- Utility Menu
- ARC Scheduler
- Student Employment
- Senior Theses
Doing a senior thesis is an exciting enterprise. It’s often the first time students are engaging in truly original research and trying to develop a significant contribution to a field of inquiry. But as joyful as an independent research process can be, you don’t have to go it alone. It’s important to have support as you navigate such a large endeavor, and the ARC is here to offer one of those layers of support.
Whether or not to write a senior thesis is just the first in a long line of questions thesis writers need to consider. In addition to questions about the topic and scope of your thesis, there are questions about timing, schedule, and support. For example, if you are collecting data, when should data collection start and when should it be completed? What kind of schedule will you write on? How will you work with your adviser? Do you want to meet with your adviser about your progress once a month? Once a week? What other resources can you turn to for information, feedback, and support?
Even though there is a lot to think about and a lot to do, doing a thesis really can be an enjoyable experience! Keep reminding yourself why you chose this topic and why you care about it.
Tips for Tackling Big Projects:

Break the process down into manageable chunks.
- When you’re approaching a big project, it can seem overwhelming to look at the whole thing at once, so it’s essential to identify the smaller steps that will move you towards the completed project.
- Your adviser is best suited to help you break down the thesis process with field-specific advice.
- If you need to refine the breakdown further so it makes sense for you, schedule an appointment with an Academic Coach . An academic coach can help you think through the steps in a way that works for you.
Schedule brief writing sessions at regular times.
- Pre-determine the time, place, and duration.
- Keep it short (15 to 60 minutes).
- Have a clear and reasonable goal for each writing session.
- Make it a regular event (every day, every other day, MWF).
- time is not wasted deciding to write if it’s already in your calendar;
- keeping sessions short reduces the competition from other tasks that are not getting done;
- having an achievable goal for each session provides a sense of accomplishment (a reward for your work);
- writing regularly can turn into a productive habit.
Create accountability structures.
- In addition to having a clear goal for each writing session, it's important to have clear goals for each week and to find someone to communicate these goals to, such as your adviser, a “thesis buddy,” your roommate, etc. Communicating your goals and progress to someone else creates a useful sense of accountability.
- If your adviser is not the person you are communicating your progress to on a weekly basis, then request to set up a structure with your adviser that requires you to check in at less frequent but regular intervals.
- Commit to attending Accountability Hours at the ARC on the same day every week. Making that commitment will add both social support and structure to your week. Use the ARC Scheduler to register for Accountability Hours.
- Set up an accountability group in your department or with thesis writers from different departments.
Create feedback structures.
- It’s important to have a means for getting consistent feedback on your work and to get that feedback early. Work on large projects often lacks the feeling of completeness, so don’t wait for a whole section (and certainly not the whole thesis) to feel “done” before you get feedback on it!
- Your thesis adviser is typically the person best positioned to give you feedback on your research and writing, so communicate with your adviser about how and how often you would like to get feedback.
- If your adviser isn’t able to give you feedback with the frequency you’d like, then fill in the gaps by creating a thesis writing group or exploring if there is already a writing group in your department or lab.
- The Harvard College Writing Center is a great resource for thesis feedback. Writing Center Senior Thesis Tutors can provide feedback on the structure, argument, and clarity of your writing and help with mapping out your writing plan. Visit the Writing Center website to schedule an appointment with a thesis tutor .
Accept that there will be some anxious moments.
- To reduce this source of anxiety, try keeping a separate document where you jot down ideas on how your research questions or central argument might be clarifying or changing as you research and write. Doing this will enable you to stay focused on the section you are working on and to stop worrying about forgetting the new ideas that are emerging.
- You might feel anxious when you realize that you need to update your argument in response to the evidence you have gathered or the new thinking your writing has unleashed. Know that that is OK. Research and writing are iterative processes – new ideas and new ways of thinking are what makes progress possible.
- Breaking down big projects into manageable chunks and mapping out a schedule for working through each chunk is one way to reduce this source of anxiety. It’s reassuring to know you are working towards the end even if you cannot quite see how it will turn out.
- It may be that your thesis or dissertation never truly feels “done” to you, but that’s okay. Academic inquiry is an ongoing endeavor.
Focus on what works for you.
- Just because your roommate wrote 10 pages in a day doesn’t mean that’s the right pace or strategy for you.
- If you are having trouble figuring out what works for you, use the ARC Scheduler to make an appointment with an Academic Coach , who can help you come up with daily, weekly, and semester-long plans.
Use your resources.
- There’s a lot of the thesis writing process that has to be done independently, but there are also a lot of free resources at Harvard to help you do the work.
- If you’re having trouble finding a source, email your question or set up a research consult via Ask a Librarian .
- If you’re looking for additional feedback or help with any aspect of writing, contact the Harvard College Writing Center . The Writing Center has Senior Thesis Tutors who will read drafts of your thesis (more typically, parts of your thesis) in advance and meet with you individually to talk about structure, argument, clear writing, and mapping out your writing plan.
- If you need help with breaking down your project or setting up a schedule for the week, the semester, or until the deadline, use the ARC Scheduler to make an appointment with an Academic Coach .
- If you would like an accountability structure for social support and to keep yourself on track, come to Accountability Hours at the ARC.
Accordion style
- Assessing Your Understanding
- Building Your Academic Support System
- Common Class Norms
- Effective Learning Practices
- First-Year Students
- How to Prepare for Class
- Interacting with Instructors
- Know and Honor Your Priorities
- Memory and Attention
- Minimizing Zoom Fatigue
- Note-taking
- Office Hours
- Perfectionism
- Scheduling Time
- Study Groups
- Tackling STEM Courses
- Test Anxiety
Important Addresses
Harvard College
University Hall Cambridge, MA 02138
Harvard College Admissions Office and Griffin Financial Aid Office
86 Brattle Street Cambridge, MA 02138
Social Links
If you are located in the European Union, Iceland, Liechtenstein or Norway (the “European Economic Area”), please click here for additional information about ways that certain Harvard University Schools, Centers, units and controlled entities, including this one, may collect, use, and share information about you.
- Application Tips
- Navigating Campus
- Preparing for College
- How to Complete the FAFSA
- What to Expect After You Apply
- View All Guides
- Parents & Families
- School Counselors
- Información en Español
- Undergraduate Viewbook
- View All Resources
Search and Useful Links
Search the site, search suggestions, alert: harvard yard closed to the public.
Please note, Harvard Yard gates are currently closed. Entry will be permitted to those with a Harvard ID only.
Last Updated: May 03, 11:02am
Open Alert: Harvard Yard Closed to the Public
Preparing for a senior thesis.

Every year, a little over half of Harvard’s senior class chooses to pursue a senior thesis. While the senior thesis looks a little different from field to field, one thing remains the same: completion of a senior thesis is a serious and challenging endeavor that requires the student to make a genuine intellectual contribution to their field of interest.
The senior thesis is a significant task for students to undertake, but there is a variety of support resources available here at Harvard to ensure that seniors can make the best of their senior thesis experience.

