Uncomplicated Reviews of Educational Research Methods
- Writing a Research Report
.pdf version of this page
This review covers the basic elements of a research report. This is a general guide for what you will see in journal articles or dissertations. This format assumes a mixed methods study, but you can leave out either quantitative or qualitative sections if you only used a single methodology.
This review is divided into sections for easy reference. There are five MAJOR parts of a Research Report:
1. Introduction 2. Review of Literature 3. Methods 4. Results 5. Discussion
As a general guide, the Introduction, Review of Literature, and Methods should be about 1/3 of your paper, Discussion 1/3, then Results 1/3.
Section 1 : Cover Sheet (APA format cover sheet) optional, if required.
Section 2: Abstract (a basic summary of the report, including sample, treatment, design, results, and implications) (≤ 150 words) optional, if required.
Section 3 : Introduction (1-3 paragraphs) • Basic introduction • Supportive statistics (can be from periodicals) • Statement of Purpose • Statement of Significance
Section 4 : Research question(s) or hypotheses • An overall research question (optional) • A quantitative-based (hypotheses) • A qualitative-based (research questions) Note: You will generally have more than one, especially if using hypotheses.
Section 5: Review of Literature ▪ Should be organized by subheadings ▪ Should adequately support your study using supporting, related, and/or refuting evidence ▪ Is a synthesis, not a collection of individual summaries
Section 6: Methods ▪ Procedure: Describe data gathering or participant recruitment, including IRB approval ▪ Sample: Describe the sample or dataset, including basic demographics ▪ Setting: Describe the setting, if applicable (generally only in qualitative designs) ▪ Treatment: If applicable, describe, in detail, how you implemented the treatment ▪ Instrument: Describe, in detail, how you implemented the instrument; Describe the reliability and validity associated with the instrument ▪ Data Analysis: Describe type of procedure (t-test, interviews, etc.) and software (if used)
Section 7: Results ▪ Restate Research Question 1 (Quantitative) ▪ Describe results ▪ Restate Research Question 2 (Qualitative) ▪ Describe results
Section 8: Discussion ▪ Restate Overall Research Question ▪ Describe how the results, when taken together, answer the overall question ▪ ***Describe how the results confirm or contrast the literature you reviewed
Section 9: Recommendations (if applicable, generally related to practice)
Section 10: Limitations ▪ Discuss, in several sentences, the limitations of this study. ▪ Research Design (overall, then info about the limitations of each separately) ▪ Sample ▪ Instrument/s ▪ Other limitations
Section 11: Conclusion (A brief closing summary)
Section 12: References (APA format)

Share this:
About research rundowns.
Research Rundowns was made possible by support from the Dewar College of Education at Valdosta State University .
- Experimental Design
- What is Educational Research?
- Writing Research Questions
- Mixed Methods Research Designs
- Qualitative Coding & Analysis
- Qualitative Research Design
- Correlation
- Effect Size
- Instrument, Validity, Reliability
- Mean & Standard Deviation
- Significance Testing (t-tests)
- Steps 1-4: Finding Research
- Steps 5-6: Analyzing & Organizing
- Steps 7-9: Citing & Writing
Create a free website or blog at WordPress.com.

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 11: Presenting Your Research
Writing a Research Report in American Psychological Association (APA) Style
Learning Objectives
- Identify the major sections of an APA-style research report and the basic contents of each section.
- Plan and write an effective APA-style research report.
In this section, we look at how to write an APA-style empirical research report , an article that presents the results of one or more new studies. Recall that the standard sections of an empirical research report provide a kind of outline. Here we consider each of these sections in detail, including what information it contains, how that information is formatted and organized, and tips for writing each section. At the end of this section is a sample APA-style research report that illustrates many of these principles.
Sections of a Research Report
Title page and abstract.
An APA-style research report begins with a title page . The title is centred in the upper half of the page, with each important word capitalized. The title should clearly and concisely (in about 12 words or fewer) communicate the primary variables and research questions. This sometimes requires a main title followed by a subtitle that elaborates on the main title, in which case the main title and subtitle are separated by a colon. Here are some titles from recent issues of professional journals published by the American Psychological Association.
- Sex Differences in Coping Styles and Implications for Depressed Mood
- Effects of Aging and Divided Attention on Memory for Items and Their Contexts
- Computer-Assisted Cognitive Behavioural Therapy for Child Anxiety: Results of a Randomized Clinical Trial
- Virtual Driving and Risk Taking: Do Racing Games Increase Risk-Taking Cognitions, Affect, and Behaviour?
Below the title are the authors’ names and, on the next line, their institutional affiliation—the university or other institution where the authors worked when they conducted the research. As we have already seen, the authors are listed in an order that reflects their contribution to the research. When multiple authors have made equal contributions to the research, they often list their names alphabetically or in a randomly determined order.
In some areas of psychology, the titles of many empirical research reports are informal in a way that is perhaps best described as “cute.” They usually take the form of a play on words or a well-known expression that relates to the topic under study. Here are some examples from recent issues of the Journal Psychological Science .
- “Smells Like Clean Spirit: Nonconscious Effects of Scent on Cognition and Behavior”
- “Time Crawls: The Temporal Resolution of Infants’ Visual Attention”
- “Scent of a Woman: Men’s Testosterone Responses to Olfactory Ovulation Cues”
- “Apocalypse Soon?: Dire Messages Reduce Belief in Global Warming by Contradicting Just-World Beliefs”
- “Serial vs. Parallel Processing: Sometimes They Look Like Tweedledum and Tweedledee but They Can (and Should) Be Distinguished”
- “How Do I Love Thee? Let Me Count the Words: The Social Effects of Expressive Writing”
Individual researchers differ quite a bit in their preference for such titles. Some use them regularly, while others never use them. What might be some of the pros and cons of using cute article titles?
For articles that are being submitted for publication, the title page also includes an author note that lists the authors’ full institutional affiliations, any acknowledgments the authors wish to make to agencies that funded the research or to colleagues who commented on it, and contact information for the authors. For student papers that are not being submitted for publication—including theses—author notes are generally not necessary.
The abstract is a summary of the study. It is the second page of the manuscript and is headed with the word Abstract . The first line is not indented. The abstract presents the research question, a summary of the method, the basic results, and the most important conclusions. Because the abstract is usually limited to about 200 words, it can be a challenge to write a good one.
Introduction
The introduction begins on the third page of the manuscript. The heading at the top of this page is the full title of the manuscript, with each important word capitalized as on the title page. The introduction includes three distinct subsections, although these are typically not identified by separate headings. The opening introduces the research question and explains why it is interesting, the literature review discusses relevant previous research, and the closing restates the research question and comments on the method used to answer it.
The Opening
The opening , which is usually a paragraph or two in length, introduces the research question and explains why it is interesting. To capture the reader’s attention, researcher Daryl Bem recommends starting with general observations about the topic under study, expressed in ordinary language (not technical jargon)—observations that are about people and their behaviour (not about researchers or their research; Bem, 2003 [1] ). Concrete examples are often very useful here. According to Bem, this would be a poor way to begin a research report:
Festinger’s theory of cognitive dissonance received a great deal of attention during the latter part of the 20th century (p. 191)
The following would be much better:
The individual who holds two beliefs that are inconsistent with one another may feel uncomfortable. For example, the person who knows that he or she enjoys smoking but believes it to be unhealthy may experience discomfort arising from the inconsistency or disharmony between these two thoughts or cognitions. This feeling of discomfort was called cognitive dissonance by social psychologist Leon Festinger (1957), who suggested that individuals will be motivated to remove this dissonance in whatever way they can (p. 191).
After capturing the reader’s attention, the opening should go on to introduce the research question and explain why it is interesting. Will the answer fill a gap in the literature? Will it provide a test of an important theory? Does it have practical implications? Giving readers a clear sense of what the research is about and why they should care about it will motivate them to continue reading the literature review—and will help them make sense of it.
Breaking the Rules
Researcher Larry Jacoby reported several studies showing that a word that people see or hear repeatedly can seem more familiar even when they do not recall the repetitions—and that this tendency is especially pronounced among older adults. He opened his article with the following humourous anecdote:
A friend whose mother is suffering symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) tells the story of taking her mother to visit a nursing home, preliminary to her mother’s moving there. During an orientation meeting at the nursing home, the rules and regulations were explained, one of which regarded the dining room. The dining room was described as similar to a fine restaurant except that tipping was not required. The absence of tipping was a central theme in the orientation lecture, mentioned frequently to emphasize the quality of care along with the advantages of having paid in advance. At the end of the meeting, the friend’s mother was asked whether she had any questions. She replied that she only had one question: “Should I tip?” (Jacoby, 1999, p. 3)
Although both humour and personal anecdotes are generally discouraged in APA-style writing, this example is a highly effective way to start because it both engages the reader and provides an excellent real-world example of the topic under study.
The Literature Review
Immediately after the opening comes the literature review , which describes relevant previous research on the topic and can be anywhere from several paragraphs to several pages in length. However, the literature review is not simply a list of past studies. Instead, it constitutes a kind of argument for why the research question is worth addressing. By the end of the literature review, readers should be convinced that the research question makes sense and that the present study is a logical next step in the ongoing research process.
Like any effective argument, the literature review must have some kind of structure. For example, it might begin by describing a phenomenon in a general way along with several studies that demonstrate it, then describing two or more competing theories of the phenomenon, and finally presenting a hypothesis to test one or more of the theories. Or it might describe one phenomenon, then describe another phenomenon that seems inconsistent with the first one, then propose a theory that resolves the inconsistency, and finally present a hypothesis to test that theory. In applied research, it might describe a phenomenon or theory, then describe how that phenomenon or theory applies to some important real-world situation, and finally suggest a way to test whether it does, in fact, apply to that situation.
Looking at the literature review in this way emphasizes a few things. First, it is extremely important to start with an outline of the main points that you want to make, organized in the order that you want to make them. The basic structure of your argument, then, should be apparent from the outline itself. Second, it is important to emphasize the structure of your argument in your writing. One way to do this is to begin the literature review by summarizing your argument even before you begin to make it. “In this article, I will describe two apparently contradictory phenomena, present a new theory that has the potential to resolve the apparent contradiction, and finally present a novel hypothesis to test the theory.” Another way is to open each paragraph with a sentence that summarizes the main point of the paragraph and links it to the preceding points. These opening sentences provide the “transitions” that many beginning researchers have difficulty with. Instead of beginning a paragraph by launching into a description of a previous study, such as “Williams (2004) found that…,” it is better to start by indicating something about why you are describing this particular study. Here are some simple examples:
Another example of this phenomenon comes from the work of Williams (2004).
Williams (2004) offers one explanation of this phenomenon.
An alternative perspective has been provided by Williams (2004).
We used a method based on the one used by Williams (2004).
Finally, remember that your goal is to construct an argument for why your research question is interesting and worth addressing—not necessarily why your favourite answer to it is correct. In other words, your literature review must be balanced. If you want to emphasize the generality of a phenomenon, then of course you should discuss various studies that have demonstrated it. However, if there are other studies that have failed to demonstrate it, you should discuss them too. Or if you are proposing a new theory, then of course you should discuss findings that are consistent with that theory. However, if there are other findings that are inconsistent with it, again, you should discuss them too. It is acceptable to argue that the balance of the research supports the existence of a phenomenon or is consistent with a theory (and that is usually the best that researchers in psychology can hope for), but it is not acceptable to ignore contradictory evidence. Besides, a large part of what makes a research question interesting is uncertainty about its answer.
The Closing
The closing of the introduction—typically the final paragraph or two—usually includes two important elements. The first is a clear statement of the main research question or hypothesis. This statement tends to be more formal and precise than in the opening and is often expressed in terms of operational definitions of the key variables. The second is a brief overview of the method and some comment on its appropriateness. Here, for example, is how Darley and Latané (1968) [2] concluded the introduction to their classic article on the bystander effect:
These considerations lead to the hypothesis that the more bystanders to an emergency, the less likely, or the more slowly, any one bystander will intervene to provide aid. To test this proposition it would be necessary to create a situation in which a realistic “emergency” could plausibly occur. Each subject should also be blocked from communicating with others to prevent his getting information about their behaviour during the emergency. Finally, the experimental situation should allow for the assessment of the speed and frequency of the subjects’ reaction to the emergency. The experiment reported below attempted to fulfill these conditions. (p. 378)
Thus the introduction leads smoothly into the next major section of the article—the method section.
The method section is where you describe how you conducted your study. An important principle for writing a method section is that it should be clear and detailed enough that other researchers could replicate the study by following your “recipe.” This means that it must describe all the important elements of the study—basic demographic characteristics of the participants, how they were recruited, whether they were randomly assigned, how the variables were manipulated or measured, how counterbalancing was accomplished, and so on. At the same time, it should avoid irrelevant details such as the fact that the study was conducted in Classroom 37B of the Industrial Technology Building or that the questionnaire was double-sided and completed using pencils.
The method section begins immediately after the introduction ends with the heading “Method” (not “Methods”) centred on the page. Immediately after this is the subheading “Participants,” left justified and in italics. The participants subsection indicates how many participants there were, the number of women and men, some indication of their age, other demographics that may be relevant to the study, and how they were recruited, including any incentives given for participation.
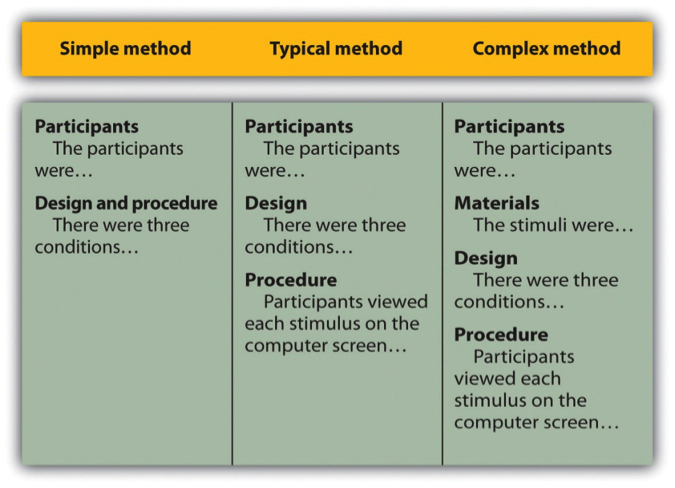
After the participants section, the structure can vary a bit. Figure 11.1 shows three common approaches. In the first, the participants section is followed by a design and procedure subsection, which describes the rest of the method. This works well for methods that are relatively simple and can be described adequately in a few paragraphs. In the second approach, the participants section is followed by separate design and procedure subsections. This works well when both the design and the procedure are relatively complicated and each requires multiple paragraphs.
What is the difference between design and procedure? The design of a study is its overall structure. What were the independent and dependent variables? Was the independent variable manipulated, and if so, was it manipulated between or within subjects? How were the variables operationally defined? The procedure is how the study was carried out. It often works well to describe the procedure in terms of what the participants did rather than what the researchers did. For example, the participants gave their informed consent, read a set of instructions, completed a block of four practice trials, completed a block of 20 test trials, completed two questionnaires, and were debriefed and excused.
In the third basic way to organize a method section, the participants subsection is followed by a materials subsection before the design and procedure subsections. This works well when there are complicated materials to describe. This might mean multiple questionnaires, written vignettes that participants read and respond to, perceptual stimuli, and so on. The heading of this subsection can be modified to reflect its content. Instead of “Materials,” it can be “Questionnaires,” “Stimuli,” and so on.
The results section is where you present the main results of the study, including the results of the statistical analyses. Although it does not include the raw data—individual participants’ responses or scores—researchers should save their raw data and make them available to other researchers who request them. Several journals now encourage the open sharing of raw data online.
Although there are no standard subsections, it is still important for the results section to be logically organized. Typically it begins with certain preliminary issues. One is whether any participants or responses were excluded from the analyses and why. The rationale for excluding data should be described clearly so that other researchers can decide whether it is appropriate. A second preliminary issue is how multiple responses were combined to produce the primary variables in the analyses. For example, if participants rated the attractiveness of 20 stimulus people, you might have to explain that you began by computing the mean attractiveness rating for each participant. Or if they recalled as many items as they could from study list of 20 words, did you count the number correctly recalled, compute the percentage correctly recalled, or perhaps compute the number correct minus the number incorrect? A third preliminary issue is the reliability of the measures. This is where you would present test-retest correlations, Cronbach’s α, or other statistics to show that the measures are consistent across time and across items. A final preliminary issue is whether the manipulation was successful. This is where you would report the results of any manipulation checks.
The results section should then tackle the primary research questions, one at a time. Again, there should be a clear organization. One approach would be to answer the most general questions and then proceed to answer more specific ones. Another would be to answer the main question first and then to answer secondary ones. Regardless, Bem (2003) [3] suggests the following basic structure for discussing each new result:
- Remind the reader of the research question.
- Give the answer to the research question in words.
- Present the relevant statistics.
- Qualify the answer if necessary.
- Summarize the result.
Notice that only Step 3 necessarily involves numbers. The rest of the steps involve presenting the research question and the answer to it in words. In fact, the basic results should be clear even to a reader who skips over the numbers.
The discussion is the last major section of the research report. Discussions usually consist of some combination of the following elements:
- Summary of the research
- Theoretical implications
- Practical implications
- Limitations
- Suggestions for future research
The discussion typically begins with a summary of the study that provides a clear answer to the research question. In a short report with a single study, this might require no more than a sentence. In a longer report with multiple studies, it might require a paragraph or even two. The summary is often followed by a discussion of the theoretical implications of the research. Do the results provide support for any existing theories? If not, how can they be explained? Although you do not have to provide a definitive explanation or detailed theory for your results, you at least need to outline one or more possible explanations. In applied research—and often in basic research—there is also some discussion of the practical implications of the research. How can the results be used, and by whom, to accomplish some real-world goal?
The theoretical and practical implications are often followed by a discussion of the study’s limitations. Perhaps there are problems with its internal or external validity. Perhaps the manipulation was not very effective or the measures not very reliable. Perhaps there is some evidence that participants did not fully understand their task or that they were suspicious of the intent of the researchers. Now is the time to discuss these issues and how they might have affected the results. But do not overdo it. All studies have limitations, and most readers will understand that a different sample or different measures might have produced different results. Unless there is good reason to think they would have, however, there is no reason to mention these routine issues. Instead, pick two or three limitations that seem like they could have influenced the results, explain how they could have influenced the results, and suggest ways to deal with them.
Most discussions end with some suggestions for future research. If the study did not satisfactorily answer the original research question, what will it take to do so? What new research questions has the study raised? This part of the discussion, however, is not just a list of new questions. It is a discussion of two or three of the most important unresolved issues. This means identifying and clarifying each question, suggesting some alternative answers, and even suggesting ways they could be studied.
Finally, some researchers are quite good at ending their articles with a sweeping or thought-provoking conclusion. Darley and Latané (1968) [4] , for example, ended their article on the bystander effect by discussing the idea that whether people help others may depend more on the situation than on their personalities. Their final sentence is, “If people understand the situational forces that can make them hesitate to intervene, they may better overcome them” (p. 383). However, this kind of ending can be difficult to pull off. It can sound overreaching or just banal and end up detracting from the overall impact of the article. It is often better simply to end when you have made your final point (although you should avoid ending on a limitation).
The references section begins on a new page with the heading “References” centred at the top of the page. All references cited in the text are then listed in the format presented earlier. They are listed alphabetically by the last name of the first author. If two sources have the same first author, they are listed alphabetically by the last name of the second author. If all the authors are the same, then they are listed chronologically by the year of publication. Everything in the reference list is double-spaced both within and between references.
Appendices, Tables, and Figures
Appendices, tables, and figures come after the references. An appendix is appropriate for supplemental material that would interrupt the flow of the research report if it were presented within any of the major sections. An appendix could be used to present lists of stimulus words, questionnaire items, detailed descriptions of special equipment or unusual statistical analyses, or references to the studies that are included in a meta-analysis. Each appendix begins on a new page. If there is only one, the heading is “Appendix,” centred at the top of the page. If there is more than one, the headings are “Appendix A,” “Appendix B,” and so on, and they appear in the order they were first mentioned in the text of the report.
After any appendices come tables and then figures. Tables and figures are both used to present results. Figures can also be used to illustrate theories (e.g., in the form of a flowchart), display stimuli, outline procedures, and present many other kinds of information. Each table and figure appears on its own page. Tables are numbered in the order that they are first mentioned in the text (“Table 1,” “Table 2,” and so on). Figures are numbered the same way (“Figure 1,” “Figure 2,” and so on). A brief explanatory title, with the important words capitalized, appears above each table. Each figure is given a brief explanatory caption, where (aside from proper nouns or names) only the first word of each sentence is capitalized. More details on preparing APA-style tables and figures are presented later in the book.
Sample APA-Style Research Report
Figures 11.2, 11.3, 11.4, and 11.5 show some sample pages from an APA-style empirical research report originally written by undergraduate student Tomoe Suyama at California State University, Fresno. The main purpose of these figures is to illustrate the basic organization and formatting of an APA-style empirical research report, although many high-level and low-level style conventions can be seen here too.

