- Essay Editor

How to Write a Methodology in a Research Proposal

In academic research, crafting a solid methodology is crucial, acting as the foundation for a reliable study structure. It provides the framework that guides the investigation towards addressing research questions and achieving study objectives. Understanding ‘What is methodology in research?’, the components it entails, its efficient organization, and the essential steps required, is vital for aspiring academics.
This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of accurately generating a methods section in a research proposal. It includes examples, insights, and strategies meticulously drawn from reputable academic sources, experienced instructors, and educational platforms.
What is a Research Proposal Methodology?
The thought-provoking part – methodology in a research paper – acts as a guide that describes the methods of analysis, research instruments, and procedures utilized to conduct the investigation. It delineates the survey design, analysis techniques, data retrieval methods, and ethics-related concerns, crucial for carrying out the investigation. Let's say that in a qualitative survey exploring the influence of social media on mental well-being, the approach section would elucidate how data is compiled through participant interviews or assessments and examined using thematic analysis.
Struggling with ‘how to write a research proposal’? Explore how our AI-powered Aithor Text Generator Assistant transforms the process, seamlessly generating content, reviewing errors, and providing suggestions for ideas and citations. Enhance your work’s proposal effortlessly with our comprehensive tool.
The Structure of the Research Proposal Methodology
In generating a research proposal, the written part for methodology serves as a pivotal element that charts the course of the investigation, delineating the stages and strategies to be employed. Let’s delve into essential elements to feature in this section.
1. Research Design: Begin by elucidating the overall academic design of your survey, whether it's a quantitative, qualitative method, or mixed. Let’s say, a quantitative investigation may employ surveys with closed-ended queries to compile numerical data.
2. Data Retrieval Methods: Delineate the specific approaches employed to compile data, comprising observations, experiments, interviews, or previously collected material – secondary data analysis. Each method must be justified based on its suitability for addressing the investigation queries.
3. Sampling Strategy: Describe the way survey participants or data samples are selected, ensuring representativeness, and minimizing bias. As an example, a random sampling method may select partakers from the population.
4. Data Analysis Techniques: Detail the analytical tools and tactics you will use to scrutinize the compiled data. This can involve various methods such as content analysis, thematic exploration, statistical evaluation, or discourse examination, based on the research queries and the data type.
5. Ethical Concerns: Consider ethical issues like informed consent, privacy-related concerns, confidentiality, and potential threats to participants. Abiding by ethical guidelines is pivotal for upholding investigation trustworthiness.
Largely, the research design outlines how the inquiry will proceed and guarantees precision and dependability in achieving its objectives.
How to Write a Methodology Section for Research Proposals: The Essential Steps
Creating a well-planned methods section is essential for precisely managing your investigation. Curious about how to write a methodology section? Begin by clearly defining your investigation issue and the hypothesis to set a robust foundation for your inquiry.
Step 1: Specify a Problem Statement and a Strong Hypothesis
Firstly, state the investigation problem, or query that your work aims to address. Here’s a sample: "The study intends to explore the correlation between youngsters' use of social media and their resulting mental well-being."
Express a strong hypothesis that predicts the expected connection between variables. For instance, "It is hypothesized that greater social site usage linked negatively to self-reported mental health records."
Step 2: Define Your Methodological Approach
Select an appropriate methodological approach depending on your investigation design from techniques named qualitative, quantitative, or mixed.
Validate your preference of approach by explaining its suitability for addressing the queries and aims. To illustrate, "A qualitative method is selected to analyze participants' lived experiences and views regarding social media usage and psychological health."
Step 3: Outline Data Collection Methods
Detail the approaches used to gather data, comprising the tools utilized.
For example, "Semi-structured interviews will be conducted to gather rich qualitative records on participants' experiences with social media platforms."
Discuss any pilot testing or validation procedures conducted for the data retrieval mechanisms.
Step 4: Detail Data Analysis Procedures
Specify the analytical methods employed to assess the gathered data. For instance, "Thematic analysis will be utilized to uncover recurring patterns and themes in the interview transcripts concerning the usage of social media impact and mental condition outcomes."
Examine how data saturation or triangulation will be achieved to establish credibility for the investigation findings.
Step 5: Address Ethical Concerns
Offer a comprehensive overview of the ethical concerns in the inquiry, comprising safeguarding participants' privacy, attaining informed consent, and addressing potential risks.
Detail any ethical approvals or permissions obtained from relevant committees that oversee investigation like ethics panels or IRBs – institution-focused review boards.
Briefly, addressing ethical concerns and obtaining necessary approvals are critical steps in safeguarding the credibility of your inquiry outcomes. Also, stay updated on the methodology outline format to make sure your analysis proposal aligns with current standards and best practices. By precisely detailing your methodology ethics and practices, you contribute significantly to advancing expertise in your domain.
Tips on Improving Your Methodology Section - Strategies and Examples
How can you guarantee that your procedures section is succinct, coherent, and easily comprehensible? Below, we provide actionable steps to guide you in constructing a methodology that elevates the clarity of your writing.
1. Clarity and Precision: Check and refine your methods section for conciseness, clarity, and lack of ambiguity. Use straightforward language and avoid words or phrases like jargon or technical terms that may hinder reader understanding.
2. Justification: Justify every methodology-based selection by explaining its rationale and relevance to your investigation objectives. For example, "The use of purposive sampling ensures the inclusion of participants with diverse experiences related to social media usage."
3. Transparency: Be sufficiently transparent about any limitations or constraints in this part, be it data collection challenges or sample size limitations. This enhances the trustworthiness of your work.
4. Validation: Discuss any validation or reliability checks conducted for your data retrieval instruments or analytical procedures. Verification improves the reliability and authenticity of your findings.
5. Peer Review: Consider obtaining feedback from researchers who are knowledgeable about study methodology to review, enhance, and polish your methodology section. Peer review acts as a helping tool to detect potential weaknesses or areas needing enhancement.
Prioritize justification, transparency, validation, and peer feedback to increase the validity and integrity of your methodology. These elements significantly contribute to the progression of knowledge in your academic field.
Final Thoughts
To wrap up, comprehending how to write a methodology section in a study proposal and eventually mastering this art is essential for carrying out impactful and rigorous studies. By following the ethical guidelines and outlined steps, and carefully organizing your methods section, you elevate the quality and credibility of your investigation. A well-designed methodology supports both your inquiry's execution and the advancement of expertise in your field. Best of luck with your research!
Related articles
Can plagiarism be detected on pdf.
Plagiarism has been a challenge for a long time in writing. It's easy to find information online, which might make some people use it without saying where it came from. But plagiarism isn't just taking someone else's words. Sometimes, we might do it by accident or even use our own old work without mentioning it. When people plagiarize, they can get into serious trouble. They might lose others' trust or even face legal problems. Luckily, we now have tools to detect plagiarism. But what about PDF ...
How to Write a Dialogue in an Essay: Useful Tips
A correct usage of dialogues in essays may seem quite difficult at first sight. Still there are special issues, for instance, narrative or descriptive papers, where this literary technique will be a good helper in depicting anyone's character. How to add dialogues to the work? How to format them correctly? Let's discuss all relevant matters to master putting conversation episodes into academic essays. Essay Dialogue: Definition & Purpose A dialogue is a literary technique for presenting a con ...
Plagiarism: 7 Types in Detail
Your professor says that it is necessary to avoid plagiarism when writing a research paper, essay, or any project based on the works of other people, so to say, any reference source. But what does plagiarism mean? What types of it exist? And how to formulate the material to get rid of potential bad consequences while rendering original texts? Today we try to answer these very questions. Plagiarism: Aspect in Brief Plagiarism is considered to be a serious breach, able to spoil your successful ...
What is Citation and Why Should You Cite the Sources When Writing Content
When we write something for school, work, or just for fun, we often use ideas and facts from other places. This makes us ask: what is a citation in writing? Let's find out what this means and why it's really important when we write. What is Citation? Citation in research refers to the practice of telling your readers where you got your information, ideas, or exact words from. It's like showing them the path to the original information you used in your writing. When you cite something, you us ...
How To Write Essays Faster Using AI?
Creating various topical texts is an obligatory assignment during studies. For a majority of students, it seems like a real headache. It is quite difficult to write a smooth and complex work, meeting all the professors' requirements. However, thanks to modern technologies there appeared a good way of getting a decent project – using AI to write essays. We'd like to acquaint you with Aithor, an effective tool of this kind, able to perform fine and elaborated texts, and, of course, inspiration, i ...
Paraphrasing vs Plagiarism: Do They Really Differ?
Academic assignments require much knowledge and skill. One of the most important points is rendering and interpreting material one has ever studied. A person should avoid presenting word-for-word plagiarism but express his or her thoughts and ideas as much as possible. However, every fine research is certain to be based on the previous issues, data given, or concepts suggested. And here it's high time to differentiate plagiarism and paraphrasing, to realize its peculiarities and cases of usage. ...
What Is Self-Plagiarism & How To Avoid It
Have you ever thought about whether using your own work again could be seen as copying? It might seem strange, but self-plagiarism is a real issue in school and work writing. Let's look at what this means and learn how to avoid self-plagiarism so your work stays original and ethical. What is self-plagiarism? Self-plagiarism, also called auto-plagiarism or duplicate plagiarism, happens when a writer uses parts of their old work without saying where it came from. This isn't just about copying w ...
Top 10 Use Cases for AI Writers
Writing is changing a lot because of AI. But don't worry — AI won't take human writers' jobs. It's a tool that can make our work easier and help us write better. When we use AI along with our own skills, we can create good content faster and better. AI can help with many parts of writing, from coming up with ideas to fixing the final version. Let's look at the top 10 ways how to use AI for content creation and how it can make your writing better. What Is AI Content Writing? AI content writin ...
📕 Studying HQ
How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Proposal
Rachel r.n..
- June 22, 2024
- How to Guides
The methods section is a critical component of your research proposal, as it outlines the specific techniques and approaches you plan to use to investigate your research question or test your hypothesis.
A well-written, comprehensive methods section demonstrates your deep understanding of different research methodologies and justifies why your selected approach is the most appropriate and rigorous for accomplishing your stated aims. This section should provide enough detail that other researchers could potentially recreate your study based on the information provided.
What You'll Learn
What is the Purpose of the Methods Section?
The main purposes of the methods section in a research proposal are as follows:
- Describe your proposed study design – Explicitly state whether you will employ an experimental, quasi-experimental, survey, ethnographic, phenomenological, case study, or other established research methodology. Providing a clear overview of your overarching design shows that you recognize the distinctions between different methodological approaches.
- Specify your methods of data collection – Outline the precise techniques you will use to gather data, such as interviews, focus groups, participant observation, document analysis, tests/measures, or surveys/questionnaires, among others. Clearly explain why these methods are suitable for your research objectives.
- Explain your sampling strategy – Describe the target population you wish to study, the specific criteria for inclusion/exclusion in your sample, your sampling technique (e.g. random, stratified, cluster, convenience/purposive), and your justification for the anticipated sample size.
- Present your plan for data analysis – Discuss in detail how you will organize, analyze, and interpret the qualitative and/or quantitative data you collect. This could include coding methods, statistical tests, analytical tools/software, etc.
- Address potential limitations and ethical issues – Acknowledge potential weaknesses, constraints, or shortcomings in your proposed methodology. Discuss strategies to enhance validity and credibility. Explain procedures to protect participants’ rights and obtain informed consent.
Step 1: Describe Your Study Design/Research Methodology
The first major section is clearly describing the overarching design or methodology that will guide your research study. Some common approaches include:
- Example: “This study will utilize a randomized controlled trial design to examine the effect of a new teaching method on student performance…”
- Example: “The quantitative portion will consist of a cross-sectional online survey of a representative national sample to assess consumer opinions…”
- Example: “An ethnographic approach will be employed, with the researcher embedding herself as a participant-observer for 6 months…”
- Example: “Using a hermeneutic phenomenological methodology enables an in-depth examination of the lived experience of chronic illness…”
- Example: “A revelatory single case study design will be used to understand the implementation and outcomes of a new policy…””
Step 2: Specify Your Data Collection Methods
Next, you need to thoroughly describe exactly how you plan to collect data based on your overarching methodology. Be sure to justify why the selected methods are optimal for answering your research question(s). Common techniques include:
- Example: “Data will be collected through a series of one-on-one, semi-structured interviews with open-ended questions to allow participants to freely discuss their views…”
- Example: “Four focus group sessions will be conducted with homogeneous groups of 6-8 millennial consumers to examine attitudes and decision processes…”
- Example: “The primary data collection method will involve overt, non-participant observation on the factory production floor over a 3-month time period…”
- Example: “A historical document analysis will be conducted on the organization’s archived memos, meeting minutes, reports and correspondence…”
- Example: “The self-administered questionnaire will contain a mix of closed-ended items with Likert scales and open-ended questions to capture nuances…”
Be sure to sufficiently detail any materials you will use, such as interview protocols, observational templates, survey instruments, etc. Describe processes for piloting or pre-testing tools before actual data collection.
Step 3: Explain Your Sampling Strategy
You must provide a clear rationale for how you will select a sample of participants from the target population of interest, including details on:
- Example: “The target population encompasses all adults ages 60+ currently receiving home-based healthcare services in urban areas of State X.”
- Probability sampling: Simple random, stratified random, cluster random sampling, etc.
- Non-probability sampling: Convenience, purposive, quota, snowball sampling, etc.
- Example: “A stratified random sampling technique will be employed to ensure the sample properly represents key demographic subgroups…”
- Example: “Inclusion criteria are: being a first-time mother, having given birth in the past 12 months, residing in County Y, and being 18-40 years old…”
- Example: “A minimum sample of 350 completed survey responses will be sought based on power analysis for detecting a medium effect size with p<0.05…”
Step 4: Present Your Data Analysis Plan
Outline in detail how you plan to organize, analyze, interpret, and extract insights from the qualitative and/or quantitative data you will collect, including:
- Example: “Thematic analysis will be used to inductively analyze interview transcripts, following Braun & Clarke’s (2006) six-step process: …”
- Example: “SPSS will be used to analyze survey data through descriptive statistics, exploratory factor analysis, correlation analysis, multiple regression, etc…”
- Example: “All qualitative codes will be tracked and analyzed using NVivo qualitative data analysis software to aid in cross-case comparison.”
If using mixed methods, specify your procedures for integrating and triangulating the different data streams during analysis and interpretation.
Step 5: Address Limitations and Ethical Considerations
While your goal is to propose a rigorous methodology, all studies have inherent limitations. A strong proposal should openly discuss potential shortcomings and how you plan to mitigate or counterbalance them:
- Example: “A key limitation is that the convenience sampling technique may overly represent those who have internet/computer access and self-select into the study.”
Constraints of data collection methods – Acknowledge potential sources of bias, measurement error, reactivity, or other issues with your chosen methods.
- Example: “The use of self-reported data is a limitation, as responses may be affected by social desirability or imperfect recall biases. However, the anonymity of the online survey aims to reduce desirability pressures.”
- Example: “All participants will provide informed consent after reviewing documentation outlining the study purpose, risks, benefits and their rights. Identifying details will be kept confidential through use of pseudonyms and secure data storage.”
- Example: “To enhance validity, the study will use data triangulation through combining findings from interviews, focus groups and document analysis. A qualitative audit trail will document all research decisions and activities.”
By forthrightly discussing the limitations, you demonstrate self-awareness about the strengths and weaknesses of your methodology. Proposing validity strategies conveys methodological rigor.
Related Articles:
How to Write a Topic Proposal for a Research Paper
How to Critically Appraise a Research Article
How to Write a Research Proposal
How to write a research proposal
Examples of Strong Methods Sections
To illustrate a complete methods section, here are two examples from different fields:
Example 1 – Experimental Psychology:
“This study will employ a double-blind randomized controlled trial design to evaluate the efficacy of a new cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) program for treating anxiety disorders among adolescents ages 13-17.
Participants will be recruited through advertisements , physician referrals, and campus/community outreach in the Greater Boston area. Those meeting inclusion criteria through an initial phone screening (being 13-17 years old, having an anxiety diagnosis, not receiving concurrent treatment) will come to the research center for a comprehensive intake assessment by trained clinicians.
Using blocked stratified randomization based on gender and anxiety severity, 120 eligible participants will be randomly assigned to one of two conditions: the CBT treatment program or a wait-list control group. The manualized CBT program consists of 12 weekly 50-minute individual sessions covering psychoeducation, cognitive restructuring, exposure, and relapse prevention…
Pre, post and 6-month follow-up assessments will be conducted…by doctoral-level psychologists blind to condition using the Anxiety Disorders Interview Schedule for Children (ADIS-C), Children’s Depression Inventory (CDI), and other validated measures of anxiety symptoms, positive thinking, therapy engagement, and quality of life…
Data will be analyzed using SPSS statistical software, with two-tailed independent samples t-tests and repeated measures ANOVA to examine between-group differences in outcomes over time. The study aims to recruit a sample providing 80% power to detect a moderate effect size with alpha = .05…”
Example 2 – Ethnography in Anthropology:
“This ethnographic study will utilize participant observation and semi-structured interviews to examine the cultural norms, practices and belief systems surrounding food and meal consumption within a suburban U.S. Bengali community.
The researcher will adopt an overt role as a participant-observer by attending and documenting daily activities, gatherings and foodways over 12 months in the Bengali community of [City, State]. This will involve immersing herself in the local Bengali organization and selected households through a gatekeeper, while building trust and rapport.
Weekly participant observation field notes will be recorded in rich detail, capturing dietary practices, food procurement, meal preparation, and the symbolic meanings and rituals surrounding eating occasions. A minimum of 20 representative Bengali families across socioeconomic levels will be recruited through snowball sampling to participate in interviews…
In-depth interviewing will utilize an interview guide covering topics like: typical Bengali foods/meals, gender roles in food practices, evaluations of “authentic” Bengali cuisine, changes in practices since immigration, and social rules around food consumption. All interviews will be conducted in Bengali, audio-recorded, and later transcribed for analysis…
A coding procedure following constructivist grounded theory will be employed to inductively analyze the data and develop a theoretical model about Bengali-American cultural ideologies surrounding food and eating…”
By providing these level of specifics, the methods sections clearly lay out the specific plans to rigorously investigate the research questions in a valid, reliable and ethical manner
How do I write the methods section of a research proposal? A Method section should show that the researcher(s) measured or described what they intended to, that they implemented research procedures in a precise and consistent manner, and that they interpreted their data in strategic, unbiased way. The section should provide readers with enough detail to replicate the study.
What is an example of a research methodology? Five examples of research could be surveys, observations, generating research questions, interviews, and focus groups. These examples are dependent on the type of research methodology used.
How long should the methods section be? You should be clear about the academic basis for all the choices of research methods that you have made. Methodology (1,500 to 2,000 words) Specific issues/debates. This should include two or three chapters, each addressing specific issues in the literature (4,000 to 5,000 words)
Start by filling this short order form order.studyinghq.com
And then follow the progressive flow.
Having an issue, chat with us here
Cathy, CS.
New Concept ? Let a subject expert write your paper for You
Have a subject expert write for you now, have a subject expert finish your paper for you, edit my paper for me, have an expert write your dissertation's chapter.
Typically replies within minutes
Hey! 👋 Need help with an assignment?
🟢 Online | Privacy policy
WhatsApp us

Transcription Service for Your Academic Paper
Start Transcription now
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources

Your Step to Success
Transcription Service for Your Paper
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
APA Methods Section – How To Write It With Examples
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

