- Sustainability
- Responsible Business
- Small Medium Business
- Pitch A Story

Image Credit- Wikipedia , Pixabay (Representational)

No Tests, No Homework! Here's How Finland Has Emerged As A Global Example Of Quality, Inclusive Education
Others/world, 15 may 2022 3:40 am gmt, editor : shiva chaudhary | .

Shiva Chaudhary
Digital Editor
A post-graduate in Journalism and Mass Communication with relevant skills, specialising in content editing & writing. I believe in the precise dissemination of information based on facts to the public.
Creatives : Shiva Chaudhary
Student-oriented approach to education in finland has been recognised as the most well-developed educational system in the world and ranks third in education worldwide..
"A quality education grants us the ability to fight the war on ignorance and poverty," - Charles Rangel
The uniqueness of the Finnish education model is encapsulated in its values of neither giving homework to students every day nor conducting regular tests and exams. Instead, it is listening to what the kids want and treating them as independent thinkers of society.
In Finland, the aim is to let students be happy and respect themselves and others.
Goodbye Standardised Exams
There is absolutely no program of nationwide standard testing, such as in India or the U.S, where those exams are the decisive points of one's admission to higher education like Board Examinations or Common Entrance Tests.
In an event organised by Shiksha Sanskriti Utthan Nyas, RSS Chief Mohan Bhagwat remarked, "It is because they teach their children to face life struggles and not score in an examination," reported The Print .
Students in Finland are graded based on individual performance and evaluation criteria decided by their teachers themselves. Overall progress is tracked by their government's Ministry of Education, where they sample groups of students across schools in Finland.
Value-Based Education
They are primarily focused on making school a safe and equal space as children learn from the environment.
All Finland schools have offered since the 1980s free school meals, access to healthcare, a focus on mental health through psychological counselling for everyone and guidance sessions for each student to understand their wants and needs.
Education in Finland is not about marks or ranks but about creating an atmosphere of social equality, harmony and happiness for the students to ease learning experiences.
Most of the students spend half an hour at home after school to work on their studies. They mostly get everything done in the duration of the school timings as they only have a few classes every day. They are given several 15 -20 minutes breaks to eat, do recreational activities, relax, and do other work. There is no regiment in school or a rigid timetable, thus, causing less stress as given in the World Economic Forum .
Everyone Is Equal - Cooperate, Not Compete
The schools do not put pressure on ranking students, schools, or competitions, and they believe that a real winner doesn't compete; they help others come up to their level to make everyone on par.
Even though individualism is promoted during evaluation based on every student's needs, collectivity and fostering cooperation among students and teachers are deemed crucial.
While most schools worldwide believe in Charles Darwin's survival of the fittest, Finland follows the opposite but still comes out at the top.
Student-Oriented Model
The school teachers believe in a simple thumb rule; students are children who need to be happy when they attend school to learn and give their best. Focus is put upon teaching students to be critical thinkers of what they know, engage in society, and decide for themselves what they want.
In various schools, playgrounds are created by children's input as the architect talks to the children about what they want or what they feel like playing before setting up the playground.
Compared To The Indian Education Model
Firstly, Finnish children enrol in schools at the age of six rather than in India, where the school age is usually three or four years old. Their childhood is free from constricting education or forced work, and they are given free rein over how they socialise and participate in society.
Secondly, all schools in Finland are free of tuition fees as there are no private schools. Thus, education is not treated as a business. Even tuition outside schools is not allowed or needed, leaving no scope for commodifying education, unlike in India, where multiple coaching centres and private schools require exorbitant fees.
Thirdly, the school hours in Finland do not start early morning at 6 am, or 7 am as done in India. Finland schools begin from 9.30 am as research in World Economic Forum has indicated that schools starting at an early age is detrimental to their health and maturation. The school ends by mostly 2 pm.
Lastly, there is no homework or surprise test given to students in Finland. Teachers believe that the time wasted on assignments can be used to perform hobbies, art, sports, or cooking. This can teach life lessons and have a therapeutic stress-relieving effect on children. Indian schools tend to give a lot of homework to prove their commitment to studying and constantly revise what they learn in school.
Delhi Govt's Focus On Education
The Delhi model of education transformed under the Aam Aadmi Party's (AAP) tenure in the capital. In line with the Finnish model, Delhi government schools have adopted 'Happiness Classes' to ensure students' mental wellness through courses on mindfulness, problem-solving, social and emotional relationships, etc., from 1st to 8th classes.
Delhi government also introduced 'Entrepreneurial Mindset Classes' in 2019 to instil business and critical thinking skills among students of 9th to 12th classes. The practical approach in this class is indicated in the 'Business Blasters', a competition started by the Delhi government to encourage students to come up with start-up ideas and students were provided with ₹1000. Approximately 51,000 students participated in the first edition of the competition, according to Citizen Matters .
Through these endeavours, India is steadily investing in creating human resources that can get employment and generate employment for themselves.
India is at its demographic dividend stage; more than half of its population is within the working-age group of 14 to 60 years. Education is an essential factor in utilising this considerable advantage to grow economically and socially. Finland's education model is how India can strive closer to its goal and progress as a nation.
Also Read: Connaissance! Delhi Board of School Education Pens MoU To Add French In Government Schools

We are an independent and public-spirited digital media platform for Indian millennials. We report news and issues that matter as well as give you the opportunity to take action.

- Scandal and Gossip
- Pop Culture
- Performing Arts
- Visual Arts

Countries with Less Homework and Why More Countries Should Follow Them

Countries with less homework and why more countries should follow them: It may sound counter intuitive but studies are showing that less homework might be the right way to go in better learning.
In an ideal world, students are entitled to an evening of some revision, rest and entertainment after a whole day of study. In many school systems, however, kids are assigned tons of assignments to handle in their free time in a bid to improve their grasp of themes and keep them occupied in books.
As much as the intentions are good, more homework only keeps children drowned in books and does little in achieving the latter. A testament to this, countries with fewer homework policies have better statistics of students that join campus and even lesser dropouts.
A testament to the benefits of fewer time commitment to homework, educational systems in powerhouses like Finland and USA have adopted the policies championing for least homework with the US recommending at most 10 minutes of assignment in any unit per night.
For proper insight, here is a list of countries that embrace the motion for least homework and reasons for other countries to emulate this move. For assistance on homework and clarity on concepts, engage experts on myHomework done , thus earning your student spurs and conceptualizing various classes better.
1. Finland
On top of the list of countries giving less assignment is Finland. Apart from boasting of short school terms and extended holidays, the country limits the homework load to 2.8 hours total of homework per week.
Despite their educational system, Finland manages to rank among the top countries in math and science innovations and also with a smaller drop-out rate. Due to their approach on education, students feel a lesser burden imposed on them thus embracing learning.
Even better, Finland educational system discourages cramming of concepts and trains teachers to impart lessons to students in a matter that they all understand the information equally.
2. South Korea
Like the former, South Korea limits its homework duration per week to a maximum of 2.9 hours. By reducing the burden on students, the country boasts of more educated persons per level of education and even lesser dropout rates.
Unlike other countries, South Korea majors on continuous assessments which excel at testing the understanding of students as opposed to daily homework.
3. Japan
Among the leading countries in technology and science is Japan . Although it has the highest amount of hours for homework per week than its counterparts at 3.8 hours, the numbers are way low than the average.
Even better, the Japanese system of study trains students to gather information from social media platforms thus honing their research and creativity skills. By limiting the amounts of homework, students get to spend quality time with parents thus giving them a platform to instill morals and gain perspective for the upcoming classes.
Reasons why more countries should reduce the homework load on students
1. By assigning more homework to students, the level of anxiety increases thus leading to low motivation in school work. As such, the productivity and attitude of kids towards education is lowered which in turn leads to more dropout rates and lesser grades.
2. With alarming rates of obesity and immorality in kids, less homework creates more parent-kid time and allows kids to engage in more co-curricular activities. As such, parents get a chance to instill moral character in kids and also involve kids in sports and exercise.
3. Time off books allows kids to relax their mind thus increasing the ability to grasp more concepts hence getting the most from every session.
Apart from denying students a change for co-curricular activities, students are also deprived of social time which in turn leads to less time for parents to instill morals in children and also spikes anxiety levels in kids.
Whether more homework is helpful or not is a debatable issue. However, the burden on students leads to daunting effects. Given that academic frontiers assign lesser homework; it shows the need for change in lesser ranking countries.
Recent Posts

Customer, 57 who gunned down Houston lawyer over McDonald’s order id...

Georgia teen, 15, dies after buying fentanyl laced pill from classmate

Middle school teacher fired after student drinks her vodka thinking it...
Popular posts.

Houston attorney shot dead trying to calm down McDonald’s customer angry...

Minnesota mom stabs 2 brothers, flees with third after setting home...

Bear drags car crash victim body from Hatfield scene later euthanized
Popular categories.
- Scandal and Gossip 17884
- Pop Culture 2816
- Fashion 960
- Nightlife 550
- Visual Arts 220
- Performing Arts 213
- Eating Out 137
- Contact & Corrections:
- About S&V & Author Bio:
- Privacy Policy
- Editorial Construct:
- Countries Who Spend the Most Time Doing Homework
Homework is an important aspect of the education system and is often dreaded by the majority of students all over the world. Although many teachers and educational scholars believe homework improves education performance, many critics and students disagree and believe there is no correlation between homework and improving test scores.
The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) is an intergovernmental organization. With headquarters in Paris, the organization was formed for the purpose of stimulating global trade and economic progress among member states. In 2009, the OECD conducted a detailed study to establish the number of hours allocated for doing homework by students around the world and conducted the research in 38 member countries. The test subjects for the study were 15 year old high school students in countries that used PISA exams in their education systems. The results showed that in Shanghai, China the students had the highest number of hours of homework with 13.8 hours per week. Russia followed, where students had an average of 9.7 hours of homework per week. Finland had the least amount of homework hours with 2.8 hours per week, followed closely by South Korea with 2.9 hours. Among all the countries tested, the average homework time was 4.9 hours per week.
Interpretation of the data
Although students from Finland spent the least amount of hours on their homework per week, they performed relatively well on tests which discredits the notion of correlation between the number of hours spent on homework with exam performance. Shanghai teenagers who spent the highest number of hours doing their homework also produced excellent performances in the school tests, while students from some regions such as Macao, Japan, and Singapore increased the score by 17 points per additional hour of homework. The data showed a close relation between the economic backgrounds of students and the number of hours they invested in their homework. Students from affluent backgrounds spent fewer hours doing homework when compared to their less privileged counterparts, most likely due to access to private tutors and homeschooling. In some countries such as Singapore, students from wealthy families invested more time doing their homework than less privileged students and received better results in exams.
Decline in number of hours
Subsequent studies conducted by the OECD in 2012 showed a decrease in the average number hours per week spent by students. Slovakia displayed a drop of four hours per week while Russia declined three hours per week. A few countries including the United States showed no change. The dramatic decline of hours spent doing homework has been attributed to teenager’s increased use of the internet and social media platforms.
More in Society

Understanding Stoicism and Its Philosophy for a Better Life

Countries With Zero Income Tax For Digital Nomads

The World's 10 Most Overcrowded Prison Systems

Manichaeism: The Religion that Went Extinct

The Philosophical Approach to Skepticism

How Philsophy Can Help With Your Life

3 Interesting Philosophical Questions About Time

What Is The Antinatalism Movement?
What Americans Keep Ignoring About Finland's School Success
The Scandinavian country is an education superpower because it values equality more than excellence.

