
Popular Insights:
Best Project Management Software
Mind Mapping Software
What Is a RACI Matrix? Definition, Examples, Uses
Reviewed by
Share this Article:
Our content and product recommendations are editorially independent. We may make money when you click links to our partners. Learn more in our Editorial & Advertising Policy .
Key takeaways
Featured Partners
{{ POSITION }}. {{ TITLE }}
Successful project management depends on a team-wide understanding of roles and responsibilities. Using a RACI matrix to assign and define each role is a great way to keep a project on track and positioned for success, especially when used in conjunction with other documents like the requirement traceability matrix.
What is a RACI Matrix?
A RACI matrix is a tool in project management designed to clarify team roles and responsibilities across tasks.
Each role is categorized as Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, or Informed, ensuring that everyone understands their role in a project’s success. By assigning these roles, project managers prevent confusion and overlapping duties while increasing accountability.
The RACI framework is especially beneficial for complex projects where clear role distribution is essential for smooth workflows and improved communication.
How Does a RACI Chart Help Project Managers?
Project managers use RACI charts to keep track of team roles and relay those responsibilities to the larger team.
The matrix defines clear roles and responsibilities for individual team members across the various phases of the project, breaking the roles down into four types. Each letter of the project management acronym stands for a designation: those who are responsible and accountable for project deliverables, those who should be consulted as work begins, and stakeholders who need to be informed of ongoing progress, roadblocks, and updates.
4 Core Roles of RACI Defined
Responsible.
The individual(s) with responsibility for the task or deliverable is responsible for developing and completing the project deliverables themselves. The responsible parties are typically hands-on team members who make direct contributions toward the completion of the project. The responsible team is composed of the project’s doers, who work hands-on to ensure that each deliverable is completed.
Some examples of responsible parties are:
- Project managers
- Business analysts
- Graphic designers
- Copywriters
One risk when using a RACI matrix is unintentionally overloading a single team member with too many responsibilities. If one person is designated as Responsible for too many tasks, they may struggle to manage their workload, leading to delays or burnout. To avoid this, project managers should carefully distribute responsibilities across the team and ensure that no individual is overwhelmed. Regularly reviewing the matrix throughout the project helps identify and address any imbalances before they become critical.
Accountable
Accountable parties ensure accountability to project deadlines, and ultimately, accountability to project completion. This group frequently also falls under the informed category.
Some examples of accountable parties are:
- Product owners
- Signature authorities
- Business owners
- Key stakeholders
By clearly defining roles, a RACI matrix prevents decision-making bottlenecks and confusion in the approval process. When roles are ambiguous, critical decisions can get delayed, as team members might not know who holds final accountability. The RACI model eliminates this issue by ensuring that the individual responsible for approvals is clearly designated as Accountable . Additionally, identifying who needs to be consulted or informed reduces unnecessary back-and-forth, allowing decisions to be made quickly and efficiently without roadblocks. This clear communication flow optimizes project progression and prevents delays.
Consulted individuals’ opinions are crucial, and their feedback needs to be considered at every step of the game. These individuals provide guidance that is often a prerequisite to other project tasks, for example, providing legal guidance on a project throughout the process. If you are working on new product development or expansion, this could essentially be the entire organization.
Some examples of consulted parties are:
- Legal experts
- Information security and cybersecurity experts
- Compliance consultants
Informed persons are those that need to stay in the loop of communication throughout the project. These individuals do not have to be consulted or be a part of the decision-making, but they should be made aware of all project updates. Typically, this party are business owners or stakeholders that are more interested in viewing the project at a 30,000-foot view. Keep this group on your CC list for awareness of topics, decisions, and progress — that includes making them part of the initial project kickoff and project demos as optional attendees. This group often also falls under the accountable group.
Some examples of informed parties are:
- Project committee members
- External stakeholders
Why Are RACI Roles Important?
The same way a requirements traceability matrix provides accountability to project requirements by mapping out the relationship between these requirements and the project work, RACI roles provide a sense of organization and clarity for teams that are looking to divide roles and keep team members accountable for their contributions. Considering that 27 percent of projects go over budget, for reasons like scope creep and lack of defined roles, RACI roles help position a project for success and avoid common pitfalls.
RACI roles help ensure that communication between all roles is ongoing. When you consider that nearly half of all project spending is at risk of being wasted due to a lack of effective team-based communication, it becomes all that more important to prioritize.
How RACI helps with communication
The RACI matrix significantly enhances communication by clearly defining who needs to be involved at each stage of a project. By outlining who is Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed, it ensures that the right stakeholders are engaged at the right times.
This structured approach reduces miscommunication, which is one of the most common causes of project failure , as team members know exactly who to reach out to for input or updates. Keeping stakeholders informed also improves transparency, preventing misunderstandings and ensuring everyone is aligned with project goals and timelines.
How to Create a RACI Matrix
If you’re looking to implement a RACI matrix as part of your team’s project planning process, take these steps to create a RACI matrix.
- Plan ahead before taking action. Ensure that you have a thorough understanding of the project and its demands before outlining any further steps by communicating with key stakeholders and decision-makers.
- Define the scope of the project. List down all key activities and deliverables from the director of program management or other leadership.
- Determine who the involved parties are. Know who is needed to be a part of the project or initiative.
- Outline each project role. Determine the project roles and responsible job titles and persons for each activity and deliverable.
- Gather as a group. Hold review sessions with key members of the team for alignment, and if you haven’t already, host a kickoff meeting with the entirety of the team and key stakeholders to unveil the matrix, address questions, and more.
If the project has already started, it’s not too late to implement a RACI matrix. Just follow the following steps:
- Outline the story. Using research from multiple sources, do a, b, c, and d.
