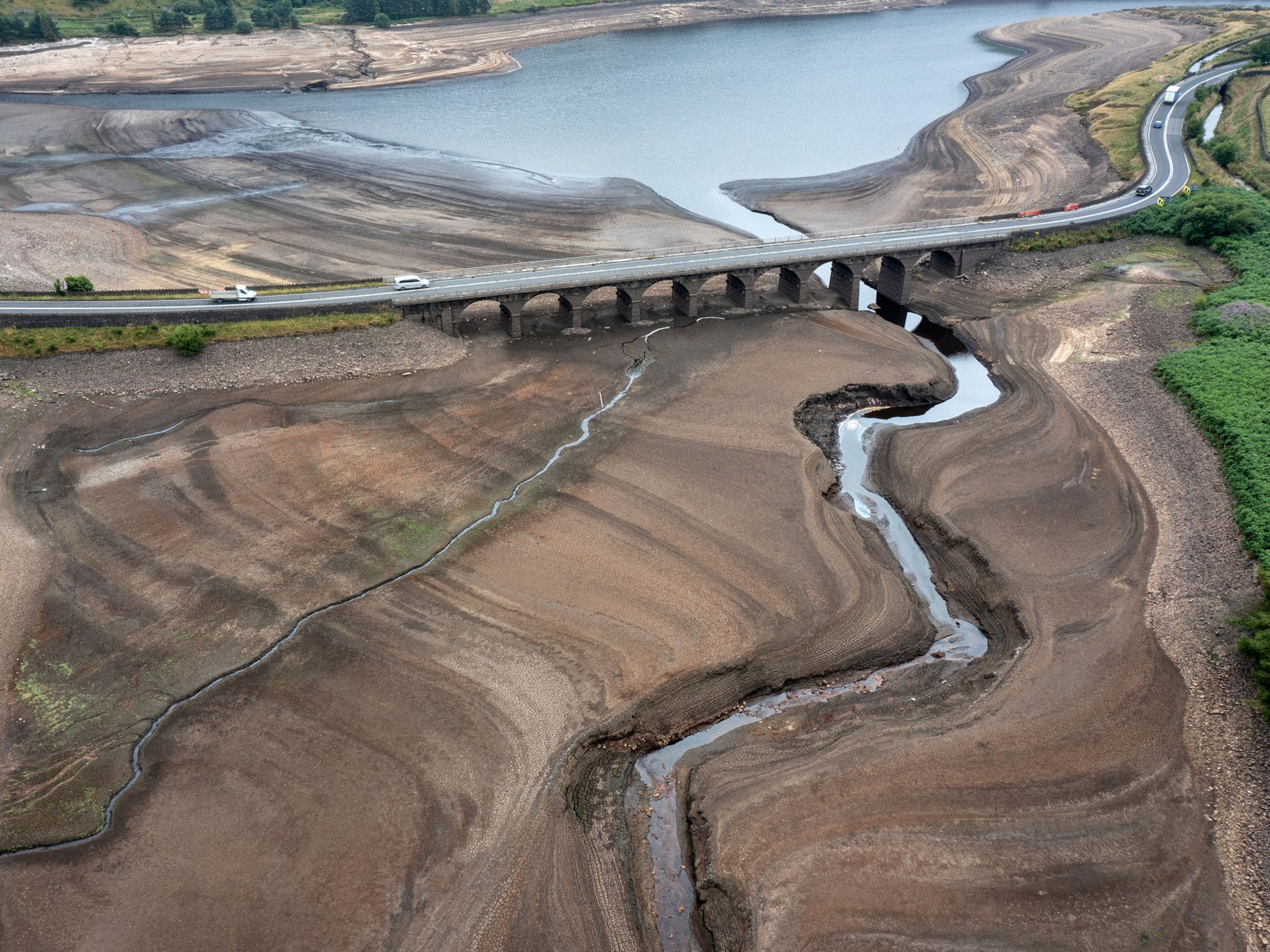
How can we solve the global water crisis?

Human activities are jeopardizing water at its source. Image: Unsplash/mrjn Photography

.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Mariana Mazzucato
Ngozi okonjo-iweala, johan rockström, tharman shanmugaratnam.

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Water is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:.
This article is produced in collaboration with Project Syndicate.
- Water-related crises around the world show that current systems of water management are unsuited for a world altered by global warming.
- Water-use restrictions, power cuts and other stopgap measures are no longer fit for purpose.
- The task now is to understand the links between water, climate change and biodiversity loss, and to properly govern water as a global common good.
- The world needs to clearly define its plans, as this will help governments steer innovation and knowhow towards meeting critical goals.
The floods, droughts, heatwaves, and fires that are devastating many parts of the world underscore two fundamental facts. First, damage to freshwater supplies is increasingly straining human societies, especially the poor, with far-reaching implications for economic, social, and political stability. Second, the combined impact of today’s extreme conditions are unprecedented in human history, and are overwhelming policymakers’ ability to respond.
In East Africa, a devastating four-year drought has destroyed millions of livelihoods and left more than 20 million people at risk of starvation. In Pakistan, recent flooding has submerged one-third of the country, killing at least 1,500 people so far and wiping out 45% of this year’s crops. In China, an unprecedented heatwave has caused acute water shortages in regions that account for one-third of the country’s rice production .
Moreover, droughts and fires in the United States and Europe, and severe floods and droughts across India, have reduced global grain yields and food exports, highlighting the extent to which our food production depends on large, stable volumes of water. Add to this the impact of the war in Ukraine on grain and fertilizer supplies, and there is a substantial risk that today’s global food crisis will persist.
For the first time in our history, human activities are jeopardizing water at its very source. Climate change and deforestation are reshaping the monsoon season, causing ice on the Tibetan plateau to melt , and affecting freshwater supplies to more than one billion people. Rising global temperatures are changing evaporation patterns and reducing moisture feedback from forests, disrupting downwind rainfall. And a destabilized global water cycle is itself aggravating climate change. For example, the depletion of water in the soil and forests is reducing their ability to sequester carbon .
Water-use restrictions, power cuts, and other stopgap measures can no longer paper over the fact that our water governance and management systems are not suited for a world of radical environmental change. All our current arrangements rest on the assumption, now invalidated, that the water supply is relatively stable (within the bounds of natural variability), predictable, and manageable in localized ways. But the water crisis is global, and it can be solved only with transformational thinking and new governance.
We must recognize that all our key environmental challenges are connected to water – whether there is too much or too little, or whether it is too polluted for human use. The task now is to understand the links between water, climate change, and biodiversity loss, and to properly define, value, and govern water as a global common good. Thinking about water in this way will allow us to mobilize collective action and design new rules that put equity and justice at the center of our response.
For too long, most governments have either ignored market failures or responded to them with quick fixes, rather than mobilizing the public and private sectors around common ambitions. The public sector must see itself as a market shaper that works with all stakeholders in the water economy to create pathways for innovation and investment, ensure universal access to clean water and sanitation, and provide enough water for food, energy, and natural systems.
A key lesson from past challenges that demanded systemic innovation is that a clearly defined mission is needed to organize our efforts. Mission-oriented policies allow governments to steer innovation and knowhow directly toward meeting critical goals. When guided by an inclusive “common-good” approach, they are uniquely capable of delivering solutions to challenges that require tremendous levels of coordination and financing across many years. Climate change, biodiversity loss, and water crises are precisely such challenges.
Mission-based strategies can help governments innovate with purpose, direction, and urgency. But to be effective, policymakers must heed the experience and wisdom of the ordinary citizens, communities, and innovators who know how to prosper in a world of water scarcity, higher temperatures, and altered coastline and river systems.
We must now recognize threats to the global freshwater system and translate our awareness into collective action. Because water scarcity will jeopardize all the other Sustainable Development Goals, it should solidify our collective determination to limit temperature increases to 1.5° Celsius above pre-industrial levels (as specified in the Paris climate agreement), and to preserve the natural systems that ensure stable rainfall and runoff patterns.
Water security – both sustainable supply and clean quality – is a critical aspect in ensuring healthy communities. Yet, our world’s water resources are being compromised.
Today, 80% of our wastewater flows untreated back into the environment, while 780 million people still do not have access to an improved water source. By 2030, we may face a 40% global gap between water supply and demand.
The World Economic Forum’s Water Possible Platform is supporting innovative ideas to address the global water challenge.
The Forum supports innovative multi-stakeholder partnerships including the 2030 Water Resources Group , which helps close the gap between global water demand and supply by 2030 and has since helped facilitate $1Billion of investments into water.
Other emerging partnerships include the 50L Home Coalition , which aims to solve the urban water crisis , tackling both water security and climate change; and the Mobilizing Hand Hygiene for All Initiative , formed in response to close the 40% gap of the global population not having access to handwashing services during COVID-19.
Want to join our mission to address the global water challenge? Read more in our impact story .
In tackling these global challenges, we must hardwire the principles of equity and justice into whatever new arrangements we devise. No community can thrive without a reliable supply of clean water. But safeguarding this global common good requires new policies and systems.
Law and economics must both be reoriented to ensure universal access to clean drinking water, sanitation, and hygiene, and to build more resilient and sustainable food systems. Incentives must change so that the private sector can do its part to provide access to technology and innovation to poor and rich countries alike. This will require long-term finance and novel mechanisms to regulate how the public and private sectors work together.
Have you read?
Ensuring sustainable water management for all by 2030, we need to rethink how we manage our water systems — before it’s too late, low-income communities lack access to clean water. it’s time for change.
The UN 2023 Water Conference – the first in almost 50 years – will be a pivotal moment for the international community to start mapping out a future that works for everyone. In preparing for it, we can take inspiration from Nicholas Stern , who rewrote the economics of climate change , and Partha Dasgupta , who rewrote the economics of biodiversity . As the four co-chairs of the Global Commission on the Economics of Water , our goal is to transform the world’s understanding of the economics and governance of water, placing a much stronger emphasis on equity, justice, effectiveness, and democracy.
We can still redefine our relationship with water and redesign our economies to value water as a global common good. But the window of opportunity is closing. To have a chance of avoiding climate catastrophe and adapting to unavoidable change, we must ensure a resilient water future for poor and rich societies alike.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Global Cooperation .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

How global joint ventures can thrive in times of turmoil
Rahul Khubchandani and Ed Gore-Randall
May 2, 2024

What bullet-proof Kevlar teaches us about cooperation and resilience
Aba Schubert
April 26, 2024

Japan and the Middle East: Japan can be a bridge in an era of global fragmentation and conflict
Kiriko Honda
April 25, 2024

Practice of long-term thinking: How to leverage foresight to address the transformational challenges ahead
Lasse Jonasson
April 24, 2024

Unlocking Africa's $1 trillion food economy: The role of global aid and sustainable technology

Energy for development: Everything you need to know from #SpecialMeeting24
Ella Yutong Lin and Kate Whiting
April 23, 2024
Press release
Imminent risk of a global water crisis, warns the UN World Water Development Report 2023

Globally, 2 billion people (26% of the population) do not have safe drinking water and 3.6 billion (46%) lack access to safely managed sanitation, according to the report, published by UNESCO on behalf of UN-Water and released today at the UN 2023 Water Conference in New York.
Between two and three billion people experience water shortages for at least one month per year, posing severe risks to livelihoods, notably through food security and access to electricity. The global urban population facing water scarcity is projected to double from 930 million in 2016 to 1.7–2.4 billion people in 2050. The growing incidence of extreme and prolonged droughts is also stressing ecosystems, with dire consequences for both plant and animal species.
There is an urgent need to establish strong international mechanisms to prevent the global water crisis from spiraling out of control. Water is our common future and it is essential to act together to share it equitably and manage it sustainably.

