Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?

A conversation with a Wheelock researcher, a BU student, and a fourth-grade teacher

“Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives,” says Wheelock’s Janine Bempechat. “It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.” Photo by iStock/Glenn Cook Photography
Do your homework.
If only it were that simple.
Educators have debated the merits of homework since the late 19th century. In recent years, amid concerns of some parents and teachers that children are being stressed out by too much homework, things have only gotten more fraught.
“Homework is complicated,” says developmental psychologist Janine Bempechat, a Wheelock College of Education & Human Development clinical professor. The author of the essay “ The Case for (Quality) Homework—Why It Improves Learning and How Parents Can Help ” in the winter 2019 issue of Education Next , Bempechat has studied how the debate about homework is influencing teacher preparation, parent and student beliefs about learning, and school policies.
She worries especially about socioeconomically disadvantaged students from low-performing schools who, according to research by Bempechat and others, get little or no homework.
BU Today sat down with Bempechat and Erin Bruce (Wheelock’17,’18), a new fourth-grade teacher at a suburban Boston school, and future teacher freshman Emma Ardizzone (Wheelock) to talk about what quality homework looks like, how it can help children learn, and how schools can equip teachers to design it, evaluate it, and facilitate parents’ role in it.
BU Today: Parents and educators who are against homework in elementary school say there is no research definitively linking it to academic performance for kids in the early grades. You’ve said that they’re missing the point.
Bempechat : I think teachers assign homework in elementary school as a way to help kids develop skills they’ll need when they’re older—to begin to instill a sense of responsibility and to learn planning and organizational skills. That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success. If we greatly reduce or eliminate homework in elementary school, we deprive kids and parents of opportunities to instill these important learning habits and skills.
We do know that beginning in late middle school, and continuing through high school, there is a strong and positive correlation between homework completion and academic success.
That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success.
You talk about the importance of quality homework. What is that?
Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives. It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.

What are your concerns about homework and low-income children?
The argument that some people make—that homework “punishes the poor” because lower-income parents may not be as well-equipped as affluent parents to help their children with homework—is very troubling to me. There are no parents who don’t care about their children’s learning. Parents don’t actually have to help with homework completion in order for kids to do well. They can help in other ways—by helping children organize a study space, providing snacks, being there as a support, helping children work in groups with siblings or friends.
Isn’t the discussion about getting rid of homework happening mostly in affluent communities?
Yes, and the stories we hear of kids being stressed out from too much homework—four or five hours of homework a night—are real. That’s problematic for physical and mental health and overall well-being. But the research shows that higher-income students get a lot more homework than lower-income kids.
Teachers may not have as high expectations for lower-income children. Schools should bear responsibility for providing supports for kids to be able to get their homework done—after-school clubs, community support, peer group support. It does kids a disservice when our expectations are lower for them.
The conversation around homework is to some extent a social class and social justice issue. If we eliminate homework for all children because affluent children have too much, we’re really doing a disservice to low-income children. They need the challenge, and every student can rise to the challenge with enough supports in place.
What did you learn by studying how education schools are preparing future teachers to handle homework?
My colleague, Margarita Jimenez-Silva, at the University of California, Davis, School of Education, and I interviewed faculty members at education schools, as well as supervising teachers, to find out how students are being prepared. And it seemed that they weren’t. There didn’t seem to be any readings on the research, or conversations on what high-quality homework is and how to design it.
Erin, what kind of training did you get in handling homework?
Bruce : I had phenomenal professors at Wheelock, but homework just didn’t come up. I did lots of student teaching. I’ve been in classrooms where the teachers didn’t assign any homework, and I’ve been in rooms where they assigned hours of homework a night. But I never even considered homework as something that was my decision. I just thought it was something I’d pull out of a book and it’d be done.
I started giving homework on the first night of school this year. My first assignment was to go home and draw a picture of the room where you do your homework. I want to know if it’s at a table and if there are chairs around it and if mom’s cooking dinner while you’re doing homework.
The second night I asked them to talk to a grown-up about how are you going to be able to get your homework done during the week. The kids really enjoyed it. There’s a running joke that I’m teaching life skills.
Friday nights, I read all my kids’ responses to me on their homework from the week and it’s wonderful. They pour their hearts out. It’s like we’re having a conversation on my couch Friday night.
It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Bempechat : I can’t imagine that most new teachers would have the intuition Erin had in designing homework the way she did.
Ardizzone : Conversations with kids about homework, feeling you’re being listened to—that’s such a big part of wanting to do homework….I grew up in Westchester County. It was a pretty demanding school district. My junior year English teacher—I loved her—she would give us feedback, have meetings with all of us. She’d say, “If you have any questions, if you have anything you want to talk about, you can talk to me, here are my office hours.” It felt like she actually cared.
Bempechat : It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Ardizzone : But can’t it lead to parents being overbearing and too involved in their children’s lives as students?
Bempechat : There’s good help and there’s bad help. The bad help is what you’re describing—when parents hover inappropriately, when they micromanage, when they see their children confused and struggling and tell them what to do.
Good help is when parents recognize there’s a struggle going on and instead ask informative questions: “Where do you think you went wrong?” They give hints, or pointers, rather than saying, “You missed this,” or “You didn’t read that.”
Bruce : I hope something comes of this. I hope BU or Wheelock can think of some way to make this a more pressing issue. As a first-year teacher, it was not something I even thought about on the first day of school—until a kid raised his hand and said, “Do we have homework?” It would have been wonderful if I’d had a plan from day one.
Explore Related Topics:
- Share this story
Senior Contributing Editor

Sara Rimer A journalist for more than three decades, Sara Rimer worked at the Miami Herald , Washington Post and, for 26 years, the New York Times , where she was the New England bureau chief, and a national reporter covering education, aging, immigration, and other social justice issues. Her stories on the death penalty’s inequities were nominated for a Pulitzer Prize and cited in the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision outlawing the execution of people with intellectual disabilities. Her journalism honors include Columbia University’s Meyer Berger award for in-depth human interest reporting. She holds a BA degree in American Studies from the University of Michigan. Profile
She can be reached at [email protected] .
Comments & Discussion
Boston University moderates comments to facilitate an informed, substantive, civil conversation. Abusive, profane, self-promotional, misleading, incoherent or off-topic comments will be rejected. Moderators are staffed during regular business hours (EST) and can only accept comments written in English. Statistics or facts must include a citation or a link to the citation.
There are 81 comments on Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?
Insightful! The values about homework in elementary schools are well aligned with my intuition as a parent.
when i finish my work i do my homework and i sometimes forget what to do because i did not get enough sleep
same omg it does not help me it is stressful and if I have it in more than one class I hate it.
Same I think my parent wants to help me but, she doesn’t care if I get bad grades so I just try my best and my grades are great.
I think that last question about Good help from parents is not know to all parents, we do as our parents did or how we best think it can be done, so maybe coaching parents or giving them resources on how to help with homework would be very beneficial for the parent on how to help and for the teacher to have consistency and improve homework results, and of course for the child. I do see how homework helps reaffirm the knowledge obtained in the classroom, I also have the ability to see progress and it is a time I share with my kids
The answer to the headline question is a no-brainer – a more pressing problem is why there is a difference in how students from different cultures succeed. Perfect example is the student population at BU – why is there a majority population of Asian students and only about 3% black students at BU? In fact at some universities there are law suits by Asians to stop discrimination and quotas against admitting Asian students because the real truth is that as a group they are demonstrating better qualifications for admittance, while at the same time there are quotas and reduced requirements for black students to boost their portion of the student population because as a group they do more poorly in meeting admissions standards – and it is not about the Benjamins. The real problem is that in our PC society no one has the gazuntas to explore this issue as it may reveal that all people are not created equal after all. Or is it just environmental cultural differences??????
I get you have a concern about the issue but that is not even what the point of this article is about. If you have an issue please take this to the site we have and only post your opinion about the actual topic
This is not at all what the article is talking about.
This literally has nothing to do with the article brought up. You should really take your opinions somewhere else before you speak about something that doesn’t make sense.
we have the same name
so they have the same name what of it?
lol you tell her
totally agree
What does that have to do with homework, that is not what the article talks about AT ALL.
Yes, I think homework plays an important role in the development of student life. Through homework, students have to face challenges on a daily basis and they try to solve them quickly.I am an intense online tutor at 24x7homeworkhelp and I give homework to my students at that level in which they handle it easily.
More than two-thirds of students said they used alcohol and drugs, primarily marijuana, to cope with stress.
You know what’s funny? I got this assignment to write an argument for homework about homework and this article was really helpful and understandable, and I also agree with this article’s point of view.
I also got the same task as you! I was looking for some good resources and I found this! I really found this article useful and easy to understand, just like you! ^^
i think that homework is the best thing that a child can have on the school because it help them with their thinking and memory.
I am a child myself and i think homework is a terrific pass time because i can’t play video games during the week. It also helps me set goals.
Homework is not harmful ,but it will if there is too much
I feel like, from a minors point of view that we shouldn’t get homework. Not only is the homework stressful, but it takes us away from relaxing and being social. For example, me and my friends was supposed to hang at the mall last week but we had to postpone it since we all had some sort of work to do. Our minds shouldn’t be focused on finishing an assignment that in realty, doesn’t matter. I completely understand that we should have homework. I have to write a paper on the unimportance of homework so thanks.
homework isn’t that bad
Are you a student? if not then i don’t really think you know how much and how severe todays homework really is
i am a student and i do not enjoy homework because i practice my sport 4 out of the five days we have school for 4 hours and that’s not even counting the commute time or the fact i still have to shower and eat dinner when i get home. its draining!
i totally agree with you. these people are such boomers
why just why
they do make a really good point, i think that there should be a limit though. hours and hours of homework can be really stressful, and the extra work isn’t making a difference to our learning, but i do believe homework should be optional and extra credit. that would make it for students to not have the leaning stress of a assignment and if you have a low grade you you can catch up.
Studies show that homework improves student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college. Research published in the High School Journal indicates that students who spent between 31 and 90 minutes each day on homework “scored about 40 points higher on the SAT-Mathematics subtest than their peers, who reported spending no time on homework each day, on average.” On both standardized tests and grades, students in classes that were assigned homework outperformed 69% of students who didn’t have homework. A majority of studies on homework’s impact – 64% in one meta-study and 72% in another – showed that take home assignments were effective at improving academic achievement. Research by the Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) concluded that increased homework led to better GPAs and higher probability of college attendance for high school boys. In fact, boys who attended college did more than three hours of additional homework per week in high school.
So how are your measuring student achievement? That’s the real question. The argument that doing homework is simply a tool for teaching responsibility isn’t enough for me. We can teach responsibility in a number of ways. Also the poor argument that parents don’t need to help with homework, and that students can do it on their own, is wishful thinking at best. It completely ignores neurodiverse students. Students in poverty aren’t magically going to find a space to do homework, a friend’s or siblings to help them do it, and snacks to eat. I feel like the author of this piece has never set foot in a classroom of students.
THIS. This article is pathetic coming from a university. So intellectually dishonest, refusing to address the havoc of capitalism and poverty plays on academic success in life. How can they in one sentence use poor kids in an argument and never once address that poor children have access to damn near 0 of the resources affluent kids have? Draw me a picture and let’s talk about feelings lmao what a joke is that gonna put food in their belly so they can have the calories to burn in order to use their brain to study? What about quiet their 7 other siblings that they share a single bedroom with for hours? Is it gonna force the single mom to magically be at home and at work at the same time to cook food while you study and be there to throw an encouraging word?
Also the “parents don’t need to be a parent and be able to guide their kid at all academically they just need to exist in the next room” is wild. Its one thing if a parent straight up is not equipped but to say kids can just figured it out is…. wow coming from an educator What’s next the teacher doesn’t need to teach cause the kid can just follow the packet and figure it out?
Well then get a tutor right? Oh wait you are poor only affluent kids can afford a tutor for their hours of homework a day were they on average have none of the worries a poor child does. Does this address that poor children are more likely to also suffer abuse and mental illness? Like mentioned what about kids that can’t learn or comprehend the forced standardized way? Just let em fail? These children regularly are not in “special education”(some of those are a joke in their own and full of neglect and abuse) programs cause most aren’t even acknowledged as having disabilities or disorders.
But yes all and all those pesky poor kids just aren’t being worked hard enough lol pretty sure poor children’s existence just in childhood is more work, stress, and responsibility alone than an affluent child’s entire life cycle. Love they never once talked about the quality of education in the classroom being so bad between the poor and affluent it can qualify as segregation, just basically blamed poor people for being lazy, good job capitalism for failing us once again!
why the hell?
you should feel bad for saying this, this article can be helpful for people who has to write a essay about it
This is more of a political rant than it is about homework
I know a teacher who has told his students their homework is to find something they are interested in, pursue it and then come share what they learn. The student responses are quite compelling. One girl taught herself German so she could talk to her grandfather. One boy did a research project on Nelson Mandela because the teacher had mentioned him in class. Another boy, a both on the autism spectrum, fixed his family’s computer. The list goes on. This is fourth grade. I think students are highly motivated to learn, when we step aside and encourage them.
The whole point of homework is to give the students a chance to use the material that they have been presented with in class. If they never have the opportunity to use that information, and discover that it is actually useful, it will be in one ear and out the other. As a science teacher, it is critical that the students are challenged to use the material they have been presented with, which gives them the opportunity to actually think about it rather than regurgitate “facts”. Well designed homework forces the student to think conceptually, as opposed to regurgitation, which is never a pretty sight
Wonderful discussion. and yes, homework helps in learning and building skills in students.
not true it just causes kids to stress
Homework can be both beneficial and unuseful, if you will. There are students who are gifted in all subjects in school and ones with disabilities. Why should the students who are gifted get the lucky break, whereas the people who have disabilities suffer? The people who were born with this “gift” go through school with ease whereas people with disabilities struggle with the work given to them. I speak from experience because I am one of those students: the ones with disabilities. Homework doesn’t benefit “us”, it only tears us down and put us in an abyss of confusion and stress and hopelessness because we can’t learn as fast as others. Or we can’t handle the amount of work given whereas the gifted students go through it with ease. It just brings us down and makes us feel lost; because no mater what, it feels like we are destined to fail. It feels like we weren’t “cut out” for success.
homework does help
here is the thing though, if a child is shoved in the face with a whole ton of homework that isn’t really even considered homework it is assignments, it’s not helpful. the teacher should make homework more of a fun learning experience rather than something that is dreaded
This article was wonderful, I am going to ask my teachers about extra, or at all giving homework.
I agree. Especially when you have homework before an exam. Which is distasteful as you’ll need that time to study. It doesn’t make any sense, nor does us doing homework really matters as It’s just facts thrown at us.
Homework is too severe and is just too much for students, schools need to decrease the amount of homework. When teachers assign homework they forget that the students have other classes that give them the same amount of homework each day. Students need to work on social skills and life skills.
I disagree.
Beyond achievement, proponents of homework argue that it can have many other beneficial effects. They claim it can help students develop good study habits so they are ready to grow as their cognitive capacities mature. It can help students recognize that learning can occur at home as well as at school. Homework can foster independent learning and responsible character traits. And it can give parents an opportunity to see what’s going on at school and let them express positive attitudes toward achievement.
Homework is helpful because homework helps us by teaching us how to learn a specific topic.
As a student myself, I can say that I have almost never gotten the full 9 hours of recommended sleep time, because of homework. (Now I’m writing an essay on it in the middle of the night D=)
I am a 10 year old kid doing a report about “Is homework good or bad” for homework before i was going to do homework is bad but the sources from this site changed my mind!
Homeowkr is god for stusenrs
I agree with hunter because homework can be so stressful especially with this whole covid thing no one has time for homework and every one just wants to get back to there normal lives it is especially stressful when you go on a 2 week vaca 3 weeks into the new school year and and then less then a week after you come back from the vaca you are out for over a month because of covid and you have no way to get the assignment done and turned in
As great as homework is said to be in the is article, I feel like the viewpoint of the students was left out. Every where I go on the internet researching about this topic it almost always has interviews from teachers, professors, and the like. However isn’t that a little biased? Of course teachers are going to be for homework, they’re not the ones that have to stay up past midnight completing the homework from not just one class, but all of them. I just feel like this site is one-sided and you should include what the students of today think of spending four hours every night completing 6-8 classes worth of work.
Are we talking about homework or practice? Those are two very different things and can result in different outcomes.
Homework is a graded assignment. I do not know of research showing the benefits of graded assignments going home.
Practice; however, can be extremely beneficial, especially if there is some sort of feedback (not a grade but feedback). That feedback can come from the teacher, another student or even an automated grading program.
As a former band director, I assigned daily practice. I never once thought it would be appropriate for me to require the students to turn in a recording of their practice for me to grade. Instead, I had in-class assignments/assessments that were graded and directly related to the practice assigned.
I would really like to read articles on “homework” that truly distinguish between the two.
oof i feel bad good luck!
thank you guys for the artical because I have to finish an assingment. yes i did cite it but just thanks
thx for the article guys.
Homework is good
I think homework is helpful AND harmful. Sometimes u can’t get sleep bc of homework but it helps u practice for school too so idk.
I agree with this Article. And does anyone know when this was published. I would like to know.
It was published FEb 19, 2019.
Studies have shown that homework improved student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college.
i think homework can help kids but at the same time not help kids
This article is so out of touch with majority of homes it would be laughable if it wasn’t so incredibly sad.
There is no value to homework all it does is add stress to already stressed homes. Parents or adults magically having the time or energy to shepherd kids through homework is dome sort of 1950’s fantasy.
What lala land do these teachers live in?
Homework gives noting to the kid
Homework is Bad
homework is bad.
why do kids even have homework?
Comments are closed.
Latest from Bostonia
Campus reacts and responds to israel-hamas war, reading list: what the pandemic revealed, remembering com’s david anable, cas’ john stone, “intellectual brilliance and brilliant kindness”, one good deed: christine kannler (cas’96, sph’00, camed’00), william fairfield warren society inducts new members, spreading art appreciation, restoring the “black angels” to medical history, in the kitchen with jacques pépin, feedback: readers weigh in on bu’s new president, com’s new expert on misinformation, and what’s really dividing the nation, the gifts of great teaching, sth’s walter fluker honored by roosevelt institute, alum’s debut book is a ramadan story for children, my big idea: covering construction sites with art, former terriers power new professional women’s hockey league, five trailblazing alums to celebrate during women’s history month, alum beata coloyan is boston mayor michelle wu’s “eyes and ears” in boston neighborhoods, bu alum nina yoshida nelsen (cfa’01,’03) named artistic director of boston lyric opera, my big idea: blending wildlife conservation and human welfare, a guide to black women’s health.
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/71970990/05_nohomework_Jiayue_Li.0.jpg)
Filed under:
- The Highlight
Nobody knows what the point of homework is
The homework wars are back.
Share this story
- Share this on Facebook
- Share this on Twitter
- Share this on Reddit
- Share All sharing options
Share All sharing options for: Nobody knows what the point of homework is
As the Covid-19 pandemic began and students logged into their remote classrooms, all work, in effect, became homework. But whether or not students could complete it at home varied. For some, schoolwork became public-library work or McDonald’s-parking-lot work.
Luis Torres, the principal of PS 55, a predominantly low-income community elementary school in the south Bronx, told me that his school secured Chromebooks for students early in the pandemic only to learn that some lived in shelters that blocked wifi for security reasons. Others, who lived in housing projects with poor internet reception, did their schoolwork in laundromats.
According to a 2021 Pew survey , 25 percent of lower-income parents said their children, at some point, were unable to complete their schoolwork because they couldn’t access a computer at home; that number for upper-income parents was 2 percent.
The issues with remote learning in March 2020 were new. But they highlighted a divide that had been there all along in another form: homework. And even long after schools have resumed in-person classes, the pandemic’s effects on homework have lingered.
Over the past three years, in response to concerns about equity, schools across the country, including in Sacramento, Los Angeles , San Diego , and Clark County, Nevada , made permanent changes to their homework policies that restricted how much homework could be given and how it could be graded after in-person learning resumed.
Three years into the pandemic, as districts and teachers reckon with Covid-era overhauls of teaching and learning, schools are still reconsidering the purpose and place of homework. Whether relaxing homework expectations helps level the playing field between students or harms them by decreasing rigor is a divisive issue without conclusive evidence on either side, echoing other debates in education like the elimination of standardized test scores from some colleges’ admissions processes.
I first began to wonder if the homework abolition movement made sense after speaking with teachers in some Massachusetts public schools, who argued that rather than help disadvantaged kids, stringent homework restrictions communicated an attitude of low expectations. One, an English teacher, said she felt the school had “just given up” on trying to get the students to do work; another argued that restrictions that prohibit teachers from assigning take-home work that doesn’t begin in class made it difficult to get through the foreign-language curriculum. Teachers in other districts have raised formal concerns about homework abolition’s ability to close gaps among students rather than widening them.
Many education experts share this view. Harris Cooper, a professor emeritus of psychology at Duke who has studied homework efficacy, likened homework abolition to “playing to the lowest common denominator.”
But as I learned after talking to a variety of stakeholders — from homework researchers to policymakers to parents of schoolchildren — whether to abolish homework probably isn’t the right question. More important is what kind of work students are sent home with and where they can complete it. Chances are, if schools think more deeply about giving constructive work, time spent on homework will come down regardless.
There’s no consensus on whether homework works
The rise of the no-homework movement during the Covid-19 pandemic tapped into long-running disagreements over homework’s impact on students. The purpose and effectiveness of homework have been disputed for well over a century. In 1901, for instance, California banned homework for students up to age 15, and limited it for older students, over concerns that it endangered children’s mental and physical health. The newest iteration of the anti-homework argument contends that the current practice punishes students who lack support and rewards those with more resources, reinforcing the “myth of meritocracy.”
But there is still no research consensus on homework’s effectiveness; no one can seem to agree on what the right metrics are. Much of the debate relies on anecdotes, intuition, or speculation.
Researchers disagree even on how much research exists on the value of homework. Kathleen Budge, the co-author of Turning High-Poverty Schools Into High-Performing Schools and a professor at Boise State, told me that homework “has been greatly researched.” Denise Pope, a Stanford lecturer and leader of the education nonprofit Challenge Success, said, “It’s not a highly researched area because of some of the methodological problems.”
Experts who are more sympathetic to take-home assignments generally support the “10-minute rule,” a framework that estimates the ideal amount of homework on any given night by multiplying the student’s grade by 10 minutes. (A ninth grader, for example, would have about 90 minutes of work a night.) Homework proponents argue that while it is difficult to design randomized control studies to test homework’s effectiveness, the vast majority of existing studies show a strong positive correlation between homework and high academic achievement for middle and high school students. Prominent critics of homework argue that these correlational studies are unreliable and point to studies that suggest a neutral or negative effect on student performance. Both agree there is little to no evidence for homework’s effectiveness at an elementary school level, though proponents often argue that it builds constructive habits for the future.
For anyone who remembers homework assignments from both good and bad teachers, this fundamental disagreement might not be surprising. Some homework is pointless and frustrating to complete. Every week during my senior year of high school, I had to analyze a poem for English and decorate it with images found on Google; my most distinct memory from that class is receiving a demoralizing 25-point deduction because I failed to present my analysis on a poster board. Other assignments really do help students learn: After making an adapted version of Chairman Mao’s Little Red Book for a ninth grade history project, I was inspired to check out from the library and read a biography of the Chinese ruler.
For homework opponents, the first example is more likely to resonate. “We’re all familiar with the negative effects of homework: stress, exhaustion, family conflict, less time for other activities, diminished interest in learning,” Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth, which challenges common justifications for homework, told me in an email. “And these effects may be most pronounced among low-income students.” Kohn believes that schools should make permanent any moratoria implemented during the pandemic, arguing that there are no positives at all to outweigh homework’s downsides. Recent studies , he argues , show the benefits may not even materialize during high school.
In the Marlborough Public Schools, a suburban district 45 minutes west of Boston, school policy committee chair Katherine Hennessy described getting kids to complete their homework during remote education as “a challenge, to say the least.” Teachers found that students who spent all day on their computers didn’t want to spend more time online when the day was over. So, for a few months, the school relaxed the usual practice and teachers slashed the quantity of nightly homework.
Online learning made the preexisting divides between students more apparent, she said. Many students, even during normal circumstances, lacked resources to keep them on track and focused on completing take-home assignments. Though Marlborough Schools is more affluent than PS 55, Hennessy said many students had parents whose work schedules left them unable to provide homework help in the evenings. The experience tracked with a common divide in the country between children of different socioeconomic backgrounds.
So in October 2021, months after the homework reduction began, the Marlborough committee made a change to the district’s policy. While teachers could still give homework, the assignments had to begin as classwork. And though teachers could acknowledge homework completion in a student’s participation grade, they couldn’t count homework as its own grading category. “Rigorous learning in the classroom does not mean that that classwork must be assigned every night,” the policy stated . “Extensions of class work is not to be used to teach new content or as a form of punishment.”
Canceling homework might not do anything for the achievement gap
The critiques of homework are valid as far as they go, but at a certain point, arguments against homework can defy the commonsense idea that to retain what they’re learning, students need to practice it.
“Doesn’t a kid become a better reader if he reads more? Doesn’t a kid learn his math facts better if he practices them?” said Cathy Vatterott, an education researcher and professor emeritus at the University of Missouri-St. Louis. After decades of research, she said it’s still hard to isolate the value of homework, but that doesn’t mean it should be abandoned.
Blanket vilification of homework can also conflate the unique challenges facing disadvantaged students as compared to affluent ones, which could have different solutions. “The kids in the low-income schools are being hurt because they’re being graded, unfairly, on time they just don’t have to do this stuff,” Pope told me. “And they’re still being held accountable for turning in assignments, whether they’re meaningful or not.” On the other side, “Palo Alto kids” — students in Silicon Valley’s stereotypically pressure-cooker public schools — “are just bombarded and overloaded and trying to stay above water.”
Merely getting rid of homework doesn’t solve either problem. The United States already has the second-highest disparity among OECD (the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) nations between time spent on homework by students of high and low socioeconomic status — a difference of more than three hours, said Janine Bempechat, clinical professor at Boston University and author of No More Mindless Homework .
When she interviewed teachers in Boston-area schools that had cut homework before the pandemic, Bempechat told me, “What they saw immediately was parents who could afford it immediately enrolled their children in the Russian School of Mathematics,” a math-enrichment program whose tuition ranges from $140 to about $400 a month. Getting rid of homework “does nothing for equity; it increases the opportunity gap between wealthier and less wealthy families,” she said. “That solution troubles me because it’s no solution at all.”
A group of teachers at Wakefield High School in Arlington, Virginia, made the same point after the school district proposed an overhaul of its homework policies, including removing penalties for missing homework deadlines, allowing unlimited retakes, and prohibiting grading of homework.
“Given the emphasis on equity in today’s education systems,” they wrote in a letter to the school board, “we believe that some of the proposed changes will actually have a detrimental impact towards achieving this goal. Families that have means could still provide challenging and engaging academic experiences for their children and will continue to do so, especially if their children are not experiencing expected rigor in the classroom.” At a school where more than a third of students are low-income, the teachers argued, the policies would prompt students “to expect the least of themselves in terms of effort, results, and responsibility.”
Not all homework is created equal
Despite their opposing sides in the homework wars, most of the researchers I spoke to made a lot of the same points. Both Bempechat and Pope were quick to bring up how parents and schools confuse rigor with workload, treating the volume of assignments as a proxy for quality of learning. Bempechat, who is known for defending homework, has written extensively about how plenty of it lacks clear purpose, requires the purchasing of unnecessary supplies, and takes longer than it needs to. Likewise, when Pope instructs graduate-level classes on curriculum, she asks her students to think about the larger purpose they’re trying to achieve with homework: If they can get the job done in the classroom, there’s no point in sending home more work.
At its best, pandemic-era teaching facilitated that last approach. Honolulu-based teacher Christina Torres Cawdery told me that, early in the pandemic, she often had a cohort of kids in her classroom for four hours straight, as her school tried to avoid too much commingling. She couldn’t lecture for four hours, so she gave the students plenty of time to complete independent and project-based work. At the end of most school days, she didn’t feel the need to send them home with more to do.
A similar limited-homework philosophy worked at a public middle school in Chelsea, Massachusetts. A couple of teachers there turned as much class as possible into an opportunity for small-group practice, allowing kids to work on problems that traditionally would be assigned for homework, Jessica Flick, a math coach who leads department meetings at the school, told me. It was inspired by a philosophy pioneered by Simon Fraser University professor Peter Liljedahl, whose influential book Building Thinking Classrooms in Mathematics reframes homework as “check-your-understanding questions” rather than as compulsory work. Last year, Flick found that the two eighth grade classes whose teachers adopted this strategy performed the best on state tests, and this year, she has encouraged other teachers to implement it.
Teachers know that plenty of homework is tedious and unproductive. Jeannemarie Dawson De Quiroz, who has taught for more than 20 years in low-income Boston and Los Angeles pilot and charter schools, says that in her first years on the job she frequently assigned “drill and kill” tasks and questions that she now feels unfairly stumped students. She said designing good homework wasn’t part of her teaching programs, nor was it meaningfully discussed in professional development. With more experience, she turned as much class time as she could into practice time and limited what she sent home.
“The thing about homework that’s sticky is that not all homework is created equal,” says Jill Harrison Berg, a former teacher and the author of Uprooting Instructional Inequity . “Some homework is a genuine waste of time and requires lots of resources for no good reason. And other homework is really useful.”
Cutting homework has to be part of a larger strategy
The takeaways are clear: Schools can make cuts to homework, but those cuts should be part of a strategy to improve the quality of education for all students. If the point of homework was to provide more practice, districts should think about how students can make it up during class — or offer time during or after school for students to seek help from teachers. If it was to move the curriculum along, it’s worth considering whether strategies like Liljedahl’s can get more done in less time.
Some of the best thinking around effective assignments comes from those most critical of the current practice. Denise Pope proposes that, before assigning homework, teachers should consider whether students understand the purpose of the work and whether they can do it without help. If teachers think it’s something that can’t be done in class, they should be mindful of how much time it should take and the feedback they should provide. It’s questions like these that De Quiroz considered before reducing the volume of work she sent home.
More than a year after the new homework policy began in Marlborough, Hennessy still hears from parents who incorrectly “think homework isn’t happening” despite repeated assurances that kids still can receive work. She thinks part of the reason is that education has changed over the years. “I think what we’re trying to do is establish that homework may be an element of educating students,” she told me. “But it may not be what parents think of as what they grew up with. ... It’s going to need to adapt, per the teaching and the curriculum, and how it’s being delivered in each classroom.”
For the policy to work, faculty, parents, and students will all have to buy into a shared vision of what school ought to look like. The district is working on it — in November, it hosted and uploaded to YouTube a round-table discussion on homework between district administrators — but considering the sustained confusion, the path ahead seems difficult.
When I asked Luis Torres about whether he thought homework serves a useful part in PS 55’s curriculum, he said yes, of course it was — despite the effort and money it takes to keep the school open after hours to help them do it. “The children need the opportunity to practice,” he said. “If you don’t give them opportunities to practice what they learn, they’re going to forget.” But Torres doesn’t care if the work is done at home. The school stays open until around 6 pm on weekdays, even during breaks. Tutors through New York City’s Department of Youth and Community Development programs help kids with work after school so they don’t need to take it with them.
As schools weigh the purpose of homework in an unequal world, it’s tempting to dispose of a practice that presents real, practical problems to students across the country. But getting rid of homework is unlikely to do much good on its own. Before cutting it, it’s worth thinking about what good assignments are meant to do in the first place. It’s crucial that students from all socioeconomic backgrounds tackle complex quantitative problems and hone their reading and writing skills. It’s less important that the work comes home with them.
Jacob Sweet is a freelance writer in Somerville, Massachusetts. He is a frequent contributor to the New Yorker, among other publications.
Will you help keep Vox free for all?
Millions rely on Vox’s journalism to understand the coronavirus crisis. We believe it pays off for all of us, as a society and a democracy, when our neighbors and fellow citizens can access clear, concise information on the pandemic. But our distinctive explanatory journalism is expensive. Support from our readers helps us keep it free for everyone. If you have already made a financial contribution to Vox, thank you. If not, please consider making a contribution today from as little as $3.
We accept credit card, Apple Pay, and Google Pay. You can also contribute via
Can we protect and profit from the oceans?
Sometimes kids need a push. here’s how to do it kindly., who gets to flourish, sign up for the newsletter today, explained, thanks for signing up.
Check your inbox for a welcome email.
Oops. Something went wrong. Please enter a valid email and try again.

