Browse Course Material
Course info, instructors.
- Prof. Eric Grimson
- Prof. John Guttag

Departments
- Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
As Taught In
- Programming Languages
Introduction to Computer Science and Programming
Assignments.

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare
- Trending Now
- Foundational Courses
- Data Science
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- System Design
- DevOps Tutorial
Basics of Computer and its Operations
Introduction :
A computer is an electronic device that can receive, store, process, and output data. It is a machine that can perform a variety of tasks and operations, ranging from simple calculations to complex simulations and artificial intelligence.
Computers consist of hardware components such as the central processing unit (CPU), memory, storage devices, input/output devices, and peripherals, as well as software components such as the operating system and applications.
The history of computers can be traced back to the 19th century when mechanical devices such as the Analytical Engine and tabulating machines were developed. However, modern computers as we know them today were developed in the mid-20th century with the invention of the transistor and the development of integrated circuits.
Today, computers are widely used in various industries such as education, finance, healthcare, and entertainment, and they have revolutionized the way we live, work, and communicate. They have also given rise to a new era of technology such as the internet, cloud computing, and mobile devices, which have further transformed our daily lives.
Computer is a device that transforms data into meaningful information. It processes the input according to the set of instructions provided to it by the user and gives the desired output quickly. A Computer can perform the following set of functions:
- Accept data
- Process data as desired
- Retrieve the stored data as and when required
- Print the result in desired format.
Data and Information: Data: It is the term used for raw facts and figures fed into the computer and along with the set of instructions which enables the computer to convert this raw data into the refined and useful information. Information: Data represented in useful and meaningful form is information.
Data and information are related concepts, but they have different meanings. Data refers to raw facts and figures that are unorganized and have no meaning on their own. Information, on the other hand, is data that has been processed, organized, and given context to make it meaningful and useful.
Data can take many forms, such as numbers, words, images, or sounds. For example, a list of sales figures for a company is data. However, this data by itself does not provide any useful information. It needs to be processed and analyzed to be turned into information that can be used for decision-making.
Information is data that has been processed and organized in a meaningful way to convey a message or answer a question. For example, using the sales figures from the earlier example, an analyst could create a graph or chart that shows the sales trends over time, providing meaningful information about the company’s performance.
In summary, data is the raw, unorganized facts and figures, while information is data that has been processed and given context to be meaningful and useful for decision-making.
Classification of Computers: Computers can be classified based on the technology being used and the way they are designed to perform the various tasks. Computers can be categorized into Digital, Analog and Hybrid based on their design and working:
- Digital Computers : These are the modern computers which are capable of processing information in discrete form. In digital technology data which can be in the form of letters, symbols or numbers is represented in binary form i.e. 0s and 1s. The digital computers are used in industrial, business and scientific applications. They are quite suitable for large volume data processing.
- Analog Computers : These computers are used to process data generated by ongoing physical processes. A thermometer is an example of an analog computer since it measures the change in mercury level continuously. Analog computers are well suited to simulating systems. A simulator helps to conduct experiments repeatedly in real time environment. Some of the common examples are simulations in aircrafts, nuclear power plants, hydraulic and electronic networks.
- Hybrid Computers : These use both analog and digital technology. It has the speed of analog computer and the accuracy of a digital computer. It may accept digital or analog signals but an extensive conversion of data from digital to analog and analog to digital has to be done. Hybrid Computers are used as a cost effective means for complex simulations.
- Supercomputers: These are the most powerful and expensive computers that are used for complex scientific calculations, simulations, and research. They are used in fields such as weather forecasting, cryptography, and nuclear research.
- Mainframe Computers: These are large and powerful computers that are used by large organizations such as banks, airlines, and government agencies to process massive amounts of data and handle multiple users simultaneously.
- Mini Computers: These are smaller and less powerful than mainframe computers, but they are still capable of handling multiple users and processing large amounts of data. They are commonly used by small to medium-sized businesses for accounting, inventory management, and other data-intensive tasks.
