

How to write a conclusion for a history essay

Every essay needs to end with a concluding paragraph. It is the last paragraph the marker reads, and this will typically be the last paragraph that you write.
What is a ‘concluding paragraph?
The conclusion is the final paragraph of your essay that reminds the reader about the points you have made and how it proves the argument which you stated in your hypothesis .
By the time your marker reads your conclusion, they have read all the evidence you have presented in your body paragraphs . This is your last opportunity to show that you have proven your points.
While your conclusion will talk about the same points you made in your introduction , it should not read exactly the same. Instead, it should state the same information in a more developed form and bring the essay to an end.
In general, you should never use quotes from sources in your conclusion.
Concluding paragraph structure
While the concluding paragraph will normally be shorter than your introductory and body paragraphs , it still has a specific role to fulfil.
A well-written concluding paragraph has the following three-part structure:
- Restate your key points
- Restate your hypothesis
- Concluding sentence
Each element of this structure is explained further, with examples, below:
1. Restate your key points
In one or two sentences, restate each of the topic sentences from your body paragraphs . This is to remind the marker about how you proved your argument.
This information will be similar to your elaboration sentences in your introduction , but will be much briefer.
Since this is a summary of your entire essay’s argument, you will often want to start your conclusion with a phrase to highlight this. For example: “In conclusion”, “In summary”, “To briefly summarise”, or “Overall”.
Example restatements of key points:
Middle Ages (Year 8 Level)
In conclusion, feudal lords had initially spent vast sums of money on elaborate castle construction projects but ceased to do so as a result of the advances in gunpowder technology which rendered stone defences obsolete.
WWI (Year 9 Level)
To briefly summarise, the initially flood of Australian volunteers were encouraged by imperial propaganda but as a result of the stories harsh battlefield experience which filtered back to the home front, enlistment numbers quickly declined.
Civil Rights (Year 10 Level)
In summary, the efforts of important First Nations leaders and activist organisations to spread the idea of indigenous political equality had a significant effect on sway public opinion in favour of a ‘yes’ vote.
Ancient Rome (Year 11/12 Level)
Overall, the Marian military reforms directly changed Roman political campaigns and the role of public opinion in military command assignments across a variety of Roman societal practices.
2. Restate your hypothesis
This is a single sentence that restates the hypothesis from your introductory paragraph .
Don’t simply copy it word-for-word. It should be restated in a different way, but still clearly saying what you have been arguing for the whole of your essay.
Make it clear to your marker that you are clearly restating you argument by beginning this sentence a phrase to highlight this. For example: “Therefore”, “This proves that”, “Consequently”, or “Ultimately”.
Example restated hypotheses:
Therefore, it is clear that while castles were initially intended to dominate infantry-dominated siege scenarios, they were abandoned in favour of financial investment in canon technologies.
This proves that the change in Australian soldiers' morale during World War One was the consequence of the mass slaughter produced by mass-produced weaponry and combat doctrine.
Consequently, the 1967 Referendum considered a public relations success because of the targeted strategies implemented by Charles Perkins, Faith Bandler and the Federal Council for the Advancement of Aborigines and Torres Strait Islanders.
Ultimately, it can be safely argued that Gaius Marius was instrumental in revolutionising the republican political, military and social structures in the 1 st century BC.
3. Concluding sentence
This is the final sentence of your conclusion that provides a final statement about the implications of your arguments for modern understandings of the topic. Alternatively, it could make a statement about what the effect of this historical person or event had on history.
Example concluding sentences:
While these medieval structures fell into disuse centuries ago, they continue to fascinate people to this day.
The implications of the war-weariness produced by these experiences continued to shape opinions about war for the rest of the 20 th century.
Despite this, the Indigenous Peoples had to lobby successive Australian governments for further political equality, which still continues today.
Ancient Rome (Year 11/12 Level)
The impact of these changes effectively prepared the way for other political figures, like Pompey, Julius Caesar and Octavian, who would ultimately transform the Roman republic into an empire.
Putting it all together
Once you have written all three parts of, you should have a completed concluding paragraph. In the examples above, we have shown each part separately. Below you will see the completed paragraphs so that you can appreciate what a conclusion should look like.
Example conclusion paragraphs:
In conclusion, feudal lords had initially spent vast sums of money on elaborate castle construction projects but ceased to do so as a result of the advances in gunpowder technology which rendered stone defences obsolete. Therefore, it is clear that while castles were initially intended to dominate infantry-dominated siege scenarios, they were abandoned in favour of financial investment in canon technologies. While these medieval structures fell into disuse centuries ago, they continue to fascinate people to this day.
To briefly summarise, the initially flood of Australian volunteers were encouraged by imperial propaganda, but as a result of the stories harsh battlefield experience which filtered back to the home front, enlistment numbers quickly declined. This proves that the change in Australian soldiers' morale during World War One was the consequence of the mass slaughter produced by mass-produced weaponry and combat doctrine. The implications of the war-weariness produced by these experiences continued to shape opinions about war for the rest of the 20th century.
In summary, the efforts of important indigenous leaders and activist organisations to spread the idea of indigenous political equality had a significant effect on sway public opinion in favour of a ‘yes’ vote. Consequently, the 1967 Referendum considered a public relations success because of the targeted strategies implemented by Charles Perkins, Faith Bandler and the Federal Council for the Advancement of Aborigines and Torres Strait Islanders. Despite this, the Indigenous Peoples had to lobby successive Australian governments for further political equality, which still continues today.
Overall, the Marian military reforms directly changed Roman political campaigns and the role of public opinion in military command assignments across a variety of Roman societal practices. Ultimately, it can be safely argued that Gaius Marius was instrumental in revolutionising the republican political, military and social structures in the 1st century BC. The impact of these changes effectively prepared the way for other political figures, like Pompey, Julius Caesar and Octavian, who would ultimately transform the Roman republic into an empire.
Additional resources

What do you need help with?
Download ready-to-use digital learning resources.

Copyright © History Skills 2014-2024.
Contact via email

Introductions & Conclusions
The introduction and conclusion serve important roles in a history paper. They are not simply perfunctory additions in academic writing, but are critical to your task of making a persuasive argument.
A successful introduction will:
- draw your readers in
- culminate in a thesis statement that clearly states your argument
- orient your readers to the key facts they need to know in order to understand your thesis
- lay out a roadmap for the rest of your paper
A successful conclusion will:
- draw your paper together
- reiterate your argument clearly and forcefully
- leave your readers with a lasting impression of why your argument matters or what it brings to light
How to write an effective introduction:
Often students get slowed down in paper-writing because they are not sure how to write the introduction. Do not feel like you have to write your introduction first simply because it is the first section of your paper. You can always come back to it after you write the body of your essay. Whenever you approach your introduction, think of it as having three key parts:
- The opening line
- The middle “stage-setting” section
- The thesis statement
“In a 4-5 page paper, describe the process of nation-building in one Middle Eastern state. What were the particular goals of nation-building? What kinds of strategies did the state employ? What were the results? Be specific in your analysis, and draw on at least one of the scholars of nationalism that we discussed in class.”
Here is an example of a WEAK introduction for this prompt:
“One of the most important tasks the leader of any country faces is how to build a united and strong nation. This has been especially true in the Middle East, where the country of Jordan offers one example of how states in the region approached nation-building. Founded after World War I by the British, Jordan has since been ruled by members of the Hashemite family. To help them face the difficult challenges of founding a new state, they employed various strategies of nation-building.”
Now, here is a REVISED version of that same introduction:
“Since 1921, when the British first created the mandate of Transjordan and installed Abdullah I as its emir, the Hashemite rulers have faced a dual task in nation-building. First, as foreigners to the region, the Hashemites had to establish their legitimacy as Jordan’s rightful leaders. Second, given the arbitrary boundaries of the new nation, the Hashemites had to establish the legitimacy of Jordan itself, binding together the people now called ‘Jordanians.’ To help them address both challenges, the Hashemite leaders crafted a particular narrative of history, what Anthony Smith calls a ‘nationalist mythology.’ By presenting themselves as descendants of the Prophet Muhammad, as leaders of the Arab Revolt, and as the fathers of Jordan’s different tribal groups, they established the authority of their own regime and the authority of the new nation, creating one of the most stable states in the modern Middle East.”
The first draft of the introduction, while a good initial step, is not strong enough to set up a solid, argument-based paper. Here are the key issues:
- This first sentence is too general. From the beginning of your paper, you want to invite your reader into your specific topic, rather than make generalizations that could apply to any nation in any time or place. Students often run into the problem of writing general or vague opening lines, such as, “War has always been one of the greatest tragedies to befall society.” Or, “The Great Depression was one of the most important events in American history.” Avoid statements that are too sweeping or imprecise. Ask yourself if the sentence you have written can apply in any time or place or could apply to any event or person. If the answer is yes, then you need to make your opening line more specific.
- Here is the revised opening line: “Since 1921, when the British first created the mandate of Transjordan and installed Abdullah I as its emir, the Hashemite rulers have faced a dual task in nation-building.”
- This is a stronger opening line because it speaks precisely to the topic at hand. The paper prompt is not asking you to talk about nation-building in general, but nation-building in one specific place.
- This stage-setting section is also too general. Certainly, such background information is critical for the reader to know, but notice that it simply restates much of the information already in the prompt. The question already asks you to pick one example, so your job is not simply to reiterate that information, but to explain what kind of example Jordan presents. You also need to tell your reader why the context you are providing matters.
- Revised stage-setting: “First, as foreigners to the region, the Hashemites had to establish their legitimacy as Jordan’s rightful leaders. Second, given the arbitrary boundaries of the new nation, the Hashemites had to establish the legitimacy of Jordan itself, binding together the people now called ‘Jordanians.’ To help them address both challenges, the Hashemite rulers crafted a particular narrative of history, what Anthony Smith calls a ‘nationalist mythology.’”
- This stage-setting is stronger because it introduces the reader to the problem at hand. Instead of simply saying when and why Jordan was created, the author explains why the manner of Jordan’s creation posed particular challenges to nation-building. It also sets the writer up to address the questions in the prompt, getting at both the purposes of nation-building in Jordan and referencing the scholar of nationalism s/he will be drawing on from class: Anthony Smith.
- This thesis statement restates the prompt rather than answers the question. You need to be specific about what strategies of nation-building Jordan’s leaders used. You also need to assess those strategies, so that you can answer the part of the prompt that asks about the results of nation-building.
- Revised thesis statement: “By presenting themselves as descendants of the Prophet Muhammad, as leaders of the Arab Revolt, and as the fathers of Jordan’s different tribal groups, they established the authority of their regime and the authority of the new nation, creating one of the most stable states in the modern Middle East.”
- It directly answers the question in the prompt. Even though you will be persuading readers of your argument through the evidence you present in the body of your paper, you want to tell them at the outset exactly what you are arguing.
- It discusses the significance of the argument, saying that Jordan created an especially stable state. This helps you answer the question about the results of Jordan’s nation-building project.
- It offers a roadmap for the rest of the paper. The writer knows how to proceed and the reader knows what to expect. The body of the paper will discuss the Hashemite claims “as descendants from the Prophet Muhammad, as leaders of the Arab Revolt, and as the fathers of Jordan’s different tribal groups.”
If you write your introduction first, be sure to revisit it after you have written your entire essay. Because your paper will evolve as you write, you need to go back and make sure that the introduction still sets up your argument and still fits your organizational structure.
How to write an effective conclusion:
Your conclusion serves two main purposes. First, it reiterates your argument in different language than you used in the thesis and body of your paper. Second, it tells your reader why your argument matters. In your conclusion, you want to take a step back and consider briefly the historical implications or significance of your topic. You will not be introducing new information that requires lengthy analysis, but you will be telling your readers what your paper helps bring to light. Perhaps you can connect your paper to a larger theme you have discussed in class, or perhaps you want to pose a new sort of question that your paper elicits. There is no right or wrong “answer” to this part of the conclusion: you are now the “expert” on your topic, and this is your chance to leave your reader with a lasting impression based on what you have learned.
Here is an example of an effective conclusion for the same essay prompt:
“To speak of the nationalist mythology the Hashemites created, however, is not to say that it has gone uncontested. In the 1950s, the Jordanian National Movement unleashed fierce internal opposition to Hashemite rule, crafting an alternative narrative of history in which the Hashemites were mere puppets to Western powers. Various tribes have also reasserted their role in the region’s past, refusing to play the part of “sons” to Hashemite “fathers.” For the Hashemites, maintaining their mythology depends on the same dialectical process that John R. Gillis identified in his investigation of commemorations: a process of both remembering and forgetting. Their myth remembers their descent from the Prophet, their leadership of the Arab Revolt, and the tribes’ shared Arab and Islamic heritage. It forgets, however, the many different histories that Jordanians champion, histories that the Hashemite mythology has never been able to fully reconcile.”
This is an effective conclusion because it moves from the specific argument addressed in the body of the paper to the question of why that argument matters. The writer rephrases the argument by saying, “Their myth remembers their descent from the Prophet, their leadership of the Arab Revolt, and the tribes’ shared Arab and Islamic heritage.” Then, the writer reflects briefly on the larger implications of the argument, showing how Jordan’s nationalist mythology depended on the suppression of other narratives.
Introduction and Conclusion checklist
When revising your introduction and conclusion, check them against the following guidelines:
Does my introduction:
- draw my readers in?
- culminate in a thesis statement that clearly states my argument?
- orient my readers to the key facts they need to know in order to understand my thesis?
- lay out a roadmap for the rest of my paper?
Does my conclusion:
- draw my paper together?
- reiterate my argument clearly and forcefully?
- leave my readers with a lasting impression of why my argument matters or what it brings to light?
Download as PDF

