- Science & Math
- Sociology & Philosophy
- Law & Politics

Kate Chopin’s The Story of An Hour: Irony & Analysis
- Kate Chopin’s The Story of…
In Kate Chopin’s short story “The Story of an Hour,” there is much irony. The first irony detected is in the way that Louise reacts to the news of the death of her husband, Brently Mallard. Before Louise’s reaction is revealed, Chopin alludes to how the widow feels by describing the world according to her perception of it after the “horrible” news.
Louise is said to “not hear the story as many women have heard the same.” Rather, she accepts it and goes to her room to be alone. Now the reader starts to see the world through Louise’s eyes, a world full of new and pure life. In her room, Louise sinks into a comfortable chair and looks out her window.
Immediately the image of comfort seems to strike an odd note. One reading this story should question the use of the word “comfortable” and why Louise is not beating the furniture instead.
Next, the newly widowed women are looking out of the window and see spring and all the new life it brings. The descriptions used now are as far away from death as possible. “The delicious breath of rain…the notes of a distant song…countless sparrows were twittering…patches of blue sky….”
All these are beautiful images of life, the reader is quite confused by this most unusual foreshadowing until Louise’s reaction is explained. The widow whispers “Free, free, free!” Louise realizes that her husband had loved her, but she goes on to explain that as men and women often inhibit each other, even if it is done with the best of intentions, they exert their own wills upon each other.
She realized that although at times she had loved him, she has regained her freedom, a state of being that all of God’s creatures strive for. Although this reaction is completely unexpected, the reader quickly accepts it because of Louise’s adequate explanation. She grows excited and begins to fantasize about living her life for herself.
With this realization, she wishes that “life might belong,” and she feels like a “goddess of Victory” as she walks down the stairs. This is an eerie foreshadowing for an even more unexpected ending. The reader has just accepted Louise’s reaction to her husband’s death when the most unexpected happens; her husband is actually alive and he enters the room shocking everyone, and Louise especially, as she is shocked to death.
The irony continues, though, because the doctors say she died of joy when the reader knows that she actually died because she had a glimpse of freedom and could not go back to living under her husband’s will again. In the title, the “story” refers to Louise’s life. She lived in the true sense of the word, with the will and freedom to live for only one hour.
Related Posts
- Kate Chopin's Désirée’s Baby: Summary & Analysis
- Kate Chopin's "The Storm": Analysis & Summary
- Kate Chopin’s A Story of An Hour: Feelings & Emotions
- Kate Chopin's A Pair of Silk Stockings: Mrs. Sommers Analysis
- Edna's Relationships in Kate Chopin's The Awakening
Author: William Anderson (Schoolworkhelper Editorial Team)
Tutor and Freelance Writer. Science Teacher and Lover of Essays. Article last reviewed: 2022 | St. Rosemary Institution © 2010-2024 | Creative Commons 4.0
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Post comment
Literary Theory and Criticism
Home › Literature › Analysis of Kate Chopin’s The Story of an Hour
Analysis of Kate Chopin’s The Story of an Hour
By NASRULLAH MAMBROL on July 28, 2021
Originally entitled “The Dream of an Hour” when it was first published in Vogue (December 1894), “The Story of an Hour” has since become one of Kate Chopin’s most frequently anthologized stories. Among her shortest and most daring works, “Story” examines issues of feminism, namely, a woman’s dissatisfaction in a conventional marriage and her desire for independence. It also features Chopin’s characteristic irony and ambiguity .
The story begins with Louise Mallard’s being told about her husband’s presumed death in a train accident. Louise initially weeps with wild abandon, then retires alone to her upstairs bedroom. As she sits facing the open window, observing the new spring life outside, she realizes with a “clear and exalted perception” that she is now free of her husband’s “powerful will bending hers” (353). She becomes delirious with the prospect that she can now live for herself and prays that her life may be long. Her newfound independence is short-lived, however. In a surprise ending, her husband walks through the front door, and Louise suffers a heart attack and dies. Her death may be considered a tragic defeat or a pyrrhic victory for a woman who would rather die than lose that “possession of self-assertion which she suddenly recognized as the strongest impulse of her being” (353). The doctors ironically attribute her death to the “joy that kills” (354).
BIBLIOGRAPHY Chopin, Kate. The Complete Works of Kate Chopin. Edited by Per Seyersted. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press, 1969. Koloski, Bernard. Kate Chopin: A Study of the Short Fiction. New York: Twayne, 1996. Seyersted, Per. Kate Chopin: A Critical Biography. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press, 1969. Toth, Emily. Kate Chopin. New York: Morrow, 1990

Share this:
Categories: Literature , Short Story
Tags: American Literature , Analysis of Kate Chopin's The Story of an Hour , calicut university materials of Kate Chopin's The Story of an Hour , criticism of Kate Chopin's The Story of an Hour , Kate Chopin , Kate Chopin's The Story of an Hour , Kate Chopin's The Story of an Hour criticism , Kate Chopin's The Story of an Hour essay , Kate Chopin's The Story of an Hour notes , Kate Chopin's The Story of an Hour plot , Literary Criticism , plotKate Chopin's The Story of an Hour , summary of Kate Chopin's The Story of an Hour , The Dream of an Hour , themes of Kate Chopin's The Story of an Hour
Related Articles

You must be logged in to post a comment.
English Studies
This website is dedicated to English Literature, Literary Criticism, Literary Theory, English Language and its teaching and learning.
- “The Story of an Hour”: Irony
“The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin is not only full of symbols but also ironic situations and comments, making it having multiplicity of meanings.
Introduction to Analysis of “The Story of an Hour”
Besides superficial meanings, a literary piece has deeper meanings to tell like Kate Chopin’s “The Story of an Hour” which is not only full of symbols but also ironic situations and comments. From the face, it seems a very simple story of a lady who receives the news of the death of her husband and feels depressed. When the same news transpires the wrong report, she immediately dies due to cardiac failure. Yet deeper meanings are not the same as superficial ones. They show not only the character of a woman of the 19 th century but also the social and financial circumstances in which she lives and how marriage traps her. Kate Chopin uses multiple symbols and ironies to convey the real meanings of false love, marriage, and social issues related to the 19 th century through her story “The Story of an Hour.”
Spotting Themes in “The Story of an Hour”
My first reaction to the story is that of stupefaction. I, at once, realized the irony and its symbolical value when I read the last sentence. The heart vulnerable to suffering in the first line stops working due to happiness. What a symbol of the fickleness of mind that the writer uses! It is also that the story has several symbols used dexterously by Kate Chopin to make her meanings clear. The story opens with the mention of heroin. The stress is upon her heart as if she is suffering from some cardiac issue, but also that she has heart problems. It has both meanings that she is an amalgamation of not only physical but also emotional problems. The story shows “Mrs. Mallard … afflicted with a heart trouble” (Chopin) which is the major reason for the great care the news breaker has taken. This heart is also a symbol of society as marriage is the heart of any society and if society must have strong foundations, the marriage institution must get strengthened. Her heart may show the situation of the peril that the family institution faced in the 19 th century. This opens up another debate when the story ends where it shows that she has died due to cardiac arrest but not on account of sorrow but happiness.
Symbolism in “The Story of an Hour”
Kate Chopin has also used symbols such as time, patches of sky, and the chair. Some of them are even personifications. The time is of spring as Kate Chopin states about her that she could watch the “trees that were all aquiver with the new spring life” (Chopin). All the next sentences show her jubilation over the situation she finds herself in. She thinks that now she is seeing all spring and no more autumn as she is going to free herself from the clutches of her marriage. In fact, spring is a symbol of happiness and shows how she views life. In this happiness, she sees all things expressing her feelings such as the patches of the blue sky. It is also a symbol of happiness and freedom. Earlier she thought of ending her life, but now the symbols have changed. Similarly, the chair has also become a significant symbol. The chair is personified when she hears the news of the death of her husband and sinks into it, but when this is over, she relaxes in it.
Irony in “The Story of an Hour”
As far as irony is concerned, Kate Chopin has used both situational as well as dramatic irony . The mere coming back of the dead husband is an example of situational irony. It is highly ironic that a person who is supposed to be dead and going through rituals comes alive home and is hardly aware of his own death. The second situational irony is that Mr. Mallard who should have come home dead, comes alive and Mrs. Mallard who is going to live a new life, dies on the spot. The greatest irony is that Mrs. Mallard is feeling happy and free, while others are worried that she might go into a comma or that this grief may cost her life. However, when the situation turns, they see that she, instead of dying of a heart attack, dies due to excessive happiness. Just read what the story says at the end, “When the doctors [states that it is] joy that kills” (Chopin). The other form is that of dramatic irony which is both when she cries though actually, she is happy that she is now free from her marriage locks. She is, in fact, thinking how wonderful life would be for her, while it is not the case for others who are thinking that life would be difficult for her and taking steps to make her comfortable. Her situation is that she is taking to her fancy imagining good old days of freedom, while her sister is taking care of her by clasping “her sister’s waist (Chopin) so that she should be consoled in any way. This shows how pretension and artificiality have been dominant in the 19 th century and how ladies are fickle-minded.
Conclusion of Analysis of “The Story of an Hour”
In short, Kate Chopin suggests the meanings through symbols and irony in this story. All the symbols used in this story have different meanings that correlate with the ironic situations and remarks. It shows that life in the 19 th century was witnessing fast transformations – the result of fast progress and modern ideas creeping into society. Marriage and false love were destroying social relationships which different symbols amply demonstrate here.
Works Cited
Chopin, Kate. The Story of an Hour . n.d. VCU. <http://www.vcu.edu/engweb/webtexts/hour/>. Accessed 12 Mar. 2020.
You may read more on Shorty Essays Below:
- “Everyday Use” and “A Man Who Was…”: African American Culture
- “Sweat” and “Everyday Use”: Feminism
- “The Cask of Amontillado”: Revenge
Related posts:
- “Araby” by James Joyce: Modernist Story
- Humanity in “The Cabuliwala”
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

