This website uses cookies to enhance the user experience.

What stage is your business at?
Tell us and we'll match you with a special liveplan discount:, new business idea, startup phase, established business, new business discount, great, we have special savings for organizing your business ideas., get full access to liveplan for 50% off, save big with any monthly package, startup discount, great, we have special savings for businesses just starting up., save big on liveplan premium, save big with any liveplan premium package, established business discount, great, we have special savings for businesses that are up and running., get annual access to liveplan for 40% off, save big with any annual package.
Enter your email address to unlock it.
We care about your privacy. See our Privacy Policy .
🎧 Real entrepreneurs. Real stories.
Subscribe to The Hurdle podcast
You can do this! Tour LivePlan to see how simple business planning can be.
Have an expert write your plan, build your forecast, and so much more.

Integrations
For Small Businesses
For Advisors & Mentors
Planning a Business
How to Write a Detailed Business Plan Step-by-Step [Free Template]

12 min. read
Updated September 23, 2024
Writing a business plan is one of the most valuable things you can do for your business.
Study after study proves that business planning significantly improves your chances of success by up to 30 percent 1 . That’s because the planning process helps you think about all aspects of your business and how it will operate and grow.
Ready to write your own detailed business plan? Here’s everything you need (along with a free business plan template ) to create your plan.
Before you write a detailed business plan, start with a one-page business plan
Despite the benefits of business planning , it’s easy to procrastinate writing a business plan.
Most people would prefer to work hands-on in their business rather than think about business strategy . That’s why, if you’re writing a business plan for the first time, we recommend you start with a simpler and shorter one-page business plan.
With a one-page plan, there’s no need to go into a lot of details or dive deep into financial projections—you just write down the fundamentals of your business and how it works.
A one-page plan should cover:
- • Value proposition
- • Market need
- • Your solution
- • Competition
- • Target market
- • Sales and marketing
- • Budget and sales goals
- • Milestones
- • Team summary
- • Key partners
- • Funding needs
A one-page business plan is a great jumping-off point in the planning process. It’ll give you an overview of your business and help you quickly refine your ideas.
Check out our guide to writing a simple one-page business plan for detailed instructions, examples, and a free downloadable one-page plan template .
When do you need a more detailed business plan?
While I will always recommend starting with the one-page plan format, there are times when a more detailed plan is necessary:
- • Flesh out sections of your plan: You need to better understand how your marketing, operations, or other business functions will operate.
- • Build a more detailed financial forecast: A one-page plan only includes a summary of your financial projections. A detailed plan includes a full financial forecast, including a profit and loss statement, balance sheet, and cash flow forecast to better measure performance.
- • Prepare for lenders and investors: While they may not read the full plan, any investor will ask in-depth questions that you can only answer by spending time writing a detailed business plan.
- • Sell your business: Use your business plan as part of your sales pitch, and show potential buyers all the details of how your business works.

How to write a detailed business plan
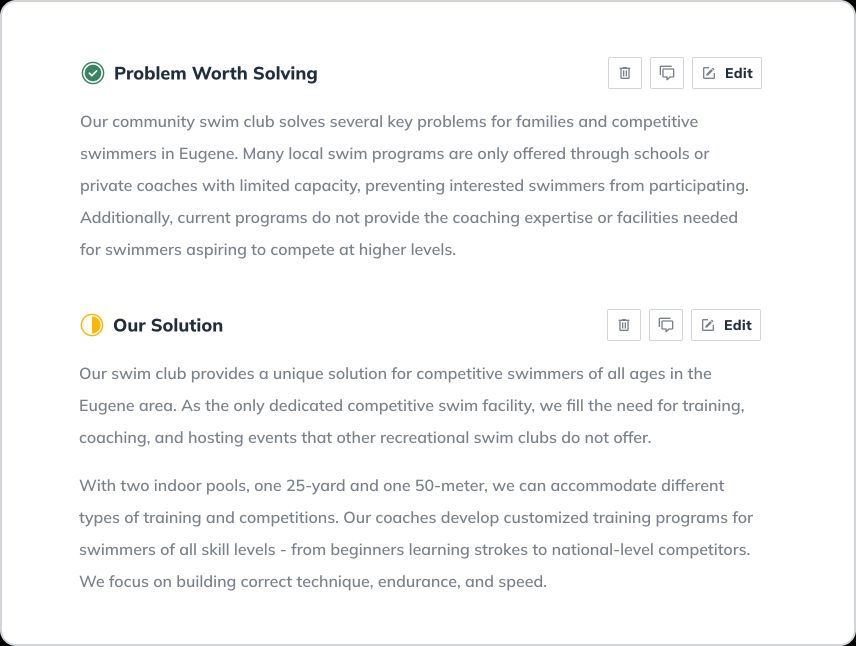
Let’s walk through writing a detailed business plan step-by-step and explore an example of what a finished business plan (for a local swim club Pools & Laps) built with LivePlan’s business plan builder looks like.
1. Executive summary
Yes, the executive summary comes first in your plan, but you should write it last—once you know all the details of your business plan.
It is just a summary of your full plan, so be careful not to be too repetitive—keep it between one or two pages and highlight:
- • Your opportunity: This summarizes what your business does, what problem it solves, and who your customers are. This is where you want readers to get excited about your business
- • Your team: For investors, your business’s team is often even more important than what the business is. Briefly highlight why your team is uniquely qualified to build the business and make it successful.
- • Financials: What are the highlights of your financial forecast ? Summarize your sales goals, when you plan to be profitable, and how much money you need to get your business off the ground.
For existing businesses, write the executive summary for your audience—whether it’s investors, business partners, or employees. Think about what your audience will want to know, and just hit the highlights.

2. Opportunity
The “opportunity” section of your business plan is all about the products and services that you are creating. The goal is to explain why your business is exciting and the problems that it solves for people. You’ll want to cover:
Problem & solution
Every successful business solves a problem for its customers. Their products and services make people’s lives easier or fill an unmet need in the marketplace.
In this section, you’ll want to explain the problem that you solve, whom you solve it for, and what your solution is. This is where you go in-depth to describe what you do and how you improve the lives of your customers.
Target market
In the previous section, you summarized your target customer. Now you’ll want to describe them in much greater detail. You’ll want to cover things like your target market’s demographics (age, gender, location, etc.) and psychographics (hobbies and other behaviors).
Ideally, you can also estimate the size of your target market so you know how many potential customers you might have.

Competition
Every business has competition , so don’t leave this section out. You’ll need to explain what other companies are doing to serve your customers or if your customers have other options for solving the problem you are solving.
Explain how your approach is different and better than your competitors, whether it’s better features, pricing, or location. Explain why a customer would come to you instead of going to another company.

3. Execution
This section of your business plan dives into how you will accomplish your goals. While the Opportunity section discussed what you’re doing, you now need to explain the specifics of how you will do it.
Marketing & sales
What marketing tactics will you use to get the word out about your business? You’ll want to explain how you get customers to your door and what the sales process looks like. For businesses with a sales force, explain how the sales team gets leads and what the process is like for closing a sale.