Key Takeaways
- An APA-style empirical research report consists of several standard sections. The main ones are the abstract, introduction, method, results, discussion, and references.
- The introduction consists of an opening that presents the research question, a literature review that describes previous research on the topic, and a closing that restates the research question and comments on the method. The literature review constitutes an argument for why the current study is worth doing.
- The method section describes the method in enough detail that another researcher could replicate the study. At a minimum, it consists of a participants subsection and a design and procedure subsection.
- The results section describes the results in an organized fashion. Each primary result is presented in terms of statistical results but also explained in words.
- The discussion typically summarizes the study, discusses theoretical and practical implications and limitations of the study, and offers suggestions for further research.
- Practice: Look through an issue of a general interest professional journal (e.g., Psychological Science ). Read the opening of the first five articles and rate the effectiveness of each one from 1 ( very ineffective ) to 5 ( very effective ). Write a sentence or two explaining each rating.
- Practice: Find a recent article in a professional journal and identify where the opening, literature review, and closing of the introduction begin and end.
- Practice: Find a recent article in a professional journal and highlight in a different colour each of the following elements in the discussion: summary, theoretical implications, practical implications, limitations, and suggestions for future research.
Long Descriptions
Figure 11.1 long description: Table showing three ways of organizing an APA-style method section.
In the simple method, there are two subheadings: “Participants” (which might begin “The participants were…”) and “Design and procedure” (which might begin “There were three conditions…”).
In the typical method, there are three subheadings: “Participants” (“The participants were…”), “Design” (“There were three conditions…”), and “Procedure” (“Participants viewed each stimulus on the computer screen…”).
In the complex method, there are four subheadings: “Participants” (“The participants were…”), “Materials” (“The stimuli were…”), “Design” (“There were three conditions…”), and “Procedure” (“Participants viewed each stimulus on the computer screen…”). [Return to Figure 11.1]
- Bem, D. J. (2003). Writing the empirical journal article. In J. M. Darley, M. P. Zanna, & H. R. Roediger III (Eds.), The compleat academic: A practical guide for the beginning social scientist (2nd ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. ↵
- Darley, J. M., & Latané, B. (1968). Bystander intervention in emergencies: Diffusion of responsibility. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 4 , 377–383. ↵
A type of research article which describes one or more new empirical studies conducted by the authors.
The page at the beginning of an APA-style research report containing the title of the article, the authors’ names, and their institutional affiliation.
A summary of a research study.
The third page of a manuscript containing the research question, the literature review, and comments about how to answer the research question.
An introduction to the research question and explanation for why this question is interesting.
A description of relevant previous research on the topic being discusses and an argument for why the research is worth addressing.
The end of the introduction, where the research question is reiterated and the method is commented upon.
The section of a research report where the method used to conduct the study is described.
The main results of the study, including the results from statistical analyses, are presented in a research article.
Section of a research report that summarizes the study's results and interprets them by referring back to the study's theoretical background.
Part of a research report which contains supplemental material.
Research Methods in Psychology - 2nd Canadian Edition Copyright © 2015 by Paul C. Price, Rajiv Jhangiani, & I-Chant A. Chiang is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications . If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
You Might Also Like:

Can you help me with a full paper template for this Abstract:
Background: Energy and sports drinks have gained popularity among diverse demographic groups, including adolescents, athletes, workers, and college students. While often used interchangeably, these beverages serve distinct purposes, with energy drinks aiming to boost energy and cognitive performance, and sports drinks designed to prevent dehydration and replenish electrolytes and carbohydrates lost during physical exertion.
Objective: To assess the nutritional quality of energy and sports drinks in Egypt.
Material and Methods: A cross-sectional study assessed the nutrient contents, including energy, sugar, electrolytes, vitamins, and caffeine, of sports and energy drinks available in major supermarkets in Cairo, Alexandria, and Giza, Egypt. Data collection involved photographing all relevant product labels and recording nutritional information. Descriptive statistics and appropriate statistical tests were employed to analyze and compare the nutritional values of energy and sports drinks.
Results: The study analyzed 38 sports drinks and 42 energy drinks. Sports drinks were significantly more expensive than energy drinks, with higher net content and elevated magnesium, potassium, and vitamin C. Energy drinks contained higher concentrations of caffeine, sugars, and vitamins B2, B3, and B6.
Conclusion: Significant nutritional differences exist between sports and energy drinks, reflecting their intended uses. However, these beverages’ high sugar content and calorie loads raise health concerns. Proper labeling, public awareness, and responsible marketing are essential to guide safe consumption practices in Egypt.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Research Report: Definition, Types + [Writing Guide]

One of the reasons for carrying out research is to add to the existing body of knowledge. Therefore, when conducting research, you need to document your processes and findings in a research report.
With a research report, it is easy to outline the findings of your systematic investigation and any gaps needing further inquiry. Knowing how to create a detailed research report will prove useful when you need to conduct research.
What is a Research Report?
A research report is a well-crafted document that outlines the processes, data, and findings of a systematic investigation. It is an important document that serves as a first-hand account of the research process, and it is typically considered an objective and accurate source of information.
In many ways, a research report can be considered as a summary of the research process that clearly highlights findings, recommendations, and other important details. Reading a well-written research report should provide you with all the information you need about the core areas of the research process.
Features of a Research Report
So how do you recognize a research report when you see one? Here are some of the basic features that define a research report.
- It is a detailed presentation of research processes and findings, and it usually includes tables and graphs.
- It is written in a formal language.
- A research report is usually written in the third person.
- It is informative and based on first-hand verifiable information.
- It is formally structured with headings, sections, and bullet points.
- It always includes recommendations for future actions.
Types of Research Report
The research report is classified based on two things; nature of research and target audience.
Nature of Research
- Qualitative Research Report
This is the type of report written for qualitative research . It outlines the methods, processes, and findings of a qualitative method of systematic investigation. In educational research, a qualitative research report provides an opportunity for one to apply his or her knowledge and develop skills in planning and executing qualitative research projects.
A qualitative research report is usually descriptive in nature. Hence, in addition to presenting details of the research process, you must also create a descriptive narrative of the information.
- Quantitative Research Report
A quantitative research report is a type of research report that is written for quantitative research. Quantitative research is a type of systematic investigation that pays attention to numerical or statistical values in a bid to find answers to research questions.
In this type of research report, the researcher presents quantitative data to support the research process and findings. Unlike a qualitative research report that is mainly descriptive, a quantitative research report works with numbers; that is, it is numerical in nature.
Target Audience
Also, a research report can be said to be technical or popular based on the target audience. If you’re dealing with a general audience, you would need to present a popular research report, and if you’re dealing with a specialized audience, you would submit a technical report.
- Technical Research Report
A technical research report is a detailed document that you present after carrying out industry-based research. This report is highly specialized because it provides information for a technical audience; that is, individuals with above-average knowledge in the field of study.
In a technical research report, the researcher is expected to provide specific information about the research process, including statistical analyses and sampling methods. Also, the use of language is highly specialized and filled with jargon.
Examples of technical research reports include legal and medical research reports.
- Popular Research Report
A popular research report is one for a general audience; that is, for individuals who do not necessarily have any knowledge in the field of study. A popular research report aims to make information accessible to everyone.
It is written in very simple language, which makes it easy to understand the findings and recommendations. Examples of popular research reports are the information contained in newspapers and magazines.
Importance of a Research Report
- Knowledge Transfer: As already stated above, one of the reasons for carrying out research is to contribute to the existing body of knowledge, and this is made possible with a research report. A research report serves as a means to effectively communicate the findings of a systematic investigation to all and sundry.
- Identification of Knowledge Gaps: With a research report, you’d be able to identify knowledge gaps for further inquiry. A research report shows what has been done while hinting at other areas needing systematic investigation.
- In market research, a research report would help you understand the market needs and peculiarities at a glance.
- A research report allows you to present information in a precise and concise manner.
- It is time-efficient and practical because, in a research report, you do not have to spend time detailing the findings of your research work in person. You can easily send out the report via email and have stakeholders look at it.
Guide to Writing a Research Report
A lot of detail goes into writing a research report, and getting familiar with the different requirements would help you create the ideal research report. A research report is usually broken down into multiple sections, which allows for a concise presentation of information.
Structure and Example of a Research Report
This is the title of your systematic investigation. Your title should be concise and point to the aims, objectives, and findings of a research report.
- Table of Contents
This is like a compass that makes it easier for readers to navigate the research report.
An abstract is an overview that highlights all important aspects of the research including the research method, data collection process, and research findings. Think of an abstract as a summary of your research report that presents pertinent information in a concise manner.
An abstract is always brief; typically 100-150 words and goes straight to the point. The focus of your research abstract should be the 5Ws and 1H format – What, Where, Why, When, Who and How.
- Introduction
Here, the researcher highlights the aims and objectives of the systematic investigation as well as the problem which the systematic investigation sets out to solve. When writing the report introduction, it is also essential to indicate whether the purposes of the research were achieved or would require more work.
In the introduction section, the researcher specifies the research problem and also outlines the significance of the systematic investigation. Also, the researcher is expected to outline any jargons and terminologies that are contained in the research.
- Literature Review
A literature review is a written survey of existing knowledge in the field of study. In other words, it is the section where you provide an overview and analysis of different research works that are relevant to your systematic investigation.
It highlights existing research knowledge and areas needing further investigation, which your research has sought to fill. At this stage, you can also hint at your research hypothesis and its possible implications for the existing body of knowledge in your field of study.
- An Account of Investigation
This is a detailed account of the research process, including the methodology, sample, and research subjects. Here, you are expected to provide in-depth information on the research process including the data collection and analysis procedures.
In a quantitative research report, you’d need to provide information surveys, questionnaires and other quantitative data collection methods used in your research. In a qualitative research report, you are expected to describe the qualitative data collection methods used in your research including interviews and focus groups.
In this section, you are expected to present the results of the systematic investigation.
This section further explains the findings of the research, earlier outlined. Here, you are expected to present a justification for each outcome and show whether the results are in line with your hypotheses or if other research studies have come up with similar results.
- Conclusions
This is a summary of all the information in the report. It also outlines the significance of the entire study.
- References and Appendices
This section contains a list of all the primary and secondary research sources.
Tips for Writing a Research Report
- Define the Context for the Report
As is obtainable when writing an essay, defining the context for your research report would help you create a detailed yet concise document. This is why you need to create an outline before writing so that you do not miss out on anything.
- Define your Audience
Writing with your audience in mind is essential as it determines the tone of the report. If you’re writing for a general audience, you would want to present the information in a simple and relatable manner. For a specialized audience, you would need to make use of technical and field-specific terms.
- Include Significant Findings
The idea of a research report is to present some sort of abridged version of your systematic investigation. In your report, you should exclude irrelevant information while highlighting only important data and findings.
- Include Illustrations
Your research report should include illustrations and other visual representations of your data. Graphs, pie charts, and relevant images lend additional credibility to your systematic investigation.
- Choose the Right Title
A good research report title is brief, precise, and contains keywords from your research. It should provide a clear idea of your systematic investigation so that readers can grasp the entire focus of your research from the title.
- Proofread the Report
Before publishing the document, ensure that you give it a second look to authenticate the information. If you can, get someone else to go through the report, too, and you can also run it through proofreading and editing software.
How to Gather Research Data for Your Report
- Understand the Problem
Every research aims at solving a specific problem or set of problems, and this should be at the back of your mind when writing your research report. Understanding the problem would help you to filter the information you have and include only important data in your report.
- Know what your report seeks to achieve
This is somewhat similar to the point above because, in some way, the aim of your research report is intertwined with the objectives of your systematic investigation. Identifying the primary purpose of writing a research report would help you to identify and present the required information accordingly.
- Identify your audience
Knowing your target audience plays a crucial role in data collection for a research report. If your research report is specifically for an organization, you would want to present industry-specific information or show how the research findings are relevant to the work that the company does.
- Create Surveys/Questionnaires
A survey is a research method that is used to gather data from a specific group of people through a set of questions. It can be either quantitative or qualitative.
A survey is usually made up of structured questions, and it can be administered online or offline. However, an online survey is a more effective method of research data collection because it helps you save time and gather data with ease.
You can seamlessly create an online questionnaire for your research on Formplus . With the multiple sharing options available in the builder, you would be able to administer your survey to respondents in little or no time.
Formplus also has a report summary too l that you can use to create custom visual reports for your research.
Step-by-step guide on how to create an online questionnaire using Formplus
- Sign into Formplus
In the Formplus builder, you can easily create different online questionnaires for your research by dragging and dropping preferred fields into your form. To access the Formplus builder, you will need to create an account on Formplus.
Once you do this, sign in to your account and click on Create new form to begin.
- Edit Form Title : Click on the field provided to input your form title, for example, “Research Questionnaire.”
- Edit Form : Click on the edit icon to edit the form.
- Add Fields : Drag and drop preferred form fields into your form in the Formplus builder inputs column. There are several field input options for questionnaires in the Formplus builder.
- Edit fields
- Click on “Save”
- Form Customization: With the form customization options in the form builder, you can easily change the outlook of your form and make it more unique and personalized. Formplus allows you to change your form theme, add background images, and even change the font according to your needs.
- Multiple Sharing Options: Formplus offers various form-sharing options, which enables you to share your questionnaire with respondents easily. You can use the direct social media sharing buttons to share your form link to your organization’s social media pages. You can also send out your survey form as email invitations to your research subjects too. If you wish, you can share your form’s QR code or embed it on your organization’s website for easy access.
Conclusion
Always remember that a research report is just as important as the actual systematic investigation because it plays a vital role in communicating research findings to everyone else. This is why you must take care to create a concise document summarizing the process of conducting any research.
In this article, we’ve outlined essential tips to help you create a research report. When writing your report, you should always have the audience at the back of your mind, as this would set the tone for the document.

Connect to Formplus, Get Started Now - It's Free!
- ethnographic research survey
- research report
- research report survey
- busayo.longe

You may also like:
Assessment Tools: Types, Examples & Importance
In this article, you’ll learn about different assessment tools to help you evaluate performance in various contexts

21 Chrome Extensions for Academic Researchers in 2022
In this article, we will discuss a number of chrome extensions you can use to make your research process even seamless
Ethnographic Research: Types, Methods + [Question Examples]
Simple guide on ethnographic research, it types, methods, examples and advantages. Also highlights how to conduct an ethnographic...
How to Write a Problem Statement for your Research
Learn how to write problem statements before commencing any research effort. Learn about its structure and explore examples
Formplus - For Seamless Data Collection
Collect data the right way with a versatile data collection tool. try formplus and transform your work productivity today..
- Academic Skills
- Reading, writing and referencing
Research reports
This resource will help you identify the common elements and basic format of a research report.
Research reports generally follow a similar structure and have common elements, each with a particular purpose. Learn more about each of these elements below.
Common elements of reports
Your title should be brief, topic-specific, and informative, clearly indicating the purpose and scope of your study. Include key words in your title so that search engines can easily access your work. For example: Measurement of water around Station Pier.
An abstract is a concise summary that helps readers to quickly assess the content and direction of your paper. It should be brief, written in a single paragraph and cover: the scope and purpose of your report; an overview of methodology; a summary of the main findings or results; principal conclusions or significance of the findings; and recommendations made.
The information in the abstract must be presented in the same order as it is in your report. The abstract is usually written last when you have developed your arguments and synthesised the results.
The introduction creates the context for your research. It should provide sufficient background to allow the reader to understand and evaluate your study without needing to refer to previous publications. After reading the introduction your reader should understand exactly what your research is about, what you plan to do, why you are undertaking this research and which methods you have used. Introductions generally include:
- The rationale for the present study. Why are you interested in this topic? Why is this topic worth investigating?
- Key terms and definitions.
- An outline of the research questions and hypotheses; the assumptions or propositions that your research will test.
Not all research reports have a separate literature review section. In shorter research reports, the review is usually part of the Introduction.
A literature review is a critical survey of recent relevant research in a particular field. The review should be a selection of carefully organised, focused and relevant literature that develops a narrative ‘story’ about your topic. Your review should answer key questions about the literature:
- What is the current state of knowledge on the topic?
- What differences in approaches / methodologies are there?
- Where are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
- What further research is needed? The review may identify a gap in the literature which provides a rationale for your study and supports your research questions and methodology.
The review is not just a summary of all you have read. Rather, it must develop an argument or a point of view that supports your chosen methodology and research questions.
The purpose of this section is to detail how you conducted your research so that others can understand and replicate your approach.
You need to briefly describe the subjects (if appropriate), any equipment or materials used and the approach taken. If the research method or method of data analysis is commonly used within your field of study, then simply reference the procedure. If, however, your methods are new or controversial then you need to describe them in more detail and provide a rationale for your approach. The methodology is written in the past tense and should be as concise as possible.
This section is a concise, factual summary of your findings, listed under headings appropriate to your research questions. It’s common to use tables and graphics. Raw data or details about the method of statistical analysis used should be included in the Appendices.
Present your results in a consistent manner. For example, if you present the first group of results as percentages, it will be confusing for the reader and difficult to make comparisons of data if later results are presented as fractions or as decimal values.
In general, you won’t discuss your results here. Any analysis of your results usually occurs in the Discussion section.
Notes on visual data representation:
- Graphs and tables may be used to reveal trends in your data, but they must be explained and referred to in adjacent accompanying text.
- Figures and tables do not simply repeat information given in the text: they summarise, amplify or complement it.
- Graphs are always referred to as ‘Figures’, and both axes must be clearly labelled.
- Tables must be numbered, and they must be able to stand-alone or make sense without your reader needing to read all of the accompanying text.
The Discussion responds to the hypothesis or research question. This section is where you interpret your results, account for your findings and explain their significance within the context of other research. Consider the adequacy of your sampling techniques, the scope and long-term implications of your study, any problems with data collection or analysis and any assumptions on which your study was based. This is also the place to discuss any disappointing results and address limitations.
Checklist for the discussion
- To what extent was each hypothesis supported?
- To what extent are your findings validated or supported by other research?
- Were there unexpected variables that affected your results?
- On reflection, was your research method appropriate?
- Can you account for any differences between your results and other studies?
Conclusions in research reports are generally fairly short and should follow on naturally from points raised in the Discussion. In this section you should discuss the significance of your findings. To what extent and in what ways are your findings useful or conclusive? Is further research required? If so, based on your research experience, what suggestions could you make about improvements to the scope or methodology of future studies?
Also, consider the practical implications of your results and any recommendations you could make. For example, if your research is on reading strategies in the primary school classroom, what are the implications of your results for the classroom teacher? What recommendations could you make for teachers?
A Reference List contains all the resources you have cited in your work, while a Bibliography is a wider list containing all the resources you have consulted (but not necessarily cited) in the preparation of your work. It is important to check which of these is required, and the preferred format, style of references and presentation requirements of your own department.
Appendices (singular ‘Appendix’) provide supporting material to your project. Examples of such materials include:
- Relevant letters to participants and organisations (e.g. regarding the ethics or conduct of the project).
- Background reports.
- Detailed calculations.
Different types of data are presented in separate appendices. Each appendix must be titled, labelled with a number or letter, and referred to in the body of the report.
Appendices are placed at the end of a report, and the contents are generally not included in the word count.
Fi nal ti p
While there are many common elements to research reports, it’s always best to double check the exact requirements for your task. You may find that you don’t need some sections, can combine others or have specific requirements about referencing, formatting or word limits.