A Summary and Analysis of Kate Chopin’s ‘The Story of an Hour’
By Dr Oliver Tearle (Loughborough University)
Some short stories can say all they need to do in just a few pages, and Kate Chopin’s three-page 1894 story ‘The Story of an Hour’ (sometimes known as ‘The Dream of an Hour’) is a classic example. Yet those three pages remain tantalisingly ambiguous, perhaps because so little is said, so much merely hinted at. Yet Chopin’s short story is, upon closer inspection, a subtle, studied analysis of death, marriage, and personal wishes.
Written in April 1894 and originally published in Vogue in December of that year, the story focuses on an hour in the life of a married woman who has just learnt that her husband has apparently died.
‘The Story of an Hour’: plot summary
What happens in that brief hour, that story of an hour? A married woman, Mrs Louise Mallard, who has heart trouble, learns that her husband has died in a railroad accident.
Her sister Josephine breaks the news to her; it was her husband’s friend Richards who first heard about the railroad disaster and saw her husband’s name, Brently Mallard, at the top of the list of fatalities. Her first reaction is to weep at the news that her husband is dead; she then takes herself off to her room to be alone.
She sinks into an armchair and finds herself attuned to a series of sensations: the trees outside the window ‘aquiver with the new spring life’, the ‘breath of rain’ in the air; the sound of a peddler crying his wares in the street below. She finds herself going into a sort of trancelike daze, a ‘suspension of intelligent thought’.
Then, gradually, a feeling begins to form within her: a sense of freedom. Now her husband is dead, it seems, she feels free. She dreads seeing her husband’s face (as she knows she must, when she goes to identify the body), but she knows that beyond that lie years and years of her life yet to be lived, and ‘would all belong to her absolutely’.
She reflects that she had loved her husband – sometimes. Sometimes she hadn’t. But now, that didn’t matter: what matters is the ‘self-assertion’, the declaration of independence, that her life alone represents a new start.
But then, her sister Josephine calls from outside the door for her to come out, worried that Louise is making herself ill. But Louise doesn’t feel ill: she feels on top of the world. She used to dread the prospect of living to a ripe old age, but now she welcomes such a prospect. Eventually she opens the door and she and Josephine go back downstairs.
Richards is still down there, waiting for them. Then, there’s a key in the front door and who should enter but … Mrs Mallard’s husband, Brently Mallard.
It turns out he was nowhere near the scene of the railroad accident, and is unharmed! Mrs Mallard is so shocked at his return that she dies, partly because of her heart disease but also, so ‘they’ said, from the unexpected ‘joy’ of her husband’s return.
‘The Story of an Hour’: analysis
In some ways, ‘The Story of an Hour’ prefigures a later story like D. H. Lawrence’s ‘ Odour of Chrysanthemums ’ (1911), which also features a female protagonist whose partner’s death makes her reassess her life with him and to contemplate the complex responses his death has aroused in her.
However, in Lawrence’s story the husband really has died (in a mining accident), whereas in ‘The Story of an Hour’, we find out at the end of the story that Mr Mallard was not involved in the railroad accident and is alive and well. In a shock twist, it is his wife who dies, upon learning that he is still alive.
What should we make of this ‘dream of an hour’? That alternative title is significant, not least because of the ambiguity surrounding the word ‘dream’. Is Louise so plunged into shock by the news of her husband’s apparent death that she begins to hallucinate that she would be better off without him? Is this her way of coping with traumatic news – to try to look for the silver lining in a very black cloud? Or should we analyse ‘dream’ as a sign that she entertains aspirations and ambitions, now her husband is out of the way?
‘The Dream of an Hour’ perhaps inevitably puts us in mind of Kate Chopin’s most famous story, the short novel The Awakening (1899), whose title reflects its female protagonist Edna Pontellier’s growing awareness that there is more to life than her wifely existence.
But Louisa Mallard’s ‘awakening’ remains a dream; when she awakes from it, upon learning that her husband is still alive and all her fancies about her future life have been in vain, she dies.
‘The Story of an Hour’ and modernism
‘The Story of an Hour’ is an early example of the impressionistic method of storytelling which was also being developed by Anton Chekhov around the same time as Chopin, and which would later be used by modernists such as Katherine Mansfield, James Joyce, and Virginia Woolf.
Although the story uses an omniscient third-person narrator, we are shown things from particular character perspectives in a way that reflects their own confusions and erratic thoughts – chiefly, of course, Louisa Mallard’s own.
But this impressionistic style – which is more interested in patterns of thought, daydreaming, and emotional responses to the world than in tightly structured plots – continues right until the end of the story.
Consider the final sentence of the story: ‘When the doctors came they said she had died of heart disease – of joy that kills.’ The irony, of course, is that Louisa appears to have accepted her husband’s death and to have taken his demise as a chance to liberate herself from an oppressive marriage (note Chopin’s reference to the lines on her face which ‘bespoke repression and even a certain strength’ – what did she need that strength for, we wonder?).
So it was not joy but disappointment, if anything, that brought on the heart attack that killed her. But the (presumably male) doctors who attended her death would not have assumed any such thing: they would have analysed her death as a result of her love for her husband, and the sheer joy she felt at having him back.
Chopin’s story also foreshadows Katherine Mansfield’s ‘The Garden Party’ , and Laura Sheridan’s enigmatic emotional reaction to seeing her first dead body (as with Chopin’s story, a man who has died in an accident). If you enjoyed this analysis of ‘The Story of an Hour’, you might also enjoy Anton Chekhov’s 1900 story ‘At Christmas Time’, to which Chopin’s story has been compared.
Discover more from Interesting Literature
Subscribe to get the latest posts to your email.
Type your email…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading

The Story of an Hour
Kate chopin, ask litcharts ai: the answer to your questions.
After Louise has locked herself in her bedroom, her sister Josephine’s attempt to coax Louise out of the bedroom is an instance of dramatic irony.
Josephine was kneeling before the closed door with her lips to the keyhole, imploring for admission. “Louise, open the door! I beg; open the door—you will make yourself ill. What are you doing, Louise? For heaven’s sake open the door.” “ Go away. I am not making myself ill.” No; she was drinking in a very elixir of life through that open window. Cite this Quote
This exchange is ironic because the reader knows how Louise is actually feeling, while Josephine doesn’t. Josephine thinks that Louise is so upset about her husband, Brently’s, death that she’s making herself sick. But the reader knows that this isn’t the case—Louise is telling the truth when says to Josephine, “I am not making myself ill.” Instead, Louise has quickly moved on from grief to excitement, as she’s realized that her husband’s death means that she’s now free.
This gap in understanding emphasizes the difference between people’s expectations of Louise—other characters believe that she’s emotionally fragile and content with being dependent on her husband—and her actual feelings and desires. Josephine’s overprotectiveness and interference seem well-intentioned, but it’s nevertheless an example of how the people in Louise’s life want to control her rather than truly understand and help her.
In this way, the dramatic irony serves two purposes. First, it prompts readers to question whether Louise’s happiness in reaction to her husband’s death is socially or morally acceptable, given that the other characters don’t expect her to feel this way and would presumably be offended if they knew. The story never takes a stance on this—it’s left up to the reader to decide whether Louise is justified in her feelings. The irony also points to how society underestimates Louise (and women of her time more generally), and how the people in her life fail to recognize that her marriage isn’t as important to her as her own independence.
The revelation near the end of the story that Brently is alive is a moment of dramatic irony.
Some one was opening the front door with a latchkey. It was Brently Mallard who entered, a little travel-stained, composedly carrying his grip-sack and umbrella. He had been far from the scene of accident, and did not even know there had been one. Cite this Quote
This passage is ironic because Brently is completely oblivious to the railroad accident, let alone the fact that Louise, Josephine, and Richards believed that he was killed in it. The reader, on the other hand, has been aware of these things all along. They’ve witnessed Louise process the news of the accident and Brently’s presumed death, undergo a process of self-discovery, and secretly envision a happy future without her husband. Brently, meanwhile, is unaware that any of this has happened.
Even more darkly ironic is the fact that seeing Brently alive is so shocking to Louise that she immediately dies of a heart attack. Brently will almost certainly interpret Louise’s death to be the product of a moment of shocking joy at discovering him alive. So, in the end, Brently will never know how Louise privately felt about their marriage, how she reacted to his death, and how his arrival actually hit her like a renewed sentence to prison as opposed to a moment of joy. This dramatic irony makes the story’s ending all the more bleak and tragic—only Louise and the reader know the truth.
Louise’s death at the end of the story is both situationally and dramatically ironic. Believing that her husband Brently was killed in a railroad accident, Louise is so shocked when he walks through the front door that she dies of a heart attack:
Some one was opening the front door with a latchkey. It was Brently Mallard who entered, a little travel-stained, composedly carrying his grip-sack and umbrella. He had been far from the scene of accident, and did not even know there had been one. He stood amazed at Josephine’s piercing cry; at Richards' quick motion to screen him from the view of his wife. But Richards was too late. When the doctors came they said she had died of heart disease—of joy that kills. Cite this Quote
This outcome is situationally ironic because it upends both the characters’ and the reader’s beliefs, and it’s dramatically ironic because the reader understands Louise’s cause of death in a way that the other characters don’t.
First, the fact that Louise, not Brently, is the one who’s dead at the end of the story subverts the characters’ and the reader’s expectations. When Louise received the news of Brently’s death, she quickly realized that her life would be happier and freer without him. It’s an ironic twist of fate, then, when it’s revealed that Brently is actually alive—this outcome is unexpected for Louise, her houseguests, and likely the reader. It completely upends Louise’s newfound excitement and expectations for her future, to the point that she dies of heart failure. Up until this point, the opposite seemed true: that Brently was dead, and that Louise would go on to live a more enjoyable and fulfilling life than ever before.
The story uses this moment of situational irony to drive home the inescapability of Louise’s situation. Trapped in her role as a housewife and eager to be independent, Brently’s death was seemingly her only way out of a dissatisfying life. But ultimately, believing that he died and allowing herself to fantasize about life as a widow is what sets her up to die of shock at the end of the story—preventing her from ever living out the freedom that she imagined for herself. The ending implies that her only escape from being dependent on her husband is, ironically, death.
Then, the doctors’ assumption that Louise died of “joy that kills” is dramatic irony, because the reader knows that Louise’s heart failure was likely caused by extreme disappointment, the opposite of extreme joy. The doctors, however, seem to assume that her weak heart is simply an extension of her natural emotional weakness as a woman, and that heart-stopping “joy” is the natural reaction to finding out her husband is still alive.
But Louise’s weak heart actually symbolizes the way her marriage limits and confines her, preventing her from being free to “live for herself” just as her heart condition prevents her from freely feeling her emotions. This is why she privately feels joy after she finds out the misinformation about Brently’s death, and why she then dies from losing joy rather than gaining it when she sees Brently alive. Thus, the final line of the story is ironic in that it fundamentally misunderstands how Louise felt about marriage—a secret that only the reader finds out, and that Louise takes to her grave.