Homework: How to Effectively Build the Learning Bridge

How has the global health crisis impacted the place that homework has in student learning and the school-home connection? Homework holds its place as a school tradition, expected by students and their parents as part of the experience of growing and learning. While there is ongoing debate about homework’s effectiveness, it is traditionally seen as a tool that strengthens academics by providing learning practice at home. John Hattie’s meta-analysis of relevant research on educational practices found that the overall effects of homework on learning are positive, and that the positive effect is highest for junior high and high school students but generally neutral for elementary students. In addition, there is variability depending on the type of homework as well as student demographics (Hattie, 2008).
Schools implementing the Responsive Classroom approach, whether in person or virtually, use homework to effectively build a learning bridge between home and school. When homework is used as a tool to build social, emotional, and academic learning beyond the school day, it takes on a different look and purpose than just more work to do at home. The goal of Responsive Classroom schools is to design homework that meets the basic needs of significance and belonging for every student by strengthening relationships, differentiating what success looks like for each child, and supporting students’ social, emotional, and academic learning.
Focus on Relationships
Homework that impedes relationships— either teacher-to-student, teacher-toparent, or student-to-parent—can potentially damage the home-school partnership. When educators examine the amount, type, and expectations of homework, they often start with the impact of homework on academic achievement. But when schools look beyond academic achievement and also include relationships, they will often rethink the look and purpose of homework.
Effectively building this school-to-home connection starts by replacing homework that impedes relationships with homework that will enhance them. Examples for building these connections include ways for students to share about family traditions, cultural practices, and/or family adventures. Lauren Komanitsky, a special education teacher at Christa McAuliffe Middle School in Jackson, New Jersey, observes:
I’ve seen tremendous enthusiasm for homework and projects that involve family members and their family history. [Students] love to learn about ancestors, interesting facts and stories, and simply getting a deeper understanding of their background. It inspires pride in them and that’s important for their identity. Students also love to do surveys and interviews of their family members. I think anything designed to create good, meaningful conversation between students and their families is time well spent. Lauren Komanitsky (personal communication, February 7, 2021)
Schools that use homework to strengthen home-school relationships embed opportunities for students to develop belonging and significance. As students share the home connections with their classmates and teachers, the classroom community will develop a larger sense of belonging because students see connections among common experiences.
Build Success for Every Student
Classrooms are diverse communities. While teachers intentionally differentiate learning during the school day, providing homework that meets the individual and cultural needs of each student requires additional attention.
One strategy for success for every student is to provide choice. Komanitsky has seen this strategy work when she has had students reflect on what they need and then select homework to meet that need:
Having kids select specific problems from a group, select what part of an overall project they are choosing to focus on, etc. . . . helps with creating a sense of autonomy. When we can give kids a choice in their learning based on their own self-reflection, they learn what it feels like to be in control of the process and this leads to more success. Lauren Komanitsky (personal communication, February 7, 2021)
When homework is designed for success for each student, the bridge between home and school supports a higher level of success and engagement.
Include Practice of Social and Emotional Learning Skills
The first guiding principle of the Responsive Classroom approach states, “Teaching social and emotional skills is as important as teaching academic content.” Social and emotional learning (SEL) is embedded in academic learning throughout the school day. Teachers can create a bridge between home and school by suggesting opportunities for students to practice SEL skills at home and in their community. For example, parents can have their children practice speaking with confidence by having them “make a request, place an order, or thank customer service workers” (Wilson, 2014, p. 67).
In addition, homework may involve students having conversations with family members about their learning histories—the successes, struggles, and strategies t hey encountered when they were students at different levels. When family members share their learning histories, students discover the application of the SEL and academic competencies of perseverance, cooperation, and responsibility. As Komanitsky points out:
When we share how we overcame struggles in certain academic subjects, it encourages perseverance and resilience in our students. Having parents and kids discuss their personal strengths and weaknesses and how they compensate when necessary is also a really good conversation. Lauren Komanitsky (personal communication, February 7, 2021)
Homework that focuses on SEL competencies provides for the transfer of these vital skills to a variety of real-life situations, both at home and in the community.
When schools approach homework as an extension of the learning day and see it as a way to strengthen relationships—between teachers and parents, students and parents, and students and teachers—homework becomes a valuable part of the school experience for every child. Students’ needs for belonging and significance are met and strengthened when homework provides for individual success. And when educators view homework as a tool to strengthen academic, social, and emotional learning, it becomes a valuable piece of the learning puzzle for every student.

- Hattie, J. (2008). Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement. Routledge.
- Wilson, M. B. (2014). The language of learning: Teaching students core thinking, listening, and speaking skills. Center for Responsive Schools, Inc
Read our research on: Abortion | Podcasts | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
What we know about online learning and the homework gap amid the pandemic.