Looking for one-on-one advice?
Get tailored advice from an Academic Skills Adviser by booking an Individual appointment, or get quick feedback from one of our Academic Writing Mentors via email through our Writing advice service.
Go to Student appointments
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Research Reports: Definition and How to Write Them

Reports are usually spread across a vast horizon of topics but are focused on communicating information about a particular topic and a niche target market. The primary motive of research reports is to convey integral details about a study for marketers to consider while designing new strategies.
Certain events, facts, and other information based on incidents need to be relayed to the people in charge, and creating research reports is the most effective communication tool. Ideal research reports are extremely accurate in the offered information with a clear objective and conclusion. These reports should have a clean and structured format to relay information effectively.
What are Research Reports?
Research reports are recorded data prepared by researchers or statisticians after analyzing the information gathered by conducting organized research, typically in the form of surveys or qualitative methods .
A research report is a reliable source to recount details about a conducted research. It is most often considered to be a true testimony of all the work done to garner specificities of research.
The various sections of a research report are:
- Background/Introduction
- Implemented Methods
- Results based on Analysis
- Deliberation
Learn more: Quantitative Research
Components of Research Reports
Research is imperative for launching a new product/service or a new feature. The markets today are extremely volatile and competitive due to new entrants every day who may or may not provide effective products. An organization needs to make the right decisions at the right time to be relevant in such a market with updated products that suffice customer demands.
The details of a research report may change with the purpose of research but the main components of a report will remain constant. The research approach of the market researcher also influences the style of writing reports. Here are seven main components of a productive research report:
- Research Report Summary: The entire objective along with the overview of research are to be included in a summary which is a couple of paragraphs in length. All the multiple components of the research are explained in brief under the report summary. It should be interesting enough to capture all the key elements of the report.
- Research Introduction: There always is a primary goal that the researcher is trying to achieve through a report. In the introduction section, he/she can cover answers related to this goal and establish a thesis which will be included to strive and answer it in detail. This section should answer an integral question: “What is the current situation of the goal?”. After the research design was conducted, did the organization conclude the goal successfully or they are still a work in progress – provide such details in the introduction part of the research report.
- Research Methodology: This is the most important section of the report where all the important information lies. The readers can gain data for the topic along with analyzing the quality of provided content and the research can also be approved by other market researchers . Thus, this section needs to be highly informative with each aspect of research discussed in detail. Information needs to be expressed in chronological order according to its priority and importance. Researchers should include references in case they gained information from existing techniques.
- Research Results: A short description of the results along with calculations conducted to achieve the goal will form this section of results. Usually, the exposition after data analysis is carried out in the discussion part of the report.
Learn more: Quantitative Data
- Research Discussion: The results are discussed in extreme detail in this section along with a comparative analysis of reports that could probably exist in the same domain. Any abnormality uncovered during research will be deliberated in the discussion section. While writing research reports, the researcher will have to connect the dots on how the results will be applicable in the real world.
- Research References and Conclusion: Conclude all the research findings along with mentioning each and every author, article or any content piece from where references were taken.
Learn more: Qualitative Observation
15 Tips for Writing Research Reports
Writing research reports in the manner can lead to all the efforts going down the drain. Here are 15 tips for writing impactful research reports:
- Prepare the context before starting to write and start from the basics: This was always taught to us in school – be well-prepared before taking a plunge into new topics. The order of survey questions might not be the ideal or most effective order for writing research reports. The idea is to start with a broader topic and work towards a more specific one and focus on a conclusion or support, which a research should support with the facts. The most difficult thing to do in reporting, without a doubt is to start. Start with the title, the introduction, then document the first discoveries and continue from that. Once the marketers have the information well documented, they can write a general conclusion.
- Keep the target audience in mind while selecting a format that is clear, logical and obvious to them: Will the research reports be presented to decision makers or other researchers? What are the general perceptions around that topic? This requires more care and diligence. A researcher will need a significant amount of information to start writing the research report. Be consistent with the wording, the numbering of the annexes and so on. Follow the approved format of the company for the delivery of research reports and demonstrate the integrity of the project with the objectives of the company.
- Have a clear research objective: A researcher should read the entire proposal again, and make sure that the data they provide contributes to the objectives that were raised from the beginning. Remember that speculations are for conversations, not for research reports, if a researcher speculates, they directly question their own research.
- Establish a working model: Each study must have an internal logic, which will have to be established in the report and in the evidence. The researchers’ worst nightmare is to be required to write research reports and realize that key questions were not included.
Learn more: Quantitative Observation
- Gather all the information about the research topic. Who are the competitors of our customers? Talk to other researchers who have studied the subject of research, know the language of the industry. Misuse of the terms can discourage the readers of research reports from reading further.
- Read aloud while writing. While reading the report, if the researcher hears something inappropriate, for example, if they stumble over the words when reading them, surely the reader will too. If the researcher can’t put an idea in a single sentence, then it is very long and they must change it so that the idea is clear to everyone.
- Check grammar and spelling. Without a doubt, good practices help to understand the report. Use verbs in the present tense. Consider using the present tense, which makes the results sound more immediate. Find new words and other ways of saying things. Have fun with the language whenever possible.
- Discuss only the discoveries that are significant. If some data are not really significant, do not mention them. Remember that not everything is truly important or essential within research reports.
Learn more: Qualitative Data
- Try and stick to the survey questions. For example, do not say that the people surveyed “were worried” about an research issue , when there are different degrees of concern.
- The graphs must be clear enough so that they understand themselves. Do not let graphs lead the reader to make mistakes: give them a title, include the indications, the size of the sample, and the correct wording of the question.
- Be clear with messages. A researcher should always write every section of the report with an accuracy of details and language.
- Be creative with titles – Particularly in segmentation studies choose names “that give life to research”. Such names can survive for a long time after the initial investigation.
- Create an effective conclusion: The conclusion in the research reports is the most difficult to write, but it is an incredible opportunity to excel. Make a precise summary. Sometimes it helps to start the conclusion with something specific, then it describes the most important part of the study, and finally, it provides the implications of the conclusions.
- Get a couple more pair of eyes to read the report. Writers have trouble detecting their own mistakes. But they are responsible for what is presented. Ensure it has been approved by colleagues or friends before sending the find draft out.
Learn more: Market Research and Analysis
MORE LIKE THIS

Techaton by QuestionPro: An Amazing Showcase of Tech Brilliance
Jul 3, 2024

Stakeholder Interviews: A Guide to Effective Engagement
Jul 2, 2024

Zero Correlation: Definition, Examples + How to Determine It
Jul 1, 2024

When You Have Something Important to Say, You want to Shout it From the Rooftops
Jun 28, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and Templates
Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and Templates
Table of Contents

