How Much Homework Is Enough? Depends Who You Ask

- Share article
Editor’s note: This is an adapted excerpt from You, Your Child, and School: Navigate Your Way to the Best Education ( Viking)—the latest book by author and speaker Sir Ken Robinson (co-authored with Lou Aronica), published in March. For years, Robinson has been known for his radical work on rekindling creativity and passion in schools, including three bestselling books (also with Aronica) on the topic. His TED Talk “Do Schools Kill Creativity?” holds the record for the most-viewed TED talk of all time, with more than 50 million views. While Robinson’s latest book is geared toward parents, it also offers educators a window into the kinds of education concerns parents have for their children, including on the quality and quantity of homework.
The amount of homework young people are given varies a lot from school to school and from grade to grade. In some schools and grades, children have no homework at all. In others, they may have 18 hours or more of homework every week. In the United States, the accepted guideline, which is supported by both the National Education Association and the National Parent Teacher Association, is the 10-minute rule: Children should have no more than 10 minutes of homework each day for each grade reached. In 1st grade, children should have 10 minutes of daily homework; in 2nd grade, 20 minutes; and so on to the 12th grade, when on average they should have 120 minutes of homework each day, which is about 10 hours a week. It doesn’t always work out that way.
In 2013, the University of Phoenix College of Education commissioned a survey of how much homework teachers typically give their students. From kindergarten to 5th grade, it was just under three hours per week; from 6th to 8th grade, it was 3.2 hours; and from 9th to 12th grade, it was 3.5 hours.
There are two points to note. First, these are the amounts given by individual teachers. To estimate the total time children are expected to spend on homework, you need to multiply these hours by the number of teachers they work with. High school students who work with five teachers in different curriculum areas may find themselves with 17.5 hours or more of homework a week, which is the equivalent of a part-time job. The other factor is that these are teachers’ estimates of the time that homework should take. The time that individual children spend on it will be more or less than that, according to their abilities and interests. One child may casually dash off a piece of homework in half the time that another will spend laboring through in a cold sweat.
Do students have more homework these days than previous generations? Given all the variables, it’s difficult to say. Some studies suggest they do. In 2007, a study from the National Center for Education Statistics found that, on average, high school students spent around seven hours a week on homework. A similar study in 1994 put the average at less than five hours a week. Mind you, I [Robinson] was in high school in England in the 1960s and spent a lot more time than that—though maybe that was to do with my own ability. One way of judging this is to look at how much homework your own children are given and compare it to what you had at the same age.
Many parents find it difficult to help their children with subjects they’ve not studied themselves for a long time, if at all.
There’s also much debate about the value of homework. Supporters argue that it benefits children, teachers, and parents in several ways:
- Children learn to deepen their understanding of specific content, to cover content at their own pace, to become more independent learners, to develop problem-solving and time-management skills, and to relate what they learn in school to outside activities.
- Teachers can see how well their students understand the lessons; evaluate students’ individual progress, strengths, and weaknesses; and cover more content in class.
- Parents can engage practically in their children’s education, see firsthand what their children are being taught in school, and understand more clearly how they’re getting on—what they find easy and what they struggle with in school.
Want to know more about Sir Ken Robinson? Check out our Q&A with him.
Q&A With Sir Ken Robinson
Ashley Norris is assistant dean at the University of Phoenix College of Education. Commenting on her university’s survey, she says, “Homework helps build confidence, responsibility, and problem-solving skills that can set students up for success in high school, college, and in the workplace.”
That may be so, but many parents find it difficult to help their children with subjects they’ve not studied themselves for a long time, if at all. Families have busy lives, and it can be hard for parents to find time to help with homework alongside everything else they have to cope with. Norris is convinced it’s worth the effort, especially, she says, because in many schools, the nature of homework is changing. One influence is the growing popularity of the so-called flipped classroom.
In the stereotypical classroom, the teacher spends time in class presenting material to the students. Their homework consists of assignments based on that material. In the flipped classroom, the teacher provides the students with presentational materials—videos, slides, lecture notes—which the students review at home and then bring questions and ideas to school where they work on them collaboratively with the teacher and other students. As Norris notes, in this approach, homework extends the boundaries of the classroom and reframes how time in school can be used more productively, allowing students to “collaborate on learning, learn from each other, maybe critique [each other’s work], and share those experiences.”
Even so, many parents and educators are increasingly concerned that homework, in whatever form it takes, is a bridge too far in the pressured lives of children and their families. It takes away from essential time for their children to relax and unwind after school, to play, to be young, and to be together as a family. On top of that, the benefits of homework are often asserted, but they’re not consistent, and they’re certainly not guaranteed.

Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

- Skip to Nav
- Skip to Main
- Skip to Footer

- Saved Articles
- Newsletters

How Important Is Homework, And How Much Should Parents Help?
Please try again

A version of this post was originally published by Parenting Translator. Sign up for the newsletter and follow Parenting Translator on Instagram .
In recent years, homework has become a very hot topic . Many parents and educators have raised concerns about homework and questioned how effective it is in enhancing students’ learning. There are also concerns that students may be getting too much homework, which ultimately interferes with quality family time and opportunities for physical activity and play . Research suggests that these concerns may be valid. For example, one study reported that elementary school students, on average, are assigned three times the recommended amount of homework.
So what does the research say? What are the potential risks and benefits of homework, and how much is too much?
Academic benefits
First, research finds that homework is associated with higher scores on academic standardized tests for middle and high school students, but not elementary school students . A recent experimental study in Romania found some benefit for a small amount of writing homework in elementary students but not math homework. Yet, interestingly, this positive impact only occurred when students were given a moderate amount of homework (about 20 minutes on average).
Non-academic benefits
The goal of homework is not simply to improve academic skills. Research finds that homework may have some non-academic benefits, such as building responsibility , time management skills, and task persistence . Homework may also increase parents’ involvement in their children’s schooling. Yet, too much homework may also have some negative impacts on non-academic skills by reducing opportunities for free play , which is essential for the development of language, cognitive, self-regulation and social-emotional skills. Homework may also interfere with physical activity and too much homework is associated with an increased risk for being overweight . As with the research on academic benefits, this research also suggests that homework may be beneficial when it is minimal.
What is the “right” amount of homework?
Research suggests that homework should not exceed 1.5 to 2.5 hours per night for high school students and no more than one hour per night for middle school students. Homework for elementary school students should be minimal and assigned with the aim of building self-regulation and independent work skills. Any more than this and homework may no longer have a positive impact.
The National Education Association recommends 10 minutes of homework per grade and there is also some experimental evidence that backs this up.
Overall translation
Research finds that homework provides some academic benefit for middle and high school students but is less beneficial for elementary school students. Research suggests that homework should be none or minimal for elementary students, less than one hour per night for middle school students, and less than 1.5 to 2.5 hours for high school students.
What can parents do?
Research finds that parental help with homework is beneficial but that it matters more how the parent is helping rather than how often the parent is helping.
So how should parents help with homework, according to the research?
- Focus on providing general monitoring, guidance and encouragement, but allow children to generate answers on their own and complete their homework as independently as possible . Specifically, be present while they are completing homework to help them to understand the directions, be available to answer simple questions, or praise and acknowledge their effort and hard work. Research shows that allowing children more autonomy in completing homework may benefit their academic skills.
- Only provide help when your child asks for it and step away whenever possible. Research finds that too much parental involvement or intrusive and controlling involvement with homework is associated with worse academic performance .
- Help your children to create structure and develop some routines that help your child to independently complete their homework . Have a regular time and place for homework that is free from distractions and has all of the materials they need within arm’s reach. Help your child to create a checklist for homework tasks. Create rules for homework with your child. Help children to develop strategies for increasing their own self-motivation. For example, developing their own reward system or creating a homework schedule with breaks for fun activities. Research finds that providing this type of structure and responsiveness is related to improved academic skills.
- Set specific rules around homework. Research finds an association between parents setting rules around homework and academic performance.
- Help your child to view homework as an opportunity to learn and improve skills. Parents who view homework as a learning opportunity (that is, a “mastery orientation”) rather than something that they must get “right” or complete successfully to obtain a higher grade (that is, a “performance orientation”) are more likely to have children with the same attitudes.
- Encourage your child to persist in challenging assignments and emphasize difficult assignments as opportunities to grow . Research finds that this attitude is associated with student success. Research also indicates that more challenging homework is associated with enhanced academic performance.
- Stay calm and positive during homework. Research shows that mothers showing positive emotions while helping with homework may improve children’s motivation in homework.
- Praise your child’s hard work and effort during homework. This type of praise is likely to increase motivation. In addition, research finds that putting more effort into homework may be associated with enhanced development of conscientiousness in children.
- Communicate with your child and the teacher about any problems your child has with homework and the teacher’s learning goals. Research finds that open communication about homework is associated with increased academic performance.
Cara Goodwin, PhD, is a licensed psychologist, a mother of three and the founder of Parenting Translator , a nonprofit newsletter that turns scientific research into information that is accurate, relevant and useful for parents.

Is homework a necessary evil?
After decades of debate, researchers are still sorting out the truth about homework’s pros and cons. One point they can agree on: Quality assignments matter.
By Kirsten Weir
March 2016, Vol 47, No. 3
Print version: page 36

- Schools and Classrooms
Homework battles have raged for decades. For as long as kids have been whining about doing their homework, parents and education reformers have complained that homework's benefits are dubious. Meanwhile many teachers argue that take-home lessons are key to helping students learn. Now, as schools are shifting to the new (and hotly debated) Common Core curriculum standards, educators, administrators and researchers are turning a fresh eye toward the question of homework's value.
But when it comes to deciphering the research literature on the subject, homework is anything but an open book.
The 10-minute rule
In many ways, homework seems like common sense. Spend more time practicing multiplication or studying Spanish vocabulary and you should get better at math or Spanish. But it may not be that simple.
Homework can indeed produce academic benefits, such as increased understanding and retention of the material, says Duke University social psychologist Harris Cooper, PhD, one of the nation's leading homework researchers. But not all students benefit. In a review of studies published from 1987 to 2003, Cooper and his colleagues found that homework was linked to better test scores in high school and, to a lesser degree, in middle school. Yet they found only faint evidence that homework provided academic benefit in elementary school ( Review of Educational Research , 2006).
Then again, test scores aren't everything. Homework proponents also cite the nonacademic advantages it might confer, such as the development of personal responsibility, good study habits and time-management skills. But as to hard evidence of those benefits, "the jury is still out," says Mollie Galloway, PhD, associate professor of educational leadership at Lewis & Clark College in Portland, Oregon. "I think there's a focus on assigning homework because [teachers] think it has these positive outcomes for study skills and habits. But we don't know for sure that's the case."
Even when homework is helpful, there can be too much of a good thing. "There is a limit to how much kids can benefit from home study," Cooper says. He agrees with an oft-cited rule of thumb that students should do no more than 10 minutes a night per grade level — from about 10 minutes in first grade up to a maximum of about two hours in high school. Both the National Education Association and National Parent Teacher Association support that limit.
Beyond that point, kids don't absorb much useful information, Cooper says. In fact, too much homework can do more harm than good. Researchers have cited drawbacks, including boredom and burnout toward academic material, less time for family and extracurricular activities, lack of sleep and increased stress.
In a recent study of Spanish students, Rubén Fernández-Alonso, PhD, and colleagues found that students who were regularly assigned math and science homework scored higher on standardized tests. But when kids reported having more than 90 to 100 minutes of homework per day, scores declined ( Journal of Educational Psychology , 2015).
"At all grade levels, doing other things after school can have positive effects," Cooper says. "To the extent that homework denies access to other leisure and community activities, it's not serving the child's best interest."
Children of all ages need down time in order to thrive, says Denise Pope, PhD, a professor of education at Stanford University and a co-founder of Challenge Success, a program that partners with secondary schools to implement policies that improve students' academic engagement and well-being.
"Little kids and big kids need unstructured time for play each day," she says. Certainly, time for physical activity is important for kids' health and well-being. But even time spent on social media can help give busy kids' brains a break, she says.
All over the map
But are teachers sticking to the 10-minute rule? Studies attempting to quantify time spent on homework are all over the map, in part because of wide variations in methodology, Pope says.
A 2014 report by the Brookings Institution examined the question of homework, comparing data from a variety of sources. That report cited findings from a 2012 survey of first-year college students in which 38.4 percent reported spending six hours or more per week on homework during their last year of high school. That was down from 49.5 percent in 1986 ( The Brown Center Report on American Education , 2014).
The Brookings report also explored survey data from the National Assessment of Educational Progress, which asked 9-, 13- and 17-year-old students how much homework they'd done the previous night. They found that between 1984 and 2012, there was a slight increase in homework for 9-year-olds, but homework amounts for 13- and 17-year-olds stayed roughly the same, or even decreased slightly.
Yet other evidence suggests that some kids might be taking home much more work than they can handle. Robert Pressman, PhD, and colleagues recently investigated the 10-minute rule among more than 1,100 students, and found that elementary-school kids were receiving up to three times as much homework as recommended. As homework load increased, so did family stress, the researchers found ( American Journal of Family Therapy , 2015).
Many high school students also seem to be exceeding the recommended amounts of homework. Pope and Galloway recently surveyed more than 4,300 students from 10 high-achieving high schools. Students reported bringing home an average of just over three hours of homework nightly ( Journal of Experiential Education , 2013).
On the positive side, students who spent more time on homework in that study did report being more behaviorally engaged in school — for instance, giving more effort and paying more attention in class, Galloway says. But they were not more invested in the homework itself. They also reported greater academic stress and less time to balance family, friends and extracurricular activities. They experienced more physical health problems as well, such as headaches, stomach troubles and sleep deprivation. "Three hours per night is too much," Galloway says.
In the high-achieving schools Pope and Galloway studied, more than 90 percent of the students go on to college. There's often intense pressure to succeed academically, from both parents and peers. On top of that, kids in these communities are often overloaded with extracurricular activities, including sports and clubs. "They're very busy," Pope says. "Some kids have up to 40 hours a week — a full-time job's worth — of extracurricular activities." And homework is yet one more commitment on top of all the others.
"Homework has perennially acted as a source of stress for students, so that piece of it is not new," Galloway says. "But especially in upper-middle-class communities, where the focus is on getting ahead, I think the pressure on students has been ratcheted up."
Yet homework can be a problem at the other end of the socioeconomic spectrum as well. Kids from wealthier homes are more likely to have resources such as computers, Internet connections, dedicated areas to do schoolwork and parents who tend to be more educated and more available to help them with tricky assignments. Kids from disadvantaged homes are more likely to work at afterschool jobs, or to be home without supervision in the evenings while their parents work multiple jobs, says Lea Theodore, PhD, a professor of school psychology at the College of William and Mary in Williamsburg, Virginia. They are less likely to have computers or a quiet place to do homework in peace.
"Homework can highlight those inequities," she says.
Quantity vs. quality
One point researchers agree on is that for all students, homework quality matters. But too many kids are feeling a lack of engagement with their take-home assignments, many experts say. In Pope and Galloway's research, only 20 percent to 30 percent of students said they felt their homework was useful or meaningful.
"Students are assigned a lot of busywork. They're naming it as a primary stressor, but they don't feel it's supporting their learning," Galloway says.
"Homework that's busywork is not good for anyone," Cooper agrees. Still, he says, different subjects call for different kinds of assignments. "Things like vocabulary and spelling are learned through practice. Other kinds of courses require more integration of material and drawing on different skills."
But critics say those skills can be developed with many fewer hours of homework each week. Why assign 50 math problems, Pope asks, when 10 would be just as constructive? One Advanced Placement biology teacher she worked with through Challenge Success experimented with cutting his homework assignments by a third, and then by half. "Test scores didn't go down," she says. "You can have a rigorous course and not have a crazy homework load."
Still, changing the culture of homework won't be easy. Teachers-to-be get little instruction in homework during their training, Pope says. And despite some vocal parents arguing that kids bring home too much homework, many others get nervous if they think their child doesn't have enough. "Teachers feel pressured to give homework because parents expect it to come home," says Galloway. "When it doesn't, there's this idea that the school might not be doing its job."
Galloway argues teachers and school administrators need to set clear goals when it comes to homework — and parents and students should be in on the discussion, too. "It should be a broader conversation within the community, asking what's the purpose of homework? Why are we giving it? Who is it serving? Who is it not serving?"
Until schools and communities agree to take a hard look at those questions, those backpacks full of take-home assignments will probably keep stirring up more feelings than facts.
Further reading
- Cooper, H., Robinson, J. C., & Patall, E. A. (2006). Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research, 1987-2003. Review of Educational Research, 76 (1), 1–62. doi: 10.3102/00346543076001001
- Galloway, M., Connor, J., & Pope, D. (2013). Nonacademic effects of homework in privileged, high-performing high schools. The Journal of Experimental Education, 81 (4), 490–510. doi: 10.1080/00220973.2012.745469
- Pope, D., Brown, M., & Miles, S. (2015). Overloaded and underprepared: Strategies for stronger schools and healthy, successful kids . San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
Letters to the Editor
- Send us a letter
Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?
A conversation with a Wheelock researcher, a BU student, and a fourth-grade teacher

“Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives,” says Wheelock’s Janine Bempechat. “It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.” Photo by iStock/Glenn Cook Photography
Do your homework.
If only it were that simple.
Educators have debated the merits of homework since the late 19th century. In recent years, amid concerns of some parents and teachers that children are being stressed out by too much homework, things have only gotten more fraught.
“Homework is complicated,” says developmental psychologist Janine Bempechat, a Wheelock College of Education & Human Development clinical professor. The author of the essay “ The Case for (Quality) Homework—Why It Improves Learning and How Parents Can Help ” in the winter 2019 issue of Education Next , Bempechat has studied how the debate about homework is influencing teacher preparation, parent and student beliefs about learning, and school policies.
She worries especially about socioeconomically disadvantaged students from low-performing schools who, according to research by Bempechat and others, get little or no homework.
BU Today sat down with Bempechat and Erin Bruce (Wheelock’17,’18), a new fourth-grade teacher at a suburban Boston school, and future teacher freshman Emma Ardizzone (Wheelock) to talk about what quality homework looks like, how it can help children learn, and how schools can equip teachers to design it, evaluate it, and facilitate parents’ role in it.
BU Today: Parents and educators who are against homework in elementary school say there is no research definitively linking it to academic performance for kids in the early grades. You’ve said that they’re missing the point.
Bempechat : I think teachers assign homework in elementary school as a way to help kids develop skills they’ll need when they’re older—to begin to instill a sense of responsibility and to learn planning and organizational skills. That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success. If we greatly reduce or eliminate homework in elementary school, we deprive kids and parents of opportunities to instill these important learning habits and skills.
We do know that beginning in late middle school, and continuing through high school, there is a strong and positive correlation between homework completion and academic success.
That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success.
You talk about the importance of quality homework. What is that?
Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives. It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.

What are your concerns about homework and low-income children?
The argument that some people make—that homework “punishes the poor” because lower-income parents may not be as well-equipped as affluent parents to help their children with homework—is very troubling to me. There are no parents who don’t care about their children’s learning. Parents don’t actually have to help with homework completion in order for kids to do well. They can help in other ways—by helping children organize a study space, providing snacks, being there as a support, helping children work in groups with siblings or friends.
Isn’t the discussion about getting rid of homework happening mostly in affluent communities?
Yes, and the stories we hear of kids being stressed out from too much homework—four or five hours of homework a night—are real. That’s problematic for physical and mental health and overall well-being. But the research shows that higher-income students get a lot more homework than lower-income kids.
Teachers may not have as high expectations for lower-income children. Schools should bear responsibility for providing supports for kids to be able to get their homework done—after-school clubs, community support, peer group support. It does kids a disservice when our expectations are lower for them.
The conversation around homework is to some extent a social class and social justice issue. If we eliminate homework for all children because affluent children have too much, we’re really doing a disservice to low-income children. They need the challenge, and every student can rise to the challenge with enough supports in place.
What did you learn by studying how education schools are preparing future teachers to handle homework?
My colleague, Margarita Jimenez-Silva, at the University of California, Davis, School of Education, and I interviewed faculty members at education schools, as well as supervising teachers, to find out how students are being prepared. And it seemed that they weren’t. There didn’t seem to be any readings on the research, or conversations on what high-quality homework is and how to design it.
Erin, what kind of training did you get in handling homework?
Bruce : I had phenomenal professors at Wheelock, but homework just didn’t come up. I did lots of student teaching. I’ve been in classrooms where the teachers didn’t assign any homework, and I’ve been in rooms where they assigned hours of homework a night. But I never even considered homework as something that was my decision. I just thought it was something I’d pull out of a book and it’d be done.
I started giving homework on the first night of school this year. My first assignment was to go home and draw a picture of the room where you do your homework. I want to know if it’s at a table and if there are chairs around it and if mom’s cooking dinner while you’re doing homework.
The second night I asked them to talk to a grown-up about how are you going to be able to get your homework done during the week. The kids really enjoyed it. There’s a running joke that I’m teaching life skills.
Friday nights, I read all my kids’ responses to me on their homework from the week and it’s wonderful. They pour their hearts out. It’s like we’re having a conversation on my couch Friday night.
It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Bempechat : I can’t imagine that most new teachers would have the intuition Erin had in designing homework the way she did.
Ardizzone : Conversations with kids about homework, feeling you’re being listened to—that’s such a big part of wanting to do homework….I grew up in Westchester County. It was a pretty demanding school district. My junior year English teacher—I loved her—she would give us feedback, have meetings with all of us. She’d say, “If you have any questions, if you have anything you want to talk about, you can talk to me, here are my office hours.” It felt like she actually cared.
Bempechat : It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Ardizzone : But can’t it lead to parents being overbearing and too involved in their children’s lives as students?
Bempechat : There’s good help and there’s bad help. The bad help is what you’re describing—when parents hover inappropriately, when they micromanage, when they see their children confused and struggling and tell them what to do.
Good help is when parents recognize there’s a struggle going on and instead ask informative questions: “Where do you think you went wrong?” They give hints, or pointers, rather than saying, “You missed this,” or “You didn’t read that.”
Bruce : I hope something comes of this. I hope BU or Wheelock can think of some way to make this a more pressing issue. As a first-year teacher, it was not something I even thought about on the first day of school—until a kid raised his hand and said, “Do we have homework?” It would have been wonderful if I’d had a plan from day one.
Explore Related Topics:
- Share this story
Senior Contributing Editor