The Story of an Hour Critical Analysis Essay
Looking for a critical analysis of The Story of an Hour ? The essay on this page contains a summary of Kate Chopin’s short story, its interpretation, and feminist criticism. Find below The Story of an Hour critique together with the analysis of its characters, themes, symbolism, and irony.
Introduction
Works cited.
The Story of an Hour was written by Kate Chopin in 1984. It describes a woman, Mrs. Mallard, who lost her husband in an accident, but later the truth came out, and the husband was alive. This essay will discuss The Story of an Hour with emphasis on the plot and development of the protagonist, Mrs. Mallard, who goes through contrasting emotions and feelings that finally kill her on meeting her husband at the door, yet he had been said to be dead.
The Story of an Hour Summary
Kate Chopin narrated the story of a woman named Mrs. Mallard who had a heart health problem. One day the husband was mistaken to have died in an accident that occurred. Due to her heart condition, her sister had to take care while breaking the bad news to her. She was afraid that such news of her husband’s death would cost her a heart attack. She strategized on how to break the news to her sister bit by bit, which worked perfectly well. Mrs. Mallard did not react as expected; instead, she started weeping just once.
She did not hear the story as many women have had the same with a paralyzed inability to accept its significance. She wept once, with sudden, wild abandonment, in her sister’s arms (Woodlief 2).
Mrs. Mallard wondered how she would survive without a husband. She went to one room and locked herself alone to ponder what the death of her husband brought to her life. She was sorrowful that her husband had died, like it is human to be sad at such times. This is someone very close to her, but only in a short span of time was no more. This sudden death shocked her. Her sister Josephine and friends Mr. Richard and Louise are also sorry for the loss (Taibah 1).
As she was in that room alone, she thought genuinely about the future. Unexpectedly, she meditated on her life without her husband. Apart from sorrow, she started counting the better part of her life without her husband. She saw many opportunities and freedom to do what she wanted with her life. She believed that the coming years would be perfect for her as she only had herself to worry about. She even prayed that life would be long.
After some time, she opened the door for Josephine, her sister, who had a joyous face. They went down the stairs of the house, and Mr. Mallard appeared as he opened the gate. Mr. Mallard had not been involved in the accident and could not understand why Josephine was crying. At the sight of her husband, Mr. Mallard, his wife, Mrs. Mallard, collapsed to death. The doctors said that she died because of heart disease.
The Story of an Hour Analysis
Mrs. Mallard was known to have a heart problem. Richard, who is Mr. Mallard’s friend, was the one who learned of Mr. Mallard’s death while in the office and about the railroad accident that killed him. They are with Josephine, Mrs. Mallard’s sister, as she breaks the news concerning the sudden death of her husband. The imagery clearly describes the situation.
The writer brought out the suspense in the way he described how the news was to be broken to a person with a heart problem. There is a conflict that then follows in Mrs. Mallard’s response which becomes more complicated. The death saddens Mrs. Mallard, but, on the other hand, she counts beyond the bitter moments and sees freedom laid down for her for the rest of her life. The description of the room and the environment symbolize a desire for freedom.
This story mostly focuses on this woman and a marriage institution. Sad and happy moments alternate in the protagonist, Mrs. Mallard. She is initially sad about the loss of her husband, then in a moment, ponders on the effects of his death and regains strength.
Within a short period, she is shocked by the sight of her husband being alive and even goes to the extreme of destroying her life. She then dies of a heart attack, whereas she was supposed to be happy to see her husband alive. This is an excellent contrast of events, but it makes the story very interesting.
She could see in the open square before her house the tops of trees that were all aquiver with the new spring life. The delicious breath of rain was in the air. In the street below, a peddler was crying his wares. The notes of a distant song that someone was singing reached her faintly, and countless sparrows were twittering in the eaves. There were patches of blue sky showing here and there through the clouds that had met and piled one above the other in the west facing her window (Woodlief 1).
Therefore, an open window is symbolic. It represents new opportunities and possibilities that she now had in her hands without anyone to stop her, and she refers to it as a new spring of life.
She knew that she was not in a position to bring her husband back to life.
Her feelings were mixed up. Deep inside her, she felt that she had been freed from living for another person.
She did not stop to ask if it were or were not a monstrous joy that held her… She knew that she would weep again when she saw the kind, tender hands folded in death, the face that had never looked save with love upon her, fixed and gray and dead (Sparknotes 1).
The author captured a marriage institution that was dominated by a man. This man, Mr. Mallard, did not treat his wife as she would like (the wife) at all times, only sometimes. This Cleary showed that she was peaceful even if her husband was dead. Only some sorrow because of the loss of his life but not of living without him. It seemed that she never felt the love for her husband.
And yet she had loved him sometimes. Often she had not. What did it matter! What could love the unsolved mystery, count for in the face of this procession of self-assertion which she suddenly recognized as the strongest impulse of her being! (Woodlief 1).
How could a wife be peaceful at the death of her husband? Though people thought that she treasured her husband, Mr. Mallard, so much and was afraid that she would be stressed, she did not see much of the bitterness like she found her freedom. This reveals how women are oppressed in silence but never exposed due to other factors such as wealth, money, and probably outfits.
As much as wealth is essential, the characters Mr. and Mrs. Mallard despise the inner being. Their hearts were crying amid a physical smile: “Free! Body and soul free!”…Go away. I am not making myself ill.” No; she was drinking in a very elixir of life through that open window” (Woodlief 1).
In this excerpt, Mrs. Mallard knows what she is doing and believes that she is not harming herself. Instead, she knew that though the husband was important to her, marriage had made her a subject to him. This was not in a positive manner but was against her will. It seems she had done many things against her will, against herself, but to please her husband.
Mrs. Mallard’s character is therefore developed throughout this story in a short time and reveals many values that made her what she was. She is a woman with a big desire for freedom that was deprived by a man in marriage. She is very emotional because after seeing her freedom denied for the second time by her husband, who was mistaken to have died, she collapses and dies. The contrast is when the writer says, “She had died of heart disease…of the joy that kills” (Woodlief 1).
Mrs. Mallard was not able to handle the swings in her emotions, and this cost her life. Mr. Mallard was left probably mourning for his wife, whom he never treasured. He took her for granted and had to face the consequences. Oppressing a wife or another person causes a more significant loss to the oppressor. It is quite ironic that Mr. Mallard never knew that his presence killed his wife.
Sparknotes. The Story of an Hour. Sparknotes, 2011. Web.
Taibah. The Story of an Hour. Taibah English Forum, 2011. Web.
Woodlief. The story of an hour . VCU, 2011. Web.
Further Study: FAQ
📌 who is the protagonist in the story of an hour, 📌 when was the story of an hour written, 📌 what is the story of an hour about, 📌 what is the conclusion the story of an hour.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, October 28). The Story of an Hour Critical Analysis Essay. https://ivypanda.com/essays/critical-analysis-of-the-story-of-an-hour/
"The Story of an Hour Critical Analysis Essay." IvyPanda , 28 Oct. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/critical-analysis-of-the-story-of-an-hour/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'The Story of an Hour Critical Analysis Essay'. 28 October.
IvyPanda . 2023. "The Story of an Hour Critical Analysis Essay." October 28, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/critical-analysis-of-the-story-of-an-hour/.
1. IvyPanda . "The Story of an Hour Critical Analysis Essay." October 28, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/critical-analysis-of-the-story-of-an-hour/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The Story of an Hour Critical Analysis Essay." October 28, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/critical-analysis-of-the-story-of-an-hour/.
- Louise Mallard in "The Story of an Hour" by Kate Chopin
- Kate Chopin’s The Story of an Hour
- The Novel "The Story of an Hour" by Kate Chopin
- Women and Freedom in "The Story of an Hour" by Kate Chopin
- Imagery and Symbolism in "Story of an Hour" by Kate Chopin
- Marriage in "The Story of an Hour" by Kate Chopin
- Literary Analysis: The Story of an Hour by Kate Chopin
- The Story of an Hour by Kate Chopin
- Kate Chopin’s “The Story of an Hour”
- Protagonists in Literature
- Symbolism in the "Death of a Salesman" by Arthur Miller
- The Other Wes Moore
- Henry David Thoreau: The Maine Woods, Walden, Cape Cod
- Analysis of “The Dubious Rewards of Consumption”
- Moral Dilemma’s in the Breakdown 1968 and the Missing Person

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the story of an hour: summary and analysis.
General Education

Imagine a world where women are fighting for unprecedented rights, the economic climate is unpredictable, and new developments in technology are made every year. While this world might sound like the present day, it also describes America in the 1890s .
It was in this world that author Kate Chopin wrote and lived, and many of the issues of the period are reflected in her short story, “The Story of an Hour.” Now, over a century later, the story remains one of Kate Chopin’s most well-known works and continues to shed light on the internal struggle of women who have been denied autonomy.
In this guide to Kate Chopin’s “The Story of an Hour,” we’ll discuss:
- A brief history of Kate Chopin and America the 1890s
- “The Story of an Hour” summary
- Analysis of the key story elements in “The Story of an Hour,” including themes, characters, and symbols
By the end of this article, you’ll have an expert grasp on Kate Chopin’s “The Story of an Hour.” So let’s get started!

“The Story of an Hour” Summary
If it’s been a little while since you’ve read Kate Chopin’s “The Story of an Hour,” it can be hard to remember the important details. This section includes a quick recap, but you can find “The Story of an Hour” PDF and full version here . We recommend you read it again before diving into our analyses in the next section!
For those who just need a refresher, here’s “The Story of an Hour” summary:
Mrs. Louise Mallard is at home when her sister, Josephine, and her husband’s friend, Richards, come to tell her that her husband, Brently Mallard, has been killed in a railroad accident . Richards had been at the newspaper office when the news broke, and he takes Josephine with him to break the news to Louise since they’re afraid of aggravating her heart condition. Upon hearing the news of her husband’s death, Louise is grief-stricken, locks herself in her room, and weeps.
From here, the story shifts in tone. As Louise processes the news of her husband’s death, she realizes something wonderful and terrible at the same time: she is free . At first she’s scared to admit it, but Louise quickly finds peace and joy in her admission. She realizes that, although she will be sad about her husband (“she had loved him—sometimes,” Chopin writes), Louise is excited for the opportunity to live for herself. She keeps repeating the word “free” as she comes to terms with what her husband’s death means for her life.
In the meantime, Josephine sits at Louise’s door, coaxing her to come out because she is worried about Louise’s heart condition. After praying that her life is long-lived, Louise agrees to come out. However, as she comes downstairs, the front door opens to reveal her husband, who had not been killed by the accident at all. Although Richards tries to keep Louise’s heart from shock by shielding her husband from view, Louise dies suddenly, which the doctors later attribute to “heart disease—of the joy that kills .”

Kate Chopin, the author of "The Story of an Hour," has become one of the most important American writers of the 19th century.
The History of Kate Chopin and the 1890s
Before we move into “The Story of an Hour” analysis section, it’s helpful to know a little bit about Kate Chopin and the world she lived in.
A Short Biography of Kate Chopin
Born in 1850 to wealthy Catholic parents in St. Louis, Missouri, Kate Chopin (originally Kate O’Flaherty) knew hardship from an early age. In 1855, Chopin lost her father, Thomas, when he passed away in a tragic and unexpected railroad accident. The events of this loss would stay with Kate for the rest of her life, eventually becoming the basis for “The Story of an Hour” nearly forty years later.
Chopin was well-educated throughout her childhood , reading voraciously and becoming fluent in French. Chopin was also very aware of the divide between the powerful and the oppressed in society at the time . She grew up during the U.S. Civil War, so she had first-hand knowledge of violence and slavery in the United States.
Chopin was also exposed to non-traditional roles for women through her familial situation. Her mother, grandmother, and great-grandmother chose to remain widows (rather than remarry) after their husbands died. Consequently, Chopin learned how important women’s independence could be, and that idea would permeate much of her writing later on.
As Chopin grew older, she became known for her beauty and congeniality by society in St. Louis. She was married at the age of nineteen to Oscar Chopin, who came from a wealthy cotton-growing family. The couple moved to New Orleans, where they would start both a general store and a large family. (Chopin would give birth to seven children over the next nine years!)
While Oscar adored his wife, he was less capable of running a business. Financial trouble forced the family to move around rural Louisiana. Unfortunately, Oscar would die of swamp fever in 1882 , leaving Chopin in heavy debt and with the responsibility of managing the family’s struggling businesses.
After trying her hand at managing the property for a year, Chopin conceded to her mother’s requests to return with her children to St. Louis. Chopin’s mother died the year after. In order to support herself and her children, Kate began to write to support her family.
Luckily, Chopin found immediate success as a writer. Many of her short stories and novels—including her most famous novel, The Awakening— dealt with life in Louisiana . She was also known as a fast and prolific writer, and by the end of the 1900s she had written over 100 stories, articles, and essays.
Unfortunately, Chopin would pass away from a suspected cerebral hemorrhage in 1904, at the age of 54 . But Kate Chopin’s “The Story of an Hour” and other writings have withstood the test of time. Her work has lived on, and she’s now recognized as one of the most important American writers of the 19th century.

American life was undergoing significant change in the 19th century. Technology, culture, and even leisure activities were changing.
American Life in the 1890s
“The Story of an Hour” was written and published in 1894, right as the 1800s were coming to a close. As the world moved into the new century, American life was also changing rapidly.
For instance, t he workplace was changing drastically in the 1890s . Gone were the days where most people were expected to work at a trade or on a farm. Factory jobs brought on by industrialization made work more efficient, and many of these factory owners gradually implemented more humane treatment of their workers, giving them more leisure time than ever.
Though the country was in an economic recession at this time, technological changes like electric lighting and the popularization of radios bettered the daily lives of many people and allowed for the creation of new jobs. Notably, however, work was different for women . Working women as a whole were looked down upon by society, no matter why they found themselves in need of a job.
Women who worked while they were married or pregnant were judged even more harshly. Women of Kate Chopin’s social rank were expected to not work at all , sometimes even delegating the responsibility of managing the house or child-rearing to maids or nannies. In the 1890s, working was only for lower class women who could not afford a life of leisure .
In reaction to this, the National American Woman Suffrage Association was created in 1890, which fought for women’s social and political rights. While Kate Chopin was not a formal member of the suffragette movements, she did believe that women should have greater freedoms as individuals and often talked about these ideas in her works, including in “The Story of an Hour.”

Kate Chopin's "The Story of an Hour" a short exploration of marriage and repression in America.
“The Story of an Hour” Analysis
Now that you have some important background information, it’s time to start analyzing “The Story of an Hour.”
This short story is filled with opposing forces . The themes, characters, and even symbols in the story are often equal, but opposite, of one another. Within “The Story of an Hour,” analysis of all of these elements reveals a deeper meaning.
“The Story of an Hour” Themes
A theme is a message explored in a piece of literature. Most stories have multiple themes, which is certainly the case in “The Story of an Hour.” Even though Chopin’s story is short, it discusses the thematic ideas of freedom, repression, and marriage.
Keep reading for a discussion of the importance of each theme!
Freedom and Repression
The most prevalent theme in Chopin’s story is the battle between freedom and “repression.” Simply put , repression happens when a person’s thoughts, feelings, or desires are being subdued. Repression can happen internally and externally. For example, if a person goes through a traumatic accident, they may (consciously or subconsciously) choose to repress the memory of the accident itself. Likewise, if a person has wants or needs that society finds unacceptable, society can work to repress that individual. Women in the 19th century were often victims of repression. They were supposed to be demure, gentle, and passive—which often went against women’s personal desires.
Given this, it becomes apparent that Louise Mallard is the victim of social repression. Until the moment of her husband’s supposed death, Louise does not feel free . In their marriage, Louise is repressed. Readers see this in the fact that Brently is moving around in the outside world, while Louise is confined to her home. Brently uses railroad transportation on his own, walks into his house of his own accord, and has individual possessions in the form of his briefcase and umbrella. Brently is even free from the knowledge of the train wreck upon his return home. Louise, on the other hand, is stuck at home by virtue of her position as a woman and her heart condition.
Here, Chopin draws a strong contrast between what it means to be free for men and women. While freedom is just part of what it means to be a man in America, freedom for women looks markedly different. Louise’s life is shaped by what society believes a woman should be and how a wife should behave. Once Louise’s husband “dies,” however, she sees a way where she can start claiming some of the more “masculine” freedoms for herself. Chopin shows how deeply important freedom is to the life of a woman when, in the end, it’s not the shock of her husband’s return of her husband that kills Louise, but rather the thought of losing her freedom again.
Marriage as a “The Story of an Hour” theme is more than just an idyllic life spent with a significant other. The Mallard’s marriage shows a reality of 1890s life that was familiar to many people. Marriage was a means of social control —that is to say, marriage helped keep women in check and secure men’s social and political power. While husbands were usually free to wander the world on their own, hold jobs, and make important family decisions, wives (at least those of the upper class) were expected to stay at home and be domestic.
Marriage in Louise Mallard’s case has very little love. She sees her marriage as a life-long bond in which she feels trapped, which readers see when she confesses that she loved her husband only “sometimes.” More to the point, she describes her marriage as a “powerful will bending hers in that blind persistence with which men and women believe they have a right to impose a private will upon a fellow-creature.” In other words, Louise Mallard feels injustice in the expectation that her life is dictated by the will of her husband.
Like the story, the marriages Kate witnessed often ended in an early or unexpected death. The women of her family, including Kate herself, all survived their husbands and didn’t remarry. While history tells us that Kate Chopin was happy in her marriage, she was aware that many women weren’t. By showing a marriage that had been built on control and society’s expectations, Chopin’s “The Story of an Hour” highlights the need for a world that respected women as valuable partners in marriage as well as capable individuals.