Everyone agrees the United States needs to improve its education system dramatically, but how? One of the hottest trends in education reform lately is looking at the stunning success of the West's reigning education superpower, Finland. Trouble is, when it comes to the lessons that Finnish schools have to offer, most of the discussion seems to be missing the point.
The small Nordic country of Finland used to be known -- if it was known for anything at all -- as the home of Nokia, the mobile phone giant. But lately Finland has been attracting attention on global surveys of quality of life -- Newsweek ranked it number one last year -- and Finland's national education system has been receiving particular praise, because in recent years Finnish students have been turning in some of the highest test scores in the world.
Finland's schools owe their newfound fame primarily to one study: the PISA survey , conducted every three years by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). The survey compares 15-year-olds in different countries in reading, math, and science. Finland has ranked at or near the top in all three competencies on every survey since 2000, neck and neck with superachievers such as South Korea and Singapore. In the most recent survey in 2009 Finland slipped slightly, with students in Shanghai, China, taking the best scores, but the Finns are still near the very top. Throughout the same period, the PISA performance of the United States has been middling, at best.
Compared with the stereotype of the East Asian model -- long hours of exhaustive cramming and rote memorization -- Finland's success is especially intriguing because Finnish schools assign less homework and engage children in more creative play. All this has led to a continuous stream of foreign delegations making the pilgrimage to Finland to visit schools and talk with the nation's education experts, and constant coverage in the worldwide media marveling at the Finnish miracle.
So there was considerable interest in a recent visit to the U.S. by one of the leading Finnish authorities on education reform, Pasi Sahlberg, director of the Finnish Ministry of Education's Center for International Mobility and author of the new book Finnish Lessons: What Can the World Learn from Educational Change in Finland? Earlier this month, Sahlberg stopped by the Dwight School in New York City to speak with educators and students, and his visit received national media attention and generated much discussion.
And yet it wasn't clear that Sahlberg's message was actually getting through. As Sahlberg put it to me later, there are certain things nobody in America really wants to talk about.
During the afternoon that Sahlberg spent at the Dwight School, a photographer from the New York Times jockeyed for position with Dan Rather's TV crew as Sahlberg participated in a roundtable chat with students. The subsequent article in the Times about the event would focus on Finland as an "intriguing school-reform model."
Yet one of the most significant things Sahlberg said passed practically unnoticed. "Oh," he mentioned at one point, "and there are no private schools in Finland."
This notion may seem difficult for an American to digest, but it's true. Only a small number of independent schools exist in Finland, and even they are all publicly financed. None is allowed to charge tuition fees. There are no private universities, either. This means that practically every person in Finland attends public school, whether for pre-K or a Ph.D.
The irony of Sahlberg's making this comment during a talk at the Dwight School seemed obvious. Like many of America's best schools, Dwight is a private institution that costs high-school students upward of $35,000 a year to attend -- not to mention that Dwight, in particular, is run for profit, an increasing trend in the U.S. Yet no one in the room commented on Sahlberg's statement. I found this surprising. Sahlberg himself did not.
Sahlberg knows what Americans like to talk about when it comes to education, because he's become their go-to guy in Finland. The son of two teachers, he grew up in a Finnish school. He taught mathematics and physics in a junior high school in Helsinki, worked his way through a variety of positions in the Finnish Ministry of Education, and spent years as an education expert at the OECD, the World Bank, and other international organizations.
Now, in addition to his other duties, Sahlberg hosts about a hundred visits a year by foreign educators, including many Americans, who want to know the secret of Finland's success. Sahlberg's new book is partly an attempt to help answer the questions he always gets asked.
From his point of view, Americans are consistently obsessed with certain questions: How can you keep track of students' performance if you don't test them constantly? How can you improve teaching if you have no accountability for bad teachers or merit pay for good teachers? How do you foster competition and engage the private sector? How do you provide school choice?
The answers Finland provides seem to run counter to just about everything America's school reformers are trying to do.
For starters, Finland has no standardized tests. The only exception is what's called the National Matriculation Exam, which everyone takes at the end of a voluntary upper-secondary school, roughly the equivalent of American high school.
Instead, the public school system's teachers are trained to assess children in classrooms using independent tests they create themselves. All children receive a report card at the end of each semester, but these reports are based on individualized grading by each teacher. Periodically, the Ministry of Education tracks national progress by testing a few sample groups across a range of different schools.
As for accountability of teachers and administrators, Sahlberg shrugs. "There's no word for accountability in Finnish," he later told an audience at the Teachers College of Columbia University. "Accountability is something that is left when responsibility has been subtracted."
For Sahlberg what matters is that in Finland all teachers and administrators are given prestige, decent pay, and a lot of responsibility. A master's degree is required to enter the profession, and teacher training programs are among the most selective professional schools in the country. If a teacher is bad, it is the principal's responsibility to notice and deal with it.
And while Americans love to talk about competition, Sahlberg points out that nothing makes Finns more uncomfortable. In his book Sahlberg quotes a line from Finnish writer named Samuli Paronen: "Real winners do not compete." It's hard to think of a more un-American idea, but when it comes to education, Finland's success shows that the Finnish attitude might have merits. There are no lists of best schools or teachers in Finland. The main driver of education policy is not competition between teachers and between schools, but cooperation.
Finally, in Finland, school choice is noticeably not a priority, nor is engaging the private sector at all. Which brings us back to the silence after Sahlberg's comment at the Dwight School that schools like Dwight don't exist in Finland.
"Here in America," Sahlberg said at the Teachers College, "parents can choose to take their kids to private schools. It's the same idea of a marketplace that applies to, say, shops. Schools are a shop and parents can buy what ever they want. In Finland parents can also choose. But the options are all the same."
Herein lay the real shocker. As Sahlberg continued, his core message emerged, whether or not anyone in his American audience heard it.
Decades ago, when the Finnish school system was badly in need of reform, the goal of the program that Finland instituted, resulting in so much success today, was never excellence. It was equity.
Since the 1980s, the main driver of Finnish education policy has been the idea that every child should have exactly the same opportunity to learn, regardless of family background, income, or geographic location. Education has been seen first and foremost not as a way to produce star performers, but as an instrument to even out social inequality.
In the Finnish view, as Sahlberg describes it, this means that schools should be healthy, safe environments for children. This starts with the basics. Finland offers all pupils free school meals, easy access to health care, psychological counseling, and individualized student guidance.
In fact, since academic excellence wasn't a particular priority on the Finnish to-do list, when Finland's students scored so high on the first PISA survey in 2001, many Finns thought the results must be a mistake. But subsequent PISA tests confirmed that Finland -- unlike, say, very similar countries such as Norway -- was producing academic excellence through its particular policy focus on equity.
That this point is almost always ignored or brushed aside in the U.S. seems especially poignant at the moment, after the financial crisis and Occupy Wall Street movement have brought the problems of inequality in America into such sharp focus. The chasm between those who can afford $35,000 in tuition per child per year -- or even just the price of a house in a good public school district -- and the other "99 percent" is painfully plain to see.
Pasi Sahlberg goes out of his way to emphasize that his book Finnish Lessons is not meant as a how-to guide for fixing the education systems of other countries. All countries are different, and as many Americans point out, Finland is a small nation with a much more homogeneous population than the United States.
Yet Sahlberg doesn't think that questions of size or homogeneity should give Americans reason to dismiss the Finnish example. Finland is a relatively homogeneous country -- as of 2010, just 4.6 percent of Finnish residents had been born in another country, compared with 12.7 percent in the United States. But the number of foreign-born residents in Finland doubled during the decade leading up to 2010, and the country didn't lose its edge in education. Immigrants tended to concentrate in certain areas, causing some schools to become much more mixed than others, yet there has not been much change in the remarkable lack of variation between Finnish schools in the PISA surveys across the same period.
Samuel Abrams, a visiting scholar at Columbia University's Teachers College, has addressed the effects of size and homogeneity on a nation's education performance by comparing Finland with another Nordic country: Norway. Like Finland, Norway is small and not especially diverse overall, but unlike Finland it has taken an approach to education that is more American than Finnish. The result? Mediocre performance in the PISA survey. Educational policy, Abrams suggests, is probably more important to the success of a country's school system than the nation's size or ethnic makeup.
Indeed, Finland's population of 5.4 million can be compared to many an American state -- after all, most American education is managed at the state level. According to the Migration Policy Institute , a research organization in Washington, there were 18 states in the U.S. in 2010 with an identical or significantly smaller percentage of foreign-born residents than Finland.
What's more, despite their many differences, Finland and the U.S. have an educational goal in common. When Finnish policymakers decided to reform the country's education system in the 1970s, they did so because they realized that to be competitive, Finland couldn't rely on manufacturing or its scant natural resources and instead had to invest in a knowledge-based economy.
With America's manufacturing industries now in decline, the goal of educational policy in the U.S. -- as articulated by most everyone from President Obama on down -- is to preserve American competitiveness by doing the same thing. Finland's experience suggests that to win at that game, a country has to prepare not just some of its population well, but all of its population well, for the new economy. To possess some of the best schools in the world might still not be good enough if there are children being left behind.
Is that an impossible goal? Sahlberg says that while his book isn't meant to be a how-to manual, it is meant to be a "pamphlet of hope."
"When President Kennedy was making his appeal for advancing American science and technology by putting a man on the moon by the end of the 1960's, many said it couldn't be done," Sahlberg said during his visit to New York. "But he had a dream. Just like Martin Luther King a few years later had a dream. Those dreams came true. Finland's dream was that we want to have a good public education for every child regardless of where they go to school or what kind of families they come from, and many even in Finland said it couldn't be done."
Clearly, many were wrong. It is possible to create equality. And perhaps even more important -- as a challenge to the American way of thinking about education reform -- Finland's experience shows that it is possible to achieve excellence by focusing not on competition, but on cooperation, and not on choice, but on equity.
The problem facing education in America isn't the ethnic diversity of the population but the economic inequality of society, and this is precisely the problem that Finnish education reform addressed. More equity at home might just be what America needs to be more competitive abroad.
LAST STRETCH!

You can still support your source of education news this teacher appreciation week.
The Hechinger Report
Covering Innovation & Inequality in Education
Homework matters depending upon which country you live in

Share this:
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
The Hechinger Report is a national nonprofit newsroom that reports on one topic: education. Sign up for our weekly newsletters to get stories like this delivered directly to your inbox. Consider supporting our stories and becoming a member today.

For years, researchers have been trying to figure out just how important homework is to student achievement. Back in 2009, the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) looked at homework hours around the world and found that there wasn ’t much of a connection between how much homework students of a particular country do and how well their students score on tests. Some top achieving countries, like Singapore, assign their students lots of homework. But Finland, for example, succeeds without much homework. On average, Finnish students do only about three hours of homework a week, yet in 2012 they scored sixth highest in the world in reading and 12th highest in math on the OECD’s international test, known as PISA or Programme for International Student Assessment.

But now, five years after the earlier homework study, OECD researchers have drilled down deeper into homework patterns, and they’re finding that homework does play an important role in student achievement within each country . Specifically, they found that homework hours vary by socioeconomic status. Higher income 15-year-olds tend to do more homework than lower income 15-year-olds in almost all of the 38 countries studied by the OECD*. Furthermore, the kids who are doing more homework also tend to get higher test scores. So the authors conclude that homework is reinforcing the achievement gap between the rich and the poor.
It’s not just that poor kids are more likely to skip their homework, or don’t have a quiet place at home to complete it. It’s also the case that schools serving poor kids often don’t assign as much homework as schools for the rich, especially private schools, explained Francesca Borgonovi, one of the authors of the study, titled “ Does Homework Perpetuate Inequities in Education? ”
“When you look within countries at students who are learning in the same educational system and they do more homework, then those students do much better,” said Borgonovi. “There is an advantage for putting extra hours in homework.”

