- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide

Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide
Table of Contents

Grant Proposal
Grant Proposal is a written document that outlines a request for funding from a grant-making organization, such as a government agency, foundation, or private donor. The purpose of a grant proposal is to present a compelling case for why an individual, organization, or project deserves financial support.
Grant Proposal Outline
While the structure and specific sections of a grant proposal can vary depending on the funder’s requirements, here is a common outline that you can use as a starting point for developing your grant proposal:
- Brief overview of the project and its significance.
- Summary of the funding request and project goals.
- Key highlights and anticipated outcomes.
- Background information on the issue or problem being addressed.
- Explanation of the project’s relevance and importance.
- Clear statement of the project’s objectives.
- Detailed description of the problem or need to be addressed.
- Supporting evidence and data to demonstrate the extent and impact of the problem.
- Identification of the target population or beneficiaries.
- Broad goals that describe the desired outcomes of the project.
- Specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives that contribute to the goals.
- Description of the strategies, activities, and interventions to achieve the objectives.
- Explanation of the project’s implementation plan, timeline, and key milestones.
- Roles and responsibilities of project staff and partners.
- Plan for assessing the project’s effectiveness and measuring its impact.
- Description of the data collection methods, tools, and indicators used for evaluation.
- Explanation of how the results will be used to improve the project.
- Comprehensive breakdown of project expenses, including personnel, supplies, equipment, and other costs.
- Clear justification for each budget item.
- Information about any matching funds or in-kind contributions, if applicable.
- Explanation of how the project will be sustained beyond the grant period.
- Discussion of long-term funding strategies, partnerships, and community involvement.
- Description of how the project will continue to address the identified problem in the future.
- Overview of the organization’s mission, history , and track record.
- Description of the organization’s experience and qualifications related to the proposed project.
- Summary of key staff and their roles.
- Recap of the project’s goals, objectives, and anticipated outcomes.
- Appreciation for the funder’s consideration.
- Contact information for further inquiries.
Grant Proposal Template
Here is a template for a grant proposal that you can use as a starting point. Remember to customize and adapt it based on the specific requirements and guidelines provided by the funding organization.
Dear [Grant-making Organization Name],
Executive Summary:
I. Introduction:
II. Needs Assessment:
III. Goals and Objectives:
IV. Project Methods and Approach:
V. Evaluation and Monitoring:
VI. Budget:
VII. Sustainability:
VIII. Organizational Capacity and Expertise:
IX. Conclusion:
Thank you for considering our grant proposal. We believe that this project will make a significant impact and address an important need in our community. We look forward to the opportunity to discuss our proposal further.
Grant Proposal Example
Here is an example of a grant proposal to provide you with a better understanding of how it could be structured and written:
Executive Summary: We are pleased to submit this grant proposal on behalf of [Your Organization’s Name]. Our proposal seeks funding in the amount of [Requested Amount] to support our project titled [Project Title]. This project aims to address [Describe the problem or need being addressed] in [Target Location]. By implementing a comprehensive approach, we aim to achieve [State the project’s goals and anticipated outcomes].
I. Introduction: We express our gratitude for the opportunity to present this proposal to your esteemed organization. At [Your Organization’s Name], our mission is to [Describe your organization’s mission]. Through this project, we aim to make a significant impact on [Describe the issue or problem being addressed] by [Explain the significance and relevance of the project].
II. Needs Assessment: After conducting thorough research and needs assessments in [Target Location], we have identified a pressing need for [Describe the problem or need]. The lack of [Identify key issues or challenges] has resulted in [Explain the consequences and impact of the problem]. The [Describe the target population or beneficiaries] are particularly affected, and our project aims to address their specific needs.
III. Goals and Objectives: The primary goal of our project is to [State the broad goal]. To achieve this, we have outlined the following objectives:
- [Objective 1]
- [Objective 2]
- [Objective 3] [Include additional objectives as necessary]
IV. Project Methods and Approach: To address the identified needs and accomplish our objectives, we propose the following methods and approach:
- [Describe the activities and strategies to be implemented]
- [Explain the timeline and key milestones]
- [Outline the roles and responsibilities of project staff and partners]
V. Evaluation and Monitoring: We recognize the importance of assessing the effectiveness and impact of our project. Therefore, we have developed a comprehensive evaluation plan, which includes the following:
- [Describe the data collection methods and tools]
- [Identify the indicators and metrics to measure progress]
- [Explain how the results will be analyzed and utilized]
VI. Budget: We have prepared a detailed budget for the project, totaling [Total Project Budget]. The budget includes the following key components:
- Personnel: [Salary and benefits for project staff]
- Supplies and Materials: [List necessary supplies and materials]
- Equipment: [Include any required equipment]
- Training and Capacity Building: [Specify any training or workshops]
- Other Expenses: [Additional costs, such as travel, marketing, etc.]
VII. Sustainability: Ensuring the sustainability of our project beyond the grant period is of utmost importance to us. We have devised the following strategies to ensure its long-term impact:
- [Describe plans for securing future funding]
- [Explain partnerships and collaborations with other organizations]
- [Outline community engagement and support]
VIII. Organizational Capacity and Expertise: [Your Organization’s Name] has a proven track record in successfully implementing projects of a similar nature. Our experienced team possesses the necessary skills and expertise to carry out this project effectively. Key personnel involved in the project include [List key staff and their qualifications].
IX. Conclusion: Thank you for considering our grant proposal. We firmly believe that [Project Title] will address a critical need in [Target Location] and contribute to the well-being of the [Target Population]. We are available to provide any additional information or clarification as required. We look forward to the
opportunity to discuss our proposal further and demonstrate the potential impact of this project.
Please find attached the required supporting documents, including our detailed budget, organizational information, and any additional materials that may be helpful in evaluating our proposal.
Thank you once again for considering our grant proposal. We appreciate your dedication to supporting projects that create positive change in our community. We eagerly await your response and the possibility of partnering with your esteemed organization to make a meaningful difference.
- Detailed Budget
- Organizational Information
- Additional Supporting Documents]
Grant Proposal Writing Guide
Writing a grant proposal can be a complex process, but with careful planning and attention to detail, you can create a compelling proposal. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the grant proposal writing process:
- Carefully review the grant guidelines and requirements provided by the funding organization.
- Take note of the eligibility criteria, funding priorities, submission deadlines, and any specific instructions for the proposal.
- Familiarize yourself with the funding organization’s mission, goals, and previous projects they have supported.
- Gather relevant data, statistics, and evidence to support the need for your proposed project.
- Clearly define the problem or need your project aims to address.
- Identify the specific goals and objectives of your project.
- Consider how your project aligns with the mission and priorities of the funding organization.
- Organize your proposal by creating an outline that includes all the required sections.
- Arrange the sections logically and ensure a clear flow of ideas.
- Start with a concise and engaging executive summary to capture the reader’s attention.
- Provide a brief overview of your organization and the project.
- Present a clear and compelling case for the problem or need your project addresses.
- Use relevant data, research findings, and real-life examples to demonstrate the significance of the issue.
- Clearly articulate the overarching goals of your project.
- Define specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives that align with the goals.
- Explain the strategies and activities you will implement to achieve the project objectives.
- Describe the timeline, milestones, and resources required for each activity.
- Highlight the uniqueness and innovation of your approach, if applicable.
- Outline your plan for evaluating the project’s effectiveness and measuring its impact.
- Discuss how you will collect and analyze data to assess the outcomes.
- Explain how the project will be sustained beyond the grant period, including future funding strategies and partnerships.
- Prepare a comprehensive budget that includes all the anticipated expenses and revenue sources.
- Clearly justify each budget item and ensure it aligns with the project activities and goals.
- Include a budget narrative that explains any cost assumptions or calculations.
- Review your proposal multiple times for clarity, coherence, and grammatical accuracy.
- Ensure that the proposal follows the formatting and length requirements specified by the funder.
- Consider seeking feedback from colleagues or experts in the field to improve your proposal.
- Gather all the necessary supporting documents, such as your organization’s background information, financial statements, resumes of key staff, and letters of support or partnership.
- Follow the submission instructions provided by the funding organization.
- Submit the proposal before the specified deadline, keeping in mind any additional submission requirements, such as online forms or hard copies.
- If possible, send a thank-you note or email to the funding organization for considering your proposal.
- Keep track of the notification date for the funding decision.
- In case of rejection, politely ask for feedback to improve future proposals.
Importance of Grant Proposal
Grant proposals play a crucial role in securing funding for organizations and projects. Here are some key reasons why grant proposals are important:
- Access to Funding: Grant proposals provide organizations with an opportunity to access financial resources that can support the implementation of projects and initiatives. Grants can provide the necessary funds for research, program development, capacity building, infrastructure improvement, and more.
- Project Development: Writing a grant proposal requires organizations to carefully plan and develop their projects. This process involves setting clear goals and objectives, identifying target populations, designing activities and strategies, and establishing timelines and budgets. Through this comprehensive planning process, organizations can enhance the effectiveness and impact of their projects.
- Validation and Credibility: Successfully securing a grant can enhance an organization’s credibility and reputation. It demonstrates to funders, partners, and stakeholders that the organization has a well-thought-out plan, sound management practices, and the capacity to execute projects effectively. Grant funding can provide validation for an organization’s work and attract further support.
- Increased Impact and Sustainability: Grant funding enables organizations to expand their reach and increase their impact. With financial resources, organizations can implement projects on a larger scale, reach more beneficiaries, and make a more significant difference in their communities. Additionally, grants often require organizations to consider long-term sustainability, encouraging them to develop strategies for continued project success beyond the grant period.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: Grant proposals often require organizations to form partnerships and collaborations with other entities, such as government agencies, nonprofit organizations, or community groups. These collaborations can lead to shared resources, expertise, and knowledge, fostering synergy and innovation in project implementation.
- Learning and Growth: The grant proposal writing process can be a valuable learning experience for organizations. It encourages them to conduct research, analyze data, and critically evaluate their programs and initiatives. Through this process, organizations can identify areas for improvement, refine their strategies, and strengthen their overall operations.
- Networking Opportunities: While preparing and submitting grant proposals, organizations have the opportunity to connect with funders, program officers, and other stakeholders. These connections can provide valuable networking opportunities, leading to future funding prospects, partnerships, and collaborations.
Purpose of Grant Proposal
The purpose of a grant proposal is to seek financial support from grant-making organizations or foundations for a specific project or initiative. Grant proposals serve several key purposes:
- Funding Acquisition: The primary purpose of a grant proposal is to secure funding for a project or program. Organizations rely on grants to obtain the financial resources necessary to implement and sustain their activities. Grant proposals outline the project’s goals, objectives, activities, and budget, making a compelling case for why the funding organization should invest in the proposed initiative.
- Project Planning and Development: Grant proposals require organizations to thoroughly plan and develop their projects before seeking funding. This includes clearly defining the problem or need the project aims to address, establishing measurable goals and objectives, and outlining the strategies and activities that will be implemented. Writing a grant proposal forces organizations to think critically about the project’s feasibility, anticipated outcomes, and impact.
- Communication and Persuasion: Grant proposals are persuasive documents designed to convince funding organizations that the proposed project is worthy of their investment. They must effectively communicate the organization’s mission, vision, and track record, as well as the specific problem being addressed and the potential benefits and impact of the project. Grant proposals use evidence, data, and compelling narratives to make a strong case for funding support.
- Relationship Building: Grant proposals serve as a platform for organizations to establish and strengthen relationships with funding organizations. Through the proposal, organizations introduce themselves, highlight their expertise, and demonstrate their alignment with the funding organization’s mission and priorities. A well-written grant proposal can lay the foundation for future collaborations and partnerships.
- Accountability and Evaluation: Grant proposals outline the expected outcomes, objectives, and evaluation methods for the proposed project. They establish a framework for accountability, as organizations are expected to report on their progress and outcomes if awarded the grant. Grant proposals often include plans for project evaluation and monitoring to assess the project’s effectiveness and ensure that the funding is being used appropriately.
- Sustainability and Long-Term Planning : Grant proposals often require organizations to consider the long-term sustainability of their projects beyond the grant period. This includes identifying strategies for continued funding, partnerships, and community involvement. By addressing sustainability in the proposal, organizations demonstrate their commitment to long-term impact and the responsible use of grant funds.
When to Write a Grant Proposal
Knowing when to write a grant proposal is crucial for maximizing your chances of success. Here are a few situations when it is appropriate to write a grant proposal:
- When There is a Funding Opportunity: Grants become available through various sources, including government agencies, foundations, corporations, and nonprofit organizations. Keep an eye out for grant announcements, requests for proposals (RFPs), or funding cycles that align with your organization’s mission and project goals. Once you identify a relevant funding opportunity, you can begin writing the grant proposal.
- When You Have a Well-Defined Project or Program: Before writing a grant proposal, it’s important to have a clearly defined project or program in mind. You should be able to articulate the problem or need you are addressing, the goals and objectives of your project, and the strategies and activities you plan to implement. Having a solid project plan in place will help you write a more compelling grant proposal.
- When You Have Conducted Research and Gathered Data: Grant proposals often require evidence and data to support the need for the project. Before writing the proposal, conduct thorough research to gather relevant statistics, studies, or community assessments that demonstrate the significance and urgency of the problem you aim to address. This data will strengthen your proposal and make it more persuasive.
- When You Have a Strong Organizational Profile: Funding organizations often consider the credibility and capacity of the applying organization. Before writing a grant proposal, ensure that your organization has a strong profile, including a clear mission statement, track record of accomplishments, capable staff or volunteers, and financial stability. These factors contribute to the overall credibility of your proposal.
- When You Have the Time and Resources to Dedicate to Proposal Writing: Writing a grant proposal requires time, effort, and resources. It involves conducting research, developing project plans, creating budgets, and crafting compelling narratives. Assess your organization’s capacity to commit to the grant proposal writing process. Consider the timeline, deadline, and any additional requirements specified by the funding organization before deciding to proceed.
- When You Have Identified Potential Partnerships or Collaborators: Some grant proposals may require or benefit from partnerships or collaborations with other organizations or stakeholders. If your project can be enhanced by partnering with other entities, it’s important to identify and secure these partnerships before writing the grant proposal. This demonstrates a collaborative approach and can strengthen your proposal.
- When You Are Committed to Project Evaluation and Accountability: Grant proposals often include requirements for project evaluation and reporting. If you are willing and able to commit to evaluating the project’s outcomes, tracking progress, and reporting on the use of funds, it is an appropriate time to write a grant proposal. This shows your dedication to transparency, accountability, and responsible use of grant funds.
Also see Proposal
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide...

