Are you seeking one-on-one college counseling and/or essay support? Limited spots are now available. Click here to learn more.

How to Write a Lab Report – with Example/Template
April 11, 2024

Perhaps you’re in the midst of your challenging AP chemistry class in high school, or perhaps college you’re enrolled in biology , chemistry , or physics at university. At some point, you will likely be asked to write a lab report. Sometimes, your teacher or professor will give you specific instructions for how to format and write your lab report, and if so, use that. In case you’re left to your own devices, here are some guidelines you might find useful. Continue reading for the main elements of a lab report, followed by a detailed description of the more writing-heavy parts (with a lab report example/lab report template). Lastly, we’ve included an outline that can help get you started.
What is a lab report?
A lab report is an overview of your experiment. Essentially, it explains what you did in the experiment and how it went. Most lab reports end up being 5-10 pages long (graphs or other images included), though the length depends on the experiment. Here are some brief explanations of the essential parts of a lab report:
Title : The title says, in the most straightforward way possible, what you did in the experiment. Often, the title looks something like, “Effects of ____ on _____.” Sometimes, a lab report also requires a title page, which includes your name (and the names of any lab partners), your instructor’s name, and the date of the experiment.
Abstract : This is a short description of key findings of the experiment so that a potential reader could get an idea of the experiment before even beginning.
Introduction : This is comprised of one or several paragraphs summarizing the purpose of the lab. The introduction usually includes the hypothesis, as well as some background information.
Lab Report Example (Continued)
Materials : Perhaps the simplest part of your lab report, this is where you list everything needed for the completion of your experiment.
Methods : This is where you describe your experimental procedure. The section provides necessary information for someone who would want to replicate your study. In paragraph form, write out your methods in chronological order, though avoid excessive detail.
Data : Here, you should document what happened in the experiment, step-by-step. This section often includes graphs and tables with data, as well as descriptions of patterns and trends. You do not need to interpret all of the data in this section, but you can describe trends or patterns, and state which findings are interesting and/or significant.
Discussion of results : This is the overview of your findings from the experiment, with an explanation of how they pertain to your hypothesis, as well as any anomalies or errors.
Conclusion : Your conclusion will sum up the results of your experiment, as well as their significance. Sometimes, conclusions also suggest future studies.
Sources : Often in APA style , you should list all texts that helped you with your experiment. Make sure to include course readings, outside sources, and other experiments that you may have used to design your own.
How to write the abstract
The abstract is the experiment stated “in a nutshell”: the procedure, results, and a few key words. The purpose of the academic abstract is to help a potential reader get an idea of the experiment so they can decide whether to read the full paper. So, make sure your abstract is as clear and direct as possible, and under 200 words (though word count varies).
When writing an abstract for a scientific lab report, we recommend covering the following points:
- Background : Why was this experiment conducted?
- Objectives : What problem is being addressed by this experiment?
- Methods : How was the study designed and conducted?
- Results : What results were found and what do they mean?
- Conclusion : Were the results expected? Is this problem better understood now than before? If so, how?
How to write the introduction
The introduction is another summary, of sorts, so it could be easy to confuse the introduction with the abstract. While the abstract tends to be around 200 words summarizing the entire study, the introduction can be longer if necessary, covering background information on the study, what you aim to accomplish, and your hypothesis. Unlike the abstract (or the conclusion), the introduction does not need to state the results of the experiment.
Here is a possible order with which you can organize your lab report introduction:
- Intro of the intro : Plainly state what your study is doing.
- Background : Provide a brief overview of the topic being studied. This could include key terms and definitions. This should not be an extensive literature review, but rather, a window into the most relevant topics a reader would need to understand in order to understand your research.
- Importance : Now, what are the gaps in existing research? Given the background you just provided, what questions do you still have that led you to conduct this experiment? Are you clarifying conflicting results? Are you undertaking a new area of research altogether?
- Prediction: The plants placed by the window will grow faster than plants placed in the dark corner.
- Hypothesis: Basil plants placed in direct sunlight for 2 hours per day grow at a higher rate than basil plants placed in direct sunlight for 30 minutes per day.
- How you test your hypothesis : This is an opportunity to briefly state how you go about your experiment, but this is not the time to get into specific details about your methods (save this for your results section). Keep this part down to one sentence, and voila! You have your introduction.
How to write a discussion section
Here, we’re skipping ahead to the next writing-heavy section, which will directly follow the numeric data of your experiment. The discussion includes any calculations and interpretations based on this data. In other words, it says, “Now that we have the data, why should we care?” This section asks, how does this data sit in relation to the hypothesis? Does it prove your hypothesis or disprove it? The discussion is also a good place to mention any mistakes that were made during the experiment, and ways you would improve the experiment if you were to repeat it. Like the other written sections, it should be as concise as possible.
Here is a list of points to cover in your lab report discussion:
- Weaker statement: These findings prove that basil plants grow more quickly in the sunlight.
- Stronger statement: These findings support the hypothesis that basil plants placed in direct sunlight grow at a higher rate than basil plants given less direct sunlight.
- Factors influencing results : This is also an opportunity to mention any anomalies, errors, or inconsistencies in your data. Perhaps when you tested the first round of basil plants, the days were sunnier than the others. Perhaps one of the basil pots broke mid-experiment so it needed to be replanted, which affected your results. If you were to repeat the study, how would you change it so that the results were more consistent?
- Implications : How do your results contribute to existing research? Here, refer back to the gaps in research that you mentioned in your introduction. Do these results fill these gaps as you hoped?
- Questions for future research : Based on this, how might your results contribute to future research? What are the next steps, or the next experiments on this topic? Make sure this does not become too broad—keep it to the scope of this project.
How to write a lab report conclusion
This is your opportunity to briefly remind the reader of your findings and finish strong. Your conclusion should be especially concise (avoid going into detail on findings or introducing new information).
Here are elements to include as you write your conclusion, in about 1-2 sentences each:
- Restate your goals : What was the main question of your experiment? Refer back to your introduction—similar language is okay.
- Restate your methods : In a sentence or so, how did you go about your experiment?
- Key findings : Briefly summarize your main results, but avoid going into detail.
- Limitations : What about your experiment was less-than-ideal, and how could you improve upon the experiment in future studies?
- Significance and future research : Why is your research important? What are the logical next-steps for studying this topic?
Template for beginning your lab report
Here is a compiled outline from the bullet points in these sections above, with some examples based on the (overly-simplistic) basil growth experiment. Hopefully this will be useful as you begin your lab report.
1) Title (ex: Effects of Sunlight on Basil Plant Growth )
2) Abstract (approx. 200 words)
- Background ( This experiment looks at… )
- Objectives ( It aims to contribute to research on…)
- Methods ( It does so through a process of…. )
- Results (Findings supported the hypothesis that… )
- Conclusion (These results contribute to a wider understanding about…)
3) Introduction (approx. 1-2 paragraphs)
- Intro ( This experiment looks at… )
- Background ( Past studies on basil plant growth and sunlight have found…)
- Importance ( This experiment will contribute to these past studies by…)
- Hypothesis ( Basil plants placed in direct sunlight for 2 hours per day grow at a higher rate than basil plants placed in direct sunlight for 30 minutes per day.)
- How you will test your hypothesis ( This hypothesis will be tested by a process of…)
4) Materials (list form) (ex: pots, soil, seeds, tables/stands, water, light source )
5) Methods (approx. 1-2 paragraphs) (ex: 10 basil plants were measured throughout a span of…)
6) Data (brief description and figures) (ex: These charts demonstrate a pattern that the basil plants placed in direct sunlight…)
7) Discussion (approx. 2-3 paragraphs)
- Support or reject hypothesis ( These findings support the hypothesis that basil plants placed in direct sunlight grow at a higher rate than basil plants given less direct sunlight.)
- Factors that influenced your results ( Outside factors that could have altered the results include…)
- Implications ( These results contribute to current research on basil plant growth and sunlight because…)
- Questions for further research ( Next steps for this research could include…)
- Restate your goals ( In summary, the goal of this experiment was to measure…)
- Restate your methods ( This hypothesis was tested by…)
- Key findings ( The findings supported the hypothesis because…)
- Limitations ( Although, certain elements were overlooked, including…)
- Significance and future research ( This experiment presents possibilities of future research contributions, such as…)
- Sources (approx. 1 page, usually in APA style)
Final thoughts – Lab Report Example
Hopefully, these descriptions have helped as you write your next lab report. Remember that different instructors may have different preferences for structure and format, so make sure to double-check when you receive your assignment. All in all, make sure to keep your scientific lab report concise, focused, honest, and organized. Good luck!
For more reading on coursework success, check out the following articles:
- How to Write the AP Lang Argument Essay (With Example)
- How to Write the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay (With Example)
- 49 Most Interesting Biology Research Topics
- 50 Best Environmental Science Research Topics
- High School Success

Sarah Mininsohn
With a BA from Wesleyan University and an MFA from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Sarah is a writer, educator, and artist. She served as a graduate instructor at the University of Illinois, a tutor at St Peter’s School in Philadelphia, and an academic writing tutor and thesis mentor at Wesleyan’s Writing Workshop.
- 2-Year Colleges
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Data Visualizations
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High Schools
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Private High School Spotlight
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight

“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
I am a... Student Student Parent Counselor Educator Other First Name Last Name Email Address Zip Code Area of Interest Business Computer Science Engineering Fine/Performing Arts Humanities Mathematics STEM Pre-Med Psychology Social Studies/Sciences Submit