America’s K-12 students are returning to classrooms this fall after 18 months of virtual learning at home during the COVID-19 pandemic. Some students who lacked the home internet connectivity needed to finish schoolwork during this time – an experience often called the “ homework gap ” – may continue to feel the effects this school year.
Here is what Pew Research Center surveys found about the students most likely to be affected by the homework gap and their experiences learning from home.
Children across the United States are returning to physical classrooms this fall after 18 months at home, raising questions about how digital disparities at home will affect the existing homework gap between certain groups of students.
Methodology for each Pew Research Center poll can be found at the links in the post.
With the exception of the 2018 survey, everyone who took part in the surveys is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
The 2018 data on U.S. teens comes from a Center poll of 743 U.S. teens ages 13 to 17 conducted March 7 to April 10, 2018, using the NORC AmeriSpeak panel. AmeriSpeak is a nationally representative, probability-based panel of the U.S. household population. Randomly selected U.S. households are sampled with a known, nonzero probability of selection from the NORC National Frame, and then contacted by U.S. mail, telephone or face-to-face interviewers. Read more details about the NORC AmeriSpeak panel methodology .
Around nine-in-ten U.S. parents with K-12 children at home (93%) said their children have had some online instruction since the coronavirus outbreak began in February 2020, and 30% of these parents said it has been very or somewhat difficult for them to help their children use technology or the internet as an educational tool, according to an April 2021 Pew Research Center survey .
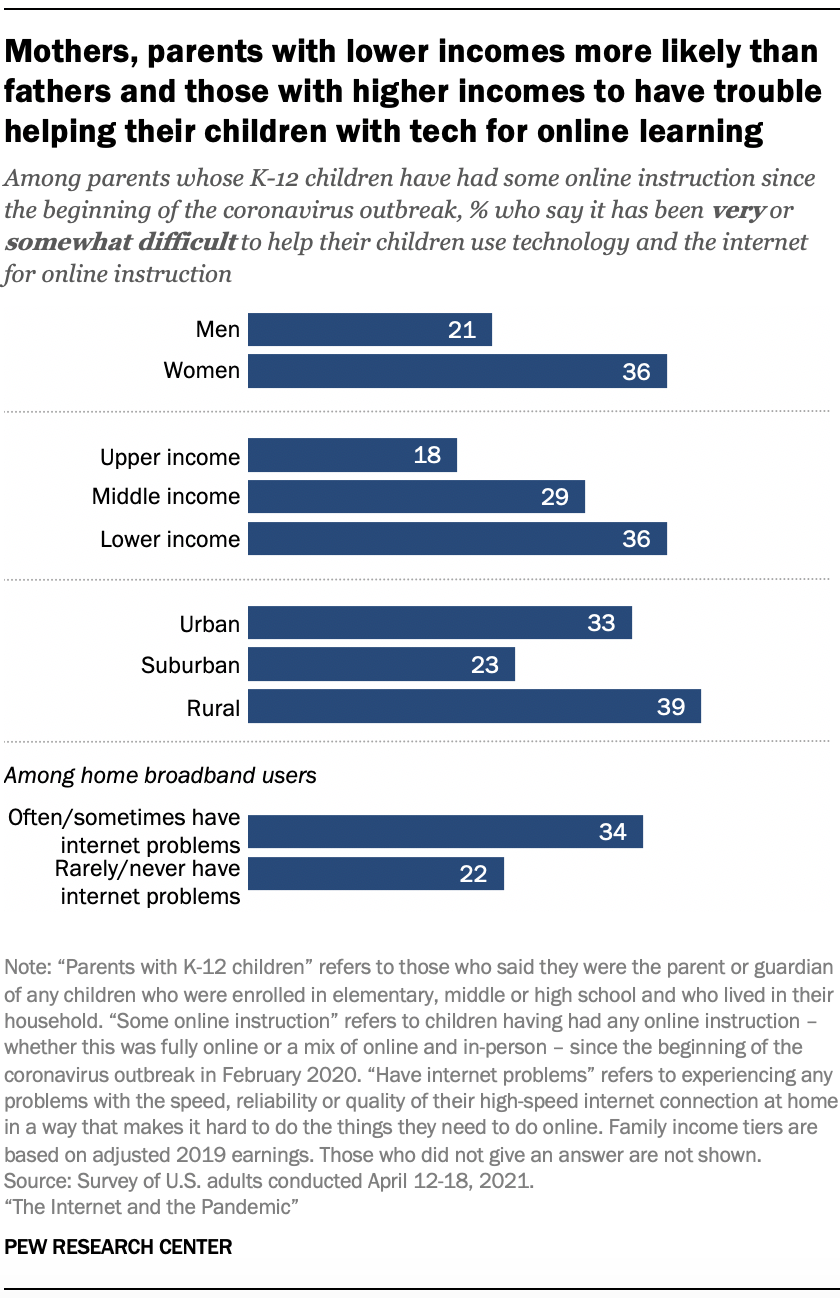
Gaps existed for certain groups of parents. For example, parents with lower and middle incomes (36% and 29%, respectively) were more likely to report that this was very or somewhat difficult, compared with just 18% of parents with higher incomes.
This challenge was also prevalent for parents in certain types of communities – 39% of rural residents and 33% of urban residents said they have had at least some difficulty, compared with 23% of suburban residents.
Around a third of parents with children whose schools were closed during the pandemic (34%) said that their child encountered at least one technology-related obstacle to completing their schoolwork during that time. In the April 2021 survey, the Center asked parents of K-12 children whose schools had closed at some point about whether their children had faced three technology-related obstacles. Around a quarter of parents (27%) said their children had to do schoolwork on a cellphone, 16% said their child was unable to complete schoolwork because of a lack of computer access at home, and another 14% said their child had to use public Wi-Fi to finish schoolwork because there was no reliable connection at home.
Parents with lower incomes whose children’s schools closed amid COVID-19 were more likely to say their children faced technology-related obstacles while learning from home. Nearly half of these parents (46%) said their child faced at least one of the three obstacles to learning asked about in the survey, compared with 31% of parents with midrange incomes and 18% of parents with higher incomes.
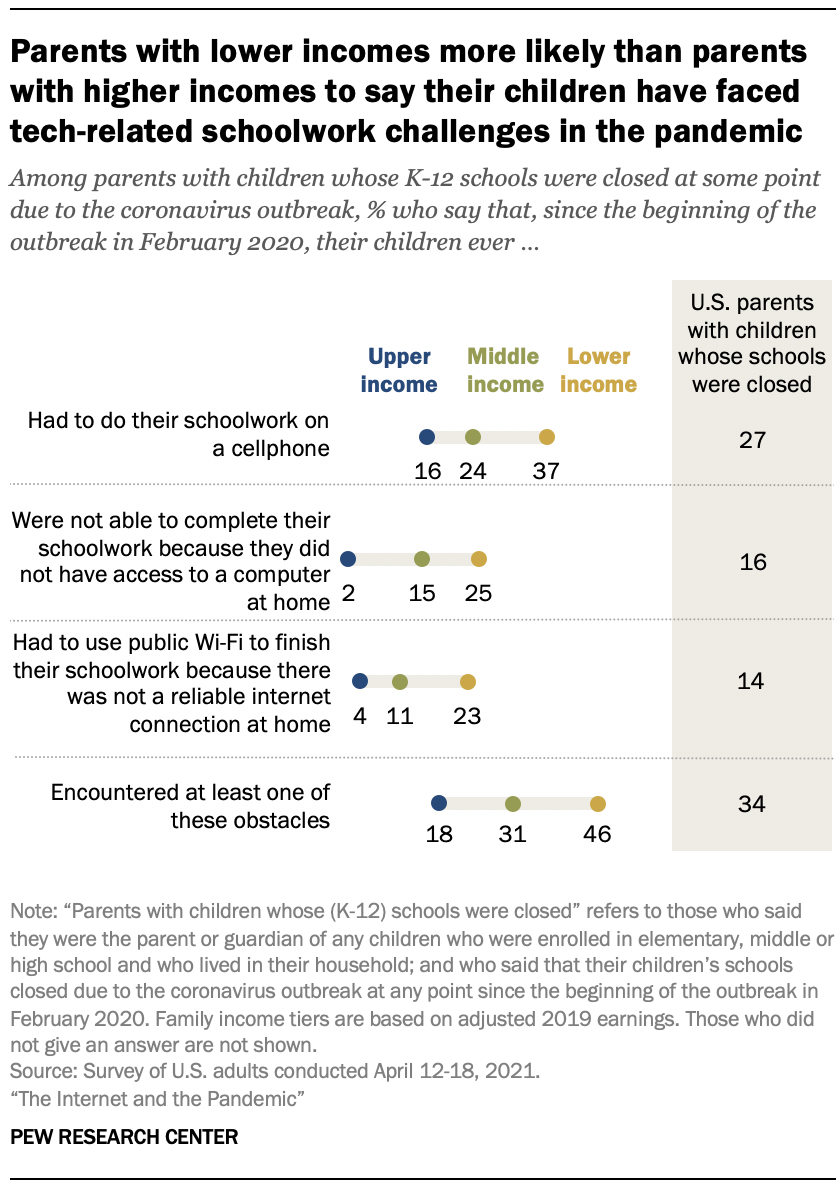
Of the three obstacles asked about in the survey, parents with lower incomes were most likely to say that their child had to do their schoolwork on a cellphone (37%). About a quarter said their child was unable to complete their schoolwork because they did not have computer access at home (25%), or that they had to use public Wi-Fi because they did not have a reliable internet connection at home (23%).
A Center survey conducted in April 2020 found that, at that time, 59% of parents with lower incomes who had children engaged in remote learning said their children would likely face at least one of the obstacles asked about in the 2021 survey.
A year into the outbreak, an increasing share of U.S. adults said that K-12 schools have a responsibility to provide all students with laptop or tablet computers in order to help them complete their schoolwork at home during the pandemic. About half of all adults (49%) said this in the spring 2021 survey, up 12 percentage points from a year earlier. An additional 37% of adults said that schools should provide these resources only to students whose families cannot afford them, and just 13% said schools do not have this responsibility.
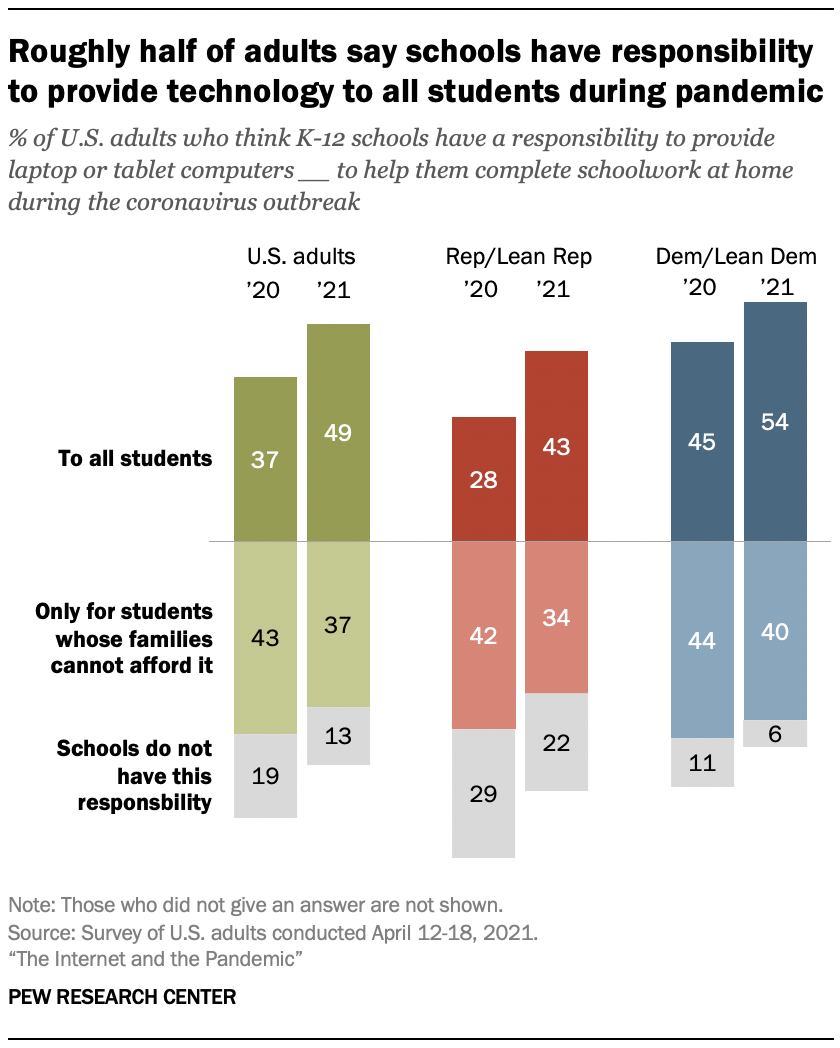
While larger shares of both political parties in April 2021 said K-12 schools have a responsibility to provide computers to all students in order to help them complete schoolwork at home, there was a 15-point change among Republicans: 43% of Republicans and those who lean to the Republican Party said K-12 schools have this responsibility, compared with 28% last April. In the 2021 survey, 22% of Republicans also said schools do not have this responsibility at all, compared with 6% of Democrats and Democratic leaners.
Even before the pandemic, Black teens and those living in lower-income households were more likely than other groups to report trouble completing homework assignments because they did not have reliable technology access. Nearly one-in-five teens ages 13 to 17 (17%) said they are often or sometimes unable to complete homework assignments because they do not have reliable access to a computer or internet connection, a 2018 Center survey of U.S. teens found.
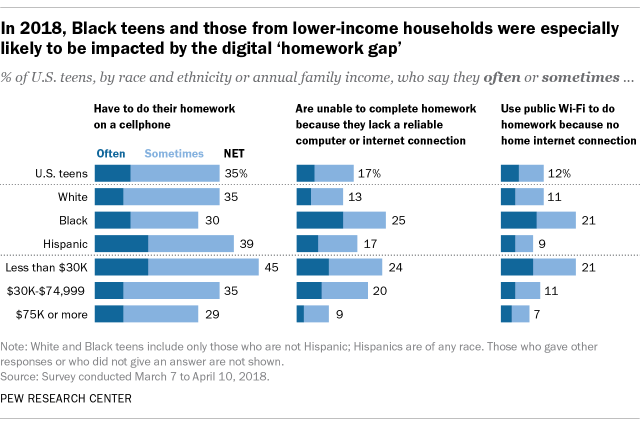
One-quarter of Black teens said they were at least sometimes unable to complete their homework due to a lack of digital access, including 13% who said this happened to them often. Just 4% of White teens and 6% of Hispanic teens said this often happened to them. (There were not enough Asian respondents in the survey sample to be broken out into a separate analysis.)
A wide gap also existed by income level: 24% of teens whose annual family income was less than $30,000 said the lack of a dependable computer or internet connection often or sometimes prohibited them from finishing their homework, but that share dropped to 9% among teens who lived in households earning $75,000 or more a year.

Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivered Saturday mornings
What federal education data shows about students with disabilities in the U.S.
Most americans who go to religious services say they would trust their clergy’s advice on covid-19 vaccines, unvaccinated americans are at higher risk from covid-19 but express less concern than vaccinated adults, americans who relied most on trump for covid-19 news among least likely to be vaccinated, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
- Our Mission

What’s the Right Amount of Homework?
Decades of research show that homework has some benefits, especially for students in middle and high school—but there are risks to assigning too much.
Many teachers and parents believe that homework helps students build study skills and review concepts learned in class. Others see homework as disruptive and unnecessary, leading to burnout and turning kids off to school. Decades of research show that the issue is more nuanced and complex than most people think: Homework is beneficial, but only to a degree. Students in high school gain the most, while younger kids benefit much less.
The National PTA and the National Education Association support the “ 10-minute homework guideline ”—a nightly 10 minutes of homework per grade level. But many teachers and parents are quick to point out that what matters is the quality of the homework assigned and how well it meets students’ needs, not the amount of time spent on it.
The guideline doesn’t account for students who may need to spend more—or less—time on assignments. In class, teachers can make adjustments to support struggling students, but at home, an assignment that takes one student 30 minutes to complete may take another twice as much time—often for reasons beyond their control. And homework can widen the achievement gap, putting students from low-income households and students with learning disabilities at a disadvantage.
However, the 10-minute guideline is useful in setting a limit: When kids spend too much time on homework, there are real consequences to consider.
Small Benefits for Elementary Students
As young children begin school, the focus should be on cultivating a love of learning, and assigning too much homework can undermine that goal. And young students often don’t have the study skills to benefit fully from homework, so it may be a poor use of time (Cooper, 1989 ; Cooper et al., 2006 ; Marzano & Pickering, 2007 ). A more effective activity may be nightly reading, especially if parents are involved. The benefits of reading are clear: If students aren’t proficient readers by the end of third grade, they’re less likely to succeed academically and graduate from high school (Fiester, 2013 ).
For second-grade teacher Jacqueline Fiorentino, the minor benefits of homework did not outweigh the potential drawback of turning young children against school at an early age, so she experimented with dropping mandatory homework. “Something surprising happened: They started doing more work at home,” Fiorentino writes . “This inspiring group of 8-year-olds used their newfound free time to explore subjects and topics of interest to them.” She encouraged her students to read at home and offered optional homework to extend classroom lessons and help them review material.
Moderate Benefits for Middle School Students
As students mature and develop the study skills necessary to delve deeply into a topic—and to retain what they learn—they also benefit more from homework. Nightly assignments can help prepare them for scholarly work, and research shows that homework can have moderate benefits for middle school students (Cooper et al., 2006 ). Recent research also shows that online math homework, which can be designed to adapt to students’ levels of understanding, can significantly boost test scores (Roschelle et al., 2016 ).
There are risks to assigning too much, however: A 2015 study found that when middle school students were assigned more than 90 to 100 minutes of daily homework, their math and science test scores began to decline (Fernández-Alonso, Suárez-Álvarez, & Muñiz, 2015 ). Crossing that upper limit can drain student motivation and focus. The researchers recommend that “homework should present a certain level of challenge or difficulty, without being so challenging that it discourages effort.” Teachers should avoid low-effort, repetitive assignments, and assign homework “with the aim of instilling work habits and promoting autonomous, self-directed learning.”
In other words, it’s the quality of homework that matters, not the quantity. Brian Sztabnik, a veteran middle and high school English teacher, suggests that teachers take a step back and ask themselves these five questions :
- How long will it take to complete?
- Have all learners been considered?
- Will an assignment encourage future success?
- Will an assignment place material in a context the classroom cannot?
- Does an assignment offer support when a teacher is not there?
More Benefits for High School Students, but Risks as Well
By the time they reach high school, students should be well on their way to becoming independent learners, so homework does provide a boost to learning at this age, as long as it isn’t overwhelming (Cooper et al., 2006 ; Marzano & Pickering, 2007 ). When students spend too much time on homework—more than two hours each night—it takes up valuable time to rest and spend time with family and friends. A 2013 study found that high school students can experience serious mental and physical health problems, from higher stress levels to sleep deprivation, when assigned too much homework (Galloway, Conner, & Pope, 2013 ).
Homework in high school should always relate to the lesson and be doable without any assistance, and feedback should be clear and explicit.
Teachers should also keep in mind that not all students have equal opportunities to finish their homework at home, so incomplete homework may not be a true reflection of their learning—it may be more a result of issues they face outside of school. They may be hindered by issues such as lack of a quiet space at home, resources such as a computer or broadband connectivity, or parental support (OECD, 2014 ). In such cases, giving low homework scores may be unfair.
Since the quantities of time discussed here are totals, teachers in middle and high school should be aware of how much homework other teachers are assigning. It may seem reasonable to assign 30 minutes of daily homework, but across six subjects, that’s three hours—far above a reasonable amount even for a high school senior. Psychologist Maurice Elias sees this as a common mistake: Individual teachers create homework policies that in aggregate can overwhelm students. He suggests that teachers work together to develop a school-wide homework policy and make it a key topic of back-to-school night and the first parent-teacher conferences of the school year.
Parents Play a Key Role
Homework can be a powerful tool to help parents become more involved in their child’s learning (Walker et al., 2004 ). It can provide insights into a child’s strengths and interests, and can also encourage conversations about a child’s life at school. If a parent has positive attitudes toward homework, their children are more likely to share those same values, promoting academic success.
But it’s also possible for parents to be overbearing, putting too much emphasis on test scores or grades, which can be disruptive for children (Madjar, Shklar, & Moshe, 2015 ). Parents should avoid being overly intrusive or controlling—students report feeling less motivated to learn when they don’t have enough space and autonomy to do their homework (Orkin, May, & Wolf, 2017 ; Patall, Cooper, & Robinson, 2008 ; Silinskas & Kikas, 2017 ). So while homework can encourage parents to be more involved with their kids, it’s important to not make it a source of conflict.