6265 Bunche Hall Box 951473 University of California, Los Angeles Los Angeles, CA 90095-1473 Phone: (310) 825-4601
Other Resources
- UCLA Library
- Faculty Intranet
- Department Forms
- Office 365 Email
- Remote Help
Campus Resources
- Maps, Directions, Parking
- Academic Calendar
- University of California
- Terms of Use
Social Sciences Division Departments
- Aerospace Studies
- African American Studies
- American Indian Studies
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Asian American Studies
- César E. Chávez Department of Chicana & Chicano Studies
- Communication
- Conservation
- Gender Studies
- Military Science
- Naval Science
- Political Science
Writing a Good History Paper
- Top Ten Reasons for Negative Comments
- Making Sure your Paper has Substance
Common Marginal Remarks on Style, Clarity, Grammar, and Syntax
Word and phrase usage problems, analyzing a historical document, writing a book review, writing a term paper or senior thesis, top ten reasons for negative comments on history papers.
(Drawn from a survey of the History Department ) 10. You engage in cheap, anachronistic moralizing . 9. You are sloppy with the chronology . 8. You quote excessively or improperly . 7. You have written a careless “one-draft wonder.” (See revise and proofread) 6. You are vague or have empty, unsupported generalizations . 5. You write too much in the passive voice. 4. You use inappropriate sources . 3. You use evidence uncritically. 2. You are wordy . 1. You have no clear thesis and little analysis.
Making Sure your History Paper has Substance
Get off to a good start..
Avoid pretentious, vapid beginnings. If you are writing a paper on, say, British responses to the rebellion in India in 1857, don't open with a statement like this: “Throughout human history people in all cultures everywhere in the world have engaged in many and long-running conflicts about numerous aspects of government policy and diplomatic issues, which have much interested historians and generated historical theories in many areas.” This is pure garbage, bores the reader, and is a sure sign that you have nothing substantive to say. Get to the point. Here’s a better start: “The rebellion in 1857 compelled the British to rethink their colonial administration in India.” This sentence tells the reader what your paper is actually about and clears the way for you to state your thesis in the rest of the opening paragraph. For example, you might go on to argue that greater British sensitivity to Indian customs was hypocritical.
State a clear thesis.
Whether you are writing an exam essay or a senior thesis, you need to have a thesis. Don’t just repeat the assignment or start writing down everything that you know about the subject. Ask yourself, “What exactly am I trying to prove?” Your thesis is your take on the subject, your perspective, your explanation—that is, the case that you’re going to argue. “Famine struck Ireland in the 1840s” is a true statement, but it is not a thesis. “The English were responsible for famine in Ireland in the 1840s” is a thesis (whether defensible or not is another matter). A good thesis answers an important research question about how or why something happened. (“Who was responsible for the famine in Ireland in the 1840s?”) Once you have laid out your thesis, don’t forget about it. Develop your thesis logically from paragraph to paragraph. Your reader should always know where your argument has come from, where it is now, and where it is going.
Be sure to analyze.
Students are often puzzled when their professors mark them down for summarizing or merely narrating rather than analyzing. What does it mean to analyze? In the narrow sense, to analyze means to break down into parts and to study the interrelationships of those parts. If you analyze water, you break it down into hydrogen and oxygen. In a broader sense, historical analysis explains the origins and significance of events. Historical analysis digs beneath the surface to see relationships or distinctions that are not immediately obvious. Historical analysis is critical; it evaluates sources, assigns significance to causes, and weighs competing explanations. Don’t push the distinction too far, but you might think of summary and analysis this way: Who, what, when, and where are the stuff of summary; how, why, and to what effect are the stuff of analysis. Many students think that they have to give a long summary (to show the professor that they know the facts) before they get to their analysis. Try instead to begin your analysis as soon as possible, sometimes without any summary at all. The facts will “shine through” a good analysis. You can't do an analysis unless you know the facts, but you can summarize the facts without being able to do an analysis. Summary is easier and less sophisticated than analysis—that’s why summary alone never earns an “A.”
Use evidence critically.
Like good detectives, historians are critical of their sources and cross-check them for reliability. You wouldn't think much of a detective who relied solely on a suspect’s archenemy to check an alibi. Likewise, you wouldn't think much of a historian who relied solely on the French to explain the origins of World War I. Consider the following two statements on the origin of World War I: 1) “For the catastrophe of 1914 the Germans are responsible. Only a professional liar would deny this...” 2) “It is not true that Germany is guilty of having caused this war. Neither the people, the government, nor the Kaiser wanted war....” They can’t both be right, so you have to do some detective work. As always, the best approach is to ask: Who wrote the source? Why? When? Under what circumstances? For whom? The first statement comes from a book by the French politician Georges Clemenceau, which he wrote in 1929 at the very end of his life. In 1871, Clemenceau had vowed revenge against Germany for its defeat of France in the Franco-Prussian War. As premier of France from 1917 to 1920, he represented France at the Paris Peace Conference in 1919. He was obviously not a disinterested observer. The second statement comes from a manifesto published by ninety-three prominent German intellectuals in the fall of 1914. They were defending Germany against charges of aggression and brutality. They too were obviously not disinterested observers. Now, rarely do you encounter such extreme bias and passionate disagreement, but the principle of criticizing and cross-checking sources always applies. In general, the more sources you can use, and the more varied they are, the more likely you are to make a sound historical judgment, especially when passions and self-interests are engaged. You don’t need to be cynical as a historian (self-interest does not explain everything), but you do need to be critical and skeptical. Competent historians may offer different interpretations of the same evidence or choose to stress different evidence. You will not find a single historical Truth with a capital “T” on any matter of significance. You can, however, learn to discriminate among conflicting interpretations, not all of which are created equal. (See also: Analyzing a Historical Document )
Be precise.
Vague statements and empty generalizations suggest that you haven't put in the time to learn the material. Consider these two sentences: “During the French Revolution, the government was overthrown by the people. The Revolution is important because it shows that people need freedom.” What people? Landless peasants? Urban journeymen? Wealthy lawyers? Which government? When? How? Who exactly needed freedom, and what did they mean by freedom? Here is a more precise statement about the French Revolution: “Threatened by rising prices and food shortages in 1793, the Parisian sans-culottes pressured the Convention to institute price controls.” This statement is more limited than the grandiose generalizations about the Revolution, but unlike them, it can open the door to a real analysis of the Revolution. Be careful when you use grand abstractions like people, society, freedom, and government, especially when you further distance yourself from the concrete by using these words as the apparent antecedents for the pronouns they and it. Always pay attention to cause and effect. Abstractions do not cause or need anything; particular people or particular groups of people cause or need things. Avoid grandiose trans-historical generalizations that you can’t support. When in doubt about the appropriate level of precision or detail, err on the side of adding “too much” precision and detail.
Watch the chronology.
Anchor your thesis in a clear chronological framework and don't jump around confusingly. Take care to avoid both anachronisms and vagueness about dates. If you write, “Napoleon abandoned his Grand Army in Russia and caught the redeye back to Paris,” the problem is obvious. If you write, “Despite the Watergate scandal, Nixon easily won reelection in 1972,” the problem is more subtle, but still serious. (The scandal did not become public until after the election.) If you write, “The revolution in China finally succeeded in the twentieth century,” your professor may suspect that you haven’t studied. Which revolution? When in the twentieth century? Remember that chronology is the backbone of history. What would you think of a biographer who wrote that you graduated from Hamilton in the 1950s?
Cite sources carefully.
Your professor may allow parenthetical citations in a short paper with one or two sources, but you should use footnotes for any research paper in history. Parenthetical citations are unaesthetic; they scar the text and break the flow of reading. Worse still, they are simply inadequate to capture the richness of historical sources. Historians take justifiable pride in the immense variety of their sources. Parenthetical citations such as (Jones 1994) may be fine for most of the social sciences and humanities, where the source base is usually limited to recent books and articles in English. Historians, however, need the flexibility of the full footnote. Try to imagine this typical footnote (pulled at random from a classic work of German history) squeezed into parentheses in the body of the text: DZA Potsdam, RdI, Frieden 5, Erzgebiet von Longwy-Briey, Bd. I, Nr. 19305, gedruckte Denkschrift für OHL und Reichsleitung, Dezember 1917, und in RWA, Frieden Frankreich Nr. 1883. The abbreviations are already in this footnote; its information cannot be further reduced. For footnotes and bibliography, historians usually use Chicago style. (The Chicago Manual of Style. 15th edition. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2003.) On the Writing Center’s website you can find a useful summary of Chicago citation style prepared by a former history major, Elizabeth Rabe ’04 ( Footnotes ). RefWorks (on the library’s website) will convert your citations to Chicago style. Don’t hesitate to ask one of the reference librarians for help if you have trouble getting started on RefWorks.
Use primary sources.
Use as many primary sources as possible in your paper. A primary source is one produced by a participant in or witness of the events you are writing about. A primary source allows the historian to see the past through the eyes of direct participants. Some common primary sources are letters, diaries, memoirs, speeches, church records, newspaper articles, and government documents of all kinds. The capacious genre “government records” is probably the single richest trove for the historian and includes everything from criminal court records, to tax lists, to census data, to parliamentary debates, to international treaties—indeed, any records generated by governments. If you’re writing about culture, primary sources may include works of art or literature, as well as philosophical tracts or scientific treatises—anything that comes under the broad rubric of culture. Not all primary sources are written. Buildings, monuments, clothes, home furnishings, photographs, religious relics, musical recordings, or oral reminiscences can all be primary sources if you use them as historical clues. The interests of historians are so broad that virtually anything can be a primary source. (See also: Analyzing a Historical Document )
Use scholarly secondary sources.
A secondary source is one written by a later historian who had no part in what he or she is writing about. (In the rare cases when the historian was a participant in the events, then the work—or at least part of it—is a primary source.) Historians read secondary sources to learn about how scholars have interpreted the past. Just as you must be critical of primary sources, so too you must be critical of secondary sources. You must be especially careful to distinguish between scholarly and non-scholarly secondary sources. Unlike, say, nuclear physics, history attracts many amateurs. Books and articles about war, great individuals, and everyday material life dominate popular history. Some professional historians disparage popular history and may even discourage their colleagues from trying their hand at it. You need not share their snobbishness; some popular history is excellent. But—and this is a big but—as a rule, you should avoid popular works in your research, because they are usually not scholarly. Popular history seeks to inform and entertain a large general audience. In popular history, dramatic storytelling often prevails over analysis, style over substance, simplicity over complexity, and grand generalization over careful qualification. Popular history is usually based largely or exclusively on secondary sources. Strictly speaking, most popular histories might better be called tertiary, not secondary, sources. Scholarly history, in contrast, seeks to discover new knowledge or to reinterpret existing knowledge. Good scholars wish to write clearly and simply, and they may spin a compelling yarn, but they do not shun depth, analysis, complexity, or qualification. Scholarly history draws on as many primary sources as practical. Now, your goal as a student is to come as close as possible to the scholarly ideal, so you need to develop a nose for distinguishing the scholarly from the non-scholarly. Here are a few questions you might ask of your secondary sources (bear in mind that the popular/scholarly distinction is not absolute, and that some scholarly work may be poor scholarship). Who is the author? Most scholarly works are written by professional historians (usually professors) who have advanced training in the area they are writing about. If the author is a journalist or someone with no special historical training, be careful. Who publishes the work? Scholarly books come from university presses and from a handful of commercial presses (for example, Norton, Routledge, Palgrave, Penguin, Rowman & Littlefield, Knopf, and HarperCollins). If it’s an article, where does it appear? Is it in a journal subscribed to by our library, listed on JSTOR , or published by a university press? Is the editorial board staffed by professors? Oddly enough, the word journal in the title is usually a sign that the periodical is scholarly. What do the notes and bibliography look like? If they are thin or nonexistent, be careful. If they are all secondary sources, be careful. If the work is about a non-English-speaking area, and all the sources are in English, then it's almost by definition not scholarly. Can you find reviews of the book in the data base Academic Search Premier? If the book was published within the last few decades, and it’s not in there, that’s a bad sign. With a little practice, you can develop confidence in your judgment—and you’re on your way to being a historian. If you are unsure whether a work qualifies as scholarly, ask your professor. (See also: Writing a Book Review )
Avoid abusing your sources.
Many potentially valuable sources are easy to abuse. Be especially alert for these five abuses: Web abuse. The Web is a wonderful and improving resource for indexes and catalogs. But as a source for primary and secondary material for the historian, the Web is of limited value. Anyone with the right software can post something on the Web without having to get past trained editors, peer reviewers, or librarians. As a result, there is a great deal of garbage on the Web. If you use a primary source from the Web, make sure that a respected intellectual institution stands behind the site. Be especially wary of secondary articles on the Web, unless they appear in electronic versions of established print journals (e.g., The Journal of Asian Studies in JSTOR). Many articles on the Web are little more than third-rate encyclopedia entries. When in doubt, check with your professor. With a few rare exceptions, you will not find scholarly monographs in history (even recent ones) on the Web. You may have heard of Google’s plans to digitize the entire collections of some of the world’s major libraries and to make those collections available on the Web. Don’t hold your breath. Your days at Hamilton will be long over by the time the project is finished. Besides, your training as a historian should give you a healthy skepticism of the giddy claims of technophiles. Most of the time and effort of doing history goes into reading, note-taking, pondering, and writing. Finding a chapter of a book on the Web (as opposed to getting the physical book through interlibrary loan) might be a convenience, but it doesn’t change the basics for the historian. Moreover, there is a subtle, but serious, drawback with digitized old books: They break the historian’s sensual link to the past. And of course, virtually none of the literally trillions of pages of archival material is available on the Web. For the foreseeable future, the library and the archive will remain the natural habitats of the historian. Thesaurus abuse. How tempting it is to ask your computer’s thesaurus to suggest a more erudite-sounding word for the common one that popped into your mind! Resist the temptation. Consider this example (admittedly, a bit heavy-handed, but it drives the point home): You’re writing about the EPA’s programs to clean up impure water supplies. Impure seems too simple and boring a word, so you bring up your thesaurus, which offers you everything from incontinent to meretricious. “How about meretricious water?” you think to yourself. “That will impress the professor.” The problem is that you don’t know exactly what meretricious means, so you don’t realize that meretricious is absurdly inappropriate in this context and makes you look foolish and immature. Use only those words that come to you naturally. Don’t try to write beyond your vocabulary. Don’t try to impress with big words. Use a thesaurus only for those annoying tip-of-the-tongue problems (you know the word and will recognize it instantly when you see it, but at the moment you just can’t think of it). Quotation book abuse. This is similar to thesaurus abuse. Let’s say you are writing a paper on Alexander Hamilton’s banking policies, and you want to get off to a snappy start that will make you seem effortlessly learned. How about a quotation on money? You click on the index of Bartlett’s Familiar Quotations , and before you know it, you’ve begun your paper with, “As Samuel Butler wrote in Hudibras , ‘For what is worth in anything/ But so much money as ’t will bring?’” Face it, you’re faking it. You don’t know who Samuel Butler is, and you’ve certainly never heard of Hudibras , let alone read it. Your professor is not fooled. You sound like an insecure after-dinner speaker. Forget Bartlett’s, unless you're confirming the wording of a quotation that came to you spontaneously and relates to your paper. Encyclopedia abuse. General encyclopedias like Britannica are useful for checking facts (“Wait a sec, am I right about which countries sent troops to crush the Boxer Rebellion in China? Better check.”). But if you are footnoting encyclopedias in your papers, you are not doing college-level research.
Dictionary Abuse. The dictionary is your friend. Keep it by your side as you write, but do not abuse it by starting papers with a definition. You may be most tempted to start this way when you are writing on a complex, controversial, or elusive subject. (“According to Webster’s Collegiate Dictionary , liberalism is defined as...”). Actually, the dictionary does you little good in such cases and makes you sound like a conscientious but dull high-school student. Save in the rare case that competing dictionary definitions are the subject at hand, keep dictionary quotations out of your paper.
Quote sparingly
Avoid quoting a secondary source and then simply rewording or summarizing the quotation, either above or below the quotation. It is rarely necessary to quote secondary sources at length, unless your essay focuses on a critical analysis of the author’s argument. (See also: Writing a Book Review ) Your professor wants to see your ability to analyze and to understand the secondary sources. Do not quote unless the quotation clarifies or enriches your analysis. When in doubt, do not quote; instead, integrate the author’s argument into your own (though be sure to acknowledge ideas from your sources, even when you are paraphrasing). If you use a lot of quotations from secondary sources, you are probably writing a poor paper. An analysis of a primary source, such as a political tract or philosophical essay, might require lengthy quotations, often in block format. In such cases, you might need to briefly repeat key points or passages as a means to introduce the author’s ideas, but your analysis and interpretation of the text’s meaning should remain the most important aim. (See also: Using primary sources and Use scholarly secondary sources .)
Know your audience
Unless instructed otherwise, you should assume that your audience consists of educated, intelligent, nonspecialists. In fact, your professor will usually be your only reader, but if you write directly to your professor, you may become cryptic or sloppy (oh well, she’ll know what I’m talking about). Explaining your ideas to someone who doesn't know what you mean forces you to be clear and complete. Now, finding the right amount of detail can, admittedly, be tricky (how much do I put in about the Edict of Nantes, the Embargo Act, or President Wilson’s background?). When in doubt, err on the side of putting in extra details. You’ll get some leeway here if you avoid the extremes (my reader’s an ignoramus/my reader knows everything).
Avoid cheap, anachronistic moralizing
Many of the people and institutions of the past appear unenlightened, ignorant, misguided, or bigoted by today’s values. Resist the temptation to condemn or to get self-righteous. (“Martin Luther was blind to the sexism and class prejudice of sixteenth-century German society.”) Like you, people in the past were creatures of their time; like you, they deserve to be judged by the standards of their time. If you judge the past by today’s standards (an error historians call “presentism”), you will never understand why people thought or acted as they did. Yes, Hitler was a bad guy, but he was bad not only by today’s standards, but also by the commonly accepted standards of his own time. Someday you’re going to look pretty foolish and ignorant yourself. (“Early twenty-first century Hamilton students failed to see the shocking inderdosherism [that’s right, you don’t recognize the concept because it doesn’t yet exist] implicit in their career plans.”)
Have a strong conclusion
Obviously, you should not just stop abruptly as though you have run out of time or ideas. Your conclusion should conclude something. If you merely restate briefly what you have said in your paper, you give the impression that you are unsure of the significance of what you have written. A weak conclusion leaves the reader unsatisfied and bewildered, wondering why your paper was worth reading. A strong conclusion adds something to what you said in your introduction. A strong conclusion explains the importance and significance of what you have written. A strong conclusion leaves your reader caring about what you have said and pondering the larger implications of your thesis. Don’t leave your reader asking, “So what?”
Revise and proofread
Your professor can spot a “one-draft wonder,” so don't try to do your paper at the last moment. Leave plenty of time for revising and proofreading. Show your draft to a writing tutor or other good writer. Reading the draft aloud may also help. Of course, everyone makes mistakes, and a few may slip through no matter how meticulous you are. But beware of lots of mistakes. The failure to proofread carefully suggests that you devoted little time and effort to the assignment. Tip: Proofread your text both on the screen and on a printed copy. Your eyes see the two differently. Don’t rely on your spell checker to catch all of your misspellings. (If ewe ken reed this ewe kin sea that a computer wood nut all ways help ewe spill or rite reel good.)
Note: The Writing Center suggests standard abbreviations for noting some of these problems. You should familiarize yourself with those abbreviations, but your professor may not use them.
Remarks on Style and Clarity
Wordy/verbose/repetitive..
Try your hand at fixing this sentence: “Due to the fact that these aspects of the issue of personal survival have been raised by recently transpired problematic conflicts, it is at the present time paramount that the ultimate psychological end of suicide be contemplated by this individual.” If you get it down to “To be or not to be, that is the question,” you’ve done well. You may not match Shakespeare, but you can learn to cut the fat out of your prose. The chances are that the five pages you’ve written for your history paper do not really contain five pages’ worth of ideas.
Misuse of the passive voice.
Write in the active voice. The passive voice encourages vagueness and dullness; it enfeebles verbs; and it conceals agency, which is the very stuff of history. You know all of this almost instinctively. What would you think of a lover who sighed in your ear, “My darling, you are loved by me!”? At its worst, the passive voice—like its kin, bureaucratic language and jargon—is a medium for the dishonesty and evasion of responsibility that pervade contemporary American culture. (“Mistakes were made; I was given false information.” Now notice the difference: “I screwed up; Smith and Jones lied to me; I neglected to check the facts.”) On history papers the passive voice usually signals a less toxic version of the same unwillingness to take charge, to commit yourself, and to say forthrightly what is really going on, and who is doing what to whom. Suppose you write, “In 1935 Ethiopia was invaded.” This sentence is a disaster. Who invaded? Your professor will assume that you don't know. Adding “by Italy” to the end of the sentence helps a bit, but the sentence is still flat and misleading. Italy was an aggressive actor, and your passive construction conceals that salient fact by putting the actor in the syntactically weakest position—at the end of the sentence as the object of a preposition. Notice how you add vigor and clarity to the sentence when you recast it in the active voice: "In 1935 Italy invaded Ethiopia." I n a few cases , you may violate the no-passive-voice rule. The passive voice may be preferable if the agent is either obvious (“Kennedy was elected in 1960”), irrelevant (“Theodore Roosevelt became president when McKinley was assassinated”), or unknown (“King Harold was killed at the Battle of Hastings”). Note that in all three of these sample sentences the passive voice focuses the reader on the receiver of the action rather than on the doer (on Kennedy, not on American voters; on McKinley, not on his assassin; on King Harold, not on the unknown Norman archer). Historians usually wish to focus on the doer, so you should stay with the active voice—unless you can make a compelling case for an exception.
Abuse of the verb to be.
The verb to be is the most common and most important verb in English, but too many verbs to be suck the life out of your prose and lead to wordiness. Enliven your prose with as many action verbs as possible. ( “In Brown v. Board of Education it was the opinion of the Supreme Court that the doctrine of ‘separate but equal’ was in violation of the Fourteenth Amendment.”) Rewrite as “ In Brown v. Board of Education the Supreme Court ruled that the doctrine of ‘separate but equal’ violated the Fourteenth ”
Explain/what’s your point?/unclear/huh?
You may (or may not) know what you’re talking about, but if you see these marginal comments, you have confused your reader. You may have introduced a non sequitur ; gotten off the subject; drifted into abstraction; assumed something that you have not told the reader; failed to explain how the material relates to your argument; garbled your syntax; or simply failed to proofread carefully. If possible, have a good writer read your paper and point out the muddled parts. Reading your paper aloud may help too.
Paragraph goes nowhere/has no point or unity.
Paragraphs are the building blocks of your paper. If your paragraphs are weak, your paper cannot be strong. Try underlining the topic sentence of every paragraph. If your topic sentences are vague, strength and precision—the hallmarks of good writing—are unlikely to follow. Consider this topic sentence (from a paper on Ivan the Terrible): “From 1538 to 1547, there are many different arguments about the nature of what happened.” Disaster looms. The reader has no way of knowing when the arguing takes place, who’s arguing, or even what the arguing is about. And how does the “nature of what happened” differ from plain “what happened”? Perhaps the writer means the following: “The childhood of Ivan the Terrible has provoked controversy among scholars of Russian history.” That's hardly deathless prose, but it does orient the reader and make the writer accountable for what follows in the paragraph. Once you have a good topic sentence, make sure that everything in the paragraph supports that sentence, and that cumulatively the support is persuasive. Make sure that each sentence follows logically from the previous one, adding detail in a coherent order. Move, delete, or add material as appropriate. To avoid confusing the reader, limit each paragraph to one central idea. (If you have a series of supporting points starting with first, you must follow with a second, third , etc.) A paragraph that runs more than a printed page is probably too long. Err on the side of shorter paragraphs.
Inappropriate use of first person.
Most historians write in the third person, which focuses the reader on the subject. If you write in the first person singular, you shift the focus to yourself. You give the impression that you want to break in and say, “Enough about the Haitian revolution [or whatever], now let’s talk about me!” Also avoid the first person plural (“We believe...”). It suggests committees, editorial boards, or royalty. None of those should have had a hand in writing your paper. And don’t refer to yourself lamely as “this writer.” Who else could possibly be writing the paper?
Tense inconsistency.
Stay consistently in the past tense when you are writing about what took place in the past. (“Truman’s defeat of Dewey in 1948 caught the pollsters by surprise.”) Note that the context may require a shift into the past perfect. (“The pollsters had not realized [past perfect] that voter opinion had been [past perfect] changing rapidly in the days before the election.”) Unfortunately, the tense problem can get a bit more complicated. Most historians shift into the present tense when describing or commenting on a book, document, or evidence that still exists and is in front of them (or in their mind) as they write. (“de Beauvoir published [past tense] The Second Sex in 1949. In the book she contends [present tense] that woman....”) If you’re confused, think of it this way: History is about the past, so historians write in the past tense, unless they are discussing effects of the past that still exist and thus are in the present. When in doubt, use the past tense and stay consistent.
Ill-fitted quotation.
This is a common problem, though not noted in stylebooks. When you quote someone, make sure that the quotation fits grammatically into your sentence. Note carefully the mismatch between the start of the following sentence and the quotation that follows: “In order to understand the Vikings, writes Marc Bloch, it is necessary, ‘To conceive of the Viking expeditions as religious warfare inspired by the ardour of an implacable pagan fanaticism—an explanation that has sometimes been at least suggested—conflicts too much with what we know of minds disposed to respect magic of every kind.’” At first, the transition into the quotation from Bloch seems fine. The infinitive (to conceive) fits. But then the reader comes to the verb (conflicts) in Bloch’s sentence, and things no longer make sense. The writer is saying, in effect, “it is necessary conflicts.” The wordy lead-in and the complex syntax of the quotation have tripped the writer and confused the reader. If you wish to use the whole sentence, rewrite as “Marc Bloch writes in Feudal Society , ‘To conceive of...’” Better yet, use your own words or only part of the quotation in your sentence. Remember that good writers quote infrequently, but when they do need to quote, they use carefully phrased lead-ins that fit the grammatical construction of the quotation.
Free-floating quotation.
Do not suddenly drop quotations into your prose. (“The spirit of the Progressive era is best understood if one remembers that the United States is ‘the only country in the world that began with perfection and aspired to progress.’”) You have probably chosen the quotation because it is finely wrought and says exactly what you want to say. Fine, but first you inconvenience the reader, who must go to the footnote to learn that the quotation comes from The Age of Reform by historian Richard Hofstadter. And then you puzzle the reader. Did Hofstadter write the line about perfection and progress, or is he quoting someone from the Progressive era? If, as you claim, you are going to help the reader to judge the “spirit of the Progressive era,” you need to clarify. Rewrite as “As historian Richard Hofstadter writes in the Age of Reform , the United States is ‘the only country in the world...’” Now the reader knows immediately that the line is Hofstadter’s.
Who’s speaking here?/your view?
Always be clear about whether you’re giving your opinion or that of the author or historical actor you are discussing. Let’s say that your essay is about Martin Luther’s social views. You write, “The German peasants who revolted in 1525 were brutes and deserved to be crushed mercilessly.” That’s what Luther thought, but do you agree? You may know, but your reader is not a mind reader. When in doubt, err on the side of being overly clear.
Jargon/pretentious theory.
Historians value plain English. Academic jargon and pretentious theory will make your prose turgid, ridiculous, and downright irritating. Your professor will suspect that you are trying to conceal that you have little to say. Of course, historians can’t get along without some theory; even those who profess to have no theory actually do—it’s called naïve realism. And sometimes you need a technical term, be it ontological argument or ecological fallacy. When you use theory or technical terms, make sure that they are intelligible and do real intellectual lifting. Please, no sentences like this: “By means of a neo-Althusserian, post-feminist hermeneutics, this essay will de/construct the logo/phallo/centrism imbricated in the marginalizing post-colonial gendered gaze, thereby proliferating the subjectivities that will re/present the de/stabilization of the essentializing habitus of post-Fordist capitalism.”
Informal language/slang.
You don’t need to be stuffy, but stay with formal English prose of the kind that will still be comprehensible to future generations. Columbus did not “push the envelope in the Atlantic.” Henry VIII was not “looking for his inner child when he broke with the Church.” Prime Minister Cavour of Piedmont was not “trying to play in the major leagues diplomatic wise.” Wilson did not “almost veg out” at the end of his second term. President Hindenburg did not appoint Hitler in a “senior moment.” Prime Minister Chamberlain did not tell the Czechs to “chill out” after the Munich Conference, and Gandhi was not an “awesome dude.”
Try to keep your prose fresh. Avoid cliches. When you proofread, watch out for sentences like these: “Voltaire always gave 110 percent and thought outside the box. His bottom line was that as people went forward into the future, they would, at the end of the day, step up to the plate and realize that the Jesuits were conniving perverts.” Ugh. Rewrite as “Voltaire tried to persuade people that the Jesuits were cony, step up to the plate and realize that the Jesuits were conniving perverts.” Ugh. Rewrite as “Voltaire tried to persuade people that the Jesuits were conniving perverts.”
Intensifier abuse/exaggeration.
Avoid inflating your prose with unsustainable claims of size, importance, uniqueness, certainty, or intensity. Such claims mark you as an inexperienced writer trying to impress the reader. Your statement is probably not certain ; your subject probably not unique , the biggest, the best, or the most important. Also, the adverb very will rarely strengthen your sentence. Strike it. (“President Truman was very determined to stop the spread of communism in Greece.”) Rewrite as “President Truman resolved to stop the spread of communism in Greece.”
Mixed image.
Once you have chosen an image, you must stay with language compatible with that image. In the following example, note that the chain, the boiling, and the igniting are all incompatible with the image of the cold, rolling, enlarging snowball: “A snowballing chain of events boiled over, igniting the powder keg of war in 1914.” Well chosen images can enliven your prose, but if you catch yourself mixing images a lot, you're probably trying to write beyond your ability. Pull back. Be more literal.