Scientific Reports
What this handout is about.
This handout provides a general guide to writing reports about scientific research you’ve performed. In addition to describing the conventional rules about the format and content of a lab report, we’ll also attempt to convey why these rules exist, so you’ll get a clearer, more dependable idea of how to approach this writing situation. Readers of this handout may also find our handout on writing in the sciences useful.
Background and pre-writing
Why do we write research reports.
You did an experiment or study for your science class, and now you have to write it up for your teacher to review. You feel that you understood the background sufficiently, designed and completed the study effectively, obtained useful data, and can use those data to draw conclusions about a scientific process or principle. But how exactly do you write all that? What is your teacher expecting to see?
To take some of the guesswork out of answering these questions, try to think beyond the classroom setting. In fact, you and your teacher are both part of a scientific community, and the people who participate in this community tend to share the same values. As long as you understand and respect these values, your writing will likely meet the expectations of your audience—including your teacher.
So why are you writing this research report? The practical answer is “Because the teacher assigned it,” but that’s classroom thinking. Generally speaking, people investigating some scientific hypothesis have a responsibility to the rest of the scientific world to report their findings, particularly if these findings add to or contradict previous ideas. The people reading such reports have two primary goals:
- They want to gather the information presented.
- They want to know that the findings are legitimate.
Your job as a writer, then, is to fulfill these two goals.
How do I do that?
Good question. Here is the basic format scientists have designed for research reports:
- Introduction
Methods and Materials
This format, sometimes called “IMRAD,” may take slightly different shapes depending on the discipline or audience; some ask you to include an abstract or separate section for the hypothesis, or call the Discussion section “Conclusions,” or change the order of the sections (some professional and academic journals require the Methods section to appear last). Overall, however, the IMRAD format was devised to represent a textual version of the scientific method.
The scientific method, you’ll probably recall, involves developing a hypothesis, testing it, and deciding whether your findings support the hypothesis. In essence, the format for a research report in the sciences mirrors the scientific method but fleshes out the process a little. Below, you’ll find a table that shows how each written section fits into the scientific method and what additional information it offers the reader.
Thinking of your research report as based on the scientific method, but elaborated in the ways described above, may help you to meet your audience’s expectations successfully. We’re going to proceed by explicitly connecting each section of the lab report to the scientific method, then explaining why and how you need to elaborate that section.
Although this handout takes each section in the order in which it should be presented in the final report, you may for practical reasons decide to compose sections in another order. For example, many writers find that composing their Methods and Results before the other sections helps to clarify their idea of the experiment or study as a whole. You might consider using each assignment to practice different approaches to drafting the report, to find the order that works best for you.
What should I do before drafting the lab report?
The best way to prepare to write the lab report is to make sure that you fully understand everything you need to about the experiment. Obviously, if you don’t quite know what went on during the lab, you’re going to find it difficult to explain the lab satisfactorily to someone else. To make sure you know enough to write the report, complete the following steps:
- What are we going to do in this lab? (That is, what’s the procedure?)
- Why are we going to do it that way?
- What are we hoping to learn from this experiment?
- Why would we benefit from this knowledge?
- Consult your lab supervisor as you perform the lab. If you don’t know how to answer one of the questions above, for example, your lab supervisor will probably be able to explain it to you (or, at least, help you figure it out).
- Plan the steps of the experiment carefully with your lab partners. The less you rush, the more likely it is that you’ll perform the experiment correctly and record your findings accurately. Also, take some time to think about the best way to organize the data before you have to start putting numbers down. If you can design a table to account for the data, that will tend to work much better than jotting results down hurriedly on a scrap piece of paper.
- Record the data carefully so you get them right. You won’t be able to trust your conclusions if you have the wrong data, and your readers will know you messed up if the other three people in your group have “97 degrees” and you have “87.”
- Consult with your lab partners about everything you do. Lab groups often make one of two mistakes: two people do all the work while two have a nice chat, or everybody works together until the group finishes gathering the raw data, then scrams outta there. Collaborate with your partners, even when the experiment is “over.” What trends did you observe? Was the hypothesis supported? Did you all get the same results? What kind of figure should you use to represent your findings? The whole group can work together to answer these questions.
- Consider your audience. You may believe that audience is a non-issue: it’s your lab TA, right? Well, yes—but again, think beyond the classroom. If you write with only your lab instructor in mind, you may omit material that is crucial to a complete understanding of your experiment, because you assume the instructor knows all that stuff already. As a result, you may receive a lower grade, since your TA won’t be sure that you understand all the principles at work. Try to write towards a student in the same course but a different lab section. That student will have a fair degree of scientific expertise but won’t know much about your experiment particularly. Alternatively, you could envision yourself five years from now, after the reading and lectures for this course have faded a bit. What would you remember, and what would you need explained more clearly (as a refresher)?
Once you’ve completed these steps as you perform the experiment, you’ll be in a good position to draft an effective lab report.
Introductions
How do i write a strong introduction.
For the purposes of this handout, we’ll consider the Introduction to contain four basic elements: the purpose, the scientific literature relevant to the subject, the hypothesis, and the reasons you believed your hypothesis viable. Let’s start by going through each element of the Introduction to clarify what it covers and why it’s important. Then we can formulate a logical organizational strategy for the section.
The inclusion of the purpose (sometimes called the objective) of the experiment often confuses writers. The biggest misconception is that the purpose is the same as the hypothesis. Not quite. We’ll get to hypotheses in a minute, but basically they provide some indication of what you expect the experiment to show. The purpose is broader, and deals more with what you expect to gain through the experiment. In a professional setting, the hypothesis might have something to do with how cells react to a certain kind of genetic manipulation, but the purpose of the experiment is to learn more about potential cancer treatments. Undergraduate reports don’t often have this wide-ranging a goal, but you should still try to maintain the distinction between your hypothesis and your purpose. In a solubility experiment, for example, your hypothesis might talk about the relationship between temperature and the rate of solubility, but the purpose is probably to learn more about some specific scientific principle underlying the process of solubility.
For starters, most people say that you should write out your working hypothesis before you perform the experiment or study. Many beginning science students neglect to do so and find themselves struggling to remember precisely which variables were involved in the process or in what way the researchers felt that they were related. Write your hypothesis down as you develop it—you’ll be glad you did.
As for the form a hypothesis should take, it’s best not to be too fancy or complicated; an inventive style isn’t nearly so important as clarity here. There’s nothing wrong with beginning your hypothesis with the phrase, “It was hypothesized that . . .” Be as specific as you can about the relationship between the different objects of your study. In other words, explain that when term A changes, term B changes in this particular way. Readers of scientific writing are rarely content with the idea that a relationship between two terms exists—they want to know what that relationship entails.
Not a hypothesis:
“It was hypothesized that there is a significant relationship between the temperature of a solvent and the rate at which a solute dissolves.”
Hypothesis:
“It was hypothesized that as the temperature of a solvent increases, the rate at which a solute will dissolve in that solvent increases.”
Put more technically, most hypotheses contain both an independent and a dependent variable. The independent variable is what you manipulate to test the reaction; the dependent variable is what changes as a result of your manipulation. In the example above, the independent variable is the temperature of the solvent, and the dependent variable is the rate of solubility. Be sure that your hypothesis includes both variables.
Justify your hypothesis
You need to do more than tell your readers what your hypothesis is; you also need to assure them that this hypothesis was reasonable, given the circumstances. In other words, use the Introduction to explain that you didn’t just pluck your hypothesis out of thin air. (If you did pluck it out of thin air, your problems with your report will probably extend beyond using the appropriate format.) If you posit that a particular relationship exists between the independent and the dependent variable, what led you to believe your “guess” might be supported by evidence?
Scientists often refer to this type of justification as “motivating” the hypothesis, in the sense that something propelled them to make that prediction. Often, motivation includes what we already know—or rather, what scientists generally accept as true (see “Background/previous research” below). But you can also motivate your hypothesis by relying on logic or on your own observations. If you’re trying to decide which solutes will dissolve more rapidly in a solvent at increased temperatures, you might remember that some solids are meant to dissolve in hot water (e.g., bouillon cubes) and some are used for a function precisely because they withstand higher temperatures (they make saucepans out of something). Or you can think about whether you’ve noticed sugar dissolving more rapidly in your glass of iced tea or in your cup of coffee. Even such basic, outside-the-lab observations can help you justify your hypothesis as reasonable.
Background/previous research
This part of the Introduction demonstrates to the reader your awareness of how you’re building on other scientists’ work. If you think of the scientific community as engaging in a series of conversations about various topics, then you’ll recognize that the relevant background material will alert the reader to which conversation you want to enter.
Generally speaking, authors writing journal articles use the background for slightly different purposes than do students completing assignments. Because readers of academic journals tend to be professionals in the field, authors explain the background in order to permit readers to evaluate the study’s pertinence for their own work. You, on the other hand, write toward a much narrower audience—your peers in the course or your lab instructor—and so you must demonstrate that you understand the context for the (presumably assigned) experiment or study you’ve completed. For example, if your professor has been talking about polarity during lectures, and you’re doing a solubility experiment, you might try to connect the polarity of a solid to its relative solubility in certain solvents. In any event, both professional researchers and undergraduates need to connect the background material overtly to their own work.
Organization of this section
Most of the time, writers begin by stating the purpose or objectives of their own work, which establishes for the reader’s benefit the “nature and scope of the problem investigated” (Day 1994). Once you have expressed your purpose, you should then find it easier to move from the general purpose, to relevant material on the subject, to your hypothesis. In abbreviated form, an Introduction section might look like this:
“The purpose of the experiment was to test conventional ideas about solubility in the laboratory [purpose] . . . According to Whitecoat and Labrat (1999), at higher temperatures the molecules of solvents move more quickly . . . We know from the class lecture that molecules moving at higher rates of speed collide with one another more often and thus break down more easily [background material/motivation] . . . Thus, it was hypothesized that as the temperature of a solvent increases, the rate at which a solute will dissolve in that solvent increases [hypothesis].”
Again—these are guidelines, not commandments. Some writers and readers prefer different structures for the Introduction. The one above merely illustrates a common approach to organizing material.
How do I write a strong Materials and Methods section?
As with any piece of writing, your Methods section will succeed only if it fulfills its readers’ expectations, so you need to be clear in your own mind about the purpose of this section. Let’s review the purpose as we described it above: in this section, you want to describe in detail how you tested the hypothesis you developed and also to clarify the rationale for your procedure. In science, it’s not sufficient merely to design and carry out an experiment. Ultimately, others must be able to verify your findings, so your experiment must be reproducible, to the extent that other researchers can follow the same procedure and obtain the same (or similar) results.
Here’s a real-world example of the importance of reproducibility. In 1989, physicists Stanley Pons and Martin Fleischman announced that they had discovered “cold fusion,” a way of producing excess heat and power without the nuclear radiation that accompanies “hot fusion.” Such a discovery could have great ramifications for the industrial production of energy, so these findings created a great deal of interest. When other scientists tried to duplicate the experiment, however, they didn’t achieve the same results, and as a result many wrote off the conclusions as unjustified (or worse, a hoax). To this day, the viability of cold fusion is debated within the scientific community, even though an increasing number of researchers believe it possible. So when you write your Methods section, keep in mind that you need to describe your experiment well enough to allow others to replicate it exactly.
With these goals in mind, let’s consider how to write an effective Methods section in terms of content, structure, and style.
Sometimes the hardest thing about writing this section isn’t what you should talk about, but what you shouldn’t talk about. Writers often want to include the results of their experiment, because they measured and recorded the results during the course of the experiment. But such data should be reserved for the Results section. In the Methods section, you can write that you recorded the results, or how you recorded the results (e.g., in a table), but you shouldn’t write what the results were—not yet. Here, you’re merely stating exactly how you went about testing your hypothesis. As you draft your Methods section, ask yourself the following questions:
- How much detail? Be precise in providing details, but stay relevant. Ask yourself, “Would it make any difference if this piece were a different size or made from a different material?” If not, you probably don’t need to get too specific. If so, you should give as many details as necessary to prevent this experiment from going awry if someone else tries to carry it out. Probably the most crucial detail is measurement; you should always quantify anything you can, such as time elapsed, temperature, mass, volume, etc.
- Rationale: Be sure that as you’re relating your actions during the experiment, you explain your rationale for the protocol you developed. If you capped a test tube immediately after adding a solute to a solvent, why did you do that? (That’s really two questions: why did you cap it, and why did you cap it immediately?) In a professional setting, writers provide their rationale as a way to explain their thinking to potential critics. On one hand, of course, that’s your motivation for talking about protocol, too. On the other hand, since in practical terms you’re also writing to your teacher (who’s seeking to evaluate how well you comprehend the principles of the experiment), explaining the rationale indicates that you understand the reasons for conducting the experiment in that way, and that you’re not just following orders. Critical thinking is crucial—robots don’t make good scientists.
- Control: Most experiments will include a control, which is a means of comparing experimental results. (Sometimes you’ll need to have more than one control, depending on the number of hypotheses you want to test.) The control is exactly the same as the other items you’re testing, except that you don’t manipulate the independent variable-the condition you’re altering to check the effect on the dependent variable. For example, if you’re testing solubility rates at increased temperatures, your control would be a solution that you didn’t heat at all; that way, you’ll see how quickly the solute dissolves “naturally” (i.e., without manipulation), and you’ll have a point of reference against which to compare the solutions you did heat.
Describe the control in the Methods section. Two things are especially important in writing about the control: identify the control as a control, and explain what you’re controlling for. Here is an example:
“As a control for the temperature change, we placed the same amount of solute in the same amount of solvent, and let the solution stand for five minutes without heating it.”
Structure and style
Organization is especially important in the Methods section of a lab report because readers must understand your experimental procedure completely. Many writers are surprised by the difficulty of conveying what they did during the experiment, since after all they’re only reporting an event, but it’s often tricky to present this information in a coherent way. There’s a fairly standard structure you can use to guide you, and following the conventions for style can help clarify your points.
- Subsections: Occasionally, researchers use subsections to report their procedure when the following circumstances apply: 1) if they’ve used a great many materials; 2) if the procedure is unusually complicated; 3) if they’ve developed a procedure that won’t be familiar to many of their readers. Because these conditions rarely apply to the experiments you’ll perform in class, most undergraduate lab reports won’t require you to use subsections. In fact, many guides to writing lab reports suggest that you try to limit your Methods section to a single paragraph.
- Narrative structure: Think of this section as telling a story about a group of people and the experiment they performed. Describe what you did in the order in which you did it. You may have heard the old joke centered on the line, “Disconnect the red wire, but only after disconnecting the green wire,” where the person reading the directions blows everything to kingdom come because the directions weren’t in order. We’re used to reading about events chronologically, and so your readers will generally understand what you did if you present that information in the same way. Also, since the Methods section does generally appear as a narrative (story), you want to avoid the “recipe” approach: “First, take a clean, dry 100 ml test tube from the rack. Next, add 50 ml of distilled water.” You should be reporting what did happen, not telling the reader how to perform the experiment: “50 ml of distilled water was poured into a clean, dry 100 ml test tube.” Hint: most of the time, the recipe approach comes from copying down the steps of the procedure from your lab manual, so you may want to draft the Methods section initially without consulting your manual. Later, of course, you can go back and fill in any part of the procedure you inadvertently overlooked.
- Past tense: Remember that you’re describing what happened, so you should use past tense to refer to everything you did during the experiment. Writers are often tempted to use the imperative (“Add 5 g of the solid to the solution”) because that’s how their lab manuals are worded; less frequently, they use present tense (“5 g of the solid are added to the solution”). Instead, remember that you’re talking about an event which happened at a particular time in the past, and which has already ended by the time you start writing, so simple past tense will be appropriate in this section (“5 g of the solid were added to the solution” or “We added 5 g of the solid to the solution”).
- Active: We heated the solution to 80°C. (The subject, “we,” performs the action, heating.)
- Passive: The solution was heated to 80°C. (The subject, “solution,” doesn’t do the heating–it is acted upon, not acting.)
Increasingly, especially in the social sciences, using first person and active voice is acceptable in scientific reports. Most readers find that this style of writing conveys information more clearly and concisely. This rhetorical choice thus brings two scientific values into conflict: objectivity versus clarity. Since the scientific community hasn’t reached a consensus about which style it prefers, you may want to ask your lab instructor.
How do I write a strong Results section?
Here’s a paradox for you. The Results section is often both the shortest (yay!) and most important (uh-oh!) part of your report. Your Materials and Methods section shows how you obtained the results, and your Discussion section explores the significance of the results, so clearly the Results section forms the backbone of the lab report. This section provides the most critical information about your experiment: the data that allow you to discuss how your hypothesis was or wasn’t supported. But it doesn’t provide anything else, which explains why this section is generally shorter than the others.
Before you write this section, look at all the data you collected to figure out what relates significantly to your hypothesis. You’ll want to highlight this material in your Results section. Resist the urge to include every bit of data you collected, since perhaps not all are relevant. Also, don’t try to draw conclusions about the results—save them for the Discussion section. In this section, you’re reporting facts. Nothing your readers can dispute should appear in the Results section.
Most Results sections feature three distinct parts: text, tables, and figures. Let’s consider each part one at a time.
This should be a short paragraph, generally just a few lines, that describes the results you obtained from your experiment. In a relatively simple experiment, one that doesn’t produce a lot of data for you to repeat, the text can represent the entire Results section. Don’t feel that you need to include lots of extraneous detail to compensate for a short (but effective) text; your readers appreciate discrimination more than your ability to recite facts. In a more complex experiment, you may want to use tables and/or figures to help guide your readers toward the most important information you gathered. In that event, you’ll need to refer to each table or figure directly, where appropriate:
“Table 1 lists the rates of solubility for each substance”
“Solubility increased as the temperature of the solution increased (see Figure 1).”
If you do use tables or figures, make sure that you don’t present the same material in both the text and the tables/figures, since in essence you’ll just repeat yourself, probably annoying your readers with the redundancy of your statements.
Feel free to describe trends that emerge as you examine the data. Although identifying trends requires some judgment on your part and so may not feel like factual reporting, no one can deny that these trends do exist, and so they properly belong in the Results section. Example:
“Heating the solution increased the rate of solubility of polar solids by 45% but had no effect on the rate of solubility in solutions containing non-polar solids.”
This point isn’t debatable—you’re just pointing out what the data show.
As in the Materials and Methods section, you want to refer to your data in the past tense, because the events you recorded have already occurred and have finished occurring. In the example above, note the use of “increased” and “had,” rather than “increases” and “has.” (You don’t know from your experiment that heating always increases the solubility of polar solids, but it did that time.)
You shouldn’t put information in the table that also appears in the text. You also shouldn’t use a table to present irrelevant data, just to show you did collect these data during the experiment. Tables are good for some purposes and situations, but not others, so whether and how you’ll use tables depends upon what you need them to accomplish.
Tables are useful ways to show variation in data, but not to present a great deal of unchanging measurements. If you’re dealing with a scientific phenomenon that occurs only within a certain range of temperatures, for example, you don’t need to use a table to show that the phenomenon didn’t occur at any of the other temperatures. How useful is this table?
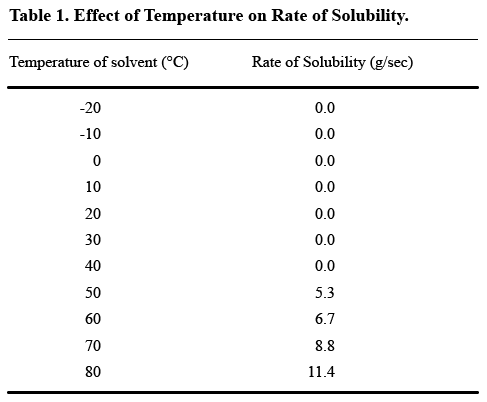
As you can probably see, no solubility was observed until the trial temperature reached 50°C, a fact that the text part of the Results section could easily convey. The table could then be limited to what happened at 50°C and higher, thus better illustrating the differences in solubility rates when solubility did occur.
As a rule, try not to use a table to describe any experimental event you can cover in one sentence of text. Here’s an example of an unnecessary table from How to Write and Publish a Scientific Paper , by Robert A. Day:
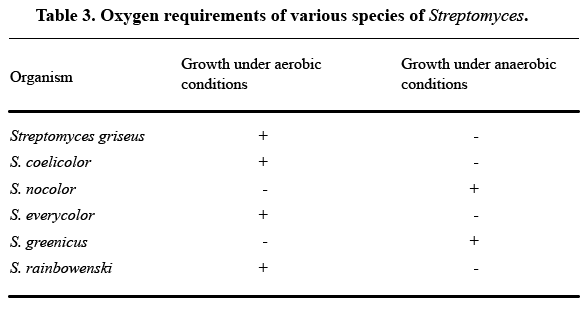
As Day notes, all the information in this table can be summarized in one sentence: “S. griseus, S. coelicolor, S. everycolor, and S. rainbowenski grew under aerobic conditions, whereas S. nocolor and S. greenicus required anaerobic conditions.” Most readers won’t find the table clearer than that one sentence.
When you do have reason to tabulate material, pay attention to the clarity and readability of the format you use. Here are a few tips:
- Number your table. Then, when you refer to the table in the text, use that number to tell your readers which table they can review to clarify the material.
- Give your table a title. This title should be descriptive enough to communicate the contents of the table, but not so long that it becomes difficult to follow. The titles in the sample tables above are acceptable.
- Arrange your table so that readers read vertically, not horizontally. For the most part, this rule means that you should construct your table so that like elements read down, not across. Think about what you want your readers to compare, and put that information in the column (up and down) rather than in the row (across). Usually, the point of comparison will be the numerical data you collect, so especially make sure you have columns of numbers, not rows.Here’s an example of how drastically this decision affects the readability of your table (from A Short Guide to Writing about Chemistry , by Herbert Beall and John Trimbur). Look at this table, which presents the relevant data in horizontal rows:
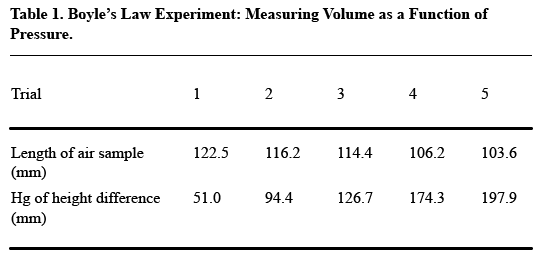
It’s a little tough to see the trends that the author presumably wants to present in this table. Compare this table, in which the data appear vertically:
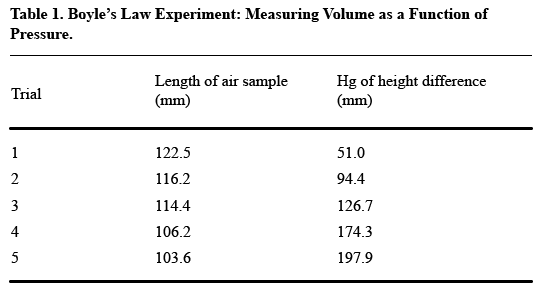
The second table shows how putting like elements in a vertical column makes for easier reading. In this case, the like elements are the measurements of length and height, over five trials–not, as in the first table, the length and height measurements for each trial.
- Make sure to include units of measurement in the tables. Readers might be able to guess that you measured something in millimeters, but don’t make them try.
- Don’t use vertical lines as part of the format for your table. This convention exists because journals prefer not to have to reproduce these lines because the tables then become more expensive to print. Even though it’s fairly unlikely that you’ll be sending your Biology 11 lab report to Science for publication, your readers still have this expectation. Consequently, if you use the table-drawing option in your word-processing software, choose the option that doesn’t rely on a “grid” format (which includes vertical lines).
How do I include figures in my report?
Although tables can be useful ways of showing trends in the results you obtained, figures (i.e., illustrations) can do an even better job of emphasizing such trends. Lab report writers often use graphic representations of the data they collected to provide their readers with a literal picture of how the experiment went.
When should you use a figure?
Remember the circumstances under which you don’t need a table: when you don’t have a great deal of data or when the data you have don’t vary a lot. Under the same conditions, you would probably forgo the figure as well, since the figure would be unlikely to provide your readers with an additional perspective. Scientists really don’t like their time wasted, so they tend not to respond favorably to redundancy.
If you’re trying to decide between using a table and creating a figure to present your material, consider the following a rule of thumb. The strength of a table lies in its ability to supply large amounts of exact data, whereas the strength of a figure is its dramatic illustration of important trends within the experiment. If you feel that your readers won’t get the full impact of the results you obtained just by looking at the numbers, then a figure might be appropriate.
Of course, an undergraduate class may expect you to create a figure for your lab experiment, if only to make sure that you can do so effectively. If this is the case, then don’t worry about whether to use figures or not—concentrate instead on how best to accomplish your task.
Figures can include maps, photographs, pen-and-ink drawings, flow charts, bar graphs, and section graphs (“pie charts”). But the most common figure by far, especially for undergraduates, is the line graph, so we’ll focus on that type in this handout.
At the undergraduate level, you can often draw and label your graphs by hand, provided that the result is clear, legible, and drawn to scale. Computer technology has, however, made creating line graphs a lot easier. Most word-processing software has a number of functions for transferring data into graph form; many scientists have found Microsoft Excel, for example, a helpful tool in graphing results. If you plan on pursuing a career in the sciences, it may be well worth your while to learn to use a similar program.
Computers can’t, however, decide for you how your graph really works; you have to know how to design your graph to meet your readers’ expectations. Here are some of these expectations:
- Keep it as simple as possible. You may be tempted to signal the complexity of the information you gathered by trying to design a graph that accounts for that complexity. But remember the purpose of your graph: to dramatize your results in a manner that’s easy to see and grasp. Try not to make the reader stare at the graph for a half hour to find the important line among the mass of other lines. For maximum effectiveness, limit yourself to three to five lines per graph; if you have more data to demonstrate, use a set of graphs to account for it, rather than trying to cram it all into a single figure.
- Plot the independent variable on the horizontal (x) axis and the dependent variable on the vertical (y) axis. Remember that the independent variable is the condition that you manipulated during the experiment and the dependent variable is the condition that you measured to see if it changed along with the independent variable. Placing the variables along their respective axes is mostly just a convention, but since your readers are accustomed to viewing graphs in this way, you’re better off not challenging the convention in your report.
- Label each axis carefully, and be especially careful to include units of measure. You need to make sure that your readers understand perfectly well what your graph indicates.
- Number and title your graphs. As with tables, the title of the graph should be informative but concise, and you should refer to your graph by number in the text (e.g., “Figure 1 shows the increase in the solubility rate as a function of temperature”).
- Many editors of professional scientific journals prefer that writers distinguish the lines in their graphs by attaching a symbol to them, usually a geometric shape (triangle, square, etc.), and using that symbol throughout the curve of the line. Generally, readers have a hard time distinguishing dotted lines from dot-dash lines from straight lines, so you should consider staying away from this system. Editors don’t usually like different-colored lines within a graph because colors are difficult and expensive to reproduce; colors may, however, be great for your purposes, as long as you’re not planning to submit your paper to Nature. Use your discretion—try to employ whichever technique dramatizes the results most effectively.
- Try to gather data at regular intervals, so the plot points on your graph aren’t too far apart. You can’t be sure of the arc you should draw between the plot points if the points are located at the far corners of the graph; over a fifteen-minute interval, perhaps the change occurred in the first or last thirty seconds of that period (in which case your straight-line connection between the points is misleading).
- If you’re worried that you didn’t collect data at sufficiently regular intervals during your experiment, go ahead and connect the points with a straight line, but you may want to examine this problem as part of your Discussion section.
- Make your graph large enough so that everything is legible and clearly demarcated, but not so large that it either overwhelms the rest of the Results section or provides a far greater range than you need to illustrate your point. If, for example, the seedlings of your plant grew only 15 mm during the trial, you don’t need to construct a graph that accounts for 100 mm of growth. The lines in your graph should more or less fill the space created by the axes; if you see that your data is confined to the lower left portion of the graph, you should probably re-adjust your scale.
- If you create a set of graphs, make them the same size and format, including all the verbal and visual codes (captions, symbols, scale, etc.). You want to be as consistent as possible in your illustrations, so that your readers can easily make the comparisons you’re trying to get them to see.
How do I write a strong Discussion section?
The discussion section is probably the least formalized part of the report, in that you can’t really apply the same structure to every type of experiment. In simple terms, here you tell your readers what to make of the Results you obtained. If you have done the Results part well, your readers should already recognize the trends in the data and have a fairly clear idea of whether your hypothesis was supported. Because the Results can seem so self-explanatory, many students find it difficult to know what material to add in this last section.
Basically, the Discussion contains several parts, in no particular order, but roughly moving from specific (i.e., related to your experiment only) to general (how your findings fit in the larger scientific community). In this section, you will, as a rule, need to:
Explain whether the data support your hypothesis
- Acknowledge any anomalous data or deviations from what you expected
Derive conclusions, based on your findings, about the process you’re studying
- Relate your findings to earlier work in the same area (if you can)
Explore the theoretical and/or practical implications of your findings
Let’s look at some dos and don’ts for each of these objectives.
This statement is usually a good way to begin the Discussion, since you can’t effectively speak about the larger scientific value of your study until you’ve figured out the particulars of this experiment. You might begin this part of the Discussion by explicitly stating the relationships or correlations your data indicate between the independent and dependent variables. Then you can show more clearly why you believe your hypothesis was or was not supported. For example, if you tested solubility at various temperatures, you could start this section by noting that the rates of solubility increased as the temperature increased. If your initial hypothesis surmised that temperature change would not affect solubility, you would then say something like,
“The hypothesis that temperature change would not affect solubility was not supported by the data.”
Note: Students tend to view labs as practical tests of undeniable scientific truths. As a result, you may want to say that the hypothesis was “proved” or “disproved” or that it was “correct” or “incorrect.” These terms, however, reflect a degree of certainty that you as a scientist aren’t supposed to have. Remember, you’re testing a theory with a procedure that lasts only a few hours and relies on only a few trials, which severely compromises your ability to be sure about the “truth” you see. Words like “supported,” “indicated,” and “suggested” are more acceptable ways to evaluate your hypothesis.
Also, recognize that saying whether the data supported your hypothesis or not involves making a claim to be defended. As such, you need to show the readers that this claim is warranted by the evidence. Make sure that you’re very explicit about the relationship between the evidence and the conclusions you draw from it. This process is difficult for many writers because we don’t often justify conclusions in our regular lives. For example, you might nudge your friend at a party and whisper, “That guy’s drunk,” and once your friend lays eyes on the person in question, she might readily agree. In a scientific paper, by contrast, you would need to defend your claim more thoroughly by pointing to data such as slurred words, unsteady gait, and the lampshade-as-hat. In addition to pointing out these details, you would also need to show how (according to previous studies) these signs are consistent with inebriation, especially if they occur in conjunction with one another. To put it another way, tell your readers exactly how you got from point A (was the hypothesis supported?) to point B (yes/no).
Acknowledge any anomalous data, or deviations from what you expected
You need to take these exceptions and divergences into account, so that you qualify your conclusions sufficiently. For obvious reasons, your readers will doubt your authority if you (deliberately or inadvertently) overlook a key piece of data that doesn’t square with your perspective on what occurred. In a more philosophical sense, once you’ve ignored evidence that contradicts your claims, you’ve departed from the scientific method. The urge to “tidy up” the experiment is often strong, but if you give in to it you’re no longer performing good science.
Sometimes after you’ve performed a study or experiment, you realize that some part of the methods you used to test your hypothesis was flawed. In that case, it’s OK to suggest that if you had the chance to conduct your test again, you might change the design in this or that specific way in order to avoid such and such a problem. The key to making this approach work, though, is to be very precise about the weakness in your experiment, why and how you think that weakness might have affected your data, and how you would alter your protocol to eliminate—or limit the effects of—that weakness. Often, inexperienced researchers and writers feel the need to account for “wrong” data (remember, there’s no such animal), and so they speculate wildly about what might have screwed things up. These speculations include such factors as the unusually hot temperature in the room, or the possibility that their lab partners read the meters wrong, or the potentially defective equipment. These explanations are what scientists call “cop-outs,” or “lame”; don’t indicate that the experiment had a weakness unless you’re fairly certain that a) it really occurred and b) you can explain reasonably well how that weakness affected your results.
If, for example, your hypothesis dealt with the changes in solubility at different temperatures, then try to figure out what you can rationally say about the process of solubility more generally. If you’re doing an undergraduate lab, chances are that the lab will connect in some way to the material you’ve been covering either in lecture or in your reading, so you might choose to return to these resources as a way to help you think clearly about the process as a whole.
This part of the Discussion section is another place where you need to make sure that you’re not overreaching. Again, nothing you’ve found in one study would remotely allow you to claim that you now “know” something, or that something isn’t “true,” or that your experiment “confirmed” some principle or other. Hesitate before you go out on a limb—it’s dangerous! Use less absolutely conclusive language, including such words as “suggest,” “indicate,” “correspond,” “possibly,” “challenge,” etc.
Relate your findings to previous work in the field (if possible)
We’ve been talking about how to show that you belong in a particular community (such as biologists or anthropologists) by writing within conventions that they recognize and accept. Another is to try to identify a conversation going on among members of that community, and use your work to contribute to that conversation. In a larger philosophical sense, scientists can’t fully understand the value of their research unless they have some sense of the context that provoked and nourished it. That is, you have to recognize what’s new about your project (potentially, anyway) and how it benefits the wider body of scientific knowledge. On a more pragmatic level, especially for undergraduates, connecting your lab work to previous research will demonstrate to the TA that you see the big picture. You have an opportunity, in the Discussion section, to distinguish yourself from the students in your class who aren’t thinking beyond the barest facts of the study. Capitalize on this opportunity by putting your own work in context.
If you’re just beginning to work in the natural sciences (as a first-year biology or chemistry student, say), most likely the work you’ll be doing has already been performed and re-performed to a satisfactory degree. Hence, you could probably point to a similar experiment or study and compare/contrast your results and conclusions. More advanced work may deal with an issue that is somewhat less “resolved,” and so previous research may take the form of an ongoing debate, and you can use your own work to weigh in on that debate. If, for example, researchers are hotly disputing the value of herbal remedies for the common cold, and the results of your study suggest that Echinacea diminishes the symptoms but not the actual presence of the cold, then you might want to take some time in the Discussion section to recapitulate the specifics of the dispute as it relates to Echinacea as an herbal remedy. (Consider that you have probably already written in the Introduction about this debate as background research.)
This information is often the best way to end your Discussion (and, for all intents and purposes, the report). In argumentative writing generally, you want to use your closing words to convey the main point of your writing. This main point can be primarily theoretical (“Now that you understand this information, you’re in a better position to understand this larger issue”) or primarily practical (“You can use this information to take such and such an action”). In either case, the concluding statements help the reader to comprehend the significance of your project and your decision to write about it.
Since a lab report is argumentative—after all, you’re investigating a claim, and judging the legitimacy of that claim by generating and collecting evidence—it’s often a good idea to end your report with the same technique for establishing your main point. If you want to go the theoretical route, you might talk about the consequences your study has for the field or phenomenon you’re investigating. To return to the examples regarding solubility, you could end by reflecting on what your work on solubility as a function of temperature tells us (potentially) about solubility in general. (Some folks consider this type of exploration “pure” as opposed to “applied” science, although these labels can be problematic.) If you want to go the practical route, you could end by speculating about the medical, institutional, or commercial implications of your findings—in other words, answer the question, “What can this study help people to do?” In either case, you’re going to make your readers’ experience more satisfying, by helping them see why they spent their time learning what you had to teach them.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
American Psychological Association. 2010. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association . 6th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Beall, Herbert, and John Trimbur. 2001. A Short Guide to Writing About Chemistry , 2nd ed. New York: Longman.
Blum, Deborah, and Mary Knudson. 1997. A Field Guide for Science Writers: The Official Guide of the National Association of Science Writers . New York: Oxford University Press.
Booth, Wayne C., Gregory G. Colomb, Joseph M. Williams, Joseph Bizup, and William T. FitzGerald. 2016. The Craft of Research , 4th ed. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Briscoe, Mary Helen. 1996. Preparing Scientific Illustrations: A Guide to Better Posters, Presentations, and Publications , 2nd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Council of Science Editors. 2014. Scientific Style and Format: The CSE Manual for Authors, Editors, and Publishers , 8th ed. Chicago & London: University of Chicago Press.
Davis, Martha. 2012. Scientific Papers and Presentations , 3rd ed. London: Academic Press.
Day, Robert A. 1994. How to Write and Publish a Scientific Paper , 4th ed. Phoenix: Oryx Press.
Porush, David. 1995. A Short Guide to Writing About Science . New York: Longman.
Williams, Joseph, and Joseph Bizup. 2017. Style: Lessons in Clarity and Grace , 12th ed. Boston: Pearson.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

