If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.

Get ready for 8th grade
Course: get ready for 8th grade > unit 1.
- Order of operations examples: exponents
- Order of operations
Order of operations example
- Worked example: Order of operations (PEMDAS)
- Order of operations with rational numbers
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

Video transcript
Practice With Order of Operations Problems and Answers
I see it happen all the time in my math classroom: students attempt math problems and get the wrong answer even though they are performing each math operation correctly. How can this be!? Isn’t math supposed to have a single correct answer?
Well, as it turns out, there is a set of rules that tells us the right order and wrong order that operations can be performed in a mathematical expression. And without knowing this very important set of rules, you can’t be sure that you will always get the correct answer! Let’s take a look at this set of rules and dig into some practice with order of operations problems and answers so that you can make sure this doesn’t happen to you!
What is the Correct Order of Operations?
In math and algebra, the order of operations is an important set of rules that tell us the correct order that arithmetic operations should be performed in when working with a numerical expression. Performing operations in the right order using a standard method makes it so that two people will always get the same correct answer when solving a given problem.
In order to help remember the standard order of operations, we can use the acronym PEMDAS.
The PEMDAS rule (sometimes known as BEDMAS or the BODMAS rule) works by matching the first letter of each operation to each of the mathematical operations.
- P (Parentheses) – We start by performing the operations inside any set of parentheses first. It is important to start with any expressions within innermost parentheses and work outward.
- E (Exponents) – The next step is to evaluate or simplify any expressions involving exponents or powers. It is important to remember that this step also includes any square root.
- MD (Multiplication and Division) – It is important to perform multiplication and division from left to right in the order that they appear in the expression. This is a common place where students make mistakes!
- AS (Addition and Subtraction) – Finally, we perform addition and subtraction from left to right as they appear in the expression. Like multiplication and division, these operations have the same priority and are performed from left to right.
To help my students, I have told them to think of the acronym PEMDAS as standing for “Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally”. There are many different ways to remember the PEMDAS acronym, but I have found that this mnemonic device is a great way to help my students remember the order of the PEMDAS acronym.
If you follow the rules of the order of operations, you should find that arriving at the correct answer isn’t as hard as you once thought!
Why Does Order of Operations Matter?
In order to understand when order of operations matters, take a look at this simple 2-step order of operations problem. Consider the following expression:
$$2 + 4 \times 3$$
There are two approaches that you could take here, and only one of them will give you the correct answer! Which one do you think is correct?
As you can see, each strategy results in different answers. The strategy on the left adds 2 + 4 first, while the strategy on the right multiplies 4 x 3 first. Remember that we use the PEMDAS rule to help us identify the right order.
PEMDAS tells us that multiplication must be performed before addition. This tells us that the second solution is correct!
Order of Operations Problems and Answers
Let’s take a look at a few more examples of order of operations problems and answers! I’ll start by introducing you to some simpler problems with two basic operations, and we’ll work our way up to more complex 4-step order of operations problems! Just be sure to review the answer key for each problem to make sure you get the same answer!
2-Step Order of Operations Problems
Example #1: \(5 – 3 \times 2\)
In this first example, following order of operations tells us to perform multiplication before subtraction. Taking a look at the given values, we know that this will result in:
\begin{split} &5 – 3 \times 2 \\ \\ =&5 – 6 \\ \\ =& -1 \end{split}
Remember, performing subtraction first is a common mistake that will prevent you from obtaining the correct answer!
Example #2: \((4 \div 2) + 7\)
The first step of the PEMDAS rule is to tackle any math expressions inside parentheses. After that, we can add 7 to the result.
\begin{split} &(4 \div 2) + 7 \\ \\ =&2 + 7 \\ \\ =& 9 \end{split}
Example #3: \(3^3 – 4\)
The first step in this example is to work out our exponent. After that, we can subtract 4 from the result.
\begin{split} &3^3 – 4 \\ \\ =&27 – 4 \\ \\ =&23 \end{split}
3-Step Order of Operations Problems
Example #4: \(\sqrt{4} \times 3 – 5\)
Remember that the ‘E’ in the PEMDAS acronym also includes the square root operation. As such, we need to evaluate the square root of 4 before multiplying by 3 and subtracting 5.
\begin{split} &\sqrt{4} \times 3 – 5 \\ \\ =&2 \times 3 – 5 \\ \\ =&6 – 5 \\ \\ =&1 \end{split}
Example #5: \((6 ÷ 2) + 3 × 2\)
In this example we must remember to tackle the parentheses first. While your instinct may be to add the 3 next, remember that you need to multiply 3 times 2 first!
\begin{split} &(6 ÷ 2) + 3 × 2 \\ \\ =&3 + 3 × 2 \\ \\ =&3 + 6\\ \\ =&9 \end{split}
Example #6: \(7 – 2 × 3 ÷ 2\)
In this example, we multiply 2 by 3 first, then divide the result by 2. Remember that multiplication and division operations are performed in the order in which they appear from left to right.
\begin{split} &7 – 2 × 3 ÷ 2 \\ \\ =&7 – 6 ÷ 2 \\ \\ =&7 – 3 \\ \\ =&4 \end{split}
4-Step Order of Operations Problems
Example #7: \(2 + 4 × 3 – 4 ÷ 2\)
\begin{split} &2 + 4 × 3 – 4 ÷ 2 \\ \\ =&2 + 12 – 4 ÷ 2 \\ \\ =&2 + 12 – 2 \\ \\ =&12 \end{split}
Example #8: \(2^3 + (4 × 3) – 6 ÷ 2\)
\begin{split} &2^3 + (4 × 3) – 6 ÷ 2 \\ \\ =&2^3 + 12 – 6 ÷ 2 \\ \\ =&8 + 12 – 6 ÷ 2 \\ \\ =&8 + 12 – 3 \\ \\ =&17 \end{split}
Using Order of Operations to Solve Math Problems
When I teach order of operations in my classes, I always encourage my students to keep the PEMDAS rule handy for every problem. Sometimes these problems can seem very simple, but may actually require more thinking. In particular, problems with both multiplication and division operations tend to confuse students!
Take the time that you need to fully understand this very important concept. You will find it comes up often in your studies of math, particularly when working with algebraic formulas !
Like all math concepts, mastering the use of order of operations takes practice and critical thinking. I am hopeful that these order of operations problems and answers have helped you feel more comfortable with this very important algebra skill!
Did you find these order of operations problems and answers helpful? Share this post and subscribe to Math By The Pixel on YouTube for more helpful mathematics content!
RECOMMENDED FOR YOU
Examples of One Solution Equations, Zero, and Infinite
Linear Equations Word Problems Worksheet with Solutions
Order of Operations Worksheets
Welcome to the order of operations worksheets page at Math-Drills.com where we definitely follow orders! This page includes Order of Operations worksheets using whole numbers, integers, decimals and fractions.
Elementary and middle school students generally use the acronyms PEMDAS or BEDMAS to help them remember the order in which they complete multi-operation questions. The 'P' or 'B' in the acronym stands for parentheses or brackets. All operations within parentheses get completed first. The 'E' refers to exponents; all exponents are calculated after the parentheses. The 'M' and 'D' are interchangeable as one completes the multiplication and division in the order that they appear from left to right. The fourth and final step is to solve for the addition and subtraction in the order that they appear from left to right.
More recently, students are being taught the acronym, PEMA, for order of operations, to avoid the confusion inherent in the other acronyms. For example, in PEMDAS, multiplication comes before division which some people incorrectly assumes means that multiplication must be done before division in an order of operations question. In fact, the two operations are completed in the order that they occur from left to right in the question. This is recognized in PEMA which more correctly shows that there are four levels to complete in an order of operations question.
Unless you want your students doing something different than the rest of the world, it would be a good idea to get them to understand these rules. There is no discovery or exploration needed here. These are rules that need to be learned and practiced and have been accepted as the standard approach to solving any multi-step mathematics problem.
Most Popular Order of Operations Worksheets this Week