Clumsy transition.
If your reader feels a jolt or gets disoriented at the beginning of a new paragraph, your paper probably lacks unity. In a good paper, each paragraph is woven seamlessly into the next. If you find yourself beginning your paragraphs with phrases such as “Another aspect of this problem...,” then you are probably “stacking note cards” rather than developing a thesis.
Unnecessary relative clause.
If you don’t need to restrict the meaning of your sentence’s subject, then don’t. (“Napoleon was a man who tried to conquer Europe.”) Here the relative clause adds nothing. Rewrite as “Napoleon tried to conquer Europe.” Unnecessary relative clauses are a classic form of wordiness.
Distancing or demeaning quotation marks.
If you believe that a frequently used word or phrase distorts historical reality, don’t put it in dismissive, sneering quotation marks to make your point (“the communist ‘threat’ to the ‘free’ world during the Cold War”). Many readers find this practice arrogant, obnoxious, and precious, and they may dismiss your arguments out of hand. If you believe that the communist threat was bogus or exaggerated, or that the free world was not really free, then simply explain what you mean.
Remarks on Grammar and Syntax
Ideally, your professor will help you to improve your writing by specifying exactly what is wrong with a particular passage, but sometimes you may find a simple awk in the margin. This all-purpose negative comment usually suggests that the sentence is clumsy because you have misused words or compounded several errors. Consider this sentence from a book review:
“However, many falsehoods lie in Goldhagen’s claims and these will be explored.”
What is your long-suffering professor to do with this sentence? The however contributes nothing; the phrase falsehoods lie is an unintended pun that distracts the reader; the comma is missing between the independent clauses; the these has no clear antecedent ( falsehoods? claims? ); the second clause is in the passive voice and contributes nothing anyway; the whole sentence is wordy and screams hasty, last-minute composition. In weary frustration, your professor scrawls awk in the margin and moves on. Buried under the twelve-word sentence lies a three-word idea: “Goldhagen often errs.” When you see awk, check for the common errors in this list. If you don’t understand what’s wrong, ask.
Unclear antecedent.
All pronouns must refer clearly to antecedents and must agree with them in number. The reader usually assumes that the antecedent is the immediately preceding noun. Do not confuse the reader by having several possible antecedents. Consider these two sentences:
“Pope Gregory VII forced Emperor Henry IV to wait three days in the snow at Canossa before granting him an audience. It was a symbolic act.”
To what does the it refer? Forcing the Emperor to wait? The waiting itself? The granting of the audience? The audience itself? The whole previous sentence? You are most likely to get into antecedent trouble when you begin a paragraph with this or it , referring vaguely back to the general import of the previous paragraph. When in doubt, take this test: Circle the pronoun and the antecedent and connect the two with a line. Then ask yourself if your reader could instantly make the same diagram without your help. If the line is long, or if the circle around the antecedent is large, encompassing huge gobs of text, then your reader probably will be confused. Rewrite. Repetition is better than ambiguity and confusion.
Faulty parallelism.
You confuse your reader if you change the grammatical construction from one element to the next in a series. Consider this sentence:
“King Frederick the Great sought to expand Prussia, to rationalize agriculture, and that the state support education.”
The reader expects another infinitive, but instead trips over the that . Rewrite the last clause as “and to promote state-supported education.” Sentences using neither/nor frequently present parallelism problems. Note the two parts of this sentence:
“After 1870 the cavalry charge was neither an effective tactic, nor did armies use it frequently.”
The sentence jars because the neither is followed by a noun, the nor by a verb. Keep the parts parallel.
Rewrite as “After 1870 the cavalry charge was neither effective nor frequently used.”
Sentences with not only/but also are another pitfall for many students. (“Mussolini attacked not only liberalism, but he also advocated militarism.”) Here the reader is set up to expect a noun in the second clause, but stumbles over a verb. Make the parts parallel by putting the verb attacked after the not only .
Misplaced modifier/dangling element.
Do not confuse the reader with a phrase or clause that refers illogically or absurdly to other words in the sentence. (“Summarized on the back cover of the American paperback edition, the publishers claim that...”) The publishers are not summarized on the back cover. (“Upon finishing the book, many questions remain.”) Who finished the book? Questions can’t read. Avoid following an introductory participial clause with the expletives it or there . Expletives are by definition filler words; they can’t be agents. (“Having examined the origins of the Meiji Restoration in Japan, it is apparent that...”) Apparent to whom? The expletive it didn’t do the examining. (“After going on the Long March, there was greater support for the Communists in China.”) Who went on the Long March? There didn’t go on the Long March. Always pay attention to who’s doing what in your sentences.
Run-on sentence.
Run-on sentences string together improperly joined independent clauses. Consider these three sentences:
“Galileo recanted his teaching that the earth moved privately he maintained his convictions.” “Galileo recanted his teaching that the earth moved, privately he maintained his convictions.” “Galileo recanted his teaching that the earth moved, however, privately he maintained his convictions.”
The first fuses two independent clauses with neither a comma nor a coordinating conjunction; the second uses a comma but omits the coordinating conjunction; and the third also omits the coordinating conjunction (however is not a coordinating conjunction). To solve the problem, separate the two clauses with a comma and the coordinating conjunction but. You could also divide the clauses with a semicolon or make separate sentences. Remember that there are only seven coordinating conjunctions ( and, but, or, nor, for, so, yet ).
Sentence fragment.
Write in sentences. A sentence has to have a subject and a predicate. If you string together a lot of words, you may lose control of the syntax and end up with a sentence fragment. Note that the following is not a sentence:
“While in Western Europe railroad building proceeded rapidly in the nineteenth century, and in Russia there was less progress.”
Here you have a long compound introductory clause followed by no subject and no verb, and thus you have a fragment. You may have noticed exceptions to the no-fragments rule. Skilful writers do sometimes intentionally use a fragment to achieve a certain effect. Leave the rule-breaking to the experts.
Confusion of restrictive and nonrestrictive clauses.
Consider these two versions of the same sentence:
1. “World War I, which raged from 1914-1918, killed millions of Europeans.” 2. “World War I that raged from 1914-1918 killed millions of Europeans.”
The first sentence has a nonrestrictive relative clause; the dates are included almost as parenthetical information. But something seems amiss with the second sentence. It has a restrictive relative clause that limits the subject (World War I) to the World War I fought between 1914 and 1918, thus implying that there were other wars called World War I, and that we need to distinguish among them. Both sentences are grammatically correct, but the writer of the second sentence appears foolish. Note carefully the distinction between that (for use in restrictive clauses, with no comma) and which (for use in nonrestrictive clauses, with a comma).
Confusion about who’s doing what.
Remember—history is about what people do, so you need to be vigilant about agency. Proofread your sentences carefully, asking yourself, “Have I said exactly who is doing or thinking what, or have I inadvertently attributed an action or belief to the wrong person or group?” Unfortunately, there are many ways to go wrong here, but faulty punctuation is among the most common. Here’s a sentence about Frantz Fanon, the great critic of European imperialism. Focus on the punctuation and its effect on agency: “Instead of a hierarchy based on class, Fanon suggests the imperialists establish a hierarchy based on race.” As punctuated, the sentence says something absurd: that Fanon is advising the imperialists about the proper kind of hierarchy to establish in the colonies. Surely, the writer meant to say that, in his analysis of imperialism, Fanon distinguishes between two kinds of hierarchy. A comma after suggests fixes the immediate problem. Now look at the revised sentence. It still needs work. Better diction and syntax would sharpen it. Fanon does not suggest (with connotations of both hinting and advocating); he states outright. What’s more, the comparison of the two kinds of hierarchy gets blurred by too many intervening words. The key point of the sentence is, in effect, “instead of A, we have B.” Clarity demands that B follow A as closely as possible, and that the two elements be grammatically parallel. But between the elements A and B, the writer inserts Fanon (a proper noun), suggests (a verb), imperialists (a noun), and establish (a verb). Try the sentence this way: “Fanon says that the imperialists establish a hierarchy based on race rather than class.” Now the agency is clear: We know what Fanon does, and we know what the imperialists do. Notice that errors and infelicities have a way of clustering. If you find one problem in a sentence, look for others.
Confusion about the objects of prepositions.
Here’s another one of those common problems that does not receive the attention it merits. Discipline your prepositional phrases; make sure you know where they end. Notice the mess in this sentence: “Hitler accused Jewish people of engaging in incest and stating that Vienna was the ‘personification of incest.’” The reader thinks that both engaging and stating are objects of the preposition of. Yet the writer intends only the first to be the object of the preposition. Hitler is accusing the Jews of engaging , but not of stating ; he is the one doing the stating . Rewrite as “Hitler accused the Jews of incest; he stated that Vienna was the ‘personification of incest.’” Note that the wordiness of the original encouraged the syntactical mess. Simplify. It can’t be said too many times: Always pay attention to who’s doing what in your sentences.
Misuse of the comparative.
There are two common problems here. The first might be called the “floating comparative.” You use the comparative, but you don’t say what you are comparing. (“Lincoln was more upset by the dissolution of the union.”) More upset than by what? More upset than who? The other problem, which is more common and takes many forms, is the unintended (and sometimes comical) comparison of unlike elements. Consider these attempts to compare President Clinton to President George H. W. Bush. Often the trouble starts with a possessive:
“President Clinton’s sexual appetite was more voracious than President Bush.”
You mean to compare appetites, but you've forgotten about your possessive, so you absurdly compare an appetite to a man. Rewrite as “more voracious than President Bush’s.” A variation of this problem is the unintended comparison resulting from the omission of a verb:
“President Clinton liked women more than President Bush.”
Re-write as “more than did President Bush.”
A misplaced modifier may also cause comparison trouble: “Unlike the Bush administration, sexual scandal nearly destroyed the Clinton administration.” Rewrite as “Unlike the Bush administration, the Clinton administration was nearly destroyed by sexual scandal.” Here the passive voice is better than the misplaced modifier, but you could rewrite as “The Bush administration had been free of sexual scandal, which nearly destroyed the Clinton administration.”
Misuse of apostrophe.
Get control of your apostrophes. Use the apostrophe to form singular or plural possessives (Washington’s soldiers; the colonies’ soldiers) or to form contractions (don’t; it’s). Do not use the apostrophe to form plurals. (“The communists [not communists’] defeated the nationalists [not nationalists’] in China.”)
Comma after although.
This is a new error, probably a carryover from the common conversational habit of pausing dramatically after although . ( “Although , coffee consumption rose in eighteenth-century Europe, tea remained far more popular.”) Delete the comma after although . Remember that although is not a synonym for the word however , so you cannot solve the problem in the sentence by putting a period after Europe . A clause beginning with although cannot stand alone as a sentence.
Comma between subject and verb.
This is a strange new error. (“Hitler and Stalin, agreed to a pact in August 1939.”) Delete the comma after Stalin. Finally, two hints: If your word-processing program underlines something and suggests changes, be careful. When it comes to grammar and syntax, your computer is a moron. Not only does it fail to recognize some gross errors, it also falsely identifies some correct passages as errors. Do not cede control of your writing decisions to your computer. Make the suggested changes only if you are positive that they are correct. If you are having trouble with your writing, try simplifying. Write short sentences and read them aloud to test for clarity. Start with the subject and follow it quickly with an active verb. Limit the number of relative clauses, participial phrases, adjectives, adverbs, and prepositional phrases. You will win no prizes for eloquence, but at least you will be clear. Add complexity only when you have learned to handle it.
An historical/an historian.
The consonant “H” is not silent in historical and historian , so the proper form of the indefinite article is “A.”
Avoid the common solecism of using feel as a synonym for think, believe, say, state, assert, contend, argue, conclude, or write. (“Marx felt that the bourgeoisie exploited the proletariat.” “Emmeline Pankhurst felt that British women should be able to vote.”) The use of feel in these sentences demeans the agents by suggesting undisciplined sentiment rather than carefully formulated conviction. Concentrate on what your historical actors said and did; leave their feelings to speculative chapters of their biographies. As for your own feelings, keep them out of your papers. (“I feel that Lincoln should have freed the slaves earlier.”) Your professor will be delighted that the material engages both your head and your heart, but your feelings cannot be graded. If you believe that Lincoln should have acted earlier, then explain, giving cogent historical reasons.
The fact that.
This is a clumsy, unnecessary construction. ( “The fact that Nixon resigned in disgrace damaged the Republican Party.”) Re-word as “Nixon resigned in disgrace, damaging the Republican Party.” Never use the hideous phrase due to the fact that.
In terms of.
This phrase is filler. Get rid of it. (“Bismarck was a success in terms of uniting Germany.) Rewrite as “Bismarck successfully united Germany.”
Attend carefully to the placement of this limiting word. Note, for example, these three sentences:
“The government only interred Japanese Americans during World War II.” “The government interred only Japanese Americans during World War II.” “The government interred Japanese Americans only during World War II.”
The first limits the action to interring (as opposed to, say, killing); the second limits the group interred (i.e., not Italian Americans); the third limits the time of interring (i.e., not during other wars).
Thus and therefore.
More than likely, you have not earned these words and are implying that you have said more than you actually have. Use them sparingly, only when you are concluding a substantial argument with a significant conclusion.
Misuse of instead.
Instead is an adverb, not a conjunction. Consider this sentence: “Charles Beard argued that the framers of the constitution were not idealists, instead they promoted their economic interests.” Revise as “The framers of the constitution, Charles Beard argued, did not uphold ideals; instead , they promoted their economic interests.” Now the instead appears properly as an adverb. (Note also that the two clauses are now parallel—both contain transitive verbs.)
Essentially and basically.
These are usually either filler words (the written equivalent of “uh” or “um”) or weasel words that merely call attention to your vagueness, lack of conviction, or lazy unwillingness to qualify precisely. (“ Essentially , Churchill believed that Nazi Germany presented a grave danger to Britain.”) Delete essentially and basically unless you are writing about essences or bases.
Both share or both agree.
These are redundant. If two people share or agree , they are both involved by definition. (“Stalin and Mao both agreed that capitalism belonged in the dustbin of history.”) Delete both .
This word means one of a kind. It is an absolute. Something cannot be very unique, more unique, or somewhat unique.
Incredible.
In casual conversation incredible often means extraordinary, astonishing, or impressive (“Yesterday’s storm was incredible.”). To avoid confusion in historical prose, you should stick with the original meaning of incredible : not believable. If you write that “William Jennings Bryan gave incredible speeches,” you’re saying that you don’t believe his speeches, or that his audiences didn’t believe them at the time—in other words, that he appeared to be lying or mistaken. You probably mean that he gave great speeches. If you write that “It’s incredible that Japan attacked Pearl Harbor,” you’re calling into question the very existence of a historical event. You probably mean that the Japanese attack was unwise or reckless. English is rich with adjectives. Finding the best one forces you to think about what you really mean.
As a synonym for subject matter, bone of contention, reservation, or almost anything else vaguely associated with what you are discussing, the word issue has lost its meaning through overuse. (“There were many issues involved with Truman’s decision to use the atomic bomb, and some historians have issues with his decision.”) Stop talking about issues and get to the point.
Beware of the word literally . It’s commonly misused, and you almost never need it in historical prose. Literally means actually, factually, exactly, directly, without metaphor. The careful writer would never say, “Roosevelt literally swamped Landon in the election of 1936.” One imagines Roosevelt (in his wheelchair no less!) dumping the hapless Landon off a pier in the Everglades on election night. The swamping was figurative, strictly a figure of speech. The adverb literally may also cause you trouble by falsely generalizing the coverage of your verb. “London was literally destroyed by the blitz.” This suggests that the whole city was destroyed, when, in fact, only parts were destroyed. Rewrite as “The blitz destroyed parts of London.” Now you’ve qualified properly (and gotten rid of the passive).
When you’re tempted to use this word, resist. Like issue , involve tells the reader too little. (“Erasmus was involved in the Renaissance.”) This statement could mean virtually anything. Delete it and discuss specifically what Erasmus said or did.
This is a fine old word with many precise meanings, but as an overused synonym for feature, side, or part, it is usually a sign of insipid prose (“Another aspect of the issues in this area is the fact that...”). Just get directly to the point.
Most good writers frown on the use of this word as a verb.(“Eisenhower’s military background impacted his foreign policy.”) Affected, influenced, or shaped would be better here. Impacted suggests painfully blocked wisdom teeth or feces. Had an impact is better than impacted , but is still awkward because impact implies a collision.
Here is another beloved but vapid word. (“Many factors led to the Reformation.”) Such a sentence usually opens a vague, boring, weaseling paragraph. If you believe (quite reasonably) that the Reformation had many causes, then start evaluating them.
Meaningful.
Overuse has drained the meaning from meaningful . (“Peter the Great took meaningful steps to westernize Russia.”) Just get to the point.
Interesting.
The adjective interesting is vague, overused, and does not earn its keep. (“Burckhardt had an interesting perspective on the Renaissance.”) This sentence is filler. Delete it and explain and analyze his perspective.
The events that transpired.
Your professor will gag on this one. Events take place or happen by definition, so the relative clause is redundant. Furthermore, most good writers do not accept transpire as a synonym for happen. Again, follow the old rule of thumb: Get right to the point, say what happened, and explain its significance. You don’t need any filler about events and transpiring .
The reason is because.
This phrase is awkward and redundant. Replace it with the reason is, or better still, simply delete it and get right to your reason.
For all intensive purposes.
The phrase is for all intents and purposes , and few good writers use it in formal prose anyway.
Take for granite.
This is an illiteracy. The phrase is “ take for granted .”
Should of/could of.
You mean should have or could have .
Center around.
Good writers frown on this phrase because it’s illogical and jarring. Use center on or center in. Attention to a small detail like this indicates that you’re thinking carefully about what you’re saying, so when the big problems confront you, you’ll be disciplined and ready.
Begs the question.
Recently, many people have started to use this phrase to mean raises, invites, or brings up the question. (“Stalin’s purges beg the question of whether he was paranoid.”) Actually, begging the question is the common logical fallacy of assuming your conclusion as part of your argument. (“In the late nineteenth century, many Americans moved to the cities because of urbanization.”) Note that the use of abstractions (e.g., urbanization) encourages begging the question . Understanding this fallacy is central to your education. The formal Latin term, petitio principii, is too fancy to catch on, so you need to preserve the simple English phrase. If something raises a question, just say so.
Historic/historical confusion.
Everything in the past or relating to the past is historical. Resist the media-driven hype that elevates the ordinary to the historic . (“A three-alarm fire last night destroyed the historic site of the first Portuguese-owned dry cleaners in Cleveland.”) Reserve the word historic for the genuinely important events, persons, or objects of the past. The Norman invasion of England in 1066 was indeed historic . Historically , historians have gathered annually for a historical convention; so far, none of the conventions has been historic .
Affect/effect confusion.
The chances are that the verb you want is affect , which means to have an influence on (“The Iranian hostage crisis affected [not effected] the presidential election of 1980”). Effect as a verb means to bring about or cause to exist ( effect change). Effect as a noun means result or consequence (“The effect of the Iranian hostage crisis on the election...”).
While/whereas confusion.
If you’re stressing contrast, the word you want is whereas . While stresses simultaneity. “Hobbes had a dismal view of human nature, whereas [not while] Rousseau believed that man had a natural sense of pity.”
It’s/its confusion.
This is the classic bonehead error. Note that the spell checker won’t help you. And remember— its’ is not a word at all.
Reign/rein confusion.
A queen reigns during her reign. You rein in a horse with reins.
Their/there/they’re confusion.
You do know the difference. Pay attention.
Everyday/every day confusion.
As an adjective, everyday (one word) means routine. If you wish to say that something happened on every successive day, then you need two words, the adjective every and the noun day . Note the difference in these two sentences: “Kant was famous for going on the same constitutional at the same time every day . For Kant, exercise and thinking were everyday activities.”
Refer/allude confusion.
To allude means to refer to indirectly or to hint at. The word you probably want in historical prose is refer , which means to mention or call direct attention to. “In the first sentence of the ‘Gettysburg Address’ Lincoln refers [not alludes ] to the fathers of the nation [he mentions them directly]; he alludes to the ‘Declaration of Independence’ [the document of four score and seven years earlier that comes to the reader’s mind, but that Lincoln doesn’t directly mention].”
Novel/book confusion.
Novel is not a synonym for book. A novel is a long work of fiction in prose. A historical monograph is not a novel —unless the historian is making everything up.
Than/then confusion.
This is an appalling new error. If you are making a comparison, you use the conjunction than . (“President Kennedy’s health was worse than [not then ] the public realized.”)
Lead/led confusion.
The past tense of the verb to lead is led (not lead ). “Sherman led [not lead ] a march to the sea.”
Lose/loose confusion.
The opposite of win is lose , not loose . “Supporters of the Equal Rights Amendment suspected that they would lose [not loose ] the battle to amend the constitution.”
However/but confusion.
However may not substitute for the coordinating conjunction but. (“Mussolini began his career as a socialist, but [not however ] he later abandoned socialism for fascism.”) The word however has many proper uses; however , [note the semicolon and comma] graceful writers use it sparingly.
Cite/site/sight confusion.
You cited a source for your paper; ancient Britons sited Stonehenge on a plain; Columbus’s lookout sighted land.
Conscience/conscious confusion.
When you wake up in the morning you are conscious , though your conscience may bother you if you’ve neglected to write your history paper.
Tenet/tenant confusion.
Your religion, ideology, or worldview all have tenets —propositions you hold or believe in. Tenants rent from landlords.
All are not/not all are confusion.
If you write, “ All the colonists did not want to break with Britain in 1776,” the chances are you really mean, “ Not all the colonists wanted to break with Britain in 1776.” The first sentence is a clumsy way of saying that no colonists wanted to break with Britain (and is clearly false). The second sentence says that some colonists did not want to break with Britain (and is clearly true, though you should go on to be more precise).
Nineteenth-century/nineteenth century confusion.
Historians talk a lot about centuries, so you need to know when to hyphenate them. Follow the standard rule: If you combine two words to form a compound adjective, use a hyphen, unless the first word ends in ly. (“ Nineteenth-century [hyphenated] steamships cut the travel time across the Atlantic.”) Leave out the hyphen if you’re just using the ordinal number to modify the noun century. (“In the nineteenth century [no hyphen] steamships cut the travel time across the Atlantic.”) By the way, while you have centuries in mind, don’t forget that the nineteenth century is the 1800s, not the 1900s. The same rule for hyphenating applies to middle-class and middle class —a group that historians like to talk about.
Bourgeois/bourgeoisie confusion.
Bourgeois is usually an adjective, meaning characteristic of the middle class and its values or habits. Occasionally, bourgeois is a noun, meaning a single member of the middle class. Bourgeoisie is a noun, meaning the middle class collectively. (“Marx believed that the bourgeoisie oppressed the proletariat; he argued that bourgeois values like freedom and individualism were hypocritical.”)
Your professor may ask you to analyze a primary document. Here are some questions you might ask of your document. You will note a common theme—read critically with sensitivity to the context. This list is not a suggested outline for a paper; the wording of the assignment and the nature of the document itself should determine your organization and which of the questions are most relevant. Of course, you can ask these same questions of any document you encounter in your research.
- What exactly is the document (e.g., diary, king’s decree, opera score, bureaucratic memorandum, parliamentary minutes, newspaper article, peace treaty)?
- Are you dealing with the original or with a copy? If it is a copy, how remote is it from the original (e.g., photocopy of the original, reformatted version in a book, translation)? How might deviations from the original affect your interpretation?
- What is the date of the document?
- Is there any reason to believe that the document is not genuine or not exactly what it appears to be?
- Who is the author, and what stake does the author have in the matters discussed? If the document is unsigned, what can you infer about the author or authors?
- What sort of biases or blind spots might the author have? For example, is an educated bureaucrat writing with third-hand knowledge of rural hunger riots?
- Where, why, and under what circumstances did the author write the document?
- How might the circumstances (e.g., fear of censorship, the desire to curry favor or evade blame) have influenced the content, style, or tone of the document?
- Has the document been published? If so, did the author intend it to be published?
- If the document was not published, how has it been preserved? In a public archive? In a private collection? Can you learn anything from the way it has been preserved? For example, has it been treated as important or as a minor scrap of paper?
- Does the document have a boilerplate format or style, suggesting that it is a routine sample of a standardized genre, or does it appear out of the ordinary, even unique?
- Who is the intended audience for the document?
- What exactly does the document say? Does it imply something different?
- If the document represents more than one viewpoint, have you carefully distinguished between the author’s viewpoint and those viewpoints the author presents only to criticize or refute?
- In what ways are you, the historian, reading the document differently than its intended audience would have read it (assuming that future historians were not the intended audience)?
- What does the document leave out that you might have expected it to discuss?
- What does the document assume that the reader already knows about the subject (e.g., personal conflicts among the Bolsheviks in 1910, the details of tax farming in eighteenth-century Normandy, secret negotiations to end the Vietnam war)?
- What additional information might help you better interpret the document?
- Do you know (or are you able to infer) the effects or influences, if any, of the document?
- What does the document tell you about the period you are studying?
- If your document is part of an edited collection, why do you suppose the editor chose it? How might the editing have changed the way you perceive the document? For example, have parts been omitted? Has it been translated? (If so, when, by whom, and in what style?) Has the editor placed the document in a suggestive context among other documents, or in some other way led you to a particular interpretation?
Your professor may ask you to write a book review, probably of a scholarly historical monograph. Here are some questions you might ask of the book. Remember that a good review is critical, but critical does not necessarily mean negative. This list is not meant to be exhaustive, nor is it a suggested outline. Of course, you can ask these same questions of any secondary historical work, even if you’re not writing a review.
- Who is the author, and what are his or her qualifications? Has the author written other books on the subject?
- When was the book written, and how does it fit into the scholarly debate on the subject? For example, is Smith writing to refute that idiot Jones; to qualify the work of the competent but unimaginative Johnson; or to add humbly to the evidence presented by the redoubtable Brown’s classic study? Be sure not to confuse the author’s argument with those arguments he or she presents only to criticize later.
- What is the book’s basic argument? (Getting this right is the foundation of your review.)
- What is the author’s method? For example, does the author rely strictly on narrative and anecdotes, or is the book analytical in some way?
- What kinds of evidence does the author use? For example, what is the balance of primary and secondary sources? Has the author done archival work? Is the source base substantial, or does it look thin? Is the author up-to-date in the scholarly literature?
- How skillfully and imaginatively has the author used the evidence?
- Does the author actually use all of the material in the bibliography, or is some of it there for display?
- What sorts of explicit or implicit ideological or methodological assumptions does the author bring to the study? For example, does he or she profess bland objectivity? A Whig view of history? Marxism?
- How persuasive is the author’s argument?
- Is the argument new, or is it old wine in new bottles?
- Is the argument important, with wide-ranging implications, or is it narrow and trivial?
- Is the book well organized and skillfully written?
- What is your overall critical assessment of the book?
- What is the general significance, if any, of the book? (Make sure that you are judging the book that the author actually wrote, not complaining that the author should have written a different book.)
Here are some tips for those long, intimidating term papers or senior theses:
- Start early. If you don’t, none of these tips will matter. Big trouble is looming if you don’t have a specific topic by the end of the first week. You should be delving into the sources during the second week.
- Keep in mind all of the dos and don’ts in this booklet.
- Work closely with your professor to assure that your topic is neither too broad nor too narrow.
- Set up a schedule with your professor and check his or her policy about reading rough drafts or parts of rough drafts. Then keep your professor informed about what you’re doing. You don’t want any unpleasant surprises. You certainly don’t want to hear, “I haven’t seen you for weeks, and it sounds like you’re way off base. How can you possibly get this done with only two weeks left in the semester?”
- Make an appointment with Kristin Strohmeyer, the history reference librarian in Burke Library. She will help you to find and use the appropriate catalogs and indexes.
- Use your imagination in compiling a bibliography. Think of all of the possible key words and subjects that may lead you to material. If you find something really good, check the subjects under which it is cataloged. Comb the notes and bibliographies of books and articles you’ve already found.
- Much of what you need will not be in our library, so get to know the friendly folks in the Interlibrary Loan department.
- Start early. This can’t be said too often.
- Use as many primary sources as you can.
- Jot down your ideas as they come to you. You may not remember them later.
- Take careful notes on your reading. Label your notes completely and precisely. Distinguish meticulously and systematically between what you are directly quoting and what you are summarizing in your own words. Unintended plagiarism is still plagiarism. Stay clean as a hound’s tooth. Write down not just the page of the quotation or idea, but also the whole run of pages where the matter is discussed. Reread all of your notes periodically to make sure that you still understand them and are compiling what you will need to write your paper. Err on the side of writing down more than you think you will need. Copious, precise notes won’t come back to haunt you; skimpy, vague notes will. Just accept that there is something anal about good note-taking.
- If you take notes directly into your computer, they will be easy to index and pull up, but there are a couple of downsides. You will not be able to see all of them simultaneously, as you can note cards laid out on a big table. What you gain in ease of access may come at the price of losing the big picture. Also, if your notes are in your computer, you may be tempted to save time and thought by pasting many of them directly into your paper. Note cards encourage you to rethink and to rework your ideas into a unified whole.
- Don’t start to write until you have a good outline.
- Make sure that your paper has a thesis. (See the entry State a clear thesis. )
- Check and recheck your facts.
- Footnote properly. (See the entry Cite sources carefully .)
- Save plenty of time to proofread.
- Start early.
Top Ten Signs that you may be Writing a Weak History Paper
10. You’re overjoyed to find that you can fill the required pages by widening all margins.
9. You haven’t mentioned any facts or cited any sources for several paragraphs.
8. You find yourself using the phrase “throughout history mankind has...”
7. You just pasted in another 100 words of quotations.
6. You haven’t a clue about the content of your next paragraph.
5. You’re constantly clicking on The Britannica, Webster’s, and Bartlett’s.
4. Your writing tutor sneaks another look at her watch as she reminds you for the third time to clarify your thesis.
3. Your main historical actors are this, it, they, the people, and society, and they are all involved with factors, aspects, impacts, and issues.
2. You just realize that you don’t understand the assignment, but it’s 3:00 A.M, the paper is due at 9:00, and you don’t dare call your professor.
1. You’re relieved that the paper counts for only 20 percent of the course grade.