Protecting and preserving this precious resource for future generations depends on partnerships. The smart management and conservation of the world’s water resources means bringing together governments, businesses, scientists, civil society and communities – including indigenous communities – to design and deliver concrete solutions.
There is much to do and time is not on our side. This report shows our ambition and we must now come together and accelerate action. This is our moment to make a difference.
International cooperation: the key to access to water for all
Nearly every water-related intervention involves some kind of cooperation. Growing crops require shared irrigation systems among farmers. Providing safe and affordable water to cities and rural areas is only possible through a communal management of water-supply and sanitation systems. And cooperation between these urban and rural communities is essential to maintaining both food security and uphold farmer incomes.
Managing rivers and aquifers crossing international borders makes matters all the more complex. While cooperation over transboundary basins and aquifers has been shown to deliver many benefits beyond water security, including opening additional diplomatic channels, only 6 of the world’s 468 internationally shared aquifers are subject to a formal cooperative agreement.
On this World Water Day, the United Nations calls for boosting international cooperation over how water is used and managed. This is the only way to prevent a global water crisis in the coming decades.
Partnerships and people’s participation increase benefits
Environmental services, such as pollution control and biodiversity, are among the shared benefits most often highlighted in the report, along with data/information-sharing and co-financing opportunities. For example, ‘water funds’ are financing schemes that bring together downstream users, like cities, businesses, and utilities, to collectively invest in upstream habitat protection and agricultural land management to improve overall water quality and/or quantity.
Mexico’s Monterrey Water Fund, launched in 2013, has maintained water quality, reduced flooding, improved infiltration and rehabilitated natural habitats through co-financing. The success of similar approaches in Sub-Saharan Africa, including the Tana-Nairobi river watershed, which supplies 95% of the Nairobi’s freshwater and 50% of Kenya’s electricity, illustrate the global potential of such partnerships.
Inclusive stakeholder participation also promotes buy-in and ownership. Involving the end-users in planning and implementing water systems creates services that better match the needs and resources of poor communities, and increases public acceptance and ownership. It also fosters accountability and transparency. In displacement camps in the Gedo region of Somalia, residents elect water committees that operate and maintain the waterpoints that supply tens of thousands of people. Committee members partner with local water authorities of the host communities to share and manage water resources.
The United Nations World Water Development Report is published by UNESCO on behalf of UN-Water and its production is coordinated by the UNESCO World Water Assessment Programme. The report gives insight into the main trends concerning the state, use and management of freshwater and sanitation, based on work by Members and Partners of UN-Water. Launched in conjunction with World Water Day, the report provides decision-makers with knowledge and tools to formulate and implement sustainable water policies. It also offers best practice examples and in-depth analyses to stimulate ideas and actions for better stewardship in the water sector and beyond.
Press contacts
UNESCO : François Wibaux, [email protected] , +33145680746
UN-Water: Daniella Bostrom Couffe, [email protected] , +41796609284
UNESCO WWAP: Simona Gallese, [email protected] , +390755911026
Related items
- Natural sciences
- UN & International cooperation
- Water resources
- Water supply
- World Water Assessment Programme (WWAP)
- World Water Day
- Country page: Switzerland
- Region: Europe and North America
- SDG: SDG 6 - Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all
- SDG: SDG 17 - Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development
- See more add
This article is related to the United Nation’s Sustainable Development Goals .

Other recent press releases
How Climate Change Impacts Water Access
The water cycle is part of our everyday lives, but climate change may have dire consequences for everyday water access.
Biology, Health, Conservation, Earth Science
Herder Collecting Water
Climate change is already hurting water access for people around the world. Here, a Samburu herder collects water for his flock in Sahara Conservancy, Kenya.
Photograph from the National Geographic image collection

Climate change is already affecting water access for people around the world, causing more severe droughts and floods. Increasing global temperatures are one of the main contributors to this problem. Climate change impacts the water cycle by influencing when, where, and how much precipitation falls. It also leads to more severe weather events over time. Increasing global temperatures cause water to evaporate in larger amounts, which will lead to higher levels of atmospheric water vapor and more frequent, heavy, and intense rains in the coming years.
Climate scientists predict that this shift will lead to more floods since more water will fall than vegetation and soil can absorb. The remaining water, or runoff , drains into nearby waterways, picking up contaminants like fertilizer on the way. Excess runoff eventually travels to larger bodies of water like lakes, estuaries, and the ocean, polluting the water supply and limiting water access for humans and ecosystems .
When fertilizers from farming wash into lakes and the ocean, they promote the rapid growth of algae. These resulting algal blooms clog coasts and waterways with clouds of green, blue-green, red, or brown algae. The blooms block sunlight from reaching underwater life and diminish oxygen levels within the water. Toxins from the blooms can kill off fish and other aquatic animals, make people sick, and even kill humans. These toxins are especially dangerous because they can survive purification processes, making tap water unfit to consume once contaminated. Algal blooms also impact industries that rely on the water for business, and often cause local waterfronts to shut down during blooms. As the climate warms, harmful algal blooms happen more often and become more severe.
As the ocean warms, freshwater glaciers around Earth begin to melt at an unsustainable rate, which results in rising sea levels. The freshwater from the melted glaciers eventually runs into the ocean. With the rising of sea levels, salt water can more easily contaminate underground freshwater-bearing rocks, called aquifers. A process called desalination removes salt from salt water, but it is a last-resort, energy-intensive, costly process for places where there are persistent droughts and freshwater is lacking. The Middle East, North Africa, and the Caribbean use desalination to produce freshwater out of necessity.
In the Northern Hemisphere—where snow, a freshwater source, typically accumulates—warmer temperatures mean less snowfall, which leaves less water available in local reservoirs after winter. This negatively impacts farmers, who are left without enough water to irrigate their crops in the growing season.
There are many things that everyone can do to lessen the impact of climate change . Some measures include growing your own fruits and vegetables or buying locally grown produce, since produce is often transported to grocery stores from far away by trucks, which add more carbon dioxide to the atmosphere . You could also walk or ride a bike instead of driving a car. On a larger scale, industries that are dependent on fossil fuels need to make the switch to renewable, cleaner energy sources to influence our planet for the better.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Production Managers
Program specialists, last updated.
January 26, 2024
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources

A trio of children bathe near the port area of Labuan Bajo on Flores Island, Indonesia.
Freshwater Crisis
There is the same amount of freshwater on earth as there always has been, but the population has exploded, leaving the world's water resources in crisis.
A Clean Water Crisis
The water you drink today has likely been around in one form or another since dinosaurs roamed the Earth , hundreds of millions of years ago.
While the amount of freshwater on the planet has remained fairly constant over time—continually recycled through the atmosphere and back into our cups—the population has exploded. This means that every year competition for a clean, copious supply of water for drinking, cooking, bathing, and sustaining life intensifies.
Water scarcity is an abstract concept to many and a stark reality for others. It is the result of myriad environmental, political, economic, and social forces.
Freshwater makes up a very small fraction of all water on the planet. While nearly 70 percent of the world is covered by water, only 2.5 percent of it is fresh. The rest is saline and ocean-based. Even then, just 1 percent of our freshwater is easily accessible, with much of it trapped in glaciers and snowfields. In essence, only 0.007 percent of the planet's water is available to fuel and feed its 6.8 billion people.
Due to geography, climate, engineering, regulation, and competition for resources, some regions seem relatively flush with freshwater, while others face drought and debilitating pollution. In much of the developing world, clean water is either hard to come by or a commodity that requires laborious work or significant currency to obtain.
Water Is Life
Wherever they are, people need water to survive. Not only is the human body 60 percent water, the resource is also essential for producing food, clothing, and computers, moving our waste stream, and keeping us and the environment healthy.
Unfortunately, humans have proved to be inefficient water users. (The average hamburger takes 2,400 liters, or 630 gallons, of water to produce, and many water-intensive crops, such as cotton, are grown in arid regions.)
According to the United Nations , water use has grown at more than twice the rate of population increase in the last century. By 2025, an estimated 1.8 billion people will live in areas plagued by water scarcity, with two-thirds of the world's population living in water-stressed regions as a result of use, growth, and climate change. The challenge we now face as we head into the future is how to effectively conserve, manage, and distribute the water we have.
For Hungry Minds
Related topics.
- WATER POLLUTION
- FRESH WATER
- ENVIRONMENT AND CONSERVATION
- WATER RESOURCES
You May Also Like

England’s chalk streams were millions of years in the making. Can they survive today?

Here’s what worries engineers the most about U.S. infrastructure

The delicate art of catching fog in the desert

Europe’s water crisis is much worse than we thought

Why snowpack is so critical to life in the West
- Environment
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Coronavirus Coverage
- Paid Content
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved

Essay on Water Crisis 500+ Words
Water, a life-sustaining resource, is essential for all living creatures on Earth. However, a water crisis is emerging as one of the most significant challenges humanity faces today. In this essay, we will explore the water crisis, its causes and consequences, and the critical need for sustainable solutions to ensure a better future for our planet.
The Growing Water Crisis
A water crisis refers to the scarcity of clean, fresh water needed for various purposes, such as drinking, agriculture, industry, and sanitation. It’s a global problem that affects people, ecosystems, and economies. According to the United Nations, by 2030, nearly half of the world’s population could be facing water scarcity.
Causes of the Water Crisis
a. Overpopulation : The world’s population is rapidly increasing, leading to higher water demand for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use.
b. Climate Change : Changing weather patterns, including prolonged droughts and more frequent extreme weather events, are affecting water availability.
c. Pollution : Water sources are often polluted by chemicals, sewage, and industrial waste, making water unsafe for consumption.
d. Wasteful Practices : Water wastage in agriculture, industry, and households contributes to the crisis.
Consequences of Water Scarcity
a. Health Issues : Lack of clean water leads to waterborne diseases like cholera and dysentery, affecting millions, especially children.
b. Food Insecurity : Agriculture heavily relies on water, and water scarcity can lead to crop failures and food shortages.
c. Conflict : Scarcity can trigger conflicts over limited water resources, leading to tensions between communities and even nations.
d. Ecosystem Damage : Wildlife and ecosystems suffer as water sources shrink, impacting biodiversity.
Sustainable Solutions to the Water Crisis
a. Water Conservation : Responsible water use, fixing leaks, and using water-saving appliances can make a significant difference.
b. Improved Infrastructure : Building and maintaining water supply and sanitation systems can help reduce water losses.
c. Rainwater Harvesting : Collecting rainwater for household use and agriculture can mitigate scarcity.
d. Desalination : Technology to turn seawater into freshwater is an option for regions with limited freshwater sources.
The Importance of Education
Education plays a vital role in raising awareness about the water crisis. Schools and communities can educate people about responsible water use, conservation, and the importance of preserving our water resources. Students can become water ambassadors, spreading the message about the need to protect our water.
Global Efforts to Combat Water Scarcity
International organizations like the United Nations and NGOs are working to address water scarcity on a global scale. They provide funding, expertise, and resources to implement sustainable water management practices in affected regions. Collaboration between countries and communities is key to finding solutions.
Conclusion of Essay on Water Crisis
In conclusion, the water crisis is a pressing global issue that affects people, ecosystems, and economies. Understanding its causes and consequences is the first step in finding solutions. It is essential for individuals, communities, and governments to take action by conserving water, improving infrastructure, and supporting sustainable practices. Education and global cooperation are vital in our fight against water scarcity.
By working together, we can ensure that future generations have access to the life-sustaining resource of clean, fresh water. Water is precious, and its conservation is our collective responsibility. As we address the water crisis, we are not only securing our own future but also safeguarding the health and well-being of our planet and all its inhabitants.
Also Check: The Essay on Essay: All you need to know
Blue Gold: Global Water Crisis Essay
The issue of water is a global affair because of the alarming rate at which limited fresh water reservoirs is depleted. Water is important for the sustenance of human life and most people treasure it. Due to its limited supply and the reduction of fresh water sources, it has become a sought after natural resource the same as oil.
The documentary ” Blue Gold: World Water Wars” talked about the disturbing rates at which individuals use water commercially and domestically to a point of altering nature including the wetlands and excessive mining of underground water.
A large number of corporate companies have control over water resources, including the distribution systems, in view of the fact that third world governments have relinquished their responsibilities in terms of protecting water supply as well as water conservation (Barlow & Clarke 4). The corporate companies in charge of managing fresh water resources are taking advantage of the increasing population.
Presently, world’s population is growing at an alarming rate and the population becomes concentrated in urban areas (Barlow & Clarke 6).
These urban areas lack proper sanitation services and fresh water for consumption, therefore the global water consumption rises (Barlow & Clarke 7) and the corporate companies obtain extreme financial benefits. The documentary illustrated that another way the corporate companies benefit from privatization of the fresh water resources is through exportation to other countries at a very high price.
Human activities are the leading cause of fresh water depletion. This natural resource becomes polluted by human activities such as dumping of solid and industrial wastes, development purposes and also for human consumption (Barlow & Clarke 5). The depletion of fresh water supply as a result of human activities especially industrial use contributes to global warming.
Since rainfall is an important aspect of the hydrological and the percentage of finite supply of fresh water that evaporates into the atmosphere is negligible, then the amount of rain pour expected becomes minimal and in the end, the arable lands becomes arid and dry (Barlow & Clarke 5). According to the interviewee, the sustainability and availability of fresh water as a natural resource becomes inevitable since the ecosystem becomes destroyed.
The issue of water is serious and should be addressed before it becomes worse. Globally, the amount of fresh water is dropping and it is believed that fresh water is a finite resource (Barlow and Clarke 5). Fresh water supply accounts for less than half the amount of the one percent water in the world and the rest is salt water, frozen ice caps and underground water.
The approximate land area fresh water accumulates is about 1.4 billion cubic kilometers (Barlow and Clarke 5). Even with this percentage, fresh water supply is not enough. People have turned to mining of underground water reservoirs up to a rate of about thirty billion gallons per day.
In conclusion, water is an important aspect for human survival. It enables people to coexist; therefore water resources should be conserved. As a result of global warming and personal interests from certain nations, water is becoming a fast moving commodity and the rate at which it is being used the human species might end up being extinct.
Even though scientists are exploring other alternatives, for example seeking other life supporting planets, it is up to every individual to conserve their environment for a future of sustainable development of natural resources.
Works Cited
Barlow, Maude, and Tony Clarke. Blue Gold: The Battle against Corporate Theft of the World’s Water . London: EarthScan, 2003. Print.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, April 28). Blue Gold: Global Water Crisis. https://ivypanda.com/essays/water-crisis-essay/
"Blue Gold: Global Water Crisis." IvyPanda , 28 Apr. 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/water-crisis-essay/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'Blue Gold: Global Water Crisis'. 28 April.
IvyPanda . 2022. "Blue Gold: Global Water Crisis." April 28, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/water-crisis-essay/.
1. IvyPanda . "Blue Gold: Global Water Crisis." April 28, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/water-crisis-essay/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Blue Gold: Global Water Crisis." April 28, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/water-crisis-essay/.
- Geotechnical Engineering: The Finite Element Software
- Effects of Ozone Depletion
- Efforts to Alleviate Ozone Depletion
- Ozone Depletion
- Finite Difference Solution to Dam seepage Problems
- Ozone Depletion: A Case of Humans Fixing What They Broke
- Geothermal Energy: What Is It and How Does It Work?
- C. Columbus and the Underground Railroad
- Blue Gold: World Water War Documentary
- The Effects of Gold Mining in the Amazons on the Environment and the Population
- Geothermal Energy in Eden Project
- Morality and Modernity: Cronon and Daston’s Understanding of Nature
- Brazil Environmental Issues
- The Ability of People Handling Global Warming
- Global Warming and Climate Change