While this painting by Johann Georg Meyer wasn't specifically of Louise Mallard, "Young Woman Looking Through a Window" is a depiction of what Louise might have looked like as she realized her freedom.
"The Story of an Hour" Characters
The best stories have developed characters, which is the case in “The Story of an Hour,” too. Five characters make up the cast of “The Story of an Hour”:
Louise Mallard
Brently mallard.
- The doctor(s)
By exploring the details of each character, we can better understand their motivations, societal role, and purpose to the story.
From the opening sentence alone, we learn a lot about Louise Mallard. Chopin writes, “Knowing that Mrs. Mallard was afflicted with a heart trouble, great care was taken to break to her as gently as possible the news of her husband’s death.”
From that statement alone, we know that she is married, has a heart condition, and is likely to react strongly to bad news . We also know that the person who is sharing the bad news views Louise as delicate and sensitive. Throughout the next few paragraphs, we also learn that Louise is a housewife, which indicates that she would be part of the middle-to-upper class in the 1890s. Chopin also describes Louise’s appearance as “young,” “fair, calm face,” with lines of “strength.” These characteristics are not purely physical, but also bleed into her character throughout the story.
Louise’s personality is described as different from other women . While many women would be struck with the news in disbelief, Louise cries with “wild abandonment”—which shows how powerful her emotions are. Additionally, while other women would be content to mourn for longer, Louise quickly transitions from grief to joy about her husband’s passing.
Ultimately, Chopin uses Louise’s character to show readers what a woman’s typical experience within marriage was in the 1890s. She uses Louise to criticize the oppressive and repressive nature of marriage, especially when Louise rejoices in her newfound freedom.
Josephine is Louise’s sister . We never hear of Josephine’s last name or whether she is married or not. We do know that she has come with Richards, a friend of Brently’s, to break the news of his death to her sister.
When Josephine tells Louise the bad news, she’s only able to tell Louise of Brently’s death in “veiled hints,” rather than telling her outright. Readers can interpret this as Josephine’s attempt at sparing Louise’s feelings. Josephine is especially worried about her sister’s heart condition, which we see in greater detail later as she warns Louise, “You will make yourself ill.” When Louise locks herself in her room, Josephine is desperate to make sure her sister is okay and begs Louise to let her in.
Josephine is the key supporting character for Louise, helping her mourn, though she never knows that Louise found new freedom from her husband’s supposed death . But from Josephine’s actions and interactions with Louise, readers can accurately surmise that she cares for her sister (even if she’s unaware of how miserable Louise finds her life).
Richards is another supporting character, though he is described as Brently’s friend, not Louise’s friend. It is Richards who finds out about Brently Mallard’s supposed death while at the newspaper office—he sees Brently’s name “leading the list of ‘killed.’” Richards’ main role in “The Story of an Hour” is to kick off the story’s plot.
Additionally, Richard’s presence at the newspaper office suggests he’s a writer, editor, or otherwise employee of the newspaper (although Chopin leaves this to readers’ inferences). Richards takes enough care to double-check the news and to make sure that Brently’s likely dead. He also enlists Josephine’s help to break the news to Louise. He tries to get to Louise before a “less careful, less tender friend” can break the sad news to her, which suggests that he’s a thoughtful person in his own right.
It’s also important to note is that Richards is aware of Louise’s heart condition, meaning that he knows Louise Mallard well enough to know of her health and how she is likely to bear grief. He appears again in the story at the very end, when he tries (and fails) to shield Brently from his wife’s view to prevent her heart from reacting badly. While Richards is a background character in the narrative, he demonstrates a high level of friendship, consideration, and care for Louise.
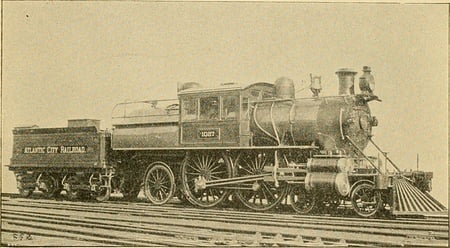
Brently Mallard would have been riding in a train like this one when the accident supposedly occurred.
Mr. Brently Mallard is the husband of the main character, Louise. We get few details about him, though readers do know he’s been on a train that has met with a serious accident. For the majority of the story, readers believe Brently Mallard is dead—though the end of “The Story of an Hour” reveals that he’s been alive all along. In fact, Brently doesn’t even know of the railroad tragedy when he arrives home “travel-stained.”
Immediately after Louise hears the news of his death, she remembers him fondly. She remarks on his “kind, tender hands” and says that Brently “never looked save with love” upon her . It’s not so much Brently as it’s her marriage to him which oppresses Louise. While he apparently always loved Louise, Louise only “sometimes” loved Brently. She constantly felt that he “impose[d] a private will” upon her, as most husbands do their wives. And while she realizes that Brently likely did so without malice, she also realized that “a kind intention or a cruel intention” makes the repression “no less a crime.”
Brently’s absence in the story does two things. First, it contrasts starkly with Louise’s life of illness and confinement. Second, Brently’s absence allows Louise to imagine a life of freedom outside of the confines of marriage , which gives her hope. In fact, when he appears alive and well (and dashes Louise’s hopes of freedom), she passes away.
The Doctor(s)
Though the mention of them is brief, the final sentence of the story is striking. Chopin writes, “When the doctors came they said she had died of heart disease—of the joy that kills.” Just as she had no freedom in life, her liberation from the death of her husband is told as a joy that killed her.
In life as in death, the truth of Louise Mallard is never known. Everything the readers know about her delight in her newfound freedom happens in Louise’s own mind; she never gets the chance to share her secret joy with anyone else.
Consequently, the ending of the story is double-sided. If the doctors are to be believed, Louise Mallard was happy to see her husband, and her heart betrayed her. And outwardly, no one has any reason to suspect otherwise. Her reaction is that of a dutiful, delicate wife who couldn’t bear the shock of her husband returned from the grave.
But readers can infer that Louise Mallard died of the grief of a freedom she never had , then found, then lost once more. Readers can interpret Louise’s death as her experience of true grief in the story—that for her ideal life, briefly realized then snatched away.

In "The Story of an Hour," the appearance of hearts symbolize both repression and hope.
“The Story of an Hour” Symbolism and Motifs
Symbols are any object, word, or other element that appear in the story and have additional meanings beyond. Motifs are elements from a story that gain meaning from being repeated throughout the narrative. The line between symbols and motifs is often hazy, but authors use both to help communicate their ideas and themes.
In “The Story of an Hour,” symbolism is everywhere, but the three major symbols present in the story are:
- The heart
- The house and the outdoors
- Joy and sorrow
Heart disease, referred to as a “heart condition” within the text, opens and closes the text. The disease is the initial cause for everyone’s concern, since Louise’s condition makes her delicate. Later, heart disease causes Louise’s death upon Brently’s safe return. In this case, Louise’s ailing heart has symbolic value because it suggests to readers that her life has left her heartbroken. When she believes she’s finally found freedom, Louise prays for a long life...when just the day before, she’d “had thought with a shudder that life might be long.”
As Louise realizes her freedom, it’s almost as if her heart sparks back to life. Chopin writes, “Now her bosom rose and fell tumultuously...she was striving to beat it back...Her pulses beat fast, and the coursing blood warmed and relaxed every inch of her body.” These words suggest that, with her newfound freedom, the symptoms of her heart disease have lifted. Readers can surmise that Louise’s diseased heart is the result of being repressed, and hope brings her heart back to life.
Unfortunately, when Brently comes back, so does Louise’s heart disease. And, although her death is attributed to joy, the return of her (both symbolic and literal) heart disease kills her in the end.

The House and the Outdoors
The second set of symbols are Louise’s house and the world she can see outside of her window. Chopin contrasts these two symbolic images to help readers better understand how marriage and repression have affected Louise.
First of all, Louise is confined to the home—both within the story and in general. For her, however, her home isn’t a place to relax and feel comfortable. It’s more like a prison cell. All of the descriptions of the house reinforce the idea that it’s closed off and inescapable . For instance, the front door is locked when Mr. Mallard returns home. When Mrs. Mallard is overcome with grief, she goes deeper inside her house and locks herself in her room.
In that room, however, Mrs. Mallard takes note of the outdoors by looking out of her window. Even in her momentary grief, she describes the “open square before her house” and “the new spring life.” The outdoors symbolize freedom in the story, so it’s no surprise that she realizes her newfound freedom as she looks out her window. Everything about the outside is free, beautiful, open, inviting, and pleasant...a stark contrast from the sadness inside the house .
The house and its differences from outdoors serve as one of many symbols for how Louise feels about her marriage: barred from a world of independence.
Joy and Sorrow
Finally, joy and sorrow are motifs that come at unexpected times throughout “The Story of an Hour.” Chopin juxtaposes joy and sorrow to highlight how tragedy releases Louise from her sorrow and gives her a joyous hope for the future.
At first, sorrow appears as Louise mourns the death of her husband. Yet, in just a few paragraphs, she finds joy in the event as she discovers a life of her own. Though Louise is able to see that feeling joy at such an event is “monstrous,” she continues to revel in her happiness.
It is later that, when others expect her to be joyful, Josephine lets out a “piercing cry,” and Louise dies. Doctors interpret this as “the joy that kills,” but more likely it’s a sorrow that kills. The reversal of the “appropriate” feelings at each event reveals how counterintuitive the “self-assertion which she suddenly recognized as the strongest impulse of her being” is to the surrounding culture. This paradox reveals something staggering about Louise’s married life: she is so unhappy with her situation that grief gives her hope...and she dies when that hope is taken away.
Key Takeaways: Kate Chopin's “The Story of an Hour”
Analyzing Chopin’s “The Story of an Hour” takes time and careful thought despite the shortness of the story. The story is open to multiple interpretations and has a lot to reveal about women in the 1890s, and many of the story’s themes, characters, and symbols critique women’s marriage roles during the period .
There’s a lot to dig through when it comes to “The Story of an Hour” analysis. If you’re feeling overwhelmed, just remember a few things :
- Events from Kate Chopin’s life and from social changes in the 1890s provided a strong basis for the story.
- Mrs. Louise Mallard’s heart condition, house, and feelings represent deeper meanings in the narrative.
- Louise goes from a state of repression, to freedom, and then back to repression, and the thought alone is enough to kill her.
Remembering the key plot points, themes, characters, and symbols will help you write any essay or participate in any discussion. Kate Chopin’s “The Story of an Hour” has much more to uncover, so read it again, ask questions, and start exploring the story beyond the page!

What’s Next?
You may have found your way to this article because analyzing literature can be tricky to master. But like any skill, you can improve with practice! First, make sure you have the right tools for the job by learning about literary elements. Start by mastering the 9 elements in every piece of literature , then dig into our element-specific guides (like this one on imagery and this one on personification .)
Another good way to start practicing your analytical skills is to read through additional expert guides like this one. Literary guides can help show you what to look for and explain why certain details are important. You can start with our analysis of Dylan Thomas’ poem, “Do not go gentle into that good night.” We also have longer guides on other words like The Great Gatsby and The Crucible , too.
If you’re preparing to take the AP Literature exam, it’s even more important that you’re able to quickly and accurately analyze a text . Don’t worry, though: we’ve got tons of helpful material for you. First, check out this overview of the AP Literature exam . Once you have a handle on the test, you can start practicing the multiple choice questions , and even take a few full-length practice tests . Oh, and make sure you’re ready for the essay portion of the test by checking out our AP Literature reading list!