Sara Rimer A journalist for more than three decades, Sara Rimer worked at the Miami Herald , Washington Post and, for 26 years, the New York Times , where she was the New England bureau chief, and a national reporter covering education, aging, immigration, and other social justice issues. Her stories on the death penalty’s inequities were nominated for a Pulitzer Prize and cited in the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision outlawing the execution of people with intellectual disabilities. Her journalism honors include Columbia University’s Meyer Berger award for in-depth human interest reporting. She holds a BA degree in American Studies from the University of Michigan. Profile
She can be reached at [email protected] .
Comments & Discussion
Boston University moderates comments to facilitate an informed, substantive, civil conversation. Abusive, profane, self-promotional, misleading, incoherent or off-topic comments will be rejected. Moderators are staffed during regular business hours (EST) and can only accept comments written in English. Statistics or facts must include a citation or a link to the citation.
There are 81 comments on Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?
Insightful! The values about homework in elementary schools are well aligned with my intuition as a parent.
when i finish my work i do my homework and i sometimes forget what to do because i did not get enough sleep
same omg it does not help me it is stressful and if I have it in more than one class I hate it.
Same I think my parent wants to help me but, she doesn’t care if I get bad grades so I just try my best and my grades are great.
I think that last question about Good help from parents is not know to all parents, we do as our parents did or how we best think it can be done, so maybe coaching parents or giving them resources on how to help with homework would be very beneficial for the parent on how to help and for the teacher to have consistency and improve homework results, and of course for the child. I do see how homework helps reaffirm the knowledge obtained in the classroom, I also have the ability to see progress and it is a time I share with my kids
The answer to the headline question is a no-brainer – a more pressing problem is why there is a difference in how students from different cultures succeed. Perfect example is the student population at BU – why is there a majority population of Asian students and only about 3% black students at BU? In fact at some universities there are law suits by Asians to stop discrimination and quotas against admitting Asian students because the real truth is that as a group they are demonstrating better qualifications for admittance, while at the same time there are quotas and reduced requirements for black students to boost their portion of the student population because as a group they do more poorly in meeting admissions standards – and it is not about the Benjamins. The real problem is that in our PC society no one has the gazuntas to explore this issue as it may reveal that all people are not created equal after all. Or is it just environmental cultural differences??????
I get you have a concern about the issue but that is not even what the point of this article is about. If you have an issue please take this to the site we have and only post your opinion about the actual topic
This is not at all what the article is talking about.
This literally has nothing to do with the article brought up. You should really take your opinions somewhere else before you speak about something that doesn’t make sense.
we have the same name
so they have the same name what of it?
lol you tell her
totally agree
What does that have to do with homework, that is not what the article talks about AT ALL.
Yes, I think homework plays an important role in the development of student life. Through homework, students have to face challenges on a daily basis and they try to solve them quickly.I am an intense online tutor at 24x7homeworkhelp and I give homework to my students at that level in which they handle it easily.
More than two-thirds of students said they used alcohol and drugs, primarily marijuana, to cope with stress.
You know what’s funny? I got this assignment to write an argument for homework about homework and this article was really helpful and understandable, and I also agree with this article’s point of view.
I also got the same task as you! I was looking for some good resources and I found this! I really found this article useful and easy to understand, just like you! ^^
i think that homework is the best thing that a child can have on the school because it help them with their thinking and memory.
I am a child myself and i think homework is a terrific pass time because i can’t play video games during the week. It also helps me set goals.
Homework is not harmful ,but it will if there is too much
I feel like, from a minors point of view that we shouldn’t get homework. Not only is the homework stressful, but it takes us away from relaxing and being social. For example, me and my friends was supposed to hang at the mall last week but we had to postpone it since we all had some sort of work to do. Our minds shouldn’t be focused on finishing an assignment that in realty, doesn’t matter. I completely understand that we should have homework. I have to write a paper on the unimportance of homework so thanks.
homework isn’t that bad
Are you a student? if not then i don’t really think you know how much and how severe todays homework really is
i am a student and i do not enjoy homework because i practice my sport 4 out of the five days we have school for 4 hours and that’s not even counting the commute time or the fact i still have to shower and eat dinner when i get home. its draining!
i totally agree with you. these people are such boomers
why just why
they do make a really good point, i think that there should be a limit though. hours and hours of homework can be really stressful, and the extra work isn’t making a difference to our learning, but i do believe homework should be optional and extra credit. that would make it for students to not have the leaning stress of a assignment and if you have a low grade you you can catch up.
Studies show that homework improves student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college. Research published in the High School Journal indicates that students who spent between 31 and 90 minutes each day on homework “scored about 40 points higher on the SAT-Mathematics subtest than their peers, who reported spending no time on homework each day, on average.” On both standardized tests and grades, students in classes that were assigned homework outperformed 69% of students who didn’t have homework. A majority of studies on homework’s impact – 64% in one meta-study and 72% in another – showed that take home assignments were effective at improving academic achievement. Research by the Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) concluded that increased homework led to better GPAs and higher probability of college attendance for high school boys. In fact, boys who attended college did more than three hours of additional homework per week in high school.
So how are your measuring student achievement? That’s the real question. The argument that doing homework is simply a tool for teaching responsibility isn’t enough for me. We can teach responsibility in a number of ways. Also the poor argument that parents don’t need to help with homework, and that students can do it on their own, is wishful thinking at best. It completely ignores neurodiverse students. Students in poverty aren’t magically going to find a space to do homework, a friend’s or siblings to help them do it, and snacks to eat. I feel like the author of this piece has never set foot in a classroom of students.
THIS. This article is pathetic coming from a university. So intellectually dishonest, refusing to address the havoc of capitalism and poverty plays on academic success in life. How can they in one sentence use poor kids in an argument and never once address that poor children have access to damn near 0 of the resources affluent kids have? Draw me a picture and let’s talk about feelings lmao what a joke is that gonna put food in their belly so they can have the calories to burn in order to use their brain to study? What about quiet their 7 other siblings that they share a single bedroom with for hours? Is it gonna force the single mom to magically be at home and at work at the same time to cook food while you study and be there to throw an encouraging word?
Also the “parents don’t need to be a parent and be able to guide their kid at all academically they just need to exist in the next room” is wild. Its one thing if a parent straight up is not equipped but to say kids can just figured it out is…. wow coming from an educator What’s next the teacher doesn’t need to teach cause the kid can just follow the packet and figure it out?
Well then get a tutor right? Oh wait you are poor only affluent kids can afford a tutor for their hours of homework a day were they on average have none of the worries a poor child does. Does this address that poor children are more likely to also suffer abuse and mental illness? Like mentioned what about kids that can’t learn or comprehend the forced standardized way? Just let em fail? These children regularly are not in “special education”(some of those are a joke in their own and full of neglect and abuse) programs cause most aren’t even acknowledged as having disabilities or disorders.
But yes all and all those pesky poor kids just aren’t being worked hard enough lol pretty sure poor children’s existence just in childhood is more work, stress, and responsibility alone than an affluent child’s entire life cycle. Love they never once talked about the quality of education in the classroom being so bad between the poor and affluent it can qualify as segregation, just basically blamed poor people for being lazy, good job capitalism for failing us once again!
why the hell?
you should feel bad for saying this, this article can be helpful for people who has to write a essay about it
This is more of a political rant than it is about homework
I know a teacher who has told his students their homework is to find something they are interested in, pursue it and then come share what they learn. The student responses are quite compelling. One girl taught herself German so she could talk to her grandfather. One boy did a research project on Nelson Mandela because the teacher had mentioned him in class. Another boy, a both on the autism spectrum, fixed his family’s computer. The list goes on. This is fourth grade. I think students are highly motivated to learn, when we step aside and encourage them.
The whole point of homework is to give the students a chance to use the material that they have been presented with in class. If they never have the opportunity to use that information, and discover that it is actually useful, it will be in one ear and out the other. As a science teacher, it is critical that the students are challenged to use the material they have been presented with, which gives them the opportunity to actually think about it rather than regurgitate “facts”. Well designed homework forces the student to think conceptually, as opposed to regurgitation, which is never a pretty sight
Wonderful discussion. and yes, homework helps in learning and building skills in students.
not true it just causes kids to stress
Homework can be both beneficial and unuseful, if you will. There are students who are gifted in all subjects in school and ones with disabilities. Why should the students who are gifted get the lucky break, whereas the people who have disabilities suffer? The people who were born with this “gift” go through school with ease whereas people with disabilities struggle with the work given to them. I speak from experience because I am one of those students: the ones with disabilities. Homework doesn’t benefit “us”, it only tears us down and put us in an abyss of confusion and stress and hopelessness because we can’t learn as fast as others. Or we can’t handle the amount of work given whereas the gifted students go through it with ease. It just brings us down and makes us feel lost; because no mater what, it feels like we are destined to fail. It feels like we weren’t “cut out” for success.
homework does help
here is the thing though, if a child is shoved in the face with a whole ton of homework that isn’t really even considered homework it is assignments, it’s not helpful. the teacher should make homework more of a fun learning experience rather than something that is dreaded
This article was wonderful, I am going to ask my teachers about extra, or at all giving homework.
I agree. Especially when you have homework before an exam. Which is distasteful as you’ll need that time to study. It doesn’t make any sense, nor does us doing homework really matters as It’s just facts thrown at us.
Homework is too severe and is just too much for students, schools need to decrease the amount of homework. When teachers assign homework they forget that the students have other classes that give them the same amount of homework each day. Students need to work on social skills and life skills.
I disagree.
Beyond achievement, proponents of homework argue that it can have many other beneficial effects. They claim it can help students develop good study habits so they are ready to grow as their cognitive capacities mature. It can help students recognize that learning can occur at home as well as at school. Homework can foster independent learning and responsible character traits. And it can give parents an opportunity to see what’s going on at school and let them express positive attitudes toward achievement.
Homework is helpful because homework helps us by teaching us how to learn a specific topic.
As a student myself, I can say that I have almost never gotten the full 9 hours of recommended sleep time, because of homework. (Now I’m writing an essay on it in the middle of the night D=)
I am a 10 year old kid doing a report about “Is homework good or bad” for homework before i was going to do homework is bad but the sources from this site changed my mind!
Homeowkr is god for stusenrs
I agree with hunter because homework can be so stressful especially with this whole covid thing no one has time for homework and every one just wants to get back to there normal lives it is especially stressful when you go on a 2 week vaca 3 weeks into the new school year and and then less then a week after you come back from the vaca you are out for over a month because of covid and you have no way to get the assignment done and turned in
As great as homework is said to be in the is article, I feel like the viewpoint of the students was left out. Every where I go on the internet researching about this topic it almost always has interviews from teachers, professors, and the like. However isn’t that a little biased? Of course teachers are going to be for homework, they’re not the ones that have to stay up past midnight completing the homework from not just one class, but all of them. I just feel like this site is one-sided and you should include what the students of today think of spending four hours every night completing 6-8 classes worth of work.
Are we talking about homework or practice? Those are two very different things and can result in different outcomes.
Homework is a graded assignment. I do not know of research showing the benefits of graded assignments going home.
Practice; however, can be extremely beneficial, especially if there is some sort of feedback (not a grade but feedback). That feedback can come from the teacher, another student or even an automated grading program.
As a former band director, I assigned daily practice. I never once thought it would be appropriate for me to require the students to turn in a recording of their practice for me to grade. Instead, I had in-class assignments/assessments that were graded and directly related to the practice assigned.
I would really like to read articles on “homework” that truly distinguish between the two.
oof i feel bad good luck!
thank you guys for the artical because I have to finish an assingment. yes i did cite it but just thanks
thx for the article guys.
Homework is good
I think homework is helpful AND harmful. Sometimes u can’t get sleep bc of homework but it helps u practice for school too so idk.
I agree with this Article. And does anyone know when this was published. I would like to know.
It was published FEb 19, 2019.
Studies have shown that homework improved student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college.
i think homework can help kids but at the same time not help kids
This article is so out of touch with majority of homes it would be laughable if it wasn’t so incredibly sad.
There is no value to homework all it does is add stress to already stressed homes. Parents or adults magically having the time or energy to shepherd kids through homework is dome sort of 1950’s fantasy.
What lala land do these teachers live in?
Homework gives noting to the kid
Homework is Bad
homework is bad.
why do kids even have homework?
Comments are closed.
Latest from Bostonia
Bu alum chompon boonnak runs mahaniyom, one of greater boston’s hottest thai restaurants, champion of indie films, china scholar merle goldman dies, cfa alum jonathan knight is head of games for the new york times, one good deed: jason hurdich (cas’97) is uniting the deaf community, one cup at a time, is our democracy at risk americans think so. bu experts talk about why—and the way forward, a commitment to early childhood education, reading list: alum bonnie hammer publishes 15 lies women are told at work —plus fiction, poetry, and short stories, space force general b. chance saltzman is a bu alum, pups wearing custom-designed veterinary collars get star treatment in alum’s new coffee-table book, using glamour for good: alum’s nonprofit organization brings clothes and beauty products to those in need, gallery: shea justice (cfa’93), oscar-nominated actor hong chau (com’01) stars in new action-comedy the instigators, alum’s new book recounts the battle for inclusion in boy scouts, feedback: readers weigh in on a bu superager, the passing of otto lerbinger, and alum’s book fat church, law alum steven m. wise, who fought for animal rights, dies, opening doors: ellice patterson (questrom’17), an alum’s new memoir recounts six decades of beatlemania, bu alum in paris keeping olympians’ minds sharp and healthy, erika jordan departs bu alumni engagement office to return to california.
- Our Mission
What’s the right amount of homework to assign? Learn about the research behind homework, how schools and teachers are handling it, and how you can differentiate it in a manageable way.

.css-13ygqr6:hover{background-color:#d1ecfa;}.css-13ygqr6:visited{color:#979797;}.css-13ygqr6.node--video:before{content:'';display:inline-block;height:20px;width:20px;margin:0 4px 0 0;background:url(data:image/svg+xml,%3Csvg%20width%3D%2242px%22%20height%3D%2242px%22%20viewBox%3D%220%200%2042%2042%22%20alt%3D%22Video%20icon%22%20data-testid%3D%22play-circle%22%20version%3D%221.1%22%20xmlns%3D%22http%3A%2F%2Fwww.w3.org%2F2000%2Fsvg%22%3E%3Ctitle%3EVideo%3C%2Ftitle%3E%3Cdefs%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Cg%20id%3D%22play-circle%22%20fill%3D%22%23000000%22%3E%3Cpath%20d%3D%22M21%2C0%20C9.38%2C0%200%2C9.38%200%2C21%20C0%2C32.62%209.38%2C42%2021%2C42%20C32.62%2C42%2042%2C32.62%2042%2C21%20C42%2C9.38%2032.62%2C0%2021%2C0%20L21%2C0%20Z%20M21%2C36.7733333%20C12.32%2C36.7733333%205.22666667%2C29.7266667%205.22666667%2C21%20C5.22666667%2C12.2733333%2012.32%2C5.22666667%2021%2C5.22666667%20C29.68%2C5.22666667%2036.7733333%2C12.32%2036.7733333%2C21%20C36.7733333%2C29.68%2029.68%2C36.7733333%2021%2C36.7733333%20L21%2C36.7733333%20Z%22%20id%3D%22circle%22%3E%3C%2Fpath%3E%3Cpath%20d%3D%22M29.54%2C19.88%20L17.7333333%2C12.9733333%20C16.8466667%2C12.46%2015.7733333%2C13.1133333%2015.7733333%2C14.0933333%20L15.7733333%2C27.9066667%20C15.7733333%2C28.9333333%2016.8933333%2C29.54%2017.7333333%2C29.0266667%20L29.5866667%2C22.12%20C30.4266667%2C21.6066667%2030.4266667%2C20.3933333%2029.54%2C19.88%20L29.54%2C19.88%20Z%22%20id%3D%22triangle%22%3E%3C%2Fpath%3E%3C%2Fg%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) no-repeat left bottom/18px 18px;} Assigning More Meaningful Math Homework

The Case Against Grading Homework
There has been an error with the video.
Homework: How Much Is Too Much?

What’s the Right Amount of Homework?

5 Ways to Make Homework More Meaningful

5 Ways to Help Students Focus on Learning Rather Than Grades

Rethinking Homework for This Year—and Beyond

Reimagining Study Hall to Promote Student Goal-Setting

4 Ways to Teach Students Backward Planning

How to Help Students Develop the Skills They Need to Complete Homework

Fact Check: Are Flexible Student Deadlines at Odds With Real Life?

The Risks of Guesstimating Homework Time

How to Get Students to Use Their Planners

5 Keys to Successful Homework Assignments During Remote Learning

A Restorative Approach to Grading
Our 62nd annual international Conference | february 27 - march 1, 2025 | orlando, florida

How Much Time Should Be Spent on Homework?

At the elementary level homework should be brief, at your child’s ability level and involve frequent, voluntary and high interest activities. Young students require high levels of feedback and/or supervision to help them complete assignments correctly. Accurate homework completion is influenced by your child’s ability, the difficulty of the task, and the amount of feedback your child receives. When assigning homework, your child’s teachers may struggle to create a balance at this age between ability, task difficulty and feedback. Unfortunately, there are no simple guiding principles.
We can assure you, however, that your input and feedback on a nightly basis is an essential component in helping your child benefit from the homework experience.
What is the recommended time in elementary school?
In first through third grade, students should receive one to three assignments per week, taking them no more than fifteen to twenty minutes. In fourth through sixth grade, students should receive two to four assignments per week, lasting between fifteen and forty-five minutes. At this age, the primarily goal of homework is to help your child develop the independent work and learning skills that will become critical in the higher grades. In the upper grades, the more time spent on homework the greater the achievement gains.
What is the recommended time in middle and high school?
For students in middle and high school grades there are greater overall benefits from time engaged in practicing and thinking about school work. These benefits do not appear to depend as much upon immediate supervision or feedback as they do for elementary students. In seventh through ninth grade we recommend students receive three to five sets of assignments per week, lasting between forty-five and seventy-five minutes per set. In high school students will receive four to five sets of homework per week, taking them between seventy-five and 150 minutes per set to complete.
As children progress through school, homework and the amount of time engaged in homework increases in importance. Due to the significance of homework at the older age levels, it is not surprising that there is more homework assigned. Furthermore, homework is always assigned in college preparatory classes and assigned at least three quarters of the time in special education and vocational training classes. Thus at any age, homework may indicate our academic expectations of children.
Regardless of the amount of homework assigned, many students unsuccessful or struggling in school spend less rather than more time engaged in homework. It is not surprising that students spending less time completing homework may eventually not achieve as consistently as those who complete their homework.
Does this mean that time devoted to homework is the key component necessary for achievement?
We are not completely certain. Some American educators have concluded that if students in America spent as much time doing homework as students in Asian countries they might perform academically as well. It is tempting to assume such a cause and effect relationship.
However, this relationship appears to be an overly simple conclusion. We know that homework is important as one of several influential factors in school success. However, other variables, including student ability, achievement, motivation and teaching quality influence the time students spend with homework tasks. Many students and their parents have told us they experience less difficulty being motivated and completing homework in classes in which they enjoyed the subject, the instruction, the assignments and the teachers.
The benefits from homework are the greatest for students completing the most homework and doing so correctly. Thus, students who devote time to homework are probably on a path to improved achievement. This path also includes higher quality instruction, greater achievement motivation and better skill levels.
Authors: Dr. Sam Goldstein and Dr. Sydney Zentall

LDA of America does not currently have an active state affiliate in Wyoming.
Make a difference in your state by volunteering to start a state affiliate to help individuals with learning disabilities in your state.
Contact LDA of America at [email protected] to inquire about starting a state affiliate.
LDA of Wisconsin’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Visit our website: https://ldaofwisconsin.org/

LDA of West Virginia’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Email: [email protected]

LDA of Washington’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Find us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=100077791775467
Visit our Website: https://ldawa.org

LDA of Virginia’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Visit our website: https://ldava.org

LDA of America does not currently have an active state affiliate in Vermont.
LDA of Utah’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Find us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/ldau.org/
Visit our website: https://www.ldau.org/
Phone: 801.553.9156

LDA of Texas’ mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Follow us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LDATexas/
Visit our Website: https://ldatx.org

LDA of Tennessee’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.