- Utilize steps 2 and 3 (as shown above) . Ensure the right groups are assigned and engaged.
- Hold a review session. Ensure that the team acknowledges and discusses the plan and the roles assigned.
If you need more information on how to create a RACI matrix, there are several RACI training courses and other resources you can use to get started.
RACI Matrix Examples
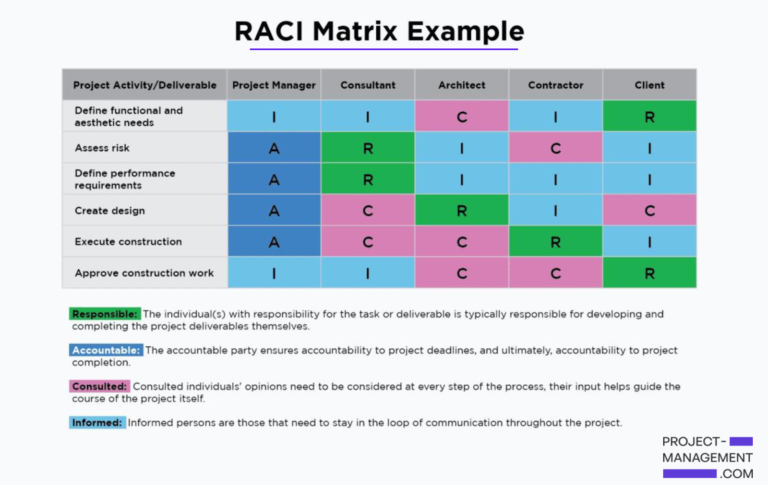
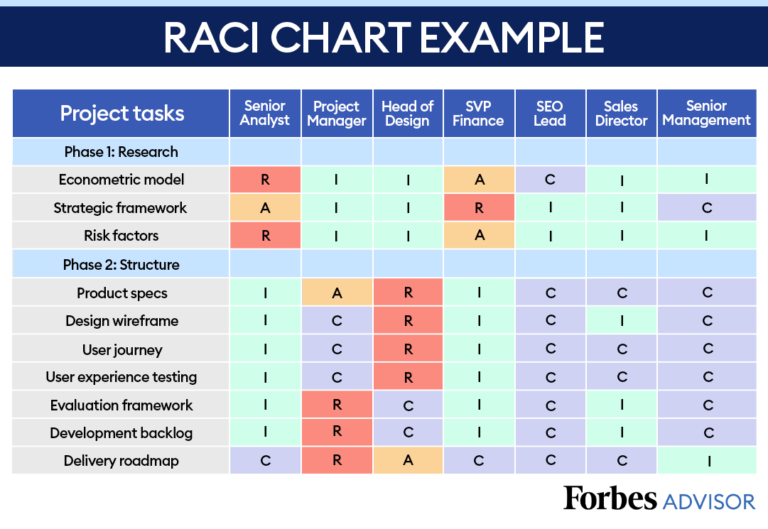
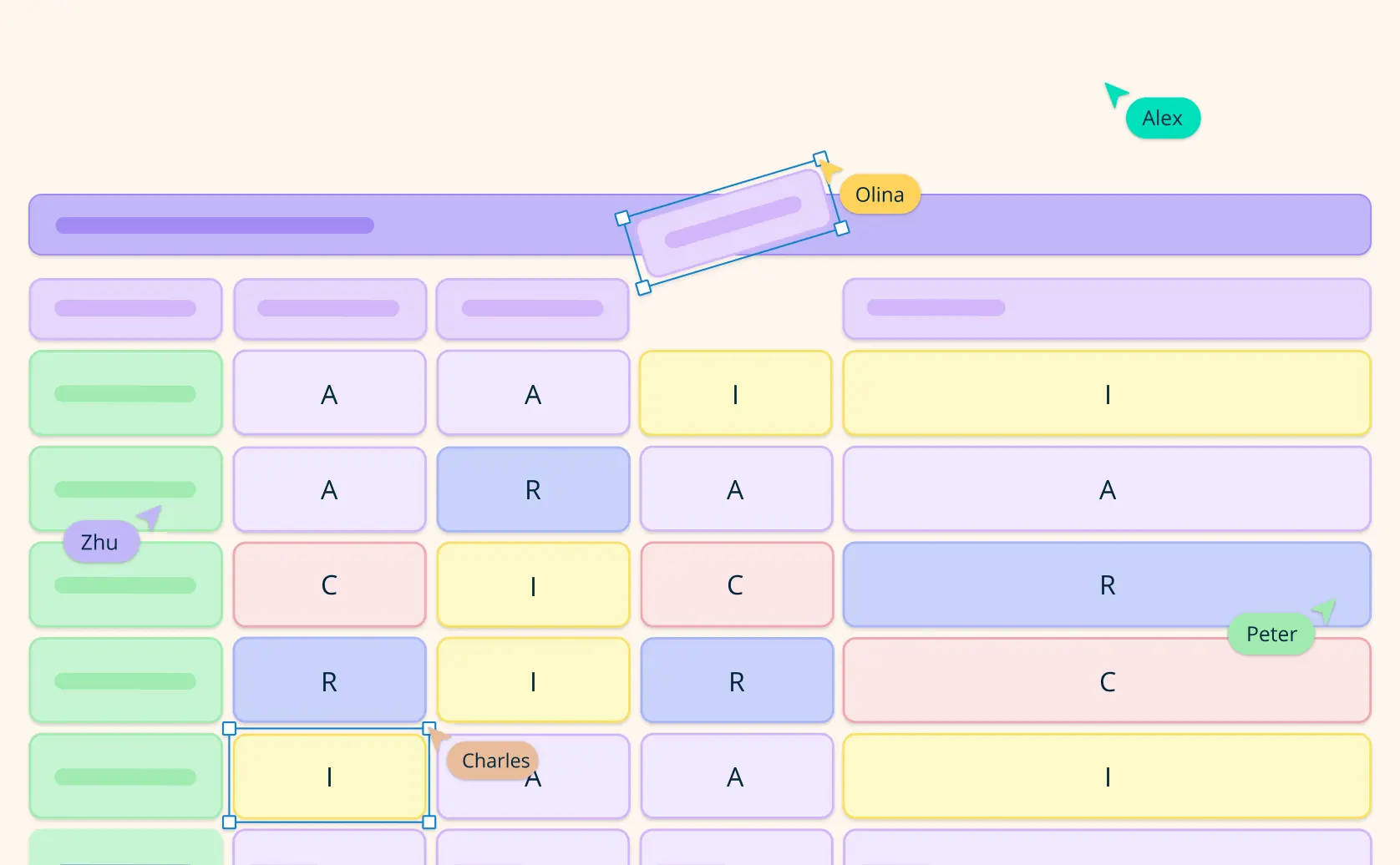
A RACI matrix helps break down what roles individuals will play as work is carried out and to what extent they will be involved in the project overall. The horizontal axis represents each person on the project team and the vertical axis represents each task.