Essay on Water Crisis
Students are often asked to write an essay on Water Crisis in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Water Crisis
The water crisis.
Water is a basic necessity, yet many people worldwide face water scarcity. It’s a crisis that affects both humans and the environment.
Causes of Water Crisis
The crisis is due to pollution, overuse of water, and climate change. Pollution contaminates water, making it unsafe. Overuse, especially in agriculture, depletes water supplies. Climate change causes unpredictable rainfall, leading to droughts or floods.
Impact of Water Crisis
The crisis affects health, agriculture, and economies. Without clean water, diseases spread. Crops fail without enough water, causing food shortages. Economies suffer as industries need water to operate.
Solutions to Water Crisis
Solutions include better water management, reducing pollution, and using water-saving technologies. Everyone can help by using water wisely.
Also check:
- 10 Lines on Water Crisis
250 Words Essay on Water Crisis
The global water crisis: an unseen emergency.
Water, the basic necessity for all life forms, is alarmingly becoming scarce. The global water crisis, often an overlooked issue, is a pressing concern that demands immediate attention.
The Root Causes
The water crisis has its roots in various factors. Rapid urbanisation and industrialisation have led to increased pollution, making vast amounts of water unfit for consumption. Climate change, with its erratic weather patterns, exacerbates water scarcity by causing droughts and floods.
The Consequences
The implications of the water crisis are far-reaching. Water scarcity hampers agricultural productivity, leading to food insecurity. It also poses serious health risks as inadequate water often results in poor sanitation, leading to the spread of waterborne diseases.
Addressing the Crisis
Addressing the water crisis requires a multi-faceted approach. Conservation efforts, such as rainwater harvesting and wastewater recycling, can help augment water supplies. Governments and corporations need to enforce stricter regulations to curb water pollution. Additionally, investing in technologies for desalination and efficient irrigation can alleviate water scarcity.
The Role of Education
Education plays a pivotal role in crisis management. By raising awareness about the water crisis and encouraging sustainable water practices, we can collectively contribute to the solution.
In conclusion, the water crisis is a multifaceted problem that requires global cooperation and innovative solutions. As the custodians of our planet, it is our responsibility to ensure that this life-giving resource is available for future generations.
500 Words Essay on Water Crisis
Introduction.
Water, the most fundamental building block of life, is becoming increasingly scarce. The world is grappling with a water crisis that poses a significant threat to both human survival and the stability of our ecosystems. This crisis is not limited to developing countries or arid regions; it is a global problem that requires urgent attention.
The Global Water Crisis
The water crisis is a complex issue with roots in various socio-economic and environmental factors. Climate change is exacerbating the situation by causing unpredictable weather patterns, leading to more frequent droughts and floods. These extreme weather events can contaminate freshwater sources and disrupt the supply of potable water.
Simultaneously, population growth and urbanization are increasing demand for water. According to the United Nations, global water demand is projected to increase by nearly 30% by 2050. This demand, combined with inefficient water use, particularly in agriculture, is rapidly depleting our freshwater resources.
Consequences of the Water Crisis
The consequences of the water crisis are far-reaching. It affects not only human health but also food security, energy production, and social stability. Lack of access to clean water leads to poor sanitation, which in turn contributes to diseases such as cholera and typhoid.
Moreover, water scarcity can exacerbate social inequalities. Poorer communities often bear the brunt of the crisis, as they lack the resources to access clean water. This can lead to conflict and displacement, further destabilizing regions already under stress.
Addressing the Water Crisis
Addressing the water crisis requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses both technological innovation and policy reform. On the technological front, advancements in desalination, water recycling, and efficient irrigation systems can play a crucial role in augmenting our water resources.
Conversely, policy reform should focus on promoting sustainable water management practices. This includes enforcing stricter regulations on water pollution and incentivizing the efficient use of water in agriculture and industry.
The water crisis is a pressing issue that demands immediate action. As we continue to grapple with this global challenge, it is crucial to remember that water is not just a commodity; it is a fundamental human right. By harnessing technological innovation and implementing effective policies, we can ensure that everyone has access to clean, safe water. This will not only alleviate the immediate water crisis but also contribute to the broader goals of social equality and environmental sustainability.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Wastage of Water
- Essay on Uses of Water
- Essay on Save Water
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Water Scarcity Essay

Essay on Water Scarcity
Water is the basic necessity of every human being, but water scarcity is a major issue that is rising very rapidly in India nowadays. The problem has become so severe that in many states the groundwater has almost dried up and people have to depend on water supply from other sources. In addition, water is one of the most misused natural resources that we still waste. It is the central point of our lives but unfortunately, not our priority concern.
Earlier, people understood the value of water and planned their lives around it. Moreover, many civilizations were born and lost around water, but today, in spite of having knowledge, we still fail to understand the value of water in our lives.
Reasons for Water Scarcity
Mismanagement of water and the growing population in our country are the two main reasons for water scarcity. There are also a number of other man made disturbances that continue to rise. Besides this, some of the reasons for water scarcity are:
Wasteful Use of Water for Agriculture
India, an agricultural country, produces a huge quantity of food to feed its population. The surplus that is left, gets exported outside.
It is not unknown that producing this much food requires a lot of water too. The traditional method of irrigation wastes a lot of water due to evaporation, water conveyance, drainage, percolation, and the overuse of groundwater. Besides, most of the areas in India use traditional irrigation techniques that stress the availability of water.
However, the technique of irrigation has changed during modern times and we provide water to plants using a sprinkler or drip irrigation.
Reduction in Water Recharges Systems
Rapid construction that uses concrete and marbles may not let the rainwater get absorbed in the soil, but still, we install some mechanism in our houses so that we can hold the rainwater. Then we can recharge the groundwater.
Lack of Water Management and Distribution
There is a need for an efficient system to manage and distribute the water in urban areas. The Indian government also needs to enhance its technology and investment in water treatment. Besides, we should ensure optimization at the planning level.
Solutions to Overcome this Problem
Close the running tap.
During dishwashing and hand washing people often let the tap run. These running taps waste thousands of liters of water per year. Therefore, closing the tap will reduce this problem.
Replace Dripping Taps
In India, it is commonly seen that most of the houses have taps or faucets that go on dripping water even when they are closed. This running tap wastes up to 30,000 liters of water that nobody bothers to change. So, we should replace these taps immediately.
Brief on Water Scarcity
Water is a basic necessity for every living being. Life without water is impossible, not just for us humans, but for all plants and animals too. Water scarcity is an issue of grave concern these days as water scarcity has become very common. Water is one of the most wasted natural resources and corrective measures should be taken before the water scarcity situation becomes worse. In spite of being aware of the implications, not much is being done today.
In India, and across the world, it has been recorded that about half a billion people face a shortage of water for about six months annually. Many well-known cities around the world are facing acute scarcity of water. Many facts and figures are available to know about the water scarcity problem, but what are the reasons for this scarcity?
With the growing population, the use of water has increased manifold. The lack of more freshwater sources and the increase in population is a major reason for this scarcity. The lack of proper Water management systems and proper drainage systems in India, especially in the urban areas is a major cause too. Kitchen wastewater should be able to be recycled but due to a poor drainage system, this is not possible. An efficient water management system is required in order to distribute water in urban areas.
Another major issue is Deforestation. Areas with more greenery and plants are known to have good rainfall. Industrialisation and urbanization are two major factors here. Due to Deforestation, and cutting down of trees, rainfall has become an issue too.
Rivers are a major source of fresh water in India. Today we see a lot of industries that have come up and all of them are mostly near the rivers and these rivers become highly polluted as a result of all the industrial waste.
Effect of Global Warming and Climate Change
Global Warming and Climate Change are also responsible for the scarcity of water. The melting of icebergs into the sea due to the rise in temperatures is a reason as to how salty water is increasing day by day instead of freshwater. The percentage of rainfall has decreased drastically these days. Climate change along with the decrease in rainfall percentage has greatly affected freshwater bodies.
Water scarcity has become a major problem and an alarming issue these days, and we must consciously strive to work together to find some solution to this issue of water scarcity. The Indian government today has formulated and come up with many plans on how to tackle and solve this problem.
To conclude, water scarcity has become an alarming issue day by day. If we do not take the problem of water scarcity seriously now, our future generations are going to suffer severely and may even have to buy this necessity at a high cost.

FAQs on Water Scarcity Essay
1. What are the reasons for Water Scarcity?
The lack of proper Water Management and proper Drainage system plays a major role. Many other factors and reasons can be held responsible for the scarcity of water. Some of the major reasons are Global Warming and Climate Change; Pollution of the rivers due to industrialization; Deforestation and the cutting down of trees is another reason; Reduced percentage of rainfall due to the climate change pattern; Increase in the population which leads to increase in the use of water. Learn more about water scarcity on Vedantu website helpful for long-term.
2. What is meant by the scarcity of water?
The scarcity of water means a shortage of water and not being able to manage the demand and supply of water. Water scarcity refers to the lack of freshwater bodies to meet the standard quantity and demand of water. Unequal distribution of water due to factors like Climate Change and Global Warming. Water Scarcity is also due to pollution and lack of rainfall. Water scarcity means a scarcity due to some physical scarcity or scarcity due to the lack of regular supply.
3. What are the two types of water scarcity?
Physical water scarcity is the result of regions' demand outpacing the limited water resources found in that location. According to the Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO) of the United Nations, about 1.2 billion people live in areas of physical scarcity and many of these people live in arid or semi-arid regions. People who are affected by this Physical kind of water scarcity are expected to grow as the population increases and as the weather patterns keep changing as a result of climate change.
Economic water scarcity is due to the lack of proper water infrastructure and a proper water management system or also because of poor management of water resources. The FAO estimates that more than 1.6 billion people face economic water shortages today. Economic water scarcity can also take place because of the unregulated use of water for agriculture and industry.
4. How can we solve the problem?
Conscious awareness is required to deal with and understand the problem of water scarcity. We can start off by consciously saving water in our homes and surroundings. Small easy steps like taking care when washing hands, or when working in the kitchen, have to be taken. The running water taps are a major reason for losing hundreds of liters of water on a daily basis. And we should be careful not to waste this water. Conscious decision to save and the need to understand the problem of water scarcity is of utmost importance.
5. How do we waste water?
Water is wasted in ways we do not even realize, in our homes and in our workplaces. When we brush our teeth, when we shave or when we wash the dishes, one of the most common things we do is to keep the water running, especially when running water is available. As soon as we begin cleaning or washing, we do not think of the water that is being wasted. While washing hands, we leave the water tap on, which results in wasting water too. Small things like these should be kept in mind and this could be our small step towards preserving water.
Home — Essay Samples — Environment — Water Scarcity — The World on the Water Crisis
The World on The Water Crisis
- Categories: Water Pollution Water Scarcity
About this sample

Words: 3016 |
16 min read
Published: Mar 28, 2023
Words: 3016 | Pages: 7 | 16 min read
Table of contents
Introduction, water issues in america.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Karlyna PhD
Verified writer
- Expert in: Environment

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
4 pages / 1974 words
3 pages / 1250 words
3 pages / 1370 words
2 pages / 815 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Water Scarcity
The subject of water consumption is a critical and multifaceted topic that holds significant importance in today's world. With growing concerns about water scarcity, environmental sustainability, and the health of our [...]
Water is an essential resource that is vital for all forms of life on Earth. It is crucial for human survival, as it is needed for drinking, cooking, sanitation, agriculture, and industry. However, the availability and access to [...]
Water, the elixir of life, is a finite resource essential for all living organisms on Earth. Yet, despite its undeniable importance, water shortage has become a critical global issue. This essay delves into the causes, [...]
Globalization, characterized by the interconnectedness of economies, cultures, and technologies across borders, has undoubtedly brought numerous benefits to our world. However, it has also given rise to a set of complex [...]
Agricultural may be a powerful tool to forge economic development of any country and to finish extreme financial condition. It is calculable that agriculture can feed a projected 9. 7 billion individuals by 2050. Growth within [...]
Professors are concerning about the knowledge of climate science and the scientific consensus on anthropogenic global warning and considering the importance of climate change education in schools. In 2016 a national survey of [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Take 10% OFF— Expires in h m s Use code save10u during checkout.
Chat with us
- Live Chat Talk to a specialist
- Self-service options
- Search FAQs Fast answers, no waiting
- Ultius 101 New client? Click here
- Messenger
International support numbers
For reference only, subject to Terms and Fair Use policies.
- How it Works
Learn more about us
- Future writers
- Explore further

Ultius Blog
Sample essay about the water crisis in flint, michigan.

