Reference management. Clean and simple.

How to write a systematic literature review [9 steps]

What is a systematic literature review?
Where are systematic literature reviews used, what types of systematic literature reviews are there, how to write a systematic literature review, 1. decide on your team, 2. formulate your question, 3. plan your research protocol, 4. search for the literature, 5. screen the literature, 6. assess the quality of the studies, 7. extract the data, 8. analyze the results, 9. interpret and present the results, registering your systematic literature review, frequently asked questions about writing a systematic literature review, related articles.
A systematic literature review is a summary, analysis, and evaluation of all the existing research on a well-formulated and specific question.
Put simply, a systematic review is a study of studies that is popular in medical and healthcare research. In this guide, we will cover:
- the definition of a systematic literature review
- the purpose of a systematic literature review
- the different types of systematic reviews
- how to write a systematic literature review
➡️ Visit our guide to the best research databases for medicine and health to find resources for your systematic review.
Systematic literature reviews can be utilized in various contexts, but they’re often relied on in clinical or healthcare settings.
Medical professionals read systematic literature reviews to stay up-to-date in their field, and granting agencies sometimes need them to make sure there’s justification for further research in an area. They can even be used as the starting point for developing clinical practice guidelines.
A classic systematic literature review can take different approaches:
- Effectiveness reviews assess the extent to which a medical intervention or therapy achieves its intended effect. They’re the most common type of systematic literature review.
- Diagnostic test accuracy reviews produce a summary of diagnostic test performance so that their accuracy can be determined before use by healthcare professionals.
- Experiential (qualitative) reviews analyze human experiences in a cultural or social context. They can be used to assess the effectiveness of an intervention from a person-centric perspective.
- Costs/economics evaluation reviews look at the cost implications of an intervention or procedure, to assess the resources needed to implement it.
- Etiology/risk reviews usually try to determine to what degree a relationship exists between an exposure and a health outcome. This can be used to better inform healthcare planning and resource allocation.
- Psychometric reviews assess the quality of health measurement tools so that the best instrument can be selected for use.
- Prevalence/incidence reviews measure both the proportion of a population who have a disease, and how often the disease occurs.
- Prognostic reviews examine the course of a disease and its potential outcomes.
- Expert opinion/policy reviews are based around expert narrative or policy. They’re often used to complement, or in the absence of, quantitative data.
- Methodology systematic reviews can be carried out to analyze any methodological issues in the design, conduct, or review of research studies.
Writing a systematic literature review can feel like an overwhelming undertaking. After all, they can often take 6 to 18 months to complete. Below we’ve prepared a step-by-step guide on how to write a systematic literature review.
- Decide on your team.
- Formulate your question.
- Plan your research protocol.
- Search for the literature.
- Screen the literature.
- Assess the quality of the studies.
- Extract the data.
- Analyze the results.
- Interpret and present the results.
When carrying out a systematic literature review, you should employ multiple reviewers in order to minimize bias and strengthen analysis. A minimum of two is a good rule of thumb, with a third to serve as a tiebreaker if needed.
You may also need to team up with a librarian to help with the search, literature screeners, a statistician to analyze the data, and the relevant subject experts.
Define your answerable question. Then ask yourself, “has someone written a systematic literature review on my question already?” If so, yours may not be needed. A librarian can help you answer this.
You should formulate a “well-built clinical question.” This is the process of generating a good search question. To do this, run through PICO:
- Patient or Population or Problem/Disease : who or what is the question about? Are there factors about them (e.g. age, race) that could be relevant to the question you’re trying to answer?
- Intervention : which main intervention or treatment are you considering for assessment?
- Comparison(s) or Control : is there an alternative intervention or treatment you’re considering? Your systematic literature review doesn’t have to contain a comparison, but you’ll want to stipulate at this stage, either way.
- Outcome(s) : what are you trying to measure or achieve? What’s the wider goal for the work you’ll be doing?
Now you need a detailed strategy for how you’re going to search for and evaluate the studies relating to your question.
The protocol for your systematic literature review should include:
- the objectives of your project
- the specific methods and processes that you’ll use
- the eligibility criteria of the individual studies
- how you plan to extract data from individual studies
- which analyses you’re going to carry out
For a full guide on how to systematically develop your protocol, take a look at the PRISMA checklist . PRISMA has been designed primarily to improve the reporting of systematic literature reviews and meta-analyses.
When writing a systematic literature review, your goal is to find all of the relevant studies relating to your question, so you need to search thoroughly .
This is where your librarian will come in handy again. They should be able to help you formulate a detailed search strategy, and point you to all of the best databases for your topic.
➡️ Read more on on how to efficiently search research databases .
The places to consider in your search are electronic scientific databases (the most popular are PubMed , MEDLINE , and Embase ), controlled clinical trial registers, non-English literature, raw data from published trials, references listed in primary sources, and unpublished sources known to experts in the field.
➡️ Take a look at our list of the top academic research databases .
Tip: Don’t miss out on “gray literature.” You’ll improve the reliability of your findings by including it.
Don’t miss out on “gray literature” sources: those sources outside of the usual academic publishing environment. They include:
- non-peer-reviewed journals
- pharmaceutical industry files
- conference proceedings
- pharmaceutical company websites
- internal reports
Gray literature sources are more likely to contain negative conclusions, so you’ll improve the reliability of your findings by including it. You should document details such as:
- The databases you search and which years they cover
- The dates you first run the searches, and when they’re updated
- Which strategies you use, including search terms
- The numbers of results obtained
➡️ Read more about gray literature .
This should be performed by your two reviewers, using the criteria documented in your research protocol. The screening is done in two phases:
- Pre-screening of all titles and abstracts, and selecting those appropriate
- Screening of the full-text articles of the selected studies
Make sure reviewers keep a log of which studies they exclude, with reasons why.
➡️ Visit our guide on what is an abstract?
Your reviewers should evaluate the methodological quality of your chosen full-text articles. Make an assessment checklist that closely aligns with your research protocol, including a consistent scoring system, calculations of the quality of each study, and sensitivity analysis.
The kinds of questions you'll come up with are:
- Were the participants really randomly allocated to their groups?
- Were the groups similar in terms of prognostic factors?
- Could the conclusions of the study have been influenced by bias?
Every step of the data extraction must be documented for transparency and replicability. Create a data extraction form and set your reviewers to work extracting data from the qualified studies.
Here’s a free detailed template for recording data extraction, from Dalhousie University. It should be adapted to your specific question.
Establish a standard measure of outcome which can be applied to each study on the basis of its effect size.
Measures of outcome for studies with:
- Binary outcomes (e.g. cured/not cured) are odds ratio and risk ratio
- Continuous outcomes (e.g. blood pressure) are means, difference in means, and standardized difference in means
- Survival or time-to-event data are hazard ratios
Design a table and populate it with your data results. Draw this out into a forest plot , which provides a simple visual representation of variation between the studies.
Then analyze the data for issues. These can include heterogeneity, which is when studies’ lines within the forest plot don’t overlap with any other studies. Again, record any excluded studies here for reference.
Consider different factors when interpreting your results. These include limitations, strength of evidence, biases, applicability, economic effects, and implications for future practice or research.
Apply appropriate grading of your evidence and consider the strength of your recommendations.
It’s best to formulate a detailed plan for how you’ll present your systematic review results. Take a look at these guidelines for interpreting results from the Cochrane Institute.
Before writing your systematic literature review, you can register it with OSF for additional guidance along the way. You could also register your completed work with PROSPERO .
Systematic literature reviews are often found in clinical or healthcare settings. Medical professionals read systematic literature reviews to stay up-to-date in their field and granting agencies sometimes need them to make sure there’s justification for further research in an area.
The first stage in carrying out a systematic literature review is to put together your team. You should employ multiple reviewers in order to minimize bias and strengthen analysis. A minimum of two is a good rule of thumb, with a third to serve as a tiebreaker if needed.
Your systematic review should include the following details:
A literature review simply provides a summary of the literature available on a topic. A systematic review, on the other hand, is more than just a summary. It also includes an analysis and evaluation of existing research. Put simply, it's a study of studies.
The final stage of conducting a systematic literature review is interpreting and presenting the results. It’s best to formulate a detailed plan for how you’ll present your systematic review results, guidelines can be found for example from the Cochrane institute .


Systematic Review
- Library Help
- What is a Systematic Review (SR)?
Steps of a Systematic Review
- Framing a Research Question
- Developing a Search Strategy
- Searching the Literature
- Managing the Process
- Meta-analysis
- Publishing your Systematic Review
Forms and templates

Image: David Parmenter's Shop
- PICO Template
- Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria
- Database Search Log
- Review Matrix
- Cochrane Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Included Studies
• PRISMA Flow Diagram - Record the numbers of retrieved references and included/excluded studies. You can use the Create Flow Diagram tool to automate the process.
• PRISMA Checklist - Checklist of items to include when reporting a systematic review or meta-analysis
PRISMA 2020 and PRISMA-S: Common Questions on Tracking Records and the Flow Diagram
- PROSPERO Template
- Manuscript Template
- Steps of SR (text)
- Steps of SR (visual)
- Steps of SR (PIECES)
Adapted from A Guide to Conducting Systematic Reviews: Steps in a Systematic Review by Cornell University Library
Source: Cochrane Consumers and Communications (infographics are free to use and licensed under Creative Commons )
Check the following visual resources titled " What Are Systematic Reviews?"
- Video with closed captions available
- Animated Storyboard
- << Previous: What is a Systematic Review (SR)?
- Next: Framing a Research Question >>
- Last Updated: May 8, 2024 1:44 PM
- URL: https://lib.guides.umd.edu/SR
Jump to navigation

Cochrane Training
Chapter 1: starting a review.
Toby J Lasserson, James Thomas, Julian PT Higgins
Key Points:
- Systematic reviews address a need for health decision makers to be able to access high quality, relevant, accessible and up-to-date information.