How To Write A Business Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Business Proposal – Templates, Examples and Guide

How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Proposal – Types, Examples, and Writing Guide

How To Write A Grant Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Grant Proposals (or Give me the money!)
What this handout is about.
This handout will help you write and revise grant proposals for research funding in all academic disciplines (sciences, social sciences, humanities, and the arts). It’s targeted primarily to graduate students and faculty, although it will also be helpful to undergraduate students who are seeking funding for research (e.g. for a senior thesis).
The grant writing process
A grant proposal or application is a document or set of documents that is submitted to an organization with the explicit intent of securing funding for a research project. Grant writing varies widely across the disciplines, and research intended for epistemological purposes (philosophy or the arts) rests on very different assumptions than research intended for practical applications (medicine or social policy research). Nonetheless, this handout attempts to provide a general introduction to grant writing across the disciplines.
Before you begin writing your proposal, you need to know what kind of research you will be doing and why. You may have a topic or experiment in mind, but taking the time to define what your ultimate purpose is can be essential to convincing others to fund that project. Although some scholars in the humanities and arts may not have thought about their projects in terms of research design, hypotheses, research questions, or results, reviewers and funding agencies expect you to frame your project in these terms. You may also find that thinking about your project in these terms reveals new aspects of it to you.
Writing successful grant applications is a long process that begins with an idea. Although many people think of grant writing as a linear process (from idea to proposal to award), it is a circular process. Many people start by defining their research question or questions. What knowledge or information will be gained as a direct result of your project? Why is undertaking your research important in a broader sense? You will need to explicitly communicate this purpose to the committee reviewing your application. This is easier when you know what you plan to achieve before you begin the writing process.
Diagram 1 below provides an overview of the grant writing process and may help you plan your proposal development.
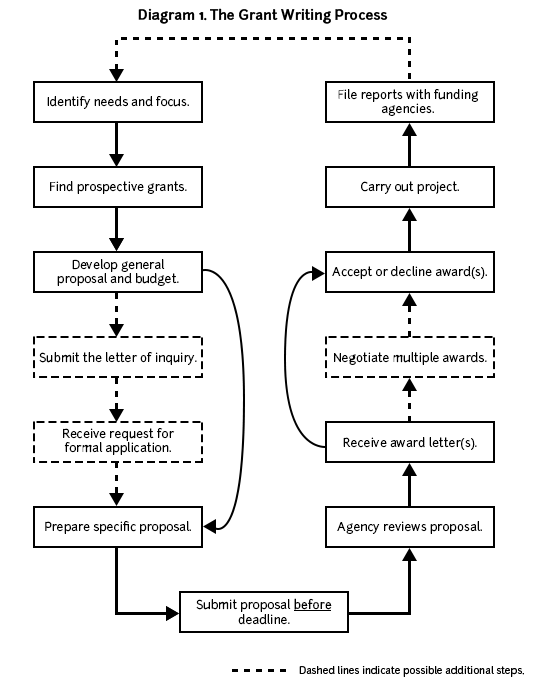
Applicants must write grant proposals, submit them, receive notice of acceptance or rejection, and then revise their proposals. Unsuccessful grant applicants must revise and resubmit their proposals during the next funding cycle. Successful grant applications and the resulting research lead to ideas for further research and new grant proposals.
Cultivating an ongoing, positive relationship with funding agencies may lead to additional grants down the road. Thus, make sure you file progress reports and final reports in a timely and professional manner. Although some successful grant applicants may fear that funding agencies will reject future proposals because they’ve already received “enough” funding, the truth is that money follows money. Individuals or projects awarded grants in the past are more competitive and thus more likely to receive funding in the future.
Some general tips
- Begin early.
- Apply early and often.
- Don’t forget to include a cover letter with your application.
- Answer all questions. (Pre-empt all unstated questions.)
- If rejected, revise your proposal and apply again.
- Give them what they want. Follow the application guidelines exactly.
- Be explicit and specific.
- Be realistic in designing the project.
- Make explicit the connections between your research questions and objectives, your objectives and methods, your methods and results, and your results and dissemination plan.
- Follow the application guidelines exactly. (We have repeated this tip because it is very, very important.)
Before you start writing
Identify your needs and focus.
First, identify your needs. Answering the following questions may help you:
- Are you undertaking preliminary or pilot research in order to develop a full-blown research agenda?
- Are you seeking funding for dissertation research? Pre-dissertation research? Postdoctoral research? Archival research? Experimental research? Fieldwork?
- Are you seeking a stipend so that you can write a dissertation or book? Polish a manuscript?
- Do you want a fellowship in residence at an institution that will offer some programmatic support or other resources to enhance your project?
- Do you want funding for a large research project that will last for several years and involve multiple staff members?
Next, think about the focus of your research/project. Answering the following questions may help you narrow it down:
- What is the topic? Why is this topic important?
- What are the research questions that you’re trying to answer? What relevance do your research questions have?
- What are your hypotheses?
- What are your research methods?
- Why is your research/project important? What is its significance?
- Do you plan on using quantitative methods? Qualitative methods? Both?
- Will you be undertaking experimental research? Clinical research?
Once you have identified your needs and focus, you can begin looking for prospective grants and funding agencies.
Finding prospective grants and funding agencies
Whether your proposal receives funding will rely in large part on whether your purpose and goals closely match the priorities of granting agencies. Locating possible grantors is a time consuming task, but in the long run it will yield the greatest benefits. Even if you have the most appealing research proposal in the world, if you don’t send it to the right institutions, then you’re unlikely to receive funding.
There are many sources of information about granting agencies and grant programs. Most universities and many schools within universities have Offices of Research, whose primary purpose is to support faculty and students in grant-seeking endeavors. These offices usually have libraries or resource centers to help people find prospective grants.
At UNC, the Research at Carolina office coordinates research support.
The Funding Information Portal offers a collection of databases and proposal development guidance.
The UNC School of Medicine and School of Public Health each have their own Office of Research.
Writing your proposal
The majority of grant programs recruit academic reviewers with knowledge of the disciplines and/or program areas of the grant. Thus, when writing your grant proposals, assume that you are addressing a colleague who is knowledgeable in the general area, but who does not necessarily know the details about your research questions.
Remember that most readers are lazy and will not respond well to a poorly organized, poorly written, or confusing proposal. Be sure to give readers what they want. Follow all the guidelines for the particular grant you are applying for. This may require you to reframe your project in a different light or language. Reframing your project to fit a specific grant’s requirements is a legitimate and necessary part of the process unless it will fundamentally change your project’s goals or outcomes.
Final decisions about which proposals are funded often come down to whether the proposal convinces the reviewer that the research project is well planned and feasible and whether the investigators are well qualified to execute it. Throughout the proposal, be as explicit as possible. Predict the questions that the reviewer may have and answer them. Przeworski and Salomon (1995) note that reviewers read with three questions in mind:
- What are we going to learn as a result of the proposed project that we do not know now? (goals, aims, and outcomes)
- Why is it worth knowing? (significance)
- How will we know that the conclusions are valid? (criteria for success) (2)
Be sure to answer these questions in your proposal. Keep in mind that reviewers may not read every word of your proposal. Your reviewer may only read the abstract, the sections on research design and methodology, the vitae, and the budget. Make these sections as clear and straightforward as possible.
The way you write your grant will tell the reviewers a lot about you (Reif-Lehrer 82). From reading your proposal, the reviewers will form an idea of who you are as a scholar, a researcher, and a person. They will decide whether you are creative, logical, analytical, up-to-date in the relevant literature of the field, and, most importantly, capable of executing the proposed project. Allow your discipline and its conventions to determine the general style of your writing, but allow your own voice and personality to come through. Be sure to clarify your project’s theoretical orientation.
Develop a general proposal and budget
Because most proposal writers seek funding from several different agencies or granting programs, it is a good idea to begin by developing a general grant proposal and budget. This general proposal is sometimes called a “white paper.” Your general proposal should explain your project to a general academic audience. Before you submit proposals to different grant programs, you will tailor a specific proposal to their guidelines and priorities.
Organizing your proposal
Although each funding agency will have its own (usually very specific) requirements, there are several elements of a proposal that are fairly standard, and they often come in the following order:
- Introduction (statement of the problem, purpose of research or goals, and significance of research)
Literature review
- Project narrative (methods, procedures, objectives, outcomes or deliverables, evaluation, and dissemination)
- Budget and budget justification
Format the proposal so that it is easy to read. Use headings to break the proposal up into sections. If it is long, include a table of contents with page numbers.
The title page usually includes a brief yet explicit title for the research project, the names of the principal investigator(s), the institutional affiliation of the applicants (the department and university), name and address of the granting agency, project dates, amount of funding requested, and signatures of university personnel authorizing the proposal (when necessary). Most funding agencies have specific requirements for the title page; make sure to follow them.
The abstract provides readers with their first impression of your project. To remind themselves of your proposal, readers may glance at your abstract when making their final recommendations, so it may also serve as their last impression of your project. The abstract should explain the key elements of your research project in the future tense. Most abstracts state: (1) the general purpose, (2) specific goals, (3) research design, (4) methods, and (5) significance (contribution and rationale). Be as explicit as possible in your abstract. Use statements such as, “The objective of this study is to …”
Introduction
The introduction should cover the key elements of your proposal, including a statement of the problem, the purpose of research, research goals or objectives, and significance of the research. The statement of problem should provide a background and rationale for the project and establish the need and relevance of the research. How is your project different from previous research on the same topic? Will you be using new methodologies or covering new theoretical territory? The research goals or objectives should identify the anticipated outcomes of the research and should match up to the needs identified in the statement of problem. List only the principle goal(s) or objective(s) of your research and save sub-objectives for the project narrative.
Many proposals require a literature review. Reviewers want to know whether you’ve done the necessary preliminary research to undertake your project. Literature reviews should be selective and critical, not exhaustive. Reviewers want to see your evaluation of pertinent works. For more information, see our handout on literature reviews .
Project narrative
The project narrative provides the meat of your proposal and may require several subsections. The project narrative should supply all the details of the project, including a detailed statement of problem, research objectives or goals, hypotheses, methods, procedures, outcomes or deliverables, and evaluation and dissemination of the research.
For the project narrative, pre-empt and/or answer all of the reviewers’ questions. Don’t leave them wondering about anything. For example, if you propose to conduct unstructured interviews with open-ended questions, be sure you’ve explained why this methodology is best suited to the specific research questions in your proposal. Or, if you’re using item response theory rather than classical test theory to verify the validity of your survey instrument, explain the advantages of this innovative methodology. Or, if you need to travel to Valdez, Alaska to access historical archives at the Valdez Museum, make it clear what documents you hope to find and why they are relevant to your historical novel on the ’98ers in the Alaskan Gold Rush.
Clearly and explicitly state the connections between your research objectives, research questions, hypotheses, methodologies, and outcomes. As the requirements for a strong project narrative vary widely by discipline, consult a discipline-specific guide to grant writing for some additional advice.
Explain staffing requirements in detail and make sure that staffing makes sense. Be very explicit about the skill sets of the personnel already in place (you will probably include their Curriculum Vitae as part of the proposal). Explain the necessary skill sets and functions of personnel you will recruit. To minimize expenses, phase out personnel who are not relevant to later phases of a project.
The budget spells out project costs and usually consists of a spreadsheet or table with the budget detailed as line items and a budget narrative (also known as a budget justification) that explains the various expenses. Even when proposal guidelines do not specifically mention a narrative, be sure to include a one or two page explanation of the budget. To see a sample budget, turn to Example #1 at the end of this handout.
Consider including an exhaustive budget for your project, even if it exceeds the normal grant size of a particular funding organization. Simply make it clear that you are seeking additional funding from other sources. This technique will make it easier for you to combine awards down the road should you have the good fortune of receiving multiple grants.
Make sure that all budget items meet the funding agency’s requirements. For example, all U.S. government agencies have strict requirements for airline travel. Be sure the cost of the airline travel in your budget meets their requirements. If a line item falls outside an agency’s requirements (e.g. some organizations will not cover equipment purchases or other capital expenses), explain in the budget justification that other grant sources will pay for the item.
Many universities require that indirect costs (overhead) be added to grants that they administer. Check with the appropriate offices to find out what the standard (or required) rates are for overhead. Pass a draft budget by the university officer in charge of grant administration for assistance with indirect costs and costs not directly associated with research (e.g. facilities use charges).
Furthermore, make sure you factor in the estimated taxes applicable for your case. Depending on the categories of expenses and your particular circumstances (whether you are a foreign national, for example), estimated tax rates may differ. You can consult respective departmental staff or university services, as well as professional tax assistants. For information on taxes on scholarships and fellowships, see https://cashier.unc.edu/student-tax-information/scholarships-fellowships/ .
Explain the timeframe for the research project in some detail. When will you begin and complete each step? It may be helpful to reviewers if you present a visual version of your timeline. For less complicated research, a table summarizing the timeline for the project will help reviewers understand and evaluate the planning and feasibility. See Example #2 at the end of this handout.
For multi-year research proposals with numerous procedures and a large staff, a time line diagram can help clarify the feasibility and planning of the study. See Example #3 at the end of this handout.
Revising your proposal
Strong grant proposals take a long time to develop. Start the process early and leave time to get feedback from several readers on different drafts. Seek out a variety of readers, both specialists in your research area and non-specialist colleagues. You may also want to request assistance from knowledgeable readers on specific areas of your proposal. For example, you may want to schedule a meeting with a statistician to help revise your methodology section. Don’t hesitate to seek out specialized assistance from the relevant research offices on your campus. At UNC, the Odum Institute provides a variety of services to graduate students and faculty in the social sciences.
In your revision and editing, ask your readers to give careful consideration to whether you’ve made explicit the connections between your research objectives and methodology. Here are some example questions:
- Have you presented a compelling case?
- Have you made your hypotheses explicit?
- Does your project seem feasible? Is it overly ambitious? Does it have other weaknesses?
- Have you stated the means that grantors can use to evaluate the success of your project after you’ve executed it?
If a granting agency lists particular criteria used for rating and evaluating proposals, be sure to share these with your own reviewers.
Example #1. Sample Budget
Jet travel $6,100 This estimate is based on the commercial high season rate for jet economy travel on Sabena Belgian Airlines. No U.S. carriers fly to Kigali, Rwanda. Sabena has student fare tickets available which will be significantly less expensive (approximately $2,000).
Maintenance allowance $22,788 Based on the Fulbright-Hays Maintenance Allowances published in the grant application guide.
Research assistant/translator $4,800 The research assistant/translator will be a native (and primary) speaker of Kinya-rwanda with at least a four-year university degree. They will accompany the primary investigator during life history interviews to provide assistance in comprehension. In addition, they will provide commentary, explanations, and observations to facilitate the primary investigator’s participant observation. During the first phase of the project in Kigali, the research assistant will work forty hours a week and occasional overtime as needed. During phases two and three in rural Rwanda, the assistant will stay with the investigator overnight in the field when necessary. The salary of $400 per month is based on the average pay rate for individuals with similar qualifications working for international NGO’s in Rwanda.
Transportation within country, phase one $1,200 The primary investigator and research assistant will need regular transportation within Kigali by bus and taxi. The average taxi fare in Kigali is $6-8 and bus fare is $.15. This figure is based on an average of $10 per day in transportation costs during the first project phase.
Transportation within country, phases two and three $12,000 Project personnel will also require regular transportation between rural field sites. If it is not possible to remain overnight, daily trips will be necessary. The average rental rate for a 4×4 vehicle in Rwanda is $130 per day. This estimate is based on an average of $50 per day in transportation costs for the second and third project phases. These costs could be reduced if an arrangement could be made with either a government ministry or international aid agency for transportation assistance.
Email $720 The rate for email service from RwandaTel (the only service provider in Rwanda) is $60 per month. Email access is vital for receiving news reports on Rwanda and the region as well as for staying in contact with dissertation committee members and advisors in the United States.
Audiocassette tapes $400 Audiocassette tapes will be necessary for recording life history interviews, musical performances, community events, story telling, and other pertinent data.
Photographic & slide film $100 Photographic and slide film will be necessary to document visual data such as landscape, environment, marriages, funerals, community events, etc.
Laptop computer $2,895 A laptop computer will be necessary for recording observations, thoughts, and analysis during research project. Price listed is a special offer to UNC students through the Carolina Computing Initiative.
NUD*IST 4.0 software $373.00 NUD*IST, “Nonnumerical, Unstructured Data, Indexing, Searching, and Theorizing,” is necessary for cataloging, indexing, and managing field notes both during and following the field research phase. The program will assist in cataloging themes that emerge during the life history interviews.
Administrative fee $100 Fee set by Fulbright-Hays for the sponsoring institution.
Example #2: Project Timeline in Table Format
Example #3: project timeline in chart format.