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!

Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Sample details
- Literature,
- Kate Chopin
- The Story of an Hour
- Views: 2,546
Related Topics
- Soviet Union
- Colonialism
- Quality of life
- West Side Story
- Nationalism
- Decision Making
- Autobiography
- Watergate scandal

Irony In The Story Of An Hour Analysis
In The Story of an Hour by Kate Chopin we observe many instances of irony. Irony is the use of words to express something different from and often opposite to their literal meaning. In this story there are three different types of irony used, they are: situational, dramatic and verbal.
Situational irony is used to show the reader that what is expected to happen sometimes doesn’t. Dramatic irony is used to fill the reader in on something that the characters in the story do not know about. Verbal irony is a figure of speech in which what is said is the opposite of what is meant.Situational irony is used in “The Story of an Hour” through Mrs.
ready to help you now
Without paying upfront
Mallard’s reaction to her husband’s death. When she first heard the news of her husband’s death, Mrs. Mallard, “wept at once, with sudden, wild abandonment” (188). It appeared to everyone in the house that she was very sad and went upstairs to be alone in her room.
This is a typical reaction after having just lost a loved one. However, once Mrs. Mallard is alone in her room, we as the reader witness that she is not saddened by the loss of her husband but rather relieved. She saw beyond that bitter moment a long procession of years to come that would belong to her absolutely.
And she opened and spread her arms out to them in welcome” (189). It turns out that Mrs. Mallard is actually happy that her husband has died and instead looks forward to her coming years being free. Dramatic irony is also used in Chopin’s “The Story of an Hour” through Mrs.
Mallard’s realization that she is free from her husband and with her death. While Mrs. Mallard was alone in her room she realized that she would no longer be bound to her husband but rather free to do whatever she should choose.However, no one else in the story knew this; they all believed that she was very sad and depressed.
Josephine, a woman in the house, even thought Mrs. Mallard was making herself sick. She said: “I beg; open the door – you will make yourself ill” (189). She did not know that Mrs.
Mallard was actually fine. Another example of dramatic irony is when Mrs. Mallard dies. When she finds out that her husband is still alive she dies from an immediate heart attack.
The narrator of the story says; “When the doctors came they said she had died of heart disease – of joy that kills” (190).Even though all of the characters in the story believe she died because she was so overwhelmingly happy her husband was alive, we, the readers know that she died because she was very upset and shocked. The final irony used is verbal irony. Verbal irony is found in the title, “The Story of an Hour”.
These words suggest a short period of time in which usually not a lot of events occur. However, in this story an hour seems like a lifetime. The main character, Mrs. Mallard, experiences grief, depression, sadness, happiness, and hope all within the time span of an hour.
Through the title, we are able to witness that quite a lot of things can occur in a short period of time. In conclusion, “The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin proves to be filled with all three different types of irony. Situational, dramatic, and verbal irony examples are found throughout the story. We can find that Kate Chopin’s writing often parallels her life.
She experienced a lot of suffering and was actually encouraged to write fiction by her doctor. Much of her writing is based on her own sufferings and is often filled with irony that is very subtle.
Cite this page
https://graduateway.com/irony-story-hour/
You can get a custom paper by one of our expert writers
- Armenian Genocide
- A Good Man Is Hard to Find
- Trail of Tears
- The Souls of Black Folk
- Ancient Rome
- Bubonic plague
Short Story
- man's search for meaning
- Cuban Missile Crisis
- The Monkey's Paw
- Stereotypes
- Volunteering
Check more samples on your topics
The theme of irony in “the story of an hour” and “the false gems” literary analysis.
Human Activities
Introduction Kate Chopin’s “The Story of an Hour” and Guy de Maupassant’s “The False Gems” display the literary technique of irony in a highly effective way to provide social criticism. Chopin made use of irony to present the seemingly never-ending struggle of women within the boundaries of marriage. On the other hand, de Maupassant used
Examples of Irony in the Story of an Hour and Richard Cory
Irony pervades our everyday lives without us always realizing it. However, if we were to pause for a moment and observe, irony would undoubtedly reveal itself. This is evident in both "The Story of an Hour" and "Richard Cory" where irony features prominently. The irony in both "The Story of an Hour" and "Richard Cory" is
The Prevalence of Irony in The Story of an Hour and Desiree’s Baby by Kate Chopin
Desiree's Baby
In her two stories, The Story of an Hour and Desirees Baby, Kate Chopin employs irony extensively. The utilization of irony is strikingly similar in both stories, leading to the tragic demise of a woman in their seemingly male-dominated society. The Short story, The Story of an Hour, initially suggests a possible happy ending. However,
Different Examples of Irony in The Story of an Hour
After reading The yellow wallpaper, The storm, and The story of an Hour, we can see that women roles today have changed dramatically. We changed politically, socially, and economically and it is making a great impact on our society today. Many years ago, women were controlled by men and did not seem to have any
“The Story of an Hour” and “How To Tell a True War Story”: Annotated Bibliography
Annotated Bibliography
The texts chosen for this annotated bibliography are “The Story of an Hour” and “How To Tell a True War Story”. These novels were at top choice because they presented a sufficient amount of evidence and detail as to how they correlate. Chopin and O’Brien effectively displayed their purpose for writing the stories with the
The Secret Life of Walter Mitty VS The Story Of An Hour Analysis
Abstract I have chosen to compare the two short stories “The Story of an Hour”, by Kate Chopin and “The Secret Life of Walter Mitty”, by James Thurber. “The Secret Life of Walter Mitty” is a short story written in 1937. The main character is an older man that drives his wife to town for
Setting Analysis of the Story of an Hour
Book Review
Nathan Valentino Setting Analysis Of “The story of an Hour” “The Story of an Hour” is a story about a woman, Mrs. Mallard, who comes to find that her beloved husband Brently Mallard was killed in a railroad incident. She mourns of his death in a different way than most would and tries to find
Analysis of the Themes in ‘The Story of An Hour’ and ‘The Chrysanthemums’
In 21 Century, most of people think that having freedom is natural; marriage of course is a happy moment in their lives. Also in many counties men and women’s status are nearly equal now. No matter you ate a man or a woman, as long as you have the ability, you can become a boss
A Literary Analysis of The Story of An Hour by Kate Chopin
In Kate Chopin's "The Story of An Hour" the theme is found within the concept of how someone can be trapped in a repressive, unsatisfying reality because of another's thoughtless oppression and manipulation. The condition of life for Mrs. Mallard is terrible; yet for some reason she doesn't seem to come to full realization until