Complete Guide to Writing a Lab Report (With Example)
Students tend to approach writing lab reports with confusion and dread. Whether in high school science classes or undergraduate laboratories, experiments are always fun and games until the times comes to submit a lab report. What if we didn’t need to spend hours agonizing over this piece of scientific writing? Our lives would be so much easier if we were told what information to include, what to do with all their data and how to use references. Well, here’s a guide to all the core components in a well-written lab report, complete with an example.
Things to Include in a Laboratory Report
The laboratory report is simply a way to show that you understand the link between theory and practice while communicating through clear and concise writing. As with all forms of writing, it’s not the report’s length that matters, but the quality of the information conveyed within. This article outlines the important bits that go into writing a lab report (title, abstract, introduction, method, results, discussion, conclusion, reference). At the end is an example report of reducing sugar analysis with Benedict’s reagent.
The report’s title should be short but descriptive, indicating the qualitative or quantitative nature of the practical along with the primary goal or area of focus.
Following this should be the abstract, 2-3 sentences summarizing the practical. The abstract shows the reader the main results of the practical and helps them decide quickly whether the rest of the report is relevant to their use. Remember that the whole report should be written in a passive voice .
Introduction
The introduction provides context to the experiment in a couple of paragraphs and relevant diagrams. While a short preamble outlining the history of the techniques or materials used in the practical is appropriate, the bulk of the introduction should outline the experiment’s goals, creating a logical flow to the next section.
Some reports require you to write down the materials used, which can be combined with this section. The example below does not include a list of materials used. If unclear, it is best to check with your teacher or demonstrator before writing your lab report from scratch.
Step-by-step methods are usually provided in high school and undergraduate laboratory practicals, so it’s just a matter of paraphrasing them. This is usually the section that teachers and demonstrators care the least about. Any unexpected changes to the experimental setup or techniques can also be documented here.
The results section should include the raw data that has been collected in the experiment as well as calculations that are performed. It is usually appropriate to include diagrams; depending on the experiment, these can range from scatter plots to chromatograms.
The discussion is the most critical part of the lab report as it is a chance for you to show that you have a deep understanding of the practical and the theory behind it. Teachers and lecturers tend to give this section the most weightage when marking the report. It would help if you used the discussion section to address several points:
- Explain the results gathered. Is there a particular trend? Do the results support the theory behind the experiment?
- Highlight any unexpected results or outlying data points. What are possible sources of error?
- Address the weaknesses of the experiment. Refer to the materials and methods used to identify improvements that would yield better results (more accurate equipment, better experimental technique, etc.)
Finally, a short paragraph to conclude the laboratory report. It should summarize the findings and provide an objective review of the experiment.
If any external sources were used in writing the lab report, they should go here. Referencing is critical in scientific writing; it’s like giving a shout out (known as a citation) to the original provider of the information. It is good practice to have at least one source referenced, either from researching the context behind the experiment, best practices for the method used or similar industry standards.
Google Scholar is a good resource for quickly gathering references of a specific style . Searching for the article in the search bar and clicking on the ‘cite’ button opens a pop-up that allows you to copy and paste from several common referencing styles.