Some closing advice
Some of us may feel ashamed or embarrassed about asking for money or promoting ourselves. Often, these feelings have more to do with our own insecurities than with problems in the tone or style of our writing. If you’re having trouble because of these types of hang-ups, the most important thing to keep in mind is that it never hurts to ask. If you never ask for the money, they’ll never give you the money. Besides, the worst thing they can do is say no.
UNC resources for proposal writing
Research at Carolina http://research.unc.edu
The Odum Institute for Research in the Social Sciences https://odum.unc.edu/
UNC Medical School Office of Research https://www.med.unc.edu/oor
UNC School of Public Health Office of Research http://www.sph.unc.edu/research/
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Holloway, Brian R. 2003. Proposal Writing Across the Disciplines. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Levine, S. Joseph. “Guide for Writing a Funding Proposal.” http://www.learnerassociates.net/proposal/ .
Locke, Lawrence F., Waneen Wyrick Spirduso, and Stephen J. Silverman. 2014. Proposals That Work . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Przeworski, Adam, and Frank Salomon. 2012. “Some Candid Suggestions on the Art of Writing Proposals.” Social Science Research Council. https://s3.amazonaws.com/ssrc-cdn2/art-of-writing-proposals-dsd-e-56b50ef814f12.pdf .
Reif-Lehrer, Liane. 1989. Writing a Successful Grant Application . Boston: Jones and Bartlett Publishers.
Wiggins, Beverly. 2002. “Funding and Proposal Writing for Social Science Faculty and Graduate Student Research.” Chapel Hill: Howard W. Odum Institute for Research in Social Science. 2 Feb. 2004. http://www2.irss.unc.edu/irss/shortcourses/wigginshandouts/granthandout.pdf.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
ANNOTATED SAMPLE GRANT PROPOSALS
How to Use Annotated Sample Grants
Are these real grants written by real students.
Yes! While each proposal represents a successfully funded application, there are two things to keep in mind: 1) The proposals below are final products; no student started out with a polished proposal. The proposal writing process requires stages of editing while a student formulates their project and works on best representing that project in writing. 2) The samples reflect a wide range of project types, but they are not exhaustive . URGs can be on any topic in any field, but all must make a successful argument for why their project should be done/can be done by the person proposing to do it. See our proposal writing guides for more advice. The best way to utilize these proposals is to pay attention to the proposal strengths and areas for improvement on each cover page to guide your reading.
How do I decide which sample grants to read?
When students first look through the database, they are usually compelled to read an example from their major (Therefore, we often hear complaints that there is not a sample proposal for every major). However, this is not the best approach because there can be many different kinds of methodologies within a single subject area, and similar research methods can be used across fields.
- Read through the Methodology Definitions and Proposal Features to identify which methodolog(ies) are most similar to your proposed project.
- Use the Annotated Sample Grant Database ( scroll below the definitions and features) filters or search for this methodology to identify relevant proposals and begin reading!
It does not matter whether the samples you read are summer grants (SURGs) or academic year grants (AYURGs). The main difference between the two grant types is that academic year proposals (AYURG) require a budget to explain how the $1,000 will be used towards research materials, while summer proposals (SURG) do not require a budget (the money is a living stipend that goes directly to the student awardee) and SURGs have a bigger project scope since they reflect a project that will take 8 weeks of full time research to complete. The overall format and style is the same across both grant cycles, so they are relevant examples for you to review, regardless of which grant cycle you are planning to apply.
How do I get my proposal to look like these sample grants?
Do not submit a first draft: These sample proposals went through multiple rounds of revisions with feedback from both Office of Undergraduate Research advisors and the student’s faculty mentor. First, it helps to learn about grant structure and proposal writing techniques before you get started. Then, when you begin drafting, it’s normal to make lots of changes as the grant evolves. You will learn a lot about your project during the editing and revision process, and you typically end up with a better project by working through several drafts of a proposal.
Work with an advisor: Students who work with an Office of Undergraduate Research Advisor have higher success rates than students who do not. We encourage students to meet with advisors well in advance of the deadline (and feel free to send us drafts of your proposal prior to our advising appointment, no matter how rough your draft is!), so we can help you polish and refine your proposal.
Review final proposal checklists prior to submission: the expectation is a two-page, single-spaced research grant proposal (1″ margins, Times New Roman 12 or Arial 11), and proposals that do not meet these formatting expectations will not be considered by the review committee. Your bibliography does not count towards this page limit.
Academic Year URG Submission Checklist
Summer URG Application Checklist
METHODOLOGY DEFINITIONS & PROPOSAL FEATURES
Research methodologies.
The proposed project involves collecting primary sources held in archives, a Special Collections library, or other repository. Archival sources might include manuscripts, documents, records, objects, sound and audiovisual materials, etc. If a student proposes a trip to collect such sources, the student should address a clear plan of what will be collected from which archives, and should address availability and access (ie these sources are not available online, and the student has permission to access the archive).
Computational/Mathematical Modeling
The proposed project involves developing models to numerically study the behavior of system(s), often through computer simulation. Students should specify what modeling tool they will be using (i.e., an off-the-shelf product, a lab-specific codebase), what experience they have with it, and what resources they have when they get stuck with the tool (especially if the advisor is not a modeler). Models often involve iterations of improvements, so much like a Design/Build project, the proposal should clearly define parameters for a “successful” model with indication of how the student will assess if the model meets these minimum qualifications.
Creative Output
The proposed project has a creative output such playwriting, play production, documentary, music composition, poetry, creative writing, or other art. Just like all other proposals, the project centers on an answerable question, and the student must show the question and method associated with the research and generation of that project. The artist also must justify their work and make an argument for why this art is needed and/or how it will add to important conversations .
Design/Build
The proposed project’s output centers around a final product or tool. The student clearly defines parameters for a “successful” project with indication of how they will assess if the product meets these minimum qualifications.
The project takes place in a lab or research group environment, though the methodology within the lab or research group vary widely by field. The project often fits within the larger goals/or project of the research group, but the proposal still has a clearly identified research question that the student is working independently to answer.
Literary/Composition Analysis
The project studies, evaluates, and interprets literature or composition. The methods are likely influenced by theory within the field of study. In the proposal, the student has clearly defined which pieces will be studied and will justify why these pieces were selected. Context will be given that provides a framework for how the pieces will be analyzed or interpreted.
Qualitative Data Analysis
The project proposes to analyze data from non-numeric information such as interview transcripts, notes, video and audio recordings, images, and text documents. The proposal clearly defines how the student will examine and interpret patterns and themes in the data and how this methodology will help to answer the defined research question.
Quantitative Data Analysis
The project proposes to analyze data from numeric sources. The proposal clearly defines variables to be compared and provides insight as to the kinds of statistical tests that will be used to evaluate the significance of the data.
The proposed project will collect data through survey(s). The proposal should clearly defined who will be asked to complete the survey, how these participants will be recruited, and/or proof of support from contacts. The proposal should include the survey(s) in an appendix. The proposal should articulate how the results from these survey(s) will be analyzed.
The proposed project will use theoretical frameworks within their proposed area of research to explain, predict, and/or challenge and extend existing knowledge. The conceptual framework serves as a lens through which the student will evaluate the research project and research question(s); it will likely contain a set of assumptions and concepts that form the basis of this lens.
Proposal Features
Group project.
A group project is proposed by two or more students; these proposals receive one additional page for each additional student beyond the two page maximum. Group projects must clearly articulate the unique role of each student researcher. While the uploaded grant proposal is the same, each student researcher must submit their own application into the system for the review.
International Travel
Projects may take place internationally. If the proposed country is not the student’s place of permanent residence, the student can additionally apply for funding to cover half the cost of an international plane ticket. Proposals with international travel should likely include travel itineraries and/or proof of support from in-country contacts in the appendix.
Non-English Language Proficiency
Projects may be conducted in a non-English language. If you have proficiency in the proposed language, you should include context (such as bilingual, heritage speaker, or by referencing coursework etc.) If you are not proficient and the project requires language proficiency, you should include a plan for translation or proof of contacts in the country who can support your research in English.
DATABASE OF ANNOTATED SAMPLE GRANTS
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a grant proposal: a step-by-step guide

