
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

1.2 The Communication Process
Learning objectives.
- Identify and define the components of the transmission model of communication.
- Identify and define the components of the interaction model of communication.
- Identify and define the components of the transaction model of communication.
- Compare and contrast the three models of communication.
- Use the transaction model of communication to analyze a recent communication encounter.
Communication is a complex process, and it is difficult to determine where or with whom a communication encounter starts and ends. Models of communication simplify the process by providing a visual representation of the various aspects of a communication encounter. Some models explain communication in more detail than others, but even the most complex model still doesn’t recreate what we experience in even a moment of a communication encounter. Models still serve a valuable purpose for students of communication because they allow us to see specific concepts and steps within the process of communication, define communication, and apply communication concepts. When you become aware of how communication functions, you can think more deliberately through your communication encounters, which can help you better prepare for future communication and learn from your previous communication. The three models of communication we will discuss are the transmission, interaction, and transaction models.
Although these models of communication differ, they contain some common elements. The first two models we will discuss, the transmission model and the interaction model, include the following parts: participants, messages, encoding, decoding, and channels. In communication models, the participants are the senders and/or receivers of messages in a communication encounter. The message is the verbal or nonverbal content being conveyed from sender to receiver. For example, when you say “Hello!” to your friend, you are sending a message of greeting that will be received by your friend.
Although models of communication provide a useful blueprint to see how the communication process works, they are not complex enough to capture what communication is like as it is experienced.
Chris Searle – Blueprint – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
The internal cognitive process that allows participants to send, receive, and understand messages is the encoding and decoding process. Encoding is the process of turning thoughts into communication. As we will learn later, the level of conscious thought that goes into encoding messages varies. Decoding is the process of turning communication into thoughts. For example, you may realize you’re hungry and encode the following message to send to your roommate: “I’m hungry. Do you want to get pizza tonight?” As your roommate receives the message, he decodes your communication and turns it back into thoughts in order to make meaning out of it. Of course, we don’t just communicate verbally—we have various options, or channels for communication. Encoded messages are sent through a channel , or a sensory route on which a message travels, to the receiver for decoding. While communication can be sent and received using any sensory route (sight, smell, touch, taste, or sound), most communication occurs through visual (sight) and/or auditory (sound) channels. If your roommate has headphones on and is engrossed in a video game, you may need to get his attention by waving your hands before you can ask him about dinner.
Transmission Model of Communication
The transmission model of communication describes communication as a linear, one-way process in which a sender intentionally transmits a message to a receiver (Ellis & McClintock, 1990). This model focuses on the sender and message within a communication encounter. Although the receiver is included in the model, this role is viewed as more of a target or end point rather than part of an ongoing process. We are left to presume that the receiver either successfully receives and understands the message or does not. The scholars who designed this model extended on a linear model proposed by Aristotle centuries before that included a speaker, message, and hearer. They were also influenced by the advent and spread of new communication technologies of the time such as telegraphy and radio, and you can probably see these technical influences within the model (Shannon & Weaver, 1949). Think of how a radio message is sent from a person in the radio studio to you listening in your car. The sender is the radio announcer who encodes a verbal message that is transmitted by a radio tower through electromagnetic waves (the channel) and eventually reaches your (the receiver’s) ears via an antenna and speakers in order to be decoded. The radio announcer doesn’t really know if you receive his or her message or not, but if the equipment is working and the channel is free of static, then there is a good chance that the message was successfully received.
Figure 1.1 The Transmission Model of Communication
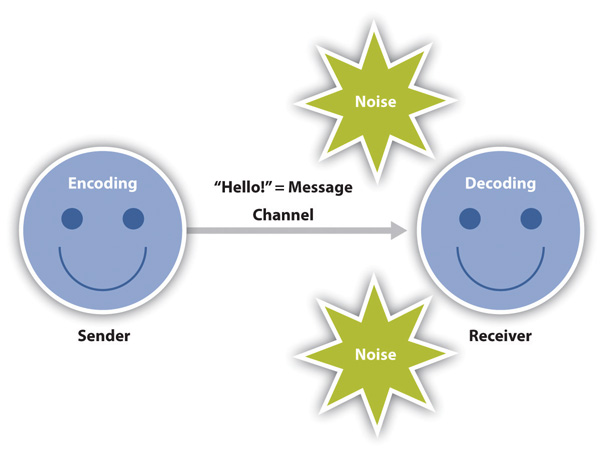
Since this model is sender and message focused, responsibility is put on the sender to help ensure the message is successfully conveyed. This model emphasizes clarity and effectiveness, but it also acknowledges that there are barriers to effective communication. Noise is anything that interferes with a message being sent between participants in a communication encounter. Even if a speaker sends a clear message, noise may interfere with a message being accurately received and decoded. The transmission model of communication accounts for environmental and semantic noise. Environmental noise is any physical noise present in a communication encounter. Other people talking in a crowded diner could interfere with your ability to transmit a message and have it successfully decoded. While environmental noise interferes with the transmission of the message, semantic noise refers to noise that occurs in the encoding and decoding process when participants do not understand a symbol. To use a technical example, FM antennae can’t decode AM radio signals and vice versa. Likewise, most French speakers can’t decode Swedish and vice versa. Semantic noise can also interfere in communication between people speaking the same language because many words have multiple or unfamiliar meanings.