Depending on the type of business that you are starting, the operations section needs to be customized to meet your needs. If you are building a mail-order business, you’ll want to cover how you source your products and how fulfillment will work.
If you’re building a manufacturing business, explain the manufacturing process and the necessary facilities. This is where you’ll talk about how your business “works,” meaning you should explain what day-to-day functions and processes are needed to make your business successful.

Milestones & metrics
So far, your business plan has mostly discussed what you’re doing and how you will do it.
The milestones and metrics section is all about timing. Your plan should highlight key dates and goals that you intend to hit. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section, just key milestones that you want to hit and when you plan to hit them.
You should also discuss key metrics : the numbers you will track to determine your success.

The Company section of your business plan should explain your business’s overall structure and the team behind it.
Organizational structure
Describe your location, facilities, and anything else about your physical location relevant to your business. You’ll also want to explain the legal structure of your business—are you an S-corp, C-corp, or an LLC? What does company ownership look like?

Arguably one of the most important parts of your plan when seeking investment is the “Team” section. This should explain who you are and who else is helping you run the business. Focus on experience and qualifications for building the type of business that you want to build.
It’s OK if you don’t have a complete team yet. Just highlight the key roles that you need to fill and the type of person you hope to hire for each role.

5. Financial plan and forecasts
Your business plan now covers the “what,” the “how,” and the “when” for your business. Now it’s time to talk about money.
Financial forecasts
What revenue do you plan on bringing in, and when? What kind of expenses will you have? How much cash will you need?
These are the types of questions you’ll answer by creating detailed forecasts. Don’t worry about getting it perfect, these are just educated guesses. Your goal is to get numbers down that seem reasonable so you can review and revise financial expectations as you run your business.
You’ll want to cover sales , expenses , personnel costs , asset purchases, cash , etc, for at least the first 12 months of your business. If you can, also create educated guesses for the following two years in annual totals.
If you intend to pursue funding, it’s worth noting that some investors and lenders might want to see a five-year forecast. For most other cases, three years is usually enough.

If you’re raising money for your business, the Financing section is where you describe how much you need. Whether you’re getting loans or investments, you should highlight what and when you need it.
Ideally, you’ll also want to summarize the specific ways you’ll use the funding once you have it.
For more specifics, check out our write-up explaining what to include in your business plan for a bank loan .

Historical Financial statements
If your business is up and running, you should also include your profit and loss statement , balance sheet , and cash flow statement . These are the historical record of your business performance and will be required by lenders, investors, and anyone considering buying your business.
If you don’t want lengthy financial statements overwhelming this section of your business plan, you can just include the most recent statements and include the rest within your appendix.

6. Appendix
The final section of your business plan is the appendix . Include detailed financial forecasts here and any other key documentation for your business.
If you have product schematics, patent information, or any other details that aren’t appropriate for the main body of the plan but need to be included for reference.
Tips to write a detailed business plan
Keep it brief.
You may not be limited to one page, but that doesn’t mean you need to write a novel. Keep your business plan focused using clear, plain language and avoiding jargon. Make your plan easier to skim by using short sentences, bulleted lists, and visuals. Remember, you can always come back and add more details.
Related Reading: 7 tips to make a high-quality business plan
Start with what you know
Don’t worry about following a strict top-to-bottom approach. Instead, build momentum by starting with sections you know well. This will help you get information down and ultimately make you more likely to complete your business plan.
Set time limits
You don’t have to write your business plan in one sitting. It may be more valuable to set a time limit, see how much you get done, and return to it again in another session. This will keep you focused and productive and help you fit plan writing into your other responsibilities.
Reference business plan examples
Real-world business plan examples from your industry can provide valuable insights into how others have successfully presented their ideas, strategies, and financials. Exploring these examples can inspire your own approach and offer practical guidance on what to include and how to tailor it to your specific needs.
Just be sure not to copy and paste anything.
Prioritize sections that really matter
When writing a detailed business plan, focus on the parts most important to you and your business.
If you plan on distributing your plan to outsiders, you should complete every section. But, if your plan is just for internal use, focus on the areas that will help you right now.
Download a free business plan template
Are you ready to write your detailed business plan? Get started by downloading our free business plan template . With that, you will be well on your way to a better business strategy, with all of the necessary information expected in a more detailed plan.
If you want to improve your ability to build a healthy, growing business, consider LivePlan.
It’s a product that makes planning easy and features a guided business plan creator , drag-and-drop financial forecasting tools , and an AI-powered LivePlan Assistant to help you write, generate ideas, and analyze your business performance.
Use your detailed business plan to grow your business
Your business plan isn’t just a document to attract investors or close a bank loan. It’s a tool that helps you better manage and grow your business. And you’ll get the most value from your business plan if you use it as part of a growth planning process .
With growth planning, you’ll easily create and execute your plan, track performance, identify opportunities and issues, and consistently revise your strategy. It’s a flexible process that encourages you to build a plan that fits your needs.
So, whether you stick with a one-page plan or expand into a more detailed business plan—you’ll be ready to start growth planning.
Sources in this article
- 1. Parsons, Noah. “Do You Need a Business Plan? This Study Says Yes” Bplans: Free Business Planning Resources and Templates , 10 May 2024, www.bplans.com/business-planning/basics/research .
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Noah Parsons
Before joining Palo Alto Software , Noah Parsons was an early Internet marketing and product expert in the Silicon Valley. He joined Yahoo! in 1996 as one of its first 101 employees and become Producer of the Yahoo! Employment property as part of the Yahoo! Classifieds team before leaving to serve as Director of Production at Epinions.com. He is a graduate of Princeton University. Noah devotes most of his free time to his three young sons. In the winter you'll find him giving them lessons on the ski slopes, and in summer they're usually involved in a variety of outdoor pursuits. Noah is currently the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan.

Table of Contents
Related articles.

August 7, 2024
Cash Flow Explained | What is it, Why it Matters, and How to Calculate

October 1, 2024
Cash Flow Statement: Definition + How to Create and Read it

October 17, 2024
What Is Accounts Receivable (AR)? [Definition + 6 Ways to Improve]

July 31, 2024
Cash Flow Vs. Profit | What’s More Important for Your Business?