The APA methods section is a very important part of your academic paper, displaying how you conducted your research by providing a precise description of the methods and procedures you used for the study. This section ensures transparency, allowing other researchers to see exactly how you conducted your experiments. In APA style , the methods section usually includes subsections on participants, materials or measures, and procedures. This article discusses the APA methods section in detail.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 APA Methods Section – In a Nutshell
- 2 Definition: APA Methods Section
- 3 APA Methods Section: Structure
- 4 APA Methods Section: Participants
- 5 APA Methods Section: Materials
- 6 APA Methods Section: Procedure
APA Methods Section – In a Nutshell
- The APA methods section covers the participants, materials, and procedures.
- Under the ‘Participants’ heading of the APA methods section, you should state the relevant demographic characteristics of your participants.
- Accurately reporting the facts of the study can help other researchers determine how much the results can be generalized.
In what format are you currently required to submit your thesis?
Definition: APA Methods Section
The APA methods section describes the procedures you used to carry out your research and explains why particular processes were selected. It allows other researchers to replicate the study and make their own conclusions on the validity of the experiment.
APA Methods Section: Structure
- The main heading of the APA methods section should be written in bold and should be capitalized. It also has to be centered.
- All subheadings should be aligned to the left and must be boldfaced. You should select subheadings that are suitable for your essay, and the most commonly used include ‘Participants’, ‘Materials’, and ‘Procedure’.
Heading formats:
| Participants | • Study participants • Sampling methods • Sample size |
| Materials | • Measures used in the study • Quality of the measurements |
| Procedure | • Methods of collecting data • The research design • The method of diagnosing and processing data • Data analysis method |
APA format has certain requirements for reporting different research designs. You should go through these guidelines to determine what you should mention for research using longitudinal designs , replication studies, and experimental designs .
Printing Your Thesis With BachelorPrint
- High-quality bindings with customizable embossing
- 3D live preview to check your work before ordering
- Free express delivery
Configure your binding now!
to the print shop
APA Methods Section: Participants
Under this subheading, you will have to report on the sample characteristics, the procedures used to collect samples, and the sample size selected.
Subject or Participant Characteristics
In academic studies, ‘participants’ refers to the people who take part in a study. If animals are used instead of human beings, the researcher can use the term ‘subjects’. In this subheading of the APA methods section, you have to describe the demographic characteristics of the participants, including their age, sex, race, ethnic group, education level, and gender identity. Depending on the nature of the study, other characteristics may be important. Some of these include:
- Education levels
- Language preference
- Immigration status
By describing the characteristics of the participants, readers will be able to determine how much the results can be generalized. Make sure you use bias-free language when writing this part of the APA methods section.
The study included 100 homosexual men and 100 homosexual women aged between 30 and 50 years from the city of London, UK.
Sampling Procedures
When selecting participants for your study, you will have to use certain sampling procedures. If the study could access all members of the population, you can say that you used random sampling methods. This section of the APA methods section should cover the percentage of respondents who participated in the research, and how they were chosen. You also need to state how participants were compensated and the ethical standard followed.
- Transgender male students from London were invited to participate in a study.
- Invites were sent to the students via email, social media posts, and posters in the schools.
- Each participant received $10 for the time spent in the study.
- The research obtained ethical approval before the participants were recruited.
Sample Size and Statistical Power
In this part of the APA methods section, you should give details on the sample size and statistical power you aimed at achieving. You should mention whether the final sample was the same as the intended sample. This section should show whether your research had enough statistical power to find any effects.
- The study aimed at a statistical power of 75% to detect an effect of 10% with an alpha of .05.
- 200 participants were required, and the study fulfilled these conditions.
APA Methods Section: Materials
Readers also need to know the materials you used for the study. This part of the APA methods section will give other researchers a good picture of the methods used to conduct the study.
Primary and secondary measures
Here, you should indicate the instruments used in the study, as well as the constructs they were meant to measure. Some of these are inventories, scales, tests, software, and hardware. Make sure you cover the following aspects:
- Reliability
- The Traumatic Stress Schedule (TSS) was used to measure the exposure to traumatic events.
- This 10-item chart requires participants to report lifelong exposure to traumatic stress.
- For example, they could indicate whether they suffered the traumatic death of a loved one.
- The Davidson Trauma Scale was also used to assess the symptoms of trauma.
Under this subheading of the APA methods section, you should also mention covariates or additional variables that can explain the outcomes.
Quality of measurements
You can mention the strategies you applied to ensure data integrity and reliability. These may include:
- Training the interviewers
- Establishing clear data nominalization procedures
- Rigorous data handling and analysis processes
- Having multiple people assess the data
If the data was subjectively coded, you should indicate the interrater reliability scores in the APA methods section.
- ✓ Post a picture on Instagram
- ✓ Get the most likes on your picture
- ✓ Receive up to $300 cash back
APA Methods Section: Procedure
This part of the APA methods section indicates the methods you used to carry out the research, process the data, and analyze the results.
Research Design and Data Collection Methods
Data collection is the systematic gathering of observations and measurements, and you have to describe all procedures used in this process. You can use supplementary materials to describe long and complicated data collection methods.
When reporting the research design, you should mention the framework of the study. This could be experimental, longitudinal, correlational, or descriptive. Additionally, you should mention whether you used a between-subjects design or within-subjects design .
In this part of the APA methods section, you should also mention whether any masking methods were used to hide condition assignments from the participants.
- Participants are told the research takes an hour covers their personal experiences in school.
- They were assured that the reports would be confidential and were asked to give consent.
- The participants were asked to fill in questionnaires .
- The control group was given an unrelated filler task, after which they filled a questionnaire.
- It was determined the experiences of homosexual and CIS-gendered students varied.
Data diagnostics
This part of the APA method section outlines the steps taken to process the data. It includes:
- Methods of identifying and controlling outliers
- Data transformation procedures
- Methods of compensating for missing values
Analytic strategies
This subheading of the APA methods section describes the analytic strategies used, but you shouldn’t mention the outcomes. The primary and secondary hypotheses use past studies or theoretical frameworks , while exploratory hypotheses focus on the data in the study.
We started by assessing the demographic differences between the two groups. We also performed an independent samples t-test on the test scores .
What are the parts of an APA methods section?
In this section, you should include the study participants, the methods used, and the procedures.
What is included in the APA methods section?
The methods section covers the participants or subject characteristics, the sampling procedures, the sample size, the measures used, the data collection methods, the research design, the data analysis strategy, and the data processing method.
Should I use the Oxford comma when writing the APA methods section?
Yes, the serial comma is required when writing the APA methods section.
Should I use the first person to write the APA methods section?
Yes, the APA language guidelines encourage researchers to use first-person pronouns when writing the methods section.
They did such an excellent job printing my dissertation! I got it fast and...
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Eigentümer dieser Website, |
| Zweck | Speichert die Einstellungen der Besucher, die in der Cookie Box von Borlabs Cookie ausgewählt wurden. |
| Cookie Name | borlabs-cookie |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Bachelorprint |
| Zweck | Erkennt das Herkunftsland und leitet zur entsprechenden Sprachversion um. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | ip-api.com |
| Cookie Name | georedirect |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Playcanvas |
| Zweck | Display our 3D product animations |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | playcanv.as, playcanvas.as, playcanvas.com |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Cookie von Google zur Steuerung der erweiterten Script- und Ereignisbehandlung. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Cookie Name | _ga,_gat,_gid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Facebook-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .facebook.com |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird zum Entsperren von Google Maps-Inhalten verwendet. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Instagram-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .instagram.com |
| Cookie Name | pigeon_state |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Sitzung |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Openstreetmap Foundation, St John’s Innovation Centre, Cowley Road, Cambridge CB4 0WS, United Kingdom |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um OpenStreetMap-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .openstreetmap.org |
| Cookie Name | _osm_location, _osm_session, _osm_totp_token, _osm_welcome, _pk_id., _pk_ref., _pk_ses., qos_token |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1-10 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Twitter International Company, One Cumberland Place, Fenian Street, Dublin 2, D02 AX07, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Twitter-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .twimg.com, .twitter.com |
| Cookie Name | __widgetsettings, local_storage_support_test |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Unbegrenzt |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Vimeo Inc., 555 West 18th Street, New York, New York 10011, USA |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Vimeo-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | player.vimeo.com |
| Cookie Name | vuid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um YouTube-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
Privacy Policy Imprint
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper

Writing a research paper is both an art and a skill, and knowing how to write the methods section of a research paper is the first crucial step in mastering scientific writing. If, like the majority of early career researchers, you believe that the methods section is the simplest to write and needs little in the way of careful consideration or thought, this article will help you understand it is not 1 .
We have all probably asked our supervisors, coworkers, or search engines “ how to write a methods section of a research paper ” at some point in our scientific careers, so you are not alone if that’s how you ended up here. Even for seasoned researchers, selecting what to include in the methods section from a wealth of experimental information can occasionally be a source of distress and perplexity.
Additionally, journal specifications, in some cases, may make it more of a requirement rather than a choice to provide a selective yet descriptive account of the experimental procedure. Hence, knowing these nuances of how to write the methods section of a research paper is critical to its success. The methods section of the research paper is not supposed to be a detailed heavy, dull section that some researchers tend to write; rather, it should be the central component of the study that justifies the validity and reliability of the research.
Are you still unsure of how the methods section of a research paper forms the basis of every investigation? Consider the last article you read but ignore the methods section and concentrate on the other parts of the paper . Now think whether you could repeat the study and be sure of the credibility of the findings despite knowing the literature review and even having the data in front of you. You have the answer!

Having established the importance of the methods section , the next question is how to write the methods section of a research paper that unifies the overall study. The purpose of the methods section , which was earlier called as Materials and Methods , is to describe how the authors went about answering the “research question” at hand. Here, the objective is to tell a coherent story that gives a detailed account of how the study was conducted, the rationale behind specific experimental procedures, the experimental setup, objects (variables) involved, the research protocol employed, tools utilized to measure, calculations and measurements, and the analysis of the collected data 2 .
In this article, we will take a deep dive into this topic and provide a detailed overview of how to write the methods section of a research paper . For the sake of clarity, we have separated the subject into various sections with corresponding subheadings.
Table of Contents
What is the methods section of a research paper ?
The methods section is a fundamental section of any paper since it typically discusses the ‘ what ’, ‘ how ’, ‘ which ’, and ‘ why ’ of the study, which is necessary to arrive at the final conclusions. In a research article, the introduction, which serves to set the foundation for comprehending the background and results is usually followed by the methods section, which precedes the result and discussion sections. The methods section must explicitly state what was done, how it was done, which equipment, tools and techniques were utilized, how were the measurements/calculations taken, and why specific research protocols, software, and analytical methods were employed.
Why is the methods section important?
The primary goal of the methods section is to provide pertinent details about the experimental approach so that the reader may put the results in perspective and, if necessary, replicate the findings 3 . This section offers readers the chance to evaluate the reliability and validity of any study. In short, it also serves as the study’s blueprint, assisting researchers who might be unsure about any other portion in establishing the study’s context and validity. The methods plays a rather crucial role in determining the fate of the article; an incomplete and unreliable methods section can frequently result in early rejections and may lead to numerous rounds of modifications during the publication process. This means that the reviewers also often use methods section to assess the reliability and validity of the research protocol and the data analysis employed to address the research topic. In other words, the purpose of the methods section is to demonstrate the research acumen and subject-matter expertise of the author(s) in their field.
Structure of methods section of a research paper
Similar to the research paper, the methods section also follows a defined structure; this may be dictated by the guidelines of a specific journal or can be presented in a chronological or thematic manner based on the study type. When writing the methods section , authors should keep in mind that they are telling a story about how the research was conducted. They should only report relevant information to avoid confusing the reader and include details that would aid in connecting various aspects of the entire research activity together. It is generally advisable to present experiments in the order in which they were conducted. This facilitates the logical flow of the research and allows readers to follow the progression of the study design.

It is also essential to clearly state the rationale behind each experiment and how the findings of earlier experiments informed the design or interpretation of later experiments. This allows the readers to understand the overall purpose of the study design and the significance of each experiment within that context. However, depending on the particular research question and method, it may make sense to present information in a different order; therefore, authors must select the best structure and strategy for their individual studies.
In cases where there is a lot of information, divide the sections into subheadings to cover the pertinent details. If the journal guidelines pose restrictions on the word limit , additional important information can be supplied in the supplementary files. A simple rule of thumb for sectioning the method section is to begin by explaining the methodological approach ( what was done ), describing the data collection methods ( how it was done ), providing the analysis method ( how the data was analyzed ), and explaining the rationale for choosing the methodological strategy. This is described in detail in the upcoming sections.
How to write the methods section of a research paper
Contrary to widespread assumption, the methods section of a research paper should be prepared once the study is complete to prevent missing any key parameter. Hence, please make sure that all relevant experiments are done before you start writing a methods section . The next step for authors is to look up any applicable academic style manuals or journal-specific standards to ensure that the methods section is formatted correctly. The methods section of a research paper typically constitutes materials and methods; while writing this section, authors usually arrange the information under each category.
The materials category describes the samples, materials, treatments, and instruments, while experimental design, sample preparation, data collection, and data analysis are a part of the method category. According to the nature of the study, authors should include additional subsections within the methods section, such as ethical considerations like the declaration of Helsinki (for studies involving human subjects), demographic information of the participants, and any other crucial information that can affect the output of the study. Simply put, the methods section has two major components: content and format. Here is an easy checklist for you to consider if you are struggling with how to write the methods section of a research paper .
- Explain the research design, subjects, and sample details
- Include information on inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Mention ethical or any other permission required for the study
- Include information about materials, experimental setup, tools, and software
- Add details of data collection and analysis methods
- Incorporate how research biases were avoided or confounding variables were controlled
- Evaluate and justify the experimental procedure selected to address the research question
- Provide precise and clear details of each experiment
- Flowcharts, infographics, or tables can be used to present complex information
- Use past tense to show that the experiments have been done
- Follow academic style guides (such as APA or MLA ) to structure the content
- Citations should be included as per standard protocols in the field
Now that you know how to write the methods section of a research paper , let’s address another challenge researchers face while writing the methods section —what to include in the methods section . How much information is too much is not always obvious when it comes to trying to include data in the methods section of a paper. In the next section, we examine this issue and explore potential solutions.

What to include in the methods section of a research paper
The technical nature of the methods section occasionally makes it harder to present the information clearly and concisely while staying within the study context. Many young researchers tend to veer off subject significantly, and they frequently commit the sin of becoming bogged down in itty bitty details, making the text harder to read and impairing its overall flow. However, the best way to write the methods section is to start with crucial components of the experiments. If you have trouble deciding which elements are essential, think about leaving out those that would make it more challenging to comprehend the context or replicate the results. The top-down approach helps to ensure all relevant information is incorporated and vital information is not lost in technicalities. Next, remember to add details that are significant to assess the validity and reliability of the study. Here is a simple checklist for you to follow ( bonus tip: you can also make a checklist for your own study to avoid missing any critical information while writing the methods section ).
- Structuring the methods section : Authors should diligently follow journal guidelines and adhere to the specific author instructions provided when writing the methods section . Journals typically have specific guidelines for formatting the methods section ; for example, Frontiers in Plant Sciences advises arranging the materials and methods section by subheading and citing relevant literature. There are several standardized checklists available for different study types in the biomedical field, including CONSORT (Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials) for randomized clinical trials, PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analysis) for systematic reviews and meta-analysis, and STROBE (STrengthening the Reporting of OBservational studies in Epidemiology) for cohort, case-control, cross-sectional studies. Before starting the methods section , check the checklist available in your field that can function as a guide.
- Organizing different sections to tell a story : Once you are sure of the format required for structuring the methods section , the next is to present the sections in a logical manner; as mentioned earlier, the sections can be organized according to the chronology or themes. In the chronological arrangement, you should discuss the methods in accordance with how the experiments were carried out. An example of the method section of a research paper of an animal study should first ideally include information about the species, weight, sex, strain, and age. Next, the number of animals, their initial conditions, and their living and housing conditions should also be mentioned. Second, how the groups are assigned and the intervention (drug treatment, stress, or other) given to each group, and finally, the details of tools and techniques used to measure, collect, and analyze the data. Experiments involving animal or human subjects should additionally state an ethics approval statement. It is best to arrange the section using the thematic approach when discussing distinct experiments not following a sequential order.
- Define and explain the objects and procedure: Experimental procedure should clearly be stated in the methods section . Samples, necessary preparations (samples, treatment, and drug), and methods for manipulation need to be included. All variables (control, dependent, independent, and confounding) must be clearly defined, particularly if the confounding variables can affect the outcome of the study.
- Match the order of the methods section with the order of results: Though not mandatory, organizing the manuscript in a logical and coherent manner can improve the readability and clarity of the paper. This can be done by following a consistent structure throughout the manuscript; readers can easily navigate through the different sections and understand the methods and results in relation to each other. Using experiment names as headings for both the methods and results sections can also make it simpler for readers to locate specific information and corroborate it if needed.
- Relevant information must always be included: The methods section should have information on all experiments conducted and their details clearly mentioned. Ask the journal whether there is a way to offer more information in the supplemental files or external repositories if your target journal has strict word limitations. For example, Nature communications encourages authors to deposit their step-by-step protocols in an open-resource depository, Protocol Exchange which allows the protocols to be linked with the manuscript upon publication. Providing access to detailed protocols also helps to increase the transparency and reproducibility of the research.
- It’s all in the details: The methods section should meticulously list all the materials, tools, instruments, and software used for different experiments. Specify the testing equipment on which data was obtained, together with its manufacturer’s information, location, city, and state or any other stimuli used to manipulate the variables. Provide specifics on the research process you employed; if it was a standard protocol, cite previous studies that also used the protocol. Include any protocol modifications that were made, as well as any other factors that were taken into account when planning the study or gathering data. Any new or modified techniques should be explained by the authors. Typically, readers evaluate the reliability and validity of the procedures using the cited literature, and a widely accepted checklist helps to support the credibility of the methodology. Note: Authors should include a statement on sample size estimation (if applicable), which is often missed. It enables the reader to determine how many subjects will be required to detect the expected change in the outcome variables within a given confidence interval.
- Write for the audience: While explaining the details in the methods section , authors should be mindful of their target audience, as some of the rationale or assumptions on which specific procedures are based might not always be obvious to the audience, particularly for a general audience. Therefore, when in doubt, the objective of a procedure should be specified either in relation to the research question or to the entire protocol.
- Data interpretation and analysis : Information on data processing, statistical testing, levels of significance, and analysis tools and software should be added. Mention if the recommendations and expertise of an experienced statistician were followed. Also, evaluate and justify the preferred statistical method used in the study and its significance.
What NOT to include in the methods section of a research paper
To address “ how to write the methods section of a research paper ”, authors should not only pay careful attention to what to include but also what not to include in the methods section of a research paper . Here is a list of do not’s when writing the methods section :
- Do not elaborate on specifics of standard methods/procedures: You should refrain from adding unnecessary details of experiments and practices that are well established and cited previously. Instead, simply cite relevant literature or mention if the manufacturer’s protocol was followed.
- Do not add unnecessary details : Do not include minute details of the experimental procedure and materials/instruments used that are not significant for the outcome of the experiment. For example, there is no need to mention the brand name of the water bath used for incubation.
- Do not discuss the results: The methods section is not to discuss the results or refer to the tables and figures; save it for the results and discussion section. Also, focus on the methods selected to conduct the study and avoid diverting to other methods or commenting on their pros or cons.
- Do not make the section bulky : For extensive methods and protocols, provide the essential details and share the rest of the information in the supplemental files. The writing should be clear yet concise to maintain the flow of the section.
We hope that by this point, you understand how crucial it is to write a thoughtful and precise methods section and the ins and outs of how to write the methods section of a research paper . To restate, the entire purpose of the methods section is to enable others to reproduce the results or verify the research. We sincerely hope that this post has cleared up any confusion and given you a fresh perspective on the methods section .
As a parting gift, we’re leaving you with a handy checklist that will help you understand how to write the methods section of a research paper . Feel free to download this checklist and use or share this with those who you think may benefit from it.