Wandering the library stacks at Widener.
I do most of my research in Widener Library. Hannah Martinez
As a rising senior in the History department, I am planning on pursuing a senior thesis on the history and use of the SAT in college admissions, and I am using the following support systems and resources to research and write my thesis:
- Staff at the History department. Every student within the department is assigned an academic advisor, who is a graduate student studying History at Harvard and knows the support available within the department. My academic advisor has helped me throughout the thesis process by connecting me with potential faculty members to advise my thesis and pick classes with a lighter course load so I can focus on completing my thesis. The Director of Undergraduate Studies in History (the History DUS) has also been pivotal in making sure that I attended a lot of information sessions about what the thesis looks like and how much of a commitment it is.
- History faculty at Harvard! All of my professors in History have been incredibly helpful in teaching me how to write like a historian, how to use primary sources in my essays, and how to undertake a serious research project over the course of a semester. Of course, while the thesis will require me to go far beyond what I’ve ever done before, I feel prepared to take on such a task because of the unwavering support from the History faculty. My mentor, Emma Rothschild, is one of the members of the faculty who has been invaluable in encouraging me to go as far as I am able.
- And last but certainly not least: funding. Funding, whether in term-time of the summer before senior year, is crucial towards making the senior thesis possible. Harvard’s Office of Undergraduate Research and Fellowships is dedicated to connecting Harvard students to funding sources across the university so they can pursue their research and get paid for it. This summer, I received a grant from the university of almost $2,000 so I am able to travel to libraries, buy books, and potentially take time off of work and do my research. Without such a grant, it would be incredibly difficult for me to do enough research so I can write a thesis this upcoming fall.
As you can see, there are multiple avenues for support and resources here at Harvard so your senior thesis is as easy as possible. While the senior thesis is still a challenging project that will take up a lot of time, Harvard’s resources make it possible for senior students to do their very best in all of their theses. I’m excited to start writing this fall!
Hannah Class of '23 Alumni
Hello! My name is Hannah, and I am a rising senior at Harvard concentrating in History from southeast Los Angeles County.

Student Voices
How the mellon mays undergraduate fellowship propelled my love of archives into academic aspirations.

Beginning my senior thesis: A personal commitment to community and justice
Amy Class of '23 Alumni
Exploring Research at Harvard: Social Studies Edition
Olga Class of '22 Alumni

Yale College Undergraduate Admissions
- A Liberal Arts Education
- Majors & Academic Programs
- Teaching & Advising
- Undergraduate Research
- International Experiences
- Science & Engineering Faculty Features
- Residential Colleges
- Extracurriculars
- Identity, Culture, Faith
- Multicultural Open House
- Virtual Tour
- Bulldogs' Blogs
- First-Year Applicants
- International First-Year Applicants
- QuestBridge First-Year Applicants
- Military Veteran Applicants
- Transfer Applicants
- Eli Whitney: Nontraditional Applicants
- Non-Degree & Alumni Auditing Applicants
- What Yale Looks For
- Putting Together Your Application
- Selecting High School Courses
- Application FAQs
- First-Generation College Students
- Rural and Small Town Students
- Choosing Where to Apply
- Inside the Yale Admissions Office Podcast
- Visit Campus
- Virtual Events
- Connect With Yale Admissions
- The Details
- Estimate Your Cost
- QuestBridge
Search form
Where do i start: how to prepare for your senior thesis.

All majors here at Yale require the completion of a senior requirement in order to graduate. For some seniors, that may mean completing a project or taking a written or oral exam. For others, like myself, that means writing a semester or year-long thesis about a topic relating to your major of study. According to the Handbook for Directors of Undergraduate Studies in Yale College, “the senior requirement measures whether the student can demonstrate some form of mastering or substantial competence in some significant aspect of the subject of the major.” In other words, this requirement exists to show the knowledge and expertise you have developed through your time here at Yale. So, where do you begin?

One of the first things to complete on your “Senior Thesis To-Do List” is finding an advisor. Having an advisor who you are not only comfortable with but who also has experience in the topic you’re interested in is incredibly important. You’ll be spending a lot of time with your advisor and ideally, you want someone who will both push you in exploring your interests and be able to guide you on how best to approach a long thesis paper.

Once you have found an advisor, you should start narrowing down your thesis idea. Do not worry if you don’t have a specific thesis topic right off the bat. I surely didn’t and I’m glad I was able to have the opportunity to talk about topics at length with my advisor before we made a final decision. Begin BIG and then slowly start finding ways to make your thesis specific. My advisor and I had several meetings where we discussed the big topics I was interested in - gender, health, political science - and the various routes my paper could go in depending on the specific question I came up with. You want to find a topic that you are generally interested or passionate about, so take your time and explore.

After deciding on the specific thesis topic that you’ll be tackling in your paper, it’s time to begin your research and prep for the writing process. Writing a senior essay is a very daunting task. For my major - political science - the senior paper needs to be 25 pages minimum. This paper has the potential of being the longest paper you’ll write during your entire Yale undergraduate career and so, preparation is necessary.
A great resource offered by Yale to undergrads writing their thesis (or any other type of paper) are library consultations, which you can schedule through the Yale Library Homepage. I recently had a consultation with a librarian in the social studies library and it was such a great experience. We spent about an hour and half talking about my thesis, sections I was possibly thinking about including in my essay and then explored the various databases I could use to find sources.
Tackling the senior thesis is all about patience and time management. It is going to be a long process, whether you’re writing it in one semester or taking the whole academic year. If you don’t pace yourself, it can soon feel overwhelming. So, ease yourself into the research process and take advantage of the resources your advisor and Yale can offer you.
More Posts by Paulina

Thank You and Goodbye: My Final Blog Post

I Transferred to Yale and Here's My Biggest Takeaway (The Final Version)
How to Tackle the Yale Transfer Application

Magical Moments in Mystic - Let’s Go Explore Connecticut!

Untraditional Classroom: Taking a Class at the Yale University Art Gallery

Toad-ally Musical: Concerts and Memories at Toad’s

Ticking Clock: Entering my Final Semester at Yale

Transfer Roundtable: “The End” - An Open Conversation with Yale Transfer Students