A stark example of this rich-poor homework gap is in Singapore. Students in the top quarter of the socio-economic spectrum spend about 11 hours on homework a week, 3 hours more than low-income students in the bottom quarter of the socio-economic spectrum. Each extra hour of homework was associated with 18 more points on the PISA math exam. So three hours adds up to more than 50 points. That’s huge. To put that in perspective, if you added 50 points to the average U.S. math score, we’d be a top 10 nation instead of number 36.
A key factor is what Borgonovi said about “learning in the same educational system.” Some school systems are designed to rely on homework, perhaps using independent study as a substitute for what could otherwise be learned in school. “If you are prepared to change the system, that’s great,” said Borgonovi. “But until you do so, if the system is based on homework, then you should do more of it.”
Students in Shanghai, a region in China that now leads the world in PISA test scores, do a whopping 14 hours of homework a week, on average. Wealthier students there do 16 hours. Poorer students do just under 11 hours. Interestingly, however, there was no association between the extra homework hours that the wealthier Shanghai kids put in and their PISA test scores. Perhaps that’s because there are diminishing marginal returns to homework after 11 hours of it!
Indeed, most countries around the world have been reducing the amount of homework assigned. Back in 2003, the average time spent on homework worldwide was about six hours a week. In 2012 that shrank to about five hours.
But the United States has been bucking this trend. The typical 15-year-old here does six hours a week, virtually unchanged from a decade ago and possibly rising. Wealthier students typically do eight hours of homework a week, about three hours more than low income students. But unlike in most countries, where more homework is associated with higher PISA test scores, that’s not the case here.
“For the United States, we don’t have homework reinforcing inequality,” Borgonovi said.
Another team of researchers, Ozkan Eren and Daniel J. Henderson, found mixed results for how effective homework is in the United States, in a 2011 study, “ Are we wasting our children’s time by giving them more homework? ” published in the Economics of Education Review. For math, there were huge benefits for the 25,000 eighth graders they studied. But not for English, science or history. And the math boost was much stronger for white students than for blacks. In other words, when a typical black student did more homework, his math test scores didn’t go up as much.
That’s perhaps a clue that even if you could magically get low-income children in other countries to do as much homework as their high-income peers, as the OECD researchers are suggesting, you might not raise their PISA test scores very much.
Indeed, Borgonovi isn’t really advocating for more homework. She says that high quality teachers and instruction are much more important to student outcomes than homework is. To be sure, some amount of homework is good, Borgonovi said, to teach kids how to plan ahead, set goals and work independently. But more than four hours of homework a week, she said, isn’t very beneficial.
“It would be better to redesign the system to have less homework,” said Borgonovi. “But that is hard to do.”
* The OECD looked at socio-economic status and not income exclusively. So the child of a university professor, for example, might still be in the high income category even if his parents don’t make very much money.
Related articles
The Hechinger Report provides in-depth, fact-based, unbiased reporting on education that is free to all readers. But that doesn't mean it's free to produce. Our work keeps educators and the public informed about pressing issues at schools and on campuses throughout the country. We tell the whole story, even when the details are inconvenient. Help us keep doing that.
Join us today.
Jill Barshay SENIOR REPORTER
(212)... More by Jill Barshay
Letters to the Editor
At The Hechinger Report, we publish thoughtful letters from readers that contribute to the ongoing discussion about the education topics we cover. Please read our guidelines for more information. We will not consider letters that do not contain a full name and valid email address. You may submit news tips or ideas here without a full name, but not letters.
By submitting your name, you grant us permission to publish it with your letter. We will never publish your email address. You must fill out all fields to submit a letter.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Sign me up for the newsletter!
- About the Hub
- Announcements
- Faculty Experts Guide
- Subscribe to the newsletter
Explore by Topic
- Arts+Culture
- Politics+Society
- Science+Technology
- Student Life
- University News
- Voices+Opinion
- About Hub at Work
- Gazette Archive
- Benefits+Perks
- Health+Well-Being
- Current Issue
- About the Magazine
- Past Issues
- Support Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Subscribe to the Magazine
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

Credit: August de Richelieu
Does homework still have value? A Johns Hopkins education expert weighs in
Joyce epstein, co-director of the center on school, family, and community partnerships, discusses why homework is essential, how to maximize its benefit to learners, and what the 'no-homework' approach gets wrong.
By Vicky Hallett
The necessity of homework has been a subject of debate since at least as far back as the 1890s, according to Joyce L. Epstein , co-director of the Center on School, Family, and Community Partnerships at Johns Hopkins University. "It's always been the case that parents, kids—and sometimes teachers, too—wonder if this is just busy work," Epstein says.
But after decades of researching how to improve schools, the professor in the Johns Hopkins School of Education remains certain that homework is essential—as long as the teachers have done their homework, too. The National Network of Partnership Schools , which she founded in 1995 to advise schools and districts on ways to improve comprehensive programs of family engagement, has developed hundreds of improved homework ideas through its Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork program. For an English class, a student might interview a parent on popular hairstyles from their youth and write about the differences between then and now. Or for science class, a family could identify forms of matter over the dinner table, labeling foods as liquids or solids. These innovative and interactive assignments not only reinforce concepts from the classroom but also foster creativity, spark discussions, and boost student motivation.
"We're not trying to eliminate homework procedures, but expand and enrich them," says Epstein, who is packing this research into a forthcoming book on the purposes and designs of homework. In the meantime, the Hub couldn't wait to ask her some questions:
What kind of homework training do teachers typically get?
Future teachers and administrators really have little formal training on how to design homework before they assign it. This means that most just repeat what their teachers did, or they follow textbook suggestions at the end of units. For example, future teachers are well prepared to teach reading and literacy skills at each grade level, and they continue to learn to improve their teaching of reading in ongoing in-service education. By contrast, most receive little or no training on the purposes and designs of homework in reading or other subjects. It is really important for future teachers to receive systematic training to understand that they have the power, opportunity, and obligation to design homework with a purpose.
Why do students need more interactive homework?
If homework assignments are always the same—10 math problems, six sentences with spelling words—homework can get boring and some kids just stop doing their assignments, especially in the middle and high school years. When we've asked teachers what's the best homework you've ever had or designed, invariably we hear examples of talking with a parent or grandparent or peer to share ideas. To be clear, parents should never be asked to "teach" seventh grade science or any other subject. Rather, teachers set up the homework assignments so that the student is in charge. It's always the student's homework. But a good activity can engage parents in a fun, collaborative way. Our data show that with "good" assignments, more kids finish their work, more kids interact with a family partner, and more parents say, "I learned what's happening in the curriculum." It all works around what the youngsters are learning.
Is family engagement really that important?
At Hopkins, I am part of the Center for Social Organization of Schools , a research center that studies how to improve many aspects of education to help all students do their best in school. One thing my colleagues and I realized was that we needed to look deeply into family and community engagement. There were so few references to this topic when we started that we had to build the field of study. When children go to school, their families "attend" with them whether a teacher can "see" the parents or not. So, family engagement is ever-present in the life of a school.
My daughter's elementary school doesn't assign homework until third grade. What's your take on "no homework" policies?
There are some parents, writers, and commentators who have argued against homework, especially for very young children. They suggest that children should have time to play after school. This, of course is true, but many kindergarten kids are excited to have homework like their older siblings. If they give homework, most teachers of young children make assignments very short—often following an informal rule of 10 minutes per grade level. "No homework" does not guarantee that all students will spend their free time in productive and imaginative play.
Some researchers and critics have consistently misinterpreted research findings. They have argued that homework should be assigned only at the high school level where data point to a strong connection of doing assignments with higher student achievement . However, as we discussed, some students stop doing homework. This leads, statistically, to results showing that doing homework or spending more minutes on homework is linked to higher student achievement. If slow or struggling students are not doing their assignments, they contribute to—or cause—this "result."
Teachers need to design homework that even struggling students want to do because it is interesting. Just about all students at any age level react positively to good assignments and will tell you so.
Did COVID change how schools and parents view homework?
Within 24 hours of the day school doors closed in March 2020, just about every school and district in the country figured out that teachers had to talk to and work with students' parents. This was not the same as homeschooling—teachers were still working hard to provide daily lessons. But if a child was learning at home in the living room, parents were more aware of what they were doing in school. One of the silver linings of COVID was that teachers reported that they gained a better understanding of their students' families. We collected wonderfully creative examples of activities from members of the National Network of Partnership Schools. I'm thinking of one art activity where every child talked with a parent about something that made their family unique. Then they drew their finding on a snowflake and returned it to share in class. In math, students talked with a parent about something the family liked so much that they could represent it 100 times. Conversations about schoolwork at home was the point.
How did you create so many homework activities via the Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork program?
We had several projects with educators to help them design interactive assignments, not just "do the next three examples on page 38." Teachers worked in teams to create TIPS activities, and then we turned their work into a standard TIPS format in math, reading/language arts, and science for grades K-8. Any teacher can use or adapt our prototypes to match their curricula.
Overall, we know that if future teachers and practicing educators were prepared to design homework assignments to meet specific purposes—including but not limited to interactive activities—more students would benefit from the important experience of doing their homework. And more parents would, indeed, be partners in education.
Posted in Voices+Opinion
You might also like
News network.
- Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Get Email Updates
- Submit an Announcement
- Submit an Event
- Privacy Statement
- Accessibility
Discover JHU
- About the University
- Schools & Divisions
- Academic Programs
- Plan a Visit
- my.JohnsHopkins.edu
- © 2024 Johns Hopkins University . All rights reserved.
- University Communications
- 3910 Keswick Rd., Suite N2600, Baltimore, MD
- X Facebook LinkedIn YouTube Instagram