School Life Balance , Tips for Online Students
The Pros and Cons of Homework

Homework is a word that most students dread hearing. After hours upon hours of sitting in class , the last thing we want is more schoolwork over our precious weekends. While it’s known to be a staple of traditional schooling, homework has also become a rather divise topic. Some feel as though homework is a necessary part of school, while others believe that the time could be better invested. Should students have homework? Have a closer look into the arguments on both sides to decide for yourself.

Photo by energepic.com from Pexels
Why should students have homework, 1. homework encourages practice.
Many people believe that one of the positive effects of homework is that it encourages the discipline of practice. While it may be time consuming and boring compared to other activities, repetition is needed to get better at skills. Homework helps make concepts more clear, and gives students more opportunities when starting their career .
2. Homework Gets Parents Involved
Homework can be something that gets parents involved in their children’s lives if the environment is a healthy one. A parent helping their child with homework makes them take part in their academic success, and allows for the parent to keep up with what the child is doing in school. It can also be a chance to connect together.
3. Homework Teaches Time Management
Homework is much more than just completing the assigned tasks. Homework can develop time management skills , forcing students to plan their time and make sure that all of their homework assignments are done on time. By learning to manage their time, students also practice their problem-solving skills and independent thinking. One of the positive effects of homework is that it forces decision making and compromises to be made.
4. Homework Opens A Bridge Of Communication
Homework creates a connection between the student, the teacher, the school, and the parents. It allows everyone to get to know each other better, and parents can see where their children are struggling. In the same sense, parents can also see where their children are excelling. Homework in turn can allow for a better, more targeted educational plan for the student.
5. Homework Allows For More Learning Time
Homework allows for more time to complete the learning process. School hours are not always enough time for students to really understand core concepts, and homework can counter the effects of time shortages, benefiting students in the long run, even if they can’t see it in the moment.
6. Homework Reduces Screen Time
Many students in North America spend far too many hours watching TV. If they weren’t in school, these numbers would likely increase even more. Although homework is usually undesired, it encourages better study habits and discourages spending time in front of the TV. Homework can be seen as another extracurricular activity, and many families already invest a lot of time and money in different clubs and lessons to fill up their children’s extra time. Just like extracurricular activities, homework can be fit into one’s schedule.

The Other Side: Why Homework Is Bad
1. homework encourages a sedentary lifestyle.
Should students have homework? Well, that depends on where you stand. There are arguments both for the advantages and the disadvantages of homework.
While classroom time is important, playground time is just as important. If children are given too much homework, they won’t have enough playtime, which can impact their social development and learning. Studies have found that those who get more play get better grades in school , as it can help them pay closer attention in the classroom.
Children are already sitting long hours in the classroom, and homework assignments only add to these hours. Sedentary lifestyles can be dangerous and can cause health problems such as obesity. Homework takes away from time that could be spent investing in physical activity.
2. Homework Isn’t Healthy In Every Home
While many people that think homes are a beneficial environment for children to learn, not all homes provide a healthy environment, and there may be very little investment from parents. Some parents do not provide any kind of support or homework help, and even if they would like to, due to personal barriers, they sometimes cannot. Homework can create friction between children and their parents, which is one of the reasons why homework is bad .
3. Homework Adds To An Already Full-Time Job
School is already a full-time job for students, as they generally spend over 6 hours each day in class. Students also often have extracurricular activities such as sports, music, or art that are just as important as their traditional courses. Adding on extra hours to all of these demands is a lot for children to manage, and prevents students from having extra time to themselves for a variety of creative endeavors. Homework prevents self discovery and having the time to learn new skills outside of the school system. This is one of the main disadvantages of homework.
4. Homework Has Not Been Proven To Provide Results
Endless surveys have found that homework creates a negative attitude towards school, and homework has not been found to be linked to a higher level of academic success.
The positive effects of homework have not been backed up enough. While homework may help some students improve in specific subjects, if they have outside help there is no real proof that homework makes for improvements.
It can be a challenge to really enforce the completion of homework, and students can still get decent grades without doing their homework. Extra school time does not necessarily mean better grades — quality must always come before quantity.
Accurate practice when it comes to homework simply isn’t reliable. Homework could even cause opposite effects if misunderstood, especially since the reliance is placed on the student and their parents — one of the major reasons as to why homework is bad. Many students would rather cheat in class to avoid doing their homework at home, and children often just copy off of each other or from what they read on the internet.
5. Homework Assignments Are Overdone
The general agreement is that students should not be given more than 10 minutes a day per grade level. What this means is that a first grader should be given a maximum of 10 minutes of homework, while a second grader receives 20 minutes, etc. Many students are given a lot more homework than the recommended amount, however.
On average, college students spend as much as 3 hours per night on homework . By giving too much homework, it can increase stress levels and lead to burn out. This in turn provides an opposite effect when it comes to academic success.
The pros and cons of homework are both valid, and it seems as though the question of ‘‘should students have homework?’ is not a simple, straightforward one. Parents and teachers often are found to be clashing heads, while the student is left in the middle without much say.
It’s important to understand all the advantages and disadvantages of homework, taking both perspectives into conversation to find a common ground. At the end of the day, everyone’s goal is the success of the student.
Related Articles
20 Reasons Why Homework is Good: Unlocking the Benefits

- Post author By admin
- October 26, 2023
Explore the compelling 20 reasons why homework is good, fostering skills and knowledge that extend beyond the classroom
Ah, homework – a topic that has fueled countless debates in the world of education. Is it a valuable learning tool or a relentless academic burden?
In this article, we’re going to shift the spotlight onto the often-overlooked positive side of homework. We’ll unveil not one or two, but a whopping 20 compelling reasons why homework is genuinely good for students.
From solidifying classroom knowledge to honing critical thinking skills, homework is far more than just an academic chore. It’s an essential building block of learning.
So, whether you’ve questioned the purpose of homework or are simply curious about its merits, join us on this journey as we explore the myriad ways homework benefits students of all ages.
Get ready to discover why homework is a treasure trove of learning opportunities!
Table of Contents
20 Reasons Why Homework is Good
Check out 20 reasons why homework is good:-
1. Reinforcement of Classroom Learning
Homework isn’t just a mundane task; it’s your secret weapon for becoming a true subject matter aficionado. It’s the place where classroom theories transform into real-world skills.
Homework, in all its wisdom, lets you roll up your sleeves and practice what you’ve learned in class, turning those lightbulb moments into permanent knowledge fixtures.
Just like a musician perfecting a melody or an artist refining their masterpiece, homework is your training ground for excellence. So, embrace it, for every assignment is a stepping stone on your path to mastery.
2. Development of Responsibility
Homework isn’t just about books and assignments; it’s a grooming ground for something equally important – responsibility.
It’s like a trusty mentor, teaching students to take charge, manage their time, and complete tasks independently.
It’s that early taste of adulthood, where you learn that success often depends on your own commitment and effort.
So, think of homework as your guide on the journey to becoming a responsible, self-reliant individual, armed with skills that will serve you well in all walks of life.
3. Improved Time Management Skills
Homework is more than just assignments; it’s a boot camp for one of life’s essential skills – time management. Think of it as a mini dress rehearsal for adulthood.
Homework teaches students to allocate their time wisely, ensuring they meet deadlines and complete tasks efficiently. It’s like learning to juggle multiple balls, a skill that will serve them well in their adult lives. So, embrace homework as your friendly time-management coach, preparing you for the real world’s challenges.
4. Enhanced Critical Thinking
Homework is not just about finding answers; it’s your secret laboratory for unleashing the power of critical thinking.
It’s the arena where you get to be the detective, dissect problems, and engineer ingenious solutions. Think of it as mental gymnastics, where your cognitive muscles get a thorough workout.
The more you dive into those homework challenges, the sharper your critical thinking skills become. So, consider homework your daily brain boot camp, molding you into a savvy problem-solver with talents that extend way beyond the classroom.
5. Preparation for the Future
Homework isn’t just about cracking textbooks; it’s your sneak peek into the future. Think of it as your personal time machine, where you’re not just solving equations but honing skills that will propel you to success in higher education and the professional arena.
It’s like laying the stepping stones to your dream career. From mastering time management to sharpening critical thinking, homework is your trusted mentor, preparing you for the exciting journey ahead.
So, when you’re poring over those assignments, remember – you’re not just studying, you’re shaping a future filled with possibilities.
6. Encouragement of Self-Discipline
Homework isn’t just about filling out worksheets; it’s the canvas on which students paint their self-discipline and self-motivation masterpieces.
It’s like training for life’s grand adventure. With homework, you’re the captain, setting sail on a sea of assignments.
Completing homework isn’t merely about meeting deadlines; it’s about cultivating skills that become your secret weapons in the real world.
So, think of homework as your personal training ground for self-discipline, sculpting you into a resilient and motivated individual who’s ready to conquer life’s challenges.
7. Review of Material
Homework isn’t just an additional task; it’s your golden opportunity to revisit and cement what you’ve learned in class.
Think of it as your personal review session, where you go through the key points and solidify your understanding. Just as an artist refines their masterpiece or a musician practices their chords, homework is your tool for perfection.
The more you review and consolidate, the stronger your grasp on the subject matter becomes. So, embrace homework as your trusted ally in mastering the art of revision, making you a confident and knowledgeable learner.
8. Practice Makes Perfect
Homework isn’t a chore; it’s your backstage pass to perfection. It’s like the endless rehearsals of a musician or the tireless drills of an athlete.
Homework is your playground for practice, where you can fine-tune your skills, ensuring you become a true master in various subjects. Just as a chef perfects a recipe through repetition, your homework is the recipe for excellence.
So, when you’re diving into those assignments, think of them as your chance to practice, practice, and practice some more, turning you into a subject maestro.
9. Teacher-Student Interaction
Homework isn’t just about cracking the books; it’s your backstage pass to building strong connections with your teachers.
It’s like sending an open invitation to ask questions and seek guidance. Homework transforms the student-teacher relationship from a formal handshake into a hearty conversation.
When you embrace homework, you’re not just solving problems; you’re forging connections that can last a lifetime.
So, think of homework as your golden opportunity for dialogue, where you can foster positive relationships with your teachers and make your educational journey all the more engaging and rewarding.
10. Parental Involvement
Homework isn’t just a student’s duty; it’s a chance for families to bond over learning. It’s like the thread that weaves the classroom and home together, allowing parents to actively participate in their child’s education.
Homework transforms the learning experience into a shared adventure where everyone can join in the fun. When parents dive into homework with their kids, it’s not just about helping with math problems.
It’s about creating moments of connection, offering support, and sharing in the educational journey. So, think of homework as the gateway to family engagement in education, making learning a joyful family affair.
11. Real-Life Application
Homework isn’t just about hitting the books; it’s your backstage pass to making knowledge practical. It’s like a secret bridge that connects the world of theory with the realm of real-life application.
Homework transforms you from a passive learner into an active doer. It’s where you take those classroom ideas and put them into action, just like a scientist testing a hypothesis or an engineer building a bridge.
So, consider homework your personal laboratory for bringing theories to life, where you turn bookish knowledge into real-world magic, making your education a thrilling adventure.
12. Different Learning Styles
Homework isn’t a one-size-fits-all deal; it’s more like a treasure map that caters to diverse learning styles. Imagine it as a chameleon, changing its colors to suit both visual and kinesthetic learners.
Homework knows that we’re all unique, with our own special ways of learning. For those who thrive on visuals, it serves up graphs and illustrations, while the hands-on learners get to dive into practical tasks.
It’s a bit like having a tailor-made suit for education. So, consider homework your personal guide, offering a learning experience that’s as unique as you are, making education a captivating and natural journey.
13. Time for Creativity
Homework isn’t a creativity crusher; it’s your chance to let your imagination soar. Think of it as a blank canvas waiting for your ideas to paint it with vibrant colors.
Homework isn’t about rules and conformity; it’s about independent thinking and the freedom to express yourself. Whether you’re crafting an essay, brainstorming a unique solution, or designing a project, homework is your invitation to let your creativity shine.
So, consider homework your personal creative playground, where you can set your ideas free, turning learning into an exciting and imaginative adventure.
14. Enhancement of Research Skills
Homework isn’t just about checking off tasks; it’s your secret lair for honing research skills, those superpowers that will supercharge your success in both academics and the real world.
Think of it as your personal training ground where you become a detective of knowledge, learning to explore, dig deep, and unearth answers.
Whether you’re delving into the depths of the library, surfing the web, or conducting surveys, research-based homework transforms you into a skilled investigator.
So, consider homework your gateway to the world of research, where you unlock skills that will not only power your academic journey but also your lifelong adventures.
15. Test Preparation
Homework isn’t just a mundane task; it’s your secret weapon for conquering exams. Think of it as your personal exam prep coach, crafting a roadmap for success.
Homework lets you revisit, revise, and sharpen your skills, so when test day arrives, you’re ready to shine. It’s not just about finishing assignments; it’s about building your confidence for those crucial exams.
So, consider homework your trusty sidekick on the path to acing tests, making your educational journey an exciting adventure.
16. Increased Engagement
Homework isn’t a homework. It’s more like an after-class adventure that keeps the excitement of learning alive. Think of it as your personal quest, where you get to explore the subjects that genuinely pique your interest.
Homework isn’t about killing time; it’s your ticket to stay engaged with your learning journey, even when the school day ends.
So, when you’re tackling your assignments, remember you’re not just checking off tasks; you’re stoking the flames of curiosity, making education an exhilarating and never-ending journey.
17. Achievement of Learning Objectives
Homework isn’t just a jumble of tasks; it’s your trusted guide leading you to specific educational victories. Picture it as your personal GPS, keeping you on track to reach those learning milestones.
Homework is where you make the connections, reinforce classroom knowledge, and make your education rock-solid. It’s not just about answering questions; it’s about ensuring you hit those educational bullseyes.
So, when you’re diving into your assignments, remember you’re not just ticking off tasks; you’re on a journey to academic success, turning each homework into a stepping stone toward your goals.
18. Inclusivity
Homework isn’t a one-size-fits-all deal; it’s your versatile tool to celebrate the uniqueness of every student. Imagine it as a buffet, serving up options for both fast learners and those who want some extra practice.
Homework understands that every student is as unique as a fingerprint, each with their own pace and learning style.
For the quick learners, it offers challenges and exciting extensions, while those who prefer more practice can dive into additional exercises.
It’s like a school that dances to your rhythm, ensuring every student has a path to success. So, think of homework as your personal learning adventure, offering choices that fit your taste, making education an exciting and inclusive journey.
19. Fosters Independence
Homework isn’t about spoon-feeding answers; it’s your nurturing ground for independent thinking and decision-making.
Think of it as a playground where you get to flex your decision muscles and spread your intellectual wings. Homework is your training camp for self-reliance, where you take charge of your learning adventure.
20. Overall Academic Improvement
Homework isn’t just a stack of assignments; it’s the secret ingredient for overall academic improvement. Think of it as the magic wand that, when waved effectively, leads to better grades and educational triumphs.
Homework isn’t a mere task list; it’s your strategic ally in the journey of learning. When used wisely, it’s your key to success, a bridge to better understanding and superior educational outcomes.
So, when you’re tackling your homework, remember you’re not just ticking off tasks; you’re paving the way for academic excellence, turning each assignment into a step towards achieving your educational goals.
What are 5 benefits of homework?
Homework is more than just a list of tasks; it’s a powerhouse of benefits that can transform a student’s learning journey. Here are the top five advantages:
1. Supercharging Learning
Homework isn’t about mindless repetition; it’s your secret weapon to reinforce what you’ve learned in class. It’s like a memory boost that makes sure you remember the important stuff for the long haul.
2. Mastering Time and Study Skills
Homework teaches you real-world skills that go way beyond the textbook. It’s your personal coach for time management and setting priorities.
Plus, it’s your go-to guide for developing top-notch study habits like staying organized, taking killer notes, and acing those tests.
3. Fueling Grit and Responsibility
Homework is your training ground for building self-discipline and a sense of responsibility. It’s where you learn to motivate yourself and tackle challenges head-on, no matter how tough they seem.
4. Sparking Creativity and Critical Thinking
Homework isn’t a one-way street. It’s your canvas for thinking outside the box and analyzing what you’re learning from all angles. It’s your chance to bring your unique ideas to the table.
5. Strengthening Home-School Bonds
Homework isn’t just about you; it’s a connection point for your parents and teachers. It’s where they get a front-row seat to your education and can lend a hand when you need it.
But, remember, like any tool, homework works best when used wisely. Too much of a good thing can lead to stress, so strike that balance, and make homework your learning ally.
Who invented homework 😡?
The roots of homework can be traced back to a frustrated Italian educator, Roberto Nevilis, who lived in the 17th century.
He was perplexed by his students’ struggles to retain their classroom lessons, and so, he devised a novel solution – homework.
By assigning tasks that required students to practice and reinforce what they’d learned in class, Nevilis hoped to bridge the knowledge gap. His ingenious idea didn’t stop at the classroom door; it spread like wildfire, first across Europe and eventually finding its way to the United States.
While Nevilis is often credited with inventing homework, history leaves some room for debate. Some scholars argue that homework may have had earlier incarnations in ancient Greece and Rome, although concrete evidence is scarce.
What’s more likely is that Nevilis was among the first to formalize the concept of homework as we understand it today.
No matter its true origin, homework has become an integral part of education worldwide. It spans across the spectrum, from the youngest elementary students to those pursuing higher education.
The purpose of homework has also evolved over time. While Nevilis initially introduced homework to help students retain information, today, its role is multifaceted. It serves as a training ground for critical thinking, problem-solving, and nurturing creativity.
Whether you view homework as a boon or a bane, one thing is certain – it has a rich and varied history, and it’s likely to continue shaping the educational landscape for the foreseeable future.
Why is homework good for your brain?
Homework isn’t just about completing assignments; it’s a brain-boosting wizard. Let’s delve into the captivating reasons why homework is a mind-enhancing elixir:
Fortifying Neural Pathways
Imagine your brain as a labyrinth of pathways. When you learn something new, it’s like carving a fresh trail. Homework? It’s your trusty path-paver, helping you practice and reinforce what you’ve learned. This makes recalling information a breeze down the road.
Mastering Executive Function Skills
Executive function skills are like your brain’s personal assistants. They help you plan, organize, and manage your time effectively.
Homework transforms you into the CEO of your tasks, requiring you to set goals, juggle priorities, and work independently.
Cultivating Cognitive Flexibility
Ever wished you could tackle problems from various angles? That’s cognitive flexibility, a superpower for your brain. Homework serves as the playground where you can flex your mental muscles, applying your knowledge to novel challenges.
Boosting Self-Efficacy
Self-efficacy is your belief in your own success. Homework is your arena for personal victories. Achieving your homework goals and witnessing your growth over time? That’s a confidence booster like no other.
Stress Alleviation
While homework might occasionally seem like a stress-inducing monster, it’s also your coach for the stress-relief Olympics. How?
It equips you with the skills to tackle challenges and manage your time wisely, ultimately reducing stress in the long run.
But, here’s the catch: balance is key. Too much homework can tip the scales. To maximize the magical benefits, you need to find harmony between homework and other essential activities like sleep, exercise, and hanging out with friends.
In a nutshell, homework isn’t just about completing assignments; it’s your secret weapon for unlocking your brain’s potential. It boosts learning and memory, nurtures executive function skills, hones cognitive flexibility, elevates self-efficacy, and even helps you conquer stress.
As we draw the curtain on our exploration of the twenty compelling reasons that make homework a valuable asset, it’s evident that homework is more than just a to-do list. It’s a treasure trove of advantages that students can unearth on their academic journey.
From fortifying those neural pathways to nurturing independence, and from honing research skills to prepping for the challenges that await in the future, homework is a versatile tool. It’s the canvas where creativity flourishes, bridging the gap between theory and practice, and inviting parents into their child’s scholastic odyssey.
Homework doesn’t just aid in academic mastery; it’s a comprehensive roadmap for personal growth and development. It nudges you towards self-discipline, sprinkles in a dash of responsibility, and offers a slice of the sweet taste of accomplishment.
However, as in any art, balance is key. The right amount of homework, harmonized with other life activities, is the secret recipe for success.
So, as you tackle your next homework assignment, remember this: you’re not just completing tasks; you’re shaping a brighter future, one thought at a time.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is homework always beneficial for students.
Homework can be beneficial when thoughtfully assigned, but excessive or irrelevant homework may have negative effects.
How can parents support their child’s homework routine?
Parents can provide a quiet, organized workspace, offer assistance when needed, and encourage good study habits.
How much homework is too much?
The right amount of homework varies by grade level and individual needs. It should challenge without overwhelming students.
What can teachers do to make homework more effective?
Teachers should assign purposeful, relevant homework, provide clear instructions, and offer support when necessary.
How does homework help prepare students for the future?
Homework instills responsibility, time management, and critical thinking skills, all of which are valuable in higher education and the workforce.
- australia (2)
- duolingo (13)
- Education (264)
- General (60)
- How To (16)
- IELTS (127)
- Latest Updates (162)
- Malta Visa (6)
- Permanent residency (1)
- Programming (31)
- Scholarship (1)
- Sponsored (4)
- Study Abroad (187)
- Technology (12)
- work permit (8)
Recent Posts

