
- Productivity
- Thoughtful learning

Become a better critical thinker with these 7 critical thinking exercises

Critical thinking is a skill you can use in any situation. Whether you're a student, entrepreneur, or business executive, critical thinking can help you make better decisions and solve problems.
But learning critical thinking skills isn't always an easy task. Many tools, techniques, and strategies are available, and choosing the right one can be challenging. Vague suggestions on the internet like "read more" aren't very helpful, and elaborate business examples don’t apply to many of us.
As average problem-solvers, we need actionable thinking exercises to improve our critical thinking skills and enhance our thinking processes. Regularly performing exercises that specifically stretch our decision-making and reasoning skills is the most effective method of improving our thinking abilities.
This article will explore several exercises that will help you develop critical thinking skills. Whether you are preparing for an exam, making an influential decision for your business, or going about your daily life, these fun activities can build your reasoning skills and creative problem-solving abilities.
Boost your logical thinking skills and start practicing a critical mindset with these 10 critical thinking exercises.
A Quick Look at Critical Thinking
As a thoughtful learner, you likely already understand the basics of critical thinking, but here's a quick refresher.
Critical thinking involves analyzing problems or issues objectively and rationally. Critical thinkers are able to understand their own biases and assumptions, as well as those of others. They’re also able to see the world from a different point of view and understand how their experiences impact their thinking.
Developing critical thinking skills is essential because it allows us to see things from multiple perspectives, identify biases and errors in reasoning, and be open to possible solutions. Making informed decisions is easier when we have a better understanding of the world around us.
Why We Need to Practice Critical Thinking

We aren't born with critical thinking skills, and they don’t naturally develop beyond survival-level thinking. To master critical thinking, we must practice it and develop it over time.
However, learning to think critically isn't as easy as learning to ride a bicycle. There aren't any step-by-step procedures to follow or supportive guides to fall back on, and it is not taught in public schools consistently or reliably. To ensure students' success, teachers must know higher-order thinking skills (HOTS) and how to teach them, research says.
Unfortunately, although teachers understand the importance of HOTS and attempt to teach it, studies show that their capacity to measure students' HOTS is low. Educator and author Dr. Kulvarn Atwal says, "It seems that we are becoming successful at producing students who are able to jump through hoops and pass tests."
As critical thinking skills become more important in higher grades, some students find it challenging to understand the concept of critical thinking. To develop necessary thinking skills, we must set aside our assumptions and beliefs. This allows us to explore and question topics from a "blank page" point of view and distinguish fact from opinion.
Be the first to try it out!
We're developing ABLE, a powerful tool for building your personal knowledge, capturing information from the web, conducting research, taking notes, and writing content.
7 Critical Thinking Exercises To Improve Your Critical Thinking Skills

The good news is that by assessing, analyzing, and evaluating our thought processes, we can improve our skills. Critical thinking exercises are key to this improvement. Our critical thinking builds and improves with regular practice, just like a muscle that gets stronger with use.
If you want to become a better critical thinker , here are some critical thinking exercises to try:
Exercise #1: The Ladder of Inference
You can exercise your critical thinking skills by using the Ladder of Inference model . This thinking model was developed by renowned organizational psychologist Chris Argyris. Each rung on the ladder of inference represents a step you take to arrive at your conclusions.
The decision-making process starts when we are faced with a problem or situation. As soon as we observe something problematic or important, we presume what is causing it, and then we use that assumption to draw conclusions. Based on those conclusions, we take action.
For example, say you're at a party and see a friend across the room. You catch their eye and wave, but they turn and walk away. Using the ladder, you might climb the rungs as follows:
- Observe that your friend walked away.
- Select a few details of the situation, including your wave and your assumption that they saw you.
- Meaning is attached based on the environment, making you think your friend must have other people to talk to at the party.
- Assumptions are made based on that meaning, assuming that means your friend doesn’t like you as much as them.
- Conclusions are drawn from the assumption, and you determine that your friend must be mad at you or doesn't want you to be at the party.
- Beliefs are formed, making you think you're not welcome.
- Action is taken, and you leave the party.
In this example, you started with a situation (someone walking away at a crowded party) and made a series of inferences to arrive at a conclusion (that the person is mad at you and doesn't want you there).
The Ladder of Inference can be a helpful tool to frame your thinking because it encourages you to examine each step of your thought process and avoid jumping to conclusions. It's easy to make assumptions without realizing it, as in this scene. Perhaps your friend never even saw you wave from across the crowded room.
Exercise #2: The Five Whys
The "Five Whys" technique is an analytical skill that can help you uncover the source of a problem. The activity was created by Sakichi Toyoda, the founder of Toyota, and consists of repeatedly asking “why?” when a problem is encountered to determine its root cause.
This exercise can be difficult because knowing if you've discovered the source of your problem is challenging. The "five" in "Five Whys" is just a guideline — you may need to ask more. When you can't ask anything else, and your response is related to the original issue, you've probably arrived at the end.
Even if you need several rounds of questioning, just keep going. The important part that helps you practice critical thinking is the process of asking "why?" and uncovering the deeper issues affecting the situation.
For instance, say you're trying to figure out why your computer keeps crashing.
- You ask " why ," and the answer is that there's a software problem.
- Why? Because the computer keeps running out of memory.
- Why? Because too many programs are running at the same time.
- Why? Because too many browser tabs are open .
- Why? Because multitasking is fragmenting your focus, you're doing too many things at once.
In this example, working through the "why's" revealed the underlying cause. As a result, you can find the best solution, which is concentrating on just one thing at a time.
Exercise #3: Inversion

Inversion is another critical thinking exercise that you can use in any situation. Inversion is sort of like taking on the role of the devil's advocate. In this exercise, adopt the opposite view of whatever issue you're exploring and consider the potential arguments for that side. This will help broaden your critical thinking skills and enable you to see other perspectives on a situation or topic more clearly.
For example, let's say you're thinking about starting your own business. Using inversion, you would explore all of the potential arguments for why starting your own business is bad. This might include concerns like:
- You could end up in debt.
- The business might fail.
- It's a lot of work.
- You might not have time for anything else.
By exploring these potentially adverse outcomes, you can identify the potential risks involved in starting your own business and make a more sound decision. You might realize that now is not the right time for you to become an entrepreneur. And if you do start the company, you'll be better prepared to deal with the issues you identified when they occur.
Exercise #4: Argument Mapping
Argument mapping can be a beneficial exercise for enhancing critical thinking skills. Like mind mapping, argument mapping is a method of visually representing an argument's structure. It helps analyze and evaluate ideas as well as develop new ones.
In critical thinking textbooks, argument diagramming is often presented to introduce students to argument constructions. It can be an effective way to build mental templates or schema for argument structures, which researchers think may make critical evaluation easier .
Argument maps typically include the following:
- Conclusion: What is being argued for or against
- Premises: The reasons given to support the conclusion
- Inferences: The connections made between the premises and conclusion
The argument map should be as clear and concise as possible, with a single word or phrase representing each element. This will help you make connections more easily. After the map is completed, you can use it to identify any weak points in the argument. If any areas aren't well-supported, additional premises can be added.
Argument mapping can be applied to any situation that requires critical thinking skills. The more time you take to map out an argument, the better you'll understand how the pieces fit together. Ultimately, this will help you think more creatively and critically, and make more informed decisions.
Exercise #5: Opinion vs. Fact
Critical thinking activities that focus on opinions and facts are particularly valuable and relevant new learning opportunities. Our constantly-connected world makes it easy to confuse opinions and facts , especially with sensationalist news articles and click-bait headlines.
How can you tell a fact from an opinion? Facts are generally objective and established, whereas opinions are subjective and unproven. For example, "the cloud is in the air" is a fact. "That dress looks good on you" is an opinion.
Practice your critical thinking skills by reading or listening to the news. See if you can identify when someone is stating an opinion rather than a fact. Ask yourself the following questions:
- Who is saying what? What reasons might be behind their statements?
- Does the claim make sense? Who would disagree with it and why?
- How can you tell if the data is reliable? Can it be fact-checked? Has it been shared by other credible publishers?
- How do you know whether or not the presenter is biased? What kind of language is being used?
This powerful exercise can train your mind to start asking questions whenever presented with a new claim. This will help you think critically about the information you're taking in and question what you're hearing before accepting it as truth.
Exercise #6: Autonomy of an Object
In her book " The Critical Thinking Tool Kit ," Dr. Marlene Caroselli describes a critical thinking exercise called "Living Problems, Lively Solutions." This exercise uses the autonomy of an object as a problem-solving tool to find a possible solution.
To do this, you'll personify your problem and place it in another context — a different time or place. This allows you to uncover unique solutions to the problem that might be tied to your mental associations with that setting.
For example, if your problem is poor time management , you might personify the issue as a thief of your time. The idea of a thief could make you think of jail, which might prompt thoughts of locking up specific distractions in your life. The idea of jail could also make you think of guards and lead you to the possible solution of checking in with an accountability buddy who can make sure you're sticking to your schedule.
The autonomy-of-object technique works because it stimulates thoughts you wouldn’t have considered without the particular context in which you place the problem.
Exercise #7: The Six Thinking Hats
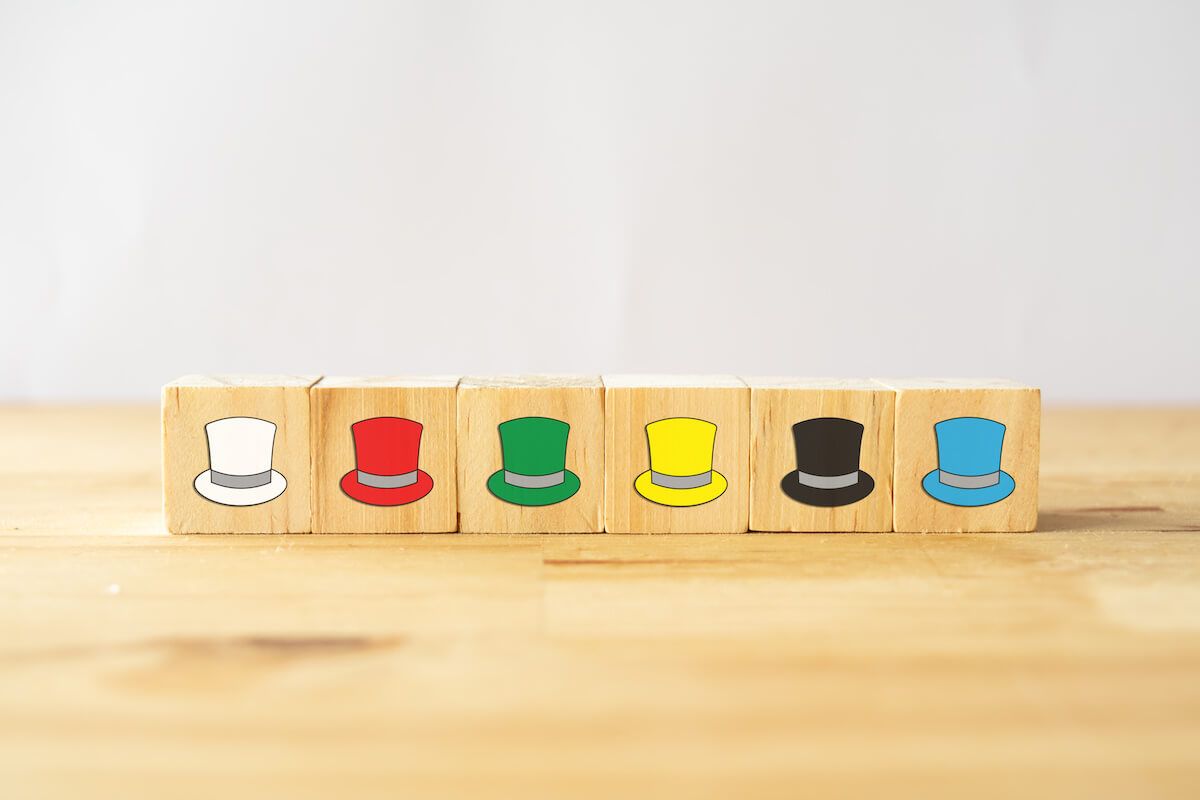

Designed by Edward de Bono, the Six Thinking Hats is a critical thinking exercise that was created as a tool for groups to use when exploring different perspectives on an issue. When people use other thinking processes, meetings can become challenging rather than beneficial.
To help teams work more productively and mindfully, de Bono suggests dividing up different styles of thinking into six categories, represented as hats:
- The white hat is objective and focuses on facts and logic
- The red hat is intuitive, focusing on emotion and instinct
- The black hat is cautious and predicts negative outcomes
- The yellow hat is optimistic and encourages positive outcomes
- The green hat is creative, with numerous ideas and little criticism
- The blue hat is the control hat used for management and organization
With each team member wearing a different hat, a group can examine an issue or problem from many different angles, preventing one viewpoint (or individual) from dominating the meeting or discussion. This means that decisions and solutions reached using the Six Thinking Hats approach will likely be more robust and effective, and everyone’s creative thinking skills will benefit.
Train Your Brain With Critical Thinking Exercises
Using critical thinking regularly in various situations can improve our ability to evaluate and analyze information. These seven critical thinking exercises train your brain for better critical thinking skills . With daily practice, they can become habits that will help you think more critically each day.
Improve your critical thinking with ABLE
Ask better questions and get better answers with ABLEs integrated web search, annotation and note-taking features. Check how ABLE helps you to improve your critical thinking.
I hope you have enjoyed reading this article. Feel free to share, recommend and connect 🙏
Connect with me on Twitter 👉 https://twitter.com/iamborisv
And follow Able's journey on Twitter: https://twitter.com/meet_able
And subscribe to our newsletter to read more valuable articles before it gets published on our blog.
Now we're building a Discord community of like-minded people, and we would be honoured and delighted to see you there.

Straight from the ABLE team: how we work and what we build. Thoughts, learnings, notes, experiences and what really matters.
Read more posts by this author
follow me :
Mental models: 13 thinking tools to boost your problem-solving skills
7 note-taking strategies to improve your study skills.