- Systematic reviews aim to minimize bias through the use of pre-specified research questions and methods that are documented in protocols, and by basing their findings on reliable research.
- Systematic reviews should be conducted by a team that includes domain expertise and methodological expertise, who are free of potential conflicts of interest.
- People who might make – or be affected by – decisions around the use of interventions should be involved in important decisions about the review.
- Good data management, project management and quality assurance mechanisms are essential for the completion of a successful systematic review.
Cite this chapter as: Lasserson TJ, Thomas J, Higgins JPT. Chapter 1: Starting a review. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.4 (updated August 2023). Cochrane, 2023. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook .
1.1 Why do a systematic review?
Systematic reviews were developed out of a need to ensure that decisions affecting people’s lives can be informed by an up-to-date and complete understanding of the relevant research evidence. With the volume of research literature growing at an ever-increasing rate, it is impossible for individual decision makers to assess this vast quantity of primary research to enable them to make the most appropriate healthcare decisions that do more good than harm. By systematically assessing this primary research, systematic reviews aim to provide an up-to-date summary of the state of research knowledge on an intervention, diagnostic test, prognostic factor or other health or healthcare topic. Systematic reviews address the main problem with ad hoc searching and selection of research, namely that of bias. Just as primary research studies use methods to avoid bias, so should summaries and syntheses of that research.
A systematic review attempts to collate all the empirical evidence that fits pre-specified eligibility criteria in order to answer a specific research question. It uses explicit, systematic methods that are selected with a view to minimizing bias, thus providing more reliable findings from which conclusions can be drawn and decisions made (Antman et al 1992, Oxman and Guyatt 1993). Systematic review methodology, pioneered and developed by Cochrane, sets out a highly structured, transparent and reproducible methodology (Chandler and Hopewell 2013). This involves: the a priori specification of a research question; clarity on the scope of the review and which studies are eligible for inclusion; making every effort to find all relevant research and to ensure that issues of bias in included studies are accounted for; and analysing the included studies in order to draw conclusions based on all the identified research in an impartial and objective way.
This Handbook is about systematic reviews on the effects of interventions, and specifically about methods used by Cochrane to undertake them. Cochrane Reviews use primary research to generate new knowledge about the effects of an intervention (or interventions) used in clinical, public health or policy settings. They aim to provide users with a balanced summary of the potential benefits and harms of interventions and give an indication of how certain they can be of the findings. They can also compare the effectiveness of different interventions with one another and so help users to choose the most appropriate intervention in particular situations. The primary purpose of Cochrane Reviews is therefore to inform people making decisions about health or health care.
Systematic reviews are important for other reasons. New research should be designed or commissioned only if it does not unnecessarily duplicate existing research (Chalmers et al 2014). Therefore, a systematic review should typically be undertaken before embarking on new primary research. Such a review will identify current and ongoing studies, as well as indicate where specific gaps in knowledge exist, or evidence is lacking; for example, where existing studies have not used outcomes that are important to users of research (Macleod et al 2014). A systematic review may also reveal limitations in the conduct of previous studies that might be addressed in the new study or studies.
Systematic reviews are important, often rewarding and, at times, exciting research projects. They offer the opportunity for authors to make authoritative statements about the extent of human knowledge in important areas and to identify priorities for further research. They sometimes cover issues high on the political agenda and receive attention from the media. Conducting research with these impacts is not without its challenges, however, and completing a high-quality systematic review is often demanding and time-consuming. In this chapter we introduce some of the key considerations for potential review authors who are about to start a systematic review.
1.2 What is the review question?
Getting the research question right is critical for the success of a systematic review. Review authors should ensure that the review addresses an important question to those who are expected to use and act upon its conclusions.
We discuss the formulation of questions in detail in Chapter 2 . For a question about the effects of an intervention, the PICO approach is usually used, which is an acronym for Population, Intervention, Comparison(s) and Outcome. Reviews may have additional questions, for example about how interventions were implemented, economic issues, equity issues or patient experience.
To ensure that the review addresses a relevant question in a way that benefits users, it is important to ensure wide input. In most cases, question formulation should therefore be informed by people with various relevant – but potentially different – perspectives (see Chapter 2, Section 2.4 ).
1.3 Who should do a systematic review?
Systematic reviews should be undertaken by a team. Indeed, Cochrane will not publish a review that is proposed to be undertaken by a single person. Working as a team not only spreads the effort, but ensures that tasks such as the selection of studies for eligibility, data extraction and rating the certainty of the evidence will be performed by at least two people independently, minimizing the likelihood of errors. First-time review authors are encouraged to work with others who are experienced in the process of systematic reviews and to attend relevant training.
Review teams must include expertise in the topic area under review. Topic expertise should not be overly narrow, to ensure that all relevant perspectives are considered. Perspectives from different disciplines can help to avoid assumptions or terminology stemming from an over-reliance on a single discipline. Review teams should also include expertise in systematic review methodology, including statistical expertise.
Arguments have been made that methodological expertise is sufficient to perform a review, and that content expertise should be avoided because of the risk of preconceptions about the effects of interventions (Gøtzsche and Ioannidis 2012). However, it is important that both topic and methodological expertise is present to ensure a good mix of skills, knowledge and objectivity, because topic expertise provides important insight into the implementation of the intervention(s), the nature of the condition being treated or prevented, the relationships between outcomes measured, and other factors that may have an impact on decision making.
A Cochrane Review should represent an independent assessment of the evidence and avoiding financial and non-financial conflicts of interest often requires careful management. It will be important to consider if there are any relevant interests that may constitute a conflict of interest. There are situations where employment, holding of patents and other financial support should prevent people joining an author team. Funding of Cochrane Reviews by commercial organizations with an interest in the outcome of the review is not permitted. To ensure that any issues are identified early in the process, authors planning Cochrane Reviews should consult the Conflict of Interest Policy . Authors should make complete declarations of interest before registration of the review, and refresh these annually thereafter until publication and just prior to publication of the protocol and the review. For authors of review updates, this must be done at the time of the decision to update the review, annually thereafter until publication, and just prior to publication. Authors should also update declarations of interest at any point when their circumstances change.
1.3.1 Involving consumers and other stakeholders
Because the priorities of decision makers and consumers may be different from those of researchers, it is important that review authors consider carefully what questions are important to these different stakeholders. Systematic reviews are more likely to be relevant to a broad range of end users if they are informed by the involvement of people with a range of experiences, in terms of both the topic and the methodology (Thomas et al 2004, Rees and Oliver 2017). Engaging consumers and other stakeholders, such as policy makers, research funders and healthcare professionals, increases relevance, promotes mutual learning, improved uptake and decreases research waste.
Mapping out all potential stakeholders specific to the review question is a helpful first step to considering who might be invited to be involved in a review. Stakeholders typically include: patients and consumers; consumer advocates; policy makers and other public officials; guideline developers; professional organizations; researchers; funders of health services and research; healthcare practitioners, and, on occasion, journalists and other media professionals. Balancing seniority, credibility within the given field, and diversity should be considered. Review authors should also take account of the needs of resource-poor countries and regions in the review process (see Chapter 16 ) and invite appropriate input on the scope of the review and the questions it will address.
It is established good practice to ensure that consumers are involved and engaged in health research, including systematic reviews. Cochrane uses the term ‘consumers’ to refer to a wide range of people, including patients or people with personal experience of a healthcare condition, carers and family members, representatives of patients and carers, service users and members of the public. In 2017, a Statement of Principles for consumer involvement in Cochrane was agreed. This seeks to change the culture of research practice to one where both consumers and other stakeholders are joint partners in research from planning, conduct, and reporting to dissemination. Systematic reviews that have had consumer involvement should be more directly applicable to decision makers than those that have not (see online Chapter II ).
1.3.2 Working with consumers and other stakeholders
Methods for working with consumers and other stakeholders include surveys, workshops, focus groups and involvement in advisory groups. Decisions about what methods to use will typically be based on resource availability, but review teams should be aware of the merits and limitations of such methods. Authors will need to decide who to involve and how to provide adequate support for their involvement. This can include financial reimbursement, the provision of training, and stating clearly expectations of involvement, possibly in the form of terms of reference.
While a small number of consumers or other stakeholders may be part of the review team and become co-authors of the subsequent review, it is sometimes important to bring in a wider range of perspectives and to recognize that not everyone has the capacity or interest in becoming an author. Advisory groups offer a convenient approach to involving consumers and other relevant stakeholders, especially for topics in which opinions differ. Important points to ensure successful involvement include the following.
- The review team should co-ordinate the input of the advisory group to inform key review decisions.
- The advisory group’s input should continue throughout the systematic review process to ensure relevance of the review to end users is maintained.
- Advisory group membership should reflect the breadth of the review question, and consideration should be given to involving vulnerable and marginalized people (Steel 2004) to ensure that conclusions on the value of the interventions are well-informed and applicable to all groups in society (see Chapter 16 ).
Templates such as terms of reference, job descriptions, or person specifications for an advisory group help to ensure clarity about the task(s) required and are available from INVOLVE . The website also gives further information on setting and organizing advisory groups. See also the Cochrane training website for further resources to support consumer involvement.
1.4 The importance of reliability
Systematic reviews aim to be an accurate representation of the current state of knowledge about a given issue. As understanding improves, the review can be updated. Nevertheless, it is important that the review itself is accurate at the time of publication. There are two main reasons for this imperative for accuracy. First, health decisions that affect people’s lives are increasingly taken based on systematic review findings. Current knowledge may be imperfect, but decisions will be better informed when taken in the light of the best of current knowledge. Second, systematic reviews form a critical component of legal and regulatory frameworks; for example, drug licensing or insurance coverage. Here, systematic reviews also need to hold up as auditable processes for legal examination. As systematic reviews need to be both correct, and be seen to be correct, detailed evidence-based methods have been developed to guide review authors as to the most appropriate procedures to follow, and what information to include in their reports to aid auditability.
