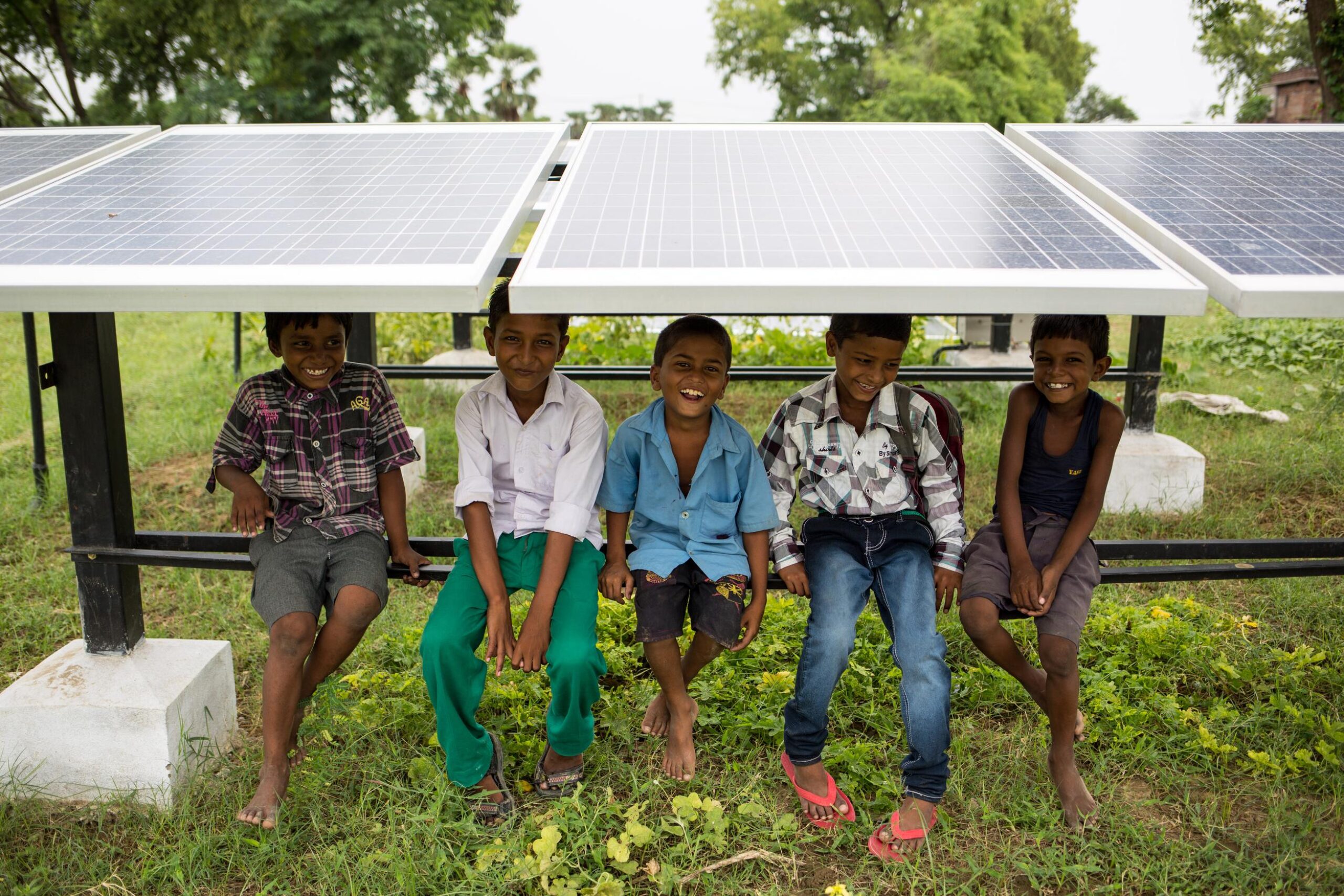


What are the solutions to climate change?
Climate change is already an urgent threat to millions of lives – but there are solutions. From changing how we get our energy to limiting deforestation, here are some of the key solutions to climate change.
Climate change is happening now, and it’s the most serious threat to life on our planet. Luckily, there are plenty of solutions to climate change and they are well-understood.
In 2015, world leaders signed a major treaty called the Paris agreement to put these solutions into practice.
Core to all climate change solutions is reducing greenhouse gas emissions , which must get to zero as soon as possible.
Because both forests and oceans play vitally important roles in regulating our climate, increasing the natural ability of forests and oceans to absorb carbon dioxide can also help stop global warming.