Hi, my name is Amy 👋
In case you can't find a relevant example, our professional writers are ready to help you write a unique paper. Just talk to our smart assistant Amy and she'll connect you with the best match.
Irony In The Story Of An Hour
Irony is a key element in “The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin. The story is full of unexpected twists and turns that keep the reader guessing. The most ironic moment in the story comes at the end, when Mrs. Mallard learns that her husband is not dead after all. This news comes as a shock to her, but it also brings relief and happiness. In this moment, the reader realizes that Mrs. Mallard’s true feelings about her marriage were not what they seemed.
Although Mrs. Mallard appears to be a victim of circumstance at first, it becomes clear that she is actually quite strong-willed and capable of making her own decisions. This is evident in the way she reacts to the news of her husband’s death. Mrs. Mallard does not immediately break down in tears or show any signs of distress. Instead, she retreats to her room and allows herself to feel the full range of emotions that come with being widowed.
It is only when Mrs. Mallard hears that her husband is alive that she shows any sign of weakness. The news comes as such a shock to her that she collapses and dies of heart failure. This final twist is ironic because it reveals that Mrs. Mallard’s true feelings about her marriage were not what they seemed. In the end, it is clear that she was not as content in her marriage as she pretended to be.
There are several types of irony, such as basic irony, which is the use of language to convey a meaning that is the opposite of its literal meaning. Situational irony occurs when a character’s behavior has the exact opposite effect than what was intended. Finally, there is dramatic irony, which occurs when there is a disconnect between the reader’s knowledge and that of the characters in a story. However, situational irony happens most frequently in Kate Chopin’s short tale “The Story of an Hour.”
The story’s title is also ironic because it’s not really a story; it’s more like a snippet of a woman’s life. The story is about a woman, Louise Mallard, who finds out that her husband has died in a train accident.
At first she is heartbroken but then she begins to feel liberated and free. She thinks about all of the things she can now do without her husband holding her back. She starts to daydream about her future and what it will be like without him. However, it turns out that he was not on the train after all and he comes home alive. When Louise sees him she has a heart attack and dies.
The ironic part is that she died of happiness, which is the opposite of what most people would expect. The story is full of situational irony because everything that Louise thinks is going to happen, happens but in the opposite way. The title is also ironic because it’s not really a story, it’s more like a snippet of a woman’s life. The story is only a few pages long but it packs a big punch. It shows how quickly things can change and how one event can have such a huge impact on someone’s life.
Mrs. Mallard’s reaction to her husband’s death in “The Story of an Hour” is a good example of situational irony. When she first learnt of her husband’ s demise, Mrs. Mallard “wept immediately, with raucous, uncontrolled sobs” (Chopin 1). Everyone in the household assumed she was grief-stricken and went upstairs to be alone in her room because this is generally how people react when they have just lost a loved one.
What they did not know was that she was actually happy. The reason why she was so happy was because now she had the freedom that she always wanted. She would no longer have to be tied down by her husband and could do whatever she pleased.
Later on, after Mrs. Mallard had some time to think about her husband’s death, she began to feel differently. She started to realize that she might not be as free as she thought she was. Even though her husband is gone, his presence is still felt throughout the house. She knows that his spirit will always be with her and that she will never truly be free. The irony in this story is that Mrs. Mallard gains her freedom through her husband’s death but also realizes that she will never be truly free.
After she is left alone in her chamber, Chopin wants the reader to observe that she is not depressed by the death of her spouse, but rather relieved. “When she gave herself up a little murmured word escaped her slightly parted lips. She said it over and over again beneath her breath: “free, free, free!”” (Chopin 1)
The relief Mrs. Mallard feels is ironic considering most people would feel grief after hearing their spouse had died. The biggest irony in the story is Mrs. Mallard’s death at the end. The joy she felt from being free suddenly turns into fear when she realizes her husband is not dead and coming up the stairs.
The shock of seeing him alive causes Mrs. Mallard to have a heart attack and die. If Mrs. Mallard had not been so quick to believe her husband was dead, she may have been able to enjoy her newfound freedom. Irony is often used by authors to create suspense or add humor to a story, but in “The Story of an Hour” it is used to show how quickly feelings can change and how easy it is to be misled.
Despite the fact that Mrs. Mallard is “free” from her marriage, it does not imply she did not love her spouse, as she looks out of an open window through which she gazes. She sees blue sky, fluffy clouds, and trees instead of being dark and sorrowful to suggest how one would expect her to feel.
The image that she sees also reflects how she feels on the inside which is free and liberated. The open window also symbolizes Mrs. Mallard’s future and what is in store for her. The story concludes with a shocking twist, as it is revealed that Mrs. Mallard’s husband was not killed in the train accident after all, and she dies of a heart attack upon seeing him alive. The irony in this story lies in the fact that Mrs. Mallard gains her freedom only to lose her life in the end.
To export a reference to this essay please select a referencing style below:
Related essays:
- The Story Of An Hour Analysis Essay
- Free Will In Kate Chopin’s The Story Of An Hour
- Trifles And Story Of An Hour Literary Analysis Essay
- Kate Chopin’s The Story of an Hour Analysis
- The Irony Of Othello
- Irony in “Pride & Prejudice”
- Ernest Hemingway’s “A Clean, Well-Lighted Place”
- Roman Fever by Edith Wharton
- Inrony in “Pride & Prejudice”
- Pride and Prejudice by Jane Austen
- Pride and Prejudice – Pride
The Story of an Hour Analysis & Summary – Essay Example
This sample will help you write a The Story of an Hour analysis essay! Here you’ll find a The Story of an Hour summary. Essay also contains a plot and character analysis.
Introduction
The story of an hour introduction, the story of an hour main plot, the story of an hour conclusion, the story of an hour analysis.
The Story of an Hour is a short story written by Kate Chopin in 1894. This famous piece of literature was controversial for its time, as the story mentioned a female protagonist who felt relieved after her husband’s death. The conclusion of The Story of an Hour is ironic, which makes the ending memorable.
The following The Story of an Hour literary analysis essay will summarize the plot and present an extensive character analysis of Mrs. Mallard. It will be helpful for those writing a The Story of an Hour critical analysis.
Kate Chopin (born Catherine O’Flaherty) was an American writer. She is best known for her narratives of delicate and brave women’s inner lives. Her novel “The Awakening” and her short stories, among them The Story of an Hour, are being read in countries all over the world today. She is widely recognized as one of the most important authors in America.
In 1984, Kate Chopin wrote The Story of an Hour. It portrays a woman, Louise Mallard, who lost her husband in an accident. However, she later discovers that the husband survived. Mrs. Mallard goes through many emotions and feelings, reevaluating her life. That ultimately kills her when she meets her presumably dead husband at the door. The following The Story of an Hour essay will focus on the plot and the protagonist’s self-development.
The Story of an Hour Summary
Louise Mallard, the main character, had always had a heart problem. It was not a secret for her friends and relatives, so everyone tried to protect her from worries.
One day her husband, Brently Mallard, was mistaken for having died in a horrible railroad accident. Richard, Mr. Mallard’s friend, was the one who learned about this death while in the office. Josephine, Louise’s sister, broke the news to her.
Josephine was very cautious because of Mrs. Mallard’s health issue. She feared such a tragedy would cause a heart attack. Bit by bit, she strategized how to tell everything to her sister, aher plan went perfectly well. Mrs. Mallard wept only once. She did not receive the story like many women would, with a helpless incapacity to acknowledge its meaning. She only cried in her sister’s arms with a feeling of a sudden, wild abandonment (Woodlief 2).
Immediately Mrs. Mallard found herself wondering how she could survive without her husband. She went to a room and locked herself to contemplate the consequences of his death. She was devastated, and this sadness was only natural. This man had been close to her, even though only for a short time. Her sister Josephine and Mr. Richard also mourned the loss (Taibah 1).
Mrs. Mallard was alone in that room, thinking about the future. As she was contemplating her fate, instead of grief, she began realizing that this was the beginning of a better part of her life. Louise saw independence and plenty of possibilities to do what her heart desired. Now, she had only to think about herself.
Later, Josephine comes to Louise’s room, crying with a joyous smile. They descend the house’s stairs, where Mr. Mallard appears at the door. He was not involved in the accident and did not understand why Josephine was crying. At the shock of seeing her husband again, Mrs. Mallard collapses. The doctors declare that she died because of the problems with her heart.
Health issues of the central character play a significant role in the story. The author managed to bring suspense in the way she described telling the bad news to a person with a heart problem. Josephine, Louise’s sister, tries her best to be careful and attentive, expecting a painful response. However, Mrs. Mallard reacts better than anticipated.
The story focuses mostly on femininity and the institution of marriage. The analysis of The Story of an Hour has to speculate on it to reveal the core message.
The author was able to illustrate that men entirely dominate the institution of marriage. Mr. Mallard, for instance, treated his wife the way she wanted only from time to time. For years, Louise has done many things to please her husband without looking after her well-being. So, having received the disturbing news, she is quite happy. It seemed that she had never cared for her husband at all.
Or did she? Mrs. Mallard’s reaction to the death of a spouse is complicated. She cannot escape the loneliness and grief that came with the loss. But the possibility of happiness prevails. Louise knew that marriage had made her a subject for him against her will. She only felt sorrow for the loss of his life but not for living without him. She felt deep inside that she had been freed from the chains of living for another person.
Mr. Mallard’s apparent death saddened Louise at first. She was devastated about his fate but regained strength quickly. Louise was well aware of the fact that she could not bring her husband back. So, she came to terms with it, which wasn’t difficult. Mrs. Mallard saw beyond the painful moment, anticipating freedom for the rest of her life.
The room and environment around Mrs. Mallard symbolize her desire for freedom. For example, Mrs. Mallard could see the tops of trees through the window. They were all aquiver with the new spring life on the open square before her house. There was a delicious breath of rain in the air. A peddler was weeping his wares in the street below. There were spots of blue sky showing up here and there through the clouds in the west facing her window, which had met and piled up one above the other (Woodlief 1).
An open window could be interpreted as a metaphor. It reflects new possibilities and resources that Mrs. Mallard now had in her sights without anybody stopping her. She referred to it as the late spring of life.
The story reveals how women were secretly marginalized. At the time, society expected them to pursue wealth and safety, which came with a husband. Liberty should be neither their worry nor their goal. When Louise felt freedom after Mr. Mallard’s death, she kept it secret for obvious reasons. But then, her sister arrived.
Mrs. Mallard was shocked by the sight of her husband alive. All of her newfound liberty and dreams came crashing down at that moment. This shattering experience even goes to the extreme of destroying her life. Whereas she was to be happy to see her husband alive, Louise died from a heart attack.
Situational irony is presented in the author’s stylistic use of words: “She had died of heart disease…of the joy that kills.” People around anticipated this tragedy from the news about Mr. Mallard’s death, not miraculous survival.
The author explored the character of Mrs. Mallard throughout this story. The reader can’t be surprised by her sudden death or miss its irony. Louise is a woman with a great desire for independence, which a man has deprived her of through marriage. Mr. Mallard represents the absence of her liberty that restores after his death. When Mrs. Mallard sees her husband at the door once again, she collapses and never wakes up.
Based on this The Story of an Hour literary analysis, we can draw several important conclusions. Mrs. Mallard couldn’t control her emotions when they concerned the most vital matters. The lack of liberty and independence may have caused her heart problems in the first place. And they cost her life in the end.
Her husband, Mr. Mallard, took Louise’s freedom when he married her. However, as it became apparent from the story, he never valued her. When she died, he had finally faced the consequences of always taking her existence for granted.
Therefore, the oppressor faced even worse tragedy than the oppressed. The dramatic irony of Mr. Mallard’s unawareness of his wife’s true feelings towards him is a big part of the story. So, in the end, it was Mr. Mallard’s presence that killed his wife.
- Chopin, Kate. The Story of an hour . The Kate Chopin International Society. Web.
- Woodlief, Ann. The Story of an Hour . 2011, Virginia Commonwealth University. Web.
What is the symbolism in The Story of an Hour?
Through The Story of an Hour, the author presents us with the inner feelings and thoughts of a woman using various symbols. Mrs. Mallard’s heart problem symbolizes her dissatisfaction with the marriage, while the open window illustrates her aspirations towards a better, independent life.
What is the meaning behind The Story of an Hour?
Kate Chopin’s The Story of an Hour analysis illustrates that the author wanted to tell us how the society of that time was unfair towards women. It also shows the delicate and complicated inner world of a woman.
What does The Story of an Hour critique?
The Story of an Hour criticizes the typical experience of marriage in the 1890s. For women, such marriage was repressive and meant their loss of personal freedoms. Therefore, the story criticizes the society of that time dominated by men.
How do you start a critical analysis of The Story of an Hour?
Start your analysis of The Story of an Hour with a short introduction. Remember to say a few words about its author and her life. Next, talk about the story and let the reader know what it is about.
What are the two main themes in The Story of an Hour?
Firstly, the theme of a female search for self-identity is featured strongly in the story. The second theme is that of repressive marriage. The reader sees it in the way Mrs. Mallard’s reaction toward her husband’s death shifts.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2020, July 9). The Story of an Hour Analysis & Summary – Essay Example. https://studycorgi.com/the-story-of-an-hour-analysis-summary-essay-example/
"The Story of an Hour Analysis & Summary – Essay Example." StudyCorgi , 9 July 2020, studycorgi.com/the-story-of-an-hour-analysis-summary-essay-example/.
StudyCorgi . (2020) 'The Story of an Hour Analysis & Summary – Essay Example'. 9 July.
1. StudyCorgi . "The Story of an Hour Analysis & Summary – Essay Example." July 9, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/the-story-of-an-hour-analysis-summary-essay-example/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "The Story of an Hour Analysis & Summary – Essay Example." July 9, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/the-story-of-an-hour-analysis-summary-essay-example/.
StudyCorgi . 2020. "The Story of an Hour Analysis & Summary – Essay Example." July 9, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/the-story-of-an-hour-analysis-summary-essay-example/.
This paper, “The Story of an Hour Analysis & Summary – Essay Example”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: January 24, 2024 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Subscriber-only Newsletter
Frank Bruni
For the sake of democracy, celebrate mike johnson.