What is a grant proposal?
Why should you write a grant proposal, format of a grant proposal, how to write a grant proposal, step 1: decide what funding opportunity to apply for, and research the grant application process, step 2: plan and research your project, preliminary research for your grant proposal, questions to ask yourself as you plan your grant proposal, developing your grant proposal, step 3: write the first draft of your grant proposal, step 4: get feedback, and revise your grant proposal accordingly, step 5: prepare to submit your grant proposal, what happens after submitting the grant proposal, final thoughts, other useful sources for writing grant proposals, frequently asked questions about writing grant proposals, related articles.
You have a vision for a future research project, and want to share that idea with the world.
To achieve your vision, you need funding from a sponsoring organization, and consequently, you need to write a grant proposal.
Although visualizing your future research through grant writing is exciting, it can also feel daunting. How do you start writing a grant proposal? How do you increase your chances of success in winning a grant?
But, writing a proposal is not as hard as you think. That’s because the grant-writing process can be broken down into actionable steps.
This guide provides a step-by-step approach to grant-writing that includes researching the application process, planning your research project, and writing the proposal. It is written from extensive research into grant-writing, and our experiences of writing proposals as graduate students, postdocs, and faculty in the sciences.
A grant proposal is a document or collection of documents that outlines the strategy for a future research project and is submitted to a sponsoring organization with the specific goal of getting funding to support the research. For example, grants for large projects with multiple researchers may be used to purchase lab equipment, provide stipends for graduate and undergraduate researchers, fund conference travel, and support the salaries of research personnel.
As a graduate student, you might apply for a PhD scholarship, or postdoctoral fellowship, and may need to write a proposal as part of your application. As a faculty member of a university, you may need to provide evidence of having submitted grant applications to obtain a permanent position or promotion.
Reasons for writing a grant proposal include:
- To obtain financial support for graduate or postdoctoral studies;
- To travel to a field site, or to travel to meet with collaborators;
- To conduct preliminary research for a larger project;
- To obtain a visiting position at another institution;
- To support undergraduate student research as a faculty member;
- To obtain funding for a large collaborative project, which may be needed to retain employment at a university.
The experience of writing a proposal can be helpful, even if you fail to obtain funding. Benefits include:
- Improvement of your research and writing skills
- Enhancement of academic employment prospects, as fellowships and grants awarded and applied for can be listed on your academic CV
- Raising your profile as an independent academic researcher because writing proposals can help you become known to leaders in your field.
All sponsoring agencies have specific requirements for the format of a grant proposal. For example, for a PhD scholarship or postdoctoral fellowship, you may be required to include a description of your project, an academic CV, and letters of support from mentors or collaborators.
For a large research project with many collaborators, the collection of documents that need to be submitted may be extensive. Examples of documents that might be required include a cover letter, a project summary, a detailed description of the proposed research, a budget, a document justifying the budget, and the CVs of all research personnel.
Before writing your proposal, be sure to note the list of required documents.
Writing a grant proposal can be broken down into three major activities: researching the project (reading background materials, note-taking, preliminary work, etc.), writing the proposal (creating an outline, writing the first draft, revisions, formatting), and administrative tasks for the project (emails, phone calls, meetings, writing CVs and other supporting documents, etc.).
Below, we provide a step-by-step guide to writing a grant proposal:
- Decide what funding opportunity to apply for, and research the grant application process
- Plan and research your project
- Write the first draft of your grant proposal
- Get feedback, and revise your grant proposal accordingly
- Prepare to submit your grant proposal

- Start early. Begin by searching for funding opportunities and determining requirements. Some sponsoring organizations prioritize fundamental research, whereas others support applied research. Be sure your project fits the mission statement of the granting organization. Look at recently funded proposals and/or sample proposals on the agency website, if available. The Research or Grants Office at your institution may be able to help with finding grant opportunities.
- Make a spreadsheet of grant opportunities, with a link to the call for proposals page, the mission and aims of the agency, and the deadline for submission. Use the information that you have compiled in your spreadsheet to decide what to apply for.
- Once you have made your decision, carefully read the instructions in the call for proposals. Make a list of all the documents you need to apply, and note the formatting requirements and page limits. Know exactly what the funding agency requires of submitted proposals.
- Reach out to support staff at your university (for example, at your Research or Grants Office), potential mentors, or collaborators. For example, internal deadlines for submitting external grants are often earlier than the submission date. Make sure to learn about your institution’s internal processes, and obtain contact information for the relevant support staff.
- Applying for a grant or fellowship involves administrative work. Start preparing your CV and begin collecting supporting documents from collaborators, such as letters of support. If the application to the sponsoring agency is electronic, schedule time to set up an account, log into the system, download necessary forms and paperwork, etc. Don’t leave all of the administrative tasks until the end.
- Map out the important deadlines on your calendar. These might include video calls with collaborators, a date for the first draft to be complete, internal submission deadlines, and the funding agency deadline.
- Schedule time on your calendar for research, writing, and administrative tasks associated with the project. It’s wise to group similar tasks and block out time for them (a process known as ” time batching ”). Break down bigger tasks into smaller ones.

Now that you know what you are applying for, you can think about matching your proposed research to the aims of the agency. The work you propose needs to be innovative, specific, realizable, timely, and worthy of the sponsoring organization’s attention.
- Develop an awareness of the important problems and open questions in your field. Attend conferences and seminar talks and follow all of your field’s major journals.
- Read widely and deeply. Journal review articles are a helpful place to start. Reading papers from related but different subfields can generate ideas. Taking detailed notes as you read will help you recall the important findings and connect disparate concepts.
- Writing a grant proposal is a creative and imaginative endeavor. Write down all of your ideas. Freewriting is a practice where you write down all that comes to mind without filtering your ideas for feasibility or stopping to edit mistakes. By continuously writing your thoughts without judgment, the practice can help overcome procrastination and writer’s block. It can also unleash your creativity, and generate new ideas and associations. Mind mapping is another technique for brainstorming and generating connections between ideas.
- Establish a regular writing practice. Schedule time just for writing, and turn off all distractions during your focused work time. You can use your writing process to refine your thoughts and ideas.
- Use a reference manager to build a library of sources for your project. You can use a reference management tool to collect papers , store and organize references , and highlight and annotate PDFs . Establish a system for organizing your ideas by tagging papers with labels and using folders to store similar references.
To facilitate intelligent thinking and shape the overall direction of your project, try answering the following questions:
- What are the questions that the project will address? Am I excited and curious about their answers?
- Why are these questions important?
- What are the goals of the project? Are they SMART (Specific, Measurable, Actionable, Relevant, and Timely)?
- What is novel about my project? What is the gap in current knowledge?
- What methods will I use, and how feasible is my approach?
- Can the work be done over the proposed period, and with the budget I am requesting?
- Do I have relevant experience? For example, have I completed similar work funded by previous grants or written papers on my proposed topic?
- What pilot research or prior work can I use, or do I need to complete preliminary research before writing the proposal?
- Will the outcomes of my work be consequential? Will the granting agency be interested in the results?
- What solutions to open problems in my field will this project offer? Are there broader implications of my work?
- Who will the project involve? Do I need mentors, collaborators, or students to contribute to the proposed work? If so, what roles will they have?
- Who will read the proposal? For example, experts in the field will require details of methods, statistical analyses, etc., whereas non-experts may be more concerned with the big picture.
- What do I want the reviewers to feel, and take away from reading my proposal?
- What weaknesses does my proposed research have? What objections might reviewers raise, and how can I address them?
- Can I visualize a timeline for my project?
Create an actionable plan for your research project using the answers to these questions.
- Now is the time to collect preliminary data, conduct experiments, or do a preliminary study to motivate your research, and demonstrate that your proposed project is realistic.
- Use your plan to write a detailed outline of the proposal. An outline helps you to write a proposal that has a logical format and ensures your thought process is rational. It also provides a structure to support your writing.
- Follow the granting agency’s guidelines for titles, sections, and subsections to inform your outline.
At this stage, you should have identified the aims of your project, what questions your work will answer, and how they are relevant to the sponsoring agency’s call for proposals. Be able to explain the originality, importance, and achievability of your proposed work.

Now that you have done your research, you are ready to begin writing your proposal and start filling in the details of your outline. Build on the writing routine you have already started. Here are some tips:
- Follow the guidelines of the funding organization.
- Keep the proposal reviewers in mind as you write. Your audience may be a combination of specialists in your field and non-specialists. Make sure to address the novelty of your work, its significance, and its feasibility.
- Write clearly, concisely, and avoid repetition. Use topic sentences for each paragraph to emphasize key ideas. Concluding sentences of each paragraph should develop, clarify, or summarize the support for the declaration in the topic sentence. To make your writing engaging, vary sentence length.
- Avoid jargon, where possible. Follow sentences that have complex technical information with a summary in plain language.
- Don’t review all information on the topic, but include enough background information to convince reviewers that you are knowledgeable about it. Include preliminary data to convince reviewers you can do the work. Cite all relevant work.
- Make sure not to be overly ambitious. Don’t propose to do so much that reviewers doubt your ability to complete the project. Rather, a project with clear, narrowly-defined goals may prove favorable to reviewers.
- Accurately represent the scope of your project; don’t exaggerate its impacts. Avoid bias. Be forthright about the limitations of your research.
- Ensure to address potential objections and concerns that reviewers may have with the proposed work. Show that you have carefully thought about the project by explaining your rationale.
- Use diagrams and figures effectively. Make sure they are not too small or contain too much information or details.
After writing your first draft, read it carefully to gain an overview of the logic of your argument. Answer the following questions:
- Is your proposal concise, explicit, and specific?
- Have you included all necessary assumptions, data points, and evidence in your proposal?
- Do you need to make structural changes like moving or deleting paragraphs or including additional tables or figures to strengthen your rationale?
- Have you answered most of the questions posed in Step 2 above in your proposal?
- Follow the length requirements in the proposal guidelines. Don't feel compelled to include everything you know!
- Use formatting techniques to make your proposal easy on the eye. Follow rules for font, layout, margins, citation styles , etc. Avoid walls of text. Use bolding and italicizing to emphasize points.
- Comply with all style, organization, and reference list guidelines to make it easy to reviewers to quickly understand your argument. If you don’t, it’s at best a chore for the reviewers to read because it doesn’t make the most convincing case for you and your work. At worst, your proposal may be rejected by the sponsoring agency without review.
- Using a reference management tool like Paperpile will make citation creation and formatting in your grant proposal quick, easy and accurate.

Now take time away from your proposal, for at least a week or more. Ask trusted mentors or collaborators to read it, and give them adequate time to give critical feedback.
- At this stage, you can return to any remaining administrative work while you wait for feedback on the proposal, such as finalizing your budget or updating your CV.
- Revise the proposal based on the feedback you receive.
- Don’t be discouraged by critiques of your proposal or take them personally. Receiving and incorporating feedback with humility is essential to grow as a grant writer.