- Personal Computers: These are small and affordable computers that are designed for individual users. They are commonly used for personal productivity, entertainment, and communication.
- Workstations: These are high-performance computers that are used by professionals such as architects, engineers, and designers to run complex software applications for tasks such as 3D modeling, animation, and scientific visualization.
- Embedded Systems: These are specialized computers that are built into other devices such as cars, appliances, and medical equipment to control their operations and perform specific functions.
- Mobile Devices: These are small and portable computers that are designed for on-the-go use, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops
Classification of Digital Computers
- Micro Computers : These are also known as Personal Computers. These type of digital computer uses a microprocessor (a CPU on a single chip) and include both desktops and laptops. These computers can work on small volume of data, are very versatile and can handle variety of applications. These computers are being used as work stations, CAD, multimedia and advertising applications. Example: portable computers such as PDAs (Personal Digital Assistants) and tablets
- Mini Computers : These computers can support multiple users working simultaneously on the same machine. These are mainly used in an organization where computers installed in various departments are interconnected. These computers are useful for small business organizations.
- Main Frames : These computers are large and very powerful computers with very high memory capacity. These can process huge databases such as census at extremely fast rate. They are suitable for big organizations, banks, industries etc. and can support hundreds of users simultaneously on the network.
- Super Computers : These are fastest and very expensive computers. They can execute billions of instructions per second. These are multiprocessor, parallel systems suitable for specialized complex scientific applications involving huge amounts of mathematical applications such as weather forecasting.
- Minicomputers: These are smaller and less powerful than mainframe computers, but they are still capable of handling multiple users and processing large amounts of data. They are commonly used by small to medium-sized businesses for accounting, inventory management, and other data-intensive tasks.
- Microcomputers: These are the most common type of digital computers, also known as personal computers or PCs. They are designed for individual users and are used for personal productivity, entertainment, and communication.
- Mobile Devices: These are small and portable computers that are designed for on-the-go use, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
Peripheral Devices
These devices are used for performing the specific functions and are connected to the computer externally. These peripheral devices enable the computer to operate according to the user requirements by feeding data in and out of the computer. Peripheral devices are as follows:
- Optical/magnetic Scanner
- Touch Screen
- Microphone for voice as input
- Monitor (Visual Display Unit)
Difference between RAM and Hard-disk
CPU process the data, and to process that data we need fast speed memory which is known as RAM.
Types of Software
- System Software : These are those software,without which our PC,laptop won’t run, i.e it is must for a device to be operating. For Example: Linux,Unix,Windows,etc.
- Application Software : These are those software,without which our PC,laptop can run, i.e these software are not necessary for a device to be operating. For Example: Facebook,What’s App,Games.
Difference between Hacker and Cracker
- Hacker : They will just warn you something about malicious activity going around in your computer.It will not steal your information.
- Cracker : They will try to steal your Information without informing you.
Basic computer operation :
- Booting up: This is the process of starting up the computer by loading the operating system (OS) into memory. The computer runs a series of checks to ensure all hardware is working correctly before loading the OS.
- Logging in: After booting up, you will need to log in to access your user account. This requires entering your username and password.
- Running programs: Once you have logged in, you can run programs on your computer. Programs can include web browsers, office applications, media players, and more.
- Accessing data: You can access data stored on your computer or other connected devices, such as external hard drives or cloud storage services. This can include files, documents, photos, and other media.
- Connecting to the internet: You can connect to the internet to access websites, download files, and communicate with others online. This typically involves using a web browser to access websites and other online services.
- Communicating with other devices: You can communicate with other devices connected to your computer, such as printers, scanners, or other peripherals. This allows you to print documents, scan images, and perform other tasks.
- Saving and backing up data: It’s important to save and back up your data regularly to avoid data loss. You can save data to your local hard drive, external hard drives, or cloud storage services.
- Shutting down: When you’re finished using your computer, you should shut it down properly. This involves closing all programs and files, saving any changes, and shutting down the OS.
- Troubleshooting: If you experience issues with your computer, you may need to troubleshoot the problem. This can involve diagnosing hardware or software issues, performing updates, or reinstalling drivers.