Final Advice
You guessed it — start early.
Studying History at Hamilton
Students will learn to use interdisciplinary methods from the humanities and social sciences to probe the sources of the past for answers to present questions. They will learn to draw comparisons and connections among diverse societies across a range of historical eras. They will further learn to convey their findings through writing that is clearly structured, precise, and persuasive.
Tutor Appointments
Peer tutor and consultant appointments are managed through TracCloud (login required). Find resources and more information about the ALEX centers using the following links.
Office / Department Name
Nesbitt-Johnston Writing Center
Contact Name
Jennifer Ambrose
Writing Center Director

Help us provide an accessible education, offer innovative resources and programs, and foster intellectual exploration.
Site Search
Chronological Order In Essay Writing
Table of contents
- 1 What Is a Chronological Order Essay
- 2 Chronological Order vs. Sequential Order
- 3 Importance of Correct Historical Occurrences
- 4 How to Write a Chronological Paragraph?
- 5.1 Pick an Idea and Make a Plan
- 5.2 Use a Variety of Sentence Structures to Keep Your Writing Interesting
- 5.3 Provide Sufficient Details
- 5.4 Use Transitional Words and Phrases, Such As “First,” “Next,” and “Then,” to Indicate the Chronological Flow
- 5.5 Use Headings and Subheadings to Organize Your Essay
- 5.6 Use Introductory and Concluding Sentences to Signal the Main Points of Each Paragraph
- 5.7 Use Appropriate Citations and References (Especially for the Historical Essay)
- 5.8 Maintain a Consistent Timeline and Avoid Jumping Back and Forth in Time
- 6 Conclusion
Writing a chronological essay is a pure pleasure. This type of university assignment is clear and structured, so knowing the basic requirements, you can easily cope with the task. Essays in chronological order require their author to have deep knowledge of the chosen subject. Not to stray from the course of the story, you need to be a real expert in this niche.
In this article, you will learn what a chronological-order essay is and how to write it. Also, you will find precious tips on making the writing process quick and enjoyable. So here are the milestones of our chronological essay guide:
- What a chronological order essay is;
- The difference between chronological and sequential order;
- Guidelines for chronological paragraph writing;
- Tips for writing an outstanding chronological essay.
Together we will consider each important point and dispel your doubts about the chronological essays. Without further ado, let’s get it started!
What Is a Chronological Order Essay
A chronological essay is an expository writing that describes historical events or a biography of a specific person. Surprisingly, not only students of the Faculty of History are faced with this type of essay. Whenever you have been given the task of writing about outstanding personalities, talking about your experiences, or presenting a life story or historical event, you will be faced with the need to use chronological order in writing.
This type of narrating writing essay requires you to present information in a logical and structured way. Expository essay writers must state all the events in the order in which they occurred. Moreover, you should dip the reader into the context of the event, explaining to him the background and the outcomes.
Chronological Order vs. Sequential Order
You may think that sequence and chronological order are identical concepts. Don’t worry, you’re not the only one who thinks so. These concepts are strongly related but not identical. Sequential order is based on the order of steps performed and how events occur relative to each other. But what is a chronological order of events?
The chronological timeline tells about the sequence of actions in time-space. Sequential order is well suited for writing step-by-step instructions and listing events. At the same time, the chronological order is excellent for narrating historical events and writing biographies.
Importance of Correct Historical Occurrences
Preliminary research is a solid foundation for your chronological essay. Take information only from reliable and trusted sources respected in science. Avoid unverified facts and loud statements. Make an effort to pre-study to avoid building an essay on false grounds. It may seem that a detailed study will take too much time, but on the contrary, it will save you the effort of rewriting the time order essay.
Check several sources for proof of the integrity of the information you found. Whenever you don’t have enough time for research, consider buying an essay rather than copying random facts from the web. After all, no matter how well you present the events in chronological order, if it does not correspond to reality, then your essay will lose all scientific value.
How to Write a Chronological Paragraph?
You can be assigned to write a chronological paragraph in your paper. This is also a type of chronological writing that you should do right if you need to get a good grade for your essay.
This paragraph should describe the sequence of events that occurred to a specific object or person. These events should be sorted chronologically, from the earliest to the latest. You should present the sequence and make logical transitions between events. This will help readers understand the connections between events and the outcomes of specific things.
You can write about anything interesting, there are almost no topics you should avoid in the essay if they meet the requirements. However, it is better when the subject is interesting to you.
When structuring these paragraphs, students not only present the facts but also explain them as causes and effects. If you don’t see connections between things, you should look closer and do more research.
To write a good chronological paragraph, you need to include crucial elements. Thus, it will be easier to structure the course of events. This guide may not only be used for chronological essays, it’s a rather versatile piece of advice on how to compose a personal statement . Among the integral components are:
- Topic sentence
- Important supporting points
- Chronological progression
- Coherence of the narrative
- Summarizing sentence
Topic sentences exist to briefly remind the reader of the main topic of your paper. Give enough detail to put the reader in the context of the chronological sequence essay. Do not jump in time, state all events clearly and unambiguously to maintain logical transitions. End your paragraph by summarizing what has been said so far.
Example of chronological order:
The Second World War was the largest bloody war, in which more than 30 countries participated and left an indelible mark on the history of mankind. (Strong topic sentence.) The prerequisites ( the supporting details ) for this historic event are considered Germany’s course for revenge in the First World War. Events began in September 1939 with the German attack on Poland. ( Chronological progression). The most important event of the Second World War is thought to be the Japanese attack on the United States of America in Pearl Harbor. After six years of fierce fighting, the Nazis were defeated by the Allies, and the war ended with the Japanese surrender on 2nd September 1945. ( Summarizing sentence)
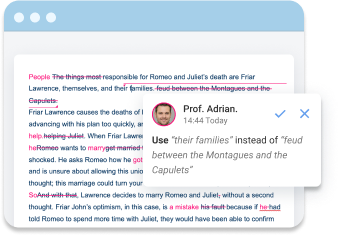
Tips on Writing a Chronological Essay
You start the writing process by choosing a topic for it. Find an interesting topic that meets your assignment’s requirements, or ask your teacher to give you a topic.
If you are stuck with creating this paper, you can use an essay editing service to prepare it. Its writers have experience working on chronological essays, they can help you with narrative and cause-and-effect paper .
Then you should research and find as much information on your topic as possible. Collect this information in a well-organized format so you can reference any of it if needed, and don’t forget to keep the dates of all events.
Pick an Idea and Make a Plan
If you need to create informative essays about a specific historical event, you should start from the beginning of this event or even with earlier events that lead to it. If a particular group organizes an event, tell the motives of this group, how they got to this idea, and how they started working on it. Then write about each step from the beginning to the conclusion of this event and arrange the events in chronological order.
Use a Variety of Sentence Structures to Keep Your Writing Interesting
If you only use simple sentences or start each sentence with the word «then», your writing will be boring to read. PapersOwl specialists advise studying several chronological ordering examples to understand the linking words and the structuring strategy. Use different stylistic devices as well as different types of complex sentences.
Provide Sufficient Details
Provide your reader with the full context of the story in time-order paragraphs. To understand the course of action of the chronological essay, the reader must be aware of the background and cause of historical events. At the same time, try not to overload your compositions with unnecessary details.
Use Transitional Words and Phrases, Such As “First,” “Next,” and “Then,” to Indicate the Chronological Flow
Sequencers help keep the story logical, they’re keywords for chronological order that make the essay flow smoothly. Use transitional words to direct the reader through the flow of your story. Don’t forget to use different expressions to avoid tautology.
Use Headings and Subheadings to Organize Your Essay
Provide clear divisions so that the paper becomes much more readable. Large arrays of text always repel the reader, so use a proper chronological structure. Also, headings and subheadings will help you further structure your essay.
Use Introductory and Concluding Sentences to Signal the Main Points of Each Paragraph
A thesis statement that summarizes the main message of your chronological essays should be restructured and repeated several times during writing. This technique is used by writers to express the main idea of the essay in the introduction and throughout the text. The thesis proposal should be catchy and memorable.
Use Appropriate Citations and References (Especially for the Historical Essay)
There could be many sources of false information on the Internet. Students should check information and put only proven citations into the chronological expositions. We know it could be challenging to deal with citation norms, so we’re always ready to write your paper for you . Be sure to check the accuracy of the quotes and the veracity of the facts you refer to.
Maintain a Consistent Timeline and Avoid Jumping Back and Forth in Time
When you have the list of essential timeline events, you can arrange the events in the order in which they happened. It helps you to use the correct order in an essay from the earliest events in your story to the latest. You can use simple editors or a spreadsheet for sorting lists.
When you write a chronological essay, nothing may cause you problems if you are well-oriented to the chosen subject. You should carefully choose topics for writing, do not forget about the preliminary study, and double-check the sources you use.
After reading our guide in detail, you will undoubtedly be able to write a decent chronological essay. However, even if you find it difficult to find inspiration for writing, this is not a problem either, as you can resort to exposition editing services. Remember that an experienced team of professionals is always ready to help you with heavy research writing essays.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a History Essay
Last Updated: December 27, 2022 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Emily Listmann, MA . Emily Listmann is a private tutor in San Carlos, California. She has worked as a Social Studies Teacher, Curriculum Coordinator, and an SAT Prep Teacher. She received her MA in Education from the Stanford Graduate School of Education in 2014. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 243,601 times.
Writing a history essay requires you to include a lot of details and historical information within a given number of words or required pages. It's important to provide all the needed information, but also to present it in a cohesive, intelligent way. Know how to write a history essay that demonstrates your writing skills and your understanding of the material.
Preparing to Write Your Essay