1.4.1 Expectations for the conduct and reporting of Cochrane Reviews
Cochrane has developed methodological expectations for the conduct, reporting and updating of systematic reviews of interventions (MECIR) and their plain language summaries ( Plain Language Expectations for Authors of Cochrane Summaries ; PLEACS). Developed collaboratively by methodologists and Cochrane editors, they are intended to describe the desirable attributes of a Cochrane Review. The expectations are not all relevant at the same stage of review conduct, so care should be taken to identify those that are relevant at specific points during the review. Different methods should be used at different stages of the review in terms of the planning, conduct, reporting and updating of the review.
Each expectation has a title, a rationale and an elaboration. For the purposes of publication of a review with Cochrane, each has the status of either ‘mandatory’ or ‘highly desirable’. Items described as mandatory are expected to be applied, and if they are not then an appropriate justification should be provided; failure to implement such items may be used as a basis for deciding not to publish a review in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR). Items described as highly desirable should generally be implemented, but there are reasonable exceptions and justifications are not required.
All MECIR expectations for the conduct of a review are presented in the relevant chapters of this Handbook . Expectations for reporting of completed reviews (including PLEACS) are described in online Chapter III . The recommendations provided in the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) Statement have been incorporated into the Cochrane reporting expectations, ensuring compliance with the PRISMA recommendations and summarizing attributes of reporting that should allow a full assessment of the methods and findings of the review (Moher et al 2009).
1.5 Protocol development
Preparing a systematic review is complex and involves many judgements. To minimize the potential for bias in the review process, these judgements should be made as far as possible in ways that do not depend on the findings of the studies included in the review. Review authors’ prior knowledge of the evidence may, for example, influence the definition of a systematic review question, the choice of criteria for study eligibility, or the pre-specification of intervention comparisons and outcomes to analyse. It is important that the methods to be used should be established and documented in advance (see MECIR Box 1.5.a , MECIR Box 1.5.b and MECIR Box 1.5.c ).
Publication of a protocol for a review that is written without knowledge of the available studies reduces the impact of review authors’ biases, promotes transparency of methods and processes, reduces the potential for duplication, allows peer review of the planned methods before they have been completed, and offers an opportunity for the review team to plan resources and logistics for undertaking the review itself. All chapters in the Handbook should be consulted when drafting the protocol. Since systematic reviews are by their nature retrospective, an element of knowledge of the evidence is often inevitable. This is one reason why non-content experts such as methodologists should be part of the review team (see Section 1.3 ). Two exceptions to the retrospective nature of a systematic review are a meta-analysis of a prospectively planned series of trials and some living systematic reviews, as described in Chapter 22 .
The review question should determine the methods used in the review, and not vice versa. The question may concern a relatively straightforward comparison of one treatment with another; or it may necessitate plans to compare different treatments as part of a network meta-analysis, or assess differential effects of an intervention in different populations or delivered in different ways.
The protocol sets out the context in which the review is being conducted. It presents an opportunity to develop ideas that are foundational for the review. This concerns, most explicitly, definition of the eligibility criteria such as the study participants and the choice of comparators and outcomes. The eligibility criteria may also be defined following the development of a logic model (or an articulation of the aspects of an extent logic model that the review is addressing) to explain how the intervention might work (see Chapter 2, Section 2.5.1 ).
MECIR Box 1.5.a Relevant expectations for conduct of intervention reviews
A key purpose of the protocol is to make plans to minimize bias in the eventual findings of the review. Reliable synthesis of available evidence requires a planned, systematic approach. Threats to the validity of systematic reviews can come from the studies they include or the process by which reviews are conducted. Biases within the studies can arise from the method by which participants are allocated to the intervention groups, awareness of intervention group assignment, and the collection, analysis and reporting of data. Methods for examining these issues should be specified in the protocol. Review processes can generate bias through a failure to identify an unbiased (and preferably complete) set of studies, and poor quality assurance throughout the review. The availability of research may be influenced by the nature of the results (i.e. reporting bias). To reduce the impact of this form of bias, searching may need to include unpublished sources of evidence (Dwan et al 2013) ( MECIR Box 1.5.b ).
MECIR Box 1.5.b Relevant expectations for the conduct of intervention reviews
Developing a protocol for a systematic review has benefits beyond reducing bias. Investing effort in designing a systematic review will make the process more manageable and help to inform key priorities for the review. Defining the question, referring to it throughout, and using appropriate methods to address the question focuses the analysis and reporting, ensuring the review is most likely to inform treatment decisions for funders, policy makers, healthcare professionals and consumers. Details of the planned analyses, including investigations of variability across studies, should be specified in the protocol, along with methods for interpreting the results through the systematic consideration of factors that affect confidence in estimates of intervention effect ( MECIR Box 1.5.c ).
MECIR Box 1.5.c Relevant expectations for conduct of intervention reviews
While the intention should be that a review will adhere to the published protocol, changes in a review protocol are sometimes necessary. This is also the case for a protocol for a randomized trial, which must sometimes be changed to adapt to unanticipated circumstances such as problems with participant recruitment, data collection or event rates. While every effort should be made to adhere to a predetermined protocol, this is not always possible or appropriate. It is important, however, that changes in the protocol should not be made based on how they affect the outcome of the research study, whether it is a randomized trial or a systematic review. Post hoc decisions made when the impact on the results of the research is known, such as excluding selected studies from a systematic review, or changing the statistical analysis, are highly susceptible to bias and should therefore be avoided unless there are reasonable grounds for doing this.
Enabling access to a protocol through publication (all Cochrane Protocols are published in the CDSR ) and registration on the PROSPERO register of systematic reviews reduces duplication of effort, research waste, and promotes accountability. Changes to the methods outlined in the protocol should be transparently declared.
This Handbook provides details of the systematic review methods developed or selected by Cochrane. They are intended to address the need for rigour, comprehensiveness and transparency in preparing a Cochrane systematic review. All relevant chapters – including those describing procedures to be followed in the later stages of the review – should be consulted during the preparation of the protocol. A more specific description of the structure of Cochrane Protocols is provide in online Chapter II .
1.6 Data management and quality assurance
Systematic reviews should be replicable, and retaining a record of the inclusion decisions, data collection, transformations or adjustment of data will help to establish a secure and retrievable audit trail. They can be operationally complex projects, often involving large research teams operating in different sites across the world. Good data management processes are essential to ensure that data are not inadvertently lost, facilitating the identification and correction of errors and supporting future efforts to update and maintain the review. Transparent reporting of review decisions enables readers to assess the reliability of the review for themselves.
Review management software, such as Covidence and EPPI-Reviewer , can be used to assist data management and maintain consistent and standardized records of decisions made throughout the review. These tools offer a central repository for review data that can be accessed remotely throughout the world by members of the review team. They record independent assessment of studies for inclusion, risk of bias and extraction of data, enabling checks to be made later in the process if needed. Research has shown that even experienced reviewers make mistakes and disagree with one another on risk-of-bias assessments, so it is particularly important to maintain quality assurance here, despite its cost in terms of author time. As more sophisticated information technology tools begin to be deployed in reviews (see Chapter 4, Section 4.6.6.2 and Chapter 22, Section 22.2.4 ), it is increasingly apparent that all review data – including the initial decisions about study eligibility – have value beyond the scope of the individual review. For example, review updates can be made more efficient through (semi-) automation when data from the original review are available for machine learning.
1.7 Chapter information
Authors: Toby J Lasserson, James Thomas, Julian PT Higgins
Acknowledgements: This chapter builds on earlier versions of the Handbook . We would like to thank Ruth Foxlee, Richard Morley, Soumyadeep Bhaumik, Mona Nasser, Dan Fox and Sally Crowe for their contributions to Section 1.3 .
Funding: JT is supported by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Collaboration for Leadership in Applied Health Research and Care North Thames at Barts Health NHS Trust. JPTH is a member of the NIHR Biomedical Research Centre at University Hospitals Bristol NHS Foundation Trust and the University of Bristol. JPTH received funding from National Institute for Health Research Senior Investigator award NF-SI-0617-10145. The views expressed are those of the author(s) and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health.
1.8 References
Antman E, Lau J, Kupelnick B, Mosteller F, Chalmers T. A comparison of results of meta-analyses of randomized control trials and recommendations of clinical experts: treatment for myocardial infarction. JAMA 1992; 268 : 240–248.
Chalmers I, Bracken MB, Djulbegovic B, Garattini S, Grant J, Gulmezoglu AM, Howells DW, Ioannidis JP, Oliver S. How to increase value and reduce waste when research priorities are set. Lancet 2014; 383 : 156–165.
Chandler J, Hopewell S. Cochrane methods – twenty years experience in developing systematic review methods. Systematic Reviews 2013; 2 : 76.
Dwan K, Gamble C, Williamson PR, Kirkham JJ, Reporting Bias Group. Systematic review of the empirical evidence of study publication bias and outcome reporting bias: an updated review. PloS One 2013; 8 : e66844.
Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JPA. Content area experts as authors: helpful or harmful for systematic reviews and meta-analyses? BMJ 2012; 345 .
Macleod MR, Michie S, Roberts I, Dirnagl U, Chalmers I, Ioannidis JP, Al-Shahi Salman R, Chan AW, Glasziou P. Biomedical research: increasing value, reducing waste. Lancet 2014; 383 : 101–104.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman D, PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Medicine 2009; 6 : e1000097.
Oxman A, Guyatt G. The science of reviewing research. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1993; 703 : 125–133.
Rees R, Oliver S. Stakeholder perspectives and participation in reviews. In: Gough D, Oliver S, Thomas J, editors. An Introduction to Systematic Reviews . 2nd ed. London: Sage; 2017. p. 17–34.
Steel R. Involving marginalised and vulnerable people in research: a consultation document (2nd revision). INVOLVE; 2004.
Thomas J, Harden A, Oakley A, Oliver S, Sutcliffe K, Rees R, Brunton G, Kavanagh J. Integrating qualitative research with trials in systematic reviews. BMJ 2004; 328 : 1010–1012.
For permission to re-use material from the Handbook (either academic or commercial), please see here for full details.