Select network
Water is one life’s most precious resources. In some organisms, water comprises as much as 90% of personal body weight, in humans, this ratio is 60%. Hence, when water is contaminated or sparse, life quality can be expected to drop dramatically. This sample environmental science essay explores the Flint Michigan water crisis that has been unfolding for two years ever since the city began to use water from the local Flint River (Foley). The case of Flint is a precautionary one and one worthy of intense public attention, both writing and speeches , as it may herald the need for a significant shift in America’s water management plant.
Background on the Flint, Michigan water crisis
Flint Michigan’s water crisis is a national crisis of eroding proportion. For two years, the locals have been continuously subjected to the ill effects of poisonous waters stemming from a recent change over in supply. Up until about April 2014, Flint had been totally reliant upon the water from Lake Huron purchased through Detroit (Foley). Due to the importance of food and water safety , plans to create a new regional water system that could bring tap water from the Lake Huron were then instated to set up a water harvesting system that could bring it into Flint at a better price were then initiated. Despite the well-meaning intentions, the project’s two-year delay caused a significantly unexpected turn of events when the temporary alternative water resource, the Flint River, was found to be highly contaminated.
The polluted water
The dissatisfactory nature of the water was realized nearly as soon as it was pumped from the river. The litany of complaints included that the water smelled, like metal, tasted, like metal, and looked ‘funny’ (Foley). Residents of flint pulled from their tap not clean and fresh water like that which is experienced almost universally across the united states but large jugs of brownish and foul liquid that may even be questionable to swim in (Bosman, Davey, Smith). Resident Bethany Hazard states that when she filled up her water from the faucet it came out not only brown but smelling of a sewer (Semuels).
The river itself has been a source of considerable pollution with a dead body being found in the river in addition to an abandoned car as well as abnormally high levels of trihalomethanes, and copper (Semuels). The mere fact, however, that such findings were only accidentally leaked underscores a lack of concern for the safety of Flint’s residents. The first tests on the water confirmed that indeed, something was quite wrong. The Environmental Protection Agency (the agency responsible for enforcing environmental policies in the U.S. ) for instance, leaked in a memo that in the water were trace amounts of the E. Coli bacteria, a serious health hazard for people of all ages (Foley unfortunate dimension of the Flint Michigan water crisis, the economic one.
How does Flint's water crisis affect the economy?
About 41% of the 100,000 residents who live in Michigan exist below or at the nation’s poverty line which makes this a socio-political issue as much as it is an environmental one (Foley). Indeed, the city actually was motivated to make the water switch over in the first place by financial concerns which held that an upgraded water resource could make serious improvements in the city’s strained budget. Unfortunately, the financial maneuver has ended up costing them several million more dollars than it saved.
It is this economic disparity that most likely contributed to the failing of the state authorities to properly address the issues in the time and manner due to the risk inherent to the contamination. Indeed, the first activist groups to call attention to the issue were labeled as no importance “anti-everything group” while other outspoken individuals were called rabble rousers playing “political football” (Bosman, Davey, Smith). All this backlash was made, in addition, in spite of increasingly worrisome findings concerning the water quality coming from scientists.
Only after months and months of complaints, of the grievous nature already once described, that the state officials began to conduct the logistical and technical response proper to the severity and vulnerability of the environment and population in question. Roughly a year after the citizens of Flint had been contending with their suspect water source that the state declared the public health emergency (like the emergency declared with the Zika virus ) proper to the situation at hand (Bosman, Davey, Smith). The local and state authorities shortly thereafter moved the water supply back to Lake Huron through Detroit however this still could not prevent or reverse the damage done.
Sociological and health impact
The water crisis in Flint Michigan is of epidemic proportions. Near the end of 2015, the state began to realize the trouble they were so direly in. Tests were conducted on the afflicted populations to discover that indeed, many a number were critically infected lead in the blood which could likely result in lasting and chronic health problems, especially in children who are more susceptible to toxins. The list of ailments from the contaminated water resource are astounding and cautionary. Rashes, hair loss, and numerous other health ailments provide a most undesirable account of the cost not only of environmental devastation but poverty as well (Foley).
The sum effect of this water pollution on top of the poverty is the literal dying away of the home. In Flint, one in 14 homes is vacant (Mallory Sidner). This means that all around the neighborhood, houses go without occupants and thus neighborhoods go without the life they need to be at maximum functioning and appreciation. As is usually the case, poverty is matched by equally disfavored social conditions. Many business have begun to close or at least shrink causing a massive shortage in available jobs and thus income for residents (Mallory Sidner).
This has the town incredibly worried not only for the longevity not only of the town but the children as well. Children are the city’s most vulnerable population who has been affected by the tap water crisis (Mallory Sidner). A prime example of the loss that has transpired within Flint’s youth is that of eighteen year old Dominque Absell. Although possessing a common and lively appearance, Dominque has begun to experience chronic headaches, passing out, seizures, and general sickness that are cutting into his life plans severely (Mallory Sidner). It is expected that the Flint water contamination is at the root of the problem and that if not properly taken care of it could prevent Dominque from graduating and going on to his desired service in the military shortly thereafter. The only proof they have that the water is the cause is that once his mother stopped using the contaminated water, her son stopped passing out (Mallory Sidner).
Government assessment and possible solutions
Flint is filled with such charged human emotion stories. Residents frequently report feelings of abandonment by their government and much hopeless for the future of their city. Such accounts are hardly unwarranted. The government had ample suspicion and evidence to act sooner than they did however they refrained from the appropriate action, no doubt lacking the compassion and urgency necessary to make the difference. Nevertheless, the government has made some progress in assisting the city, namely a $28 million dollar request from the governor which was approved by the Michigan House a few weeks ago to aid the city (Bosman, Davey, Smith). Surely the recent storm of media coverage in Flint helped to secure the recent assistance bill. Obama himself met with Karen Weaver, the Flint Michigan mayor, stating to reports that he would:
“Be beside myself” if he were a parent in Flint and that “the notion that immediately families were not notified, this were not shut down – that shouldn’t happen anywhere” (Bosman, Davey, Smith).
Unfortunately, besides having a river contamination problem contributing to the contaminated water, there is also the suspicion aging pipes are a part of the cause (Connor and Rappleye). The dying infrastructure of Flint had prevented the necessary upgrades to the city sewer system which further contributed to the disastrous sewer effects (Semuels). Despite the rising news coverage in Flint concerning water problems, there is a general trend through the U.S. in depreciatory water quality. In 2013 for instance, America received a failing grade ‘D’ in their drinking water score from the American Society for Civil Engineers’ Report Card for America’s Infrastructure (Semuels). This most undesirable metric indicates that the infrastructure in America is approaching the final stage of its utility and is likely to widely become a liability throughout much of the U.S. It is suspected that an innovation initiative totaling more than $1 trillion dollars is needed to reverse this grade into the passing (Semuels).
It may be estimated what the costs will be if the project is not quickly instated thanks to the sobering example that is Flint Michigan’s water crisis. People throughout the nation, starting most likely in the poorest cities and districts, will begin to feel the effects of subtlety being poisoned in increasing damage until they, and their regional county, will have to individually face the disaster before them. However, if taken seriously as a country, these effects may be largely circumvented through the proposal leading to improved safety and water quality across the nation. It is no doubt that this incident will spark academic analysis from essays to dissertations for years to come even if it does not translate into much needed public policy.
Concluding thoughts on the Flint, Michigan water crisis
Flint, Michigan has gone through quite the ordeal over the past two years as they transitioned to the temporary Flint River water source. The mere fact, however, as news reports and research papers have shown, that the river was polluted in the first place is a suspect as the state’s fiscal and environmental response to the issue. Perhaps instead of letting this failure go to total waste, the nation will readily accept the lesson given and set forth the initiative to improve America’s infrastructure as a country. Indeed, this would be a most positive use of tax-payers dollars that could have lasting returns on the country’s health unlike other spending programs like that of war.
Bosman, Julie, Davey, Monica, Smith, Mitch. As Water Problems Grew, Officials Belittled Complaints from Flint. NY Times . Web. Mar. 9, 2016.
Connor, Tracy, Rappley, Hannah. NBC News. 2016. Web. Mar. 9, 2016.
Foley, Kaye. The Flint Water Crisis Explained. Yahoo.com , 2016. Web. Mar. 9, 2016.
Mallory, Simon, Sidner, Sara. Children of Flint: Inheriting anxiety and giving up hope. CNN.com . Web. Mar. 9, 2016
Semuels, Alana. Aging Pipes are Poisoning America’s Tap Water. The Atlantic , 2015. Web. Mar. 9, 2016.
https://www.ultius.com/ultius-blog/entry/sample-essay-about-the-water-crisis-in-flint-michigan.html
- Chicago Style
Ultius, Inc. "Sample Essay about the Water Crisis in Flint, Michigan." Ultius | Custom Writing and Editing Services. Ultius Blog, 10 Mar. 2016. https://www.ultius.com/ultius-blog/entry/sample-essay-about-the-water-crisis-in-flint-michigan.html
Copied to clipboard
Click here for more help with MLA citations.
Ultius, Inc. (2016, March 10). Sample Essay about the Water Crisis in Flint, Michigan. Retrieved from Ultius | Custom Writing and Editing Services, https://www.ultius.com/ultius-blog/entry/sample-essay-about-the-water-crisis-in-flint-michigan.html
Click here for more help with APA citations.
Ultius, Inc. "Sample Essay about the Water Crisis in Flint, Michigan." Ultius | Custom Writing and Editing Services. March 10, 2016 https://www.ultius.com/ultius-blog/entry/sample-essay-about-the-water-crisis-in-flint-michigan.html.
Click here for more help with CMS citations.
Click here for more help with Turabian citations.
Ultius is the trusted provider of content solutions and matches customers with highly qualified writers for sample writing, academic editing, and business writing.

Tested Daily
Click to Verify
About The Author
This post was written by Ultius.