Now you are almost ready to submit. This is exciting! At this stage, you need to block out time to complete all final checks.
- Allow time for proofreading and final editing. Spelling and grammar mistakes can raise questions regarding the rigor of your research and leave a poor impression of your proposal on reviewers. Ensure that a unified narrative is threaded throughout all documents in the application.
- Finalize your documents by following a checklist. Make sure all documents are in place in the application, and all formatting and organizational requirements are met.
- Follow all internal and external procedures. Have login information for granting agency and institution portals to hand. Double-check any internal procedures required by your institution (applications for large grants often have a deadline for sign-off by your institution’s Research or Grants Office that is earlier than the funding agency deadline).
- To avoid technical issues with electronic portals, submit your proposal as early as you can.
- Breathe a sigh of relief when all the work is done, and take time to celebrate submitting the proposal! This is already a big achievement.
Now you wait! If the news is positive, congratulations!
But if your proposal is rejected, take heart in the fact that the process of writing it has been useful for your professional growth, and for developing your ideas.
Bear in mind that because grants are often highly competitive, acceptance rates for proposals are usually low. It is very typical to not be successful on the first try and to have to apply for the same grant multiple times.
Here are some tips to increase your chances of success on your next attempt:
- Remember that grant writing is often not a linear process. It is typical to have to use the reviews to revise and resubmit your proposal.
- Carefully read the reviews and incorporate the feedback into the next iteration of your proposal. Use the feedback to improve and refine your ideas.
- Don’t ignore the comments received from reviewers—be sure to address their objections in your next proposal. You may decide to include a section with a response to the reviewers, to show the sponsoring agency that you have carefully considered their comments.
- If you did not receive reviewer feedback, you can usually request it.
You learn about your field and grow intellectually from writing a proposal. The process of researching, writing, and revising a proposal refines your ideas and may create new directions for future projects. Professional opportunities exist for researchers who are willing to persevere with submitting grant applications.
➡️ Secrets to writing a winning grant
➡️ How to gain a competitive edge in grant writing
➡️ Ten simple rules for writing a postdoctoral fellowship
A grant proposal should include all the documents listed as required by the sponsoring organization. Check what documents the granting agency needs before you start writing the proposal.
Granting agencies have strict formatting requirements, with strict page limits and/or word counts. Check the maximum length required by the granting agency. It is okay for the proposal to be shorter than the maximum length.
Expect to spend many hours, even weeks, researching and writing a grant proposal. Consequently, it is important to start early! Block time in your calendar for research, writing, and administration tasks. Allow extra time at the end of the grant-writing process to edit, proofread, and meet presentation guidelines.
The most important part of a grant proposal is the description of the project. Make sure that the research you propose in your project narrative is new, important, and viable, and that it meets the goals of the sponsoring organization.
A grant proposal typically consists of a set of documents. Funding agencies have specific requirements for the formatting and organization of each document. Make sure to follow their guidelines exactly.
The Ultimate Grant Writing Guide (and How to Find and Apply for Grants)
Securing grants requires strategic planning. Identifying relevant opportunities, building collaborations, and crafting a comprehensive grant proposal are crucial steps. Read our ultimate guide on grant writing, finding grants, and applying for grants to get the funding for your research.
Updated on February 22, 2024

Embarking on a journey of groundbreaking research and innovation always requires more than just passion and dedication, it demands financial support. In the academic and research domains, securing grants is a pivotal factor for transforming these ideas into tangible outcomes.
Grant awards not only offer the backing needed for ambitious projects but also stand as a testament to the importance and potential impact of your work. The process of identifying, pursuing, and securing grants, however, is riddled with nuances that necessitate careful exploration.
Whether you're a seasoned researcher or a budding academic, navigating this complex world of grants can be challenging, but we’re here to help. In this comprehensive guide, we'll walk you through the essential steps of applying for grants, providing expert tips and insights along the way.
Finding grant opportunities
Prior to diving into the application phase, the process of finding grants involves researching and identifying those that are relevant and realistic to your project. While the initial step may seem as simple as entering a few keywords into a search engine, the full search phase takes a more thorough investigation.
By focusing efforts solely on the grants that align with your goals, this pre-application preparation streamlines the process while also increasing the likelihood of meeting all the requirements. In fact, having a well thought out plan and a clear understanding of the grants you seek both simplifies the entire activity and sets you and your team up for success.
Apply these steps when searching for appropriate grant opportunities:
1. Determine your need
Before embarking on the grant-seeking journey, clearly articulate why you need the funds and how they will be utilized. Understanding your financial requirements is crucial for effective grant research.
2. Know when you need the money
Grants operate on specific timelines with set award dates. Align your grant-seeking efforts with these timelines to enhance your chances of success.
3. Search strategically
Build a checklist of your most important, non-negotiable search criteria for quickly weeding out grant options that absolutely do not fit your project. Then, utilize the following resources to identify potential grants:
- Online directories
- Small Business Administration (SBA)
- Foundations
4. Develop a tracking tool
After familiarizing yourself with the criteria of each grant, including paperwork, deadlines, and award amounts, make a spreadsheet or use a project management tool to stay organized. Share this with your team to ensure that everyone can contribute to the grant cycle.
Here are a few popular grant management tools to try:
- Jotform : spreadsheet template
- Airtable : table template
- Instrumentl : software
- Submit : software
Tips for Finding Research Grants
Consider large funding sources : Explore major agencies like NSF and NIH.
Reach out to experts : Consult experienced researchers and your institution's grant office.
Stay informed : Regularly check news in your field for novel funding sources.
Know agency requirements : Research and align your proposal with their requisites.
Ask questions : Use the available resources to get insights into the process.
Demonstrate expertise : Showcase your team's knowledge and background.
Neglect lesser-known sources : Cast a wide net to diversify opportunities.
Name drop reviewers : Prevent potential conflicts of interest.
Miss your chance : Find field-specific grant options.
Forget refinement : Improve proposal language, grammar, and clarity.
Ignore grant support services : Enhance the quality of your proposal.
Overlook co-investigators : Enhance your application by adding experience.
Grant collaboration
Now that you’ve taken the initial step of identifying potential grant opportunities, it’s time to find collaborators. The application process is lengthy and arduous. It requires a diverse set of skills. This phase is crucial for success.
With their valuable expertise and unique perspectives, these collaborators play instrumental roles in navigating the complexities of grant writing. While exploring the judiciousness that goes into building these partnerships, we will underscore why collaboration is both advantageous and indispensable to the pursuit of securing grants.
Why is collaboration important to the grant process?
Some grant funding agencies outline collaboration as an outright requirement for acceptable applications. However, the condition is more implied with others. Funders may simply favor or seek out applications that represent multidisciplinary and multinational projects.
To get an idea of the types of collaboration major funders prefer, try searching “collaborative research grants” to uncover countless possibilities, such as:
- National Endowment for the Humanities
- American Brain Tumor Association
For exploring grants specifically for international collaboration, check out this blog:
- 30+ Research Funding Agencies That Support International Collaboration
Either way, proposing an interdisciplinary research project substantially increases your funding opportunities. Teaming up with multiple collaborators who offer diverse backgrounds and skill sets enhances the robustness of your research project and increases credibility.
This is especially true for early career researchers, who can leverage collaboration with industry, international, or community partners to boost their research profile. The key lies in recognizing the multifaceted advantages of collaboration in the context of obtaining funding and maximizing the impact of your research efforts.
How can I find collaborators?
Before embarking on the search for a collaborative partner, it's essential to crystallize your objectives for the grant proposal and identify the type of support needed. Ask yourself these questions:
1)Which facet of the grant process do I need assistance with:
2) Is my knowledge lacking in a specific:
- Population?
3) Do I have access to the necessary:
Use these questions to compile a detailed list of your needs and prioritize them based on magnitude and ramification. These preliminary step ensure that search for an ideal collaborator is focused and effective.
Once you identify targeted criteria for the most appropriate partners, it’s time to make your approach. While a practical starting point involves reaching out to peers, mentors, and other colleagues with shared interests and research goals, we encourage you to go outside your comfort zone.
Beyond the first line of potential collaborators exists a world of opportunities to expand your network. Uncover partnership possibilities by engaging with speakers and attendees at events, workshops, webinars, and conferences related to grant writing or your field.
Also, consider joining online communities that facilitate connections among grant writers and researchers. These communities offer a space to exchange ideas and information. Sites like Collaboratory , NIH RePorter , and upwork provide channels for canvassing and engaging with feasible collaborators who are good fits for your project.
Like any other partnership, carefully weigh your vetted options before committing to a collaboration. Talk with individuals about their qualifications and experience, availability and work style, and terms for grant writing collaborations.
Transparency on both sides of this partnership is imperative to forging a positive work environment where goals, values, and expectations align for a strong grant proposal.
Putting together a winning grant proposal
It’s time to assemble the bulk of your grant application packet – the proposal itself. Each funder is unique in outlining the details for specific grants, but here are several elements fundamental to every proposal:
- Executive Summary
- Needs assessment
- Project description
- Evaluation plan
- Team introduction
- Sustainability plan
This list of multi-faceted components may seem daunting, but careful research and planning will make it manageable.
Start by reading about the grant funder to learn:
- What their mission and goals are,
- Which types of projects they have funded in the past, and
- How they evaluate and score applications.
Next, view sample applications to get a feel for the length, flow, and tone the evaluators are looking for. Many funders offer samples to peruse, like these from the NIH , while others are curated by online platforms , such as Grantstation.
Also, closely evaluate the grant application’s requirements. they vary between funding organizations and opportunities, and also from one grant cycle to the next. Take notes and make a checklist of these requirements to add to an Excel spreadsheet, Google smartsheet, or management system for organizing and tracking your grant process.
Finally, understand how you will submit the final grant application. Many funders use online portals with character or word limits for each section. Be aware of these limits beforehand. Simplify the editing process by first writing each section in a Word document to be copy and pasted into the corresponding submission fields.
If there is no online application platform, the funder will usually offer a comprehensive Request for Proposal (RFP) to guide the structure of your grant proposal. The RFP:
- Specifies page constraints
- Delineates specific sections
- Outlines additional attachments
- Provides other pertinent details
Components of a grant proposal
Cover letter.
Though not always explicitly requested, including a cover letter is a strategic maneuver that could be the factor determining whether or not grant funders engage with your proposal. It’s an opportunity to give your best first impression by grabbing the reviewer’s attention and compelling them to read further.
Cover letters are not the place for excessive emotion or detail, keep it brief and direct, stating your financial needs and purpose confidently from the outset. Also, try to clearly demonstrate the connection between your project and the funder’s mission to create additional value beyond the formal proposal.
Executive summary
Like an abstract for your research manuscript, the executive summary is a brief synopsis that encapsulates the overarching topics and key points of your grant proposal. It must set the tone for the main body of the proposal while providing enough information to stand alone if necessary.
Refer to How to Write an Executive Summary for a Grant Proposal for detailed guidance like:
- Give a clear and concise account of your identity, funding needs, and project roadmap.
- Write in an instructive manner aiming for an objective and persuasive tone
- Be convincing and pragmatic about your research team's ability.
- Follow the logical flow of main points in your proposal.
- Use subheadings and bulleted lists for clarity.
- Write the executive summary at the end of the proposal process.
- Reference detailed information explained in the proposal body.
- Address the funder directly.
- Provide excessive details about your project's accomplishments or management plans.
- Write in the first person.
- Disclose confidential information that could be accessed by competitors.
- Focus excessively on problems rather than proposed solutions.
- Deviate from the logical flow of the main proposal.
- Forget to align with evaluation criteria if specified