Although the transmission model may seem simple or even underdeveloped to us today, the creation of this model allowed scholars to examine the communication process in new ways, which eventually led to more complex models and theories of communication that we will discuss more later. This model is not quite rich enough to capture dynamic face-to-face interactions, but there are instances in which communication is one-way and linear, especially computer-mediated communication (CMC). As the following “Getting Plugged In” box explains, CMC is integrated into many aspects of our lives now and has opened up new ways of communicating and brought some new challenges. Think of text messaging for example. The transmission model of communication is well suited for describing the act of text messaging since the sender isn’t sure that the meaning was effectively conveyed or that the message was received at all. Noise can also interfere with the transmission of a text. If you use an abbreviation the receiver doesn’t know or the phone autocorrects to something completely different than you meant, then semantic noise has interfered with the message transmission. I enjoy bargain hunting at thrift stores, so I just recently sent a text to a friend asking if she wanted to go thrifting over the weekend. After she replied with “What?!?” I reviewed my text and saw that my “smart” phone had autocorrected thrifting to thrusting ! You have likely experienced similar problems with text messaging, and a quick Google search for examples of text messages made funny or embarrassing by the autocorrect feature proves that many others do, too.
“Getting Plugged In”
Computer-Mediated Communication
When the first computers were created around World War II and the first e-mails exchanged in the early 1960s, we took the first steps toward a future filled with computer-mediated communication (CMC) (Thurlow, Lengel, & Tomic, 2004). Those early steps turned into huge strides in the late 1980s and early 1990s when personal computers started becoming regular features in offices, classrooms, and homes. I remember getting our first home computer, a Tandy from Radio Shack, in the early 1990s and then getting our first Internet connection at home in about 1995. I set up my first e-mail account in 1996 and remember how novel and exciting it was to send and receive e-mails. I wasn’t imagining a time when I would get dozens of e-mails a day, much less be able to check them on my cell phone! Many of you reading this book probably can’t remember a time without CMC. If that’s the case, then you’re what some scholars have called “digital natives.” When you take a moment to think about how, over the past twenty years, CMC has changed the way we teach and learn, communicate at work, stay in touch with friends, initiate romantic relationships, search for jobs, manage our money, get our news, and participate in our democracy, it really is amazing to think that all that used to take place without computers. But the increasing use of CMC has also raised some questions and concerns, even among those of you who are digital natives. Almost half of the students in my latest communication research class wanted to do their final research projects on something related to social media. Many of them were interested in studying the effects of CMC on our personal lives and relationships. This desire to study and question CMC may stem from an anxiety that people have about the seeming loss or devaluing of face-to-face (FtF) communication. Aside from concerns about the digital cocoons that many of us find ourselves in, CMC has also raised concerns about privacy, cyberbullying, and lack of civility in online interactions. We will continue to explore many of these issues in the “Getting Plugged In” feature box included in each chapter, but the following questions will help you begin to see the influence that CMC has in your daily communication.
- In a typical day, what types of CMC do you use?
- What are some ways that CMC reduces stress in your life? What are some ways that CMC increases stress in your life? Overall, do you think CMC adds to or reduces your stress more?
- Do you think we, as a society, have less value for FtF communication than we used to? Why or why not?
Interaction Model of Communication
The interaction model of communication describes communication as a process in which participants alternate positions as sender and receiver and generate meaning by sending messages and receiving feedback within physical and psychological contexts (Schramm, 1997). Rather than illustrating communication as a linear, one-way process, the interaction model incorporates feedback, which makes communication a more interactive, two-way process. Feedback includes messages sent in response to other messages. For example, your instructor may respond to a point you raise during class discussion or you may point to the sofa when your roommate asks you where the remote control is. The inclusion of a feedback loop also leads to a more complex understanding of the roles of participants in a communication encounter. Rather than having one sender, one message, and one receiver, this model has two sender-receivers who exchange messages. Each participant alternates roles as sender and receiver in order to keep a communication encounter going. Although this seems like a perceptible and deliberate process, we alternate between the roles of sender and receiver very quickly and often without conscious thought.
The interaction model is also less message focused and more interaction focused. While the transmission model focused on how a message was transmitted and whether or not it was received, the interaction model is more concerned with the communication process itself. In fact, this model acknowledges that there are so many messages being sent at one time that many of them may not even be received. Some messages are also unintentionally sent. Therefore, communication isn’t judged effective or ineffective in this model based on whether or not a single message was successfully transmitted and received.