Order of Operations With Whole Numbers and Integers
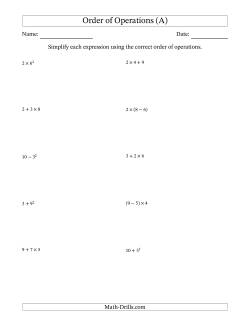
The worksheets in this section include questions with parentheses, addition, and multiplication. Exponents, subtraction, and division are excluded. The purpose of excluding some parts of PEMDAS is to ease students into how the order of operations works. To help students see a purpose for the order of operations, try to associate the expressions with related scenarios. For example, 2 + 7 × 3 could refer to the number of days in two days and three weeks. (9 + 2) × 15 could mean the total amount earned if someone worked 9 hours yesterday and 2 hours today for $15 an hour.
- Order of Operations With Whole Numbers (Addition and Multiplication Only) 2-Step Order of Operations with Whole Numbers ( Addition & Multiplication Only ) 3-Step Order of Operations with Whole Numbers ( Addition & Multiplication Only ) 4-Step Order of Operations with Whole Numbers ( Addition & Multiplication Only ) 5-Step Order of Operations with Whole Numbers ( Addition & Multiplication Only ) 6-Step Order of Operations with Whole Numbers ( Addition & Multiplication Only )
The worksheets in this section include questions with parentheses, addition, subtraction, and multiplication. Exponents and division are excluded. This section is similar to the previous one in that it is meant to help ease students into the order of operations without complicating things with exponents and division.
- Order of Operations With Whole Numbers (Addition, Subtraction and Multiplication Only) 2-Step Order of Operations with Whole Numbers ( Addition, Subtraction & Multiplication Only ) 3-Step Order of Operations with Whole Numbers ( Addition, Subtraction & Multiplication Only ) 4-Step Order of Operations with Whole Numbers ( Addition, Subtraction & Multiplication Only ) 5-Step Order of Operations with Whole Numbers ( Addition, Subtraction & Multiplication Only ) 6-Step Order of Operations with Whole Numbers ( Addition, Subtraction & Multiplication Only )
One last section to help ease students into the order of operations or simply for students who haven't learned about exponents yet. The questions on the worksheets in this section include parentheses and all four operations.
- Order of Operations With Whole Numbers (No Exponents) 2-Step Order of Operations with Whole Numbers ( No Exponents ) 3-Step Order of Operations with Whole Numbers ( No Exponents ) 4-Step Order of Operations with Whole Numbers ( No Exponents ) 5-Step Order of Operations with Whole Numbers ( No Exponents ) 6-Step Order of Operations with Whole Numbers ( No Exponents )
The worksheets in this section include questions with parentheses, exponents and all four operations.
- Order of Operations With Whole Numbers (All Operations, Parentheses and Exponents) 2-Step Order of Operations with Whole Numbers 3-Step Order of Operations with Whole Numbers 4-Step Order of Operations with Whole Numbers 5-Step Order of Operations with Whole Numbers 6-Step Order of Operations with Whole Numbers
- Order of Operations With Integers (No Exponents) 2-Step Order of Operations with Integers and No Exponents 3-Step Order of Operations with Integers and No Exponents 4-Step Order of Operations with Integers and No Exponents 5-Step Order of Operations with Integers and No Exponents 6-Step Order of Operations with Integers and No Exponents
The worksheets in this section include parentheses, exponents, and all four operations.
- Order of Operations With Integers (All Operations, Parentheses and Exponents) 2-Step Order of Operations with Integers 3-Step Order of Operations with Integers 4-Step Order of Operations with Integers 5-Step Order of Operations with Integers 6-Step Order of Operations with Integers
Order of Operations With Fractions and Decimals
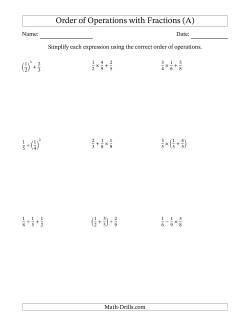
As with other order of operation worksheets, the fractions order of operations worksheets require some prerequisite knowledge. If your students struggle with these questions, it probably has more to do with their ability to work with fractions than the questions themselves. Observe closely and try to pin point exactly what prerequisite knowledge is missing then spend some time going over those concepts/skills before proceeding. Otherwise, the worksheets below should have fairly straight-forward answers and shouldn't result in too much hair loss.
- Order of Operations with Positive Fractions (No Exponents) 2-Step Order of Operations with Positive Fractions (No Exponents) 3-Step Order of Operations with Positive Fractions (No Exponents) 4-Step Order of Operations with Positive Fractions (No Exponents) 5-Step Order of Operations with Positive Fractions (No Exponents) 6-Step Order of Operations with Positive Fractions (No Exponents)
- Order of Operations with Positive Fractions 2-Step Order of Operations with Positive Fractions 3-Step Order of Operations with Positive Fractions 4-Step Order of Operations with Positive Fractions 5-Step Order of Operations with Positive Fractions 6-Step Order of Operations with Positive Fractions
- Order of Operations with Positive and Negative Fractions 2-Step Order of Operations with Positive & Negative Fractions 3-Step Order of Operations with Positive & Negative Fractions 4-Step Order of Operations with Positive & Negative Fractions 5-Step Order of Operations with Positive & Negative Fractions 6-Step Order of Operations with Positive & Negative Fractions
- Order of Operations With Positive Decimals 2-Step Order of Operations with Positive Decimals 3-Step Order of Operations with Positive Decimals 4-Step Order of Operations with Positive Decimals 5-Step Order of Operations with Positive Decimals 6-Step Order of Operations with Positive Decimals
- Order of Operations With Positive and Negative Decimals 2-Step Order of Operations with Positive & Negative Decimals 3-Step Order of Operations with Positive & Negative Decimals 4-Step Order of Operations with Positive & Negative Decimals 5-Step Order of Operations with Positive & Negative Decimals 6-Step Order of Operations with Positive & Negative Decimals
- Order of Operations With Positive Decimals (European Format: Comma Decimal) 2-Step Order of Operations with Positive Decimals (Comma Decimal) 3-Step Order of Operations with Positive Decimals (Comma Decimal) 4-Step Order of Operations with Positive Decimals (Comma Decimal) 5-Step Order of Operations with Positive Decimals (Comma Decimal) 6-Step Order of Operations with Positive Decimals (Comma Decimal)
- Order of Operations With Positive and Negative Decimals (European Format: Comma Decimal) 2-Step Order of Operations with Positive & Negative Decimals (Comma Decimal) 3-Step Order of Operations with Positive & Negative Decimals (Comma Decimal) 4-Step Order of Operations with Positive & Negative Decimals (Comma Decimal) 5-Step Order of Operations with Positive & Negative Decimals (Comma Decimal) 6-Step Order of Operations with Positive & Negative Decimals (Comma Decimal)
- Order of Operations With Fractions and Decimals Mixed Order of Operations with Fractions & Decimals Mixed Order of Operations with Fractions & Decimals Mixed with some Negative Values
Copyright © 2005-2024 Math-Drills.com You may use the math worksheets on this website according to our Terms of Use to help students learn math.
High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Order of op
Order of operations
Here you will learn about order of operations , including what it means and how to calculate and solve order of operations problems using PEMDAS .
Students will first learn about order of operations as a part of operations and algebraic thinking in elementary school.
What is the order of operations?
Order of operations refers to the rule that explains the sequence of steps necessary for correctly evaluating a mathematical expression or math problem.
You will use the acronym PEMDAS to help recall the correct order, or priority, in which you complete mathematical operations.
Mathematical operations such as multiplication and addition have to be completed in a specific order. This sequence of steps helps us to evaluate any mathematical expression, both with numerical values and algebraic expressions.
To evaluate an expression using PEMDAS, you need to understand what PEMDAS represents and be able to apply the PEMDAS rule to any calculation.
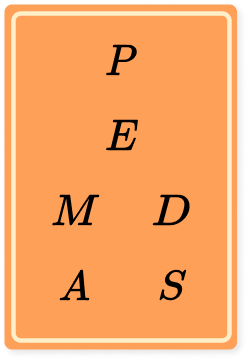
PEMDAS stands for:
P arentheses, E xponents, M ultiplication and D ivision, A ddition and S ubtraction
Parentheses have a higher priority than exponents, so we calculate what is inside a pair of parentheses first. Exponents have a higher priority than division and multiplication, so any exponent that can be evaluated is calculated next, and so on.
The order can be remembered using the mnemonic device for PEMDAS, ‘Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally.’
It is important to note that multiplication and division are given equal priority , and addition and subtraction are given equal priority.
When completing calculations that involve multiplication and division or addition and subtraction, you work from left to right.
For example,
Consider the following expression 12-7+6.
12-7=5 and then 5+6=11
Consider the following expression 10 \div 5 \times 2.
10 \div 5=2 and then calculate 2 \times 2=4.
Visually you could represent PEMDAS as:
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to 5th grade math and 6th grade math?
- Grade 5: Operations and Algebraic Thinking (5.OA.1) Use parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical expressions, and evaluate expressions with these symbols.
- Grade 5: Operations and Algebraic Thinking (5.OA.2) Write simple expressions that record calculations with numbers, and interpret numerical expressions without evaluating them.
- Grade 6: Expressions and Equations (6.EE.1) Write and evaluate numerical expressions involving whole-number exponents.
How to evaluate using order of operations
In order to evaluate expressions using order of operations , you would use PEMDAS :
Solve any calculations within parentheses.
Solve for any exponents.
Solve any division and multiplication calculations.
Solve any addition and subtraction calculations.
![order of operations problem solving tes [FREE] Properties of Equality Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 3 to 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/properties-of-equality-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image-.png)
[FREE] Properties of Equality Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 3 to 6)
Use this quiz to check your grade 3 to 6 students’ understanding of properties of equality. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 3rd, 5th and 6th grade properties of equality topics to identify areas of strength and support!