With Love, From Oxford - Photo Essay


Senior Thesis in Comparative Literature and Society
Senior Thesis in Medical Humanities
A vademecum
General Information
The Senior Thesis in Comparative Literature and Society and the Senior Thesis in Medical Humanities give students the opportunity to deepen and refine their interest in a particular subject, establish a sustained intellectual relationship with a Columbia or Barnard Faculty member, and be considered for ICLS Departmental Honors.
Students are advised to start thinking about their thesis, including possible topics and faculty members who might serve as Thesis Supervisors, in the Spring Semester of their junior year.
CLS and Medical Humanities majors are encouraged to consult with the DUS early in the process. The DUS can offer early advice on topic and Supervisor selection.
Note: Medical Humanities majors are also encouraged to consult with Professor Rishi Goyal ( [email protected] ), Director of Medical Humanities, for advice on the early steps of thesis construction. If you plan to use the Health Sciences Library, please see the slide show from this Fall 2022 orientation.
Students who decide to write a thesis will enroll in a year-long course (CPLS3995) starting in the Fall of their Senior Year. This year-long, 3-credit course (1.5 credits in Fall, 1.5 credits in Spring) will allow students to receive academic credits for their thesis, and to count the thesis towards completion of their major requirement when necessary (Requirement #10 of the CLS Course Chart).
The Thesis: What Is It?
The Senior Thesis is a piece of scholarly research, the model for which is an academic journal article. A translation or a piece of creative work, such as a piece of creative writing, can be submitted with the prior approval of the DUS, and must be accompanied by an explanatory introduction or foreword of no less than 5000 words in length.
The Senior Thesis must be between 11,000 and 15,000 words, in 12-point font, and double-spaced. The total page count includes the preface or introduction, the main body of the thesis, references and/or a bibliography, and appendices (when applicable). The following items (all of which are optional and are not required) do not count toward the total page number: Title page; Table of contents; List of charts, graphs, and illustrations.
The Thesis must be written in English unless the student has received permission to write in another language. The citational and bibliographical style will be decided in consultation with the Thesis Supervisor.
Who Can Be Your Thesis Supervisor?
Any Columbia and Barnard faculty member can serve as Thesis Supervisor. This is usually a person you have worked with previously or taken a class with, or who is an expert in your subject matter. You are encouraged to discuss with your DUS before finalizing your choice.
Why Write A Senior Thesis?
The Senior Thesis is the culmination of a student’s journey through the major. It presents a unique opportunity to utilize one’s skills in research, critical analysis, and sustained written argumentation while developing a topic of choice and, in the process, gain valuable scholarly expertise. Being completed in close collaboration with a Faculty member, the Senior Thesis provides an occasion to develop a close academic relationship with someone who is an expert in their field, and to experience the rewards and demands of academic research during this year-long process.
The Senior Thesis is the capstone of a student’s undergraduate studies, and represents valuable experience – and precious training – for those considering a graduate career in academia, as well as any other endeavor involving research and writing.
Thesis Proposal in Junior Year
Students interested in writing a senior thesis (or, in the case of Barnard students, students who have to write one) will submit a thesis proposal in the Spring semester of their junior year. The proposal should be short, no longer than 1 page single-spaced , and should include the name of your advisor. This early preliminary work on your thesis will help you prepare better for the challenge of writing it. The thesis proposal should ideally indicate your topic, justification, methodology, aims, questions that concern you, and a sketch of the overall argument. Your proposal should also include a tentative title. Of course, it is to be expected that all these might change over the course of your research and writing. For Spring 2024, thesis proposals for juniors are due on May 3. Contact Profs. Bugnevicius and Goyal to discuss your thesis idea or if you need help with finding an advisor.
On the Construction and Completion of the Thesis
1 How to Find and Shape a topic?
If you are still reading, you may indeed end up writing a Senior Thesis in ICLS! Let me now address you directly, (future) thesis writer.
First, how do you find a topic? Topics arise from curiosity, interest, love at first sight with a text or work of art, and the desire to explore and learn more about a particular issue or a complicated question. In the early steps of the process of identifying a topic, you should cast a wide net: What is it that you like to study? What are the areas, events, authors, exchanges, issues, or archives that have nourished your curiosity? How are they connected? In answering the last of these questions, you are beginning to shape your thesis comparatively . The way you decide to explore and organize the comparison will shape the structure of your work.
The topic for your thesis is often – but not necessarily – the result of your engagement with a particular question, theme, or set of works in a class you have taken. You have the option, in accordance with your Supervisor, to develop the Senior Thesis from a research paper you have already written.
After identifying the broader contours of your topic, your focus should shift to progressively scaling down and refining your topic so that a limited, manageable, yet clear and fruitful set of questions will guide your thesis. The nature of your revised frame of inquiry should remain comparative: How do texts, contexts, events, images, or social practices inform each other and amplify information when they are brought into shared frames of analysis? What might comparing, contrasting, or otherwise juxtaposing material allow us to see that we might not otherwise see when we read or interpret materials separately, or solely within their tradition, context, or medium?
Identifying your sources is crucial to defining your topic and to constructing an appropriate set of methodology(ies) for your thesis. Like other aspects of writing a senior thesis, deciding what kind of sources to use or what text/material to include or exclude is a process of refinement that will require time and that will invariably involve making a set of difficult choices. It is not possible, nor should one try, to write about everything at once!
Some helpful tips:
* Start locating and assembling the corpus of your thesis early, in terms of both primary sources (novels, art pieces, archival sources, etc.) and relevant secondary sources (scholarship).
* Continue to refine that corpus in conversation with your Supervisor while remaining attentive to your evolving interests and preoccupations, until the final core texts or authors become clear.
* Do not be afraid to change your mind, but at the same time bear in mind that this is just one serious piece of writing. There will be others.
* Because the thesis is limited in scope – and one of your first research experiences – it cannot encompass all of your interests. If you are dealing with a large quantity of material, in the very early stages of the process your attention should be directed to breaking down your interests (and the materials that will allow you to develop them) into smaller, more manageable chunks. Your thesis will grow out of this process of selection, execution, and imagination.
3) Research and early Writing: the Outline and a Preliminary Bibliography:
The goal of the Fall semester of your Senior year should be completing a good amount of research and reading. Do not wait for research to finish to start writing: research never finishes. To start and grow your work, take advantage of the structure of the Senior Seminar, which is aimed to encourage you to start writing early, even if that only means a few sentences, a paragraph, or a page. Make an outline and keep it up-to-date and useful. As you keep reading and narrowing the scope of your intervention, keep revising the outline and, in light of it, readjust the direction of your writing. Submit your abstract and writing to your Supervisor throughout the Fall semester, and by the time Spring comes, you will have a clear roadmap, as well as sufficient progress, to finish the thesis as thoroughly and carefully as it deserves, while preventing the April 15 th deadline from becoming a source of anxiety.
4) Funding your research You may apply through research funding through your college. Students in Columbia College see this page . Note the deadline is usually in the Fall term. Students in the College of General Studies may apply in either term, information can be found here . Consult these websites for application details and updated deadlines. Barnard College students can find funding resources here . *Note that this page also has additional funding resources for which CC and GS students may be eligible.
5) Coversheet details We do not have strict guidelines regarding the format of the coversheet but we ask that you include: the thesis title, the date, your name, the phrase “Senior Thesis in (your major) at the Institute for Comparative Literature and Society at Columbia University,” and your thesis advisor and their department.
Submission Deadline and Grading
The deadline for submitting the Senior Thesis is April 15 th .The Thesis will be submitted electronically to the DUS of ICLS and to the Thesis Supervisor. Medical Humanities majors will also submit, at the same time, to Professor Rishi Goyal, Director of Medical Humanities. The Thesis Supervisor is solely responsible for the final grade.
Submission Extension Policy
Short extensions of the submission deadline can be requested with prior approval of your Thesis Supervisor. Any request for extension should be submitted to your DUS by email as early as possible, and your Supervisor should be copied. Please be advised that being granted an extension makes you ineligible for Departmental Honors and Prizes .
Click here to watch the 2020 Senior Thesis presentations .
DOWNLOAD MATERIALS
Students who decide to write a thesis will enroll in a year-long course (CPLS3995) starting in the Fall of their Senior Year. This year-long, 3-credit course (1 credit in Fall, 2 credits in Spring) will allow students to receive academic credits for their thesis, and to count the thesis towards completion of their major requirement when necessary (Requirement #10 of the CLS Course Chart).
The deadline for submitting the Senior Thesis is April 15 th .The Thesis will be submitted both electronically and in hard copy to the DUS of ICLS and to the Thesis Supervisor. Medical Humanities majors will also submit, at the same time, to Professor Rishi Goyal, Director of Medical Humanities. The Thesis Supervisor is solely responsible for the final grade.