References
- Bhattacharya, D. How to write the Methods section of a research paper. Editage Insights, 2018. https://www.editage.com/insights/how-to-write-the-methods-section-of-a-research-paper (2018).
- Kallet, R. H. How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper. Respiratory Care 49, 1229–1232 (2004). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15447808/
- Grindstaff, T. L. & Saliba, S. A. AVOIDING MANUSCRIPT MISTAKES. Int J Sports Phys Ther 7, 518–524 (2012). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3474299/
Editage All Access is a subscription-based platform that unifies the best AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline every step of a researcher’s journey. The Editage All Access Pack is a one-of-a-kind subscription that unlocks full access to an AI writing assistant, literature recommender, journal finder, scientific illustration tool, and exclusive discounts on professional publication services from Editage.
Based on 22+ years of experience in academia, Editage All Access empowers researchers to put their best research forward and move closer to success. Explore our top AI Tools pack, AI Tools + Publication Services pack, or Build Your Own Plan. Find everything a researcher needs to succeed, all in one place – Get All Access now starting at just $14 a month !
Related Posts

Back to School – Lock-in All Access Pack for a Year at the Best Price

Research Paper Appendix: Format and Examples
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Sweepstakes
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Methods Section for a Psychology Paper
Tips and Examples of an APA Methods Section
Verywell / Brianna Gilmartin
The methods section of an APA format psychology paper provides the methods and procedures used in a research study or experiment . This part of an APA paper is critical because it allows other researchers to see exactly how you conducted your research.
Method refers to the procedure that was used in a research study. It included a precise description of how the experiments were performed and why particular procedures were selected. While the APA technically refers to this section as the 'method section,' it is also often known as a 'methods section.'
The methods section ensures the experiment's reproducibility and the assessment of alternative methods that might produce different results. It also allows researchers to replicate the experiment and judge the study's validity.
This article discusses how to write a methods section for a psychology paper, including important elements to include and tips that can help.
What to Include in a Method Section
So what exactly do you need to include when writing your method section? You should provide detailed information on the following:
- Research design
- Participants
- Participant behavior
The method section should provide enough information to allow other researchers to replicate your experiment or study.
Components of a Method Section
The method section should utilize subheadings to divide up different subsections. These subsections typically include participants, materials, design, and procedure.
Participants
In this part of the method section, you should describe the participants in your experiment, including who they were (and any unique features that set them apart from the general population), how many there were, and how they were selected. If you utilized random selection to choose your participants, it should be noted here.
For example: "We randomly selected 100 children from elementary schools near the University of Arizona."
At the very minimum, this part of your method section must convey:
- Basic demographic characteristics of your participants (such as sex, age, ethnicity, or religion)
- The population from which your participants were drawn
- Any restrictions on your pool of participants
- How many participants were assigned to each condition and how they were assigned to each group (i.e., randomly assignment , another selection method, etc.)
- Why participants took part in your research (i.e., the study was advertised at a college or hospital, they received some type of incentive, etc.)
Information about participants helps other researchers understand how your study was performed, how generalizable the result might be, and allows other researchers to replicate the experiment with other populations to see if they might obtain the same results.
In this part of the method section, you should describe the materials, measures, equipment, or stimuli used in the experiment. This may include:
- Testing instruments
- Technical equipment
- Any psychological assessments that were used
- Any special equipment that was used
For example: "Two stories from Sullivan et al.'s (1994) second-order false belief attribution tasks were used to assess children's understanding of second-order beliefs."
For standard equipment such as computers, televisions, and videos, you can simply name the device and not provide further explanation.
Specialized equipment should be given greater detail, especially if it is complex or created for a niche purpose. In some instances, such as if you created a special material or apparatus for your study, you might need to include an illustration of the item in the appendix of your paper.
In this part of your method section, describe the type of design used in the experiment. Specify the variables as well as the levels of these variables. Identify:
- The independent variables
- Dependent variables
- Control variables
- Any extraneous variables that might influence your results.
Also, explain whether your experiment uses a within-groups or between-groups design.
For example: "The experiment used a 3x2 between-subjects design. The independent variables were age and understanding of second-order beliefs."
The next part of your method section should detail the procedures used in your experiment. Your procedures should explain:
- What the participants did
- How data was collected
- The order in which steps occurred
For example: "An examiner interviewed children individually at their school in one session that lasted 20 minutes on average. The examiner explained to each child that he or she would be told two short stories and that some questions would be asked after each story. All sessions were videotaped so the data could later be coded."
Keep this subsection concise yet detailed. Explain what you did and how you did it, but do not overwhelm your readers with too much information.
Tips for How to Write a Methods Section
In addition to following the basic structure of an APA method section, there are also certain things you should remember when writing this section of your paper. Consider the following tips when writing this section:
- Use the past tense : Always write the method section in the past tense.
- Be descriptive : Provide enough detail that another researcher could replicate your experiment, but focus on brevity. Avoid unnecessary detail that is not relevant to the outcome of the experiment.
- Use an academic tone : Use formal language and avoid slang or colloquial expressions. Word choice is also important. Refer to the people in your experiment or study as "participants" rather than "subjects."
- Use APA format : Keep a style guide on hand as you write your method section. The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association is the official source for APA style.
- Make connections : Read through each section of your paper for agreement with other sections. If you mention procedures in the method section, these elements should be discussed in the results and discussion sections.
- Proofread : Check your paper for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.. typos, grammar problems, and spelling errors. Although a spell checker is a handy tool, there are some errors only you can catch.
After writing a draft of your method section, be sure to get a second opinion. You can often become too close to your work to see errors or lack of clarity. Take a rough draft of your method section to your university's writing lab for additional assistance.
A Word From Verywell
The method section is one of the most important components of your APA format paper. The goal of your paper should be to clearly detail what you did in your experiment. Provide enough detail that another researcher could replicate your study if they wanted.
Finally, if you are writing your paper for a class or for a specific publication, be sure to keep in mind any specific instructions provided by your instructor or by the journal editor. Your instructor may have certain requirements that you need to follow while writing your method section.
Frequently Asked Questions
While the subsections can vary, the three components that should be included are sections on the participants, the materials, and the procedures.
- Describe who the participants were in the study and how they were selected.
- Define and describe the materials that were used including any equipment, tests, or assessments
- Describe how the data was collected
To write your methods section in APA format, describe your participants, materials, study design, and procedures. Keep this section succinct, and always write in the past tense. The main heading of this section should be labeled "Method" and it should be centered, bolded, and capitalized. Each subheading within this section should be bolded, left-aligned and in title case.
The purpose of the methods section is to describe what you did in your experiment. It should be brief, but include enough detail that someone could replicate your experiment based on this information. Your methods section should detail what you did to answer your research question. Describe how the study was conducted, the study design that was used and why it was chosen, and how you collected the data and analyzed the results.
Erdemir F. How to write a materials and methods section of a scientific article ? Turk J Urol . 2013;39(Suppl 1):10-5. doi:10.5152/tud.2013.047
Kallet RH. How to write the methods section of a research paper . Respir Care . 2004;49(10):1229-32. PMID: 15447808.
American Psychological Association. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). Washington DC: The American Psychological Association; 2019.
American Psychological Association. APA Style Journal Article Reporting Standards . Published 2020.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on October 12, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 21, 2023.

A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organized and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research proposals.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
| Show your reader why your project is interesting, original, and important. | |
| Demonstrate your comfort and familiarity with your field. Show that you understand the current state of research on your topic. | |
| Make a case for your . Demonstrate that you have carefully thought about the data, tools, and procedures necessary to conduct your research. | |
| Confirm that your project is feasible within the timeline of your program or funding deadline. |
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: “A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management”
- Example research proposal #2: “Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use”
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesize prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
| ? or ? , , or research design? | |
| , )? ? | |
| , , , )? | |
| ? |
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasize again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
| Research phase | Objectives | Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Background research and literature review | 20th January | |
| 2. Research design planning | and data analysis methods | 13th February |
| 3. Data collection and preparation | with selected participants and code interviews | 24th March |
| 4. Data analysis | of interview transcripts | 22nd April |
| 5. Writing | 17th June | |
| 6. Revision | final work | 28th July |
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved August 29, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- Locations and Hours
- UCLA Library
- Research Guides
- Research Tips and Tools
Advanced Research Methods
- Writing a Research Proposal
- What Is Research?
- Library Research
What Is a Research Proposal?
Reference books.
- Writing the Research Paper
- Presenting the Research Paper
When applying for a research grant or scholarship, or, just before you start a major research project, you may be asked to write a preliminary document that includes basic information about your future research. This is the information that is usually needed in your proposal:
- The topic and goal of the research project.
- The kind of result expected from the research.
- The theory or framework in which the research will be done and presented.
- What kind of methods will be used (statistical, empirical, etc.).
- Short reference on the preliminary scholarship and why your research project is needed; how will it continue/justify/disprove the previous scholarship.
- How much will the research project cost; how will it be budgeted (what for the money will be spent).
- Why is it you who can do this research and not somebody else.
Most agencies that offer scholarships or grants provide information about the required format of the proposal. It may include filling out templates, types of information they need, suggested/maximum length of the proposal, etc.
Research proposal formats vary depending on the size of the planned research, the number of participants, the discipline, the characteristics of the research, etc. The following outline assumes an individual researcher. This is just a SAMPLE; several other ways are equally good and can be successful. If possible, discuss your research proposal with an expert in writing, a professor, your colleague, another student who already wrote successful proposals, etc.
- Author, author's affiliation
- Explain the topic and why you chose it. If possible explain your goal/outcome of the research . How much time you need to complete the research?
- Give a brief summary of previous scholarship and explain why your topic and goals are important.
- Relate your planned research to previous scholarship. What will your research add to our knowledge of the topic.
- Break down the main topic into smaller research questions. List them one by one and explain why these questions need to be investigated. Relate them to previous scholarship.
- Include your hypothesis into the descriptions of the detailed research issues if you have one. Explain why it is important to justify your hypothesis.
- This part depends of the methods conducted in the research process. List the methods; explain how the results will be presented; how they will be assessed.
- Explain what kind of results will justify or disprove your hypothesis.
- Explain how much money you need.
- Explain the details of the budget (how much you want to spend for what).
- Describe why your research is important.
- List the sources you have used for writing the research proposal, including a few main citations of the preliminary scholarship.
- << Previous: Library Research
- Next: Writing the Research Paper >>
- Last Updated: Aug 22, 2024 3:43 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.ucla.edu/research-methods
17 Research Proposal Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process

A research proposal systematically and transparently outlines a proposed research project.
The purpose of a research proposal is to demonstrate a project’s viability and the researcher’s preparedness to conduct an academic study. It serves as a roadmap for the researcher.
The process holds value both externally (for accountability purposes and often as a requirement for a grant application) and intrinsic value (for helping the researcher to clarify the mechanics, purpose, and potential signficance of the study).
Key sections of a research proposal include: the title, abstract, introduction, literature review, research design and methods, timeline, budget, outcomes and implications, references, and appendix. Each is briefly explained below.
Watch my Guide: How to Write a Research Proposal
Get your Template for Writing your Research Proposal Here (With AI Prompts!)
Research Proposal Sample Structure
Title: The title should present a concise and descriptive statement that clearly conveys the core idea of the research projects. Make it as specific as possible. The reader should immediately be able to grasp the core idea of the intended research project. Often, the title is left too vague and does not help give an understanding of what exactly the study looks at.
Abstract: Abstracts are usually around 250-300 words and provide an overview of what is to follow – including the research problem , objectives, methods, expected outcomes, and significance of the study. Use it as a roadmap and ensure that, if the abstract is the only thing someone reads, they’ll get a good fly-by of what will be discussed in the peice.
Introduction: Introductions are all about contextualization. They often set the background information with a statement of the problem. At the end of the introduction, the reader should understand what the rationale for the study truly is. I like to see the research questions or hypotheses included in the introduction and I like to get a good understanding of what the significance of the research will be. It’s often easiest to write the introduction last
Literature Review: The literature review dives deep into the existing literature on the topic, demosntrating your thorough understanding of the existing literature including themes, strengths, weaknesses, and gaps in the literature. It serves both to demonstrate your knowledge of the field and, to demonstrate how the proposed study will fit alongside the literature on the topic. A good literature review concludes by clearly demonstrating how your research will contribute something new and innovative to the conversation in the literature.
Research Design and Methods: This section needs to clearly demonstrate how the data will be gathered and analyzed in a systematic and academically sound manner. Here, you need to demonstrate that the conclusions of your research will be both valid and reliable. Common points discussed in the research design and methods section include highlighting the research paradigm, methodologies, intended population or sample to be studied, data collection techniques, and data analysis procedures . Toward the end of this section, you are encouraged to also address ethical considerations and limitations of the research process , but also to explain why you chose your research design and how you are mitigating the identified risks and limitations.
Timeline: Provide an outline of the anticipated timeline for the study. Break it down into its various stages (including data collection, data analysis, and report writing). The goal of this section is firstly to establish a reasonable breakdown of steps for you to follow and secondly to demonstrate to the assessors that your project is practicable and feasible.
Budget: Estimate the costs associated with the research project and include evidence for your estimations. Typical costs include staffing costs, equipment, travel, and data collection tools. When applying for a scholarship, the budget should demonstrate that you are being responsible with your expensive and that your funding application is reasonable.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: A discussion of the anticipated findings or results of the research, as well as the potential contributions to the existing knowledge, theory, or practice in the field. This section should also address the potential impact of the research on relevant stakeholders and any broader implications for policy or practice.
References: A complete list of all the sources cited in the research proposal, formatted according to the required citation style. This demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the relevant literature and ensures proper attribution of ideas and information.
Appendices (if applicable): Any additional materials, such as questionnaires, interview guides, or consent forms, that provide further information or support for the research proposal. These materials should be included as appendices at the end of the document.
Research Proposal Examples
Research proposals often extend anywhere between 2,000 and 15,000 words in length. The following snippets are samples designed to briefly demonstrate what might be discussed in each section.
1. Education Studies Research Proposals
See some real sample pieces:
- Assessment of the perceptions of teachers towards a new grading system
- Does ICT use in secondary classrooms help or hinder student learning?
- Digital technologies in focus project
- Urban Middle School Teachers’ Experiences of the Implementation of
- Restorative Justice Practices
- Experiences of students of color in service learning
Consider this hypothetical education research proposal:
The Impact of Game-Based Learning on Student Engagement and Academic Performance in Middle School Mathematics
Abstract: The proposed study will explore multiplayer game-based learning techniques in middle school mathematics curricula and their effects on student engagement. The study aims to contribute to the current literature on game-based learning by examining the effects of multiplayer gaming in learning.
Introduction: Digital game-based learning has long been shunned within mathematics education for fears that it may distract students or lower the academic integrity of the classrooms. However, there is emerging evidence that digital games in math have emerging benefits not only for engagement but also academic skill development. Contributing to this discourse, this study seeks to explore the potential benefits of multiplayer digital game-based learning by examining its impact on middle school students’ engagement and academic performance in a mathematics class.
Literature Review: The literature review has identified gaps in the current knowledge, namely, while game-based learning has been extensively explored, the role of multiplayer games in supporting learning has not been studied.
Research Design and Methods: This study will employ a mixed-methods research design based upon action research in the classroom. A quasi-experimental pre-test/post-test control group design will first be used to compare the academic performance and engagement of middle school students exposed to game-based learning techniques with those in a control group receiving instruction without the aid of technology. Students will also be observed and interviewed in regard to the effect of communication and collaboration during gameplay on their learning.
Timeline: The study will take place across the second term of the school year with a pre-test taking place on the first day of the term and the post-test taking place on Wednesday in Week 10.
Budget: The key budgetary requirements will be the technologies required, including the subscription cost for the identified games and computers.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: It is expected that the findings will contribute to the current literature on game-based learning and inform educational practices, providing educators and policymakers with insights into how to better support student achievement in mathematics.
2. Psychology Research Proposals
See some real examples:
- A situational analysis of shared leadership in a self-managing team
- The effect of musical preference on running performance
- Relationship between self-esteem and disordered eating amongst adolescent females
Consider this hypothetical psychology research proposal:
The Effects of Mindfulness-Based Interventions on Stress Reduction in College Students
Abstract: This research proposal examines the impact of mindfulness-based interventions on stress reduction among college students, using a pre-test/post-test experimental design with both quantitative and qualitative data collection methods .
Introduction: College students face heightened stress levels during exam weeks. This can affect both mental health and test performance. This study explores the potential benefits of mindfulness-based interventions such as meditation as a way to mediate stress levels in the weeks leading up to exam time.
Literature Review: Existing research on mindfulness-based meditation has shown the ability for mindfulness to increase metacognition, decrease anxiety levels, and decrease stress. Existing literature has looked at workplace, high school and general college-level applications. This study will contribute to the corpus of literature by exploring the effects of mindfulness directly in the context of exam weeks.
Research Design and Methods: Participants ( n= 234 ) will be randomly assigned to either an experimental group, receiving 5 days per week of 10-minute mindfulness-based interventions, or a control group, receiving no intervention. Data will be collected through self-report questionnaires, measuring stress levels, semi-structured interviews exploring participants’ experiences, and students’ test scores.
Timeline: The study will begin three weeks before the students’ exam week and conclude after each student’s final exam. Data collection will occur at the beginning (pre-test of self-reported stress levels) and end (post-test) of the three weeks.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: The study aims to provide evidence supporting the effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in reducing stress among college students in the lead up to exams, with potential implications for mental health support and stress management programs on college campuses.
3. Sociology Research Proposals
- Understanding emerging social movements: A case study of ‘Jersey in Transition’
- The interaction of health, education and employment in Western China
- Can we preserve lower-income affordable neighbourhoods in the face of rising costs?
Consider this hypothetical sociology research proposal:
The Impact of Social Media Usage on Interpersonal Relationships among Young Adults
Abstract: This research proposal investigates the effects of social media usage on interpersonal relationships among young adults, using a longitudinal mixed-methods approach with ongoing semi-structured interviews to collect qualitative data.
Introduction: Social media platforms have become a key medium for the development of interpersonal relationships, particularly for young adults. This study examines the potential positive and negative effects of social media usage on young adults’ relationships and development over time.
Literature Review: A preliminary review of relevant literature has demonstrated that social media usage is central to development of a personal identity and relationships with others with similar subcultural interests. However, it has also been accompanied by data on mental health deline and deteriorating off-screen relationships. The literature is to-date lacking important longitudinal data on these topics.
Research Design and Methods: Participants ( n = 454 ) will be young adults aged 18-24. Ongoing self-report surveys will assess participants’ social media usage, relationship satisfaction, and communication patterns. A subset of participants will be selected for longitudinal in-depth interviews starting at age 18 and continuing for 5 years.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of five years, including recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide insights into the complex relationship between social media usage and interpersonal relationships among young adults, potentially informing social policies and mental health support related to social media use.
4. Nursing Research Proposals
- Does Orthopaedic Pre-assessment clinic prepare the patient for admission to hospital?
- Nurses’ perceptions and experiences of providing psychological care to burns patients
- Registered psychiatric nurse’s practice with mentally ill parents and their children
Consider this hypothetical nursing research proposal:
The Influence of Nurse-Patient Communication on Patient Satisfaction and Health Outcomes following Emergency Cesarians
Abstract: This research will examines the impact of effective nurse-patient communication on patient satisfaction and health outcomes for women following c-sections, utilizing a mixed-methods approach with patient surveys and semi-structured interviews.
Introduction: It has long been known that effective communication between nurses and patients is crucial for quality care. However, additional complications arise following emergency c-sections due to the interaction between new mother’s changing roles and recovery from surgery.
Literature Review: A review of the literature demonstrates the importance of nurse-patient communication, its impact on patient satisfaction, and potential links to health outcomes. However, communication between nurses and new mothers is less examined, and the specific experiences of those who have given birth via emergency c-section are to date unexamined.
Research Design and Methods: Participants will be patients in a hospital setting who have recently had an emergency c-section. A self-report survey will assess their satisfaction with nurse-patient communication and perceived health outcomes. A subset of participants will be selected for in-depth interviews to explore their experiences and perceptions of the communication with their nurses.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of six months, including rolling recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing within the hospital.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide evidence for the significance of nurse-patient communication in supporting new mothers who have had an emergency c-section. Recommendations will be presented for supporting nurses and midwives in improving outcomes for new mothers who had complications during birth.
5. Social Work Research Proposals
- Experiences of negotiating employment and caring responsibilities of fathers post-divorce
- Exploring kinship care in the north region of British Columbia
Consider this hypothetical social work research proposal:
The Role of a Family-Centered Intervention in Preventing Homelessness Among At-Risk Youthin a working-class town in Northern England
Abstract: This research proposal investigates the effectiveness of a family-centered intervention provided by a local council area in preventing homelessness among at-risk youth. This case study will use a mixed-methods approach with program evaluation data and semi-structured interviews to collect quantitative and qualitative data .
Introduction: Homelessness among youth remains a significant social issue. This study aims to assess the effectiveness of family-centered interventions in addressing this problem and identify factors that contribute to successful prevention strategies.
Literature Review: A review of the literature has demonstrated several key factors contributing to youth homelessness including lack of parental support, lack of social support, and low levels of family involvement. It also demonstrates the important role of family-centered interventions in addressing this issue. Drawing on current evidence, this study explores the effectiveness of one such intervention in preventing homelessness among at-risk youth in a working-class town in Northern England.
Research Design and Methods: The study will evaluate a new family-centered intervention program targeting at-risk youth and their families. Quantitative data on program outcomes, including housing stability and family functioning, will be collected through program records and evaluation reports. Semi-structured interviews with program staff, participants, and relevant stakeholders will provide qualitative insights into the factors contributing to program success or failure.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of six months, including recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing.
Budget: Expenses include access to program evaluation data, interview materials, data analysis software, and any related travel costs for in-person interviews.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide evidence for the effectiveness of family-centered interventions in preventing youth homelessness, potentially informing the expansion of or necessary changes to social work practices in Northern England.
Research Proposal Template
Get your Detailed Template for Writing your Research Proposal Here (With AI Prompts!)
This is a template for a 2500-word research proposal. You may find it difficult to squeeze everything into this wordcount, but it’s a common wordcount for Honors and MA-level dissertations.
| Section | Checklist |
|---|---|
| Title | – Ensure the single-sentence title clearly states the study’s focus |
| Abstract (Words: 200) | – Briefly describe the research topicSummarize the research problem or question – Outline the research design and methods – Mention the expected outcomes and implications |
| Introduction (Words: 300) | – Introduce the research topic and its significance – Clearly state the research problem or question – Explain the purpose and objectives of the study – Provide a brief overview of |
| Literature Review (Words: 800) | – Gather the existing literature into themes and ket ideas – the themes and key ideas in the literature – Identify gaps or inconsistencies in the literature – Explain how the current study will contribute to the literature |
| Research Design and Methods (Words; 800) | – Describe the research paradigm (generally: positivism and interpretivism) – Describe the research design (e.g., qualitative, quantitative, or mixed-methods) – Explain the data collection methods (e.g., surveys, interviews, observations) – Detail the sampling strategy and target population – Outline the data analysis techniques (e.g., statistical analysis, thematic analysis) – Outline your validity and reliability procedures – Outline your intended ethics procedures – Explain the study design’s limitations and justify your decisions |
| Timeline (Single page table) | – Provide an overview of the research timeline – Break down the study into stages with specific timeframes (e.g., data collection, analysis, report writing) – Include any relevant deadlines or milestones |
| Budget (200 words) | – Estimate the costs associated with the research project – Detail specific expenses (e.g., materials, participant incentives, travel costs) – Include any necessary justifications for the budget items – Mention any funding sources or grant applications |
| Expected Outcomes and Implications (200 words) | – Summarize the anticipated findings or results of the study – Discuss the potential implications of the findings for theory, practice, or policy – Describe any possible limitations of the study |
Your research proposal is where you really get going with your study. I’d strongly recommend working closely with your teacher in developing a research proposal that’s consistent with the requirements and culture of your institution, as in my experience it varies considerably. The above template is from my own courses that walk students through research proposals in a British School of Education.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 15 Green Flags in a Relationship
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 15 Signs you're Burnt Out, Not Lazy
8 thoughts on “17 Research Proposal Examples”
Very excellent research proposals
very helpful
Very helpful
Dear Sir, I need some help to write an educational research proposal. Thank you.