- Teaching & Learning
Home truths about homework

Teaching during lockdown has presented a vast range of challenges within education but, when we eventually move into the post-Covid world, there could be some opportunities, too. It is unlikely that many teachers are thinking about “building back better” just now, as they try to keep their heads above the water. But one area that could eventually present opportunities for recovery and improvement is homework.
One of the biggest challenges faced by teachers has been trying to provide coherent learning opportunities that support positive and productive engagement. Parents and carers have undoubtedly found this difficult, with the phrase “that’s not how I did it when I was at school” being heard at kitchen tables around the country. Of course, home learning is not new: in Scotland, official figures pre-pandemic suggested that only around 0.1 per cent of school-age pupils were home educated, although the reality may have been higher.
A far more commonplace example of out-of-school education is homework. Obviously, the lockdown experience has involved far more than typical homework activities, such as practising spelling and times tables, or completing a consolidation worksheet. As a result, parents and carers will be more acutely aware than ever of what it is like to be a teacher - and this might be a good thing.
Homework vs homeschooling
The evidence for the value of traditional homework is mixed. The Education Endowment Foundation research summary suggests minimal evidence for effectiveness of homework in primary and slightly stronger justification for use in the secondary sector.
There is a variety of factors relating to students, teachers, parents and the task itself, making homework a complex area of study. It has been suggested that homework can be used effectively, especially in older age groups, for consolidation of learning and for developing traits such as autonomy and self-regulation. At its worst, homework is allocated simply because of long-established expectations or tradition: “It is what we did in school, so you can do it, too.”
It can also affect the home environment, which is especially pertinent during Covid-19, with demands on students and parents exacerbated by financial pressures and a reported increase in mental health issues. These pressures will not end with the return of students to school buildings.
The evidence for the value of homework with young children isn’t great. In fact, a review of the homework literature shows little - if any - influence of homework on academic achievement at primary level. And it is not even clear, on balance, that homework is a positive influence on primary-age students. The challenges that parents, teachers and students face with homework have also been problems for home learning. Notably, many parents and carers - even those who are teachers - will have found it difficult to get the youngest learners to focus. This might not be an issue with the learners themselves but, with our perception of what homework has always been, there is a lack of shared understanding about the very purpose of the activity.
Self-regulation
Advocates of homework often stress its importance in developing self-regulatory skills. This may differ from the experience of many teachers who have to relentlessly chase homework or receive homework that is incomplete, rushed or copied.
The Sutton Trust reported that only 51 per cent of teachers in the most advantaged state schools were getting at least three-quarters of work back during home learning, with just 20 per cent in the most deprived schools.
Unfortunately, the reality is that homework does not necessarily teach learners to be independent; it often has the opposite effect, depending on the nature of the task. It may even kill a love of learning.
But it doesn’t have to be that way. During Covid-19, teachers have had to innovate and experiment with various techniques, tools and apps to keep learners engaged and focused on learning, and averted from the myriad distractions and lures of the internet.
In fact, home learning is a great opportunity to make links between what children learn in school and experience at home. Students can apply what they learn at home and report this back to their teacher, giving unique opportunities for teachers to assess student understanding.
Instead of focusing on independence as a self-regulatory skill, home learning could demonstrate the usefulness and benefits of what they learn in school, transforming homework from an oppressive task that must be completed to an empowering educational tool.
The role of technology
Covid-19 has put a spotlight on the inequalities that exist in society and in education. Learners from low-income backgrounds have suffered most, with many not having the full access needed for home learning. The impact of a learner’s background is not new or surprising, and homework research has long shown inequalities relating to a range of variables, including parental income and educational history. Although undoubtedly a challenge, homework could be used more effectively to close rather than extend educational gaps. Perhaps the holy grail here is to transform the way we view education as a society, into a process rather than the pursuit of an end product.
Homework can be used to extend learning beyond the classroom but, without the correct support, it may end up cementing misunderstandings or aggravating learner anxieties or frustrations towards learning. Battles with parents and carers over task completion can end up being counterproductive and kill the joy of learning.
Technology may be able to help: adaptive learning software, such as that used within the Khan Academy, is a promising way of supporting learners at their level and could be used to revolutionise homework, although all students would need access.
The big tech firms, including the ubiquitous Microsoft and Google, meanwhile, have the resources and expertise to develop user-focused solutions: with the right educational and pedagogical input, they could create fantastic resources to bridge school and home learning. The possibilities to enhance additional support needs provision, especially relating to accessibility, are also an exciting prospect.
We could, too, look at what was already working well before lockdown. Some schools had developed approaches such as “takeaway homework” - whereby pupils choose from a “menu” of different homework options - that proved popular with teachers and learners alike.
At classroom level, some teachers have successfully involved learners in the development of weekly homework planning, co-constructing activities that consolidate the previous week’s learning. This has been well received, with high engagement, but it requires considerable dedicated teaching time and so lends itself more to the primary sector.
As teachers, we are constantly looking for ways to best support our learners. By pushing back against the status quo and reassessing how homework is used, we can transform the value of homework for teachers, learners and parents alike.
Reinventing home learning
Many teachers are sceptical about traditional approaches to homework, whereas others have simply gone along with it because “’twas ever thus”. We need to move away from homework being a tick-box burden and reinvent home learning with activities that nurture students’ interests and reduce learning disparities, rather than the contrary.
Technology has changed the way we live, learn and experience the world, yet homework practices often reflect more traditional methods, such as rote learning or pen-and-paper activities.
So, where do we start? Research from New Zealand during Covid-19 suggests that there are three pedagogical characteristics that influence learners’ experiences of online learning: personalisation, authenticity and collaboration. These could be the guiding principles to transform homework practice.
Starting with personalisation - and building on our new post-Covid understanding of technology - provides a unique opportunity to link learning to students’ life experiences, making it more personalised and authentic.
Homework is rarely collaborative, yet numerous apps, software and platforms give learners the opportunity to share and give each other feedback. Such collaboration helps to develop social-emotional skills, which have suffered during lockdown; it’s also relevant in the modern-day working environments that learners may experience once they leave education. We also, of course, need to provide teachers and learners with the resources to access this effectively.
When learning at home, an adult is not always around to help to engage or motivate the learner, and we cannot expect them to always do this themselves. But by redesigning home-learning activities, making the task more meaningful and engaging, students can get more out of homework.
Likewise, teachers can find homework more rewarding when it is informative and eases rather than adds to their workload. With the advancement of education software, teachers can assess understanding, collect data and give feedback. Such software can also help promote the home-school link and inform parents how to support their child. Where parental support is not available - a problem sometimes overlooked when setting homework - education software can help to scaffold students while they are working independently.
Home learning during the pandemic has provided us with many challenges but, more importantly, it has given us the experience with which to reinvent homework and transform learning in the future. Crucial to this are the relationships between learners, parents or carers, and the teachers, because - as we have found last year - they may not always be on the same educational page.
What should we do next?
Post-lockdown, it is likely that many learners and their parents or carers will, understandably, want a break from home learning. In contrast, some school leaders and politicians may be keen to ramp up homework in a desperate scramble to close attainment gaps.
Perhaps, though, there is another way. Given the skills teachers have learned, especially using technology, and the experiences of parents and carers during home learning, there may now be a better understanding of each other than ever before. Teachers and school leaders could build on this by using the post-lockdown period to pause homework and develop something new, from the ground up. Aims and objectives could be agreed between schools and families, limitations with technology could be considered, and parents and carers could be given support from teachers to help young people learn better and more independently.
To do this, school leaders and teachers might want to go back to the drawing board. Existing homework policies should be abandoned with learners, teachers, parents and carers collaborating to find a better way forward that suits everyone. The label “homework” could even be replaced by something less task focused.
Once implemented, policies and practices should be reviewed on a regular basis by everyone involved. If they aren’t working, then further refinement should be welcomed.
The experiences of home learning have undoubtedly been challenging, but they present an opportunity to reinforce the idea that learning is a lifelong process, something that goes well beyond the confines of school and classroom - whether or not we refer to it as “homework” anymore.
Rick Grammatica is a primary school teacher in Bangkok. Richard Holme is a lecturer in education at the University of Dundee. He blogs at richardholme.wordpress.com and tweets @richardjholme
This article originally appeared in the 30 April 2021 issue
You need a Tes subscription to read this article
Subscribe now to read this article and get other subscriber-only content:.
- Unlimited access to all Tes magazine content
- Exclusive subscriber-only stories
- Award-winning email newsletters
Already a subscriber? Log in
You need a subscription to read this article
Subscribe now to read this article and get other subscriber-only content, including:.
topics in this article


Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, how to do homework: 15 expert tips and tricks.
Coursework/GPA

Everyone struggles with homework sometimes, but if getting your homework done has become a chronic issue for you, then you may need a little extra help. That’s why we’ve written this article all about how to do homework. Once you’re finished reading it, you’ll know how to do homework (and have tons of new ways to motivate yourself to do homework)!
We’ve broken this article down into a few major sections. You’ll find:
- A diagnostic test to help you figure out why you’re struggling with homework
- A discussion of the four major homework problems students face, along with expert tips for addressing them
- A bonus section with tips for how to do homework fast
By the end of this article, you’ll be prepared to tackle whatever homework assignments your teachers throw at you .
So let’s get started!

How to Do Homework: Figure Out Your Struggles
Sometimes it feels like everything is standing between you and getting your homework done. But the truth is, most people only have one or two major roadblocks that are keeping them from getting their homework done well and on time.
The best way to figure out how to get motivated to do homework starts with pinpointing the issues that are affecting your ability to get your assignments done. That’s why we’ve developed a short quiz to help you identify the areas where you’re struggling.
Take the quiz below and record your answers on your phone or on a scrap piece of paper. Keep in mind there are no wrong answers!
1. You’ve just been assigned an essay in your English class that’s due at the end of the week. What’s the first thing you do?
A. Keep it in mind, even though you won’t start it until the day before it’s due B. Open up your planner. You’ve got to figure out when you’ll write your paper since you have band practice, a speech tournament, and your little sister’s dance recital this week, too. C. Groan out loud. Another essay? You could barely get yourself to write the last one! D. Start thinking about your essay topic, which makes you think about your art project that’s due the same day, which reminds you that your favorite artist might have just posted to Instagram...so you better check your feed right now.
2. Your mom asked you to pick up your room before she gets home from work. You’ve just gotten home from school. You decide you’ll tackle your chores:
A. Five minutes before your mom walks through the front door. As long as it gets done, who cares when you start? B. As soon as you get home from your shift at the local grocery store. C. After you give yourself a 15-minute pep talk about how you need to get to work. D. You won’t get it done. Between texts from your friends, trying to watch your favorite Netflix show, and playing with your dog, you just lost track of time!
3. You’ve signed up to wash dogs at the Humane Society to help earn money for your senior class trip. You:
A. Show up ten minutes late. You put off leaving your house until the last minute, then got stuck in unexpected traffic on the way to the shelter. B. Have to call and cancel at the last minute. You forgot you’d already agreed to babysit your cousin and bake cupcakes for tomorrow’s bake sale. C. Actually arrive fifteen minutes early with extra brushes and bandanas you picked up at the store. You’re passionate about animals, so you’re excited to help out! D. Show up on time, but only get three dogs washed. You couldn’t help it: you just kept getting distracted by how cute they were!
4. You have an hour of downtime, so you decide you’re going to watch an episode of The Great British Baking Show. You:
A. Scroll through your social media feeds for twenty minutes before hitting play, which means you’re not able to finish the whole episode. Ugh! You really wanted to see who was sent home! B. Watch fifteen minutes until you remember you’re supposed to pick up your sister from band practice before heading to your part-time job. No GBBO for you! C. You finish one episode, then decide to watch another even though you’ve got SAT studying to do. It’s just more fun to watch people make scones. D. Start the episode, but only catch bits and pieces of it because you’re reading Twitter, cleaning out your backpack, and eating a snack at the same time.
5. Your teacher asks you to stay after class because you’ve missed turning in two homework assignments in a row. When she asks you what’s wrong, you say:
A. You planned to do your assignments during lunch, but you ran out of time. You decided it would be better to turn in nothing at all than submit unfinished work. B. You really wanted to get the assignments done, but between your extracurriculars, family commitments, and your part-time job, your homework fell through the cracks. C. You have a hard time psyching yourself to tackle the assignments. You just can’t seem to find the motivation to work on them once you get home. D. You tried to do them, but you had a hard time focusing. By the time you realized you hadn’t gotten anything done, it was already time to turn them in.
Like we said earlier, there are no right or wrong answers to this quiz (though your results will be better if you answered as honestly as possible). Here’s how your answers break down:
- If your answers were mostly As, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is procrastination.
- If your answers were mostly Bs, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is time management.
- If your answers were mostly Cs, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is motivation.
- If your answers were mostly Ds, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is getting distracted.
Now that you’ve identified why you’re having a hard time getting your homework done, we can help you figure out how to fix it! Scroll down to find your core problem area to learn more about how you can start to address it.
And one more thing: you’re really struggling with homework, it’s a good idea to read through every section below. You may find some additional tips that will help make homework less intimidating.

How to Do Homework When You’re a Procrastinator
Merriam Webster defines “procrastinate” as “to put off intentionally and habitually.” In other words, procrastination is when you choose to do something at the last minute on a regular basis. If you’ve ever found yourself pulling an all-nighter, trying to finish an assignment between periods, or sprinting to turn in a paper minutes before a deadline, you’ve experienced the effects of procrastination.
If you’re a chronic procrastinator, you’re in good company. In fact, one study found that 70% to 95% of undergraduate students procrastinate when it comes to doing their homework. Unfortunately, procrastination can negatively impact your grades. Researchers have found that procrastination can lower your grade on an assignment by as much as five points ...which might not sound serious until you realize that can mean the difference between a B- and a C+.
Procrastination can also negatively affect your health by increasing your stress levels , which can lead to other health conditions like insomnia, a weakened immune system, and even heart conditions. Getting a handle on procrastination can not only improve your grades, it can make you feel better, too!
The big thing to understand about procrastination is that it’s not the result of laziness. Laziness is defined as being “disinclined to activity or exertion.” In other words, being lazy is all about doing nothing. But a s this Psychology Today article explains , procrastinators don’t put things off because they don’t want to work. Instead, procrastinators tend to postpone tasks they don’t want to do in favor of tasks that they perceive as either more important or more fun. Put another way, procrastinators want to do things...as long as it’s not their homework!
3 Tips f or Conquering Procrastination
Because putting off doing homework is a common problem, there are lots of good tactics for addressing procrastination. Keep reading for our three expert tips that will get your homework habits back on track in no time.
#1: Create a Reward System
Like we mentioned earlier, procrastination happens when you prioritize other activities over getting your homework done. Many times, this happens because homework...well, just isn’t enjoyable. But you can add some fun back into the process by rewarding yourself for getting your work done.
Here’s what we mean: let’s say you decide that every time you get your homework done before the day it’s due, you’ll give yourself a point. For every five points you earn, you’ll treat yourself to your favorite dessert: a chocolate cupcake! Now you have an extra (delicious!) incentive to motivate you to leave procrastination in the dust.
If you’re not into cupcakes, don’t worry. Your reward can be anything that motivates you . Maybe it’s hanging out with your best friend or an extra ten minutes of video game time. As long as you’re choosing something that makes homework worth doing, you’ll be successful.

#2: Have a Homework Accountability Partner
If you’re having trouble getting yourself to start your homework ahead of time, it may be a good idea to call in reinforcements . Find a friend or classmate you can trust and explain to them that you’re trying to change your homework habits. Ask them if they’d be willing to text you to make sure you’re doing your homework and check in with you once a week to see if you’re meeting your anti-procrastination goals.
Sharing your goals can make them feel more real, and an accountability partner can help hold you responsible for your decisions. For example, let’s say you’re tempted to put off your science lab write-up until the morning before it’s due. But you know that your accountability partner is going to text you about it tomorrow...and you don’t want to fess up that you haven’t started your assignment. A homework accountability partner can give you the extra support and incentive you need to keep your homework habits on track.
#3: Create Your Own Due Dates
If you’re a life-long procrastinator, you might find that changing the habit is harder than you expected. In that case, you might try using procrastination to your advantage! If you just can’t seem to stop doing your work at the last minute, try setting your own due dates for assignments that range from a day to a week before the assignment is actually due.
Here’s what we mean. Let’s say you have a math worksheet that’s been assigned on Tuesday and is due on Friday. In your planner, you can write down the due date as Thursday instead. You may still put off your homework assignment until the last minute...but in this case, the “last minute” is a day before the assignment’s real due date . This little hack can trick your procrastination-addicted brain into planning ahead!