Example: Writing a Lab Report
Title : Semi-Quantitative Analysis of Food Products using Benedict’s Reagent
Abstract : Food products (milk, chicken, bread, orange juice) were solubilized and tested for reducing sugars using Benedict’s reagent. Milk contained the highest level of reducing sugars at ~2%, while chicken contained almost no reducing sugars.
Introduction : Sugar detection has been of interest for over 100 years, with the first test for glucose using copper sulfate developed by German chemist Karl Trommer in 1841. It was used to test the urine of diabetics, where sugar was present in high amounts. However, it wasn’t until 1907 when the method was perfected by Stanley Benedict, using sodium citrate and sodium carbonate to stabilize the copper sulfate in solution. Benedict’s reagent is a bright blue because of the copper sulfate, turning green and then red as the concentration of reducing sugars increases.
Benedict’s reagent was used in this experiment to compare the amount of reducing sugars between four food items: milk, chicken solution, bread and orange juice. Following this, standardized glucose solutions (0.0%, 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, 2.0%) were tested with Benedict’s reagent to determine the color produced at those sugar levels, allowing us to perform a semi-quantitative analysis of the food items.
Method : Benedict’s reagent was prepared by mixing 1.73 g of copper (II) sulfate pentahydrate, 17.30 g of sodium citrate pentahydrate and 10.00 g of sodium carbonate anhydrous. The mixture was dissolved with stirring and made up to 100 ml using distilled water before filtration using filter paper and a funnel to remove any impurities.
4 ml of milk, chicken solution and orange juice (commercially available) were measured in test tubes, along with 4 ml of bread solution. The bread solution was prepared using 4 g of dried bread ground with mortar and pestle before diluting with distilled water up to 4 ml. Then, 4 ml of Benedict’s reagent was added to each test tube and placed in a boiling water bath for 5 minutes, then each test tube was observed.
Next, glucose solutions were prepared by dissolving 0.5 g, 1.0 g, 1.5 g and 2.0 g of glucose in 100 ml of distilled water to produce 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5% and 2.0% solutions, respectively. 4 ml of each solution was added to 4 ml of Benedict’s reagent in a test tube and placed in a boiling water bath for 5 minutes, then each test tube was observed.
Results : Food Solutions (4 ml) with Benedict’s Reagent (4 ml)
Glucose Solutions (4 ml) with Benedict’s Reagent (4 ml)
Semi-Quantitative Analysis from Data
Discussion : From the analysis of food solutions along with the glucose solutions of known concentrations, the semi-quantitative analysis of sugar levels in different food products was performed. Milk had the highest sugar content of 2%, with orange juice at 1.5%, bread at 0.5% and chicken with 0% sugar. These values were approximated; the standard solutions were not the exact color of the food solutions, but the closest color match was chosen.
One point of contention was using the orange juice solution, which conferred color to the starting solution, rendering it green before the reaction started. This could have led to the final color (and hence, sugar quantity) being inaccurate. Also, since comparing colors using eyesight alone is inaccurate, the experiment could be improved with a colorimeter that can accurately determine the exact wavelength of light absorbed by the solution.
Another downside of Benedict’s reagent is its inability to react with non-reducing sugars. Reducing sugars encompass all sugar types that can be oxidized from aldehydes or ketones into carboxylic acids. This means that all monosaccharides (glucose, fructose, etc.) are reducing sugars, while only select polysaccharides are. Disaccharides like sucrose and trehalose cannot be oxidized, hence are non-reducing and will not react with Benedict’s reagent. Furthermore, Benedict’s reagent cannot distinguish between different types of reducing sugars.
Conclusion : Using Benedict’s reagent, different food products were analyzed semi-quantitatively for their levels of reducing sugars. Milk contained around 2% sugar, while the chicken solution had no sugar. Overall, the experiment was a success, although the accuracy of the results could have been improved with the use of quantitative equipment and methods.
Reference :
- Raza, S. I., Raza, S. A., Kazmi, M., Khan, S., & Hussain, I. (2021). 100 Years of Glucose Monitoring in Diabetes Management. Journal of Diabetes Mellitus , 11 (5), 221-233.
- Benedict, Stanley R (1909). A Reagent for the Detection of Reducing Sugars. Journal of Biological Chemistry , 5 , 485-487.
Using this guide and example, writing a lab report should be a hassle-free, perhaps even enjoyable process!
About the Author

Sean is a consultant for clients in the pharmaceutical industry and is an associate lecturer at La Trobe University, where unfortunate undergrads are subject to his ramblings on chemistry and pharmacology.
You Might Also Like…

Are Left-Handers More Creative? Science Can’t Really Answer

Is Open Access Really the Ideal Future for Academic Publishing?

If our content has been helpful to you, please consider supporting our independent science publishing efforts: for just $1 a month.
© 2023 FTLOScience • All Rights Reserved
How to Write a Lab Report
Lab Reports Describe Your Experiment
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Scientific Method
- Biochemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
Lab reports are an essential part of all laboratory courses and usually a significant part of your grade. If your instructor gives you an outline for how to write a lab report, use that. Some instructors require a lab report to be included in a lab notebook , while others will request a separate report. Here's a format for a lab report you can use if you aren't sure what to write or need an explanation of what to include in the different parts of the report.
A lab report is how you explain what you did in your experiment, what you learned, and what the results meant.
Lab Report Essentials
Not all lab reports have title pages, but if your instructor wants one, it would be a single page that states:
- The title of the experiment.
- Your name and the names of any lab partners.
- Your instructor's name.
- The date the lab was performed or the date the report was submitted.
The title says what you did. It should be brief (aim for ten words or less) and describe the main point of the experiment or investigation. An example of a title would be: "Effects of Ultraviolet Light on Borax Crystal Growth Rate". If you can, begin your title using a keyword rather than an article like "The" or "A".
Introduction or Purpose
Usually, the introduction is one paragraph that explains the objectives or purpose of the lab. In one sentence, state the hypothesis. Sometimes an introduction may contain background information, briefly summarize how the experiment was performed, state the findings of the experiment, and list the conclusions of the investigation. Even if you don't write a whole introduction, you need to state the purpose of the experiment, or why you did it. This would be where you state your hypothesis .
List everything needed to complete your experiment.
Describe the steps you completed during your investigation. This is your procedure. Be sufficiently detailed that anyone could read this section and duplicate your experiment. Write it as if you were giving direction for someone else to do the lab. It may be helpful to provide a figure to diagram your experimental setup.
Numerical data obtained from your procedure usually presented as a table. Data encompasses what you recorded when you conducted the experiment. It's just the facts, not any interpretation of what they mean.
Describe in words what the data means. Sometimes the Results section is combined with the Discussion.
Discussion or Analysis
The Data section contains numbers; the Analysis section contains any calculations you made based on those numbers. This is where you interpret the data and determine whether or not a hypothesis was accepted. This is also where you would discuss any mistakes you might have made while conducting the investigation. You may wish to describe ways the study might have been improved.
Conclusions
Most of the time the conclusion is a single paragraph that sums up what happened in the experiment, whether your hypothesis was accepted or rejected, and what this means.
Figures and Graphs
Graphs and figures must both be labeled with a descriptive title. Label the axes on a graph, being sure to include units of measurement. The independent variable is on the X-axis, the dependent variable (the one you are measuring) is on the Y-axis. Be sure to refer to figures and graphs in the text of your report: the first figure is Figure 1, the second figure is Figure 2, etc.
If your research was based on someone else's work or if you cited facts that require documentation, then you should list these references.
- How to Format a Biology Lab Report
- Science Lab Report Template - Fill in the Blanks
- How to Write a Science Fair Project Report
- How to Write an Abstract for a Scientific Paper
- Six Steps of the Scientific Method
- How To Design a Science Fair Experiment
- Understanding Simple vs Controlled Experiments
- Make a Science Fair Poster or Display
- What Is an Experiment? Definition and Design
- How to Organize Your Science Fair Poster
- What Are the Elements of a Good Hypothesis?
- Scientific Method Lesson Plan
- How to Write a Film Review
- The 10 Most Important Lab Safety Rules
- 6 Steps to Writing the Perfect Personal Essay
Lab Report Format: Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
In psychology, a lab report outlines a study’s objectives, methods, results, discussion, and conclusions, ensuring clarity and adherence to APA (or relevant) formatting guidelines.
A typical lab report would include the following sections: title, abstract, introduction, method, results, and discussion.
The title page, abstract, references, and appendices are started on separate pages (subsections from the main body of the report are not). Use double-line spacing of text, font size 12, and include page numbers.
The report should have a thread of arguments linking the prediction in the introduction to the content of the discussion.
This must indicate what the study is about. It must include the variables under investigation. It should not be written as a question.
Title pages should be formatted in APA style .
The abstract provides a concise and comprehensive summary of a research report. Your style should be brief but not use note form. Look at examples in journal articles . It should aim to explain very briefly (about 150 words) the following:
- Start with a one/two sentence summary, providing the aim and rationale for the study.
- Describe participants and setting: who, when, where, how many, and what groups?
- Describe the method: what design, what experimental treatment, what questionnaires, surveys, or tests were used.
- Describe the major findings, including a mention of the statistics used and the significance levels, or simply one sentence summing up the outcome.
- The final sentence(s) outline the study’s “contribution to knowledge” within the literature. What does it all mean? Mention the implications of your findings if appropriate.
The abstract comes at the beginning of your report but is written at the end (as it summarises information from all the other sections of the report).
Introduction
The purpose of the introduction is to explain where your hypothesis comes from (i.e., it should provide a rationale for your research study).
Ideally, the introduction should have a funnel structure: Start broad and then become more specific. The aims should not appear out of thin air; the preceding review of psychological literature should lead logically into the aims and hypotheses.
- Start with general theory, briefly introducing the topic. Define the important key terms.
- Explain the theoretical framework.
- Summarise and synthesize previous studies – What was the purpose? Who were the participants? What did they do? What did they find? What do these results mean? How do the results relate to the theoretical framework?
- Rationale: How does the current study address a gap in the literature? Perhaps it overcomes a limitation of previous research.
- Aims and hypothesis. Write a paragraph explaining what you plan to investigate and make a clear and concise prediction regarding the results you expect to find.
There should be a logical progression of ideas that aids the flow of the report. This means the studies outlined should lead logically to your aims and hypotheses.
Do be concise and selective, and avoid the temptation to include anything in case it is relevant (i.e., don’t write a shopping list of studies).
USE THE FOLLOWING SUBHEADINGS:
Participants
- How many participants were recruited?
- Say how you obtained your sample (e.g., opportunity sample).
- Give relevant demographic details (e.g., gender, ethnicity, age range, mean age, and standard deviation).
- State the experimental design .
- What were the independent and dependent variables ? Make sure the independent variable is labeled and name the different conditions/levels.
- For example, if gender is the independent variable label, then male and female are the levels/conditions/groups.
- How were the IV and DV operationalized?
- Identify any controls used, e.g., counterbalancing and control of extraneous variables.
- List all the materials and measures (e.g., what was the title of the questionnaire? Was it adapted from a study?).
- You do not need to include wholesale replication of materials – instead, include a ‘sensible’ (illustrate) level of detail. For example, give examples of questionnaire items.
- Include the reliability (e.g., alpha values) for the measure(s).
- Describe the precise procedure you followed when conducting your research, i.e., exactly what you did.
- Describe in sufficient detail to allow for replication of findings.
- Be concise in your description and omit extraneous/trivial details, e.g., you don’t need to include details regarding instructions, debrief, record sheets, etc.
- Assume the reader has no knowledge of what you did and ensure that he/she can replicate (i.e., copy) your study exactly by what you write in this section.
- Write in the past tense.
- Don’t justify or explain in the Method (e.g., why you chose a particular sampling method); just report what you did.
- Only give enough detail for someone to replicate the experiment – be concise in your writing.
- The results section of a paper usually presents descriptive statistics followed by inferential statistics.
- Report the means, standard deviations, and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for each IV level. If you have four to 20 numbers to present, a well-presented table is best, APA style.
- Name the statistical test being used.
- Report appropriate statistics (e.g., t-scores, p values ).
- Report the magnitude (e.g., are the results significant or not?) as well as the direction of the results (e.g., which group performed better?).
- It is optional to report the effect size (this does not appear on the SPSS output).
- Avoid interpreting the results (save this for the discussion).
- Make sure the results are presented clearly and concisely. A table can be used to display descriptive statistics if this makes the data easier to understand.
- DO NOT include any raw data.
- Follow APA style.
Use APA Style
- Numbers reported to 2 d.p. (incl. 0 before the decimal if 1.00, e.g., “0.51”). The exceptions to this rule: Numbers which can never exceed 1.0 (e.g., p -values, r-values): report to 3 d.p. and do not include 0 before the decimal place, e.g., “.001”.
- Percentages and degrees of freedom: report as whole numbers.
- Statistical symbols that are not Greek letters should be italicized (e.g., M , SD , t , X 2 , F , p , d ).
- Include spaces on either side of the equals sign.
- When reporting 95%, CIs (confidence intervals), upper and lower limits are given inside square brackets, e.g., “95% CI [73.37, 102.23]”
- Outline your findings in plain English (avoid statistical jargon) and relate your results to your hypothesis, e.g., is it supported or rejected?
- Compare your results to background materials from the introduction section. Are your results similar or different? Discuss why/why not.
- How confident can we be in the results? Acknowledge limitations, but only if they can explain the result obtained. If the study has found a reliable effect, be very careful suggesting limitations as you are doubting your results. Unless you can think of any c onfounding variable that can explain the results instead of the IV, it would be advisable to leave the section out.
- Suggest constructive ways to improve your study if appropriate.
- What are the implications of your findings? Say what your findings mean for how people behave in the real world.
- Suggest an idea for further research triggered by your study, something in the same area but not simply an improved version of yours. Perhaps you could base this on a limitation of your study.
- Concluding paragraph – Finish with a statement of your findings and the key points of the discussion (e.g., interpretation and implications) in no more than 3 or 4 sentences.
Reference Page
The reference section lists all the sources cited in the essay (alphabetically). It is not a bibliography (a list of the books you used).
In simple terms, every time you refer to a psychologist’s name (and date), you need to reference the original source of information.
If you have been using textbooks this is easy as the references are usually at the back of the book and you can just copy them down. If you have been using websites then you may have a problem as they might not provide a reference section for you to copy.
References need to be set out APA style :
Author, A. A. (year). Title of work . Location: Publisher.
Journal Articles
Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (year). Article title. Journal Title, volume number (issue number), page numbers
A simple way to write your reference section is to use Google scholar . Just type the name and date of the psychologist in the search box and click on the “cite” link.
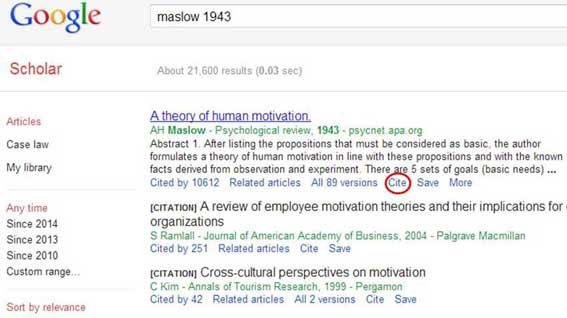
Next, copy and paste the APA reference into the reference section of your essay.