Hi Levi, use the site search bar to ask a question and I’ll likely have a guide already written for your specific question. Thanks for reading!
very good research proposal
Thank you so much sir! ❤️
Very helpful 👌
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

How To Write A Research Proposal
A Straightforward How-To Guide (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | August 2019 (Updated April 2023)
Writing up a strong research proposal for a dissertation or thesis is much like a marriage proposal. It’s a task that calls on you to win somebody over and persuade them that what you’re planning is a great idea. An idea they’re happy to say ‘yes’ to. This means that your dissertation proposal needs to be persuasive , attractive and well-planned. In this post, I’ll show you how to write a winning dissertation proposal, from scratch.
Before you start:
– Understand exactly what a research proposal is – Ask yourself these 4 questions
The 5 essential ingredients:
- The title/topic
- The introduction chapter
- The scope/delimitations
- Preliminary literature review
- Design/ methodology
- Practical considerations and risks
What Is A Research Proposal?
The research proposal is literally that: a written document that communicates what you propose to research, in a concise format. It’s where you put all that stuff that’s spinning around in your head down on to paper, in a logical, convincing fashion.
Convincing is the keyword here, as your research proposal needs to convince the assessor that your research is clearly articulated (i.e., a clear research question) , worth doing (i.e., is unique and valuable enough to justify the effort), and doable within the restrictions you’ll face (time limits, budget, skill limits, etc.). If your proposal does not address these three criteria, your research won’t be approved, no matter how “exciting” the research idea might be.
PS – if you’re completely new to proposal writing, we’ve got a detailed walkthrough video covering two successful research proposals here .

How do I know I’m ready?
Before starting the writing process, you need to ask yourself 4 important questions . If you can’t answer them succinctly and confidently, you’re not ready – you need to go back and think more deeply about your dissertation topic .
You should be able to answer the following 4 questions before starting your dissertation or thesis research proposal:
- WHAT is my main research question? (the topic)
- WHO cares and why is this important? (the justification)
- WHAT data would I need to answer this question, and how will I analyse it? (the research design)
- HOW will I manage the completion of this research, within the given timelines? (project and risk management)
If you can’t answer these questions clearly and concisely, you’re not yet ready to write your research proposal – revisit our post on choosing a topic .
If you can, that’s great – it’s time to start writing up your dissertation proposal. Next, I’ll discuss what needs to go into your research proposal, and how to structure it all into an intuitive, convincing document with a linear narrative.
The 5 Essential Ingredients
Research proposals can vary in style between institutions and disciplines, but here I’ll share with you a handy 5-section structure you can use. These 5 sections directly address the core questions we spoke about earlier, ensuring that you present a convincing proposal. If your institution already provides a proposal template, there will likely be substantial overlap with this, so you’ll still get value from reading on.
For each section discussed below, make sure you use headers and sub-headers (ideally, numbered headers) to help the reader navigate through your document, and to support them when they need to revisit a previous section. Don’t just present an endless wall of text, paragraph after paragraph after paragraph…
Top Tip: Use MS Word Styles to format headings. This will allow you to be clear about whether a sub-heading is level 2, 3, or 4. Additionally, you can view your document in ‘outline view’ which will show you only your headings. This makes it much easier to check your structure, shift things around and make decisions about where a section needs to sit. You can also generate a 100% accurate table of contents using Word’s automatic functionality.

Ingredient #1 – Topic/Title Header
Your research proposal’s title should be your main research question in its simplest form, possibly with a sub-heading providing basic details on the specifics of the study. For example:
“Compliance with equality legislation in the charity sector: a study of the ‘reasonable adjustments’ made in three London care homes”
As you can see, this title provides a clear indication of what the research is about, in broad terms. It paints a high-level picture for the first-time reader, which gives them a taste of what to expect. Always aim for a clear, concise title . Don’t feel the need to capture every detail of your research in your title – your proposal will fill in the gaps.
Need a helping hand?
Ingredient #2 – Introduction
In this section of your research proposal, you’ll expand on what you’ve communicated in the title, by providing a few paragraphs which offer more detail about your research topic. Importantly, the focus here is the topic – what will you research and why is that worth researching? This is not the place to discuss methodology, practicalities, etc. – you’ll do that later.
You should cover the following:
- An overview of the broad area you’ll be researching – introduce the reader to key concepts and language
- An explanation of the specific (narrower) area you’ll be focusing, and why you’ll be focusing there
- Your research aims and objectives
- Your research question (s) and sub-questions (if applicable)
Importantly, you should aim to use short sentences and plain language – don’t babble on with extensive jargon, acronyms and complex language. Assume that the reader is an intelligent layman – not a subject area specialist (even if they are). Remember that the best writing is writing that can be easily understood and digested. Keep it simple.

Note that some universities may want some extra bits and pieces in your introduction section. For example, personal development objectives, a structural outline, etc. Check your brief to see if there are any other details they expect in your proposal, and make sure you find a place for these.
Ingredient #3 – Scope
Next, you’ll need to specify what the scope of your research will be – this is also known as the delimitations . In other words, you need to make it clear what you will be covering and, more importantly, what you won’t be covering in your research. Simply put, this is about ring fencing your research topic so that you have a laser-sharp focus.
All too often, students feel the need to go broad and try to address as many issues as possible, in the interest of producing comprehensive research. Whilst this is admirable, it’s a mistake. By tightly refining your scope, you’ll enable yourself to go deep with your research, which is what you need to earn good marks. If your scope is too broad, you’re likely going to land up with superficial research (which won’t earn marks), so don’t be afraid to narrow things down.
Ingredient #4 – Literature Review
In this section of your research proposal, you need to provide a (relatively) brief discussion of the existing literature. Naturally, this will not be as comprehensive as the literature review in your actual dissertation, but it will lay the foundation for that. In fact, if you put in the effort at this stage, you’ll make your life a lot easier when it’s time to write your actual literature review chapter.
There are a few things you need to achieve in this section:
- Demonstrate that you’ve done your reading and are familiar with the current state of the research in your topic area.
- Show that there’s a clear gap for your specific research – i.e., show that your topic is sufficiently unique and will add value to the existing research.
- Show how the existing research has shaped your thinking regarding research design . For example, you might use scales or questionnaires from previous studies.
When you write up your literature review, keep these three objectives front of mind, especially number two (revealing the gap in the literature), so that your literature review has a clear purpose and direction . Everything you write should be contributing towards one (or more) of these objectives in some way. If it doesn’t, you need to ask yourself whether it’s truly needed.
Top Tip: Don’t fall into the trap of just describing the main pieces of literature, for example, “A says this, B says that, C also says that…” and so on. Merely describing the literature provides no value. Instead, you need to synthesise it, and use it to address the three objectives above.

Ingredient #5 – Research Methodology
Now that you’ve clearly explained both your intended research topic (in the introduction) and the existing research it will draw on (in the literature review section), it’s time to get practical and explain exactly how you’ll be carrying out your own research. In other words, your research methodology.
In this section, you’ll need to answer two critical questions :
- How will you design your research? I.e., what research methodology will you adopt, what will your sample be, how will you collect data, etc.
- Why have you chosen this design? I.e., why does this approach suit your specific research aims, objectives and questions?
In other words, this is not just about explaining WHAT you’ll be doing, it’s also about explaining WHY. In fact, the justification is the most important part , because that justification is how you demonstrate a good understanding of research design (which is what assessors want to see).
Some essential design choices you need to cover in your research proposal include:
- Your intended research philosophy (e.g., positivism, interpretivism or pragmatism )
- What methodological approach you’ll be taking (e.g., qualitative , quantitative or mixed )
- The details of your sample (e.g., sample size, who they are, who they represent, etc.)
- What data you plan to collect (i.e. data about what, in what form?)
- How you plan to collect it (e.g., surveys , interviews , focus groups, etc.)
- How you plan to analyse it (e.g., regression analysis, thematic analysis , etc.)
- Ethical adherence (i.e., does this research satisfy all ethical requirements of your institution, or does it need further approval?)
This list is not exhaustive – these are just some core attributes of research design. Check with your institution what level of detail they expect. The “ research onion ” by Saunders et al (2009) provides a good summary of the various design choices you ultimately need to make – you can read more about that here .

Don’t forget the practicalities…
In addition to the technical aspects, you will need to address the practical side of the project. In other words, you need to explain what resources you’ll need (e.g., time, money, access to equipment or software, etc.) and how you intend to secure these resources. You need to show that your project is feasible, so any “make or break” type resources need to already be secured. The success or failure of your project cannot depend on some resource which you’re not yet sure you have access to.
Another part of the practicalities discussion is project and risk management . In other words, you need to show that you have a clear project plan to tackle your research with. Some key questions to address:
- What are the timelines for each phase of your project?
- Are the time allocations reasonable?
- What happens if something takes longer than anticipated (risk management)?
- What happens if you don’t get the response rate you expect?
A good way to demonstrate that you’ve thought this through is to include a Gantt chart and a risk register (in the appendix if word count is a problem). With these two tools, you can show that you’ve got a clear, feasible plan, and you’ve thought about and accounted for the potential risks.
Tip – Be honest about the potential difficulties – but show that you are anticipating solutions and workarounds. This is much more impressive to an assessor than an unrealistically optimistic proposal which does not anticipate any challenges whatsoever.
Final Touches: Read And Simplify
The final step is to edit and proofread your proposal – very carefully. It sounds obvious, but all too often poor editing and proofreading ruin a good proposal. Nothing is more off-putting for an assessor than a poorly edited, typo-strewn document. It sends the message that you either do not pay attention to detail, or just don’t care. Neither of these are good messages. Put the effort into editing and proofreading your proposal (or pay someone to do it for you) – it will pay dividends.
When you’re editing, watch out for ‘academese’. Many students can speak simply, passionately and clearly about their dissertation topic – but become incomprehensible the moment they turn the laptop on. You are not required to write in any kind of special, formal, complex language when you write academic work. Sure, there may be technical terms, jargon specific to your discipline, shorthand terms and so on. But, apart from those, keep your written language very close to natural spoken language – just as you would speak in the classroom. Imagine that you are explaining your project plans to your classmates or a family member. Remember, write for the intelligent layman, not the subject matter experts. Plain-language, concise writing is what wins hearts and minds – and marks!
Let’s Recap: Research Proposal 101
And there you have it – how to write your dissertation or thesis research proposal, from the title page to the final proof. Here’s a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- The purpose of the research proposal is to convince – therefore, you need to make a clear, concise argument of why your research is both worth doing and doable.
- Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper.
- Title – provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms
- Introduction – explains what you’ll be researching in more detail
- Scope – explains the boundaries of your research
- Literature review – explains how your research fits into the existing research and why it’s unique and valuable
- Research methodology – explains and justifies how you will carry out your own research
Hopefully, this post has helped you better understand how to write up a winning research proposal. If you enjoyed it, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach Blog . If your university doesn’t provide any template for your proposal, you might want to try out our free research proposal template .

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
30 Comments
Thank you so much for the valuable insight that you have given, especially on the research proposal. That is what I have managed to cover. I still need to go back to the other parts as I got disturbed while still listening to Derek’s audio on you-tube. I am inspired. I will definitely continue with Grad-coach guidance on You-tube.
Thanks for the kind words :). All the best with your proposal.
First of all, thanks a lot for making such a wonderful presentation. The video was really useful and gave me a very clear insight of how a research proposal has to be written. I shall try implementing these ideas in my RP.
Once again, I thank you for this content.
I found reading your outline on writing research proposal very beneficial. I wish there was a way of submitting my draft proposal to you guys for critiquing before I submit to the institution.
Hi Bonginkosi
Thank you for the kind words. Yes, we do provide a review service. The best starting point is to have a chat with one of our coaches here: https://gradcoach.com/book/new/ .
Hello team GRADCOACH, may God bless you so much. I was totally green in research. Am so happy for your free superb tutorials and resources. Once again thank you so much Derek and his team.
You’re welcome, Erick. Good luck with your research proposal 🙂
thank you for the information. its precise and on point.
Really a remarkable piece of writing and great source of guidance for the researchers. GOD BLESS YOU for your guidance. Regards
Thanks so much for your guidance. It is easy and comprehensive the way you explain the steps for a winning research proposal.
Thank you guys so much for the rich post. I enjoyed and learn from every word in it. My problem now is how to get into your platform wherein I can always seek help on things related to my research work ? Secondly, I wish to find out if there is a way I can send my tentative proposal to you guys for examination before I take to my supervisor Once again thanks very much for the insights
Thanks for your kind words, Desire.
If you are based in a country where Grad Coach’s paid services are available, you can book a consultation by clicking the “Book” button in the top right.
Best of luck with your studies.
May God bless you team for the wonderful work you are doing,
If I have a topic, Can I submit it to you so that you can draft a proposal for me?? As I am expecting to go for masters degree in the near future.
Thanks for your comment. We definitely cannot draft a proposal for you, as that would constitute academic misconduct. The proposal needs to be your own work. We can coach you through the process, but it needs to be your own work and your own writing.
Best of luck with your research!
I found a lot of many essential concepts from your material. it is real a road map to write a research proposal. so thanks a lot. If there is any update material on your hand on MBA please forward to me.
GradCoach is a professional website that presents support and helps for MBA student like me through the useful online information on the page and with my 1-on-1 online coaching with the amazing and professional PhD Kerryen.
Thank you Kerryen so much for the support and help 🙂
I really recommend dealing with such a reliable services provider like Gradcoah and a coach like Kerryen.
Hi, Am happy for your service and effort to help students and researchers, Please, i have been given an assignment on research for strategic development, the task one is to formulate a research proposal to support the strategic development of a business area, my issue here is how to go about it, especially the topic or title and introduction. Please, i would like to know if you could help me and how much is the charge.
This content is practical, valuable, and just great!
Thank you very much!
Hi Derek, Thank you for the valuable presentation. It is very helpful especially for beginners like me. I am just starting my PhD.
This is quite instructive and research proposal made simple. Can I have a research proposal template?
Great! Thanks for rescuing me, because I had no former knowledge in this topic. But with this piece of information, I am now secured. Thank you once more.
I enjoyed listening to your video on how to write a proposal. I think I will be able to write a winning proposal with your advice. I wish you were to be my supervisor.
Dear Derek Jansen,
Thank you for your great content. I couldn’t learn these topics in MBA, but now I learned from GradCoach. Really appreciate your efforts….
From Afghanistan!
I have got very essential inputs for startup of my dissertation proposal. Well organized properly communicated with video presentation. Thank you for the presentation.
Wow, this is absolutely amazing guys. Thank you so much for the fruitful presentation, you’ve made my research much easier.
this helps me a lot. thank you all so much for impacting in us. may god richly bless you all
How I wish I’d learn about Grad Coach earlier. I’ve been stumbling around writing and rewriting! Now I have concise clear directions on how to put this thing together. Thank you!
Fantastic!! Thank You for this very concise yet comprehensive guidance.
Even if I am poor in English I would like to thank you very much.
Thank you very much, this is very insightful.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Privacy Policy