Order of operations examples
Example 1: pemdas with addition and multiplication.
Evaluate 3+6\times{7}.
There are no parentheses.
2 Solve for any exponents.
There are no exponents.
3 Solve any division and multiplication calculations.
The multiplication that we need to calculate is 6\times{7}=42.
Replacing 6\times{7} with 42 gives us the calculation 3+42.
4 Solve any addition and subtraction calculations.
So 3+6\times{7}=45
Example 2: PEMDAS with division and subtraction
Evaluate 12-8\div{2}.
The division you need to calculate is 8\div{2}=4.
Replacing 8\div{2} with 4 gives us the calculation 12-4.
So 12-8\div{4}=8
Example 3: PEMDAS with parentheses and multiplication
Evaluate 3(2+4\times{6}-3).
You have a pair of parentheses and so you need to resolve what is inside the set of parentheses first. This is the calculation 2+4\times{6}-3.
Using PEMDAS, multiplication comes before addition and subtraction so you need to solve the multiplication 4\times{6}=24.
Replacing 4\times{6} with 24 in the calculation, you have 2+24-3.
Addition and subtraction should be completed from left to right and so you have 2+24=26 and 26-3=23. Therefore 2+24-3=23.
As 2+4\times{6}-3=23 and 3(2+4\times{6}-3) means 3\times(2+4\times{6}-3), you have the updated calculation 3\times{23}.
3\times{23}=69
There is nothing else to solve, so the final answer is:
3(2+4\times{6}-3)=69
Example 4: PEMDAS with an exponent and multiplication
Evaluate 4\times{3}^{2}.
Here you have to resolve 3^{2}=3\times{3}=9.
Replacing 3^{2} with 9 in the calculation, you now have:
The final step needed is to calculate 4\times{9}=36
4\times{3}^{2}=36
Example 5: PEMDAS with brackets, an exponent and division
Evaluate 3+(10\div{4}\times{20})^{2}.
Within the set of parentheses, you have the calculation 10\div{4}\times{20}.
You need to work from left to right.
Completing the division, you have 10\div{4}=2.5
Next, 2.5\times{20}=50
Therefore, 10\div{4}\times{20}=50.
Replacing 10\div{4}\times{20} with 50, you now have the updated calculation,
You now have to solve 50^{2}=50\times{50}=2500.
Updating the calculation, you now have 3+2500.
There are no divisions or multiplications to solve.
3+2500=2503 which gives us the final answer:
3+(10\div{4}\times{20})^{2}=2503
Example 6: PEMDAS with everything
Evaluate 4^{2}+2(14-8)\div{3}.
Within the brackets is the calculation 14-8=6.
Updating the calculation by changing the value in the bracket to 6, you have
4^{2}+2\times{6}\div{3}
As 4^2=4 \times 4=16, you now have
16+2\times{6}\div{3}
Here you have to calculate 2\times{6}\div{3}. Working from left to right, you calculate 2\times{6} and then divide the solution by 3.
2\times{6}=12
12\div{3}=4
Updating the calculation, you now have 16+4.
As 16+4=20, our final answer is:
4^{2}+2(14-8)\div{3}=20
Teaching tips for order of operations
- While PEMDAS is a great way for students to remember the order of operations, it’s important that the students understand how to solve for each of the operations required, not simply giving them the acronym to memorize.
- It is important to find a way for students to practice outside of order of operations worksheets. The more practice a student gets, the better. For example you can physically separate word problems from the answer choices in the classroom. Students would have to walk around to discuss and solve the problem and then find the answer that matches.
- Students could be given an expression without the symbols. They would have to then decide which operations/symbols would make the expression true.
Easy mistakes to make
- Multiplication/division and addition/subtraction in the incorrect order When you have a chain of multiplication and division calculations or a chain of addition and subtraction calculations, you work from left to right. For example, If you put parentheses into the calculation 12\div{4}\times{3} with the purpose of keeping the calculation exactly the same, you must place the parentheses around 12\div{4}. This is because 12\div{4}\times{3}=9, and (12\div{4})\times{3}=3\times{3}=9. If you placed parentheses around 4\times{3} you would have 12\div{(4\times{3})}=12\div{12}=1 which is a different answer that you would get without the parenthesis.
- Exponents as multiplying a number by 2 When introducing exponents, some students will interpret 4^2 as 4 \times 2 instead of 4 \times 4. The use of a number line to represent this expression or using expanded notation when introducing the concept can help students internalize the learning.
- Multiplying before exponents Take 2\times{3}^{4}. Because you would perform exponents before you perform multiplication within PEMDAS, you need to calculate the exponent term first, and then multiply the solution by 2. Inserting a pair of parentheses with the purpose of keeping the calculation exactly the same, 2\times{3}^{4}=2\times(3^{4})=162. A common misconception is that the multiplication is carried out first, and then the value is raised to the power; here this would look like (2\times{3})^{4} and is equal to 6^{4}=1296 which is the wrong answer.
Related properties of equality lessons
- Properties of equality
- Associative property
- Commutative property
- Distributive property
Practice order of operations questions
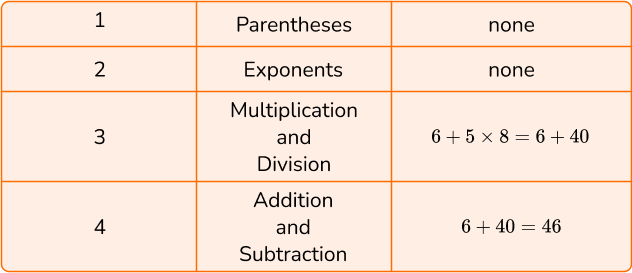
1. Calculate 6+5 \times 8.