Be the first to know
Be first to know when there’s a chance make a difference. Sign up to get Greenpeace action alerts, straight to your inbox.
The main ways to stop climate change are to pressure government and business to:
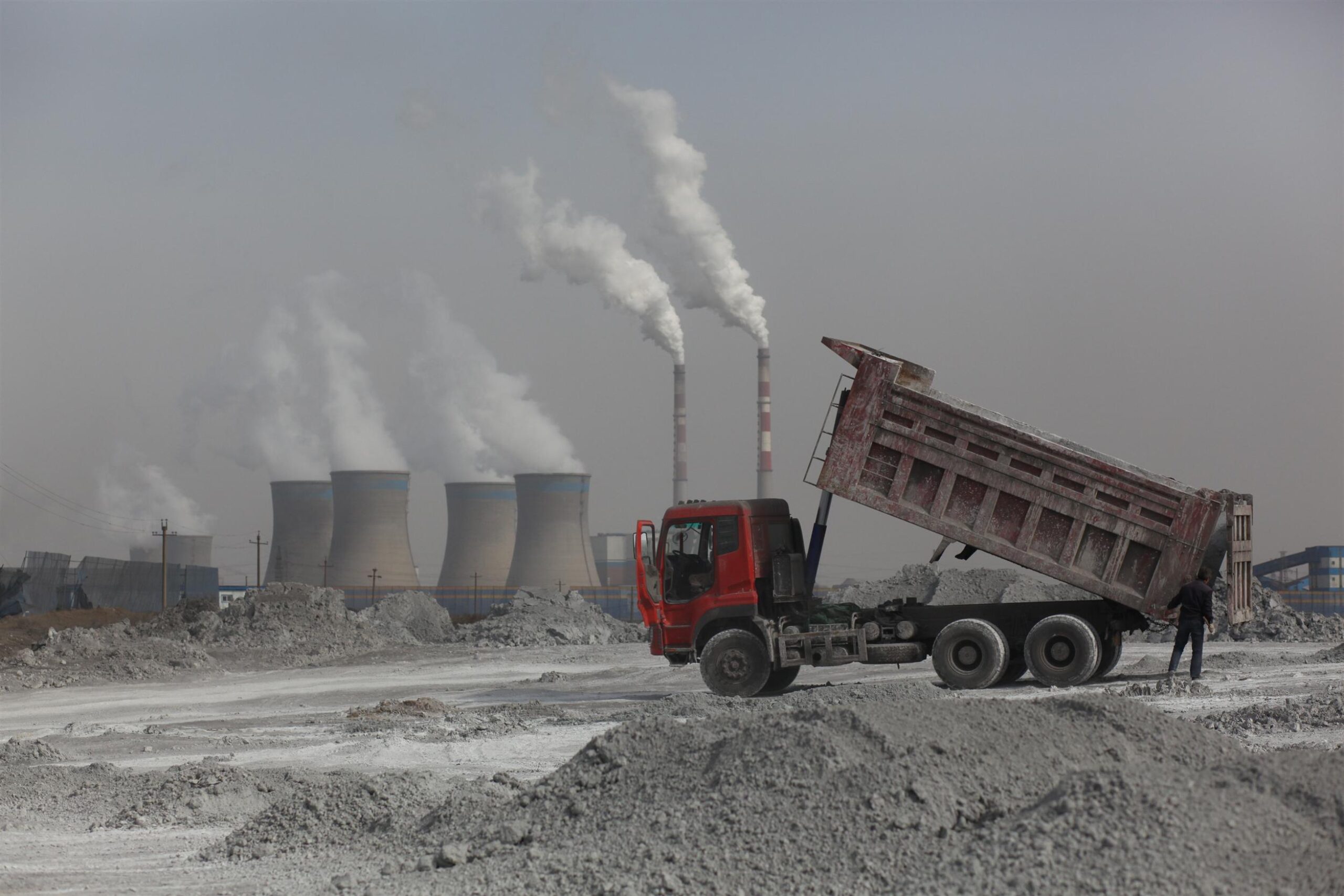
- Keep fossil fuels in the ground . Fossil fuels include coal, oil and gas – and the more that are extracted and burned, the worse climate change will get. All countries need to move their economies away from fossil fuels as soon as possible.
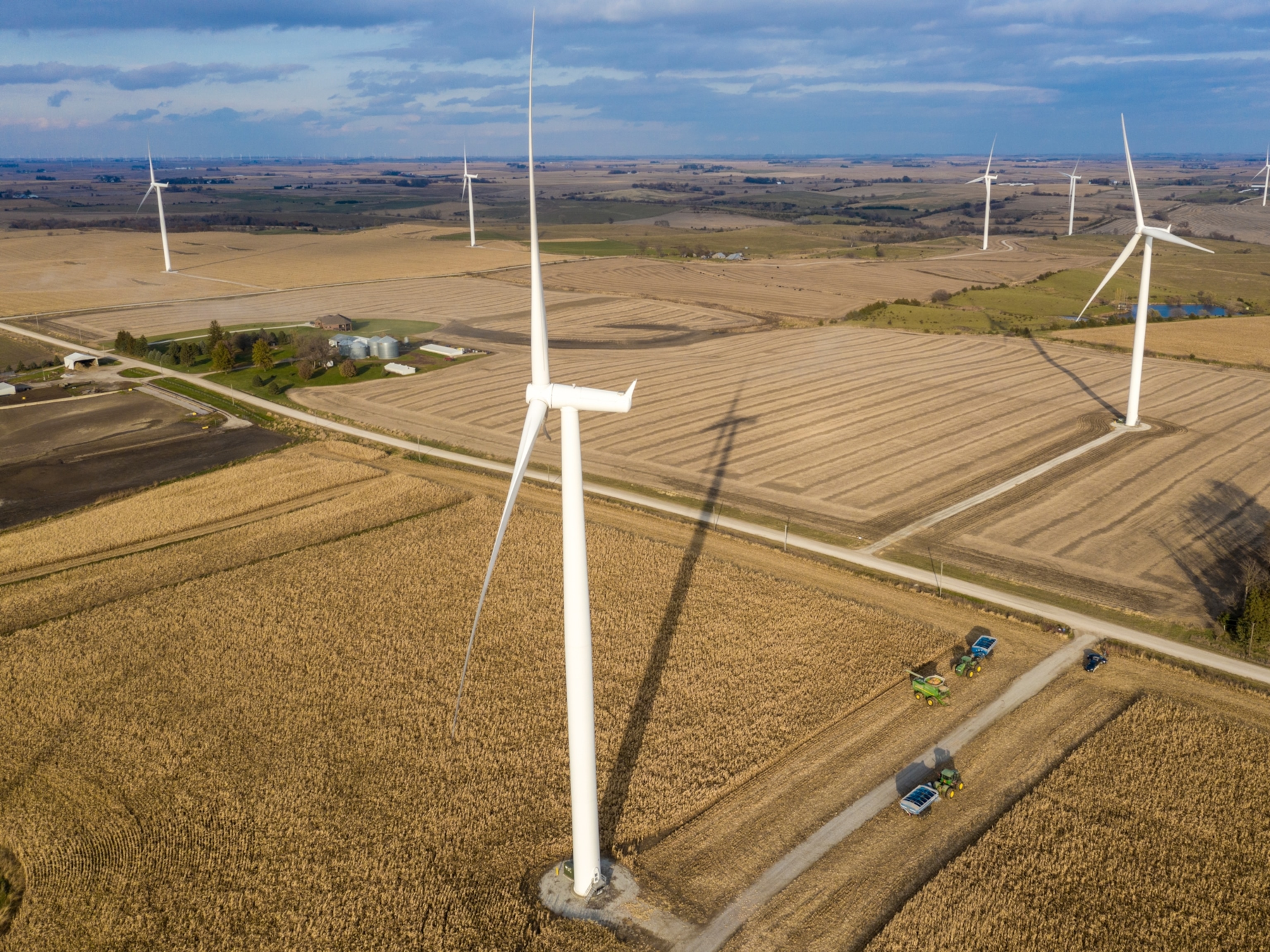
- Invest in renewable energy . Changing our main energy sources to clean and renewable energy is the best way to stop using fossil fuels. These include technologies like solar, wind, wave, tidal and geothermal power.
- Switch to sustainable transport . Petrol and diesel vehicles, planes and ships use fossil fuels. Reducing car use, switching to electric vehicles and minimising plane travel will not only help stop climate change, it will reduce air pollution too.
- Help us keep our homes cosy . Homes shouldn’t be draughty and cold – it’s a waste of money, and miserable in the winter. The government can help households heat our homes in a green way – such as by insulating walls and roofs and switching away from oil or gas boilers to heat pumps .
- Improve farming and encourage vegan diets . One of the best ways for individuals to help stop climate change is by reducing their meat and dairy consumption, or by going fully vegan. Businesses and food retailers can improve farming practices and provide more plant-based products to help people make the shift.
- Restore nature to absorb more carbon . The natural world is very good at cleaning up our emissions, but we need to look after it. Planting trees in the right places or giving land back to nature through ‘rewilding’ schemes is a good place to start. This is because photosynthesising plants draw down carbon dioxide as they grow, locking it away in soils.
- Protect forests like the Amazon . Forests are crucial in the fight against climate change, and protecting them is an important climate solution. Cutting down forests on an industrial scale destroys giant trees which could be sucking up huge amounts of carbon. Yet companies destroy forests to make way for animal farming, soya or palm oil plantations. Governments can stop them by making better laws.
- Protect the oceans . Oceans also absorb large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, which helps to keep our climate stable. But many are overfished , used for oil and gas drilling or threatened by deep sea mining. Protecting oceans and the life in them is ultimately a way to protect ourselves from climate change.