What is abstract thinking? 10 activities to improve your abstract thinking skills

5 examples of cognitive learning theory (and how you can use them)
0 results found.
- Aegis Alpha SA
- We build in public
Building with passion in
Critical Thinking Exercises
- Writing Research Papers
- Writing Essays
- English Grammar
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
Critical thinking is a skill that students develop gradually as they progress in school. While the skill becomes more important in higher grades, some students find it difficult to understand the concept of critical thinking .
The reason critical thinking can be difficult to grasp is because it requires students to set aside assumptions and beliefs to learn to think without bias or judgment.
Critical thinking involves suspending your beliefs to explore and question topics from a "blank page" point of view. It also involves the ability to distinguish fact from opinion when exploring a topic.
These exercises are designed to help develop critical thinking skills.
Critical Thinking Exercise 1: Tour Guide for an Alien
This exercise provides an opportunity to think outside your normal way of thinking.
Pretend that you have been assigned the task of conducting a tour for aliens who are visiting the earth and observing human life. You're riding along in a blimp, viewing the landscape below, and you float over a professional baseball stadium. One of the aliens looks down and is very confused by what he sees. You explain that there is a game going on and he asks several important questions.
- What is a game?
- Why are there no female players?
- Why do people get so excited about watching other people play games?
- What is a team?
- Why can't the people in the seats go down on the field and join in?
If you try to answer these questions fully, it will quickly become apparent that we carry around certain assumptions and values. We support a certain team, for instance, because it makes us feel like we're a part of a community. This sense of community is a value that matters to some people more than others.
Furthermore, when trying to explain team sports to an alien, you have to explain the value we place on winning and losing.
When you think like an alien tour guide, you are forced to take a deeper look at the things we do and things we value. Sometimes they don't sound logical from the outside looking in.
Critical Thinking Exercise 2: Fact or Opinion
Do you think you know the difference between fact and opinion? It's not always easy to discern. When you visit websites, do you believe everything you read? The abundance of available information makes it more important than ever for students to develop critical thinking skills. Additionally, it's an important reminder that you must use trustworthy sources in your school work.
If you don't learn the difference between fact and opinion, you may end up reading and watching things that continue to reinforce beliefs and assumptions you already own.
For this exercise, read each statement and try to determine whether it sounds like a fact or an opinion. This can be completed alone or with a study partner .
- My mom is the best mom on earth.
- My dad is taller than your dad.
- My telephone number is difficult to memorize.
- The deepest part of the ocean is 35,813 feet deep.
- Dogs make better pets than turtles.
- Smoking is bad for your health.
- Eighty-five percent of all cases of lung cancer in the U.S. are caused by smoking.
- If you flatten and stretch out a Slinky toy it will be 87 feet long.
- Slinky toys are fun.
- One out of every one hundred American citizens is color blind.
- Two out of ten American citizens are boring.
You will probably find some of the statements easy to judge but other statements difficult. If you can effectively debate the truthfulness of a statement with your partner, then it's most likely an opinion.
- Critical Thinking Definition, Skills, and Examples
- 2020-21 Common Application Essay Option 4—Solving a Problem
- What Does It Mean to Make a Claim During an Argument?
- 10 Ways to Make Learning Fun for Students
- Common Application Essay Option 3 Tips: Challenging a Belief
- Building Character Vocabulary
- The Horse Problem: A Math Challenge
- 6 Tips to Liven Up Your Lectures
- 6 Steps to Master Small Talk
- Common Application Essay Option 2 Tips: Learning from Failure
- Ethos, Logos, Pathos for Persuasion
- How to Facilitate Learning and Critical Thinking
- Impromptu Speech Activities
- Moving Past the Five Paragraph Essay
- 100 Persuasive Speech Topics for Students
- College Interview Tips: "Tell Me About a Challenge You Overcame"

7 Puzzles to Challenge Your Critical Thinking
Can you spot the connections and sort these items.
Posted March 5, 2015 | Reviewed by Ekua Hagan

The theme of this post is critical thinking—and the kinds of puzzles that can be constructed around it. This term is used frequently in psychology and education . There are various definitions, but the one that best suits our purpose and which is, in the end, perhaps the best, is the ability to comprehend the logical connections among ideas, words, phrases, and concepts . In the relevant scientific literature, of course, the term is used much more broadly as a framework for understanding human cognition . But in my opinion, the best way to understand things is to construct puzzles to illustrate their basic essence.
Critical thinking involves skill at recognizing a pattern in given information and especially recognizing how the information is connected to the real world. Here are a couple of very simple examples. First, consider the five words below:
- Cruise ship
- Walking on foot
- Automobile (not a race car)
Now, put them in order from the slowest to the fastest, when they are going at maximum speed. The solution, of course, is: 4-2-5-1-3.
As with all such puzzles, there might be slightly different solutions—one could claim that some automobiles go faster than cruise ships. This “indeterminacy” characterizes this kind of thinking. However, some puzzles are straightforward. For instance, what do the following five things have in common?
The answer? These are all words referring to shades of blue.
The seven puzzles below are to the ones above, though hopefully more challenging. Some involve knowledge of facts, but critical thinking is still involved in such cases because the organization of the facts according to some principle is always involved—for example, a puzzle may ask you to put five items in order of their dates of invention.
The following tongue-in-cheek definition of critical thinking by Richard W. Paul, a leading expert on critical thinking theory, says it all: “Critical thinking is thinking about your thinking while you’re thinking in order to make your thinking better.”
I. What do the following 5 things have in common?
- Orange juice
II. Put the following buildings or structures in order of height, from the shortest to the tallest.
- Typical camping tent
III. What do the following animals have in common?
IV. Put the following inventions in order from earliest to most recent.
V. What feature do the following words have in common?
- Imagination
VI. Put these bodies of water in order in terms of volume, from smallest to largest .
VII. What do the following landmasses have in common?
I. They are all drinkable liquids. II. 5-1-4-3-2 III. They all have a tail. They are also all quadrupeds. IV. To the best of my knowledge: 5-4-3-1-2 V. They start with a vowel: a, e, i, o, u VI. 4-2-1-5-3 VII. They are all peninsulas.

Marcel Danesi, Ph.D. , is a professor of semiotics and anthropology at Victoria College, University of Toronto. His books include The Puzzle Instinct and The Total Brain Workout .
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Teletherapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Email Newsletter
Receive free lesson plans, printables, and worksheets by email:
Critical Thinking Worksheets
- Brain Teasers - A great way to stimulate thinking. Don't worry, they come complete with answer keys.
- Compare and Contrast - Students examine differences and similarities in a variety situations.
- Dictionary Practice Worksheets - Practice your dictionary skills.
- Fact And Opinion - Students determine the validity of a body of work.
- How Many Are There? - Fun activities for examining patterns.
- Internet Search Worksheets - Fun Internet searches for students.
- Logic Puzzle - Each scenario is thought provoking. Lots of brain power needed here.
- Making Predictions - A good warm-up for inferences.
- Mazes - Your run-of-the-mill start and finish mazes.
- Name People That ...- Good creative thinking exercises.
- Name Places That ...- Good creative thinking exercises.
- Name Things That ...- Good creative thinking exercises.
- Secret Code - Students answer riddles through secret codes.
- Study Skills Worksheets - Great for test preparation.
- Sorting and Classifying - Great for meeting national standards.
- What Do You Remember? - A visual memory activity.
Activities That Improve Student Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is perhaps the most important skill we need. It is paramount not just for job success but also for making the best decisions in crucial life matters.
As an educator, you should explain to your students that almost all our mistakes can be attributed to a lack of critical thinking. You can pick just about any big blunder you made in the past. You will invariably find that it transpired because of a failure to think critically.
Remember, the best thing you can do as a teacher is to inculcate a strong sense of critical thinking in your students.
Here are the activities that will help students to develop critical thinking.
Discuss Cognitive Biases
There are myriad cognitive biases.
The fact of the matter is we succumb to these biases at some point in our lives. Hence, it pays to study these biases.
You can pick those biases you think are the most detrimental and insidious. You should then explain them to your students to learn to identify and avoid these biases.
Perhaps the most dangerous bias by far is the Optimism bias. It may sound rather innocuous because of the word ‘optimism’. However, it is far more sinister in reality.
Optimism bias tends to think that bad things won't happen to us - they will happen to others only. For example, many think they won't suffer a fatal car crash. Hence, some get involved in overspeeding and texting while driving despite knowing their perils. No wonder these two reckless acts are the main reasons for fatal car crashes.
Writing About Biases
After elucidating various biases and providing simple examples to help them grasp these concepts, you can instruct your students to write about adverse events in their lives when they succumbed to these biases.
What did you learn? What were the consequences? These are further questions you can ask.
Talking about one’s mistakes is never easy. It is hard to concede that we are wrong at times. However, if we want to become better human beings and find success, we must learn from our mistakes. But the first step entails admitting one’s mistakes.
This will also instill humility and reduce overconfidence.
Avoiding Biases – The Easy Way
All biases and ensuring blunders are avoidable with one simple trick.
It just takes one word to get smarter – “why”. That is, you should question everything. As simple as that.
In particular, you should question all that you do and think.
Write it down first whenever you are about to take action or form an opinion about something. Then in front of it, just write “why?” You can then brainstorm and write for and against the idea in logical points.
If you make this a regular habit, you will avoid many mistakes and regrets. You will also maximize positive returns from your decisions.
Explain It to a 6-Year Old
This is something that can greatly benefit students in their academic endeavors.
We are inclined to think that we understand what has been just said. But just nodding along is not enough. You should be able to explain it to others.
The good news is that this goes far beyond altruism. In truth, it is self-empowerment. When you explain an abstruse concept to others, you bolster your own understanding of the same. Reiterating something embeds it more deeply into your long-term memory.
The social factor may also be beneficial and fruitful.
Do Your Research
Teach students to challenge common perceptions and conventional wisdom.
Explain carefully that this entails walking a fine line. You don't want to be dismissive, nor do you want to be naive. Instead, you should have an open mind and a willingness to do your research carefully.
Inform students about consulting reliable online sources. Explain that it is best to consider multiple authentic sources. Don't be satisfied with just the first entry in Google search results.
Here's how you can instill the importance of research in your students.
Instruct your students to research air pollution in the US. Those who do their research more meticulously will find that indoor air pollution is far deadlier than outdoor air pollution.
Tell them that they found out this key health fact courtesy of research. You can further instruct them to find ways of mitigating these risks.
Motivate your students to do research by telling them that they will be pleasantly surprised at the wealth of knowledge that they can uncover via dedicated research.
Beware of Disinformation
Disinformation is ubiquitous these days. It has become a weapon of choice for bad actors ranging from rogue states to unscrupulous individuals.
Critical thinking can help dispel misinformation and prevent you from becoming its victim.
You should help kids to detect and deal with weapons of mass distraction.
There was a time when fake news was disseminated largely via social media.
It is being spread by state-sponsored groups masquerading as legitimate media outlets on the internet. The scope and scale of these fake news campaigns are staggering to say the least.
One such fake news campaign involved no less than 750 fake sites posing as media outlets. Disinformation from this notorious racket reached millions around the globe and even found its way to UN and European Parliament meetings.
You can instruct kids in your class to do a project on internet disinformation, complete with case studies. You should also tell them to write about all possible ways to spot fakes and scams.
Bottom Line
Shown above are the activities to develop critical thinking in students.
You might agree that cultivating this key ability in your students is one of the best things you did for them.
Want a daily email of lesson plans that span all subjects and age groups?
Subjects all subjects all subjects the arts all the arts visual arts performing arts value of the arts back business & economics all business & economics global economics macroeconomics microeconomics personal finance business back design, engineering & technology all design, engineering & technology design engineering technology back health all health growth & development medical conditions consumer health public health nutrition physical fitness emotional health sex education back literature & language all literature & language literature linguistics writing/composition speaking back mathematics all mathematics algebra data analysis & probability geometry measurement numbers & operations back philosophy & religion all philosophy & religion philosophy religion back psychology all psychology history, approaches and methods biological bases of behavior consciousness, sensation and perception cognition and learning motivation and emotion developmental psychology personality psychological disorders and treatment social psychology back science & technology all science & technology earth and space science life sciences physical science environmental science nature of science back social studies all social studies anthropology area studies civics geography history media and journalism sociology back teaching & education all teaching & education education leadership education policy structure and function of schools teaching strategies back thinking & learning all thinking & learning attention and engagement memory critical thinking problem solving creativity collaboration information literacy organization and time management back, filter by none.
- Elementary/Primary
- Middle School/Lower Secondary
- High School/Upper Secondary
- College/University
- TED-Ed Animations
- TED Talk Lessons
- TED-Ed Best of Web
- Under 3 minutes
- Under 6 minutes
- Under 9 minutes
- Under 12 minutes
- Under 18 minutes
- Over 18 minutes
- Algerian Arabic
- Azerbaijani
- Cantonese (Hong Kong)
- Chinese (Hong Kong)
- Chinese (Singapore)
- Chinese (Taiwan)
- Chinese Simplified
- Chinese Traditional
- Chinese Traditional (Taiwan)
- Dutch (Belgium)
- Dutch (Netherlands)
- French (Canada)
- French (France)
- French (Switzerland)
- Kurdish (Central)
- Luxembourgish
- Persian (Afghanistan)
- Persian (Iran)
- Portuguese (Brazil)
- Portuguese (Portugal)
- Spanish (Argentina)
- Spanish (Latin America)
- Spanish (Mexico)
- Spanish (Spain)
- Spanish (United States)
- Western Frisian
sort by none
- Longest video
- Shortest video
- Most video views
- Least video views
- Most questions answered
- Least questions answered

Can you solve the magical maze riddle?
Lesson duration 04:51
282,896 Views

How to make smart decisions more easily
Lesson duration 05:16
976,841 Views

Can you solve a mystery before Sherlock Holmes?
Lesson duration 05:17
443,871 Views

Can you solve the secret assassin society riddle?
Lesson duration 05:01
624,157 Views

How to overcome your mistakes
Lesson duration 04:52
849,414 Views

Can you solve the cursed dice riddle?
Lesson duration 04:31
634,756 Views

Why some people don't have an inner monologue
Lesson duration 12:03
2,617,492 Views

Science vs. Pseudoscience
Lesson duration 05:48
342,707 Views
Can you solve the time traveling car riddle?
Lesson duration 05:18
599,612 Views

This one weird trick will get you infinite gold
Lesson duration 05:08
924,042 Views

How to quit your job — without ruining your career - Gala Jackson
Lesson duration 06:13
100,904 Views

What if you experienced every human life in history?
Lesson duration 05:21
2,702,628 Views

How to design climate-resilient buildings - Alyssa-Amor Gibbons
Lesson duration 14:12
42,569 Views

The case for free, universal basic services - Aaron Bastani
Lesson duration 19:09
79,530 Views

Can you steal the most powerful wand in the wizarding world?
Lesson duration 05:20
740,162 Views

History vs. Thomas Jefferson
437,433 Views

The best way to apologize (according to science)
Lesson duration 05:06
1,384,492 Views

How do we determine the value of a life?
Lesson duration 06:06
636,451 Views

What’s the smartest age?
Lesson duration 04:53
1,511,172 Views

The Boltzmann brain paradox
Lesson duration 05:40
1,094,233 Views

The 4 greatest threats to the survival of humanity
Lesson duration 05:24
482,547 Views

Can you outsmart the college admissions fallacy?
Lesson duration 06:17
804,807 Views

Can you solve the fortress riddle?
Lesson duration 05:23
1,173,833 Views

Can you solve the private eye riddle?
1,264,376 Views
All Formats
Resource types, all resource types.
- Rating Count
- Price (Ascending)
- Price (Descending)
- Most Recent
Free critical thinking worksheets

Fairy Tales 2nd Grade Fairytales, Folktales, & Fables Unit Lessons & Activities

Creativity Activities and Challenges MEGA Bundle Finish the Picture, STEM

Spring Creativity Challenges and Earth Day Activities Finish the Picture

Cause and Effect- Paragraphs

Book vs. Movie Compare & Contrast FREEBIE! No-Prep Worksheets | Fun Movie Day!