- The key words will often need to be defined at the start of your essay, and will serve as its boundaries. [2] X Research source
- For example, if the question was "To what extent was the First World War a Total War?", the key terms are "First World War", and "Total War".
- Do this before you begin conducting your research to ensure that your reading is closely focussed to the question and you don't waste time.

- Explain: provide an explanation of why something happened or didn't happen.
- Interpret: analyse information within a larger framework to contextualise it.
- Evaluate: present and support a value-judgement.
- Argue: take a clear position on a debate and justify it. [3] X Research source

- Your thesis statement should clearly address the essay prompt and provide supporting arguments. These supporting arguments will become body paragraphs in your essay, where you’ll elaborate and provide concrete evidence. [4] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- Your argument may change or become more nuanced as your write your essay, but having a clear thesis statement which you can refer back to is very helpful.
- For example, your summary could be something like "The First World War was a 'total war' because civilian populations were mobilized both in the battlefield and on the home front".

- Pick out some key quotes that make your argument precisely and persuasively. [5] X Research source
- When writing your plan, you should already be thinking about how your essay will flow, and how each point will connect together.
Doing Your Research

- Primary source material refers to any texts, films, pictures, or any other kind of evidence that was produced in the historical period, or by someone who participated in the events of the period, that you are writing about.
- Secondary material is the work by historians or other writers analysing events in the past. The body of historical work on a period or event is known as the historiography.
- It is not unusual to write a literature review or historiographical essay which does not directly draw on primary material.
- Typically a research essay would need significant primary material.

- Start with the core texts in your reading list or course bibliography. Your teacher will have carefully selected these so you should start there.
- Look in footnotes and bibliographies. When you are reading be sure to pay attention to the footnotes and bibliographies which can guide you to further sources a give you a clear picture of the important texts.
- Use the library. If you have access to a library at your school or college, be sure to make the most of it. Search online catalogues and speak to librarians.
- Access online journal databases. If you are in college it is likely that you will have access to academic journals online. These are an excellent and easy to navigate resources.
- Use online sources with discretion. Try using free scholarly databases, like Google Scholar, which offer quality academic sources, but avoid using the non-trustworthy websites that come up when you simply search your topic online.
- Avoid using crowd-sourced sites like Wikipedia as sources. However, you can look at the sources cited on a Wikipedia page and use them instead, if they seem credible.

- Who is the author? Is it written by an academic with a position at a University? Search for the author online.
- Who is the publisher? Is the book published by an established academic press? Look in the cover to check the publisher, if it is published by a University Press that is a good sign.
- If it's an article, where is published? If you are using an article check that it has been published in an academic journal. [8] X Research source
- If the article is online, what is the URL? Government sources with .gov addresses are good sources, as are .edu sites.

- Ask yourself why the author is making this argument. Evaluate the text by placing it into a broader intellectual context. Is it part of a certain tradition in historiography? Is it a response to a particular idea?
- Consider where there are weaknesses and limitations to the argument. Always keep a critical mindset and try to identify areas where you think the argument is overly stretched or the evidence doesn't match the author's claims. [9] X Research source

- Label all your notes with the page numbers and precise bibliographic information on the source.
- If you have a quote but can't remember where you found it, imagine trying to skip back through everything you have read to find that one line.
- If you use something and don't reference it fully you risk plagiarism. [10] X Research source
Writing the Introduction

- For example you could start by saying "In the First World War new technologies and the mass mobilization of populations meant that the war was not fought solely by standing armies".
- This first sentences introduces the topic of your essay in a broad way which you can start focus to in on more.

- This will lead to an outline of the structure of your essay and your argument.
- Here you will explain the particular approach you have taken to the essay.
- For example, if you are using case studies you should explain this and give a brief overview of which case studies you will be using and why.

Writing the Essay

- Try to include a sentence that concludes each paragraph and links it to the next paragraph.
- When you are organising your essay think of each paragraph as addressing one element of the essay question.
- Keeping a close focus like this will also help you avoid drifting away from the topic of the essay and will encourage you to write in precise and concise prose.
- Don't forget to write in the past tense when referring to something that has already happened.

- Don't drop a quote from a primary source into your prose without introducing it and discussing it, and try to avoid long quotations. Use only the quotes that best illustrate your point.
- If you are referring to a secondary source, you can usually summarise in your own words rather than quoting directly.
- Be sure to fully cite anything you refer to, including if you do not quote it directly.

- Think about the first and last sentence in every paragraph and how they connect to the previous and next paragraph.
- Try to avoid beginning paragraphs with simple phrases that make your essay appear more like a list. For example, limit your use of words like: "Additionally", "Moreover", "Furthermore".
- Give an indication of where your essay is going and how you are building on what you have already said. [15] X Research source

- Briefly outline the implications of your argument and it's significance in relation to the historiography, but avoid grand sweeping statements. [16] X Research source
- A conclusion also provides the opportunity to point to areas beyond the scope of your essay where the research could be developed in the future.
Proofreading and Evaluating Your Essay

- Try to cut down any overly long sentences or run-on sentences. Instead, try to write clear and accurate prose and avoid unnecessary words.
- Concentrate on developing a clear, simple and highly readable prose style first before you think about developing your writing further. [17] X Research source
- Reading your essay out load can help you get a clearer picture of awkward phrasing and overly long sentences. [18] X Research source

- When you read through your essay look at each paragraph and ask yourself, "what point this paragraph is making".
- You might have produced a nice piece of narrative writing, but if you are not directly answering the question it is not going to help your grade.

- A bibliography will typically have primary sources first, followed by secondary sources. [19] X Research source
- Double and triple check that you have included all the necessary references in the text. If you forgot to include a reference you risk being reported for plagiarism.
Sample Essay

Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.historytoday.com/robert-pearce/how-write-good-history-essay
- ↑ https://www.hamilton.edu/academics/centers/writing/writing-resources/writing-a-good-history-paper
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/thesis_statement_tips.html
- ↑ http://history.rutgers.edu/component/content/article?id=106:writing-historical-essays-a-guide-for-undergraduates
- ↑ https://guides.lib.uw.edu/c.php?g=344285&p=2580599
- ↑ http://www.hamilton.edu/documents/writing-center/WritingGoodHistoryPaper.pdf
- ↑ http://www.bowdoin.edu/writing-guides/
- ↑ https://www.wgtn.ac.nz/hppi/publications/Writing-History-Essays.pdf
About This Article

To write a history essay, read the essay question carefully and use source materials to research the topic, taking thorough notes as you go. Next, formulate a thesis statement that summarizes your key argument in 1-2 concise sentences and create a structured outline to help you stay on topic. Open with a strong introduction that introduces your thesis, present your argument, and back it up with sourced material. Then, end with a succinct conclusion that restates and summarizes your position! For more tips on creating a thesis statement, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Lea Fernandez
Nov 23, 2017
Did this article help you?