Project narrative
After the executive summary is the project narrative . This is the main body of your grant proposal and encompasses several distinct elements that work together to tell the story of your project and justify the need for funding.
Include these primary components:
Introduction of the project team
Briefly outline the names, positions, and credentials of the project’s directors, key personnel, contributors, and advisors in a format that clearly defines their roles and responsibilities. Showing your team’s capacity and ability to meet all deliverables builds confidence and trust with the reviewers.
Needs assessment or problem statement
A compelling needs assessment (or problem statement) clearly articulates a problem that must be urgently addressed. It also offers a well-defined project idea as a possible solution. This statement emphasizes the pressing situation and highlights existing gaps and their consequences to illustrate how your project will make a difference.
To begin, ask yourself these questions:
- What urgent need are we focusing on with this project?
- Which unique solution does our project offer to this urgent need?
- How will this project positively impact the world once completed?
Here are some helpful examples and templates.
Goals and objectives
Goals are broad statements that are fairly abstract and intangible. Objectives are more narrow statements that are concrete and measurable. For example :
- Goal : “To explore the impact of sleep deprivation on cognitive performance in college students.”
- Objective : “To compare cognitive test scores of students with less than six hours of sleep and those with 8 or more hours of sleep.”
Focus on outcomes, not processes, when crafting goals and objectives. Use the SMART acronym to align them with the proposal's mission while emphasizing their impact on the target audience.
Methods and strategies
It is vitally important to explain how you intend to use the grant funds to fulfill the project’s objectives. Detail the resources and activities that will be employed. Methods and strategies are the bridge between idea and action. They must prove to reviewers the plausibility of your project and the significance of their possible funding.
Here are some useful guidelines for writing your methods section that are outlined in " Winning Grants: Step by Step ."
- Firmly tie your methods to the proposed project's objectives and needs assessment.
- Clearly link them to the resources you are requesting in the proposal budget.
- Thoroughly explain why you chose these methods by including research, expert opinion, and your experience.
- Precisely list the facilities and capital equipment that you will use in the project.
- Carefully structure activities so that the program moves toward the desired results in a time-bound manner.
A comprehensive evaluation plan underscores the effectiveness and accountability of a project for both the funders and your team. An evaluation is used for tracking progress and success. The evaluation process shows how to determine the success of your project and measure the impact of the grant award by systematically gauging and analyzing each phase of your project as it compares to the set objectives.
Evaluations typically fall into two standard categories:
1. Formative evaluation : extending from project development through implementation, continuously provides feedback for necessary adjustments and improvements.
2. Summative evaluation : conducted post-project completion, critically assesses overall success and impact by compiling information on activities and outcomes.
Creating a conceptual model of your project is helpful when identifying these key evaluation points. Then, you must consider exactly who will do the evaluations, what specific skills and resources they need, how long it will take, and how much it will cost.
Sustainability
Presenting a solid plan that illustrates exactly how your project will continue to thrive after the grant money is gone builds the funder's confidence in the project’s longevity and significance. In this sustainability section, it is vital to demonstrate a diversified funding strategy for securing the long-term viability of your program.
There are three possible long term outcomes for projects with correlated sustainability options:
- Short term projects: Though only implemented once, will have ongoing maintenance costs, such as monitoring, training, and updates.
(E.g., digitizing records, cleaning up after an oil spill)
- Projects that will generate income at some point in the future: must be funded until your product or service can cover operating costs with an alternative plan in place for deficits.
(E.g., medical device, technology, farming method)
- Ongoing projects: will eventually need a continuous stream of funding from a government entity or large organization.
(E.g., space exploration, hurricane tracking)
Along with strategies for funding your program beyond the initial grant, reference your access to institutional infrastructure and resources that will reduce costs.
Also, submit multi-year budgets that reflect how sustainability factors are integrated into the project’s design.
The budget section of your grant proposal, comprising both a spreadsheet and a narrative, is the most influential component. It should be able to stand independently as a suitable representation of the entire endeavor. Providing a detailed plan to outline how grant funds will be utilized is crucial for illustrating cost-effectiveness and careful consideration of project expenses.
A comprehensive grant budget offers numerous benefits to both the grantor , or entity funding the grant, and the grantee , those receiving the funding, such as:
- Grantor : The budget facilitates objective evaluation and comparison between multiple proposals by conveying a project's story through responsible fund management and financial transparency.
- Grantee : The budget serves as a tracking tool for monitoring and adjusting expenses throughout the project and cultivates trust with funders by answering questions before they arise.
Because the grant proposal budget is all-encompassing and integral to your efforts for securing funding, it can seem overwhelming. Start by listing all anticipated expenditures within two broad categories, direct and indirect expenses , where:
- Direct : are essential for successful project implementation, are measurable project-associated costs, such as salaries, equipment, supplies, travel, and external consultants, and are itemized and detailed in various categories within the grant budget.
- Indirect : includes administrative costs not directly or exclusively tied to your project, but necessary for its completion, like rent, utilities, and insurance, think about lab or meeting spaces that are shared by multiple project teams, or Directors who oversee several ongoing projects.
After compiling your list, review sample budgets to understand the typical layout and complexity. Focus closely on the budget narratives , where you have the opportunity to justify each aspect of the spreadsheet to ensure clarity and validity.

While not always needed, the appendices consist of relevant supplementary materials that are clearly referenced within your grant application. These might include:
- Updated resumes that emphasize staff members' current positions and accomplishments.
- Letters of support from people or organizations that have authority in the field of your research, or community members that may benefit from the project.
- Visual aids like charts, graphs, and maps that contribute directly to your project’s story and are referred to previously in the application.
Finalizing your grant application
Now that your grant application is finished, make sure it's not just another document in the stack Aim for a grant proposal that captivates the evaluator. It should stand out not only for presenting an excellent project, but for being engaging and easily comprehended .
Keep the language simple. Avoid jargon. Prioritizing accuracy and conciseness. Opt for reader-friendly formatting with white space, headings, standard fonts, and illustrations to enhance readability.
Always take time for thorough proofreading and editing. You can even set your proposal aside for a few days before revisiting it for additional edits and improvements. At this stage, it is helpful to seek outside feedback from those familiar with the subject matter as well as novices to catch unnoticed mistakes and improve clarity.
If you want to be absolutely sure your grant proposal is polished, consider getting it edited by AJE .
How can AI help the grant process?
When used efficiently, AI is a powerful tool for streamlining and enhancing various aspects of the grant process.
- Use AI algorithms to review related studies and identify knowledge gaps.
- Employ AI for quick analysis of complex datasets to identify patterns and trends.
- Leverage AI algorithms to match your project with relevant grant opportunities.
- Apply Natural Language Processing for analyzing grant guidelines and tailoring proposals accordingly.
- Utilize AI-powered tools for efficient project planning and execution.
- Employ AI for tracking project progress and generating reports.
- Take advantage of AI tools for improving the clarity, coherence, and quality of your proposal.
- Rely solely on manual efforts that are less comprehensive and more time consuming.
- Overlook the fact that AI is designed to find patterns and trends within large datasets.
- Minimize AI’s ability to use set parameters for sifting through vast amounts of data quickly.
- Forget that the strength of AI lies in its capacity to follow your prompts without divergence.
- Neglect tools that assist with scheduling, resource allocation, and milestone tracking.
- Settle for software that is not intuitive with automated reminders and updates.
- Hesitate to use AI tools for improving grammar, spelling, and composition throughout the writing process.
Remember that AI provides a diverse array of tools; there is no universal solution. Identify the most suitable tool for your specific task. Also, like a screwdriver or a hammer, AI needs informed human direction and control to work effectively.
Looking for tips when writing your grant application?
Check out these resources:
- 4 Tips for Writing a Persuasive Grant Proposal
- Writing Effective Grant Applications
- 7 Tips for Writing an Effective Grant Proposal
- The best-kept secrets to winning grants
- The Best Grant Writing Books for Beginner Grant Writers
- Research Grant Proposal Funding: How I got $1 Million
Final thoughts
The bottom line – applying for grants is challenging. It requires passion, dedication, and a set of diverse skills rarely found within one human being.
Therefore, collaboration is key to a successful grant process . It encourages everyone’s strengths to shine. Be honest and ask yourself, “Which elements of this grant application do I really need help with?” Seek out experts in those areas.
Keep this guide on hand to reference as you work your way through this funding journey. Use the resources contained within. Seek out answers to all the questions that will inevitably arise throughout the process.
The grants are out there just waiting for the right project to present itself – one that shares the funder’s mission and is a benefit to our communities. Find grants that align with your project goals, tell your story through a compelling proposal, and get ready to make the world a better place with your research.

The AJE Team
See our "Privacy Policy"
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on October 12, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 21, 2023.

A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organized and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research proposals.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: “A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management”
- Example research proposal #2: “Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use”
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesize prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasize again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Grant Proposal Writing is Exciting, Imaginative Work
Download this Handout PDF
Overview Additional Resources about Grants and Grant Writing Considering the Audience, Purpose, and Expectations of a Grant Proposal Common Elements of Grant Proposals General Tips Successful Sample Proposals
So, you want to write a grant proposal? This is exciting! This means that you have valuable research to do or a particular nonprofit to build or a community resource you’re passionate about developing. You have a distinct vision for how something could be improved or advanced, and you’re ready to ask for funding or other support to help this vision become a reality.

As you reach toward this unrealized vision by developing a grant proposal, you should think about successful grant writing as an act of imagination. Professor Kate Vieira, a Curriculum and Instruction professor at UW-Madison with considerable grant writing experience, describes grant proposal writing as a creative process akin to fiction writing—these are works of imagination. Professor Vieira recommends approaching the task of writing a grant proposal with an attitude of wonder and excitement as you strive to turn your ideas into something real. You have a great idea, and you think that you’re the best person to achieve a specific goal. Now you just need to convince others to get excited about this vision as well.
On this page, we offer some ways of thinking about grant proposals and advice about the process of planning and writing a proposal. We consider grant proposals; overall purposes, audiences, and expectations in order to make this information applicable across a range of contexts. However, this general approach has important limits . First, you will need to get more tailored advice about grant writing within your specific discipline or sphere. Second, you’ll need to follow very carefully the exact instructions about proposals from the granting agencies to which you are applying.
Talk with professors, mentors, previous grant recipients, the funding agency/group you are applying to, and trusted advisers in your field to learn more about what successful grant proposals look like in your situation and to get feedback on your plan and on your drafting process.
Before you start writing your grant proposal, you’ll want to make sure that you:
- develop a specific, meaningful, actionable plan for what you want to do and why you want to do it;
- consider how your plan will achieve positive results;
- locate a granting organization or source that funds projects like the one you have in mind;
- research that organization to make sure that its mission aligns with your plan;
- review the organization’s proposal guidelines; and
- examine sample proposals from your department, peers, and/or the organization.
When you’ve done all of this, you’re ready to start drafting your proposal!
Additional Resources about Grants and Grant Writing
For students, faculty, or staff at UW–Madison, a great place to learn more about grants, grant proposal writing, and granting institutions is the Grants Information Collection at UW–Madison’s Memorial Library. Check out their website and our review of some of their materials as well as links to other useful grant resources here.
Considering the Audience, Purpose, and Expectations of a Grant Proposal
A grant proposal is a very clear, direct document written to a particular organization or funding agency with the purpose of persuading the reviewers to provide you with support because: (1) you have an important and fully considered plan to advance a valuable cause, and (2) you are responsible and capable of realizing that plan.
As you begin planning and drafting your grant proposal, ask yourself:
- Who is your audience? Think about the people from the agency offering this grant who will read this proposal. What are the agency’s mission and goals? What are its values? How is what you want to do aligned with what this agency is all about? How much do these readers know about what you are interested in? Let your answers to these questions inform how you present your plan, what vocabulary you use, how much background you provide, and how you frame your goals. In considering your audience, you should think about the kind of information these readers will find to be the most persuasive. Is it numbers? If so, make sure that you provide and explain your data. Is it testimonials? Recommendations from other collaborators? Historical precedent? Think closely about how you construct your argument in relationship to your readers.
- What are the particular expectations for this grant? Pay attention to everything the granting organization requires of you. Your proposal should adhere exactly to these requirements. If you receive any advice that contradicts the expectations of your particular situation ( including from this website ), ignore it! Study representative samples of successful proposals in your field or proposals that have received the particular grant you are applying for.
- How do you establish your credibility? Make sure that you present yourself as capable, knowledgeable, and forward thinking. Establish your credibility through the thoroughness of your plan, the intentional way that you present its importance and value, and the knowledge you have of what has already been learned or studied. Appropriately reference any past accomplishments that verify your ability to succeed and your commitment to this project. Outline any partnerships you have built with complementary organizations and individuals.
- How can you clearly and logically present your plan? Make sure that your organization is logical. Divide your proposal into predictable sections and label them with clear headings. Follow exactly the headings and content requirements established by the granting agency’s call for proposals.Grant proposals are direct and to–the–point. This isn’t a good place for you to embroider your prose with flowery metaphors or weave in subtle literary allusions. Your language should be uncluttered and concise. Match the concepts and language your readers use and are familiar with. Your readers shouldn’t have to work hard to understand what you are communicating. For information about writing clear sentences, see this section of our writer’s handbook. However, use a vivid image, compelling anecdote, or memorable phrase if it conveys the urgency or importance of what you are proposing to do.
Common Elements of Grant Proposals
General tips, pay attention to the agency’s key interests..
As mentioned earlier, if there are keywords in the call for proposals—or in the funding organization’s mission or goal—be sure to use some of those terms throughout your proposal. But don’t be too heavy–handed. You want to help your readers understand the connections that exist between your project and their purpose without belaboring these connections.
Organize ideas through numbered lists.
Some grant writers use numbered lists to organize their ideas within their proposal. They set up these lists with phrases like, “This project’s three main goals are . . . ” or, “This plan will involve four stages . . . ” Using numbers in this way may not be eloquent, but it can an efficient way to present your information in a clear and skimmable manner.
Write carefully customized proposals.
Because grant funding is so competitive, you will likely be applying for several different grants from multiple funding agencies. But if you do this, make sure that you carefully design each proposal to respond to the different interests, expectations, and guidelines of each source. While you might scavenge parts of one proposal for another, never use the exact same proposal twice . Additionally when you apply to more than one source at the same time, be sure to think strategically about the kind of support you are asking from which organization. Do your research to find out, for example, which source is more likely to support a request for materials and which is more interested in covering the cost of personnel.
Go after grants of all sizes.
Pay attention to small grant opportunities as well as big grant opportunities. In fact, sometimes securing a smaller grant can make your appeal for a larger grant more attractive. Showing that one or two stakeholders have already supported your project can bolster your credibility.
Don’t give up! Keep on writing!
Writing a grant proposal is hard work. It requires you to closely analyze your vision and consider critically how your solution will effectively respond to a gap, problem, or deficiency. And often, even for seasoned grant writers, this process ends with rejection. But while grant writers don’t receive many of the grants they apply to, they find the process of carefully delineating and justifying their objectives and methods to be productive. Writing closely about your project helps you think about and assess it regardless of what the grant committee decides. And of course, if you do receive a grant, the writing won’t be over. Many grants require progress reports and updates, so be prepared to keep on writing!
Successful Sample Grant Proposals
One of the best ways to learn how to write grant proposals is to analyze successful samples. We’ve annotated and uploaded three very different kinds of successful proposals written by colleagues associated with UW–Madison. We encourage you to carefully read these samples along with the annotations we’ve provided that direct your attention to specific ways each one is doing the work of a strong proposal. But don’t stop with these! Find additional samples on your own of successful proposals like the one you’re writing to help guide and further your understanding of what has worked and been persuasive.
- Sample Grant Proposal 1 (PDF) Fellowship Proposal for UW–Madison’s Center for the Humanities’ Public Humanities Exchange (HEX)
- Sample Grant Proposal 2 (PDF) Proposal for a 3–Year National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship
- Sample Grant Proposal 3 (PDF) Madison Writing Assistance’s grant proposal to the Evjue Foundation