How to Perform a Systematic Literature Review
A Guide for Healthcare Researchers, Practitioners and Students
- © 2020
- Edward Purssell ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3748-0864 0 ,
- Niall McCrae ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9776-7694 1
School of Health Sciences, City, University of London, London, UK
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Florence Nightingale Faculty of Nursing Midwifery & Palliative Care, King’s College London, London, UK
- Presents a logical approach to systematic literature reviewing
- offers a corrective to flawed guidance in existing books
- An accessible but intellectually stimulating guide with illuminating examples and analogies
77k Accesses
28 Citations
10 Altmetric
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this book
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Other ways to access
Licence this eBook for your library
Institutional subscriptions
Table of contents (11 chapters)
Front matter, introduction.
- Edward Purssell, Niall McCrae
A Brief History of the Systematic Review
The aim and scope of a systematic review: a logical approach, searching the literature, screening search results: a 1-2-3 approach, critical appraisal: assessing the quality of studies, reviewing quantitative studies: meta-analysis and narrative approaches, reviewing qualitative studies and metasynthesis, reviewing qualitative and quantitative studies and mixed-method reviews, meaning and implications: the discussion, making an impact: dissemination of results, back matter.
- Methodology
- Evidence-based practice
About this book
The systematic review is a rigorous method of collating and synthesizing evidence from multiple studies, producing a whole greater than the sum of parts. This textbook is an authoritative and accessible guide to an activity that is often found overwhelming. The authors steer readers on a logical, sequential path through the process, taking account of the different needs of researchers, students and practitioners. Practical guidance is provided on the fundamentals of systematic reviewing and also on advanced techniques such as meta-analysis. Examples are given in each chapter, with a succinct glossary to support the text.
This up-to-date, accessible textbook will satisfy the needs of students, practitioners and educators in the sphere of healthcare, and contribute to improving the quality of evidence-based practice. The authors will advise some freely available or inexpensive open source/access resources (such as PubMed, R and Zotero) to help students how to perform a systemic review, in particular those with limited resources.
Authors and Affiliations
Edward Purssell
Florence Nightingale Faculty of Nursing Midwifery & Palliative Care, King’s College London, London, UK
Niall McCrae
About the authors
Dr. Niall McCrae teaches mental health nursing and research methods at the Florence Nightingale Faculty of Nursing, Midwifery & Palliative Care at King’s College London. His research interests are dementia, depression, the impact of social media on younger people, and the history of mental health care. Niall has written two previous books: The Moon and Madness (Imprint Academic, 2011) and The Story of Nursing in British Mental Hospitals: Echoes from the Corridors (Routledge, 2016). He is a regular writer for Salisbury Review magazine.
In partnershipPurssell and McCrae have written several papers on research methodology and literature reviewing for healthcare journals. Both have extensive experience of teaching literature reviewing at all academic levels, and explaining complex concepts in a way that is accessible to all
Bibliographic Information
Book Title : How to Perform a Systematic Literature Review
Book Subtitle : A Guide for Healthcare Researchers, Practitioners and Students
Authors : Edward Purssell, Niall McCrae
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-49672-2
Publisher : Springer Cham
eBook Packages : Medicine , Medicine (R0)
Copyright Information : The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2020
Softcover ISBN : 978-3-030-49671-5 Published: 05 August 2020
eBook ISBN : 978-3-030-49672-2 Published: 04 August 2020
Edition Number : 1
Number of Pages : VII, 188
Number of Illustrations : 7 b/w illustrations, 12 illustrations in colour
Topics : Nursing Research , Nursing Education , Research Skills
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
The Graduate Health & Life Sciences Research Library at Georgetown University Medical Center
Systematic reviews.
- Should I do a systematic review?
- Writing the Protocol
- Building a Systematic Search
- Where to Search
- Managing Project Data
- How can a DML librarian help?
How do I write a protocol?
The protocol serves as a roadmap for your review and specifies the objectives, methods, and outcomes of primary interest of the systematic review. Having a protocol promotes transparency and can be helpful for project management. Some journals require you to submit your protocol along with your manuscript.
A good way to familiarize yourself with research protocols is to take a look at those registered on PROSPERO. PROSPERO's registration form includes 22 mandatory fields and 18 optional fields which will help you to explain every aspect of your research plan.
- PROSPERO - International prospective register of systematic reviews
A protocol ideally includes the following:
- Databases to be searched and additional sources (particularly for grey literature)
- Keywords to be used in the search strategy
- Limits applied to the search
- Screening process
- Data to be extracted
- Summary of data to be reported
Once you have written your protocol, it is advisable to register it. Registering your protocol is a good way to announce that you are working on a review, so that others do not start working on it.
The University of Warwick's protocol template is available below and is a great tool for planning your protocol.
- << Previous: Should I do a systematic review?
- Next: Building a Systematic Search >>
- Last Updated: May 1, 2024 1:01 PM
- URL: https://guides.dml.georgetown.edu/systematicreviews
The Responsible Use of Electronic Resources policy governs the use of resources provided on these guides. © Dahlgren Memorial Library, Georgetown University Medical Center. Unless otherwise stated, these guides may be used for educational or academic purposes as long as proper attribution is given. Please seek permission for any modifications, adaptations, or for commercial purposes. Email [email protected] to request permission. Proper attribution includes: Written by or adapted from, Dahlgren Memorial Library, URL.
Browse Econ Literature
- Working papers
- Software components
- Book chapters
- JEL classification
More features
- Subscribe to new research
RePEc Biblio
Author registration.
- Economics Virtual Seminar Calendar NEW!

How to Undertake an Impactful Literature Review: Understanding Review Approaches and Guidelines for High-impact Systematic Literature Reviews
- Author & abstract
- Related works & more
Corrections
- Amrita Chakraborty
- Arpan Kumar Kar

Suggested Citation
Download full text from publisher.
Follow serials, authors, keywords & more
Public profiles for Economics researchers
Various research rankings in Economics
RePEc Genealogy
Who was a student of whom, using RePEc
Curated articles & papers on economics topics
Upload your paper to be listed on RePEc and IDEAS
New papers by email
Subscribe to new additions to RePEc
EconAcademics
Blog aggregator for economics research
Cases of plagiarism in Economics
About RePEc
Initiative for open bibliographies in Economics
News about RePEc
Questions about IDEAS and RePEc
RePEc volunteers
Participating archives
Publishers indexing in RePEc
Privacy statement
Found an error or omission?
Opportunities to help RePEc
Get papers listed
Have your research listed on RePEc
Open a RePEc archive
Have your institution's/publisher's output listed on RePEc
Get RePEc data
Use data assembled by RePEc
How-To Create an Orthopaedic Systematic Review: A Step-by-Step Guide Part II: Study Execution
Affiliations.
- 1 Maimonides Medical Center, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Brooklyn, NY.
- 2 Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Cleveland, OH.
- 3 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California.
- 4 Sinai Hospital of Baltimore, Rubin Institute for Advanced Orthopedics, Baltimore, Maryland.
- 5 Sinai Hospital of Baltimore, Rubin Institute for Advanced Orthopedics, Baltimore, Maryland; Northwell Health Orthopaedics, Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, NY. Electronic address: [email protected].
- PMID: 38692416
- DOI: 10.1016/j.arth.2024.03.055
Systematic reviews are the apex of the evidence-based pyramid, representing the strongest form of evidence synthesizing results from multiple primary studies. In particular, a quantitative systematic review, or meta-analysis, pools results from multiple studies to help answer a respective research question. The aim of this review is to serve as a guide on how to: 1) design; 2) execute, and 3) publish an orthopaedic arthroplasty systematic review. In Part II, we focus on methods to assess data quality through the Cochrane Risk of Bias, Methodological Index for Non-Randomized Studies (MINORS) criteria, or Newcastle-Ottawa scale; enumerate various methods for appropriate data interpretation and analysis; and summarize how to convert respective findings to a publishable manuscript (providing a previously published example). Use of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines is recommended and standard in all scientific literature, including that of orthopaedic surgery. Pooled analyses with forest plots and associated odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals are common ways to present data. When converting to a manuscript, it is important to consider and discuss the inherent limitations of systematic reviews, including their inclusion and/or exclusion criteria and overall quality, which can be limited based on the quality of individual studies (e.g., publication bias, heterogeneity, search/selection bias). We hope our papers will serve as starting points for those interested in performing an orthopaedic arthroplasty systematic review.
Keywords: Arthroplasty research; Clinical orthopaedic research; Data Analysis; Meta-analysis; Study design; Systematic review.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
- Open access
- Published: 17 August 2023
Data visualisation in scoping reviews and evidence maps on health topics: a cross-sectional analysis
- Emily South ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2187-4762 1 &
- Mark Rodgers 1
Systematic Reviews volume 12 , Article number: 142 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
3602 Accesses
13 Altmetric
Metrics details
Scoping reviews and evidence maps are forms of evidence synthesis that aim to map the available literature on a topic and are well-suited to visual presentation of results. A range of data visualisation methods and interactive data visualisation tools exist that may make scoping reviews more useful to knowledge users. The aim of this study was to explore the use of data visualisation in a sample of recent scoping reviews and evidence maps on health topics, with a particular focus on interactive data visualisation.
Ovid MEDLINE ALL was searched for recent scoping reviews and evidence maps (June 2020-May 2021), and a sample of 300 papers that met basic selection criteria was taken. Data were extracted on the aim of each review and the use of data visualisation, including types of data visualisation used, variables presented and the use of interactivity. Descriptive data analysis was undertaken of the 238 reviews that aimed to map evidence.
Of the 238 scoping reviews or evidence maps in our analysis, around one-third (37.8%) included some form of data visualisation. Thirty-five different types of data visualisation were used across this sample, although most data visualisations identified were simple bar charts (standard, stacked or multi-set), pie charts or cross-tabulations (60.8%). Most data visualisations presented a single variable (64.4%) or two variables (26.1%). Almost a third of the reviews that used data visualisation did not use any colour (28.9%). Only two reviews presented interactive data visualisation, and few reported the software used to create visualisations.