The Business Guide to Customer Engagement Metrics and Analysis
Get in-depth insights, practical formulas, and strategies to optimize engagement.
- Business Growth

Writing a Business Plan: A Guide for New and Experienced Entrepreneurs
For entrepreneurs, a business plan serves as a roadmap that outlines a company’s goals, strategies, and operational approach. It’s more than just a formality; having a well-structured plan can provide clear direction for decision making and increase the likelihood of long-term success.
A full 93% of mid-sized business owners plan to obtain funding for new technology and equipment, showing the importance of long-term planning for a healthy, resilient business. Proactive preparation helps anticipate challenges, manage resources effectively, and align teams and stakeholders with a shared vision.
This guide breaks down the elements of a business plan, offering step-by-step insights for those looking to launch or grow a successful venture.
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a comprehensive document that sets out a company’s goals, strategies, and the steps needed to reach them. It serves as a roadmap, guiding businesses through each stage of their growth, from the initial idea to scaling operations. Typically, a business plan covers main sections, including market analysis, competitive landscape, target audience, marketing plan approach, and financial projections.
Beyond its role in securing funding, a business plan helps entrepreneurs change their ideas, evaluate market opportunities, and identify risks. It also serves as a tool for improving retention by aligning offerings with specific customer needs and adapting to market changes.
Benefits of a Business Plan
A solid business plan supports any company by enhancing decision-making, improving funding access, and building a competitive advantage. Here’s a closer look at its benefits:
Direction for Decision Making
A business plan sets clear goals and priorities, guiding founders and teams to make decisions that align with the company’s mission. This focused direction helps allocate resources efficiently and keeps the team on track, ensuring each choice supports long-term growth.
Attracting Investors and Funding
A well-structured plan demonstrates the business's potential to investors and lenders, providing a clear roadmap for growth and operational improvement, which builds confidence in its viability.
Operational Focus and Efficiency
With clear goals and detailed strategies, a business plan helps streamline operations by pinpointing gaps early and keeping the team focused on key customer engagement metrics and performance analysis. This alignment supports more efficient workflows and proactive decision-making.
Market Assessment and Competitive Positioning
A business plan helps you understand your target market and position your business effectively against competitors. It supports analysis of market trends and customer needs, guiding adjustments to improve market fit.
Resource Allocation
Teams can distribute resources more effectively, making sure that funds, time, and efforts are directed toward high-impact areas for growth.
Risk Management
Early identification of potential challenges prepares teams to manage risks and adapt strategies, strengthening resilience in a changing market.

How to Create a Business Plan
Crafting a business plan begins with a strong idea and builds toward a detailed, actionable strategy. Here are twelve steps to guide you through:
Step 1: Start with Your Business Idea
Begin by clarifying your core business idea, define what your business will offer, who it will serve, and what sets it apart. This step creates the foundation for your entire plan, aligning your vision from the start. If you’re a small business owner exploring options, here are business ideas to help inspire your next steps.
Step 2: Write the Executive Summary
Provide a brief overview of your business, including its purpose, target market, and goals. Summarize the highlights of each section to offer readers a quick snapshot of your plan. The executive summary should be concise yet compelling, capturing the essence of your business and demonstrating its potential for success. This section often serves as the first impression for investors or stakeholders, so make it impactful to encourage further interest in the detailed plan that follows.
Step 3: Define Your Company
Describe your company’s structure, mission, and vision, giving a clear picture of its foundational principles. Highlight what makes your business unique, such as a proprietary product, innovative approach, or market niche, and share any significant milestones or achievements that add to its credibility. This section should communicate your company’s identity and purpose, setting it apart in the eyes of investors, partners, and customers.
Step 4: Address Legal Considerations
Include the legal foundations of your business, such as your chosen business structure (e.g., LLC, corporation, sole proprietorship) and any required licenses or permits. Outline regulatory requirements specific to your industry, and detail any intellectual property protections like trademarks or patents. Covering these aspects helps prevent legal issues and reassures investors and stakeholders of the business’s compliance and integrity.
Step 5: Conduct Market Analysis
Research your target market thoroughly. Identify customer needs, analyze competitors, and study relevant market trends. This analysis helps you understand demand, pricing strategies, and areas for differentiation, setting a strong foundation for your business positioning.
Step 6: SWOT Analysis
In addition to market analysis, a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) provides a structured view of your business’s internal and external factors. Highlighting strengths, identifying areas for improvement, recognizing growth opportunities, and acknowledging potential threats creates a balanced assessment of your business’s position. This transparency strengthens credibility, demonstrating a realistic approach to navigating challenges and maximizing potential.
.png)
Step 7: Outline Organization and Management
Describe your business structure, ownership, and key personnel. Outline the roles and expertise of each team member, emphasizing their contributions to your business goals.
Step 8: Describe Products or Services
Provide details on your products or services, focusing on their unique features, stages of development, and how they solve customer problems. Highlight how these offerings can help capture market share by differentiating your business from competitors.
Step 9: Develop Your Marketing Strategy
Describe how you will reach and engage your ideal customer profile and attract potential customers. An effective marketing strategy builds brand awareness, generates demand, and helps capture market share. Outline your customer acquisition tactics, engagement metrics, and the specific channels that align with your target audience’s habits to show how these efforts will drive growth and sustain customer relationships.
Step 10: Draft a Funding Request
If seeking funding, specify your financial needs, intended use of funds, and expected impact on growth. Clarify your projections for returns on investment, showing how funding will drive a successful business.
Step 11: Prepare Financial Projections
Prepare a comprehensive financial projection covering revenue, expenses, and anticipated growth over the next three to five years. Presenting this data on a quarterly or yearly basis strengthens the demonstration of your business’s financial viability. Incorporating a break-even analysis within these projections further enhances your plan by showing when your business is expected to reach profitability—an essential metric for lenders and investors seeking assurance of your venture’s potential success.
Step 12: Compile the Appendix
Use this section for any additional documents, like team resumes, legal agreements, or product visuals, to provide extra context and depth.
Business Plan Formats
Business plans vary in length and detail, ranging from simple, one-page summaries to comprehensive, data-heavy documents. Choose a format that matches your audience and purpose here are some examples:
- Traditional Plan : Detailed and thorough, this format is ideal for complex businesses or when seeking significant investment. It includes in-depth sections on financials, market research, and competitive analysis.
- Lean Startup Plan: A shorter, focused document, helpful for quickly evaluating feasibility and developing small business ideas. This format highlights core assumptions and metrics to track early progress.
- One-Page Plan: A concise overview that summarizes points on a single page, suitable for early-stage planning or quick presentations. It’s the best way to communicate necessary information without overwhelming detail.
- Operational Plan: Primarily used internally, this format focuses on day-to-day operations, helping teams stay aligned on tasks and timelines. It includes specifics on staffing, workflows, and resource management.
- Growth Plan: Custom for expansion, this format includes strategies for growing operations, entering new markets, and increasing revenue. It also includes projections and market insights to guide the company’s future direction.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Writing a Business Plan
The strength of a business plan often lies in avoiding typical missteps. Make sure to be mindful of these pitfalls:

Overly Optimistic Projections
Projecting high revenue without factoring in potential setbacks can lead to unrealistic expectations. Expenses often rise unexpectedly, and without a buffer, financial stability can be at risk. A balanced approach to projections helps create a more sustainable financial outlook.
Ignoring Market Research
Market fit is fundamental for success. In fact, 42% of businesses fail due to a lack of market fit, highlighting the importance of thorough research as it uncovers trends and competitor strategies, helping to change your approach.
Forgetting Customer Retention
Strengthening customer relationship through retention drives sustainable growth. Loyal customers often generate more long-term revenue than new ones, making retention a strategic focus. Regular engagement and feedback collection from these customers can also inspire meaningful product improvements.
Lack of Flexibility
A rigid plan can become outdated as markets and customer needs change. Building in room for adjustments allows the business to adapt to changing conditions and new insights. Flexibility also helps in responding quickly to unforeseen challenges or opportunities. An adaptable plan keeps the company aligned with current trends and customer expectations.
Underestimating Financial Needs
Misjudging initial financial plan and ongoing funding requirements can derail operations. It's important to estimate realistic financial needs, including reserves for unexpected costs, to ensure adequate resources for growth and stability.
Overlooking Competitive Analysis
Focusing solely on your own offerings can blind you to competitors’ strengths. Understanding competitor positioning, pricing, and weaknesses allows for smarter differentiation and helps in capturing market share effectively.
Weak Marketing Strategy
A lackluster marketing approach can stifle growth, regardless of product quality. A well-defined strategy that targets ideal customers with the right channels is essential for brand visibility and customer acquisition.
Neglecting Team Dynamics and Culture
Overlooking the importance of team structure and company culture can impact employee retention and productivity. Aligning team roles and fostering a supportive culture contributes to long-term stability and operational efficiency.
Turning Plans into Actions: Steps for Meaningful Growth
A well-crafted business plan is more than just a tool for investors; it’s a comprehensive guide that aligns your strategies with customer satisfaction and high-quality service. The feel, felt, found approach can add depth to your planning, helping you empathize with customer concerns, offer solutions and adapt to changing market demands. Through detailed planning, you can better predict challenges and develop solutions that strengthen customer trust.
A solid business plan serves as a roadmap for assessing progress, adapting to change, and driving sustainable growth. It’s an investment in resilience, helping you set clear priorities, make informed decisions, and build stronger connections with your customers. Starting fresh or refining an existing approach, a well-defined plan keeps you focused and prepared through each stage of growth.
Support customers better with Velaro’s AI-powered chat, making it simple to engage effectively. Book a personalized demo today .
Stay informed. get exclusive offers and news delivered straight to your inbox..
Thank you for joining our blog family!
As a subscriber, you'll get exclusive access to insights, expert tips, and more. Stay tuned for our upcoming posts.
Find more valuable articles

The Complete Guide to Customer Service: Addressing Challenges, Types, and Best Practices
This complete guide to customer service covers types, challenges, and effective practices to improve customer experiences and build long-term loyalty.

Getting Started with Live Chat Performance Management in 5 Steps
Learn how to collect baseline data and how to take action to the collected data with live chat performance management.