Home » How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step [Template]
How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step [Template]
Table of Contents

How To Write a Research Proposal
Writing a Research proposal involves several steps to ensure a well-structured and comprehensive document. Here is an explanation of each step:
1. Title and Abstract
- Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research.
- Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal.
2. Introduction:
- Provide an introduction to your research topic, highlighting its significance and relevance.
- Clearly state the research problem or question you aim to address.
- Discuss the background and context of the study, including previous research in the field.
3. Research Objectives
- Outline the specific objectives or aims of your research. These objectives should be clear, achievable, and aligned with the research problem.
4. Literature Review:
- Conduct a comprehensive review of relevant literature and studies related to your research topic.
- Summarize key findings, identify gaps, and highlight how your research will contribute to the existing knowledge.
5. Methodology:
- Describe the research design and methodology you plan to employ to address your research objectives.
- Explain the data collection methods, instruments, and analysis techniques you will use.
- Justify why the chosen methods are appropriate and suitable for your research.
6. Timeline:
- Create a timeline or schedule that outlines the major milestones and activities of your research project.
- Break down the research process into smaller tasks and estimate the time required for each task.
7. Resources:
- Identify the resources needed for your research, such as access to specific databases, equipment, or funding.
- Explain how you will acquire or utilize these resources to carry out your research effectively.
8. Ethical Considerations:
- Discuss any ethical issues that may arise during your research and explain how you plan to address them.
- If your research involves human subjects, explain how you will ensure their informed consent and privacy.
9. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
- Clearly state the expected outcomes or results of your research.
- Highlight the potential impact and significance of your research in advancing knowledge or addressing practical issues.
10. References:
- Provide a list of all the references cited in your proposal, following a consistent citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
11. Appendices:
- Include any additional supporting materials, such as survey questionnaires, interview guides, or data analysis plans.
Research Proposal Format
The format of a research proposal may vary depending on the specific requirements of the institution or funding agency. However, the following is a commonly used format for a research proposal:
1. Title Page:
- Include the title of your research proposal, your name, your affiliation or institution, and the date.
2. Abstract:
- Provide a brief summary of your research proposal, highlighting the research problem, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes.
3. Introduction:
- Introduce the research topic and provide background information.
- State the research problem or question you aim to address.
- Explain the significance and relevance of the research.
- Review relevant literature and studies related to your research topic.
- Summarize key findings and identify gaps in the existing knowledge.
- Explain how your research will contribute to filling those gaps.
5. Research Objectives:
- Clearly state the specific objectives or aims of your research.
- Ensure that the objectives are clear, focused, and aligned with the research problem.
6. Methodology:
- Describe the research design and methodology you plan to use.
- Explain the data collection methods, instruments, and analysis techniques.
- Justify why the chosen methods are appropriate for your research.
7. Timeline:
8. Resources:
- Explain how you will acquire or utilize these resources effectively.
9. Ethical Considerations:
- If applicable, explain how you will ensure informed consent and protect the privacy of research participants.
10. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
11. References:
12. Appendices:
Research Proposal Template
Here’s a template for a research proposal:
1. Introduction:
2. Literature Review:
3. Research Objectives:
4. Methodology:
5. Timeline:
6. Resources:
7. Ethical Considerations:
8. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
9. References:
10. Appendices:
Research Proposal Sample
Title: The Impact of Online Education on Student Learning Outcomes: A Comparative Study
1. Introduction
Online education has gained significant prominence in recent years, especially due to the COVID-19 pandemic. This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of online education on student learning outcomes by comparing them with traditional face-to-face instruction. The study will explore various aspects of online education, such as instructional methods, student engagement, and academic performance, to provide insights into the effectiveness of online learning.
2. Objectives
The main objectives of this research are as follows:
- To compare student learning outcomes between online and traditional face-to-face education.
- To examine the factors influencing student engagement in online learning environments.
- To assess the effectiveness of different instructional methods employed in online education.
- To identify challenges and opportunities associated with online education and suggest recommendations for improvement.
3. Methodology
3.1 Study Design
This research will utilize a mixed-methods approach to gather both quantitative and qualitative data. The study will include the following components:
3.2 Participants
The research will involve undergraduate students from two universities, one offering online education and the other providing face-to-face instruction. A total of 500 students (250 from each university) will be selected randomly to participate in the study.
3.3 Data Collection
The research will employ the following data collection methods:
- Quantitative: Pre- and post-assessments will be conducted to measure students’ learning outcomes. Data on student demographics and academic performance will also be collected from university records.
- Qualitative: Focus group discussions and individual interviews will be conducted with students to gather their perceptions and experiences regarding online education.
3.4 Data Analysis
Quantitative data will be analyzed using statistical software, employing descriptive statistics, t-tests, and regression analysis. Qualitative data will be transcribed, coded, and analyzed thematically to identify recurring patterns and themes.
4. Ethical Considerations
The study will adhere to ethical guidelines, ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of participants. Informed consent will be obtained, and participants will have the right to withdraw from the study at any time.
5. Significance and Expected Outcomes
This research will contribute to the existing literature by providing empirical evidence on the impact of online education on student learning outcomes. The findings will help educational institutions and policymakers make informed decisions about incorporating online learning methods and improving the quality of online education. Moreover, the study will identify potential challenges and opportunities related to online education and offer recommendations for enhancing student engagement and overall learning outcomes.
6. Timeline
The proposed research will be conducted over a period of 12 months, including data collection, analysis, and report writing.
The estimated budget for this research includes expenses related to data collection, software licenses, participant compensation, and research assistance. A detailed budget breakdown will be provided in the final research plan.
8. Conclusion
This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of online education on student learning outcomes through a comparative study with traditional face-to-face instruction. By exploring various dimensions of online education, this research will provide valuable insights into the effectiveness and challenges associated with online learning. The findings will contribute to the ongoing discourse on educational practices and help shape future strategies for maximizing student learning outcomes in online education settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How To Write A Grant Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Research Proposal – Types, Template and Example

How To Write A Business Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide

How to choose an Appropriate Method for Research?

Business Proposal – Templates, Examples and Guide
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Anaesth
- v.60(9); 2016 Sep
How to write a research proposal?
Department of Anaesthesiology, Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
Devika Rani Duggappa
Writing the proposal of a research work in the present era is a challenging task due to the constantly evolving trends in the qualitative research design and the need to incorporate medical advances into the methodology. The proposal is a detailed plan or ‘blueprint’ for the intended study, and once it is completed, the research project should flow smoothly. Even today, many of the proposals at post-graduate evaluation committees and application proposals for funding are substandard. A search was conducted with keywords such as research proposal, writing proposal and qualitative using search engines, namely, PubMed and Google Scholar, and an attempt has been made to provide broad guidelines for writing a scientifically appropriate research proposal.
INTRODUCTION
A clean, well-thought-out proposal forms the backbone for the research itself and hence becomes the most important step in the process of conduct of research.[ 1 ] The objective of preparing a research proposal would be to obtain approvals from various committees including ethics committee [details under ‘Research methodology II’ section [ Table 1 ] in this issue of IJA) and to request for grants. However, there are very few universally accepted guidelines for preparation of a good quality research proposal. A search was performed with keywords such as research proposal, funding, qualitative and writing proposals using search engines, namely, PubMed, Google Scholar and Scopus.
Five ‘C’s while writing a literature review

BASIC REQUIREMENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
A proposal needs to show how your work fits into what is already known about the topic and what new paradigm will it add to the literature, while specifying the question that the research will answer, establishing its significance, and the implications of the answer.[ 2 ] The proposal must be capable of convincing the evaluation committee about the credibility, achievability, practicality and reproducibility (repeatability) of the research design.[ 3 ] Four categories of audience with different expectations may be present in the evaluation committees, namely academic colleagues, policy-makers, practitioners and lay audiences who evaluate the research proposal. Tips for preparation of a good research proposal include; ‘be practical, be persuasive, make broader links, aim for crystal clarity and plan before you write’. A researcher must be balanced, with a realistic understanding of what can be achieved. Being persuasive implies that researcher must be able to convince other researchers, research funding agencies, educational institutions and supervisors that the research is worth getting approval. The aim of the researcher should be clearly stated in simple language that describes the research in a way that non-specialists can comprehend, without use of jargons. The proposal must not only demonstrate that it is based on an intelligent understanding of the existing literature but also show that the writer has thought about the time needed to conduct each stage of the research.[ 4 , 5 ]
CONTENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
The contents or formats of a research proposal vary depending on the requirements of evaluation committee and are generally provided by the evaluation committee or the institution.
In general, a cover page should contain the (i) title of the proposal, (ii) name and affiliation of the researcher (principal investigator) and co-investigators, (iii) institutional affiliation (degree of the investigator and the name of institution where the study will be performed), details of contact such as phone numbers, E-mail id's and lines for signatures of investigators.
The main contents of the proposal may be presented under the following headings: (i) introduction, (ii) review of literature, (iii) aims and objectives, (iv) research design and methods, (v) ethical considerations, (vi) budget, (vii) appendices and (viii) citations.[ 4 ]
Introduction
It is also sometimes termed as ‘need for study’ or ‘abstract’. Introduction is an initial pitch of an idea; it sets the scene and puts the research in context.[ 6 ] The introduction should be designed to create interest in the reader about the topic and proposal. It should convey to the reader, what you want to do, what necessitates the study and your passion for the topic.[ 7 ] Some questions that can be used to assess the significance of the study are: (i) Who has an interest in the domain of inquiry? (ii) What do we already know about the topic? (iii) What has not been answered adequately in previous research and practice? (iv) How will this research add to knowledge, practice and policy in this area? Some of the evaluation committees, expect the last two questions, elaborated under a separate heading of ‘background and significance’.[ 8 ] Introduction should also contain the hypothesis behind the research design. If hypothesis cannot be constructed, the line of inquiry to be used in the research must be indicated.
Review of literature
It refers to all sources of scientific evidence pertaining to the topic in interest. In the present era of digitalisation and easy accessibility, there is an enormous amount of relevant data available, making it a challenge for the researcher to include all of it in his/her review.[ 9 ] It is crucial to structure this section intelligently so that the reader can grasp the argument related to your study in relation to that of other researchers, while still demonstrating to your readers that your work is original and innovative. It is preferable to summarise each article in a paragraph, highlighting the details pertinent to the topic of interest. The progression of review can move from the more general to the more focused studies, or a historical progression can be used to develop the story, without making it exhaustive.[ 1 ] Literature should include supporting data, disagreements and controversies. Five ‘C's may be kept in mind while writing a literature review[ 10 ] [ Table 1 ].
Aims and objectives
The research purpose (or goal or aim) gives a broad indication of what the researcher wishes to achieve in the research. The hypothesis to be tested can be the aim of the study. The objectives related to parameters or tools used to achieve the aim are generally categorised as primary and secondary objectives.
Research design and method
The objective here is to convince the reader that the overall research design and methods of analysis will correctly address the research problem and to impress upon the reader that the methodology/sources chosen are appropriate for the specific topic. It should be unmistakably tied to the specific aims of your study.
In this section, the methods and sources used to conduct the research must be discussed, including specific references to sites, databases, key texts or authors that will be indispensable to the project. There should be specific mention about the methodological approaches to be undertaken to gather information, about the techniques to be used to analyse it and about the tests of external validity to which researcher is committed.[ 10 , 11 ]
The components of this section include the following:[ 4 ]
Population and sample
Population refers to all the elements (individuals, objects or substances) that meet certain criteria for inclusion in a given universe,[ 12 ] and sample refers to subset of population which meets the inclusion criteria for enrolment into the study. The inclusion and exclusion criteria should be clearly defined. The details pertaining to sample size are discussed in the article “Sample size calculation: Basic priniciples” published in this issue of IJA.
Data collection
The researcher is expected to give a detailed account of the methodology adopted for collection of data, which include the time frame required for the research. The methodology should be tested for its validity and ensure that, in pursuit of achieving the results, the participant's life is not jeopardised. The author should anticipate and acknowledge any potential barrier and pitfall in carrying out the research design and explain plans to address them, thereby avoiding lacunae due to incomplete data collection. If the researcher is planning to acquire data through interviews or questionnaires, copy of the questions used for the same should be attached as an annexure with the proposal.
Rigor (soundness of the research)
This addresses the strength of the research with respect to its neutrality, consistency and applicability. Rigor must be reflected throughout the proposal.
It refers to the robustness of a research method against bias. The author should convey the measures taken to avoid bias, viz. blinding and randomisation, in an elaborate way, thus ensuring that the result obtained from the adopted method is purely as chance and not influenced by other confounding variables.
Consistency
Consistency considers whether the findings will be consistent if the inquiry was replicated with the same participants and in a similar context. This can be achieved by adopting standard and universally accepted methods and scales.
Applicability
Applicability refers to the degree to which the findings can be applied to different contexts and groups.[ 13 ]
Data analysis
This section deals with the reduction and reconstruction of data and its analysis including sample size calculation. The researcher is expected to explain the steps adopted for coding and sorting the data obtained. Various tests to be used to analyse the data for its robustness, significance should be clearly stated. Author should also mention the names of statistician and suitable software which will be used in due course of data analysis and their contribution to data analysis and sample calculation.[ 9 ]
Ethical considerations
Medical research introduces special moral and ethical problems that are not usually encountered by other researchers during data collection, and hence, the researcher should take special care in ensuring that ethical standards are met. Ethical considerations refer to the protection of the participants' rights (right to self-determination, right to privacy, right to autonomy and confidentiality, right to fair treatment and right to protection from discomfort and harm), obtaining informed consent and the institutional review process (ethical approval). The researcher needs to provide adequate information on each of these aspects.
Informed consent needs to be obtained from the participants (details discussed in further chapters), as well as the research site and the relevant authorities.
When the researcher prepares a research budget, he/she should predict and cost all aspects of the research and then add an additional allowance for unpredictable disasters, delays and rising costs. All items in the budget should be justified.
Appendices are documents that support the proposal and application. The appendices will be specific for each proposal but documents that are usually required include informed consent form, supporting documents, questionnaires, measurement tools and patient information of the study in layman's language.
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used in composing your proposal. Although the words ‘references and bibliography’ are different, they are used interchangeably. It refers to all references cited in the research proposal.
Successful, qualitative research proposals should communicate the researcher's knowledge of the field and method and convey the emergent nature of the qualitative design. The proposal should follow a discernible logic from the introduction to presentation of the appendices.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.

Chapter 12: Writing Research Proposals and Reports
Research is of no use unless it gets to the people who need to use it.
— Chris Whitty [1]
Learning Objectives
After reading this chapter, students should be able to do the following:
- Outline the main components of a research proposal.
- Explain the purpose of a method section in a research proposal.
- Identify key ethical considerations that need to be addressed in a research proposal.
- Outline the structure and format of a scholarly research report.
INTRODUCTION
Just as research is conducted for a variety of purposes, such as to explore or to explain a phenomenon of interest, as discussed at the start of this book, research is also carried out with its eventual target audience in mind, as implied by the opening quote. Basic research is generally undertaken for an academic audience, and research findings are disseminated (communicated) in reports that form the basis of conference talks or published works such as books, chapters, or journal articles read by scholars in affiliated disciplines. Disciplines recommend their own writing style for academic papers and reports. Three common documentation styles used in the social sciences throughout North America are American Psychological Association (APA) style, American Sociological Association (ASA) style, and Modern Language Association (MLA) style. All three provide direction for quoting and paraphrasing the work of others, for setting up the format of documents (e.g., spacing, headers, and the presentation of material in tables and figures), and for referencing sources. APA format is based on the most current edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association . MLA style is based on the most current edition of the MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers , and ASA is based on the American Sociological Association Style Guide . Consult with your instructor, your course syllabus, your library’s writing resources, or the instructions for contributors at a journal to determine the exact style you should use for preparing course work, research proposals, or research reports.
Research Proposals versus Reports
Most everyone who takes a research methods course or who plans to carry out basic research for an honours project, an independent study, or graduate studies (e.g., master’s research or a research-based dissertation for a doctorate degree) is expected to develop a research proposal. Similarly, researchers and other academics who wish to carry out studies at universities, in community settings, and in the private or business sector typically submit a research proposal to an ethics board and/or to a funding agency prior to beginning the research project. A research proposal is a comprehensive plan, created in advance of carrying out research, that details what a research project is about and what the process entails for obtaining the data needed to address the research questions and objectives. Included in the proposal is a description of the relevant literature, the main research questions or hypotheses the study hopes to address, the methods for obtaining data, and anticipated ethical considerations. A research report , in contrast, is written after research is conducted. The report is a detailed account that describes the area of interest, provides the specific research questions or hypotheses addressed in the study, spells out the methods used to obtain the data, and communicates the main results from the study. In addition, a research report discusses the findings in relation to the wider literature on the subject matter, indicates any limitations of the study, and offers suggestions for future research on that topic. The next section provides you with some guidance for what to include in a research proposal.

The Research Proposal
A research proposal is meant to address two primary questions: (1) What purpose does the research serve? and (2) How will the research be carried out to meet the intended objective? The research purpose is articulated in the introduction section and the planned process for carrying out the research is detailed in the method section. A research proposal is usually divided into five main sections consisting of an introduction, a method section, a section on data analysis and dissemination, a section on ethical considerations, and a listing of prospective references. These sections are described in detail below.
Introduction
To explain the research purpose in a manner that is accessible to a wide audience of readers, a researcher should frame the general research interest within a theoretical context, briefly describe what other researchers have done and found on the topic, state the current research interest, and explain how the present study will contribute to the literature by posing specific research questions and/or by testing hypotheses. Begin with a broad opening statement that identifies the area of interest. For example, a student of mine who planned to compare the portrayal of masculinity in the lyrics of country versus hip-hop songs began by pointing out the increasing popularity of both genres of music and went on to point out the earnings and prevalence of the two genres in order to introduce the general topic (Holub, 2012). After introducing the general topic, a researcher can begin to narrow the topic by linking the topic to previous research on the proposed area of interest. This is where central concepts are discussed and the theoretical context is established. Continuing with the previous example, my student went on to point out prevalent masculinity themes identified in previous research on lyrics of music from the two genres. The same student ended the introduction by noting that the proposed study would compare depictions of masculinity across genres to see if there were common underlying features. A qualitative study with an exploratory focus is going to include a general question, such as “Are there similarities in the way masculinity is depicted in country and hip-hop music lyrics?” In contrast, a quantitative study with a more descriptive focus would likely include a directional hypothesis, such as “H1: The proposed study predicts that masculinity will be more evident in hip-hop than in country music lyrics.” Ask yourself the following questions as you prepare the introductory section:
- What is my broad area of interest?
- Did I identify a narrow focus within this area of interest?
- Did I summarize the relevant literature in this area?
- Did I include clear conceptual definitions for the main concepts?
- Is a theoretical context established for my study?
- What will my research contribute to this area?
- What is my research question or hypothesis?
The method section outlines who the participants will be and how they will be selected. In addition, the method section includes details about the setting and materials needed to conduct the study, the procedures for carrying out the study, and the main variables examined in the study, as discussed in more detail below.
Participants and How They Will be Obtained or Sample Selection
First, if the study will include research participants, such as interview participants, survey respondents, or experimental subjects, a researcher needs to detail who the potential research participants will be and how they will be identified and recruited. In addition, the researcher should note any relevant criteria that may be used to include or exclude participants. For example, an honours student working under one of the author’s supervision examined the prevalence of aggressive and dangerous forms of driving in a sample of 300 university students (Haje & Symbaluk, 2014). In an ethics application, Bruno Haje proposed that participants would be recruited from the university’s research subject pool in accordance with the department’s procedures for online survey research participation. Bruno also pointed out that since this study was specifically about driving behaviours, participants would need to be volunteers who drive a motor vehicle at least on occasion.
Note that not all forms of research involve research participants. A researcher planning to use unobtrusive methods, such as physical trace analysis, or wanting to carry out a content analysis would instead describe proposed units of analysis. Recall Gackenbach et al.’s (2011) study on the video game player’s online dream diary. Although there was a person to whom the dreams belonged, it was the content of 447 of his 831 dream postings that constituted the units of analysis. In a qualitative study, this section is usually titled sample selection. Here, a researcher articulates how the sample (e.g., of dream postings) will be obtained, including any inclusion or exclusion criteria that will determine eligibility (Padgett, 2012). For example, of the 831 posted dreams, a dream was included in the analysis if it was more than 50 but fewer than 500 words, had a clear date as to when it occurred, included an activity blog entry from the night before the dream, and fit one of the defined dream categories, resulting in a sample of 447 dreams (Gackenbach et al., 2011).