- Reduce how much people consume . Our transport, fashion, food and other lifestyle choices all have different impacts on the climate. This is often by design – fashion and technology companies, for example, will release far more products than are realistically needed. But while reducing consumption of these products might be hard, it’s most certainly worth it. Reducing overall consumption in more wealthy countries can help put less strain on the planet.
- Reduce plastic . Plastic is made from oil, and the process of extracting, refining and turning oil into plastic (or even polyester, for clothing) is surprisingly carbon-intense . It doesn’t break down quickly in nature so a lot of plastic is burned, which contributes to emissions. Demand for plastic is rising so quickly that creating and disposing of plastics will account for 17% of the global carbon budget by 2050 (this is the emissions count we need to stay within according to the Paris agreement ).
It’s easy to feel overwhelmed, and to feel that climate change is too big to solve. But we already have the answers, now it’s a question of making them happen. To work, all of these solutions need strong international cooperation between governments and businesses, including the most polluting sectors.
Individuals can also play a part by making better choices about where they get their energy, how they travel, and what food they eat. But the best way for anyone to help stop climate change is to take collective action. This means pressuring governments and corporations to change their policies and business practices.
Governments want to be re-elected. And businesses can’t survive without customers. Demanding action from them is a powerful way to make change happen.
The fossil fuel industry is blocking climate change action
Major oil and gas companies including BP, Exxon and Shell have spent hundreds of millions of pounds trying to delay or stop government policies that would have helped tackle the climate crisis.
Despite the effects of climate change becoming more and more obvious, big polluting corporations – the ones responsible for the majority of carbon emissions – continue to carry on drilling for and burning fossil fuels.
Industries including banks, car and energy companies also make profits from fossil fuels. These industries are knowingly putting money over the future of our planet and the safety of its people.
What are world leaders doing to stop climate change?
With such a huge crisis facing the entire planet, the international response should be swift and decisive. Yet progress by world governments has been achingly slow. Many commitments to reduce carbon emissions have been set, but few are binding and targets are often missed.