Figure 1.2 The Interaction Model of Communication
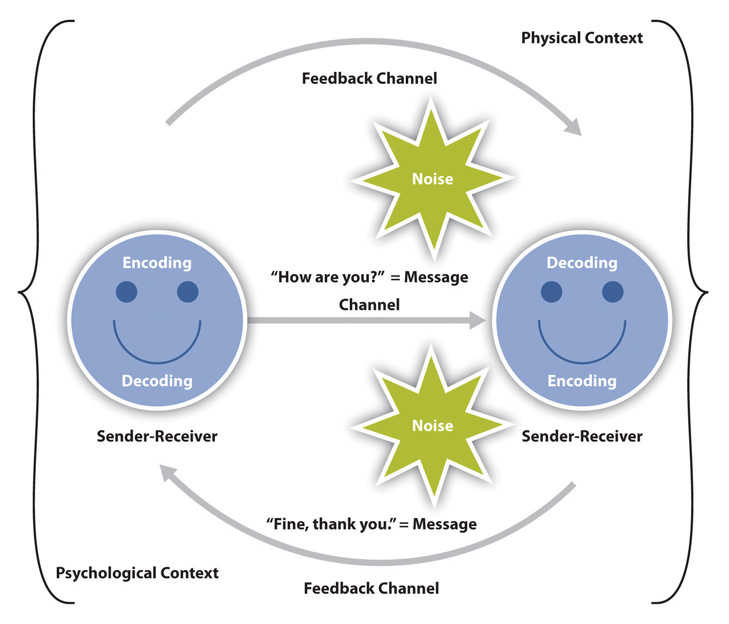
The interaction model takes physical and psychological context into account. Physical context includes the environmental factors in a communication encounter. The size, layout, temperature, and lighting of a space influence our communication. Imagine the different physical contexts in which job interviews take place and how that may affect your communication. I have had job interviews on a sofa in a comfortable office, sitting around a large conference table, and even once in an auditorium where I was positioned on the stage facing about twenty potential colleagues seated in the audience. I’ve also been walked around campus to interview with various people in temperatures below zero degrees. Although I was a little chilly when I got to each separate interview, it wasn’t too difficult to warm up and go on with the interview. During a job interview in Puerto Rico, however, walking around outside wearing a suit in near 90 degree temperatures created a sweating situation that wasn’t pleasant to try to communicate through. Whether it’s the size of the room, the temperature, or other environmental factors, it’s important to consider the role that physical context plays in our communication.
Psychological context includes the mental and emotional factors in a communication encounter. Stress, anxiety, and emotions are just some examples of psychological influences that can affect our communication. I recently found out some troubling news a few hours before a big public presentation. It was challenging to try to communicate because the psychological noise triggered by the stressful news kept intruding into my other thoughts. Seemingly positive psychological states, like experiencing the emotion of love, can also affect communication. During the initial stages of a romantic relationship individuals may be so “love struck” that they don’t see incompatible personality traits or don’t negatively evaluate behaviors they might otherwise find off-putting. Feedback and context help make the interaction model a more useful illustration of the communication process, but the transaction model views communication as a powerful tool that shapes our realities beyond individual communication encounters.
Transaction Model of Communication
As the study of communication progressed, models expanded to account for more of the communication process. Many scholars view communication as more than a process that is used to carry on conversations and convey meaning. We don’t send messages like computers, and we don’t neatly alternate between the roles of sender and receiver as an interaction unfolds. We also can’t consciously decide to stop communicating, because communication is more than sending and receiving messages. The transaction model differs from the transmission and interaction models in significant ways, including the conceptualization of communication, the role of sender and receiver, and the role of context (Barnlund, 1970).
To review, each model incorporates a different understanding of what communication is and what communication does. The transmission model views communication as a thing, like an information packet, that is sent from one place to another. From this view, communication is defined as sending and receiving messages. The interaction model views communication as an interaction in which a message is sent and then followed by a reaction (feedback), which is then followed by another reaction, and so on. From this view, communication is defined as producing conversations and interactions within physical and psychological contexts. The transaction model views communication as integrated into our social realities in such a way that it helps us not only understand them but also create and change them.
The transaction model of communication describes communication as a process in which communicators generate social realities within social, relational, and cultural contexts. In this model, we don’t just communicate to exchange messages; we communicate to create relationships, form intercultural alliances, shape our self-concepts, and engage with others in dialogue to create communities. In short, we don’t communicate about our realities; communication helps to construct our realities.
The roles of sender and receiver in the transaction model of communication differ significantly from the other models. Instead of labeling participants as senders and receivers, the people in a communication encounter are referred to as communicators . Unlike the interaction model, which suggests that participants alternate positions as sender and receiver, the transaction model suggests that we are simultaneously senders and receivers. For example, on a first date, as you send verbal messages about your interests and background, your date reacts nonverbally. You don’t wait until you are done sending your verbal message to start receiving and decoding the nonverbal messages of your date. Instead, you are simultaneously sending your verbal message and receiving your date’s nonverbal messages. This is an important addition to the model because it allows us to understand how we are able to adapt our communication—for example, a verbal message—in the middle of sending it based on the communication we are simultaneously receiving from our communication partner.