Once again, remember that references need to be in alphabetical order according to surname.
Psychology Lab Report Example
Quantitative paper template.
Quantitative professional paper template: Adapted from “Fake News, Fast and Slow: Deliberation Reduces Belief in False (but Not True) News Headlines,” by B. Bago, D. G. Rand, and G. Pennycook, 2020, Journal of Experimental Psychology: General , 149 (8), pp. 1608–1613 ( https://doi.org/10.1037/xge0000729 ). Copyright 2020 by the American Psychological Association.
Qualitative paper template
Qualitative professional paper template: Adapted from “‘My Smartphone Is an Extension of Myself’: A Holistic Qualitative Exploration of the Impact of Using a Smartphone,” by L. J. Harkin and D. Kuss, 2020, Psychology of Popular Media , 10 (1), pp. 28–38 ( https://doi.org/10.1037/ppm0000278 ). Copyright 2020 by the American Psychological Association.
- How To Find Articles with Databases
- How To Evaluate Articles
- How To Read A Scientific Paper
- How To Interpret Data
- How To Write A Lab Report
- How To Write A Scientific Paper
- Get More Help
- Reference: Encyclopedia, Handbooks & Dictionaries
- Research Tools: Databases, Protocols & Citation Locators
- E-Journal Lists by Subject
- Scholarly vs Popular
- Search Tips
- Open Resources
- E-Journal lists by subject
- Develop a Research Question
Writing Lab Reports
Writing lab reports follows a straightforward and structured procedure. It is important to recognize that each part of a lab report is important, so take the time to complete each carefully. A lab report is broken down into eight sections: title, abstract, introduction, methods and materials, results, discussion, conclusion, and references.
- Ex: "Determining the Free Chlorine Content of Pool Water"
- Abstracts are a summary of the experiment as a whole and should familiarize the reader with the purpose of the research.
- Abstracts will always be written last, even though they are the first paragraph of a lab report.
- Not all lab reports will require an abstract. However, they are often included in upper-level lab reports and should be studied carefully.
- Why was the research done or experiment conducted?
- What problem is being addressed?
- What results were found?
- What are the meaning of the results?
- How is the problem better understood now than before, if at all?
Introduction
- The introduction of a lab report discusses the problem being studied and other theory that is relevant to understanding the findings.
- The hypothesis of the experiment and the motivation for the research are stated in this section.
- Write the introduction in your own words. Try not to copy from a lab manual or other guidelines. Instead, show comprehension of the experiment by briefly explaining the problem.
Methods and Materials
- Ex: pipette, graduated cylinder, 1.13mg of Na, 0.67mg Ag
- List the steps taken as they actually happened during the experiment, not as they were supposed to happen.
- If written correctly, another researcher should be able to duplicate the experiment and get the same or very similar results.
- The results show the data that was collected or found during the experiment.
- Explain in words the data that was collected.
- Tables should be labeled numerically, as "Table 1", "Table 2", etc. Other figures should be labeled numerically as "Figure 1", "Figure 2", etc.
- Calculations to understand the data can also be presented in the results.
- The discussion section is one of the most important parts of the lab report. It analyzes the results of the experiment and is a discussion of the data.
- If any results are unexpected, explain why they are unexpected and how they did or did not effect the data obtained.
- Analyze the strengths and weaknesses of the design of the experiment and compare your results to other similar experiments.
- If there are any experimental errors, analyze them.
- Explain your results and discuss them using relevant terms and theories.
- What do the results indicate?
- What is the significance of the results?
- Are there any gaps in knowledge?
- Are there any new questions that have been raised?
- The conclusion is a summation of the experiment. It should clearly and concisely state what was learned and its importance.
- If there is future work that needs to be done, it can be explained in the conclusion.
- If using any outside sources to support a claim or explain background information, those sources must be cited in the references section of the lab report.
- In the event that no outside sources are used, the references section may be left out.
Other Useful Sources
- The Lab Report
- Sample Laboratory Report #2
- Some Tips on Writing Lab Reports
- Writing a Science Lab Report
- << Previous: How To Interpret Data
- Next: How To Write A Scientific Paper >>
- Last Updated: Mar 8, 2024 2:26 PM
- URL: https://guides.libraries.indiana.edu/STEM
Social media
- Instagram for Herman B Wells Library
- Facebook for IU Libraries
Additional resources
Featured databases.
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) OneSearch@IU
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Academic Search (EBSCO)
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) ERIC (EBSCO)
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Nexis Uni
- Resource available without restriction HathiTrust Digital Library
- Databases A-Z
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Google Scholar
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) JSTOR
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Web of Science
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Scopus
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) WorldCat
IU Libraries
- Diversity Resources
- About IU Libraries
- Alumni & Friends
- Departments & Staff
- Jobs & Libraries HR
- Intranet (Staff)
- IUL site admin
Writing Studio
Writing a lab report: introduction and discussion section guide.
In an effort to make our handouts more accessible, we have begun converting our PDF handouts to web pages. Download this page as a PDF: Writing a Lab Report Return to Writing Studio Handouts
Part 1 (of 2): Introducing a Lab Report
The introduction of a lab report states the objective of the experiment and provides the reader with background information. State the topic of your report clearly and concisely (in one or two sentences). Provide background theory, previous research, or formulas the reader should know. Usually, an instructor does not want you to repeat whatever the lab manual says, but to show your understanding of the problem.
Questions an Effective Lab Report Introduction Should Answer
What is the problem.
Describe the problem investigated. Summarize relevant research to provide context, key terms, and concepts so that your reader can understand the experiment.
Why is it important?
Review relevant research to provide a rationale for the investigation. What conflict, unanswered question, untested population, or untried method in existing research does your experiment address? How will you challenge or extend the findings of other researchers?
What solution (or step toward a solution) do you propose?
Briefly describe your experiment : hypothesis , research question , general experimental design or method , and a justification of your method (if alternatives exist).
Tips on Composing Your Lab Report’s Introduction
- Move from the general to the specific – from a problem in research literature to the specifics of your experiment.
- Engage your reader – answer the questions: “What did I do?” “Why should my reader care?”
- Clarify the links between problem and solution, between question asked and research design, and between prior research and the specifics of your experiment.
- Be selective, not exhaustive, in choosing studies to cite and the amount of detail to include. In general, the more relevant an article is to your study, the more space it deserves and the later in the introduction it appears.
- Ask your instructor whether or not you should summarize results and/or conclusions in the Introduction.
- “The objective of the experiment was …”
- “The purpose of this report is …”
- “Bragg’s Law for diffraction is …”
- “The scanning electron microscope produces micrographs …”
Part 2 (of 2): Writing the “Discussion” Section of a Lab Report
The discussion is the most important part of your lab report, because here you show that you have not merely completed the experiment, but that you also understand its wider implications. The discussion section is reserved for putting experimental results in the context of the larger theory. Ask yourself: “What is the significance or meaning of the results?”
Elements of an Effective Discussion Section
What do the results indicate clearly? Based on your results, explain what you know with certainty and draw conclusions.
Interpretation
What is the significance of your results? What ambiguities exist? What are logical explanations for problems in the data? What questions might you raise about the methods used or the validity of the experiment? What can be logically deduced from your analysis?
Tips on the Discussion Section
1. explain your results in terms of theoretical issues..
How well has the theory been illustrated? What are the theoretical implications and practical applications of your results?
For each major result:
- Describe the patterns, principles, and relationships that your results show.
- Explain how your results relate to expectations and to literature cited in your Introduction. Explain any agreements, contradictions, or exceptions.
- Describe what additional research might resolve contradictions or explain exceptions.
2. Relate results to your experimental objective(s).
If you set out to identify an unknown metal by finding its lattice parameter and its atomic structure, be sure that you have identified the metal and its attributes.
3. Compare expected results with those obtained.
If there were differences, how can you account for them? Were the instruments able to measure precisely? Was the sample contaminated? Did calculated values take account of friction?
4. Analyze experimental error along with the strengths and limitations of the experiment’s design.
Were any errors avoidable? Were they the result of equipment? If the flaws resulted from the experiment design, explain how the design might be improved. Consider, as well, the precision of the instruments that were used.
5. Compare your results to similar investigations.
In some cases, it is legitimate to compare outcomes with classmates, not in order to change your answer, but in order to look for and to account for or analyze any anomalies between the groups. Also, consider comparing your results to published scientific literature on the topic.
The “Introducing a Lab Report” guide was adapted from the University of Toronto Engineering Communications Centre and University of Wisconsin-Madison Writing Center.
The “Writing the Discussion Section of a Lab Report” resource was adapted from the University of Toronto Engineering Communications Centre and University of Wisconsin-Madison Writing Center.
Last revised: 07/2008 | Adapted for web delivery: 02/2021
In order to access certain content on this page, you may need to download Adobe Acrobat Reader or an equivalent PDF viewer software.
CrelioHealth For Diagnostics

How To Write a Laboratory Report: Guide 2024
Why are lab reports important? Lab reports are essential for communicating the findings of medical diagnosis or scientific research & experiments. L ab Report Writing by researchers, clinicians, and other healthcare professionals helps them to make informed decisions about patient care, drug development, and other essential matters.
To write a laboratory report in the correct format is essential, ensuring your findings are clearly and accurately communicated. A lab report writing guide provides a comprehensive framework to help you navigate the process of creating a well-structured and informative lab report. So, this guide will provide you with a step-by-step guide on how to write a laboratory report, including tips on structure, content, and style.
I. Understanding Lab Reports
The key to decoding lab reports lies in grasping the specific terminology, understanding the significance of data, and appreciating the overall narrative that the report conveys. Further, learn how to understand lab reports under these headings:
A. What is a Lab Report?
A lab report is a written document that describes the findings of a medical diagnosis, research, or scientific experiment. Lab report writing includes information on the purpose of the investigation, the methods used, the results obtained, and the conclusions drawn.
B. Lab Reports Types
There are many types of different lab reports. And, they can generally be classified into two categories:
- Qualitative lab reports: These reports describe the results of diagnosis that produce non-numerical data, such as observations, descriptions, and images.
- Quantitative lab reports: These reports describe the results of studies/findings that produce numerical data, such as counts, measurements, and calculations.
C. Purpose of Lab Reports
The purpose of a lab report is to communicate the findings of a diagnosis, experimental study, or research to others. This may be done for a variety of reasons, such as:
- To share findings with other healthcare providers or scientists
- To report on the results of a clinical diagnosis or trial
- To fulfill the requirements of a course or degree
- To document the results of a quality control test
II. Preparing for Laboratory Reporting
Before you begin with the steps to writing a lab report, it is essential to:
Familiarize yourself with the diagnosis: Make sure you understand the purpose of the investigation, the approach used, and the expected results.
Gather necessary references: This includes data, charts, graphs, and other relevant information.
Consider safety considerations: Make sure to follow all safety protocols when conducting the experiment and writing the report.
III. Structure of a Lab Report
A typical structure of a lab report is as follows:
- Title: The title should be clear and concise, and it should accurately reflect the content of the report.
- Abstract: The abstract is a brief summary of the report, including the diagnostic’s purpose of the diagnosis, methodologies, results, and conclusions.
- Introduction: The introduction provides background information on the experiment, including the purpose of the experiment, the hypothesis, and any relevant literature review.
- Materials and Methods: This section describes the materials used and the procedures followed in conducting the diagnosis.
- Results: This section presents the results of the clinical studies in a clear and concise manner. Data may be offered in tables, charts, and graphs.
- Discussion: The discussion section interprets the medical diagnosis results and discusses their implications. It is important to compare your results to those of other studies and to discuss any limitations of the study.
- Conclusion: The conclusion summarizes the main findings of the experiment and states the conclusions that can be drawn.
- References: This section lists all of the sources cited in the report.
IV. Lab Report Templates
Let’s explore and enhance your understanding of the most critical aspect of Lab Report Layout.
A. Importance of Using Templates
- Enhanced Consistency: Templates provide a structured laboratory report format that ensures consistency across all reports. This is crucial in the healthcare and medical field, where precision and standardization are essential. Consistent reports are easier to review, understand, and compare.
- Time and Effort Savings: Ready-to-use templates significantly reduce the time and effort required to create lab reports. Instead of starting from scratch with each report, you can fill in the necessary information and focus on the content. According to a study by the University of Toronto, professionals using templates save an average of 25% of their report creation time.
- Error Reduction: Templates include predefined sections and lab reporting formatting guidelines, reducing the likelihood of errors in your lab reports. This minimizes the risk of oversight or omission, improving the overall quality of the report.
B. Sample Lab Report Template
Toxicology laboratory report template.
A toxicology template in a structured laboratory report writing format is specifically designed for reporting findings related to toxic substances and their effects on living organisms. Moreover, this template typically includes sections detailing the toxic agents, exposure levels, symptoms, and recommendations.
View an example of a simplified toxicology laboratory report template here.

Molecular Diagnostics Report Template
Molecular diagnostics reports provide information about examining tissues at the molecular level. Also, a molecular testing report template contains sections detailing patient information, gene & variant information, observations, and diagnostic conclusions.
Here’s an example of a Next Generation Sequencing report template:

Difference Between Report Templates
The key difference between report templates lies in their focus and content. While both templates share common elements like title, abstract, methods, and references, a toxicology report template is tailored to the specific needs of toxicological analysis. In contrast, a molecular test report template is designed for reporting on tissue examination. The choice of a template depends on the type of study or experiment.
C. Examples and Sample Lab Reports
Analyzing well-written lab reports :.
To understand the importance of templates, let’s analyze a well-written lab report. In a study conducted by the University of Nottingham, it was found that the structure of a lab report using templates had a 15% higher clarity score than those without templates. Furthermore, this demonstrates the immediate impact on report quality.