Each square of the matrix represents an individual, a task, and that individual’s role within the project, either responsible, accountable, consulted, or informed.
In this situation, for example, the project manager is accountable for assessing risk, defining performance requirements, creating designs, executing construction, and approving construction work. However, they are only informed about approving construction work and defining functional and aesthetic needs.
Who Creates the RACI Matrix?
The RACI matrix — sometimes called RACI model, RACI diagram, or simply just RAC — is created by the project manager at the start of the project as a key part of establishing the initial human resources planning for the project.
Because miscommunication is a common threat to any project, RACI charts are a great asset to teams dealing with any type of work, from very simple projects to extremely complex ones.
Software Integration with Common PM Tools
Integrating the RACI Matrix into project management software makes it easier to assign roles and responsibilities. Here’s how the RACI Matrix works with popular tools:

Asana allows you to assign tasks and label roles like Responsible or Accountable directly in its project boards. By integrating RACI, project managers can easily track who is accountable for each phase, preventing miscommunication and task overlap. This tool also supports team collaboration by keeping all RACI role assignments visible in one place.

In Jira, RACI roles can be linked directly to project tickets. This integration helps project managers oversee who is accountable for each task while tracking the project’s progress through detailed reporting. Jira’s focus on issue tracking aligns perfectly with the RACI framework, ensuring that each decision and approval process is well-defined.

Trello utilizes labels and categories to represent RACI roles. With its simple, card-based format, project managers can visually assign and manage tasks, ensuring clarity on who is responsible or consulted at each stage. This tool is especially effective for smaller teams needing a clear overview of task assignments.
Integrating the RACI matrix into these tools enhances accountability and clarity, making it easier for teams to stay aligned on task responsibilities and avoid delays.
RACI Alternatives
While the RACI matrix is a widely used tool, several alternatives may be more suitable depending on your project’s needs:
- RASCI : Adds a Support role to the traditional RACI structure, providing extra assistance where necessary.
- DACI : The DACI framework focuses on decision-making by identifying clear Decision Makers and those accountable for final outcomes.
- RAPID : A decision-making framework that defines who Recommends, Agrees, Performs, Inputs, and Decides on critical decisions.
- Gantt chart : Provides a comprehensive view of who does what and when, combining responsibilities with timelines in a visual format.
- Work breakdown structure : Breaks down the entire scope of work in a project, offering a detailed view of all tasks in a hierarchical structure.
- Project dashboard : Offers dynamic, real-time oversight, keeping teams informed with up-to-date information on project progress, roles, and responsibilities.
Each RACI alternative differs on task ownership and project management. The best project managers choose the right approach based on their project’s needs.
RACI and Stakeholder Analysis
Stakeholder analysis is a crucial step that directly connects to the RACI matrix. By identifying all relevant stakeholders, project managers can effectively assign roles within the matrix.
This process helps clarify who has a vested interest in the project and ensures their roles are properly reflected in the matrix.
To run a stakeholder analysis:
- Identify key stakeholders : Determine who has a vested interest in the project’s success (e.g., clients, executives, team members).
- Define stakeholder influence : Assess how much influence each stakeholder has over project decisions.
- Align stakeholder roles with RACI : Assign stakeholders as Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, or Informed based on their role in the project.
- Maintain communication channels : Ensure stakeholders are appropriately informed of project progress, updates, and changes.
- Review regularly : Reassess stakeholder involvement as project phases evolve.
Aligning stakeholder involvement with RACI creates a roadmap for communication and decision-making that keeps everyone engaged and informed throughout the project life cycle.
Common Mistakes When Creating a RACI Matrix
- Failure to plan ahead : A RACI matrix should not be the first step in your project planning. Before preparing the matrix, ensure you have a fully assembled project team and a clear understanding of your project scope and key tasks. Without a basic structure in place, the matrix can become chaotic and difficult to manage. Starting with a rough project plan helps ensure that the RACI matrix aligns with your overall goals.
- Working with too large a team : The larger the team, the more complex the RACI matrix can become, leading to confusion rather than clarity. A matrix with too many roles or stakeholders can make responsibilities difficult to track and dilute accountability. For larger teams, consider breaking the project into smaller, manageable components, or you can use alternative frameworks. Between the DACI vs RACI model , DACI may be better at accommodating scale.