Figure 1.3 The Transaction Model of Communication
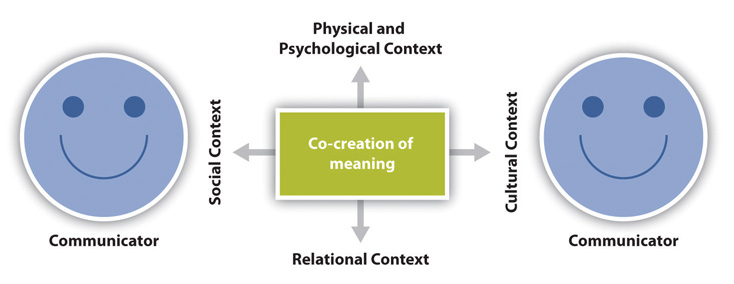
The transaction model also includes a more complex understanding of context. The interaction model portrays context as physical and psychological influences that enhance or impede communication. While these contexts are important, they focus on message transmission and reception. Since the transaction model of communication views communication as a force that shapes our realities before and after specific interactions occur, it must account for contextual influences outside of a single interaction. To do this, the transaction model considers how social, relational, and cultural contexts frame and influence our communication encounters.
Social context refers to the stated rules or unstated norms that guide communication. As we are socialized into our various communities, we learn rules and implicitly pick up on norms for communicating. Some common rules that influence social contexts include don’t lie to people, don’t interrupt people, don’t pass people in line, greet people when they greet you, thank people when they pay you a compliment, and so on. Parents and teachers often explicitly convey these rules to their children or students. Rules may be stated over and over, and there may be punishment for not following them.
Norms are social conventions that we pick up on through observation, practice, and trial and error. We may not even know we are breaking a social norm until we notice people looking at us strangely or someone corrects or teases us. For example, as a new employee you may over- or underdress for the company’s holiday party because you don’t know the norm for formality. Although there probably isn’t a stated rule about how to dress at the holiday party, you will notice your error without someone having to point it out, and you will likely not deviate from the norm again in order to save yourself any potential embarrassment. Even though breaking social norms doesn’t result in the formal punishment that might be a consequence of breaking a social rule, the social awkwardness we feel when we violate social norms is usually enough to teach us that these norms are powerful even though they aren’t made explicit like rules. Norms even have the power to override social rules in some situations. To go back to the examples of common social rules mentioned before, we may break the rule about not lying if the lie is meant to save someone from feeling hurt. We often interrupt close friends when we’re having an exciting conversation, but we wouldn’t be as likely to interrupt a professor while they are lecturing. Since norms and rules vary among people and cultures, relational and cultural contexts are also included in the transaction model in order to help us understand the multiple contexts that influence our communication.
Relational context includes the previous interpersonal history and type of relationship we have with a person. We communicate differently with someone we just met versus someone we’ve known for a long time. Initial interactions with people tend to be more highly scripted and governed by established norms and rules, but when we have an established relational context, we may be able to bend or break social norms and rules more easily. For example, you would likely follow social norms of politeness and attentiveness and might spend the whole day cleaning the house for the first time you invite your new neighbors to visit. Once the neighbors are in your house, you may also make them the center of your attention during their visit. If you end up becoming friends with your neighbors and establishing a relational context, you might not think as much about having everything cleaned and prepared or even giving them your whole attention during later visits. Since communication norms and rules also vary based on the type of relationship people have, relationship type is also included in relational context. For example, there are certain communication rules and norms that apply to a supervisor-supervisee relationship that don’t apply to a brother-sister relationship and vice versa. Just as social norms and relational history influence how we communicate, so does culture.
Cultural context includes various aspects of identities such as race, gender, nationality, ethnicity, sexual orientation, class, and ability. We will learn more about these identities in Chapter 2 “Communication and Perception” , but for now it is important for us to understand that whether we are aware of it or not, we all have multiple cultural identities that influence our communication. Some people, especially those with identities that have been historically marginalized, are regularly aware of how their cultural identities influence their communication and influence how others communicate with them. Conversely, people with identities that are dominant or in the majority may rarely, if ever, think about the role their cultural identities play in their communication.

Cultural context is influenced by numerous aspects of our identities and is not limited to race or ethnicity.
Wikimedia Commons – public domain.
When cultural context comes to the forefront of a communication encounter, it can be difficult to manage. Since intercultural communication creates uncertainty, it can deter people from communicating across cultures or lead people to view intercultural communication as negative. But if you avoid communicating across cultural identities, you will likely not get more comfortable or competent as a communicator. Difference, as we will learn in Chapter 8 “Culture and Communication” , isn’t a bad thing. In fact, intercultural communication has the potential to enrich various aspects of our lives. In order to communicate well within various cultural contexts, it is important to keep an open mind and avoid making assumptions about others’ cultural identities. While you may be able to identify some aspects of the cultural context within a communication encounter, there may also be cultural influences that you can’t see. A competent communicator shouldn’t assume to know all the cultural contexts a person brings to an encounter, since not all cultural identities are visible. As with the other contexts, it requires skill to adapt to shifting contexts, and the best way to develop these skills is through practice and reflection.