If you feel like Kevin Hart in this meme, then our tips for doing homework when you're busy are for you.
How to Do Homework When You’re too Busy
If you’re aiming to go to a top-tier college , you’re going to have a full plate. Because college admissions is getting more competitive, it’s important that you’re maintaining your grades , studying hard for your standardized tests , and participating in extracurriculars so your application stands out. A packed schedule can get even more hectic once you add family obligations or a part-time job to the mix.
If you feel like you’re being pulled in a million directions at once, you’re not alone. Recent research has found that stress—and more severe stress-related conditions like anxiety and depression— are a major problem for high school students . In fact, one study from the American Psychological Association found that during the school year, students’ stress levels are higher than those of the adults around them.
For students, homework is a major contributor to their overall stress levels . Many high schoolers have multiple hours of homework every night , and figuring out how to fit it into an already-packed schedule can seem impossible.
3 Tips for Fitting Homework Into Your Busy Schedule
While it might feel like you have literally no time left in your schedule, there are still ways to make sure you’re able to get your homework done and meet your other commitments. Here are our expert homework tips for even the busiest of students.
#1: Make a Prioritized To-Do List
You probably already have a to-do list to keep yourself on track. The next step is to prioritize the items on your to-do list so you can see what items need your attention right away.
Here’s how it works: at the beginning of each day, sit down and make a list of all the items you need to get done before you go to bed. This includes your homework, but it should also take into account any practices, chores, events, or job shifts you may have. Once you get everything listed out, it’s time to prioritize them using the labels A, B, and C. Here’s what those labels mean:
- A Tasks : tasks that have to get done—like showing up at work or turning in an assignment—get an A.
- B Tasks : these are tasks that you would like to get done by the end of the day but aren’t as time sensitive. For example, studying for a test you have next week could be a B-level task. It’s still important, but it doesn’t have to be done right away.
- C Tasks: these are tasks that aren’t very important and/or have no real consequences if you don’t get them done immediately. For instance, if you’re hoping to clean out your closet but it’s not an assigned chore from your parents, you could label that to-do item with a C.
Prioritizing your to-do list helps you visualize which items need your immediate attention, and which items you can leave for later. A prioritized to-do list ensures that you’re spending your time efficiently and effectively, which helps you make room in your schedule for homework. So even though you might really want to start making decorations for Homecoming (a B task), you’ll know that finishing your reading log (an A task) is more important.
#2: Use a Planner With Time Labels
Your planner is probably packed with notes, events, and assignments already. (And if you’re not using a planner, it’s time to start!) But planners can do more for you than just remind you when an assignment is due. If you’re using a planner with time labels, it can help you visualize how you need to spend your day.
A planner with time labels breaks your day down into chunks, and you assign tasks to each chunk of time. For example, you can make a note of your class schedule with assignments, block out time to study, and make sure you know when you need to be at practice. Once you know which tasks take priority, you can add them to any empty spaces in your day.
Planning out how you spend your time not only helps you use it wisely, it can help you feel less overwhelmed, too . We’re big fans of planners that include a task list ( like this one ) or have room for notes ( like this one ).
#3: Set Reminders on Your Phone
If you need a little extra nudge to make sure you’re getting your homework done on time, it’s a good idea to set some reminders on your phone. You don’t need a fancy app, either. You can use your alarm app to have it go off at specific times throughout the day to remind you to do your homework. This works especially well if you have a set homework time scheduled. So if you’ve decided you’re doing homework at 6:00 pm, you can set an alarm to remind you to bust out your books and get to work.
If you use your phone as your planner, you may have the option to add alerts, emails, or notifications to scheduled events . Many calendar apps, including the one that comes with your phone, have built-in reminders that you can customize to meet your needs. So if you block off time to do your homework from 4:30 to 6:00 pm, you can set a reminder that will pop up on your phone when it’s time to get started.

This dog isn't judging your lack of motivation...but your teacher might. Keep reading for tips to help you motivate yourself to do your homework.
How to Do Homework When You’re Unmotivated
At first glance, it may seem like procrastination and being unmotivated are the same thing. After all, both of these issues usually result in you putting off your homework until the very last minute.
But there’s one key difference: many procrastinators are working, they’re just prioritizing work differently. They know they’re going to start their homework...they’re just going to do it later.
Conversely, people who are unmotivated to do homework just can’t find the willpower to tackle their assignments. Procrastinators know they’ll at least attempt the homework at the last minute, whereas people who are unmotivated struggle with convincing themselves to do it at a ll. For procrastinators, the stress comes from the inevitable time crunch. For unmotivated people, the stress comes from trying to convince themselves to do something they don’t want to do in the first place.
Here are some common reasons students are unmotivated in doing homework :
- Assignments are too easy, too hard, or seemingly pointless
- Students aren’t interested in (or passionate about) the subject matter
- Students are intimidated by the work and/or feels like they don’t understand the assignment
- Homework isn’t fun, and students would rather spend their time on things that they enjoy
To sum it up: people who lack motivation to do their homework are more likely to not do it at all, or to spend more time worrying about doing their homework than...well, actually doing it.
3 Tips for How to Get Motivated to Do Homework
The key to getting homework done when you’re unmotivated is to figure out what does motivate you, then apply those things to homework. It sounds tricky...but it’s pretty simple once you get the hang of it! Here are our three expert tips for motivating yourself to do your homework.
#1: Use Incremental Incentives
When you’re not motivated, it’s important to give yourself small rewards to stay focused on finishing the task at hand. The trick is to keep the incentives small and to reward yourself often. For example, maybe you’re reading a good book in your free time. For every ten minutes you spend on your homework, you get to read five pages of your book. Like we mentioned earlier, make sure you’re choosing a reward that works for you!
So why does this technique work? Using small rewards more often allows you to experience small wins for getting your work done. Every time you make it to one of your tiny reward points, you get to celebrate your success, which gives your brain a boost of dopamine . Dopamine helps you stay motivated and also creates a feeling of satisfaction when you complete your homework !
#2: Form a Homework Group
If you’re having trouble motivating yourself, it’s okay to turn to others for support. Creating a homework group can help with this. Bring together a group of your friends or classmates, and pick one time a week where you meet and work on homework together. You don’t have to be in the same class, or even taking the same subjects— the goal is to encourage one another to start (and finish!) your assignments.
Another added benefit of a homework group is that you can help one another if you’re struggling to understand the material covered in your classes. This is especially helpful if your lack of motivation comes from being intimidated by your assignments. Asking your friends for help may feel less scary than talking to your teacher...and once you get a handle on the material, your homework may become less frightening, too.
#3: Change Up Your Environment
If you find that you’re totally unmotivated, it may help if you find a new place to do your homework. For example, if you’ve been struggling to get your homework done at home, try spending an extra hour in the library after school instead. The change of scenery can limit your distractions and give you the energy you need to get your work done.
If you’re stuck doing homework at home, you can still use this tip. For instance, maybe you’ve always done your homework sitting on your bed. Try relocating somewhere else, like your kitchen table, for a few weeks. You may find that setting up a new “homework spot” in your house gives you a motivational lift and helps you get your work done.

Social media can be a huge problem when it comes to doing homework. We have advice for helping you unplug and regain focus.
How to Do Homework When You’re Easily Distracted
We live in an always-on world, and there are tons of things clamoring for our attention. From friends and family to pop culture and social media, it seems like there’s always something (or someone!) distracting us from the things we need to do.
The 24/7 world we live in has affected our ability to focus on tasks for prolonged periods of time. Research has shown that over the past decade, an average person’s attention span has gone from 12 seconds to eight seconds . And when we do lose focus, i t takes people a long time to get back on task . One study found that it can take as long as 23 minutes to get back to work once we’ve been distracte d. No wonder it can take hours to get your homework done!
3 Tips to Improve Your Focus
If you have a hard time focusing when you’re doing your homework, it’s a good idea to try and eliminate as many distractions as possible. Here are three expert tips for blocking out the noise so you can focus on getting your homework done.
#1: Create a Distraction-Free Environment
Pick a place where you’ll do your homework every day, and make it as distraction-free as possible. Try to find a location where there won’t be tons of noise, and limit your access to screens while you’re doing your homework. Put together a focus-oriented playlist (or choose one on your favorite streaming service), and put your headphones on while you work.
You may find that other people, like your friends and family, are your biggest distraction. If that’s the case, try setting up some homework boundaries. Let them know when you’ll be working on homework every day, and ask them if they’ll help you keep a quiet environment. They’ll be happy to lend a hand!
#2: Limit Your Access to Technology
We know, we know...this tip isn’t fun, but it does work. For homework that doesn’t require a computer, like handouts or worksheets, it’s best to put all your technology away . Turn off your television, put your phone and laptop in your backpack, and silence notifications on any wearable tech you may be sporting. If you listen to music while you work, that’s fine...but make sure you have a playlist set up so you’re not shuffling through songs once you get started on your homework.
If your homework requires your laptop or tablet, it can be harder to limit your access to distractions. But it’s not impossible! T here are apps you can download that will block certain websites while you’re working so that you’re not tempted to scroll through Twitter or check your Facebook feed. Silence notifications and text messages on your computer, and don’t open your email account unless you absolutely have to. And if you don’t need access to the internet to complete your assignments, turn off your WiFi. Cutting out the online chatter is a great way to make sure you’re getting your homework done.
#3: Set a Timer (the Pomodoro Technique)
Have you ever heard of the Pomodoro technique ? It’s a productivity hack that uses a timer to help you focus!
Here’s how it works: first, set a timer for 25 minutes. This is going to be your work time. During this 25 minutes, all you can do is work on whatever homework assignment you have in front of you. No email, no text messaging, no phone calls—just homework. When that timer goes off, you get to take a 5 minute break. Every time you go through one of these cycles, it’s called a “pomodoro.” For every four pomodoros you complete, you can take a longer break of 15 to 30 minutes.
The pomodoro technique works through a combination of boundary setting and rewards. First, it gives you a finite amount of time to focus, so you know that you only have to work really hard for 25 minutes. Once you’ve done that, you’re rewarded with a short break where you can do whatever you want. Additionally, tracking how many pomodoros you complete can help you see how long you’re really working on your homework. (Once you start using our focus tips, you may find it doesn’t take as long as you thought!)

Two Bonus Tips for How to Do Homework Fast
Even if you’re doing everything right, there will be times when you just need to get your homework done as fast as possible. (Why do teachers always have projects due in the same week? The world may never know.)
The problem with speeding through homework is that it’s easy to make mistakes. While turning in an assignment is always better than not submitting anything at all, you want to make sure that you’re not compromising quality for speed. Simply put, the goal is to get your homework done quickly and still make a good grade on the assignment!
Here are our two bonus tips for getting a decent grade on your homework assignments , even when you’re in a time crunch.
#1: Do the Easy Parts First
This is especially true if you’re working on a handout with multiple questions. Before you start working on the assignment, read through all the questions and problems. As you do, make a mark beside the questions you think are “easy” to answer .
Once you’ve finished going through the whole assignment, you can answer these questions first. Getting the easy questions out of the way as quickly as possible lets you spend more time on the trickier portions of your homework, which will maximize your assignment grade.
(Quick note: this is also a good strategy to use on timed assignments and tests, like the SAT and the ACT !)
#2: Pay Attention in Class
Homework gets a lot easier when you’re actively learning the material. Teachers aren’t giving you homework because they’re mean or trying to ruin your weekend... it’s because they want you to really understand the course material. Homework is designed to reinforce what you’re already learning in class so you’ll be ready to tackle harder concepts later.
When you pay attention in class, ask questions, and take good notes, you’re absorbing the information you’ll need to succeed on your homework assignments. (You’re stuck in class anyway, so you might as well make the most of it!) Not only will paying attention in class make your homework less confusing, it will also help it go much faster, too.

What’s Next?
If you’re looking to improve your productivity beyond homework, a good place to begin is with time management. After all, we only have so much time in a day...so it’s important to get the most out of it! To get you started, check out this list of the 12 best time management techniques that you can start using today.
You may have read this article because homework struggles have been affecting your GPA. Now that you’re on the path to homework success, it’s time to start being proactive about raising your grades. This article teaches you everything you need to know about raising your GPA so you can
Now you know how to get motivated to do homework...but what about your study habits? Studying is just as critical to getting good grades, and ultimately getting into a good college . We can teach you how to study bette r in high school. (We’ve also got tons of resources to help you study for your ACT and SAT exams , too!)
Need more help with this topic? Check out Tutorbase!
Our vetted tutor database includes a range of experienced educators who can help you polish an essay for English or explain how derivatives work for Calculus. You can use dozens of filters and search criteria to find the perfect person for your needs.

These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to help provide a better website experience for you, and help us to understand how people use our website. Our partners will also collect data and use cookies for ad personalisation and measurement.
Clicking "Accept" will allow us and our partners to use cookies, learn more in our cookie policy or to change your cookie preferences, click "Manage".
To find out more about cookies and the types of cookies we are setting please visit our cookie policy .
If you'd prefer that certain types of cookie are not saved on your browser when visiting our website, use the toggles below to adjust those preferences and click "Save choices".
Strictly Necessary
These cookies are necessary for the website to function and without them you would not be able to reliably use the website. For example, logging into your account or completing forms.
Analytics Cookies
A series of cookies that collect anonymised data on how users interact with our website. This anonymous data helps us improve the website with a focus on its users, for example, ensuring the most popular content is easier to access.
View associated providers +
Marketing Cookies
These cookies track your online activity to help advertisers deliver more relevant and personalised advertising or to limit how many times you see an ad. These cookies can share that information with other organisations or advertisers.

We're honoured to be chosen as the best Secondary Digital Learning Resource at the 2024 Bett Awards!

The award-winning literacy platform for schools
A love of learning through language.
Join our mission to prepare learners for the demands of their future with captivating and aspirational EdTech.

Each year, learners need to add up to 3,000 words to their vocabulary. That's just to keep up with the demands of the curriculum.
With that challenge in mind, can any one teacher consistently teach, assess, re-teach and monitor this knowledge across a class of more than 30 learners? Can leadership monitor the progress of an entire school of learners?
Traditional methods alone fall well short of meeting this challenge.
Here’s where Bedrock Learning steps in...
Why Bedrock Learning?

Tier 2 vocabulary and grammar
Our core curriculum explicitly teaches vocabulary and grammar, all in the context of original and engaging prose, ensuring learners are reading a diverse range of high-quality texts that draw them in, expanding their cultural capital whilst they learn.

Coverage of 38 curriculum areas
With over 30,000 subject-specific Tier 3 words across 38 subjects from maths to music, Bedrock unlocks the language demands of the curriculum, providing targeted and personalised instruction that moves beyond definitions…

Comprehensive CPD and support
Bedrock's in-house Teaching & Learning Team consists exclusively of qualified teachers, all here to support you in maximising your partnership with Bedrock. From CPD workshops to webinars, free resources, podcasts and more.

A multi-award winner
We don't like to blow our own trumpet, but we are hugely proud of how often Bedrock has been independently recognised by leading national and international educational bodies.

Trusted by MATs nationwide
We’re proud to be a trusted resource partner with dozens of Multi Academy Trusts across the UK, providing outstanding education resources into their classrooms, supporting their curriculum development and sharing trust-wide data insights.

Data & Reporting within Harris Federation academies

Impacting outcomes for Pupil Premium, EAL and SEND learners at Harris Federation

Using Bedrock for the humanities at St. Anselm's

Partnering with Bedrock across the Harris Federation

Why the Harris Federation chose to partner with Bedrock

Key Stage 3 success at Taverham High School

Success in every subject at St Anselm's Catholic School

Literacy success at St Mary's Primary School

How we use Bedrock Learning at Coston Primary
Meet bedrock's award-winning curriculum....
Our comprehensive vocabulary curriculum teaches academic vocabulary through original fiction and non-fiction and develops literacy for reading, writing and oracy.
Tier 3 vocabulary
Bedrock enables schools to deliver quality teaching and learning of Tier 3 vocabulary across 38 curriculum areas and tens of thousands of words, ensuring that learners can communicate like experts in every subject across the school.
Bedrock Grammar immerses students in engaging learning experiences, using stories, video, interactive activities and scaffolded writing opportunities.
GCSE English
Bedrock English provides curriculum schemes specially designed to support English Literature and English Language study at GCSE level, from Years 9-11.
Subscription Options
The right solution for your school.
Bedrock’s personalised and adaptive approach goes beyond our teaching. Every school is different, so our subscription packages can be mixed by year group. For example, start your Year 7s on Accelerate, expand to Consolidate with your Year 8 cohort and prepare your older learners for GCSEs with Master.
Book a conversation with one of our team to discuss the best option for your school.
- Tier 2 vocabulary curriculum
- Grammar curriculum
- Bedrock Library
- Remote support
- Subject-specific Tier 3 vocabulary content for 1 subject of your choice, PLUS create unlimited custom content for your school
Consolidate
- Subject-specific Tier 3 vocabulary content for 3 subjects of your choice, PLUS create unlimited custom content for your school
- 37 Common Greek and Latin Roots
- Bedrock for GCSE English: 102 terms and example analysis
- 1 dedicated CPD workshop for your team (remote/virtual or held on-site)
- Subject-specific Tier 3 vocabulary content for all 38 subjects, PLUS create unlimited custom content for your school
- 2 dedicated CPD workshops for your team (remote/virtual or held on-site)
- School Impact Analysis report and data triangulation each year
Visit Bedrock Primary here


A.I. Is Learning What It Means to Be Alive
Given troves of data about genes and cells, A.I. models have made some surprising discoveries. What could they teach us someday?
Credit... Doug Chayka
Supported by
- Share full article

By Carl Zimmer
- Published March 10, 2024 Updated March 12, 2024
In 1889, a French doctor named Francois-Gilbert Viault climbed down from a mountain in the Andes, drew blood from his arm and inspected it under a microscope. Dr. Viault’s red blood cells, which ferry oxygen, had surged 42 percent. He had discovered a mysterious power of the human body: When it needs more of these crucial cells, it can make them on demand.
In the early 1900s, scientists theorized that a hormone was the cause. They called the theoretical hormone erythropoietin, or “red maker” in Greek. Seven decades later, researchers found actual erythropoietin after filtering 670 gallons of urine .
And about 50 years after that, biologists in Israel announced they had found a rare kidney cell that makes the hormone when oxygen drops too low. It’s called the Norn cell , named after the Norse deities who were believed to control human fate.
It took humans 134 years to discover Norn cells. Last summer, computers in California discovered them on their own in just six weeks.
The discovery came about when researchers at Stanford programmed the computers to teach themselves biology. The computers ran an artificial intelligence program similar to ChatGPT, the popular bot that became fluent with language after training on billions of pieces of text from the internet. But the Stanford researchers trained their computers on raw data about millions of real cells and their chemical and genetic makeup.
The researchers did not tell the computers what these measurements meant. They did not explain that different kinds of cells have different biochemical profiles. They did not define which cells catch light in our eyes, for example, or which ones make antibodies.
The computers crunched the data on their own, creating a model of all the cells based on their similarity to each other in a vast, multidimensional space. When the machines were done, they had learned an astonishing amount . They could classify a cell they had never seen before as one of over 1,000 different types. One of those was the Norn cell.
“That’s remarkable, because nobody ever told the model that a Norn cell exists in the kidney,” said Jure Leskovec, a computer scientist at Stanford who trained the computers.
The software is one of several new A.I.-powered programs, known as foundation models, that are setting their sights on the fundamentals of biology. The models are not simply tidying up the information that biologists are collecting. They are making discoveries about how genes work and how cells develop.
As the models scale up, with ever more laboratory data and computing power, scientists predict that they will start making more profound discoveries. They may reveal secrets about cancer and other diseases. They may figure out recipes for turning one kind of cell into another.
“A vital discovery about biology that otherwise would not have been made by the biologists — I think we’re going to see that at some point,” said Dr. Eric Topol, the director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute.
Just how far they will go is a matter of debate. While some skeptics think the models are going to hit a wall, more optimistic scientists believe that foundation models will even tackle the biggest biological question of them all: What separates life from nonlife?
Heart Cells and Mole Rats