- BSW Scholarships
- How to Transition to a Social Work Career
- Social Worker Salary and Jobs in Social Work
- Is a Master of Social Work MSW Really Worth It?
- Social Worker Resource Guide
- Doctor of Social Work Salary and Careers
- How to Become a School Superintendent
- Faculty Interview: Dr. Lee Nabb, Morehead State University
- Scholarships for Doctor of Education (EdD) Students
- What is a Terminal Degree?
- Is It Worth Getting a Doctorate in Education (EdD)?
- Faculty Interview: Tracy Caddell, Ball State University
- Doctor of Education EdD Salary and Career Outlook
- EdD vs. PhD
- What is Organizational Change?
- Faculty Interview: Michael Poe, Northwest Nazarene University
- How to Transition to a Teaching Career
- Applying for Your Master’s
- Preparing for Your Interview
- Crafting Your Resume
- How to Write a Personal Statement
- How to Get the Right References
- Is a Master of Teaching Worth It?
- The Ultimate Guide to the Praxis® Tests
- Finance your Teaching Education
- Online Master of Arts in Teaching – TESOL Programs
- HBCU Undergraduate Scholarships Guide
- Librarian Resource Guide
- Explore Librarian Salary, Jobs, and Careers in Library Science
- Online Master of Science in Teaching
- Online Master of Education Programs
- Our Guide to Entry-Level Nursing
- What Type of Nurse Should You Be?
- Guide to Transitioning RN to MSN Programs
- What Can You Do With a Bachelor’s in Public Health?
- Bachelor of Public Health Scholarships and Grants
- Kinesiology and Exercise Science Salaries
- How to Make a Career Change from Teaching to Speech Pathology
- Speech Pathology School Scholarships
- How to Get into Speech Pathology School
- ASHA Certification for Speech-Language Pathologists
- Is a Master’s in Speech Pathology Really Worth It?
- Professional Development Guide for Speech Pathologists
- What Speech Pathology Students Should Do Before Graduating
- Speech-Language Pathologist Resume Guide
- Speech-Language Pathology Job Interview Guide
- Speech Pathologist Resource Guide
- Speech Pathologist Salary and Career Outlook
- What Is an AGACNP?
- What Is a Women’s Health Nurse Practitioner
- Guide to Making a Career Change to Nursing
- How To Get Into Nursing School
- Is Nursing School Really Worth It?
- Nursing Salary by State
- Nursing Resources
- Which Nursing Degree Is Right for Me?
- Types of Nursing Degrees
- Nursing School Scholarships
- Explore Midwife Salary, Jobs, and Careers in Midwifery
- What is a Midwife
- The 2022 Guide to Online Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) Programs
- Nursing Careers Infographic
- Nurse Practitioner Career & Salary
- Our Guide to APRN License and Certification
- NP vs DNP: Nurse Practitioner vs Doctor of Nursing Practice
- Family Nurse Practitioner (FNP)
- Registered Nurse vs. Nurse Practitioner
- Acute Care Nurse Practitioner ACNP Salary and Careers
- Women’s Health Nurse Practitioner WHNP Salary and Careers
- Online Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner Programs (PMHNP)
- Occupational Therapy Salary and Career Outlook
- Scholarships for Occupational Therapy Students
- How to Get into Occupational Therapy School
- Is a Doctor of Occupational Therapy Worth It?
- What is Occupational Therapy?
- What Is the Difference Between Physical Therapy and Occupational Therapy?
- What Is Physical Therapy?
- How to Get Into Physical Therapy School
- Is a Doctor of Physical Therapy DPT Really Worth It?
- Physical Therapy Careers and Salaries
- How to Make a Career Transition to Physical Therapy
- Chiropractor vs. Physical Therapist
- Physical Therapy Scholarships
- What’s the Difference Between a Physician Assistant and a Doctor?
- Scholarships for Physician Assistant PA Students
- Physician Assistant vs. Nurse Practitioner: What Are the Differences?
- Physician Assistant Salary, Jobs and Career Path
- How to Become a Physician Assistant
- How to Get Into PA School
- Is a Physician Assistant PA Degree Really Worth It?
- Physician Assistant Certification Guide
- Pharmacy Doctorate Salary and Career Outlook
- How to Get into Pharmacy (PharmD) School
- Master of Health Informatics Career and Salary
- Master of Public Health Salary and Career Outlook
- Online Master’s in Health Administration Programs (MHA)
- Top Paying Healthcare Careers
- Bachelor of Psychology Scholarships
- Digital Resources for Students with Autism – Helpful for Teachers and Parents
- What is a Functional Behavior Assessment?
- What is Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)?
- Applied Behavior Analysis ABA Scholarships
- Psychologist Salary and Career Outlook
- Types of Psychology Degrees
- Clinical Psychologist Careers and Salary
- Marriage and Family Therapist Salary and Jobs for MFT Careers
- Behavioral Psychology
- Counseling Skills and Techniques
- Is a Master’s in Counseling Worth It?
- 25 Counseling Scholarships for Graduate Students
- School Psychologist vs School Counselor
- Bullying Resources for Educators and Parents
- The Comprehensive College Planning Resource
- School Counselor Certification Guide
- Resources for School Counselors
- School Counselor Salary and Career Outlook
- LMHC vs. LCSW
- How to Become a Counselor
- Mental Health Counselor Salary and Career Outlook
- MPA vs MPH: Which Degree is Best for You?
- MPA vs. International Relations
- MPA vs. MPP
- Masters in Business Administration (MBA) vs. Masters of Public Administration (MPA)
- Is an MPA Degree Really Worth It?
- MPA Careers and Salaries
- Master of Public Administration MPA Scholarships
- Online Masters in Urban Planning Programs
- What Can I Do With an International Relations Degree?
- International Relations Salary and Career Paths
- How to Make a Career Transition to Financial Planner
- Can You Change Careers with an MBA
- MBA Concentrations Guide
- Online MBA in Financial Planning Programs
- Find Online MBA in Entrepreneurship Programs
- Find Online MBA in Marketing Programs
- Find Online MBA in Business Analytics Programs
- Find Online MBA in Finance Programs
- MBA or CFA: Which Is Better for a Finance Career
- How to Get Into Business School
- MBA or JD: Which Is the Better Career Path?
- Is an MBA Degree Really Worth It? Decide Here
- Explore MBA Salary, Jobs, and Careers in Business
- MBA Scholarships
- Bachelor’s of Business Scholarships
- What Can You Do With a Bachelor’s in Business and Management?
- What Can You Do with a Bachelor’s in Marketing?
- Bachelor of Marketing Scholarships
- Is a Master of Accounting Worth It?
- Accountant Salary and Career Outlook
- Guide to Transition into an Accounting Career
- Master’s in HR Salary and Career Outlook
- How to Break into Supply Chain Management
- Supply Chain Management Salary and Career Outlook
- Online Master’s in Management and Leadership
- Online Master’s in Finance Programs
- Explore Our LSAT Study Guide
- How to Get into Law School
- How to Study for the Bar Exam
- Is a JD Really Worth It?
- MPA vs JD: Which Is Better?
- Is a Master of Legal Studies Worth It?
- Online Master’s in Taxation Law Programs
- Online Master of Laws LLM Programs
- Online Master of Legal Studies in Compliance Programs
- What You Can Do with a Bachelor’s in Communications
- Bachelor of Communications Scholarships
- Online Master of Communication Management Programs
- Master’s in Communications Salary and Careers
- Is a Communications Degree Worth It?
- How to Become a Communications Director
- How to Become an Architect
- Guide to Online Economics Certificates and Courses
- How to Become a Public Policy Analyst
- Public Policy Analyst Salary and Job Outlook
- Guide to Online Sustainability Certificates and Short Courses
- Data Science Salary and Career Outlook
- Is a Data Science Degree Worth It?
- Online Business Management Courses
- How to Become a Finance Manager
- Finance Salary and Careers
- Web Developer Salary and Career Paths
- How to Become a Cyber Security Specialist
- Guide to Cybersecurity Salaries and Careers
- AI Engineer Salary and Career Outlook
- How to Become an AI Engineer
- How to Become a Blockchain Developer
- Systems and IT Salary and Career Outlook
- Online Human Resources HR Courses
- How to Become a Project Manager
- Project Manager Salary and Career Outlook
- Become a Marketing Manager
- Is a Marketing Degree Worth It?
- Marketing Salary and Careers
- Online Healthcare Courses
- Online Nutrition Courses
- Online Education Courses
- Online Business Negotiations Courses
- Online Leadership Courses
- Online Conflict Resolution Courses
- Become a Data Analyst
- Online Real Estate Courses
- What is an HBCU?
- Reasons to Choose a Degree From an HBCU
- Teaching Methods
- Learning Styles
- Testing Effect
- School Media
- Motivating Students
- Dropout Prevention
- Teachers Care
- Grants for Teachers
- Teacher Appreciation
- Debra Rose Howell
- Dr. David Lazerson
- Dr. Penny Ferguson
- Genein Letford
- Lynne Kesselman
- Susan Evans
- Valerie Kibler
- How To Become a Lawyer Online
- How to Become a Principal
- Guide to Becoming a Doctor of Social Work
- Masters Degree Program Accreditation
- Teacher Certification Tests (The Praxis and Beyond)
- Teacher Salary, Career and Benefits Guide
- Summer Vacation for Teachers
- Teaching STEM
- Teaching Art
- Teaching Music
- Teaching Gifted Education
- Teaching Social Studies
- Teaching English as a Second Language (ESL)
- Teaching English and Language Arts
- Teaching Special Education
- Teacher Shortage Areas by State
- How To Become an Online Teacher
- Become a Licensed Mental Health Counselor
- How to Become a School Counselor
- LMHC Licensure Guide for Mental Health Counselors
- What does an LMHC do?
- Become a Psychologist
- How to Become a Clinical Psychologist
- What Does a Licensed Marriage & Family Therapist (LMFT) Do?
- Become a Behavior Analyst
- How to Become a Pediatric Nurse
- Become a Women’s Health Nurse Practitioner
- How to Become a Pharmacist
- Become a Speech Pathologist
- Become a Physical Therapist
- How to Become an Occupational Therapist
- Become a Registered Nurse (RN)
- Become a Nurse Practitioner
- Become a Nurse Midwife
- Become an Acute Care Nurse Practitioner
- Become a Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner
- Become an Advanced Practice Registered Nurse APRN
- How to Become a Business Consultant
- Become an Accountant
- Become a Human Resources Specialist
- Become a Public Administrator
- Become a Librarian
Teach.com / Resources
Homework Around the World
January 12, 2017
The verdict is in, and when it comes to homework, it appears that less is more. Research shows that several of the countries scoring top in the world for education, surprisingly dole out the least amount of homework to their students.
South Korea leads the world in education, and on average, students receive less than 3 hours of homework per week.
On the other hand, the United States leads the charge with the most money spent on education per student and students receive a significantly greater amount of homework, but clocks in at number 17 in the world for education. So, why the disparity?
Let’s take a look at this infographic to see how homework and different types of education systems factor into academic rankings around the world.

Homeschooler Pro

What Country Has No Homework
Homework can be a lifelong nightmare for students, while others find it to be a necessary part of the educative process. Nonetheless, some countries have abolished the requirement of homework, while others have adopted it.
Table of Contents
This article will discuss which country has abolished homework and the reasoning behind such decision.
Overview of Homework in Different Countries
The opinion on homework is controversial. In some cases, students develop a sense of responsibility, organization, and improved grades by doing homework.
On the other hand, too much or too little homework can be a source of stress for students and parents, detracting from the quality of life. The amount of homework assigned and the amount of hours spent on it greatly vary from country to country. Students in Asian countries, like Japan, South Korea, and China, are amongst those who spend the most time on homework.
On the other hand, countries such as Finland and Denmark assign less homework, but still allow students to get enough practice on their academic skills to excel in exams.
History of Homework in Finland
Finland is a country located in the Nordic region known for its educational advancements and standards. During the eighties, Finland started an education reform. Since then, the country has abolished mandatory homework and included the practice of less is more into their school system.
Rather than assigning students hours of homework, teachers prefer to give more meaningful and creative tasks and projects. No longer must students worry about homework, as students can dedicate their time to leisure and extra-curricular activities while having the same grade level as students in countries where homework is mandatory.
Finns have a culture of knowing how to read, rather than what to read, and classroom activities and short exercises provide enough practice for students.
The Effects of Abolishing Homework
The decision to abolish homework has proved to be a successful and beneficial plan for the future of Finland. Students have more time to have a balanced life and to pursue activities, such as music, team sports, and part-time jobs.
Also, the decision gives more time and space to students to focus more on their studies and projects. For example, Finland implements a philosophy known as de-emphasis of testing. This means that the focus is not entirely placed on top results, but rather in the acquisition of knowledge.
Therefore, instead of focusing solely on grades, the emphasis is placed on learning how to think and how to learn.
International Recognition of Finland’s System
Finland has a universal, publicly funded educational system that is completely free and voluntary for students between the ages of 6 and 1 Other countries, such as Sweden and Denmark, follow the Finnish system and accomplishment of de-emphasizing on the testing and exam scores.
The policy of no-homework has even been recognized internationally. Books, such as The World’s Best Education System by Melinda Schawacher, and Pasi Silander’s book, The Education Revolution in Finland have given Finland’s system credit.
Criticisms of Abolishing Homework
Although Finland has achieved success with its system and educational advancements, there still remain some critics to the decision to abolish homework. For example, opponents argue that students are not compelled to sit down and study and that this decision allows students to succumb to distraction.
Moreover, some may argue that students develop better time management skills when managing their own time and dedicating it to homework; this way, they learn how to structure their studies and better manage their academic life.
Alternative Homework Policies
Not all countries are ready or willing to completely abolish homework. Therefore, other policy suggestions have been made to reduce the amount of homework assigned.
For example, in the United States, the Homework Policy Council suggests limiting homework to 10 minutes per grade level. In Brazil, the Justa Causa movement urges for the reduction of homework for primary school students. Also, in some countries, parents have started movements to reduce the number of hours spent on homework.

The Pros and Cons of Homework
Overall, some students receive beneficial results from doing homework while others find it to be a stressful obligation. Homework has both pros and cons, as it allows students to acquire more knowledge and practice, as well as improve their grades, but it also has shortcomings, as it takes away from the quality of life and social life of students.
The education system ultimately needs to address the needs of the students and address the proper amount and type of homework. Too much or too little homework can be a source of stress.
In conclusion, Finland has revolutionized the use of less is more in the educational system by abolishing homework. This decision has proven to be beneficial for Finland’s students, as they can dedicate their time to leisure and have more potential to excel academically.
The decision to abolish homework has also been recognized worldwide, as other countries have followed the Finnish system with similar results. Nonetheless, other countries have adopted alternative homework policies in order to prevent the burden of too much homework on students. Finland’s no-homework policy has pros and cons, from allowing the students to dedicate their free time to other activities, to not allowing the students to better manage their own learning process.
Despite the criticism, the decision to abolish homework has been a success for the Finnish; therefore, it is worth considering for other countries as well.
Related posts:
- does homeschooling affect food stamps?
- how to skip grades homeschooling?
- why is homeschooling illegal in sweden?
- how to date when homeschooled?
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Terms and Conditions - Privacy Policy
Take the Quiz: Find the Best State for You »
What's the best state for you », study: homework matters more in certain countries.
Homework is reinforcing the achievement gap between the rich and the poor, say authors of a new study.
Homework Matters, Depending on Your Country
For years, researchers have been trying to figure out just how important homework is to student achievement. Back in 2009, the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development looked at homework hours around the world and found that there wasn’t much of a connection between how much homework students of a particular country do and how well their students score on tests.
Some top achieving countries, like Singapore, assign their students lots of homework. But Finland, for example, succeeds without much homework. On average, Finnish students do only about three hours of homework a week, yet in 2012 they scored sixth highest in the world in reading and 12th highest in math on the OECD’s international test, known as PISA or Programme for International Student Assessment.
But now, five years after the earlier homework study, OECD researchers have drilled down deeper into homework patterns, and they’re finding that homework does play an important role in student achievement within each country . Specifically, they found that homework hours vary by socioeconomic status. Higher income 15-year-olds tend to do more homework than lower income 15-year-olds in almost all of the 38 countries studied by the OECD*. Furthermore, the kids who are doing more homework also tend to get higher test scores. So the authors conclude that homework is reinforcing the achievement gap between the rich and the poor.