Research paper format is an essential aspect of academic writing that plays a crucial role in the communication of research findings . The format of a research paper depends on various factors such as the discipline, style guide, and purpose of the research. It includes guidelines for the structure, citation style, referencing , and other elements of the paper that contribute to its overall presentation and coherence. Adhering to the appropriate research paper format is vital for ensuring that the research is accurately and effectively communicated to the intended audience. In this era of information, it is essential to understand the different research paper formats and their guidelines to communicate research effectively, accurately, and with the required level of detail. This post aims to provide an overview of some of the common research paper formats used in academic writing.
Research Paper Formats
Research Paper Formats are as follows:
- APA (American Psychological Association) format
- MLA (Modern Language Association) format
- Chicago/Turabian style
- IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) format
- AMA (American Medical Association) style
- Harvard style
- Vancouver style
- ACS (American Chemical Society) style
- ASA (American Sociological Association) style
- APSA (American Political Science Association) style
APA (American Psychological Association) Format
Here is a general APA format for a research paper:
- Title Page: The title page should include the title of your paper, your name, and your institutional affiliation. It should also include a running head, which is a shortened version of the title, and a page number in the upper right-hand corner.
- Abstract : The abstract is a brief summary of your paper, typically 150-250 words. It should include the purpose of your research, the main findings, and any implications or conclusions that can be drawn.
- Introduction: The introduction should provide background information on your topic, state the purpose of your research, and present your research question or hypothesis. It should also include a brief literature review that discusses previous research on your topic.
- Methods: The methods section should describe the procedures you used to collect and analyze your data. It should include information on the participants, the materials and instruments used, and the statistical analyses performed.
- Results: The results section should present the findings of your research in a clear and concise manner. Use tables and figures to help illustrate your results.
- Discussion : The discussion section should interpret your results and relate them back to your research question or hypothesis. It should also discuss the implications of your findings and any limitations of your study.
- References : The references section should include a list of all sources cited in your paper. Follow APA formatting guidelines for your citations and references.
Some additional tips for formatting your APA research paper:
- Use 12-point Times New Roman font throughout the paper.
- Double-space all text, including the references.
- Use 1-inch margins on all sides of the page.
- Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches.
- Use a hanging indent for the references (the first line should be flush with the left margin, and all subsequent lines should be indented).
- Number all pages, including the title page and references page, in the upper right-hand corner.
APA Research Paper Format Template
APA Research Paper Format Template is as follows:
Title Page:
- Title of the paper
- Author’s name
- Institutional affiliation
- A brief summary of the main points of the paper, including the research question, methods, findings, and conclusions. The abstract should be no more than 250 words.
Introduction:
- Background information on the topic of the research paper
- Research question or hypothesis
- Significance of the study
- Overview of the research methods and design
- Brief summary of the main findings
- Participants: description of the sample population, including the number of participants and their characteristics (age, gender, ethnicity, etc.)
- Materials: description of any materials used in the study (e.g., survey questions, experimental apparatus)
- Procedure: detailed description of the steps taken to conduct the study
- Presentation of the findings of the study, including statistical analyses if applicable
- Tables and figures may be included to illustrate the results
Discussion:
- Interpretation of the results in light of the research question and hypothesis
- Implications of the study for the field
- Limitations of the study
- Suggestions for future research
References:
- A list of all sources cited in the paper, in APA format
Formatting guidelines:
- Double-spaced
- 12-point font (Times New Roman or Arial)
- 1-inch margins on all sides
- Page numbers in the top right corner
- Headings and subheadings should be used to organize the paper
- The first line of each paragraph should be indented
- Quotations of 40 or more words should be set off in a block quote with no quotation marks
- In-text citations should include the author’s last name and year of publication (e.g., Smith, 2019)
APA Research Paper Format Example
APA Research Paper Format Example is as follows:
The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health
University of XYZ
This study examines the relationship between social media use and mental health among college students. Data was collected through a survey of 500 students at the University of XYZ. Results suggest that social media use is significantly related to symptoms of depression and anxiety, and that the negative effects of social media are greater among frequent users.
Social media has become an increasingly important aspect of modern life, especially among young adults. While social media can have many positive effects, such as connecting people across distances and sharing information, there is growing concern about its impact on mental health. This study aims to examine the relationship between social media use and mental health among college students.
Participants: Participants were 500 college students at the University of XYZ, recruited through online advertisements and flyers posted on campus. Participants ranged in age from 18 to 25, with a mean age of 20.5 years. The sample was 60% female, 40% male, and 5% identified as non-binary or gender non-conforming.
Data was collected through an online survey administered through Qualtrics. The survey consisted of several measures, including the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) for depression symptoms, the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7) for anxiety symptoms, and questions about social media use.
Procedure :
Participants were asked to complete the online survey at their convenience. The survey took approximately 20-30 minutes to complete. Data was analyzed using descriptive statistics, correlations, and multiple regression analysis.
Results indicated that social media use was significantly related to symptoms of depression (r = .32, p < .001) and anxiety (r = .29, p < .001). Regression analysis indicated that frequency of social media use was a significant predictor of both depression symptoms (β = .24, p < .001) and anxiety symptoms (β = .20, p < .001), even when controlling for age, gender, and other relevant factors.
The results of this study suggest that social media use is associated with symptoms of depression and anxiety among college students. The negative effects of social media are greater among frequent users. These findings have important implications for mental health professionals and educators, who should consider addressing the potential negative effects of social media use in their work with young adults.
References :
References should be listed in alphabetical order according to the author’s last name. For example:
- Chou, H. T. G., & Edge, N. (2012). “They are happier and having better lives than I am”: The impact of using Facebook on perceptions of others’ lives. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 15(2), 117-121.
- Twenge, J. M., Joiner, T. E., Rogers, M. L., & Martin, G. N. (2018). Increases in depressive symptoms, suicide-related outcomes, and suicide rates among U.S. adolescents after 2010 and links to increased new media screen time. Clinical Psychological Science, 6(1), 3-17.
Note: This is just a sample Example do not use this in your assignment.
MLA (Modern Language Association) Format
MLA (Modern Language Association) Format is as follows:
- Page Layout : Use 8.5 x 11-inch white paper, with 1-inch margins on all sides. The font should be 12-point Times New Roman or a similar serif font.
- Heading and Title : The first page of your research paper should include a heading and a title. The heading should include your name, your instructor’s name, the course title, and the date. The title should be centered and in title case (capitalizing the first letter of each important word).
- In-Text Citations : Use parenthetical citations to indicate the source of your information. The citation should include the author’s last name and the page number(s) of the source. For example: (Smith 23).
- Works Cited Page : At the end of your paper, include a Works Cited page that lists all the sources you used in your research. Each entry should include the author’s name, the title of the work, the publication information, and the medium of publication.
- Formatting Quotations : Use double quotation marks for short quotations and block quotations for longer quotations. Indent the entire quotation five spaces from the left margin.
- Formatting the Body : Use a clear and readable font and double-space your text throughout. The first line of each paragraph should be indented one-half inch from the left margin.
MLA Research Paper Template
MLA Research Paper Format Template is as follows:
- Use 8.5 x 11 inch white paper.
- Use a 12-point font, such as Times New Roman.
- Use double-spacing throughout the entire paper, including the title page and works cited page.
- Set the margins to 1 inch on all sides.
- Use page numbers in the upper right corner, beginning with the first page of text.
- Include a centered title for the research paper, using title case (capitalizing the first letter of each important word).
- Include your name, instructor’s name, course name, and date in the upper left corner, double-spaced.
In-Text Citations
- When quoting or paraphrasing information from sources, include an in-text citation within the text of your paper.
- Use the author’s last name and the page number in parentheses at the end of the sentence, before the punctuation mark.
- If the author’s name is mentioned in the sentence, only include the page number in parentheses.
Works Cited Page
- List all sources cited in alphabetical order by the author’s last name.
- Each entry should include the author’s name, title of the work, publication information, and medium of publication.
- Use italics for book and journal titles, and quotation marks for article and chapter titles.
- For online sources, include the date of access and the URL.
Here is an example of how the first page of a research paper in MLA format should look:
Headings and Subheadings
- Use headings and subheadings to organize your paper and make it easier to read.
- Use numerals to number your headings and subheadings (e.g. 1, 2, 3), and capitalize the first letter of each word.
- The main heading should be centered and in boldface type, while subheadings should be left-aligned and in italics.
- Use only one space after each period or punctuation mark.
- Use quotation marks to indicate direct quotes from a source.
- If the quote is more than four lines, format it as a block quote, indented one inch from the left margin and without quotation marks.
- Use ellipses (…) to indicate omitted words from a quote, and brackets ([…]) to indicate added words.
Works Cited Examples
- Book: Last Name, First Name. Title of Book. Publisher, Publication Year.
- Journal Article: Last Name, First Name. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal, volume number, issue number, publication date, page numbers.
- Website: Last Name, First Name. “Title of Webpage.” Title of Website, publication date, URL. Accessed date.
Here is an example of how a works cited entry for a book should look:
Smith, John. The Art of Writing Research Papers. Penguin, 2021.
MLA Research Paper Example
MLA Research Paper Format Example is as follows:
Your Professor’s Name
Course Name and Number
Date (in Day Month Year format)
Word Count (not including title page or Works Cited)
Title: The Impact of Video Games on Aggression Levels
Video games have become a popular form of entertainment among people of all ages. However, the impact of video games on aggression levels has been a subject of debate among scholars and researchers. While some argue that video games promote aggression and violent behavior, others argue that there is no clear link between video games and aggression levels. This research paper aims to explore the impact of video games on aggression levels among young adults.
Background:
The debate on the impact of video games on aggression levels has been ongoing for several years. According to the American Psychological Association, exposure to violent media, including video games, can increase aggression levels in children and adolescents. However, some researchers argue that there is no clear evidence to support this claim. Several studies have been conducted to examine the impact of video games on aggression levels, but the results have been mixed.
Methodology:
This research paper used a quantitative research approach to examine the impact of video games on aggression levels among young adults. A sample of 100 young adults between the ages of 18 and 25 was selected for the study. The participants were asked to complete a questionnaire that measured their aggression levels and their video game habits.
The results of the study showed that there was a significant correlation between video game habits and aggression levels among young adults. The participants who reported playing violent video games for more than 5 hours per week had higher aggression levels than those who played less than 5 hours per week. The study also found that male participants were more likely to play violent video games and had higher aggression levels than female participants.
The findings of this study support the claim that video games can increase aggression levels among young adults. However, it is important to note that the study only examined the impact of video games on aggression levels and did not take into account other factors that may contribute to aggressive behavior. It is also important to note that not all video games promote violence and aggression, and some games may have a positive impact on cognitive and social skills.
Conclusion :
In conclusion, this research paper provides evidence to support the claim that video games can increase aggression levels among young adults. However, it is important to conduct further research to examine the impact of video games on other aspects of behavior and to explore the potential benefits of video games. Parents and educators should be aware of the potential impact of video games on aggression levels and should encourage young adults to engage in a variety of activities that promote cognitive and social skills.
Works Cited:
- American Psychological Association. (2017). Violent Video Games: Myths, Facts, and Unanswered Questions. Retrieved from https://www.apa.org/news/press/releases/2017/08/violent-video-games
- Ferguson, C. J. (2015). Do Angry Birds make for angry children? A meta-analysis of video game influences on children’s and adolescents’ aggression, mental health, prosocial behavior, and academic performance. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 10(5), 646-666.
- Gentile, D. A., Swing, E. L., Lim, C. G., & Khoo, A. (2012). Video game playing, attention problems, and impulsiveness: Evidence of bidirectional causality. Psychology of Popular Media Culture, 1(1), 62-70.
- Greitemeyer, T. (2014). Effects of prosocial video games on prosocial behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 106(4), 530-548.
Chicago/Turabian Style
Chicago/Turabian Formate is as follows:
- Margins : Use 1-inch margins on all sides of the paper.
- Font : Use a readable font such as Times New Roman or Arial, and use a 12-point font size.
- Page numbering : Number all pages in the upper right-hand corner, beginning with the first page of text. Use Arabic numerals.
- Title page: Include a title page with the title of the paper, your name, course title and number, instructor’s name, and the date. The title should be centered on the page and in title case (capitalize the first letter of each word).
- Headings: Use headings to organize your paper. The first level of headings should be centered and in boldface or italics. The second level of headings should be left-aligned and in boldface or italics. Use as many levels of headings as necessary to organize your paper.
- In-text citations : Use footnotes or endnotes to cite sources within the text of your paper. The first citation for each source should be a full citation, and subsequent citations can be shortened. Use superscript numbers to indicate footnotes or endnotes.
- Bibliography : Include a bibliography at the end of your paper, listing all sources cited in your paper. The bibliography should be in alphabetical order by the author’s last name, and each entry should include the author’s name, title of the work, publication information, and date of publication.
- Formatting of quotations: Use block quotations for quotations that are longer than four lines. Indent the entire quotation one inch from the left margin, and do not use quotation marks. Single-space the quotation, and double-space between paragraphs.
- Tables and figures: Use tables and figures to present data and illustrations. Number each table and figure sequentially, and provide a brief title for each. Place tables and figures as close as possible to the text that refers to them.
- Spelling and grammar : Use correct spelling and grammar throughout your paper. Proofread carefully for errors.
Chicago/Turabian Research Paper Template
Chicago/Turabian Research Paper Template is as folows:
Title of Paper
Name of Student
Professor’s Name
I. Introduction
A. Background Information
B. Research Question
C. Thesis Statement
II. Literature Review
A. Overview of Existing Literature
B. Analysis of Key Literature
C. Identification of Gaps in Literature
III. Methodology
A. Research Design
B. Data Collection
C. Data Analysis
IV. Results
A. Presentation of Findings
B. Analysis of Findings
C. Discussion of Implications
V. Conclusion
A. Summary of Findings
B. Implications for Future Research
C. Conclusion
VI. References
A. Bibliography
B. In-Text Citations
VII. Appendices (if necessary)
A. Data Tables
C. Additional Supporting Materials
Chicago/Turabian Research Paper Example
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Political Engagement
Name: John Smith
Class: POLS 101
Professor: Dr. Jane Doe
Date: April 8, 2023
I. Introduction:
Social media has become an integral part of our daily lives. People use social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram to connect with friends and family, share their opinions, and stay informed about current events. With the rise of social media, there has been a growing interest in understanding its impact on various aspects of society, including political engagement. In this paper, I will examine the relationship between social media use and political engagement, specifically focusing on how social media influences political participation and political attitudes.
II. Literature Review:
There is a growing body of literature on the impact of social media on political engagement. Some scholars argue that social media has a positive effect on political participation by providing new channels for political communication and mobilization (Delli Carpini & Keeter, 1996; Putnam, 2000). Others, however, suggest that social media can have a negative impact on political engagement by creating filter bubbles that reinforce existing beliefs and discourage political dialogue (Pariser, 2011; Sunstein, 2001).
III. Methodology:
To examine the relationship between social media use and political engagement, I conducted a survey of 500 college students. The survey included questions about social media use, political participation, and political attitudes. The data was analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Iv. Results:
The results of the survey indicate that social media use is positively associated with political participation. Specifically, respondents who reported using social media to discuss politics were more likely to have participated in a political campaign, attended a political rally, or contacted a political representative. Additionally, social media use was found to be associated with more positive attitudes towards political engagement, such as increased trust in government and belief in the effectiveness of political action.
V. Conclusion:
The findings of this study suggest that social media has a positive impact on political engagement, by providing new opportunities for political communication and mobilization. However, there is also a need for caution, as social media can also create filter bubbles that reinforce existing beliefs and discourage political dialogue. Future research should continue to explore the complex relationship between social media and political engagement, and develop strategies to harness the potential benefits of social media while mitigating its potential negative effects.
Vii. References:
- Delli Carpini, M. X., & Keeter, S. (1996). What Americans know about politics and why it matters. Yale University Press.
- Pariser, E. (2011). The filter bubble: What the Internet is hiding from you. Penguin.
- Putnam, R. D. (2000). Bowling alone: The collapse and revival of American community. Simon & Schuster.
- Sunstein, C. R. (2001). Republic.com. Princeton University Press.
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) Format
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) Research Paper Format is as follows:
- Title : A concise and informative title that accurately reflects the content of the paper.
- Abstract : A brief summary of the paper, typically no more than 250 words, that includes the purpose of the study, the methods used, the key findings, and the main conclusions.
- Introduction : An overview of the background, context, and motivation for the research, including a clear statement of the problem being addressed and the objectives of the study.
- Literature review: A critical analysis of the relevant research and scholarship on the topic, including a discussion of any gaps or limitations in the existing literature.
- Methodology : A detailed description of the methods used to collect and analyze data, including any experiments or simulations, data collection instruments or procedures, and statistical analyses.
- Results : A clear and concise presentation of the findings, including any relevant tables, graphs, or figures.
- Discussion : A detailed interpretation of the results, including a comparison of the findings with previous research, a discussion of the implications of the results, and any recommendations for future research.
- Conclusion : A summary of the key findings and main conclusions of the study.
- References : A list of all sources cited in the paper, formatted according to IEEE guidelines.
In addition to these elements, an IEEE research paper should also follow certain formatting guidelines, including using 12-point font, double-spaced text, and numbered headings and subheadings. Additionally, any tables, figures, or equations should be clearly labeled and referenced in the text.
AMA (American Medical Association) Style
AMA (American Medical Association) Style Research Paper Format:
- Title Page: This page includes the title of the paper, the author’s name, institutional affiliation, and any acknowledgments or disclaimers.
- Abstract: The abstract is a brief summary of the paper that outlines the purpose, methods, results, and conclusions of the study. It is typically limited to 250 words or less.
- Introduction: The introduction provides a background of the research problem, defines the research question, and outlines the objectives and hypotheses of the study.
- Methods: The methods section describes the research design, participants, procedures, and instruments used to collect and analyze data.
- Results: The results section presents the findings of the study in a clear and concise manner, using graphs, tables, and charts where appropriate.
- Discussion: The discussion section interprets the results, explains their significance, and relates them to previous research in the field.
- Conclusion: The conclusion summarizes the main points of the paper, discusses the implications of the findings, and suggests future research directions.
- References: The reference list includes all sources cited in the paper, listed in alphabetical order by author’s last name.
In addition to these sections, the AMA format requires that authors follow specific guidelines for citing sources in the text and formatting their references. The AMA style uses a superscript number system for in-text citations and provides specific formats for different types of sources, such as books, journal articles, and websites.
Harvard Style
Harvard Style Research Paper format is as follows:
- Title page: This should include the title of your paper, your name, the name of your institution, and the date of submission.
- Abstract : This is a brief summary of your paper, usually no more than 250 words. It should outline the main points of your research and highlight your findings.
- Introduction : This section should introduce your research topic, provide background information, and outline your research question or thesis statement.
- Literature review: This section should review the relevant literature on your topic, including previous research studies, academic articles, and other sources.
- Methodology : This section should describe the methods you used to conduct your research, including any data collection methods, research instruments, and sampling techniques.
- Results : This section should present your findings in a clear and concise manner, using tables, graphs, and other visual aids if necessary.
- Discussion : This section should interpret your findings and relate them to the broader research question or thesis statement. You should also discuss the implications of your research and suggest areas for future study.
- Conclusion : This section should summarize your main findings and provide a final statement on the significance of your research.
- References : This is a list of all the sources you cited in your paper, presented in alphabetical order by author name. Each citation should include the author’s name, the title of the source, the publication date, and other relevant information.
In addition to these sections, a Harvard Style research paper may also include a table of contents, appendices, and other supplementary materials as needed. It is important to follow the specific formatting guidelines provided by your instructor or academic institution when preparing your research paper in Harvard Style.
Vancouver Style
Vancouver Style Research Paper format is as follows:
The Vancouver citation style is commonly used in the biomedical sciences and is known for its use of numbered references. Here is a basic format for a research paper using the Vancouver citation style:
- Title page: Include the title of your paper, your name, the name of your institution, and the date.
- Abstract : This is a brief summary of your research paper, usually no more than 250 words.
- Introduction : Provide some background information on your topic and state the purpose of your research.
- Methods : Describe the methods you used to conduct your research, including the study design, data collection, and statistical analysis.
- Results : Present your findings in a clear and concise manner, using tables and figures as needed.
- Discussion : Interpret your results and explain their significance. Also, discuss any limitations of your study and suggest directions for future research.
- References : List all of the sources you cited in your paper in numerical order. Each reference should include the author’s name, the title of the article or book, the name of the journal or publisher, the year of publication, and the page numbers.
ACS (American Chemical Society) Style
ACS (American Chemical Society) Style Research Paper format is as follows:
The American Chemical Society (ACS) Style is a citation style commonly used in chemistry and related fields. When formatting a research paper in ACS Style, here are some guidelines to follow:
- Paper Size and Margins : Use standard 8.5″ x 11″ paper with 1-inch margins on all sides.
- Font: Use a 12-point serif font (such as Times New Roman) for the main text. The title should be in bold and a larger font size.
- Title Page : The title page should include the title of the paper, the authors’ names and affiliations, and the date of submission. The title should be centered on the page and written in bold font. The authors’ names should be centered below the title, followed by their affiliations and the date.
- Abstract : The abstract should be a brief summary of the paper, no more than 250 words. It should be on a separate page and include the title of the paper, the authors’ names and affiliations, and the text of the abstract.
- Main Text : The main text should be organized into sections with headings that clearly indicate the content of each section. The introduction should provide background information and state the research question or hypothesis. The methods section should describe the procedures used in the study. The results section should present the findings of the study, and the discussion section should interpret the results and provide conclusions.
- References: Use the ACS Style guide to format the references cited in the paper. In-text citations should be numbered sequentially throughout the text and listed in numerical order at the end of the paper.
- Figures and Tables: Figures and tables should be numbered sequentially and referenced in the text. Each should have a descriptive caption that explains its content. Figures should be submitted in a high-quality electronic format.
- Supporting Information: Additional information such as data, graphs, and videos may be included as supporting information. This should be included in a separate file and referenced in the main text.
- Acknowledgments : Acknowledge any funding sources or individuals who contributed to the research.
ASA (American Sociological Association) Style
ASA (American Sociological Association) Style Research Paper format is as follows:
- Title Page: The title page of an ASA style research paper should include the title of the paper, the author’s name, and the institutional affiliation. The title should be centered and should be in title case (the first letter of each major word should be capitalized).
- Abstract: An abstract is a brief summary of the paper that should appear on a separate page immediately following the title page. The abstract should be no more than 200 words in length and should summarize the main points of the paper.
- Main Body: The main body of the paper should begin on a new page following the abstract page. The paper should be double-spaced, with 1-inch margins on all sides, and should be written in 12-point Times New Roman font. The main body of the paper should include an introduction, a literature review, a methodology section, results, and a discussion.
- References : The reference section should appear on a separate page at the end of the paper. All sources cited in the paper should be listed in alphabetical order by the author’s last name. Each reference should include the author’s name, the title of the work, the publication information, and the date of publication.
- Appendices : Appendices are optional and should only be included if they contain information that is relevant to the study but too lengthy to be included in the main body of the paper. If you include appendices, each one should be labeled with a letter (e.g., Appendix A, Appendix B, etc.) and should be referenced in the main body of the paper.
APSA (American Political Science Association) Style
APSA (American Political Science Association) Style Research Paper format is as follows:
- Title Page: The title page should include the title of the paper, the author’s name, the name of the course or instructor, and the date.
- Abstract : An abstract is typically not required in APSA style papers, but if one is included, it should be brief and summarize the main points of the paper.
- Introduction : The introduction should provide an overview of the research topic, the research question, and the main argument or thesis of the paper.
- Literature Review : The literature review should summarize the existing research on the topic and provide a context for the research question.
- Methods : The methods section should describe the research methods used in the paper, including data collection and analysis.
- Results : The results section should present the findings of the research.
- Discussion : The discussion section should interpret the results and connect them back to the research question and argument.
- Conclusion : The conclusion should summarize the main findings and implications of the research.
- References : The reference list should include all sources cited in the paper, formatted according to APSA style guidelines.
In-text citations in APSA style use parenthetical citation, which includes the author’s last name, publication year, and page number(s) if applicable. For example, (Smith 2010, 25).
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

APA Research Paper Format – Example, Sample and...

Informed Consent in Research – Types, Templates...

Scope of the Research – Writing Guide and...

Research Objectives – Types, Examples and...

Figures in Research Paper – Examples and Guide

Implications in Research – Types, Examples and...
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide
Published on September 24, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on March 27, 2023.

The introduction to a research paper is where you set up your topic and approach for the reader. It has several key goals:
- Present your topic and get the reader interested
- Provide background or summarize existing research
- Position your own approach
- Detail your specific research problem and problem statement
- Give an overview of the paper’s structure
The introduction looks slightly different depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or constructs an argument by engaging with a variety of sources.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: introduce your topic, step 2: describe the background, step 3: establish your research problem, step 4: specify your objective(s), step 5: map out your paper, research paper introduction examples, frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
The first job of the introduction is to tell the reader what your topic is and why it’s interesting or important. This is generally accomplished with a strong opening hook.
The hook is a striking opening sentence that clearly conveys the relevance of your topic. Think of an interesting fact or statistic, a strong statement, a question, or a brief anecdote that will get the reader wondering about your topic.
For example, the following could be an effective hook for an argumentative paper about the environmental impact of cattle farming:
A more empirical paper investigating the relationship of Instagram use with body image issues in adolescent girls might use the following hook:
Don’t feel that your hook necessarily has to be deeply impressive or creative. Clarity and relevance are still more important than catchiness. The key thing is to guide the reader into your topic and situate your ideas.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