Setting and Materials
In addition to describing the participants and how they will be recruited or the units of analysis, the method section also indicates the proposed setting or location for data collection and any materials needed to carry out the study. Research is often carried out at a university where the primary researcher holds a faculty position. However, if the study is an in-depth qualitative interview, the setting may be the respondent’s place of residence or a public location that the respondent feels comfortable in and one that provides some degree of needed privacy, such as a booth in a local coffee shop. Similarly, if the study involves ethnographic fieldwork, the research setting is likely to be wherever that group or process is located and can best be examined from within a natural context.
Materials for a study include items that need to be purchased ahead of time to carry out the study. For example, to carry out my master’s research on pain perception and endurance, I needed to purchase a heart rate monitor to assess participants, for health and safety reasons, throughout the exercise. I also needed equipment that could be used to assist in the measurement of pain endurance. Specifically, participants performed an isometric sitting exercise above a box with a pressure plate. A participant who was too tired to continue sat down on the box, thereby activating the pressure plate to stop a timer that recorded endurance.
As another example, an online ethnography might require a computer, internet access, and possibly some kind of registration or software needed to gain access to a group of interest, such as through a membership or user account. Finally, a researcher conducting an interview-based study might wish to use incentives to compensate interviewees for their time and would therefore need to purchase gift cards or prepare some comparable remuneration in advance of the study.
Main Variables
Next, researchers describe the main variables or measures of interest. If the approach is quantitative, as in the case of an experimental method, this section describes the dependent variables. (The independent variables are discussed as part of the procedures for how the manipulation will be carried out.) For example, in the pain study, the main dependent variable was pain endurance, defined as the length of a time a participant was able to maintain an isometric sitting exercise in minutes and seconds. Each dependent variable should be listed, along with the operational definition for how it will be measured. For a quantitative survey, each main variable is likely to be measured using a question or multiple questions on a self-report questionnaire. For example, in a study on aggressive driving, aggressive behaviour might be measured using Deffenbacher et al.’s (2002) shortened version of the Driver Anger Expression Inventory, consisting of 21 items. The inventory assesses verbally aggressive behaviour (e.g., yelling at other drivers), physically aggressive behaviour (e.g., giving someone the finger), and/or constructive expressions of anger (e.g., thinking about other things). Survey items are usually summarized in this section and the full inventory is included in an appendix. If the measures are already established, you can report on the reliability and validity of the measure as described in the literature.
Alternatively, if a study is based on a qualitative content analysis, an in-depth interview, or an unstructured observation, this section elaborates on how the researcher plans to identify main themes and patterns from the data once it is collected and transcribed, as opposed to operationalizing variables ahead of time. This section is sometimes called coding procedures and it can take the place of the main variables and procedures sections. For example, a researcher who wishes to examine a television series for depictions of violence enacted by the main characters might indicate a plan to use an open coding scheme to detail every separate and distinct act of violence committed by a main character as a first-cycle coding method. This can be followed by second phase of coding directed at identifying main themes and categorizing the patterns to the violence identified in the first round of coding. Similarly, an ethnographer might plan to use descriptive coding for field notes and documents collected on a group of interest that will be later subjected to a more structured coding process. A qualitative researcher might also adopt existing coding schemes from the established literature to conduct a content analysis. When possible, the researcher should articulate the coding schemes and tie them back to the theoretical context in which they developed. Since the content of any method section is going to vary considerably depending on the approach and methodology (e.g., quantitative survey versus qualitative interview), you should examine published journal articles based on the same methodology you plan to use for a more definitive sense of what you need to include here.

Finally, the procedures section outlines the detailed plan for carrying out the study as the last main component of the method section. This section needs to include enough detail that a reader could replicate the study exactly, based on how it is described in writing. For example, if a researcher intends to conduct online survey research, the procedures will detail how the participants are to access the online survey through a link they receive in an email invitation sent to their university email account. Once a participant clicks on the study link, what happens next? The procedures walk the reader through the study. For an online survey, the first page that is likely to appear on the screen following the link to the study is the informed consent statement. The procedures will then go into detail about how the online consent form describes the study, provides details about what is expected of participants, notes the benefits and risk of participation, indicates that participation is voluntary, and explains how privacy will be maintained and what the plans are for dissemination of findings. The procedures also indicate how consent is obtained. In the case of an online survey, potential participants are likely to be asked to click on a box that reads something like “I agree to participate in this study” or “I do not agree to participate in this study.” Procedures can also note that upon agreeing to participate in the study, the participants then receive the first screen page of the survey. What happens to those who choose not to participate? The procedures should also note that participants who do not consent to participate instead receive a debriefing statement that provides additional details about the study and contact information for the principal researcher.
In addition to describing the process leading up to survey access, the procedures also describe the survey instrument by noting how many questions are on the questionnaire, indicating whether questions are grouped into sections, noting the topic of each section, and listing the order in which the information will be received by the participant. For example, perhaps the questionnaire begins with 10 items that assess background information, followed by a 5-item personality scale or a 12-item behaviour inventory. The procedures also note what happens once participants complete the survey. In most cases, after completing an online survey, participants will receive the debriefing statement mentioned above. Finally, a copy of the questionnaire in its entirety, along with the consent form and debriefing statement, should be attached at the end of the proposal as an appendix.
Again, we would advise you to look at how the procedures are described in a couple of published journal articles, based on studies like the one you are planning, for additional ideas on what you need to include as necessary steps. Ask yourself the following questions as you prepare the method section:
- Did I indicate who the target participants will be and how I plan to obtain them?
- If I don’t have participants, did I explain what my units of analysis will be and how I plan to sample for them?
- Did I explain any relevant inclusion or exclusion criteria for selection?
- Have I noted where the proposed study will take place?
- Have I identified all materials that need to be obtained in advance of the study?
- For a quantitative study, have I listed and operationalized all main variables I plan to examine in my study?
- For a qualitative study, have I explained how I plan to code or categorize the information I will be collecting?
- Have I explained all steps I will undertake to carry out the study?
Data Analysis and Dissemination
In addition to describing the main variables and/or coding procedures, a research proposal also includes a brief section outlining the plan for data analysis and dissemination of findings. A quantitative study is likely to include statistical analysis using a software package especially designed for the social sciences, such as IBM SPSS or Stata statistical software. Data analysis in a qualitative study may be carried out by developing codes through transcription and textual analysis, or it can be assisted through specialized software programs such as NVivo, which helps to manage data by treating units of analysis as cases and organizing ideas, concepts, and themes into codes so that patterns and trends can be made apparent (Jackson & Bazeley, 2019). Here researchers can also indicate any strategies they plan to use to establish reliability, including inter-rater reliability and methods for obtaining rigour. Finally, a proposal outlines the plan for what will be done with the data once it is collected. Perhaps the researcher intends to report on the findings at an upcoming conference by presenting a conference poster (see Appendix B: Sample Student Poster for an example) or submit the main findings to a journal for peer review and possible publication.
Ethical Considerations
If a researcher plans to undertake a study that will include university students (or any humans) as research participants, as in the case of an experimental design, a survey project, an in-depth qualitative interview, or a focus group, the researcher would need to first obtain ethical approval through a university’s research ethics board. Even in the case of non-reactive research, if a researcher wishes to carry out a project that will in some way involve a university’s assets (directly or indirectly), as in the case of non-participatory observation in public spaces on campus, ethical approval will need to be sought from that university’s research ethics board. A research proposal always includes relevant ethical concerns along with the ways in which the planned study will address the concerns.
Minimal Risk for Harm
Recognizing that all research involving humans has at least a minimum potential for harm, a researcher should identify whether the proposed study can be judged as a minimal risk. While it is up to the research ethics board to determine whether the study is deemed minimal risk, a researcher can and should provide rationale for why the proposed project should be assessed as such. For example, a researcher who plans to conduct a survey on driving may indicate that there are no anticipated risks associated with participating in the proposed study. However, since the participants are disclosing information about their own driving habits, there is a minimal risk that participants may experience psychological discomfort when answering questions about the extent to which they engage in dangerous or aggressive driving practices. Specifically, participants could feel remorse or embarrassment while responding to certain questions. In addition, participants could later reflect on responses given and regret having disclosed information about their driving.
Mitigating Minimal Risk of Harm
To help mitigate this potential likelihood of harm, a researcher can include explicit information in the initial consent form to give the potential participants an idea of the type of questions they can anticipate being asked during the survey. For example, participants might be informed that they will be asked to report on safe and unsafe driving practices. In addition, the researcher can even include examples of specific items on the survey (e.g., Question #25 asks “How often do you send or receive text messages while stopped at a red light?”).
Researchers can also include a statement within the questionnaire itself that reiterates that participation is voluntary, that participants may skip over questions they do not want to answer, and that they can choose to end their participation at any time without penalty. Finally, a researcher can include additional self-help resources with the debriefing statement, such as resources for driver education and training.
Addressing Beneficence
Recall from chapter 3 the importance of designing a study in a manner that minimizes harm while maximizing the overall benefit of the research. Where possible, a research proposal should include a statement about the benefits of the proposed study for the researcher. For example, might the research help to fulfill the requirements for an honours project or a master’s thesis? In addition, it is important to list potential benefits for the participants, such as the opportunity to learn more about themselves or research processes. Finally, the proposal should also indicate benefits to the wider research community and/or society more generally. For example, may the proposed study contribute toward our understanding of some group, phenomenon, or process?
Upholding Privacy and Confidentiality
A researcher also needs to detail the planned procedures for upholding privacy through the anonymity of participants, how safe and secure storage of data will be achieved, and how confidentiality will be upheld in the disclosure of findings. For example, a researcher will need to note whether any personally identifying information is going to be collected and, if so, how the researcher plans to safeguard the identity of individual participants. Note that participants need to be made aware of this prior to providing consent.
Part of the process of ensuring privacy includes a consideration and disclosure of who is going to participate in data collection (e.g., Will research assistants help to collect information?); who is expected to access to the data once it is collected (e.g., Will anyone other than the principal researcher assist in the transcription or coding?); and where data is going to be stored (e.g., Will the data be transferred onto a computer file that will be kept on a password-protected computer in a locked office of the principal researcher? Will field notes be kept in a locked cabinet in the secure office of the principal researcher?). A research ethics board will ask for information on these items as well as additional information, including how long any sensitive data will need to be stored (the recommended length being about two years) and how the data will eventually be disposed of (e.g., Will the notes be shredded?).

Prospective References
Finally, a research proposal ends with a list of relevant references. References included in a research proposal help to establish a scholarly context for the planned study. The references help identify, for example, the appropriate and relevant theories, theorists, and concepts that inform the proposed research. In addition, references can help to validate the proposed methodology. For example, perhaps the researcher plans to use a grounded theory approach such as one described by Kathy Charmaz in 2014.
References are listed on a separate page in a standard citation format such as the one provided by the seventh edition of the American Psychological Association’s (2020) publication manual (APA format). In APA format, an author of a book is listed by last name, followed by first initials, year of publication, title, edition (if applicable, and then the publisher according to specific rules for style and punctuation. As illustrated here, in APA format, only the first word of the title of a book is capitalized, and the title appears in italics. MLA and ASA format are similar, as shown below.
APA format :
Charmaz, K. (2014). Constructing grounded theory (2nd ed.). Sage.
ASA format:
Charmaz, Kathy. (2014). Constructing Grounded Theory. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
MLA format:
Charmaz, Kathy. Constructing Grounded Theory . 2nd ed., Sage, 2014.
Activity: Research Proposals Review
Test Yourself
- What are the two primary questions addressed by a research proposal?
- Does the introduction section in a research proposal begin with a broad or narrow statement?
- In which section of a research proposal would you expect to find information on the setting and materials for a study?
- Which subsection of a research proposal walks the reader through the study?
- What suggestions might researchers propose to mitigate the risk of harm to participants?
THE RESEARCH REPORT
A research report is a formalized summary of a completed research project. A research report is written in a standard format that you can use to describe the research you have carried out for an undergraduate research class, an honours project, an independent study, a community-based project or some kind of field placement. This format includes a title page, an abstract, an introduction, a method section, a results section, a discussion section, references, and if applicable, tables, figures, and an appendix, as described in detail in this section and demonstrated in Appendix A: Sample Student Report . Research reports submitted to an academic journal may require additional elements depending on the journal submission guidelines, the most common of which are referred to below and discussed in more detail in this APA Sample Professional Paper produced by the Purdue Online Writing Lab.
The title page is much more than just a placeholder for the title of the study—it not only identifies what was studied, it provides additional information that helps to locate and establish the study within the greater context of the discipline in which it is situated. First, a title page includes a long title that summarizes what the study was about. There is no required minimum or maximum word length; however, the title should contain enough information to give the reader a sense of the specific research objectives. For example, “Sleep Quality” as a title would help identify the area of interest but not what the study was about. In contrast, Semplonius and Willoughby’s (2018) full title, “Psychosocial Adjustment Throughout University: A Longitudinal Investigation of the Roles of Sleep Quality and Emotion Dysregulation,” informs readers that the relationship between sleep and emotions is being studied over time.
In addition to the full title, a title page for a student report usually includes the names of student authors, the university, the course, the instructor, and the due date. Meanwhile, a professional paper submitted to a journal for publication usually includes the names of authors listed in order according to who contributed most to the research project and a running head , which is a shortened version of the title that appears in the header of the manuscript. Further down the page, title pages for professional papers also often include an author note that includes a recognition statement for the source of any relevant funding and how to correspond with the principal researcher for more information about the study. The recognition statement cites the source of support for the study, such as an external research grant (e.g., the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council) or an internal source of funding (e.g., a research fund from within a department or school, or a university’s research office). The correspondence statement lists the name and email address of the main contact person or the principal researcher for the study so that interested readers and other researchers can reach the person for more information about the study.
Located at the beginning of a research project, an abstract is a brief overview of the research project. It summarizes what the research is about, how many participants there were and how they were obtained (or what the units of analysis were), what the procedures were for carrying out the study, what the design consisted of, and what the main findings were. This can be considered the most important section in the entire report, as it is generally the first and sometimes the only section that is read by other academics and researchers conducting searches for relevant articles of interest. Although it appears at the beginning of a report, it should be the last thing the researcher writes, to ensure that it is both succinct (i.e., usually 150–250 words) and comprehensive. This is one of the most difficult sections to write, as it needs to include a lot of information in what amounts to only a few sentences. A good strategy for writing an abstract that is under 250 words is to first write an abstract that includes all relevant information (this will likely be about 300–400 words on your first try), and then rework it a few times, paring it down word by word, until it is as concise as possible.
If submitting an article for publication, journals may also require a short list of relevant keywords beneath the abstract, which are concepts used to locate the article via database searches once it is in print. Keywords also give the reader additional insight into the study. For example, readers interested in the interrelations between sleep , depression , emotion dysregulation , and alcohol might benefit from reading Semplonius and Willoughby’s (2018) study.