Logic Puzzle FREEBIE

Thanksgiving Gratitude Worksheet FREEBIE - Print or Use with Digital Easel
- Easel Activity

Presidents' Day Early Finisher Activities - Crack the Code | Word Search | Maze

Halloween Logic Puzzles | Printable & Digital | Free

- Google Apps™

Leap Day Challenge FREEBIE - Fun, Engaging, No-Prep Activities for February 29th

FREE No Prep Math and Literacy - Critical Thinking Skills

Fact Families/Missing Addend/Open-Ended Worksheets

FREE download - All About Me Ice-Breaker Worksheet - Kindergarten, 1st Grade

Articulation Activity Booklets /TH/

Spring Mystery Logic Puzzle FREEBIE #2

Valentine's Day Worksheets FREEBIE - No-Prep Fun Critical Thinking Activities

Word Search Mini Escape Room Puzzle Game Pack - No Prep Easel Activity Freebie

Thanksgiving Mystery Logic Puzzle Freebie #7

Save Fred! Community and Teamwork Builder

- Word Document File

FREE Winter Logic Puzzles Math Activities: No Prep Sudoku Puzzle Math Worksheets

SPOT your Emotions

Points, Lines, Planes, and Angles: Always, Sometimes, or Never (FREE)

Current Events FREEBIE | Print or Easel Activity | Use with any Article or Post

What's Your Learning Style- Student Quiz/Worksheet with Results

Mystery Logic Puzzle Freebie #1

Spring Break Survival Printable Activities Pack Sample Freebie

Self Esteem: Positive Thinking Worksheets

Fact and Opinion Sorting, Identifying, Writing, Reading Activities

- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
FREE Book Bracket Template. For March and Beyond!
5 Critical Thinking Skills Every Kid Needs To Learn (And How To Teach Them)
Teach them to thoughtfully question the world around them.

Little kids love to ask questions. “Why is the sky blue?” “Where does the sun go at night?” Their innate curiosity helps them learn more about the world, and it’s key to their development. As they grow older, it’s important to encourage them to keep asking questions and to teach them the right kinds of questions to ask. We call these “critical thinking skills,” and they help kids become thoughtful adults who are able to make informed decisions as they grow older.
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking allows us to examine a subject and develop an informed opinion about it. First, we need to be able to simply understand the information, then we build on that by analyzing, comparing, evaluating, reflecting, and more. Critical thinking is about asking questions, then looking closely at the answers to form conclusions that are backed by provable facts, not just “gut feelings” and opinion.
Critical thinkers tend to question everything, and that can drive teachers and parents a little crazy. The temptation to reply, “Because I said so!” is strong, but when you can, try to provide the reasons behind your answers. We want to raise children who take an active role in the world around them and who nurture curiosity throughout their entire lives.
Key Critical Thinking Skills
So, what are critical thinking skills? There’s no official list, but many people use Bloom’s Taxonomy to help lay out the skills kids should develop as they grow up.
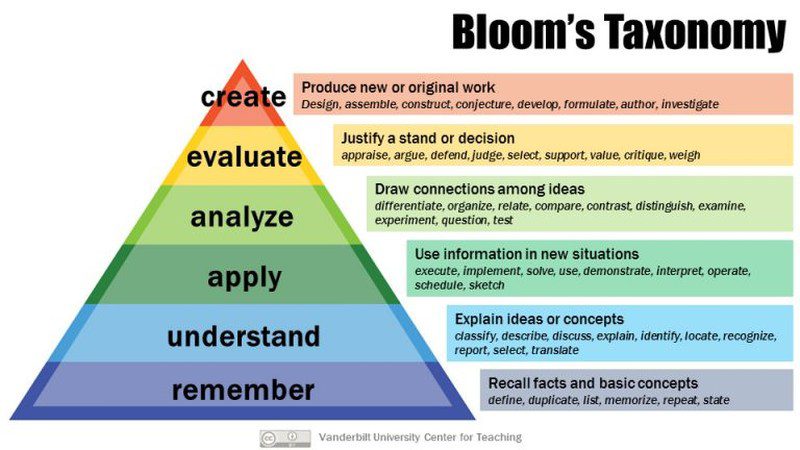
Source: Vanderbilt University
Bloom’s Taxonomy is laid out as a pyramid, with foundational skills at the bottom providing a base for more advanced skills higher up. The lowest phase, “Remember,” doesn’t require much critical thinking. These are the skills kids use when they memorize math facts or world capitals or practice their spelling words. Critical thinking doesn’t begin to creep in until the next steps.
Understanding requires more than memorization. It’s the difference between a child reciting by rote “one times four is four, two times four is eight, three times four is twelve,” versus recognizing that multiplication is the same as adding a number to itself a certain number of times. Schools focus more these days on understanding concepts than they used to; pure memorization has its place, but when a student understands the concept behind something, they can then move on to the next phase.
Application opens up whole worlds to students. Once you realize you can use a concept you’ve already mastered and apply it to other examples, you’ve expanded your learning exponentially. It’s easy to see this in math or science, but it works in all subjects. Kids may memorize sight words to speed up their reading mastery, but it’s learning to apply phonics and other reading skills that allows them to tackle any new word that comes their way.
Analysis is the real leap into advanced critical thinking for most kids. When we analyze something, we don’t take it at face value. Analysis requires us to find facts that stand up to inquiry, even if we don’t like what those facts might mean. We put aside personal feelings or beliefs and explore, examine, research, compare and contrast, draw correlations, organize, experiment, and so much more. We learn to identify primary sources for information, and check into the validity of those sources. Analysis is a skill successful adults must use every day, so it’s something we must help kids learn as early as possible.
Almost at the top of Bloom’s pyramid, evaluation skills let us synthesize all the information we’ve learned, understood, applied, and analyzed, and to use it to support our opinions and decisions. Now we can reflect on the data we’ve gathered and use it to make choices, cast votes, or offer informed opinions. We can evaluate the statements of others too, using these same skills. True evaluation requires us to put aside our own biases and accept that there may be other valid points of view, even if we don’t necessarily agree with them.
In the final phase, we use every one of those previous skills to create something new. This could be a proposal, an essay, a theory, a plan—anything a person assembles that’s unique.
Note: Bloom’s original taxonomy included “synthesis” as opposed to “create,” and it was located between “apply” and “evaluate.” When you synthesize, you put various parts of different ideas together to form a new whole. In 2001, a group of cognitive psychologists removed that term from the taxonomy , replacing it with “create,” but it’s part of the same concept.
How To Teach Critical Thinking
Using critical thinking in your own life is vital, but passing it along to the next generation is just as important. Be sure to focus on analyzing and evaluating, two multifaceted sets of skills that take lots and lots of practice. Start with these 10 Tips for Teaching Kids To Be Awesome Critical Thinkers . Then try these critical thinking activities and games. Finally, try to incorporate some of these 100+ Critical Thinking Questions for Students into your lessons. They’ll help your students develop the skills they need to navigate a world full of conflicting facts and provocative opinions.
One of These Things Is Not Like the Other
This classic Sesame Street activity is terrific for introducing the ideas of classifying, sorting, and finding relationships. All you need are several different objects (or pictures of objects). Lay them out in front of students, and ask them to decide which one doesn’t belong to the group. Let them be creative: The answer they come up with might not be the one you envisioned, and that’s OK!
The Answer Is …
Post an “answer” and ask kids to come up with the question. For instance, if you’re reading the book Charlotte’s Web , the answer might be “Templeton.” Students could say, “Who helped save Wilbur even though he didn’t really like him?” or “What’s the name of the rat that lived in the barn?” Backwards thinking encourages creativity and requires a good understanding of the subject matter.
Forced Analogies
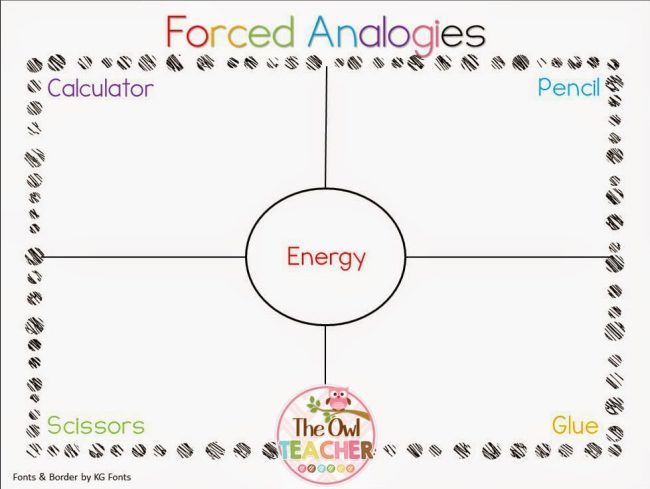
Practice making connections and seeing relationships with this fun game. Kids write four random words in the corners of a Frayer Model and one more in the middle. The challenge? To link the center word to one of the others by making an analogy. The more far out the analogies, the better!
Learn more: Forced Analogies at The Owl Teacher
Primary Sources
Tired of hearing “I found it on Wikipedia!” when you ask kids where they got their answer? It’s time to take a closer look at primary sources. Show students how to follow a fact back to its original source, whether online or in print. We’ve got 10 terrific American history–based primary source activities to try here.
Science Experiments
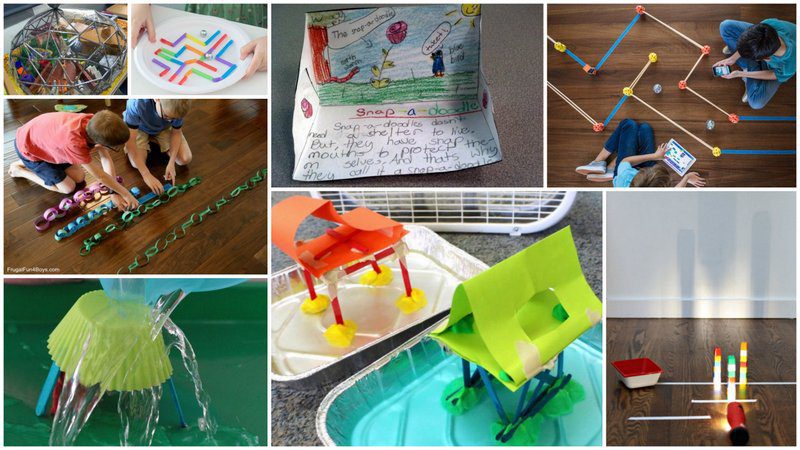

Hands-on science experiments and STEM challenges are a surefire way to engage students, and they involve all sorts of critical thinking skills. We’ve got hundreds of experiment ideas for all ages on our STEM pages , starting with 50 Stem Activities To Help Kids Think Outside the Box .
Not the Answer
Multiple-choice questions can be a great way to work on critical thinking. Turn the questions into discussions, asking kids to eliminate wrong answers one by one. This gives them practice analyzing and evaluating, allowing them to make considered choices.
Learn more: Teaching in the Fast Lane
Correlation Tic-Tac-Toe

Here’s a fun way to work on correlation, which is a part of analysis. Show kids a 3 x 3 grid with nine pictures, and ask them to find a way to link three in a row together to get tic-tac-toe. For instance, in the pictures above, you might link together the cracked ground, the landslide, and the tsunami as things that might happen after an earthquake. Take things a step further and discuss the fact that there are other ways those things might have happened (a landslide can be caused by heavy rain, for instance), so correlation doesn’t necessarily prove causation.
Learn more: Critical Thinking Tic-Tac-Toe at The Owl Teacher
Inventions That Changed the World
Explore the chain of cause and effect with this fun thought exercise. Start it off by asking one student to name an invention they believe changed the world. Each student then follows by explaining an effect that invention had on the world and their own lives. Challenge each student to come up with something different.
Learn more: Teaching With a Mountain View
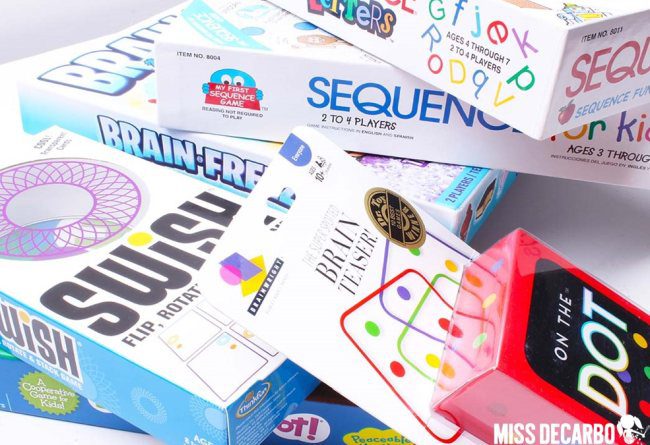
Critical Thinking Games

There are so many board games that help kids learn to question, analyze, examine, make judgments, and more. In fact, pretty much any game that doesn’t leave things entirely up to chance (Sorry, Candy Land) requires players to use critical thinking skills. See one teacher’s favorites at the link below.
Learn more: Miss DeCarbo
This is one of those classic critical thinking activities that really prepares kids for the real world. Assign a topic (or let them choose one). Then give kids time to do some research to find good sources that support their point of view. Finally, let the debate begin! Check out 100 Middle School Debate Topics , 100 High School Debate Topics , and 60 Funny Debate Topics for Kids of All Ages .
How do you teach critical thinking skills in your classroom? Come share your ideas and ask for advice in the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook .
Plus, check out 38 simple ways to integrate social-emotional learning throughout the day ..