- Writer Options
- Custom Writing
- Business Documents
- Support Desk
- +1-800-405-2972
- Submit bug report
- A+ BBB Rating!
Ultius is the trusted provider of content solutions for consumers around the world. Connect with great American writers and get 24/7 support.
© 2024 Ultius, Inc.
- Refund & Cancellation Policy
Free Money For College!
Yeah. You read that right —We're giving away free scholarship money! Our next drawing will be held soon.
Our next winner will receive over $500 in funds. Funds can be used for tuition, books, housing, and/or other school expenses. Apply today for your chance to win!
* We will never share your email with third party advertisers or send you spam.
** By providing my email address, I am consenting to reasonable communications from Ultius regarding the promotion.
Past winner

- Name Samantha M.
- From Pepperdine University '22
- Studies Psychology
- Won $2,000.00
- Award SEED Scholarship
- Awarded Sep. 5, 2018
Thanks for filling that out.
Check your inbox for an email about the scholarship and how to apply.
About . Click to expand section.
- Our History
- Team & Board
- Transparency and Accountability
What We Do . Click to expand section.
- Cycle of Poverty
- Climate & Environment
- Emergencies & Refugees
- Health & Nutrition
- Livelihoods
- Gender Equality
- Where We Work
Take Action . Click to expand section.
- Attend an Event
- Partner With Us
- Fundraise for Concern
- Work With Us
- Leadership Giving
- Humanitarian Training
- Newsletter Sign-Up
Donate . Click to expand section.
- Give Monthly
- Donate in Honor or Memory
- Leave a Legacy
- DAFs, IRAs, Trusts, & Stocks
- Employee Giving
Ten causes of the global water crisis
Mar 22, 2022

Nothing survives without water; it’s the most basic fact of life. Humans need a steady and clean supply of H2O to live, something which is becoming more and more difficult to come by.
Water affects our lives in countless ways . We use it to eat, to fuel our businesses, to keep our homes (and hands) clean… But less than 1% of the world’s water supply is usable to us. The rest is saltwater, ice, or underground. And we have to make that <1% last for 7.9 billion people. The global water crisis is proof that we’ve come up dry: The latest reports from the WHO and UNICEF show that over hundreds of millions of people are caught in a cycle of thirst — one that feeds into the cycle of poverty .
The Global Water Crisis At A Glance
- According to UN-Water 2.3 billion people live in water-stressed countries
- According to UNICEF, 1.42 billion people – including 450 million children – live in areas of high or extremely high water vulnerability
- 785 million people lack access to basic water services
- The WHO reports that 884 million people lack access to safe drinking water
- Two-thirds of the world’s population experience severe water scarcity during at least one month of the year
- The Global Water Institute estimates that 700 million people could be displaced by intense water scarcity by 2030
- 3.2 billion people live in agricultural areas with high water shortages or scarcity
- Approximately 73% of people affected by water shortages live in Asia
- The global water crisis is a women’s issue : In what UNICEF calls “a colossal waste of time,” women and girls spend an estimated 200 million hours hauling water every day
- Diarrhea kills 2,195 children every day—more than AIDS, malaria, and measles combined—and can be caused by lack of access to clean water and sanitation services
Add Impact to Your Inbox
Learn more about Concern's response to the global water crisis.
What’s Causing The Global Water Crisis?
There are a number of root causes for our current water crisis, which in turn affect everything from harvests to public health. By addressing these causes, we can do better with the 1% we have.
1. Climate Change
Unsurprisingly, climate change is one of the main reasons behind the global water crisis. The areas most vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, such as Somalia’s decade-plus of drought or increasingly severe monsoons in Bangladesh , are often water-stressed to begin with. As the climate crisis continues to deepen, those resources become all the more scarce. One of the main causes of climate change, deforestation, leads to “heat islands” that impact the surrounding land. In sub-Saharan Africa, for example, 80% of farmland has been affected by soil degradation due to climate-related droughts. On the opposite end of the spectrum, rising sea levels are salinating freshwater sources, meaning that they’re no longer potable as-is.

2. Natural Disasters
Whether related to climate change or not, according to one UNICEF report nearly 75% of all natural disasters between 2001 and 2018 were water-related. This includes droughts, but also floods — which can destroy or contaminate clean water sources for communities. This not only cuts people off from clean drinking water, but also opens up the risk for waterborne diseases like diarrhea. The frequency of these events are expected to increase as we continue to feel the effects of climate change.

3. War and Conflict
The ongoing crisis in Syria has led to a well-developed middle-class country lapsing into a water crisis thanks to the destruction of its infrastructure. This poses a serious threat to public health for the millions of Syrians still living inside the country. Another protracted conflict in the Central African Republic has seen armed groups target village water-points and wells — much like hunger as a weapon of war , water can also be leveraged in times of violence.

4. Wastewater
Let’s talk about contaminated water and the role it plays in the global water crisis: Sometimes water can be plentiful in an area. But whether that water is safe to drink…that’s another story. Many areas of the world have poor systems for dealing with wastewater — water that is affected by human use, like washing dishes at home or used in an industrial process. At a global scale, 44% of household wastewater is reused without being treated, and 80% of wastewater overall flows back into the ecosystem without being treated or reused, which by the UN’s numbers leaves 1.8 billion people using water that can be contaminated by feces, chemicals, or other contaminants that can prove toxic. Wastewater is one of the leading causes for many of the world’s most pervasive diseases, including cholera, dysentery, typhoid, and polio.
The average family can waste 180 gallons per week, or 9,400 gallons per year, due to household leaks.
5. Water Waste
Different from wastewater, water waste is what happens when we ignore dripping faucets, over-water our lawns, or ignore the free tap water served to us at a restaurant. Some of these may seem like minor inconveniences, but they add up: Speaking with VOX, water management expert Shafiqul Islam estimates that these minor annoyances can account for anywhere between 30 and 40% of a city’s lost water. The average family can waste 180 gallons per week, or 9,400 gallons per year, due to household leaks. Add this all up and we’re looking at roughly 900 billion gallons of water lost annually.
In 2018, Cape Town managed to avert “Day Zero” — the day in which the city would need to turn off all water taps for its 4 million residents — by limiting water use and focusing on the necessities first.
6. Lack of Water Data
We know that data is never the most exciting entry on a list, but it’s still key: UN Water reports a lack of water quality data for over 3 billion people around the world. These are usually in areas where other factors on this list are at play, meaning that they’re at a credible risk for using non-potable water. Knowledge is power, and the only way we can ensure that we have a handle on the global water crisis is by ensuring that we know the health of all the world’s rivers, lakes, and groundwater reserves.
7. Lack of International Cooperation On Shared Water Sources
Many bodies of water sit across two or more countries, meaning that they’re effectively the subjects of joint-custody between nations. However, according to the latest update from the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals , only 24 countries report that all internationally-shared rivers, lakes, and groundwater sources are covered by cooperative arrangements. This means that, if one country is following all of the protocol necessary to keep its side of a lake clean, that may be irrelevant if the waters on the opposite shore are not being treated with the same degree of care.

8. Lack Of Infrastructure
It’s not that countries willingly mismanage their water supplies. Whether through deliberate destruction or unwitting mismanagement, many governments lack the infrastructure to properly invest in their water resources, allowing clean water to reach those that need it most. Losses related to water insecurity cost the US an estimated $470 billion per year . While water infrastructure is a resource that has high financial implications, the value of water is taken for granted. As the UN notes in its High Level Panel on Water, water “is typically capital intensive, long-lived with high sunk costs. It calls for a high initial investment followed by a very long payback period.”
Countless water points were left unusable due to violence, disrepair, and overuse in the Central African Republic with some water sources purposely contaminated by armed groups. Fortunately solutions don’t necessarily need to be high-tech. We’ve brought clean water solutions to villages using manually operated “village drills,” removing the need for electricity. They’re also 33% cheaper than typical mechanized drills, and can be transported to remote areas and assembled on site.
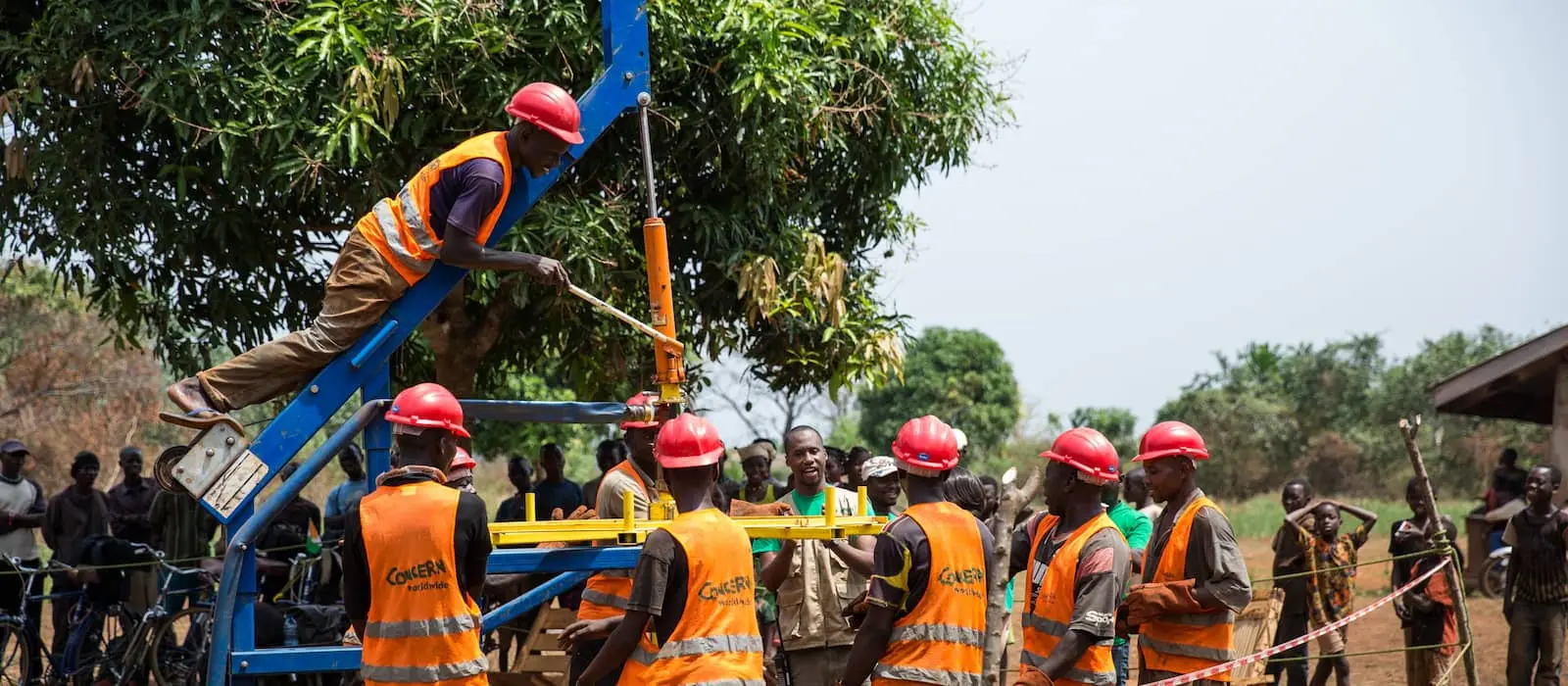

People power brings clean water to Central African Republic
Years of conflict have decimated wells in Central African Republic, putting the population at risk of disease from drinking dirty water. But with a little bit of innovation — and a lot of people power — communities in the Kouango region are finally getting access to clean water.
9. Forced Migration and The Refugee Crisis
Even before the crisis in Ukraine uprooted 10 million people, we were facing unprecedented levels of displacement. In many of the world’s largest host communities , informal settlements for refugees create high-density areas of people, and can put pressure on available infrastructure. In many cases, people will cross the nearest open border to flee conflict or other crises, which often leaves them in areas that face similar climate events, or have similarly stressed resources. This is why water trucking — which is, effectively, exactly what it sounds like — is one of the key elements of Concern’s emergency response plans.

10. Inequality and An Imbalance of Power
Even in high-income countries, water management isn’t a priority as seen in budget allocations. It’s not the most photogenic issue, especially when you’re showing solutions in action, and “emergency food distribution” is a much easier concept to grasp compared to “watershed management.” This has led to an unacceptable imbalance between those setting federal and local government budgets — and foreign aid budgets — and those who are in the direst need of clean water and adequate sanitation. In 2015, the UN reported that, underlying all of the barriers to solving the water crisis, was one simple fact: “The people suffering the most from the water and sanitation crisis — poor people in general and poor women in particular — often lack the political voice needed to assert their claims to water.” This disparity in power and lack of representation has widened that chasm. Closing it is a critical step to ensuring clean water for all.
“The people suffering the most from the water and sanitation crisis — poor people in general and poor women in particular — often lack the political voice needed to assert their claims to water.”
The Global Water Crisis: Concern’s Approach
Ensuring access to clean water and sanitation and providing hygiene information and training are key aspects of Concern’s work, with active water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) programs in 18 countries.
Over the last 55 years, we have dug, drilled, and bored thousands of wells in remote and vulnerable communities across dozens of countries, and built countless latrines in their schools and health centers. The hours saved and the illnesses prevented make it one of the most effective things we do.
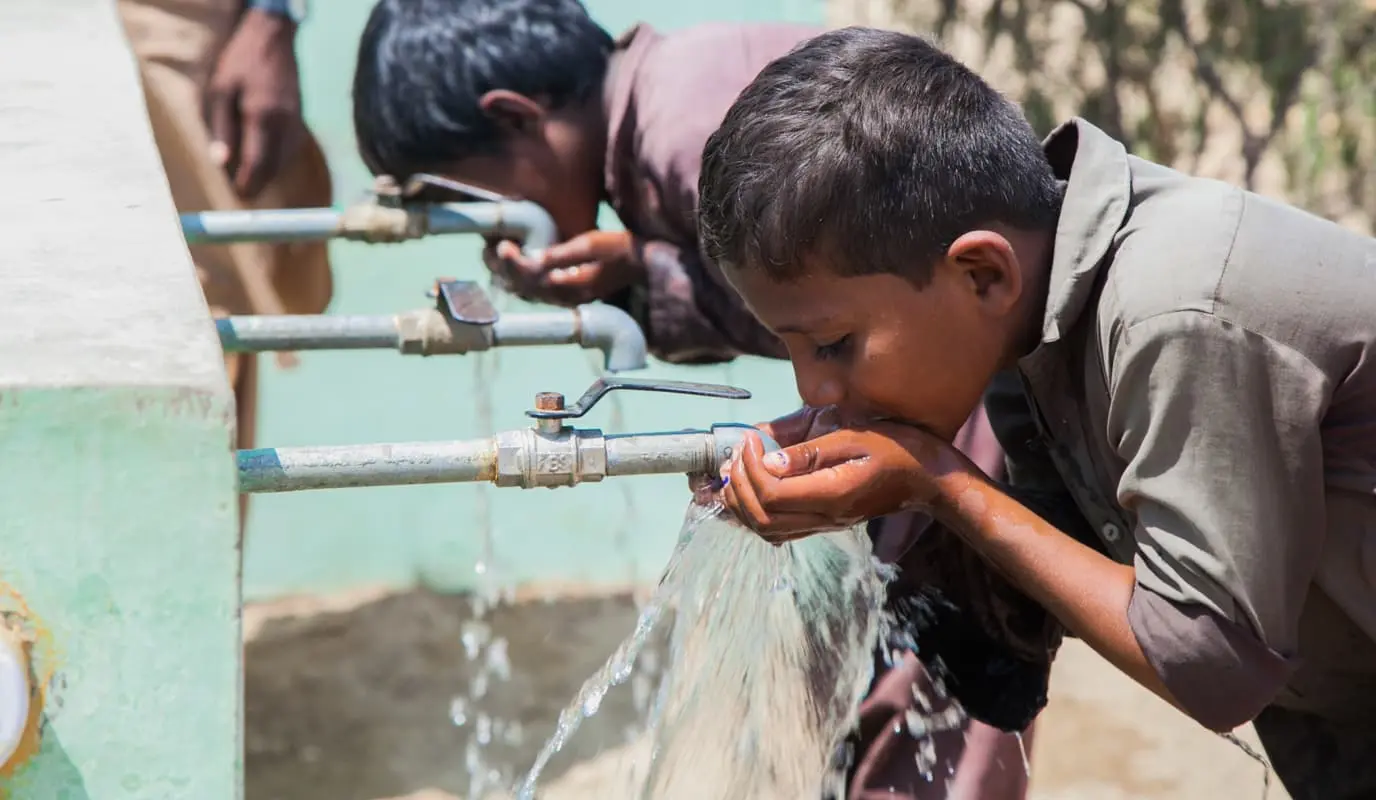