Make Complex Engagements Easy
Press & Media. Better assist your customers with automated workflows. Discover more on CIO Applications Magazine.
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Tips White Papers
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- United Kingdom
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
How to Prepare and Write the Perfect Business Plan for Your Company Here's how to write a business plan that will formalize your company's goals and optimize your organization.
By Matthew McCreary May 5, 2021
Are you preparing to start your own business but uncertain about how to get started? A business plan ought to be one of the first steps in your entrepreneurial journey because it will organize the ideas that have been spinning around in your brain and prepare you to seek funding, partners and more.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a detailed document that outlines a company's goals and how the business, well, plans to achieve those goals over the next three or more years. It helps define expected profits and challenges, providing a road map that will help you avoid bumps in the road.
Stever Robbins writes in an Entrepreneur article titled, "Why You Must Have a Business Plan," that a business plan "is a tool for understanding how your business is put together…. Writing out your business plan forces you to review everything at once: your value proposition, marketing assumptions, operations plan, financial plan and staffing plan." But, a business plan is about more than just reviewing the past state of your business or even what your business looks like today.
Robbins writes that a well-written business plan will help you drive the future by "laying out targets in all major areas: sales, expense items, hiring positions and financing goals. Once laid out, the targets become performance goals."
The business plan can help your company attract talent and funding, because when prospects ask about your business, you already have an articulated overview to offer them. How they react can allow you to quickly understand how others see your business and pivot if necessary.
What should you do before you write your business plan?
It might sound redundant, but you actually need to plan your business plan. Business plans can be complicated, and you'll be held accountable for the goals you set. For example, if you plan to open five locations of your business within the first two years, your investors might get angry if you only manage to open two.
That's why it's essential that, before writing your business plan, you spend some time determining exactly which objectives are essential to your business. If you're struggling to come up with a list of goals on your own, Entrepreneur article "Plan Your Business Plan" offers some questions you can ask yourself to spark some inspiration.
How determined am I to see this venture succeed?
Am I willing to invest my own money and work long hours for no pay, sacrificing personal time and lifestyle, maybe for years?
What's going to happen to me if this venture doesn't work out?
If it does succeed, how many employees will this company eventually have?
What will be the business's annual revenue in a year? What about in five years?
What will be the company's market share in that amount of time?
Will the business have a niche market, or will it sell a broad spectrum of goods and services?
What are my plans for geographic expansion? Should it be local or national? Can it be global?
Am I going to be a hands-on manager, or will I delegate a large proportion of tasks to others?
If I delegate, what sorts of tasks will I share? Will it be sales, technical work or something else?
How comfortable am I taking direction from others? Can I work with partners or investors who demand input into the company's management?
Is the business going to remain independent and privately owned, or will it eventually be acquired or go public?
It's also essential to consider your financial goals. Your business might not require a massive financial commitment upfront, but it probably will if you're envisioning rapid growth. Unless you're making your product or service from scratch, you'll have to pay your suppliers before your customers can pay you, and as "Plan Your Business Plan" points out, "this cash flow conundrum is the reason so many fast-growing companies have to seek bank financing or equity sales to finance their growth. They are literally growing faster than they can afford."
How much financing will you need to start your business? What will you be willing to accept? If you're desperate for that first influx of cash, you might be tempted to accept any offer, but doing so might force you to either surrender too much control or ask investors for a number that's not quite right for either side.
These eight questions can help you determine a few financial aspects of your planning stages:
What initial investment will the business require?
How much control of the business are you willing to relinquish to investors?
When will the business turn a profit?
When can investors, including you, expect a return on investment?
What are the business's projected profits over time?
Will you be able to devote yourself full-time to the business?
What kind of salary or profit distribution can you expect to take home?
What are the chances the business will fail, and what will happen if it does?
You should also consider who, primarily, is going to be reading your business plan, and how you plan to use it. Is it a means of raising money or attracting employees? Will suppliers see it?
Lastly, you need to assess the likelihood of whether you actually have the time and resources to see your plan through. It might hurt to realize the assumptions you've made so far don't actually make a successful business, but it's best to know early on, before you make further commitments.
Related: Need a Business Plan Template? Here Is Apple's 1981 Plan for the Mac.
How to Write a Business Plan
Once you've worked out all the questions above and you know exactly what goals you have for your business plan, the next step is to actually write the darn thing. A typical business plan runs 15 to 20 pages but can be longer or shorter, depending on the complexity of the business and the needs of your venture. Regardless of whether you intend to use the business plan for self-evaluation or to seek a seven-figure investment, it should include nine key components, many of which are outlined in Entrepreneur 's introduction to business plans:
1. Title page and contents
Presentation is important, and a business plan should be presented in a binder with a cover that lists the business's name, the principals' names and other relevant information like a working address, phone number, email and web address and date. Write the information in a font that's easy to read and include it on the title page inside, too. Add in the company logo and a table of contents that follows the executive summary.
2. Executive summary
Think of the executive summary as the SparkNotes version of your business plan . It should tell the reader in as few words as possible what your business wants and why. The executive summary should address these nine things:
The business idea and why it is necessary. (What problem does it solve?)
How much will it cost, and how much financing are you seeking?
What will the return be to the investor? Over what length of time?
What is the perceived risk level?
Where does your idea fit into the marketplace?
What is the management team?
What are the product and competitive strategies?
What is your marketing plan?
What is your exit strategy?
When writing the executive summary, remember that it should be somewhere between one-half page to a full page. Anything longer, and you risk losing your reader's attention before they can dig into your business plan. Try to answer each of the questions above in two or three sentences, and you'll wind up with an executive summary that's about the right length.
Related: First Steps: Writing the Executive Summary of Your Business Plan
3. Business description
You can fill anywhere from a few paragraphs to a few pages when writing your business description, but try again to keep it short, with the understanding that more sections will follow. The business description typically starts with a short explanation of your chosen industry, including its present outlook and future possibilities. Use data and sources (with proper footnotes) to explain the markets the industry offers, along with the developments that will affect your business. That way, everyone who reads the business description, particularly investors, will see that they can trust the various information contained within your business plan.
When you pivot to speaking of your business, start with its structure. How does your business work? Is it retail, service-oriented or wholesale? Is the business new or established? Is the company a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation? Who are the principals and who are your customers? What do the distribution channels look like, and how can you support sales?
Next, break down your business's offerings. Are you selling a physical product, SaaS or a service? Explain it in a way that a reader knows what you're planning to sell and how it differentiates itself from the competition (investors call this a Unique Selling Proposition, or USP, and it's important that you find yours). Whether it's a trade secret or a patent, you should be specific about your competitive advantage and why your business is going to be profitable. If you plan to use your business plan for fundraising, you can use the business description section to explain why new investments will help make the business even more profitable.
This, like everything else, can be brief, but you can tell the reader about your business's efficiency or workflow. You can write about other key people within the business or cite industry experts' support of your idea, as well as your base of operations and reasons for starting in the first place.
4. Market strategies
Paint a picture about your market by remembering the four Ps: product, price, place and promotion.
Start this section by defining the market's size, structure and sales potential. What are the market's growth prospects? What do the demographics and trends look like right now?
Next, outline the frequency at which your product or service will be purchased by the target market and the potential annual purchase. What market share can you possibly expect to win? Try to be realistic here, and keep in mind that even a number like 25% might be a dominant share.
Next, break down your business's plan for positioning, which relates to the market niche your product or service can fill. Who is your target market, how will you reach them and what are they buying from you? Who are your competitors, and what is your USP?
The positioning statement within your business plan should be short and to the point, but make sure you answer each of those questions before you move on to, perhaps, the most difficult and important aspect of your market strategy: pricing.
In fact, settling on a price for your product or service is one of the most important decisions you have to make in the entire business plan. Pricing will directly determine essential aspects of your business, like profit margin and sales volume. It will influence all sorts of areas, too, from marketing to target consumer.
There are two primary ways to determine your price: The first is to look inward, adding up the costs of offering your product or service, and then adding in a profit margin to find your number. The second is called competitive pricing, and it involves research into how your competitors will either price their products or services now or in the future. The difficult aspect of this second pricing method is that it often sets a ceiling on pricing, which, in turn, could force you to adjust your costs.
Then, pivot the market strategies section toward your distribution process and how it relates to your competitors' channels. How, exactly, are you going to get your offerings from one place to the next? Walk the reader step by step through your process. Do you want to use the same strategy or something else that might give you an advantage?
Last, explain your promotion strategy. How are you going to communicate with your potential customers? This part should talk about not only marketing or advertising, but also packaging, public relations and sales promotions.
Related: Creating a Winning Startup Business Plan
5. Competitive analysis
The next section in your business plan should be the competitive analysis, which helps explain the differences between you and your competitors … and how you can keep it that way. If you can start with an honest evaluation of your competitors' strengths and weaknesses within the marketplace, you can also provide the reader with clear analysis about your advantage and the barriers that either already exist or can be developed to keep your business ahead of the pack. Are there weaknesses within the marketplace, and if so, how can you exploit them?
Remember to consider both your direct competition and your indirect competition, with both a short-term and long-term view.
6. Design and development plan
If you plan to sell a product, it's smart to add a design and development section to your business plan. This part should help your readers understand the background of that product. How have the production, marketing and company developed over time? What is your developmental budget?
For the sake of organization, consider these three aspects of the design and development plan:
Product development
Market development
Organizational development
Start by establishing your development goals, which should logically follow your evaluation of the market and your competition. Make these goals feasible and quantifiable, and be sure to establish timelines that allow your readers to see your vision. The goals should address both technical and marketing aspects.
Once the reader has a clear idea of your development goals, explain the procedures you'll develop to reach them. How will you allocate your resources, and who is in charge of accomplishing each goal?
The Entrepreneur guide to design and development plans offers this example on the steps of producing a recipe for a premium lager beer:
Gather ingredients.
Determine optimum malting process.
Gauge mashing temperature.
Boil wort and evaluate which hops provide the best flavor.
Determine yeast amounts and fermentation period.
Determine aging period.
Carbonate the beer.
Decide whether or not to pasteurize the beer.
Make sure to also talk about scheduling. What checkpoints will the product need to pass to reach a customer? Establish timeframes for each step of the process. Create a chart with a column for each task, how long that task will take and when the task will start and end.
Next, consider the costs of developing your product, breaking down the costs of these aspects:
General and administrative (G&A) costs
Marketing and sales
Professional services, like lawyers or accountants
Miscellaneous costs
Necessary equipment
The next section should be about the personnel you either have or plan to hire for that development. If you already have the right person in place, this part should be easy. If not, then this part of the business plan can help you create a detailed description of exactly what you need. This process can also help you formalize the hierarchy of your team's positions so that everyone knows their roles and responsibilities.
Finish the development and design section of your business plan by addressing the risks in developing the product and how you're going to address those risks. Could there be technical difficulties? Are you having trouble finding the right person to lead the development? Does your financial situation limit your ability to develop the product? Being honest about your problems and solutions can help answer some of your readers' questions before they ask them.
Related: The Essential Guide to Writing a Business Plan
7. Operations and management plan
Want to learn everything you'll ever need to know about the operations and management section of your business plan, and read a real, actual web article from 1997? Check out our guide titled, "Writing A Business Plan: Operations And Management."
Here, we'll more briefly summarize the two areas that need to be covered within your operations and management plan: the organizational structure is first, and the capital requirement for the operation are second.
The organizational structure detailed within your business plan will establish the basis for your operating expenses, which will provide essential information for the next part of the business plan: your financial statements. Investors will look closely at the financial statements, so it's important to start with a solid foundation and a realistic framework. You can start by dividing your organizational structure into these four sections:
Marketing and sales (including customer relations and service)
Production (including quality assurance)
Research and development
Administration
After you've broken down the organization's operations within your business plan, you can look at the expenses, or overhead. Divide them into fixed expenses, which typically remain constant, and variable, which will change according to the volume of business. Here are some of the examples of overhead expenses:
Maintenance and repair
Equipment leases
Advertising and promotion
Packaging and shipping
Payroll taxes and benefits
Uncollectible receivables
Professional services
Loan payments
Depreciation
Having difficulty calculating what some of those expenses might be for your business? Try using the simple formulas in "Writing A Business Plan: Operations And Management."
8. Financial factors
The last piece of the business plan that you definitely need to have covers the business's finances. Specifically, three financial statements will form the backbone of your business plan: the income statement, the cash-flow statement and balance sheet . Let's go through them one by one.
The income statement explains how the business can make money in a simple way. It draws on financial models already developed and discussed throughout the business plan (revenue, expenses, capital and cost of goods) and combines those numbers with when sales are made and when expenses are incurred. When the reader finishes going through your income statement, they should understand how much money your company makes or loses by subtracting your costs from your revenue, showing either a loss or a profit. If you like, you or a CPA can add a very short analysis at the end to emphasize some important aspects of the statement.
Second is the cash-flow statement, which explains how much cash your business needs to meet its obligations, as well as when you're going to need it and how you're going to get it. This section shows a profit or loss at the end of each month or year that rolls over to the next time period, which can create a cycle. If your business plan shows that you're consistently operating at a loss that gets bigger as time goes on, this can be a major red flag for both you and potential investors. This part of the business plan should be prepared monthly during your first year in business, quarterly in your second year and annually after that.
Our guide on cash-flow statements includes 17 items you'll need to add to your cash-flow statement.
Cash. Cash on hand in the business.
Cash sales . Income from sales paid for by cash.
Receivables. Income from collecting money owed to the business due to sales.
Other income. The liquidation of assets, interest on extended loans or income from investments are examples.
Total income. The sum of the four items above (total cash, cash sales, receivables, other income).
Material/merchandise . This will depend on the structure of your business. If you're manufacturing, this will include your raw materials. If you're in retail, count your inventory of merchandise. If you offer a service, consider which supplies are necessary.
Direct labor . What sort of labor do you need to make your product or complete your service?
Overhead . This includes both the variable expenses and fixed expenses for business operations.
Marketing/sales . All salaries, commissions and other direct costs associated with the marketing and sales departments.
Research and development . Specifically, the labor expenses required for research and development.
General and administrative expenses. Like the research and development costs, this centers on the labor for G&A functions of the business.
Taxes . This excludes payroll taxes but includes everything else.
Capital. Required capital for necessary equipment.
Loan payments. The total of all payments made to reduce any long-term debts.
Total expenses. The sum of items six through 14 (material/merchandise, direct labor, overhead, marketing/sales, research and development, general and administrative expenses, taxes, capital and loan payments).
Cash flow. Subtract total expenses from total income. This is how much cash will roll over to the next period.
Cumulative cash flow . Subtract the previous period's cash flow from your current cash flow.
Just like with the income statement, it's a good idea to briefly summarize the figures at the end. Again, consulting with a CPA is probably a good idea.
The last financial statement is the balance sheet. A balance sheet is, as our encyclopedia says, "a financial statement that lists the assets, liabilities and equity of a company at a specific point in time and is used to calculate the net worth of a business." If you've already started the business, use the balance sheet from your last reporting period. If the business plan you wrote is for a business you hope to start, do your best to project your assets and liabilities over time. If you want to earn investors, you'll also need to include a personal financial statement. Then, as with the other two sections, add a short analysis that hits the main points.
9. Supporting documents
If you have other documents that your readers need to see, like important contracts, letters of reference, a copy of your lease or legal documents, you should add them in this section.
Related: 7 Steps to a Perfectly Written Business Plan
What do I do with my business plan after I've written it?
The simplest reason to create a business plan is to help people unfamiliar with your business understand it quickly. While the most obvious use for a document like this is for financing purposes, a business plan can also help you attract talented employees — and, if you share the business plan internally, help your existing employees understand their roles.
But it's also important to do for your own edification, too. It's like the old saying goes, "The best way to learn something is to teach it." Writing down your plans, your goals and the state of your finances helps clarify the thoughts in your own mind. From there, you can more easily lead your business because you'll know whether the business is reaching the checkpoints you set out to begin with. You'll be able to foresee difficulties before they pop up and be able to pivot quickly.
That's why you should continue to update your business plan when the conditions change, either within your business (you might be entering a new period or undergoing a change in management) or within your market (like a new competitor popping up). The key is to keep your business plan ready so that you don't have to get it ready when opportunity strikes.
Entrepreneur Staff
Associate Editor, Contributed Content
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- U.S. Diners Are Feeding the $1 Trillion Restaurant Industry Like Never Before. Here's Why — and What They're Hungry for, According to Resy's CEO.
- Lock SearchGPT is About to Change How Customers Find Your Business. Are You Ready?
- AI Startups Received $2.9 Billion in Funding Last Quarter. These 3 U.S. Companies Received a Lot of It — And You've Probably Never Heard of Them.
- Lock Gen Xers Earning Up to $100,000 a Year Won't Retire Like Boomers Did. They're Embracing This Strategy Instead.
- 'We Are Not Red or Blue — We Are Golden': McDonald's Tells Employees It's Non-Political After Trump Visit
- Lock In Her Late 30s, She Pursued Another Creative Side Hustle — Then Turned It Into a Multimillion-Dollar Business
Most Popular Red Arrow
You have one month left to buy a house, according to barbara corcoran. here's why..
"If you are planning on waiting a year and seeing where interest rates go, you are out of your mind," Corcoran said.
These 3 Side Hustles Make the Most Money While Working Fewer Hours, According to a New Survey
The survey also found that having a side hustle doubled as a path to becoming more employable.
The McRib Is Back, But Only at Select McDonald's — Here's Where to Find It
This scarcity is nothing new. In 2022, McDonald's announced a "Farewell Tour" for the McRib, suggesting that it might be the last time customers could get their hands on it.
This New Restaurant Is Banking on One Dish — Because It's the Only Entrée on the Menu
The new hotspot is gaining buzz on social media for its innovative yet super simple concept.
Adobe Says Creators 'Need to Embrace' AI — It's Now Built Into Photoshop and Can't Be Turned Off
Adobe announced the new AI tools last week.
Stop Chasing Algorithms — Here's How Creators Can Take Control of Their Content and Monetize on Their Own Terms
Social media platforms promise creators visibility, but the real challenge lies in relying on algorithms for income.
Successfully copied link
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Simple Business Plan
By Joe Weller | October 11, 2021
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
A business plan is the cornerstone of any successful company, regardless of size or industry. This step-by-step guide provides information on writing a business plan for organizations at any stage, complete with free templates and expert advice.
Included on this page, you’ll find a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan and a chart to identify which type of business plan you should write . Plus, find information on how a business plan can help grow a business and expert tips on writing one .
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that communicates a company’s goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered.
A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals. That said, a typical business plan will include the following benchmarks:
- Product goals and deadlines for each month
- Monthly financials for the first two years
- Profit and loss statements for the first three to five years
- Balance sheet projections for the first three to five years
Startups, entrepreneurs, and small businesses all create business plans to use as a guide as their new company progresses. Larger organizations may also create (and update) a business plan to keep high-level goals, financials, and timelines in check.
While you certainly need to have a formalized outline of your business’s goals and finances, creating a business plan can also help you determine a company’s viability, its profitability (including when it will first turn a profit), and how much money you will need from investors. In turn, a business plan has functional value as well: Not only does outlining goals help keep you accountable on a timeline, it can also attract investors in and of itself and, therefore, act as an effective strategy for growth.
For more information, visit our comprehensive guide to writing a strategic plan or download free strategic plan templates . This page focuses on for-profit business plans, but you can read our article with nonprofit business plan templates .
Business Plan Steps
The specific information in your business plan will vary, depending on the needs and goals of your venture, but a typical plan includes the following ordered elements:
- Executive summary
- Description of business
- Market analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Description of organizational management
- Description of product or services
- Marketing plan
- Sales strategy
- Funding details (or request for funding)
- Financial projections
If your plan is particularly long or complicated, consider adding a table of contents or an appendix for reference. For an in-depth description of each step listed above, read “ How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step ” below.
Broadly speaking, your audience includes anyone with a vested interest in your organization. They can include potential and existing investors, as well as customers, internal team members, suppliers, and vendors.
Do I Need a Simple or Detailed Plan?
Your business’s stage and intended audience dictates the level of detail your plan needs. Corporations require a thorough business plan — up to 100 pages. Small businesses or startups should have a concise plan focusing on financials and strategy.
How to Choose the Right Plan for Your Business
In order to identify which type of business plan you need to create, ask: “What do we want the plan to do?” Identify function first, and form will follow.
Use the chart below as a guide for what type of business plan to create:
Is the Order of Your Business Plan Important?
There is no set order for a business plan, with the exception of the executive summary, which should always come first. Beyond that, simply ensure that you organize the plan in a way that makes sense and flows naturally.
The Difference Between Traditional and Lean Business Plans
A traditional business plan follows the standard structure — because these plans encourage detail, they tend to require more work upfront and can run dozens of pages. A Lean business plan is less common and focuses on summarizing critical points for each section. These plans take much less work and typically run one page in length.
In general, you should use a traditional model for a legacy company, a large company, or any business that does not adhere to Lean (or another Agile method ). Use Lean if you expect the company to pivot quickly or if you already employ a Lean strategy with other business operations. Additionally, a Lean business plan can suffice if the document is for internal use only. Stick to a traditional version for investors, as they may be more sensitive to sudden changes or a high degree of built-in flexibility in the plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step
Writing a strong business plan requires research and attention to detail for each section. Below, you’ll find a 10-step guide to researching and defining each element in the plan.
Step 1: Executive Summary
The executive summary will always be the first section of your business plan. The goal is to answer the following questions:
- What is the vision and mission of the company?
- What are the company’s short- and long-term goals?
See our roundup of executive summary examples and templates for samples. Read our executive summary guide to learn more about writing one.
Step 2: Description of Business
The goal of this section is to define the realm, scope, and intent of your venture. To do so, answer the following questions as clearly and concisely as possible:
- What business are we in?
- What does our business do?
Step 3: Market Analysis
In this section, provide evidence that you have surveyed and understand the current marketplace, and that your product or service satisfies a niche in the market. To do so, answer these questions:
- Who is our customer?
- What does that customer value?
Step 4: Competitive Analysis
In many cases, a business plan proposes not a brand-new (or even market-disrupting) venture, but a more competitive version — whether via features, pricing, integrations, etc. — than what is currently available. In this section, answer the following questions to show that your product or service stands to outpace competitors:
- Who is the competition?
- What do they do best?
- What is our unique value proposition?
Step 5: Description of Organizational Management
In this section, write an overview of the team members and other key personnel who are integral to success. List roles and responsibilities, and if possible, note the hierarchy or team structure.
Step 6: Description of Products or Services
In this section, clearly define your product or service, as well as all the effort and resources that go into producing it. The strength of your product largely defines the success of your business, so it’s imperative that you take time to test and refine the product before launching into marketing, sales, or funding details.
Questions to answer in this section are as follows:
- What is the product or service?
- How do we produce it, and what resources are necessary for production?
Step 7: Marketing Plan
In this section, define the marketing strategy for your product or service. This doesn’t need to be as fleshed out as a full marketing plan , but it should answer basic questions, such as the following:
- Who is the target market (if different from existing customer base)?
- What channels will you use to reach your target market?
- What resources does your marketing strategy require, and do you have access to them?
- If possible, do you have a rough estimate of timeline and budget?
- How will you measure success?
Step 8: Sales Plan
Write an overview of the sales strategy, including the priorities of each cycle, steps to achieve these goals, and metrics for success. For the purposes of a business plan, this section does not need to be a comprehensive, in-depth sales plan , but can simply outline the high-level objectives and strategies of your sales efforts.
Start by answering the following questions:
- What is the sales strategy?
- What are the tools and tactics you will use to achieve your goals?
- What are the potential obstacles, and how will you overcome them?
- What is the timeline for sales and turning a profit?
- What are the metrics of success?
Step 9: Funding Details (or Request for Funding)
This section is one of the most critical parts of your business plan, particularly if you are sharing it with investors. You do not need to provide a full financial plan, but you should be able to answer the following questions:
- How much capital do you currently have? How much capital do you need?
- How will you grow the team (onboarding, team structure, training and development)?
- What are your physical needs and constraints (space, equipment, etc.)?
Step 10: Financial Projections
Apart from the fundraising analysis, investors like to see thought-out financial projections for the future. As discussed earlier, depending on the scope and stage of your business, this could be anywhere from one to five years.
While these projections won’t be exact — and will need to be somewhat flexible — you should be able to gauge the following:
- How and when will the company first generate a profit?
- How will the company maintain profit thereafter?
Business Plan Template