- Utility Menu
GA4 Tracking Code
fa51e2b1dc8cca8f7467da564e77b5ea
- Make a Gift
- Join Our Email List
- Advising Senior Theses
Every thesis writer and thesis project is unique, and arguably the single most important thing that you can do as a thesis adviser is to get to know your student well and to be supportive and attentive as they work towards their spring deadline. The amount of structure that different concentrations offer their students can also have a significant impact on how you think about your role as an adviser. In some cases you may feel like an extension of the department’s undergraduate office, encouraging your student to follow its well-articulated pathway towards completion and nudging your student to heed (albeit perhaps with some discretion) its recommended proposal or draft deadlines. In other cases you may be the one responsible for translating the concentration’s somewhat vague guidelines into an actionable roadmap of recommended thresholds and dates. It’s well worth establishing a healthy line of communication with the concentration’s undergraduate office (and with anyone else involved in advising your student’s academic work) from the start of your advising relationship.
Regardless of the precise structure and obligations surrounding your position as an adviser, there are a number of things which you can do to help just about any student have a meaningful, and successful, experience with the senior thesis. Here are five key contributions which you can make:
Manage expectations
In an ideal world, every student would enter the thesis process fully prepared for every aspect of scholarly work. They all would know how to ask an analytical question suitable for a 60- or 100-page paper, how to find relevant data, how to draw lucid figures, how to format every footnote or methods section, … . Likewise, we might wish that every thesis topic lent itself equally well to the particular constraints of Harvard’s resources and academic calendar. If only that essential cache of Russian manuscripts existed in a published English translation in Widener! If only this experimental protocol took two weeks rather than four months! In reality, however, every thesis involves some compromise—perhaps significant compromise. One of your most important jobs as a thesis adviser is to roleplay your student’s future audience, and to help your student understand that the most successful theses ask questions that are not only meaningful, but that can be answered at least somewhat plausibly by the set of skills, resources, and time that is available to a Harvard undergraduate. Insofar as a student is determined to tackle a dissertation-sized question, the adviser can at least remind the student that it will be important to frame the results as a “partial” answer or a “contribution towards” an answer in the introduction.
Encourage self-knowledge
As with the previous point about managing expectations, it is important that an adviser be able to remind their student that the senior thesis is not, and will not be, the moment when students magically become “better” people than they already are. Students who have been night owls during their first three years of college are unlikely to transform miraculously into the type of scholars who rise at 6am and write 1000 words before breakfast—no matter how much they yearn to emulate some academic role model. Students who have participated actively in a sport or other extracurricular are unlikely to be able to simply recoup those hours for thesis work—cutting back three hours/week at The Crimson is at least as likely to translate into three more hours spent bantering in the dining hall as it is into three hours spent poring over the administrative structure of the Byzantine Empire. The point is that students can benefit from being reminded that they already know how to do the kind of work expected of them on the thesis, and that it may be counterproductive—if not downright unhealthy—to hold themselves to new or arbitrary standards.
Motivate to start writing early
With relatively few exceptions, most of the writing projects assigned in college are sufficiently modest that students can wait to start writing until they have figured out the full arc of what they want to say and how they want to say it. It’s possible, in other words, to plan and hold the entirety of a five-page essay in one’s head. This is simply not true of a senior thesis. Theses require the author to take a leap of faith—to start writing before the research is done and long before they know exactly what they want to say. Students may be reluctant to do this, fearing that they might “waste” precious time drafting a section of a chapter that ultimately doesn’t fit in the final thesis. You can do your student a world of good by reminding them that there is no such thing as wasted writing. In a project as large as a thesis, writing is not merely about reporting one’s conclusions—it is the process through which students come to figure out what their conclusions might be, and which lines of research they will need to pursue to get there.