Chart created by Jill Barshay | Hechinger Report; data from OECD
It’s not just that poor kids are more likely to skip their homework, or don’t have a quiet place at home to complete it. It’s also the case that schools serving poor kids often don’t assign as much homework as schools for the rich, especially private schools, explained Francesca Borgonovi, one of the authors of the study, titled “ Does Homework Perpetuate Inequities in Education? ”
“When you look within countries at students who are learning in the same educational system and they do more homework, then those students do much better,” said Borgonovi. “There is an advantage for putting extra hours in homework.”
A stark example of this rich-poor homework gap is in Singapore. Students in the top quarter of the socio-economic spectrum spend about 11 hours on homework a week, 3 hours more than low-income students in the bottom quarter of the socio-economic spectrum. Each extra hour of homework was associated with 18 more points on the PISA math exam. So three hours adds up to more than 50 points. That’s huge. To put that in perspective, if you added 50 points to the average U.S. math score, we’d be a top 10 nation instead of number 36.
A key factor is what Borgonovi said about “learning in the same educational system.” Some school systems are designed to rely on homework, perhaps using independent study as a substitute for what could otherwise be learned in school. “If you are prepared to change the system, that’s great,” said Borgonovi. “But until you do so, if the system is based on homework, then you should do more of it.”

Students in Shanghai, a region in China that now leads the world in PISA test scores, do a whopping 14 hours of homework a week, on average. Wealthier students there do 16 hours. Poorer students do just under 11 hours. Interestingly, however, there was no association between the extra homework hours that the wealthier Shanghai kids put in and their PISA test scores. Perhaps that’s because there are diminishing marginal returns to homework after 11 hours of it!
Indeed, most countries around the world have been reducing the amount of homework assigned. Back in 2003, the average time spent on homework worldwide was about six hours a week. In 2012 that shrank to about five hours.
But the United States has been bucking this trend. The typical 15-year-old here does six hours a week, virtually unchanged from a decade ago and possibly rising. Wealthier students typically do eight hours of homework a week, about three hours more than low income students. But unlike in most countries, where more homework is associated with higher PISA test scores, that’s not the case here.
“For the United States, we don’t have homework reinforcing inequality,” Borgonovi said.
Another team of researchers, Ozkan Eren and Daniel J. Henderson, found mixed results for how effective homework is in the United States, in a 2011 study, “ Are we wasting our children’s time by giving them more homework? “ published in the Economics of Education Review. For math, there were huge benefits for the 25,000 eighth graders they studied. But not for English, science or history. And the math boost was much stronger for white students than for blacks. In other words, when a typical black student did more homework, his math test scores didn’t go up as much.
That’s perhaps a clue that even if you could magically get low-income children in other countries to do as much homework as their high-income peers, as the OECD researchers are suggesting, you might not raise their PISA test scores very much.
Indeed, Borgonovi isn’t really advocating for more homework. She says that high quality teachers and instruction are much more important to student outcomes than homework is. To be sure, some amount of homework is good, Borgonovi said, to teach kids how to plan ahead, set goals and work independently. But more than four hours of homework a week, she said, isn’t very beneficial.
“It would be better to redesign the system to have less homework,” said Borgonovi. “But that is hard to do.”
* The OECD looked at socio-economic status and not income exclusively. So the child of a university professor, for example, might still be in the high income category even if his parents don’t make very much money.
Join the Conversation
Tags: education , K-12 education , students , Finland , Singapore
America 2024

Health News Bulletin
Stay informed on the latest news on health and COVID-19 from the editors at U.S. News & World Report.
Sign in to manage your newsletters »
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
You May Also Like
The 10 worst presidents.
U.S. News Staff Feb. 23, 2024

Cartoons on President Donald Trump
Feb. 1, 2017, at 1:24 p.m.

Photos: Obama Behind the Scenes
April 8, 2022

Photos: Who Supports Joe Biden?
March 11, 2020

The Cicadas Are Coming: Grab Your Fork?
Laura Mannweiler May 10, 2024

U.S. Report Stings Israeli War Effort
Aneeta Mathur-Ashton May 10, 2024

Inflation, High Rates Spook Consumers
Tim Smart May 10, 2024

Stormy Daniels' Testimony Gets Heated
Laura Mannweiler and Lauren Camera May 9, 2024