- Not communicating with the project team : A RACI matrix is meant to formalize responsibilities, not introduce them for the first time. Ensure that all team members are briefed on their roles and the project’s objectives before creating the matrix. Holding a kickoff meeting where tasks and responsibilities are discussed ensures everyone is aligned and prepared, preventing misunderstandings or confusion about their roles in the execution of the project.
- Overburdening team members : Assigning too many roles to a single person can lead to burnout and inefficiencies. If one team member is designated as both Responsible and Accountable for multiple tasks, they may become overwhelmed and unable to perform effectively. Regularly review the RACI matrix to ensure workload distribution is balanced and that no individual is shouldering too much responsibility.
- Hitting decision-making roadblocks : Without a clear assignment of who is Accountable for decision-making, tasks can get delayed as teams wait for approvals. This bottleneck can slow progress and create frustration. By explicitly identifying who has the authority to make final decisions, you ensure a smoother workflow and prevent key tasks from stalling due to indecision or unclear lines of accountability.
RACI Matrix Pros & Cons
- Increased engagement: RACI helps engage project participants throughout the project life cycle.
- Enhanced project planning: Project managers make project planning more organized, efficient, and detailed.
- Identifiable improvement opportunities: Areas of improvement are more easily identified.
- Easier collaboration: Use of a RACI matrix creates a clear path for leadership to sign off on project steps, as project documentation in the RACI model is heavily emphasized.
- Better communication: Improves overall group communication.
- Group accountability: Assists groups, especially larger project teams, stay connected and accountable to their roles and project goals.
- Limitations on role scope: The RACI model does not provide details on role scope, especially for responsible parties. These gaps in detail also affect other team roles; for example, the RACI model does not determine who is responsible for verification and signatory.
- Limits on task details and scope: While a RACI matrix can provide an overview of who is responsible for different tasks, it will not state what needs to be done.
- Not aligned to the agile methodology: Project managers using an agile methodology like scrum may find it redundant since accountability, ownership, and ongoing communication is built into the scrum framework (i.e., product owner, scrum master, and daily standups with the team). Additionally, agile focuses on team-based delivery and accountability, while the RACI framework and alternatives focus on individual responsibility and autonomous accountability.
Free RACI Matrix Templates
A number of project management software solutions include a native RACI matrix template. Here are just a few we found:
Colorful RACI chart template
We love this template from Smartsheet because it’s colorful, thorough, and includes room for every party involved in the project.
Pastel-colored RACI matrix template
This template from the Academy to Innovate HR is a great choice for project managers who want to organize their team roles with an easy-on-the-eyes chart that evolves beyond the simple spreadsheet.
Simple RACI chart
These RACI templates from ClickUp have enough variety to fit any of your project needs, but are simple enough for even beginner PMs to use.
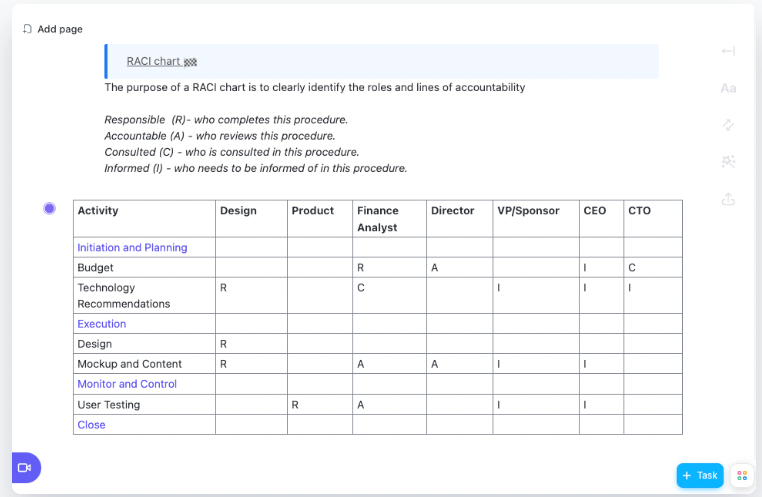
Detailed RACI matrix template
This template is a great starter template for anyone looking to explore RACI charts in their project management strategy. As an added bonus, it comes with the RACI definitions already built in!