Matthew Sayers
Mar 31, 2019
Millie Jenkerinx
Nov 11, 2017
Oct 18, 2019
Shannon Harper
Mar 9, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter

Subscription Offers
Give a Gift

How To Write a Good History Essay
The former editor of History Review Robert Pearce gives his personal view.
First of all we ought to ask, What constitutes a good history essay? Probably no two people will completely agree, if only for the very good reason that quality is in the eye – and reflects the intellectual state – of the reader. What follows, therefore, skips philosophical issues and instead offers practical advice on how to write an essay that will get top marks.
Witnesses in court promise to tell the truth, the whole truth and nothing but the truth. All history students should swear a similar oath: to answer the question, the whole question and nothing but the question. This is the number one rule. You can write brilliantly and argue a case with a wealth of convincing evidence, but if you are not being relevant then you might as well be tinkling a cymbal. In other words, you have to think very carefully about the question you are asked to answer. Be certain to avoid the besetting sin of those weaker students who, fatally, answer the question the examiners should have set – but unfortunately didn’t. Take your time, look carefully at the wording of the question, and be certain in your own mind that you have thoroughly understood all its terms.
If, for instance, you are asked why Hitler came to power, you must define what this process of coming to power consisted of. Is there any specific event that marks his achievement of power? If you immediately seize on his appointment as Chancellor, think carefully and ask yourself what actual powers this position conferred on him. Was the passing of the Enabling Act more important? And when did the rise to power actually start? Will you need to mention Hitler’s birth and childhood or the hyperinflation of the early 1920s? If you can establish which years are relevant – and consequently which are irrelevant – you will have made a very good start. Then you can decide on the different factors that explain his rise.
Or if you are asked to explain the successes of a particular individual, again avoid writing the first thing that comes into your head. Think about possible successes. In so doing, you will automatically be presented with the problem of defining ‘success’. What does it really mean? Is it the achievement of one’s aims? Is it objective (a matter of fact) or subjective (a matter of opinion)? Do we have to consider short-term and long-term successes? If the person benefits from extraordinary good luck, is that still a success? This grappling with the problem of definition will help you compile an annotated list of successes, and you can then proceed to explain them, tracing their origins and pinpointing how and why they occurred. Is there a key common factor in the successes? If so, this could constitute the central thrust of your answer.
Save 35% with a student subscription to History Today
The key word in the above paragraphs is think . This should be distinguished from remembering, daydreaming and idly speculating. Thinking is rarely a pleasant undertaking, and most of us contrive to avoid it most of the time. But unfortunately there’s no substitute if you want to get the top grade. So think as hard as you can about the meaning of the question, about the issues it raises and the ways you can answer it. You have to think and think hard – and then you should think again, trying to find loopholes in your reasoning. Eventually you will almost certainly become confused. Don’t worry: confusion is often a necessary stage in the achievement of clarity. If you get totally confused, take a break. When you return to the question, it may be that the problems have resolved themselves. If not, give yourself more time. You may well find that decent ideas simply pop into your conscious mind at unexpected times.
You need to think for yourself and come up with a ‘bright idea’ to write a good history essay. You can of course follow the herd and repeat the interpretation given in your textbook. But there are problems here. First, what is to distinguish your work from that of everybody else? Second, it’s very unlikely that your school text has grappled with the precise question you have been set.
The advice above is relevant to coursework essays. It’s different in exams, where time is limited. But even here, you should take time out to do some thinking. Examiners look for quality rather than quantity, and brevity makes relevance doubly important. If you get into the habit of thinking about the key issues in your course, rather than just absorbing whatever you are told or read, you will probably find you’ve already considered whatever issues examiners pinpoint in exams.
The Vital First Paragraph
Every part of an essay is important, but the first paragraph is vital. This is the first chance you have to impress – or depress – an examiner, and first impressions are often decisive. You might therefore try to write an eye-catching first sentence. (‘Start with an earthquake and work up to a climax,’ counselled the film-maker Cecil B. De Mille.) More important is that you demonstrate your understanding of the question set. Here you give your carefully thought out definitions of the key terms, and here you establish the relevant time-frame and issues – in other words, the parameters of the question. Also, you divide the overall question into more manageable sub-divisions, or smaller questions, on each of which you will subsequently write a paragraph. You formulate an argument, or perhaps voice alternative lines of argument, that you will substantiate later in the essay. Hence the first paragraph – or perhaps you might spread this opening section over two paragraphs – is the key to a good essay.
On reading a good first paragraph, examiners will be profoundly reassured that its author is on the right lines, being relevant, analytical and rigorous. They will probably breathe a sign of relief that here is one student at least who is avoiding the two common pitfalls. The first is to ignore the question altogether. The second is to write a narrative of events – often beginning with the birth of an individual – with a half-hearted attempt at answering the question in the final paragraph.
Middle Paragraphs
Philip Larkin once said that the modern novel consists of a beginning, a muddle and an end. The same is, alas, all too true of many history essays. But if you’ve written a good opening section, in which you’ve divided the overall question into separate and manageable areas, your essay will not be muddled; it will be coherent.
It should be obvious, from your middle paragraphs, what question you are answering. Indeed it’s a good test of an essay that the reader should be able to guess the question even if the title is covered up. So consider starting each middle paragraph will a generalisation relevant to the question. Then you can develop this idea and substantiate it with evidence. You must give a judicious selection of evidence (i.e. facts and quotations) to support the argument you are making. You only have a limited amount of space or time, so think about how much detail to give. Relatively unimportant background issues can be summarised with a broad brush; your most important areas need greater embellishment. (Do not be one of those misguided candidates who, unaccountably, ‘go to town’ on peripheral areas and gloss over crucial ones.)
The regulations often specify that, in the A2 year, students should be familiar with the main interpretations of historians. Do not ignore this advice. On the other hand, do not take historiography to extremes, so that the past itself is virtually ignored. In particular, never fall into the trap of thinking that all you need are sets of historians’ opinions. Quite often in essays students give a generalisation and back it up with the opinion of an historian – and since they have formulated the generalisation from the opinion, the argument is entirely circular, and therefore meaningless and unconvincing. It also fatuously presupposes that historians are infallible and omniscient gods. Unless you give real evidence to back up your view – as historians do – a generalisation is simply an assertion. Middle paragraphs are the place for the real substance of an essay, and you neglect this at your peril.
Final Paragraph
If you’ve been arguing a case in the body of an essay, you should hammer home that case in the final paragraph. If you’ve been examining several alternative propositions, now is the time to say which one is correct. In the middle paragraph you are akin to a barrister arguing a case. Now, in the final paragraph, you are the judge summing up and pronouncing the verdict.
It’s as well to keep in mind what you should not be doing. Do not introduce lots of fresh evidence at this stage, though you can certainly introduce the odd extra fact that clinches your case. Nor should you go on to the ‘next’ issue. If your question is about Hitler coming to power, you should not end by giving a summary of what he did once in power. Such an irrelevant ending will fail to win marks. Remember the point about answering ‘nothing but the question’? On the other hand, it may be that some of the things Hitler did after coming to power shed valuable light on why he came to power in the first place. If you can argue this convincingly, all well and good; but don’t expect the examiner to puzzle out relevance. Examiners are not expected to think; you must make your material explicitly relevant.
Final Thoughts
A good essay, especially one that seems to have been effortlessly composed, has often been revised several times; and the best students are those who are most selfcritical. Get into the habit of criticising your own first drafts, and never be satisfied with second-best efforts. Also, take account of the feedback you get from teachers. Don’t just look at the mark your essay gets; read the comments carefully. If teachers don’t advise how to do even better next time, they are not doing their job properly.
Relevance is vital in a good essay, and so is evidence marshalled in such a way that it produces a convincing argument. But nothing else really matters. The paragraph structure recommended above is just a guide, nothing more, and you can write a fine essay using a very different arrangement of material. Similarly, though it would be excellent if you wrote in expressive, witty and sparklingly provocative prose, you can still get top marks even if your essay is serious, ponderous and even downright dull.
There are an infinite number of ways to write an essay because any form of writing is a means of self-expression. Your essay will be unique because you are unique: it’s up to you to ensure that it’s uniquely good, not uniquely mediocre.
Robert Pearce is the editor of History Review .
Popular articles

When Did Britain’s Age of Deference End – and Why?

Why Were the Jews Persecuted?

How to Write a Conclusion For a History Essay Step-by-Step

A historical essay is a short piece of writing that answers a question or addresses a topic. It shows a student’s historical knowledge and ability to express themselves. The conclusion is a final summary that explains why the topic is significant. A well-written conclusion ends a historical essay on a strong note. It often is what the reader remembers the most.
What Is A History Essay?
An essay is a short piece of writing that answers a question (“Who are the funniest presidents ”) discusses a subject (“What is Japanese feudalism ”), or addresses a topic (“ Causes and Effects of the Industrial Revolution ”). A historical essay specifically addresses historical matters.
These essays are used to judge a student’s progress in understanding history. They also are used to teach and analyze a student’s ability to write and express their knowledge. A person can know their stuff and still have problems expressing their knowledge.
Skillful communication is an essential tool. When you write your conclusion to a historical essay remember that both the information and how you express it are both very important.
Final Chance To Impress
The conclusion of a historical essay is the final paragraph.
This is important. It is the final thing that the reader reads. It provides a final impression that can be the thing that is remembered the most. It is one last chance to impress.
Conclusion Is A Summary
The conclusion is a summary of your argument or topic. This is an example of the importance of crisp writing. The summary provides the reader with a final brief chance (do not ramble!) to know what you are trying to say. Try not to be boring. Do not write in the first person (“I”).
The summary does two basic things. If your historical essay has a specific thesis, a question that you have to answer, you summarize your answer. And, you summarize the main points of your essay. In both cases, you do not just repeat what you said before.
Conclusion Says Why It All Matters
The conclusion should not provide new information to make your case. That is what the body of the essay is for. The conclusion does say why your topic matters.
It provides the historical implications or significance of your topic. It offers a final chance for the reader to think about the subject of your historical essay. End on a strong note!
Step-By-Step Guide To Writing A Conclusion
Step 1: restate your thesis statement.
A “thesis” is a fancy way of saying what you are trying to convince the reader is true. It is your argument. For instance, you might have to argue that Catherine the Great truly was impressive. You would start a conclusion with a one-sentence summary of your basic viewpoint.
For these reasons, Catherine the Great was an impressive monarch given the restraints she had to live under.
If the historical essay does not answer a specific question, the opening statement can summarize the subject of the essay itself:
Donata Badoer , a Venetian noblewoman, married Marco Polo in 1300.
The restatement sentence does not provide an explanation. It simply summarizes your basic conclusion. Note that the thesis sentence might have a qualifier, something that must be true for the argument to work. Catherine was great “given the restraints” of the times.
The restatement sentence also can include various words that signal to the reader that the essay is coming to a close. These “summary words” include: in summary, as a result, on the whole, for these reasons, this proves, overall, therefore, this study reveals, and the evidence shows.
The appropriate words tend to be a matter of personal taste and judgment. They sometimes can be left out (“for these reasons” is a bit redundant) but are popular flourishes.
Step 2: Restate Your Key Points
This part of the conclusion summarizes the key points of your historical essay.
Remember, you are not supposed to be introducing anything new. This is also not a long explanation of the topic. You already did that.
The restatement can be as short as one sentence. It should not be much longer than two to three sentences. This is a conclusion paragraph, not a separate chapter.
Catherine the Great rose from humble beginnings to lead a great empire, providing many benefits such as supporting women’s education, improving the country’s image, and promoting vaccination.
Note that you are summarizing your main points without being vague (not just “many benefits” or “people say” but specific examples). The reader has a crisp summary of your argument.
Step 3: Final Statement and Thoughts
The conclusion ends with a statement on why this all matters.
The reader learns how the topic fits into a wider historical context . How did the topic affect the future, including the current day? Is there an unanswered question or something that can be a helpful subject of research? The reader is left thinking and intrigued.
For instance, a historical essay on new weapons in World War I can end thusly:
Those who fought in World I did manage to retain their humanity but the new weapons foreshadowed even more deadly battles and weapons in the future.
Again, the conclusion is a brief summary. This final thought should be a sentence or two long.
This section especially provides you some room to provide a bit of a personal touch. A quotation or suggestion for further research can be added. The reader is left wanting to learn more.
Conclusion About Conclusions
The conclusion of a historical essay ties everything together. It reminds the reader what your argument is and why it matters. A well-written conclusion is not just a cherry on top of the sundae. It leaves the reader with a content feeling that they did not waste their time reading your essay. They won’t be confused or bored. They will be left content and intrigued for more.
Teach and Thrive
A Bronx, NY veteran high school social studies teacher who has learned most of what she has learned through trial and error and error and error.... and wants to save others that pain.
RELATED ARTICLES:
How to Write an Introduction For a History Essay Step-by-Step
An introduction of a historical essay acquaints the reader with the topic and how the writer will explain it. It is an important first impression. The introduction is a paragraph long and about five...
The Ultimate Guide to Crafting a Winning Historical Essay Body: Tips and Tricks for Success
A historical essay answers a question or addresses a specific topic. The format is like a sandwich: a body cushioned between the introduction and conclusion paragraphs. Each body paragraph is a...
So much is at stake in writing a conclusion. This is, after all, your last chance to persuade your readers to your point of view, to impress yourself upon them as a writer and thinker. And the impression you create in your conclusion will shape the impression that stays with your readers after they've finished the essay.
The end of an essay should therefore convey a sense of completeness and closure as well as a sense of the lingering possibilities of the topic, its larger meaning, its implications: the final paragraph should close the discussion without closing it off.
To establish a sense of closure, you might do one or more of the following:
- Conclude by linking the last paragraph to the first, perhaps by reiterating a word or phrase you used at the beginning.
- Conclude with a sentence composed mainly of one-syllable words. Simple language can help create an effect of understated drama.
- Conclude with a sentence that's compound or parallel in structure; such sentences can establish a sense of balance or order that may feel just right at the end of a complex discussion.
To close the discussion without closing it off, you might do one or more of the following:
- Conclude with a quotation from or reference to a primary or secondary source, one that amplifies your main point or puts it in a different perspective. A quotation from, say, the novel or poem you're writing about can add texture and specificity to your discussion; a critic or scholar can help confirm or complicate your final point. For example, you might conclude an essay on the idea of home in James Joyce's short story collection, Dubliners , with information about Joyce's own complex feelings towards Dublin, his home. Or you might end with a biographer's statement about Joyce's attitude toward Dublin, which could illuminate his characters' responses to the city. Just be cautious, especially about using secondary material: make sure that you get the last word.
- Conclude by setting your discussion into a different, perhaps larger, context. For example, you might end an essay on nineteenth-century muckraking journalism by linking it to a current news magazine program like 60 Minutes .
- Conclude by redefining one of the key terms of your argument. For example, an essay on Marx's treatment of the conflict between wage labor and capital might begin with Marx's claim that the "capitalist economy is . . . a gigantic enterprise of dehumanization "; the essay might end by suggesting that Marxist analysis is itself dehumanizing because it construes everything in economic -- rather than moral or ethical-- terms.
- Conclude by considering the implications of your argument (or analysis or discussion). What does your argument imply, or involve, or suggest? For example, an essay on the novel Ambiguous Adventure , by the Senegalese writer Cheikh Hamidou Kane, might open with the idea that the protagonist's development suggests Kane's belief in the need to integrate Western materialism and Sufi spirituality in modern Senegal. The conclusion might make the new but related point that the novel on the whole suggests that such an integration is (or isn't) possible.
Finally, some advice on how not to end an essay:
- Don't simply summarize your essay. A brief summary of your argument may be useful, especially if your essay is long--more than ten pages or so. But shorter essays tend not to require a restatement of your main ideas.
- Avoid phrases like "in conclusion," "to conclude," "in summary," and "to sum up." These phrases can be useful--even welcome--in oral presentations. But readers can see, by the tell-tale compression of the pages, when an essay is about to end. You'll irritate your audience if you belabor the obvious.
- Resist the urge to apologize. If you've immersed yourself in your subject, you now know a good deal more about it than you can possibly include in a five- or ten- or 20-page essay. As a result, by the time you've finished writing, you may be having some doubts about what you've produced. (And if you haven't immersed yourself in your subject, you may be feeling even more doubtful about your essay as you approach the conclusion.) Repress those doubts. Don't undercut your authority by saying things like, "this is just one approach to the subject; there may be other, better approaches. . ."
Copyright 1998, Pat Bellanca, for the Writing Center at Harvard University
How to Write a History Essay?
04 August, 2020
10 minutes read
Author: Tomas White
There are so many types of essays. It can be hard to know where to start. History papers aren’t just limited to history classes. These tasks can be assigned to examine any important historical event or a person. While they’re more common in history classes, you can find this type of assignment in sociology or political science course syllabus, or just get a history essay task for your scholarship. This is Handmadewriting History Essay Guide - let's start!