In Paris in 2015, world leaders from 197 countries pledged to put people first and reduce their countries’ greenhouse gas emissions. The Paris agreement has the aim of limiting global warming to well below 2ºC and ideally to 1.5°C.
If governments act swiftly on the promises they made in the Paris climate agreement, and implement the solutions now, there’s still hope of avoiding the worst consequences of climate change .
World leaders and climate negotiators meet at annual COPs – which stands for Conference of the Parties (the countries that signed the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, or UNFCCC).
At COPs and other climate talks, nations take stock of their ability to meet their commitments to reduce emissions.
Recently, talks have focused on climate finance – money to help poorer countries adapt to climate change and reduce emissions. Rich countries have pledged $100 billion in annual funding to help developing countries reduce emissions and manage the impacts of climate change. This is yet to materialise, and much more money is needed.
As the impacts of climate change are increasing, important talks have also started on “loss and damage” funding. This is money needed by worst-impacted countries to deal with extreme weather and other climate change impacts.
Global climate change activism
Around the world, millions of us are taking steps to defend our climate. People of all ages and from all walks of life are desperately demanding solutions to the climate emergency.
Over the years, Greenpeace has challenged oil companies chasing new fossil fuels to extract and burn. We’ve also called out the governments for their failure to act fast enough on the climate emergency. Greenpeace activists are ordinary people taking extraordinary action, to push the solutions to climate change.
Indigenous Peoples are most severely affected by both the causes and effects of climate change . They are often on the front lines, facing down deforestation or kicking out fossil fuel industries polluting their water supplies.
Communities in the Pacific Islands are facing sea level rises and more extreme weather. But they are using their strength and resilience to demand world leaders take quicker climate action.
For many of these communities, the fight against climate change is a fight for life itself.
Even in the UK, climate change is impacting people more severely. As a country with the wealth and power to really tackle climate change, it’s never been more important to demand action.
Beginner's guides
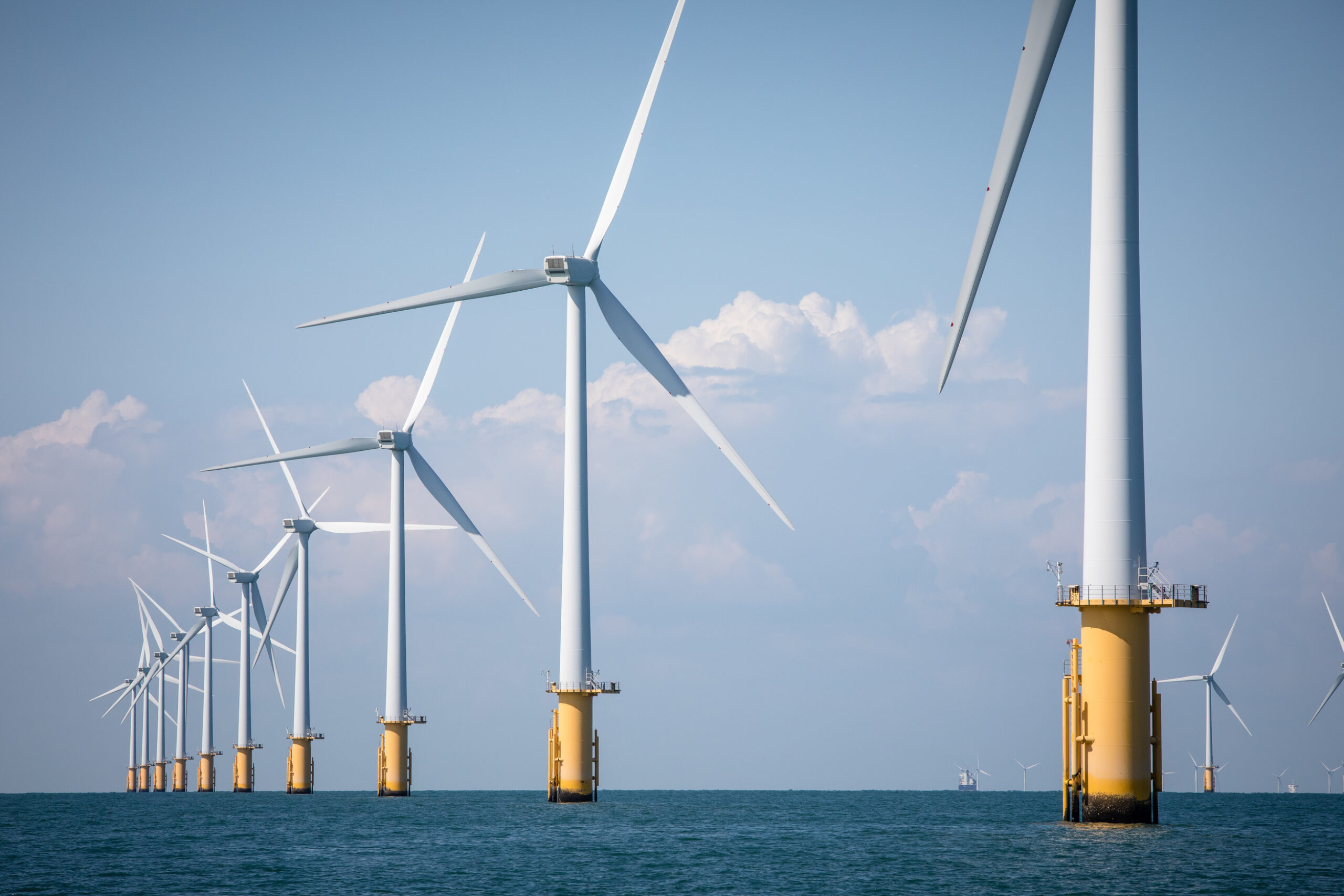