To solve, follow the order of operations by using PEMDAS.
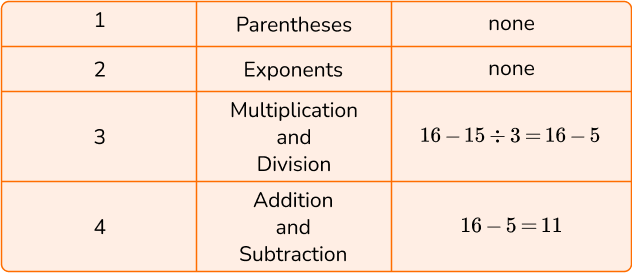
2. Calculate 16-15 \div 3.
To solve, follow the order of operations by using PEMDAS .
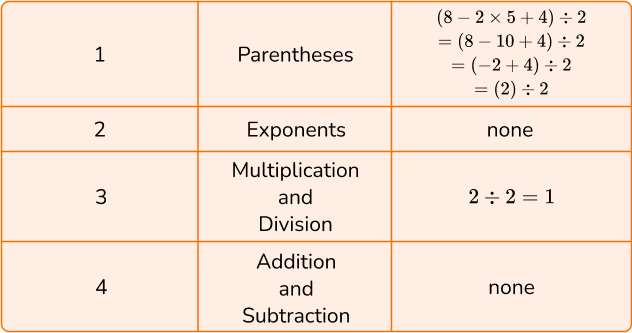
3. Calculate (8-2 \times 5+4) \div 2.
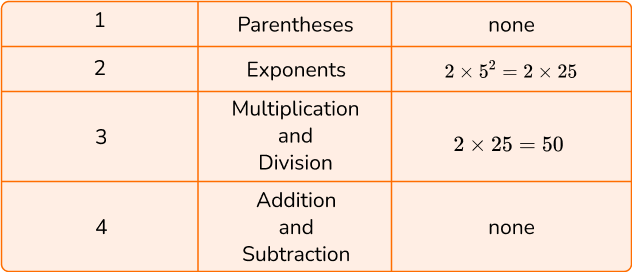
4. Calculate 2 \times 5^2.
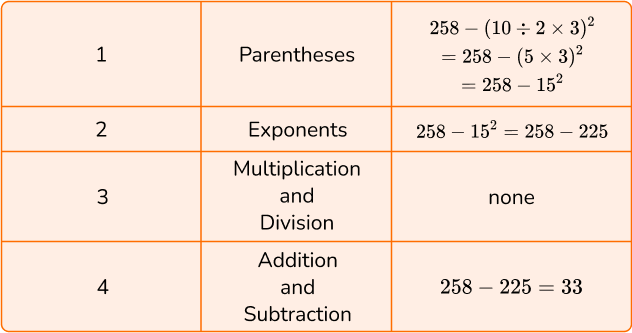
5. Calculate 258-(10 \div 2 \times 3)^2.
6. Calculate 3(7-5)^3 \div 6+4.
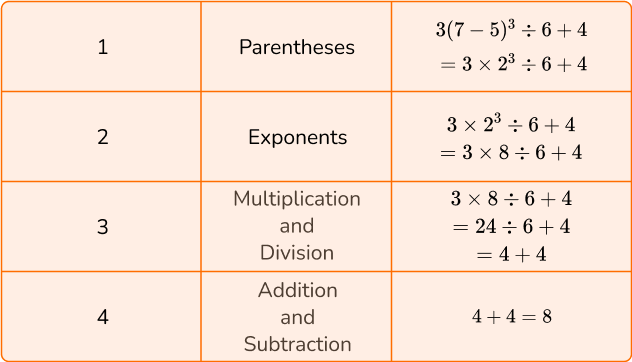
Order of operations FAQs
In the order of operations, multiplication and division are seen as equal and would be performed as they are stated within the expression, starting from left to right. The same is true with addition and subtraction.
Both PEMDAS and BODMAS are correct. The acronym BODMAS is the UK version of the same rules. It can also be referred to as BIDMAS or BEDMAS . The acronym in the UK would read as: B rackets, I ndices, D ivision and M ultiplication, A ddition and S ubtraction.
An exponent refers to the number of times a number is multiplied by itself. For example 7^2 = 7 \times 7 or 4^3 = 4 \times 4 \times 4.
Parentheses are used within mathematical expressions to note a modification is the normal order of operations. In the expression, (3+4) \times 3, because the addition is within parentheses, it is solved before the multiplication.
The next lessons are
- Addition and subtraction
- Multiplication and division
- Types of numbers
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs .
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 6)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these Grade 3 to Grade 6 practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
40 multiple choice questions and detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math experts covering a range of topics!
Privacy Overview

Teaching Order of Operations: No-fail Strategies that Work!
Order of operations can be frustrating to teach, but it doesn’t have to be. There’s no question that this is an extremely challenging topic for elementary students. Fortunately, there are loads of strategies for teaching order of operations that are both fun and effective.
One reason kids struggle with this concept is that there are so many rules to learn and follow. Even worse, rules that appear to be simple often prove to be deceptively complex.
For example, most kids can easily remember that multiplication and division are always performed before addition and subtraction, especially after they learn to follow the order described by “PEMDAS.”
However, they tend to get stuck when an equation includes both multiplication AND division. Most kids automatically multiply before dividing, but order of operations tells us to perform the operation that comes first when reading the problem from left to right. No wonder kids find order of operations to be super confusing!
Another reason kids struggle is that even when they understand how to use order of operations correctly, they don’t apply the rules systematically. Because the problems look easy, students try to rely on mental math alone to solve them. This may work with the easy problems, but mental math isn’t effective with more complex problems that include multiple operations, parentheses, exponents.
Order of Operations Lesson
The lesson begins with a quick activity to get students thinking about why we need rules for solving equations. This lesson “hook” is followed by an order of operations mini-lesson, a guided practice session, and a fast-paced game that doubles as a formative assessment activity.
To get the most from the activities, each student will need a dry erase board or tablet where they can work out the problems. You’ll also need at least one calculator for the class that uses order of operations correctly. A physical calculator is fine if displayed under a document camera, or you can use an online calculator. Be sure to test the calculator prior to the lesson to be sure it can handle order of operations problems. To find out, enter 1 + 2 x 3 and press the = sign. The correct answer is 7, so if your calculator displays 9 as the answer, it does NOT use order of operations correctly.