- Security: It’s important to keep your computer secure by using antivirus software, firewalls, and other security measures. This helps protect your data and prevent unauthorized access to your system.
Issues of basic computers and computer operations :
some common issues that can arise with basic computers and computer operations:
- Slow performance: Computers can become slow and unresponsive due to a variety of factors, such as lack of storage space, outdated hardware, or malware.
- Malware and viruses: Malware and viruses can infect computers and cause a range of problems, including data loss, system crashes, and identity theft.
- Hardware failures: Computer hardware components can fail over time, leading to issues like system crashes, data loss, and display problems.
- Software glitches: Software applications can sometimes malfunction or crash, leading to issues like data loss or unresponsive programs.
- Driver problems: Drivers are software components that enable hardware devices to communicate with the operating system. If drivers become outdated or corrupted, it can lead to issues like hardware failures or system crashes.
- Compatibility issues: Sometimes software applications or hardware components may not be compatible with each other, leading to issues like system crashes or display problems.
- Internet connectivity issues: Problems with internet connectivity can lead to issues like slow loading web pages, interrupted downloads, and difficulty accessing online services.
- User error: Users can sometimes make mistakes or accidentally delete files or programs, leading to issues like data loss or unresponsive programs.
Reference :
Some references for learning about basic computers and computer operations:
- “Computer Basics” by GCFGlobal: This is a comprehensive guide to learning about computers, including hardware components, software, and basic operations.
- “Computer Science Basics” by Khan Academy: This course covers the fundamentals of computer science, including how computers work, programming basics, and algorithms.
- “Introduction to Computers” by Udemy: This course covers the basics of computer hardware, software, and operations, including topics like file management, computer security, and troubleshooting.
- “Computer Operations” by Techopedia: This article provides an overview of computer operations, including booting up, running programs, and saving and backing up data.
- “How Computers Work” by HowStuffWorks: This website provides a detailed explanation of how computers work, including the role of hardware components, operating systems, and software applications.
- “The Basics of Computer Operations” by The Tech Academy: This guide provides an overview of basic computer operations, including starting up, running programs, and shutting down.
- “Introduction to Computing” by Georgia Tech: This course provides an introduction to computing, including basic computer operations, programming, and algorithms.
Similar Reads
Improve your coding skills with practice.
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Introduction to Computer
- Computer Science

What is a Computer?
A computer is an electronic machine that processes raw data and outputs information. An electronic device that takes data as input and transforms it using a set of special instructions known as Programs to produce the desired output. A computer has an internal memory that stores data and instructions that are temporarily awaiting processing, as well as the intermediate result (information) before it is communicated to the recipients via the Output devices
What Does the Computer Require in Order to be Operational?
A Computer requires hardware devices and an operating system in order to be operational.
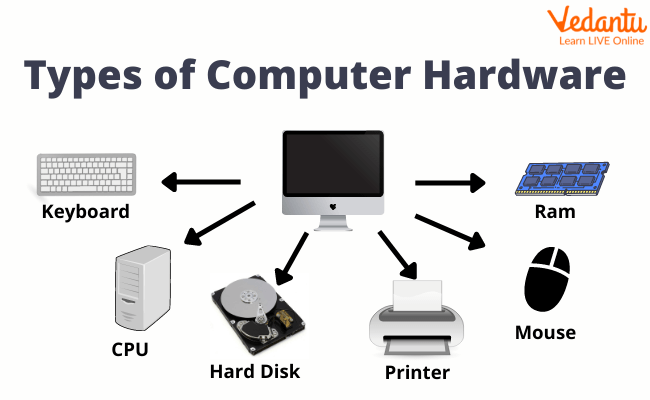
1. Hardware Devices
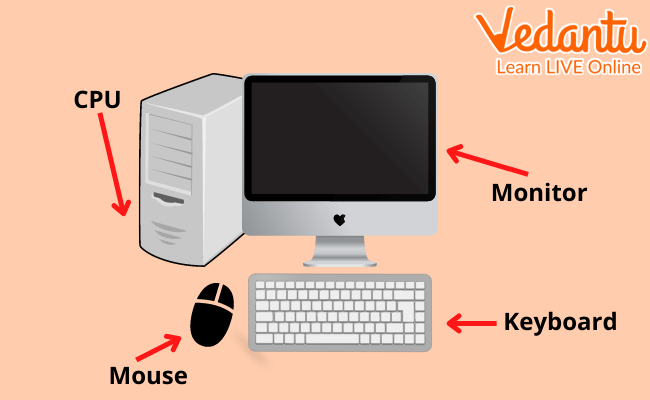
Monitor: It is a big television-like screen. It is an output device where you see what is happening on the computer.