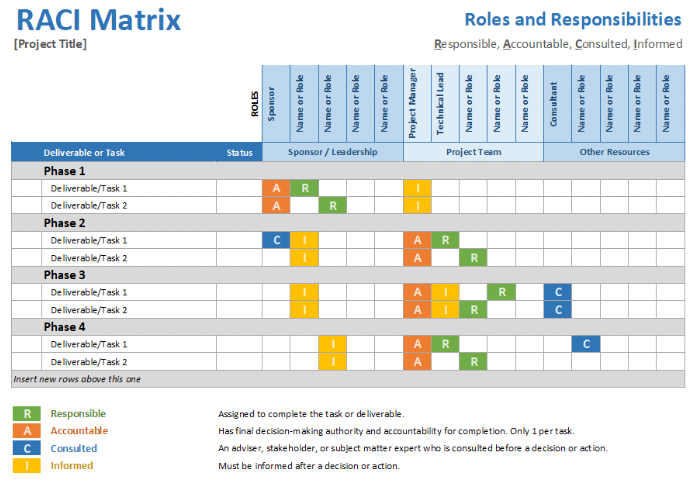
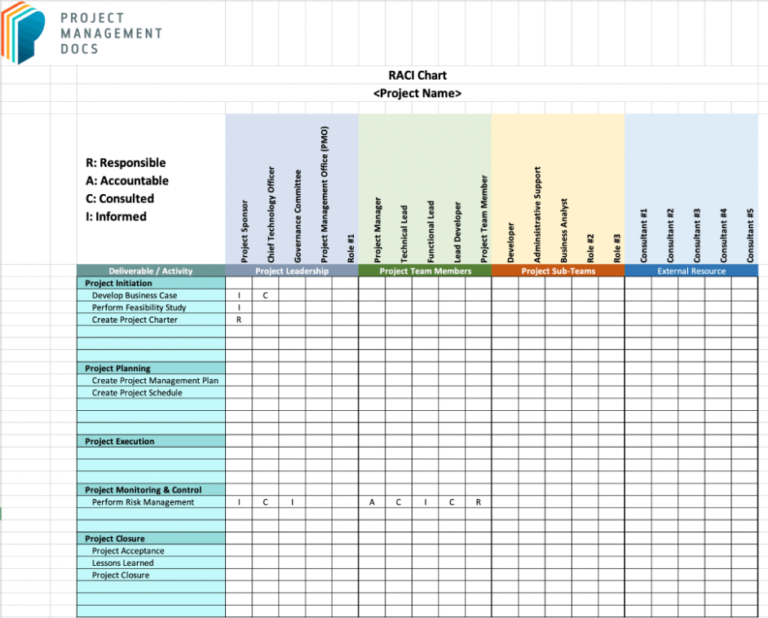
Excel-based RACI chart template
Are you an Excel or Google Sheets user looking to take advantage of the RACI matrix? An Excel-formatted template from Project Management Docs might just be the solution for you. This template is a great template for users who want a chart that comes in a preformatted structure.
The four components of a RACI matrix are Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed. Responsible refers to the individual(s) who completes the task, while Accountable is the person who ensures the task is done. Consulted are those who provide input, and Informed are those who need to be updated on progress.
The difference between Responsible and Accountable lies in execution versus oversight. Responsible refers to the person who performs the work, while Accountable is the individual who ensures the task is completed successfully and takes ultimate ownership.
RACI is still widely used, but for more complex decision-making processes, alternatives like DACI and RAPID may be better suited. However, it remains a popular tool for establishing clear roles in projects, especially for smaller teams.
The Bottom Line on the RACI Matrix
The RACI matrix remains a powerful tool for defining roles and responsibilities in project management, helping teams avoid confusion and delays. By clearly assigning who is Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed, project managers can streamline communication, prevent decision-making bottlenecks, and ensure accountability.
While alternatives like RASCI or DACI exist, RACI is especially useful for smaller teams and simpler projects. When used correctly, it significantly enhances project clarity and efficiency, leading to smoother execution and more successful outcomes.
Join our newsletter
Subscribe to Project Management Insider for best practices, reviews and resources.
You might also like:
{{ title }}, you should also read.

10 Tips for Succeeding in Project Management
Best Methods to Assess & Estimate Project Risks

Airtable vs Monday 2024 Comparison: Which Is Best for You?

Get the Free Newsletter!
You might also like.

Business Process Management (BPM) vs Project Management Process (PM)
What is Smartsheet? 2024 Beginner’s Guide
Technical Project Manager (TPM) vs Project Manager (PM)
What is a Responsibility Assignment Matrix And How to Create One
Projects often falter not from lack of talent or resources, but from unclear responsibilities and misaligned expectations. When deadlines loom and stakeholders grow anxious, the difference between success and failure often comes down to one fundamental question: Does everyone know exactly what they’re supposed to do?
The Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) addresses this critical need for clarity in project execution. It transforms vague roles and loose accountability into clear, actionable responsibilities. By establishing who owns what, who decides what, and who needs to know what, RAM helps teams move from confusion to confidence, turning project plans into delivered results.
What is the Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM)?
The Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) is an essential project management tool designed to clarify roles and responsibilities within a project. At its core, RAM serves as a blueprint for project execution by categorizing stakeholders into defined roles. These roles are Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed, commonly referred to as the RACI matrix. By employing a RAM, project managers can effectively delegate tasks, enhance team communication, and reduce ambiguity in project workflows.
RAM’s primary value lies in its ability to facilitate clear communication and role demarcation among team members. By outlining who is Responsible for task execution, who holds the ultimate Accountable authority, who should be Consulted for input, and who ought to be Informed of progress, the matrix ensures that all bases are covered. This structure simplifies task management and helps prevent project delays by ensuring that everyone understands their duties and expectations.
In project management practices, a well-developed RAM boosts efficiency by establishing transparent pathways for delegation and consultation. It also serves as a helpful guide for integrating cross-functional team dynamics, which are vital in collaborative workspaces. Difference Between Responsibility Assignment Matrix and RACI Matrix
In project management, both the Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) and the RACI matrix serve as frameworks to define clear roles and responsibilities. However, they differ in their approach and application, necessitating a distinct understanding for effective project implementation.
- Ready to use
- Fully customizable template
- Get Started in seconds

Roles and Responsibilities Explained
The Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM), an integral tool for project management, demystifies and assigns specific roles among team members, ensuring efficiency and clarity. The key components, known as the RACI model, divide responsibilities as follows:
Responsible:
This role entails the individual(s) who physically perform a task or activity. They are the action-takers who ensure the deliverables are executed. For instance, developers who are coding the features outlined in a project are tagged as responsible.
Accountable:
Crucial to the project’s success, the accountable individual is the decision-maker. They oversee the completion of work by the responsible parties, ensuring standards and timelines are met. In web development, a product manager often holds this role, signing off on a sprint before it is released.
These are the subject-matter experts whose opinions are sought during a task’s lifecycle. They offer guidance and feedback, ensuring insightful integration into the project. A legal consultant might review compliance documentation, providing essential advice to the project leads.