By Frank Bruni
Mr. Bruni is a contributing Opinion writer who was on the staff of The Times for more than 25 years.
We’ve seen movies aplenty in which a deeply flawed protagonist, someone we’d pretty much given up hope on, has a stirring of conscience or change of heart and puts his immediate interests at risk for the sake of something bigger. The music swells. The credits roll.
I never expected the music to swell and the credits to roll with Mike Johnson’s face in the center of the frame.
Johnson, the House speaker, reversed a position that he’d previously held, banded with Democrats and infuriated some of the loudest, meanest and most vengeful members of his party — that’s Marjorie Taylor Greene you hear wailing in the wings — to pass a $95 billion aid package for Ukraine, Israel and Taiwan last weekend. We’ve read all about it.
But before we move on to the next congressional melodrama, let’s make sure we’ve given Johnson his due. I say that not as any fan of his — he had no business being elected speaker, given his assertive role in trying to overturn the 2020 election — and I think that’s all the more reason to say it. In an era this intensely and corrosively partisan, it’s especially important that we give warranted praise and appropriate thanks to people with whom we usually disagree. Tribalism discourages that, but a healthy democracy demands it.
I strongly support the aid package while understanding the qualms about it, but its merits aren’t my focus here. Johnson’s principled course is. He made common cause with political adversaries. He potentially put his speakership in greater jeopardy than if he’d taken a different tack (though these matters are tricky and time will tell).
What impresses and encourages me most, though, are accounts of how he arrived at his backing of the bill: He educated himself. As Catie Edmondson reported in an article in The Times on Sunday, Johnson “attributed his turnabout in part to the intelligence briefings he received, a striking assertion from a leader of a party that has embraced former President Donald J. Trump’s deep mistrust of the intelligence community.”
Seeking more information. Not dismissing it out of hand because of its provenance. Humbly conceding that your prior understanding was faulty or incomplete. Encouraging others to look beyond their stubbornness to the possibility of enlightenment.
None of that should be exceptional. All of it is. May it be a model for the lawmakers around him, for all politicians, for the rest of us.
And may we take another lesson from this: All is not lost. What Johnson did and how this episode ultimately played out constitute another instance of the government pulling through — a budget passes at the final hour, a debt ceiling is finally raised — after terrifying signs that it might not. That doesn’t redeem all the wasted time and what it cost. But it’s an important counter to the very worst of our pessimism, a reminder not to let our premonitions of doom utterly consume us and become self-fulfilling prophecies.
In Politico on Tuesday, Jonathan Martin presented an insightful take along those lines, also noting the manner in which Johnson and others had neutered Trump, whose opposition to Ukraine funding sort of petered out before last weekend’s vote: “The Republican Party is drifting from its Reaganite past, but when faced with the burden of leadership, there’s still muscle memory to be found; Donald Trump is more committed to self-interest than any ideological anchorage and can be managed accordingly; and bipartisanship remains possible when bad actors are removed from the negotiating table.”
Martin quoted a previous House speaker, Nancy Pelosi, calling Johnson “courageous.” He quoted the Democratic strategist James Carville, who said, “This is a country saved by unexpected people.”
”Saved” may be going too far. It has an out-of-the-woods music to it that even the most optimistic part of me can’t hum along to. But all of me believes the following, which is the moral of Mike Johnson’s arc: While the times we live in are profoundly dysfunctional, they are by no means hopeless.
For the Love of Sentences
In Time Out, Adam Feldman reviewed a Broadway revival of “Cabaret” and questioned Eddie Redmayne’s performance in the role that Joel Grey played in the movie version. “The theory seems to be that increasing the Emcee’s power exponentially will make him more exciting: That energy, if you will, is equal to Emcee squared,” Feldman wrote. (Thanks to Christine Tralongo of Manhattan for nominating this.)
In The Guardian, the characteristically caustic critic Jay Rayner thrilled to the look of a new Spanish restaurant in London: “When I die, a moment keenly anticipated by certain chefs, I want the team that did the interiors at Lita in Marylebone to knock up my coffin. Because darling, the joinery! It’s an orgy of tongue and groove, dovetail and pocket. They haven’t stinted on the finish either. There’s a soft gloss and polish to the place that would, I think, lend a comely glow to my corpse in repose.” (James Bullock, Edmonton, Alberta)
In Esquire, Charles P. Pierce reflected on an emblematic American newspaper: “Ever since USA Today first darkened the doors of our rooms in various Marriott properties, we’ve all had fun mocking the way it served up the news in easily digestible nuggets (and also pie charts!). Of course, given the aerosolized way we get our news these days, the old USA Today looks like The Paris Review.” (Stephen Wertheimer, Boca Raton, Fla.)
In The Times, David Brooks rued the contemporary retreat from reason: “Since the Trump years, this habit of not consulting the evidence has become the underlying crisis in so many realms. People segregate into intellectually cohesive teams, which are always dumber than intellectually diverse teams. Issues are settled by intimidation, not evidence.” (Mary Ann Skold, Detroit)
Also in The Times, Ross Douthat identified pessimism and apathy as main culprits of American drift and dysfunction: “We are more melancholic than choleric; more disillusioned than fanatical.” (Jeanine F. Jewell, Lincoln, Neb.)
In The Washington Post, Ron Charles marveled approvingly at the construction of “The Spoiled Heart,” a new novel by Sunjeev Sahota: “Along the way, Sahota throws so many disparate parts into this story that it’s something of a miracle when they begin to coalesce — like a box of gears and springs tumbling down the stairs and coming to rest in the shape of a clock.” (Lynn Boatwright, Chattanooga, Tenn.)
Robin Givhan considered Donald Trump’s appearances in a Manhattan courtroom last week: “This is a trial that reminds us of the smallness of Trump even as the idea of him, the myth of him has become outsize.” (Betsy Snider, Acworth, N.H.)
And Karen Tumulty chronicled the Kennedy clan’s effort to quash the candidacy of Robert F. Kennedy Jr.: “In an election fueled by fear and resentment, there is no torch to be passed — except for the one that the Kennedys fear would be used to set fire to what’s left of the family’s name.” (Greg Howard, Vancouver, Wash.)
Bonus Miscellany: Several readers nominated the words of a Manhattan woman who did not make the cut of Trump-trial jurors after Trump’s lawyers discovered that she wrote on social media that she wouldn’t trust Trump even if his tongue were notarized. That’s a wickedly funny gibe — but I immediately had the feeling that it must have been said by someone else previously, if not about Trump, then about another serial liar. Thank you, Google! Turns out that Alair Townsend, who was a deputy to former New York City Mayor Ed Koch, once said, “I wouldn’t believe Donald Trump if his tongue were notarized.” A sane assessment. Also a prophetic one.
To nominate favorite bits of recent writing from The Times or other publications to be mentioned in “For the Love of Sentences,” please email me here and include your name and place of residence.
What I’m Writing, Doing and Reading
In this rancorous era, too many Americans interpret one group’s actual or possible gains as another group’s actual or possible losses. Too many of us conflate real offenses with imagined ones — and forget that the common good deserves as much consideration as our individual lots. It’s a crisis of humility, as I observed in this essay in Times Opinion, adapted from my new book , “The Age of Grievance.” But it’s also connected to a new American pessimism, which was the subject of an excerpt from the book that The Atlantic published this week. I’ll examine those dynamics — and how we might pivot to a better way and better days — in a conversation with Katie Couric next Wednesday evening that allows for virtual attendance. Details are here .
I loved Alex Ross’s recent essay in The New Yorker on the nature of noise. From start to finish, it’s inventive, imaginative, intelligent — and I might have missed it but for an email from Shelley G. Allison of Carrollton, Texas, who sang the praises of this representative passage: “The irony is that the atomized buzz common to so much late-20th-century technology — fax machines, dial-up modems, the hiss between stations on a radio dial, the ‘Poltergeist’ snow of a TV left on overnight — has largely faded. Such noise now resides in our minds, as we fend off notifications, updates, ‘Just for You’ suggestions, consumer-feedback requests, obscene spam, clickbait headlines, A.I.-generated news stories, A.I.-generated news stories about A.I., and the whole silently screaming rest of it.”
The competition for our attention has produced a glut of curiosity-piquing, cleverly enticing headlines, so I can be numb to the come-ons. But “ In Defense of Annette Bening’s Face ,” an essay by Valerie Monroe in The Cut, caught my attention: Why does Bening’s face need defending? It’s gorgeous! That’s Monroe’s well-turned point: Natural beauty like hers is too often the exception among aging Hollywood stars, so that eternal youthful perfection becomes yet another of those illusions that needlessly torment us wrinkled, puffy, pudgy mortals.
On a Personal (By Which I Mean Regan) Note
The picture above is a font of false impressions.
You look at it and you think: What a spoiled girl. Gets to flop down wherever she likes.
Wrong! She is allowed on any and all furniture upstairs in the house, where the blue futon in question resides. Never, ever downstairs.
You think: Frank positioned that throw pillow there.
Wrong! Regan may not have opposable thumbs — and I shudder to imagine what she’d do with them if she did — but those white-gloved paws of hers are busy little appendages, and she’s dexterous with her snout. She’ll nudge or bat one or more of the three throw pillows on the futon to the floor if she feels that they’re in her way. Or she’ll rearrange them for maximum comfort.
I wouldn’t be entirely shocked if one of these days, I come home to find that she has moved one of the pillows to the love seat in the first-floor living room because its placement there makes more sense to her. She’s a mysterious creature with a mind of her own.
But with a sense of limits and boundaries. You think: Frank’s a softy and she gets the better of him. Half wrong! Yes, I’m too liberal with treats. Yes, I tell her I love her about as often as I exhale. Yes, I let her in and out, out and in, as if I’m a hotel doorman.
But when I firmly tell her to do something, she does it. When I lay down clear rules, she doesn’t break them. At the risk of romanticizing and anthropomorphizing the hell out of Regan, I like to believe that what we have with our dogs is what we have with so many of the people in our lives: an understanding. A truce. Indulge me this much and I’ll indulge you that much.
And if that’s pure fiction, well, it’s harmless, and it makes me and Regan happy.
Frank Bruni is a professor of journalism and public policy at Duke University, the author of the book "The Age of Grievance" and a contributing Opinion writer. He writes a weekly email newsletter . Instagram Threads @ FrankBruni • Facebook
Turmoil at NPR after editor rips network for political bias
The public radio network is being targeted by conservative activists over the editor’s essay, which many staffers say is misleading and inaccurate.

Uri Berliner had worked at NPR for a quarter-century when he wrote the essay that would abruptly end his tenure. On April 9, the Free Press published 3,500 words from Berliner, a senior business editor, about how the public radio network is guilty of journalistic malpractice — for conforming to a politically liberal worldview at the expense of fairness and accuracy.
“It’s true NPR has always had a liberal bent, but during most of my tenure here, an open-minded, curious culture prevailed,” Berliner wrote. “We were nerdy, but not knee-jerk, activist, or scolding. In recent years, however, that has changed.”
The essay, whose arguments were disputed by NPR management and many staffers, plunged the network into a week-long public controversy.
Last week NPR’s new CEO, Katherine Maher, indirectly referenced Berliner’s essay in a note to staff that NPR also published online. “Asking a question about whether we’re living up to our mission should always be fair game: after all, journalism is nothing if not hard questions,” she wrote. “Questioning whether our people are serving our mission with integrity, based on little more than the recognition of their identity, is profoundly disrespectful, hurtful, and demeaning.”
The drama reached a pinnacle Wednesday, when Berliner resigned while taking a shot at Maher.
In his resignation letter, Berliner called NPR “a great American institution” that should not be defunded. “I respect the integrity of my colleagues and wish for NPR to thrive and do important journalism,” he wrote in the letter, posted on his X account. “But I cannot work in a newsroom where I am disparaged by a new CEO whose divisive views confirm the very problems I cite in my Free Press essay.”
Berliner’s comments have angered many of his now-former colleagues, who dismissed as inaccurate his depiction of their workplace and who say his faulty criticisms have been weaponized against them.
Berliner’s essay is titled “ I’ve Been at NPR for 25 Years. Here’s How We Lost America’s Trust .” On its face, it seemed to confirm the worst suspicions held by NPR’s critics on the right: that the legendary media organization had an ideological, progressive agenda that dictates its journalism. The Free Press is an online publication started by journalist Bari Weiss, whose own resignation from the New York Times in 2020 was used by conservative politicians as evidence that the Times stifled certain ideas and ideologies; Weiss accused the Times of catering to a rigid, politically left-leaning worldview and of refusing to defend her against online “bullies” when she expressed views to the contrary. Berliner’s essay was accompanied by several glossy portraits and a nearly hour-long podcast interview with Weiss. He also went on NewsNation, where the host Chris Cuomo — who had been cast out from CNN for crossing ethical lines to help his governor-brother — called Berliner a “whistleblower.”
Initially, Berliner was suspended for not getting approval for doing work for another publication. NPR policy requires receiving written permission from supervisors “for all outside freelance and journalistic work,” according to the employee handbook.
An NPR spokeswoman said Wednesday that the network does not comment on personnel matters. Berliner declined The Washington Post’s request for further comment.
In an interview Tuesday with NPR’s David Folkenflik — whose work is also criticized in the Free Press essay — Berliner said “we have great journalists here. If they shed their opinions and did the great journalism they’re capable of, this would be a much more interesting and fulfilling organization for our listeners.”
Berliner’s future at NPR became an open question. NPR leaders were pressed by staff in meetings this week as to why he was still employed there. And some reporters made clear they didn’t want to be edited by Berliner anymore because they now questioned his journalistic judgment, said one prominent NPR journalist, who spoke on the condition of anonymity to preserve relationships. “How are you supposed to have honest debates about coverage if you think it’s going to be fodder for the point he’s trying to make?” the staffer said.
Berliner had written that “there’s an unspoken consensus” about stories to pursue at NPR — “of supposed racism, transphobia, signs of the climate apocalypse, Israel doing something bad, and the dire threat of Republican policies” — and that the network operated without friction, “almost like an assembly line.”
Several prominent NPR journalists countered that impression. “We have strong, heated editorial debates every day to try and get the most appropriate language and nuanced reporting in a landscape that is divisive and difficult to work in as a journalist,” Leila Fadel, host of “Morning Edition,” told The Post. “Media and free independent press are often under attack for the fact-based reporting that we do.” She called Berliner’s essay “a bad-faith effort” and a “factually inaccurate take on our work that was filled with omissions to back his arguments.”
Other staffers noted that Berliner did not seek comment from NPR for his piece. No news organization is above reproach, “Weekend Edition” host Ayesha Rascoe told The Post, but someone should not “be able to tear down an entire organization’s work without any sort of response or context provided, or pushback.” There are many legitimate critiques to make of NPR’s coverage, she added, “but the way this has been done — it’s to invalidate all the work NPR does.”
NPR is known to have a very collegial culture, and the manner in which Berliner aired his criticism — perhaps even more than the substance of it — is what upset so many of his co-workers, according to one staffer.
“Morning Edition” host Steve Inskeep, writing on his Substack on Tuesday , fact-checked or contextualized several of the arguments Berliner made. For instance: Berliner wrote that he once asked “why we keep using that word that many Hispanics hate — Latinx.” Inskeep said he searched 90 days of NPR’s content and found “Latinx” was used nine times — “usually by a guest” — compared to the nearly 400 times “Latina” and “Latino” were used.
“This article needed a better editor,” Inskeep wrote. “I don’t know who, if anyone, edited Uri’s story, but they let him publish an article that discredited itself. … A careful read of the article shows many sweeping statements for which the writer is unable to offer evidence.”
This week conservative activist Christopher Rufo — who rose to fame for targeting “critical race theory,” and whose scrutiny of Harvard President Claudine Gay preceded her resignation — set his sights on Maher, surfacing old social media posts she wrote before she joined the news organization. In one 2020 tweet, she referred to Trump as a “deranged racist.” Others posts show her wearing a Biden hat, or wistfully daydreaming about hanging out with Kamala D. Harris. Rufo has called for Maher’s resignation.
“In America everyone is entitled to free speech as a private citizen,” Maher wrote in a statement to The Post, when asked about the social media posts. “What matters is NPR’s work and my commitment as its CEO: public service, editorial independence, and the mission to serve all of the American public.”
Maher, who started her job as NPR CEO last month, previously was the head of the Wikimedia Foundation, the nonprofit that operates the online encyclopedia Wikipedia. An NPR spokesperson said in a statement Tuesday that Maher “was not working in journalism at the time” of the social media posts; she was “exercising her first amendment right to express herself like any other American citizen,” and “the CEO is not involved in editorial decisions.”
In a statement, an NPR spokesperson described the outcry over Maher’s old posts as “a bad faith attack that follows an established playbook, as online actors with explicit agendas work to discredit independent news organizations.”
Meanwhile, some NPR staffers want a more forceful defense of NPR journalism by management. An internal letter — signed by about 50 NPR staffers as of Wednesday afternoon — called on Maher and NPR editor in chief Edith Chapin to “publicly and directly” call out Berliner’s “factual inaccuracies and elisions.”
In the essay, Berliner accuses NPR of mishandling three major stories: the allegations of the 2016 Trump campaign’s collusion with Russia, the origins of the coronavirus , and the authenticity and relevance of Hunter Biden’s laptop. Berliner’s critics note that he didn’t oversee coverage of these stories. They also say that his essay indirectly maligns employee affinity groups — he name-checks groups for Muslim, Jewish, queer and Black employees, which he wrote “reflect broader movement in the culture of people clustering together based on ideology or a characteristic at birth.” (Berliner belonged to the group for Jewish employees, according to an NPR staffer with knowledge of membership.) He also writes that he found NPR’s D.C. newsroom employed 87 registered Democrats and zero Republicans in editorial positions in 2021. His critics say this figure lacks proper context.
Tony Cavin, NPR’s managing editor of standards and practices, told The Post that “I have no idea where he got that number,” that NPR’s newsroom has 660 employees, and that “I know a number of our hosts and staff are registered as independents.” That includes Inskeep, who, on his Substack, backed up Cavin’s assessment.
Berliner also wrote that, during the administration of Donald Trump , NPR “hitched our wagon” to top Trump antagonist Rep. Adam Schiff (D-Calif.) by interviewing him 25 times about Trump and Russia. Cavin told The Post NPR aired 900 interviews with lawmakers during the same period of time, “so that’s 3 percent. He’s a business reporter, he knows about statistics and it seems he’s selectively using statistics.”
Cavin said some inside the organization agree with points Berliner made, even if they “don’t like the way he went about it. The irony of this is it tells you how diverse as an organization we are, in ideological terms.”
“There are a few bits of truth in this,” NPR international correspondent Eyder Peralta wrote on Facebook. But he said the essay “uses a selecting reading to serve the author’s own world views” and paints with “too broad a brush.”
“I have covered wars, I have been thrown in jail for my work,” Peralta told The Post, “and for him to question part of what is in our nature, which is intellectual curiosity and that we follow our noses where they lead us, that hurts. And I think that damages NPR.”
Some staffers have also been attacked online since the essay’s publication. Rascoe, who, as a Black woman host for NPR, says she’s no stranger to online vitriol, but one message after Berliner’s essay labeled her as a “DEI hire” who has “never read a book in her life.”
“What stung about this one was it came on the basis of a supposed colleague’s op-ed,” whose words were “being used as fodder to attack me,” Rascoe said. “And my concern is not about me, but all the younger journalists who don’t have the platform I have and who will be attacked and their integrity questioned simply on the basis of who they are.”
NPR, like much of the media industry, has struggled in recent years with a declining audience and a tough ad market. NPR laid off 100 workers in 2023, one of its largest layoffs ever , citing fewer sponsorships and a projected $30 million decline in revenue.
Going forward, some staffers worry about the ramifications of Berliner’s essay and the reactions to it. The open letter to Maher and Chapin said that “sending the message that a public essay is the easiest way to make change is setting a bad precedent, regardless of the ideologies being expressed.”
An earlier version of this article included a reference to Uri Berliner's Free Press essay in which Berliner cited voter registration data for editorial employees of NPR's D.C. newsroom. The article has been updated to clarify that this data was from 2021, not the present day.
- Gateway Pundit to file for bankruptcy amid election conspiracy lawsuits April 24, 2024 Gateway Pundit to file for bankruptcy amid election conspiracy lawsuits April 24, 2024
- A history of CNN’s Laura Coates, who calmly narrated a self-immolation April 20, 2024 A history of CNN’s Laura Coates, who calmly narrated a self-immolation April 20, 2024
- Are some reporters putting Trump jurors at risk? April 18, 2024 Are some reporters putting Trump jurors at risk? April 18, 2024