An introduction section follows the abstract. Like the research proposal, an introduction in a research report should include a general opening and a broad discussion of the research interest and area, followed by a narrowing of the research topic. In addition, the research topic should be situated within the relevant literature, and the theoretical context and key concepts should all be well articulated. After summarizing the relevant literature, the introduction ends with a statement of the research problem, key question(s), issues explored, and/or hypotheses tested.
For example, in a research project on pain that I conducted for my master’s research, the broad opening statement in the journal article I published was “Pain is a fundamental fact of life” (Symbaluk et al., 1997, p. 258). From there, the introduction narrowed to discuss forms of acute and chronic pain in everyday life. It further narrowed as we brought in the social psychology of pain and established how monetary incentives and social modelling have been used in experimental research to increase pain endurance. It continued to narrow as we identified gaps in the literature and explained how this experiment was the first to look at the role of self-efficacy and pain perception as potential mediators for the anticipated effects of money and modelling on pain endurance. The introduction ended with specific hypotheses, including one predicting that pain endurance would increase as a function of money for participants who were exposed to pain-tolerant social models.
Note that the introduction section for a qualitative research project also summarizes the relevant literature and ties that literature to the research interests of the present study. However, in lieu of hypotheses, this section is likely to conclude with a statement of the research objective or the main question (or questions) explored in the study that follow logically from the literature review (Pyrczak & Bruce, 2017). For example, a qualitative study conducted by one of my students in an introduction to research methods course focused on the reproduction of common stereotypes in popular media. Finlay’s (2012) research question was “Does the popular television series Crime Scene Investigation promote or resist common stereotypical media representations of gender?”
The method (sometimes called methodology) section of the research report is next. The method section is generally the longest in a report, as it contains subsections on the participants or selection of a sample, setting and materials, procedures or coding scheme, dependent or main variables, and data analysis.
Participants and How They Were Obtained or Sample and Sample Selection
For research involving humans as participants, this section notes how many participants were included in the study, who the participants were, and how they were obtained. For example, Sabbane et al. (2009) experiment on the effects of anti-smoking warnings on attitudes and smoking intentions included 178 teenagers ( N = 178) as participants. Specifically, participants were males and females between the ages of 12 and 17 who were non-smokers ( n = 158) or occasional smokers ( n = 15) recruited, with parental consent, from Secondary I classes in a Montreal secondary school.
As a second example, Boyd et al. (2009) analyzed the content of media representations of bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), more commonly known as “mad cow disease” for the first 10 days following an outbreak in Alberta on May 20, 2003. Their sampling frame consisted of The Globe and Mail and the National Post (as leading national papers), as well as The Lethbridge Herald (as a local Alberta newspaper) and the Edmonton Journal (as a regional newspaper). The sampling procedure involved online searches of these papers for articles on mad cow disease identified through keywords. From this potential sample, articles were included if they met additional criteria. For example, articles that only peripherally mentioned BSE (i.e., it was not the focus of the study) were excluded, resulting in 309 articles in the sample used (Boyd et al., 2009).
Finally, as a third example, Dr. Rosemary Ricciardelli interviewed 14 men as part of a study on the role of hair in self-identification. The interviewees were recruited through convenience sampling via four means of advertising the study, including business card advertisements for the study given out and left in coffee shops and shopping centres in the Greater Toronto Area, an email invitation sent out to students in a small suburban university, an advertisement in Fab magazine, and an ad in a free gay publication (Ricciardelli, 2011).
As addressed in the research proposals section above, the setting refers to the location where the data collection takes place. For example, in a study looking at the meaning of recovery from the perspective of Canadian consumers receiving mental health services, Piat et al. (2009) conducted interviews at major mental health service sources, including the Wellington Centre of the Douglas Mental Health University Institute, the Canadian Mental Health Association Waterloo/Wellington-Dufferin branches, and at the Programme d’encadrement clinique et d’hébergement. If the setting does not apply, as might be the case if the study was conducted over the internet, then this section would refer to materials only.
The materials refer to the main instruments and supplies used to carry out the procedures of the study. In an experiment, whatever is manipulated as the independent variable likely constitutes a material that requires preparation in advance of the study. For example, in a study on social-information processing as a function of psychopathic traits, Wilson et al. (2008) showed participants artificially created characters and then examined recall and recognition. The characters were profiles developed ahead of time that consisted of eight stimulus characters created with images of faces from the Pictures of Facial Affect (POFA) series put together with descriptions that contained a name, an occupation, and a set of likes and dislikes.
Note that indexes, scales, and other items used to compose a questionnaire given as part of survey research are generally described as main variables or measures after the procedures (not as materials needed to carry out the study).
The procedures section of a research report details how the study was carried out. This subsection within the methods is written in the past tense, and it includes a description of all phases of the study, beginning with any instructions given to participants and the consent process, followed by details on the type of techniques employed to gather data and to later examine it. For example, if interviews were conducted, the researcher needs to indicate how many times each participant was interviewed and the time frame over which data collection (interviewing) took place. Alternatively, if observations occurred, when, where, and under what conditions did these take place? As another example, if an experiment was employed, how did participants experience the independent variable? Instead, if the study was based on ethnography, how did the researcher access the setting? Who were the gatekeepers and how was the gatekeeping process navigated? How was rapport with group members established? What role did the researcher engage in for data collection purposes (e.g., participant observation)? What methods were used to collect data? How did the researcher disengage from the setting at the completion of the study?
Note that if the study was based on content analysis, instead of procedures, a research report could include a section on coding procedures or a coding scheme. Similarly, if the study was based on secondary analysis of existing data, this section would outline why and how that source was selected and obtained, and how the archival material was organized and synthesized for subsequent data analysis (Neuman & Robson, 2024).
Main Variables or Measures
A research report always includes a section that outlines the main variables examined in the study. If the study is an experiment, the dependent variables are listed along with their operationalized definitions. For example, in the pain experiment I conducted for my master’s research, pain perception was operationalized as the time elapsed prior to the first sensation of pain in seconds, and pain endurance referred to how long a participant held an isometric sitting position in minutes and seconds (Symbaluk et al., 1997).
As another example, in a study looking at alcohol content as a mediating factor for brand preference, Segal and Stockwell (2008) employed measures of intoxication and enjoyment completed by participants after they drank two low-alcohol- or two regular-alcohol-content beers. Their measures section included a description of an objective variable based on blood-alcohol content assessed using a standard instrument called the Alco-Sensor IV, and it included a description of three subjective measures. Each subjective measure was listed along with appropriate citations for the originating source and an account of the measure. For example, one measure was The Sensation Scale, which they note was originally developed by Maisto et al. (1980) and consists of 31 items about the effects of alcohol. The measures section also notes that participants scored the items using Likert responses ranging from 0 (not at all) to 9 (extremely), with the higher ratings referring to higher intoxication.
If the study is based on qualitative research, as would be the case for in-depth interviews or most focus group sessions, the research report might not have a section for the main variables or measures. This is because concepts, themes, and main ideas may emerge during data collection and analysis in response to open-ended questions. However, if interviews or focus-group sessions are more structured, a researcher may include the questions or describe items that compose an interview guide as part of a section titled interview guide (in lieu of main variables).
Data Analysis
The last part of the method section of a research report details how data analysis was carried out. For example, if content analyses employed the frequency of occurrence of certain categories of events, how were the categories developed? Specifically, did the researcher use categories already established in the literature, modify categories based on previous literature, or develop new ones? Were categories counted once or every time there was an instance of that category? And how was reliability assessed? Did the researchers employ inter-coder reliability and, if so, what was the reliability rate achieved?
As another example, the process for data analysis in an ethnographic study of young homeless men in Calgary was described as follows: “Interviews were transcribed verbatim and checked for accuracy against the digital recordings. A thematic framework was agreed upon by the authors (SP and LM), based on the reported significance of daily routines, coping strategies, and access to services. This was used along with an open coding strategy to recursively analyze these findings using NVivo 7, a qualitative analysis software (QRS International, 2007). Data analysis was concurrent with data collection and uncovered common themes among the interviewees” (Persaud et al., 2010, p. 345).
Writing Resources
Academic writing is challenging. You want to be clear and concise, avoiding jargon and unnecessary details, while at the same time having to explain complex practices and procedures that go into conducting social research. The good news is that most universities have writing centres with online resources and expert staff to help you learn how to write research reports and other forms of scholarly communication. As an example, the University of York Writing Centre has created a useful video on how to write a methods section:
[Video transcript – See Appendix D 12.1 ] Methods: structure is by University of York Writing Centre. Used with permission.
Alongside free online resources, s everal universities also provide students with tools like Grammarly, a writing assistant that uses artificial intelligence to give you immediate feedback on your writing.
The results section of a research report outlines the main findings of the study in the appropriate technical terms. If there are several dependent variables or measures, each variable might be listed as a subheading in this section. Note that the results section states only facts, as succinctly as possible. In the case of quantitative research, the results section for an experiment is likely to report on findings based on tests of differences between means using t -tests for two groups or analysis of variance for variation between and within more than two groups or categories. The results section for quantitative survey research is likely to describe main variables (e.g., using measures of central tendency and variability), as well as report on tests for associations between variables of interest, such as correlations, regression analysis, or nonparametric measures of correlation.
The results section may include figures and tables, as discussed below, if they are necessary to help the reader understand the information being shared. If they are instead supplementary information that may distract a reader from the content, they can instead go in an appendix at the end of the report. When submitting a report to a journal for publication, you may also ask to include figures and tables after the references at the end of a report; an editor then styles and includes them to the text when preparing the file for publication. In each of these instances, the text of your paper should include a “callout” referencing each figure or table, which should be labelled sequentially, to draw the reader’s attention to this information (e.g., for an example of a pie chart included in the text, see Figure 12.1; to review how a table may appear in an appendix, see Appendix A of this book).
Coding and the Development of Categories
In a qualitative research report, results typically document the findings from the coding methods employed in the study. The coding methods involve stages or phases, beginning with initial codes. As described in various earlier chapters, data obtained in a study are assigned labels or codes. Specifically, a code “is most often a word or short phrase that symbolically assigns a summative, salient, essence-capturing, and/or evocative attribute for a portion of language-based or visual data” (Saldaña, 2021, p. 5). Recall that qualitative data includes a range of information, from narrative and text based on interviews and field notes to drawings and images presented in magazine ads, shown through character portrayals on television, and so on. A posting on RateMyProfessor.com, for example, might contain the passage “She really knows her stuff,” coded as “instructor” and “knowledge” since the passage refers to the instructor and it contains a comment about an attribute of the instructor. To begin with, each unit of data is usually assigned its own specific code.
After the initial codes are determined, the next phase includes going back over the data to determine if there are patterns in the data that can be coded into categories based on their common elements. For example, perhaps lots of comments refer to the instructor. Some of the comments might pertain to instructor attributes, such as comments about the instructor’s knowledge of the subject matter and comments about the instructor’s willingness to help students. Other items might have to do with an instructor’s grading, such as “The instructor is a hard marker” or “The instructor grades fairly.” Finally, other comments might pertain to assignments in the course, such as “This course has a lot of papers!” One large category to emerge from this data might be “comments about the instructor.” Another category might be “comments about the course content.” Within the “comments about the instructor” category, other subcategories could also be identified. For example, there may be a subcategory for “instructor attributes.” Within the subcategory for “instructor attributes,” researchers could also list codes for “clarity,” “helpfulness,” “knowledge,” and so on.
Qualitative data analysis is a lengthy process that eventually culminates in the development of themes, as Saldaña (2021) points out, “a theme can be an outcome of coding, categorization, or analytic reflection, but it is not something that is, in itself, coded” (p. 19). Results from qualitative studies, then, highlight main themes or claims that are descriptive outcomes identifying the main overall findings that emerged from the data collection and analysis processes. To substantiate the results, qualitative researchers need to carefully articulate each of the coding stages and categories that developed within each stage. Each main theme is generally discussed within its own subsection in the results, similar to how each main dependent variable is discussed for a quantitative study.
Results from research studies are often depicted in figures . Figures are charts or graphs used to display results based on how a variable is measured. A pie chart, for example, is used to depict the results in a picture format for a single, qualitative variable that is measured at the nominal level. For example, a researcher doing a content analysis on gender portrayals in the media might use a pie chart to convey that there are more males than females depicted as central characters on television. Or a researcher conducting an online survey on attitudes toward healthcare might use a pie chart to describe the respondents who completed the survey. Perhaps the largest slice of the pie indicates that many participants were married, followed by single, common-law, divorced, and separated (see figure 12.1). If none of the respondents claimed they were in a category (e.g., widowed), that category would not be included in the pie chart.
If it is important to indicate the frequency distribution for the categories of a variable, a bar graph would be used instead of a pie chart, since it emphasizes the number of respondents in each category of a variable and it can even be used to show the concurrent pattern of findings for two variables measured at the nominal level. In figure 12.2 we can still determine that more than half of the participants in this fictitious study on the effectiveness of a drug treatment program were married (86 + 11 = 97 out of 181). However, we can also note that there may be a relationship between treatment completion and marital status, since a higher proportion of respondents who were in a relationship (married or common-law) completed treatment relative to participants who were single or divorced (see figure 12.2).
Bar graphs can also be used to display the distributions of responses across or within categories of a nominal variable, shown in percentages. For example, figure 12.3 shows the percentage of respondents in each marital status category who completed or failed to complete treatment. This figure more clearly illustrates the relationship between relationship status and treatment completion, as it is now obvious to the reader that the clear majority of those in relationships completed treatment, whereas those who are not in relationships appear to have just slightly higher than a 50-50 chance of success (see figure 12.3).
Tables are typically summaries of the main findings from quantitative research, such as the percentage of respondents who gave answers in each category of a variable on a questionnaire or the differences in means between groups on dependent measures. For example, Symbaluk and Howell’s (2010) study showed that students gave higher ratings to teaching-award winning instructors than to research-award winners on the popular website RateMyProfessors.com. In the results section, a table compared teaching-award and research-award recipients by listing the mean rating given by students for easiness, helpfulness, and clarity for the two groups of instructors (see table 12.1). Tables are also especially useful for indicating patterns in data over time (Nardi, 2006).
| Rating Variable | Teaching-Award Recipients | Research-Award Recipients |
|---|---|---|
| Easiness | ||
| 3.29 | 2.84 | |
| .61 | .81 | |
| Helpfulness | ||
| 4.10 | 3.42 | |
| .76 | 1.07 | |
| Clarity | ||
| 4.10 | 3.51 | |
| .72 | 1.10 | |
| : Means and standard deviations are based on sample sizes of 120 for teaching-award recipients and 119 for research-award recipients. Ratings were made on five-point scales, with higher scores reflecting greater ease, helpfulness, or clarity. | ||
In the discussion section of a research report, researchers summarize and elaborate on the main findings, highlight the importance of the findings, and tie them back into the wider literature. In addition, the discussion section notes limitations of the current study and identifies directions for future research. Since the results section focuses only on the findings, the discussion section is where the researcher can indicate what the results mean and whether the results are consistent with prior expectations, previous research, and/or the hypotheses tested in the study. In addition, researchers can elaborate on what the findings mean, why they are important, and how they can best be interpreted within the context of existing literature. A research report is often described as having the overall shape of an hourglass. Just as the introduction section began broad and narrowed to the focus of the current study, wherein the methods and the results sections are exclusive to the present study, the discussion broadens again until it finally generalizes back to the wider topic of interest.
After discussing the results in relation to the original research questions and wider literature, limitations are raised and suggestions for improvements are provided. All studies have strengths and weaknesses. Usually, a researcher will point out a few of the methodological limitations of the current study. Perhaps the sample size was smaller than desired, or perhaps the sampling method used was not ideal but was necessary under the present circumstances. Even if the most appropriate sampling method was used, as might be the case for a sample of convenience employed in an interview-based study on centenarians (people who live to be more than 100 years of age), inherent limitations such as the resulting inability to generalize the findings should be mentioned in the discussion. If secondary sources are used, there may be restrictions in terms of what can be explored given the different originating purpose of data collection. Usually, a researcher will indicate ways to improve on the present study or offer suggestions for future studies given the limitations discussed. A discussion typically ends with a statement of direction for academics interested in conducting further research in this area. Note that some authors choose to include a conclusion section as a separate section to end the report. A conclusion section summarizes the contributions of the present study and provides suggestions for future research and/or includes directives for policy initiatives.
The last section of a research report is a list of the sources cited throughout the report. The list is generally double-spaced in accordance with the rest of the report and is written in a standard style, such as the one provided by the most current version of the American Psychological Association’s (2020) style guide discussed earlier on.
Research on the Net
APA is the most commonly used citation style in the social sciences. Most, if not all, academic libraries provide students with online resources and staff support to help with citation questions. Additionally, the American Psychological Association’s APA Style website provides examples of how to reference sources , including less commonly used sources like social media posts and audiovisual materials such as podcasts and YouTube videos. The website also provides guidance on how to set up tables and figures , and how to format your paper .
- What seven sections compose a standard academic research report?
- Why is an abstract so important?
- What is provided at the end of an introduction?
- What five subsections are described in the method section of a research report?
- Which section(s) include figures or tables?
- Where would a researcher indicate whether the findings obtained were the ones anticipated prior to the onset of the study?
OTHER ITEMS
Other optional items that may be included in a research report are an appendix and a list of acknowledgements.
The appendix is a section or placeholder where a researcher can include additional information that may be relevant to other researchers, such as a scale or index used to construct questionnaire items, an interview guide used to assist a moderator in a focus group, a set of instructions provided to participants in an experiment, or a coding scheme adapted from the literature for use in a content analysis. Since the appendix is an extra section, it is generally not included in the page count for a research report.
List of Acknowledgements
A list of acknowledgements is sometimes included to pay tribute to individuals and organizations that helped to support the research. For example, research assistants, graduate students, or paid assistants who are not primary researchers or contributing authors are generally acknowledged at the end of the report. The researcher can also list agencies, groups, or organizations that provided funding in the form of grants, scholarships, and/or awards, along with any individual or organization that provided necessary materials, such as meeting space, for carrying out the study.
- Why is a list of acknowledgements important to include in a research report?
Activity: Research Reports Review
Chapter summary.
- Outline the main components of a research proposal. A research proposal includes five main sections: an introduction, a method section, a section on data analysis and dissemination, a section on ethical considerations, and a listing of prospective references.
- Explain the purpose of a method section in a research proposal. The method section outlines who the participants will be and how they will be selected or how the sample will be obtained. In addition, a method section includes information on the setting and materials needed to conduct the study, the procedures for carrying out the study, and the main variables that are examined in the study.
- Identify key ethical considerations that need to be addressed in a research proposal. If a researcher plans to conduct research using humans as participants, the proposal should indicate why the study can be deemed minimal risk and how the minimal risk will be mitigated. The proposal should also include a statement that outlines the benefits of the study for participants, for the researchers, and for the wider academic community. Finally, the proposal should also include a discussion about how privacy and confidentiality will be upheld in the planned study.
- Outline the structure and format of a scholarly research report. A research report includes a title page, an abstract, an introduction, a method section, a results section, a discussion section, and references. The method section includes subsections on participants and how they were selected or the sample and how it was obtained, the setting and materials, the main variables or measures, and how data analysis was conducted.
RESEARCH REFLECTION
- Suppose you are interested in studying the prevalence of texting while driving. What method do you think would be most suitable for examining this phenomenon? If you were going use that method to study texting while driving, what ethical considerations would you need to address in a research proposal?
- Suppose you are interested in learning about effective strategies used by university students to prepare for final exams. Indicate what you would include in a research proposal in the section on participants. Specifically, who would your sample comprise and how you would go about obtaining participants?
- Suppose you want to explore the ways in which people treat their pets in comparison to how they treat members of their immediate family in an exploratory study for your master’s thesis. What kind of method would you employ to study this topic? Based on your choice of method, what sorts of information would you need to include in the results section of a research report based on the findings?
LEARNING THROUGH PRACTICE
Objective: To develop a research outline
Directions:
- First, decide on one area of the mass media where you wish to examine gender, such as music, television, or social media.
- Next, identify relevant secondary sources for data on gender within the selected area of the mass media. For example, if you want to study gender in music, a relevant source would be music lyrics in songs within a genre, such as rap.
- Develop one or two general research questions that you could (potentially) examine using the secondary source identified in the previous step.
- Explain whether your study will be based on qualitative or quantitative research. Justify your approach.
- Describe the main method you plan to use to examine your question of interest. For example, will you be conducting a content analysis?
- Describe a main research question or hypothesis examined in the article.
- Describe the method or methods used to answer the question of interest.
- Explain whether this article has provided you with any ideas or guidance for how to develop your own study in the area.
- Do you think this source of data is a good one to include in your eventual sample? Why or why not?
- Describe the sampling procedure you would use to conduct your planned study.
- Examining the secondary source of data with your research questions in mind, what kind of data analysis do you think you would need to do? Explain the procedures for how you would carry out this analysis on a larger scale in your eventual study.
RESEARCH RESOURCES
- For step-by-step instructions on how to write research proposals and reports, refer to chapters 6 and 7 in Symbaluk, D., Hall, R., & Champoux, G. (2019). Navigating an undergraduate degree in the social sciences: Tips and strategies . MacEwan Open Books.
- For more information on ways to code qualitative data (e.g., descriptive coding, process coding, emotion coding, axial coding, theoretical coding), refer to Saldaña, J. (2021). The coding manual for qualitative researchers (4th ed.). Sage.
- To learn how to code qualitative data using NVivo software, refer to Jackson, K., & Bazeley, P. (2019). Qualitative data analysis with NVivo (3rd ed.) . Sage.
- To learn about data analysis based on qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods, refer to Bergin, T. (2018). An introduction to data analysis: Quantitative, qualitative and mixed methods . Sage.
- Opening quote by Professor Chris Whitty, chief scientific advisor for the Department of Health, published on January 1, 2019, from the National Institute for Health Research home page at nihr.ac.uk. ↵
A comprehensive plan created in advance of carrying out research that details what the purpose of the project is and what the process will be for obtaining data.
A detailed account, following research, that describes the research interest, questions or hypotheses addressed, methods used, and findings from the study.
A brief overview of a research project, which describes the participants or units of observation, the design, the procedures, and the main findings in no more than 250 words.
Charts or graphs used to display results based on how a variable is measure.
Summaries of main findings from quantitative research, such as the percentage of respondents who gave answers in each category of a variable on a questionnaire or the differences in means between groups on dependent measures.
Research Methods: Exploring the Social World in Canadian Context Copyright © 2024 by Diane Symbaluk & Robyn Hall is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on 13 June 2023.
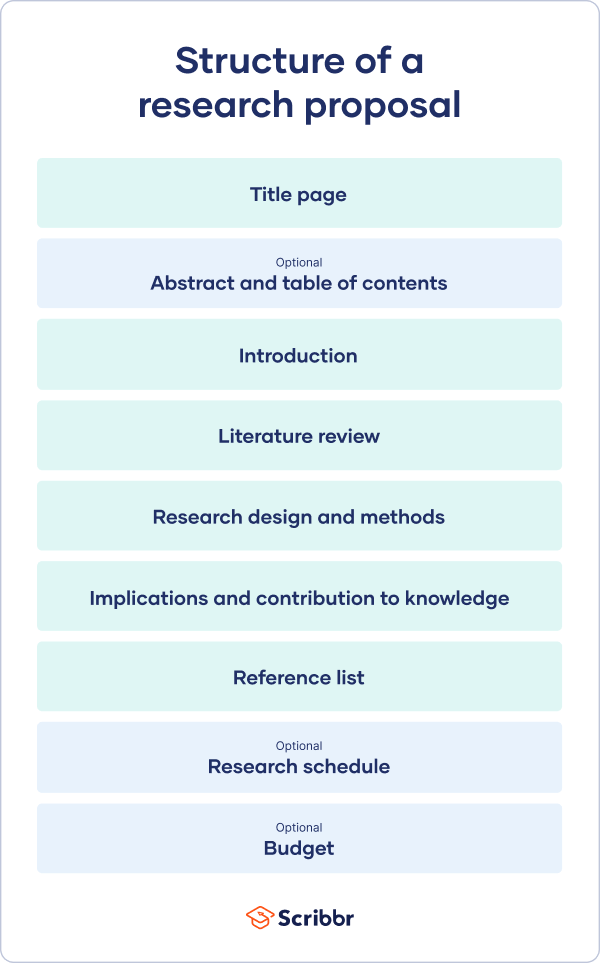
A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organised and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, frequently asked questions.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
| Show your reader why your project is interesting, original, and important. | |
| Demonstrate your comfort and familiarity with your field. Show that you understand the current state of research on your topic. | |
| Make a case for your . Demonstrate that you have carefully thought about the data, tools, and procedures necessary to conduct your research. | |
| Confirm that your project is feasible within the timeline of your program or funding deadline. |
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: ‘A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management’
- Example research proposal #2: ‘ Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use’
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesise prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
| ? or ? , , or research design? | |
| , )? ? | |
| , , , )? | |
| ? |
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasise again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
| Research phase | Objectives | Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Background research and literature review | 20th January | |
| 2. Research design planning | and data analysis methods | 13th February |
| 3. Data collection and preparation | with selected participants and code interviews | 24th March |
| 4. Data analysis | of interview transcripts | 22nd April |
| 5. Writing | 17th June | |
| 6. Revision | final work | 28th July |
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, June 13). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 26 August 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-proposal-explained/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
How to Write a Research Proposal: A Complete Guide
.webp)
A research proposal is a piece of writing that basically serves as your plan for a research project. It spells out what you’ll study, how you’ll go about it, and why it matters. Think of it as your pitch to show professors or funding bodies that your project is worth their attention and support.
This task is standard for grad students, especially those in research-intensive fields. It’s your chance to showcase your ability to think critically, design a solid study, and articulate why your research could make a difference.
In this article, we'll talk about how to craft a good research proposal, covering everything from the standard format of a research proposal to the specific details you'll need to include.
Feeling overwhelmed by the idea of putting one together? That’s where DoMyEssay comes in handy. Whether you need a little push or more extensive guidance, we’ll help you nail your proposal and move your project forward.
Research Proposal Format
When you're putting together a research proposal, think of it as setting up a roadmap for your project. You want it to be clear and easy to follow so everyone knows what you’re planning to do, how you’re going to do it, and why it matters.
Whether you’re following APA or Chicago style, the key is to keep your formatting clean so that it’s easy for committees or funding bodies to read through and understand.
Here’s a breakdown of each section, with a special focus on formatting a research proposal:
- Title Page : This is your first impression. Make sure it includes the title of your research proposal, your name, and your affiliations. Your title should grab attention and make it clear what your research is about.
- Abstract : This is your elevator pitch. In about 250 words, you need to sum up what you plan to research, how you plan to do it, and what impact you think it will have.
- Introduction : Here’s where you draw them in. Lay out your research question or problem, highlight its importance, and clearly outline what you aim to achieve with your study.
- Literature Review : Show that you’ve done your homework. In this section, demonstrate that you know the field and how your research fits into it. It’s your chance to connect your ideas to what’s already out there and show off a bit about what makes your approach unique or necessary.
- Methodology : Dive into the details of how you’ll get your research done. Explain your methods for gathering data and how you’ll analyze it. This is where you reassure them that your project is doable and you’ve thought through all the steps.
- Timeline : Keep it realistic. Provide an estimated schedule for your research, breaking down the process into manageable stages and assigning a timeline for each phase.
- Budget : If you need funding, lay out a budget that spells out what you need money for. Be clear and precise so there’s no guesswork involved about what you’re asking for.
- References/Bibliography : List out all the works you cited in your proposal. Stick to one citation style to keep things consistent.
Get Your Research Proposal Right
Let our experts guide you through crafting a research proposal that stands out. From idea to submission, we've got you covered.