LDA of America does not currently have an active state affiliate in South Dakota.
LDA of South Carolina’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Find us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LDAofSC

LDA of America does not currently have an active state affiliate in Rhode Island.
LDA of Pennsylvania’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Find us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/ldapa
Visit our website: https://ldaofpa.org
Phone: 412.212.7087

LDA of America does not currently have an active state affiliate in Oregon.
LDA of America does not currently have an active state affiliate in Oklahoma.
LDA of Ohio’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Visit our website: https://lda-oh.org

LDA of America does not currently have an active state affiliate in North Dakota.
LDA of North Carolina’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Find us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LDAofNorthCarolina
Visit our Website: https://ldanc.org

LDA of New York’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Visit our website: https://ldanys.org

LDA of America does not currently have an active state affiliate in New Mexico.
LDA of New Jersey’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Find us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LearningDisabilitiesAssociationofNJ/
Visit our website: https://ldanj.org

LDA of New Hampshire’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Visit our website: https://nhlda.org

LDA of America does not currently have an active state affiliate in Nevada.
LDA of Nebraska’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Find us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LearningDisabilityNE/

The Learning Disabilities Association of Montana (LDA-MT) is one of the state affiliates of the Learning Disabilities Association of America, as a nonprofit volunteer organization of parents, professionals, and adults with learning disabilities. Our mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education, and advocacy.
Visit our website: https://ldamontana.org

LDA of America does not currently have an active state affiliate in Missouri.
LDA of America does not currently have an active state affiliate in Mississippi.
LDA of Minnesota’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Find us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LDAMinnesota/
Follow us on X (formerly Twitter): https://x.com/ldaminnesota
Visit our Website: https://www.ldaminnesota.org/
Phone: 952.582.6000

LDA of Illinois’ mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Find us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=100063726155725
Visit our website: https://ldaillinois.org
Phone: 708.430.7532

The Learning Disabilities Association of Iowa is dedicated to identifying causes and promoting prevention of learning disabilities and to enhancing the quality of life for all individuals with learning disabilities and their families by:
- Encouraging effective identification and intervention,
- Fostering research, and
- Protecting the rights of individuals with learning disabilities under the law.
Find us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LDA.Iowa
Follow us on X (formerly Twitter): https://x.com/ldaofiowa
Visit our website: https://ldaiowa.org
Phone: 515.209.2290

LDA of Michigan’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Find us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LDAmichigan
Follow us on X (formerly Twitter): https://x.com/LDAmichigan
Visit our Website: https://ldaofmichigan.org
Phone: 616.284.1650

The mission of LDA of Massachusetts is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Affiliate Contact: Kristen Lech Contact Email: [email protected]

LDA of Maryland’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Find us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/ldamd/
Visit our website: https://ldamd.org/

LDA of Maine’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Find us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/ldame
Visit our website: https://ldame.org

The Learning Disabilities Association of Louisiana (LDA-LA) is one of the state affiliates of the Learning Disabilities Association of America, as a nonprofit volunteer organization of parents, professionals, and adults with learning disabilities. Our mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education, and advocacy.
Find us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LDAofLouisiana/

LDA of Kentucky’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Find us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=100067524906403
Visit our Website: https://www.ldaofky.org/

LDA of America does not currently have an active state affiliate in Kansas.
LDA of Indiana’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Find us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LearningDisabilitiesAssociationofIndiana/

LDA of America does not currently have an active state affiliate in Idaho.
LDA of America does not currently have an active state affiliate in Hawaii.
LDA of Georgia’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Find us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LearningDisabilitiesAssociationofGeorgia/
Visit our website: https://ldaga.org

LDA of Florida’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Find us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LDAFlorida/
Visit our website: https://lda-florida.org

LDA of America does not currently have an active state affiliate in the District of Columbia.
LDA of Connecticut’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Find us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LDAofCT
Visit our Website: https://sites.google.com/view/ldaofconnecticut/

LDA of Delaware’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Affiliate Contact: Fern Goldstein
Find us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/ldadelaware/
Visit our Website: https://ldadelaware.org/

LDA of America does not currently have an active state affiliate in Colorado.
LDA of California’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Visit our website: https://ldacalifornia.org
Affiliate Contact: EunMi Cho

LDA of Arkansas’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Find us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/ldarkansas/
Visit our website: https://lda-arkansas.org

LDA of Arizona’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Visit our website: https://ldaofarizona.org

LDA of Alabama’s mission is to create opportunities for success for all individuals affected by learning disabilities through support, education and advocacy.
Find Us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LDAAlabama/
Visit Our Website: https://ldaalabama.org/

LDA of America does not currently have an active state affiliate in Alaska.

Let’s talk
How can we help you?

Email Address

High-Quality Homework: How to Assign the Right Amount, and the Most Effective Formats of Homework
by Chandra Williams | Jul 16, 2019

SHARE THIS STORY
Although studies have shown that homework offers some benefits to students, assigning too much homework can actually cause students to experience higher stress levels and physical and mental health issues . In this article, we’ll discuss guidelines you can use to assign high quality homework for your students.
What is the “ten-minute homework guideline?”
The National PTA and National Education Association support the “ ten minute homework guideline ,” which suggests each student should have about ten minutes of homework per grade level. First-grade students should have between ten to twenty minutes of homework, with an additional ten minutes added for each subsequent grade level.
The ten-minute homework rule offers several benefits to students, including:
- Reduces the likelihood of students becoming overwhelmed.
- Prevents diminishing returns for academic success.
- Reduces the impact of the “homework gap,” a term indicating the disproportionate challenges faced by students who do not have access to the internet and other resources to complete homework assignments at their homes.
- Reduces impact on students who naturally take longer to complete homework assignments.
What purposes should homework accomplish?
Most homework assignments fall into one of the following four categories :
- Practice — Students have learned skills in class and practice using those skills on their own at home. For example, students learned the order of operations in math class and practice using these skills by solving some multi-step equations.
- Preparation — Students prepare to learn about a new concept in class the next day. For example, students read the first chapter of a new book which will be discussed in tomorrow’s English class.
- Study — Students review content they have already learned and practiced to prepare for a formative, unit, or benchmark assessment.
- Extend or Elaborate — Students have learned about a general concept in class, and complete individual work to expand their knowledge on the topic. For example, students learned about the formation of the United States in class, and each student will individually create a project exploring the history of a different state.
When students’ complete homework for the purpose of practicing skills, they may have single-skill assignments or cumulative assignments.
- Single-skill assignments are most effective when students need to master the skill taught in class. For example, students may list the steps of the scientific method.
- Cumulative assignments require students to decide which skill they need to use when solving a particular problem, and then properly use the skill. For example, students are presented with an experiment, must determine which steps in the scientific method need to be completed, and then must complete the experiment and demonstrate its results.
What is the most effective type of homework?
Existing studies have found that student performance is most positively affected when homework is used to build fluency, master new concepts, and proficiency. Students retain information better when the practice is conducted over several shorter sessions, rather than through one marathon session. Additionally, students should be able to use the same processes and skills with their homework assignments, which were modeled and demonstrated during class. In other words, homework assignments should be presented in the same format as classroom practices.
What are best practices for assigning homework?
Research suggests that homework is most effective when:.
- Assignments promote curiosity, leading to “ autonomous, self-directed learning .”
- Students have already “ demonstrated competence in the skill…before being asked to do it independently.”
- Teachers consider some students do not have access to the internet, a quiet working space, or homework help from parents or a tutor.
- Students understand the purpose of completing each homework assignment.
- Teachers provide feedback quickly, minimizing the chance for students to forget the assignment before they learn their scores.
- Teachers keep in mind that middle school and high school students may be assigned homework from all of their classes, and the ten-minute homework guideline applies to the combined homework load.
FILED UNDER
Instructional Strategies
Recent Posts
- Parent Engagement and Student Success
- Reflect and Set Goals for Student Success
- Creating Proactive and Positive Classrooms
Browse by Topic
Select month, join our newsletter.

How Much Homework is the Right Amount of Homework?
In the past, assigning mounds of homework was a way of life for most teachers. But now, many schools and teachers are opting to pull back on heavy homework to allow for more quality time at home—reading a good book, enjoying a family dinner, or playing outside. This change is in response to the growing question about the real value of homework and the changing dynamics of families with two working parents and multiple children with extra-curricular activities.
In the current debate of how much homework is the right amount, many schools rely on the 10-Minute Rule that is supported by the National PTA and the National Education Association. It equates to assigning 10 minutes of homework per grade level, per night. So, 20 minutes for second graders, 60 minutes for sixth graders, and so on, maxing at 2 hours of work for high school seniors. However, studies have shown that students may be spending three times the recommended time to complete their assignments.
- The Homework Debate
Those in support of nightly homework suggest that it:
- Helps students develop soft skills that include good study habits, time management, organization, prioritization, and personal responsibility
- Allows students to display their understanding of what they’ve learned without help from their teacher
- Keeps families involved in their children’s learning
- Fills in the gaps when teachers have less time to reinforce lessons and concepts in class
Those pushing for less homework (or none at all), especially for elementary students, argue that it does more harm than good. They point to these facts :
- The link between homework and academic achievement is not as strong as previously thought, especially for students in elementary school.
- Too much parent involvement can lessen the positive effects students should gain through after-school work.
- Homework is being blamed for increased stress, sleep deprivation, and other physical health problems in students.
- Breaking the Homework Mold
When determining your approach , remember this key point: quality over quantity. Consider the four common categories/purposes of additional work when creating assignments:
Practice Problems
Tailor, tailor, tailor! It’s easy to get lost in the sea of homework resources at hand these days. By keeping each student’s needs in mind, you’ll find the right practice for everyone. Zero in on review for the specific skills that individual students need to master. Using a variety of tools for different students, or even assigning a cluster of problems instead of the entire worksheet or book, can help you differentiate homework to make it more impactful.
Preparation Work
If a lack of classroom time is a real concern, use outside work to give your students a jumpstart on the next day’s lessons. This can include watching a video or completing a reading assignment that will give them valuable background on what they’ll be learning next. This concept is successfully used in many flipped classroom lessons.
Extension Activities
This allows you to see how well your students can take what they’ve learned and apply it to new situations.
Integration Assignments
Integration requires your students to apply several skills into a single assignment, whether it’s a research assignment, science project, presentation, or book report. It may be more time-intensive, but students are practicing many different disciplines.
- Homework Tips for Parents
Homework time can be a little difficult for a busy family, resulting in stumped parents and frustrated kids. Read on for advice that you can share with the families in your classroom to help create more positive experiences, no matter how much work is assigned.
Set a routine, but be sure to get your child’s input.
Some kids are okay to tackle homework as soon as they get home, while others may need to decompress for a while before they get back to work. Bookworms might want to save their reading for bedtime and early risers might knock out a math worksheet first thing in the morning.
Homework time should be free from distractions.
Unless a tablet or computer is required to complete the assignment, homework time should be done without TV or cell phone distractions.
Be a low-key homework helper.

The daily practice in this updated, standards-based series helps students build and maintain skills covered over the school year. Ideal for summer school students.
520 East Bainbridge Street Elizabethtown, PA 17022 Phone: 800.233.0759 Fax: 888.834.1303
- Privacy Policy
©2024 Continental. All Rights Reserved.
Found the perfect materials for your classroom? Email your shopping cart to your school/district contacts to request purchasing approval. Step #1: Save My Cart Step #2: Personalize My Email