This part of the introduction differs depending on what approach your paper is taking.
In a more argumentative paper, you’ll explore some general background here. In a more empirical paper, this is the place to review previous research and establish how yours fits in.
Argumentative paper: Background information
After you’ve caught your reader’s attention, specify a bit more, providing context and narrowing down your topic.
Provide only the most relevant background information. The introduction isn’t the place to get too in-depth; if more background is essential to your paper, it can appear in the body .
Empirical paper: Describing previous research
For a paper describing original research, you’ll instead provide an overview of the most relevant research that has already been conducted. This is a sort of miniature literature review —a sketch of the current state of research into your topic, boiled down to a few sentences.
This should be informed by genuine engagement with the literature. Your search can be less extensive than in a full literature review, but a clear sense of the relevant research is crucial to inform your own work.
Begin by establishing the kinds of research that have been done, and end with limitations or gaps in the research that you intend to respond to.
The next step is to clarify how your own research fits in and what problem it addresses.
Argumentative paper: Emphasize importance
In an argumentative research paper, you can simply state the problem you intend to discuss, and what is original or important about your argument.
Empirical paper: Relate to the literature
In an empirical research paper, try to lead into the problem on the basis of your discussion of the literature. Think in terms of these questions:
- What research gap is your work intended to fill?
- What limitations in previous work does it address?
- What contribution to knowledge does it make?
You can make the connection between your problem and the existing research using phrases like the following.
| Although has been studied in detail, insufficient attention has been paid to . | You will address a previously overlooked aspect of your topic. |
| The implications of study deserve to be explored further. | You will build on something suggested by a previous study, exploring it in greater depth. |
| It is generally assumed that . However, this paper suggests that … | You will depart from the consensus on your topic, establishing a new position. |
Now you’ll get into the specifics of what you intend to find out or express in your research paper.
The way you frame your research objectives varies. An argumentative paper presents a thesis statement, while an empirical paper generally poses a research question (sometimes with a hypothesis as to the answer).
Argumentative paper: Thesis statement
The thesis statement expresses the position that the rest of the paper will present evidence and arguments for. It can be presented in one or two sentences, and should state your position clearly and directly, without providing specific arguments for it at this point.
Empirical paper: Research question and hypothesis
The research question is the question you want to answer in an empirical research paper.
Present your research question clearly and directly, with a minimum of discussion at this point. The rest of the paper will be taken up with discussing and investigating this question; here you just need to express it.
A research question can be framed either directly or indirectly.
- This study set out to answer the following question: What effects does daily use of Instagram have on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls?
- We investigated the effects of daily Instagram use on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls.
If your research involved testing hypotheses , these should be stated along with your research question. They are usually presented in the past tense, since the hypothesis will already have been tested by the time you are writing up your paper.
For example, the following hypothesis might respond to the research question above:
Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
The final part of the introduction is often dedicated to a brief overview of the rest of the paper.
In a paper structured using the standard scientific “introduction, methods, results, discussion” format, this isn’t always necessary. But if your paper is structured in a less predictable way, it’s important to describe the shape of it for the reader.
If included, the overview should be concise, direct, and written in the present tense.
- This paper will first discuss several examples of survey-based research into adolescent social media use, then will go on to …
- This paper first discusses several examples of survey-based research into adolescent social media use, then goes on to …
Full examples of research paper introductions are shown in the tabs below: one for an argumentative paper, the other for an empirical paper.
- Argumentative paper
- Empirical paper
Are cows responsible for climate change? A recent study (RIVM, 2019) shows that cattle farmers account for two thirds of agricultural nitrogen emissions in the Netherlands. These emissions result from nitrogen in manure, which can degrade into ammonia and enter the atmosphere. The study’s calculations show that agriculture is the main source of nitrogen pollution, accounting for 46% of the country’s total emissions. By comparison, road traffic and households are responsible for 6.1% each, the industrial sector for 1%. While efforts are being made to mitigate these emissions, policymakers are reluctant to reckon with the scale of the problem. The approach presented here is a radical one, but commensurate with the issue. This paper argues that the Dutch government must stimulate and subsidize livestock farmers, especially cattle farmers, to transition to sustainable vegetable farming. It first establishes the inadequacy of current mitigation measures, then discusses the various advantages of the results proposed, and finally addresses potential objections to the plan on economic grounds.
The rise of social media has been accompanied by a sharp increase in the prevalence of body image issues among women and girls. This correlation has received significant academic attention: Various empirical studies have been conducted into Facebook usage among adolescent girls (Tiggermann & Slater, 2013; Meier & Gray, 2014). These studies have consistently found that the visual and interactive aspects of the platform have the greatest influence on body image issues. Despite this, highly visual social media (HVSM) such as Instagram have yet to be robustly researched. This paper sets out to address this research gap. We investigated the effects of daily Instagram use on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls. It was hypothesized that daily Instagram use would be associated with an increase in body image concerns and a decrease in self-esteem ratings.
The introduction of a research paper includes several key elements:
- A hook to catch the reader’s interest
- Relevant background on the topic
- Details of your research problem
and your problem statement
- A thesis statement or research question
- Sometimes an overview of the paper
Don’t feel that you have to write the introduction first. The introduction is often one of the last parts of the research paper you’ll write, along with the conclusion.
This is because it can be easier to introduce your paper once you’ve already written the body ; you may not have the clearest idea of your arguments until you’ve written them, and things can change during the writing process .
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis —a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, March 27). Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved July 4, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-paper/research-paper-introduction/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, writing a research paper conclusion | step-by-step guide, research paper format | apa, mla, & chicago templates, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
How to format a research paper
Last updated
7 February 2023
Reviewed by
Miroslav Damyanov
Short on time? Get an AI generated summary of this article instead
Writing a research paper can be daunting if you’re not experienced with the process. Getting the proper format is one of the most challenging aspects of the task. Reviewers will immediately dismiss a paper that doesn't comply with standard formatting, regardless of the valuable content it contains.
In this article, we'll delve into the essential characteristics of a research paper, including the proper formatting.
Make research less tedious
Dovetail streamlines research to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- What is a research paper?
A research paper is a document that provides a thorough analysis of a topic , usually for an academic institution or professional organization. A research paper may be of any length, but they are typically 2,000–10,000 words.
Unlike less formal papers, such as articles or essays, empirical evidence and data are key to research papers. In addition to students handing in papers, scientists, attorneys, medical researchers, and independent scholars may need to produce research papers.
People typically write research papers to prove a particular point or make an argument. This could support or disprove a theoretical point, legal case, scientific theory, or an existing piece of research on any topic.
One of the distinguishing characteristics of research papers is that they contain citations to prior research. Citing sources using the correct format is essential for creating a legitimate research paper.
- Top considerations for writing a research paper
To write a research paper, you must consider several factors. Fields such as the sciences, humanities, and technical professions have certain criteria for writing research papers.
You’ll write a research paper using one of several types of formatting. These include APA, MLA, and CMOS styles, which we’ll cover in detail to guide you on citations and other formatting rules.
Specific requirements of the assignment
If the paper is for a college, university, or any specific organization, they’ll give you certain requirements, such as the range of topics, length, and formatting requirements.
You should study the specifics of the assignment carefully, as these will override more general guidelines you may find elsewhere. If you're writing for a particular professor, they may ask for single or double spacing or a certain citation style.
- Components of a research paper
Here are the basic steps to writing a quality research paper, assuming you've chosen your topic and considered the requirements of the paper. Depending on the specific conditions of the paper you're writing, you may need the following elements:
Thesis statement
The thesis statement provides a blueprint for the paper. It conveys the theme and purpose of the paper. It also informs you and readers what your paper will argue and the type of research it will contain. As you write the paper, you can refer to the thesis statement to help you decide whether or not to include certain items.
Most research papers require an abstract as well as a thesis. While the thesis is a short (usually a single sentence) summary of the work, an abstract contains more detail. Many papers use the IMRaD structure for the abstract, especially in scientific fields. This consists of four elements:
Introduction : Summarize the purpose of the paper
Methods : Describe the research methods (e.g., collecting data , interviews , field research)
Results: Summarize your conclusions.
Discussion: Discuss the implications of your research. Mention any significant limitations to your approach and suggest areas for further research.
The thesis and abstract come at the beginning of a paper, but you should write them after completing the paper. This approach ensures a clear idea of your main topic and argument, which can evolve as you write the paper.
Table of contents
Like most nonfiction books, a research paper usually includes a table of contents.
Tables, charts, and illustrations
If your paper contains multiple tables, charts, illustrations, or other graphics, you can create a list of these.
Works cited or reference page
This page lists all the works you cited in your paper. For MLA and APA styles, you will use in-text citations in the body of the paper. For Chicago (CMOS) style, you'll use footnotes.
Bibliography
While you use a reference page to note all cited papers, a bibliography lists all the works you consulted in your research, even if you don't specifically cite them.
While references are essential, a bibliography is optional but usually advisable to demonstrate the breadth of your research.
Dedication and acknowledgments
You may include a dedication or acknowledgments at the beginning of the paper directly after the title page and before the abstract.
- Steps for writing a research paper
These are the most critical steps for researching, writing, and formatting a research paper:
Create an outline
The outline is not part of the published paper; it’s for your use. An outline makes it easier to structure the paper, ensuring you include all necessary points and research.
Here you can list all topics and subtopics that will support your argument. When doing your research, you can refer to the outline to ensure you include everything.
Gather research
Solid research is the hallmark of a research paper. In addition to accumulating research, you need to present it clearly. However, gathering research is one of the first tasks. If you compile each piece of research correctly, it will be easier to format the paper correctly. You want to avoid having to go back and look up information constantly.
Start by skimming potentially useful sources and putting them aside for later use. Reading each source thoroughly at this stage will be time-consuming and slow your progress. You can thoroughly review the sources to decide what to include and discard later. At this stage, note essential information such as names, dates, page numbers, and website links. Citing sources will be easier when you’ve written all the information down.
Be aware of the quality of your sources. A research paper should reference scholarly, academic, or scientific journals. It’s vital to understand the difference between primary and secondary sources.
A primary source is an original, firsthand account of a topic. A secondary source is someone else covering the topic, as in a popular article or interview. While you may include secondary sources, your paper should also include primary research . Online research can be convenient, but you need to be extra careful when assessing the quality of your sources.
Write the first draft
Create a first draft where you put together all your research and address the topic described in your thesis and abstract.
Edit and format the paper
Proofread, edit, and make any necessary adjustments and improvements to the first draft. List your citations as described below. Ensure your thesis and abstract describe your research accurately.
- Formatting a research paper: MLA, APA, and CMOS styles
There are several popular formats for research papers: MLA (Modern Language Association) and APA (American Psychological Association). Certain academic papers use CMOS (Chicago Manual of Style). Other formats may apply to particular fields.
For example, medical research may use AMA (American Medical Association) formatting and IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) for particular technical papers. The following are the guidelines and examples of the most popular formats:
The humanities typically use MLA format, including literature, history, and culture. Look over examples of papers created in MLA format . Here are the main rules to keep in mind:
Double-spaced lines.
Indent new paragraphs 1/2 inch.
Title case for headings, where all major words are capitalized, as in "How to Write a Research Paper."
Use a popular font such as Times New Roman. This applies to all formatting styles.
Use one-inch margins on all sides.
Number sections of the paper using Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, etc.).
Use a running head for each page on the upper right-hand corner, which consists of your last name and the page number.
Use an in-text citation within the text, using the author's last name followed by the page number: "Anything worth dying for is certainly worth living for" (Heller 155).
On the citations page, list the full name, book or periodical, and other information. For MLA, you will not need footnotes, only in-text citations.
List citations in alphabetical order on a separate page at the end of the paper entitled “Works Cited.”
Continuing with the above example from Heller, the listing would be: Heller, Joseph. Catch-22, Simon & Schuster, 1961.
For a periodical, the format is "Thompson, Hunter S. "The Kentucky Derby is Decadent and Depraved" Scanlon's, June 1970."
Use title case for source titles, as in "On the Origin of Species."
The sciences typically use APA format, including physical sciences such as physics and social sciences such as psychology. Simply Psychology provides examples of APA formatting . The following are the most important rules of the APA format.
Begin the paper with a title page, which is not required for MLA.
Use double-line spacing.
Use a running head for each page in the upper right-hand corner, which consists of the paper's title in capital letters followed by the page number.
The citations page at the end should be titled "References."
In-text citations should include the publication date: (Smith, 1999, p. 50). Note also that there's a "p" for "page," whereas in MLA, you write the page number without a "p."
As with MLA, use title case for headings, as in "Most Popular Treatments for Cognitive Disorders."
Use sentence case for titles of sources, as in "History of the decline and fall of the Roman empire." Note "Roman" starts with a capital because it's a proper noun.
When citing in-text references, use the author's last name and the first and middle initials.
Always use the Oxford comma. This comma goes before the words "or" and "and" in a list. For example, "At the store, I bought oranges, paper towels, and pasta."
CMOS formatting
Book publishers and many academic papers use CMOS formatting based on the Chicago Manual of Style. CMOS is also called Turabian, named after Kate L. Turabian, who wrote the first manual for this style. Here are examples of CMOS style formatting and citations.
Include an unnumbered title page.
Place page numbers on the upper right-hand corner of the page. Do not list your name or the paper's title as you would for MLA or APA styles.
Use title case for both headings and sources (same as MLA).
Unlike MLA and APA, the Chicago style uses footnotes for citations. Use a superscript for footnotes: "Smith argues against Jones' theory¹.” Footnotes may appear at the bottom of the page or the end of the document.
CMOS supports both short notes and full notes. In most cases, you'll use the full note: "Michael Pollan, The Omnivore's Dilemma: A Natural History of Four Meals (New York: Penguin, 2006), 76." For further references to the same source, use a short note: " Pollan, Omnivore's Dilemma, 45." The requirements of some papers may specify using only short notes for all footnotes.
- General guidelines for writing and formatting research papers
Keep these guidelines in mind for all types of research papers:
Initial formatting
As you create your first draft, don't worry about formatting. If you try to format it perfectly as you write the paper, it will be difficult to progress and develop a flow of thought. With the first draft, you don't have to be concerned about ordering the sections. You can rearrange headings and sections later.
Citation tools
Use automation tools for citations . Some useful tools make citations easier by automatically generating a citation list and bibliography. Many work with APA, MLA, and CMOS styles.
Check for plagiarism
Use a plagiarism detector to make sure your paper isn't unintentionally plagiarizing. There are many free and paid plagiarism checkers online, such as Grammarly.
Proofread your work
Do several rounds of editing and proofreading. Editing is necessary for any type of writing, but you’ll need to revisit several distinct areas with a research paper:
Check for spelling and grammatical errors.
Read the paper to make sure it's well-argued and that you’ve organized it properly.
Check that you’ve correctly formatted citations. It's easy to make errors, such as incorrect numbering of footnotes (e.g., Chicago style) or forgetting to include a source on your citations page.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 6 February 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 7 March 2023
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
- Design for Business
- Most Recent
- Presentations
- Infographics
- Data Visualizations
- Forms and Surveys
- Video & Animation
- Case Studies
- Digital Marketing
- Design Inspiration
- Visual Thinking
- Product Updates
- Visme Webinars
- Artificial Intelligence

Report Writing Format with Templates and Sample Report

Written by: Orana Velarde

If you’re probably wondering how to write a good report, you’re not alone. Many individuals face difficulties when it comes to report writing, as it requires a specific format and structure that can be confusing to navigate.
With so many types of reports - sales reports , marketing reports , school reports, social media reports and more, how do you know the best structure and organize your thoughts or data that would positively reflect your work?
It all lies in following the right report writing format. With the right format, you’ll be able to write your report with guidelines and make it easy to read and understand and make it easier for you to write as well.
Just as there are different types of reports, there are also different report formats and ways to deliver them. In this article, we’ll walk you through the best report writing formats, examples of reports, report layouts and templates for report writing.
Here's a short selection of 6 easy-to-edit report templates you can edit, share and download with Visme. View more templates below:

Table of Contents
6 types of reports, the ultimate report writing format, top report writing tips, how to write a report, sample report in standard report writing format, report writing format faqs.
- A report is unlike an essay, blog post or journalistic article. The main idea of a report is to present facts about a specific topic, situation, or event. It should always be in a clear and concise way.
- There are six main types of reports: annual reports, weekly reports, project reports, sales and marketing reports, research reports and academic reports.
- A report writing format includes a title, table of contents, summary, introduction, body, conclusion, recommendations and appendices.
- Top report writing tips include writing a report outline, creating the body of the report before the introduction or conclusion, sticking to facts, and keeping your appendix at a reasonable size.
- Visme offers not only hundreds of pre-made report templates but an initiative online report maker to provide you with everything you need to create high-quality reports for any niche, topic or industry.
There are six main types of reports you might encounter based on your goal or niche. In this section we’ll highlight and showcase what these reports are along with reports writing samples, each populated with a similar reporting writing format to what we'll cover further in this article.
1. Annual Reports
The first type of report we'll cover is an annual report . This type of company report format typically rounds up a business's year of progress and performance to let supervisors and team members know what they've accomplished.
It can include anything from website analytics to sales profits, depending on who the report is meant for.

2. Weekly Reports
One report that is helpful to provide your team is a weekly report based on your progress in various projects and goals. This can be a simple one-pager, or a more in-depth report with specific updates.

3. Project Reports
Keep clients and team members up-to-date on the status of various projects you're working on by providing them with a project report. This can include a timeline of your report progress and the deadline for each segment to keep everyone on the same page.

4. Sales/Marketing Reports
It's essential to keep your team updated on how your sales and/or marketing strategies are going. Put together graphs showing profit margins, increases in engagement and more.
These types of reports are also a great way to determine whether your strategies are working or if they need some tweaking in the future.

5. Research Report
Sometimes if you need to do some in-depth research, the best way to present that information is with a research report. Whether it's scientific findings, data and statistics from a study, etc., a research report is a great way to share your results.
For the visuals in your research report, Visme offers millions of free stock photos . But if you can’t find what you need, or are looking for something out of the box, try the Visme AI image generator . Prompt the AI tool to quickly create an image that matches your research, your brand and your report.

6. Academic Report
An academic report is one created for a class, often in a graduate or undergraduate university. This report format follows a formal writing style and dives into a topic related to the student's academic studies.

For more report examples you can learn from, check out our guide on Report Examples With Sample Templates .
Now we're getting to the good part — the ultimate report writing format. While this may vary based on the data and information you pull, it provides enough leeway for you to follow standard report formats.
Keep in mind that good report writing depends on first writing a report outline to start organizing the content in the best way possible.
A standard report format goes a little something like this:
- Title: A clear and concise report title.
- Table of Contents: A page dedicated to the contents of your report.
- Summary: An overview of your entire report — you'll need to wait until you've completed the full report to write this section.
- Introduction: Introduce your report topic and what readers will find throughout the pages.
- Body: The longest section of your report — compile all of your information and use data visualization to help present it.
- Conclusion: Different from the summary, this concludes the report body and summarizes all of your findings.
- Recommendations: A set of recommended goals or steps to complete with the information provided in this report.
- Appendices: A list of your sources used to compile the information in your report.
Each of these eight elements ensures that you leave no stone unturned and that your reader knows exactly what they're learning in your report and how you gathered this information.
Your next step is to get started with an outline. At each point of the outline, use one or two sentences to describe what will go in there. It doesn’t need to say much, just an idea for you to follow later. Input some design ideas for the overall design and report layout as well.
For example, in the Table of Contents section, simply add that you want it to only cover one page or slide, make a note if you’d like to add the pages for only the main sections or maybe also the subsections.
In the Appendices section, list all the links to the sources you used and add on as you do more research. Every source you reference in your report must be listed here.
The most important part of your outline is the Body section. In there, create an internal outline of sections and subsections that you can follow later when writing.

After you’ve drafted the outline, it’s time to put together all of the content into the report. The outline we provided above is the only report writing format you’ll ever need. You can add sections if needed but don’t take any away.
Let’s take a look at every section in detail.

Create your own Report with this easy-to-edit template! Edit and Download
The title of your report should be clear in its wording. It must say exactly what the report is about. Remember that this isn’t a novel. Include a subtitle if necessary, making sure the font size of each subtitle is smaller than the title.
In terms of design , your title can be designed as an inviting cover page. There needs to be a clear hierarchy in how the title looks.
On your title or cover page , be sure to include the following:
- Report title
- Report subtitle (if necessary)
- Author of the report
- Who the report is meant for
- Date the report was written
If you’re having trouble coming up with an interesting title or report content, you can get some help from the Visme AI Writer . Describe your report in the text prompt and ask the AI to write a few optional titles. If the first results aren’t to your liking, ask it to do some edits until you have just what you need.

Always leave the Table of Contents page until the end. After all, you can’t write a table of contents if you don’t know all of your page numbers yet.
However, if your Body outline already has each of your section and subsection titles defined, you can add those to the contents and leave the numbering for later.
Having a Table of Content pages makes it easy for your readers to find the information they're most interested in quickly and easily, improving overall readability. So you absolutely do not want to skip this step.

Likewise, the summary (also known as the abstract) of the report is best done after you’ve finished writing the report. You can draft a summary at the beginning to help guide your work, but you’ll definitely want to revisit it at the end. When you do, try using different paraphrasing techniques to ensure that you're not using repetitive phrases already present throughout the report.
A summary is a blurb of the entire report . It must include the purpose, the process and a snippet of the resolution. This should be no longer than a single paragraph or two.
Alternatively, if your report is data-heavy, the summary can also be a detail report where you share detailed data. Plus, you can add a hyperlink to further data analysis regarding what you’re reporting about.
Introduction

In the introduction, state what the report is about and why it has been created. Depending on the length of your report, the introduction format could range from one single paragraph to an entire page long.
For example, one paragraph is enough for a social media report introduction while an entire page would be more suitable for an annual report .
Take this time to introduce why your topic is so important, especially if it's a research report. You need to focus on why your readers should care about what you have uncovered.

The body of your report is where all the information is put together and will be the longest section of your report. This will likely span several (anywhere from 5-50) pages. Follow your initial outline to maintain consistent flow in the content creation. Write the body content as sections and subsections.
Furthermore, use bullet points and data visualization as visual cues . These will help your audience to better understand the content of your report.
Check out this video from Visme for some tips on visualizing all that data!

Close your report with a well-crafted conclusion . Formulate it as a brief summary of what was covered within the report, and be sure to include a mention to the recommendations section and the resources in the appendix.
This section should never bring new information to the table — instead, it should simply summarize all of the findings you've already mentioned into one concise final section.
Recommendations

Craft the recommendations section as a set of actionable steps with smart goals associated along with possible solutions. This section is irrelevant for school reports or book reports, but is essential for business reports or corporate settings.

This is the section where you list all your sources if it’s a research report. You should also add any links that are relevant to the report — or previous reports about the same topic.
You could even link an interactive version of the report you just created with Visme. Visme allows you to create interactive and animated documents that can be published to the web with a single click, offering a new dimension to your report.
A good rule of thumb when creating your appendices is to only add information that is relevant to the report or that you referenced when writing your report. Use reference annotations inside the report to link to the content in the appendix.
The report content used in this sample report design can be found here .
Following a report writing format is only a portion of the report writing process. When it comes to the content being placed in that context, it needs to be executed in a professional manner that will not only inform your reader but engage them from start to finish as well.
Here are some writing tips and best practices you should follow to complete your report in style.

Looking to create a stand-out visual report?
- Choose from dozens of professionally designed templates
- Create animated charts and creatively visualize stats and figures
- Customize anything to fit your brand image and content needs
Start With the Body of the Report
It's helpful to write the body of the report before the introduction or conclusion so you have a comprehensive overview of what key points should be covered in each section. This rule applies whether you're writing the report independently or as a team.
For the body of your report, you can assign specific sections to your team members and then appoint someone to write the conclusion and intro once it's complete.
Visme provides a space for team collaboration where you and your team members can work on your report simultaneously, adding comments, real-time updates and more. This feature helps to ensure everyone contributes and each section of your report is completed and well-rounded.
Use Visuals with Purpose
Don’t simply add visuals for the sake of adding them. Instead, by adding data visualization, you can condense complex information, pinpoint relationships and showcase values and risk. Not to mention a single chart can save you from adding unnecessary text to your report. Give each visual a strong purpose in your report.
Next to data visualization, you should also be mindful of what images you choose to include in your report, whether they’re used as a backdrop or illustration of the topic at hand. You can dive into Visme’s extensive library of royalty-free images, upload your own or create your own with Visme’s AI-powered Image Generator .
Tap into the infinite possibilities of AI image generation right inside your Visme editor. Available inside any project, old or new, just type in your prompts and generate creative and unique visuals for your report.
Write a Well Crafted Report
To ensure your report holds credibility, it must be error-free with proper spelling, grammar and tone. You should only use acronyms or jargon that are associated with your industry or profession, only if needed.
Try to use simple language and avoid adding unnecessary fluff. Lastly, before you send off your report, be sure to review it or ask for a colleague's opinion to ensure everything is in place.
You can send your report as a shareable link for a quick review or invite your colleague directly into your Visme project to decide if they can view, edit or comment on it. Make updates and share changes in real-time to streamline a faster editing process and have your report polished and ready to share with your audience.
Keep Your Appendix Short
Avoid creating a large appendix, as it can be intimidating or burdensome for the reader. It’s best only to add information or sources relevant to the report’s main points. One way to implement this tip is to review your appendix only after your report’s been completed, then do an extensive review to see what needs to stay or be removed until you're satisfied with the size of your appendix.
Use a Grammar Checker
If it’s accessible, ask an editor or writer to review your article. You can also use tools like Hemmingway, ProWritingAid or Grammarly . Even your best KPIs and ROIs won’t save you from bad grammar.
Writing a report may seem challenging, but anyone can do it with a proper plan, the right tools and some practice. You can sign up for Visme's AI Report Writer and follow these simple steps to write your own report.
Step 1: Define Your Objective
Before you put pen to paper, identify your reasons for writing the report. What do you want to accomplish with it? What is the purpose of your research, and why will it be important to others?
You might need to create a monthly , weekly , or annual report . Or, it could be a business report, including sales, marketing or social media reports .
No matter what type of report you are writing, the objective will guide you through the rest of the process.
Also, consider your target audience who will be reading it. For example, if you are writing a sales repor t for your team, it might be important to include data that shows their performance compared to the previous month, like the example below.