Renewable energy
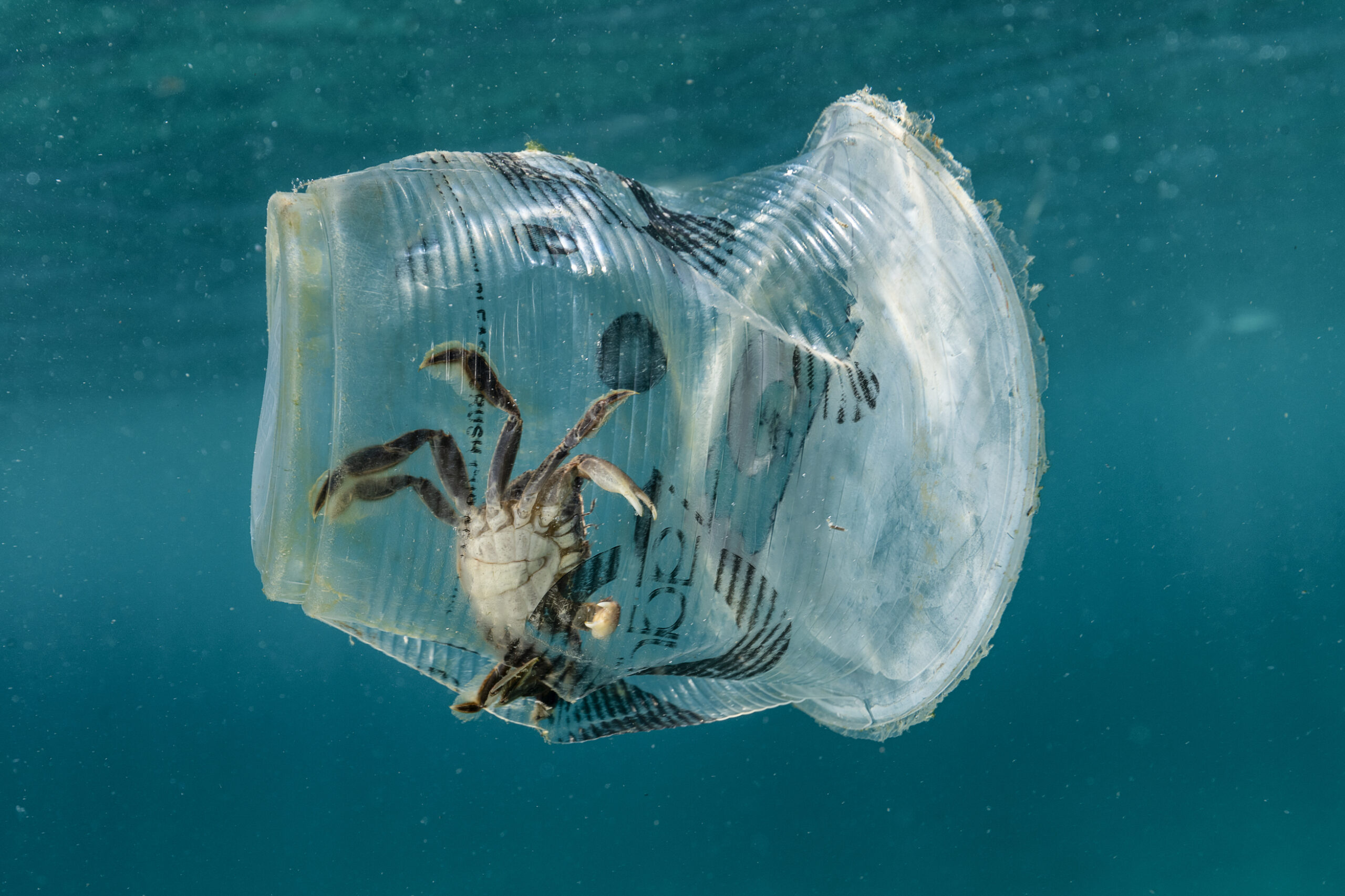

Plastic pollution

Fossil fuels

Wildlife and biodiversity
Get action alerts.
Be first to know when there’s a chance make a difference. Sign up for Greenpeace action alerts, straight to your inbox.
If you sign up, we’ll keep you updated on how you can get involved through petitions, campaigning, volunteering and donating. You can opt out at any time . Read our privacy policy .
Our website uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site you agree to our privacy policy
Can we slow or even reverse global warming?
Yes. While we cannot stop global warming overnight, we can slow the rate and limit the amount of global warming by reducing human emissions of heat-trapping gases and soot (“black carbon”).
If all human emissions of heat-trapping gases were to stop today, Earth’s temperature would continue to rise for a few decades as ocean currents bring excess heat stored in the deep ocean back to the surface. Once this excess heat radiated out to space, Earth’s temperature would stabilize. Experts think the additional warming from this “hidden” heat are unlikely to exceed 0.9° Fahrenheit (0.5°Celsius). With no further human influence, natural processes would begin to slowly remove the excess carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, and global temperatures would gradually begin to decline.
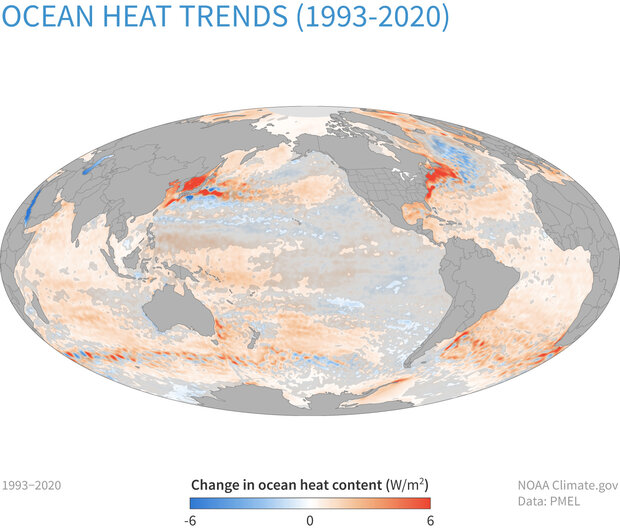
Change in heat content in the upper 2,300 feet (700 meters) of the ocean from 1993-2020. Between 1993–2019, heat content rose by up to 6 Watts per square meter in parts of the ocean (dark orange). Some areas lost heat (blue), but overall, the ocean gained more heat than it lost. The changes in areas covered with the gray shading were not statistically significant. NOAA Climate.gov image, based on data from NCEI.
It’s true that without dramatic action in the next couple of decades, we are unlikely to keep global warming in this century below 2.7° Fahrenheit (1.5° Celsius) compared to pre-industrial temperatures—a threshold that experts say offers a lower risk of serious negative impacts. But the more we overshoot that threshold, the more serious and widespread the negative impacts will be, which means that it is never “too late” to take action.
In response to a request from the U.S. Congress, the U.S. National Academy of Sciences published a series of peer-reviewed reports, titled America's Climate Choices , to provide authoritative analyses to inform and guide responses to climate change across the nation. Relevant to this question, the NAS report titled Limiting the Magnitude of Future Climate Change explains policies that could be adopted to slow or even reverse global warming. The report says, "Meeting internationally discussed targets for limiting atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations and associated increases in global average temperatures will require a major departure from business as usual in how the world uses and produces energy."