Biologists have long sought to understand how the different cells in our bodies use genes to do the many things we need to stay alive.
About a decade ago, researchers started industrial-scale experiments to fish out genetic bits from individual cells. They recorded what they found in catalogs, or “ cell atlases ,” that swelled with billions of pieces of data.
Dr. Christina Theodoris, a medical resident at Boston Children’s Hospital, was reading about a new kind of A.I. model made by Google engineers in 2017 for language translations. The researchers provided the model with millions of sentences in English, along with their translations into German and French. The model developed the power to translate sentences it hadn’t seen before. Dr. Theodoris wondered if a similar model could teach itself to make sense of the data in cell atlases.
In 2021, she struggled to find a lab that might let her try to build one. “There was a lot of skepticism that this approach would work at all,” she said.
Shirley Liu, a computational biologist at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, gave her a shot. Dr. Theodoris pulled data from 106 published human studies, which collectively included 30 million cells, and fed it all into a program she created called GeneFormer.
The model gained a deep understanding of how our genes behave in different cells. It predicted, for example, that shutting down a gene called TEAD4 in a certain type of heart cell would severely disrupt it. When her team put the prediction to the test in real cells called cardiomyocytes, the beating of the heart cells grew weaker.
In another test, she and her colleagues showed GeneFormer heart cells from people with defective heartbeat rhythms as well as from healthy people. “Then we said, Now tell us what changes we need to happen to the unhealthy cells to make them healthy,” said Dr. Theodoris, who now works as a computational biologist at the Gladstone Institutes in San Francisco.
GeneFormer recommended reducing the activity of four genes that had never before been linked to heart disease. Dr. Theodoris’s team followed the model’s advice, knocking down each of the four genes. In two out of the four cases, the treatment improved how the cells contracted.
The Stanford team got into the foundation-model business after helping to build one of the biggest databases of cells in the world, known as CellXGene . Beginning in August, the researchers trained their computers on the 33 million cells in the database, focusing on a type of genetic information called messenger RNA. They also fed the model the three-dimensional structures of proteins, which are the products of genes.
From this data, the model — known as Universal Cell Embedding, or U.C.E. — calculated the similarity among cells, grouping them into more than 1,000 clusters according to how they used their genes. The clusters corresponded to types of cells discovered by generations of biologists.
U.C.E. also taught itself some important things about how the cells develop from a single fertilized egg. For example, U.C.E. recognized that all the cells in the body can be grouped according to which of three layers they came from in the early embryo.
“It essentially rediscovered developmental biology,” said Stephen Quake, a biophysicist at Stanford who helped develop U.C.E.
The model was also able to transfer its knowledge to new species. Presented with the genetic profile of cells from an animal that it had never seen before — a naked mole rat, say — U.C.E. could identify many of its cell types.
“You can bring a completely new organism — chicken, frog, fish, whatever — you can put it in, and you will get something useful out,” Dr. Leskovec said.
After U.C.E. discovered the Norn cells, Dr. Leskovec and his colleagues looked in the CellXGene database to see where they had come from. While many of the cells had been taken from kidneys, some had come from lungs or other organs. It was possible, the researchers speculated, that previously unknown Norn cells were scattered across the body.
Dr. Katalin Susztak, a physician-scientist at the University of Pennsylvania who studies Norn cells, said that the finding whetted her curiosity. “I want to check these cells,” she said.
She is skeptical that the model found true Norn cells outside the kidneys, since the erythropoietin hormone hasn’t been found in other places. But the new cells may sense oxygen as Norn cells do.
In other words, U.C.E. may have discovered a new type of cell before biologists did.
An ‘Internet of Cells’
Just like ChatGPT , biological models sometimes get things wrong. Kasia Kedzierska, a computational biologist at the University of Oxford, and her colleagues recently gave GeneFormer and another foundation model , scGPT, a battery of tests . They presented the models with cell atlases they hadn’t seen before and had them perform tasks such as classifying the cells into types. The models performed well on some tasks, but in other cases they fared poorly compared with simpler computer programs.
Dr. Kedzierska said she had great hopes for the models but that, for now, “they should not be used out of the box without a proper understanding of their limitations.”
Dr. Leskovec said that the models were improving as scientists trained them on more data. But compared with ChatGPT’s training on the entire internet, the latest cell atlases offer only a modest amount of information. “I’d like an entire internet of cells,” he said.
More cells are on the way as bigger cell atlases come online. And scientists are gleaning different kinds of data from each of the cells in those atlases. Some scientists are cataloging the molecules that stick to genes, or taking photographs of cells to illuminate the precise location of their proteins. All of that information will allow foundation models to draw lessons about what makes cells work.
Scientists are also developing tools that let foundation models combine what they’re learning on their own with what flesh-and-blood biologists have already discovered. The idea would be to connect the findings in thousands of published scientific papers to the databases of cell measurements.
With enough data and computing power, scientists say, they may eventually create a complete mathematical representation of a cell.
“That’s going to be hugely revolutionary for the field of biology,” said Bo Wang, a computational biologist at the University of Toronto and the creator of scGPT. With this virtual cell, he speculated, it would be possible to predict what a real cell would do in any situation. Scientists could run entire experiments on their computers rather than in petri dishes.
Dr. Quake suspects that foundation models will learn not just about the kinds of cells that currently reside in our bodies but also about kinds of cells that could exist. He speculates that only certain combinations of biochemistry can keep a cell alive. Dr. Quake dreams of using foundation models to make a map showing the realm of the possible, beyond which life cannot exist.
“I think these models are going to help us get some really fundamental understanding of the cell, which is going to provide some insight into what life really is,” Dr. Quake said.
Having a map of what’s possible and impossible to sustain life might also mean that scientists could actually create new cells that don’t yet exist in nature. The foundation model might be able to concoct chemical recipes that transform ordinary cells into new, extraordinary ones. Those new cells might devour plaque in blood vessels or explore a diseased organ to report back on its condition.
“It’s very ‘Fantastic Voyage ’- ish,” Dr. Quake admitted. “But who knows what the future is going to hold?”
If foundation models live up to Dr. Quake’s dreams, they will also raise a number of new risks. On Friday, more than 80 biologists and A.I. experts signed a call for the technology to be regulated so that it cannot be used to create new biological weapons. Such a concern might apply to new kinds of cells produced by the models.
Privacy breaches could happen even sooner. Researchers hope to program personalized foundation models that would look at an individual’s unique genome and the particular way that it works in cells. That new dimension of knowledge could reveal how different versions of genes affect the way cells work. But it could also give the owners of a foundation model some of the most intimate knowledge imaginable about the people who donated their DNA and cells to science.
Some scientists have their doubts about how far foundational models will make it down the road to “Fantastic Voyage,” however. The models are only as good as the data they are fed. Making an important new discovery about life may depend on having data on hand that we haven’t figured out how to collect. We might not even know what data the models need.
“They might make some new discoveries of interest,” said Sara Walker, a physicist at Arizona State University who studies the physical basis of life. “But ultimately they are limited when it comes to new fundamental advances.”
Still, the performance of foundation models has already led their creators to wonder about the role of human biologists in a world where computers make important insights on their own. Traditionally, biologists have been rewarded for creative and time-consuming experiments that uncover some of the workings of life. But computers may be able to see those workings in a matter of weeks, days or even hours by scanning billions of cells for patterns we can’t see.
“It’s going to force a complete rethink of what we consider creativity,” Dr. Quake said. “Professors should be very, very nervous.”
Carl Zimmer covers news about science for The Times and writes the Origins column . More about Carl Zimmer
Explore Our Coverage of Artificial Intelligence
News and Analysis
Gov. Bill Lee of Tennessee signed a bill to prevent the use of A.I. to copy a performer’s voice. It is the first such measure in the United States.
French regulators said Google failed to notify news publishers that it was using their articles to train its A.I. algorithms, part of a wider ruling against the company for its negotiating practices with media outlets.
Apple is in discussions with Google about using Google’s generative A.I. model called Gemini for its next iPhone.
The Age of A.I.
The Caribbean island Anguilla made $32 million last year, more than 10 percent of its G.D.P., from companies registering web addresses that end in .ai .
When it comes to the A.I. that powers chatbots like ChatGPT, China lags behind the United States. But when it comes to producing the scientists behind a new generation of humanoid technologies, China is pulling ahead .
By interacting with data about genes and cells, A.I. models have made some surprising discoveries and are learning what it means to be alive. What could they teach us someday ?
Covariant, a robotics start-up, is using the technology behind chatbots to build robots that learn skills much like ChatGPT does.
Advertisement
Our websites may use cookies to personalize and enhance your experience. By continuing without changing your cookie settings, you agree to this collection. For more information, please see our University Websites Privacy Notice .
UConn Today
- School and College News
- Arts & Culture
- Community Impact
- Entrepreneurship
- Health & Well-Being
- Research & Discovery
- UConn Health
- University Life
- UConn Voices
- University News
March 26, 2024 | Jennifer Walker - UConn Health
Medical Students Embrace Interactive Experience Learning the Care of Older Adults
The UConn School of Medicine students immerse in an interactive experience at Duncaster Independent Life Care Community to learn first hand from aging population how to care for their medical, physical and social needs.

Audrey Grotheer, UConn medical student, Ami Desai, COO, Duncaster, Tia Kozar, UConn medical student, Tiffany Smith, Marketing Manager, Duncaster, Emma Carlson, UConn medical student, Kelly Papa, President and CEO Duncaster
Victoria “Tia” Kozar, a fourth-year medical student at the University of Connecticut School of Medicine found her biggest inspiration in the field of Geriatric Psychiatry during her undergraduate education at Quinnipiac University when she participated in the first Quinnipiac Students-In-Residence Program. She resided at a Masonicare assisted living community and it was her neighbor and friend Beth who began exhibiting signs of cognitive lapse and was later diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease that drove Kozar’s passion for this field.
Connecticut is a quickly aging state and the Center on Aging at UConn Health is at the epicenter of important outcomes for older adults. It is estimated that most physicians spend more than half of their time providing care for older individuals. In addition, there is an expanding body of knowledge specific to the care of older patients.
By engaging in community-based learning experiences, medical students have the opportunity to interact with older adults in a real-world setting, learn about their needs and experiences, and develop empathy and understanding toward them.
When speaking with older adults in the community Kozar all too often had the conversation that included statements such as “I wished my doctor listened more,” “I feel like I don’t have a voice in my care,” “there are so many things that I wished they knew.” Kozar knew this was a conversation that had to happen on a larger scale, and she wanted to develop a program and experience where the dialogue could go both ways.
The UConn School of Medicine is teaching all students how to care for an aging population and the leadership at both UConn Health and Duncaster Independent Life Care Community were on board for this immersive experience and eager to have students participate in the program Kozar spent two years creating.
“Duncaster is proud to partner with UConn School of Medicine to offer this learning experience to students,” says Kelly Papa, President and CEO of Duncaster.
Audrey Grotheer and Emma Carlson, both second year medical students at the University of Connecticut School of Medicine were chosen as the pioneers of this pilot program through an application process. They spent three days at Duncaster’s facility in Bloomfield, Connecticut. A curriculum complemented their stay included dementia, spectrum of senior care and the variety of roles they could have in the care of older adults. The program was experiential, and the students participated in activities and meals with the residents.
Grotheer, is still exploring which area of medicine she will study and describes the experience as the “most amazing sleep away camp you would ever experience.” Having lost all her grandparents she thinks of them often and has happy memories but regrets that they passed before she grew up enough to ask them about them. Growing in this awareness that people have interesting stories to share about their life, she thought this would be a great program to participate in.
In her weekly clinical rotation at a local cardiac center, many of the patients are older and she appreciated that the program would assist her in learning skills to interact with older adults. The patients come with life stories that really contribute to their care and the relationship that they form with their providers.
Carlson is from Montana and after earning her undergraduate degree from Colorado College, she took two gap years in England and DC to decided what she wanted to do with a MD/Ph.D. degree she was planning on pursuing. She wanted to come to a place that would emphasize the patient as much as the science itself and she found that at UConn.
Her plan is to obtain her MD in infectious disease and a Ph.D. in immunology and knows that in her field she will see many older adults and this program helped her with how to apply judgment to help patients in different stages of their health longevity.
Papa has a post it above her desk that says, “by 2027 Aging services will be a career destination for graduating professionals.” She wrote this in 2017, with that goal that in CT we would embrace the vision that students saw working with older adults as a rewarding career path, rather than finding it as an unexpected path.
“Geriatrics is not part of a silo, it’s important to have that experience and be invested in a population that is getting older and getting older fast and to arm our future doctors with the tools to care for older adults,” says Kozar.
While at Duncaster, Grotheer and Carlson stayed in their own separate suite, and both admit that it was not what they expected. They had a luncheon with residents and had structured groups to have conversations about health care. They went to a few meetings and attended a very active residents’ association monthly meeting,
They were able to experience how each area operated in the full continuum of care at Duncaster’s independent life plan community, including independent living facility, assisted living, skilled nursing care and the memory unit.
“This whole experience demystified the care of older adults, a lot of what I have seen through life experiences and media is the downsides of aging, the difficulties and complications of dealing with older adults,” says Grotheer. “I saw happy aging, being in an environment that was engaging and active.”
Carlson met a retired physician who acknowledged the gap in health care and encouraged her to make change and speak more into policy. He also told her to be aware of patients and their circumstances and give more when you can.
As part of the curriculum, the students kept journals and also participated in a Dementia Friends seminar. They went away with certificate of a Dementia Friend. They will go into their clinical rotations with these experiences and certifications preparing them to be the best clinical student.
“Almost immediately after experience ended several of the residents at Duncaster reached out asking for the students contact information to stay in touch,” says Kozar. “They had such a lovely time chatting with them and getting to know them and that they wanted to keep that open as friendships blossomed.
Both Grotheer and Carlson would highly recommend that other students participate in this opportunity. It helps them counsel patients better and be well informed to give advice that is feasible for the people they are taking care of. While they both recognize that Duncaster is not what all aging care facilities look like, they would like to see the program expand and there to be a longitudinal mentorship that includes visiting a variety of facilities to see differences.
Kozar, who will graduate from medical school in May and will start her fellowship at Yale Psychiatry, hopes to continue to grow and expand on these programs to provide more training and experience in the care of older adults.
“As a Registered Nurse, now CEO, I am grateful my career path led me on an unexpected journey to aging services where I found a very rewarding career. If you ask most professionals working with older adults if geriatrics was their career destination as a college student, most say no, something happened, and they found it. But what if students selected it from the beginning? That is why programs like Masonicare’s and Duncaster’s exist. Let’s make working with older adults a career destination,” says Papa.
According to Dr George Kuchel, Director of the UConn Center on Aging and the UConn Older Americans Independence Pepper Center, “In the future, our country will be facing even greater challenges when it comes to training sufficient numbers of physicians and other health professions in skills needed to provide high quality evidence-based care for older adults. This is especially true when it comes to mental health issues. With that in mind, I am delighted to see such interest amongst our next generation of physicians. Having served on the Board of Directors at Duncaster for many years, I could not think of a better place for our medical students to go through this type of life changing experience.”
Recent Articles