You Might Also Like

30+ Awesome Career-Readiness Activities That Teach Soft Skills
Students need these skills to succeed in the workplace. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
Critical thinking definition

Critical thinking, as described by Oxford Languages, is the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement.
Active and skillful approach, evaluation, assessment, synthesis, and/or evaluation of information obtained from, or made by, observation, knowledge, reflection, acumen or conversation, as a guide to belief and action, requires the critical thinking process, which is why it's often used in education and academics.
Some even may view it as a backbone of modern thought.
However, it's a skill, and skills must be trained and encouraged to be used at its full potential.
People turn up to various approaches in improving their critical thinking, like:
- Developing technical and problem-solving skills
- Engaging in more active listening
- Actively questioning their assumptions and beliefs
- Seeking out more diversity of thought
- Opening up their curiosity in an intellectual way etc.
Is critical thinking useful in writing?
Critical thinking can help in planning your paper and making it more concise, but it's not obvious at first. We carefully pinpointed some the questions you should ask yourself when boosting critical thinking in writing:
- What information should be included?
- Which information resources should the author look to?
- What degree of technical knowledge should the report assume its audience has?
- What is the most effective way to show information?
- How should the report be organized?
- How should it be designed?
- What tone and level of language difficulty should the document have?
Usage of critical thinking comes down not only to the outline of your paper, it also begs the question: How can we use critical thinking solving problems in our writing's topic?
Let's say, you have a Powerpoint on how critical thinking can reduce poverty in the United States. You'll primarily have to define critical thinking for the viewers, as well as use a lot of critical thinking questions and synonyms to get them to be familiar with your methods and start the thinking process behind it.
Are there any services that can help me use more critical thinking?
We understand that it's difficult to learn how to use critical thinking more effectively in just one article, but our service is here to help.
We are a team specializing in writing essays and other assignments for college students and all other types of customers who need a helping hand in its making. We cover a great range of topics, offer perfect quality work, always deliver on time and aim to leave our customers completely satisfied with what they ordered.
The ordering process is fully online, and it goes as follows:
- Select the topic and the deadline of your essay.
- Provide us with any details, requirements, statements that should be emphasized or particular parts of the essay writing process you struggle with.
- Leave the email address, where your completed order will be sent to.
- Select your prefered payment type, sit back and relax!
With lots of experience on the market, professionally degreed essay writers , online 24/7 customer support and incredibly low prices, you won't find a service offering a better deal than ours.
- WordPress.org
- Documentation
- Learn WordPress
- Members Newsfeed
20 Critical Thinking Activities for Middle Schoolers
- Middle School Education

Introduction:
Critical thinking is vital for middle school students, as it helps them develop problem-solving skills, make informed decisions, and understand different perspectives. Integrating critical thinking activities into classroom learning experiences can greatly enhance students’ cognitive abilities. The following are 20 engaging critical thinking activities designed for middle school students.
1. Brain Teasers: Use age-appropriate puzzles to challenge students’ cognitive abilities and encourage them to find creative solutions.
2. Socratic Circles: Divide the class into groups and encourage them to participate in a philosophical discussion on a given topic, asking questions that stimulate critical thinking and deeper understanding.
3. Compare and Contrast: Assign two similar but different texts for students to compare and contrast, analyzing similarities and differences between each author’s perspective.
4. What-If Questions: Encourage children to think critically about hypothetical scenarios by asking what-if questions, such as “What if the internet didn’t exist?”
5. Debate Club: Organize a debate club where students are encouraged to research and defend differing viewpoints on a topic.
6. Mind Mapping: Teach students how to create a mind map – a visual representation of their thoughts – to help them brainstorm complex issues effectively.
7. Mystery Bag: In small groups, give students a bag containing several random objects and ask them to invent an innovative product or story using all items in the bag.
8. Critical Thinking Journal: Have students maintain journals where they analyze their thought processes after completing activities, promoting self-reflection and metacognition.
9. Moral Dilemmas: Present students with moral dilemmas, requiring them to weigh pros and cons before making ethical decisions.
10. Fact or Opinion?: Give students various statements and ask them to differentiate between fact or opinion, helping them build critical thinking skills when handling information.
11. Research Projects: Assign project topics that require deep research from multiple sources, developing students’ abilities to sift through information and synthesize their findings.
12. Think-Pair-Share: Have students think individually about a complex question, then pair up to discuss their thoughts, and finally share with the class.
13. Art Interpretation: Display an artwork and ask students to interpret its meaning, theme, or message, pushing them to look beyond the surface.
14. Reverse Role Play: Assign roles for a scenario where students exchange positions (e.g., teacher-student, parent-child), fostering empathetic understanding and critical thinking skills.
15. Critical Evaluation of Media: Analyze news articles, commercials, or social media posts by asking questions about their purpose, target audience, and accuracy.
16. Six Thinking Hats: Teach students Edward de Bono’s “Six Thinking Hats” technique to improve critical thinking by exploring diverse perspectives when solving problems.
17. Analogy Building: Encourage students to create analogies from one concept to another, enhancing abstract thinking and problem-solving abilities.
18. Current Events Analysis: Keep track of current events and have students critically evaluate news stories or blog posts to encourage informed decision-making in real-world contexts.
19. Brainstorming Sessions: Hold group brainstorming sessions where students invent solutions for complex problems while practicing active listening and critical thinking.
20. Reflection Activities: Use reflective writing prompts at the end of lessons or activities to foster metacognition, self-awareness, and the development of critical thinking skills.
Conclusion:
Critical thinking activities are vital for middle schoolers as they foster intellectual growth and prepare them for future learning experiences. By incorporating these 20 activities into your classroom curriculum, you can help students develop essential critical thinking skills that will serve them throughout their academic careers and beyond.

Related Articles

Starting at a new school can be an exciting yet nerve-wracking experience…

Middle school can be a challenging time for students, but lunch breaks…

Introduction Morning meetings are a great opportunity for middle school students to…

Pedagogue is a social media network where educators can learn and grow. It's a safe space where they can share advice, strategies, tools, hacks, resources, etc., and work together to improve their teaching skills and the academic performance of the students in their charge.
If you want to collaborate with educators from around the globe, facilitate remote learning, etc., sign up for a free account today and start making connections.
Pedagogue is Free Now, and Free Forever!
- New? Start Here
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Registration
Don't you have an account? Register Now! it's really simple and you can start enjoying all the benefits!
We just sent you an Email. Please Open it up to activate your account.
I allow this website to collect and store submitted data.
Educationise
11 Activities That Promote Critical Thinking In The Class
52 Critical Thinking Flashcards for Problem Solving
Critical thinking activities encourage individuals to analyze, evaluate, and synthesize information to develop informed opinions and make reasoned decisions. Engaging in such exercises cultivates intellectual agility, fostering a deeper understanding of complex issues and honing problem-solving skills for navigating an increasingly intricate world. Through critical thinking, individuals empower themselves to challenge assumptions, uncover biases, and constructively contribute to discourse, thereby enriching both personal growth and societal progress.
Critical thinking serves as the cornerstone of effective problem-solving, enabling individuals to dissect challenges, explore diverse perspectives, and devise innovative solutions grounded in logic and evidence. For engaging problem solving activities, read our article problem solving activities that enhance student’s interest.
What is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is a 21st-century skill that enables a person to think rationally and logically in order to reach a plausible conclusion. A critical thinker assesses facts and figures and data objectively and determines what to believe and what not to believe. Critical thinking skills empower a person to decipher complex problems and make impartial and better decisions based on effective information.
More Articles from Educationise
- 10 Innovative Strategies for Promoting Critical Thinking in the Classroom
- How to Foster Critical Thinking Skills in Students? Creative Strategies and Real-World Examples
- 9 Must-Have AI Tools for Teachers to Create Interactive Learning Materials
- The Future of Education: 8 Predictions for the Next Decade
- The Latest in EdTech: 5 Innovative Tools and Technologies for the Classroom
- 8 Free Math Problem Solving Websites and Applications
Critical thinking skills cultivate habits of mind such as strategic thinking, skepticism, discerning fallacy from the facts, asking good questions and probing deep into the issues to find the truth.
Importance of Acquiring Critical Thinking Skills
Acquiring critical thinking skills was never as valuable as it is today because of the prevalence of the modern knowledge economy. Today, information and technology are the driving forces behind the global economy. To keep pace with ever-changing technology and new inventions, one has to be flexible enough to embrace changes swiftly.
Read our article: How to Foster Critical Thinking Skills in Students? Creative Strategies and Real-World Examples
Today critical thinking skills are one of the most sought-after skills by the companies. In fact, critical thinking skills are paramount not only for active learning and academic achievement but also for the professional career of the students. The lack of critical thinking skills catalyzes memorization of the topics without a deeper insight, egocentrism, closed-mindedness, reduced student interest in the classroom and not being able to make timely and better decisions.
Benefits of Critical Thinking Skills in Education
Certain strategies are more eloquent than others in teaching students how to think critically. Encouraging critical thinking in the class is indispensable for the learning and growth of the students. In this way, we can raise a generation of innovators and thinkers rather than followers. Some of the benefits offered by thinking critically in the classroom are given below:
- It allows a student to decipher problems and think through the situations in a disciplined and systematic manner
- Through a critical thinking ability, a student can comprehend the logical correlation between distinct ideas
- The student is able to rethink and re-justify his beliefs and ideas based on facts and figures
- Critical thinking skills make the students curious about things around them
- A student who is a critical thinker is creative and always strives to come up with out of the box solutions to intricate problems
- Critical thinking skills assist in the enhanced student learning experience in the classroom and prepares the students for lifelong learning and success
- The critical thinking process is the foundation of new discoveries and inventions in the world of science and technology
- The ability to think critically allows the students to think intellectually and enhances their presentation skills, hence they can convey their ideas and thoughts in a logical and convincing manner
- Critical thinking skills make students a terrific communicator because they have logical reasons behind their ideas
Critical Thinking Lessons and Activities
11 Activities that Promote Critical Thinking in the Class
We have compiled a list of 11 activities that will facilitate you to promote critical thinking abilities in the students. We have also covered problem solving activities that enhance student’s interest in our another article. Click here to read it.
1. Worst Case Scenario
Divide students into teams and introduce each team with a hypothetical challenging scenario. Allocate minimum resources and time to each team and ask them to reach a viable conclusion using those resources. The scenarios can include situations like stranded on an island or stuck in a forest. Students will come up with creative solutions to come out from the imaginary problematic situation they are encountering. Besides encouraging students to think critically, this activity will enhance teamwork, communication and problem-solving skills of the students.
Read our article: 10 Innovative Strategies for Promoting Critical Thinking in the Classroom
2. If You Build It
It is a very flexible game that allows students to think creatively. To start this activity, divide students into groups. Give each group a limited amount of resources such as pipe cleaners, blocks, and marshmallows etc. Every group is supposed to use these resources and construct a certain item such as building, tower or a bridge in a limited time. You can use a variety of materials in the classroom to challenge the students. This activity is helpful in promoting teamwork and creative skills among the students.
It is also one of the classics which can be used in the classroom to encourage critical thinking. Print pictures of objects, animals or concepts and start by telling a unique story about the printed picture. The next student is supposed to continue the story and pass the picture to the other student and so on.
4. Keeping it Real
In this activity, you can ask students to identify a real-world problem in their schools, community or city. After the problem is recognized, students should work in teams to come up with the best possible outcome of that problem.
5. Save the Egg
Make groups of three or four in the class. Ask them to drop an egg from a certain height and think of creative ideas to save the egg from breaking. Students can come up with diverse ideas to conserve the egg like a soft-landing material or any other device. Remember that this activity can get chaotic, so select the area in the school that can be cleaned easily afterward and where there are no chances of damaging the school property.
6. Start a Debate
In this activity, the teacher can act as a facilitator and spark an interesting conversation in the class on any given topic. Give a small introductory speech on an open-ended topic. The topic can be related to current affairs, technological development or a new discovery in the field of science. Encourage students to participate in the debate by expressing their views and ideas on the topic. Conclude the debate with a viable solution or fresh ideas generated during the activity through brainstorming.
7. Create and Invent
This project-based learning activity is best for teaching in the engineering class. Divide students into groups. Present a problem to the students and ask them to build a model or simulate a product using computer animations or graphics that will solve the problem. After students are done with building models, each group is supposed to explain their proposed product to the rest of the class. The primary objective of this activity is to promote creative thinking and problem-solving skills among the students.
8. Select from Alternatives
This activity can be used in computer science, engineering or any of the STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) classes. Introduce a variety of alternatives such as different formulas for solving the same problem, different computer codes, product designs or distinct explanations of the same topic.
Form groups in the class and ask them to select the best alternative. Each group will then explain its chosen alternative to the rest of the class with reasonable justification of its preference. During the process, the rest of the class can participate by asking questions from the group. This activity is very helpful in nurturing logical thinking and analytical skills among the students.
9. Reading and Critiquing
Present an article from a journal related to any topic that you are teaching. Ask the students to read the article critically and evaluate strengths and weaknesses in the article. Students can write about what they think about the article, any misleading statement or biases of the author and critique it by using their own judgments.
In this way, students can challenge the fallacies and rationality of judgments in the article. Hence, they can use their own thinking to come up with novel ideas pertaining to the topic.
10. Think Pair Share
In this activity, students will come up with their own questions. Make pairs or groups in the class and ask the students to discuss the questions together. The activity will be useful if the teacher gives students a topic on which the question should be based.
For example, if the teacher is teaching biology, the questions of the students can be based on reverse osmosis, human heart, respiratory system and so on. This activity drives student engagement and supports higher-order thinking skills among students.
11. Big Paper – Silent Conversation
Silence is a great way to slow down thinking and promote deep reflection on any subject. Present a driving question to the students and divide them into groups. The students will discuss the question with their teammates and brainstorm their ideas on a big paper. After reflection and discussion, students can write their findings in silence. This is a great learning activity for students who are introverts and love to ruminate silently rather than thinking aloud.
Read our next article: 10 Innovative Strategies for Promoting Critical Thinking in the Classroom
Share this:
4 thoughts on “ 11 activities that promote critical thinking in the class ”.
- Pingback: What is Growth Mindset? 50+ Motivational Quotes on Growth Mindset - Educationise
- Pingback: 6 Steps To Implement Project-Based Learning In The Classroom - Educationise
- Pingback: Engaging Problem-Solving Activities That Spark Student Interest - Educationise
Thanks for the great article! Especially with the post-pandemic learning gap, these critical thinking skills are essential! It’s also important to teach them a growth mindset. If you are interested in that, please check out The Teachers’ Blog!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Discover more from educationise.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

Mental Health Worksheets
Mental health worksheets & workbooks for adolescents, mental health worksheets & workbooks for adults, mental health worksheets & workbooks for couples, mental health worksheets & workbooks for families.
Search by topic:
Table of Contents
50 Activities for Developing Critical Thinking Skills Worksheet

The Happier Therapy editorial team is made up of Masters and PhD counselling psychologists. Each worksheet is created by a team member with exposure to and experience in the subject matter. The worksheet then gets reviewed by a more senior editorial member. This is someone with extensive knowledge of the subject matter and highly cited published material.
What is the theory behind 50 activities for developing a critical thinking skills worksheet?
Critical thinking is the ability to solve problems, give logic and reasons, and think independently. It involves creativity, absorbing knowledge and ideas, interpreting information, and applying knowledge to solve problems. Because critical thinking is not an inborn quality and can be learned through different strategies and exercises, kids can learn it and improve their thinking processes.
How will this worksheet help you?
This worksheet will help you with fifty different critical thinking-improving exercises and activities. It is beneficial for parents, teachers, and caregivers to use this worksheet for new ideas to practice these activities with their children. This is not just a guide to improve critical thinking, but you can practice these exercises as a fun way to learn new skills.
How to use this worksheet?
This worksheet can be used by teachers, parents, caregivers, or therapists as a way to find new activities to perform with your children to improve their critical thinking. In every session, you can choose a new activity and perform it with your children and help them learn these skills in new fun ways.
Was this helpful?
Heyman GD. Children’s Critical Thinking When Learning From Others. Curr Dir Psychol Sci. 2008 Oct 1;17(5):344-347.
Find a supportive therapist who can help with mental health.