How Rare Are Brain Worms Like RFK Jr.’s?
Laura Mannweiler May 8, 2024

QUOTES: Israel's Rafah Attack
Cecelia Smith-Schoenwalder May 8, 2024

Live In Abroad Blog
Settle, study or earn living in abroad
Which country has no exams?
Exploring the Finnish Education System: The Country with No Exams
Introduction
Education is not just about scoring high grades. It’s about nurturing creativity, critical thinking, collaboration and communication. What if there was a country that emphasizes these aspects more than examinations? Yes, such a country exists, and it’s none other than Finland. In this article, we provide valuable insights into the Finnish education system, a model that promotes learning over testing. If you’re seeking consultancy for abroad studies, this article is a must-read!
Understanding the Finnish Education System
The concept of no exams in finland, benefits of studying in finland, faqs about studying in finland.
Finland’s education system is renowned worldwide for its innovative and student-centric approach. The system doesn’t stress on exams or homework, but on holistic development. The focus is on fostering creativity, critical thinking skills, and a love for learning. But, how does Finland achieve this?
Equal Opportunities for All
The Finnish system believes in providing equal opportunities to all students, irrespective of their social or economic background. Every child has access to free education, meals, and healthcare services, ensuring a level playing field for all.
More Play, Less Work
Finnish schools believe in the power of play. They emphasize extracurricular activities, fostering creativity and team spirit. Children spend less time in classrooms and more in nature, learning from real-life experiences.
One of the unique aspects of the Finnish education system is its “no exams” policy. Yes, you read it right. Until the age of 16, Finnish students don’t undergo any national standardized tests. So, how do they assess the learning?
Focus on Individual Progress
In Finland, the focus is on individual progress rather than competition. Teachers monitor students’ progress through continuous assessment. They provide personalized feedback and guidance, ensuring every child learns at their own pace.
Trust in Teachers
Finland places immense trust in its teachers. They are given the freedom to design their curriculum and teaching methods. They are respected professionals, considered on par with doctors and lawyers.
Here are some key takeaways why studying in Finland can be a perfect choice for your abroad studies:
- Well-rounded Development: The Finnish system nurtures creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills.
- Less Stress: The absence of exams and homework reduces stress, leading to happier students.
- High-Quality Education: Finland ranks among the top countries in the world for education quality.
- Excellent Teachers: Finnish teachers are highly qualified, ensuring the best guidance for students.
Do Finnish universities also have no exams?
While Finnish basic education doesn’t have exams, universities do have exams. However, they focus more on research, projects, and practical knowledge.
Is it expensive to study in Finland?
Most Finnish universities offer free education for EU students. For non-EU students, the tuition fees vary, but scholarships are available.
The Finnish education system offers a fresh perspective on learning, emphasizing overall development over rote learning. If you’re seeking a consultancy for abroad studies, consider Finland. It’s not just about studying; it’s about learning, experiencing, and growing.
Remember, exams might test your memory, but real education enhances your thinking skills, creativity, and personality. And that’s what the Finnish education system aims for!
By bishwasbh
Related post, what are the three goals for study abroad.
Does IDP do visa processing?
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
How long does it take to complete Django?
How do i know if my chest pain is serious, is it still profitable to make an app.
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/71970990/05_nohomework_Jiayue_Li.0.jpg)
Filed under:
- The Highlight
Nobody knows what the point of homework is
The homework wars are back.
Share this story
- Share this on Facebook
- Share this on Twitter
- Share this on Reddit
- Share All sharing options
Share All sharing options for: Nobody knows what the point of homework is
As the Covid-19 pandemic began and students logged into their remote classrooms, all work, in effect, became homework. But whether or not students could complete it at home varied. For some, schoolwork became public-library work or McDonald’s-parking-lot work.
Luis Torres, the principal of PS 55, a predominantly low-income community elementary school in the south Bronx, told me that his school secured Chromebooks for students early in the pandemic only to learn that some lived in shelters that blocked wifi for security reasons. Others, who lived in housing projects with poor internet reception, did their schoolwork in laundromats.
According to a 2021 Pew survey , 25 percent of lower-income parents said their children, at some point, were unable to complete their schoolwork because they couldn’t access a computer at home; that number for upper-income parents was 2 percent.
The issues with remote learning in March 2020 were new. But they highlighted a divide that had been there all along in another form: homework. And even long after schools have resumed in-person classes, the pandemic’s effects on homework have lingered.
Over the past three years, in response to concerns about equity, schools across the country, including in Sacramento, Los Angeles , San Diego , and Clark County, Nevada , made permanent changes to their homework policies that restricted how much homework could be given and how it could be graded after in-person learning resumed.
Three years into the pandemic, as districts and teachers reckon with Covid-era overhauls of teaching and learning, schools are still reconsidering the purpose and place of homework. Whether relaxing homework expectations helps level the playing field between students or harms them by decreasing rigor is a divisive issue without conclusive evidence on either side, echoing other debates in education like the elimination of standardized test scores from some colleges’ admissions processes.
I first began to wonder if the homework abolition movement made sense after speaking with teachers in some Massachusetts public schools, who argued that rather than help disadvantaged kids, stringent homework restrictions communicated an attitude of low expectations. One, an English teacher, said she felt the school had “just given up” on trying to get the students to do work; another argued that restrictions that prohibit teachers from assigning take-home work that doesn’t begin in class made it difficult to get through the foreign-language curriculum. Teachers in other districts have raised formal concerns about homework abolition’s ability to close gaps among students rather than widening them.
Many education experts share this view. Harris Cooper, a professor emeritus of psychology at Duke who has studied homework efficacy, likened homework abolition to “playing to the lowest common denominator.”
But as I learned after talking to a variety of stakeholders — from homework researchers to policymakers to parents of schoolchildren — whether to abolish homework probably isn’t the right question. More important is what kind of work students are sent home with and where they can complete it. Chances are, if schools think more deeply about giving constructive work, time spent on homework will come down regardless.
There’s no consensus on whether homework works
The rise of the no-homework movement during the Covid-19 pandemic tapped into long-running disagreements over homework’s impact on students. The purpose and effectiveness of homework have been disputed for well over a century. In 1901, for instance, California banned homework for students up to age 15, and limited it for older students, over concerns that it endangered children’s mental and physical health. The newest iteration of the anti-homework argument contends that the current practice punishes students who lack support and rewards those with more resources, reinforcing the “myth of meritocracy.”
But there is still no research consensus on homework’s effectiveness; no one can seem to agree on what the right metrics are. Much of the debate relies on anecdotes, intuition, or speculation.
Researchers disagree even on how much research exists on the value of homework. Kathleen Budge, the co-author of Turning High-Poverty Schools Into High-Performing Schools and a professor at Boise State, told me that homework “has been greatly researched.” Denise Pope, a Stanford lecturer and leader of the education nonprofit Challenge Success, said, “It’s not a highly researched area because of some of the methodological problems.”
Experts who are more sympathetic to take-home assignments generally support the “10-minute rule,” a framework that estimates the ideal amount of homework on any given night by multiplying the student’s grade by 10 minutes. (A ninth grader, for example, would have about 90 minutes of work a night.) Homework proponents argue that while it is difficult to design randomized control studies to test homework’s effectiveness, the vast majority of existing studies show a strong positive correlation between homework and high academic achievement for middle and high school students. Prominent critics of homework argue that these correlational studies are unreliable and point to studies that suggest a neutral or negative effect on student performance. Both agree there is little to no evidence for homework’s effectiveness at an elementary school level, though proponents often argue that it builds constructive habits for the future.
For anyone who remembers homework assignments from both good and bad teachers, this fundamental disagreement might not be surprising. Some homework is pointless and frustrating to complete. Every week during my senior year of high school, I had to analyze a poem for English and decorate it with images found on Google; my most distinct memory from that class is receiving a demoralizing 25-point deduction because I failed to present my analysis on a poster board. Other assignments really do help students learn: After making an adapted version of Chairman Mao’s Little Red Book for a ninth grade history project, I was inspired to check out from the library and read a biography of the Chinese ruler.
For homework opponents, the first example is more likely to resonate. “We’re all familiar with the negative effects of homework: stress, exhaustion, family conflict, less time for other activities, diminished interest in learning,” Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth, which challenges common justifications for homework, told me in an email. “And these effects may be most pronounced among low-income students.” Kohn believes that schools should make permanent any moratoria implemented during the pandemic, arguing that there are no positives at all to outweigh homework’s downsides. Recent studies , he argues , show the benefits may not even materialize during high school.
In the Marlborough Public Schools, a suburban district 45 minutes west of Boston, school policy committee chair Katherine Hennessy described getting kids to complete their homework during remote education as “a challenge, to say the least.” Teachers found that students who spent all day on their computers didn’t want to spend more time online when the day was over. So, for a few months, the school relaxed the usual practice and teachers slashed the quantity of nightly homework.
Online learning made the preexisting divides between students more apparent, she said. Many students, even during normal circumstances, lacked resources to keep them on track and focused on completing take-home assignments. Though Marlborough Schools is more affluent than PS 55, Hennessy said many students had parents whose work schedules left them unable to provide homework help in the evenings. The experience tracked with a common divide in the country between children of different socioeconomic backgrounds.
So in October 2021, months after the homework reduction began, the Marlborough committee made a change to the district’s policy. While teachers could still give homework, the assignments had to begin as classwork. And though teachers could acknowledge homework completion in a student’s participation grade, they couldn’t count homework as its own grading category. “Rigorous learning in the classroom does not mean that that classwork must be assigned every night,” the policy stated . “Extensions of class work is not to be used to teach new content or as a form of punishment.”
Canceling homework might not do anything for the achievement gap
The critiques of homework are valid as far as they go, but at a certain point, arguments against homework can defy the commonsense idea that to retain what they’re learning, students need to practice it.
“Doesn’t a kid become a better reader if he reads more? Doesn’t a kid learn his math facts better if he practices them?” said Cathy Vatterott, an education researcher and professor emeritus at the University of Missouri-St. Louis. After decades of research, she said it’s still hard to isolate the value of homework, but that doesn’t mean it should be abandoned.
Blanket vilification of homework can also conflate the unique challenges facing disadvantaged students as compared to affluent ones, which could have different solutions. “The kids in the low-income schools are being hurt because they’re being graded, unfairly, on time they just don’t have to do this stuff,” Pope told me. “And they’re still being held accountable for turning in assignments, whether they’re meaningful or not.” On the other side, “Palo Alto kids” — students in Silicon Valley’s stereotypically pressure-cooker public schools — “are just bombarded and overloaded and trying to stay above water.”
Merely getting rid of homework doesn’t solve either problem. The United States already has the second-highest disparity among OECD (the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) nations between time spent on homework by students of high and low socioeconomic status — a difference of more than three hours, said Janine Bempechat, clinical professor at Boston University and author of No More Mindless Homework .
When she interviewed teachers in Boston-area schools that had cut homework before the pandemic, Bempechat told me, “What they saw immediately was parents who could afford it immediately enrolled their children in the Russian School of Mathematics,” a math-enrichment program whose tuition ranges from $140 to about $400 a month. Getting rid of homework “does nothing for equity; it increases the opportunity gap between wealthier and less wealthy families,” she said. “That solution troubles me because it’s no solution at all.”
A group of teachers at Wakefield High School in Arlington, Virginia, made the same point after the school district proposed an overhaul of its homework policies, including removing penalties for missing homework deadlines, allowing unlimited retakes, and prohibiting grading of homework.
“Given the emphasis on equity in today’s education systems,” they wrote in a letter to the school board, “we believe that some of the proposed changes will actually have a detrimental impact towards achieving this goal. Families that have means could still provide challenging and engaging academic experiences for their children and will continue to do so, especially if their children are not experiencing expected rigor in the classroom.” At a school where more than a third of students are low-income, the teachers argued, the policies would prompt students “to expect the least of themselves in terms of effort, results, and responsibility.”
Not all homework is created equal
Despite their opposing sides in the homework wars, most of the researchers I spoke to made a lot of the same points. Both Bempechat and Pope were quick to bring up how parents and schools confuse rigor with workload, treating the volume of assignments as a proxy for quality of learning. Bempechat, who is known for defending homework, has written extensively about how plenty of it lacks clear purpose, requires the purchasing of unnecessary supplies, and takes longer than it needs to. Likewise, when Pope instructs graduate-level classes on curriculum, she asks her students to think about the larger purpose they’re trying to achieve with homework: If they can get the job done in the classroom, there’s no point in sending home more work.
At its best, pandemic-era teaching facilitated that last approach. Honolulu-based teacher Christina Torres Cawdery told me that, early in the pandemic, she often had a cohort of kids in her classroom for four hours straight, as her school tried to avoid too much commingling. She couldn’t lecture for four hours, so she gave the students plenty of time to complete independent and project-based work. At the end of most school days, she didn’t feel the need to send them home with more to do.
A similar limited-homework philosophy worked at a public middle school in Chelsea, Massachusetts. A couple of teachers there turned as much class as possible into an opportunity for small-group practice, allowing kids to work on problems that traditionally would be assigned for homework, Jessica Flick, a math coach who leads department meetings at the school, told me. It was inspired by a philosophy pioneered by Simon Fraser University professor Peter Liljedahl, whose influential book Building Thinking Classrooms in Mathematics reframes homework as “check-your-understanding questions” rather than as compulsory work. Last year, Flick found that the two eighth grade classes whose teachers adopted this strategy performed the best on state tests, and this year, she has encouraged other teachers to implement it.
Teachers know that plenty of homework is tedious and unproductive. Jeannemarie Dawson De Quiroz, who has taught for more than 20 years in low-income Boston and Los Angeles pilot and charter schools, says that in her first years on the job she frequently assigned “drill and kill” tasks and questions that she now feels unfairly stumped students. She said designing good homework wasn’t part of her teaching programs, nor was it meaningfully discussed in professional development. With more experience, she turned as much class time as she could into practice time and limited what she sent home.
“The thing about homework that’s sticky is that not all homework is created equal,” says Jill Harrison Berg, a former teacher and the author of Uprooting Instructional Inequity . “Some homework is a genuine waste of time and requires lots of resources for no good reason. And other homework is really useful.”
Cutting homework has to be part of a larger strategy
The takeaways are clear: Schools can make cuts to homework, but those cuts should be part of a strategy to improve the quality of education for all students. If the point of homework was to provide more practice, districts should think about how students can make it up during class — or offer time during or after school for students to seek help from teachers. If it was to move the curriculum along, it’s worth considering whether strategies like Liljedahl’s can get more done in less time.
Some of the best thinking around effective assignments comes from those most critical of the current practice. Denise Pope proposes that, before assigning homework, teachers should consider whether students understand the purpose of the work and whether they can do it without help. If teachers think it’s something that can’t be done in class, they should be mindful of how much time it should take and the feedback they should provide. It’s questions like these that De Quiroz considered before reducing the volume of work she sent home.
More than a year after the new homework policy began in Marlborough, Hennessy still hears from parents who incorrectly “think homework isn’t happening” despite repeated assurances that kids still can receive work. She thinks part of the reason is that education has changed over the years. “I think what we’re trying to do is establish that homework may be an element of educating students,” she told me. “But it may not be what parents think of as what they grew up with. ... It’s going to need to adapt, per the teaching and the curriculum, and how it’s being delivered in each classroom.”
For the policy to work, faculty, parents, and students will all have to buy into a shared vision of what school ought to look like. The district is working on it — in November, it hosted and uploaded to YouTube a round-table discussion on homework between district administrators — but considering the sustained confusion, the path ahead seems difficult.
When I asked Luis Torres about whether he thought homework serves a useful part in PS 55’s curriculum, he said yes, of course it was — despite the effort and money it takes to keep the school open after hours to help them do it. “The children need the opportunity to practice,” he said. “If you don’t give them opportunities to practice what they learn, they’re going to forget.” But Torres doesn’t care if the work is done at home. The school stays open until around 6 pm on weekdays, even during breaks. Tutors through New York City’s Department of Youth and Community Development programs help kids with work after school so they don’t need to take it with them.
As schools weigh the purpose of homework in an unequal world, it’s tempting to dispose of a practice that presents real, practical problems to students across the country. But getting rid of homework is unlikely to do much good on its own. Before cutting it, it’s worth thinking about what good assignments are meant to do in the first place. It’s crucial that students from all socioeconomic backgrounds tackle complex quantitative problems and hone their reading and writing skills. It’s less important that the work comes home with them.
Jacob Sweet is a freelance writer in Somerville, Massachusetts. He is a frequent contributor to the New Yorker, among other publications.
Will you support Vox today?
Millions rely on Vox’s journalism to understand the coronavirus crisis. We believe it pays off for all of us, as a society and a democracy, when our neighbors and fellow citizens can access clear, concise information on the pandemic. But our distinctive explanatory journalism is expensive. Support from our readers helps us keep it free for everyone. If you have already made a financial contribution to Vox, thank you. If not, please consider making a contribution today from as little as $3.
We accept credit card, Apple Pay, and Google Pay. You can also contribute via
Social media platforms aren’t equipped to handle the negative effects of their algorithms abroad. Neither is the law.
The real science behind the billionaire pursuit of immortality, if you want to belong, find a third place, sign up for the newsletter today, explained, thanks for signing up.
Check your inbox for a welcome email.
Oops. Something went wrong. Please enter a valid email and try again.
Why I Think All Schools Should Abolish Homework

H ow long is your child’s workweek? Thirty hours? Forty? Would it surprise you to learn that some elementary school kids have workweeks comparable to adults’ schedules? For most children, mandatory homework assignments push their workweek far beyond the school day and deep into what any other laborers would consider overtime. Even without sports or music or other school-sponsored extracurriculars, the daily homework slog keeps many students on the clock as long as lawyers, teachers, medical residents, truck drivers and other overworked adults. Is it any wonder that,deprived of the labor protections that we provide adults, our kids are suffering an epidemic of disengagement, anxiety and depression ?
With my youngest child just months away from finishing high school, I’m remembering all the needless misery and missed opportunities all three of my kids suffered because of their endless assignments. When my daughters were in middle school, I would urge them into bed before midnight and then find them clandestinely studying under the covers with a flashlight. We cut back on their activities but still found ourselves stuck in a system on overdrive, returning home from hectic days at 6 p.m. only to face hours more of homework. Now, even as a senior with a moderate course load, my son, Zak, has spent many weekends studying, finding little time for the exercise and fresh air essential to his well-being. Week after week, and without any extracurriculars, Zak logs a lot more than the 40 hours adults traditionally work each week — and with no recognition from his “bosses” that it’s too much. I can’t count the number of shared evenings, weekend outings and dinners that our family has missed and will never get back.
How much after-school time should our schools really own?
In the midst of the madness last fall, Zak said to me, “I feel like I’m working towards my death. The constant demands on my time since 5th grade are just going to continue through graduation, into college, and then into my job. It’s like I’m on an endless treadmill with no time for living.”
My spirit crumbled along with his.
Like Zak, many people are now questioning the point of putting so much demand on children and teens that they become thinly stretched and overworked. Studies have long shown that there is no academic benefit to high school homework that consumes more than a modest number of hours each week. In a study of high schoolers conducted by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), researchers concluded that “after around four hours of homework per week, the additional time invested in homework has a negligible impact on performance.”
In elementary school, where we often assign overtime even to the youngest children, studies have shown there’s no academic benefit to any amount of homework at all.
Our unquestioned acceptance of homework also flies in the face of all we know about human health, brain function and learning. Brain scientists know that rest and exercise are essential to good health and real learning . Even top adult professionals in specialized fields take care to limit their work to concentrated periods of focus. A landmark study of how humans develop expertise found that elite musicians, scientists and athletes do their most productive work only about four hours per day .
Yet we continue to overwork our children, depriving them of the chance to cultivate health and learn deeply, burdening them with an imbalance of sedentary, academic tasks. American high school students , in fact, do more homework each week than their peers in the average country in the OECD, a 2014 report found.
It’s time for an uprising.
Already, small rebellions are starting. High schools in Ridgewood, N.J. , and Fairfax County, Va., among others, have banned homework over school breaks. The entire second grade at Taylor Elementary School in Arlington, Va., abolished homework this academic year. Burton Valley Elementary School in Lafayette, Calif., has eliminated homework in grades K through 4. Henry West Laboratory School , a public K-8 school in Coral Gables, Fla., eliminated mandatory, graded homework for optional assignments. One Lexington, Mass., elementary school is piloting a homework-free year, replacing it with reading for pleasure.
More from TIME
Across the Atlantic, students in Spain launched a national strike against excessive assignments in November. And a second-grade teacher in Texas, made headlines this fall when she quit sending home extra work , instead urging families to “spend your evenings doing things that are proven to correlate with student success. Eat dinner as a family, read together, play outside and get your child to bed early.”
It is time that we call loudly for a clear and simple change: a workweek limit for children, counting time on the clock before and after the final bell. Why should schools extend their authority far beyond the boundaries of campus, dictating activities in our homes in the hours that belong to families? An all-out ban on after-school assignments would be optimal. Short of that, we can at least sensibly agree on a cap limiting kids to a 40-hour workweek — and fewer hours for younger children.
Resistance even to this reasonable limit will be rife. Mike Miller, an English teacher at Thomas Jefferson High School for Science and Technology in Alexandria, Va., found this out firsthand when he spearheaded a homework committee to rethink the usual approach. He had read the education research and found a forgotten policy on the county books limiting homework to two hours a night, total, including all classes. “I thought it would be a slam dunk” to put the two-hour cap firmly in place, Miller said.
But immediately, people started balking. “There was a lot of fear in the community,” Miller said. “It’s like jumping off a high dive with your kids’ future. If we reduce homework to two hours or less, is my kid really going to be okay?” In the end, the committee only agreed to a homework ban over school breaks.
Miller’s response is a great model for us all. He decided to limit assignments in his own class to 20 minutes a night (the most allowed for a student with six classes to hit the two-hour max). His students didn’t suddenly fail. Their test scores remained stable. And they started using their more breathable schedule to do more creative, thoughtful work.
That’s the way we will get to a sane work schedule for kids: by simultaneously pursuing changes big and small. Even as we collaboratively press for policy changes at the district or individual school level, all teachers can act now, as individuals, to ease the strain on overworked kids.
As parents and students, we can also organize to make homework the exception rather than the rule. We can insist that every family, teacher and student be allowed to opt out of assignments without penalty to make room for important activities, and we can seek changes that shift practice exercises and assignments into the actual school day.
We’ll know our work is done only when Zak and every other child can clock out, eat dinner, sleep well and stay healthy — the very things needed to engage and learn deeply. That’s the basic standard the law applies to working adults. Let’s do the same for our kids.
Vicki Abeles is the author of the bestseller Beyond Measure: Rescuing an Overscheduled, Overtested, Underestimated Generation, and director and producer of the documentaries “ Race to Nowhere ” and “ Beyond Measure. ”
More Must-Reads From TIME
- What Student Photojournalists Saw at the Campus Protests
- How Far Trump Would Go
- Why Maternity Care Is Underpaid
- Saving Seconds Is Better Than Hours
- Welcome to the Golden Age of Ryan Gosling
- Scientists Are Finding Out Just How Toxic Your Stuff Is
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at [email protected]
The truth about homework in America
by: Carol Lloyd | Updated: May 6, 2024
Print article