Conclusions
Data visualisation is currently underused by scoping review authors. In particular, there is potential for much greater use of more innovative forms of data visualisation and interactive data visualisation. Where more innovative data visualisation is used, scoping reviews have made use of a wide range of different methods. Increased use of these more engaging visualisations may make scoping reviews more useful for a range of stakeholders.
Peer Review reports
Scoping reviews are “a type of evidence synthesis that aims to systematically identify and map the breadth of evidence available on a particular topic, field, concept, or issue” ([ 1 ], p. 950). While they include some of the same steps as a systematic review, such as systematic searches and the use of predetermined eligibility criteria, scoping reviews often address broader research questions and do not typically involve the quality appraisal of studies or synthesis of data [ 2 ]. Reasons for conducting a scoping review include the following: to map types of evidence available, to explore research design and conduct, to clarify concepts or definitions and to map characteristics or factors related to a concept [ 3 ]. Scoping reviews can also be undertaken to inform a future systematic review (e.g. to assure authors there will be adequate studies) or to identify knowledge gaps [ 3 ]. Other evidence synthesis approaches with similar aims have been described as evidence maps, mapping reviews or systematic maps [ 4 ]. While this terminology is used inconsistently, evidence maps can be used to identify evidence gaps and present them in a user-friendly (and often visual) way [ 5 ].
Scoping reviews are often targeted to an audience of healthcare professionals or policy-makers [ 6 ], suggesting that it is important to present results in a user-friendly and informative way. Until recently, there was little guidance on how to present the findings of scoping reviews. In recent literature, there has been some discussion of the importance of clearly presenting data for the intended audience of a scoping review, with creative and innovative use of visual methods if appropriate [ 7 , 8 , 9 ]. Lockwood et al. suggest that innovative visual presentation should be considered over dense sections of text or long tables in many cases [ 8 ]. Khalil et al. suggest that inspiration could be drawn from the field of data visualisation [ 7 ]. JBI guidance on scoping reviews recommends that reviewers carefully consider the best format for presenting data at the protocol development stage and provides a number of examples of possible methods [ 10 ].
Interactive resources are another option for presentation in scoping reviews [ 9 ]. Researchers without the relevant programming skills can now use several online platforms (such as Tableau [ 11 ] and Flourish [ 12 ]) to create interactive data visualisations. The benefits of using interactive visualisation in research include the ability to easily present more than two variables [ 13 ] and increased engagement of users [ 14 ]. Unlike static graphs, interactive visualisations can allow users to view hierarchical data at different levels, exploring both the “big picture” and looking in more detail ([ 15 ], p. 291). Interactive visualizations are often targeted at practitioners and decision-makers [ 13 ], and there is some evidence from qualitative research that they are valued by policy-makers [ 16 , 17 , 18 ].
Given their focus on mapping evidence, we believe that scoping reviews are particularly well-suited to visually presenting data and the use of interactive data visualisation tools. However, it is unknown how many recent scoping reviews visually map data or which types of data visualisation are used. The aim of this study was to explore the use of data visualisation methods in a large sample of recent scoping reviews and evidence maps on health topics. In particular, we were interested in the extent to which these forms of synthesis use any form of interactive data visualisation.
This study was a cross-sectional analysis of studies labelled as scoping reviews or evidence maps (or synonyms of these terms) in the title or abstract.
The search strategy was developed with help from an information specialist. Ovid MEDLINE® ALL was searched in June 2021 for studies added to the database in the previous 12 months. The search was limited to English language studies only.
The search strategy was as follows:
Ovid MEDLINE(R) ALL
(scoping review or evidence map or systematic map or mapping review or scoping study or scoping project or scoping exercise or literature mapping or evidence mapping or systematic mapping or literature scoping or evidence gap map).ab,ti.
limit 1 to english language
(202006* or 202007* or 202008* or 202009* or 202010* or 202011* or 202012* or 202101* or 202102* or 202103* or 202104* or 202105*).dt.
The search returned 3686 records. Records were de-duplicated in EndNote 20 software, leaving 3627 unique records.
A sample of these reviews was taken by screening the search results against basic selection criteria (Table 1 ). These criteria were piloted and refined after discussion between the two researchers. A single researcher (E.S.) screened the records in EPPI-Reviewer Web software using the machine-learning priority screening function. Where a second opinion was needed, decisions were checked by a second researcher (M.R.).
Our initial plan for sampling, informed by pilot searching, was to screen and data extract records in batches of 50 included reviews at a time. We planned to stop screening when a batch of 50 reviews had been extracted that included no new types of data visualisation or after screening time had reached 2 days. However, once data extraction was underway, we found the sample to be richer in terms of data visualisation than anticipated. After the inclusion of 300 reviews, we took the decision to end screening in order to ensure the study was manageable.
Data extraction
A data extraction form was developed in EPPI-Reviewer Web, piloted on 50 reviews and refined. Data were extracted by one researcher (E. S. or M. R.), with a second researcher (M. R. or E. S.) providing a second opinion when needed. The data items extracted were as follows: type of review (term used by authors), aim of review (mapping evidence vs. answering specific question vs. borderline), number of visualisations (if any), types of data visualisation used, variables/domains presented by each visualisation type, interactivity, use of colour and any software requirements.
When categorising review aims, we considered “mapping evidence” to incorporate all of the six purposes for conducting a scoping review proposed by Munn et al. [ 3 ]. Reviews were categorised as “answering a specific question” if they aimed to synthesise study findings to answer a particular question, for example on effectiveness of an intervention. We were inclusive with our definition of “mapping evidence” and included reviews with mixed aims in this category. However, some reviews were difficult to categorise (for example where aims were unclear or the stated aims did not match the actual focus of the paper) and were considered to be “borderline”. It became clear that a proportion of identified records that described themselves as “scoping” or “mapping” reviews were in fact pseudo-systematic reviews that failed to undertake key systematic review processes. Such reviews attempted to integrate the findings of included studies rather than map the evidence, and so reviews categorised as “answering a specific question” were excluded from the main analysis. Data visualisation methods for meta-analyses have been explored previously [ 19 ]. Figure 1 shows the flow of records from search results to final analysis sample.
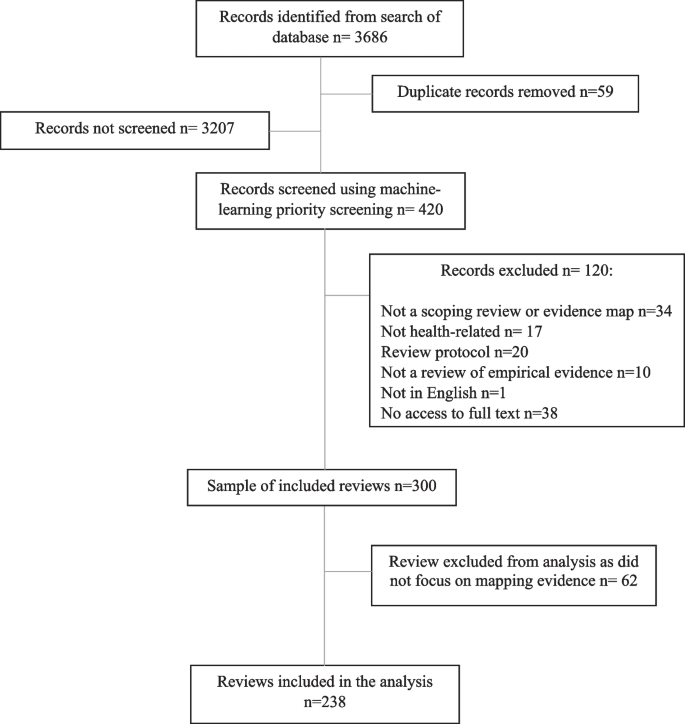
Flow diagram of the sampling process
Data visualisation was defined as any graph or diagram that presented results data, including tables with a visual mapping element, such as cross-tabulations and heat maps. However, tables which displayed data at a study level (e.g. tables summarising key characteristics of each included study) were not included, even if they used symbols, shading or colour. Flow diagrams showing the study selection process were also excluded. Data visualisations in appendices or supplementary information were included, as well as any in publicly available dissemination products (e.g. visualisations hosted online) if mentioned in papers.
The typology used to categorise data visualisation methods was based on an existing online catalogue [ 20 ]. Specific types of data visualisation were categorised in five broad categories: graphs, diagrams, tables, maps/geographical and other. If a data visualisation appeared in our sample that did not feature in the original catalogue, we checked a second online catalogue [ 21 ] for an appropriate term, followed by wider Internet searches. These additional visualisation methods were added to the appropriate section of the typology. The final typology can be found in Additional file 1 .
We conducted descriptive data analysis in Microsoft Excel 2019 and present frequencies and percentages. Where appropriate, data are presented using graphs or other data visualisations created using Flourish. We also link to interactive versions of some of these visualisations.
Almost all of the 300 reviews in the total sample were labelled by review authors as “scoping reviews” ( n = 293, 97.7%). There were also four “mapping reviews”, one “scoping study”, one “evidence mapping” and one that was described as a “scoping review and evidence map”. Included reviews were all published in 2020 or 2021, with the exception of one review published in 2018. Just over one-third of these reviews ( n = 105, 35.0%) included some form of data visualisation. However, we excluded 62 reviews that did not focus on mapping evidence from the following analysis (see “ Methods ” section). Of the 238 remaining reviews (that either clearly aimed to map evidence or were judged to be “borderline”), 90 reviews (37.8%) included at least one data visualisation. The references for these reviews can be found in Additional file 2 .
Number of visualisations
Thirty-six (40.0%) of these 90 reviews included just one example of data visualisation (Fig. 2 ). Less than a third ( n = 28, 31.1%) included three or more visualisations. The greatest number of data visualisations in one review was 17 (all bar or pie charts). In total, 222 individual data visualisations were identified across the sample of 238 reviews.