Discover the convenience of BetterHelp, an online therapy platform connecting you with licensed and accredited therapists specialized in addressing issues such as depression, anxiety, relationships, and more. Complete the assessment and find your ideal therapist within just 48 hours.
HappierTherapy is user-supported. We may earn a commission if you sign up for BetterHelp’s services after clicking through from this site
Related Posts
Asperger’s therapy worksheet
Autism Worksheet Emotions

Autism Worksheet Social Skills
- Search the site

9 Critical Thinking Exercises That Actually Improve Your Mind
Anthony Metivier | August 25, 2023 | Thinking

After all, the Internet is loaded with generic exercises like “read books written by leaders.”
Sorry, but that’s not a specific exercise. That’s a generic activity.
On this page, we’ll dive into specific exercise for critical thinking targeted at specific outcomes. Each exercise is designed to help you boost precise aspects of thinking so you can feel improvement as you go.
First, however, it’s good to understand what makes an exercise worthwhile. And understand why critical thinking has gotten more and more important as time moves on.
Since that is kind of counterintuitive in the age of AI, let’s dive in with a critical thinking exercise of our own.
Why Critical Thinking Skills Are More Important Now Than Ever
As the author of this blog on memory and thinking for over a decade, people ask me often if any of these skills matter anymore.
I’ve gotten the question even more frequently since AI tools like chat-GPT and Midjourney have appeared.
“Do we really need memory techniques anymore, now that I can search the Internet for anything at any time?”
“Why should I improve my thinking skills when I can read a simple summary of any book just by asking an AI?”
First, it’s still the case that a vast percentage of information has never appeared online. It’s imperative that people understand this and do hands-on, practical research with a variety of sources offline.
That said, there are certain use cases where using an AI seems to make sense. I recently published a case study demonstrating the positive use of chat-GPT for language learning , for example. But there are a few reasons we don’t want to relegate our thinking and learning to machines.
The big one is that we don’t own the platform and we certainly don’t own the data. Nor do we have general access to the people who do.
That’s troublesome because I’ve noticed bias that makes the text generators much different than the kinds of bias produced by a standard search engine. For example, instead of just getting the results, you might get a mini-discussion that essentially assumes it knows the intent behind your question.

This happened to me while working on my “Memory Detective” series. I thought it would be fun to get some feedback and ideas from chat-GPT, but it was anything but amusing.
In fact, the software effectively accused me of being biased about the bad guy I was exploring – which of course I was, just not in the way the software assumed. It’s a bad guy I was developing, after all. And moreover, I was working on fiction and made this evident in my request, even though the AI seems to have ignored this crucial point.
Here’s the kicker and the reason I’m dwelling on this point: Discovering that chat-GPT is itself biased let me to the point of feeling, however briefly, offended by the people who designed such preachy features into the program.
It’s only because I’ve done some of the critical thinking exercises below that I’m aware of my own memory biases , and was able to continue using the software objectively. We are all going to need to be increasingly objective as “the powers that be” inject their agendas into the tools we use.
In sum, even if each and everyone one of us ultimately winds up owning and designing our own personal Artificial Intelligences, we’re still going to need to think critically about both inputs, outputs and our interpretations of them. And in order to keep our critical thinking skills mobile, we’re going to need ongoing mental training .
9 Critical Thinking Exercises That Create Laser Sharp Intelligence
Authentic critical thinking exercises must always involve:
- New learning by working with information you have not encountered before
- Variety so that you experience growth in multiple areas and don’t “burn out” on just one area
- Varying levels of complexity so you experience different challenges
- Consistent practice over time
Follow those guidelines and you will succeed.
Critical Thinking Exercises For Students
Students have many needs. Above all, they need to be able to understand how people make arguments and substantiate their claims with evidence.
One: The News Exercise
One great source for practice is the news.
For this exercise, head over to any news website. Look for an article that includes graphs, numbers, or any representation involving numerical data.
Here’s the kind of news representation I’m talking about:
As you examine the news, ask the following questions:
- How is the news trying to help you understand the data?
- Does the representation of the data make sense?
- How can you determine whether or not the graph is reliable?
- How can you determine whether or not the presenter is reliable and free from bias?
- Who gets any kind of special benefit if the interpretation of the data falls in their favor?
Asking questions like these provides a powerful exercise that will sharpen your mind whenever you are presented with scientific data.
Two: The Abilities Exercise
Do you know anyone living with a disability?
I do and you can learn more about my mentor Jon Morrow in his article 7 Life Lessons from a Guy Who Can’t Move Anything but His Face .
After reading his post, imagine what it would be like if you could only move one part of your body. Write an essay that describes how exactly your life would change from the way it is.
Another version of this exercise is to think of ways you can use your mind to box with one hand tied behind your back.
For example, you can practice debating with a timer on and give yourself increasingly smaller amounts of time to make your case. There are many lists of debate topics online to choose from, and you can sharpen your skills anytime by going through the Rhetorica ad Herennium .
Three: The Research Response Exercise
Take the following argument:
Pesticides harm the environment more than they’re worth.
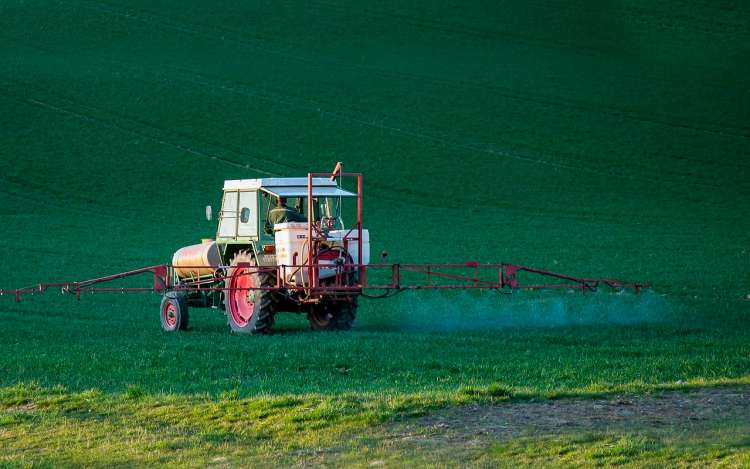

As you think through this statement, answer the following questions:
- What kind of research do you need to conduct in order to answer both for or against this statement?
- How would you outline your responses? Use a structure like this: “if A then B, and if B then C, and if C then D, and in conclusion, if A then D.”
Critical Thinking Exercises For Business
People in business need to successfully navigate sales meetings and negotiate multiple levels of management in their careers. Here are some critical thinking exercises that will help you develop skills in these areas.
Four: The Prison Exercise
Pretend that you’ve been hired to sell a neighborhood council on building a new maximum security prison. This particular neighborhood is upper-class and filled with mansions.
What benefits can you bring together to explain why it would be a great thing for this neighborhood to house prisoners in this area?
What incentives can you include in the full package? As you consider both the benefits and the incentives, reign yourself in.
You want to think logically in order to make this a critical thinking exercise. If you indulge in flights of fancy, then it will be creative thinking exercise instead.
Anytime you get off track, these critical thinking examples will help you get back on this path.
Five: The Facial Expression Exercise
One way to improve business success is to develop your empathy.

For this exercise, gather a number of photographs from the newspaper or some magazines.
As you look through the photographs, practice identifying the emotions. If you feel like you’re lacking in vocabulary for the task, consider reading The Dictionary of Emotions . You can also use an online dictionary or thesaurus to come up with words.
Next, do some role playing. Pick one person from the photographs and imagine meeting them in real life.
List all the questions you would ask them in order to connect with them better based on the emotion you listed when you first saw the photograph.
Six: The Competitor Exercise
Think about your competitors in business.
As you go through each, list their purpose for being in business. What is it that they are trying to accomplish?
Be non judgemental, realistic and focus on the most significant aspects of their purpose.
Then, think about how you can contribute to the growth of their success without damaging your own.
Obviously, this is a very tricky critical thinking exercise, but I’m confident you’ll find it beneficial. If you’re into sports or any other realm where competition plays a role, this exercise is also helpful.
And if you really want to learn about critical thinking so you’re a master, check out these critical thinking books .
Critical Thinking Exercises For Adults
As mentioned, exercises that stimulate our thinking abilities are best if they are targeted at a particular outcome.

However, there is some room for general exercises that are good for everyone. Let’s have a look at some of my favorites.
Seven: The Stakes Exercise
Many times when you’re listening to an argument, it’s easy to get hung up on the details.
A great exercise is to simply ask: What’s at stake?
This means, what’s the real core issue? And who benefits the most if they get to be right on the issue?
As you complete this exercise, but sure to go through both the objective and subjective reasoning of both sides.
Also, you’ll benefit if you continually focus on how many possible answers might exist. It’s not always the case that there’s one and only one correct answer, even if situations require us to pick just one.
You’ll want to also spend time interpreting the information on both sides of the argument, and possibly doing follow-up research. In fact, if you don’t, it’s unlikely that you’ll improve your reasoning skills as much as you’d like.
Eight: Make An “Argument Map”
I’ve talked a lot about mind mapping on this blog. But there’s another powerful process called argument mapping .
This technique goes back to Plato. If you’ve read the Meno , you might remember how Socrates draws a set of figures in the dirt to display the concepts that come up during the discussion.
These days, we can use pen and paper or software to create an argument map. Here’s one from Evan Rodriguez .
To create one yourself, pick an argument where multiple reasons are involved and break things down.
In this example, Rodriquez has separated the “because” reasons and then used the graph to help him sort through the truth by visualizing a set of if/then parameters.
Creating such argument maps provide tremendous exercise. They’re also relatively quick to produce.
You might also enjoy learning more about the history of what is sometimes called “graphicacy.” Look up people and processes like:
- Ars combinatoria
- Giordano Bruno
- Petrus Ramus
- John Venn (who introduced Venn diagrams)
- Peirce’s Existential Graphs
Nine: Memorize the Fallacies
One of the best critical thinking exercises is to learn the fallacies so well you know them when you see them or hear them in a conversation .
There are at least two kinds of fallacies: Formal and informal. This list of fallacies is very thorough.
To commit as many of these as possible to memory, you’ll want to learn a technique called the Memory Palace . I’m happy to help you learn it here:

Let’s say you want to memorize argumentum ad lapidem or the “ appeal to the stone ” fallacy.
You can memorize the Latin and English along with the meaning by thinking about a chair in your home and imagining yourself having an argument with a stone. In this image, you’re calling the stone’s arguments absurd without providing any evidence for why you believe this to be the case.
It’s a powerful technique and will help you spot fallacies in everyday life. Commit as many to memory as you can.
The Ultimate Critical Thinking Exercise to Reach Peak Critical Thinking
For thousands of years, people have asked “Who am I?”
You might not think about this as an exercise that relates to critical thinking strategies at large, but if you really submit to the question as a practice, it helps your thinking across the board.
When you take away your name, your title, the roles you play in your profession and all the games of life, who are you really? Is there a “true self” in the mix that you can always trust to be the same?

To practice this exercise with more structure, get 15-20 index cards and write down personal qualities on each. They can be qualities like:
- Versatility
Sit down, take a deep breath and mix the cards.
Then, pick one of the cards and reflect on how that quality is perceived by others in your life:
Family, friends, co-workers. You might want to learn about how to think about yourself through the perspective of authors through my autobiographical memory post first. Or just dive in.
Next, imagine what it would be like if that quality was completely gone from your life. Who would you be without it? Can you glimpse your true self without this label?
Then pick up another card and repeat the process, linking each with a deep breath. Then follow-up by journaling on your experiences. Making sure to write after completing each of the exercises on this page is key to benefiting from the reflective thinking skills you’ll also want to grow.
Thank you for reading this article, and if you enjoyed these exercises, please consider going through these powerful brain exercises next.
Related Posts
Critical thinking provides so many benefits. But did you know there's more than one kind…
Real life critical thinking examples are hard to come by. This post gives you 7…
Most critical thinking quotes have nothing to do with the critical part. These 5 quotes…
Most barriers to critical to critical thinking are easily removed. Read this post to boost…
Last modified: August 25, 2023
About the Author / Anthony Metivier
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
I accept the Privacy Policy
POPULAR POSTS
- How to Remember Things: 18 Proven Memory Techniques
- How to Build a Memory Palace: Proven Memory Palace Technique Approach
- How to Learn a New Language Fast: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Digital Amnesia: 5 Ways To Stop The Internet From Ruining Your Memory
- 15 Brain Exercises & Memory Exercises For Rapid Remembering
- The Memory Palace of Matteo Ricci
- Effortless Conference Interpreting: 7 Career-Making Memory Tips
- How To Teach Your Kids Memory Techniques
- 5 Unconventional, But Proven Note Taking Techniques
Recent Posts
- Lifelong Learning: The Benefits in Life and in Today’s Job Market
- How To Stop Losing Things: 6 Proven Tips
- How To Be A Renaissance Man: 8 Traits For Epic Well-Roundedness
- 8 Productive Study Habits That Guarantee You’ll Excel In School
- Real Life Sherlock Holmes Ben Cardall On What to Memorize
Pay with Confidence

Memory Courses
- The Magnetic Memory Method Masterclass
- The Magnetic Memory Method Masterplan
- How To Learn And Memorize The Vocabulary Of Any Language
- How To Learn And Memorize Poetry
- How To Memorize Names and Faces
- How to Memorize Math, Numbers, Simple Arithmetic and Equations
- How to Remember Your Dreams
Quick Links
- Testimonials
- Privacy Policy
- Privacy Tools
- Terms of Service
P.O. Box 933 Mooloolaba, QLD 4557 Australia
Memory Improvement Blog
- How to Build A Memory Palace
- Eidetic Memory
- Episodic Memory
- Photographic Memory
- Improve Memory for Studying
- Memorization Techniques
- How to Memorize Things Fast
- Brain Exercises

- The Magnetic Memory Method Podcast
- Memory Improvement Resources for Learning And Remembering

COOL MEMORY TECHNIQUES!