When drought or displacement prevent access to clean water supplies, we do what it takes to connect communities, including trucking water to temporary tanks and installing pumps in camps. We work hand-in-hand with communities to help them assess the longstanding challenges they face, change behaviors, and ensure water and sanitation infrastructure will be maintained for the long term. And we foster a sense of ownership, build sustainable maintenance practices, and create transparent financial management systems that benefit the community.
One example of our approach can be seen in the Democratic Republic of Congo , where Concern has been the lead partner in a consortium that has already achieved some extraordinary results. Over the course of six years, our teams worked closely with 600 of the country’s most isolated communities to help them achieve sustainable water, sanitation, and hygiene solutions. This program has reached over 650,000 people in a country that has faced 40+ years of protracted crisis .
Support Our Work
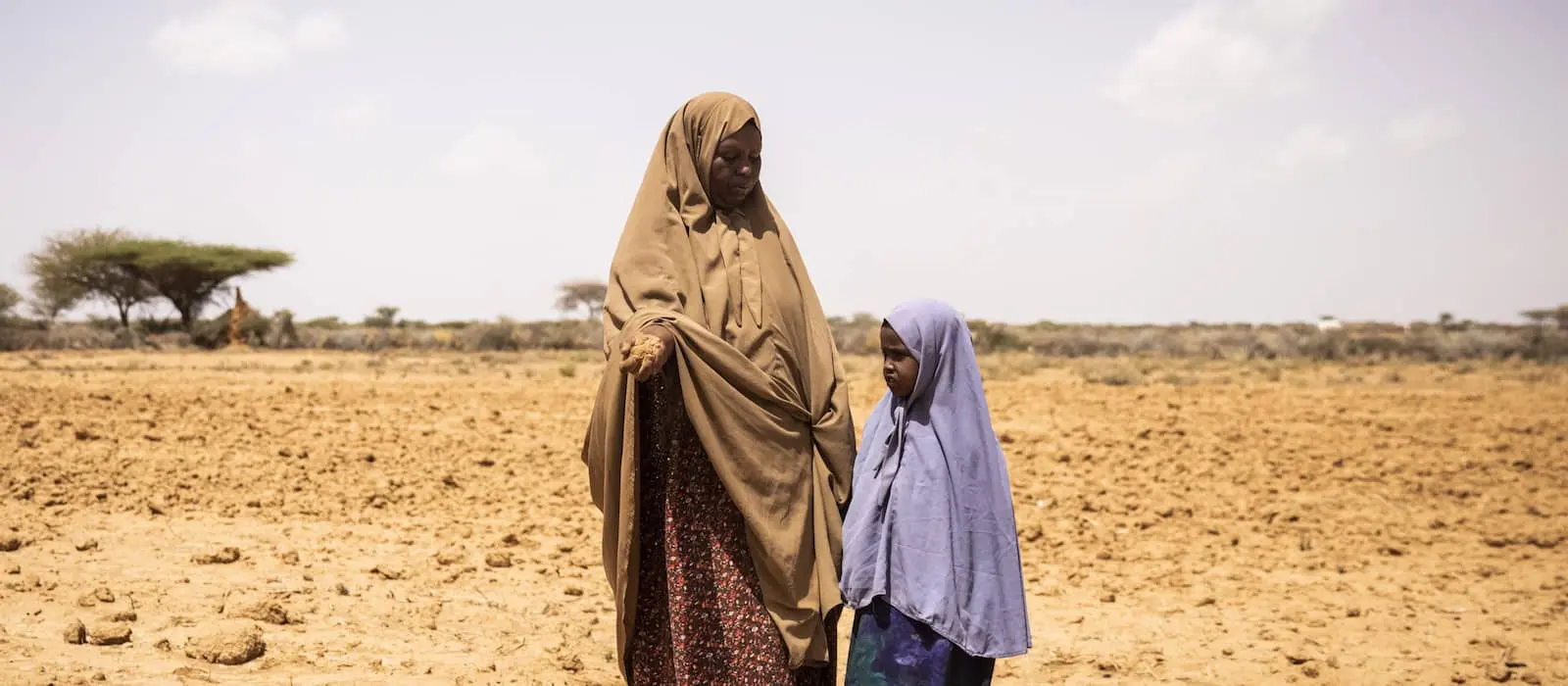

Timeline: Breaking down more than a decade of drought in Somalia
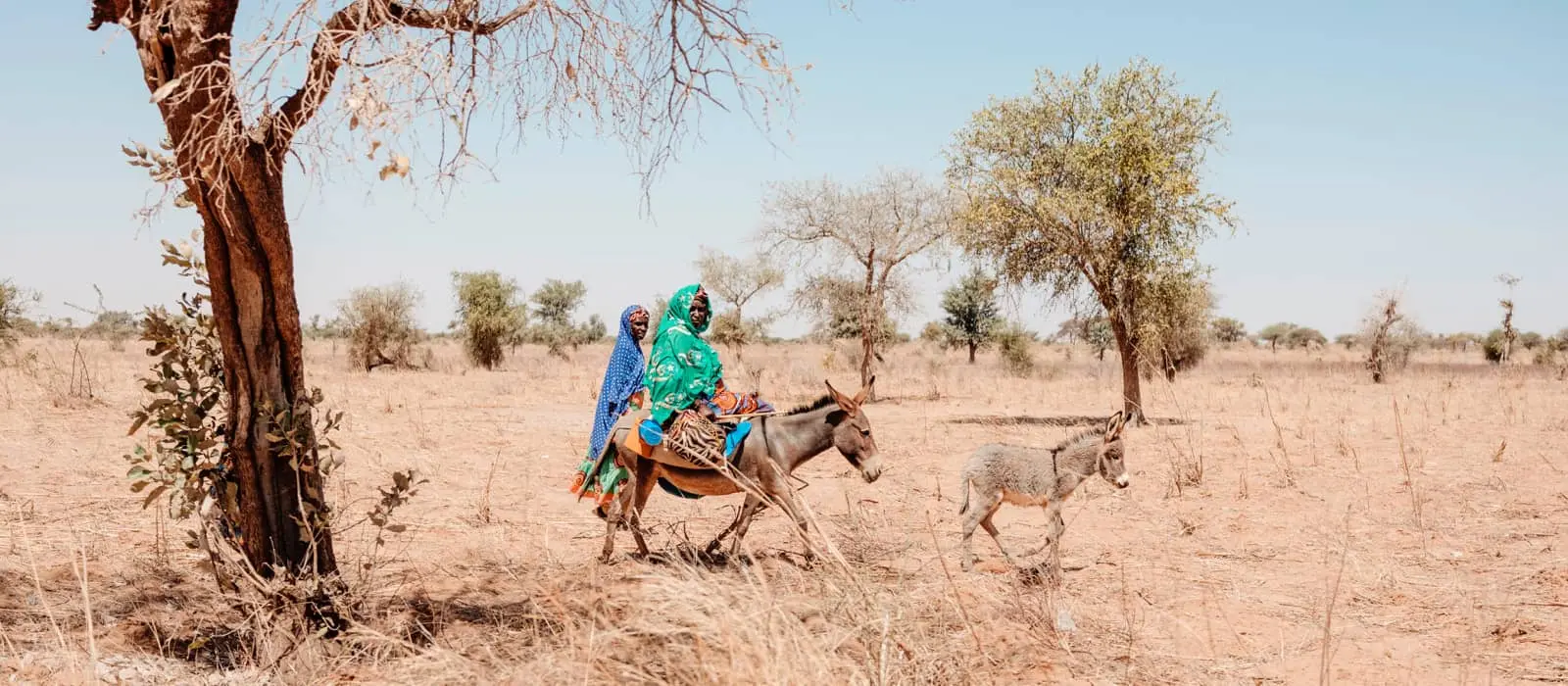

Ten countries with water stress and scarcity — and how we're helping

With nearly 75% of Bangladesh underwater, can crisis be avoided?
Sign up for our newsletter.
Get emails with stories from around the world.
You can change your preferences at any time. By subscribing, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
India’s Water Crisis – How to Solve it?
From Current Affairs Notes for UPSC » Editorials & In-depths » This topic
Water is the most valuable natural resource as it is essential for human survival and life on earth. However, the availability of freshwater for human consumption is highly under stress because of a variety of factors. This crisis of water scarcity is most visible in India as well as in other developing countries.

This topic of “India’s Water Crisis – How to Solve it?” is important from the perspective of the UPSC IAS Examination , which falls under General Studies Portion.
What is water scarcity?
- Water scarcity is the lack of freshwater resources to satisfy water demand.
- It is manifested by partial or no satisfaction of expressed demand, economic competition for water quantity or quality, disputes between users, irreversible groundwater depletion, and negative effects on the environment.
- It affects every continent and was categorised in 2019 by the World Economic Forum as one of the largest global risks with respect to its potential impact over the next decade.
- One-third of the global population (2 billion people) live under situations of severe water scarcity at least one month of the year.
- Half a billion people in the world affected by severe water scarcity all year round.
- Half of the world’s largest cities have been facing water scarcity.
Express Learning Programme (ELP)
- Optional Notes
- Study Hacks
- Prelims Sureshots (Repeated Topic Compilations)
- Current Affairs (Newsbits, Editorials & In-depths)
- Ancient Indian History
- Medieval Indian History
- Modern Indian History
- Post-Independence Indian History
- World History
- Art & Culture
- Geography (World & Indian)
- Indian Society & Social Justice
- Indian Polity
- International Relations
- Indian Economy
- Environment
- Agriculture
- Internal Security
- Disasters & its Management
- General Science – Biology
- General Studies (GS) 4 – Ethics
- Syllabus-wise learning
- Political Science
- Anthropology
- Public Administration
SIGN UP NOW
How is the water scarcity measured?
- The absolute minimum water requirement for domestic usage is 50 litres per person per day, though 100-200 litres is often recommended.
- Considering the needs of agriculture, industry and energy sectors, the recommended minimum annual per capita requirement is about 1700 cubic meters .
- If a country like India has only about 1700 cu. meters water per person per year, it will experience only occasional or local water distress .
- If the availability falls below this threshold level, the country will start to experience periodic or regular water stress .
- If the water availability declines below 1000 cu. meters, the country will suffer from chronic water scarcity . Lack of water will then start to severely affect human health and well-being as well as economic development.
- If the annual per capita supply declines below 500 cu. meters, the country will reach the stage of absolute scarcity .
Prelims Sureshots – Most Probable Topics for UPSC Prelims
A Compilation of the Most Probable Topics for UPSC Prelims, including Schemes, Freedom Fighters, Judgments, Acts, National Parks, Government Agencies, Space Missions, and more. Get a guaranteed 120+ marks!
What is the status of water availability in India?
- India receives 4000 bcm (billion cubic metres) rainfall each year. Out of this, 1869 bcm remains after evaporation = The actual availability is only 1137 bcm.
- Even in that 1137 bcm of water, there is a lot of temporal as well as regional variations in the availability.
- For instance, on the one side, there are water surplus states such as Uttar Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh and on the other side, there are water scarce states such as Maharashtra (Vidarbha, Beed), Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Rajasthan and parts of Gujarat.
- Moreover, some states that are known to be water abundant such as Punjab, Haryana have their own issues.
What is the magnitude of the water crisis in India?
- Currently, the annual availability of water is 1123 bcm in India and the demand is around 750 bcm. However, by 2050 the annual demand for water will be 1180 bcm which will exceed the water availability = wide ramifications for the country.
- 70% of India’s water is contaminated.
- 75% of households do not have drinking water on its premises.
- 84% of rural households do not have access to piped water.
- 54% of the country’s groundwater is declining rapidly than it is being replenished.
- India’s water table is declining in most regions. Also, there is a presence of toxic elements like fluoride, arsenic, mercury, even uranium in our groundwater.
- Water levels in India’s major reservoirs have fallen to 21% of the average of the last decade.
- Hundreds of small and seasonal rivers are perishing permanently.
- Almost all the major perennial rivers remain stagnant.
- Cauvery and its tributaries haven’t met the ocean for decades; the upstream dams choke its flows downstream, affecting people in Tamil Nadu.
- Krishna river runs dry in her delta region for most of the year.
- According to NITI Aayog’s water quality index, India ranks 120 th among 122 countries.