Where endless possibilities for growth, fun, and lifelong memories await. Sat, Feb 10, 2024: Meet top camps & kids programs. One afternoon. RSVP for free tickets .
- Private Schools
- Advice Guide
- Trends in Education
Homework wars: how much homework is enough?
Evaluating the homework policies of schools.
In choosing a school for your child, you’ll want to look at its homework policies. You might be surprised by how much these vary between schools.
The perfect private school?
It’s one of the biggest decisions you’ll make for your child. Let our experts and school insiders guide you through your best options, red flags to watch out for, and tips to a successful application.
Private School Expo - Fall 2024 Yes, I want to attend
Figure 1: The distribution for the amount of homework assigned in Grade 6 among schools featured on OurKids.net.
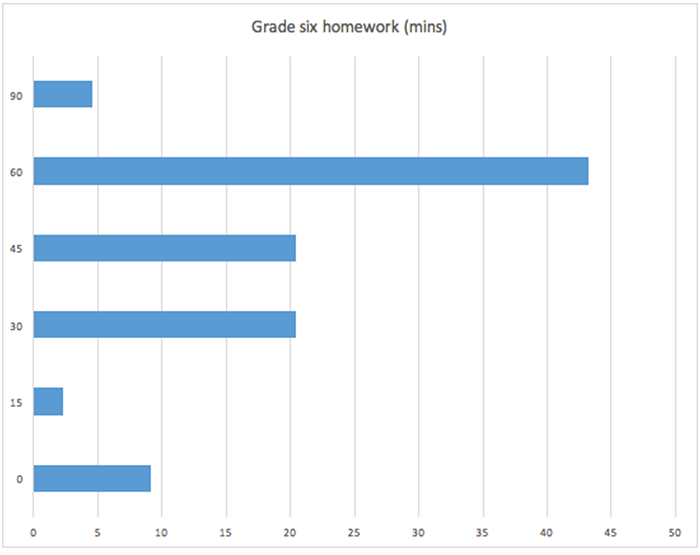
There’s a long-standing and contentious debate over homework . Should homework be assigned to school-age children? If so, in what grades? And how much homework should be assigned? There’s no shortage of disagreement about these questions.
On the one hand, traditionalists are pro-homework. They claim that homework helps students learn. They also claim schools should start assigning it in Grade 1, and increase the amount in each grade.
Progressives , on the other hand, are anti-homework. They claim that homework is mostly ineffective, and that schools should assign little, if any, homework—especially in the earlier grades.
Understanding this debate can help you evaluate the homework policy of any prospective school. And this can help you decide if a school’s a good fit for your family.
Figure 2: The average amount of homework assigned by grade for schools featured on OurKids.net.
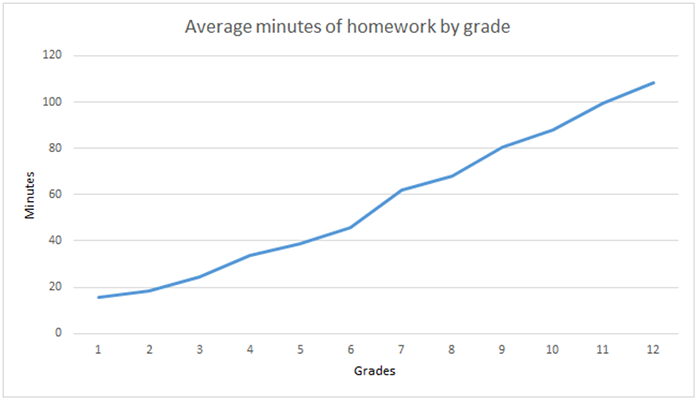
(1) The case for homework
(2) the case against homework, (3) recent research on homework, (4) homework in public schools, (5) homework in canadian private schools, (6) guidelines for evaluating homework policies.
It has long been held that homework—assuming it’s well-designed—is crucial to learning and development.
In Cultural Literacy (1987), the traditionalist Hirsch argues for the value of homework. Homework, he urges, gives students more time to reinforce knowledge they’ve learned in the classroom. And this gives them a stronger basis for future learning.
For example, by memorizing the multiplication tables or the location of every country in Europe, students can learn important concepts and expand their body of knowledge. Coming back to material after a period away from it is a time-tested strategy for retaining information. Homework provides exactly that, supporters argue. And this enables students to move on to new material during class.
In addition, it’s argued, regular homework also helps students practice skills. Many skills require lots of practice to become ingrained habits, says Michael Zwaagstra, a well-known homework advocate. Why, he asks (in What’s Wrong with our Schools? (2009)), would academic skills be any different?
A pianist can improve by practicing scales and a basketball player can improve by spending hours in the gym. In the same way, students can improve skills learned in school through practice.
Basic skills like grammar, spelling, and multiplication tables require drill, says Barr (2007). Learning how to begin projects, searching for answers, and problem-solving are skills that adults use daily, and must be learned early through homework.
Homework not only helps with academics, but it also builds study skills and character.
This view aligns with the frequently discussed “practice principle.” According to Malcolm Gladwell, among others, one needs at least 10,000 hours of practice to master challenging skills, such as playing the guitar, writing a short story, or serving a tennis ball.
Arguments for homework:
- It gives students a time and context to reinforce knowledge gained in the classroom.
- It gives students a time and context to practice skills learned in the classroom and needed for future studies, and life.
- It can instill study habits and organization skills.
- It can lead to better self-direction and self-discipline.
- It can allow students to work on things not directly covered in class (for instance, through independent studies or book reports). This can expand the breadth and depth of learning.
- It allows parents to be more involved in their children’s studies by encouraging them to help out with homework.
- It can lead to a willingness to learn during leisure time, and inspire a love of learning.
Sometimes homework can be frustrating for students and parents. Often, though, these problems stem from homework being poorly designed, it’s argued. In other words, we shouldn’t throw the baby out with the bathwater:
The best way to address the homework issue is for teachers to ensure they have a good reason for assigning the homework. Homework should be meaningful and provide students with the opportunity to practice skills and concepts they have recently learned in school. Ensuring that homework is properly designed and relevant to what students are learning is the best way to alleviate concerns about its effectiveness. (Zwaagstra, 2009)
- 84% of schools featured on OurKids.net start assigning homework in Grade 1 or earlier.
- 9% of schools featured on OurKids.net don’t start assigning homework until Grade 7 or higher.
- 5.6% of schools featured on OurKids.net don’t assign homework at any grade level.
Figure 3: The average amount of homework assigned by grade for traditional schools featured on OurKids.net.
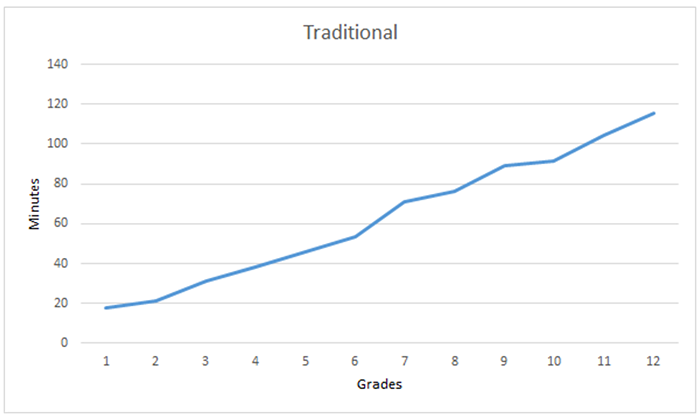
The case for homework seems pretty straightforward, right? Well, not according to homework’s critics. In the last 40 years or so, homework has been criticized by many.
Critics claim homework can interfere with student motivation and family life. Alfie Kohn (in “ The Homework Myth ”), a well-known progressivist and homework opponent, sums up this line of thinking:
"The negative effects of homework are well known. They include children’s frustration and exhaustion, lack of time for other activities, and possible loss of interest in learning. Many parents lament the impact of homework on their relationships with their children; t hey may also resent having to play the role of enforcer and worry that they will be criticized either for not being involved enough with the homework or for becoming too involved."
Kralovec and Buell (in “ End Homework Now ”, 2001), two other homework opponents, describe how homework can be a major source of stress for families:
Homework squeezes family life. All parents have educational agendas for their children. They want to pass on their cultural heritage, religious beliefs , and important life skills. They want to teach their children how to be good citizens and how to share in the responsibilities of running a home. More homework makes parents put their own agendas on hold even as they often struggle to help their children cope with homework assignments. Additionally, families need time to constitute themselves as families. According to a 1998 survey by Public Agenda, nearly 50 percent of parents reported having a serious argument with their children over homework, and 34 percent reported homework as a source of stress and struggle. Parents often have conflicting feelings about homework, viewing it as a way for their children to succeed but also as imposing serious limits on family time.
Zwaagstra (2009), meanwhile, tries to address this kind of claim:
Perhaps the most specious and troublesome claim is that homework takes away time for more valuable activities for students, such as exercising or talking to parents. Using the University of Michigan Institute for Social Research data—often quoted by homework opponents—one quickly finds that the average television viewing for school-aged children is more than two hours a day. If there is anything that takes time away from constructive childhood activities, it is watching mindless television programs. (One wonders whether homework opponents plan to encourage governments to pass laws that restrict the number of hours that children are permitted to watch television during weeknights.)
But parent concerns over homework are real. In Canada, a 2007 study from the Ontario Institute for Studies in Education (OISE) showed that—at least in Ontario —many parents question both the amount of homework and the nature of homework.
The study revealed that much assigned homework seems unnecessary to parents, isn’t taken up in class, shared or evaluated, and when it is, it’s often not quick enough. It also revealed that many parents are concerned about the affect homework has on their family life.
Responses to the parent survey included:
“ I feel that my child is being asked to complete homework that is too difficult for her to do on her own. She needs the help of one or both parents. This seems to me to be inappropriate. I do not mind helping my child with homework, but it seems that at least she should be given at least some homework that she can complete on her own. ”
It would seem that the teachers are either too rushed or can't be bothered to communicate well what is expected from the homework assignments.
That there is so much quantity, I wonder if the benefits of learning from the work is being outweighed by the negative effects such as less ‘down’ time, less family time, stress of completing assignments, emphasis on completing work instead of learning something.
I think most of the assigned homework thus far has been either busy work and a complete waste of time, or it is part of the curriculum that the teacher has not had time to cover and is sending it home to extend the school day.
Homework starts too young. Children are in structured activities all day between school and daycare . For working parents —as soon as you get home you have to start in on all of the assigned homework. This is impacting the quality time you are able to spend as a family unit. Under the age of 10 I highly question how homework actually contributes to learning outcomes. I believe that if kids had time for free play, family time, and outdoor activity —academic results would actually be higher in the end.
Indeed, the argument against homework goes beyond the question of infringing on family time and being annoying. Homework’s critics also question how effective it is at improving grades—especially in the early school years (such as preschool and elementary school).
In fact, Kohn, one of homework’s harshest critics, has argued homework has no positive effects. This is a common view in the anti-homework camp.
Numerous studies conducted since the 1980s have looked at the benefits of homework, and according to Kohn (not to mention Kralovec, Buell and others), none have proven its value. In particular, they show no positive correlation between homework and high grades.
Arguments for less homework:
- For children, spending time on homework means that they aren’t spending as much time on other valuable activities. These may include spending time with family and friends, and engaging in sports and other extracurricular activities . For teens , too much homework makes it hard to balance their academic and social lives.
- Homework is often assigned as “busy-time” work, with little pedagogical value.
- The research on homework outcomes, critics maintain, doesn’t support assigning it, especially in the younger grades.
- Homework—especially in large amounts —can lead to frustration, exhaustion, and poor mental and physical health in some students.
- For some students, homework can interfere with the love of learning that’s crucial, both in the school years and beyond.
- There’s a strong correlation between homework and dropout rates, studies show .
Assigning homework often turns into a way for teachers to offload the job of teaching students in class, critics argue. Students should be able to learn the required material and skills within class—even if that means finding more class time for practice and review.
Figure 4: The average amount of homework assigned by grade for progressive schools featured on OurKids.net.
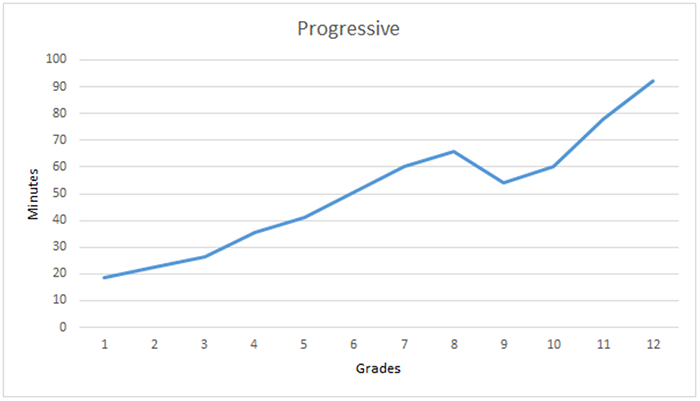
So, who’s right? Is homework a good thing or not? And in terms of what academic outcomes? And, what does research say about the effectiveness of homework?
The Duke homework study
Well, there have been several studies on homework. One of the biggest was the Duke study , led by Harrison Cooper. In this study, Duke University researchers reviewed more than sixty research studies on the effectiveness of homework between 1987 and 2003. It concluded that homework does have a positive effect on student achievement, such as grades.
According to Cooper, the study shows the right amount of homework depends on the grade level. For elementary school students, no amount of homework—large or small—affects academic achievement.
For middle school students, academic achievement continues to improve with more homework, until assignments last between one and two hours a night. For high school students, the more homework, the higher the achievement, up to a limit of about two to three hours a night.
While the study seemed to show that homework’s a critical part of the learning process, Cooper noted it also showed that too much homework can be counter-productive for students at all levels.
The research appeared to be consistent with the “10-minute” rule, now quite commonly accepted, at least in traditional , academically-oriented schools. According to the 10-minute rule, teachers should add 10 minutes of homework for each grade a student completes, starting with the first grade. In other words, a first-grader would be assigned 10 minutes of homework, a second-grader 20 minutes, a third-grader 30 minutes, and so on.
Criticisms of the Duke study
Yet many have disputed these results. Kohn, for example, has argued that the results, taken as a whole, are inconclusive. At best, the research shows that homework can have minor benefits on the achievement levels of high school students:
There is absolutely no evidence of any academic benefit from assigning homework in elementary or middle school. For younger students, in fact, there isn’t even a correlation between whether children do homework (or how much they do) and any meaningful measure of achievement. At the high school level , the correlation is weak and tends to disappear when more sophisticated statistical measures are applied. Meanwhile, no study has ever substantiated the belief that homework builds character or teaches good study habits.
The results of the Duke study have also been disputed for other reasons. First, many of the research studies were poorly designed. Second, the research focused mostly on academic achievement as the desirable outcome. Only a few studies looked at homework’s affect on attitudes toward school and subject matter. And no studies looked at other outcomes such as study habits, cheating, or participation in community activities.
Overall, research on the effectiveness of homework is less than conclusive. Some studies have led to different, and in some cases, conflicting interpretations of the data. Yet we can draw some tentative conclusions from the research. These conclusions include the following:
What the research says about homework:
- Completing homework seems to have little or no impact on the academic achievement of elementary school students.
- Completing homework seems at least weakly correlated with academic achievement in high school and possibly middle school students.
- There’s an upper limit to the amount of homework that should be assigned to students at any level.
- It becomes counter-productive to assign very large amounts of homework.
- Some homework is not well-designed, given feedback, or returned promptly by teachers .
- Some homework is not monitored very closely by teachers.
- The question of how homework influences attitudes towards school, study habits, and work ethic requires further study.
As a parent, it’s important to select a school that’s the right fit for your child. Part of this decision will involve looking at a school’s homework policy.
In both the public and private school system , homework policies vary widely. Different schools have different homework policies, and these policies can vary among classes and teachers within the same school.
Yet in public schools , unlike private schools, homework policies can be regulated by the government. If your child is in a public school, it’s important to know whether the government regulates homework policies in your school district, and if so, how.
Consider the following example:
TDSB homework policy
One homework policy was recently enacted by the Toronto District School Board (TDSB) , in April of 2008. This policy emerged in response to complaints from parents and students about the amount of homework assigned.
The new policy allowed teachers in Toronto to assign only a minimal amount of homework to elementary students: no more than one hour per evening to Grade 7 and 8 students (in total), and no more than two hours per evening to high school students (in total). In addition, the policy forbid teachers from assigning homework over holidays and from disciplining students who fail to complete their homework on time.
This policy has received mixed reviews, and it’s unclear whether it’s achieved its objectives. Some teachers claim that the restrictions on homework significantly slow down the pace of class. This results in more advanced students sometimes feeling unchallenged and unstimulated in class. This is because much in-class time is spent covering material that could be completed as homework.
On the other hand, some have defended these kinds of policies. They’ve claimed they tend to free up extra time. Children can spend more time with their families, participate in extracurricular activities, socialize with friends, and pursue other interests and hobbies.
In private schools, like public schools, there’s a wide range of homework policies. Unlike in public schools, though, private school policies aren’t regulated by the government. Private schools are normally free to come up with their own homework policies.
Yet, private schools vary in their educational objectives. And these objectives affect their homework policies.
Private schools can be divided into two main homework camps:
Traditional private schools
On the one hand, traditional, academic schools tend to be more pro-homework. These schools have a standard curriculum which is content-based and rooted in the core disciplines. Their teachers typically deliver a unified and tightly structured curriculum through direct instruction.
These schools also tend to have what we at Our Kids define as a rigorous academic culture . This means they highly value academic performance and use many tests and assignments to evaluate it.
Traditional schools view homework as essential to education. They assign homework to school-age students on a regular basis, increasing the amount and level of difficulty with each grade.
Progressive private schools
On the other hand, progressive schools tend to be more anti-homework. These schools include (but aren’t limited to) Montessori , Waldorf , and Reggio Emilia schools . They typically provide little direct instruction, and less objective evaluation than traditional schools.
Instead of teaching core subjects through transmitting factual knowledge, progressive schools place children’s interests and ideas at the heart of the learning experience. They also tend to have what we at Our Kids call a supportive academic culture , one focused largely on instilling a love of learning and lifelong curiosity in students.
Many progressive schools view homework as less essential to education and assign less homework to students than traditional schools, especially in the upper grades. In fact, some progressive schools do not assign homework in any grade.
Classroom flipping
Many of these anti-homework progressivist schools use a practice called classroom flipping . In these schools, students do more “sit-down” learning at home, such as reading or writing . Meanwhile, they do more applied learning activities in class, such as group exercises or in-class presentations.
Classroom flipping is similar to the way some university courses are taught. At this level, students often do “sit-down” reading and studying at home, and then have class and group discussions in school.
Because classroom flipping is a fairly new practice, there’s been little to no research done on it. We’ve begun, though, to compile some data on classroom flipping, including which schools featured on OurKids.net use this practice. Our main aim is to be able to draw some conclusions about its value, in comparison with more traditional approaches to homework.
- 20.3% of schools featured on OurKids.net use the practice of classroom flipping.
Figure 5: The average amount of homework assigned by grade for traditional versus progressive schools, as featured on OurKids.net. Note that while traditional schools on average assign more homework than progressive schools, a significant difference doesn’t emerge until the high school years, from Grade 9 to 12.
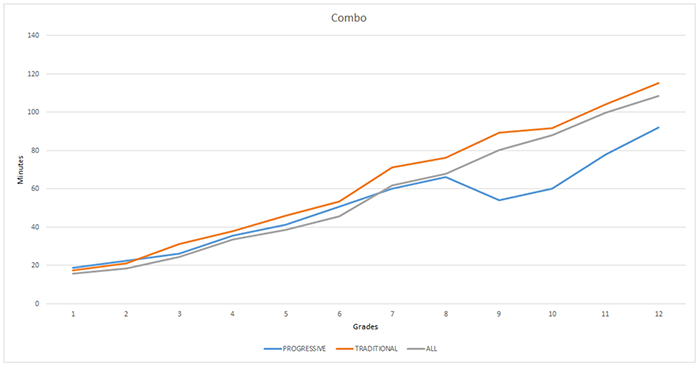
The jury is still out on homework. Despite lots of research, there’s little agreement on the merits of homework, and its merits versus its costs. But research seems to suggest, if nothing else, that homework can enhance learning in many ways.
Part of choosing the right school for your child involves looking at schools’ homework policies. To start, you should find out whether your child’s current or prospective school has a homework policy. If the school doesn’t have a homework policy, you should find out whether any of its programs, classes, or teachers have homework policies.
If your child’s school (or program or class) does have a homework policy, you should ask for a hard or softcopy of the homework policy document. With this in hand, you can take a close look at the homework policy, and decide whether it’s appropriate and well-suited for your child.
Although there’s no such thing as the perfect or “one-size-fits-all” homework policy, good ones provide an explicit set of guidelines for assigning homework.
These guidelines should be well-supported by the relevant research. Ideally, they should also be clearly communicated to teachers and educators, and in some cases, students and parents .
Below, we provide you our own set of guidelines for evaluating a school’s homework policy. This is meant to help you decide whether a school's homework policy passes muster. Keep in mind, this list is not exhaustive.
Best homework practices
- Homework should be carefully designed and monitored to achieve the right learning outcomes for students: improved learning, better study habits, higher academic achievement, and the like.
- Homework should have a specific purpose: “busy time” homework with no pedagogical value isn’t permissible.
- Homework should be differentiated according to students’ particular learning needs , where appropriate.
- Teachers should typically provide written or oral feedback on homework within a reasonable time-period.
- Too much homework shouldn’t be assigned: the maximum should be approximately one to two hours a day for high school students and one hour a day for elementary and middle school students.
- The amount of homework assigned to students should be gradually increased with each grade, by around ten minutes.
- Homework may be designed to involve parents/guardians in supporting their children’s learning. But parents should rarely, if ever, be asked to play a formal instructional role in their homework.
- Homework shouldn’t require resources or technology to which students may not have access.
- Homework should be designed and communicated so that students understand what’s expected of them before leaving school.
- Homework should be designed to require no additional teaching outside the classroom.
- Ideally, homework help should be offered.
Series: Choosing a School
- Education experts discuss how to know when a school isn't working
- Parents discuss choosing a school
- School heads discuss red flags to look out for when choosing a school
- School heads discuss choosing a school
- Profile of Stuart Grainger, Headmaster, Trinity College School
- Why your school needs Zebra Robotics
- Finding an academic home in the online world
- Parents' step-by-step guide to choosing the right school
- Questions to ask private schools
- Must Read: Five steps to choosing the perfect school