Extracting Key Elements :
Well-written lab reports often share common elements, such as a clear introduction, hypothesis, detailed methods, comprehensive results, and insightful discussions. Therefore, by analyzing numerous sample reports, you can learn to identify and extract these key elements to incorporate into your reports effectively.
Learning from Successful Reports :
Successful lab reports set a benchmark for quality. For instance, a published clinical trial report that adheres to industry standards can serve as a valuable reference. Also, learning from such reports can help you understand the level of detail required, ethical considerations, and the integration of statistical data.
D. Customizing Templates for Your Needs
Branding & whitelabeling:.
In healthcare institutions or research organizations, it’s essential to maintain a professional brand identity. Moreover, templates can be customized to include the organization’s logo, color scheme, and fonts. This branding not only reinforces the organization’s image but also distinguishes reports as official documents.
Personalization & Localization:
Lab report templates can be personalized for individual researchers, specific study requirements, or for engaging customers. For instance, a researcher may need to add credentials, contact information, or a personalized header. Templates can also be localized for different regions, taking into account language preferences, lab reporting formatting standards, and specific regulatory requirements.
Customizing templates for branding, personalization, and localization adds a layer of professionalism to your reports, making them more reader-friendly and aligned with the organization’s identity and the specific needs of your target audience.
V. Tips for Effective Lab Reporting
Comprehensive detailing of medical test reports helps in effective lab reporting skills. As a result, it becomes practical to produce high-quality reports that meet industry standards and ethical lab report guidelines.
A. Clarity and Precision in Writing
- Use Clear and Concise Language : When writing a lab report, it’s vital to use clear, straightforward language. Avoid jargon or overly technical terms that might confuse readers who are not experts in your field. Your goal is to ensure that anyone, regardless of their background, can understand the report. To keep it clear and simple to patients, smart reports and trend reports have become popular today. Get an example of smart reports here .
- Define Technical Terms : While clarity is crucial, there will be instances where specialized terminology is necessary. In such cases, provide definitions or explanations for these terms, either in the text or through a glossary. This aids comprehension and ensures your patients, stakeholders, and other readers are on the same page.
- Avoid Ambiguity : Ambiguity can lead to misinterpretation. Be explicit in your descriptions and explanations. Use precise language to leave no room for doubt or multiple interpretations of your findings.
B. Data Presentation
- Choose the Right Visual Aids : When presenting data, select appropriate visual aids like tables, charts, graphs, and figures. The choice should depend on the data type and what will best illustrate your findings.
- Label and Caption Clearly : Ensure that every visual aid is properly labeled and captioned. These labels and captions should be informative, providing context for the reader. Readers should be able to understand the significance of the visual without having to reference the main text extensively.
- Consistency in Data Presentation: Maintain a consistent style for presenting data throughout the report. Consistency in fonts, colors, and medical lab report formatting makes the information visually appealing and easier to follow.
- Avoid Data Overload : While it’s essential to present relevant data, avoid overwhelming the reader with an excessive amount of information. Select the most crucial data points and present them clearly.
By adhering to such lab report layout and these tips for effective lab reporting, you’ll create reports that are not only accurate and comprehensive but also highly readable and professional. Hence, clear writing, precise data presentation, ethical considerations, and thorough validation & approval are vital in producing reports that make a significant impact in the field of healthcare and medical research.
VI. Common Mistakes to Avoid
While lab report writing, it is crucial to avoid the following common mistakes:
- Factual errors: Carefully check your results and conclusions for factual errors.
- Inconsistent formatting: Use a consistent lab reporting format throughout your report. This includes using the same font, font size, and margins throughout.
- Neglecting data analysis: Do not simply present your data without analyzing it. Interpret the results of your diagnosis and discuss their implications.
- Ignoring ethical considerations: Discuss any ethical considerations that apply to your methods.
VII. Lab Report Submission
Submitting a lab report is the culmination of meticulous work and precision. Additionally, ensuring that the laboratory report writing format is correct, adheres to submission protocols, and is submitted on time is essential.
A. Formatting Guidelines
Follow the Prescribed Laboratory Report Format : Each type of lab report, whether a clinical report, research report, or analytical report, often has specific formatting guidelines. It is crucial to adhere to these lab report guidelines to maintain consistency and readability. Moreover, inconsistencies in medical lab report format can distract readers and lead to misinterpretations.
Font and Spacing: Pay attention to the prescribed font type and size. Common choices are Times New Roman or Arial, with font size typically set at 12 points. Ensure that your report has proper line spacing, often set at double spacing, to enhance readability.
Margin Requirements: Be aware of margin requirements. Standard margins are usually set at 1 inch (2.54 cm) on all sides. Also, following these margin guidelines ensures that your document looks clean and professional.
Page Numbering: Lab reports may require specific page numbering, such as placing page numbers in the upper right or lower right corner. Ensure that page numbers are consistent throughout the document.
Tables and Figures: If your report includes tables and figures, make sure they are labeled and formatted per the lab report guidelines. Further, this includes consistent table and figure titles, numbering, and sources. Tables and figures in the structure of laboratory reports enhance the report’s visual appeal.
B. Submission Protocols
Submission Method: Different institutions and organizations may have distinct methods for submitting lab reports. Standard methods include email submissions, online portals, or physical submissions. Verify the method specified by your institution.
Cover Page: In some cases, lab reports require a cover page with essential information like your name, course or title, submission date, and any other relevant details. Ensure this cover page is included if required.
Lab Report Title: When submitting the report, ensure that the title accurately represents the content of your report. A well-chosen title helps readers and reviewers quickly understand the report’s focus.
Acknowledgment of Collaborators: If you collaborated with other researchers or medical professionals on the lab report, acknowledge their contributions. This is not only an ethical practice but also enhances the credibility of your work.
Submission Deadlines: Meeting deadlines is non-negotiable in lab report submission. Your lab’s TAT depends on it. Be aware of this submission deadline, and make sure your report is submitted well in advance to account for any unforeseen issues.
C. Deadlines and Extensions
Timely Submission: Timely submission is a hallmark of professionalism. Failing to meet deadlines can have serious repercussions. For example, the punishment for late submissions of the COVID-19 reports to the state government or the federal government was severely strict and non-negotiable.
Requesting Extensions: If you foresee that you might not be able to meet the submission deadline, it’s advisable to request an extension well in advance. Most institutions have formal procedures for extension requests. Explain your reasons for needing an extension clearly and provide a realistic new submission date.
Consequences of Missed Deadlines: Be aware that missed deadlines can lead to academic penalties, reduced credibility, and the loss of opportunities. The impact can be severe in clinical settings, where timely reporting is critical for patient care.
Remember that lab report submission is the last critical step in the lab reporting process. Proper laboratory report writing format, adherence to submission protocols, and timely submissions are essential to ensure that your hard work and research are effectively communicated and contribute to the advancement of healthcare and medical knowledge. Always verify specific requirements with your institution or organization, and make it a practice to submit your lab reports with precision and professionalism.
Lab reports are essential for communicating the findings of scientific experiments to other scientists, clinicians, and healthcare professionals. It is vital to encourage all staff and researchers to be familiar with the best practices for writing lab reports. Lab report templates can be a helpful tool for writing a well-structured and informative report. These structure of laboratory reports can also be used to personalize and brand your reports.
Additional Resources
Here are some additional resources that you may find helpful:
- Writing the Laboratory Report by Pamela J. Saltman
- A Guide to Scientific Writing by Robert A. Day
- The ACS Style Guide by the American Chemical Society
- CrelioHealth
- LabArchives
- How to Write a Lab Report by the University of Nottingham
- Lab Report Guidelines by the University of Toronto
- Writing a Lab Report by Phoenix College
Here are some Answers to Common Questions for Understanding Lab Reports better:
- What is the purpose of a lab report? The purpose of a lab report is to communicate the findings of an experiment to others. This may be done for a variety of reasons, such as to share findings with other scientists, to report on the results of a clinical trial, or to fulfill the requirements of a course or degree.
- What are the parts of a lab report? A typical lab report includes the following sections: title, abstract, introduction, materials and methods, results, discussion, conclusion, and references.
- What is the format of a lab report? Lab reports should be written in a clear and concise style. The lab reporting format will vary depending on the specific requirements of your instructor or supervisor. However, most lab reports follow a standard format, as described in this lab report writing guide.
- https://www.nottingham.ac.uk/studyingeffectively/writing/writingtasks/labreports.aspx
- https://advice.writing.utoronto.ca/types-of-writing/lab-report/
- https://phoenixcollege.libguides.com/LabReportWriting/labreportformat
- https://phoenixcollege.libguides.com/LabReportWriting/introduction
Related Posts

Exploring the Benefits and Opportunities Of Lab Provider Portals

The Truth About External Lab Partnerships to Enhance Specialized Services
Leave a reply cancel reply, discover more from creliohealth for diagnostics.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

- Science Notes Posts
- Contact Science Notes
- Todd Helmenstine Biography
- Anne Helmenstine Biography
- Free Printable Periodic Tables (PDF and PNG)
- Periodic Table Wallpapers
- Interactive Periodic Table
- Periodic Table Posters
- How to Grow Crystals
- Chemistry Projects
- Fire and Flames Projects
- Holiday Science
- Chemistry Problems With Answers
- Physics Problems
- Unit Conversion Example Problems
- Chemistry Worksheets
- Biology Worksheets
- Periodic Table Worksheets
- Physical Science Worksheets
- Science Lab Worksheets
- My Amazon Books
Lab Report Format – How to Write a Laboratory Report

A science laboratory experiment isn’t truly complete until you’ve written the lab report. You may have taken excellent notes in your laboratory notebook, but it isn’t the same as a lab report. The lab report format is designed to present experimental results so they can be shared with others. A well-written report explains what you did, why you did it, and what you learned. It should also generate reader interest, potentially leading to peer-reviewed publication and funding.
Sections of a Lab Report
There is no one lab report format. The format and sections might be specified by your instructor or employer. What really matters is covering all of the important information.
Label the sections (except the title). Use bold face type for the title and headings. The order is:
You may or may not be expected to provide a title page. If it is required, the title page includes the title of the experiment, the names of the researchers, the name of the institution, and the date.
The title describes the experiment. Don’t start it with an article (e.g., the, an, a) because it messes up databases and isn’t necessary. For example, a good title might be, “Effect of Increasing Glucose Concentration on Danio rerio Egg Hatching Rates.” Use title case and italicize the scientific names of any species.
Introduction
Sometimes the introduction is broken into separate sections. Otherwise, it’s written as a narrative that includes the following information:
- State the purpose of the experiment.
- State the hypothesis.
- Review earlier work on the subject. Refer to previous studies. Cover the background so a reader understands what is known about a subject and what you hope to learn that is new.
- Describe your approach to answering a question or solving a problem. Include a theory or equation, if appropriate.
This section describes experimental design. Identify the parameter you changed ( independent variable ) and the one you measured ( dependent variable ). Describe the equipment and set-up you used, materials, and methods. If a reader can’t picture the apparatus from your description, include a photograph or diagram. Sometimes this section is broken into “Materials” and “Methods.”
Your lab notebook contains all of the data you collected in the experiment. You aren’t expected to reproduce all of this in a lab report. Instead, provide labelled tables and graphs. The first figure is Figure 1, the second is Figure 2, etc. The first graph is Graph 1. Refer to figures and graphs by their figure number. For some experiments, you may need to include labelled photographs. Cite the results of any calculations you performed, such as slope and standard deviation. Discuss sources of error here, including instrument, standard, and random errors.
Discussion or Conclusions
While the “Results” section includes graphs and tables, the “Discussion” or “Conclusions” section focuses on what the results mean. This is where you state whether or not the objective of the experiment was met and what the outcome means. Propose reasons for discrepancies between expected and actual outcomes. Finally, describe the next logical step in your research and ways you might improve on the experiment.
References or Bibliography
Did you build upon work conducted by someone else? Cite the work. Did you consult a paper relating to the experiment? Credit the author. If you’re unsure whether to cite a reference or not, a good rule of thumb is to include a reference for any fact not known to your audience. For some reports, it’s only necessary to list publications directly relating to your procedure and conclusions.
The Tone of a Lab Report
Lab reports should be informative, not entertaining. This isn’t the place for humor, sarcasm, or flowery prose. A lab report should be:
- Concise : Cover all the key points without getting crazy with the details.
- Objective : In the “Conclusions” section, you can propose possible explanations for your results. Otherwise, keep your opinions out of the report. Instead, present facts and an analysis based on logic and math.
- Critical : After presenting what you did, the report focuses on what the data means. Be on the lookout for sources of error and identify them. Use your understanding of error to determine how reliable your results are and gauge confidence in your conclusions.
Related Posts
- 301 Academic Skills Centre
- Study skills online
Scientific writing and lab reports
Information on how to structure and format a lab report, also known as a scientific report.

What is a lab report?
Lab reports, or scientific reports, are the primary vehicle used to disseminate and communicate scientific research methods across science and engineering disciplines.
They are structured and formulaic, to make it as easy as possible for a reader to understand the background, aims, methodology and findings of a particular experiment or technique.
Lab reports usually follow very closely prescribed formats. It's essential that you pay very careful attention to the specific guidelines issued with your experimental brief.
Typically, a lab report is broken down into discrete sections, separated by subheadings. These will include the following:
- an abstract, outlining in brief what was done and what was found
- a point-by-point description of the experimental method followed (a bit like following a recipe)
- a clear presentation of all of the results observed, some of which may be placed in an appendix to the main report
- a discussion of those results
- a brief conclusion and references
Lab reports are written in a neutral and objective tone and are kept as short, concise and to the point as possible.
They are not the place to experiment with elaborate language, which might impact on the clarity of their information.
301 Recommends:
Our Scientific Writing and Lab Report workshop provides a practical guide to communicating your findings with a focus on the scientific lab report as a model. You will learn why it is important to record experiments in this way and gain a detailed understanding of how to structure your reports based on the IMRaD format (Introduction, Methods, Results and Discussion). This interactive session is packed with top tips and best practice to enhance your report writing skills.
Introduction
Establish the reason or context for doing the experiment. It might help to think of your introduction as a funnel.
Start broad and focus down to the specifics of your research including the aims/objectives and hypothesis for testing.
Provides a descriptive protocol of your experiment so it could be replicated by another researcher.
Your methods section should be written avoiding the first person and using the passive voice where possible (ie a sample was taken...). Reproducibility of methods is the foundation for evidence-based science.
Present your data using tables or graphical representations as appropriate.
Interpret the results and explain their significance.
Reverse the funnel: put the specific results from your experiment back into a wider context, ie
- what do they mean?
- what applications do they have?
- what recommendations can you make?
- what are the limitations?
- what gaps remain for further research?
Restate your main findings and key points from the discussion.
Strengthen your arguments with support from existing literature.
Summary of the entire report: Interesting, easy to read, concise. This will usually be the last part of the report that you write.
Title, appendix and acknowledgements
Guidance for Writing Lab Reports by Faculty of Engineering (pdf. 1677 kb)
Lab Reports Writing Template (pdf. 662 kb)
Proofreading Your Work
Writing numbers and presenting data
Consider the best way to present your data clearly. If this is best done using a table or chart, then consider what format makes things clearest.
Make sure all important aspects of the data are included in your chart or table, including units where relevant. Don't include charts just for the sake of it – data display should help the reader understand the data.
Report the results of any statistical tests using the appropriate conventions for your subject.
Data display
Displaying Data in Tables
Displaying Data in Graphs
Hypothesis tests
Writing Numbers in Standard Form
Library resources
Library workshops.
The Come Together, Write Now sessions are now open to all students. These virtual sessions for academic reading and writing will help you focus on your work, providing the time and space to come together as a reading and writing community and support each other.
You can view our upcoming sessions and book a place here .
Online guidance
Reading other publications can help you to become familiar with the structure, tone and language of scientific writing.
Take a look at the Library resources on scientific literature:
Evaluating the Scientific Literature
Finding Scientific Journal Papers
Types of Scientific Paper
Always read the guidance notes
Methods • Use past tense • Write in the third person • Include detailed materials • State the study design • Cite/reference the lab protocol
Results • Organise your data in a logical order • Include tables and graphs • Label clearly and include units • Include figure legends and titles • State statistical tests and p-values • Refer to all tables and figures in the text
Leave it until the last minute
Methods • Copy the lab protocol • Forget to include statistics and calculation methods • Write a set of instructions (cookbook!) • Interpret your results
Results • Include raw data • Present same data in a graph and table • Overcomplicate the results section • Interpret your results • Copy other people’s data or exclude unexpected results
Academic Skills Certificate
The 301 Academic Skills Certificate gives you an opportunity to gain recognition for developing your skills and reflecting on this experience.
Through this reflection, you will be able to identify changes and improvements to your academic skills that will lead to long-term benefits to your studies.
The 301 Academic Skills Certificate acknowledges your commitment to enhancing your academic and employability skills and personal development.
Related information
The conventions of academic writing
Dissertation planning