What is the recent water crisis in India?
- Maharashtra is facing a water crisis of unprecedented proportions. After years of drought, the river currents have ebbed, water in dams and reservoirs have depleted and over-exploitation of groundwater has raised concerns regarding the long-term availability of water.
- Meanwhile, media reports claim IT firms in Chennai are asking employees to work from home. The reason is that they don’t have enough water to sustain their operations. It hasn’t rained for almost 200 days in the city and it may not get adequate rain to get over the water crisis for the next 3 months.
- In North India, the people of arid Thar Desert of Rajasthan are spending Rs. 2500 for getting 2500 litres of water which they share with their cattle.
- With Punjab facing the threat of desertification and the state struggling to break away from the wheat-paddy cycle, farmers in the state have been adopting a decade-old scheme to utilise underground pipeline system for irrigation.
- In light of this crisis, Central government on its part has created a Jal Shakti Ministry under a full-fledged cabinet minister to resolve the water crisis but a lot more needs to be done.
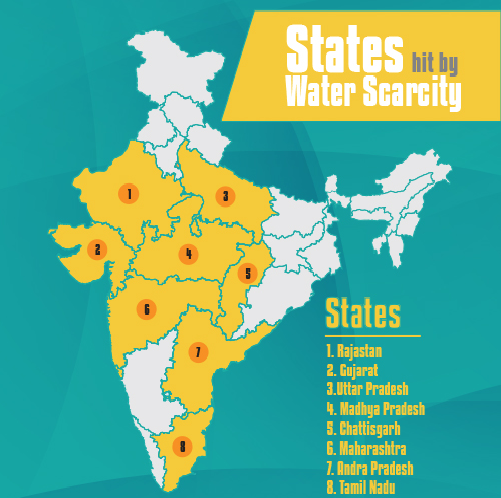
What are the reasons for this crisis?
Monsoon dependence:.
There is a huge dependence on monsoon rains to replenish most of India’s important water sources such as underground aquifers, lakes, rivers, and reservoirs . But monsoon is vulnerable to factors such as climate change, El-Nino , etc.
Uneven distribution of water and Rainfall pattern :
Certain regions have surplus amounts of water for their need while others face perennial droughts for most of the year. For instance, Drought is a recurrent phenomenon in Andhra Pradesh where no district is entirely free of droughts. Rajasthan is one of the most drought-prone areas of India.
Increasing demand :
Population growth, industrialization, rapid urbanisation, rising needs of irrigation and increase in domestic water usage have accelerated the demand for water. Since urbanization increases in India at a rapid pace = water demand will increase rapidly as city dwellers consume more water than rural people.
Urbanisation & Water scarcity:
- Currently, about 285 million or 33% of India’s total population resides in urban areas. By 2050 this figure will reach 50%.
- Rapid urbanisation is adding to the water scarcity issue in the country.
- Presence of buildings, tar, and cement roads = even if a city like Mumbai gets good rains, the rainwater is not retained in the area as the water is not allowed to percolate underground.
- Therefore, water required for cities is largely drawn from neighbouring villages and far-off rivers and lakes = threatening the availability in those areas.
- Large cities also generate large quantities of urban sewage which pollutes the freshwater sources and ocean waters. However, only about 20% of urban wastewater is currently treated globally. In India, the figure is even lower.
Overexploitation :
- In developing countries like India, groundwater fulfills nearly 80% of irrigation requirement = resulted in a fast depletion of groundwater sources.
- Free power and inefficient utilisation of water by farmers has added to the issue of groundwater depletion.
- The groundwater and sand extraction from most river beds and basins has turned unsustainable.
- Tanks and ponds are encroached upon.
- Dug-wells and borewells are carelessly built to slide deeper and deeper to suck water from greater depths.
Shift to cash-crops:
Water is being diverted from food crops to cash crops that consume an enormous quantity of water.
Inefficient cultivation practices:
- In India, around 70% of the population is still dependent on agriculture for its livelihood.
- Since the adoption of Green Revolution in the 1960s, nearly 50% of the food production comes from irrigated land.
- But inefficient cultivation practices have led to the flooding of fertile land which in turn has caused salinization, siltation of reservoirs, etc = causing groundwater reserves of major agricultural states to be depleted at an alarming rate.
Water Pollution :
- Release of industrial and domestic waste, including urban sewage, into rivers, lakes, and estuaries has polluted freshwater sources at an alarming rate in India = those fresh water sources are not fit for drinking or other activities.
- Eutrophication of surface water and coastal zones is expected to increase almost everywhere leads to nitrogen pollution .
What are the impacts of the water crisis?
Economic growth: A Niti Aayog report predicted that water demand will be twice the present supply by 2030 and India could lose up to 6% of its GDP during that time.
Power supply: Water shortages are hurting India’s capacity to generate electricity because 40% of thermal power plants are located in areas where water scarcity is high.
Agricultural crisis: Indian agriculture is heavily dependent on monsoon (not dependable) + Ineffective agricultural practices in irrigated areas = Water stress in agriculture = Poor Cultivation = Farmer suicides .
Drinking water scarcity: Not only farmers are affected by the water crisis, urban dwellers in cities and towns across India are also facing a never seen before drinking water scarcity.
Conflicts over water : In India, there are conflicts between Karnataka and Tamil Nadu over sharing of Cauvery waters, between Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh over sharing of Narmada waters, between Andhra Pradesh and Telangana over sharing of Krishna waters, etc.
What are the measures taken by the government?
Across the country, states are taking the lead:.
- In Rajasthan, there is a scheme named ‘Mukhya Mantri Jal Swavlamban Abhiyan’. One of its objectives is to facilitate effective implementation of water conservation and water harvesting related activities in rural areas.
- Maharashtra has launched a project called ‘Jalyukt-Shivar’, which seeks to make 5000 villages free of water scarcity every year.
- accelerating the development of minor irrigation infrastructure,
- strengthening community-based irrigation management and
- adopting a comprehensive programme for restoration of tanks.
Jal Shakti Abhiyan:
- It is a collaborative initiative of various Union Ministries and State Governments, being coordinated by the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (DDWS).
- Focus Area: is water-stressed districts (256) and blocks (1592).
- Team: Central government officers, headed by joint secretaries and additional secretaries, are assigned to these 256 districts and district administration will also select 2 members to join the team. This team of officers from the central government and district administration will visit and work on water-stressed districts and blocks to ensure water conservation initiatives.
- The campaign is centered on 5 aspects
- Water conservation and rainwater harvesting
- Renovation of traditional and other water bodies/tanks
- Reuse of water and recharging of structures like bore well
- Watershed development
- Intensive afforestation
- Significance: With this initiative, the government seeks to provide drinking water to all households on a priority and in a sustainable way. It is also expected to bring a positive mindset in people for water conservation. The campaign will assist people to work for rainwater harvesting, maintenance, and upkeep of ponds and village tanks and conservation of water.
Jal Shakti Mantralaya
- The government has created a new Ministry named ‘Jal Shakti’after merging Ministry of Water Resources, River Development & Ganga Rejuvenation with the Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation.
- Providing clean drinking water,
- International and inter-states water disputes,
- Namami Gange project aimed at cleaning Ganga and its tributaries, and sub-tributaries.
- The ministry will launch the government’s ambitious plan (‘Nal se Jal’ scheme under jal jivan plan) to provide piped drinking water supply to every household in India by 2024.
- This Move seeks to consolidate the administration and bringing water-related issues such as conservation, development, management, and abatement of pollution under a single ministry.
- National River Conservation Directorate (NRCD) is responsible for implementing the centrally sponsored national river conservation plan for all rivers across the country except river Ganga and its tributaries (as issues regarding Ganga and its tributaries are taken up by National Mission for Clean Ganga).
Jal Jeevan Mission *

Atal Bhujal Yojana *
- It is a world bank funded central scheme that aims to improve groundwater management at the national level… Read More .
Can a new water ministry tackle the worst water crisis in Indian history?
- Experts are of the opinion that an exclusive ministry can only bring about a cosmetic but not a real change.
- Water is a state subject = Unless states make specific requests the centre cannot intervene.
What are the solutions to the water crisis in India?
Good water management practices :
- India receives adequate annual rainfall through the south-west monsoon. However, most regions of the country are still water deficient mainly because of inefficient water management practices.
- Rainwater harvesting should be encouraged on a large scale, especially, in cities where the surface runoff of rainwater is very high.
- Roof-top rainwater harvesting can also be utilised to recharge groundwater by digging percolation pits around the house and filling it with gravel.
- Indian cities need to learn from Cape Town of South Africa which when faced with the water crisis in 2018 had announced “ Day Zero “. During that day, water-taps in the city turned off = people had to use communal water-taps to conserve water. Restrictions on water use per person were also fixed.
- Since water is a state subject in India state governments should take active measures and create awareness for the minimal use of water.
Interlinking of rivers :
- Interlinking of rivers is a topic that has been discussed and debated for several years as a possible permanent solution to the water crisis in the country.
- The 3 primary advantages mentioned in favour of the scheme are (1) droughts will never occur (2) there will be no more floods in the major rivers and (3) an additional 30,000 MW of hydropower will be generated.
Coordination in aquifer usage: There is an urgent need for coordination among users for aquifers. There should be laws and contracts for sharing of aquifers. Groundwater aquifer mapping has started only recently in India which is a welcome step.
River basin authority: There should be a River Basin Authority for sharing information among states since most of the rivers in India pass through different states.
Coordinated efforts among states for management of groundwater at a localized level.
Community-level management: At the village level, there can be decentralized management of water at the community level.
Charging money for efficient use of water (like electricity). For example- Water ATMs at Marathwada provide water @25 paisa per litre a day.
Good Cultivation practices:
- Changing the cropping pattern, crop diversification and encouraging water use efficiency in agriculture by moving towards food crops from cash crops.
- Innovative farming practices like precision farming , zero budget natural farming , etc. could be employed for efficient water utilisation.
Incentive-based water conservation in rural parts of the water-stressed regions is another solution.
- For example, if a particular level of groundwater level is maintained, higher MSP can be provided to the farmers of that region.
- MSP can also be provided based on crop’s water usage = Crops that consume a high amount of water will get less MSP.
Way forward
India is not a water deficit country, but due to severe neglect and lack of monitoring of water resource development projects, many regions in the country face water stress from time to time. Therefore balancing water demand with available supply is the need of the hour for future economic growth and development as well as for the sustenance of human life.
New National Water Policy (NWP)
In November 2019, the Ministry of Jal Shakti had set up a committee to draft the new National Water Policy (NWP). This was the first time that the government asked a committee of independent experts to draft the policy.
Highlights of NWP
1) demand-side: diversification of public procurement operations.
- Irrigation utilizes 80-90% of India’s water , most of which is used by rice, wheat, and sugarcane.
- Therefore, crop diversification is the single most crucial step in addressing India’s water crisis.
- The policy recommends diversifying public procurement operations to include Nutri-cereals, pulses, and oilseeds.
- This would incentivize farmers to diversify their cropping patterns, resulting in huge savings of water.
2) Reduce-Recycle-Reuse
- Reduce-Recycle-Reuse has been suggested as the basic mantra of integrated urban water supply and wastewater management, with the treatment of sewage and eco-restoration of urban river stretches, as far as possible via decentralised wastewater management.
- All non-potable use like flushing, fire protection, vehicle washing should mandatorily shift to treated wastewater.
3) Supply-side measure: Using technology to use stored water in dams
- Within supply-side options, the NWP points to trillions of litres stored in big dams, that are still not reaching farmers.
- NWP recommends how the irrigated areas could be considerably expanded at very low cost by using pressurised closed conveyance pipelines, in addition to Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems and pressurised micro-irrigation.
4) Supply of water through “nature-based solutions”
- The NWP places major importance on the supply of water via “nature-based solutions” like the rejuvenation of catchment areas, to be incentivised through compensation for ecosystem services.
- Specially curated “blue-green infrastructure” like rain gardens and bio-swales, restored rivers with wet meadows, wetlands constructed for bio-remediation, urban parks, permeable pavements, green roofs etc are suggested for urban areas.
5) Sustainable and equitable management of groundwater
- Information on aquifer boundaries , water storage capacities and flows provided in a user-friendly manner to stakeholders, assigned as custodians of their aquifers, would allow them to create protocols for effective management of groundwater.
6) Rights of Rivers
- The NWP accords river protection and revitalisation prior and primary importance.
- Steps to restore river flows include: Re-vegetation of catchments, regulation of groundwater extraction, river-bed pumping and mining of sand and boulders.
- The NWP outlines a process to draft a Rights of Rivers Act, including their right to flow, to meander and to meet the sea.
7) Emphasis on water quality
- The new NWP considers water quality as the most serious un-addressed issue in India today.
- It proposes that every water ministry, at the Centre and states, include a water quality department.
- The policy advocates adoption of state-of-the-art, low-cost, low-energy, eco-sensitive technologies for sewage treatment.
- Widespread use of reverse osmosis has led to huge water wastage and adverse impact on water quality.
- The policy wants RO units to be discouraged if the total dissolved solids count in water is less than 500mg/L.
- It suggests a task force on emerging water contaminants to better understand and tackle the threats they are likely to pose.
8) Reforming governance of water
- The policy makes radical proposals for improving the governance of water, which suffers from three kinds of issues: That between irrigation and drinking water, surface and groundwater, as also water and wastewater.
- Government departments, working in silos, have generally dealt with just one side of these binaries.
- Dealing with drinking water and irrigation in silos has meant that aquifers providing assured sources of drinking water dry up because the same aquifers are used for irrigation, which consumes much more water.
- And when water and wastewater are separated in planning, the result is a fall in water quality.
9) Creation of National Water Commission
- The NWP also suggests the creation of a unified multi-disciplinary, multi-stakeholder National Water Commission (NWC), which would become an exemplar for states to follow.
- Governments should build enduring partnerships with primary stakeholders of water , who must become an integral part of the NWC and its counterparts in the states.
How Gujarat transformed from Water-deficit state to surplus state?
- The Gujarat government created the state-level Bhaskaracharya Institute for Space Applications and Geoinformatics (BISAG) to aid in the supply of services and solutions for the deployment of map-based GeoSpatial Information Systems.
- Micro-level check dams.
- Macro-level projects particularly in the Saurashtra, Kutch, and North Gujarat areas.
- Gujarat launched the Kutch branch canal from the Narmada Main canal, which helps provide water to the most distant parts.
- Sujalam Sufalam Yojana: to irrigate the areas of North Gujarat.
- The SAUNI Yojana (Saurashtra Narmada Avtaran Irrigation Yojana), which means literally “reincarnation of the Narmada River in the region,” was thus introduced.
- Administrative and Governance reforms.
GET MONTHLY COMPILATIONS
Related Posts