If you are writing a project status report like this, you must focus on showing the project's performance over a period of time.

In either case, your objective will help you determine what information is essential in your report and how much should be included.
Step 2: Conduct Research
Start by gathering relevant data and information from various sources, such as books, articles, interviews and online resources. Also, you can find data from your company's files, sheets, CRM or sales software and any other source you can.
As you explore different perspectives and evidence, you'll better understand the topic and be equipped to present a comprehensive analysis.
While researching, take notes and keep track of your sources for easy referencing later. In-depth research lays a solid foundation for a credible and insightful report.
Step 3: Prepare an Outline
Creating an outline provides a structured framework that guides your writing and keeps you focused. Start with the main headings like introduction, body and conclusion. Under each, add subheadings of key points or arguments you will cover.
An outline organizes your thoughts and lets you see where information fits best, ensuring a logical flow of ideas in your report. This planning tool ultimately makes the writing process easier and more efficient.
Step 4: Write the First Draft
After conducting research and preparing an outline, it's time to write your first draft. Start by stating your purpose in the introduction. Expand on your main points and provide necessary information and arguments in the body section.
Lastly, summarize and conclude your ideas. Don't focus on perfection in this stage; just get your thoughts down. It might look rough, but that's okay. This draft is your starting point, where you'll improve in the next revision and editing stages.
You can use Visme's AI writer to simplify the report writing process. It can help you prepare structured outlines, generate compelling report content and proofread text to ensure it's error-free. Just explain what you want to generate, and the AI writer will do the rest.
Step 5: Revise and Edit
This is one of the most important steps in this whole process. It involves reviewing the structure, flow and content of your report. Check your arguments, their logical presentation and if your evidence supports the claims.
Also, focus on editing the report by checking language, spelling, punctuation, style and formatting. You can use grammar checker tools like Grammarly and Hemmingway editor.
The more time you spend editing your report, the more clearly it conveys your message.
Step 6: Share the Report
Once your report is complete and you are satisfied with the results, it’s time to share it with your audience. You may need to share your report in various file formats and channels.
If you use Visme to write your report, you can download and share your report in many different ways:
- Download your report in various formats, including PDF, JPG, PNG and HTLM5.
- Publish it on social media or share it via email using a shareable link generated in the editor.
- Generate a code snippet in Visme to embed it anywhere online.
Click through the image below to use this customizable template to create your report. It follows the standard report writing format so you won’t get confused or miss a section.

Do you still have questions about good report writing and the best report writing formats? These FAQs will help.
What Are the Five Steps in Report Writing?
Writing a report effectively is best done by following a format and a set of guidelines. These are the five steps to follow to create a good report.
1. Understand your report’s purpose: Begin by having a clear understanding of the report's intent.
Whether it's an annual summary, weekly update, or research findings, knowing your report's purpose is crucial for effective writing. Compile and write the content with the purpose in mind as if it were a problem to be solved.
2. Follow the Right Report Writing Format: Adhere to a structured format, including a clear title, table of contents, summary, introduction, body, conclusion, recommendations, and appendices. This ensures clarity and coherence. Follow the format suggestions in this article to start off on the right foot.
3. Plan Your Writing: Create an outline to organize your thoughts and prioritize the body of the report. Stick to factual information, providing accuracy and reliability throughout. Be as detailed as possible in the outline; this will help build the report effectively.
4. Choose the Right Report Template: Utilize templates tailored to your report type, whether it's annual, weekly, project-related, sales/marketing, research, or academic. Templates streamline formatting and enhance professionalism. Visme has hundreds of report templates to choose from. Browse the gallery to find the perfect one.
5. Keep Your Audience in Mind: Tailor your report to meet your audience's needs. Whether it's supervisors, team members, clients, or peers, consider what information is most relevant and valuable to them. Make it easy for them to skim the report with clear headlines, titles and data visualizations.
How Do You Format a Report Nicely?
Formatting a report nicely involves attention to detail and adherence to specific guidelines. Here are some key characteristics that will ensure your report looks polished and professional:
1. Consistent Font and Size: Use a readable font like Arial or Verdana, and maintain consistency in font size throughout the report. Typically, a 12-point font is standard for most reports.
2. Clear Headings and Subheadings: Employ clear and descriptive headings and subheadings to organize your content. Use a consistent hierarchy, i.e., Heading 1, Heading 2, body text, etc, for a neat structure.
3. Adequate Margins: Ensure proper margins on all sides of the page (usually 1 inch or 2.54 cm) to provide white space and enhance readability.
4. Line Spacing: Use 1.5 or double spacing for the main text to prevent overcrowding and improve readability. Single spacing is acceptable for footnotes, references, and captions.
5. Page Numbers: Include page numbers, typically in the header or footer, to aid navigation. Ensure they are placed consistently and formatted appropriately.
6. Bullet Points and Numbering : When listing items or creating outlines, use bullet points or numbering for clarity. Maintain uniformity in style and indentation.
7. Tables and Figures: Format tables and figures consistently by providing clear labels and captions. Ensure they are properly aligned within the text.
8. Alignment: Align text and paragraphs consistently. Use left-justified text for most reports, as it's the easiest to read. Justify text only when necessary.
9. Page Breaks: Insert page breaks as needed to avoid awkward page transitions within sections or paragraphs.
10. Use of Color: If your report allows for color, use it sparingly and consistently. Ensure that text and background colors provide sufficient contrast for readability.
11. Proofreading and Editing: Always proofread and edit your report for grammar, spelling, and formatting errors. Consistency in formatting is essential for a polished look
12. Citations and References: If your report includes citations and references, follow a specific citation style guide (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago) consistently throughout the document.
13. Review for Accessibility: Consider accessibility guidelines, such as providing alternative text for images and using accessible color choices, to ensure all readers can access your report.
What Are the Five Qualities of a Good Report?
A well-crafted report possesses five key qualities that make it effective and valuable. Here they are:
1. Clarity and Conciseness: A good report is clear and concise. It presents information in a straightforward manner, avoiding unnecessary jargon or overly complex language. Readers should easily understand the content without confusion.
2. Relevance: Every piece of information in a good report is relevant to the report's purpose and objectives. Irrelevant or extraneous details are omitted, ensuring that the report focuses on what truly matters.
3. Structure and Organization: Reports are structured logically, with a clear beginning, middle, and end. They typically include sections like an introduction, body, and conclusion, ensuring a logical flow of information. Headings and subheadings help organize content effectively.
4. Accuracy and Reliability: Accurate and reliable data is a hallmark of a good report. Information presented should be based on thorough research, sound methodology, and credible sources. Any data or facts should be verifiable.
5. Actionable Recommendations: In many cases, a good report includes actionable recommendations or insights. After presenting the data and analysis, the report should offer practical suggestions or solutions that readers can implement or consider for decision-making.
Over to You
Hopefully, this post has helped you to better understand the best way to put together a report using a standard report format and layout. Following a standard report writing format is just what you need to create engaging, memorable reports . Follow the tips above and you’ll never make a boring report again.
Just how following a report writing format will help you create a better report, a Visme subscription will help you create a full suite of visual content.
Create stunning business reports faster using Visme

Trusted by leading brands
Recommended content for you:

Create Stunning Content!
Design visual brand experiences for your business whether you are a seasoned designer or a total novice.
About the Author
Orana is a multi-faceted creative. She is a content writer, artist, and designer. She travels the world with her family and is currently in Istanbul. Find out more about her work at oranavelarde.com
Writing up a Research Report
- First Online: 10 November 2021
Cite this chapter

- Stefan Hunziker 3 &
- Michael Blankenagel 3
A research report is one big argument how and why you came up with your conclusions. To make it a convincing argument, a typical guiding structure has developed. In the different chapters, distinct issues need to be addressed to explain to the reader why your conclusions are valid. The governing principle for writing the report is full disclosure: to explain everything and ensure replicability by another researcher.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or Ebook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Barros, L. O. (2016). The only academic phrasebook you’ll ever need. Createspace Independent Publishing Platform.
Google Scholar
Field, A. (2016). An adventure in statistics. The reality enigma . SAGE.
Field, A. (2020). Discovering statistics using IBM SPSS statistics (5th ed.). SAGE.
Früh, M., Keimer, I., & Blankenagel, M. (2019). The impact of Balanced Scorecard excellence on shareholder returns. IFZ Working Paper No. 0003/2019. Retrieved June 09, 2021, from https://zenodo.org/record/2571603#.YMDUafkzZaQ .
Yin, R. K. (2013). Case study research: Design and methods (5th ed.). SAGE.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Wirtschaft/IFZ – Campus Zug-Rotkreuz, Hochschule Luzern, Zug-Rotkreuz, Zug , Switzerland
Stefan Hunziker & Michael Blankenagel
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Stefan Hunziker .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden GmbH, part of Springer Nature
About this chapter
Hunziker, S., Blankenagel, M. (2021). Writing up a Research Report. In: Research Design in Business and Management. Springer Gabler, Wiesbaden. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-34357-6_4
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-34357-6_4
Published : 10 November 2021
Publisher Name : Springer Gabler, Wiesbaden
Print ISBN : 978-3-658-34356-9
Online ISBN : 978-3-658-34357-6
eBook Packages : Business and Economics (German Language)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Reference.com
What's Your Question?
- History & Geography
- Science & Technology
- Business & Finance
- Pets & Animals
The Key Components of a Winning Report Writing Format: Best Practices Revealed
Reports are an essential tool in the business world, providing valuable insights and analysis that guide decision-making processes. However, a poorly structured report can easily confuse readers and undermine its purpose. To ensure your reports are clear, concise, and effective, it’s crucial to follow a winning report writing format. In this article, we will uncover the key components of a successful report writing format and share best practices to help you create impactful reports.
I. Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for your report and should provide a brief overview of its purpose and scope. Start by stating the problem or issue that the report aims to address. Clearly define any key terms or concepts that may be unfamiliar to readers. Additionally, include any relevant background information to provide context for your analysis.
II. Methodology
The methodology section outlines the research methods used to gather data for your report. This section is particularly important as it establishes the credibility and reliability of your findings. Describe in detail how you collected data – whether through surveys, interviews, experiments, or secondary research – and explain why these methods were chosen.
Furthermore, discuss any limitations or challenges encountered during the research process that may have impacted the results. By transparently sharing your methodology, you allow readers to evaluate the validity of your conclusions.
III. Findings and Analysis
This section forms the core of your report and presents the findings from your research in a clear and organized manner. Start by summarizing your results in a concise manner before delving into more detailed analysis.
Present numerical data using tables, charts, or graphs to facilitate understanding and make complex information more accessible. Use relevant headings and subheadings throughout this section to guide readers through different aspects of your analysis.
Additionally, provide explanations for any trends or patterns observed in the data while relating them back to your original research question or objective. Avoid making subjective statements or unsupported claims; instead, back up your analysis with evidence and logical reasoning.
IV. Conclusion and Recommendations
The conclusion sums up the main findings of your report and provides a concise answer to the research question or objective stated in the introduction. This section should not introduce any new information but rather reaffirm the key points discussed in the previous sections.
If appropriate, include recommendations based on your findings. These recommendations should be actionable and specific, offering practical steps for addressing the problem or issue outlined in your report. Support your recommendations with evidence from your analysis to increase their credibility.
In conclusion, a winning report writing format comprises several key components that ensure clarity, coherence, and effectiveness. By structuring your report with an informative introduction, a detailed methodology section, a comprehensive findings and analysis section, and a concise conclusion with actionable recommendations, you can create reports that provide valuable insights for decision-making processes. Remember to tailor each component to suit the specific needs of your audience and convey information in a professional manner. With these best practices in mind, you’ll be well-equipped to produce impactful reports that stand out in any business setting.
This text was generated using a large language model, and select text has been reviewed and moderated for purposes such as readability.
MORE FROM REFERENCE.COM

- How it works
- Pay for essays
- Do my homework
- Term Paper Writing Service
- Do my assignment
- Coursework help
- Our Writers

Understanding MLA research proposal format: a comprehensive guide

A historian and political analyst by training, Jay Brines offers six years of experience in academic writing. His in-depth understanding of political theories and historical contexts brings a rich perspective to his papers, making them a valuable resource for students in these fields. You can always count on this paper writer.
How to write a research paper MLA format? It's a common question among students and researchers who are preparing papers in the humanities. A research paper proposal outlines the objective, scope, and direction of your academic endeavor. Academic proposals are essential because they allow researchers to explain their study's purpose and request comments or financing. Formatting this text in MLA style follows humanities field standards and makes it organized and readable. This introduction to MLA style paper will explain why writing guidelines are essential for academic achievement and how they help you write a clear, professional, and convincing MLA research proposal format.
Coherent and well-structured proposals are crucial. They prepare the basis for the study and provide a clear path for it, ensuring all project issues are examined and adequately expressed. When drafting such proposals, it's beneficial to understand "What is MLA format?" as this style guide can help organize your documentation and citations effectively, ensuring clarity and consistency throughout the academic writing process. Using the right proposal structure helps you communicate your work's research significance and persuade others to do the study. This introductory section emphasizes the importance of MLA proposal formatting in academic writing and research preparation before diving into the details.
Mastering the essentials of MLA style for crafting research proposals
Modern Language Association (MLA) style is popular in language and literary writing. It's essential to familiarize yourself with the specific guidelines that govern this style. Understanding MLA rules helps research proposals sound professional and scholarly. MLA style paper format organizes proposals, making research aims obvious to reviewers and researchers. MLA proposal format, citations, and organization are crucial for academic legitimacy. The style basics will be covered in this part to help you write a solid MLA research proposal.
The crucial role of following MLA guidelines in writing
Following MLA formatting basics while writing an academic paper is essential to scholarly communication. These standards organize material simply and consistently, making the text easier to read. Researchers should follow MLA formatting principles to guarantee that their work is regarded seriously and evaluated on its merits rather than formatting problems.
Understanding and using MLA style paper format in a study proposal helps generate a professional tone and structure, which is crucial to convincing review panels of its viability and need. It shows attention to detail and adherence to "academic writing" norms, which are appreciated in scholarship. This section will explain MLA style paper format and how to use it to write a research proposal, covering citation styles and formatting a research paper.
Developing a compelling title and abstract
The title page for research proposal writings generally makes the initial impression. A brief title summarizes your study and engages readers. It should be concise, informative, and reflect your idea. Meanwhile, the abstract, much like you might find in a research proposal sample MLA format, condenses your study goals, methods, and consequences. Well-written abstracts instantly convey the scope and relevance of your study, inspiring additional investigation. Title and abstract efficiency can greatly affect study publicity and accessibility.
Crafting a compelling abstract: a quick guide for 100-200 words
Any study project needs an abstract writing to summarize its aims, methodologies, and implications. Effective abstract tips include beginning with a clear problem or purpose, a quick summary of the research methodology used, and a picture of the expected outcomes.
This section of the proposal frequently decides the reader's interest in reading the whole thing. It is the first substantive description of your work viewed by an external scholar, and a well-written abstract may greatly improve its reception. Thus, abstract writing is essential for researchers who want their proposal to stand out. Writing services can help you learn how to start a paper effectively, ensuring your abstract catches the reader's attention immediately. Moreover, services such as write my paper for me can provide guidance on structuring and refining your abstract, making it a powerful introduction to your proposal.
Strategies and insights for crafting engaging titles and abstracts
The title of your MLA research proposal format sets the tone and identifies the subject. A short, detailed, and informative title structure should convey the study's substance and entice the reader to learn more. A strong title quickly tells the reader about the study topic, which is vital in academic writing that prioritizes clarity and accuracy.
To write a good title and abstract, be clear when reading the research proposal example MLA and avoid unclear terminology. Additionally, connecting the title and abstract with the primary research challenges and approaches helps give a comprehensive preview of the proposal's content and persuasively argues for the research's necessity and relevance.
Organizing your research proposal: a strategic approach
Effectively communicating your research proposal sample MLA strategy requires a well-structured research proposal. This section helps you organize your proposal to include all important elements. Your study topic, technique, and projected results should flow together to make a cohesive paper. A logical MLA proposal format helps your proposal flow and emphasizes the importance and viability of your research idea.
Blueprint for organizing your proposal with defined sections
A well-organized proposal organization is crucial to a clear document. A well-organized proposal helps the reviewer identify crucial material and evaluate the study's feasibility and relevance. The parts should be organized from topic introduction to research methodology approaches, expected results implications, and conclusions.
The introduction proposal example, literature review, methodology, expected outcomes, and conclusion should be clearly divided. Each part should explain the research's goals, importance, and methodology and add to the proposal's narrative. This systematic technique helps deliver material effectively and shows the researcher's extensive planning and comprehension of the academic project's needs.
Guidelines for numbering and formatting subsections to enhance clarity and coherence
Effective structuring extends to the detailed organization of your content. Numbering and MLA formatting sub-sections enhance the readability and navigability of your proposal. Here are key practices to consider:
- Consistent sub-section headings: Use uniform styles for headings and subheadings to maintain a coherent MLA structure.
- Sequential numbering: Number sections and sub-sections in a sequential manner to guide the reader through your proposal.
- Logical flow: Arrange sections in a logical order, starting with the introduction proposal example and proceeding through methods, results, and conclusions.
- Visual distinction: Make use of bold or italicized fonts sparingly to emphasize important points without distracting from the main text.
Crafting the introduction and conducting the literature review
The beginning of your MLA research proposal example should set the stage for your investigation. It presents the study issue, emphasizes its relevance, and specifies your research goals. You must demonstrate your understanding of existing research and its relevance to your subject in the literature review after the introduction. This part places your research in the existing scholarly conversation and highlights gaps your study seeks to fill.
Advice for crafting a powerful introduction to frame your research
Introduction writing in a research proposal sample MLA includes background information, the research topic, and study goals. A good beginning sets the stage for the subject, engages the reader, and persuades them that it is important. The study scope and desired contributions to knowledge must be clearly defined.
A good introduction should flow into a Literature review that critically evaluates pertinent research. Literature review guidelines recommend that this part show a deep awareness of the academic environment around the research issue and identify gaps that the present study will fill.
Best practices for performing a literature review in MLA-style research proposals
When conducting a literature review for an MLA research proposal, consider the following MLA guidelines for essay projects:
- Relevant sources: Focus on recent and pertinent literature to support your research context.
- Citation consistency: Adhere strictly to MLA citation guidelines to maintain uniformity and avoid plagiarism.
- Critical analysis: Evaluate and synthesize the literature; don't just summarize. Highlight debates, major themes, and gaps in the research.
- Integration with proposal: Clearly link the literature review to your research questions and objectives, demonstrating its direct relevance.
Formulating the research methodology and anticipating outcomes
Define your research methodology by detailing data collection and analysis methods. The research design, data-collecting techniques, and analytic procedures should be clearly stated in this section to support the study's goals. Describe methodology limitations to honestly examine your approach's flaws and display critical thinking and problem-solving.
Outlining expected results predicts what the research seeks and what it may mean in the area. This indicates the study's direction, likely influence, and relevance. This section addresses research challenges to prepare the proposal for skepticism and scrutiny by showing that the researcher has examined and planned for probable hurdles.
A conclusion of your MLA research proposal is a conclusion summary of the article's main elements. This section revisits key topics like the structured approach to proposal development, MLA formatting, and strategic considerations for each section — from writing an impactful title to writing a clear and concise abstract. The conclusion summarizes these essential elements to help the reader comprehend the MLA structure and substance.
How should I format the title page in an MLA research proposal?
MLA research proposal does not need a title page; instead, write your name, instructor's name, course name, and date in the upper left corner of the first page and the title centered on the following line.
Can I use bullet points in an MLA research proposal?
Bullet points can assist in clarifying procedures or list topics in the methodology section, even though MLA style prioritizes paragraph form.
How do I cite sources within the proposal?
Use parenthetical citations with the author's last name and page number, and list all books cited at the conclusion of your proposal.
Related posts