Before you teach PEMDAS or any other strategy, challenge your students to solve a simple equation such as this one: 3 + 8 x 2 = ? Ask your students to write the equation on a dry erase board or tablet, and then solve it and show you the answer.
You’re likely to see two different answers, but resist the urge to reveal the correct answer at this point. Most students will say the answer is 22 because they added 3 and 8 and then multiplied the sum by 2. However, who have studied order of operations in the past will say the answer is 19 because they multiplied 8 times 2 and added 3 to the product. Your students might be a bit confused when they notice that some of their classmates have different answers, but they are about to become even more confused!
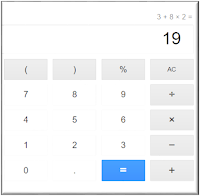
Tell your students that you’re going to use a calculator to check the answer, and as they watch, enter the problem above. When the calculator displays 19 as the answer, act surprised and say you must have entered the problem wrong. Enter it carefully again, and when you get the same answer, try a different calculator. When you get the same answer yet again, ask your students to pair up with a partner to discuss why the calculator keeps giving the “wrong” answer. After they talk it over for a few minutes, tell them that 19 is actually the correct answer, and that you’re going to teach them some important rules for solving problems that involve more than one operation.
This activity is a great way to start your order of operations lesson because it creates a feeling of “cognitive dissonance,” a state of mind in which we struggle to assimilate new facts that don’t match what we thought we knew about a topic. When students experience cognitive dissonance, they become eager to learn and open to new ideas, so it’s the perfect time to start the actual instruction.
2. Direct Instruction: Introduce Order of Operations
How you introduce order of operations will depend on your students’ readiness and their prior experiences with algebraic concepts. You might want to start by teaching your students how to use parentheses to indicate which part of an equation should be solved first. Write an equation two different ways, keeping the numbers the same but placing the parentheses around different pairs of numbers like this: (5 + 3) x 2 = ? and 5 + (3 x 2) = ?
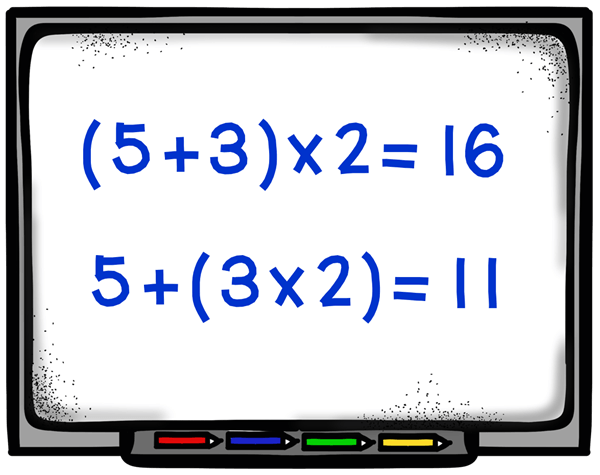
Show your students how to solve both problems, and point out that even though the numbers used in the equations are the same, the solutions are different. Give your students several more pairs of problems that have the same numbers and the parentheses in different locations. Stop after each problem to discuss the solution and clear up misunderstandings.
Next, display an equation that doesn’t have parentheses, like 15 – 5 x 2 = x. Point out that it’s not clear which part of the problem should be solved first, and as they’ve seen with the previous example, the order in which you perform the operations DOES matter.
Tell your students that mathematicians have agreed upon a set of rules called the “order of operations” that must be followed when solving problems. If your students have already studied exponents, you can teach the acronym PEMDAS which stands for Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication, Division, Addition, and Subtraction. The phrase “Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally” will help them remember the order of those letters. If your students haven’t studied exponents, you can substitute the acronym PMDAS and the phrase “Pass My Dad a Sandwich.”

3. Guided Practice: Teaching the Step-by-Step Method for Solving Problems
For the next part of the lesson, you’ll need to download the Order of Operations Freebie shown above. This freebie consists of three pages from Order of Operations Bingo Level 1 . Exponents are not mentioned on these pages, and the acronym PMDAS is used instead of PEMDAS.
After using the Order of Operations Review to explain the PMDAS acronym, display a copy of the practice page or give each student a paper copy. Introduce the step-by-step method for evaluating algebraic expressions by explaining the example at the top of the page. Using this strategy, each step is written on a separate line.
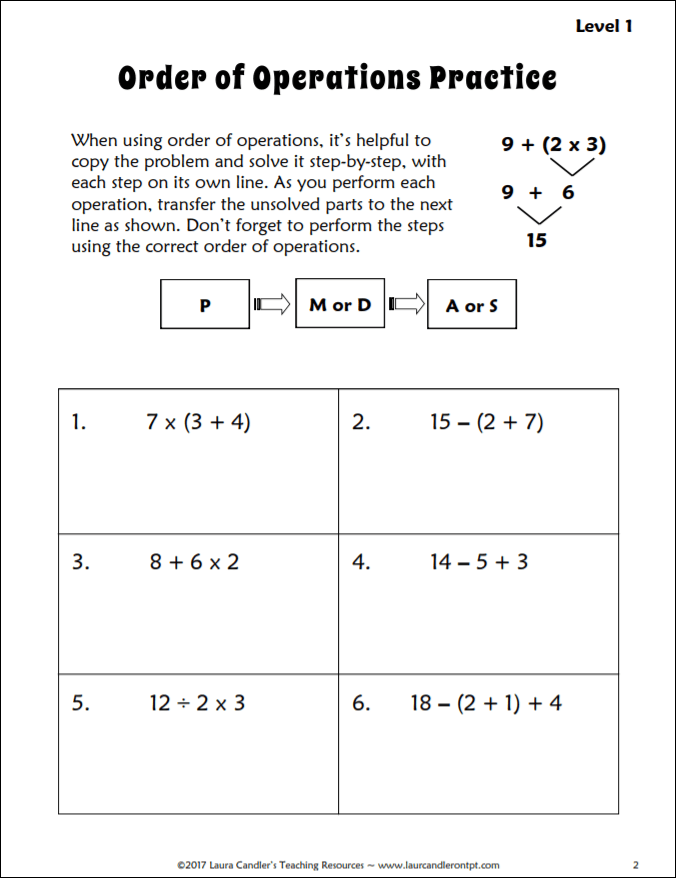
Guide your students through the process of solving the 6 practice problems one at a time. Check and discuss the solutions after each problem, and be sure to have them show you their work. If needed, refer to the answer key on page 3 of the freebie for step-by-step solutions.
If you have not taught this step-by step-method of solving order of operations problems, you might be tempted to skip it and let your students use mental math. Most of the problems are so easy that your students may be able to solve them without writing out each step.
However, relying on mental math to solve more challenging problems results in a lot of careless mistakes, so I recommending teaching your students to follow this step-by-step strategy with EVERY problem. If they get in the habit of using this systematic approach, they will be able to solve more complex problems with ease later. Trust me on this!
4. Play an Order of Operations Game
After your students understand how to solve order of operations problems, they’ll need lots of practice while the concepts are fresh in their minds. Games are far more effective for practice than worksheets because they are fast-pace and fun, motivating students to solve dozens of problems in a short time.
If you play the game as a class and discuss the answers after each problem, your students will know within a few round of the game if they are solving the problems correctly. If they aren’t, they will be motivated to ask questions and seek help to improve. Furthermore, many games can serve as formative assessment activities if you walk around while students are solving each problem to observe their work. Without having to administer a formal test, you’ll be able to see who understands the concepts and who needs more help.