Find Private Schools:
In the spotlight.

Balancing academics and social-emotional well-being
The art of providing holistic learning environments for teens

School size matters
How school size impacts the student experience at TCS

Out of the class and into the community
TCS’s service learning program provides the hands-on experience of giving back

The benefits of multilingualism
What language education at Alexander von Humboldt German International School Montreal provides

Fostering connection in online classrooms
How HTS is building a state-of-the-art online education platform that focuses on student relationships

Creating real-world impact in classrooms
How The Linden School paves the way for global change through their STEM programs

Leveraging performing arts to boost self-confidence and communication skills
How a new on-site theatre will support Villanova College’s rich arts programming

Preparing high school students for a changing world
How St. Michael’s College School brings the real world into classrooms [ Read more ]

Helping kids deal with climate anxiety
An one-of-a-kind program that promotes science and critical thinking [ Read more ]


Combining high academics with prep hockey
Chase your passion with a one-of-a-kind sports opportunity at Académie Ste-Cécile International School [ Read more ]

Sustainability, responsibility, and accessibility (in service of student success)
ERA’s environmental and social mandate [ Read more ]

Focusing on more than just academics
Well-being and belonging at Trinity College School [ Read more ]

Focusing on affordability in private education
Trinity College School’s financial assistance program [ Read more ]

Where learning takes root
The progressive Kindergarten program at Hudson College [ Read more ]

Preparing for the future
Learn about your U.S. college and university choices [ Read more ]

Planning ahead
Cambridge International Academy innovates in customized student planning. [ Read more ]

The must-attend event for families researching schools.
Meet with admissions. Attend info sessions. Find the best-fit school. [ Get my ticket ]

Association Montessori Internationale Schools
In Canada, participation in AMI (Canada’s) MQA program ensures that a school is committed to the principles of Montessori pedagogy while aligning with current child development research (through the AMI Scientific Pedagogy Group). [ Read more ]

What does it mean to be socially engaged?
Rosthern Junior College High School has been answering that question for more than 100 years. [ Read more ]

From 18 months to 18 years, HSC is where I grow into my best self.
From the moment a student walks onto the 50+ acre campus in Hamilton, Ontario, their journey begins. They grow up in a strong, healthy community whose members share their zest for learning. [ Read more ]

Teaching girls to change the world
We spoke with Tara Silver about what girls need, how girls learn, and how the Linden School has pioneered in all of that. [ Read more ]
Start here: Five steps to finding the perfect school.
Tickets on sale now: private school expos..
- Meet with all the top schools in just one day.
- Attend info seminars with education experts.
- Consult with school heads and admissions teams.
Latest Articles
Regina Christian schools Find the top private and independent Christian schools in Regina (May 16, 2024)
Concord private schools Find the top private and independent schools in Concord (May 16, 2024)
Kimberley private schools Find the top private and independent schools in Kimberley (May 16, 2024)
Riverview private schools Find the top private and independent schools in Riverview (May 16, 2024)
Balancing academics and social-emotional well-being The art of providing holistic learning environments for teens (May 13, 2024)
| Ask a Question |
| Ask a question and get it answered in our community Q&A section |
| Get News & Updates |
| Sign up for our free e-Newsletter to get news straight to your inbox |
| Meet With Schools |
| Come to our Canada-wide Private School Expos to meet with top schools |
Please sign in to continue
Your FREE Our Kids account helps you manage your search, save your favourites, and RSVP for upcoming events.
Signing in allows us to save your selections and customize your experience.
NEW USER? Create an account in 10 seconds using the same path above.
Meet top schools, speak with current students and parents, and consult with experts. All in one afternoon.
- ABOUT OUR KIDS
- PRINT/DIGITAL GUIDES
- OUR KIDS ACCOUNT
- PRIVATE SCHOOLS
- Browse Schools
- Shortlist Schools
- Compare Schools
- School Reviews
- Private School Expos
- Camp Reviews
- Camp & Program Guide
- KIDS' PROGRAMS
- Find Programs & Classes
- Virtual Programs
- Upcoming Events
By logging in or creating an account, you agree to Our Kids' Terms and Conditions . Information presented on this page may be paid advertising provided by the advertisers [schools/camps/programs] and is not warranted or guaranteed by OurKids.net or its associated websites. By using this website, creating or logging into an Our Kids account, you agree to Our Kids' Terms and Conditions . Please also see our Privacy Policy . Our Kids ™ © 2023 All right reserved.
Sign up to receive our exclusive eNews twice a month.
| Verify Code | |

Is Homework Good for Kids?
Research suggests that homework may be most beneficial when it is minimal..
Updated October 3, 2023 | Reviewed by Devon Frye
- Why Education Is Important
- Take our ADHD Test
- Find a Child Therapist
- Research finds that homework can academically benefit middle and high schoolers, but not elementary students.
- There are non-academic benefits to homework, but too much work may interfere with other areas of development.
- Research suggests students should be given about 10 minutes of homework per grade level.
- Parents can help with homework by encouraging a growth mindset and supporting their child's autonomy.
In recent years, homework has become a very hot topic. Many parents and educators have raised concerns about homework and questioned how effective it is in enhancing students’ learning. There are also concerns that students may simply be getting too much homework, which ultimately interferes with quality family time and opportunities for physical activity and play.
Research suggests that these concerns may be valid. For example, one study reported that elementary school students, on average, are assigned three times the recommended amount of homework.
What does the research say? What are the potential risks and benefits of homework, and how much is “too much”?
Academic vs. Non-Academic Benefits
First, research finds that homework is associated with higher scores on academic standardized tests for middle and high school students, but not elementary school students . A recent experimental study in Romania found some benefits for a small amount of writing homework in elementary students but not math homework. Yet, interestingly, this positive impact only occurred when students were given a moderate amount of homework (about 20 minutes on average).
Yet the goal of homework is not simply to improve academic skills. Research finds that homework may have some non-academic benefits, such as building responsibility , time management skills, and task persistence . Homework may also increase parents’ involvement in their children’s schooling.
Yet too much homework may also have some negative impacts on non-academic skills by reducing opportunities for free play , which is essential for the development of language, cognitive, self-regulation , and social-emotional skills. Homework may also interfere with physical activity ; indeed, too much homework is associated with an increased risk of being overweight . As with the research on academic benefits, this research also suggests that homework may be beneficial when it is minimal.
What is the “Right” Amount of Homework?
Research suggests that homework should not exceed 1.5 to 2.5 hours per night for high school students and no more than 1 hour per night for middle school students. Homework for elementary school students should be minimal and assigned with the aim of building self-regulation and independent work skills. Any more than this and homework may no longer have a positive impact.
The National Education Association recommends 10 minutes of homework per grade and there is also some experimental evidence that backs this up.
What Can Parents Do?
Research finds that parental help with homework is beneficial but that it matters more how the parent is helping rather than how often the parent is helping.
So how should parents help with homework (according to the research)?
- Focus on providing general monitoring, guidance, and encouragement, but allow children to complete their homework as independently as possible. Research shows that allowing children more autonomy in completing homework may benefit their academic skills.
- Only provide help when your child asks for it and step away whenever possible. Research finds that too much parental involvement or intrusive and controlling involvement with homework is associated with worse academic performance .
- Help your children to create structure and develop some routines that help your child to independently complete their homework. Research finds that providing this type of structure and responsiveness is related to improved academic skills.
- Set specific rules around homework. Research finds an association between parents setting rules around homework and academic performance.
- Help your child to view homework as an opportunity to learn and improve skills. Parents who view homework as a learning opportunity (that is, a “mastery orientation”) rather than something that they must get “right” or complete successfully to obtain a higher grade (that is, a “performance orientation”) are more likely to have children with the same attitudes.
- Encourage your child to persist in challenging assignments and emphasize difficult assignments as opportunities to grow. Research finds that this attitude is associated with student success. Research also indicates that more challenging homework is associated with enhanced academic performance.
- Stay calm and positive during homework. Research shows that mothers’ showing positive emotions while helping with homework may improve children’s motivation in homework.
- Praise your child’s hard work and effort during homework. This type of praise is likely to increase motivation. In addition, research finds that putting more effort into homework may be associated with enhanced development of conscientiousness in children.
- Communicate with your child and the teacher about any problems your child has with homework and the teacher’s learning goals. Research finds that open communication about homework is associated with increased academic performance.