Key Takeaways
- Communication models are not complex enough to truly capture all that takes place in a communication encounter, but they can help us examine the various steps in the process in order to better understand our communication and the communication of others.
- The transmission model of communication describes communication as a one-way, linear process in which a sender encodes a message and transmits it through a channel to a receiver who decodes it. The transmission of the message many be disrupted by environmental or semantic noise. This model is usually too simple to capture FtF interactions but can be usefully applied to computer-mediated communication.
- The interaction model of communication describes communication as a two-way process in which participants alternate positions as sender and receiver and generate meaning by sending and receiving feedback within physical and psychological contexts. This model captures the interactive aspects of communication but still doesn’t account for how communication constructs our realities and is influenced by social and cultural contexts.
- The transaction model of communication describes communication as a process in which communicators generate social realities within social, relational, and cultural contexts. This model includes participants who are simultaneously senders and receivers and accounts for how communication constructs our realities, relationships, and communities.
- Getting integrated: How might knowing the various components of the communication process help you in your academic life, your professional life, and your civic life?
- What communication situations does the transmission model best represent? The interaction model? The transaction model?
- Use the transaction model of communication to analyze a recent communication encounter you had. Sketch out the communication encounter and make sure to label each part of the model (communicators; message; channel; feedback; and physical, psychological, social, relational, and cultural contexts).
Barnlund, D. C., “A Transactional Model of Communication,” in Foundations of Communication Theory , eds. Kenneth K. Sereno and C. David Mortensen (New York, NY: Harper and Row, 1970), 83–92.
Ellis, R. and Ann McClintock, You Take My Meaning: Theory into Practice in Human Communication (London: Edward Arnold, 1990), 71.
Schramm, W., The Beginnings of Communication Study in America (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1997).
Shannon, C. and Warren Weaver, The Mathematical Theory of Communication (Urbana, IL: University of Illinois Press, 1949), 16.
Thurlow, C., Laura Lengel, and Alice Tomic, Computer Mediated Communication: Social Interaction and the Internet (London: Sage, 2004), 14.
Communication in the Real World Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
The Basic Elements of the Communication Process
ThoughtCo / Hilary Allison
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
Whenever you've had a conversation, texted a friend, or given a business presentation, you have engaged in communication . Any time two or more people get together to exchange messages, they are engaging in this basic process. Although it seems simple, communication is actually quite complex and has a number of components.
Communication Process Definition
The term communication process refers to the exchange of information (a message ) between two or more people. For communication to succeed, both parties must be able to exchange information and understand each other. If the flow of information is blocked for some reason or the parties cannot make themselves understood, then communication fails.
The communication process begins with the sender , who is also called the communicator or source . The sender has some kind of information — a command, request, question, or idea — that he or she wants to present to others. For that message to be received, the sender must first encode the message in a form that can be understood, such as by the use of a common language or industry jargon, and then transmit it.
The Receiver
The person to whom a message is directed is called the receiver or the interpreter . To comprehend the information from the sender, the receiver must first be able to receive the sender's information and then decode or interpret it.
The Message
The message or content is the information that the sender wants to relay to the receiver. Additional subtext can be conveyed through body language and tone of voice. Put all three elements together — sender, receiver, and message — and you have the communication process at its most basic.
Also called the channel , the medium is the means by which a message is transmitted. Text messages, for example, are transmitted through the medium of cell phones.
The communication process reaches its final point when the message has been successfully transmitted, received, and understood. The receiver, in turn, responds to the sender, indicating comprehension. Feedback may be direct, such as a written or verbal response, or it may take the form of an act or deed in response (indirect).
Other Factors
The communication process isn't always so simple or smooth, of course. These elements can affect how information is transmitted, received, and interpreted:
- Noise : This can be any sort of interference that affects the message being sent, received, or understood. It can be as literal as static over a phone line or radio or as esoteric as misinterpreting a local custom.
- Context : This is the setting and situation in which communication takes place. Like noise, context can have an impact on the successful exchange of information. It may have a physical, social, or cultural aspect to it. In a private conversation with a trusted friend, you would share more personal information or details about your weekend or vacation, for example, than in a conversation with a work colleague or in a meeting.
The Communication Process in Action
Brenda wants to remind her husband, Roberto, to stop by the store after work and buy milk for dinner. She forgot to ask him in the morning, so Brenda texts a reminder to Roberto. He texts back and then shows up at home with a gallon of milk under his arm. But something's amiss: Roberto bought chocolate milk when Brenda wanted regular milk.
In this example, the sender is Brenda. The receiver is Roberto. The medium is a text message. The code is the English language they're using. And the message itself is "Remember the milk!" In this case, the feedback is both direct and indirect. Roberto texts a photo of milk at the store (direct) and then came home with it (indirect). However, Brenda did not see the photo of the milk because the message didn't transmit (noise) and Roberto didn't think to ask what kind of milk (context).
- A Receiver's Role in Clear, Effective Communication Is an Important One
- What Is a Message in Communication?