Home — Essay Samples — Literature — The Story of An Hour — What Is the Irony and Reading Twists in ‘The Story of an Hour’
What is The Irony and Reading Twists in 'The Story of an Hour'
- Categories: Irony Symbolism The Story of An Hour
About this sample

Words: 686 |
Published: Jul 3, 2023
Words: 686 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read
What is the Irony in 'The Story of an Hour'?

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Literature

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 928 words
1 pages / 802 words
1 pages / 648 words
4.5 pages / 1980 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on The Story of An Hour
First published in 1894, Kate Chopin's "The Story of an Hour" is a short but powerful story that explores the complex emotions of a woman who learns of her husband's death. The narrative delves into the theme of female [...]
Women’s role in society has always been a widely-discussed topic. The Yellow Wallpaper by Charlotte Perkins Gilman and The Story of an Hour by Kate Chopin are two stories that explore this issue. Do you want to compare and [...]
Situational irony refers to a literary device where the outcome of a situation is different from what was expected or intended, often resulting in a reversal of expectations for the characters and readers. This aspect of irony [...]
Kate Chopin's "The Story of an Hour" is a short story that explores the internal conflict of the protagonist, Mrs. Mallard, and her pursuit of personal freedom. The story is set during the late 19th century, a time when societal [...]
Charlotte Perkins Gilman’s “The Yellow Wallpaper,” and Kate Chopin’s “The Story of an Hour” explore ideas of female identity and selfhood, and more importantly, female liberation. These authors present their female characters as [...]
American literature varies from other literary works across the world. Every story seems to express a different theme, and yet somehow they all seem similar. The Gift of the Magi and The Story of an Hour, written within 15 years [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In the essay analyzing Kate Chopin's short story "The Story of an Hour," the author delves into the use of irony as a literary technique to support the central theme that "nothing is as it seems." The essay highlights how Chopin employs both situational and verbal irony to underscore the transformation of the protagonist, Mrs. Mallard.
In Kate Chopin's short story "The Story of an Hour," there is much irony. The first irony detected is in the way that Louise reacts to the news of the death of her husband, Brently Mallard. Before Louise's reaction is revealed, Chopin alludes to how the widow feels by describing the world according to her.
The irony in "The Story of an Hour" is that other characters mistakenly attribute Mrs. Mallard's death to her shocked elation that her husband Brently is alive. Supposedly killed in a train ...
Among her shortest and most daring works, "Story" examines issues of feminism, namely, a woman's dissatisfaction in a conventional marriage and her desire for independence. It also features Chopin's characteristic irony and ambiguity. The story begins with Louise Mallard's being told about her husband's presumed death in a train ...
Conclusion of Analysis of "The Story of an Hour". In short, Kate Chopin suggests the meanings through symbols and irony in this story. All the symbols used in this story have different meanings that correlate with the ironic situations and remarks. It shows that life in the 19 th century was witnessing fast transformations - the result of ...
After her initial sobs of grief subside, Louise escapes into her bedroom and locks the door. She refuses to let Josephine or Richards follow her. Alone, she falls into a chair placed before an open window. Absolutely drained by her own anguish and haunted by exhaustion, she rests in the chair and looks out the window.
In Chopin's " The Story of an Hour ," irony is one of the elements of the story that reveals and contributes to the theme. Everyone in the story assumes the wife will be heart-broken when her ...
Yet Chopin's short story is, upon closer inspection, a subtle, studied analysis of death, marriage, and personal wishes. Written in April 1894 and originally published in Vogue in December of that year, the story focuses on an hour in the life of a married woman who has just learnt that her husband has apparently died.
The revelation near the end of the story that Brently is alive is a moment of dramatic irony. Some one was opening the front door with a latchkey. It was Brently Mallard who entered, a little travel-stained, composedly carrying his grip-sack and umbrella. He had been far from the scene of accident, and did not even know there had been one.
The tragic timing of Louise's newfound will to live underscores Chopin's use of irony throughout the story. Readers, along with Louise Mallard, are led to believe that Brently Mallard is dead ...
Published: Mar 5, 2024. Situational irony refers to a literary device where the outcome of a situation is different from what was expected or intended, often resulting in a reversal of expectations for the characters and readers. This aspect of irony plays a significant role in Kate Chopin's short story "The Story of an Hour," where the ...
In "The Story of an Hour", Chopin uses both irony and imagery to convey her theme of freedom versus confinement. As the story begins to unravel, it become abundantly clear that the reader's expectations are about to be challenged. ... Situational Irony In The Story Of An Hour Essay. Situational irony refers to a literary device where the ...
The Story of an Hour was written by Kate Chopin in 1984. It describes a woman, Mrs. Mallard, who lost her husband in an accident, but later the truth came out, and the husband was alive. This essay will discuss The Story of an Hour with emphasis on the plot and development of the protagonist, Mrs. Mallard, who goes through contrasting emotions ...
In this guide to Kate Chopin's "The Story of an Hour," we'll discuss: A brief history of Kate Chopin and America the 1890s. "The Story of an Hour" summary. Analysis of the key story elements in "The Story of an Hour," including themes, characters, and symbols. By the end of this article, you'll have an expert grasp on Kate ...
Full Plot Analysis. As the brief nature of the story suggests, "The Story of an Hour" explores the sudden struggle that Louise Mallard faces as she reaches a major turning point in her life. The possibilities that exist in a world without her husband captivate her, but she also experiences guilt regarding the relief she feels after hearing ...
Quick answer: The best example of verbal irony in Kate Chopin's "The Story of An Hour" is the story's final line. Louise dies of a heart attack upon seeing her husband alive. Her doctors believe ...
Kate Chopin's short story, "The Story of an Hour," is a masterpiece of American literature, recognized for its exploration of complex themes such as freedom, marriage, and societal expectations. In this critical essay, we will delve into the narrative's underlying messages, character development, and the literary devices employed to convey its ...
Verbal irony is found in the title, "The Story of an Hour". These words suggest a short period of time in which usually not a lot of events occur. However, in this story an hour seems like a lifetime. The main character, Mrs. Mallard, experiences grief, depression, sadness, happiness, and hope all within the time span of an hour.
Irony is a key element in "The Story of an Hour" by Kate Chopin. The story is full of unexpected twists and turns that keep the reader guessing. The most ironic moment in the story comes at the end, when Mrs. Mallard learns that her husband is not dead after all. This news comes as a shock to her, but it also brings relief and happiness.
The Story of an Hour is a short story written by Kate Chopin in 1894. This famous piece of literature was controversial for its time, as the story mentioned a female protagonist who felt relieved after her husband's death. The conclusion of The Story of an Hour is ironic, which makes the ending memorable.
In The Story of an Hour, Kate Chopin uses a variety of literary devices ranging from third person narration, juxtaposition and irony to vividly illustrate the dramatic process of grievance, and alternately liberation, that Mrs. Mallard experiences under the impression that her husband has died.In the beginning of the short story, Chopin attempts to extend inklings to the reader of what is ...
I loved Alex Ross's recent essay in The New Yorker on the nature of noise. From start to finish, it's inventive, imaginative, intelligent — and I might have missed it but for an email from ...
Uri Berliner had worked at NPR for a quarter-century when he wrote the essay that would abruptly end his tenure. On April 9, the Free Press published 3,500 words from Berliner, a senior business ...
Often hailed as classics of feminist literature, "The Story of an Hour" by Kate Chopin and "Sweat" by Zora Neale Hurston both employ the literary device of irony to illuminate the oppression, societal expectations, and ultimately, the liberation of women during their respective time periods.This essay delves into the intricacies of irony in these stories, exploring how it shapes the characters ...
Many stories needed to be long or extended to be able to tell the message. Kate Chopins an American author of short stories and novels who is also the author of "The Story of an Hour" conveys her message through this short literature with the use of irony. "The Story of an Hour' is a short story with great and interesting flow to read.