Transitioning to energy sources that do not emit greenhouse gases, such as solar, wind, biofuels, and nuclear, can slow the pace of climate change, though these energy sources face hurdles ranging from manufacturing capacity to debates about where to install some facilities. Images courtesy Energy.gov.
Alternative methods to slow or reduce global warming have been proposed that are, collectively, known as "climate engineering" or "geoengineering." Some geoengineering proposals involve cooling Earth's surface by injecting reflective particles into the upper atmosphere to scatter and reflect sunlight back to space. Other proposals involve seeding the oceans with iron to stimulate large-scale phytoplankton blooms, thereby drawing down carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere through photosynthesis. Such methods could work, in principle, but many climate scientists oppose undertaking geoengineering until we have a much better understanding of the possible side effects. Additionally, there are unresolved legal and ethical issues surrounding geoengineering.
Given these concerns, the American Meteorological Society published a position paper (readopted in January 2013) in which it said: "...research to date has not determined whether there are large-scale geoengineering approaches that would produce significant benefits, or whether those benefits would substantially outweigh the detriments. Indeed, geoengineering must be viewed with caution because manipulating the Earth system has considerable potential to trigger adverse and unpredictable consequences."
Martinich, J., B.J. DeAngelo, D. Diaz, B. Ekwurzel, G. Franco, C. Frisch, J. McFarland, and B. O’Neill. (2018). Reducing Risks Through Emissions Mitigation. In Impacts, Risks, and Adaptation in the United States: Fourth National Climate Assessment, Volume II [Reidmiller, D.R., C.W. Avery, D.R. Easterling, K.E. Kunkel, K.L.M. Lewis, T.K. Maycock, and B.C. Stewart (eds.)]. U.S. Global Change Research Program, Washington, DC, USA, pp. 1346–1386. doi: 10.7930/NCA4.2018.CH29 .
Allen, M.R., O.P. Dube, W. Solecki, F. Aragón-Durand, W. Cramer, S. Humphreys, M. Kainuma, J. Kala, N. Mahowald, Y. Mulugetta, R. Perez, M.Wairiu, and K. Zickfeld (2018). Framing and Context. In: Global Warming of 1.5°C. An IPCC Special Report on the impacts of global warming of 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels and related global greenhouse gas emission pathways, in the context of strengthening the global response to the threat of climate change, sustainable development, and efforts to eradicate poverty [Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, H.-O. Pörtner, D. Roberts, J. Skea, P.R. Shukla, A. Pirani, W. Moufouma-Okia, C. Péan, R. Pidcock, S. Connors, J.B.R. Matthews, Y. Chen, X. Zhou, M.I. Gomis, E. Lonnoy, T. Maycock, M. Tignor, and T. Waterfield (eds.)]. In Press.
We value your feedback
Help us improve our content
Related Content
News & features, natural variability in earth’s reflectiveness would limit our ability to detect effects of climate engineering, climate science 101: ethics and issues surrounding geo-engineering to mitigate climate change, what's the difference between global warming and climate change, maps & data, climate forcing, ocean heat content - seasonal difference from average, ocean heat content - yearly difference from average, teaching climate, toolbox for teaching climate & energy, imatternow campaign, climate youth engagement, climate resilience toolkit, climate change 2023 - ar6 synthesis report, food production, international food security.

A sunset lights a glacier in New Zealand's Fiordland National Park. Around the world, many glaciers are melting quickly as the planet warms.
- ENVIRONMENT

Are there real ways to fight climate change? Yes.
Humans have the solutions to fight a global environmental crisis. Do we have the will?
The evidence that humans are causing climate change, with drastic consequences for life on the planet, is overwhelming .
Experts began raising the alarm about global warming in 1979 , a change now referred to under the broader term climate change , preferred by scientists to describe the complex shifts now affecting our planet’s weather and climate systems. Climate change encompasses not only rising average temperatures but also extreme weather events, shifting wildlife populations and habitats, rising seas , and a range of other impacts.
Over 200 countries—193 countries plus the 27 members of the European Union—have signed the Paris Climate Agreement , a treaty created in 2015 to fight climate change on a global scale. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), which synthesizes the scientific consensus on the issue, has set a goal of keeping warming under 2°C (3.6°F) and pursuing an even lower warming cap of 1.5 °C (2.7° F).
But no country has created policies that will keep the world below 1.5 °C, according to the Climate Action Tracker . Current emissions have the world on track to warm 2.8°C by the end of this century.
Addressing climate change will require many solutions —there's no magic bullet. Yet nearly all of these solutions exist today. They range from worldwide changes to where we source our electricity to protecting forests from deforestation.
The promise of new technology
Better technology will help reduce emissions from activities like manufacturing and driving.
Scientists are working on ways to sustainably produce hydrogen, most of which is currently derived from natural gas, to feed zero-emission fuel cells for transportation and electricity.
Renewable energy is growing, and in the U.S., a combination of wind, solar, geothermal, and other renewable sources provide 20 percen t of the nation’s electricity.
New technological developments promise to build better batteries to store that renewable energy, engineer a smarter electric grid, and capture carbon dioxide from power plants and store it underground or turn it into valuable products such as gasoline . Some argue that nuclear power—despite concerns over safety, water use, and toxic waste—should also be part of the solution, because nuclear plants don't contribute any direct air pollution while operating.
Should we turn to geoengineering?
While halting new greenhouse gas emissions is critical, scientists say we need to extract existing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, effectively sucking it out of the sky.
Pulling carbon out of the atmosphere is a type of geoengineering , a science that interferes with the Earth’s natural systems, and it’s a controversial approach to fighting climate change.
Other types of geoengineering involve spraying sunlight-reflecting aerosols into the air or blocking the sun with a giant space mirror. Studies suggest we don’t know enough about the potential dangers of geoengineering to deploy it.