GET YOUR FREE 4-PART VIDEO MINI-COURSE
Improve your memory in record time! Just enter your email below now to subscribe.
- How to learn anything at lightning fast speeds
- Improve your short and long term memory almost overnight
- Learn any language with and recall any information with ease

- Search Search Search …
- Search Search …
Critical Thinking Exercises for Employees: Boosting Workplace Problem-Solving Skills

In today’s fast-paced work environment, critical thinking skills are essential for success. By engaging in critical thinking exercises, employees can refine their ability to evaluate information, solve complex problems, and communicate effectively. These skills not only contribute to individual success but also promote a more innovative and productive work environment.
Critical thinking also plays a crucial role in leadership and management, as well as fostering effective teamwork. Managers who possess strong critical thinking skills are better equipped to guide their teams in problem-solving and decision-making processes. By incorporating critical thinking exercises into employee training, organizations can cultivate a culture that values innovation, creativity, and adaptability.
Key Takeaways
- Critical thinking exercises help employees develop problem-solving and communication skills.
- Strong critical thinking is essential for effective leadership, management, and teamwork.
- Fostering critical thinking in the workplace leads to a more innovative and productive environment.
Understanding Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is a vital skill for employees in the business world, as it enables individuals to analyze complex situations, identify biases, and make informed decisions through creative problem-solving methods. This cognitive process encourages a deeper understanding of problems and promotes the ability to approach them from multiple perspectives.
Developing critical thinking skills involves being aware of one’s own biases and working towards eliminating them. Bias can significantly impact how we approach problems and may result in making distorted decisions. By recognizing and addressing these biases, employees can harness their critical thinking abilities to make impartial and robust decisions in the business landscape.
One essential component of critical thinking is the ability to analyze information. This involves breaking down a problem into its constituent parts, understanding their relationships, and evaluating the significance of each element. Through thorough analysis, employees can gain a comprehensive view of the situation and consider various aspects before making well-informed decisions.
In the context of problem-solving, critical thinking encourages employees to explore new perspectives and think beyond conventional solutions. By adopting a creative approach, individuals can generate novel ideas and innovations, which can lead to improved business results and overall growth.
In conclusion, it is crucial for employees to develop and hone their critical thinking skills, as they enable individuals to navigate complex business environments effectively. By addressing biases, conducting robust analysis, and adopting creative problem-solving strategies, employees can make well-informed decisions that contribute to the success and longevity of the organization.
The Importance of Critical Thinking in the Workplace
Critical thinking is an essential skill for employees to possess in the modern workplace. It involves the ability to carefully and systematically analyze information, consider multiple perspectives, and make well-informed decisions. By enhancing decision-making abilities, critical thinking can lead to improved workplace performance and increased job satisfaction.
In the workplace , critical thinking allows for a more thorough evaluation of issues, helping to identify potential problems or opportunities. This is particularly important in today’s fast-paced, competitive environment, where companies need to stay ahead of industry trends and anticipate the needs of their customers. Employees who possess strong critical thinking skills can help their team effectively navigate the challenges that arise in any industry.
Furthermore, critical thinking plays a significant role in evaluating evidence and determining the credibility of information sources. Employees who can scrutinize data, identify patterns, and draw inferences can make more informed decisions and contribute to their team’s success. As a result, employers often seek to hire individuals with strong critical thinking abilities.
In a team setting, critical thinking helps facilitate productive discussions and collaboration. Members of a team who can effectively analyze situations, question assumptions, and remain open-minded to the opinions of others contribute positively to the decision-making process. This ensures that a diverse range of perspectives is considered, leading to better outcomes for the company.
Ultimately, developing critical thinking skills in employees is not just beneficial for the individual worker and their direct colleagues, but it also impacts the overall success of the organization. By fostering an environment that encourages the growth of critical thinking skills, employers can not only increase productivity but also create a more positive and engaged work culture.
Developing Critical Thinking Skills
Mindful observation.
Mindful observation is a valuable exercise for enhancing critical thinking skills. Encourage employees to take a step back and observe their surroundings, paying close attention to details that may have previously gone unnoticed. This practice helps employees develop the ability to analyze situations more thoroughly and interpret information more effectively.
Active Listening
Active listening is essential for effective communication and leadership. Encourage employees to practice active listening by giving their full attention to the speaker, avoiding interrupting, and providing constructive feedback. Active listening promotes the development of critical thinking skills by fostering open-mindedness, empathy, and understanding in the workplace.
Asking Questions
Asking questions is a key component of critical thinking, as it encourages employees to inquire deeper into subjects and analyze all aspects of an issue. Employers can foster a work environment that supports curiosity by encouraging team members to ask both open-ended and closed-ended questions and offering guidance when needed.
Assessing Evidence and Drawing Conclusions
Teaching employees how to evaluate evidence and draw informed conclusions is crucial for the development of critical thinking skills. Use thinking exercises that involve employees analyzing and evaluating various sources of information, ultimately forming an inference that leads to an informed decision. Pairing employees with a mentor is helpful for providing guidance and support throughout the process.
Recognizing and Managing Biases
Biases can greatly impact critical thinking and decision-making. Encourage employees to recognize their own biases and learn how to manage them effectively. Employees can benefit from understanding the impact of these biases on their thought process and how to minimize their influence to make objective, well-reasoned conclusions.
By incorporating these exercises and strategies into the workplace, employees can develop critical thinking skills that strengthen their overall performance, communication, and leadership abilities.
Critical Thinking and Communication
Critical thinking and communication go hand in hand in the workplace. Developing both skills can enhance employees’ ability to solve problems, make decisions, and work effectively in teams. By engaging in critical thinking exercises that involve clear communication and open discussion, employees can improve their cognitive abilities and interpersonal skills.
One exercise to improve critical thinking and communication is explaining a problem to someone else. This allows employees to fully understand a situation and consider all possible options for resolution. Encouraging employees to articulate their thought processes and rationale can lead to improved cognitive skills .
Another useful technique is group discussions, which can stimulate critical thinking and promote clear communication. By engaging in conversations where various perspectives are considered, employees can develop the ability to analyze information objectively and reevaluate their initial assumptions. Fostering open-mindedness and empathy for others’ viewpoints can also build strong communication skills in the workplace .
In addition to exercises, employees should continuously practice self-awareness. Becoming more conscious of their thought processes, values, ethics, and beliefs will enhance their critical thinking abilities . Developing self-awareness also encourages employees to reflect on their communication styles and identify areas that need improvement.
Implementing these critical thinking and communication exercises in the workplace can lead to more efficient problem-solving, enhanced team dynamics, and improved performance across the organization. By fostering a culture of open discussion and clear communication, employers can empower their teams to make well-informed decisions and excel in their respective roles.
Applying Critical Thinking to Problem Solving
Effective problem solving requires employees to utilize critical thinking skills. By carefully analyzing information, asking questions, and determining the best course of action, employees will be more likely to arrive at creative and innovative solutions to challenges.
A key aspect of critical thinking in problem solving is to question assumptions. Employees should be encouraged to identify any preconceived notions or biases that may be influencing their thought processes. This will help them approach the problem with a more open and objective perspective.
Another essential component is seeking alternative viewpoints, even if it means playing the devil’s advocate. By considering different perspectives and exploring various possibilities, employees will be better equipped to discover innovative solutions that might not have been immediately apparent.
Critical thinking also involves evaluating the effectiveness of potential solutions. Employees should be encouraged to analyze the pros and cons of each option, as well as consider any potential long-term impacts. This process can help identify the most viable and successful solutions for a given problem.
In order to foster a culture of critical thinking within the workplace, managers can provide support by encouraging employees to ask questions, challenge assumptions, and explore alternative perspectives. Additionally, providing opportunities for learning and growth can help employees further develop their critical thinking skills, ultimately leading to more effective problem solving and increased innovation.
In summary, critical thinking is essential for effective problem-solving at work. By questioning assumptions, exploring various perspectives, and evaluating potential solutions, employees can confidently recommend creative and innovative approaches to overcoming challenges. This will not only lead to better outcomes for the organization, but also foster a culture of continuous improvement and growth.
Critical Thinking in Leadership and Management
Developing critical thinking skills in leadership and management positions is crucial for making informed decisions, driving company growth, and ensuring employee satisfaction. By enhancing their cognitive abilities, leaders and managers become better at decision-making, hiring processes, and overall performance.
In the realm of leadership, critical thinking helps leaders to understand the logical relationships between ideas and recognize the importance of an argument. This enables them to identify mistakes in reasoning and make well-informed choices, thus driving superior organizational outcomes as mentioned here .
Certainly, nurturing critical thinking in management is essential for improving cognition . This includes decision-making skills, the ability to identify potential pitfalls, and dealing with complex situations. By integrating critical thinking into management practices, companies can boost employee engagement, improve workplace morale, and ultimately succeed in a competitive business landscape.
Incorporating critical thinking exercises into hiring processes allows employers to better assess candidates’ abilities objectively. By focusing on problem-solving and communication skills during the interview process, managers can identify high-potential talent who demonstrate strong critical thinking competencies.
Investing time in building and improving critical thinking skills not only benefits individuals but also the overall success of an organization. By supporting employees in developing their cognitive abilities, leaders and managers both play a crucial role in promoting a culture of critical thinking that will lead to better decision-making and stronger company performance.
In conclusion, fostering critical thinking in leadership and management enables better decision-making, more effective hiring processes, and improved organizational performance. Strong cognitive abilities empower leaders and managers to approach complex situations with confidence and clarity, driving overall growth and success.
Critical Thinking in Team Building
Incorporating critical thinking exercises within team building activities is essential for fostering creativity, collaboration, and problem-solving amongst employees. By engaging team members in activities that require them to consider multiple perspectives and work together to reach a conclusion, companies can significantly improve their team’s performance.
One effective critical thinking activity for team building is Debate It Out . In this exercise, teams are assigned a controversial topic and asked to come to a consensus. Participants must research and present opposing viewpoints, encouraging the consideration of multiple perspectives. This debate process encourages employees to challenge preconceived notions, question assumptions, and ultimately strengthen their critical thinking skills.
Another beneficial exercise involves conducting Reverse-engineering Google activities. In this scenario, participants work together to reverse-engineer a successful past project or campaign. This collaborative approach allows team members to learn from each other’s experiences, assumptions, and mistakes while analyzing the factors that contributed to the project’s success.
Brainstorming is another critical thinking team building activity that can generate diverse ideas and encourage innovation. By setting specific goals or challenges, team members collaborate to provide multiple solutions to a given problem. Encourage employees to think beyond the obvious answers, providing a safe space for innovative and unusual ideas.
In summary, promoting critical thinking within team building exercises is essential for strengthening collaboration, problem-solving, and decision-making skills. Implementing activities such as debates, reverse-engineering Google tasks, and brainstorming can foster robust critical thinking skills amongst team members and ultimately lead to improved team performance.
Evaluating Potential Job Candidates for Critical Thinking Skills
Screening for critical thinking.
When evaluating potential job candidates, it’s important to assess their critical thinking skills as part of the hiring process. These skills are essential for both hard and soft skills, making them valuable across various roles and industries.
A vital step to measure critical thinking is through the initial screening process. To do this effectively, recruiters can utilize pre-employment tests that focus on evaluating candidates’ analytical skills, problem-solving abilities, and decision-making skills. These assessments can be administered online for a more efficient process while narrowing down the applicant pool.
In addition, it’s helpful to include open-ended questions on job application forms, which require a demonstration of critical thinking. For instance, candidates can be asked to provide examples of situations where they needed to use critical thinking skills to resolve a problem.
Assessing Analytical Skills during Interviews
During the interview stage, hiring managers have the opportunity to further evaluate a candidate’s critical thinking abilities. Incorporating critical-thinking interview questions can reveal valuable insights into their thought processes and how they approach problem-solving.
Asking situational and behavioral questions can provide excellent insight into a candidate’s analytical capabilities. Employers may ask questions that require candidates to analyze specific scenarios, or they may inquire about past experiences where candidates employed their critical thinking skills.
Using case studies or real-life scenarios during interviews is also an effective method for assessing critical thinking abilities. Presenting candidates with a complex problem or task can help gauge their skills in problem-solving, decision-making, and evaluation.
It’s essential to have a structured approach when evaluating candidates’ analytical skills, as it enables hiring managers to compare their abilities objectively. This will ultimately help them make informed decisions when selecting the best-suited candidate for the job.
By effectively screening and assessing job candidates’ critical thinking skills, companies can confidently hire employees with the necessary abilities to contribute successfully to their organization’s goals and vision.
The Role of Emotional Intelligence in Critical Thinking
Emotional Intelligence (EI) plays a significant part in facilitating critical thinking skills for employees. EI is defined as the ability to understand and manage one’s emotions , as well as recognizing and influencing the emotions of others. In the context of critical thinking, high emotional intelligence allows individuals to be more reflective and open to different perspectives.
A key aspect of emotional intelligence in critical thinking is self-awareness. When employees are aware of their own emotions and biases, they can step back and reflect on their thoughts and decisions objectively. By doing so, they are better able to analyze and evaluate various media and sources of information, leading to more informed decisions.
Emotional intelligence also helps employees consider the ethical implications of their decisions. With a heightened understanding of emotions, individuals are more likely to empathize with others and take their perspectives into account. This ability enables them to navigate complex ethical dilemmas and make fair judgments that adhere to the organization’s values.
Moreover, employees with high emotional intelligence can easily adapt to different perspectives and opinions. They demonstrate a willingness to engage in meaningful dialogues with co-workers and are receptive to feedback. This collaborative spirit nurtures a culture of learning and continuous improvement, fostering an environment in which critical thinking can thrive.
In summary, emotional intelligence plays a crucial role in enhancing critical thinking skills among employees. By being aware of their emotions and biases, reflecting on decisions objectively, considering ethics, and embracing diverse perspectives, individuals with high emotional intelligence contribute enormously to creating a productive and innovative workplace.
Fostering an Innovative Work Environment through Critical Thinking
Promoting open discussions.
One way to encourage innovation in the workplace is by promoting open discussions. These encourage employees to share their ideas and contribute to the collaborative push for creative solutions. When a culture of open communication is established, employees feel valued and are more likely to take risks, making it easier for them to come up with innovative solutions. Conducting regular brainstorming sessions and encouraging the exchange of opinions during meetings can further enhance the creative thinking process.
Encouragement of Reflective Practice
Another essential aspect of fostering an innovative work environment is the encouragement of reflective practice. Reflection allows employees to learn from their experiences and identify areas for improvement. By consistently implementing reflective practices, employees can develop a better understanding of their thought processes, leading to more confident and knowledgeable decision-making. This can be done through regular self-assessments, group discussions, or by providing constructive feedback from managers and peers.
By focusing on open discussions and reflective practices, businesses can effectively nurture a culture of critical thinking and creativity, leading to more innovative solutions and long-term success in the ever-changing business landscape.
Enhancing critical thinking skills in the workplace is an essential step towards cultivating a culture of effective decision-making and problem-solving. By engaging in various training exercises, employees can strengthen their ability to analyze situations, interpret data, and make informed choices.
Introducing critical thinking exercises into an organization demonstrates the company’s commitment to fostering employee growth and harnessing their full potential. Such exercises are not only beneficial in honing analytical and problem-solving skills, but also in improving communication, collaboration, and adaptability among team members.
Incorporating critical thinking training into existing programs can lead to a more efficient and productive workplace. Employees with strong critical thinking skills are better prepared to face challenges, remain flexible and adaptive to changes in the market, and contribute positively to an organization’s overall success. By prioritizing critical thinking development, businesses can invest in their employees and, in turn, reap the benefits of a well-equipped workforce.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are effective group exercises to improve critical thinking.
There are various group exercises that can help improve critical thinking skills among employees. One example is the Socratic questioning technique in which a facilitator poses a series of questions designed to uncover assumptions and stimulate critical thinking. Another effective activity is the “Case Study Analysis,” where employees are tasked with analyzing real-life business scenarios to identify challenges, gather data, and make informed decisions.
How can team building games enhance critical thinking skills?
Team building games can be an engaging way to enhance critical thinking skills. These games often require collaboration, problem-solving, and decision-making under pressure, which can help participants sharpen their analytical abilities. Incorporating team-building exercises that promote critical thinking into regular team meetings or training sessions can create an environment of intellectual growth and mutual support.
What are some fun activities to develop critical thinking in adults?
Fun activities for adults aimed at developing critical thinking skills might include puzzles, escape room games, and debate clubs. These activities encourage individuals to challenge their assumptions, think outside the box, and use logical reasoning, ultimately improving their cognition and problem-solving abilities .
How can a workbook aid in critical thinking development?
A workbook designed for critical thinking development typically contains structured exercises, real-world examples, and reflective activities. These materials guide individuals through a step-by-step process of improving their critical thinking skills by encouraging self-awareness, fostering curiosity, and promoting constructive feedback. Using a workbook can provide an organized and personalized approach to enhancing critical thinking abilities.
What are the top 5 skills essential for critical thinking?
The top 5 skills essential for critical thinking include:
- Analytical thinking: The ability to break complex problems into smaller, manageable components.
- Evaluation: Assessing information and making judgments based on evidence and reasoning.
- Problem-solving: Identifying challenges and proposing effective solutions.
- Creativity: Generating innovative ideas, insights, and approaches.
- Communication: Articulating thoughts clearly and persuasively to convey complex ideas to others.
How can virtual activities benefit employees’ critical thinking?
Virtual activities can be an effective way to enhance critical thinking skills for remote or hybrid teams. Online tools and platforms can facilitate group discussions, brainstorming sessions, and collaborative problem-solving exercises, allowing employees to engage with diverse perspectives and develop their critical thinking skills. Employing virtual critical thinking activities can create an inclusive environment, encouraging employees to learn from each other, and adapt to changing circumstances.
You may also like