Virtual Water Trade

Precision Farming in India – Features, Merits, Demerits and Challenges...

Rural Economy in Pandemic Times
Excellent essay indeed!
Great explanation.
worth a praise! well done :)
Wish you could mention the references for all the statistics and facts.
Please add features to include this article in PDF.
Where are effects🙄
Haven’t you seen the impacts heading in this article?
Great explanation and essay. This is exactly what I have been searching for.
There was a problem reporting this post.
Block Member?
Please confirm you want to block this member.
You will no longer be able to:
- See blocked member's posts
- Mention this member in posts
Please allow a few minutes for this process to complete.

DA KZN secures trial date against eThekwini in sewage and water case
- Loadshedding
- South African News
- African News
- International News
- All Opinions
- Latest Opinions
- Raymond Suttner - Suttner's View
- Politics 360 - Ebrahim Fakir
- Institute for Security Studies
- South African Institute of International Affairs
- Saliem Fakir - Low Carbon Future
- The Conversation
- Real Economy
- Other Opinions
- Author Interviews
- All Legislation
- Constitution
- Audio Articles
- Recommendations
- All Case Law
- Constitutional Court
- Supreme Court of Appeal
- High Courts
- All Legal Briefs
- Company Posts
- Legal Notice

Note: Search is limited to the most recent 250 articles. To access earlier articles, click Advanced Search and set an earlier date range. To search for a term containing the '&' symbol, click Advanced Search and use the 'search headings' and/or 'in first paragraph' options.
And must exclude these words...
Sponsored by
Please enter the email address that you used to register on Polity.org.za. Your password will be sent to this address.
Email this article
separate emails by commas, maximum limit of 4 addresses
Article Enquiry
Embed video.

Embed Video Popup Video Instagram

Download Buy Photos
6th May 2024
ARTICLE ENQUIRY SAVE THIS ARTICLE EMAIL THIS ARTICLE
Font size: - +
/ MEDIA STATEMENT / The content on this page is not written by Polity.org.za, but is supplied by third parties. This content does not constitute news reporting by Polity.org.za.
The Democratic Alliance in KwaZulu-Natal has become the first political party to secure a trial date in the High Court against the eThekwini Municipality for the ongoing sewage and water crisis in the city. The trial is set to begin on the 8th of August 2024.
After launching the case in February 2023, the ANC-run eThekwini Municipality has done everything possible to evade this day of reckoning. It even required the KZN Judge President, Thoba Portia Poyo-Dlwati, to instruct eThekwini by way of a court order to file answering affidavits to the DA’s papers so the case could proceed.
The DA has spared no expense and hired the very best lawyers to bring this case before the courts in terms of the National Environmental Management Act (NEMA) because we understand the importance of this issue not only to the people of eThekwini, but all of KwaZulu-Natal.
The DA is the only party that has taken this issue seriously while other parties have done nothing except post pictures of themselves pointing at broken pipes.
This is the kind of response and commitment that the residents of KwaZulu-Natal can expect from a DA Provincial Government. Less words, more delivery.
Furthermore, this marks a series of court cases that the DA is fighting on behalf of residents across the province and we will soon be announcing further action that we will be taking against other municipalities.
There is only one party with a proven track record of getting things done and that is the Democratic Alliance.
Issued by Chris Pappas - DA KZN Premier Candidate
EMAIL THIS ARTICLE SAVE THIS ARTICLE ARTICLE ENQUIRY
To subscribe email [email protected] or click here To advertise email [email protected] or click here
Polity.org.za is a product of Creamer Media. www.creamermedia.co.za
Other Creamer Media Products include: Engineering News Mining Weekly Research Channel Africa
Newsletters
Sign up for our FREE daily email newsletter
Subscriptions
We offer a variety of subscriptions to our Magazine, Website, PDF Reports and our photo library.
Subscriptions are available via the Creamer Media Store.
Advertising on Polity.org.za is an effective way to build and consolidate a company's profile among clients and prospective clients. Email [email protected]


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The top five countries that contribute to humanity's total water footprint appear below—along with South Africa, where the city of Cape Town is facing a crisis-level water shortage. WORLDWIDE ...
Water Crisis. Unlimited access to clean, safe water is taken for granted in many places, but water scarcity is a growing concern worldwide. Overuse, increasing demand, pollution, poor management, lack of infrastructure, and changes in weather patterns due to global warming are key stressors that affect the availability of fresh water.
Water stress or scarcity occurs when demand for safe, usable water in a given area exceeds the supply. On the demand side, the vast majority—roughly 70 percent—of the world's freshwater is ...
In this regard the following discussion will elaborate on the major causes and implication of water shortage in the planet today. First, both industrial and domestic water pollution is one of the major causes of water shortage because as more water is polluted the more water is wasted (Oxfam.org.uk, 2011).
As the four co-chairs of the Global Commission on the Economics of Water, our goal is to transform the world's understanding of the economics and governance of water, placing a much stronger emphasis on equity, justice, effectiveness, and democracy. We can still redefine our relationship with water and redesign our economies to value water as ...
The water crisis is a health crisis. Nearly 1 million people die each year from water, sanitation and hygiene-related diseases which could be reduced with access to safe water or sanitation. Every 2 minutes a child dies from a water-related disease. Access to safe water and sanitation contributes to improved health and helps prevent the spread ...
Between two and three billion people worldwide experience water shortages. These shortages will worsen in the coming decades, especially in cities, if international cooperation in this area is not boosted, warn UNESCO and UN-Water in the latest edition of the UN World Water Development Report. UNESCO/D. Bonazzi. 22 March 2023.
Climate change is already affecting water access for people around the world, causing more severe droughts and floods. Increasing global temperatures are one of the main contributors to this problem. Climate change impacts the water cycle by influencing when, where, and how much precipitation falls. It also leads to more severe weather events ...
It is the result of myriad environmental, political, economic, and social forces. Freshwater makes up a very small fraction of all water on the planet. While nearly 70 percent of the world is ...
This essay on water crisis causes and solutions embarks on a comprehensive exploration of the causes that underlie the water crisis and examines the profound consequences it imposes on societies and ecosystems. Furthermore, it delves into a myriad of potential solutions and strategies that hold the key to mitigating this critical issue ...
Water Shortage: a Global Crisis. Water, the elixir of life, is a finite resource essential for all living organisms on Earth. Yet, despite its undeniable importance, water shortage has become a critical global issue. This essay delves into the causes, consequences, and potential solutions to the growing problem of water scarcity.
Essay on Water Crisis 500+ Words. Water, a life-sustaining resource, is essential for all living creatures on Earth. However, a water crisis is emerging as one of the most significant challenges humanity faces today. In this essay, we will explore the water crisis, its causes and consequences, and the critical need for sustainable solutions to ...
Blue Gold: Global Water Crisis Essay. Exclusively available on IvyPanda. The issue of water is a global affair because of the alarming rate at which limited fresh water reservoirs is depleted. Water is important for the sustenance of human life and most people treasure it. Due to its limited supply and the reduction of fresh water sources, it ...
500 Words Essay on Water Crisis Introduction. Water, the most fundamental building block of life, is becoming increasingly scarce. The world is grappling with a water crisis that poses a significant threat to both human survival and the stability of our ecosystems. This crisis is not limited to developing countries or arid regions; it is a ...
Brief on Water Scarcity. Water is a basic necessity for every living being. Life without water is impossible, not just for us humans, but for all plants and animals too. Water scarcity is an issue of grave concern these days as water scarcity has become very common. Water is one of the most wasted natural resources and corrective measures ...
There are several more statistical facts on the U.S.' water issues that shows our water isn't, per se, clean. "The ASCE estimates that a water main breaks every 2 minutes, or 240,000 breaks a year in the U.S.". Some water pipes in the US can be up to 150 years old, most of which are lead pipes, which were banned over three decades ago.
This sample environmental science essay explores the Flint Michigan water crisis that has been unfolding for two years ever since the city began to use water from the local Flint River (Foley). The case of Flint is a precautionary one and one worthy of intense public attention, both writing and speeches, as it may herald the need for a ...
The existing water source was protected from flooding and the access point raised for better access. 4. Wastewater. Let's talk about contaminated water and the role it plays in the global water crisis: Sometimes water can be plentiful in an area. But whether that water is safe to drink…that's another story.
The Water Crisis and Solutions Essay. There is a global shortage of drinking water. A person might wonder how this can be if seventy percent of the earth's surface is covered by water. Most of the Earth's water is unsuitable for human consuption. Ocean water is salt water, which makes up 97.5% of all water on the planet.
Water Crisis Essay. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. Contemporarily there are many global issues that are affecting the citizens of the world as a single community; disrupting natural framework and disturbing the social and economic ...
In this water crisis essay, we had describe about water crisis in details. Water is the basic requirement for the survival and promotion of humans, animals, birds and vegetation. Environmental pollution is a major cause of 'water crisis' as a result the underground layer increases rapidly. In 1951, the per capita water availability was ...
54% of the country's groundwater is declining rapidly than it is being replenished. India's water table is declining in most regions. Also, there is a presence of toxic elements like fluoride, arsenic, mercury, even uranium in our groundwater. Water levels in India's major reservoirs have fallen to 21% of the average of the last decade.
This study examines the impact of an increasing water footprint on exacerbating water scarcity and the crisis in Isfahan province, Iran. It highlights the significance of considering the water footprint approach in water resource management. To achieve this goal, a comprehensive analysis of water availability limitations, population growth, the agricultural sector, and the industrial sector ...
The Democratic Alliance in KwaZulu-Natal has become the first political party to secure a trial date in the High Court against the eThekwini Municipality for the ongoing sewage and water crisis in the city. The trial is set to begin on the 8th of August 2024. After launching the case in February 2023, the ANC-run eThekwini Municipality has done everything possible to evade this day of reckoning.