Download Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Smartsheet
This basic business plan template has space for all the traditional elements: an executive summary, product or service details, target audience, marketing and sales strategies, etc. In the finances sections, input your baseline numbers, and the template will automatically calculate projections for sales forecasting, financial statements, and more.
For templates tailored to more specific needs, visit this business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy.
If you are looking for a particular template by file type, visit our pages dedicated exclusively to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates.
How to Write a Simple Business Plan
A simple business plan is a streamlined, lightweight version of the large, traditional model. As opposed to a one-page business plan , which communicates high-level information for quick overviews (such as a stakeholder presentation), a simple business plan can exceed one page.
Below are the steps for creating a generic simple business plan, which are reflected in the template below .
- Write the Executive Summary This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what’s in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company.
- Add a Company Overview Document the larger company mission and vision.
- Provide the Problem and Solution In straightforward terms, define the problem you are attempting to solve with your product or service and how your company will attempt to do it. Think of this section as the gap in the market you are attempting to close.
- Identify the Target Market Who is your company (and its products or services) attempting to reach? If possible, briefly define your buyer personas .
- Write About the Competition In this section, demonstrate your knowledge of the market by listing the current competitors and outlining your competitive advantage.
- Describe Your Product or Service Offerings Get down to brass tacks and define your product or service. What exactly are you selling?
- Outline Your Marketing Tactics Without getting into too much detail, describe your planned marketing initiatives.
- Add a Timeline and the Metrics You Will Use to Measure Success Offer a rough timeline, including milestones and key performance indicators (KPIs) that you will use to measure your progress.
- Include Your Financial Forecasts Write an overview of your financial plan that demonstrates you have done your research and adequate modeling. You can also list key assumptions that go into this forecasting.
- Identify Your Financing Needs This section is where you will make your funding request. Based on everything in the business plan, list your proposed sources of funding, as well as how you will use it.
Simple Business Plan Template