Individuals in this category need to be kept in the loop about major project updates and decisions, though they do not directly contribute to task completion. Stakeholders, such as business owners, often fall into this group, ensuring higher-ups are aware of project progress and outcomes.
Assigning clear roles is paramount to avoiding project delays and confusion. A well-implemented RAM facilitates timely communication, ensuring everyone understands their responsibilities in the broader project ecosystem. Task mismatches or overlaps can hinder productivity, but with Roles and Responsibilities , such issues can be preemptively addressed. Furthermore, using tools like Creately’s templates enhances team understanding and engagement with precise role allocation, leading to a well-oiled project management process.
By effectively utilizing a RAM, teams can synchronize efforts, maintain accountability at every project stage, and achieve a harmonious workflow. This structured approach not only defines expectations clearly but also empowers team members to contribute to the project’s success confidently.
Types of Responsibility Assignment Matrix
The versatility of a Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) allows it to be customized to fit the specific needs of various projects. Below, we explore a few prominent types of Responsibility Assignment Matrices that can be utilized in diverse scenarios:
Functional RAM (F-RAM):
This type is ideal for projects where tasks align closely with specific departmental functions. It leverages the expertise of functional leaders, ensuring tasks are executed within the domain knowledge, enhancing precision and efficiency.

Projectized RAM (P-RAM):
Employed in projects where focus shifts to specialized skills required for a specific project. Roles are tightly aligned with project goals rather than functional departments, allowing teams to tackle unique challenges effectively.
These variations in RAM frameworks demonstrate the flexibility in aligning matrices to the unique demands of projects, making them invaluable tools for project managers striving for clarity and efficiency in responsibility assignments.
How to Create a Responsibility Assignment Matrix
Creating a Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) is an essential aspect of effective project management. It provides clarity and direction by mapping out roles and responsibilities across team members, thereby optimizing collaboration and accountability. Here’s a step-by-step guide to creating a RAM:
1. List Project Activities
The foundation of an effective RAM begins with a thorough breakdown of project activities. This step requires careful analysis of the project scope to identify all significant components, deliverables, and ongoing tasks. Work with project stakeholders to ensure no critical activities are overlooked. Break down larger activities into manageable components while keeping them substantial enough to avoid micromanagement.
Define project phases with clear start and end points
Identify major deliverables that represent significant project outcomes
List critical milestones that mark important project transitions
Include key operational tasks required for project execution
Document ongoing support activities and maintenance requirements
Specify quality control and validation activities
Add project management and coordination tasks
2. Identify Team Members
A comprehensive understanding of your project team is crucial for accurate responsibility assignment. This step involves mapping out all individuals and their roles within the project context. Consider both direct team members and those who may have periodic involvement. Document their positions, departments, and general areas of expertise to facilitate appropriate responsibility assignments.
List project managers and their specific areas of oversight
Include team leaders responsible for different project components
Document technical staff members and their specializations
Identify support personnel who provide auxiliary services
Add department representatives who need involvement
Note external resources and contractors
Specify backup personnel for critical roles
Include subject matter experts who may provide specialized input
3. Define Responsibility Types
A clear definition of responsibility types ensures consistent assignment and understanding across the project team. Unlike more complex matrices, RAM focuses on straightforward responsibility levels that clearly indicate who does what. Each type should be clearly defined and understood by all team members to prevent confusion or overlap.
Primary Responsibility
Full ownership of task completion
Authority to make decisions
Accountability for outcomes
Direct reporting obligations
Secondary Responsibility
Backup support for primary owner
Shared task execution
Collaborative decision-making
Regular involvement
Support Role
Assists primary and secondary owners
Provides specific expertise
Limited decision-making authority
Task-specific involvement
Optional Involvement
As-needed participation
Advisory capacity
No direct responsibility
Periodic consultation
4. Create the Matrix Structure
The matrix’s visual organization is crucial for usability and clarity. Create a clear, easy-to-read format that allows quick identification of responsibilities and relationships. The structure should facilitate both detailed review and quick reference, with clear headers and consistent formatting throughout.
Select appropriate software tools for matrix creation and maintenance
Design vertical activity listing grouped by project phase
Create horizontal team member listing organized by department
Include clear column and row headers
Add department and role information
Implement consistent formatting for easy reading
Consider color coding for visual clarity
Include space for notes and clarifications
5. Assign Responsibilities
This critical step involves matching team members with activities based on their skills, availability, and authority levels. Each assignment should reflect both the needs of the task and the capabilities of the team member. Ensure balanced distribution of responsibilities while maintaining clear lines of accountability.
Designate primary responsibilities with clear markers
Assign secondary responsibilities to ensure backup coverage
Indicate support roles where additional assistance is needed
Mark optional involvement for consultative roles
Verify every activity has appropriate coverage
Balance workload across team members
Consider dependencies between activities
Account for team member capacity and availability
6. Review and Validate
Thorough review ensures the matrix accurately reflects project needs and team capabilities. Conduct structured reviews with stakeholders to verify assignments, identify gaps, and resolve potential conflicts. This step is crucial for gaining team buy-in and ensuring the matrix will be an effective project management tool.
Schedule review sessions with key stakeholders
Verify all activities have appropriate coverage
Check for balanced workload distribution
Confirm team member availability and capacity
Address any gaps or overlaps in responsibility
Document team agreement and acceptance
Incorporate feedback from review sessions
Finalize responsibility assignments
7. Distribute and Maintain
Implementation of the RAM requires clear communication and ongoing maintenance. Establish processes for distribution, updates, and regular reviews to ensure the matrix remains current and useful throughout the project lifecycle. Create clear protocols for handling changes and maintaining version control.