Cara Goodwin, Ph.D., is a licensed clinical psychologist who specializes in translating scientific research into information that is useful, accurate, and relevant for parents.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Sticking up for yourself is no easy task. But there are concrete skills you can use to hone your assertiveness and advocate for yourself.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Homework Guidelines for Elementary and Middle School Teachers
- Homework Tips
- Learning Styles & Skills
- Study Methods
- Time Management
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- M.Ed., Educational Administration, Northeastern State University
- B.Ed., Elementary Education, Oklahoma State University
Homework; the term elicits a myriad of responses. Students are naturally opposed to the idea of homework. No student ever says, “I wish my teacher would assign me more homework.” Most students begrudge homework and find any opportunity or possible excuse to avoid doing it.
Educators themselves are split on the issue. Many teachers assign daily homework seeing it as a way to further develop and reinforce core academic skills, while also teaching students responsibility. Other educators refrain from assigning daily homework. They view it as unnecessary overkill that often leads to frustration and causes students to resent school and learning altogether.
Parents are also divided on whether or not they welcome homework. Those who welcome it see it as an opportunity for their children to reinforce critical learning skills. Those who loathe it see it as an infringement of their child’s time. They say it takes away from extra-curricular activities, play time, family time, and also adds unnecessary stress.
Research on the topic is also inconclusive. You can find research that strongly supports the benefits of assigning regular homework, some that denounce it as having zero benefits, with most reporting that assigning homework offers some positive benefits, but also can be detrimental in some areas.
The Effects of Homework
Since opinions vary so drastically, coming to a consensus on homework is nearly impossible. We sent a survey out to parents of a school regarding the topic, asking parents these two basic questions:
- How much time is your child spending working on homework each night?
- Is this amount of time too much, too little, or just right?
The responses varied significantly. In one 3 rd grade class with 22 students, the responses regarding how much time their child spends on homework each night had an alarming disparity. The lowest amount of time spent was 15 minutes, while the largest amount of time spent was 4 hours. Everyone else fell somewhere in between. When discussing this with the teacher, she told me that she sent home the same homework for every child and was blown away by the vastly different ranges in time spent completing it. The answers to the second question aligned with the first. Almost every class had similar, varying results making it really difficult to gauge where we should go as a school regarding homework.
While reviewing and studying my school’s homework policy and the results of the aforementioned survey, I discovered a few important revelations about homework that I think anyone looking at the topic would benefit from:
1. Homework should be clearly defined. Homework is not unfinished classwork that the student is required to take home and complete. Homework is “extra practice” given to take home to reinforce concepts that they have been learning in class. It is important to note that teachers should always give students time in class under their supervision to complete class work. Failing to give them an appropriate amount of class time increases their workload at home. More importantly, it does not allow the teacher to give immediate feedback to the student as to whether or not they are doing the assignment correctly. What good does it do if a student completes an assignment if they are doing it all incorrectly? Teachers must find a way to let parents know what assignments are homework and which ones are classwork that they did not complete.
2. The amount of time required to complete the same homework assignment varies significantly from student to student. This speaks to personalization. I have always been a big fan of customizing homework to fit each individual student. Blanket homework is more challenging for some students than it is for others. Some fly through it, while others spend excessive amounts of time completing it. Differentiating homework will take some additional time for teachers in regards to preparation, but it will ultimately be more beneficial for students.
The National Education Association recommends that students be given 10-20 minutes of homework each night and an additional 10 minutes per advancing grade level. The following chart adapted from the National Education Associations recommendations can be used as a resource for teachers in Kindergarten through the 8 th grade.
|
|
Kindergarten | 5 – 15 minutes |
1 Grade | 10 – 20 minutes |
2 Grade | 20 – 30 minutes |
3 Grade | 30 – 40 minutes |
4 Grade | 40 – 50 minutes |
5 Grade | 50 – 60 minutes |
6 Grade | 60 – 70 minutes |
7 Grade | 70 – 80 minutes |
8 Grade | 80 – 90 minutes |
It can be difficult for teachers to gauge how much time students need to complete an assignment. The following charts serve to streamline this process as it breaks down the average time it takes for students to complete a single problem in a variety of subject matter for common assignment types. Teachers should consider this information when assigning homework. While it may not be accurate for every student or assignment, it can serve as a starting point when calculating how much time students need to complete an assignment. It is important to note that in grades where classes are departmentalized it is important that all teachers are on the same page as the totals in the chart above is the recommended amount of total homework per night and not just for a single class.
Kindergarten – 4th Grade (Elementary Recommendations)
|
|
Single Math Problem | 2 minutes |
English Problem | 2 minutes |
Research Style Questions (i.e. Science) | 4 minutes |
Spelling Words – 3x each | 2 minutes per word |
Writing a Story | 45 minutes for 1-page |
Reading a Story | 3 minutes per page |
Answering Story Questions | 2 minutes per question |
Vocabulary Definitions | 3 minutes per definition |
*If students are required to write the questions, then you will need to add 2 additional minutes per problem. (i.e. 1-English problem requires 4 minutes if students are required to write the sentence/question.)
5th – 8th Grade (Middle School Recommendations)
|
|
Single-Step Math Problem | 2 minutes |
Multi-Step Math Problem | 4 minutes |
English Problem | 3 minutes |
Research Style Questions (i.e. Science) | 5 minutes |
Spelling Words – 3x each | 1 minutes per word |
1 Page Essay | 45 minutes for 1-page |
Reading a Story | 5 minutes per page |
Answering Story Questions | 2 minutes per question |
Vocabulary Definitions | 3 minutes per definition |
*If students are required to write the questions, then you will need to add 2 additional minutes per problem. (i.e. 1-English problem requires 5 minutes if students are required to write the sentence/question.)
Assigning Homework Example
It is recommended that 5 th graders have 50-60 minutes of homework per night. In a self-contained class, a teacher assigns 5 multi-step math problems, 5 English problems, 10 spelling words to be written 3x each, and 10 science definitions on a particular night.
|
|
|
|
Multi-Step Math | 4 minutes | 5 | 20 minutes |
English Problems | 3 minutes | 5 | 15 minutes |
Spelling Words – 3x | 1 minute | 10 | 10 minutes |
Science Definitions | 3 minutes | 5 | 15 minutes |
|
|
3. There are a few critical academic skill builders that students should be expected to do every night or as needed. Teachers should also consider these things. However, they may or may not, be factored into the total time to complete homework. Teachers should use their best judgment to make that determination:
- Independent Reading – 20-30 minutes per day
- Study for Test/Quiz - varies
- Multiplication Math Fact Practice (3-4) – varies - until facts are mastered
- Sight Word Practice (K-2) – varies - until all lists are mastered
4. Coming to a general consensus regarding homework is almost impossible. School leaders must bring everyone to the table, solicit feedback, and come up with a plan that works best for the majority. This plan should be reevaluated and adjusted continuously. What works well for one school may not necessarily be the best solution for another.
- Is Homework Good or Bad for Students?
- How to Change Your Habits and Improve Your Grades
- Tips to Write a Great Letter to the Editor
- Fourth Grade School Supplies List
- Cheating with Technology
- 18 Ways to Practice Spelling Words
- MLA Style Parenthetical Citations
- How to Give an Impromptu Speech
- How to Memorize the Names of the US Presidents
- Mock Election Ideas For Students
- 8 Locker Organization Ideas for Back to School
- Field Trip Rules
- Study Tips for Middle School Students
- 20 Tips for Success in High School
- External and Internal Motivation
- How to Write and Structure a Persuasive Speech
- August 15 Mighty Cardinal Band attends summer camp to practice show
- July 17 International Thespian Festival
- June 15 Future Problem Solvers place second in Texas with community project
- May 28 Engi-near the finish line
- May 17 Love is in the air

Three Penny Press

Students spend three times longer on homework than average, survey reveals
Sonya Kulkarni and Pallavi Gorantla | Jan 9, 2022

Graphic by Sonya Kulkarni
The National Education Association and the National Parent Teacher Association have suggested that a healthy number of hours that students should be spending can be determined by the “10-minute rule.” This means that each grade level should have a maximum homework time incrementing by 10 minutes depending on their grade level (for instance, ninth-graders would have 90 minutes of homework, 10th-graders should have 100 minutes, and so on).
As ‘finals week’ rapidly approaches, students not only devote effort to attaining their desired exam scores but make a last attempt to keep or change the grade they have for semester one by making up homework assignments.
High schoolers reported doing an average of 2.7 hours of homework per weeknight, according to a study by the Washington Post from 2018 to 2020 of over 50,000 individuals. A survey of approximately 200 Bellaire High School students revealed that some students spend over three times this number.
The demographics of this survey included 34 freshmen, 43 sophomores, 54 juniors and 54 seniors on average.
When asked how many hours students spent on homework in a day on average, answers ranged from zero to more than nine with an average of about four hours. In contrast, polled students said that about one hour of homework would constitute a healthy number of hours.
Junior Claire Zhang said she feels academically pressured in her AP schedule, but not necessarily by the classes.
“The class environment in AP classes can feel pressuring because everyone is always working hard and it makes it difficult to keep up sometimes.” Zhang said.
A total of 93 students reported that the minimum grade they would be satisfied with receiving in a class would be an A. This was followed by 81 students, who responded that a B would be the minimum acceptable grade. 19 students responded with a C and four responded with a D.
“I am happy with the classes I take, but sometimes it can be very stressful to try to keep up,” freshman Allyson Nguyen said. “I feel academically pressured to keep an A in my classes.”
Up to 152 students said that grades are extremely important to them, while 32 said they generally are more apathetic about their academic performance.
Last year, nine valedictorians graduated from Bellaire. They each achieved a grade point average of 5.0. HISD has never seen this amount of valedictorians in one school, and as of now there are 14 valedictorians.
“I feel that it does degrade the title of valedictorian because as long as a student knows how to plan their schedule accordingly and make good grades in the classes, then anyone can be valedictorian,” Zhang said.
Bellaire offers classes like physical education and health in the summer. These summer classes allow students to skip the 4.0 class and not put it on their transcript. Some electives also have a 5.0 grade point average like debate.
Close to 200 students were polled about Bellaire having multiple valedictorians. They primarily answered that they were in favor of Bellaire having multiple valedictorians, which has recently attracted significant acclaim .
Senior Katherine Chen is one of the 14 valedictorians graduating this year and said that she views the class of 2022 as having an extraordinary amount of extremely hardworking individuals.
“I think it was expected since freshman year since most of us knew about the others and were just focused on doing our personal best,” Chen said.
Chen said that each valedictorian achieved the honor on their own and deserves it.
“I’m honestly very happy for the other valedictorians and happy that Bellaire is such a good school,” Chen said. “I don’t feel any less special with 13 other valedictorians.”
Nguyen said that having multiple valedictorians shows just how competitive the school is.
“It’s impressive, yet scary to think about competing against my classmates,” Nguyen said.
Offering 30 AP classes and boasting a significant number of merit-based scholars Bellaire can be considered a competitive school.
“I feel academically challenged but not pressured,” Chen said. “Every class I take helps push me beyond my comfort zone but is not too much to handle.”
Students have the opportunity to have off-periods if they’ve met all their credits and are able to maintain a high level of academic performance. But for freshmen like Nguyen, off periods are considered a privilege. Nguyen said she usually has an hour to five hours worth of work everyday.
“Depending on the day, there can be a lot of work, especially with extra curriculars,” Nguyen said. “Although, I am a freshman, so I feel like it’s not as bad in comparison to higher grades.”
According to the survey of Bellaire students, when asked to evaluate their agreement with the statement “students who get better grades tend to be smarter overall than students who get worse grades,” responders largely disagreed.
Zhang said that for students on the cusp of applying to college, it can sometimes be hard to ignore the mental pressure to attain good grades.
“As a junior, it’s really easy to get extremely anxious about your GPA,” Zhang said. “It’s also a very common but toxic practice to determine your self-worth through your grades but I think that we just need to remember that our mental health should also come first. Sometimes, it’s just not the right day for everyone and one test doesn’t determine our smartness.”
Your donation will support the student journalists of Bellaire High School. Your contribution will allow us to purchase equipment and cover our annual website hosting costs.

HUMANS OF BELLAIRE – Aiden Gross
![recommended amount of homework AP Physics 1 teacher Gary Johnson stands with his wife and three kids in Solitude, Utah on a ski trip. "My kids really took to [skiing] fast," Johnson said. "It's a fun time as a family to get out there. You leave everything behind and just hang out together."](https://threepennypress.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/fam-600x450.jpg)
HUMANS OF BELLAIRE – GARY JOHNSON

From a spark to an Edaburn

Lifelong friends

Future Problem Solvers place second in Texas with community project

Mighty Cardinal Band attends summer camp to practice show

International Thespian Festival

Engi-near the finish line
Love is in the air
Comments (8).
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Anonymous • Jul 16, 2024 at 3:27 pm
didnt realy help
Anonymous • Nov 21, 2023 at 10:32 am
It’s not really helping me understand how much.
josh • May 9, 2023 at 9:58 am
Kassie • May 6, 2022 at 12:29 pm
Im using this for an English report. This is great because on of my sources needed to be from another student. Homework drives me insane. Im glad this is very updated too!!
Kaylee Swaim • Jan 25, 2023 at 9:21 pm
I am also using this for an English report. I have to do an argumentative essay about banning homework in schools and this helps sooo much!
Izzy McAvaney • Mar 15, 2023 at 6:43 pm
I am ALSO using this for an English report on cutting down school days, homework drives me insane!!
E. Elliott • Apr 25, 2022 at 6:42 pm
I’m from Louisiana and am actually using this for an English Essay thanks for the information it was very informative.
Nabila Wilson • Jan 10, 2022 at 6:56 pm
Interesting with the polls! I didn’t realize about 14 valedictorians, that’s crazy.

How much time should you spend studying? Our ‘Goldilocks Day’ tool helps find the best balance of good grades and well-being
Senior Research Fellow, Allied Health & Human Performance, University of South Australia
Professor of Health Sciences, University of South Australia
Disclosure statement
Dot Dumuid is supported by an Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Early Career Fellowship GNT1162166 and by the Centre of Research Excellence in Driving Global Investment in Adolescent Health funded by NHMRC GNT1171981.
Tim Olds receives funding from the NHMRC and the ARC.
University of South Australia provides funding as a member of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
For students, as for all of us, life is a matter of balance, trade-offs and compromise. Studying for hours on end is unlikely to lead to best academic results. And it could have negative impacts on young people’s physical, mental and social well-being.
Our recent study found the best way for young people to spend their time was different for mental health than for physical health, and even more different for school-related outcomes. Students needed to spend more time sitting for best cognitive and academic performance, but physical activity trumped sitting time for best physical health. For best mental health, longer sleep time was most important.
It’s like a game of rock, paper, scissors with time use. So, what is the sweet spot, or as Goldilocks put it, the “just right” amount of study?
Read more: Back to school: how to help your teen get enough sleep
Using our study data for Australian children aged 11 and 12, we are developing a time-optimisation tool that allows the user to define their own mental, physical and cognitive health priorities. Once the priorities are set, the tool provides real-time updates on what the user’s estimated “Goldilocks day” looks like.