Restoring nature to protect the planet
Planting trees, restoring seagrasses, and boosting the use of agricultural cover crops could help clean up significant amounts of carbon dioxide .
The Amazon rainforest is an important reservoir of the Earth’s carbon, but a study published in 2021, showed deforestation was transforming this reservoir into a source of pollution.
Restoring and protecting nature may provide as much as 37 percent of the climate mitigation needed to reach the Paris Agreement’s 203o targets. Protecting these ecosystems can also benefit biodiversity, providing a win-win for nature .
Adapt—or else
Communities around the world are already recognizing that adaptation must also be part of the response to climate change . From flood-prone coastal towns to regions facing increased droughts and fires, a new wave of initiatives focuses on boosting resilience . Those include managing or preventing land erosion, building microgrids and other energy systems built to withstand disruptions, and designing buildings with rising sea levels in mind.
Last year, the Inflation Reduction Act was signed into law and was a historic investment in fighting and adapting to climate change.
( Read more about how the bill will dramatically reduce emissions. )
Recent books such as Drawdown and Designing Climate Solutions have proposed bold yet simple plans for reversing our current course. The ideas vary, but the message is consistent: We already have many of the tools needed to address climate change. Some of the concepts are broad ones that governments and businesses must implement, but many other ideas involve changes that anyone can make— eating less meat , for example, or rethinking your modes of transport .
"We have the technology today to rapidly move to a clean energy system," write the authors of Designing Climate Solutions . "And the price of that future, without counting environmental benefits, is about the same as that of a carbon-intensive future."
Sarah Gibbens contributed reporting to this article.

LIMITED TIME OFFER
Related topics.
- CLIMATE CHANGE
- ENVIRONMENT AND CONSERVATION
- AIR POLLUTION
- RENEWABLE ENERGY
You May Also Like

Another weapon to fight climate change? Put carbon back where we found it

Which cities will still be livable in a world altered by climate change?

Listen to 30 years of climate change transformed into haunting music

Could seaweed be the 'fastest and least expensive' tool to fight climate change?

How the historic climate bill will dramatically reduce U.S. emissions
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
November 26, 2007
10 Solutions for Climate Change
Ten possibilities for staving off catastrophic climate change
By David Biello