Model strategies
While academic research and writing can and should be a creative endeavor, it is also undeniably true that even professional scholars draw upon a relatively constrained set of well-known strategies when framing their work. How many different ways, after all, are there to say that the conventional wisdom on a topic has ignored a certain genre of evidence? Or that two competing schools of thought actually agree more than they disagree? Or that fiddling with one variable has the power to reframe an entire discussion? Students may struggle to see how to plug their research into the existing scholarly conversation around their topic. Showing them models or templates that demystify the ways in which scholars frame their interventions can be enormously powerful.
Keep contact and avoid the "shame spiral"
As noted above, the senior thesis is a long process, and while it’s rarely a good idea for students to change their work habits in an effort to complete it, it is important that they be working early and often. Occasionally students do become overwhelmed by the scope of the project, and begin to feel defeated by the incremental nature of progress they are making. Even a good week of work may yield only a couple of pages of passable writing. Ideally a student feeling overwhelmed would come to their adviser for some help putting things into perspective. But for a student used to having a fair amount of success, the struggles involved in a senior thesis may be disorienting, and they may worry that they are “disappointing” you. For some, this will manifest as a retreat from your deadlines and oversight—even as they outwardly project confidence. They may begin bargaining with themselves in ways that only serve to sink them deeper into a sense of panic or shame. (“I’m long past the deadline for my first ten pages—but if I give my adviser a really brilliant fifteen-page section, he won’t mind! Surely I can turn these four pages into fifteen if I stay up all night!”) One of the best things that you can do as an adviser is keep contact with your student and make sure to remind them that your dynamic is not one of “approval” or “disapproval.” It is important that they maintain a healthy and realistic approach to the incremental process of completing the thesis over several months.
For more information...
The Art of Thesis Writing: A handout for students
Harvard's Academic Resource Center on Senior Theses
Senior Thesis Tutors at the Harvard College Writing Center
- Designing Your Course
- In the Classroom
- Getting Feedback
- Equitable & Inclusive Teaching
- Writing Letters of Recommendation
- Teaching and Your Career
- Teaching Remotely
- Tools and Platforms
- The Science of Learning
- Bok Publications
- Other Resources Around Campus
What Is a Senior Thesis?
Daniel Ingold/Cultura/Getty Images
- Writing Research Papers
- Writing Essays
- English Grammar
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
A senior thesis is a large, independent research project that students take on during their senior year of high school or college to fulfill their graduation requirement. It is the culminating work of their studies at a particular institution, and it represents their ability to conduct research and write effectively. For some students, a senior thesis is a requirement for graduating with honors.
Students typically work closely with an advisor and choose a question or topic to explore before carrying out an extensive research plan.
Style Manuals and the Paper's Organization
The structure of your research paper will depend, in part, on the style manual that is required by your instructor. Different disciplines, such as history, science, or education, have different rules to abide by when it comes to research paper construction, organization, and modes of citation. The styles for different types of assignment include:
Modern Language Association (MLA): The disciplines that tend to prefer the MLA style guide include literature, arts, and the humanities, such as linguistics, religion, and philosophy. To follow this style, you will use parenthetical citations to indicate your sources and a works cited page to show the list of books and articles you consulted.
American Psychological Association (APA): The APA style manual tends to be used in psychology, education, and some of the social sciences. This type of report may require the following:
- Introduction
Chicago style: "The Chicago Manual of Style" is used in most college-level history courses as well as professional publications that contain scholarly articles. Chicago style may call for endnotes or footnotes corresponding to a bibliography page at the back or the author-date style of in-text citation, which uses parenthetical citations and a references page at the end.
Turabian style: Turabian is a student version of Chicago style. It requires some of the same formatting techniques as Chicago, but it includes special rules for writing college-level papers, such as book reports. A Turabian research paper may call for endnotes or footnotes and a bibliography.
Science style: Science instructors may require students to use a format that is similar to the structure used in publishing papers in scientific journals. The elements you would include in this sort of paper include:
- List of materials and methods used
- Results of your methods and experiments
- Acknowledgments
American Medical Association (AMA): The AMA style book might be required for students in medical or premedical degree programs in college. Parts of an AMA research paper might include:
- Proper headings and lists
- Tables and figures
- In-text citations
- Reference list
Choose Your Topic Carefully
Starting off with a bad, difficult, or narrow topic likely won't lead to a positive result. Don't choose a question or statement that's so broad that it's overwhelming and could comprise a lifetime of research or a topic that's so narrow you'll struggle to compose 10 pages. Consider a topic that has a lot of recent research so you won't struggle to put your hands on current or adequate sources.
Select a topic that interests you. Putting in long hours on a subject that bores you will be arduous—and ripe for procrastination. If a professor recommends an area of interest, make sure it excites you.
Also, consider expanding a paper you've already written; you'll hit the ground running because you've already done some research and know the topic. Last, consult with your advisor before finalizing your topic. You don't want to put in a lot of hours on a subject that is rejected by your instructor.
Organize Your Time
Plan to spend half of your time researching and the other half writing. Often, students spend too much time researching and then find themselves in a crunch, madly writing in the final hours. Give yourself goals to reach along certain "signposts," such as the number of hours you want to have invested each week or by a certain date or how much you want to have completed in those same timeframes.
Organize Your Research
Compose your works cited or bibliography entries as you work on your paper. This is especially important if your style manual requires you to use access dates for any online sources that you review or requires page numbers be included in the citations. You don't want to end up at the very end of the project and not know what day you looked at a particular website or have to search through a hard-copy book looking for a quote that you included in the paper. Save PDFs of online sites, too, as you wouldn't want to need to look back at something and not be able to get online or find that the article has been removed since you read it.
Choose an Advisor You Trust
This may be your first opportunity to work with direct supervision. Choose an advisor who's familiar with the field, and ideally select someone you like and whose classes you've already taken. That way you'll have a rapport from the start.
Consult Your Instructor
Remember that your instructor is the final authority on the details and requirements of your paper. Read through all instructions, and have a conversation with your instructor at the start of the project to determine his or her preferences and requirements. Have a cheat sheet or checklist of this information; don't expect yourself to remember all year every question you asked or instruction you were given.
- What Is a Bibliography?
- Turabian Style Guide With Examples
- What Is a Citation?
- Formatting Papers in Chicago Style
- What Is a Style Guide and Which One Do You Need?
- Definition of Appendix in a Book or Written Work
- Bibliography: Definition and Examples
- What Are Endnotes, Why Are They Needed, and How Are They Used?
- Tips for Typing an Academic Paper on a Computer
- How to Organize Research Notes
- Bibliography, Reference List or Works Cited?
- What's the Preferred Way to Write the Abbreviation for United States?
- How to Write a Research Paper That Earns an A
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- MLA Style Parenthetical Citations
- Formatting APA Headings and Subheadings

- Library Search
- View Library Account
- The Claremont Colleges Library
- Research Guides
Senior Thesis Resources
How to use this guide, brush up on your research skills, we're here to help.
- Basic Research Skills
- Advanced Research Skills
- Library-Specific Resources
- Uploading to Scholarship@Claremont
This guide includes a range of library and writing center resources that will help you with the skills and tools you need to be successful in completing your senior thesis. The guide is divided into sections on the left of the page. You can skip ahead to the section that is relevant to you or browse through all the sections.
For most students, their senior thesis is the most sustained research project of their academic career. This guide is designed for students to spend some time up front to build the research skills necessary for a successful senior thesis. Finding and filling the gaps in your research knowledge will save you time in the long run and help you build a stronger senior thesis.
Use the Basic Research Skills and Advanced Research Skills options in the navigation menu to get started.
In addition to your senior thesis advisor, there are people who can help with different aspects of your senior thesis. It's a good idea to identify the librarian for your subject area early in your research, as well as finding out what kinds of support your campus writing center provides for students working on theses.
Head, Information Literacy & Student Engagement

- Next: Basic Research Skills >>
- : Sep 27, 2023 1:23 PM
- URL: https://libguides.libraries.claremont.edu/senior_thesis_help