Keyboard: It is an input device. It is a way of giving commands to a computer with the help of keys over it.
Central Processing Unit (CPU): It is a processing unit.It is considered the brain of the computer as it can’t perform any activity without CPU.
Mouse: It is an input device. This is the alternate method for cooperating with your PC. Most mice have two buttons — a right and a left button — and a looking over wheel.
Hardware Devices
2. Operating System (OS)

Operating System
PCs without an OS are precisely similar to TVs without a signal. They will turn on, yet you will be checking a clear screen out without any desire to collaborate with it. The most famous working framework is "Microsoft Windows," and it is used by most PC.
The OS acts as the sensory system of the PC, interfacing the computer processor to all the PC programs. The OS permits you to run other programs, work on projects, and do essentially all the other things that PCs are prepared to do.
There are a wide range of renditions of Microsoft Windows, and a new adaptation is delivered every several years.

How to Operate a Computer
There are three states in which a computer is at any given time.
OFF : This is precisely the exact thing it seems like: The PC is off, and no parts are running or working. The screen is dark (no pictures), there is no "humming" sound from the central processor, and the PC is inert to mouse developments or pressing keys on the keyboard.
ON : When a PC is on, you ought to see pictures on the screen, conceivably hear a "buzzing" commotion coming from the central processor and the pointer on the screen ought to answer when you move the mouse.
Rest Mode : Most PCs have a mode called "Rest," in which the PC is on, yet has expected an energy-productive, insignificant power mode. To "wake" the PC, basically move the mouse around or press the spacebar on the console, and it will "awaken" and return to the identical spot that it was at the point at which it fell asleep.
Signing on Screen
When you turn the PC on, the PC will go through a progression of mechanized undertakings before it is prepared for you to associate with it; this cycle is called "startup." This cycle will endure somewhere in the range of one and two minutes. Assuming the PC is not working accurately, you might see a blunder message during startup.
After you sign on, the PC will show what is known as your work area inside a couple of moments to a couple of moments. Here you will see a computerized portrayal of something almost identical to real-life office space, complete with a work area, documents and record organizers, and a recycling bin.
Features of Computer
Below mentioned are some of the features of a computer..
When executing mathematical computations, a computer works significantly faster and more accurately than a human.
Speed of Computer
Calculations made by computers are always accurate. Data inaccuracy or consistency might lead to errors.
A computer contains internal storage for data called main memory. Data is also stored on removable media like CDs, pen drives, and other types of secondary storage.
Computer Memory
Reliability
When given the same set of data repeatedly, a computer will consistently provide the same output, demonstrating its dependability.
The computer completes every task automatically, that is, without human interaction.

Computer Automation
Drawbacks of Computer
Although using a computer has numerous benefits, there are also risks and drawbacks. If used improperly, computers can cause a number of health problems.
The computer is emotionless.
It can't function alone. It requires somebody to work on it and give it instructions.
The computer must be supplied with each command.
No choice can be made by a computer on its own.
What is a Machine?
A machine is a tool that facilitates our job.
It helps us save time and effort.
Humans are not as productive as machines .
Machine Examples Include the Following:
For enjoyment, people use televisions.

To iron the clothes, use an iron box.
An automobile is used for transportation.
Calling is done on a mobile device.