Download Simple Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | Smartsheet
Use this simple business plan template to outline each aspect of your organization, including information about financing and opportunities to seek out further funding. This template is completely customizable to fit the needs of any business, whether it’s a startup or large company.
Read our article offering free simple business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options. You can also explore our collection of one page business templates .
How to Write a Business Plan for a Lean Startup
A Lean startup business plan is a more Agile approach to a traditional version. The plan focuses more on activities, processes, and relationships (and maintains flexibility in all aspects), rather than on concrete deliverables and timelines.
While there is some overlap between a traditional and a Lean business plan, you can write a Lean plan by following the steps below:
- Add Your Value Proposition Take a streamlined approach to describing your product or service. What is the unique value your startup aims to deliver to customers? Make sure the team is aligned on the core offering and that you can state it in clear, simple language.
- List Your Key Partners List any other businesses you will work with to realize your vision, including external vendors, suppliers, and partners. This section demonstrates that you have thoughtfully considered the resources you can provide internally, identified areas for external assistance, and conducted research to find alternatives.
- Note the Key Activities Describe the key activities of your business, including sourcing, production, marketing, distribution channels, and customer relationships.
- Include Your Key Resources List the critical resources — including personnel, equipment, space, and intellectual property — that will enable you to deliver your unique value.
- Identify Your Customer Relationships and Channels In this section, document how you will reach and build relationships with customers. Provide a high-level map of the customer experience from start to finish, including the spaces in which you will interact with the customer (online, retail, etc.).
- Detail Your Marketing Channels Describe the marketing methods and communication platforms you will use to identify and nurture your relationships with customers. These could be email, advertising, social media, etc.
- Explain the Cost Structure This section is especially necessary in the early stages of a business. Will you prioritize maximizing value or keeping costs low? List the foundational startup costs and how you will move toward profit over time.
- Share Your Revenue Streams Over time, how will the company make money? Include both the direct product or service purchase, as well as secondary sources of revenue, such as subscriptions, selling advertising space, fundraising, etc.
Lean Business Plan Template for Startups