The Senior Thesis
From the outset of their time at Princeton, students are encouraged and challenged to develop their scholarly interests and to evolve as independent thinkers.
The culmination of this process is the senior thesis, which provides a unique opportunity for students to pursue original research and scholarship in a field of their choosing. At Princeton, every senior writes a thesis or, in the case of some engineering departments, undertakes a substantial independent project.
Integral to the senior thesis process is the opportunity to work one-on-one with a faculty member who guides the development of the project. Thesis writers and advisers agree that the most valuable outcome of the senior thesis is the chance for students to enhance skills that are the foundation of future success, including creativity, intellectual engagement, mental discipline and the ability to meet new challenges.
Many students develop projects from ideas sparked in the classes they’ve taken; others fashion their topics on the basis of long-standing personal passions. Most thesis writers encounter the intellectual twists and turns of any good research project, where the questions emerge as they proceed, often taking them in unexpected directions.
Planning for the senior thesis starts in earnest in the junior year, when students complete a significant research project known as the junior paper. Students who plan ahead can make good use of the University's considerable resources, such as receiving University funds to do research in the United States or abroad. Other students use summer internships as a launching pad for their thesis. For some science and engineering projects, students stay on campus the summer before their senior year to get a head start on lab work.
Writing a thesis encourages the self-confidence and high ambitions that come from mastering a difficult challenge. It fosters the development of specific skills and habits of mind that augur well for future success. No wonder generations of graduates look back on the senior thesis as the most valuable academic component of their Princeton experience.
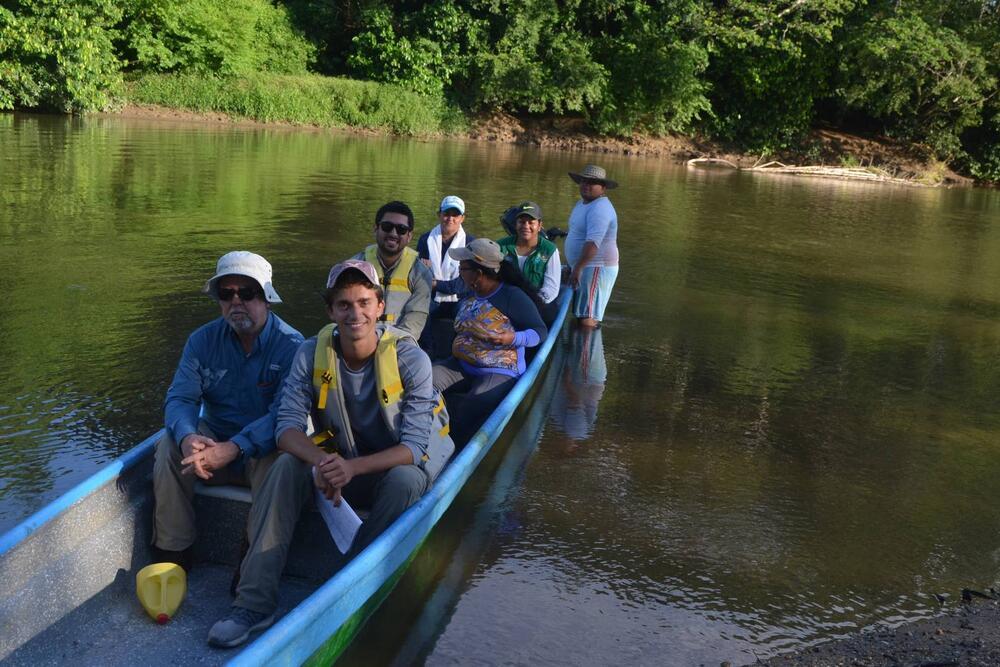
Navigating Colombia’s Magdalena River, One Story At A Time
For his senior thesis, Jordan Salama, a Spanish and Portuguese major, produced a nonfiction book of travel writing about the people and places along Colombia’s main river, the Magdalena.

Embracing the Classics to Inform Policymaking for Public Education
For her senior thesis, Emma Treadwayconsiders how the basic tenets of Stoicism — a school of philosophy that dates from 300 BCE — can teach students to engage empathetically with the world and address inequities in the classroom.

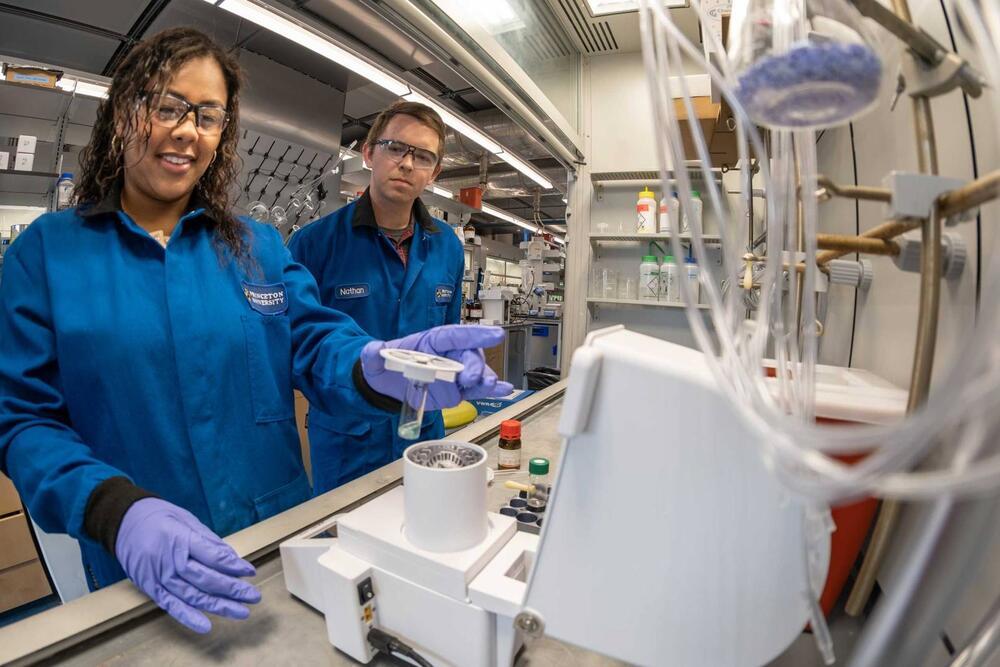
Creating A Faster, Cheaper and Greener Chemical Reaction
One way to make drugs more affordable is to make them cheaper to produce. For her senior thesis research, Cassidy Humphreys, a chemistry major with a passion for medicine, took on the challenge of taking a century-old formula at the core of many modern medications — and improving it.

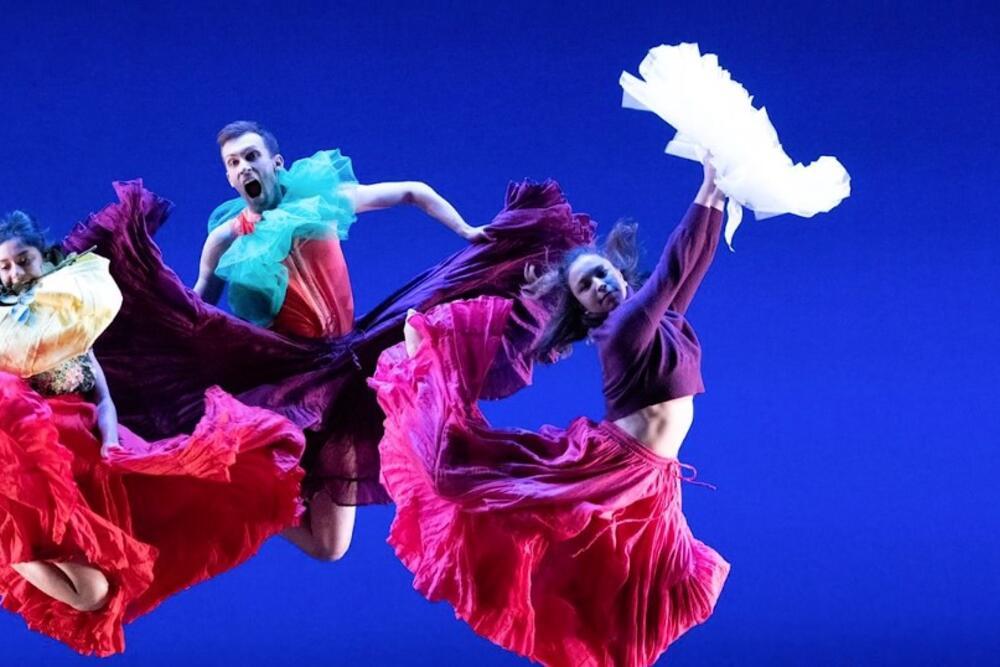
The Humanity of Improvisational Dance
Esin Yunusoglu investigated how humans move together and exist in a space — both on the dance floor and in real life — for the choreography she created as her senior thesis in dance, advised by Professor of Dance Susan Marshall.