How to Write an Exemplification Essay | A Guide from WritePaperFor.Me

How to Create a Dissertation Outline. Writing Tips and Free Template

How to Write a Dissertation: Helpful Tips and Impressive Ideas
What are you waiting for?
You are a couple of clicks away from tranquility at an affordable price!
Verify originality of an essay
Get ideas for your paper
Find top study documents
How to write a survey paper: structure and tips for effective writing
Updated 04 Jul 2024

All students dream of an easier way to learn a subject. Writing a survey paper example can effectively synthesize and consolidate information, helping you master a topic. It’s a valuable skill for anyone involved in academic research. This article will guide you through the essential steps of crafting an effective review. From understanding its purpose and structure to gathering and synthesizing information, you will learn how to write a survey paper and present a comprehensive overview of existing studies on a specific topic. You’ll be equipped with the tools to produce a well-organized and insightful text highlighting key findings and gaps in the literature.
What is a survey?
This is a comprehensive overview of the current knowledge and research on a particular topic. Unlike a sociology research paper and other original academic papers that present new findings, this writing summarizes and synthesizes existing studies, emphasizing significant developments, trends, and gaps in the literature. Its primary goal is to deliver readers a lucid explanation of the state of the art in a specific field.
Where is it used?
Also known as review papers, paper survey examples are commonly used in academic and professional contexts where a broad topic overview is needed. They are prevalent in:
- Academic journals: Researchers publish review articles in scholarly journals to explain the current academic landscape, often to introduce a special issue on a particular subject.
- Theses and dissertations: Graduate students frequently use this writing the same way as a precis paper as part of their thesis or dissertation work to demonstrate their understanding of the existing literature.
- Conference proceedings: Papers based on good survey topics are presented at conferences to summarize current exploration directions and trends, creating a foundation for discussions and further study.
- Grant proposals: Researchers include them in grant applications to justify the need for their proposed exploration by highlighting gaps and unresolved issues in the existing science literature.
When do you need it?
- Project beginning: Researchers turn to this genre to gather and summarize existing knowledge, which helps identify gaps and formulate research questions.
- Curriculum development: Educators use review papers to develop course materials that give students a comprehensive understanding of a subject.
- Policymaking: Policymakers rely on a survey introduction example to gain insights into current research trends and evidence, which inform decision-making processes.
- Professional development: Professionals use papers on technology research topics to stay updated on the latest developments and advancements in their field.
Survey paper format and structure
To ensure adherence to academic standards, format your writing as follows. Use Times New Roman, 12-point font, and double-space the text. Set 1-inch margins on all sides for a professional look. Format headings and subheadings clearly and consistently. Include page numbers in the upper right corner. Follow the chosen citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, or Chicago) for in-text citations. Label and number all tables and figures, placing them in the appropriate sections and referring to them within the text.
Below is a general guideline on how to format a survey and structure it:
Your survey title examples should be clear and concise, reflecting the main topic to convey the paper’s focus quickly. This page should include the name(s) of the author(s), institutional affiliation(s), date of submission, and contact details.
How to introduce a survey? Complete the abstract (typically 150-250 words) with a summary of the objectives, scope, key findings, and conclusions, offering a snapshot of the research. List 3-5 keywords that represent the main topic.
Introduction
In your research survey introduction example, provide the background, significance, objectives, and an outline of the document to set the context, explain its importance, and guide the reader.
Literature review
This section summarizes and evaluates the strengths and weaknesses of existing studies and discloses patterns, trends, and gaps, establishing a foundation and context.
Methodologies and approaches
This section is the same as you use in a communication paper . It describes, compares, and critiques study approaches, informing readers about various methods and assessing their effectiveness.
Key terms and definitions
This section explains key terms and concepts used in research to ensure a clear understanding of the terminology.
Recent trends and developments
This section offers an overview of the latest exploration and emerging trends, describing the current state of the art and highlighting new directions.
It synthesizes the reviewed literature and trends, analyzes findings and implications, and identifies science areas requiring further exploration.
In this part, summarize the main points and findings, significance, and recommendations to wrap up the text and suggest future research directions.
This is a complete list of cited sources in the proper format, crediting original authors and offering further reading resources.
Follow these guidelines to ensure your survey paper template is well-organized, clearly written, and academically rigorous. Always check for any specific requirements provided by your instructor, institution, or the journal to which you submit the text.
How to write a survey: step-by-step guide
An overview involves a systematic approach that ensures the final document is comprehensive, well-structured, and insightful. Below is an extended step-by-step guide to help you craft a thorough paper:
Step 1. Select a topic.
Choose a topic relevant to your study area with ample existing research. Ensure your survey topic examples are specific enough to be manageable but broad enough to cover significant exploration.
Step 2. Define the scope.
Clearly outline the scope of your work. This task will be easy if you know the answer to “ What is a term paper ”. Specify the aspects of the topic you will focus on to maintain clarity and focus throughout your document.
Step 3. Conduct a preliminary literature review.
Begin by reviewing the available literature to gain a general understanding of your topic's current state of research. Identify key studies, influential papers, and major findings to inform your subsequent detailed review.
Step 4. Formulate a research question.
To understand how to write a survey introduction, you should develop a clear and concise research question or thesis statement that will guide your work. Ensure your question is specific, focused, and researchable.
Step 5. Gather and organize relevant sources.
Collect literature directly addressing your research question using academic databases, journals, books, and credible online sources. Categorize it into themes, methodologies, or chronological order.
Step 6. Analyze and critique the literature.
Critically evaluate the studies, identifying their strengths, weaknesses, and contributions to the field. Look for patterns, trends, gaps, and areas of consensus or controversy in the existing study.
Step 7. Create an outline and conduct your research.
Develop a detailed outline for your work to guide your writing process. Create a document containing an introduction to a survey, body paragraphs with methodologies, key findings, and discussion, and finalize with a conclusion.
Step 8. Edit and proofread.
Review your paper for clarity, coherence, and consistency. Check for grammatical errors, proper citation, and adherence to formatting guidelines. Revise for improved quality and readability. Proofread the final draft to eliminate the mistakes. Seek feedback from peers or mentors for a polished, high-quality paper.
Step 9. Check formatting and presentation.
Ensure your document follows the provided formatting guidelines. Pay attention to font, margins, spacing, and heading styles. Correctly label and reference tables, figures, and appendices.
Step 10. Review and submit.
Conduct a final review for any errors or inconsistencies. Ensure logical flow and integration of all sections. Submit your text according to the given submission guidelines.
How to make your research stand out?
Creating a paper survey template can significantly advance your understanding of a topic, but to truly excel, there are a few essential recommendations to keep in mind. Let’s see how to write a survey paper to ensure your text stands out.
Understand your topic.
Begin by thoroughly understanding the topic. If any part of the question is unclear, seek clarification from your instructor. A solid grasp of the topic's basics will help identify key points of your exploration.
Select relevant literature.
Stay focused on your survey topics ideas by selecting sources that directly address them. Avoid hoarding unrelated sources and systematically review and filter appropriate studies.
Construct a concise research question.
Even if you prefer controversial research topics , keep your thesis statement short and clear to guide your paper’s direction and help you stay focused. This way, it will be easier for you to select relevant literature and avoid unnecessary information.
Use your library.
A preliminary investigation is crucial. Start with your college library, which offers a wealth of resources like encyclopedias and introductory texts to help outline your topic. Use these references to delve deeper into specific academic texts, enhancing your study outcomes.
Prioritize different up-to-date sources.
Base your work on current literature, ideally published within the last 5 years, and ensure you have more than 10 relevant sources. This balance maintains the relevance and depth of your exploration.
Use reputable sources.
One of the key secrets of how to write a good survey is to choose peer-reviewed and recognized sources in your field. Quality trumps quantity, so focus on highly regarded publications.
Use a logical sequence.
Be sure you understand how to structure a paragraph and that each element of your work ties into the research question and overall objective. This requires revising, editing, and proofreading your work multiple times.
Follow an appropriate format.
When learning how to write a survey report, remember to follow academic guidelines and use a standard format, including suitable headings, spacing, font, margins, and referencing style. Adhering to word limits and maintaining concise wording is also crucial.
With these tips, you can produce high-quality, well-organized reviews that effectively communicate your study outcomes. If you need professional assistance, do not hesitate to contact our research paper writing service . Our dedicated experts are ready to help complete your work, provide valuable recommendations, and edit and proofread your work.
Final thoughts
Writing surveys is a crucial academic skill that allows you to synthesize existing research and present a comprehensive overview of a specific topic. Following the steps outlined in this article, you can produce well-structured and compelling writing that highlights key findings, identifies gaps in the literature, and provides a clear direction for future exploration. From understanding the purpose and scope of your research to organizing your findings and refining your writing, each step is essential to creating a high-quality text.
However, the process can be challenging and time-consuming. If you need additional assistance, EduBirdie is here to help. We offer expert guidance and support for every aspect of survey writing, from conducting thorough research and organizing your paper to editing and proofreading. With our help, you can ensure your survey study example meets the highest academic standards and effectively communicates your findings.
Whether you are just starting your research or need help polishing your final draft, EduBirdie's professional services can make a significant difference in the quality of your work. Don’t hesitate to seek the support you need to excel in your academic endeavors.
Was this helpful?
Thanks for your feedback.