Be the first to hear about our new and upcoming workshops!
The 301 Academic Skills Centre newsletter is a fortnightly email for study skills, mathematics and statistics.
Be the first to find out about our:
- new and upcoming workshops,
- special events and programmes, and
- new and relevant online materials and resources.
Sheffield is a research university with a global reputation for excellence. We're a member of the Russell Group: one of the 24 leading UK universities for research and teaching.
- Writing Home
- Writing Advice Home
The Lab Report
- Printable PDF Version
- Fair-Use Policy
This document describes a general format for lab reports that you can adapt as needed. Lab reports are the most frequent kind of document written in engineering and can count for as much as 25% of a course yet little time or attention is devoted to how to write them well. Worse yet, each professor wants something a little different. Regardless of variations, however, the goal of lab reports remains the same: document your findings and communicate their significance. With that in mind, we can describe the report’s format and basic components. Knowing the pieces and purpose, you can adapt to the particular needs of a course or professor.
A good lab report does more than present data; it demonstrates the writer’s comprehension of the concepts behind the data. Merely recording the expected and observed results is not sufficient; you should also identify how and why differences occurred, explain how they affected your experiment, and show your understanding of the principles the experiment was designed to examine. Bear in mind that a format, however helpful, cannot replace clear thinking and organized writing. You still need to organize your ideas carefully and express them coherently.
Typical Components
- Introduction
- Methods and Materials (or Equipment)
- Experimental Procedure
- Further Reading
1. The Title Page needs to contain the name of the experiment, the names of lab partners, and the date. Titles should be straightforward, informative, and less than ten words (i.e. Not “Lab #4” but “Lab #4: Sample Analysis using the Debye-Sherrer Method”). 2. The Abstract summarizes four essential aspects of the report: the purpose of the experiment (sometimes expressed as the purpose of the report), key findings, significance and major conclusions. The abstract often also includes a brief reference to theory or methodology. The information should clearly enable readers to decide whether they need to read your whole report. The abstract should be one paragraph of 100-200 words (the sample below is 191 words).
Quick Abstract Reference
- Key result(s)
- Most significant point of discussion
- Major conclusion
May Include:
- Brief method
- Brief theory
Restrictions:
ONE page 200 words MAX.
Sample Abstract
This experiment examined the effect of line orientation and arrowhead angle on a subject’s ability to perceive line length, thereby testing the Müller-Lyer illusion. The Müller-Lyer illusion is the classic visual illustration of the effect of the surrounding on the perceived length of a line. The test was to determine the point of subjective equality by having subjects adjust line segments to equal the length of a standard line. Twenty-three subjects were tested in a repeated measures design with four different arrowhead angles and four line orientations. Each condition was tested in six randomized trials. The lines to be adjusted were tipped with outward pointing arrows of varying degrees of pointedness, whereas the standard lines had inward pointing arrows of the same degree. Results showed that line lengths were overestimated in all cases. The size of error increased with decreasing arrowhead angles. For line orientation, overestimation was greatest when the lines were horizontal. This last is contrary to our expectations. Further, the two factors functioned independently in their effects on subjects’ point of subjective equality. These results have important implications for human factors design applications such as graphical display interfaces.
3. The introduction is more narrowly focussed than the abstract. It states the objective of the experiment and provides the reader with background to the experiment. State the topic of your report clearly and concisely, in one or two sentences:
Quick Intro Reference
- Purpose of the experiment
- Important background and/or theory
May include:
- Description of specialized equipment
- Justification of experiment’s importance
Example: The purpose of this experiment was to identify the specific element in a metal powder sample by determining its crystal structure and atomic radius. These were determined using the Debye-Sherrer (powder camera) method of X-ray diffraction.
A good introduction also provides whatever background theory, previous research, or formulas the reader needs to know. Usually, an instructor does not want you to repeat the lab manual, but to show your own comprehension of the problem. For example, the introduction that followed the example above might describe the Debye-Sherrer method, and explain that from the diffraction angles the crystal structure can be found by applying Bragg’s law. If the amount of introductory material seems to be a lot, consider adding subheadings such as: Theoretical Principles or Background.
Note on Verb Tense
Introductions often create difficulties for students who struggle with keeping verb tenses straight. These two points should help you navigate the introduction:
“The objective of the experiment was…”
“The purpose of this report is…” “Bragg’s Law for diffraction is …” “The scanning electron microscope produces micrographs …”
4. Methods and Materials (or Equipment) can usually be a simple list, but make sure it is accurate and complete. In some cases, you can simply direct the reader to a lab manual or standard procedure: “Equipment was set up as in CHE 276 manual.” 5. Experimental Procedure describes the process in chronological order. Using clear paragraph structure, explain all steps in the order they actually happened, not as they were supposed to happen. If your professor says you can simply state that you followed the procedure in the manual, be sure you still document occasions when you did not follow that exactly (e.g. “At step 4 we performed four repetitions instead of three, and ignored the data from the second repetition”). If you’ve done it right, another researcher should be able to duplicate your experiment. 6. Results are usually dominated by calculations, tables and figures; however, you still need to state all significant results explicitly in verbal form, for example:
Quick Results Reference
- Number and Title tables and graphs
- Use a sentence or two to draw attention to key points in tables or graphs
- Provide sample calculation only
- State key result in sentence form
Using the calculated lattice parameter gives, then, R = 0.1244nm.
Graphics need to be clear, easily read, and well labeled (e.g. Figure 1: Input Frequency and Capacitor Value). An important strategy for making your results effective is to draw the reader’s attention to them with a sentence or two, so the reader has a focus when reading the graph.
In most cases, providing a sample calculation is sufficient in the report. Leave the remainder in an appendix. Likewise, your raw data can be placed in an appendix. Refer to appendices as necessary, pointing out trends and identifying special features. 7. Discussion is the most important part of your report, because here, you show that you understand the experiment beyond the simple level of completing it. Explain. Analyse. Interpret. Some people like to think of this as the “subjective” part of the report. By that, they mean this is what is not readily observable. This part of the lab focuses on a question of understanding “What is the significance or meaning of the results?” To answer this question, use both aspects of discussion:
More particularly, focus your discussion with strategies like these:
Compare expected results with those obtained.
If there were differences, how can you account for them? Saying “human error” implies you’re incompetent. Be specific; for example, the instruments could not measure precisely, the sample was not pure or was contaminated, or calculated values did not take account of friction.
Analyze experimental error.
Was it avoidable? Was it a result of equipment? If an experiment was within the tolerances, you can still account for the difference from the ideal. If the flaws result from the experimental design explain how the design might be improved.
Explain your results in terms of theoretical issues.
Often undergraduate labs are intended to illustrate important physical laws, such as Kirchhoff’s voltage law, or the Müller-Lyer illusion. Usually you will have discussed these in the introduction. In this section move from the results to the theory. How well has the theory been illustrated?
Relate results to your experimental objective(s).
If you set out to identify an unknown metal by finding its lattice parameter and its atomic structure, you’d better know the metal and its attributes.
Compare your results to similar investigations.
In some cases, it is legitimate to compare outcomes with classmates, not to change your answer, but to look for any anomalies between the groups and discuss those.
Analyze the strengths and limitations of your experimental design.
This is particularly useful if you designed the thing you’re testing (e.g. a circuit). 8. Conclusion can be very short in most undergraduate laboratories. Simply state what you know now for sure, as a result of the lab:
Quick Conclusion Reference
- State what’s known
- State significance
- Suggest further research
Example: The Debye-Sherrer method identified the sample material as nickel due to the measured crystal structure (fcc) and atomic radius (approximately 0.124nm).
Notice that, after the material is identified in the example above, the writer provides a justification. We know it is nickel because of its structure and size. This makes a sound and sufficient conclusion. Generally, this is enough; however, the conclusion might also be a place to discuss weaknesses of experimental design, what future work needs to be done to extend your conclusions, or what the implications of your conclusion are. 9. References include your lab manual and any outside reading you have done. Check this site’s documentation page to help you organize references in a way appropriate to your field. 10. Appendices typically include such elements as raw data, calculations, graphs pictures or tables that have not been included in the report itself. Each kind of item should be contained in a separate appendix. Make sure you refer to each appendix at least once in your report. For example, the results section might begin by noting: “Micrographs printed from the Scanning Electron Microscope are contained in Appendix A.”
To learn more about writing science papers, visit our handout on writing in the sciences .

Why — and How — to Write Lab Reports
Why write lab reports?
Milena Shahu, Chemistry
Chemistry is an experimental science. The theoretical concepts and principles are usually introduced in the lecture part of the course. The laboratory is important as well because it helps students discover/prove what they learned in the lecture and consolidate their understanding through experimentation. While conducting an experiment in the laboratory, students are expected to understand the scientific process behind the principle they are testing, create a hypothesis, design and complete an experimental study, obtain useful data, and analyze/interpret the data to reach conclusions. It is important for students to communicate their findings with the scientific community (in this case, the professor of the course, teaching assistants and their classmates). This enhances students’ learning and helps faculty evaluate how well students are learning. The best way to convey their findings (or prove if they are legitimate) to the scientific community is by writing a clear and concise scientific lab report. The practice of writing a scientific report is useful and pedagogical if taught as part of the learning process, because it strengthens skills important for chemists, including logical organization, attention to detail, writing, communication, and critical thinking.
The lab report has a similar format to a chemistry journal article. In general, journal articles mirror the scientific method and comprise four major sections: Introduction, Experimental Methods, Results, and Discussion. Journal articles also include a title, abstract, conclusions, references, and acknowledgements. The lab report handout guides students through the process of properly writing of each of the above sections. As a result, students’ scientific writing skills improve throughout a laboratory course. Other faculty in the Chemistry Department use similar handouts to guide students in this writing process.
Since the lab courses count for the Integrated Writing requirement at Georgetown, the goal is to ensure that our chemistry/biochemistry majors master college level writing skills. Students improve gradually over four undergraduate years, as they move to the more advanced level lab courses, where they are required to write a more detailed report, which includes statistical data analysis and error analysis. By the time our majors graduate, they are well prepared and possess the necessary skills to write a chemistry journal article.
Here are the guidelines we give to our students.
LAB REPORT FORMAT
Besides the experimental work, an important part of the laboratory is the written report, which should clearly show what was done and what results were obtained. It should be original, which means that you should not copy the lab manual or other materials. Your lab reports are to be in the format of a manuscript to be submitted to a Journal of American Chemical Society (JACS).
Title page contains the title of the report, the names of the authors, the section, group number, and the date of submission.
Abstract consists of a few paragraphs, usually no longer than a half page. In this part, you should summarize the results of the experimental work and give the main conclusions. Be quantitative. The abstract is generally written after you have evaluated your results.
The Introduction section should give an introduction of the theory, and explain why you are doing this experiment and what is the purpose/problem that the experiment is focused on. What significance does the problem that you are trying to solve have? If you need to present some equations, they should be presented here in separate lines and also be numbered. The symbols used in the equations must be explained clearly when they appear for the first time.
In the Experimental section you should describe the experimental procedure. You should not repeat the information given in the lab manual, but make a reference to it. You should give details of the procedure only if it is not given in your lab manual or if you modified it. A figure of the apparatus should be illustrated only if you assembled it or you were using a special apparatus, compared to the one given in the lab manual.
The Results section should include tables, graphs, and sample calculations. All the results should be presented even if there is any inconsistency with the theory or with what is expected. You should explain why this happens in the “Discussion” section. If you are using any computer program, you should make a reference to it. All the tables should have titles and should be numbered. The column headings should be labeled with the units specified. Graphs should be presented as figures. All the graphs should have numbers and a short legend. Graphs should have labeled axes and clearly show the scales and units of the axes.
In the Discussion section you should present your final results. What do they mean? Your results can be compared with the theory or experimental values from literature. If there is any inconsistency, you should try to explain it. You should give a discussion of probable experimental errors, such as random and systematic errors. You should calculate the experimental errors if you are provided with literature or actual values of the parameters that you are determining. Other topics you can discuss are: comparison of the experimental method used with other methods, suggestion for a better experimental method, discussion of any difficulties that you might have faced or any approximation you used, etc.
Conclusions section is a brief summary of your results. You can talk about your interesting findings.
References must be listed at the end of the report and should have at least two primary sources. You should cite all the sources used.

- Langson Library
- Science Library
- Grunigen Medical Library
- Law Library
- Connect From Off-Campus
- Accessibility
- Gateway Study Center

Email this link
Writing a scientific paper, the scientific paper, scientific communication, guides from other universities and professional societies.
- INTRODUCTION
- LITERATURE CITED
- Bibliography of guides to scientific writing and presenting
- Peer Review
- Presentations
- Lab Report Writing Guides on the Web

Dear Novice Writer,
When I was in your shoes and preparing my first paper, I consulted a book on how to write. I found there a sentence encouraging the reader to do the following:
" After standing in boiling water for an hour, examine the contents of the flask."
I had a pretty good idea what was wrong with the sentence but, at the time I couldn't figure out how to revise it, and the author didn't tell me.
From: How to write and Illustrate a Scientific Paper (2nd ed.) Bjorn Gustavii.
No one knows how to write a scientific paper without practice and help. Many science students practice this skill when they are asked to write lab reports. This guide will describe some best practices for scientific writing and give you some additional sources to explore.
If you have read scientific papers, you will have noticed that a standard format is frequently used. This format allows a researcher to present information clearly and concisely. Scientists communicate new ideas by publishing their research in a specialized format called the journal article .
This form usually includes 6 parts:
1) abstract (a summary of the article)
2) introduction (a brief review of why they chose this experiment)
3) materials and methods (what organisms and equipment were used)
4) results (what was found)
5) discussion (what it means)
6) references (the list of journal articles and books that the scientist referred to in the paper).
- George Mason University Guide
- Bates College Guide
- Writing Resources on the World Wide Web
- University of Toronto Engineering Communication Centre Online Writing Handbook
- North Carolina State University Guide to Writing Lab Reports (LABWRITE)
- Next: TITLE >>
- Last Updated: Aug 4, 2023 9:33 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uci.edu/scientificwriting
Off-campus? Please use the Software VPN and choose the group UCIFull to access licensed content. For more information, please Click here
Software VPN is not available for guests, so they may not have access to some content when connecting from off-campus.
Tips on How to Write a Lab Report: A Full Guide

What Is a Lab Report
Let's start with a burning question: what is lab report? A lab report is an overview of your scientific experiment. It describes what you did (the course of the experiment), how you did it (what equipment and materials you used), and what outcome your experiment led to.
If you take any science classes involving a lab experiment – or full-fledged laboratory courses, you'll have to do your share of lab report writing.
Unlike the format of case study writing , lab reports have to follow a different structure. They, along with other lab report guidelines, are likely defined by your instructor. Your lab notebook may also contain the requirements.
But if it's not your case, here's what to include in a lab report:
- title page;
- introduction;
- equipment and materials list;
- conclusion;
- appendices.
If this structure looks intimidating now, don't worry: we'll break down every component below.
Format for Lab Reports
Different instructors require different formats for lab reports. So, look through the requirements you've received and see if a science lab report format is specified.
If no format is specified, see if your school, college, or university has specific formatting guidelines or a lab report template to follow.
If that's also not the case, then you can choose the most common formatting style for research papers and lab reports alike: the APA (American Psychology Association) format. Other options include the MLA (Modern Language Association) and Chicago styles.
APA Lab Report Style
Let's break down the main particularities of using the APA style for lab reports. When it comes to the lab report outline, this style dictates that you should include the following:
- a title page;
- an abstract;
- sources (as a References page).
How to format references under the APA format deserves a separate blog post. But here's a short example:
Smith, J. (2021). A lab report introduction guide. Cambridge Press.
To cite this source in the text, style it like this: (Smith, 2021)
As for the text formatting, here are the key APA guidelines to keep in mind:
- page margins: 1" (on all sides);
- indent: 0.5";
- page number: in the upper right corner;
- spacing: double;
- font: Times New Roman 12 pt.
How Long Should a Lab Report Be?
The appropriate report length depends heavily on the kind of experiment conducted – and on the requirements set by your instructor. That said, most lab reports are five to ten pages long, in our experience. That includes all the raw data, appendices, and graphs.
Need a lab report example? You'll find three below!
What's the Difference Between Lab Reports & Research Papers?
While lab report format and structure are similar to that of a research paper, they differ. But unfortunately, in our work as a college essay writing service , we see them confused often enough.
The key differences between lab reports and research papers are:
- Lab reports require you to conduct a hands-on experiment, while research papers are focused on the interpretation of existing data;
- A lab report's purpose is to show that you understand the scientific methods central to the experimental procedure – that's why the lab report template is different, too;
- A lab experiment doesn't require you to have an original hypothesis or argument;
- Research papers are usually longer than lab reports.
How to Do a Lab Report: Outline
Like with any other papers, from SWOT analysis to case studies, writing lab reports is easier when you have a clear college lab report outline in front of you. Luckily for you, the lab report structure is the same in most cases.
So, here's how to do a lab report – follow this outline (unless your instructor's requirements contradict it!):
- Title page: your name, course, instructor, and the report title;
- Abstract: a short description of the key findings and their significance;
- Introduction: the purpose of the lab experiment and its background information;
- Methods and materials: what you used during the experiment (e.g., a lab manual, certain reagents, etc.);
- Procedure: the detailed description of the lab experiment;
- Results: the outcome of your experiment and its interpretation;
- Conclusion: what your findings may mean for the field;
- References: the list of your sources;
- Appendices: raw data, calculations, graphs, etc.
Feeling Stuck With Your Lab Report?
Let our qualified writers handle it for you and relieve you of this burden!
Guide on How to Write a Lab Report
If the outline above is overwhelming at first, don't worry! As a paper and essay writing service , we've had our share of experience in writing lab reports. Today, we'd like to share this experience with you in this lab report guide.
So, below you'll find everything you need to know on how to write a good lab report, along with handy lab report guidelines!

Lab Report Title Page
The lab report title page should include your name, student code, and any lab partners you may have had. It should also contain the date of the experiment and the title of your report.
The title length should be less than ten words. You'll also need to include the name of the academic supervisor in your lab report title page if you have one.
This paragraph describes your experiment, its main point, and its findings in a nutshell. Here are several guidelines on how to write an abstract for a lab report:
- Keep it under 200 words;
- Start with the purpose of your experiment;
- Describe the experimental procedure;
- State the results;
- Include 2-3 keywords (optional).
Lab Report Introduction
The first paragraph is where you explain your hypothesis and the purpose of your experiment. You can also add any previous research on the matter and any background information worth including. Here's a short lab report introduction example with a hypothesis:
This experiment examined the correlation between the levels of CO2 and the rate of photosynthesis in Chlorella algae. The latter was quantified by measuring the levels of RuBisCO.
Equipment (Methods and Materials)
Next in the lab report structure is the equipment section (also known as methods and materials). This is where you mention your lab manual, methods used during the experimental procedure, and the materials list.
In this part of the report, ensure to include all the details of the experimental procedure. It should provide readers with everything they need to know to replicate your study.
Procedure (with Graphs & Figures)
This part is, perhaps, the easiest (unlike how to write a hypothesis for a lab report). You should simply document the course of the lab experiment step-by-step, in chronological order.
This is usually a significant part of the report, taking up most of it. So make sure to provide detailed information on your hands-on experience!
Results Section
This is the overview of your experiment's findings (also known as the discussion section). Here's how to write a results section for a lab report:
- Discuss the outcome of the experiment;
- Explain how it pertains to your hypothesis (whether it proves or disproves it);
- Keep it brief and concise.
Note . You might notice that describing future work or further studies is absent from the tips on how to write the discussion section of a lab report. That's because it's a part of the conclusion, not the discussion.
This is where you sum up the results of your experiment and draw any major conclusions. You may also suggest future laboratory experiments or further research.
Here's how to write a conclusion for a lab report in three steps:
- Explain the results of your experiment;
- Determine their significance – and any limitations to the experimental design;
- Suggest future studies (if applicable).
The conclusion part of lab reports is typically short. So, don't worry if you can't write a lengthy one – you don't have to!
This is the part of your lab report outline where you list all of the sources you relied on in your lab experiments. It should include your lab manual, along with any relevant recommended reading from your course. You may also include any extra sources you used.
Remember to format your references list according to the formatting style you have to follow. Apart from every entry's formatting, you'll also have to present your references in alphabetical order based on the author's last name (for APA lab reports).
Finally, any lab report format includes appendices – your figures and graphs, in other words. This is where you add your raw data in tables, complete calculations, charts, etc.
Keep in mind: just like with sources, you need to cite each of the appendices in the main body of the report. Remember to format the appendix and its citation according to the chosen formatting style.
Lab Report Examples
As a paper and dissertation writing service , we know that sometimes it's better to see a great example of how to write a lab report once than to read dozens of tips. So, we've asked our lab report writing service to prepare a lab report template for three disciplines: chemistry, biology, and science.
Look at these samples if you keep wondering how to do a lab report! But keep in mind: you won't be able to use them as-is. So instead, use them as examples for your writing.
Note . References to lab manuals are made up – you should refer to the one you use in the experiment!