Research Proposal Structure
When you're writing a research proposal, you're laying out your questions and explaining the path you're planning to take to tackle them. Here’s how to structure your proposal so that it speaks to why your research matters and should get some attention.
Introduction
An introduction is where you grab attention and make everyone see why what you're doing matters. Here, you’ll pose the big question of your research proposal topic and show off the potential of your research right from the get-go:
- Grab attention : Start with something that makes the reader sit up — maybe a surprising fact, a challenging question, or a brief anecdote that highlights the urgency of your topic.
- Set the scene : What’s the broader context of your work? Give a snapshot of the landscape and zoom in on where your research fits. This helps readers see the big picture and the niche you’re filling.
- Lay out your plan : Briefly mention the main goals or questions of your research. If you have a hypothesis, state it clearly here.
- Make it matter : Show why your research needs to happen now. What gaps are you filling? What changes could your findings inspire? Make sure the reader understands the impact and significance of your work.
Literature Review
In your research proposal, the literature review does more than just recap what’s already out there. It's where you get to show off how your research connects with the big ideas and ongoing debates in your field. Here’s how to make this section work hard for you:
- Connect the dots : First up, highlight how your study fits into the current landscape by listing what others have done and positioning your research within it. You want to make it clear that you’re not just following the crowd but actually engaging with and contributing to real conversations.
- Critique what’s out there : Explore what others have done well and where they’ve fallen short. Pointing out the gaps or where others might have missed the mark helps set up why your research is needed and how it offers something different.
- Build on what’s known : Explain how your research will use, challenge, or advance the existing knowledge. Are you closing a key gap? Applying old ideas in new ways? Make it clear how your work is going to add something new or push existing boundaries.
Aims and Objectives
Let's talk about the aims and objectives of your research. This is where you set out what you want to achieve and how you plan to get there:
- Main Goal : Start by stating your primary aim. What big question are you trying to answer, or what hypothesis are you testing? This is your research's main driving force.
- Detailed Objectives : Now, break down your main goal into smaller, actionable objectives. These should be clear and specific steps that will help you reach your overall aim. Think of these as the building blocks of your research, each one designed to contribute to the larger goal.
Research Design and Method
This part of your proposal outlines the practical steps you’ll take to answer your research questions:
- Type of Research : First off, what kind of research are you conducting? Will it be qualitative or quantitative research , or perhaps a mix of both? Clearly define whether you'll be gathering numerical data for statistical analysis or exploring patterns and theories in depth.
- Research Approach : Specify whether your approach is experimental, correlational, or descriptive. Each of these frameworks has its own way of uncovering insights, so choose the one that best fits the questions you’re trying to answer.
- Data Collection : Discuss the specifics of your data. If you’re in the social sciences, for instance, describe who or what you’ll be studying. How will you select your subjects or sources? What criteria will you use, and how will you gather your data? Be clear about the methods you’ll use, whether that’s surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments.
- Tools and Techniques : Detail the tools and techniques you'll use to collect your data. Explain why these tools are the best fit for your research goals.
- Timeline and Budget : Sketch out a timeline for your research activities. How long will each phase take? This helps everyone see that your project is organized and feasible.
- Potential Challenges : What might go wrong? Think about potential obstacles and how you plan to handle them. This shows you’re thinking ahead and preparing for all possibilities.
Ethical Considerations
When you're conducting research, especially involving people, you've got to think about ethics. This is all about ensuring everyone's rights are respected throughout your study. Here’s a quick rundown:
- Participant Rights : You need to protect your participants' rights to privacy, autonomy, and confidentiality. This means they should know what the study involves and agree to participate willingly—this is what we call informed consent.
- Informed Consent : You've got to be clear with participants about what they’re signing up for, what you’ll do with the data, and how you'll keep it confidential. Plus, they need the freedom to drop out any time they want.
- Ethical Approval : Before you even start collecting data, your research plan needs a green light from an ethics committee. This group checks that you’re set up to keep your participants safe and treated fairly.
You need to carefully calculate the costs for every aspect of your project. Make sure to include a bit extra for those just-in-case scenarios like unexpected delays or price hikes. Every dollar should have a clear purpose, so justify each part of your budget to ensure it’s all above board. This approach keeps your project on track financially and avoids any surprises down the line.
The appendices in your research proposal are where you stash all the extra documents that back up your main points. Depending on your project, this could include things like consent forms, questionnaires, measurement tools, or even a simple explanation of your study for participants.
Just like any academic paper, your research proposal needs to include citations for all the sources you’ve referenced. Whether you call it a references list or a bibliography, the idea is the same — crediting the work that has informed your research. Make sure every source you’ve cited is listed properly, keeping everything consistent and easy to follow.
Research Proposal Got You Stuck?
Get expert help with your literature review, ensuring your research is grounded in solid scholarship.

How to Write a Research Proposal?
Whether you're new to this process or looking to refine your skills, here are some practical tips to help you create a strong and compelling proposal.
| Tip | What to Do |
|---|---|
| Stay on Target 🎯 | Stick to the main points and avoid getting sidetracked. A focused proposal is easier to follow and more compelling. |
| Use Visuals 🖼️ | Consider adding charts, graphs, or tables if they help explain your ideas better. Visuals can make complex info clearer. |
| Embrace Feedback 🔄 | Be open to revising your proposal based on feedback. The best proposals often go through several drafts. |
| Prepare Your Pitch 🎤 | If you’re going to present your proposal, practice explaining it clearly and confidently. Being able to pitch it well can make a big difference. |
| Anticipate Questions ❓ | Think about the questions or challenges reviewers might have and prepare clear responses. |
| Think Bigger 🌍 | Consider how your research could impact your field or even broader society. This can make your proposal more persuasive. |
| Use Strong Sources 📚 | Always use credible and up-to-date sources. This strengthens your arguments and builds trust with your readers. |
| Keep It Professional ✏️ | While clarity is key, make sure your tone stays professional throughout your proposal. |
| Highlight What’s New 💡 | Emphasize what’s innovative or unique about your research. This can be a big selling point for your proposal. |
Research Proposal Template
Here’s a simple and handy research proposal example in PDF format to help you get started and keep your work organized:
Writing a research proposal can be straightforward if you break it down into manageable steps:
- Pick a strong research proposal topic that interests you and has enough material to explore.
- Craft an engaging introduction that clearly states your research question and objectives.
- Do a thorough literature review to see how your work fits into the existing research landscape.
- Plan out your research design and method , deciding whether you’ll use qualitative or quantitative research.
- Consider the ethical aspects to ensure your research is conducted responsibly.
- Set up a budget and gather any necessary appendices to support your proposal.
- Make sure all your sources are cited properly to add credibility to your work.
If you need some extra support, DoMyEssay is ready to help with any type of paper, including crafting a strong research proposal.
What Is a Research Proposal?
How long should a research proposal be, how do you start writing a research proposal.
Examples of Research proposals | York St John University. (n.d.). York St John University. https://www.yorksj.ac.uk/study/postgraduate/research-degrees/apply/examples-of-research-proposals/
.webp)

Style and Grammar Guidelines
APA Style provides a foundation for effective scholarly communication because it helps writers present their ideas in a clear, concise, and inclusive manner. When style works best, ideas flow logically, sources are credited appropriately, and papers are organized predictably. People are described using language that affirms their worth and dignity. Authors plan for ethical compliance and report critical details of their research protocol to allow readers to evaluate findings and other researchers to potentially replicate the studies. Tables and figures present information in an engaging, readable manner.
The style and grammar guidelines pages present information about APA Style as described in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, Seventh Edition and the Concise Guide to APA Style, Seventh Edition . Any updates to APA Style are noted on the applicable topic pages. If you are still using the sixth edition, helpful resources are available in the sixth edition archive .
Looking for more style?

- Accessibility of APA Style
- Line Spacing
- Order of Pages
- Page Header
- Paragraph Alignment and Indentation
- Sample Papers
- Title Page Setup
- Appropriate Level of Citation
- Basic Principles of Citation
- Classroom or Intranet Sources
- Paraphrasing
- Personal Communications
- Quotations From Research Participants
- Secondary Sources
- Abbreviations
- Capitalization
- Italics and Quotation Marks
- Punctuation
- Spelling and Hyphenation
- General Principles for Reducing Bias
- Historical Context
- Intersectionality
- Participation in Research
- Racial and Ethnic Identity
- Sexual Orientation
- Socioeconomic Status
- Accessible Use of Color in Figures
- Figure Setup
- Sample Figures
- Sample Tables
- Table Setup
- Archival Documents and Collections
- Basic Principles of Reference List Entries
- Database Information in References
- DOIs and URLs
- Elements of Reference List Entries
- Missing Reference Information
- Reference Examples
- References in a Meta-Analysis
- Reference Lists Versus Bibliographies
- Works Included in a Reference List
- Active and Passive Voice
- Anthropomorphism
- First-Person Pronouns
- Logical Comparisons
- Plural Nouns
- Possessive Adjectives
- Possessive Nouns
- Singular “They”
- Adapting a Dissertation or Thesis Into a Journal Article
- Correction Notices
- Cover Letters
- Journal Article Reporting Standards (JARS)
- Open Science
- Response to Reviewers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The main heading of "Methods" should be centered, boldfaced, and capitalized. Subheadings within this section are left-aligned, boldfaced, and in title case. You can also add lower level headings within these subsections, as long as they follow APA heading styles. To structure your methods section, you can use the subheadings of ...
The methods section should describe what was done to answer the research question, describe how it was done, justify the experimental design, and explain how the results were analyzed. Scientific writing is direct and orderly. Therefore, the methods section structure should: describe the materials used in the study, explain how the materials ...
A quality example of a research proposal shows one's above-average analytical skills, including the ability to coherently synthesize ideas and integrate lateral and vertical thinking. Communication skills. The proposal also demonstrates your proficiency to communicate your thoughts in concise and precise language.
In generating a research proposal, the written part for methodology serves as a pivotal element that charts the course of the investigation, delineating the stages and strategies to be employed. Let's delve into essential elements to feature in this section. 1. Research Design: Begin by elucidating the overall academic design of your survey ...
The main purposes of the methods section in a research proposal are as follows: Describe your proposed study design - Explicitly state whether you will employ an experimental, quasi-experimental, survey, ethnographic, phenomenological, case study, or other established research methodology. Providing a clear overview of your overarching design ...
This section of the APA methods section should cover the percentage of respondents who participated in the research, and how they were chosen. You also need to state how participants were compensated and the ethical standard followed. Example. Transgender male students from London were invited to participate in a study.
The methods section is a fundamental section of any paper since it typically discusses the 'what', 'how', 'which', and 'why' of the study, which is necessary to arrive at the final conclusions. In a research article, the introduction, which serves to set the foundation for comprehending the background and results is usually ...
Do yourself a favour and start with the end in mind. Section 1 - Introduction. As with all chapters in your dissertation or thesis, the methodology chapter should have a brief introduction. In this section, you should remind your readers what the focus of your study is, especially the research aims. As we've discussed many times on the blog ...
To write your methods section in APA format, describe your participants, materials, study design, and procedures. Keep this section succinct, and always write in the past tense. The main heading of this section should be labeled "Method" and it should be centered, bolded, and capitalized. Each subheading within this section should be bolded ...
Your Methods Section contextualizes the results of your study, giving editors, reviewers and readers alike the information they need to understand and interpret your work. Your methods are key to establishing the credibility of your study, along with your data and the results themselves. A complete methods section should provide enough detail ...
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
1. Research Proposal Format Example. Following is a general outline of the material that should be included in your project proposal. I. Title Page II. Introduction and Literature Review (Chapters 2 and 3) A. Identification of specific problem area (e.g., what is it, why it is important). B. Prevalence, scope of problem.
The new Third Edition covers every section of the proposal, telling you all you need to know on how to structure it, bring rigor to your methods section, impress your readers, and get your proposal accepted. Developing Effective Research Proposals provides an authoritative and accessible guide for anyone tackling a research proposal.
3. Follow the order of the results: To improve the readability and flow of your manuscript, match the order of specific methods to the order of the results that were achieved using those methods. 4. Use subheadings: Dividing the Methods section in terms of the experiments helps the reader to follow the section better.
Research Design and Methods: This section needs to clearly demonstrate how the data will be gathered and analyzed in a systematic and academically sound manner. Here, you need to demonstrate that the conclusions of your research will be both valid and reliable. ... Research Proposal Examples. Research proposals often extend anywhere between ...
Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper. Your research proposal should include (at least) 5 essential components : Title - provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms. Introduction - explains what you'll be researching in more detail.
Here is an explanation of each step: 1. Title and Abstract. Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research. Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal. 2.
Research proposals, like all other kinds of academic writing, are written in a formal, objective tone. Keep in mind that being concise is a key component of academic writing; formal does not mean flowery. Adhere to the structure outlined above. Your reader knows how a research proposal is supposed to read and expects it to fit this template.
INTRODUCTION. A clean, well-thought-out proposal forms the backbone for the research itself and hence becomes the most important step in the process of conduct of research.[] The objective of preparing a research proposal would be to obtain approvals from various committees including ethics committee [details under 'Research methodology II' section [Table 1] in this issue of IJA) and to ...
Explain the purpose of a method section in a research proposal. The method section outlines who the participants will be and how they will be selected or how the sample will be obtained. In addition, a method section includes information on the setting and materials needed to conduct the study, the procedures for carrying out the study, and the ...
A Sample Quantitative Research Proposal Written in the APA 6th Style. [Note: This sample proposal is based on a composite of past proposals, simulated information and references, and material I've included for illustration purposes - it is based roughly on a fairly standard research proposal; I say roughly because there is no one set way of ...
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: 'A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management'.
Purpose: To provide an overview of the study, which you will expand on in detail in later sections of the research proposal. What you should do: Provide a brief overview of your project. Include the goals of your research proposal and clearly specify the research questions you want to address. Explain the hypotheses you want to test.
The structure of a research proposal includes eight different sections and is approximately 2000 to about 2500 words maximum. Remember that number. It should never be too short, but also shouldn't be too long. So it includes the following sections, a title, an abstract research background, research questions, the research methods.
To Sum Up. Writing a research proposal can be straightforward if you break it down into manageable steps: Pick a strong research proposal topic that interests you and has enough material to explore.; Craft an engaging introduction that clearly states your research question and objectives.; Do a thorough literature review to see how your work fits into the existing research landscape.
People are described using language that affirms their worth and dignity. Authors plan for ethical compliance and report critical details of their research protocol to allow readers to evaluate findings and other researchers to potentially replicate the studies. Tables and figures present information in an engaging, readable manner.
The methods a student selects should relate to their dissertation area. Below are several analytic/research methods in which students have been examined in recent years. Numerous analytic/research methods are appropriate, and students need not be restricted to choices on the list: Anthropological methods; Case study methods; Complex systems ...