More study improves grades, but not as much as you think
Over 30 years of research shows that students doing more homework get better grades. However, extra study doesn’t make as much difference as people think. An American study found the average grades of high school boys increased by only about 1.5 percentage points for every extra hour of homework per school night.
What these sorts of studies don’t consider is that the relationship between time spent doing homework and academic achievement is unlikely to be linear. A high school boy doing an extra ten hours of homework per school night is unlikely to improve his grades by 15 percentage points.
There is a simple explanation for this: doing an extra ten hours of homework after school would mean students couldn’t go to bed until the early hours of the morning. Even if they could manage this for one day, it would be unsustainable over a week, let alone a month. In any case, adequate sleep is probably critical for memory consolidation .
Read more: What's the point of homework?
As we all know, there are only 24 hours in a day. Students can’t devote more time to study without taking this time from other parts of their day. Excessive studying may become detrimental to learning ability when too much sleep time is lost.
Another US study found that, regardless of how long a student normally spent studying, sacrificing sleep to fit in more study led to learning problems on the following day. Among year 12s, cramming in an extra three hours of study almost doubled their academic problems. For example, students reported they “did not understand something taught in class” or “did poorly on a test, quiz or homework”.
Excessive study could also become unhelpful if it means students don’t have time to exercise. We know exercise is important for young people’s cognition , particularly their creative thinking, working memory and concentration.
On the one hand, then, more time spent studying is beneficial for grades. On the other hand, too much time spent studying is detrimental to grades.
We have to make trade-offs
Of course, how young people spend their time is not only important to their academic performance, but also to their health. Because what is the point of optimising school grades if it means compromising physical, mental and social well-being? And throwing everything at academic performance means other aspects of health will suffer.
US sleep researchers found the ideal amount of sleep for for 15-year-old boys’ mental health was 8 hours 45 minutes a night, but for the best school results it was one hour less.
Clearly, to find the “Goldilocks Zone” – the optimal balance of study, exercise and sleep – we need to think about more than just school grades and academic achievement.
Read more: 'It was the best five years of my life!' How sports programs are keeping disadvantaged teens at school
Looking for the Goldilocks Day
Based on our study findings , we realised the “Goldilocks Day” that was the best on average for all three domains of health (mental, physical and cognitive) would require compromises. Our optimisation algorithm estimated the Goldilocks Day with the best overall compromise for 11-to-12-year-olds. The breakdown was roughly:
10.5 hours of sleep
9.5 hours of sedentary behaviour (such as sitting to study, chill out, eat and watch TV)
2.5 hours of light physical activity (chores, shopping)
1.5 hours of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (sport, running).
We also recognised that people – or the same people at different times — have different priorities. Around exam time, academic performance may become someone’s highest priority. They may then wish to manage their time in a way that leads to better study results, but without completely neglecting their mental or physical health.
To better explore these trade-offs, we developed our time-use optimisation tool based on Australian data . Although only an early prototype, the tool shows there is no “one size fits all” solution to how young people should be spending their time. However, we can be confident the best solutions will involve a healthy balance across multiple daily activities.
Just like we talk about the benefits of a balanced diet, we should start talking about the benefits of balanced time use. The better equipped young people and those supporting them are to find their optimal daily balance of sleep, sedentary behaviours and physical activities, the better their learning outcomes will be, without compromising their health and well-being.
- Mental health
- Physical activity
- Children's mental health
- Children and sleep
- Children's well-being
- children's physical health
- Sleep research

OzGrav Postdoctoral Research Fellow

Student Administration Officer

Casual Facilitator: GERRIC Student Programs - Arts, Design and Architecture

Senior Lecturer, Digital Advertising

Manager, Centre Policy and Translation
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

You are here
- News Center
In the Media
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
Repair Your Relationship With Your Child In Less Than 17 Seconds!

How to Know What’s the “Right” Amount of Homework
You dread the moment your child needs to do assignments because homework takes all night to complete!
Your kids are miserable, we are miserable.
But how do you know when it’s really a problem?
How do you know what’s the “right” amount of homework for your child?

Worry no more!
Here’s 4 simple tips to help you determine if your kid’s homework is appropriate and what to do if you need some help.
1.Look at the Time
How long does it typically take your kid to complete all their homework for one day?
The PTA and NEA recommend 10 minutes for every year in school , and this includes assigned reading. Many districts have their homework policy written out as well. This can often be found in Parent and/or Student handbook.
If homework is taking way longer than the recommended amount, something is amiss.
Bring it up with your kid’s teacher.
Either the teacher, like me, doesn’t realize this strain of homework, or your child needs extra help grasping a skill and by contacting your kid’s teacher, they will know that they may need to offer some extra time with your child on this skill.
2.You Shouldn’t Re-teach
This one is very simple. Appropriate homework asks kids to use a skill they already learned in class. It doesn’t require re-teaching by you.
So if your kid is saying over and over how they “didn’t learn how to do this in class” or they truly don’t understand how to complete the work, there’s a red flag.
3.Look at the task
Is it busy work or are they practicing a valuable skill?
Not all homework is created equal. And this is so true, especially in elementary school homework.
In my honest opinion, writing your spelling words 20 times each and completing 100 math facts in 2 minutes isn’t always as helpful as understanding the learning concept.
So for instance in spelling, that would be understanding the syllables, and phonic sounds.
If it seems like your kid is just getting busy work, then ask the teacher about it. Ask what the learning goal is and explain the impact the current homework is having on your kid.
4.You shouldn’t need a PhD to figure out the homework task
Your child should be able to figure out how to do it with little to no help from you.
If homework causes a strain in your home and is taking WAY longer than the recommended amount, bring it up with your kid’s teacher.
Whatever it is, know that it isn’t your sole responsibility for your kid to get all his or her homework done.
Resources We Shared:
Drama Free Homework Checklist
Homework Simplified
Download the transcripts HERE
The best mom is a happy mom. To better take care of you, download our No Guilt Mom mindset here . These reminders will help you second guess less, and feel more confidence every day in your parenting.
Recommended Posts

How do you know if your kid’s homework is appropriate?

When “I’m Sorry” Doesn’t Cut It – How to Teach Kids to Apologize

The one tip you need to master your kid’s homework organization

5 Ways to Say “No” Without The Guilt

Everything You Need to Know About How to Hang Art the Right Way

3 Simple Ways to Make Homework Fun

What is Homework 911?

Podcast Episode: Why You Don’t Know What You Find Fun

Homework is NOT Wrecking our Kids. The Four Skills Kids Master in Elementary School Homework.

3 Simple Ways to Stop the Homework Power Struggle

Podcast Episode 134: How Your “Mom” Qualities Will Help You Thrive at Work

How to Easily Get Your Kids to Focus on Homework

10 Ways to Stop the Homework Hassle

5 Mistakes Every Parent Makes with Homework

The “one-phrase” you need to get your kids to stop nagging you

Podcast Episode 75: How to Ditch That Nasty “Stop and Drop” Habit

3 Things to Do When Your Kid Cries over Homework

When you have no clue how to help your child with their math homework

4 Steps to Take When Your Child Says “I Hate You”
Podcast episode: why you don’t know what you find fun transcript, article info, popular posts.
- Brie Tucker
COO/ Podcast Producer at No Guilt Mom
- No Guilt Mom Podcast
- Podcast Episode 292: Lies You’ve Been Told About Being the Good Girl Transcripts
- Podcast Episode 292: Lies You’ve Been Told About Being the Good Girl with Elise Loehnen
- Podcast Episode 291: 4 Ways You Can Rekindle Your Sexual Spark: Going From Meh to Magic
- Podcast Episode #146: How to Parent Like a Spy with Christina Hillsberg
- Podcast Episode 112: What is Social Justice Parenting?
- Podcast Episode #98: Talking about the Birds and the Bees with Brittany McBride
- Podcast Episode 86: Parenting on the Same Page with Amy McCready
- Podcast Episode 72: How to Reclaim Your Joy as a Mom
- Podcast Episode 61: How Logical Consequences are More Effective Than Punishments at Home
- How to Calm Down When Stressed
- Podcast Episode 028: Why Don’t Our Kids Listen Anymore?
- 5 Tips to Calm Your Anxiety
Similar Posts

Podcast Episode 73: 4 Ways to Tackle an Upper Limit Problem You Probably Didn’t Know You Had
Do you ever feel guilty when things are going good for you? Do you engage in negative self-talk? Have you ever thought that you just might be self-sabotaging good things in your life? If so, you are not alone. And, according to Gay Hendricks, you may have what he calls an “upper limit problem.” Here’s 4 ways you can kick it to the curb.

Podcast Episode 89: Why We Absolutely Need Mom Friends
You’ve heard us talk about “back in times of B.C.” (Before Children) and how life worked differently then. One of those things that worked differently were friendships (for many of us). We had school, or work, or outside hobbies where we could meet people with similar interests. But when you become a mom, some of us are cut off from those outside things and we struggle trying to make those friendships going forward. And the truth is that mom friends are absolutely essential to your journey through parenthood!
Well, no need to fear, we’ve got 3 tips on how to make (and keep) those mommy friendships going strong!

Podcast Episode 97: 7 Ways to get RESPECT in your home
Do you feel like your kids don’t respect you? They talk back, won’t listen when you ask them to do chores, the list goes on. As kids, many of us were taught a generation ago to simply listen to and follow adults. We give you 7 simple ways to get RESPECT in your home!

My daughter used to leave the kitchen table and throw herself on the couch.
“I can’t DO it,” she wailed, “It’s TOO hard.”
Every afternoon became a neverending negotiation – one I dreaded.
I just wanted to pour myself a glass of wine and hide in the closet.
What do you do at that point?

Podcast Episode 262: Why You Should Focus on Your BUT with Marielle Melling
Discover expert parenting tips for building strong relationships with your children in our latest blog post. Learn how to embrace imperfect parenting moments, regulate your emotions, and foster authentic connections with your little ones. Say goodbye to shame and hello to joy as you navigate the beautiful chaos of motherhood. Dive in and start building stronger relationships today!

Podcast Episode 59: Simple Steps to Help Your Kids be Laser-Focused on BIG Tasks
We all feel stressed when our kids can’t focus…3 easy steps to help your kid focus on projects…When these are used, school projects will be so easy and stress free for you and your kids.
Kids Receive 3 Times the Recommended Homework Load, Study Says
E lementary school children often receive far more homework than recommended by a leading education group, according to new research. The study , published in the American Journal of Family Therapy , found that the average first and second grader had three times the recommended homework load.
The National Education Association recommends that elementary school students receive 10-20 minutes of homework per night in first grade. That figure should grow by 10 minutes per year, the NEA recommends. The study found that teachers regularly assign homework that exceeds that recommendation.
The survey, based on an analysis of survey results from more than 500 parents in Rhode Island, suggests that the average student spends nearly 30 minutes on homework in the first grade, a number that grows steadily over the years. Time spent on homework peaks in 10th grade at 54 minutes per night, according to the study.
Researchers also found a disparity in homework patterns based on parents’ education level as well as a family’s racial background. On average, parents of Hispanic students said their children spent significantly more time on homework than their non-Hispanic counterparts in second, third and 12th grades.
For children with parents of different education levels, time spent on homework was consistent in early years. However, a sharp disparity emerges in high school, where children of parents with college degrees spent significantly more time on homework.
More Must-Reads from TIME
- Breaking Down the 2024 Election Calendar
- Heman Bekele Is TIME’s 2024 Kid of the Year
- The Reintroduction of Kamala Harris
- A Battle Over Fertility Law in China
- For the Love of Savoring Sandwiches : Column
- The 1 Heart-Health Habit You Should Start When You’re Young
- Cuddling Might Help You Get Better Sleep
- The 50 Best Romance Novels to Read Right Now
Write to Justin Worland at [email protected]

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The National PTA and the National Education Association support the " 10-minute homework guideline "—a nightly 10 minutes of homework per grade level. But many teachers and parents are quick to point out that what matters is the quality of the homework assigned and how well it meets students' needs, not the amount of time spent on it.
The amount of homework young people are given varies a lot from school to school and from grade to grade. In some schools and grades, children have no homework at all. In others, they may have 18 ...
Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school. • Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered ...
Many districts follow the guideline of 10 minutes per grade level. This is a good rule of thumb and can be modified for specific students or subjects that need more or less time for assignments. This can also be helpful to gauge if you are providing too much (or too little) homework. Consider surveying your students on how much time is needed ...
In that poll teens reported spending, on average, more than three hours on homework each school night, with 11th graders spending more time on homework than any other grade level. By contrast ...
And homework has a greater positive effect on students in secondary school (grades 7-12) than those in elementary. "Every child should be doing homework, but the amount and type that they're doing ...
What is the "right" amount of homework? Research suggests that homework should not exceed 1.5 to 2.5 hours per night for high school students and no more than one hour per night for middle school students. Homework for elementary school students should be minimal and assigned with the aim of building self-regulation and independent work skills.
For decades, the homework standard has been a "10-minute rule," which recommends a daily maximum of 10 minutes of homework per grade level. Second graders, for example, should do about 20 ...
Many high school students also seem to be exceeding the recommended amounts of homework. Pope and Galloway recently surveyed more than 4,300 students from 10 high-achieving high schools. Students reported bringing home an average of just over three hours of homework nightly (Journal of Experiential Education, 2013).
Homework is too severe and is just too much for students, schools need to decrease the amount of homework. When teachers assign homework they forget that the students have other classes that give them the same amount of homework each day. ... As a student myself, I can say that I have almost never gotten the full 9 hours of recommended sleep ...
What's the right amount of homework to assign? Learn about the research behind homework, how schools and teachers are handling it, and how you can differentiate it in a manageable way. ... Recommended. Recommended Latest. Assigning More Meaningful Math Homework. A small set of problems or even one substantial problem can be enough to ...
In high school students will receive four to five sets of homework per week, taking them between seventy-five and 150 minutes per set to complete. As children progress through school, homework and the amount of time engaged in homework increases in importance. Due to the significance of homework at the older age levels, it is not surprising ...
Research suggests that homework is most effective when: Assignments promote curiosity, leading to " autonomous, self-directed learning .". Students have already " demonstrated competence in the skill…before being asked to do it independently.". Teachers consider some students do not have access to the internet, a quiet working space ...
In the current debate of how much homework is the right amount, many schools rely on the 10-Minute Rule that is supported by the National PTA and the National Education Association. It equates to assigning 10 minutes of homework per grade level, per night. So, 20 minutes for second graders, 60 minutes for sixth graders, and so on, maxing at 2 ...
According to Cooper, the study shows the right amount of homework depends on the grade level. For elementary school students, no amount of homework—large or small—affects academic achievement. For middle school students, academic achievement continues to improve with more homework, until assignments last between one and two hours a night.
What is the "Right" Amount of Homework? Research suggests that homework should not exceed 1.5 to 2.5 hours per night for high school students and no more than 1 hour per night for middle ...
The following chart adapted from the National Education Associations recommendations can be used as a resource for teachers in Kindergarten through the 8 th grade. Grade Level. Recommended Amount of Homework Per Night. Kindergarten. 5 - 15 minutes. 1 st Grade. 10 - 20 minutes. 2 nd Grade. 20 - 30 minutes.
High schoolers reported doing an average of 2.7 hours of homework per weeknight, according to a study by the Washington Post from 2018 to 2020 of over 50,000 individuals. A survey of approximately 200 Bellaire High School students revealed that some students spend over three times this number. The demographics of this survey included 34 ...
US sleep researchers found the ideal amount of sleep for for 15-year-old boys' mental health was 8 hours 45 minutes a night, but for the best school results it was one hour less.
Stanford Graduate School of Education. 482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
Published: June 19, 2020. Homework often gets a bad rap. It can be time-consuming for both students and teachers, stressful, and—as some unengaged students love to point out— "boring.". But savvy educators know that the right assignment can engage students on a more meaningful level and lead to better student involvement in the classroom.
The PTA and NEA recommend 10 minutes for every year in school, and this includes assigned reading. Many districts have their homework policy written out as well. This can often be found in Parent and/or Student handbook. If homework is taking way longer than the recommended amount, something is amiss. Bring it up with your kid's teacher.
The study, published in the American Journal of Family Therapy, found that the average first and second grader had three times the recommended homework load. The National Education Association ...