Order of Operations Bingo is my favorite activity for practicing this skill because players can’t win without using order of operations correctly. To foster math skill development, ask your students to work out each problem on a dry erase board or tablet, using the step-by-step method. Stop after each problem to discuss each solution before presenting the next task card. Remind your students that they can only cover the answer on their Bingo boards with a chip if they had the correct answer BEFORE you revealed the solution to the class. If you enforce this rule, I can guarantee a huge drop in careless errors after the first round of the game!
5. Review and Practice with Order of Operations Task Cards or digital Boom Cards
The first four strategies are extremely effective for teaching kids how to use order of operations correctly. However, in order to retain what they’ve learned, your students will need opportunities for more review and practice throughout the year.
Whether you’re teaching students remotely or in the classroom, the Order of Operations Boom Cards below will meet this need perfectly! Boom Cards are self-checking, interactive, digital task cards that can be played on almost any device with Internet access. They are hosted on the Boom Learning platform, but free accounts are available. My Boom Cards also include optional audio directions; students can click the sound icon in the corner of each card to hear the words on the card read aloud! Kids love these interactive task cards because they’re fun, and teachers love them because they’re so effective!

If you prefer printable task cards, the Order of Operations Task Cards below will make it easy for your students keep these skills fresh. You can use the task cards shown below in math centers and with cooperative learning activities like Showdown or Team Scoot .
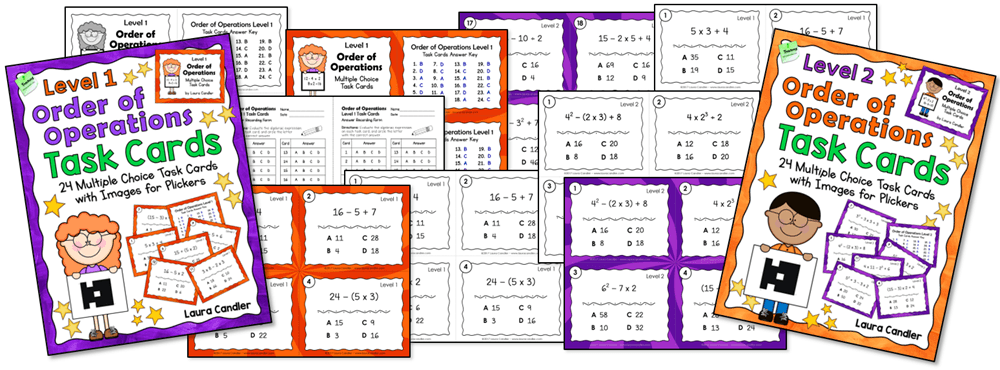
Differentiating Instruction is Easy
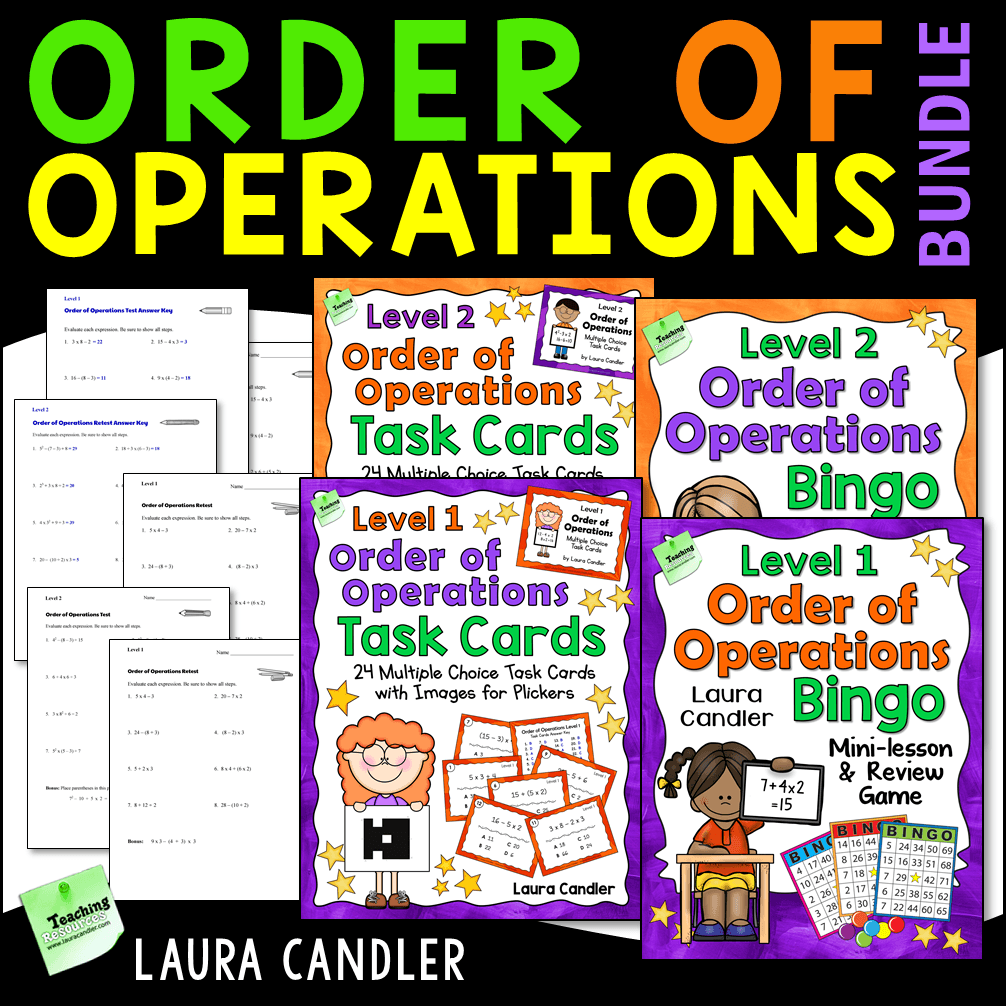
Differentiating instruction is easy because there are two levels of instructional materials, including the task cards, bingo game, and assessments. Level 1 includes basic problems like the ones used in the freebie. The materials for Level 2 have more complex problems and some of the problems include exponents. Both sets of bingo games, the printable task cards, and the assessments are included in one cost-saving bundle. If your curriculum includes exponents, the Order of Operations Games and Tests Bundle is your best option. If you use both levels in your classroom, you might want to print the task cards and game materials for each level on different colored card stock to keep them separate. (Boom Cards must be purchased separately.)
Classroom-Tested: Teacher and Student Approved
I love having teachers field test my products with their students. Several teachers tested Order of Operations Bingo with their students, and two of them sent pictures of their students playing the game. I love to see photos of kids using my lessons and activities, and I couldn’t resist sharing a few of them with you!
Fourth grade teacher Christina Ashburn tested Order of Operations Bingo and had her students solve the problems on dry erase boards as described in the lesson. She didn’t have bingo chips, so she laminated the game boards and had her students color over the answers with dry erase markers. I honestly never thought of doing that, but it’s a brilliant idea! For one thing, if kids are solving problems on dry erase boards, their markers should be handy. Also, you don’t have to worry about plastic Bingo chips ending up all over the classroom floor!
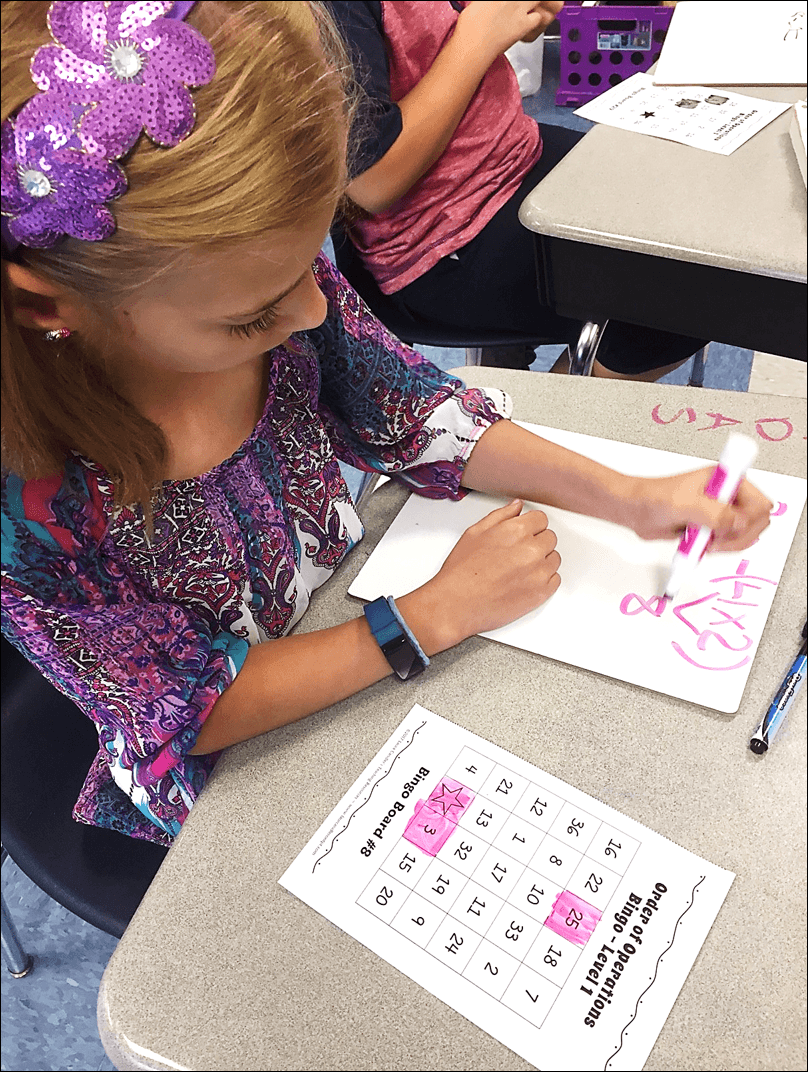
Fifth grade teacher Sheryl Nicholas also tested the game in her class. After observing her students play Order of Operations Bingo , she discovered an unexpected benefit. Sheryl explained, “My favorite part was how my non-English speakers immediately felt involved in the review. So much lately is ‘drill and test,’ but this made it a lot more interesting for the students. All were engaged in the activity and there was quite a bit of math talk as well as individual practicing of skills.”