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics
Dynamic title for modals
Are you sure.
- About Grants
- How to Apply - Application Guide
Samples: Applications, Attachments, and Other Documents
As you learn about grantsmanship and write your own applications and progress reports, examples of how others presented their ideas can help. NIH also provides attachment format examples, sample language, and more resources below.
On This Page:
Sample Grant Applications
Nih formats, sample language, and other examples.
With the gracious permission of successful investigators, some NIH institutes have provided samples of funded applications, summary statements, and more. When referencing these examples, it is important to remember:
- The applications below used the form version and instructions that were in effect at the time of their submission. Forms and instructions change regularly. Read and carefully follow the instructions in your chosen funding opportunity and the Application Guide .
- The best way to present your science may differ substantially from the approaches used in these examples. Seek feedback on your draft application from mentors and others.
- Talk to an NIH program officer in your area of science for advice about which grant program would be a good fit for you and the Institute or Center that might be interested in your idea.
- Samples are not available for all grant programs. Because many programs have common elements, the available samples can still provide helpful information and demonstrate effective ways to present information.
National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- Sample Applications and Summary Statements (R01, R03, R15, R21, R33, U01, SBIR, STTR, G11, K, and F)
- NIAID Sample Forms, Plans, Letters, Emails, and More
National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- Behavioral Research Grant Applications (R01, R21, R03)
- Cancer Epidemiology Grant Applications (R01, R21, R03, R37)
- Cancer Control and Population Sciences Grant Applications (R01, R21, R37)
- Healthcare Delivery Research Grant Applications (R01, R03, R21, R50)
National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI)
- ELSI Applications and Summary Statements and biosketches (K99/R00, K01, R01, R03, and R21)
- NHGRI Sample Consent Forms
National Institute on Aging (NIA)
- K99/R00: Pathway to Independence Awards Sample Applications
- NIA Small Business Sample Applications (SBIR and STTR Phase 1, Phase 2, and Fast-Track)
National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD)
- Research Project Grants (R01) Sample Applications and Summary Statements
- Early Career Research (ECR) R21 Sample Applications and Summary Statements
- Exploratory/Developmental Research Grant (R21) Sample Applications and Summary Statements
NIH provides additional examples of completed forms, templates, plans, and other sample language for reference. Your chosen approach must follow the instructions in your funding opportunity and the Application Guide .
- Application Format Pages
- Annotated Form Sets
- Animal Document Samples from Office of Laboratory Animal Welfare (OLAW) for animal welfare assurances, study proposals, Memorandum of Understanding , and more
- Allowable Appendix Materials Examples
- Authentication of Key Biological and/or Chemical Resources Plan Examples
- Biosketch Format Pages, Instructions, and Samples
- Data Management and Sharing (DMS) Plan Samples
- Informed Consent Example for Certificates of Confidentiality
- Informed Consent Sample Language for secondary research with data and biospecimens and for genomic research
- Model Organism Sharing Plans
- Multiple PI Leadership Plan Examples
- Other Support format page, samples, and instructions
- Scientific Rigor Examples
- Person Months FAQ with example calculations
- Plain Language Examples for application title, abstract, and public health relevance statements
- Project Outcome Description Examples for interim or final Research Performance Progress Report (RPPR)
This page last updated on: February 7, 2024
- Bookmark & Share
- E-mail Updates
- Help Downloading Files
- Privacy Notice
- Accessibility
- National Institutes of Health (NIH), 9000 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, Maryland 20892
- NIH... Turning Discovery Into Health
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PMC10250258

How to write a successful grant application: guidance provided by the European Society of Clinical Pharmacy
Anita e. weidmann.
1 Department of Clinical Pharmacy, Innsbruck University, Innsbruck, Austria
Cathal A. Cadogan
2 School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin, Ireland
Daniela Fialová
3 Department of Social and Clinical Pharmacy, Faculty of Pharmacy in Hradec Králové, Charles University, Hradec Králové, Czech Republic
4 Department of Geriatrics and Gerontology, 1st Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic
Ankie Hazen
5 Julius Centre for Health Sciences and Primary Care, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Martin Henman
6 Trinity College Dublin, Dublin, Ireland
Monika Lutters
7 Kantonsspital Aarau, Aarau, Switzerland
Betul Okuyan
8 Department of Clinical Pharmacy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Marmara University, Istanbul, Turkey
Vibhu Paudyal
9 University of Birmingham, Birmingham, United Kingdom
Francesca Wirth
10 Department of Pharmacy, University of Malta, Msida, Malta
Considering a rejection rate of 80–90%, the preparation of a research grant is often considered a daunting task since it is resource intensive and there is no guarantee of success, even for seasoned researchers. This commentary provides a summary of the key points a researcher needs to consider when writing a research grant proposal, outlining: (1) how to conceptualise the research idea; (2) how to find the right funding call; (3) the importance of planning; (4) how to write; (5) what to write, and (6) key questions for reflection during preparation. It attempts to explain the difficulties associated with finding calls in clinical pharmacy and advanced pharmacy practice, and how to overcome them. The commentary aims to assist all pharmacy practice and health services research colleagues new to the grant application process, as well as experienced researchers striving to improve their grant review scores. The guidance in this paper is part of ESCP’s commitment to stimulate “ innovative and high-quality research in all areas of clinical pharmacy ”.
Writing research grants is a central part of any good quality research. Once a detailed research proposal has been submitted, it is subjected to an expert peer review process. Such reviews are designed to reach a funding decision, with feedback provided to improve the study for this and any future submissions. Depending on the length of the proposal, complexity of the research and experience of the research team, a proposal can take between six to twelve months to write [ 1 ]. Ample time must be given to the writing of hypothesis/research aim, budgeting, discussion with colleagues and several rounds of feedback [ 2 ]. The draft research proposal should always be completed well before the deadline to allow for last minute delays. An application which is not fully developed should not be submitted since it will most likely be rejected [ 3 ].
Despite the large effort that goes into each grant application, success rates are low. Application success rates for Horizon 2020 were < 15% [ 4 ] and < 20% for the National Institute of Health (NIH) [ 5 – 8 ]. With these statistics in mind, it is evident that often repeated submissions are required before securing funding. Due to a paucity of specific clinical pharmacy grant awarding bodies, writing a grant application for a clinical pharmacy or pharmacy practice research project often involves multidisciplinary collaborations with other healthcare professions and focus on a specific patient population or condition. There is no guarantee of success when trying to secure funding for research. Even the most seasoned researchers will have applications rejected. The key is to never give up. This commentary provides useful pointers for the planning and execution of grant writing.
Conceptualising your research idea
Before writing a research grant proposal/application, consider what the research should achieve in the short, medium, and long term, and how the research goals will serve patients, science and society [ 9 , 10 ]. Practical implications of research, policy impact or positive impact on society and active patient/public involvement are highly valued by many research agencies as research should not be conducted “only for research”, serving the researchers’ interests. EU health policy and action strategies (CORDIS database) and other national strategies, such as national mental health strategy for grants within mental disorders, should be considered, as well as dissemination strategies, project deliverables, outcomes and lay public invitations to participate. The Science Community COMPASS has developed a useful “Message Box Tool” that can help in the identification of benefits and solutions, as well as the all-important “So What?” of the research [ 11 ]. Clearly determine what the lead researcher’s personal and professional strengths, expertise and past experiences are, and carefully select the research team to close these gaps [ 12 – 14 ].
How to find the right funding call
When trying to identify the right type of grant according to the research ambitions, one should be mindful that several types of grants exist, including small project grants (for equipment, imaging costs), personal fellowships (for salary costs, sometimes including project costs), project grants (for a combination of salary and project costs), programme grants (for comprehensive project costs and salary for several staff members), start-up grants and travel grants [ 15 ]. Types of grants include EU grants (e.g. Horizon, Norway Grant), commercial grants (e.g. healthcare agencies and insurance companies), New Health Program grants ideal for new, reimbursed clinical pharmacy service projects and national grants (e.g. FWF (Austria), ARRS (Slovenia), NKFIH (Hungary), NCN (Poland), FWO (Belgium), HRZZ (Croatia), GAČR (Czech Republic), SNSF (Switzerland), SSF (Sweden). It is worth remembering that early career researchers, normally within ten years of finishing a PhD, have a particular sub-category within most grants.
Many national agencies only have one “Pharmacy” category. This results in clinical pharmacy and advanced clinical pharmacy practice projects competing with pharmaceutical chemistry, pharmaceutical biology and pharmacy technology submissions, thereby reducing the success rate as these research areas can often be very advanced in most EU countries compared to clinical and advanced pharmacy practice. A second possible submission category is “Public Health”. Several essential factors can impact the grant selection, such as research field, budget capacity, leading researcher’s experience and bilateral grants. Examples of successful clinical pharmacy funded research studies can be found in the published literature [ 16 – 20 ].
Plan, plan, plan
One key element of successful grant writing is the ability to plan and organise time. In order to develop a realistic work plan and achieve milestones, it is imperative to note deadlines and to be well-informed about the details of what is required. The development of a table or Gantt Chart that notes milestones, outcomes and deliverables is useful [ 21 ].
All funders are quite specific about what they will and will not fund. Research your potential funders well in advance. It is vital to pay attention to the aims, ambitions and guidelines of the grant awarding bodies and focus your proposal accordingly. Submitting an application which does not adhere to the guidelines may lead to very early rejection. It is helpful to prepare the grant application in such a way that the reviewers can easily find the information they are looking for [ 15 , 22 ]. This includes checking the reviewers’ reports and adding “bolded” sentences into the application to allow immediate emphasis. Reviewers’ reports are often available on the agencies’ websites. It is extremely useful to read previously submitted and funded or rejected proposals to further help in the identification of what is required in each application. Most funding agencies publish a funded project list, and the ‘Centre for Open Science (COS) Database of Funded Research’ enables tracking of funding histories from leading agencies around the world [ 23 ]. Another useful recommendation is to talk to colleagues who have been successful when applying to that particular funder. Funding agency grant officers can provide advice on the suitability of the proposal and the application process.
It is important to pay particular attention to deadlines for the grant proposal and ensure that sufficient time is allocated for completion of all parts of the application, particularly those that are not fully within one’s own control, for example, gathering any required signatures/approvals. Funders will generally not review an application submitted beyond the deadline.
Lastly, it is important to obtain insight into the decision process of grants. Research applications are sent to several reviewers, who are either volunteers or receive a small compensation to judge the application on previously determined criteria. While the judging criteria may vary from funder to funder, the key considerations are:
- Is there a clear statement of the research aim(s)/research question(s)/research objective(s)?
- Is the proposed research “state-of-the-art” in its field and has all relevant literature been reviewed?
- Is the method likely to yield valid, reliable, trustworthy data to answer question 1.?
- If the answer to the second question is ’yes’, then what is the impact of financing this study on patient care, professional practice, society etc.?
- Is there sufficient confidence that the research team will deliver this study on time with expected quality outputs and on budget?
- Does the study provide value for money?
How to write
The key to good grant proposal writing is to be concise yet engaging. The use of colour and modern web-based tools such as #hashtags, webpage links, and links to YouTube presentations are becoming increasingly popular to improve the interest of a submission and facilitate a swift decision-making process. Ensure use of the exact section headings provided in the guidance, and use the keywords provided in the funding call documentation to reflect alignment with the funding bodies’ key interests. Attention to detail cannot be overstated; the quality and accuracy of the research proposal reflect the quality and accuracy of the research [ 24 ]. Try to adopt a clear, succinct, and simple writing style, making the grant easy to read. Having a clear focus can help to boost a grant to the top of a reviewer’s pile [ 25 , 26 ]. A clearly stated scientific question, hypothesis, and rationale are imperative. The reviewer should not have to work to understand the project [ 27 ]. Allow for plenty of time to incorporate feedback from trusted individuals with the appropriate expertise and consider having reviews for readability by non-experts.
What to write
Abstract, lay summary and background/rationale.
Take sufficient time to draft the scientific abstract and summary for the lay public. These should clearly state the long-term goal of the research, the aim and specific testable objectives, as well as the potential impact of the work. The research aim is a broad statement of research intent that sets out what the project hopes to achieve at the end. Research objectives are specific statements that define measurable outcomes of the project [ 28 , 29 ].
The lay summary is important for non-subject experts to quickly grasp the purpose and aims of the research. This is important in light of the increased emphasis on patient and public involvement in the design of the research. The abstract is often given little attention by the applicants, yet is essential. If reviewers have many applications to read, they may form a quick judgement when reading the abstract. The background should develop the argument for the study. It should flow and highlight the relevant literature and policy or society needs statements which support the argument, but at the same time must be balanced. It should focus on the need for the study at the local, national and international level, highlighting the knowledge gap the study addresses and what the proposed research adds. Ensure this section is well-referenced. The innovation section addresses the ‘‘So what?’’ question and should clearly explain how this research is important to develop an understanding in this field of practice and its potential impact. Will it change practice, or will it change the understanding of the disease process or its treatment? Will it generate new avenues for future scientific study? [ 30 ].
Hypothesis/aims and objectives
For the hypothesis, state the core idea of the grant in one or two sentences. It should be concise, and lead to testable specific aims. This section is fundamental; if it is unclear or poorly written, the reviewers may stop reading and reject the application. Do not attempt to make the aims overly complex. Well-written aims should be simply stated. Criteria such as PICO (population, intervention, comparison, outcomes) [ 31 ], and FINER (feasible, interesting, novel, ethical, relevant) [ 32 ], provide useful frameworks to help in writing aim(s), research question(s), objective(s) and hypotheses. Pay attention to the distinction between aim(s), research question(s), objective(s) and hypotheses. While it is tempting to want to claim that enormously complex problems can be solved in a single project, do not overreach. It is important to be realistic [ 25 ].
Experimental design, methods and expertise
The methodology is one of the most important parts of getting a grant proposal accepted. The reviewing board should be convinced that the relevant methodology is well within the research teams’ expertise. Any evidence of potential success, such as preliminary results or pilot studies strengthen the application significantly [ 33 ]. The methodology must relate directly to the aim. Structuring this section into specific activities/ set of activities that address each research question or objective should be considered. This clarifies how each question/ objective will be addressed. Each work-package should clearly define the title of the research question/objective to be addressed, the activities to be carried out including milestones and deliverables, and the overall duration of the proposed work-package. Deliverables should be presented in table format for ease of review. Each subsequent work-package should start once the previous one has been completed to provide a clear picture of timelines, milestones and deliverables which reflect stakeholder involvement and overall organisation of the proposed project. Using relevant EQUATOR Network reporting guidelines enhances the quality of detail included in the design [ 34 ]. Key elements of this methodology are detailed in Table 1 .
Summary of the key elements of the experimental design, methods and expertise
Proposed budget
The budget should be designed based on the needs of the project and the funding agency’s policies and instructions. Each aspect of the budget must be sufficiently justified to ensure accountability to the grant awarding body [ 35 ]. Costing and justification of the time of those involved, any equipment, consumables, travel, payment for participants, dissemination costs and other relevant costs are required. The funders will be looking for value for money and not necessarily a low-cost study. Ensure that the total budget is within the allocated funding frame.
Provide a breakdown of the key work packages and tasks to be completed, as well as an indication of the anticipated duration. Include a Gantt chart (A table detailing the most general project content milestones and activities) to demonstrate that all aspects of the proposal have been well thought through [ 21 ].
Critical appraisal, limitations, and impact of the proposed research
It is important to detail any strengths and limitations of the proposed project. Omitting these will present the reviewing board with sufficient grounds to reject the proposal [ 36 ]. Provide a clear statement about the short and long-term impact of the research [ 37 , 38 ]. The reviewers will pay particular attention to the differences the study can make and how potential impact aligns with the funding bodies goals as well as national policies. This statement is essential to make an informed decision whether or not to support the application. Useful diagrams summarise the different levels of impact [ 39 ].
Table 2 provides a summary of the key elements of project grants and key questions to ask oneself.
Summary of the key elements of project grants and key questions to ask oneself.
(Adapted from [ 5 ]: Koppelmann GH, Holloway JW. Successful grant writing. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2012; 13:63–66.)
Although the grant writing process is time-consuming and complex, support is widely available at each stage. It is important to involve colleagues and collaborators to improve the proposal as much as possible and invest time in the detailed planning and execution. Even if the grant is not awarded, do not be disheartened. Use the feedback for improvement and exercise resilience and persistence in pursuing your research ambition.
The guidance in this paper is part of ESCP’s commitment to stimulate “innovative and high-quality research in all areas of clinical pharmacy”. In a previous ESCP survey, it was found that few opportunities for collaboration (especially for grant applications) was one of the key barriers for members towards conducting research [ 40 ]. ESCP promotes networking, which is essential for multi-centre grant applications, both among ESCP members and with other organisations as it recognises the need for “multi-centre research in all areas of clinical pharmacy both within countries and between countries or differing healthcare delivery systems”. ESCP is planning to relaunch its own research grant which was paused during the pandemic, and it is also planning to provide ESCP members with information about the research grants offered by other organizations. ESCP is exploring partnering with other organisations to develop research proposals in areas of common interest and, in the near future, it will ask its members about their research priorities. Taken together, these initiatives will inform ESCP’s research strategy and help it to formulate policies to address the challenges its members face.
Acknowledgements
Research works of Assoc. Prof. Fialová were also supported by the institutional program Cooperation of the Faculty of Pharmacy, Charles University.
Open access funding provided by University of Innsbruck and Medical University of Innsbruck. This work was conducted without external funding.
Conflicts of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Academic Resources
- Academic Calendar
- Academic Catalog
- Academic Success
- BlueM@il (Email)
- Campus Connect
- DePaul Central
- Desire2Learn (D2L)
Campus Resources
- Campus Security
- Campus Maps
University Resources
- Technology Help Desk
Information For
- Alumni & Friends
- Current Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Research Development
- Identifying External Funding
- Internal Grants
Grant Writing
- Identifying Collaborators
- Technology for Research
- Trainings for Researchers
- Become a Peer Reviewer
- Academic Growth and Innovation Fund
- DPU-RFUMS Collaborative Grants
- Research & Innovation Leadership Fellows Program
- Pre-Award Services
- Award Management
- Research Protections
DePaul University Research Services > Research Development > Grant Writing
ORS offers grant writing support for the narrative portions of proposals to federal agencies and other governmental funders, with a special focus on projects that are multidisciplinary in nature or that involve partnerships between DePaul and other institutions. We directly support faculty to succeed in their efforts to acquire funding, and also work with Dean's Offices and other leaders to develop innovative program and proposal ideas, identify faculty for research initiatives, and offer targeted training.
- Edit part or all of a narrative before submission.
- Help you revise a proposal that was not successful to prepare for resubmission.
- Help you think through your project idea and decide how to structure your narrative.
- Draft select sections of your narrative.
- Provide project management for larger submissions, including hosting regular check-in meetings, coordinating letters of support and collaboration, and facilitating additional documents for the submission.
Interested in learning more about grant writing generally? The Grant Writer offers trainings, lunch-and-learn sessions, and other events to support general faculty learning around the grant writing process. Check the ORS News & Events page for upcoming training sessions, or reach out directly to request assistance.