Mobile Device
Points to Remember
Computer is an electronic machine.
The main components required for a computer are mouse, monitor and keyboard.
The CPU is also known as the “Brain” of the computer.
OS stands for operating system.
The first screen you see when it starts is called the desktop.
Learning by Doing
Choose the correct answer:.
1. Which part of the computer contains the computer's brains?
B. Keyboard
D. All of above
Write True or False
1. Windows, Linux, and Android are examples of Operating devices(True/False)
2. Keyboard is an Input device. (True/False)
Sample Questions
1. Choose the correct statement
A. Computer is an electronic machine
B. It performs arithmetic operation
C. Both A) and B)
2. What is an OS?
Ans: OS stands for operating system.The OS permits you to run other programs, work on projects, and do essentially all the other things that PCs are prepared to do.
3. List various primary parts of the computer.
1. A Motherboard
2. A CPU i.e. Central Processing Unit’
3. RAM i.e. Random Access Memory
5. Hard drives
6. Computer Mouse
The monitor, CPU, keyboard, mouse, printer, sound system, RAM, hard drive, and many other components make up the computer system's hardware. There are various operating systems in computers such as Microsoft Windows, Linux and so on.
FAQs on Introduction to Computer
1. Which OS does Apple use?
An Apple Computer is called a Macintosh (Mac). Its Operating System is OS X while other PCs use windows.
2. Do computers require the Internet to operate?
A computer does not need to access the Internet in order to run properly. The Internet is a way of connecting to other computer users. You can interface with the web utilizing a telephone line, a link association, or by utilizing a remote interfacing gadget (wi-fi). For most home PC clients, this is a paid help, however you can use the Web for free in a few public areas, similar to the library or a café. A PC will actually want to carry out most normal roles (play music, type records, alter pictures) and run programs without a Web association. Notwithstanding, to see a page or send an email, you will require a Web association.
3. What “My Computer is Possessed!” means?
“My Computer is Possessed!” It is a common misconception that computers have “a mind of their own.” In spite of the fact that PCs can play out specific assignments significantly more effectively and quicker than people (like counting, performing numerical computations, and so on), they are, eventually, machines and can't have an independent mind. Any reasonable person would agree that the PC can do nothing that you don't advise it to do.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In computer programming, an assignment statement sets and/or re-sets the value stored in the storage location(s) denoted by a variable name; in other words, it copies a value into the variable.
Assignments Course Description 6.0001 Introduction to Computer Science and Programming in Python is intended for students with little or no programming experience.
This course is based on Python 3.5. See the Anaconda for Python 3.5 FAQ. Please review the 6.0001 Style Guide (PDF) before attempting the problem sets. If you need additional help, please consult the 6.0001 list of Programming Resources (PDF). Solutions are not available.
Assignments. MIT OpenCourseWare is a web based publication of virtually all MIT course content. OCW is open and available to the world and is a permanent MIT activity.
Understanding computer fundamentals is essential for anyone looking to navigate the digital world confidently. This tutorial Computer fundamental has covered the basics of hardware, software, operating systems, and networking, providing you with a solid foundation.
Components of a Computer. There are basically three important components of a computer: Input Unit; Central Processing Unit(CPU) Output Unit; 1. Input Unit: The input unit consists of input devices that are attached to the computer. These devices take input and convert it into binary language that the computer understands.
A computer is an electronic device that can receive, store, process, and output data. It is a machine that can perform a variety of tasks and operations, ranging from simple calculations to complex simulations and artificial intelligence.
Chapter Overview. Th is chapter introduces you to the computer, inside and out. You’ll learn about the types of computers that are in use today, and you’ll get an overview of dif erent ways that computers are used in our society.
A computer is an electronic machine that processes raw data and outputs information. An electronic device that takes data as input and transforms it using a set of special instructions known as Programs to produce the desired output.
In this week you will learn about the computer science concepts of state and modularity and how they can help you understand the computer applications that you use every day. What's included 9 videos 1 reading 4 assignments 1 peer review 3 discussion prompts