After they played the game, Sheryl interviewed her students to get their feedback and shared some of their comments with me. I especially loved reading two comments about having to write out the steps of each problem. One student said, “I liked that you wouldn’t let me do them in my head but made me write the problems on the iPad and do them.” Another student wasn’t quite as enthusiastic about that part of the lesson, stating, “I wish you would have let me do these problems in my head. But then again, I always work too fast so I probably did better since I had to write them down.”
I just laughed when I read that last comment because it’s exactly the sort of thing some of my students would have said! This “no-fail” order of operations lesson is fun for students, and the step-by-step strategies make it highly effective, too. After playing the game, even kids recognize the importance of writing out the steps when solving order of operations problems, whether they like it or not!

Candler's Classroom Connections
- Growth Mindset
- Literature Circles
- Cooperative Learning

- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

Order of Operations | mixed operations BOOM Math Maze Game
Subject: Mathematics
Age range: 11-14
Resource type: Game/puzzle/quiz
Last updated
19 December 2022
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

Practice solving order of operations and challenge your students with this fun BOOM cards math game! The perfect alternative to a math worksheet, this digital puzzle game will give students plenty of practice at solving order of operations problems (mixed operators). The perfect math challenge for 5th grade, 6th grade or 7th grade.
Captivate your class with these simple puzzles and engage even your most reluctant students in learning that is meaningful AND fun! Who said math had to be boring?!
The game framework focuses on mastery - students must enter a correct sequence of answers to get the hero through the maze. Students will need to choose their path wisely because only the most efficient and accurate route will succeed!
See my BLOG POST for more details or PREVIEW THE DECK right now!
This product is a part of a Bundle on order of operations which you can get for a big discount HERE
WHAT YOU GET:
· 8 introduction puzzles teaching the game (with included audio narration) · 10 math puzzles that gradually get harder as students progress
Hi I’m Gil, the teacher behind GameWise. I make fun educational games to inspire students and make education more fun for teachers too. I do this because education these days is more challenging than ever. My aim is to empower teachers with digital games that hook students on learning that is fun AND meaningful. My resources are simple to use, but highly interactive and challenging enough to engage the whole class.
IMPORTANT NOTES:
To use Boom Cards, you must be connected to the Internet. Boom Cards play on modern browsers (Chrome, Safari, Firefox, and Edge). Apps are available for Android, iPads, iPhones, and Kindle Fires. For security and privacy, adults must have a Boom Learning account to use and assign Boom Cards. You will be able to assign the Boom Cards you are buying with “Fast Pins,” (play provides instant feedback for self-grading Boom Cards). Fast Play is always a free way for students to engage with Boom Cards decks. For additional assignment options, you’ll need a premium account.
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Solver Title
Generating PDF...
- Pre Algebra Order of Operations Factors & Primes Fractions Long Arithmetic Decimals Exponents & Radicals Ratios & Proportions Percent Modulo Number Line Expanded Form Mean, Median & Mode
- Algebra Equations Inequalities System of Equations System of Inequalities Basic Operations Algebraic Properties Partial Fractions Polynomials Rational Expressions Sequences Power Sums Interval Notation Pi (Product) Notation Induction Logical Sets Word Problems
- Pre Calculus Equations Inequalities Scientific Calculator Scientific Notation Arithmetics Complex Numbers Polar/Cartesian Simultaneous Equations System of Inequalities Polynomials Rationales Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Coordinate Geometry Plane Geometry Solid Geometry Conic Sections Trigonometry
- Calculus Derivatives Derivative Applications Limits Integrals Integral Applications Integral Approximation Series ODE Multivariable Calculus Laplace Transform Taylor/Maclaurin Series Fourier Series Fourier Transform
- Functions Line Equations Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Conic Sections Transformation
- Linear Algebra Matrices Vectors
- Trigonometry Identities Proving Identities Trig Equations Trig Inequalities Evaluate Functions Simplify
- Statistics Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Average Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability Mid-Range Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile Upper Quartile Interquartile Range Midhinge Standard Normal Distribution
- Physics Mechanics
- Chemistry Chemical Reactions Chemical Properties
- Finance Simple Interest Compound Interest Present Value Future Value
- Economics Point of Diminishing Return
- Conversions Roman Numerals Radical to Exponent Exponent to Radical To Fraction To Decimal To Mixed Number To Improper Fraction Radians to Degrees Degrees to Radians Hexadecimal Scientific Notation Distance Weight Time Volume
- Pre Algebra
- Two-step without parentheses
- Two-step with parentheses
- Three/four steps without parentheses
- Three/four steps with parentheses
- Multi-step without parentheses
- Multi-step with parentheses
- Prime Factorization
- Negative Factors
- Positive Factors
- Odd Factors
- Even Factors
- Biggest Factor
- Equivalent Fractions
- Add, Subtract
- Add, Subtract Like Denominators
- Add, Subtract Unlike Denominators
- Multiply with Whole Number
- Divide with Whole Number
- Mixed Numbers
- Complex Fractions
- Improper Fractions
- Long Addition
- Long Subtraction
- Long Multiplication
- Long Division
- Add/Subtract
- Multiplication
- Decimal to Fraction
- Fraction to Decimal
- Square Root
- Ratios & Proportions
Number Line
- Expanded Form
- Pre Calculus
- Linear Algebra
- Trigonometry
- Conversions