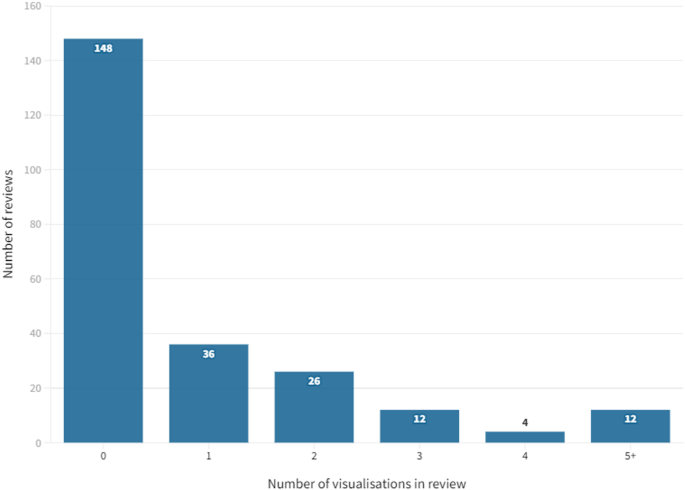
Number of data visualisations per review
Categories of data visualisation
Graphs were the most frequently used category of data visualisation in the sample. Over half of the reviews with data visualisation included at least one graph ( n = 59, 65.6%). The least frequently used category was maps, with 15.6% ( n = 14) of these reviews including a map.
Of the total number of 222 individual data visualisations, 102 were graphs (45.9%), 34 were tables (15.3%), 23 were diagrams (10.4%), 15 were maps (6.8%) and 48 were classified as “other” in the typology (21.6%).
Types of data visualisation
All of the types of data visualisation identified in our sample are reported in Table 2 . In total, 35 different types were used across the sample of reviews.
The most frequently used data visualisation type was a bar chart. Of 222 total data visualisations, 78 (35.1%) were a variation on a bar chart (either standard bar chart, stacked bar chart or multi-set bar chart). There were also 33 pie charts (14.9% of data visualisations) and 24 cross-tabulations (10.8% of data visualisations). In total, these five types of data visualisation accounted for 60.8% ( n = 135) of all data visualisations. Figure 3 shows the frequency of each data visualisation category and type; an interactive online version of this treemap is also available ( https://public.flourish.studio/visualisation/9396133/ ). Figure 4 shows how users can further explore the data using the interactive treemap.
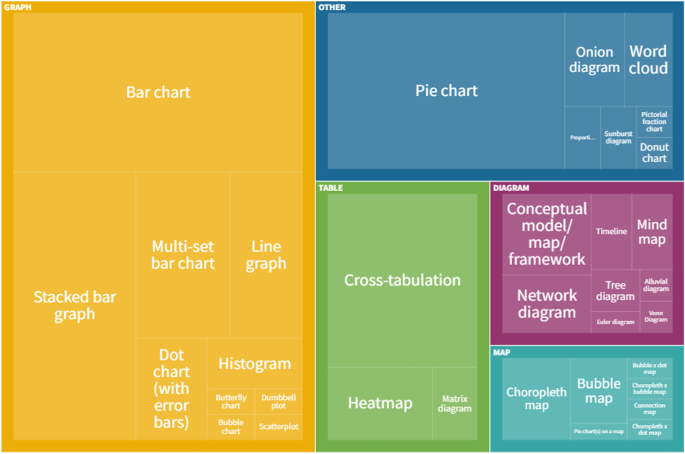
Data visualisation categories and types. An interactive version of this treemap is available online: https://public.flourish.studio/visualisation/9396133/ . Through the interactive version, users can further explore the data (see Fig. 4 ). The unit of this treemap is the individual data visualisation, so multiple data visualisations within the same scoping review are represented in this map. Created with flourish.studio ( https://flourish.studio )
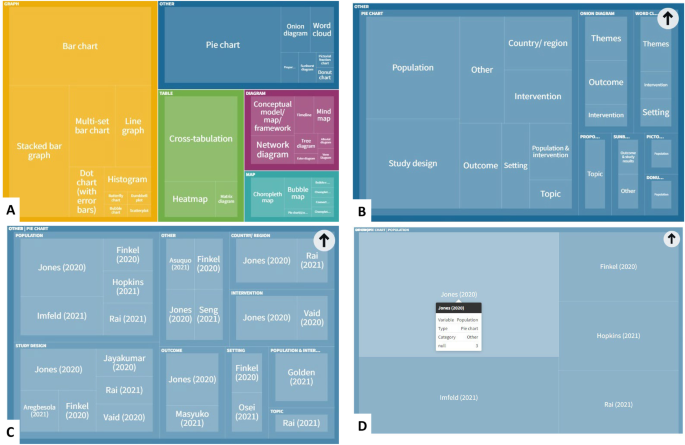
Screenshots showing how users of the interactive treemap can explore the data further. Users can explore each level of the hierarchical treemap ( A Visualisation category > B Visualisation subcategory > C Variables presented in visualisation > D Individual references reporting this category/subcategory/variable permutation). Created with flourish.studio ( https://flourish.studio )
Data presented
Around two-thirds of data visualisations in the sample presented a single variable ( n = 143, 64.4%). The most frequently presented single variables were themes ( n = 22, 9.9% of data visualisations), population ( n = 21, 9.5%), country or region ( n = 21, 9.5%) and year ( n = 20, 9.0%). There were 58 visualisations (26.1%) that presented two different variables. The remaining 21 data visualisations (9.5%) presented three or more variables. Figure 5 shows the variables presented by each different type of data visualisation (an interactive version of this figure is available online).
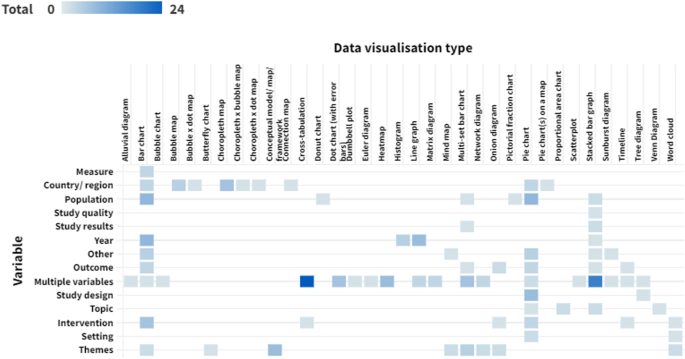
Variables presented by each data visualisation type. Darker cells indicate a larger number of reviews. An interactive version of this heat map is available online: https://public.flourish.studio/visualisation/10632665/ . Users can hover over each cell to see the number of data visualisations for that combination of data visualisation type and variable. The unit of this heat map is the individual data visualisation, so multiple data visualisations within a single scoping review are represented in this map. Created with flourish.studio ( https://flourish.studio )
Most reviews presented at least one data visualisation in colour ( n = 64, 71.1%). However, almost a third ( n = 26, 28.9%) used only black and white or greyscale.
Interactivity
Only two of the reviews included data visualisations with any level of interactivity. One scoping review on music and serious mental illness [ 22 ] linked to an interactive bubble chart hosted online on Tableau. Functionality included the ability to filter the studies displayed by various attributes.
The other review was an example of evidence mapping from the environmental health field [ 23 ]. All four of the data visualisations included in the paper were available in an interactive format hosted either by the review management software or on Tableau. The interactive versions linked to the relevant references so users could directly explore the evidence base. This was the only review that provided this feature.
Software requirements
Nine reviews clearly reported the software used to create data visualisations. Three reviews used Tableau (one of them also used review management software as discussed above) [ 22 , 23 , 24 ]. Two reviews generated maps using ArcGIS [ 25 ] or ArcMap [ 26 ]. One review used Leximancer for a lexical analysis [ 27 ]. One review undertook a bibliometric analysis using VOSviewer [ 28 ], and another explored citation patterns using CitNetExplorer [ 29 ]. Other reviews used Excel [ 30 ] or R [ 26 ].
To our knowledge, this is the first systematic and in-depth exploration of the use of data visualisation techniques in scoping reviews. Our findings suggest that the majority of scoping reviews do not use any data visualisation at all, and, in particular, more innovative examples of data visualisation are rare. Around 60% of data visualisations in our sample were simple bar charts, pie charts or cross-tabulations. There appears to be very limited use of interactive online visualisation, despite the potential this has for communicating results to a range of stakeholders. While it is not always appropriate to use data visualisation (or a simple bar chart may be the most user-friendly way of presenting the data), these findings suggest that data visualisation is being underused in scoping reviews. In a large minority of reviews, visualisations were not published in colour, potentially limiting how user-friendly and attractive papers are to decision-makers and other stakeholders. Also, very few reviews clearly reported the software used to create data visualisations. However, 35 different types of data visualisation were used across the sample, highlighting the wide range of methods that are potentially available to scoping review authors.
Our results build on the limited research that has previously been undertaken in this area. Two previous publications also found limited use of graphs in scoping reviews. Results were “mapped graphically” in 29% of scoping reviews in any field in one 2014 publication [ 31 ] and 17% of healthcare scoping reviews in a 2016 article [ 6 ]. Our results suggest that the use of data visualisation has increased somewhat since these reviews were conducted. Scoping review methods have also evolved in the last 10 years; formal guidance on scoping review conduct was published in 2014 [ 32 ], and an extension of the PRISMA checklist for scoping reviews was published in 2018 [ 33 ]. It is possible that an overall increase in use of data visualisation reflects increased quality of published scoping reviews. There is also some literature supporting our findings on the wide range of data visualisation methods that are used in evidence synthesis. An investigation of methods to identify, prioritise or display health research gaps (25/139 included studies were scoping reviews; 6/139 were evidence maps) identified 14 different methods used to display gaps or priorities, with half being “more advanced” (e.g. treemaps, radial bar plots) ([ 34 ], p. 107). A review of data visualisation methods used in papers reporting meta-analyses found over 200 different ways of displaying data [ 19 ].