How to Write a Formal Lab Report for Chemistry?
The same lab report guidelines listed above apply to chemistry lab reports. Here's a short example that includes a lab report introduction, equipment, procedure, results, and references for an electrolysis reaction.
How to Write a Lab Report for Biology?
Next up in your lab report guide, it's a biology lab report! Like in any other lab report, its main point is to describe your experiment and explain its findings. Below you can find an example of one biology lab report that seeks to explain how to extract DNA from sliced fruit and make it visible to the naked eye.
How to Write a Science Lab Report?
Finally, let's look at a general science lab report. In this case, the science lab report format is the same as for other disciplines: start with the introduction and hypothesis, describe the equipment and procedure, and explain the outcome.
Here's a science lab report example on testing the density of different juices.
7 More Tips on How to Write a Lab Report
Need some more guidance on writing lab reports? Then, we've got you covered! Here are seven more tips on writing an excellent report:
- Carefully examine your lab manual before starting the experiment;
- Take detailed notes throughout the process;
- Be conscious of any limitations of your experimental design – and mention them in conclusion;
- Stick to the lab report structure defined by your instructor;
- Be transparent about any experimental error that may occur;
- Search for examples if you feel stuck with writing lab reports;
- Triple-check your lab report before submitting it: look for formatting issues, sources forgotten, and grammar and syntax mistakes.
Need Qualified Help With an Assignment?
You're seconds away from it! Hire a professional writer now – and stop worrying about a deadline coming up!
Related Articles
.webp)

- Scientific Lab Reports
- Understanding the Assignment
- Need a Topic?
- Evaluating Sources
- Brainstorming Strategies
- Drafting Strategies
- Thesis Formulation
- Introductions
- Conclusions
- Show Don't Tell
- Expand Your Draft
- Flow & Lexical Coherence
- Revision Checklist
- Introduction to Style and Grammar
- Apostrophes
- Article Usage for ESL Learners
- Capitalization
- Clarity: Get Rid of Nominalizations
- Cohesion: Does my Paragraph Flow?
- Commas and Colons
- Conciseness
- Confusing Words
- Parallel Structure
- Passive Voice
- Quotation Marks
- Run-on Sentences
- Subject-Verb Agreement
- Writing Mechanics
- Other Styles
- Art History This link opens in a new window
- Programming Lab Reports
Writing a Lab Report
Link to other resources.
- Screenwriting
- Publication Opportunities
- Meet with a Tutor This link opens in a new window
Academic Resource Center Hours :
Monday-Thursday: 8:00 AM-6:00 PM
Friday: 8:00 AM-4:00 PM
Phone Number : 310-338-2847
Email : [email protected]
www.lmu.edu/arc
We are located in Daum Hall on the 2nd floor!
Writing a scientific lab report is significantly different from writing for other classes like philosophy, English, and history. The most prominent form of writing in biology, chemistry, and environmental science is the lab report, which is a formally written description of results and discoveries found in an experiment. College lab reports should emulate and follow the same formats as reports found in scholarly journals, such as Nature , Cell , and The American Journal of Biochemistry .
Report Format
Title: The title says what you did. It should be brief (aim for ten words or less) and describe the main point of the experiment or investigation.
- Example: Caffeine Increases Amylase Activity in the Mealworm ( Tenebrio molitar).
- If you can, begin your title using a keyword rather than an article like “The” or “A.”
Abstract: An abstract is a very concise summary of the purpose of the report, data presented, and major conclusions in about 100 - 200 words. Abstracts are also commonly required for conference/presentation submissions because they summarize all of the essential materials necessary to understand the purpose of the experiment. They should consist of a background sentence , an introduction sentence , your hypothesis/purpose of the experiment, and a sentence about the results and what this means.
Introduction: The introduction of a lab report defines the subject of the report, provides background information and relevant studies, and outlines scientific purpose(s) and/or objective(s).
- The introduction is a place to provide the reader with necessary research on the topic and properly cite sources used.
- Summarizes the current literature on the topic including primary and secondary sources.
- Introduces the paper’s aims and scope.
- States the purpose of the experiment and the hypothesis.
Materials and Methods: The materials and methods section is a vital component of any formal lab report. This section of the report gives a detailed account of the procedure that was followed in completing the experiment as well as all important materials used. (This includes bacterial strains and species names in tests using living subjects.)
- Discusses the procedure of the experiment in as much detail as possible.
- Provides information about participants, apparatus, tools, substances, location of experiment, etc.
- For field studies, be sure to clearly explain where and when the work was done.
- It must be written so that anyone can use the methods section as instructions for exact replications.
- Don’t hesitate to use subheadings to organize these categories.
- Practice proper scientific writing forms. Be sure to use the proper abbreviations for units. Example: The 50mL sample was placed in a 5ºC room for 48hrs.
Results: The results section focuses on the findings, or data, in the experiment, as well as any statistical tests used to determine their significance.
- Concentrate on general trends and differences and not on trivial details.
- Summarize the data from the experiments without discussing their implications (This is where all the statistical analyses goes.)
- Organize data into tables, figures, graphs, photographs, etc. Data in a table should not be duplicated in a graph or figure. Be sure to refer to tables and graphs in the written portion, for example, “Figure 1 shows that the activity....”
- Number and title all figures and tables separately, for example, Figure 1 and Table 1 and include a legend explaining symbols and abbreviations. Figures and graphs are labeled below the image while tables are labeled above.
Discussion: The discussion section interprets the results, tying them back to background information and experiments performed by others in the past.This is also the area where further research opportunities shold be explored.
- Interpret the data; do not restate the results.
- Observations should also be noted in this section, especially anything unusual which may affect your results.
For example, if your bacteria was incubated at the wrong temperature or a piece of equipment failed mid-experiment, these should be noted in the results section.
- Relate results to existing theories and knowledge.This can tie back to your introduction section because of the background you provided.
- Explain the logic that allows you to accept or reject your original hypotheses.
- Include suggestions for improving your techniques or design, or clarify areas of doubt for further research.
Acknowledgements and References: A references list should be compiled at the end of the report citing any works that were used to support the paper. Additionally, an acknowledgements section should be included to acknowledge research advisors/ partners, any group or person providing funding for the research and anyone outside the authors who contributed to the paper or research.
General Tips
- In scientific papers, passive voice is perfectly acceptable. On the other hand, using “I” or “we” is not.
Incorrect: We found that caffeine increased amylase levels in Tenebrio molitar. Correct: It was discovered that caffeine increased amylase levels in Tenebrio molitar.
- It is expected that you use as much formal (bland) language and scientific terminology as you can. There should be no emphasis placed on “expressing yourself” or “keeping it interesting”; a lab report is not a narrative.
- In a lab report, it is important to get to the point. Be descriptive enough that your audience can understand the experiment, but strive to be concise.
- << Previous: Programming Lab Reports
- Next: Screenwriting >>
- Last Updated: Mar 14, 2024 12:00 PM
- URL: https://libguides.lmu.edu/writing
- My Allegheny
- Student Resources
- Office of the President
- Give to Allegheny
Laboratory Reports
Note: All students are expected to read and understand the following guidelines.
The lab report presents pertinent data, procedure(s) used, conclusions drawn, and a discussion explaining and defending these conclusions. It must be written with care. Its intended audience is anyone who might have an interest in the outcome of the particular experiment. A report, as with scientific writing in general, is brief, but complete with no superfluous information or words. The report should be as compact as possible, well written (grammatically, at least), and must use the language of the discipline.
(i) Title: The title should describe the chemical reaction(s) or study that you performed. It should be specific, but without unnecessary verbiage.
(ii) Abstract: In two or three sentences, describe what was done in the experiment. Briefly state the problem involved and type of reaction or techniques used, summarize the principal findings, and note the major conclusions.
(iii) Chemical Equation: Present the chemistry occurring during the experiment. You must use ChemDraw (available on all Doane Hall computers), or another chemical drawing program.
(iv) Narrative Experimental: The experimental procedure written in paragraph form (do not write as commands). This part of the report is complete and detailed so that an experienced chemist could repeat your experiments exactly. However, you can be too detailed. Therefore, you need not explain the procedure for conducting standard techniques–extraction, distillation, etc.–but merely state that the technique was employed.
Be sure to identify materials and give the chemical names of all compounds used. Although raw data is included in this section, do not bother to include trivial things such as the mass of glassware, the separate pieces of equipment in a standard apparatus, or simple calculations. Include observations only if relevant to the experiment.
(v) Results and Discussion: This is one section, not two separate sections. Summarize the pertinent data you have collected. Use tables and graphs as necessary for clarity (eg. large amounts of data). Tables and other figures should be numbered and appropriately titled. The purpose of the discussion is to interpret, compare, and contrast the results. Interpret the data and draw conclusions. Conclusions should be based on the evidence presented. This is the place to discuss % yields, purity (spectra and melting pt. information), and sources of error. Also, general theory may be included here if it is relevant to the results being discussed. But, be brief! This section must be written with great care.
Answer such questions as: Is the product pure? How do you know? Spectra should be fully analyzed. Is the yield high or low? If it is low, why? “Experimental error” is not an acceptable reason! Observations may be noted if pertinent.
General Information
The general form of the lab report is journal style. All data, conclusions, observations, etc. must be presented in paragraph form. Data must be coupled with procedures or conclusions, not listed separately. All writing must be past tense, passive voice. For example:
(correct) Three fractions were collected.
(incorrect) I collected three fractions; or, Collect three fractions.
Lab reports are graded both on the quality of results you obtain and the manner in which you communicate these to others. A good resource for the latter is the ACS Style Guide. A portion of this is available on the Web. Your instructor may provide more specific requirements or expectations.
Honor Code Considerations
You are expected to keep your own lab notebook and write your own lab report. If you work with a partner, that person must be acknowledged in your notebook and on the cover page of your report. Even though you may be using data collected by a partner, all conclusions must be your own. You should not work on reports together. Texts and tables of constants (i.e., CRC) must be referenced.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Introduction. Your lab report introduction should set the scene for your experiment. One way to write your introduction is with a funnel (an inverted triangle) structure: Start with the broad, general research topic. Narrow your topic down your specific study focus. End with a clear research question.
She served as a graduate instructor at the University of Illinois, a tutor at St Peter's School in Philadelphia, and an academic writing tutor and thesis mentor at Wesleyan's Writing Workshop. How to Write a Lab Report - We of a lab report example as well as a template and suggested format to get you started.
What this handout is about. This handout provides a general guide to writing reports about scientific research you've performed. In addition to describing the conventional rules about the format and content of a lab report, we'll also attempt to convey why these rules exist, so you'll get a clearer, more dependable idea of how to approach ...
As with all forms of writing, it's not the report's length that matters, but the quality of the information conveyed within. This article outlines the important bits that go into writing a lab report (title, abstract, introduction, method, results, discussion, conclusion, reference). At the end is an example report of reducing sugar ...
Title Page. Not all lab reports have title pages, but if your instructor wants one, it would be a single page that states: . The title of the experiment. Your name and the names of any lab partners. Your instructor's name. The date the lab was performed or the date the report was submitted.
A typical lab report would include the following sections: title, abstract, introduction, method, results, and discussion. The title page, abstract, references, and appendices are started on separate pages (subsections from the main body of the report are not). Use double-line spacing of text, font size 12, and include page numbers.
Writing lab reports follows a straightforward and structured procedure. It is important to recognize that each part of a lab report is important, so take the time to complete each carefully. A lab report is broken down into eight sections: title, abstract, introduction, methods and materials, results, discussion, conclusion, and references. Title.
reports, grants, and research proposals to authoring books, scientists encounter several instances where they need to execute profound and convincing writing skills. All forms of technical writing are equally significant, but this article categorically emphasizes the skills and techniques required for writing a comprehensive experimental lab ...
Download this page as a PDF: Writing a Lab Report. Return to Writing Studio Handouts. Part 1 (of 2): Introducing a Lab Report. The introduction of a lab report states the objective of the experiment and provides the reader with background information. State the topic of your report clearly and concisely (in one or two sentences).
A. What is a Lab Report? A lab report is a written document that describes the findings of a medical diagnosis, research, or scientific experiment. Lab report writing includes information on the purpose of the investigation, the methods used, the results obtained, and the conclusions drawn. B. Lab Reports Types
In scientific writing, particularly in lab reports, the use of personal pronouns is generally discouraged. The emphasis in these reports is on presenting objective, unbiased information rather than personal experiences or opinions. By avoiding personal pronouns such as "I," "we," or "you," the writer maintains a sense of impartiality and ...
A typical lab report format includes a title, introduction, procedure, results, discussion, and conclusions. A science laboratory experiment isn't truly complete until you've written the lab report. You may have taken excellent notes in your laboratory notebook, but it isn't the same as a lab report. The lab report format is designed to ...
301 Recommends: Our Scientific Writing and Lab Report workshop provides a practical guide to communicating your findings with a focus on the scientific lab report as a model. You will learn why it is important to record experiments in this way and gain a detailed understanding of how to structure your reports based on the IMRaD format (Introduction, Methods, Results and Discussion).
For any lab report, use a professional font and size. For example, 12-point Times New Roman. Double-space the report. Include a page number, usually either in the top or bottom right corner of each page. Clearly separate specific sections of the report with headings and subheadings.
Not "Lab #4" but "Lab #4: Sample Analysis using the Debye-Sherrer Method"). 2. The Abstract summarizes four essential aspects of the report: the purpose of the experiment (sometimes expressed as the purpose of the report), key findings, significance and major conclusions. The abstract often also includes a brief reference to theory or ...
List all the sources you consulted while writing the lab report. Include the full bibliographic information in the appropriate format. For lab reports in sciences and social sciences, the APA citation style is usually followed. Students of business, fine arts, and history will use Chicago style citations in their lab reports.
Experimental reports (also known as "lab reports") are reports of empirical research conducted by their authors. You should think of an experimental report as a "story" of your research in which you lead your readers through your experiment. As you are telling this story, you are crafting an argument about both the validity and reliability of ...
The lab report handout guides students through the process of properly writing of each of the above sections. As a result, students' scientific writing skills improve throughout a laboratory course. Other faculty in the Chemistry Department use similar handouts to guide students in this writing process. Since the lab courses count for the ...
Lab Report Writing Guides on the Web; Librarian. Reference Department The Scientific Paper. Dear Novice Writer, When I was in your shoes and preparing my first paper, I consulted a book on how to write. I found there a sentence encouraging the reader to do the following:
Lab Report Examples. Lab Report Example from Manchester Community Collge. This page shows a good example of a lab report, but a few things are different from the guidelines in your assignment (e.g., separating materials and experimental procedure).
How to Do a Lab Report: Outline. Like with any other papers, from SWOT analysis to case studies, writing lab reports is easier when you have a clear college lab report outline in front of you. Luckily for you, the lab report structure is the same in most cases. So, here's how to do a lab report - follow this outline (unless your instructor's requirements contradict it!):
Writing a Lab Report. Writing a scientific lab report is significantly different from writing for other classes like philosophy, English, and history. The most prominent form of writing in biology, chemistry, and environmental science is the lab report, which is a formally written description of results and discoveries found in an experiment.
Students struggle with writing lab reports, because they are used to writing for ENG 111 and similar classes. Scientific writing is different! Use the tips on this page to avoid common problems, and check out the tabs above for "What to Include" and an "Example" of a successful lab report.
The lab report presents pertinent data, procedure (s) used, conclusions drawn, and a discussion explaining and defending these conclusions. It must be written with care. Its intended audience is anyone who might have an interest in the outcome of the particular experiment. A report, as with scientific writing in general, is brief, but complete ...
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out ...
For example, when writing a personal statement, you must deal with personal statements for different levels, including writing for a job and adjusting things for a company or working for an undergraduate school. ... This blog post will assist you in learning how to write a lab report in the concluding section, as we shall help you master what a ...