Fun critical thinking online games for adults
Critical thinking can be a difficult skill to hone, but with some practice and a fun incentive, you can be thinking deeper […]
How to Use Artificial Intelligence in the Critical Thinking Process: Enhancing Human Decision-Making
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the way critical thinking is approached in various sectors. By integrating AI into the critical thinking process, […]

Critical thinking questions for quizzes
Whether you’re a teacher looking to challenge your students to think critically, or you’re studying up in preparation for the LSAT, we’ve […]

When To Use Critical Thinking – What You Need To Know
There is a time and a place to use different skills in life. When faced with a problem that requires calm, logical […]
404 Not found
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
This article is part of the research topic.
Psychological Transformation in Technology-Enhanced Learning Environments (TELEs): Focus on Teachers and Learners
Developing Community of Inquiry using Educational Blog in Higher Education of Bangladesh Perspective Provisionally Accepted

- 1 Institute of Education and Research (IER), University of Dhaka, Bangladesh
The final, formatted version of the article will be published soon.
Web 2.0 tools such as blogs, wikis, social networking, podcasting etc. have received concentration in educational research over the last decade. Blogs enable students to reflect their learning experiences, disseminate ideas, and participate in analytical thinking. The Community of Inquiry (CoI) framework has been widely utilized in educational research to understand and enhance online and blended learning environments. There is insufficient research evidence to demonstrate the impact of educational blogging utilizing the CoI model as a framework. This paper explores how blogs can be used to support collaborative learning and how such interaction upholds CoI through enhancing critical thinking and meaningful learning in the context of Higher Education (HE). An exploratory mixed method research approach has been followed in this study. A convenience sampling method was employed to choose 75 undergraduate students from Dhaka University for a 24-week blogging project. Every publication on the blog was segmented into meaningful units. Whole texts of posts and comments are extracted from the blog and the transcripts are analyzed in Qualitative manner considering CoI framework, more specifically, through the lens of cognitive, social, and teaching presence. In addition, the semi-structured questionnaire is used to collect data from students whether blogging expediated students' learning or not. The research findings indicate that cognitive presence, namely the exploration component, is dominant in blog-based learning activity. Moreover, this research has demonstrated that blogs build reliable virtual connections among students through exchanging ideas and information and by offering opportunities for reflective practice and asynchronous feedback. This study also revealed challenges related to blogging in the context of developing countries, including lack of familiarity with blogs, restricted internet connectivity, limited access to devices, and low levels of social interaction. It is recommended that different stakeholders including policy makers, curriculum developers and teachers may take the initiative to synchronize the utilization of educational blogs with the formal curriculum, guaranteeing that blog activities supplement and improve traditional teaching-learning activities.
Keywords: web 2.0, Community of inquiry (COI), Blog, Collaborative Learning, Learning outcome
Received: 26 Sep 2023; Accepted: 25 Mar 2024.
Copyright: © 2024 Chowdhury and Siddique. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Mr. Sabbir A. Chowdhury, University of Dhaka, Institute of Education and Research (IER), Dhaka, Bangladesh
People also looked at
.a{fill:#396;}.b{fill:#fff;} 4-H clover Exploring your future: April 1 session
Event information.
7 - 8:15 p.m. Central time
Webinar series
Jennifer Cable, Extension youth development curriculum library coordinator [email protected] or 920-207-6815
Joanna Tzenis, State specialist, 4-H education & career pathways [email protected] or 612-625-9771
Erin Corcoran, Extension executive office and administrative specialist [email protected] or 612-624-9893
Exploring your future is a five-session series designed for youth to explore and identify their personal aspirations for the future through interactive activities that encourage creativity, self-awareness, critical thinking, goal setting and self-discovery.
Personalized for youth in grades 7-11, session content is designed to spark curiosity and plant the seeds that will motivate youth to make plans for their personal pathway to the valued future of their choice. Youth will have the opportunity to learn about financial planning, admission processes, career exploration and more!
This web series begins Monday April 1st and continues Monday April 8th, Monday April 15th, Monday April 22nd, and Monday April 29th.
Open to youth in grades 7-11 statewide.
Registration
Registration opens in 4-H Online on March 8 and closes on March 27.
For assistance, please refer to the event registration guide .
Accessibility
University of Minnesota Extension is committed to providing equal opportunity for participation in all programs, services, and activities. To request accommodations for persons with disabilities, contact Jennifer Cable two weeks before the start of the event. Requests received after this date will be honored whenever possible.
Related events
© 2024 Regents of the University of Minnesota. All rights reserved. The University of Minnesota is an equal opportunity educator and employer.
- Report Web Disability-Related Issue |
- Privacy Statement |
- Staff intranet
- Pharmaceutical Engineering Magazine
- Online Exclusives
- Special Reports
- Facilities & Equipment
- Information Systems
- Product Development
- Production Systems
- Quality Systems
- Regulatory Compliance
- Research + Development
- Supply Chain Management
- White Papers
- iSpeak Blog
- Editorial Calendar
- Article of the Year
- Submit an Article
- Editorial Team
Computer Software Assurance and the Critical Thinking Approach

In 2022, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued their draft guidance “Computer Software Assurance for Production and Quality System Software” 1 to enhance the computer validation process required by predicate rules, either in the pharmaceutical or medical device space. The critical thinking approach was introduced by ISPE GAMP® Guides and emphasizes a focus on clear thinking through a plan, then creating documentation from a process perspective. These methods combined create the optimal replacement for computer system validation (CSV).
- 1 US Food and Drug Administration. “Computer Software Assurance for Production and Quality System Software. Draft Guidance for Industry and Food and Drug Administration Staff.” September 2022. https://www.fda.gov/media/161521/download
New FDA draft guidance marked a transition to computer software assurance (CSA) in 2022 1 . Historically, CSV practices unfortunately focused on generating great amounts of paper-based testing records, and it was believed that the larger the stack of documentation, the better the quality and effort when validating a computerized system and eventually presenting it to the FDA.
The reality is that a mountain of paperwork did not equate to proper CSV, which resulted in a failure to fully ensure the product quality, data integrity, or patient safety. Critical thinking is a term that was introduced by GAMP guidance (initially in ISPE GAMP® Good Practice Guide: Enabling Innovation 2 and then more recently in ISPE GAMP® 5: A Risk-Based Approach to Compliant GxP Computerized Systems (Second Edition) 3 ), and it focuses on those critical considerations missed by CSV.
When applied, this critical thinking approach potentially results in the conclusion that a tremendous amount of documentation cannot possibly represent quality, especially when inspectors continue to identify a multitude of issues during inspections. These issues stem from items including, but not limited to, segregation of duties, data integrity potential violations, and whether the system works as intended after testing.
The FDA draft guidance states 1 : “Computer software assurance is a risk-based approach for establishing and maintaining confidence that software is fit for its intended use. This approach considers the risk of compromised safety and/or quality of the device (should the software fail to perform as intended) to determine the level of assurance effort and activities appropriate to establish confidence in the software. Because the computer software assurance effort is risk-based, it follows a least-burdensome approach, where the burden of validation is no more than necessary to address the risk. Such an approach supports the efficient use of resources, in turn promoting product quality.”
UTILIZATION OF THE CRITICAL THINKING APPROACH
The critical thinking approach can be used in potentially limiting testing evidence for low-risk functionalities through the following use of innovative testing approaches: unscripted and scripted testing.
Unscripted Testing
This is dynamic testing in which the tester’s actions are not prescribed by written instructions in a test case. This can include:
- Ad hoc testing: A concept derived from unscripted practice that focuses primarily on performing testing that does not rely on large amounts of documentation (e.g., test procedures) to execute
- Error-guessing: A test design technique in which test cases are derived on the basis of the tester’s knowledge of past failures or general knowledge of failure modes
- Exploratory testing: Experience-based testing in which the tester spontaneously designs and executes tests based on the tester’s existing relevant knowledge, prior exploration of the test item (including results from previous tests), and heuristic logical rules regarding common software behaviors and types of failure
Scripted Testing
This is dynamic testing in which the tester’s actions are prescribed by written instructions in a test case. It includes:
- Robust scripted testing: Scripted testing efforts in which the risk of the computer system or automation includes evidence of repeatability, traceability to requirements, and auditability
- Limited scripted testing: A hybrid approach of scripted and unscripted testing that is appropriately scaled according to the risk of the computer system or automation. These test methods require that the tester, through training and/or experience, has the knowledge to devise appropriate tests
WHY SOFTWARE ASSURANCE IS CRITICAL
Software assurance saves time and money. Software quality assurance ensures that developers find bugs and errors at the early stages of software development when less amount of time and money is required to fix them. The CSA approach provides flexibility and agility in helping ensure that the software is maintained in a validated state.
In determining the risk-based approach for software systems, the main intent is to use a risk-based methodology to ensure targeted and focused validation. This confirms that the computerized system is functioning for its prescribed, intended use, focusing (i.e., limiting a larger amount of documented evidence) on those functionalities that may directly impact patient safety and product quality.
For example, a software feature, function, or operation might pose a high process risk when its failure to perform as intended may result in a quality problem that foreseeably could compromise patient safety. In addition, software features and functions may maintain process parameters—such as temperature, pressure, or humidity—that affect the physical properties of product or manufacturing processes which are identified as essential to product safety and quality.
THE CSA RISK FRAMEWORK
The CSA risk framework is a risk-based approach intended to help manufacturers establish and maintain the reliability and safety of computer software throughout the life cycle, reducing the testing effort. Several steps must be taken to ensure the successful implementation of the CSA approach.
Identifying the Intended Use
Manufacturers must first determine whether the software is intended for use as part of production or the quality system. In general, software is either used directly as part of production or the quality system, or it supports production or the quality system.
Software that is used directly as part of production or the quality system includes software intended for automating production processes, inspection, testing, or the collection and processing of production data. It also includes software intended for automating quality system processes, collection, and the processing of quality system data, or maintaining a quality record established under the quality system regulation.
Manufacturers must validate software with these intended uses to ensure that it is reliable and functions as intended according to the associated risk. This is critical for both the pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical industries, as well as medical device manufacturers.
Determining the Risk-Based Approach
The CSA risk framework provides guidance on identifying and mitigating the risks associated with software validation and includes examples of applying the framework to various CSA situations. Once it has been determined that a software feature, function, or operation is intended for use as part of production or the quality system, a risk-based approach should be used to determine the appropriate assurance activities.
This approach involves identifying historical software failures, determining whether such a failure poses a high process risk, and systematically selecting and performing assurance activities commensurate with the medical device or process risk. The risk-based analysis for production or quality system software should consider which failures are historically known (as opposed to likely) and the risks resulting from each such failure.
Process risks refer to the potential to compromise production or the quality system, whereas direct system risks refer to the potential for a device to harm the patient or user. In CSA, the risk determination is therefore a key element to be carefully designed and executed to focus validation testing on the functionalities oriented to manage high-risk processes.
The CSA risk framework is a risk-based approach intended to help manufacturers establish and maintain the reliability and safety of computer software throughout the life cycle, reducing the testing e ort. Several steps must be taken to ensure the successful implementation of the CSA approach.
Determining the Appropriate Assurance Activities
Different types of assurance activities should be considered, corresponding with the system risk or process risk. For software features, functions, or operations that pose a high process risk, assurance activities should be considered higher corresponding with the system risk. Conversely, for software features, functions, or operations that do not pose a high process risk, appropriate assurance activities should be considered lower corresponding to the risk identified.
- 1 a b US Food and Drug Administration. “Computer Software Assurance for Production and Quality System Software. Draft Guidance for Industry and Food and Drug Administration Staff.” September 2022. https://www.fda.gov/media/161521/download
- 2 International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering. ISPE GAMP® Good Practice Guide: Enabling Innovation. North Bethesda, MD: International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering, 2021.
- 3 International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering. ISPE GAMP® 5 Guide: A Risk-Based Approach to Compliant GxP Computerized Systems (Second Edition). North Bethesda, MD: International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering, 2022.