Written by Mary O. Spears
Mary O. Spears is a dedicated writer specializing in crafting insightful guides on essay and paper writing. With a profound understanding of academic standards and a talent for demystifying complex topics, Mary offers invaluable guidance to students aiming for academic excellence. Outside of her professional work, Mary is passionate about cooking and eating healthy, bringing creativity and balance to both her culinary and writing endeavors.
Related Blog Posts
How to overcome writer’s block.
Our article will help you learn how to overcome writer's block with the best practical methods. You will learn the symptoms that define it and rece...
PESTLE analysis example: explanation & tips
Understanding the larger environment in which a company operates is vital for planning and making decisions. One of the most effective tools for th...
How to Write a College Paper Successfully
Writing a college paper is an undeniably challenging task. It is one of those chances you are expected to show your professors the kind of student ...
Join our 150K of happy users
- Get original papers written according to your instructions
- Save time for what matters most
Free All-in-One Office Suite with PDF Editor
Edit Word, Excel, and PPT for FREE.
Read, edit, and convert PDFs with the powerful PDF toolkit.
Microsoft-like interface, easy to use.
Windows • MacOS • Linux • iOS • Android
Select areas that need to improve
- Didn't match my interface
- Too technical or incomprehensible
- Incorrect operation instructions
- Incomplete instructions on this function
Fields marked * are required please
Please leave your suggestions below
- Quick Tutorials
- Practical Skills
How to Write a Conclusion - Steps with Examples
I remember my college days when one of the most dreadful assignments was writing a research paper. It made me wonder if there was an easier way to help me through it. The worst part was writing the conclusion, which meant wrapping up the entire paper and finally drawing conclusions. It sounds pretty intimidating, doesn't it? How are you supposed to fit all that information into such a short space, and what else might you be missing? In this guide, I will show you how to write a conclusion so you can spare yourself from the distress of it all.
What to Include/ Not Include in a Conclusion?
Professors often stress a lot on writing a good conclusion that includes a wrap-up for your paper or essay. These are some factors you must consider to include in your conclusion:
Restate Your Thesis:
Begin by restating the main argument or thesis of your paper. This reinforces the central point you have been arguing throughout your work.
Summarize Key Points:
Provide a concise summary of the key points and findings from your paper. Highlight the most significant pieces of evidence that support your thesis.
Discuss the Implications:
Explain the broader implications of your findings. How do they contribute to the field of study? What practical applications or theoretical advancements arise from your research?
Address Limitations:
Acknowledge any limitations or weaknesses in your study. This demonstrates a critical and reflective approach to your research and provides a foundation for future work.
Suggest Future Research:
Propose areas for future research. What questions remain unanswered? What further investigations could build on your findings?
End with a Strong Closing Statement:
Conclude with a strong, impactful statement that leaves a lasting impression on your reader. This could be a call to action, a prediction, or a thought-provoking question related to your research topic.
There may also be certain things you would unknowingly add in your conclusion that would ultimately leave a bad impression on the reader. Keep these factors in mind so you may avoid when writing your conclusion for your paper:
New Information:
Avoid introducing new information or ideas that were not covered in the body of the paper. The conclusion is for synthesizing and reflecting on the information already presented.
Detailed Methodology:
Do not include detailed descriptions of your research methods. This information belongs in the methodology section of your paper.
Repetitive Summaries:
Refrain from simply reiterating points that were already made in the results or discussion sections. Instead, focus on synthesizing the information and highlighting its significance.
Speculative Statements:
Avoid idle speculation or guesswork about potential outcomes or implications that are not supported by your research findings.
Apologies or Undermining Your Work:
Do not undermine your work by apologizing for any perceived shortcomings. Present your conclusions confidently and assert the value of your research.
Excessive Length:
Keep the conclusion concise and to the point. Long, drawn-out conclusions can dilute the impact of your final statements.
To put things into perspective, here's what a good and bad conclusion example look like:
Good Example:
Bad Example:
Types of Conclusion
Summarizing conclusion:.
This type is the most common and involves summarizing the main points of the research, reiterating the research question, and restating the significance of the findings.
It is broadly used across different disciplines.
Example: If a study investigated the impact of social media on adolescents' mental health, a summarizing conclusion would reiterate key findings, such as the association between high social media use and increased anxiety and depression levels among adolescents, and emphasize the importance of these findings for developing effective interventions.
Editorial Conclusion:
This type is used less frequently and is suited for research papers that advocate for a particular viewpoint or policy. It presents a strong editorial opinion based on the research findings and offers recommendations or calls to action.
It is suitable for papers focusing on policy recommendations or advocating a specific viewpoint.
Example: For a study on the environmental impact of plastic waste, an editorial conclusion might call for a comprehensive ban on single-use plastics and increased recycling initiatives, urging governments, businesses, and individuals to take immediate action to protect the environment.
Externalizing Conclusion:
This type extends the research beyond the scope of the paper by suggesting future research directions or discussing broader implications of the findings. It is often used in theoretical or exploratory research papers.
It is Ideal for theoretical or exploratory studies.
Example: In a study exploring AI applications in healthcare, an externalizing conclusion might suggest future research into the ethical, legal, and social implications of AI in healthcare and emphasize the need for interdisciplinary collaboration to harness AI's potential while addressing its challenges.
How to Write a Conclusion in 4 Steps [With Examples]
Writing a conclusion may seem a bit tricky, but once you fully understand the essence of what goes into a conclusion, it will become much easier. To demonstrate how to write a conclusion, I will be using WPS Office , a tool designed to be convenient for students, thanks to its easy-to-use interface and free features. You can also utilize WPS AI, as I am in these simple 4 steps, to make the entire process smoother for yourself.
Step 1: Restate The Thesis Statement
Start your conclusion by restating the thesis statement of your research paper. This reminds the reader of the main focus and purpose of your study.
Example: If your thesis statement is "This study investigates the impact of social media on adolescents' mental health, revealing a significant association between high social media usage and increased levels of anxiety and depression.", you can use WPS AI to help improve and rewrite your thesis statement.
Here's how WPS AI can assist you with your thesis statement.
Write your thesis statement in WPS Writer and select the entire text using your mouse.
After selecting the text, a small hover menu will appear. Click on the "WPS AI" icon in this menu.
This will open a list of AI assistance options you can choose from. To ask WPS AI to improve your thesis statement, click on "Improve Writing".
WPS AI will process and return an improved thesis statement. If you don’t like the improved version, click on "Rewrite", or click on "Accept" to replace your text with the improved version.
Step 2: Review Main Supporting Points
Next, we need to summarize the key points of our research. When summarizing the key findings of your research, it’s important to highlight the most significant results and their implications.
Example: Let's say that from our research the most important findings were:
The study found that high social media usage negatively affects adolescents' self-esteem due to constant exposure to idealized images and lifestyles.
Excessive use of social media, particularly before bedtime, was linked to disrupted sleep patterns and insufficient rest, contributing to mental health issues.
Despite being a tool for connection, high social media usage can lead to feelings of loneliness and social isolation as face-to-face interactions decrease.
Here's how WPS AI can assist you summarize the key points of your research for your conclusion.
Let's switch to WPS Office again, and this time let's select the key points that we have written down from our research.
Click on the WPS AI icon from the hover menu to open the list of options you can choose from.
From the list, let's click on "Summarize" to shorten and summarize the key points from our research.
You can now choose to either accept or ask WPS AI to rewrite this summary of key points again.
Step 3: Show Why It Matters
Now that you have laid out all the findings from your paper and WPS AI has effectively summarized them, you can further prompt it to broaden the implications of your findings and follow up with real-world problems.
To get real-world insights using WPS AI, follow these steps:
Click on the WPS AI widget at the top right corner of the WPS Writer interface.
The WPS AI pane will open on the right. Here, simply type in your prompt. Here is an example of a prompt:
"Explain the significance of high social media usage leading to increased anxiety and depression in adolescents, and discuss potential real-world problems and solutions."
WPS AI will display the results, which can now be a part of your summary or can be further summarized or improved with the help of WPS AI.
Step 4: Offer Meaningful Insights
Lastly, provide some final thoughts or insights that will leave a lasting impression on your reader. This can include suggestions for future research, practical applications of your findings, or a call to action based on your conclusions.
Example: Here is an example of how Meaningful Insights can be presented:
Further research is needed to explore the long-term effects of social media usage on adolescent mental health and to identify effective interventions.
Developing and promoting apps that encourage healthy social media use and provide mental health support could mitigate the negative effects identified in the study.
Stakeholders, including policymakers, educators, and parents, should collaborate to create environments that foster healthy digital habits and support adolescents' mental health.
Now, with the help of WPS AI, these points can simply be summarized to get more concise and structured Meaningful Insights for our conclusion.
Bonus Tips: How to Polish your Conclusion with WPS AI
Writing a strong conclusion for your research paper is crucial, and WPS Office is designed to be exceptionally student-friendly. It offers accessible options and advanced features for free, making it an excellent tool for students. One of the standout features is WPS AI, which integrates AI into its writing and proofreading abilities.
Draft Generation: WPS AI can assist you in writing a conclusion by generating an initial draft. This draft serves as a solid foundation, ensuring that all essential elements are included and properly structured.
Grammar and Style Check: WPS AI can identify grammar errors, awkward phrasing, and inconsistencies in your conclusion paragraph. This ensures that your writing is polished and professional.
Sentence Structure Enhancement: The AI can suggest improvements to sentence structures, helping you to vary sentence lengths and styles for better readability and flow. This makes your conclusion more engaging and easier to read.
Vocabulary Enhancement: WPS AI offers synonyms and alternative word choices to enhance the vocabulary in your conclusion, making your writing more sophisticated and engaging.
Clarity and Conciseness: WPS AI can help you refine your conclusion to ensure it effectively summarizes your main points without unnecessary repetition or tangents. This keeps your conclusion focused and impactful.
Refinement and Customization: Once WPS AI has generated the draft, you can refine and personalize it to align with your research and style. This step allows you to inject your voice and insights into the conclusion, making it uniquely yours.
Polishing and Proofreading: After refining the draft, you can use WPS AI to polish the conclusion further. WPS AI's advanced proofreading capabilities ensure that your conclusion is not only coherent and concise but also free of grammatical errors and stylistic inconsistencies.
ByIncorporating WPS AI into your writing routine you can significantly improve your efficiency and the overall quality of your academic work. You can streamline the process of writing your research paper conclusion, saving time and effort while ensuring a high-quality result. Whether you’re summarizing key findings, making policy recommendations, or suggesting future research directions, WPS AI helps you create a compelling and impactful conclusion.
So we have seen how WPS AI can help us write more effective and accurate conclusions, but is this all the help it offers? Absolutely not! With the help of WPS AI, you can further improve your conclusion by making it more fluent and easier to read.
Furthermore, WPS AI is not just a writing tool; it also offers AI spell check features, which can help students proofread their work according to their academic style such as APA, MLA, or Chicago style.
WPS Office has a lot to offer and is a perfect tool for students who need help writing not just effective conclusions but also effective research papers. So if you are stuck with a conclusion or a research paper, consider turning to WPS AI for help.
FAQs about writing a conclusion for paper/ essay
1. how long should a conclusion be.
A well-constructed conclusion typically constitutes approximately 10% of your document's total word count. For instance, in a 1,500-word paper, aim for a conclusion of about 150 words. This provides sufficient space to summarize key points and offer a final overview of the main ideas discussed.
2. How can I make my Conclusion impactful?
Here are some effective strategies for creating an impactful conclusion:
Utilize compelling language to engage the reader effectively.
Ensure the conclusion remains clear and concise, omitting insignificant specifics.
Conclude with a stimulating statement, a call to action, or a reflection on the broader implications of your research findings to make a lasting impact.
3. How do I avoid simply repeating what I've already said in the Conclusion?
To avoid repeating yourself in your conclusion, focus on cohesively summarizing your main ideas rather than reiterating them. Additionally, consider exploring the wider impact of your arguments or suggesting directions for future research on your topic. This approach ensures your conclusion provides fresh perspectives and maintains reader interest.
Perfect Your Conclusion With WPS Office
Your research paper is not complete without a strong conclusion. The person who reads your paper should feel like they have taken away significant key insights from your work. Writing an effective conclusion can sometimes be challenging, but WPS Office, with its AI capabilities, can assist you in helping you with how to write a conclusion to perfection. Incorporate WPS AI into your writing routine to significantly improve your efficiency and the overall quality of your academic work. Try WPS Office today and experience the benefits of AI-assisted writing firsthand.
- 1. 10 Professional Company Presentation Templates: To Write a Great Company Profile
- 2. How to Write a Cover Letter [Tips with Examples]
- 3. How to write meter square in powerpoint
- 4. How to Write an Essay in MLA Format | For Students
- 5. How to write matrix in Word
- 6. How to Write an Abstract - Steps with Examples
15 years of office industry experience, tech lover and copywriter. Follow me for product reviews, comparisons, and recommendations for new apps and software.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
- As Partisan Hostility Grows, Signs of Frustration With the Two-Party System
Nearly half of younger adults say they ‘wish there were more parties to choose from’
Table of contents.
- Leaners’ ratings of the opposing party are quite negative, but ratings of their ‘own’ party are lukewarm
- A rise in the share of Americans with unfavorable views of both parties
- The partisan gap in presidential approval ratings has grown over time
- About half of Republicans like leaders who contend Trump won 2020 election
- Views of political leaders’ approach to the other party
- Does support for a political party reflect on a person’s character?
- Majority of public sees a great deal of difference between Republican and Democratic parties
- Most Americans say at least one candidate for office shares their views
- Why partisan leaners lean – and why they don’t identify with a party
- Non-college adults are more likely than college graduates to cite the party ‘sticking up for people like them’ as a major reason for identifying with it
- Few voters say it is likely they will vote for the other party
- Leaners hold fewer negative stereotypes about the other party than partisans, but rising shares attribute negative traits
- Most Democrats view those in their party as more open-minded than other Americans; most GOP see co-partisans as more hardworking
- Across the political spectrum, a rise in the number of negative traits attributed to opposing partisans
- Acknowledgments
- Methodology
Pew Research Center conducted this study to better understand Americans’ feelings about the country’s major political parties and the reasons why they choose to affiliate with or lean toward a party. For this analysis, we surveyed 6,174 U.S. adults between June 27 and July 4, 2022. Everyone who took part in this survey is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used for the report and its methodology .
Partisan polarization has long been a fact of political life in the United States. But increasingly, Republicans and Democrats view not just the opposing party but also the people in that party in a negative light. Growing shares in each party now describe those in the other party as more closed-minded, dishonest, immoral and unintelligent than other Americans.
Perhaps the most striking change is the extent to which partisans view those in the opposing party as immoral. In 2016, about half of Republicans (47%) and slightly more than a third of Democrats (35%) said those in the other party were a lot or somewhat more immoral than other Americans. Today, 72% of Republicans regard Democrats as more immoral, and 63% of Democrats say the same about Republicans.
The pattern is similar with other negative partisan stereotypes: 72% of Republicans and 64% of Democrats say people in the opposing party are more dishonest than other Americans. Fewer than half in each party said this six years ago. Large majorities in both parties also describe those in the other party as more closed-minded than other Americans (83% of Democrats and 69% of Republicans say this), and this sentiment also has increased in recent years.
Yet there is one negative trait that Republicans are far more likely than Democrats to link to their political opponents. A 62% majority of Republicans say Democrats are “more lazy” than other Americans, up from 46% in previous studies in 2019 and 2016 . Only about a quarter of Democrats (26%) say Republicans are lazier than others, and this has changed only modestly since 2016.
The new survey on parties and partisanship by Pew Research Center, conducted among 6,174 Americans between June 27 and July 4, 2022, on the nationally representative American Trends Panel, finds that negative sentiment – the belief that the opposing party’s policies are harmful to the country – remains a major factor in why Republicans and Democrats choose to affiliate with their party.
In fact, nearly equal shares of Republicans cite the harm caused by Democratic policies (78%) and the positive impact of GOP policies (76%) as major reasons why they identify with their party. This also is the case for Democrats, with identical shares (68% each) citing these negative and positive reasons for their decision to affiliate with the Democratic Party.
The belief that the opposing party’s policies are harmful to the country is a particularly prominent factor in why independents lean toward the Republican and Democratic parties. It is the only one, among the five included on this survey, cited by majorities of both Republican-leaning (57%) and Democratic-leaning independents (55%) as a major reason why they lean toward their parties.
The survey finds that while negative partisanship remains extensive – and in many cases is increasing – there also are signs of frustration with the two-party system and the parties themselves. This frustration is more evident among partisan leaners – who tend to be younger and less politically engaged than partisans – than among those who identify as Republicans or Democrats.
Among the public overall, 39% say the following describes their views extremely or very well: “I often wish there were more political parties to choose from in this country.” Another 32% say the statement describes their views somewhat well, while 28% say it describes their views not too well or not at all well.
Notably, Democrats are more likely than Republicans to express a desire for more political parties: 38% of those who identify with the Democratic Party say this describes their views extremely or very well, compared with 21% of Republicans. Yet it is among independents and others who do not identify with a party that the sentiment is most pronounced: 48% say it describes their views extremely or very well, including 48% of those who lean Republican and 53% of those who lean Democratic.
Overall, interest in having more political parties is higher among younger Americans than older adults. Nearly half of those ages 18 to 49 say they often wish there were more parties to choose from (47% say it describes their views extremely or very well); that compares with 35% of those ages 50 to 64 and just 23% of those 65 and older.
Neither party is very popular with the public : Roughly four-in-ten Americans (41%) have a very or somewhat favorable view of the Democratic Party, while even fewer (37%) have a favorable impression of the Republican Party.
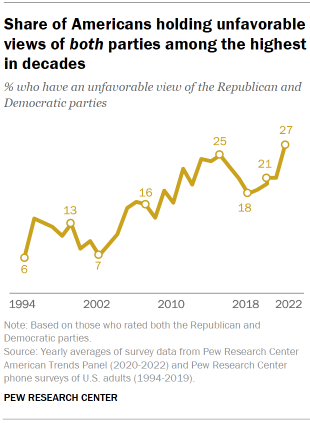
Over the past several decades, the share of Americans who express unfavorable opinions of both major parties has grown: In 1994, just 6% of the public had an unfavorable view of the Republican and Democratic parties. Today, about a quarter (27%) have negative views of both parties. This view is especially pronounced among partisan leaners: 44% of Republican-leaning independents – and an identical share of Democratic leaners – currently have negative views of both parties.
The Democratic Party has advantages over the GOP on several traits and attributes, particularly when it comes to tolerance for different types of people and not making excuses for hateful views among members of their own party. About six-in-ten adults (57%) say the phrase “respectful and tolerant of different types of people” describes the Democratic Party very or somewhat well, compared with 38% who say it describes the Republican Party.
And while 61% say the phrase “too often makes excuses for party members who have hateful views” describes the Republican Party, a smaller share (51%) say it describes the Democratic Party.
At the same time, there are more modest differences in views of the parties’ respect for the nation’s democratic institutions. About half of adults (51%) say “respects the country’s democratic institutions and traditions” describes the Democratic Party very or somewhat well, while 45% say it applies to the GOP. And neither party gets high ratings for honesty: 43% say the phrase “governs in an honest and ethical way” describes the Democratic Party, compared with 37% who characterize the Republican Party this way.
Other important findings from the survey
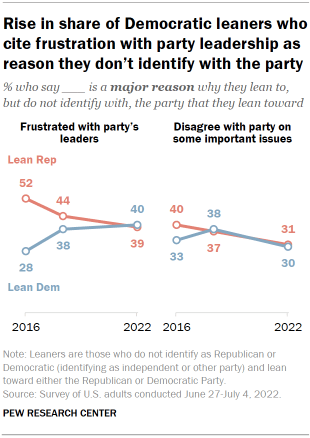
Those who lean to the Democratic Party have become more critical of Democratic leaders. When asked why they lean toward a party – rather than identify with it – many leaners say they do not want to put a political label on their views, while nearly as many offer that they are frustrated with the leadership of the party they lean toward. The share of Democratic leaners who cite frustration with the party’s leaders as a major reason for why they do not more closely associate with the party has risen from 28% in 2016 to 40% currently. Over the same period, the share of Republican leaners who express frustration with GOP leadership has declined from 52% to 39%.
The GOP is divided over leaders who endorse Trump’s unproven election claims. About half of Republicans (51%) say they like political leaders who publicly assert that Donald Trump was the legitimate winner of the 2020 presidential election; 17% say they do not like such leaders, while 31% neither like nor dislike them. Those who identify strongly with the GOP – strong Republicans, who make up 70% of all Republicans – are far more likely than those who identify with the party less strongly or Republican leaners to express positive views of such leaders. About six-in-ten strong Republicans (59%) express positive views of leaders who say Trump won in 2020, compared with 31% of less strong Republicans and 24% of Republican-leaning independents.
Republicans and Democrats express increasingly positive views of themselves . While Republicans and Democrats express increasingly negative views of those in the other party, they have become more positive about the people in their party. For example, a majority of Republicans (63%) now say that members of their party are a lot or somewhat more moral than other Americans; about half of Republicans (51%) said that in 2016 and 2019. The share of Democrats who say their fellow Democrats are more moral than other Americans has increased from 38% in 2016 to 51% currently.
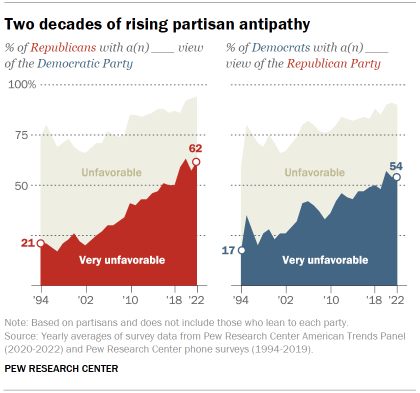
Deeply negative views of the opposing party are far more widespread than in the past. About six-in ten Republicans (62%) and more than half of Democrats (54%) have a very unfavorable view of the other party in Pew Research Center surveys conducted this year. While these highly negative views of the opposing party are little changed in the last few years, the share expressing this level of antipathy is higher than it was even five years ago, and considerably higher than it was a few decades ago. In 1994, fewer than a quarter in both parties rated the other party very unfavorably.
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Political Animosity
- Political Parties
- Political Polarization
Most Americans say elected officials should avoid heated or aggressive speech
Americans’ dismal views of the nation’s politics, partisan antipathy: more intense, more personal, most popular, report materials.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Thesis. Thesis is a type of research report. A thesis is a long-form research document that presents the findings and conclusions of an original research study conducted by a student as part of a graduate or postgraduate program. It is typically written by a student pursuing a higher degree, such as a Master's or Doctoral degree, although it ...
Use the section headings (outlined above) to assist with your rough plan. Write a thesis statement that clarifies the overall purpose of your report. Jot down anything you already know about the topic in the relevant sections. 3 Do the Research. Steps 1 and 2 will guide your research for this report.
Formatting an MLA paper. The main guidelines for writing an MLA style paper are as follows: Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman. Set 1 inch page margins. Apply double line spacing. Indent every new paragraph ½ inch. Use title case capitalization for headings. Check out the video below to see how to set up the format in ...
You can begin writing the introductory section of the report as soon as you have decided on the general approach your study will follow. You don't have to wait until you have determined all the details of the method. 2. You can write the method section of the report before you have analyzed the data.
There are five MAJOR parts of a Research Report: 1. Introduction 2. Review of Literature 3. Methods 4. Results 5. Discussion. As a general guide, the Introduction, Review of Literature, and Methods should be about 1/3 of your paper, Discussion 1/3, then Results 1/3. Section 1: Cover Sheet (APA format cover sheet) optional, if required.
Figures 11.2, 11.3, 11.4, and 11.5 show some sample pages from an APA-style empirical research report originally written by undergraduate student Tomoe Suyama at California State University, Fresno. The main purpose of these figures is to illustrate the basic organization and formatting of an APA-style empirical research report, although many ...
Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch. Use double-spaced text throughout your paper. Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point). Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section.
Write up a state-of-the-art research report. Understand how to use scientific language in research reports. Develop a structure for your research report that comprises all relevant sections. Assess the consistency of your research design. Avoid dumbfounding your reader with surprising information.
We've covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are: To choose a research question and review the literature. To plan your paper structure and draft an outline. To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing.
Guide to Writing a Research Report. A lot of detail goes into writing a research report, and getting familiar with the different requirements would help you create the ideal research report. A research report is usually broken down into multiple sections, which allows for a concise presentation of information. Structure and Example of a ...
An outline of the research questions and hypotheses; the assumptions or propositions that your research will test. Literature Review. Not all research reports have a separate literature review section. In shorter research reports, the review is usually part of the Introduction. A literature review is a critical survey of recent relevant ...
Do not use a period after your title or after any heading in the paper (e.g., Works Cited). Begin your text on a new, double-spaced line after the title, indenting the first line of the paragraph half an inch from the left margin. Fig. 1. The top of the first page of a research paper.
Research reports are recorded data prepared by researchers or statisticians after analyzing the information gathered by conducting organized research, typically in the form of surveys or qualitative methods. A research report is a reliable source to recount details about a conducted research. It is most often considered to be a true testimony ...
There's endless good advice for writing effective research reports, and it almost all depends on the subjective aims of the people behind the report. ... For any research-report format, the outline should create momentum along a chain of logic that builds up to a conclusion or interpretation.
Research paper format is an essential aspect of academic writing that plays a crucial role in the communication of research findings.The format of a research paper depends on various factors such as the discipline, style guide, and purpose of the research. It includes guidelines for the structure, citation style, referencing, and other elements of the paper that contribute to its overall ...
When reporting the methods used in a sample -based study, the usual convention is to. discuss the following topics in the order shown: Chapter 13 Writing a Research Report 8. • Sample (number in ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
Here's a commonly used process for successful writers: Sample Writing Process. Prewriting. Make notes, scribble ideas: start generating text, drawing figures, sketching out presentation ideas. Ignore neatness, spelling, and sentence structure--get the ideas down. Analyze audience and purpose to focus your writing. Writing.
Indent new paragraphs 1/2 inch. Use a running head for each page in the upper right-hand corner, which consists of the paper's title in capital letters followed by the page number. The citations page at the end should be titled "References." In-text citations should include the publication date: (Smith, 1999, p. 50).
Preparation of a comprehensive written research report is an essential part of a valid research experience, and the student should be aware of this requirement at the outset of the project. Interim reports may also be required, usually at the termination of the quarter or semester. Sufficient time should be allowed for satisfactory completion ...
2. Follow the Right Report Writing Format: Adhere to a structured format, including a clear title, table of contents, summary, introduction, body, conclusion, recommendations, and appendices. This ensures clarity and coherence. Follow the format suggestions in this article to start off on the right foot. 3.
Grammar Checker to make sure your grammar, spelling, and punctuation are correct; Paraphraser to understand ideas you read in your research and improve the fluency of your writing; Summarizer to compose a potential thesis statement and concluding sentences for paragraphs and sections; QuillBot Flow to work on your research paper from start to finish; Writing a research paper requires a lot of ...
Thus, you must write up a research report to add your research to the body of knowledge. To make sure readers find the information regarding conclusion validity and to facilitate the writing process, a commonly used structure for research reports has emerged. The standard research report comprises the following 7 sections: introduction,
Avoid making subjective statements or unsupported claims; instead, back up your analysis with evidence and logical reasoning. IV. Conclusion and Recommendations. The conclusion sums up the main findings of your report and provides a concise answer to the research question or objective stated in the introduction.
MLA style paper format organizes proposals, making research aims obvious to reviewers and researchers. MLA proposal format, citations, and organization are crucial for academic legitimacy. The style basics will be covered in this part to help you write a solid MLA research proposal. The crucial role of following MLA guidelines in writing
Report on Administrative Proceedings for October 1, 1998 through Mar. 31, 1999- Rule 900 of the Commission's Rules of Practice (17 CFR 201.900) requires the Commission's Office of the Secretary to publish in the SEC Docket each October and Apr. a status report on the Commission's administrative proceedings caseload. (Apr. 30, 1999.
Survey paper format and structure To ensure adherence to academic standards, format your writing as follows. Use Times New Roman, 12-point font, and double-space the text. Set 1-inch margins on all sides for a professional look. Format headings and subheadings clearly and consistently. Include page numbers in the upper right corner.
Writing a strong conclusion for your research paper is crucial, and WPS Office is designed to be exceptionally student-friendly. It offers accessible options and advanced features for free, making it an excellent tool for students. One of the standout features is WPS AI, which integrates AI into its writing and proofreading abilities. WPS AI
Pew Research Center conducted this study to understand Americans' attitudes about U.S. government, such as its size and role. This report is based primarily on a survey of 8,709 adults, including 7,166 registered voters, from April 8 to 14, 2024. Some of the analysis in this report is based on a survey of 8,638 adults from May 13 to 19, 2024.
Partisan polarization has long been a fact of political life in the United States. But increasingly, Republicans and Democrats view not just the opposing party but also the people in that party in a negative light. Growing shares in each party now describe those in the other party as more closed-minded, dishonest, immoral and unintelligent than other Americans.