Share final matrix with all team members
Establish regular review intervals
Create update procedures
Track changes and modifications
Maintain version control system
Document change history
Set up accessibility protocols
Schedule periodic reviews
Create backup and archive procedures
Establish change approval process
Embracing these steps ensures that the Responsibility Assignment Matrix not only maps roles accurately but also fosters a collaborative environment, driving project success and reducing miscommunication risks.
For further visual assistance, consider exploring the Matrix Org Chart Template that can help visualize the responsibility distribution effectively, keeping alignment with project goals and organizational structure.
Helpful Resources
Create a work breakdown structure.
A hierarchical decomposition method that breaks down project deliverables into smaller, more manageable components.
Free RACI Model Template
A responsibility assignment framework that defines four key roles in task completion and decision-making processes.
Kanban Board Software
Kanban boards provide real-time visualization of work progress through distinct stages of completion.
When Should a Responsibility Assignment Matrix be Created?
A Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) should be created at the beginning of a project and maintained throughout its lifecycle. It is an essential tool for project planning and execution, and should be developed as one of the first steps in the project management process.
The ideal time to create a RAM is during the project initiation and planning phases, for the following reasons:
Establish Clarity from the Start:
Creating a RAM early on helps set clear expectations and responsibilities from the very beginning of the project. This prevents confusion, overlapping work, and gaps in accountability as the project progresses.
Support Project Planning:
The RAM serves as a crucial input to other project planning artifacts, such as the work breakdown structure, project schedule, and resource planning. Defining roles and responsibilities upfront makes these downstream planning activities much more effective.
Facilitate Team Formation:
When a new project team is assembled, the RAM helps onboard members by clearly delineating their roles and expectations. This promotes faster team cohesion and productivity.
Manage Changing Scope:
As project scope evolves over time, the RAM can be updated to reflect new responsibilities and assignments. Maintaining a current RAM ensures the project stays on track despite changes.
Enable Monitoring and Control:
The RAM provides a framework for monitoring project progress and controlling task completion. Project managers can easily track whether work is being done as expected based on the assigned responsibilities.
Support Handoffs and Knowledge Transfer:
When team members join or leave the project, the RAM serves as a reference to quickly understand who is accountable for what, facilitating a smooth transition.
While the RAM is most critical during project initiation, it should be reviewed and updated regularly throughout the project lifecycle. This ensures the matrix remains an accurate and useful tool for managing responsibilities and facilitating project success.
Why a Responsibility Assignment Matrix is Essential for Project Success
Clarity and accountability.
A Responsibility Assignment Matrix serves as the cornerstone of project role definition, eliminating ambiguity and confusion that often plague complex projects. By clearly delineating who is responsible for each task and deliverable, RAM creates a transparent framework where every team member understands their precise role and obligations. This clarity extends beyond simple task assignment – it establishes clear decision-making pathways, enables efficient performance tracking, and ensures that accountability is maintained throughout the project lifecycle. When challenges arise, team members can quickly identify the appropriate person to address issues, reducing response time and improving project efficiency.
Enhanced Cross-Functional Collaboration
The implementation of RAM transforms how cross-functional teams interact and coordinate their efforts. By providing a clear structure for inter-departmental collaboration, a Responsibility Assignment Matrixffectively breaks down traditional organizational silos that often impede project progress. Team members from different departments gain a comprehensive understanding of how their work impacts others, leading to more effective communication and coordinated effort. This enhanced collaboration reduces redundant work, minimizes misunderstandings, and creates a more cohesive project environment where resources and knowledge are shared efficiently across departmental boundaries.
Risk Management and Mitigation
Responsibility Assignment Matrix serves as a powerful risk management tool by establishing clear ownership of potential project risks and their associated mitigation strategies. Through explicit responsibility assignment, potential gaps in resource allocation or skill coverage become immediately apparent, allowing for proactive resolution before they impact project delivery. The matrix ensures that risk responses have clear owners, establishing structured escalation procedures when issues arise. This systematic approach to risk management significantly reduces the likelihood of missed deliverables and strengthens quality control measures across the project lifecycle.
Operational Efficiency
The implementation of RAM dramatically streamlines project operations by optimizing decision-making processes and resource utilization. Clear responsibility assignments reduce the need for excessive meetings and expedite issue resolution by eliminating confusion about who should address specific challenges. The matrix provides a framework for efficient workflow management, enabling better capacity planning and resource allocation. This improved operational efficiency translates directly into enhanced productivity and more effective use of project resources.
Team Empowerment
A Responsibility Assignment Matrix creates an environment of empowerment by providing team members with clear understanding of their authority and responsibilities. This clarity enables confident decision-making within defined parameters and increases job satisfaction through reduced role ambiguity. Team members can better plan their career development as they understand the full scope of their responsibilities and can identify areas for growth. The resulting increase in engagement and morale leads to higher productivity and better project outcomes.
Project Control and Monitoring
A Responsibility Assignment Matrixsignificantly enhances project oversight capabilities by providing a clear framework for progress tracking and performance monitoring. Project managers can easily track milestone completion, resource utilization, and deadline adherence through the lens of assigned responsibilities. This improved visibility enables more effective status reporting and budget control, allowing for timely interventions when projects deviate from planned parameters. The matrix serves as a foundation for establishing clear performance metrics and ensuring consistent project delivery.
Stakeholder Management
Effective stakeholder management is greatly enhanced through RAM implementation. The matrix clearly defines communication channels and information flow patterns, ensuring that all stakeholders receive appropriate updates and are engaged at the right level. This structured approach to stakeholder management leads to better expectation management, improved client satisfaction, and more effective vendor relationships. Clear responsibility assignments for stakeholder communication reduce the risk of mixed messages and ensure consistent engagement throughout the project lifecycle.