Download Lean Business Plan Template for Startups
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Startup leaders can use this Lean business plan template to relay the most critical information from a traditional plan. You’ll find all the sections listed above, including spaces for industry and product overviews, cost structure and sources of revenue, and key metrics, and a timeline. The template is completely customizable, so you can edit it to suit the objectives of your Lean startups.
See our wide variety of startup business plan templates for more options.
How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
A business plan for a loan, often called a loan proposal , includes many of the same aspects of a traditional business plan, as well as additional financial documents, such as a credit history, a loan request, and a loan repayment plan.
In addition, you may be asked to include personal and business financial statements, a form of collateral, and equity investment information.
Download free financial templates to support your business plan.
Tips for Writing a Business Plan
Outside of including all the key details in your business plan, you have several options to elevate the document for the highest chance of winning funding and other resources. Follow these tips from experts:.
- Keep It Simple: Avner Brodsky , the Co-Founder and CEO of Lezgo Limited, an online marketing company, uses the acronym KISS (keep it short and simple) as a variation on this idea. “The business plan is not a college thesis,” he says. “Just focus on providing the essential information.”
- Do Adequate Research: Michael Dean, the Co-Founder of Pool Research , encourages business leaders to “invest time in research, both internal and external (market, finance, legal etc.). Avoid being overly ambitious or presumptive. Instead, keep everything objective, balanced, and accurate.” Your plan needs to stand on its own, and you must have the data to back up any claims or forecasting you make. As Brodsky explains, “Your business needs to be grounded on the realities of the market in your chosen location. Get the most recent data from authoritative sources so that the figures are vetted by experts and are reliable.”
- Set Clear Goals: Make sure your plan includes clear, time-based goals. “Short-term goals are key to momentum growth and are especially important to identify for new businesses,” advises Dean.
- Know (and Address) Your Weaknesses: “This awareness sets you up to overcome your weak points much quicker than waiting for them to arise,” shares Dean. Brodsky recommends performing a full SWOT analysis to identify your weaknesses, too. “Your business will fare better with self-knowledge, which will help you better define the mission of your business, as well as the strategies you will choose to achieve your objectives,” he adds.
- Seek Peer or Mentor Review: “Ask for feedback on your drafts and for areas to improve,” advises Brodsky. “When your mind is filled with dreams for your business, sometimes it is an outsider who can tell you what you’re missing and will save your business from being a product of whimsy.”
Outside of these more practical tips, the language you use is also important and may make or break your business plan.
Shaun Heng, VP of Operations at Coin Market Cap , gives the following advice on the writing, “Your business plan is your sales pitch to an investor. And as with any sales pitch, you need to strike the right tone and hit a few emotional chords. This is a little tricky in a business plan, because you also need to be formal and matter-of-fact. But you can still impress by weaving in descriptive language and saying things in a more elegant way.
“A great way to do this is by expanding your vocabulary, avoiding word repetition, and using business language. Instead of saying that something ‘will bring in as many customers as possible,’ try saying ‘will garner the largest possible market segment.’ Elevate your writing with precise descriptive words and you'll impress even the busiest investor.”
Additionally, Dean recommends that you “stay consistent and concise by keeping your tone and style steady throughout, and your language clear and precise. Include only what is 100 percent necessary.”
Resources for Writing a Business Plan
While a template provides a great outline of what to include in a business plan, a live document or more robust program can provide additional functionality, visibility, and real-time updates. The U.S. Small Business Association also curates resources for writing a business plan.
Additionally, you can use business plan software to house data, attach documentation, and share information with stakeholders. Popular options include LivePlan, Enloop, BizPlanner, PlanGuru, and iPlanner.
How a Business Plan Helps to Grow Your Business
A business plan — both the exercise of creating one and the document — can grow your business by helping you to refine your product, target audience, sales plan, identify opportunities, secure funding, and build new partnerships.
Outside of these immediate returns, writing a business plan is a useful exercise in that it forces you to research the market, which prompts you to forge your unique value proposition and identify ways to beat the competition. Doing so will also help you build (and keep you accountable to) attainable financial and product milestones. And down the line, it will serve as a welcome guide as hurdles inevitably arise.
Streamline Your Business Planning Activities with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Read our simple guide to learn how to write a business plan quickly and easily. A solid business plan is essential for any new business.
For entrepreneurs, a business plan serves as a roadmap that outlines a company’s goals, strategies, and operational approach. It’s more than just a formality; having a well …
Learn how to use a business plan to launch, grow, and fund your business along with a few additional use cases. Read now.
Here's how to write a business plan that will formalize your company's goals and optimize your organization.
A business plan — both the exercise of creating one and the document — can grow your business by helping you to refine your product, target audience, sales plan, identify opportunities, secure funding, and build new …