Not excited about homework? We can hardly blame you. But how families handle homework in America can have a huge impact on their child’s short-term and long-term academic success. Here’s a glimpse at how American families approach homework, and some tips that may help you decide how to handle homework in your home.
Model how much you value your child’s education
Think of your child’s nightly homework as a time to model how much you value your child’s learning and education. Get in the habit of asking your child what homework they have each evening, looking over their homework when they’re done each night, praising their hard work, and marveling at all that they are learning. Your admiration and love is the best magic learning potion available.
Set up a homework routine American parents who want their children to graduate from high school and go to college take learning at home seriously. They turn off the TV and radio at homework time. They take away access to video games and smartphones. They make sure the child gets some exercise and has a healthy snack before starting homework because both are shown to help kids focus. When it’s time for homework, they (try to) ensure their child has a quiet place where they can focus and have access to the grade-appropriate homework basics, like paper, pencils, erasers, crayons, and tape for kids in younger grades and calculators and writing materials for kids in older grades.
Helping with homework when you don’t read/speak English
So how can you help with homework if you can’t read your child’s homework because it’s in English — or because the math is being presented in a way you’ve never seen? If you can’t understand your child’s homework, you can still do a lot to help them. Your physical presence (and your authority to turn off the TV) can help them take homework time seriously. Your encouragement that they take their time and not rush through the work also will help. Finally, your ability to ask questions can do two important things: you can show your interest in their work (and thus reinforce the importance you place on learning and education) and you can help your child slow down and figure things out when they’re lost or frustrated. A lot of learning happens when children have a chance to talk through problems and ideas. Sometimes, just describing the assignment or problem to you can help the solution click for your child.
What’s the right amount of homework?
It’s often in first grade that kids start receiving regular homework and feel stressed and lost if they don’t complete it. If your child is having trouble adjusting to their new routines, know that it’s not just your child. Families all across America are having the same issues in terms of figuring out how to create quiet, focussed time for a young child to read, write, and do math inside a bustling home. In first grade, your child will likely be asked to do somewhere between 10 and 30 minutes of homework a night, sometimes in addition to 20 minutes of bedtime reading. ( The National PTA’s research-based recommendation is 10 to 20 minutes of homework a night in first grade and an additional 10 minutes per grade level thereafter.) If your child is getting a lot more than that, talk to your child’s teacher about how long your child should be spending on homework and what you can do to help.
Comparing U.S. homework time to other countries
If you’ve come from another country and recall your childhood homework taking less time, you may think it’s because you’re foreign. The truth is, most parents who grew up in the U.S. are feeling the same way. In the past few decades homework for younger grades has intensified in many schools. “The amount of homework that younger kids — ages 6 to 9 — have to do has gone up astronomically since the late ’80s,” says Alfie Kohn, author of the 2006 book The Homework Myth: Why Our Kids Get Too Much of a Bad Thing. So if you feel surprised about the quantity of homework your child is bringing home, you’re not alone.
According to an international study of homework, 15-year-olds in Shanghai do 13.8 hours of homework per week compared to 6.1 hours in the U.S. and 5.3 hours in Mexico and 3.4 hours in Costa Rica. But here’s the thing: academic expectations in the U.S. vary widely from school to school. Some American elementary schools have banned homework. Others pile on hours a night — even in the younger grades. By high school, though, most American students who are seriously preparing for four-year college are doing multiple hours of homework most nights.
Not into homework? Try this.
Homework detractors point to research that shows homework has no demonstrated benefits for students in the early elementary grades. “The research clearly shows that there is no correlation between academic achievement and homework, especially in the lower grades,” says Denise Pope, senior lecturer at the Stanford University Graduate School of Education and the author of the 2015 book, Overloaded and Underprepared: Strategies for Stronger Schools and Healthy Successful Kids .
On the other hand, nightly reading is hugely important.
“One thing we know does have a correlation with academic achievement is free reading time,” says Pope. “We know that that is something we want schools to encourage.” Since the scientific evidence shows the most impact comes from reading for pleasure, don’t skip bedtime reading. If your child is not being given any homework, make sure to spend some of that extra time reading books in either English or Spanish.
Homes Nearby
Homes for rent and sale near schools

How our schools are (and aren't) addressing race

What should I write my college essay about?
What the #%@!& should I write about in my college essay?

Should your teen take the PSAT — and if so, when?
Yes! Sign me up for updates relevant to my child's grade.
Please enter a valid email address
Thank you for signing up!
Server Issue: Please try again later. Sorry for the inconvenience
Planning is one of the keys to success in college.

Prosperous countries that allocate less homework to students
Reflecting old days in school, and one cannot forget the dramas with homework assignments that we did every evening after all day in school learning. We could struggle with sleep and homework on the study table. During playtime, school days were excellent, and we longed never to end, but when it came to homework, the school was not so excited and fun. However, there are countries out there who offer students less or no homework, and they are successful. Yes, you heard me right, successful and offered fewer homework assignments. Is the offering of less homework, the secret to success? What are their homework solutions ? In this article, we explore the countries that provide less homework and are thriving.
On top of the list of successful countries that offer less homework and is Finland. Finland is a European country that prides itself on offering 2.8 hours of assignments per week, long holiday vacations, and short school days. Besides, Finnish children are not obligated to begin school before they are seven years of age that sounds weird, child staying at home until the age of seven. Despite all these, the Finnish education system equips her students with requisite skills and knowledge, and they come at the top of matters examinations globally. For example, in science and mathematics knowledge, Finnish students rank sixth in the entire world. According to Finnish people, their education system works on absolute trust. Instead of overloading students with homework assignments at home, parents have faith that teachers will provide their children with the required education while they are in school. However, studies have proven that homework translates to better results, but the Finnish education system is proofing otherwise.
South Korea
Similar to Finland, South Korea allocate their students an average of 2.9 hours of assignments per week. Despite South Korea allocating relatively less homework per week, South Korea is positioned two in the entire world in their reading knowledge. South Korean schools had no structure until the last few years when South Koreans restructured their education system, and it became a significant part of their country’s development. South Korean restructured education system seeks to provide education to everyone regardless of his or her background. Though South Korean students rank at the top globally and enjoy fewer homework assignments, many questions linger as to whether they are successful. Instead of South Korean schools allocating more homework assignments to students, they pay close attention to constant testing and always pressure students.
The Japanese education system is the most unique, globally. Instead of teachers utilizing their knowledge to impart knowledge and skills to students, they teach them how to use internet resources to find answers to their problems. On average Japanese schools, offer her students 3.8 hours of assignments per week. Japanese students do not engage in brainwork. Instead, schools throughout the country do not hire janitors. Students themselves keep their buildings tidy and clean. Therefore, while schools in Japan do not overload students with homework, they prepare for other skills they will require to succeed in life.
Homework is a topic that draws varied opinions amongst people. Others believe that homework is the best strategy for students to learn, while others believe that students should learn everything in school without homework assignments. Finally, the successful countries that offer less homework have demonstrated that it is possible to succeed without giving students extra work after school.
Follow us to get more information!
And subscribe
Our No Homework Policy