Purpose of a History Essay
Wondering how to write a history essay? First of all, it helps to understand its purpose. Secondly, this essay aims to examine the influences that lead to a historical event. Thirdly, it can explore the importance of an individual’s impact on history.
However, the goal isn’t to stay in the past. Specifically, a well-written history essay should discuss the relevance of the event or person to the “now”. After finishing this essay, a reader should have a fuller understanding of the lasting impact of an event or individual.
Need basic essay guidance? Find out what is an essay with this 101 essay guide: What is an Essay?
Elements for Success
Indeed, understanding how to write a history essay is crucial in creating a successful paper. Notably, these essays should never only outline successful historic events or list an individual’s achievements. Instead, they should focus on examining questions beginning with what , how , and why . Here’s a pro tip in how to write a history essay: brainstorm questions. Once you’ve got questions, you have an excellent starting point.
Preparing to Write

Evidently, a typical history essay format requires the writer to provide background on the event or person, examine major influences, and discuss the importance of the forces both then and now. In addition, when preparing to write, it’s helpful to organize the information you need to research into questions. For example:
- Who were the major contributors to this event?
- Who opposed or fought against this event?
- Who gained or lost from this event?
- Who benefits from this event today?
- What factors led up to this event?
- What changes occurred because of this event?
- What lasting impacts occurred locally, nationally, globally due to this event?
- What lessons (if any) were learned?
- Why did this event occur?
- Why did certain populations support it?
- Why did certain populations oppose it?
These questions exist as samples. Therefore, generate questions specific to your topic. Once you have a list of questions, it’s time to evaluate them.
Evaluating the Question

Seasoned writers approach writing history by examining the historic event or individual. Specifically, the goal is to assess the impact then and now. Accordingly, the writer needs to evaluate the importance of the main essay guiding the paper. For example, if the essay’s topic is the rise of American prohibition, a proper question may be “How did societal factors influence the rise of American prohibition during the 1920s? ”
This question is open-ended since it allows for insightful analysis, and limits the research to societal factors. Additionally, work to identify key terms in the question. In the example, key terms would be “societal factors” and “prohibition”.
Summarizing the Argument
The argument should answer the question. Use the thesis statement to clarify the argument and outline how you plan to make your case. In other words. the thesis should be sharp, clear, and multi-faceted. Consider the following tips when summarizing the case:
- The thesis should be a single sentence
- It should include a concise argument and a roadmap
- It’s always okay to revise the thesis as the paper develops
- Conduct a bit of research to ensure you have enough support for the ideas within the paper
Outlining a History Essay Plan

Once you’ve refined your argument, it’s time to outline. Notably, many skip this step to regret it then. Nonetheless, the outline is a map that shows where you need to arrive historically and when. Specifically, taking the time to plan, placing the strongest argument last, and identifying your sources of research is a good use of time. When you’re ready to outline, do the following:
- Consider the necessary background the reader should know in the introduction paragraph
- Define any important terms and vocabulary
- Determine which ideas will need the cited support
- Identify how each idea supports the main argument
- Brainstorm key points to review in the conclusion
Gathering Sources
As a rule, history essays require both primary and secondary sources . Primary resources are those that were created during the historical period being analyzed. Secondary resources are those created by historians and scholars about the topic. It’s a good idea to know if the professor requires a specific number of sources, and what kind he or she prefers. Specifically, most tutors prefer primary over secondary sources.
Where to find sources? Great question! Check out bibliographies included in required class readings. In addition, ask a campus Librarian. Peruse online journal databases; In addition, most colleges provide students with free access. When in doubt, make an appointment and ask the professor for guidance.
Writing the Essay
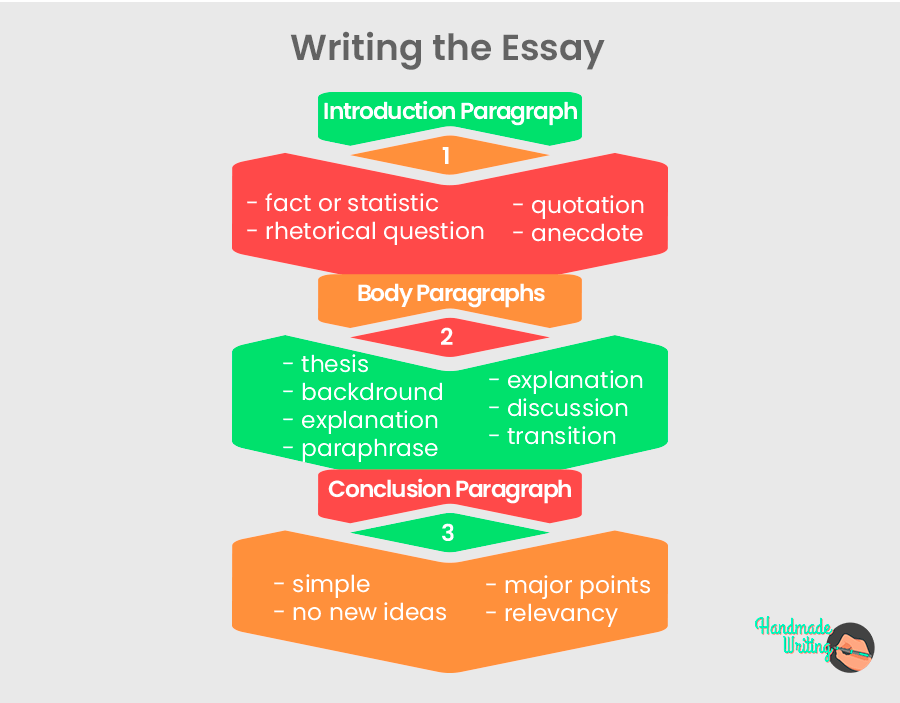
Now that you have prepared your questions, ideas, and arguments; composed the outline ; and gathered sources – it’s time to write your first draft. In particular, each section of your history essay must serve its purpose. Here is what you should include in essay paragraphs.
Introduction Paragraph
Unsure of how to start a history essay? Well, like most essays, the introduction should include an attention-getter (or hook):
- Relevant fact or statistic
- Rhetorical Question
- Interesting quotation
- Application anecdote if appropriate
Once you’ve captured the reader’s interest, introduce the topic. Similarly, present critical historic context. Namely, it is necessary to introduce any key individuals or events that will be discussed later in the essay. At last, end with a strong thesis which acts as a transition to the first argument.
Body Paragraphs
Indeed, each body paragraph should offer a single idea to support the argument. Then, after writing a strong topic sentence, the topic should be supported with correctly cited research. Consequently, a typical body paragraph is arranged as follows:
- Topic sentence linking to the thesis
- Background of the topic
- Research quotation or paraphrase #1
- Explanation and analysis of research
- Research quotation or paraphrase #2
- Transition to the next paragraph
Equally, the point of body paragraphs is to build the argument. Hence, present the weakest support first and end with the strongest. Admittedly, doing so leaves the reader with the best possible evidence.
Conclusion Paragraph
You’re almost there! Eventually, conclusion paragraphs should review the most important points in the paper. In them, you should prove that you’ve supported the argument proposed in the thesis. When writing a conclusion paragraph keep these tips in mind:
- Keep it simple
- Avoid introducing new information
- Review major points
- Discuss the relevance to today
Problems with writing Your History essay ? Try our Essay Writer Service!

Proofreading Your Essay
Once the draft is ready and polished, it’s time to proceed to final editing. What does this process imply? Specifically, it’s about removing impurities and making the essay look just perfect. Here’s what you need to do to improve the quality of your paper:
- Double check the content. In the first place, it’s recommended to get rid of long sentences, correct vague words. Also, make sure that all your paragrahps contain accurate sentences with transparent meaning.
- Pay attention to style. To make the process of digesting your essay easier, focus on crafting a paper with readable style, the one that is known to readers. Above all, the main mission here is to facilitate the perception of your essay. So, don’t forget about style accuracy.
- Practice reading the essay. Of course, the best practice before passing the paper is to read it out loud. Hence, this exercise will help you notice fragments that require rewriting or a complete removal.
History Essay Example
Did you want a history essay example? Take a look at one of our history essay papers.
Make it Shine
An A-level essay takes planning and revision, but it’s achievable. Firstly, avoid procrastination and start early. Secondly, leave yourself plenty of time to brainstorm, outline, research and write. Finally, follow these five tips to make your history essay shine:
- Write a substantial introduction. Particularly, it’s the first impression the professor will have of the paper.
- State a clear thesis. A strong thesis is easier to support.
- Incorporate evidence critically. If while researching you find opposing arguments, include them and discuss their flaws.
- Cite all the research. Whether direct quotations or paraphrases, citing evidence is crucial to avoiding plagiarism, which can have serious academic consequences.
- Include primary and secondary resources. While primary resources may be harder to find, the professor will expect them—this is, after all, a history essay.
History Essay Sample
Ready to tackle the history essay format? Great! Check out this history essay sample from an upper-level history class. While the essay isn’t perfect, the professor points out its many strengths.
Remember: start early and revise, revise, revise . We can’t revise history, but you can revise your ideas until they’re perfect.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
College of Arts and Sciences
History and American Studies
- What courses will I take as an History major?
- What can I do with my History degree?
- History 485
- History Resources
- What will I learn from my American Studies major?
- What courses will I take as an American Studies major?
- What can I do with my American Studies degree?
- American Studies 485
- For Prospective Students
- Student Research Grants
- Honors and Award Recipients
- Phi Alpha Theta
Alumni Intros
- Internships
Introduction and Conclusion
INTRODUCTIONS The introduction of a paper must introduce its thesis and not just its topic. Readers will lose some—if not much—of what the paper says if the introduction does not prepare them for what is coming (and tell them what to look for and how to evaluate it).
For example, an introduction that says, “The British army fought in the battle of Saratoga” gives the reader virtually no guidance about the paper’s thesis (i.e., what the paper concludes/argues about the British army at Saratoga).
History papers are not mystery novels. Historians WANT and NEED to give away the ending immediately. Their conclusions—presented in the introduction—help the reader better follow/understand their ideas and interpretations.
In other words, an introduction is a MAP that lays out “the trip the author is going to take [readers] on” and thus “lets readers connect any part of the argument with the overall structure. Readers with such a map seldom get confused or lost.”1
Introductions do four things:
attract the ATTENTION of the reader convince the reader that he/she NEEDS TO READ what the author has to say define the paper’s SPECIFIC TOPIC state and explain the paper’s THESIS Writing the introduction: Consider writing the introduction AFTER finishing your paper. By then, you will know what your paper says. You will have thought it through and provided arguments and supporting evidence; therefore, you will know what the reader needs to know—in brief form—in the introduction. (Always think of your initial introduction as “getting started” and as something that “won’t count.” It is for your eyes only; discard it when you know exactly what your paper says.) A common technique is to turn your conclusion into an introduction. It usually reflects what is in the paper—topic, thesis, arguments, evidence—and can be easily adjusted to be a clear and useful introduction.
Some types of introductions:
Quotation Historical overview (provides introduction to topic AND background so that fewer explanations are needed later in paper) Review of literature or a controversy Statistics or startling evidence Anecdote or illustration Question From general to specific OR specific to general Avoid:
“The purpose of this paper is . . .” OR “This paper is about . . . .” First person (e.g., “I will argue that”) Too many questions Dictionary definitions Length: There is no rule other than to be logical. Short papers require short introductions (e.g., a short paragraph); longer ones may require a page or more to provide all that a reader needs. Longer papers require ELABORATION of the thesis; a sentence is not sufficient to prepare the reader for the many pages of arguments and evidence that follow.
CONCLUSIONS Conclusions are the last thing that readers read; they define readers’ final impression of a paper. A flat, boring conclusion means a flat, boring (or, at least, disappointing) paper.
Conclusions should be a climax, not an anti-climax. They do not just restate what has already been said; they interpret, speculate, and provoke thinking.
Some types of conclusions:
Statement of subject’s significance Call for further research Recommendation or speculation Comparison of part to present Anecdote Quotation Questions (with or without answers) Avoid:
“In conclusion”; “finally”; “thus” Additional or new ideas that introduce a new paper First person Length: Again, there is no rule, although too short conclusions should definitely be avoided. Short conclusions leave the reader on the edge of a cliff with no directions on how to get down.
You are the expert – help your reader pull together and appreciate what he/she has read.
____________________________ 1Howard Becker, Writing for Social Scientists (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1986).

How have History & American Studies majors built careers after earning their degrees? Learn more by clicking the image above.
Recent Posts
- History and American Studies Symposium–April 26, 2024
- Fall 2024 Courses
- Fall 2023 Symposium – 12/8 – All Welcome!
- Spring ’24 Course Flyers
- Internship Opportunity – Chesapeake Gateways Ambassador
- Congratulations to our Graduates!
- History and American Studies Symposium–April 21, 2023
- View umwhistory’s profile on Facebook
- View umwhistory’s profile on Twitter
How to Write a Good History Essay. A Sequence of Actions and Useful Tips
/rating_on.png)
Before you start writing your history essay, there is quite a lot of work that has to be done in order to gain success.
You may ask: what is history essay? What is the difference between it and other kinds of essays? Well, the main goal of a history essay is to measure your progress in learning history and test your range of skills (such as analysis, logic, planning, research, and writing), it is necessary to prepare yourself very well.
Your plan of action may look like this. First of all, you will have to explore the topic. If you are going to write about a certain historical event, think of its causes and premises, and analyze what its impact on history was. In case you are writing about a person, find out why and how he or she came to power and how they influenced society and historical situations.
The next step is to make research and collect all the available information about the person or event, and also find evidence.
Finally, you will have to compose a well-organized response.
During the research, make notes and excerpts of the most notable data, write out the important dates and personalities. And of course, write down all your thoughts and findings.
It all may seem complicated at first sight, but in fact, it is not so scary! To complete this task successfully and compose a good history essay, simply follow several easy steps provided below.
Detailed Writing Instruction for Students to Follow
If you want to successfully complete your essay, it would be better to organize the writing process. You will complete the assignment faster and more efficient if you divide the whole work into several sections or steps.
- Introduction
Writing a good and strong introduction part is important because this is the first thing your reader will see. It gives the first impression of your essay and induces people to reading (or not reading) it.
To make the introduction catchy and interesting, express the contention and address the main question of the essay. Be confident and clear as this is the moment when you define the direction your whole essay will take. And remember that introduction is not the right place for rambling! The best of all is, to begin with, a brief context summary, then go to addressing the question and express the content. Finally, mark the direction your essay about history will take.
Its quality depends on how clear you divided the whole essay into sections in the previous part. As long as you have provided a readable and understandable scheme, your readers will know exactly what to expect.
The body of your essay must give a clear vision of what question you are considering. In this section, you can develop your idea and support it with the evidence you have found. Use certain facts and quotations for that. When being judicial and analytical, they will help you to easily support your point of view and argument.
As long as your essay has a limited size, don’t be too precise. It is allowed to summarize the most essential background information, for example, instead of giving a precise list of all the issues that matter.
It is also good to keep in mind that each paragraph of your essay’s body must tell about only one issue. Don’t make a mess out of your paper!
It is not only essential to start your essay well. How you will end it also matters. A properly-written conclusion is the one that restates the whole paper’s content and gives a logical completion of the issue or question discussed above. Your conclusion must leave to chance for further discussion or arguments on the case. It’s time, to sum up, give a verdict.
That is why it is strongly forbidden to provide any new evidence or information here, as well as start a new discussion, etc.
After you finish writing, give yourself some time and put the paper away for a while. When you turn back to it will be easier to take a fresh look at it and find any mistakes or things to improve. Of course, remember to proofread your writing and check it for any grammar, spelling and punctuation errors. All these tips will help you to learn how to write a history essay.

History Essay Examples

Top History Essay Examples To Get Inspired By
Published on: May 4, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 31, 2024

Share this article
History essays are a crucial component of many academic programs, helping students to develop their critical thinking, research, and writing skills.
However, writing a great history essay is not always easy, especially when you are struggling to find the right approach. This is where history essay examples come in handy.
By reading and examining samples of successful history essays, you can gain inspiration, learn new ways to approach your topic. Moreover, you can develop a better understanding of what makes a great history essay.
In this blog, you will find a range of history essay examples that showcase the best practices in history essay writing.
Read on to find useful examples.
On This Page On This Page -->
Sample History Essays
Explore our collection of excellent history paper examples about various topics. Download the pdf examples for free and read to get inspiration for your own essay.
History Essay Samples for Middle School
The Impact of Ancient Civilizations on Modern Society
The Rise and Fall of the Roman Empire
The Causes and Consequences of the American Revolution
History Writing Samples for High School Students
The Impact of the Industrial Revolution on Society
Grade 10 History Essay Example: World War 1 Causes and Effects
Grade 12 History Essay Example: The Impact of Technology on World War II
Ancient History Essay Examples
The Societal and Political Structures of the Maya Civilization
The Role of Phoenicians in the Development of Ancient Mediterranean World
The Contributions of the Indus Civilization
Medieval History Essay Examples
The Crusades Motivations and Consequences
The Beginning of Islamic Golden Age
The Black Death
Modern History Essay Examples
The Suez Crisis and the End of British Dominance
The Rise of China as an Economic Powerhouse
World History Essay Examples
The Role of the Silk Road in Shaping Global Trade and Culture
The Rise and Fall of the Ottoman Empire
The Legacy of Ancient Greek Philosophy and Thought

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
American History Essay Examples
The Civil Rights Movement and its Impact on American Society
The American Civil War and its Aftermath
The Role of Women in American Society Throughout History
African History Essay Examples
The Impact of Colonialism on African Societies
The Rise and Fall of the Mali Empire
European History Essay Examples
The Protestant Reformation and the Rise of Protestantism in Europe
The French Revolution and its Impact on European Politics and Society
The Cold War and the Division of Europe
Argumentative History Essay Examples
Was the US Civil War Primarily About Slavery or States
The Effects of British Colonization on Colonies
Art History Essay Examples
The Influence of Greek and Roman Art on Neoclassicism
The Depiction of Women in Art Throughout History
The Role of Art in the Propaganda of Fascist Regimes
How to Use History Essay Examples
History essay examples are a valuable tool for students looking for inspiration and guidance on how to approach their own essays.
By analyzing successful essays, you can learn effective writing techniques that can be expected in a high-quality history essay.
Here are some tips that will help you take full advantage of the samples above.
Tips for Effectively Using History Essay Examples
- Analyze the Structure:
Pay close attention to how the essay is organized, including the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Look for how the author transitions between paragraphs and the use of evidence to support their argument.
- Study the Thesis Statement:
The thesis statement is the backbone of any successful history essay. Analyze how the author crafted their thesis statement, and consider how you can apply this to your own writing.
- Take Note of the Evidence:
Effective history essays rely on using strong evidence to support their arguments. Take note of the sources and types of evidence used in the essay. Consider how you can apply similar evidence to support your own arguments.
- Pay Attention to the Formatting and Other Academic Formalities:
The sample essays also demonstrate how you can incorporate academic formalities and standards while keeping the essay engaging. See how these essays fulfill academic standards and try to follow them in your own writing.
- Practice Writing:
While analyzing history essay examples can be helpful, it is important to also practice writing your own essays. Use the examples as inspiration, but try to craft your own unique approach to your topic.
History essays are an essential aspect of learning and understanding the past. By using history essay examples, students can gain inspiration on how to develop their history essays effectively.
Furthermore, following the tips outlined in this blog, students can effectively analyze these essay samples and learn from them.
However, writing a history essay can still be challenging.
Looking for an online essay writing service that specializes in history essays? Look no further!
Our history essay writing service is your go-to source for well-researched and expertly crafted papers.
And for an extra edge in your academic journey, explore our AI essay writing tool . Make history with your grades by choosing our online essay writing service and harnessing the potential of our AI essay writing tool.
Get started today!
Cathy A. (Law, Marketing)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
I Thought the Bragg Case Against Trump Was a Legal Embarrassment. Now I Think It’s a Historic Mistake.