From the Blog
The infamous senior thesis, revisiting wwii: my senior thesis, independent work in its full glory, advisers, independent work and beyond.
PROGRAM IN AMERICAN STUDIES
- Undergraduate
- Writing a Good Thesis
writing a good senior thesis
Notes towards writing a good senior thesis.
An honors paper has to present a thesis , or argument. It's important to understand what this means. Though in the sciences it might be enough to master a certain body of facts or information derived from class (or from your research) and to rehearse them articulately, interpretation is an analytic skill that requires you to move beyond the specific ideas that you have encountered in your critical and/or background reading. You need to show that you have learned ways of interpreting based on your research, and to demonstrate those skills on new material--that is, to apply different concepts and/or to discuss different parts of the literary text than were discussed in the scholarship you consulted.
An argument is a claim about the meaning of a text combined with a claim about the way the text's formal features are related to its meaning. Thus your interpretation has to take into account both the ideas or concepts of the text, and its recursive formal features (i.e., some strand or strands in its pattern of images, phrases, figures, or plot elements). And it has to identify characteristics of the text that distinguish it sufficiently from other texts. In addition, your honors paper has to have a thesis that extends beyond individual literary works. It may be an argument about the shape of a literary career, about the relationship of a given set of literary texts to their historical context, about the relationship of one writer's work to another's, or about the development of certain formal features or themes over time and/or across the work of several different writers.
Since this is a research paper, your argument must have a relationship to previous research and scholarship. It isn't sufficient, for instance, to reach the exact same conclusion as a previous critic but simply point to additional evidence. Your new evidence must point to a revised conclusion. And the argument must be non-trivial. In other words, it can't simply attend to a theme or aspect of the literary work that hasn't been noticed before, and leave it at that (e.g., "No one's ever looked at images of birds in Dickens . . ."). You have to argue why the things you've noticed are important, e.g., why they make a difference. A good critical paper anticipates what the most obvious objections, counter-arguments or counter-evidence to its thesis might be. If you can't imagine any evidence or argument contrary to your thesis, it may not be the world's most interesting thesis. The best essay is one in which you consider how evidence or scholarship which might seem to contradict your thesis in fact supports it. Or you may want to leave your reader with choices (e.g. "While from one perspective, the novel seems to suggest . . ., seen from another perspective, it seems to suggest . . . These two perspectives appear irreconcilable"). In any case, don't assume either that your argument is obvious, or on the other hand that its mere novelty is interesting.
Scale: there are no rules here, but you should anticipate writing on roughly 3-4 novels (or a dozen or so poems), or the equivalent of this for other genres. The texts you analyze in depth will of course be only the tip of the iceberg. For instance, to make an argument about the relationship of Dickens's portrayal of women to Hardy's portrayal of women you could hypothetically write only on Bleak House and Tess of the D'Urbervilles, but your generalizations would have to be ones that genuinely held up for their other novels—and thus you would have had to research and think about many other Dickens and Hardy novels well enough to know that. You would probably also have to make at least passing gestures towards their other novels, in addition to considering the arguments of other critics who had looked at this topic. If you were arguing about the attitude toward technology in 20th-century American literature, you might write on only 3 or 4 authors, but you would obviously have had to read well beyond these particular authors in order to make a generalization about a period.
Remember that your honors work is supposed to be the equivalent of at least two full courses. Think about the reading list for a typical upper-level course in English, and double that in order to get a sense of how much reading and research you should be doing. If you're working on novels, you will probably read 6-8 novels for your honors paper, in addition to maybe a half-dozen scholarly books (critical, biographical, historical, etc.) and a couple of dozen articles. The amount of reading you can do determines the rough scope of the questions you can ask and answer in your thesis. You probably can't make an argument about "what the Victorians thought," though you can make a very good argument about how novels shifted in their portrayal of, e.g., capitalism, over the course of the Victorian period.
Think about posing a question for yourself in your thesis. It has to be a question that can be answered (i.e., it can't be too speculative or subjective), and one which specific kinds of material or inquiry would help you answer. It must also be either a question which other scholars have asked, or one which indirectly helps answer (or re-orient) the question(s) that other scholars have asked.
Secondary Menu
- Senior Thesis: Frequently Asked Questions
What kinds of topics do students explore?
Students writing theses in the department work on a broad range of issues, including health care; migration and refugees; gender and sexuality; photography and material culture; social media and politics. For some students, ethnographic research lies at the core of this project. Others may choose to work chiefly with documents (popular or mass media, photography, film, digital texts, social networks, etc.). Some students conduct thesis research over the previous summer. Others base their study on a prior study abroad experience, fieldwork methods project, or final paper for a CA class. Alternately, you may certainly choose to work on something completely new.
Why should I write a thesis?
The senior thesis is a chance for you to put your classroom studies to work on something you care deeply about. Many writers attest that the experience is among the most rewarding in the course of their college career.
Who is eligible to write a thesis?
Qualified juniors will be notified each year by DUS about their eligibility.
Can I join the CA thesis class as an IDM or Program II student?
Yes, with DUS approval .
How does thesis advising work and how do I select an advisor?
When you enroll in the seminar, you will work closely with a faculty advisor to design an independent program of original research culminating in a senior thesis. We encourage you to discuss your ideas with professors who know your work and who can help you think realistically about the feasibility of the research. These prior relationships generate the best advisor-advisee relationships.
What kind of approval is required for my research?
Ethnographic research often entails seeking “human subjects” approval through the Duke IRB, institutional review board.
Is funding available for summer fieldwork?
Yes, it is available, on a competitive basis, through the Undergraduate Research Support Office .
The two-semester senior seminar (CULANTH 498S and 499S) is open to students with an overall 3.0 GPA in their academic record and a 3.3 GPA in the major. Qualified juniors will be notified each year by DUS about their eligibility.
Do thesis writers need to take the two-semester class?
Thesis writers must complete both terms of the course to receive credit. Students who wish to exit the Senior Seminar Distinction Program sequence after completion of 489S, must petition the course instructor, their advisor and the DUS. The student will be given course credit and a final grade given the instructor, their advisor and the DUS determine the student has done adequate work.
Do thesis writers receive distinction?
The thesis must be judged to be of at least B+ quality by the student’s supervisory committee to receive distinction. In addition, the student must pass an oral examination on the thesis, which is given upon its completion by the supervisory committee. Students must also maintain their requisite GPAs.
How is the thesis evaluated?
The student forms a supervisory committee for the thesis during the fall of the senior year. It should consist of three faculty members who offer the student advice and support in preparing the thesis. At least two of the members must be faculty from the Cultural Anthropology department.
When is the thesis due?
In April of the senior year.
How do I apply?
If you are interested in writing a thesis and taking the requisite courses (CULANTH 498S and 499S), please submit the following materials (hard copy, in box) to the current DUS in the spring of your junior year:
- A 500-word proposal that outlines the direction of the thesis including topic; central research question; possible findings or hypothesis about the material; designation of the fieldwork site (where relevant) or primary materials that will be used as the basis of this analysis. Please indicate whether your research will be based on ethnography.
- Provisional bibliography of 10 works (essays or books) that will be drawn on during this project.
- Name and signature of the Cultural Anthropology faculty member who has agreed to direct your thesis and mentor you during the writing process.
- A one paragraph reference from a Cultural Anthropology faculty member attesting to your preparedness to carry out the thesis (someone other than your advisor for the thesis).
- What is Cultural Anthropology?
- Educational Objectives
- Assessment Plan
- Anthropology & Activism
- Majors & Minor
- Building Your Focus
- Career Options
- For Current Students
- CA Graduation with Distinction: Eligibility and Courses
- For Double Majors
- For Interdepartmental Majors
- Typical Course of Study
- How to Apply
- Program Key Features
- Financial Support
- Visiting Our Department
- Living in Durham
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Recent Graduates
- Plan of Study
- Field Specializations Workshop
- Language Requirements
- Funding & Grants
- Teaching Service Requirement
- Department Colloquia
- Conference Travel
- Summer Field Research
- Dissertation
- Receipt of the MA "on the way"
- Primary Faculty
- Affiliated Faculty
- Visiting Faculty
- Professors Emeriti
- Graduate Students
- Diane Nelson
- Selected Faculty Books
- Assisting Duke Students
- Native American Studies Initiative