At The Country School, children have no homework until the second trimester of 5th grade. There is no evidence of a clear connection between homework, improved test scores and academic achievement in the lower grades. Traditional homework also limits valuable family time, and may even be detrimental to students’ mental health. Once homework is introduced in the latter part of 5th grade, teachers are conscientious about balancing the homework load, teaching students the skills to manage the work, and making sure that the homework assigned always serves a purpose and is connected to helping students achieve the highest academic standards
“ We want kids to spend their afternoons playing, exploring and getting recharged for the next day. We want to give our students their lives back, and our parents their kids back. This is a bold move, and we have our work cut out for us, but we don’t want to spend another minute tied to traditional ways of doing things when we know they are not right for our kids. With our roots firmly planted in progressive education, we place an emphasis on learning by doing, through hands on projects and teachers who engage students in understanding and experiencing – rather than just memorizing and regurgitating for tests. I believe this approach creates students with a lifelong love of learning, and the skills and confidence to succeed both inside and outside the classroom – academically, socially, and emotionally. ”
The Parent/School Partnership
Learning should still take place at home with or without homework. Our policy gives families the freedom to let their interests and passions guide their learning. Science experiments, playing outside, cooking and reading books together become an equally important part of a child’s development, along with the curriculum they learn at school. At the elementary level, it is expected that parents will support their child’s learning through nightly reading, reviewing math facts, practicing spelling words, etc. Teachers are happy to help provide ideas and resources for continuing the learning at home if needed.
Our no homework policy in lower grades allows you to be a partner in your child’s education. While our rigorous academic standards are fostered in the classroom, your family is empowered to explore and create your own path for learning at home.
- Share a Simcha
Subscribe for Simcha Updates!
- Remove a Simcha
University leaders face calls for accountability after crackdowns on pro-Palestinian encampments
Pro-Palestinian activists have launched encampments at more than 70 campuses to bring attention to Israel’s monthslong military assault on the Gaza Strip and to demand that schools divest from companies doing business with the country. The nationwide movement has led to clashes with police and more than 2,300 protesters being arrested in the past few weeks, according to an NBC News tally.
Now, as many students face legal and disciplinary action and universities are reassessing commencement plans , school communities are expressing frustration with administrators’ management of campus protests.
On Wednesday, a group of pro-Palestinian protesters formed an encampment at Fordham University’s Lincoln Center campus in New York City. The school called on the New York Police Department to assist, and police arrested 15 protesters.
In a statement addressed to the school community released later that evening, Fordham President Tania Tetlow characterized the encampment inside the Leon Lowenstein academic building and the protest directly outside as “different” from previously held events on the college campus, and added that “hundreds of protesters came from elsewhere.”
“We draw the line at intrusions into a classroom building, especially by people who are not members of our community. (There is a difference between free speech and people barging into your home to shout.),” she wrote.
In a letter shared exclusively with NBC News, two Fordham faculty members presented an analysis of what they consider to be Tetlow’s “inaccurate and misleading statements” to the Fordham community.
Assistant professor Leo Guardado and associate professor Carey Kasten provided an in-depth timeline of the May 1 events to the Fordham Faculty Senate on Friday. They also presented a compilation of photos and videos taken by faculty members who elected to serve as observers of the encampment.
The evidence was used to dispute almost 10 claims Tetlow made in her letter. NBC News has not independently verified either side’s claims.
One of those contentions includes an exaggeration of the size of the indoor encampment. The professors claim that, based on eyewitness accounts and video evidence, about 20 people were a part of the encampment, when Tetlow said “several dozen people pushed inside the lobby.”
Guardado and Kasten also claimed the language in Tetlow’s letter suggested that the majority of individuals involved in the encampment and protest were not affiliated with Fordham.
“The arrested protesters were students and alums. Many of the people outside were students, faculty and alums,” Kasten said. “This is our community.”
Tetlow said the university remains committed to allowing peaceful protests, but the professors’ letter to the Fordham Faculty Senate argued that the encampment was nonviolent and that “all participants remained peaceful in their protest throughout the day.”
Danie Taylor, a professor in the Fordham theater program, said he was disheartened by the university’s failure to “uphold its own mission statement,” which includes the “promotion of justice” and the “protection of human rights.”
“We must hold our institution accountable to its stated values of social responsibility and ethical conduct,” he said.
Fordham University did not immediately respond to a request for comment Saturday.
School administrators face pushback
University administrators are experiencing pushback and fielding criticism for their decisions to use police to crack down on encampments and protests.
Last week, after a pro-Palestinian encampment began on Emory University’s campus, police arrested 28 individuals — 20 of whom were Emory community members.
After the incident, the Faculty Senate of the Emory College of Arts and Sciences, one of the university’s nine schools, passed a vote of no confidence in President Gregory Fenves, with 75% of members voting in favor of its passage, according to Laura Diamond, assistant vice president of university communications.
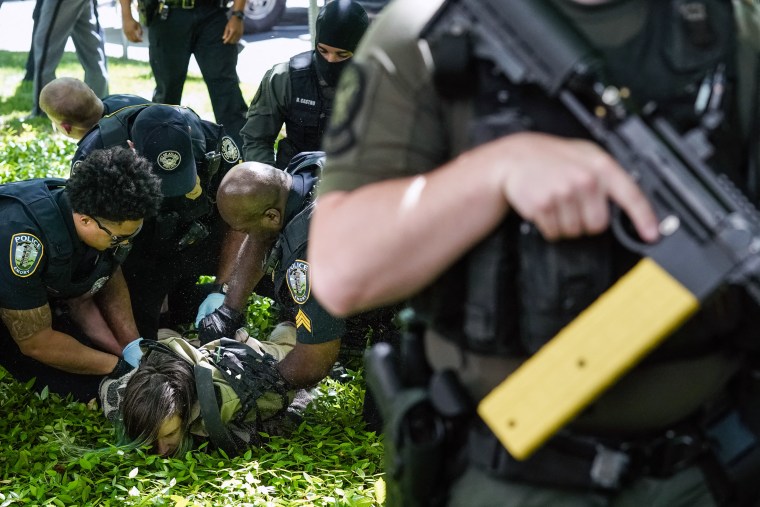

In response to the vote, the university said in a statement: “While we take any concerns expressed by members of our community seriously, there are a wide range of perspectives being shared.”
On Friday, the NYPD arrested 43 individuals while the New School’s encampment was cleared. Later that afternoon, more than 200 faculty and staff members from all five colleges within the university convened an emergency meeting.
The meeting, hosted by the New School chapter of the American Association of University Professors, held three votes, including a vote of no confidence in President Donna Shalala and the board of trustees. More than 90% of members voted in favor.
A vast majority of the group also voted for all charges and disciplinary actions against students to be dropped.
“The results of this emergency meeting are simply a first step, initiated by workers at The New School profoundly angered and distressed by the administration’s treatment of our students,” the group said in a statement on Friday. “President Donna Shalala’s decision to invite police onto campus under the flimsiest of premises, to arrest students involved in nonviolent protest, at a time when no faculty support was on hand, is intolerable.”
At University of Texas at Austin, where police arrested 57 pro-Palestinian protesters on April 24, more than 600 members of the university’s teaching staff signed an open letter claiming no confidence in President Jay Hartzell.
“The President has shown himself to be unresponsive to urgent faculty, staff, and student concerns. He has violated our trust. The University is no longer a safe and welcoming place for the diverse community of students and scholars who until now have called this campus home,” the letter stated.
It was sent to Hartzell on April 29, after some faculty members declined to hold class or grade assignments earlier in the week to protest the university’s response to the encampment.
The faculty members of the Columbia University history department condemned the use of police force against students and referred to the similar anti-war protests that took place on campus in 1968.
“Since the last time the police were called on this campus in large numbers, in 1968, Columbia has worked hard to restore community, build shared governance, deal peacefully with protest, and maintain a culture of respectful debate. We must hold on to this legacy,” the department said in a statement.

Students are also taking action against university administration after the crackdown on pro-Palestinian activism.
At the University of Southern California, the undergraduate student government sent a letter to President Carol Folt expressing disappointment in the administration’s use of force, after the Los Angeles Police Department arrested nearly 100 people on April 24.
“The escalation of police violence on our campus is an experience we never imagined — much less one being fronted by our university,” the letter, released on April 28, stated.
The USC students called for no further “retaliatory action” against them for participating in peaceful assemblies.
“We expect the university’s disproportionate response to the demonstration on April 24th to never recur on this campus,” the letter continued. “To the administration, we expect better.”
At Columbia University, students filed a complaint with the U.S. Department of Education’s Office for Civil Rights to investigate discrimination against Palestinian students and their allies.
In addition to faculty and student efforts to demand accountability from administrators, organizations such as Palestine Legal are stepping in.
In Florida, a coalition of seven organizations — including the state’s chapters of the ACLU and NAACP — delivered a letter to Florida college and university presidents on Friday to express concern over “unnecessary use of force by law enforcement and encroachments on First Amendment rights,” citing university responses to the peaceful protests as “troubling and dangerous.”
Joe Kottke is a researcher at the NBC News Network Desk.
Militants bomb a girls school in northwestern Pakistan, once a Taliban stronghold. No one was harmed
Police say suspected militants bombed a girls school in a former stronghold of the Pakistani Taliban in the country’s volatile northwest, badly damaging the structure
DERA ISMAIL KHAN, Pakistan — Militants detonated a bomb at a girls school in a former stronghold of the Pakistani Taliban in the country’s volatile northwest, badly damaging the structure, police said Thursday. No one was harmed in the overnight attack.
There was no immediate claim of responsibility for the attack late Wednesday that targeted the only girls school in Shawa, a town in the North Waziristan district in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province bordering Afghanistan, local police chief Amjad Wazir said.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Finland schools begin from 9.30 am as research in World Economic Forum has indicated that schools starting at an early age is detrimental to their health and maturation. The school ends by mostly 2 pm. Lastly, there is no homework or surprise test given to students in Finland.
1. Finland. On top of the list of countries giving less assignment is Finland. Apart from boasting of short school terms and extended holidays, the country limits the homework load to 2.8 hours total of homework per week. Despite their educational system, Finland manages to rank among the top countries in math and science innovations and also ...
The Pontus School is a new primary school and kindergarten for some 550 children from ages 1 to 12. It was built three years ago to support the pedagogy and spirit of the 2014 NCC.
The test subjects for the study were 15 year old high school students in countries that used PISA exams in their education systems. The results showed that in Shanghai, China the students had the highest number of hours of homework with 13.8 hours per week. Russia followed, where students had an average of 9.7 hours of homework per week.
Moore discusses Finland's education policy (almost no homework, no standardized testing), speaking with Krista Kiuru, the Finnish Minister of Education. Moor...
The Finnish system is excellent for a largely homogenous country in a relatively small area with a similar culture that values education. In short: the Finnish system is great for Finns.
Educational policy, Abrams suggests, is probably more important to the success of a country's school system than the nation's size or ethnic makeup. Indeed, Finland's population of 5.4 million can ...
Indeed, most countries around the world have been reducing the amount of homework assigned. Back in 2003, the average time spent on homework worldwide was about six hours a week. In 2012 that shrank to about five hours. But the United States has been bucking this trend. The typical 15-year-old here does six hours a week, virtually unchanged ...
"No homework" does not guarantee that all students will spend their free time in productive and imaginative play. ... Within 24 hours of the day school doors closed in March 2020, just about every school and district in the country figured out that teachers had to talk to and work with students' parents. This was not the same as homeschooling ...
Homework Around the World. January 12, 2017. The verdict is in, and when it comes to homework, it appears that less is more. Research shows that several of the countries scoring top in the world for education, surprisingly dole out the least amount of homework to their students. South Korea leads the world in education, and on average, students ...
Finland is a country located in the Nordic region known for its educational advancements and standards. During the eighties, Finland started an education reform. Since then, the country has abolished mandatory homework and included the practice of less is more into their school system. Rather than assigning students hours of homework, teachers ...
Higher income 15-year-olds tend to do more homework than lower income 15-year-olds in almost all of the 38 countries studied by the OECD*. Furthermore, the kids who are doing more homework also ...
Here are some key takeaways why studying in Finland can be a perfect choice for your abroad studies: Well-rounded Development: The Finnish system nurtures creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills. Less Stress: The absence of exams and homework reduces stress, leading to happier students. High-Quality Education: Finland ranks ...
A World Without Homework. Published On: February 6, 2020. In recent years, researchers and teachers have been experimenting with a "no homework" policy in the classroom. Though it may sound dubious, some evidence suggests "no homework" might be a good idea. Studies have shown that more homework in elementary and middle school does not ...
The homework wars are back. By Jacob Sweet Updated Feb 23, 2023, 6:04am EST. As the Covid-19 pandemic began and students logged into their remote classrooms, all work, in effect, became homework ...
American high school students, in fact, do more homework each week than their peers in the average country in the OECD, a 2014 report found. It's time for an uprising. Already, small rebellions ...
The truth is, most parents who grew up in the U.S. are feeling the same way. In the past few decades homework for younger grades has intensified in many schools. "The amount of homework that younger kids — ages 6 to 9 — have to do has gone up astronomically since the late '80s," says Alfie Kohn, author of the 2006 book The Homework ...
Finland. On top of the list of successful countries that offer less homework and is Finland. Finland is a European country that prides itself on offering 2.8 hours of assignments per week, long holiday vacations, and short school days. Besides, Finnish children are not obligated to begin school before they are seven years of age that sounds ...
Homework does not help younger students, and may not help high school students. We've known for a while that homework does not help elementary students. A 2006 study found that "homework had no association with achievement gains" when measured by standardized tests results or grades. [ 7]
At The Country School, children have no homework until the second trimester of 5th grade. There is no evidence of a clear connection between homework, improved test scores and academic achievement in the lower grades. Traditional homework also limits valuable family time, and may even be detrimental to students' mental health. Once homework ...
There's one country in the world where little kids get no homework, no GPAs, and no exams! Let us take you on a trip to the one country who... | school, homework Video. Home. Live. Reels. Shows. Explore. More. Home. Live. Reels. Shows. Explore. Country With No Exams. Like. Comment. Share. 464K · 23K comments · 11M views. Nas Daily ...
It means that standardized homework is eliminated. 3.South Korea. A South Korean student is supposed to have no more than 2.8 hours of homework each week. It is one of the best examples of homework management around the world. The country recognizes that each student is different and a standardized assessment only crashes the confidence of some ...
On Wednesday, a group of pro-Palestinian protesters formed an encampment at Fordham University's Lincoln Center campus in New York City. The school called on the New York Police Department to ...
DERA ISMAIL KHAN, Pakistan — Militants detonated a bomb at a girls school in a former stronghold of the Pakistani Taliban in the country's volatile northwest, badly damaging the structure ...