Implementing a Responsibility Assignment Matrix within collaborative workspaces can further smooth workflows and support dynamic project environments. The framework allows for efficient task execution while balancing diverse team inputs. Retrospective Meetings can be a great way to uncover insights and foster better collaboration
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Implementing a Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) can transform project management by creating clarity and structure. However, some common mistakes can hinder its effectiveness. Here’s how to avoid them:
Lack of Clarity:
Ambiguities in role definitions can lead to confusion. Ensure all team members understand their roles and responsibilities clearly within the RAM framework.
Overcomplication:
A RAM should be straightforward. Avoid including unnecessary details that complicate its purpose. Keep it streamlined for efficient communication.
Static Assignments:
Projects evolve, and so should your RAM. Regularly update role assignments to adapt to changes in project scope or personnel.
Missed Stakeholder Alignment:
Failing to engage stakeholders throughout the RAM process can result in oversight. Ensure ongoing collaboration and buy-in from all parties involved.
Tool Over-Reliance:
While templates and software tools can aid RAM creation, relying solely on them without input from your team may lead to gaps. Encourage regular discussions to complement these tools.
Avoid these pitfalls to harness the full potential of a RAM, ensuring that it remains a key resource for achieving seamless project outcomes.
How Creately Enhances Visual Project Management for Seamless Collaboration and Execution
Creately offers a comprehensive visual platform that transforms traditional project management workflows into dynamic, interactive processes. Here’s how Creately empowers teams to plan, manage, and collaborate effectively:
1. Visual Task Tracking for Clear Progress Monitoring
Creately makes task tracking intuitive by offering visual tools such as Kanban boards, Gantt charts, timelines, and flow diagrams. Teams can break down complex projects into manageable tasks and milestones, making it easier to see where things stand at any given moment. The visual approach ensures that tasks, deadlines, and progress are clear and accessible, helping teams stay on track while preventing bottlenecks.
2. Simplified Role and Responsibility Assignment
Creately simplifies the process of assigning roles and responsibilities using templates like the Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) and RACI charts. Project managers can clearly define who is responsible, accountable, consulted, and informed (RACI) for every task. This ensures that all team members understand their roles, fostering accountability and reducing misunderstandings about who owns each task.
3. Common Workspace to Share and Manage Progress
Creately provides a centralized workspace where team members can easily share and manage all project-related materials. This workspace acts as a single source of truth, allowing teams to store diagrams, documents, and updates in one place. The shared environment ensures that everyone has access to the latest project information, avoiding confusion from outdated versions or fragmented files across different platforms.
4. Real-Time Collaboration for Faster Decision-Making
Creately’s real-time collaboration features enable team members to work together, regardless of location. Multiple users can simultaneously edit diagrams, add comments, and update progress. This immediate feedback loop encourages rapid decision-making and problem-solving, significantly reducing the time it takes to respond to issues or changes in project scope. Teams can brainstorm, strategize, and plan in real time, ensuring faster project delivery.
5. Customizable Visual Templates for Diverse Project Needs
Creately offers a wide variety of customizable templates, allowing teams to tailor their project management approach to their unique needs. Whether you need a work breakdown structure (WBS), flowcharts, mind maps, or specific methodologies like Agile or Waterfall, Creately’s visual templates help structure projects in the most effective way. This flexibility allows teams to visualize complex processes and workflows, leading to better planning and execution.
6. Integration with Other Tools for a Unified Workflow
Creately integrates seamlessly with other popular tools like Google Workspace, Slack, and Jira, ensuring that project management remains cohesive across platforms. Teams can link their visual diagrams with tasks, milestones, or communications in other tools, creating a unified project ecosystem that keeps everyone aligned and reduces duplication of work.
By fostering a workspace where ideas, tasks, and updates flow seamlessly, Creately enhances both individual accountability and collective productivity. This not only improves project outcomes but also nurtures a culture of collaboration and innovation within teams. As projects continue to evolve in complexity, having a platform that adapts to diverse needs and simplifies task management will become an indispensable asset. Creately is more than just a tool—it’s a strategic partner in transforming how teams work together to achieve success.
AcqNotes. “Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) - AcqNotes.” AcqNotes, 20 July 2017, www.acqnotes.com/acqnote/careerfields/responsibility-assignment-matrix .
Malsam, William. “How to Make a Responsibility Assignment Matrix for a Project (Template Included).” ProjectManager.com, 10 June 2021, www.projectmanager.com/blog/responsibility-assignment-matrix .
Six, Ten. “What Is a Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) in Project Management?” Ten Six Consulting, 11 Apr. 2024, www.tensix.com/what-is-a-responsibility-assignment-matrix-ram-in-project-management/ .
FAQ about RAM
What is a responsibility assignment matrix (ram) in project management, what can a responsibility assignment matrix (ram) eliminate.
A RAM eliminates several common project management challenges:
- Role ambiguity and confusion about task ownership
- Duplicate efforts and redundant work
- Communication gaps and information silos
- Decision-making bottlenecks
- Unclear escalation paths
- Resource allocation conflicts
- Accountability issues
How does a RAM differ from other project management tools?
Unlike other project management tools:
RAM focuses specifically on responsibility assignment rather than scheduling or task management
- It provides a clear framework for decision-making authority
- It explicitly defines different levels of involvement for each task
- It helps balance workload and authority across the team

Chiraag George is a communication specialist here at Creately. He is a marketing junkie that is fascinated by how brands occupy consumer mind space. A lover of all things tech, he writes a lot about the intersection of technology, branding and culture at large.
Related Tools and Resources
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.

IMAGES
VIDEO