By Jed Handelsman Shugerman
Mr. Shugerman is a law professor at Boston University.
About a year ago, when Alvin Bragg, the Manhattan district attorney, indicted former President Donald Trump, I was critical of the case and called it an embarrassment. I thought an array of legal problems would and should lead to long delays in federal courts.
After listening to Monday’s opening statement by prosecutors, I still think the district attorney has made a historic mistake. Their vague allegation about “a criminal scheme to corrupt the 2016 presidential election” has me more concerned than ever about their unprecedented use of state law and their persistent avoidance of specifying an election crime or a valid theory of fraud.
To recap: Mr. Trump is accused in the case of falsifying business records. Those are misdemeanor charges. To elevate it to a criminal case, Mr. Bragg and his team have pointed to potential violations of federal election law and state tax fraud. They also cite state election law, but state statutory definitions of “public office” seem to limit those statutes to state and local races.
Both the misdemeanor and felony charges require that the defendant made the false record with “intent to defraud.” A year ago, I wondered how entirely internal business records (the daily ledger, pay stubs and invoices) could be the basis of any fraud if they are not shared with anyone outside the business. I suggested that the real fraud was Mr. Trump’s filing an (allegedly) false report to the Federal Election Commission, and that only federal prosecutors had jurisdiction over that filing.
A recent conversation with Jeffrey Cohen, a friend, Boston College law professor and former prosecutor, made me think that the case could turn out to be more legitimate than I had originally thought. The reason has to do with those allegedly falsified business records: Most of them were entered in early 2017, generally before Mr. Trump filed his Federal Election Commission report that summer. Mr. Trump may have foreseen an investigation into his campaign, leading to its financial records. He may have falsely recorded these internal records before the F.E.C. filing as consciously part of the same fraud: to create a consistent paper trail and to hide intent to violate federal election laws, or defraud the F.E.C.
In short: It’s not the crime; it’s the cover-up.
Looking at the case in this way might address concerns about state jurisdiction. In this scenario, Mr. Trump arguably intended to deceive state investigators, too. State investigators could find these inconsistencies and alert federal agencies. Prosecutors could argue that New York State agencies have an interest in detecting conspiracies to defraud federal entities; they might also have a plausible answer to significant questions about whether New York State has jurisdiction or whether this stretch of a state business filing law is pre-empted by federal law.
However, this explanation is a novel interpretation with many significant legal problems. And none of the Manhattan district attorney’s filings or today’s opening statement even hint at this approach.
Instead of a theory of defrauding state regulators, Mr. Bragg has adopted a weak theory of “election interference,” and Justice Juan Merchan described the case , in his summary of it during jury selection, as an allegation of falsifying business records “to conceal an agreement with others to unlawfully influence the 2016 election.”
As a reality check: It is legal for a candidate to pay for a nondisclosure agreement. Hush money is unseemly, but it is legal. The election law scholar Richard Hasen rightly observed , “Calling it election interference actually cheapens the term and undermines the deadly serious charges in the real election interference cases.”
In Monday’s opening argument, the prosecutor Matthew Colangelo still evaded specifics about what was illegal about influencing an election, but then he claimed , “It was election fraud, pure and simple.” None of the relevant state or federal statutes refer to filing violations as fraud. Calling it “election fraud” is a legal and strategic mistake, exaggerating the case and setting up the jury with high expectations that the prosecutors cannot meet.
The most accurate description of this criminal case is a federal campaign finance filing violation. Without a federal violation (which the state election statute is tethered to), Mr. Bragg cannot upgrade the misdemeanor counts into felonies. Moreover, it is unclear how this case would even fulfill the misdemeanor requirement of “intent to defraud” without the federal crime.
In stretching jurisdiction and trying a federal crime in state court, the Manhattan district attorney is now pushing untested legal interpretations and applications. I see three red flags raising concerns about selective prosecution upon appeal.
First, I could find no previous case of any state prosecutor relying on the Federal Election Campaign Act either as a direct crime or a predicate crime. Whether state prosecutors have avoided doing so as a matter of law, norms or lack of expertise, this novel attempt is a sign of overreach.
Second, Mr. Trump’s lawyers argued that the New York statute requires that the predicate (underlying) crime must also be a New York crime, not a crime in another jurisdiction. The district attorney responded with judicial precedents only about other criminal statutes, not the statute in this case. In the end, the prosecutors could not cite a single judicial interpretation of this particular statute supporting their use of the statute (a plea deal and a single jury instruction do not count).
Third, no New York precedent has allowed an interpretation of defrauding the general public. Legal experts have noted that such a broad “election interference” theory is unprecedented, and a conviction based on it may not survive a state appeal.
Mr. Trump’s legal team also undercut itself for its decisions in the past year: His lawyers essentially put all of their eggs in the meritless basket of seeking to move the trial to federal court, instead of seeking a federal injunction to stop the trial entirely. If they had raised the issues of selective or vindictive prosecution and a mix of jurisdictional, pre-emption and constitutional claims, they could have delayed the trial past Election Day, even if they lost at each federal stage.
Another reason a federal crime has wound up in state court is that President Biden’s Justice Department bent over backward not to reopen this valid case or appoint a special counsel. Mr. Trump has tried to blame Mr. Biden for this prosecution as the real “election interference.” The Biden administration’s extra restraint belies this allegation and deserves more credit.
Eight years after the alleged crime itself, it is reasonable to ask if this is more about Manhattan politics than New York law. This case should serve as a cautionary tale about broader prosecutorial abuses in America — and promote bipartisan reforms of our partisan prosecutorial system.
Nevertheless, prosecutors should have some latitude to develop their case during trial, and maybe they will be more careful and precise about the underlying crime, fraud and the jurisdictional questions. Mr. Trump has received sufficient notice of the charges, and he can raise his arguments on appeal. One important principle of “ our Federalism ,” in the Supreme Court’s terms, is abstention , that federal courts should generally allow state trials to proceed first and wait to hear challenges later.
This case is still an embarrassment, in terms of prosecutorial ethics and apparent selectivity. Nevertheless, each side should have its day in court. If convicted, Mr. Trump can fight many other days — and perhaps win — in appellate courts. But if Monday’s opening is a preview of exaggerated allegations, imprecise legal theories and persistently unaddressed problems, the prosecutors might not win a conviction at all.
Jed Handelsman Shugerman (@jedshug) is a law professor at Boston University.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
A Columbia professor wanted to document history. NYPD arrested him outside his home
Gregory Pflugfelder had just finished the final class of his career at Columbia. In 28 years at the university, he achieved many accolades as a professor of history who taught a popular course on Japanese monsters – mostly focused on Godzilla and "the role of the monstrous in the cultural imagination."
He didn't know it, but a cultural monster of sorts would soon be at his door.
The next night, on Tuesday, the 64-year-old silver-haired scholar stepped outside his apartment building, located off campus across the street from Columbia. He wanted to record iPhone video of hundreds of police responding to historic student protests against Israel’s war in Gaza . Fifteen minutes later, the NYPD arrested him.
The New York Police Department listed Pflugfelder among 112 arrests made at Columbia on Tuesday night , according to police records obtained by USA TODAY. But Pflugfelder was never on campus.
“I certainly posed no danger to anybody,” he told USA TODAY. “I was literally standing in the street and not blocking anybody.”
As protests and opposition to the war in Gaza has swept across U.S. campuses, universities and police have increasingly pointed to "outside agitators" and off-campus disruptors as the insurgents behind the campus unrest. Pflugfelder's arrest – on a charge of obstructing government administration – is among the first of 282 people put in custody at or near Columbia and City College of New York during police raids. The arrests have raised claims of heavy-handed police tactics to suppress largely peaceful demonstrations against the Israel-Hamas war.
Columbia University referred questions about the professor’s arrest to NYPD. Neither NYPD nor New York Mayor Eric Adams’ office responded to email requests from USA TODAY.
Live updates: NYPD says officer fired gun on Columbia campus; NYU, New School protests cleared
'Historic mistake'
Pflugfelder's last class, Introduction to Japanese Civilization, is a course he taught since he started teaching at Columbia in 1996. He's only taught at the Ivy League school. His plan Tuesday was to do “absolutely nothing,” he recalled. This included reading and watching the Hulu show, "Shōgun."
In the afternoon, he heard protests nearby, around the corner from his apartment on West 114th Street. His apartment building is located across the street from campus, where demonstrators gathered for weeks and formed an encampment calling on the university to divest from Israel.
He knew about the heightened police response because of a prior protest at Columbia, on April 18, at which police arrested over 100 people at the encampment in the center of campus. Police buses blocked Pflugfelder's street to take protesters to NYPD headquarters.
He supported students right to demonstrate. He wrote a letter to Columbia President Minouche Shafik, who requested NYPD respond to the encampment on campus. It was his first time writing to the president’s office. “I urge you not to compound the historic mistake you've made by repeating it,” he wrote on April 23.
A week later, on Tuesday, he felt history would be made again, and he wanted to document it. He stepped out of his apartment building to record video on his iPhone.
By about 9 p.m., he estimated hundreds of police, donning helmets and batons, had formed lines on the street. He recorded students forced inside fraternity houses and dorm buildings, with video of them knocking on the windows. Then, he turned to look at the street, where officers formed lines ahead of their siege on campus.
At most, he said, he stood 7 feet onto the street from the curb. Police ordered him inside, but he told them his address was about 300 feet down the block. They told him to go home, but he said he wanted to continue recording. An officer said, “OK, put him down,” Pflugfelder recalled, though he was not forced to the ground. Nonetheless, he ended up cuffed in zip ties.
“I just stayed on my block, relatively well behaved,” he said. “Poorly located, unfortunately.”
He said he told the female police officer arresting him: “You’ve just arrested your first faculty member.” He said she responded, “This is for your protection.”
Police response to NYC schools showed 'precision policing,' Adams says
Mayor Adams has said police acted with professionalism in mass arrests on college campuses, which included police using a SWAT vehicle to enter Hamilton Hall, the occupied Columbia building.
"The NYPD's precision policing ensured that the operation was organized, calm, and that there were no injuries or violent clashes,” Adams told reporters on Wednesday, the day after the arrests.
But Jennvine Wong, supervising attorney at the nonprofit Legal Aid Society’s cop accountability project, said Pflugfelder's arrest raises questions about whether NYPD escalated rather than deescalated situations. It also may have violated laws protecting citizens’ right to record police interactions.
“Generally speaking, there is still a First Amendment right to record in public as long as they’re not interfering with police,” Wong told USA TODAY. “To me, this sounds like a devious arrest.”
War in Gaza: Biden to meet with King of Jordan as US, Israel go 'back and forth' over Rafah invasion
By Pflugfelder’s account, he was the third arrested person to enter an NYPD van. Ten people would fill the van that took him downtown. At 6-foot-5-inches, Pflugfelder said he felt cramped. He also has “claustrophobic tendencies,” and during the ride, he asked others to help him take his mind off his feelings, so they asked about his classes. He gathered during the ride that most people inside were Columbia students, based on the questions they asked.
At NYPD headquarters, he was in a holding cell with about 60 other men. He stayed there for about five hours. One person next to him on the bench said he was from Columbia and had been at Hamilton Hall, the occupied school building police raided using flash-bang grenades, and where police errantly fired a gunshot indoors. The man Pflugfelder saw was visibly bruised, including a black eye.
“The violence against protesters was extreme,” said Corinna Mullin, an adjunct assistant professor of political science at John Jay College of Criminal Justice, part of CUNY, at a recent news conference. Mullin was among those arrested Tuesday night at City College.
Conclusions drawn, then data collected
Police released Pflugfelder from custody at about 5 a.m. with a ticket to appear in Manhattan Criminal Court on May 20. He called an Uber and went home, though since has found it hard to rest. He’s hasn't yet communicated with university administration. He’s not looking forward to it.
“I would not put myself in a vulnerable situation vis-a-vis an institution that has assaulted me,” he said.
Irene Mulvey, the president of the American Association of University Professors, said the group has several firsthand, eyewitness accounts of what she called unnecessarily violent and disproportionate responses to what started as peaceful protests.
Information released by police, including on the number of “outside agitators,” has not answered important questions about the rationale to send police to college campuses, including at Columbia, said Mulvey, a mathematician and professor emeritus at Fairfield University, in Connecticut. A central reason police responded to Columbia was people from outside who indoctrinated students with training and ideology, though officials have disclosed little evidence to date.
“Scientists, we would collect data and draw conclusions,” she told USA TODAY. “In this case, it seems a conclusion was drawn, and then data was collected, which may or may not justify it.”
Pflugfelder has yet to have the relaxing day he’s sought after nearly three decades of teaching. In jail, police made him remove the shoelaces of his black and white Vessi sneakers. He’s kept them unlaced since then, as a reminder.
Contributing: Mike James, USA TODAY

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Restate your key points. In one or two sentences, restate each of the topic sentences from your body paragraphs. This is to remind the marker about how you proved your argument. This information will be similar to your elaboration sentences in your introduction, but will be much briefer. Since this is a summary of your entire essay's ...
Some papers emphasize social or cultural history, others political or military history, and still others intellectual or economic (or any other genre of) history. In undergraduate courses, you'll most likely notice a distinc-tion between review essays (often based on your responses to assigned readings from the course syllabus) and research ...
Writing a history essay. An essay is a piece of sustained writing in response to a question, topic or issue. Essays are commonly used for assessing and evaluating student progress in history. History essays test a range of skills including historical understanding, interpretation and analysis, planning, research and writing.
Introductions & Conclusions. The introduction and conclusion serve important roles in a history paper. They are not simply perfunctory additions in academic writing, but are critical to your task of making a persuasive argument. A successful introduction will: draw your readers in. culminate in a thesis statement that clearly states your argument.
Step 1: Return to your thesis. To begin your conclusion, signal that the essay is coming to an end by returning to your overall argument. Don't just repeat your thesis statement —instead, try to rephrase your argument in a way that shows how it has been developed since the introduction. Example: Returning to the thesis.
Historical essay writing is based upon the thesis. A thesis is a statement, an argument which will be presented by the writer. The thesis is in effect, your position, your particular interpretation, your way of seeing a problem. Resist the temptation, which many students have, to think of a thesis as simply "restating" an instructor's question.
this, history essays are more than narrative accounts of the past. The purpose of a history essay is to communicate useful conclusions about past events in a purposeful and persuasive manner. History essays that are mere narratives of historical events without being analytical are, therefore, of limited value. Analytical essays are also called
Paragraph goes nowhere/has no point or unity. Paragraphs are the building blocks of your paper. If your paragraphs are weak, your paper cannot be strong. Try underlining the topic sentence of every paragraph. If your topic sentences are vague, strength and precision—the hallmarks of good writing—are unlikely to follow.
history. in undergraduate courses, you'll most likely notice a distinction between review essays (often based on your responses to assigned readings from the course syllabus) and research papers (typically requiring additional research in a library or archive on a topic of your own choosing). Different types of history papers naturally
Step 1: Understand the History Paper Format. You may be assigned one of several types of history papers. The most common are persuasive essays and research papers. History professors might also ask you to write an analytical paper focused on a particular source or an essay that reviews secondary sources.
5 Tips on Writing a Chronological Essay. 5.1 Pick an Idea and Make a Plan. 5.2 Use a Variety of Sentence Structures to Keep Your Writing Interesting. 5.3 Provide Sufficient Details. 5.4 Use Transitional Words and Phrases, Such As "First," "Next," and "Then," to Indicate the Chronological Flow. 5.5 Use Headings and Subheadings to ...
Download Article. 1. Have a clear structure. When you come to write the body of the essay it is important that you have a clear structure to your argument and to your prose. If your essay drifts, loses focus, or becomes a narrative of events then you will find your grade dropping.
Relevance. Witnesses in court promise to tell the truth, the whole truth and nothing but the truth. All history students should swear a similar oath: to answer the question, the whole question and nothing but the question. This is the number one rule. You can write brilliantly and argue a case with a wealth of convincing evidence, but if you ...
A historical essay is a short piece of writing that answers a question or addresses a topic. It shows a student's historical knowledge and ability to express themselves. The conclusion is a final summary that explains why the topic is significant. A well-written conclusion ends a historical essay on a strong note.
Finally, some advice on how not to end an essay: Don't simply summarize your essay. A brief summary of your argument may be useful, especially if your essay is long--more than ten pages or so. But shorter essays tend not to require a restatement of your main ideas. Avoid phrases like "in conclusion," "to conclude," "in summary," and "to sum up ...
Make it Shine. An A-level essay takes planning and revision, but it's achievable. Firstly, avoid procrastination and start early. Secondly, leave yourself plenty of time to brainstorm, outline, research and write. Finally, follow these five tips to make your history essay shine: Write a substantial introduction.
History papers are not mystery novels. Historians WANT and NEED to give away the ending immediately. Their conclusions—presented in the introduction—help the reader better follow/understand their ideas and interpretations. ... Short papers require short introductions (e.g., a short paragraph); longer ones may require a page or more to ...
Writing a history essay requires a lot of work and experience. A student needs to show a high level of knowledge and understanding of historical events, as well analytical and research skills. No wonder many students find it challenging to compose a well-written essay! To achieve success, use the following tips to level-up your writing abilities
The long essay question on the AP U.S. History exam is designed to test your ability to apply knowledge of history in a complex, analytic manner. ... historiography—the skills and strategies historians use to analyze and interpret historical evidence to reach a conclusion. Thus, when writing an effective essay, you must be able to write a ...
Tips for Effectively Using History Essay Examples. Analyze the Structure: Pay close attention to how the essay is organized, including the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Look for how the author transitions between paragraphs and the use of evidence to support their argument. Study the Thesis Statement:
She Wrote 'The History of White People.' She Has a Lot More to Say. "I Just Keep Talking," a collection of essays and artwork by the historian Nell Irvin Painter, captures her wide-ranging ...
Mr. Shugerman is a law professor at Boston University. About a year ago, when Alvin Bragg, the Manhattan district attorney, indicted former President Donald Trump, I was critical of the case and ...
Conclusions drawn, then data collected Police released Pflugfelder from custody at about 5 a.m. with a ticket to appear in Manhattan Criminal Court on May 20. He called an Uber and went home ...
University dean fears '99.9 per cent' of his students are using AI to write essays Professor Laurent Muzellec, Dean of Trinity Business School at Trinity College Dublin, said the technology is ...