Only two reviews in our sample used interactive data visualisation, and one of these was an example of systematic evidence mapping from the environmental health field rather than a scoping review (in environmental health, systematic evidence mapping explicitly involves producing a searchable database [ 35 ]). A scoping review of papers on the use of interactive data visualisation in population health or health services research found a range of examples but still limited use overall [ 13 ]. For example, the authors noted the currently underdeveloped potential for using interactive visualisation in research on health inequalities. It is possible that the use of interactive data visualisation in academic papers is restricted by academic publishing requirements; for example, it is currently difficult to incorporate an interactive figure into a journal article without linking to an external host or platform. However, we believe that there is a lot of potential to add value to future scoping reviews by using interactive data visualisation software. Few reviews in our sample presented three or more variables in a single visualisation, something which can easily be achieved using interactive data visualisation tools. We have previously used EPPI-Mapper [ 36 ] to present results of a scoping review of systematic reviews on behaviour change in disadvantaged groups, with links to the maps provided in the paper [ 37 ]. These interactive maps allowed policy-makers to explore the evidence on different behaviours and disadvantaged groups and access full publications of the included studies directly from the map.
We acknowledge there are barriers to use for some of the data visualisation software available. EPPI-Mapper and some of the software used by reviews in our sample incur a cost. Some software requires a certain level of knowledge and skill in its use. However numerous online free data visualisation tools and resources exist. We have used Flourish to present data for this review, a basic version of which is currently freely available and easy to use. Previous health research has been found to have used a range of different interactive data visualisation software, much of which does not required advanced knowledge or skills to use [ 13 ].
There are likely to be other barriers to the use of data visualisation in scoping reviews. Journal guidelines and policies may present barriers for using innovative data visualisation. For example, some journals charge a fee for publication of figures in colour. As previously mentioned, there are limited options for incorporating interactive data visualisation into journal articles. Authors may also be unaware of the data visualisation methods and tools that are available. Producing data visualisations can be time-consuming, particularly if authors lack experience and skills in this. It is possible that many authors prioritise speed of publication over spending time producing innovative data visualisations, particularly in a context where there is pressure to achieve publications.
Limitations
A limitation of this study was that we did not assess how appropriate the use of data visualisation was in our sample as this would have been highly subjective. Simple descriptive or tabular presentation of results may be the most appropriate approach for some scoping review objectives [ 7 , 8 , 10 ], and the scoping review literature cautions against “over-using” different visual presentation methods [ 7 , 8 ]. It cannot be assumed that all of the reviews that did not include data visualisation should have done so. Likewise, we do not know how many reviews used methods of data visualisation that were not well suited to their data.
We initially relied on authors’ own use of the term “scoping review” (or equivalent) to sample reviews but identified a relatively large number of papers labelled as scoping reviews that did not meet the basic definition, despite the availability of guidance and reporting guidelines [ 10 , 33 ]. It has previously been noted that scoping reviews may be undertaken inappropriately because they are seen as “easier” to conduct than a systematic review ([ 3 ], p.6), and that reviews are often labelled as “scoping reviews” while not appearing to follow any established framework or guidance [ 2 ]. We therefore took the decision to remove these reviews from our main analysis. However, decisions on how to classify review aims were subjective, and we did include some reviews that were of borderline relevance.
A further limitation is that this was a sample of published reviews, rather than a comprehensive systematic scoping review as have previously been undertaken [ 6 , 31 ]. The number of scoping reviews that are published has increased rapidly, and this would now be difficult to undertake. As this was a sample, not all relevant scoping reviews or evidence maps that would have met our criteria were included. We used machine learning to screen our search results for pragmatic reasons (to reduce screening time), but we do not see any reason that our sample would not be broadly reflective of the wider literature.
Data visualisation, and in particular more innovative examples of it, is currently underused in published scoping reviews on health topics. The examples that we have found highlight the wide range of methods that scoping review authors could draw upon to present their data in an engaging way. In particular, we believe that interactive data visualisation has significant potential for mapping the available literature on a topic. Appropriate use of data visualisation may increase the usefulness, and thus uptake, of scoping reviews as a way of identifying existing evidence or research gaps by decision-makers, researchers and commissioners of research. We recommend that scoping review authors explore the extensive free resources and online tools available for data visualisation. However, we also think that it would be useful for publishers to explore allowing easier integration of interactive tools into academic publishing, given the fact that papers are now predominantly accessed online. Future research may be helpful to explore which methods are particularly useful to scoping review users.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Organisation formerly known as Joanna Briggs Institute
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Munn Z, Pollock D, Khalil H, Alexander L, McLnerney P, Godfrey CM, Peters M, Tricco AC. What are scoping reviews? Providing a formal definition of scoping reviews as a type of evidence synthesis. JBI Evid Synth. 2022;20:950–952.
Peters MDJ, Marnie C, Colquhoun H, Garritty CM, Hempel S, Horsley T, Langlois EV, Lillie E, O’Brien KK, Tunçalp Ӧ, et al. Scoping reviews: reinforcing and advancing the methodology and application. Syst Rev. 2021;10:263.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Munn Z, Peters MDJ, Stern C, Tufanaru C, McArthur A, Aromataris E. Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2018;18:143.
Sutton A, Clowes M, Preston L, Booth A. Meeting the review family: exploring review types and associated information retrieval requirements. Health Info Libr J. 2019;36:202–22.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Miake-Lye IM, Hempel S, Shanman R, Shekelle PG. What is an evidence map? A systematic review of published evidence maps and their definitions, methods, and products. Syst Rev. 2016;5:28.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien K, Colquhoun H, Kastner M, Levac D, Ng C, Sharpe JP, Wilson K, et al. A scoping review on the conduct and reporting of scoping reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2016;16:15.
Khalil H, Peters MDJ, Tricco AC, Pollock D, Alexander L, McInerney P, Godfrey CM, Munn Z. Conducting high quality scoping reviews-challenges and solutions. J Clin Epidemiol. 2021;130:156–60.
Lockwood C, dos Santos KB, Pap R. Practical guidance for knowledge synthesis: scoping review methods. Asian Nurs Res. 2019;13:287–94.
Article Google Scholar
Pollock D, Peters MDJ, Khalil H, McInerney P, Alexander L, Tricco AC, Evans C, de Moraes ÉB, Godfrey CM, Pieper D, et al. Recommendations for the extraction, analysis, and presentation of results in scoping reviews. JBI Evidence Synthesis. 2022;10:11124.
Google Scholar
Peters MDJ GC, McInerney P, Munn Z, Tricco AC, Khalil, H. Chapter 11: Scoping reviews (2020 version). In: Aromataris E MZ, editor. JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis. JBI; 2020. Available from https://synthesismanual.jbi.global . Accessed 1 Feb 2023.
Tableau Public. https://www.tableau.com/en-gb/products/public . Accessed 24 January 2023.
flourish.studio. https://flourish.studio/ . Accessed 24 January 2023.
Chishtie J, Bielska IA, Barrera A, Marchand J-S, Imran M, Tirmizi SFA, Turcotte LA, Munce S, Shepherd J, Senthinathan A, et al. Interactive visualization applications in population health and health services research: systematic scoping review. J Med Internet Res. 2022;24: e27534.
Isett KR, Hicks DM. Providing public servants what they need: revealing the “unseen” through data visualization. Public Adm Rev. 2018;78:479–85.
Carroll LN, Au AP, Detwiler LT, Fu T-c, Painter IS, Abernethy NF. Visualization and analytics tools for infectious disease epidemiology: a systematic review. J Biomed Inform. 2014;51:287–298.
Lundkvist A, El-Khatib Z, Kalra N, Pantoja T, Leach-Kemon K, Gapp C, Kuchenmüller T. Policy-makers’ views on translating burden of disease estimates in health policies: bridging the gap through data visualization. Arch Public Health. 2021;79:17.
Zakkar M, Sedig K. Interactive visualization of public health indicators to support policymaking: an exploratory study. Online J Public Health Inform. 2017;9:e190–e190.
Park S, Bekemeier B, Flaxman AD. Understanding data use and preference of data visualization for public health professionals: a qualitative study. Public Health Nurs. 2021;38:531–41.
Kossmeier M, Tran US, Voracek M. Charting the landscape of graphical displays for meta-analysis and systematic reviews: a comprehensive review, taxonomy, and feature analysis. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2020;20:26.
Ribecca, S. The Data Visualisation Catalogue. https://datavizcatalogue.com/index.html . Accessed 23 November 2021.
Ferdio. Data Viz Project. https://datavizproject.com/ . Accessed 23 November 2021.
Golden TL, Springs S, Kimmel HJ, Gupta S, Tiedemann A, Sandu CC, Magsamen S. The use of music in the treatment and management of serious mental illness: a global scoping review of the literature. Front Psychol. 2021;12: 649840.
Keshava C, Davis JA, Stanek J, Thayer KA, Galizia A, Keshava N, Gift J, Vulimiri SV, Woodall G, Gigot C, et al. Application of systematic evidence mapping to assess the impact of new research when updating health reference values: a case example using acrolein. Environ Int. 2020;143: 105956.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Jayakumar P, Lin E, Galea V, Mathew AJ, Panda N, Vetter I, Haynes AB. Digital phenotyping and patient-generated health data for outcome measurement in surgical care: a scoping review. J Pers Med. 2020;10:282.
Qu LG, Perera M, Lawrentschuk N, Umbas R, Klotz L. Scoping review: hotspots for COVID-19 urological research: what is being published and from where? World J Urol. 2021;39:3151–60.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Rossa-Roccor V, Acheson ES, Andrade-Rivas F, Coombe M, Ogura S, Super L, Hong A. Scoping review and bibliometric analysis of the term “planetary health” in the peer-reviewed literature. Front Public Health. 2020;8:343.
Hewitt L, Dahlen HG, Hartz DL, Dadich A. Leadership and management in midwifery-led continuity of care models: a thematic and lexical analysis of a scoping review. Midwifery. 2021;98: 102986.