- Definition and Examples of Senders in Communication
- What Does Medium Mean in the Communication Process?
- What Is Communication?
- Noise and Interference in Various Types of Communication
- Science Says You Should Leave the Period Out of Text Messages
- Feedback in Communication Studies
- The Definition of Listening and How to Do It Well
- Text Message Smishing Scams
- Multiple Literacies: Definition, Types, and Classroom Strategies
- What is a Rhetorical Situation?
- Email Message
- Definition and Examples of Discourse
- What Is Wei Xin?
- Texting (Text Messaging)

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.1: Communication- Definition and The Communication Process
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 114736

- Pamela J. Gerber & Heidi Murphy
- Central New Mexico Community College via https://www.cnm.edu/
In this section, we will define communication and discuss the components of the communication process.
Definition of Communication
In this text, we define communication as symbol using and meaning making. Communicators exchange two types of symbols, verbal and/or nonverbal, and attach meaning to said symbols. For example, the meaning attached to the verbal symbol “hello” is a greeting. You can also convey this greeting by using a nonverbal symbol, such as a hand wave. However, it is important note that the meanings we attach to symbols can vary from person to person. For example, another communicator might instead interpret a hand wave as trying to get their attention.

The Communication Process
In order to better understand how verbal and nonverbal symbols are produced, interpreted, and coordinated in interactions, it is necessary to understand the components of the communication process.
Senders and receivers of messages in a communicative interaction. Because we are continuously sending and receiving verbal and/or nonverbal messages, we are simultaneously both a sender and receiver in interactions. For example, in a face-to-face interaction, the other communicator may be recounting an experience verbally with words and nonverbally with hand gestures, while we are sending our own nonverbal messages via eye contact, facial expressions, posture, etc.
The process of turning our thoughts, ideas, and feelings into verbal and/or nonverbal messages.
The process of interpreting and adding meaning to the verbal and/or nonverbal messages we receive.
A thing that represents or stands for something else. In communication, symbols can be verbal, such as words, or nonverbal, such as the ‘okay’ hand symbol.
Verbal and nonverbal symbols that represent thoughts, feelings, and ideas. Messages can be both intentional (conscious) and unintentional (unconscious). For example, we may intentionally smile at a friend but unintentionally fidget with our hands when nervous.
The means through which the message is sent from one communicator to the other, such spoken words, a text message, or our hands to make a gesture.
The verbal and nonverbal messages sent by one communicator in response to the other communicator’s message(s). For example, if someone says a word we are unfamiliar with, we may frown in response or give them a confused look to let them know we do not understand.
Noise is a type of interference in the communication process that results from the physical, relational, individual, and/or cultural context. Noise can occur in various places in the process, such as in the people, in the channel, in the message, and even outside the interaction.
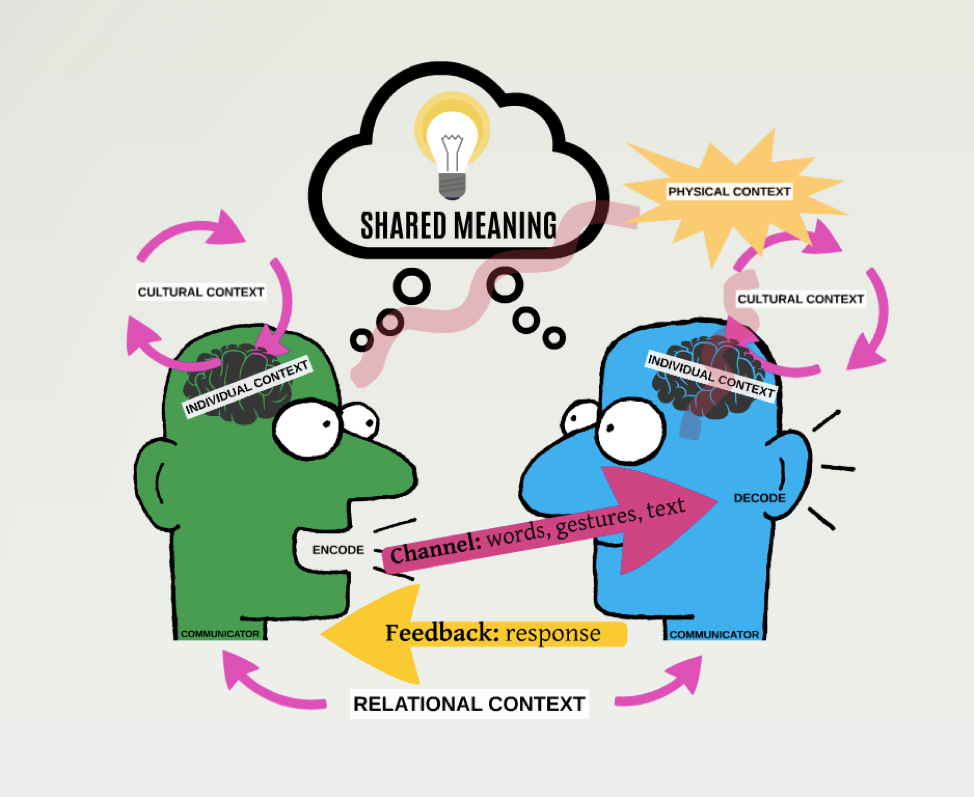
In any interpersonal interaction, there are at least two communicators and both communicators are generating and creating meaning by simultaneously sending and receiving messages . For example, in a face-to-face interaction, we may be telling a story about our horrible day and the other person may be listening. While we are telling our story, we are encoding our thoughts and feelings and considering which details to leave out and which ones to talk about. Think about the last time you recapped your experience at a social gathering for a friend and then again for a family member. Did you focus on different details with each person? That’s encoding. While telling the story, we may use both verbal and nonverbal symbols to create the content of our message. The channel we send our message through can be spoken words (for verbal symbols) or hand gestures (for nonverbal symbols). The other communicator, who is listening, decodes the message by interpreting and adding meaning to it. In addition, the listener is also simultaneously communicating messages back to us. This is called feedback . They may be nonverbally establishing eye contact (or not), yawning, or verbally interrupting or asking questions.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences

Good Feedback Is a Two-Way Conversation

Start by asking these questions.