View all events...

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Grant Proposal. Grant Proposal is a written document that outlines a request for funding from a grant-making organization, such as a government agency, foundation, or private donor. The purpose of a grant proposal is to present a compelling case for why an individual, organization, or project deserves financial support.
Applicants must write grant proposals, submit them, receive notice of acceptance or rejection, and then revise their proposals. Unsuccessful grant applicants must revise and resubmit their proposals during the next funding cycle. Successful grant applications and the resulting research lead to ideas for further research and new grant proposals.
Do not submit a first draft: These sample proposals went through multiple rounds of revisions with feedback from both Office of Undergraduate Research advisors and the student's faculty mentor.First, it helps to learn about grant structure and proposal writing techniques before you get started. Then, when you begin drafting, it's normal to make lots of changes as the grant evolves.
Create your grant proposal. Create, send and eSign your grant proposals. Receive automatic follow-up reminders to keep the conversation going. Start a free trial. Step 1. Write a strong cover letter. Your cover letter is the perfect opportunity to capture the funder's attention and get your foot in the door.
Step 2: Plan and research your project. Preliminary research for your grant proposal. Questions to ask yourself as you plan your grant proposal. Developing your grant proposal. Step 3: Write the first draft of your grant proposal. Step 4: Get feedback, and revise your grant proposal accordingly.
Simplify the editing process by first writing each section in a Word document to be copy and pasted into the corresponding submission fields. If there is no online application platform, the funder will usually offer a comprehensive Request for Proposal (RFP) to guide the structure of your grant proposal. The RFP:
1. Abstract. The abstract is a summary of your research proposal. It should be around 150 to 200 words and summarize your aims, the gap in literature, the methods you plan to use, and how long you might take. 2. Literature Review. The literature review is a review of the literature related to your field.
Preparing a grant proposal is often an involved process. Begin by developing a plan of attack. We suggest you generate a list of tasks and assign different members of your team to different tasks, along with specific due dates. This will help you monitor the progress of your grant proposal.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management" Example research proposal #2: "Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use" Title page
Make sure that your organization is logical. Divide your proposal into predictable sections and label them with clear headings. Follow exactly the headings and content requirements established by the granting agency's call for proposals.Grant proposals are direct and to-the-point.
Purpose of A Proposal. To show you have a worthwhile research project to undertake. To demonstrate that YOU have the competence to complete it. To discuss all relevant aspects of the research process. To enable others to evaluate whether enough information exists to want to support the proposed study. As a supervisor (e.g. a thesis)
There might be some disagreements between the surgeons and patients perspectives. 1 The purpose of the background and significance chapter is to justify the study you are proposing. Describe how the result of your study will benefit society. You need to convince the granting agencies that it is worth their money.
Unfortunately, grant writing is generally considered very difficult, more so than the actual research. In this post, we will discuss how to write a grant proposal. 10 characteristics of an effective scientific research grant proposal. Aims to advance science and benefit human knowledge, society, or the environment; Has focused and measurable aims
Include a sentence or two about what your organization does, and one research-based point that shows the need that your organization addresses. Limit your cover letter to one page with three or four paragraphs. Use the same date that you'll be sending the complete grant application to the funding source.
Abstract. This article aims to provide a step-by-step overview of the process of applying for research funding and will be most relevant to either a new academic joining a group or a young clinician wanting to establish their own research. The article covers the steps involved in preparing, writing and submitting an application.
research grant proposal. − Receiving relevant and up-to-date information about new research methods. − Establishing collaborative associations with peers. − Constructive feedback on research proposals and throughout the research process. − Assistance in the development of a long-term research and writing plan.
Research: Includes traditional research by individual investigators, broadly based traditional research and other, research-related career programs, and the SBIR/STTR mechanism. 2. Services: Includes grants to deliver health, social, or other types of services; treatment and rehabilitation programs; education and information programs. 3. Training:
An effective grant writer creates a proposal that: (1) matches the funding organization's goals, (2) conveys strong research objectives on the first page, (3) tells a compelling research story, (4) details sound logistics for executing the research plan, and (5) adds credibility to the research proposal in every section. 1.
As you learn about grantsmanship and write your own applications and progress reports, examples of how others presented their ideas can help. NIH also provides attachment format examples, sample language, and more resources below. On This Page: Sample Grant Applications; NIH Formats, Sample Language, and Other Examples; Sample Grant Applications
Step 1. Write a strong cover letter. When writing the cover letter, keep it short (three to four paragraphs), precise (amount needed, purpose, and reasons why you deserve the grant), and relatable to the reader. You should avoid repetition and compare yourself to other applicants.
Writing a grant proposal is not something to be undertaken alone. Even the most seasoned of researchers will need advice, guidance and constructive criticism from trusted and experienced colleagues when developing new grant proposals. For many junior researchers, a supervisor will be the appropriate person to provide this support.
Conceptualising your research idea. Before writing a research grant proposal/application, consider what the research should achieve in the short, medium, and long term, and how the research goals will serve patients, science and society [9, 10].Practical implications of research, policy impact or positive impact on society and active patient/public involvement are highly valued by many ...
responsibilities. 9. Be prepared as time from call for proposal to last date may only be 1 2 weeks. 10. Have a maximum of three to four research objectives in the grant application. 11. Detail the ...
ORS offers grant writing support for the narrative portions of proposals to federal agencies and other governmental funders, with a special focus on projects that are multidisciplinary in nature or that involve partnerships between DePaul and other institutions. ... and also work with Dean's Offices and other leaders to develop innovative ...