Xia H, Tan S, Huang S, Gan P, Zhong C, Lu M, Peng Y, Zhou X, Tang X. Scoping review and bibliometric analysis of the most influential publications in achalasia research from 1995 to 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:8836395.
Vigliotti V, Taggart T, Walker M, Kusmastuti S, Ransome Y. Religion, faith, and spirituality influences on HIV prevention activities: a scoping review. PLoS ONE. 2020;15: e0234720.
van Heemskerken P, Broekhuizen H, Gajewski J, Brugha R, Bijlmakers L. Barriers to surgery performed by non-physician clinicians in sub-Saharan Africa-a scoping review. Hum Resour Health. 2020;18:51.
Pham MT, Rajić A, Greig JD, Sargeant JM, Papadopoulos A, McEwen SA. A scoping review of scoping reviews: advancing the approach and enhancing the consistency. Res Synth Methods. 2014;5:371–85.
Peters MDJ, Marnie C, Tricco AC, Pollock D, Munn Z, Alexander L, McInerney P, Godfrey CM, Khalil H. Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI Evid Synth. 2020;18:2119–26.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, Moher D, Peters MDJ, Horsley T, Weeks L, et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169:467–73.
Nyanchoka L, Tudur-Smith C, Thu VN, Iversen V, Tricco AC, Porcher R. A scoping review describes methods used to identify, prioritize and display gaps in health research. J Clin Epidemiol. 2019;109:99–110.
Wolffe TAM, Whaley P, Halsall C, Rooney AA, Walker VR. Systematic evidence maps as a novel tool to support evidence-based decision-making in chemicals policy and risk management. Environ Int. 2019;130:104871.
Digital Solution Foundry and EPPI-Centre. EPPI-Mapper, Version 2.0.1. EPPI-Centre, UCL Social Research Institute, University College London. 2020. https://eppi.ioe.ac.uk/cms/Default.aspx?tabid=3790 .
South E, Rodgers M, Wright K, Whitehead M, Sowden A. Reducing lifestyle risk behaviours in disadvantaged groups in high-income countries: a scoping review of systematic reviews. Prev Med. 2022;154: 106916.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Melissa Harden, Senior Information Specialist, Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, for advice on developing the search strategy.
This work received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, University of York, York, YO10 5DD, UK
Emily South & Mark Rodgers
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Both authors conceptualised and designed the study and contributed to screening, data extraction and the interpretation of results. ES undertook the literature searches, analysed data, produced the data visualisations and drafted the manuscript. MR contributed to revising the manuscript, and both authors read and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Emily South .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1..
Typology of data visualisation methods.
Additional file 2.
References of scoping reviews included in main dataset.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
South, E., Rodgers, M. Data visualisation in scoping reviews and evidence maps on health topics: a cross-sectional analysis. Syst Rev 12 , 142 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-023-02309-y
Download citation
Received : 21 February 2023
Accepted : 07 August 2023
Published : 17 August 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-023-02309-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Scoping review
- Evidence map
- Data visualisation
Systematic Reviews
ISSN: 2046-4053
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]

COMMENTS
Method details Overview. A Systematic Literature Review (SLR) is a research methodology to collect, identify, and critically analyze the available research studies (e.g., articles, conference proceedings, books, dissertations) through a systematic procedure [12].An SLR updates the reader with current literature about a subject [6].The goal is to review critical points of current knowledge on a ...
The best reviews synthesize studies to draw broad theoretical conclusions about what a literature means, linking theory to evidence and evidence to theory. This guide describes how to plan, conduct, organize, and present a systematic review of quantitative (meta-analysis) or qualitative (narrative review, meta-synthesis) information.
Screen the literature. Assess the quality of the studies. Extract the data. Analyze the results. Interpret and present the results. 1. Decide on your team. When carrying out a systematic literature review, you should employ multiple reviewers in order to minimize bias and strengthen analysis.
Image by TraceyChandler. Steps to conducting a systematic review. Quick overview of the process: Steps and resources from the UMB HSHSL Guide. YouTube video (26 min); Another detailed guide on how to conduct and write a systematic review from RMIT University; A roadmap for searching literature in PubMed from the VU Amsterdam; Alexander, P. A. (2020).
Reasons for inclusion and exclusion should be recorded. Step 3: Assessing the quality of studies. Study quality assessment is relevant to every step of a review. Question formulation (Step 1) and study selection criteria (Step 2) should describe the minimum acceptable level of design.
Systematic review allows the assessment of primary study quality, identifying the weaknesses in current experimental efforts and guiding the methodology of future research. Choosing the features of study design to review and critique is dependent on the subject and design of the literature identified.
Investing effort in designing a systematic review will make the process more manageable and help to inform key priorities for the review. Defining the question, referring to it throughout, and using appropriate methods to address the question focuses the analysis and reporting, ensuring the review is most likely to inform treatment decisions ...
Systematic reviews are characterized by a methodical and replicable methodology and presentation. They involve a comprehensive search to locate all relevant published and unpublished work on a subject; a systematic integration of search results; and a critique of the extent, nature, and quality of evidence in relation to a particular research question. The best reviews synthesize studies to ...
A systematic review is a type of review that uses repeatable methods to find, select, and synthesize all available evidence. It answers a clearly formulated research question and explicitly states the methods used to arrive at the answer. Example: Systematic review. In 2008, Dr. Robert Boyle and his colleagues published a systematic review in ...
Literature reviews establish the foundation of academic inquires. However, in the planning field, we lack rigorous systematic reviews. In this article, through a systematic search on the methodology of literature review, we categorize a typology of literature reviews, discuss steps in conducting a systematic literature review, and provide suggestions on how to enhance rigor in literature ...
A systematic review aims to bring evidence together to answer a pre-defined research question. This involves the identification of all primary research relevant to the defined review question, the critical appraisal of this research, and the synthesis of the findings.13 Systematic reviews may combine data from different.
Our goal with this paper is to conduct a narrative review of the literature about systematic reviews and outline the essential elements of a systematic review along with the limitations of such a review. Keywords: systematic reviews, meta-analysis, narrative literature review, prisma checklist. A literature review provides an important insight ...
How to Perform a Systematic Literature Review A Guide for Healthcare Researchers, Practitioners and Students. ... The systematic review is a rigorous method of collating and synthesizing evidence from multiple studies, producing a whole greater than the sum of parts. This textbook is an authoritative and accessible guide to an activity that is ...
A literature search is distinguished from, but integral to, a literature review. Literature reviews are conducted for the purpose of (a) locating information on a topic or identifying gaps in the literature for areas of future study, (b) synthesising conclusions in an area of ambiguity and (c) helping clinicians and researchers inform decision-making and practice guidelines.
The meticulous nature of the systematic review research methodology differentiates a systematic review from a narrative review (literature review or authoritative review). This paper provides a brief step by step summary of how to conduct a systematic review, which may be of interest for clinicians and researchers.
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Abstract. Performing a literature review is a critical first step in research to understanding the state-of-the-art and identifying gaps and challenges in the field. A systematic literature review is a method which sets out a series of steps to methodically organize the review. In this paper, we present a guide designed for researchers and in ...
Creating a systematic review protocol is an important step in the planning process for your review. A review protocol is beneficial for a number of reasons: It helps to ensure that all team members are on the same page when it comes to the research question, inclusion/exclusion criteria, etc.
How do I write a protocol? The protocol serves as a roadmap for your review and specifies the objectives, methods, and outcomes of primary interest of the systematic review. Having a protocol promotes transparency and can be helpful for project management. Some journals require you to submit your protocol along with your manuscript.
Performing a literature review is a critical first step in research to understanding the state-of-the-art and identifying gaps and challenges in the field. A systematic literature review is a method which sets out a series of steps to methodically organize the review. In this paper, we present a guide designed for researchers and in particular ...
Learn how to draft a systematic literature review chapter for your thesis with this comprehensive guide. I'll break down each step of the process, providing ...
A systematic review collects all possible studies related to a given topic and design, and reviews and analyzes their results [ 1 ]. During the systematic review process, the quality of studies is evaluated, and a statistical meta-analysis of the study results is conducted on the basis of their quality. A meta-analysis is a valid, objective ...
Downloadable! Literature reviews lay the foundation for academic investigations, especially for early career researchers. However, in the planning phase, we generally lack clarity on approaches, due to which a lot of review articles are rejected or fail to create a significant impact. The systematic literature review (SLR) is one of the important review methodologies which is increasingly ...
Systematic review methodology can be distinguished from narrative reviews of the literature through its emphasis on transparent, structured and comprehensive approaches to searching the literature ...
Systematic reviews (SRs) are a rigorous method for synthesizing empirical evidence to answer specific research questions. However, they are labor-intensive because of their collaborative nature, strict protocols, and typically large number of documents. Large language models (LLMs) and their applications such as gpt-4/ChatGPT have the potential to reduce the human workload of the SR process ...
In particular, a quantitative systematic review, or meta-analysis, pools results from multiple studies to help answer a respective research question. The aim of this review is to serve as a guide on how to: 1) design; 2) execute, and 3) publish an orthopaedic arthroplasty systematic review. In Part II, we focus on methods to assess data quality ...
Scoping reviews and evidence maps are forms of evidence synthesis that aim to map the available literature on a topic and are well-suited to visual presentation of results. A range of data visualisation methods and interactive data visualisation tools exist that may make scoping reviews more useful to knowledge users. The aim of this study was to explore the use of data visualisation in a ...
The topic must at least be: interesting to you (ideally, you should have come across a series of recent papers related to your line of work that call for a critical summary), an important aspect of the field (so that many readers will be interested in the review and there will be enough material to write it), and.
A systematic review shows the potential of metabolomic and proteomic analysis to discover new disease biomarkers that may influence diagnostics and disease management in glomerulonephritis. BACKGROUND Glomerulonephritis inherently leads to the development of chronic kidney disease. It is the second most common diagnosis in patients requiring renal replacement therapy in the United Kingdom ...