Rather than relying on a feedback hierarchy, managers should consider a partnership model that distributes power and increases two-way conversation with their employees. It’s a humbler approach to managing people that focuses on asking questions, not giving orders. The author calls it the difference between “window gazing” and “mirror holding.”
“Window gazing” is a process of see-and-tell. Ask two people gazing out the same window to describe what they see, and you’re likely to get a pair of perspectives that are substantively different but remain equally valid. Not so in the context of work, where the imbalance of power allows only one view — the manager’s — to prevail. That changes with “mirror holding,” a dramatic shift in the tone and trajectory of feedback conversations. Instead of telling their employees what to see, managers guide them where to look. They engage employees in thoughtful conversation about their current strengths, future goals, and how to bring those elements closer in line.
Getting others to accept our feedback can prove challenging, especially when it’s critical. Worried that their feedback may lead to hurt feelings or diminished productivity , managers resort to face-saving techniques like the “praise sandwich” that end up doing more harm than good. The result is a tenuous feedback culture built largely upon evasion, confusion, and self-delusion.
- Joe Hirsch is the managing director of Semaca Partners, a boutique communications firm, a TEDx and keynote speaker, the author of The Feedback Fix and an award-winning educational leader. His work and research on high-performance feedback has been featured in Forbes, CNBC, Inc. and other major outlets. Connect with him at www.joehirsch.me or @joemhirsch .
Partner Center
Essay on Importance of Communication for Students and Children
500+ words essay on importance of communication:.
Communication is one of the important tools that aid us to connect with people. Either you are a student or a working professional, good communication is something that will connect you far ahead. Proper communication can help you to solve a number of issues and resolve problems. This is the reason that one must know how to communicate well. The skills of communication essential to be developed so that you are able to interact with people. And able to share your thoughts and reach out to them. All this needs the correct guidance and self-analysis as well.

Meaning of Communication
The word communication is basically a process of interaction with the people and their environment . Through such type of interactions, two or more individuals influence the ideas, beliefs, and attitudes of each other.
Such interactions happen through the exchange of information through words, gestures, signs, symbols, and expressions. In organizations, communication is an endless process of giving and receiving information and to build social relationships.
Importance of Communication
Communication is not merely essential but the need of the hour. It allows you to get the trust of the people and at the same time carry better opportunities before you. Some important points are as follows –
Help to Build Relationships
No matter either you are studying or working, communication can aid you to build a relationship with the people. If you are studying you communicate with classmates and teachers to build a relationship with them. Likewise in offices and organizations too, you make relationships with the staff, your boss and other people around.
Improve the Working Environment
There are a number of issues which can be handled through the right and effective communication. Even planning needs communication both written as well as verbal. Hence it is essential to be good in them so as to fill in the communication gap.
Foster strong team
Communication helps to build a strong team environment in the office and other places. Any work which requires to be done in a team. It is only possible if the head communicates everything well and in the right direction.
Find the right solutions
Through communication, anyone can find solutions to even serious problems. When we talk, we get ideas from people that aid us to solve the issues. This is where communication comes into play. Powerful communication is the strength of any organization and can help it in many ways.
Earns more respect
If your communication skills are admirable, people will love and give you respect. If there is any problem, you will be the first person to be contacted. Thus it will increase your importance. Hence you can say that communications skills can make a big change to your reputation in society.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Don’t Go Overboard With Your Point
The conversation is about to express your thoughts. And to let the other person know what you feel. It is not mean to prove that your point is correct and the other person is wrong. Don’t Overboard other With Your Point.