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A senior thesis in literature, on the other hand, will likely involve studying a movement, trope, author, or theme, and your sources will involve a combination of fiction, historical context, literary criticism, and literary theory. At many schools, a thesis ranges from 80 to 125 pages. At other universities, as few as 25 pages might fill the ...
2 Q: Why should I write a Senior Thesis? A: While writing a thesis is one way to become eligible for honors, and the only way to become eligible for the summa cum laude level of honors, the best motivations are a love of research and/or a burning question. You should not consider a Senior Thesis if your primary motivations are not intellectually based, but are instead more practical—i.e ...
Doing a senior thesis is an exciting enterprise. It's often the first time students are engaging in truly original research and trying to develop a significant contribution to a field of inquiry. But as joyful as an independent research process can be, you don't have to go it alone. It's important to have support as you navigate such a ...
Before coming to Yale, I thought a thesis was the main argument of a paper. I quickly learned that an undergraduate thesis is about fifty times harder and fifty pages longer than any thesis arguments I wrote in high school. At Yale, every senior has some sort of senior requirement, but thesis projects vary by department. Some departments require students to do a semester-long
The senior thesis is a significant task for students to undertake, but there is a variety of support resources available here at Harvard to ensure that seniors can make the best of their senior thesis experience. Wandering the library stacks at Widener. I do most of my research in Widener Library.
For my major - political science - the senior paper needs to be 25 pages minimum. This paper has the potential of being the longest paper you'll write during your entire Yale undergraduate career and so, preparation is necessary. A great resource offered by Yale to undergrads writing their thesis (or any other type of paper) are library ...
• A senior thesis must be an original research project of no fewer than 10,000 words and no more than 20,000 words, not counting notes and bibliography. ... some of the material from said essays in your thesis if you must (it's not necessary to reinvent the wheel). However, your senior thesis should be a completely new project. If you wrote ...
Whether you're a junior or an ambitious sophomore or freshman, there are many things you can do to prepare for the possibility of writing a senior thesis. This short guide aims to share some practices and activities you can engage in . before . your senior year to help you have a successful thesis experience. Do I really want to write a ...
Senior Thesis Writing Guides. The senior thesis is typically the most challenging writing project undertaken by undergraduate students. The writing guides below aim to introduce students both to the specific methods and conventions of writing original research in their area of concentration and to effective writing process. The senior thesis is ...
Provide the student the tools necessary to answer the research question. This includes getting the student started with literature, contacts (e.g. grad students and postdocs), equipme nt and ... • Senior thesis students are required to take either 99A or 99B, though it is very strongly recommended that students enroll in both courses.
A senior thesis is a capstone research project at the end of a student's undergraduate career. To complete a senior thesis, you conceive, conduct, analyze, and then present an original research ... apply for any necessary funding from departmental, university, or other sources. • September and October: Complete a full-fledged research ...
We do not have strict guidelines regarding the format of the coversheet but we ask that you include: the thesis title, the date, your name, the phrase "Senior Thesis in (your major) at the Institute for Comparative Literature and Society at Columbia University," and your thesis advisor and their department. Submission Deadline and Grading.
SENIOR THESIS PROSPECTUS . In preparation for doing two semesters of focused research during your senior year you are required to prepare an initial report that serves as a prospectus or guide for your Senior Thesis research. This Senior Thesis Prospectus is due on Tuesday, September 20, 2022.
2 keeping in mind the standards below as norms (for a creative thesis). The Senior Champagne Reception follows the thesis deadline, in the Thompson Room, Barker Center. April 30, May 1, May 4, 2020 Oral examinations scheduled for those thesis writers who might be candidates for the summa cum laude degree. *Note for JOINT CONCENTRATORS: you must follow the deadlines and formatting/style guidelines
As noted above, the senior thesis is a long process, and while it's rarely a good idea for students to change their work habits in an effort to complete it, it is important that they be working early and often. Occasionally students do become overwhelmed by the scope of the project, and begin to feel defeated by the incremental nature of ...
Updated on January 24, 2019. A senior thesis is a large, independent research project that students take on during their senior year of high school or college to fulfill their graduation requirement. It is the culminating work of their studies at a particular institution, and it represents their ability to conduct research and write effectively.
This guide is designed for students to spend some time up front to build the research skills necessary for a successful senior thesis. Finding and filling the gaps in your research knowledge will save you time in the long run and help you build a stronger senior thesis. Use the Basic Research Skills and Advanced Research Skills options in the ...
Integral to the senior thesis process is the opportunity to work one-on-one with a faculty member who guides the development of the project. Thesis writers and advisers agree that the most valuable outcome of the senior thesis is the chance for students to enhance skills that are the foundation of future success, including creativity, intellectual engagement, mental discipline and the ability ...
Notes Towards Writing a Good Senior Thesis. An honors paper has to present a thesis, or argument. It's important to understand what this means. Though in the sciences it might be enough to master a certain body of facts or information derived from class (or from your research) and to rehearse them articulately, interpretation is an analytic ...
A senior thesis project is best suited for students who have an interest in exploring a specific question and/or field of knowledge beyond their previous course work. A thesis is an in-depth analysis of a specific topic with the emphasis on original research. Writing a good thesis requires a significant amount of work well beyond what is ...
This senior thesis guide applies to all CEE students who are satisfying the senior thesis requirement by signing up for CEE 478. Senior thesis can be co-advised by several faculty from CEE or out of CEE; however, at least one faculty from CEE must be co-advisor. Students in the "Architecture and Engineering - Architecture Focus" track are ...
A 500-word proposal that outlines the direction of the thesis including topic; central research question; possible findings or hypothesis about the material; designation of the fieldwork site (where relevant) or primary materials that will be used as the basis of this analysis. Please indicate whether your research will be based on ethnography.
• A Senior Thesis must be an original research project of no fewer than 10,000 words and no more than 20,000 words, not counting notes and bibliography. ... the material from said essays in your thesis if you must (it's not necessary to reinvent the wheel). However, your senior thesis should be a completely new project. If you wrote on ...