March 27, 2024
UConn Health Minute: Colon Cancer
Read the article

Podcast: Bilingual Tool to Spot Signs of MS Earlier

Accounting Ph.D. Candidate Kangkang Zhang Receives Deloitte Foundation Fellowship
Pic Answer - AI Solver 12+
Math photo solve your homework, tech consolidated inc, designed for ipad.
- #62 in Education
- 4.6 • 8.1K Ratings
- Offers In-App Purchases
Screenshots
Description.
Pic Answer - AI Solver: Snap, Ask, Learn! Step into a world of effortless learning with Pic Answer - AI Solver, where each photo brings you closer to understanding. This app goes beyond traditional math solvers, offering a unique blend of AI-driven solutions and interactive chat for a variety of academic subjects. Why Choose Pic Answer? • Instant Photo Answers: Just snap a picture of your homework and watch as our AI provides accurate solutions in seconds. • All-Subject AI Chat: Whether you need help in math, science, or literature, our AI chat is ready to assist with personalized guidance. • Comprehensive Learning Made Simple: Our focus isn't just on answers, but on helping you understand the concepts behind them. • Intuitive and User-Friendly: We've designed our app to be easy and enjoyable for learners of all ages and abilities. Key Features: • AI-Powered Scanner: Simply snap a picture of the problem, and our app swiftly analyzes and resolves it with precision. • Real-Time AI Chat Assistance: Engage in interactive conversations for in-depth explanations and study tips. • Broad Subject Coverage: From complex math equations to science experiments and literary analysis, we've got you covered. Your Educational Companion: • Always Evolving: We constantly enhance our app with the latest AI advancements and user feedback. • Perfect for Everyone: Whether you're a student, teacher, or just curious, our app is tailored to fit your learning needs. The app includes optional subscriptions to unlock pro features. terms and conditions: http://techconsolidated.org/terms.html Download "Pic Answer - AI Solver" today and revolutionize the way you learn!
Version 1.33.1
Bug fixes for improved app performance
Ratings and Reviews
8.1K Ratings
VERY USEFUL APP!!! - Sherry ⚡️
I’m not failing my grades as I used to be and thank god I found this app. I been failing my tests but now that I found this app I’m passing all my classes! Tysm to the owner to whoever made this :) gladly I rate this a 5 star app it’s useful for people who have low grades or are failing classes. I use this app with my brother and he isn’t getting b’s anymore he’s getting straight A’s. Ty ty ty ty for this app to be made! Share all the love with this app 💓💓
Developer Response ,
Thank you for taking the time to submit your feedback! We value our users’ loyalty greatly and our team is always dedicated to improving the quality of your experience.
This app is horrible. I expected to be accurate it wasn’t. For starters, I downloaded this app so it could help me with my math. I wanted to be sure is was accurate so I took a picture of a old math problem and see if it would work. I looked at the answer key with the answer. For example, let’s say the answer from this app was 26. The answer key said it was 78. It was confusing so it has a respond feature and I typed this is not accurate. Then it gave me a complete different answer and the new answer was 12! I was puzzled. So I solved the question on my own and the answer key was correct. I took a another photo and the same answer, 12. I searched up on google the problem and it was 78. I paid $6.99 for this trash.
We apologize for any issues you've encountered while using our app. Our team is currently working on enhancing the app, so please keep an eye out for the upcoming update.
My honest opinion
It’s a good app, but most of the time you have to re-take a photo, or the answer is wrong. 40% of the time the app doesn’t want to work, or closes on me when I’m using it. It’s a good app for easy, quick, answers.. but not so much big ones. I do like that it works for questions with pictures.. and it has a specific mode for math questions. Would I recommend you download it.. yes. It is a good app, maybe just needs a couple of updates/bug fixes.
App Privacy
The developer, Tech Consolidated Inc , indicated that the app’s privacy practices may include handling of data as described below. For more information, see the developer’s privacy policy .
Data Used to Track You
The following data may be used to track you across apps and websites owned by other companies:
Data Not Linked to You
The following data may be collected but it is not linked to your identity:
- Identifiers
- Diagnostics
Privacy practices may vary, for example, based on the features you use or your age. Learn More
Information
- PA 6.99 Weekly, 3 days trial $6.99
- PA 4.99 Weekly Trial $4.99
- PA 6.99 Weekly, No Trial $6.99
- PA 9.99 Monthly With Trial $9.99
- PA 29.99 Yearly $29.99
- PA 69.99 Yearly With Trial $69.99
- Pic Answer Lifetime Purchase $39.99
- Pic Answer 4.99 Weekly $4.99
- PA 14.99 Monthly Trial $14.99
- Developer Website
- App Support
- Privacy Policy
More By This Developer
Simulife - Life Simulator Game
Shredder Simulator Games ASMR
Photoshoot - AI Headshot Maker
Sequin Simulator Games
Real Life Moments
Squishy Simulator Games
You Might Also Like
Quizard AI - Scan and Solve
PhotoSolve: Answer Pic Solver
Homework AI - Math Helper
Answer.AI - Your AI tutor
Solvely-AI math solver
March 26, 2024
The Battleground 2024: Texas
Marist Texas Poll
Trump With Double-Digit Lead Over Biden in Texas; Margin Narrows Among Definite Voters… Cruz Leads Allred in Senate Race
In Texas, where former President Donald Trump carried the state by about five-and-a-half percentage points in 2020, Trump now leads Biden by double that (11 percentage points) among registered voters. However, Trump’s lead narrows to seven percentage points among those who say they will definitely vote in November’s election. In the race for U.S. Senate, Republican incumbent Ted Cruz leads his Democratic challenger, Colin Allred, by 6 percentage points among Texas registered voters. The contest changes little among those definite to vote.
55% of Texas registered voters support Trump against Biden (44%) in this year’s presidential election. Among those who definitely plan to vote, Trump (53%) has a seven-percentage point lead (46%) against Biden.
Independents, who Biden carried by 6-percentage points in 2020, now break for Trump. Trump receives 56% of Texas independents to 41% for Biden.
Biden’s support among younger voters has diminished. Trump (57%) leads Biden (43%) by 14-percentage points among those between the ages of 18 and 29 years. According to the Exit Polls of the 2020 General Election in Texas, Biden (57%) handily defeated Trump (40%) with this group. While voters aged 30 to 44 years divided between Biden and Trump in 2020, Trump (60%) has a wide lead against Biden (40%) among these voters in the state.
Trump has made inroads among Black voters. While Biden (64%) leads Trump (34%) by nearly two-to-one among Black voters, Biden received the support of a much greater proportion of Black voters (90%) in the 2020 election. Biden has also lost support among Latino voters. Biden (52%) edges Trump (47%) by five percentage points. He carried this group of voters by 17 percentage points in 2020.
In a three-candidate race, including Robert F. Kennedy Jr., who is yet to achieve ballot status in Texas, Trump (48%) has a 12-percentage point lead over Biden (36%) among the Texas electorate. Kennedy receives 15% of the vote.
"Trump’s lead among independents and younger voters and his improved standing among Black and Latino voters is a striking change from four years ago," says Lee M. Miringoff, Director of the Marist College Institute for Public Opinion. "Democrats have a long way to go to put Texas in play in November."
Biden Approval Rating Upside Down in Texas
38% of Texas adults approve of the job Biden is doing as President. 55% disapprove. By more than two-to-one, Texas residents strongly disapprove (42%) of the job Biden is doing in office than strongly approve (18%). This is little changed from 2022.
Mental Fitness a Political Liability for Biden in Texas, Not So Much for Trump
62% of Texas residents — including 88% of Republicans, 61% of independents, and 28% of Democrats — say Biden’s mental fitness to be president is a real concern. 36% think it is a campaign strategy used by his opponents.
A majority of Texas residents are not worried about Trump’s mental ability to be President. 54% — including 81% of Republicans, 60% of independents, and 20% of Democrats — believe questions about Trump’s mental fitness are a campaign strategy used by his opponents. 43% are concerned about his mental acumen.
Texans Have Negative View of Biden, Divide About Trump… RFK Jr. Little-Known
55% of Texas residents have an unfavorable impression of President Biden, including 58% of independents. 37% have a positive impression of him.
In contrast, Texas residents divide about Trump. 46% have an unfavorable opinion of the former president while 47% have a favorable one.
About one in three residents statewide (33%) views Kennedy positively. 27% have a negative image of him, and 40% have either never heard of Kennedy or are unsure how to rate him.
Trump’s Actions Below Board, Say More than Seven in Ten
73% of Texans think Trump’s actions while president were either illegal (42%) or unethical but not illegal (31%). 26% say Trump did nothing wrong.
Most Democrats (83%) and a plurality of independents (42%) say Trump broke the law. An additional 30% of independents think Trump engaged in unethical behavior but did not break the law. While a plurality of Republicans (48%) say Trump did nothing wrong, 44% think he did something unethical.
Many residents (61%), including 89% of Democrats, 67% of independents, and 30% of Republicans do not think Trump should receive immunity from criminal prosecution for actions taken while president. 38%, including 68% of Republicans, think he should be granted immunity.
A majority of Texans (53%) say the investigations into the former president are fair and are intended to find out if he broke the law. This includes 89% of Democrats and 55% of independents but only 18% of Republicans. Fueled by Republicans (81%), 46% of Texas residents say the investigations are unfair and are a means of getting in the way of the 2024 presidential campaign.
Trump Viewed Stronger on Economy, Immigration, and Preserving Democracy
Six in ten Texas adults (60%) think Trump would better handle the economy as president than Biden (38%). Trump (59%) also has the advantage over Biden (39%) on the issue of immigration. Texans give Trump (51%) an edge over Biden (47%) on preserving democracy. However, they divide about whether Biden (48%) or Trump (47%) would better handle the issue of abortion.
Immigration, Inflation, and Preserving Democracy Top Voting Issues
27% of Texas residents say immigration is top of mind for them when deciding their vote for president. 26% mention inflation, and 24% cite preserving democracy. Nine percent say abortion is their number-one voting issue while the same proportion (9%) cite healthcare. Five percent say crime is a pressing concern when thinking about November’s elections.
While 43% of Republicans mention immigration, 40% of Democrats choose preserving democracy as their top concern. Among independents, immigration (29%) is the priority followed closely by preserving democracy (24%) and inflation (23%).
Cruz is +6 Percentage Points Over Allred in Texas Senate Race
Republican incumbent Ted Cruz (51%) leads his Democratic challenger Colin Allred (45%) by six percentage points among Texas registered voters. Among independents, Cruz (50%) is up by eight percentage points against Allred (42%). There is a wide gender gap. Cruz (59%) carries men by 21 percentage points over Allred (38%). Allred (52%) tops Cruz (44%) among women.
Opinions of Cruz Mixed… Allred Mostly Unknown
45% of Texas residents have a favorable opinion of Cruz, and 43% have an unfavorable one. Allred has low name recognition in the state. A majority (53%) have either never heard of Allred or are unsure how to rate him. 30% have a positive view of Allred while only 17% have an unfavorable one.
Texas Republicans Best Democrats in Early Look at the Generic Ballot
A majority of registered voters statewide (54%) say they are more likely to vote for the Republican candidate on the ballot in their district rather than the Democratic candidate (44%). Among independent voters, 55% say they are more likely to cast their ballot for the Republican congressional candidate.
More Than Seven in Ten Confident in Electoral Process
72% of Texans are either very confident or confident that their state or local government will conduct a fair and accurate election in November. Regardless of party affiliation, a strong majority of residents believe in the integrity of Texas’ elections.
Domestic Issues Should be the Priority, Say a Majority of Texas Residents
56% of Texans, including 62% of Republicans and 58% of independents, think the U.S. should focus on its own problems and play less of a leadership role globally. 43% of residents, including 57% of Democrats, think it is crucial for the U.S. to play a major leadership role in world events.
- Survey Data
ME 274: Basic Mechanics II
Homework h5.c - sp24.
DISCUSSION THREAD

NOTE: The view of the figure provided is that of the rod as seen from above the surface on which the rod lies.
Any questions?? Please ask/answer questions regarding this homework problem through the "Leave a Comment" link above.
20 thoughts on “Homework H5.C - Sp24”
Does a frictionless horizontal surface mean that it is on a horizontal plane?
Correct. This means that gravity does not need to be taken into account
Is there a normal force to account for in this question?
The only normal force would be opposing gravity, coming out of the page. Since this is in the horizontal plane we do not need to account for gravity and therefore we do not need to account for the normal force. The only force in your FBD should be force F
Would kinamatics be required for this question? If F is the only force acting on the rod I believe the question can be solved just through Newton/Eulers, would this be correct?
If in any kinetics problem in this course that you find that you do not need kinematics, then simply write: "Step 3: kinematics - NOT NEEDED.
In this problem, you do not need kinematics.
This is correct. You do not need kinematics in this problem since there isn't a problem where we have too many unknowns. The inertia is of the center of mass which is 1/12mL^2 based on the chart for inertia in our lecture book. Dividing F by g will give you your mass to solve a and b. Acceleration can be found by finding the force in the x and y directions and angular acceleration can be found by finding the torques that correspond to inertia times alpha.
MOI for a uniform rod around its center is 1/12 * m * L^2.
After solving for the acceleration of G, you will need to use M = IA (where I is moment of inertia and A is angular acceleration of the rod).
The mass is given in terms of pounds, which is mass*gravity. It's important to remember to divide this value by gravity in imperial units to find the mass alone when plugging into equations
Please note that the "weight" of the bar is given in terms of pounds.
I know that we need to use the M = IA Formula. However, I am confused on when we would use the (r cross ma) term if we are using the same equation and why it crosses out here.
For different problems, the 'r cross ma' term could be 'crossed out' for different reasons. Your goal should be to choose a point A such that this term goes to zero/ is 'crossed out'. In this problem specifically, if you choose the point A as the center of mass, then the position vector from A to G becomes a zero vector , and the whole cross product term goes to zero - simplifying our math.
I think it would be helpful to reference pg. 298 in the lecture book which explains it. This problem essentially falls into the first bullet point: by choosing the point of interest to be the center of mass, then the position vector is 0 and (r cross ma)=0. You would need to use the r cross ma when the point you choose is NOT 1) center of mass 2) fixed 3) with r(G/A) parallel to acceleration vector
All of the above cases have (r cross ma)=0, and we purposely choose a point such that we do not have to calculate r cross ma
When solving this hw, I did not need to use either accelerations to solve for each other. They were separate equations from the book. Similar to lecture
What helped solve this problem more easily is to remember that the Y component of the force being applied is cancels out when taking the moment around the center of mass.
The weight of the bar and the force acting on the bar are both given in lbs, so no unit conversion is necessary such as mg --> m
When dealing with a frictionless horizontal surface, we don't need to worry about gravity or its effect on the surface. We mainly focus on the force F acting on the rod, without considering motion equations. Remembering to use the moment of inertia formula M=IA is important, especially when figuring out how the rod rotates. Choosing A to be at the same location as the center of mass G, helps simplify calculations by eliminating unnecessary terms like r×ma. This method is all about making the math easier, as explained in the lectures.
In this problem, because the rod is in the horizontal plane and there is only one force, only kinetics are required to solve
You do not need kinematics in this problem since there isn't a problem where we have too many unknowns. The inertia is of the center of mass which is 1/12mL^2 based on the chart for inertia in our lecture book. Dividing F by g will give you your mass to solve a and b. Acceleration can be found by finding the force in the x and y directions and angular acceleration can be found by finding the torques that correspond to inertia times alpha.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Purdue University

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Less commonly, homework is assigned to extend student learning to different contexts or to integrate learning by applying multiple skills around a project. Little research exists on the effects of these different kinds of homework on student achievement, leaving policymakers with little evidence on which to base decisions (Cooper 1989; Foyle ...
Yes, and the stories we hear of kids being stressed out from too much homework—four or five hours of homework a night—are real. That's problematic for physical and mental health and overall well-being. But the research shows that higher-income students get a lot more homework than lower-income kids.
Homework can also help clue parents in to the existence of any learning disabilities their children may have, allowing them to get help and adjust learning strategies as needed. Duke University Professor Harris Cooper noted, "Two parents once told me they refused to believe their child had a learning disability until homework revealed it to ...
Is homework, including the projects and writing assignments you do at home, an important part of your learning experience? Or, in your opinion, is it not a good use of time? Explain.
Pro 1: Homework Helps to Improve Student Achievement. Homework teaches students various beneficial skills that they will carry with them throughout their academic and professional life, from time management and organization to self-motivation and autonomous learning. Homework helps students of all ages build critical study abilities that help ...
Students reported bringing home an average of just over three hours of homework nightly (Journal of Experiential Education, 2013). On the positive side, students who spent more time on homework in that study did report being more behaviorally engaged in school — for instance, giving more effort and paying more attention in class, Galloway says.
In this paper, I also present the results of a small-scale study into 90 first-year English Department students' perceptions of homework vs. home-learning in the context of Abu Dhabi, the UAE ...
Nobody knows what the point of homework is. The homework wars are back. As the Covid-19 pandemic began and students logged into their remote classrooms, all work, in effect, became homework. But ...
A schoolwide effort to reduce homework has led to a renewed focus on ensuring that all work assigned really aids students' learning. I used to pride myself on my high expectations, including my firm commitment to accountability for regular homework completion among my students. But the trauma of Covid-19 has prompted me to both reflect and adapt.
When homework is used as a tool to build social, emotional, and academic learning beyond the school day, it takes on a different look and purpose than just more work to do at home. The goal of Responsive Classroom schools is to design homework that meets the basic needs of significance and belonging for every student by strengthening ...
America's K-12 students are returning to classrooms this fall after 18 months of virtual learning at home during the COVID-19 pandemic. Some students who lacked the home internet connectivity needed to finish schoolwork during this time - an experience often called the "homework gap" - may continue to feel the effects this school year. Here is what Pew Research Center surveys found ...
As young children begin school, the focus should be on cultivating a love of learning, and assigning too much homework can undermine that goal. And young students often don't have the study skills to benefit fully from homework, so it may be a poor use of time (Cooper, 1989; Cooper et al., 2006; Marzano & Pickering, 2007). A more effective ...
Homework allows for more time to complete the learning process. School hours are not always enough time for students to really understand core concepts, and homework can counter the effects of time shortages, benefiting students in the long run, even if they can't see it in the moment. 6. Homework Reduces Screen Time.
The research cited by educators just doesn't seem to make sense. If a child wants to learn to play the violin, it's obvious she needs to practice at home between lessons (at least, it's ...
1. Supercharging Learning. Homework isn't about mindless repetition; it's your secret weapon to reinforce what you've learned in class. It's like a memory boost that makes sure you remember the important stuff for the long haul. 2. Mastering Time and Study Skills. Homework teaches you real-world skills that go way beyond the textbook.
Homework can affect both students' physical and mental health. According to a study by Stanford University, 56 per cent of students considered homework a primary source of stress. Too much homework can result in lack of sleep, headaches, exhaustion and weight loss. Excessive homework can also result in poor eating habits, with families ...
Home truths about homework. The challenges of home learning, highlighted by the pandemic, should make us question the traditional tasks we set for students to complete outside school. Now is the perfect time to rethink our approach, say Rick Grammatica and Richard Holme. 30th April 2021, 12:00am.
Here's how it works: first, set a timer for 25 minutes. This is going to be your work time. During this 25 minutes, all you can do is work on whatever homework assignment you have in front of you. No email, no text messaging, no phone calls—just homework. When that timer goes off, you get to take a 5 minute break.
Homework is an opportunity to learn and retain information in an environment where they feel most comfortable, which can help accelerate their development. 5. Using Learning Materials. Throughout a child's education, understanding how to use resources such as libraries and the internet is important. Homework teaches children to actively ...
The challenge: Learning independently. It's important for kids to learn how to do homework without help. Using a homework contract can help your child set realistic goals. Encourage "thinking out loud." Get tips for helping grade-schoolers do schoolwork on their own. Sometimes, homework challenges don't go away despite your best efforts.
Some pupils may not have a quiet space for home learning - it is important for schools to consider how home learning can be supported (e.g. through providing homework clubs for pupils). 3. Homework that is linked to classroom work tends to be more effective. ... In the most effective examples homework was an integral part of learning, rather ...
Happy teachers. Our department leadership team has noted significant change in students' mathematical confidence and resilience. Based on the impact we have seen so far, we are highly confident that as we roll out the White Rose Education scheme of work and premium resources to future year groups, our students will flourish.
Bedrock for GCSE English: 102 terms and example analysis. 2 dedicated CPD workshops for your team (remote/virtual or held on-site) School Impact Analysis report and data triangulation each year. Bedrock Learning's digital literacy curriculum explicitly teaches Tier 2 and Tier 3 vocabulary and grammar, across 38 subject areas & all Key Stages.
For closure lengths, the study averaged district-level estimates of time spent in remote and hybrid learning compiled by the Covid-19 School Data Hub (C.S.D.H.) and American Enterprise Institute ...
From this data, the model — known as Universal Cell Embedding, or U.C.E. — calculated the similarity among cells, grouping them into more than 1,000 clusters according to how they used their ...
Studdy is the most accurate app for solving word problems, math problems, and college-level science problems. With more than 1 million problems solved, Studdy is the go-to AI homework helper anytime, anywhere. FEATURES: - Makes learning tough subjects super easy, with step by step guidance and the ability to ask questions along the way
Victoria "Tia" Kozar, a fourth-year medical student at the University of Connecticut School of Medicine found her biggest inspiration in the field of Geriatric Psychiatry during her undergraduate education at Quinnipiac University when she participated in the first Quinnipiac Students-In-Residence Program. She resided at a Masonicare assisted living community and it was her neighbor and ...
Pic Answer - AI Solver: Snap, Ask, Learn! Step into a world of effortless learning with Pic Answer - AI Solver, where each photo brings you closer to understanding. This app goes beyond traditional math solvers, offering a unique blend of AI-driven solutions and interactive chat for a variety of ac…
The Marist Institute for Public Opinion (MIPO) is a survey research center. MIPO is home to the Marist Poll and conducts polls on politics, the economy, sports, technology and more at the local, state, and national level.
HOME PAGE; Course material; Exams; Homework/Discussion; Daily Schedule - Sp 24; Instructor material - Sp 24; Search for: Chapter 5 Homework. ... Previous Post Homework H5.D - Sp24 Next Post Homework H5.F - Sp24. 14 thoughts on "Homework H5.C - Sp24" Jiahao He says: March 22, 2024 at 4:10 pm.