Watch Your Words
Before you say something to Watch Your Words. At times, out of anger or anxiousness, we say somethings that we must not say. Whenever you are in a professional meeting or in some formal place, where there is a necessity of communicating about your product or work then it is advised to practice the same beforehand
Communication is the greatest importance. It is important to sharing out one’s thoughts and feelings to live a fuller and happier life. The more we communicate the less we suffer and the better we feel about everything around. However, it is all the more necessary to learn the art of effective communication to put across ones point well.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Communication is regarded as the process by which individuals send and receive thoughts, ideas as well as feelings in a manner in which the recipient comprehends the message in its intended form. Thus, communication is taken as a two way process where the binding force is assumed to be the feedback loop.
Rather than illustrating communication as a linear, one-way process, the interaction model incorporates feedback, which makes communication a more interactive, two-way process. For example: A question-and-answer session, in which a question is asked and a response given, is an example of an interactional model of communication. Feedback and ...
Communication is a two way process of sharing or transferring information. This information can be formal as in business meetings and presentations, and can be informal as talking about daily lives, opinions, suggestions etc. Whether communication is formal or informal, verbal or non verbal, it helps in mutual understanding and helps people to ...
546 Words. 3 Pages. Open Document. The Communication Process: Communication is a process where we share our feelings, ideas, thoughts, suggestion, experience, feedback, opinions, etc. It's a dialogue in which the sharing of meaningful information are constantly coming in and going out between two or more people in order to reach an understanding.
Although the one-way approach might be convincing in relation to information giving and persuasive communication, more recent approaches to the concept of communication view it as a fundamental two-way process that is interactive by nature and participatory at all levels (for an overview, see Servaes, Citation 1999). This involves the ...
Rather than illustrating communication as a linear, one- way process, the interaction model incorporates feedback, which makes communication a more interactive, two- way process. Feedback includes messages sent in response to other messages. For example, your instructor may respond to a point you raise during class discussion or you may point ...
Transmission Model of Communication. The transmission model of communication describes communication as a linear, one-way process in which a sender intentionally transmits a message to a receiver (Ellis & McClintock, 1990). This model focuses on the sender and message within a communication encounter. Although the receiver is included in the model, this role is viewed as more of a target or ...
The communication process reaches its final point when the message has been successfully transmitted, received, and understood. The receiver, in turn, responds to the sender, indicating comprehension. Feedback may be direct, such as a written or verbal response, or it may take the form of an act or deed in response (indirect).
The process of turning our thoughts, ideas, and feelings into verbal and/or nonverbal messages. Decoding: The process of interpreting and adding meaning to the verbal and/or nonverbal messages we receive. Symbol: A thing that represents or stands for something else. In communication, symbols can be verbal, such as words, or nonverbal, such as ...
The two-way communication cycle is a complete verbal communication process that helps provide a smooth transmission of information. The response that the receiver sends provides essential feedback ...
The author calls it the difference between "window gazing" and "mirror holding." "Window gazing" is a process of see-and-tell. Ask two people gazing out the same window to describe ...
Here are four examples of two-way communication: 1. Conversing between two people. One type of two-way communication is a basic conversation between two parties. For example, this may include two colleagues discussing the plans they have to complete a project.
The word communication is basically a process of interaction with the people and their environment. Through such type of interactions, two or more individuals influence the ideas, beliefs, and attitudes of each other. Such interactions happen through the exchange of information through words, gestures, signs, symbols, and expressions.
In the workplace, effective communication can help you: Manage employees and build teams. Grow your organization more rapidly and retain employees. Benefit from enhanced creativity and innovation. Become a better public speaker. Build strong relationships and attract more opportunities for you or your organization.
The act of communication is also known as the process of passing information in oral or written form. It is the transfer of a person's thoughts in the way of talking or writing to another person. Communication has four actions that are, encoding, sending, receiving, and decoding. The sender encodes the information and transfers it to the ...
Communication Essay 4 (400 words) Communication, the bridge that binds us all, serves as the cornerstone of human civilization. It transcends barriers, united minds, and propels progress. At its core, communication is an art, an ever-evolving dance of words, gestures, and expressions that molds our relationships and shapes our understanding of ...
Deepening the understanding of leaders' decision-making, philosophy, and priorities; Communicating information; Creating connections within and without a unit. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like No matter the purpose, there are some characteristics common to all effective writing, it: ____________.
Fig.2.1 Communication process, verbal and non-verbal communications. Source: 3.bp.blogspot.com Fig 2.1 above shows that one can safely conclude that communication is carried out, to
Essay, Pages 5 (1182 words) Views. 156. Communication is a process which has many steps. The primary goal of communication is to exchange information, thoughts, and feelings between people through verbal and nonverbal channels. Communication is an essential need in law enforcement and individuals in the field must become proficient in sending ...
Oral Communication Communication is a two-way process of reaching mutual understanding, in which participants not only exchange (encode-decode) information, news, ideas and feelings but also create and share meaning. (businessdictionary, 2017). The types of communication are Interpersonal, Written and Oral.
1. Communication is a two-way process in which information is delivered and ___________. received. 2. What is the role of a project manager? to oversee a project from beginning to end. to complete an assessment of a project's quality. to hire all of the workers for a project. to decide that a project should be begun.