Mark Garlick Getty Images
The enormity of global warming can be daunting and dispiriting. What can one person, or even one nation, do on their own to slow and reverse climate change ? But just as ecologist Stephen Pacala and physicist Robert Socolow, both at Princeton University, came up with 15 so-called " wedges " for nations to utilize toward this goal—each of which is challenging but feasible and, in some combination, could reduce greenhouse gas emissions to safer levels —there are personal lifestyle changes that you can make too that, in some combination, can help reduce your carbon impact. Not all are right for everybody. Some you may already be doing or absolutely abhor. But implementing just a few of them could make a difference.
Forego Fossil Fuels —The first challenge is eliminating the burning of coal , oil and, eventually, natural gas. This is perhaps the most daunting challenge as denizens of richer nations literally eat, wear, work, play and even sleep on the products made from such fossilized sunshine. And citizens of developing nations want and arguably deserve the same comforts, which are largely thanks to the energy stored in such fuels.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
Oil is the lubricant of the global economy, hidden inside such ubiquitous items as plastic and corn, and fundamental to the transportation of both consumers and goods. Coal is the substrate, supplying roughly half of the electricity used in the U.S. and nearly that much worldwide—a percentage that is likely to grow, according to the International Energy Agency. There are no perfect solutions for reducing dependence on fossil fuels (for example, carbon neutral biofuels can drive up the price of food and lead to forest destruction, and while nuclear power does not emit greenhouse gases, it does produce radioactive waste), but every bit counts.
So try to employ alternatives when possible—plant-derived plastics, biodiesel, wind power—and to invest in the change, be it by divesting from oil stocks or investing in companies practicing carbon capture and storage.
Infrastructure Upgrade —Buildings worldwide contribute around one third of all greenhouse gas emissions (43 percent in the U.S. alone), even though investing in thicker insulation and other cost-effective, temperature-regulating steps can save money in the long run. Electric grids are at capacity or overloaded, but power demands continue to rise. And bad roads can lower the fuel economy of even the most efficient vehicle. Investing in new infrastructure, or radically upgrading existing highways and transmission lines, would help cut greenhouse gas emissions and drive economic growth in developing countries.
Of course, it takes a lot of cement, a major source of greenhouse gas emissions, to construct new buildings and roads. The U.S. alone contributed 50.7 million metric tons of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere in 2005 from cement production, which requires heating limestone and other ingredients to 1,450 degrees Celsius (2,642 degrees Fahrenheit). Mining copper and other elements needed for electrical wiring and transmission also causes globe-warming pollution.
But energy-efficient buildings and improved cement-making processes (such as using alternative fuels to fire up the kiln) could reduce greenhouse gas emissions in the developed world and prevent them in the developing world.
Move Closer to Work —Transportation is the second leading source of greenhouse gas emissions in the U.S. (burning a single gallon of gasoline produces 20 pounds of CO 2 ). But it doesn't have to be that way.
One way to dramatically curtail transportation fuel needs is to move closer to work, use mass transit, or switch to walking, cycling or some other mode of transport that does not require anything other than human energy. There is also the option of working from home and telecommuting several days a week.
Cutting down on long-distance travel would also help, most notably airplane flights, which are one of the fastest growing sources of greenhouse gas emissions and a source that arguably releases such emissions in the worst possible spot (higher in the atmosphere). Flights are also one of the few sources of globe-warming pollution for which there isn't already a viable alternative: jets rely on kerosene, because it packs the most energy per pound, allowing them to travel far and fast, yet it takes roughly 10 gallons of oil to make one gallon of JetA fuel. Restricting flying to only critical, long-distance trips—in many parts of the world, trains can replace planes for short- to medium-distance trips—would help curb airplane emissions.
Consume Less —The easiest way to cut back on greenhouse gas emissions is simply to buy less stuff. Whether by forgoing an automobile or employing a reusable grocery sack, cutting back on consumption results in fewer fossil fuels being burned to extract, produce and ship products around the globe.
Think green when making purchases. For instance, if you are in the market for a new car, buy one that will last the longest and have the least impact on the environment. Thus, a used vehicle with a hybrid engine offers superior fuel efficiency over the long haul while saving the environmental impact of new car manufacture.
Paradoxically, when purchasing essentials, such as groceries, buying in bulk can reduce the amount of packaging—plastic wrapping, cardboard boxes and other unnecessary materials. Sometimes buying more means consuming less.
Be Efficient —A potentially simpler and even bigger impact can be made by doing more with less. Citizens of many developed countries are profligate wasters of energy, whether by speeding in a gas-guzzling sport-utility vehicle or leaving the lights on when not in a room.
Good driving—and good car maintenance, such as making sure tires are properly inflated—can limit the amount of greenhouse gas emissions from a vehicle and, perhaps more importantly, lower the frequency of payment at the pump.
Similarly, employing more efficient refrigerators, air conditioners and other appliances, such as those rated highly under the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's Energy Star program, can cut electric bills while something as simple as weatherproofing the windows of a home can reduce heating and cooling bills. Such efforts can also be usefully employed at work, whether that means installing more efficient turbines at the power plant or turning the lights off when you leave the office .
Eat Smart, Go Vegetarian? —Corn grown in the U.S. requires barrels of oil for the fertilizer to grow it and the diesel fuel to harvest and transport it. Some grocery stores stock organic produce that do not require such fertilizers, but it is often shipped from halfway across the globe. And meat, whether beef, chicken or pork, requires pounds of feed to produce a pound of protein.
Choosing food items that balance nutrition, taste and ecological impact is no easy task. Foodstuffs often bear some nutritional information, but there is little to reveal how far a head of lettuce, for example, has traveled.
University of Chicago researchers estimate that each meat-eating American produces 1.5 tons more greenhouse gases through their food choice than do their vegetarian peers. It would also take far less land to grow the crops necessary to feed humans than livestock, allowing more room for planting trees.
Stop Cutting Down Trees —Every year, 33 million acres of forests are cut down . Timber harvesting in the tropics alone contributes 1.5 billion metric tons of carbon to the atmosphere. That represents 20 percent of human-made greenhouse gas emissions and a source that could be avoided relatively easily.
Improved agricultural practices along with paper recycling and forest management—balancing the amount of wood taken out with the amount of new trees growing—could quickly eliminate this significant chunk of emissions.
And when purchasing wood products, such as furniture or flooring, buy used goods or, failing that, wood certified to have been sustainably harvested. The Amazon and other forests are not just the lungs of the earth, they may also be humanity's best short-term hope for limiting climate change.
Unplug —Believe it or not, U.S. citizens spend more money on electricity to power devices when off than when on. Televisions, stereo equipment, computers, battery chargers and a host of other gadgets and appliances consume more energy when seemingly switched off, so unplug them instead.
Purchasing energy-efficient gadgets can also save both energy and money—and thus prevent more greenhouse gas emissions. To take but one example, efficient battery chargers could save more than one billion kilowatt-hours of electricity—$100 million at today's electricity prices—and thus prevent the release of more than one million metric tons of greenhouse gases.
Swapping old incandescent lightbulbs for more efficient replacements, such as compact fluorescents (warning: these lightbulbs contain mercury and must be properly disposed of at the end of their long life), would save billions of kilowatt-hours. In fact, according to the EPA, replacing just one incandescent lightbulb in every American home would save enough energy to provide electricity to three million American homes.
One Child —There are at least 6.6 billion people living today, a number that is predicted by the United Nations to grow to at least nine billion by mid-century. The U.N. Environmental Program estimates that it requires 54 acres to sustain an average human being today—food, clothing and other resources extracted from the planet. Continuing such population growth seems unsustainable.
Falling birth rates in some developed and developing countries (a significant portion of which are due to government-imposed limits on the number of children a couple can have) have begun to reduce or reverse the population explosion. It remains unclear how many people the planet can comfortably sustain, but it is clear that per capita energy consumption must go down if climate change is to be controlled.
Ultimately, a one child per couple rule is not sustainable either and there is no perfect number for human population. But it is clear that more humans means more greenhouse gas emissions.
Future Fuels —Replacing fossil fuels may prove the great challenge of the 21st century. Many contenders exist, ranging from ethanol derived from crops to hydrogen electrolyzed out of water, but all of them have some drawbacks, too, and none are immediately available at the scale needed.
Biofuels can have a host of negative impacts, from driving up food prices to sucking up more energy than they produce. Hydrogen must be created, requiring either reforming natural gas or electricity to crack water molecules. Biodiesel hybrid electric vehicles (that can plug into the grid overnight) may offer the best transportation solution in the short term, given the energy density of diesel and the carbon neutral ramifications of fuel from plants as well as the emissions of electric engines. A recent study found that the present amount of electricity generation in the U.S. could provide enough energy for the country's entire fleet of automobiles to switch to plug-in hybrids , reducing greenhouse gas emissions in the process.
But plug-in hybrids would still rely on electricity, now predominantly generated by burning dirty coal. Massive investment in low-emission energy generation, whether solar-thermal power or nuclear fission , would be required to radically reduce greenhouse gas emissions. And even more speculative energy sources—hyperefficient photovoltaic cells, solar energy stations in orbit or even fusion—may ultimately be required.
The solutions above offer the outline of a plan to personally avoid contributing to global warming. But should such individual and national efforts fail, there is another, potentially desperate solution:
Experiment Earth —Climate change represents humanity's first planetwide experiment. But, if all else fails, it may not be the last. So-called geoengineering , radical interventions to either block sunlight or reduce greenhouse gases, is a potential last resort for addressing the challenge of climate change.
Among the ideas: releasing sulfate particles in the air to mimic the cooling effects of a massive volcanic eruption; placing millions of small mirrors or lenses in space to deflect sunlight; covering portions of the planet with reflective films to bounce sunlight back into space; fertilizing the oceans with iron or other nutrients to enable plankton to absorb more carbon; and increasing cloud cover or the reflectivity of clouds that already form.
All may have unintended consequences, making the solution worse than the original problem. But it is clear that at least some form of geoengineering will likely be required: capturing carbon dioxide before it is released and storing it in some fashion, either deep beneath the earth, at the bottom of the ocean or in carbonate minerals. Such carbon capture and storage is critical to any serious effort to combat climate change.
Additional reporting by Larry Greenemeier and Nikhil Swaminathan .

IMAGES