Most Used Actions
- 3+4-5\cdot 6
- 4+3-2\cdot 6(6-9)
- 3\cdot(1+2)^{2}\div9-12(1+(3-2)^{3})^{2}
- 3+4\div 2-5
- (1+6\div 3)\div(6-5)
order-of-operations-calculator
- Practice Makes Perfect Learning math takes practice, lots of practice. Just like running, it takes practice and dedication. If you want...
Please add a message.
Message received. Thanks for the feedback.

VIDEO
COMMENTS
Flipchart contains fulls lesson, including starter and plenary, and examples for students. Students have opportunity to use the order of operations on whiteboards. Questions then move on to fluency, reasoning and problem solving. Worksheet containing fluency questions (including placing brackets in the correct place), reasoning and problem ...
Good luck! Part 1: Order of Operations problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Problem 1:Simplify the numerical expression below. Answer. Problem 2:Simplify the numerical expression below. Answer. Problem 3:Simplify the numerical expression below. Answer.
Step 3: Multiply and divide whichever comes first, from left to right. Step 4: Add and subtract whichever comes first, from left to right. Examples on How to Apply the Order of Operations to Simplify Numerical Expressions. Example 1:Simplify the expression below using the Order of Operations. Examining the numerical expressions with multiple ...
The order of operations (PEMDAS) is essential for solving complex math problems. PEMDAS stands for Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division (same level), and Addition and Subtraction (same level). By following these steps, you can simplify and accurately solve mathematical expressions, ensuring a correct final answer. Created by Sal ...
Order of operations example. The order of operations tells us the order to solve steps in expressions with more than one operation. First, we solve any operations inside of parentheses or brackets. Second, we solve any exponents. Third, we solve all multiplication and division from left to right. Fourth, we solve all addition and subtraction ...
Example #1: In this first example, following order of operations tells us to perform multiplication before subtraction. Taking a look at the given values, we know that this will result in: Remember, performing subtraction first is a common mistake that will prevent you from obtaining the correct answer! Example #2:
Order of Operations Answers - Corbettmaths. Watch on. BODMAS, BIDMAS, bodmas, Practice Questions. Ordering Numbers Practice Questions. Cube Numbers and Cube Roots Practice Questions. The Corbettmaths Practice Questions on the Order of Operations.
Next: Best Buys Textbook Exercise GCSE Revision Cards. 5-a-day Workbooks
This page includes Order of Operations worksheets using whole numbers, integers, decimals and fractions. Elementary and middle school students generally use the acronyms PEMDAS or BEDMAS to help them remember the order in which they complete multi-operation questions. The 'P' or 'B' in the acronym stands for parentheses or brackets.
What is the order of operations? Order of operations refers to the rule that explains the sequence of steps necessary for correctly evaluating a mathematical expression or math problem.. You will use the acronym PEMDAS to help recall the correct order, or priority, in which you complete mathematical operations.. Mathematical operations such as multiplication and addition have to be completed ...
Questions 3, 6 and 9 (Problem Solving) Developing Match the calculation to the correct answer using knowledge of the order of operations. Calculations with two operations. Using all four operations and tables knowledge up to 12 x 12. Expected Match the calculation to the correct answer using knowledge of the order of operations.
4. Play an Order of Operations Game. After your students understand how to solve order of operations problems, they'll need lots of practice while the concepts are fresh in their minds. Games are far more effective for practice than worksheets because they are fast-pace and fun, motivating students to solve dozens of problems in a short time.
The order of operations is a mathematical convention for arithmetic computation. The below list indicates the order to do arithmetic, from top to bottom. The order of operations is usually summarized by the acronym PEMDAS. An AoPS mnemonic you can use to remember the order of operations is "Please Evaluate, My Dear AoPS Students".
It helps us solve problems in a systematic way to find the answers. The rule — or order — of operations that we follow is: P arentheses — When there are parentheses in an expression, we need to solve the operations inside the parentheses first. This is the first step in the order. E xponents —Exponents show how many times a number is ...
Algebra 01/31 Order of Operations. This lesson titled 'The Order of Operations' is fully differentiated, and uses whiteboard questions as a scaffolding and Assessment for Learning method. These whiteboard questions are also particularly useful for reducing students' maths anxiety by providing them with multiple answer they can choose from.
Teach Starter, part of Tes. ... Results for ‛Order Of Operations Problem Solving' 729 teaching resources Order Of Operations Problem Solving Sort: Relevance . Grades Grade 1 200. Grade 2 271. Grade 3 353. Grade 4 242. Grade 5 231. Grade 6 131. Grade 7 5. Kindergarten 88.
Order of Operations Activity. Once your students understand how to solve equations with one operation, it may be time for them to move on to multiple operations within an equation. If students are presented with an equation such as 6 + 9 × 12 ÷ 3 - 1, would they know what to do first?. Students typically approach problems such as this one in the same manner as they read a book, from left ...
Worksheets and presentations on word problems, order of operations and PEMDAS Order of Operations MP4 works with the Order of Operations PPT . Creative Commons "Sharealike" Review. 5 Something went wrong, please try again later. ... Tes Global Ltd is registered in England (Company No 02017289) with its registered office at Building 3, St Paul ...
pdf, 360.77 KB. Practice solving order of operations and challenge your students with this fun BOOM cards math game! The perfect alternative to a math worksheet, this digital puzzle game will give students plenty of practice at solving order of operations problems (mixed operators). The perfect math challenge for 5th grade, 6th grade or 7th grade.
Teach Starter, part of Tes. Search. Trending. ... Order Of Operations Problem Solving Sort: Relevance . Year Levels Foundation Year 58. Preschool / Kindergarten 14. Year 1 185. Year 2 271. Year 3 315. Year 4 250. Year 5 199. Year 6 190. Year 7 72. Resource Types Worksheet 379.
Free Order of Operations (PEMDAS) calculator - solve algebra problems following PEMDAS order step-by-step