CSA AND REQUIRED RECORDS
CSA enforces the need for regulated companies to establish the appropriate record. When establishing the record, the manufacturer should capture sufficient objective evidence to demonstrate that the software feature, function, or operation was assessed and performs as intended. In general, the record should include:
- The intended use of the software feature, function, or operation
- The determination of risk of the software feature, function, or operation
- Documentation of the assurance activities conducted
- The date of testing activities and the name of the person conducting them
- Establishing review and approval, when appropriate
The documentation of assurance activities should not include more evidence than necessary. However, it should retain sufficient details to serve as a baseline for improvements or as a reference point if issues occur. To reduce the need for manual or paper-based documentation, the FDA recommends that manufacturers “leverage automated traceability, testing, and the electronic capture of work performed to document the results. As a least burdensome method, FDA recommends the use of electronic records, such as system logs, audit trails, and other data generated by the software . . . in establishing the record associated with assurance activities” 1 .
THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN CSV AND CSA
CSA is a new way of looking at the traditional CSV approach through consideration of risk whereby the focus is on what matters—patient safety, product quality, and data integrity. A comparison of the two approaches for assurance activities and records is shown in Table 1.
The focus of CSV is a decision to carry out excessive and unnecessary tasks/testing, which creates excessive documentation, and too much time is spent on testing on all system functionalities. In comparison, when using CSA, the primary focus allows manufacturers to leverage principles such as risk-based testing, unscripted testing, continuous performance monitoring, and data monitoring, as well as validation activities performed by other entities (e.g., developers, suppliers). The CSA approach provides flexibility and agility in helping assure that the software maintains a validated state. This allows for assurance that the data provided is accurate, compliant, and more efficient.
In Figure 1, the left triangle represents the CSV approach, and the right triangle shows the differences that occur with CSA. As shown, in CSV, the decision to carry out excessive and unnecessary tasks/testing with documentation is the primary function, whereas critical thinking comes last. Issues and potential enhancements are identified in the last stages of the processes, resulting in a need for reworking and a waste of resources.

Current thinking with respect to GAMP® 5 Second Edition promotes a risk-based approach to ensure fitness of the system for its intended use 3 . In many instances of validation strategy, people do not apply critical thinking to ensure that the approach they are taking is customized and proportionate to the needs of the specific system they are validating: for example, when implementing the 21 CFR Part 11 requirement of segregation of duties (SOD), where roles and privileges are properly defined, configured, and followed 4 5 .
Using critical thinking (instead of having general training on the system regarding SOD), a customized/tailored approach to system training around the routine tasks of the different system user types should be followed. This will ensure that each user type is given training centered on their specific tasks and responsibilities so that SOD is clearly defined and followed.
Critical thinking is the most advantageous process for companies and manufacturers. It ensures that issues and enhancements are determined in the first stages, thereby focusing proper efforts toward assurance needs. Thus, it results in better-defined testing activities to ultimately ensure proper intended use and working functionality of the computerized system.
TRANSITIONING FROM CSV TO CSA
Organizations that want to pivot from a CSV to a CSA approach need to properly invest in activities and apply critical thinking to how software assurance will be performed and to how time and efforts will be allocated to achieve these tasks. For example, if a firm is implementing a new laboratory or manufacturing software/computerized system, the firm should apply critical thinking to assess the system and functional requirements risks as well as the intended use of the system, instead of spending significant time on excessive testing or documentation. This is because risk determination is the CSA core process.
The computerized system should be explored for what its intended use will be, what the key functions are, and what risks lie with its functionalities. Its potential impact on product quality and patient safety, historical issues, data integrity, and potential violations should also be assessed. This is necessary to properly outline the strategy of assurance and testing activities before the true efforts on documentation begin.
In addition, after the initial critical thinking phase of the process, teams should decide the key software assurance activities that must be performed to determine what needs to be tested and how testing should be documented. This will determine the amount of testing and evidence required to prove that the test function is working as intended.
The culmination of the activities previously mentioned should then be combined with a proper vendor risk management inspection program—especially for information technology service providers and technology vendors—that should include equipment and software-computerized systems.
Vendor risk management, audits, and inspection programs currently represent significant industry gaps. Performing these activ ities and having vendors’ quality systems assessed, when in good standing and documented, can potentially be further leveraged. This is especially true with commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) and software as a service (SaaS) platforms when leveraging these vendor audits/inspections to minimize out-of-the-box functionality testing or excessive service testing/verification.
The activities previously mentioned are a recommended way of pivoting from CSV to CSA in practice—and from a CSA perspective. It is equally important to shift and develop an organization’s mindset and culture to change from CSV to a CSA approach with critical thinking.
Having a proper quality system with a good foundation that establishes a vendor risk management or vendor audit program is a necessity.
The risk-based analysis for production or quality system software considers factors that may impact or prevent the software from performing as intended, such as proper system configuration and management, security of the system, data storage, data transfer, or operation error. Thus, a risk-based analysis for production or quality system software should consider which failures are reasonably foreseeable (as opposed to likely) and the risks resulting from each such failure.
Pivoting from CSV to CSA and using critical thinking can help the industry become more compliant and drive processes to be more agile while also ensuring better data integrity, product quality, and patient safety. It will also concurrently ensure that a stronger focus on validation of computerized systems will come with a more focused risk-based approach. Industry examples of CSA implementation while demonstrating new strategies with effective critical thinking can help ensure that the new paradigm will result in also using a risk-based approach to work smarter and not harder.
KEY STRATEGIES FOR CSA IMPLEMENTATION
Key strategies for effective implementation of better computerized systems with more efficient and agile processes and less work can produce more targeted efficiency with improved outcomes for product quality, patient safety, and data integrity.
As an example, COTS spreadsheet software may be composed of various functions with different intended uses. Based on FDA guidance on CSA, when using the basic input functions of the COTS spreadsheet software for the intended use of documenting the time and temperature readings for a curing process, a manufacturer may not need to perform additional assurance activities beyond those conducted by the COTS software developer and initial installation and configuration 1 .
The intended use of the software—documenting readings—only supports maintaining the quality system record and poses a low process risk. As such, initial activities such as the vendor assessment and software installation and configuration may be sufficient to establish that the software is fit for its intended use and is maintained in a validated state.
However, if a manufacturer uses built-in functions of the COTS spreadsheet to create custom formulas that are directly used in production or the quality system, then additional risks may be present. For example, if a custom formula automatically calculates time and temperature statistics to monitor the performance and suitability of the curing process, then additional validation by the manufacturer might be necessary. Therefore, having a proper quality system with a good foundation that establishes a vendor risk management or vendor audit program is a necessity.
Using the SaaS Model
The increased utilization of SaaS solutions with cloud computing combined with proper and actual vendor audits (i.e., focused to verify the current practices of the vendor and not limited to high-level verifications) and a third-party vendor risk management program produces benefits. It allows for leveraging within the CSA approach (with SaaS solutions that have a good audit history) and for a reduction of the overall scope of SaaS solution and COTS functionality validation testing.
Manufacturers are responsible for determining the appropriate assurance activities to ensure the software features, functions, or operations are in a validated state. Some possible assurance activities and considerations (such as leveraging vendor risk management programs or third-party vendor audits, e.g., in SaaS or cloud computing vendors) reduce the amount of testing while leveraging any of the aforementioned activities. This is potentially combined with historical vendor testing data, COTS functionality, and overall historical data/experience with the software or vendor.
Benefits of the SaaS model
The SaaS model of selling software has become increasingly popular over the years due to its many advantages. The SaaS model allows customers to pay for only the services they use, eliminating upfront costs associated with purchasing and maintaining physical infrastructure or exhaustively upgrading on-premise versions.
Advantages of cloud technologies
The benefits of cloud computing for pharmaceutical companies are numerous, and include faster time to market, scalability, flexibility, cost savings, better collaboration, advanced security, and data loss prevention. In addition, new instances can be implemented, or old instances can be retired in seconds, allowing developers to accelerate development with quicker deployments.
Cloud computing enables the pharmaceutical community to innovate rapidly, manage changes effortlessly, and deliver new medicines to the market faster. Cloud-based infrastructure offers secure storage for sizable and sensitive information. It also supports data security, integrity, and compliance with regulatory entities.
Key Metrics for Success
An important step to determine successful implementation and delivery of a CSA approach is to ensure proper formulation and monitoring of key metrics or key performance indicators (KPIs). Examples include:
- Return on investment: Cost savings for overall reduction in the duration needed to ensure the software is working as intended
- Writing: Significant reduction in the writing of test scripts and protocols
- Execution: Significant reduction in the execution and testing of test scripts and protocols
- Review of key deliverables: Significant reduction in the review of key deliverables
- Approval of key deliverables: Significant reduction in the approval of key deliverables
The overall benefits include a shorter duration for testing with quicker approval times and less production issues. This also potentially produces fewer issues during an audit or inspection where the system can be shown to be tested properly to ensure it is functioning correctly. Thus, it also potentially reduces risk in data integrity, product quality, and patient safety.
GAMP® 5 Second Edition provides further detailed guidance on how to apply CSA and critical thinking. The opportunities and concepts discussed in the FDA draft guidance on scope of testing and the use of the most appropriate types of testing can readily be adopted and implemented within the system life cycle approach described in GAMP® 5 Second Edition .
Critical thinking emphasizes a focus on, first, clearly thinking through a plan and then creating documentation from a process perspective. Although this critical thinking theory started with medical devices, it can apply to any pharmaceutical or biotechnology product. Instead of companies generating mountains of paperwork that “say” the product is safe, CSA can reduce the amount of testing and documentation. It offers greater efficiency, creates fewer steps, and ensures safer products, and, therefore, better patient outcomes.
Digital systems are increasingly being proliferated by industry, and manufacturers must eventually become up to date with technology. Electronic data can be more readily accessible, retrieved, analyzed, and presented with more efficiency, especially during an audit or inspection. This is another benefit of a CSA approach.
CSA, with GAMP in mind, starts with critical thinking instead of first developing the documentation; this can work for paper documents as well as computer system digital formats. The focus is on quality aspects—assurance means more focus on patient safety and data integrity, which is where the most risk lies. Documentation should then be created accordingly. Rather than focusing on paper-based exercises, which can create problems, the focus should be on thought. This means thinking through a plan, testing to minimize risks (ensuring the software and its functions are working as intended), focusing on quality, and then creating documentation from a process perspective.
However, pharmaceutical companies should be careful to consider that FDA guidance is still a draft when deciding how to apply it: It may change before the issue is in its final version. Furthermore, at this stage, it is unclear how many other different national authorities around the world will accept the CSA draft guidance. Pharmaceutical facilities that must concurrently comply with US FDA and other national authorities will need to balance to what extent they apply the CSA draft guidance. This will ensure that they do not inadvertently fail to adhere to the mix of different regulatory expectations that are applicable to their facilities.
The current draft of the FDA guidance applies to the medical device and biologics space, although the governing principles are expected to be agreed on and recommended by regulatory agencies also in the pharmaceutical space. Meanwhile, a number of regulated companies of all the previously mentioned regulated spaces have initiated the process of switching from a CSV repetitive strategy (where persons are used just to re-execute the validation approach established in the past) to a critical thinking approach. This transition should be carefully planned and deployed because it requires a substantial change in the mindset of all actors involved in the assurance activities related to a computer system.
- 4 US Food and Drug Administration. “CFR - Code of Federal Regulations Title 21, Annex 11.” March 1997. www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?CFRPart=11
- 5 US Food and Drug Administration. “Part 11, Electronic Records; Electronic Signatures - Scope and Application, Guidance for Industry.” September 2003. www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/part-11-electronic-records-electronic-signatures-scope-and-application
Not a Member Yet?
To continue reading this article and to take advantage of full access to Pharmaceutical Engineering magazine articles, technical reports, white papers and exclusive content on the latest pharmaceutical engineering news, join ISPE today. In addition to exclusive access to all of the content in Pharmaceutical Engineering magazine, you will get online access to 24 ISPE Good Practice Guides, exclusive networking events, regulatory resources, Communities of Practice, and more.
Learn more about the valuable benefits you'll receive with an ISPE membership.
Join Today Member Login
Related Articles

The FDA recommended CSA seeks to speed Computer System Validation (CSV) without sacrificing quality, but there’s a lot to know before you get started. This eBook, authored by CSV expert Darren Geaney, will give you a foundation of understanding so you can take the first step in your CSA journey with confidence.

Pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities produce a variety of products, including highly potent products that require safety measures to prevent adverse health effects on patients and operators. To ensure safety, these facilities use containment equipment to minimize the risk of contamination. This article presents criteria for selecting containment equipment, considering both...

The world is beginning to grasp the huge challenge of achieving net-zero carbon emissions, or carbon neutrality, by 2050. Many countries have committed to achieving this ambitious goal. As a major global industry, the pharmaceutical sector has a significant role to play. For thermal energy–intensive industries, such as pharmaceutical manufacturing, the long-term future options to maintain...

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Exercise #1: The Ladder of Inference. You can exercise your critical thinking skills by using the Ladder of Inference model. This thinking model was developed by renowned organizational psychologist Chris Argyris. Each rung on the ladder of inference represents a step you take to arrive at your conclusions.
It's thinking on purpose! Critical thinking involves mindful communication, problem-solving, and a freedom from bias or. About This Workbook. egocentric tendency. You can apply critical thinking to any kind of subject, problem, or situation you choose. The activity pages in the Critical Thinking Workbook are meant to be shared and explored.
Critical Thinking Exercise 1: Tour Guide for an Alien. Introduction to Critical Thinking. By Grace Fleming. Read More. This exercise provides an opportunity to think outside your normal way of thinking. Pretend that you have been assigned the task of conducting a tour for aliens who are visiting the earth and observing human life.
This arrangement will help you and your students more clearly understand and identify the specific critical-thinking skills they are using. For each thinking skill in this book, there are two kinds of activities: (1) those that you, as the teacher, will lead, and (2) student reproducibles for indepen-dent work.
First, consider the five words below: Cruise ship. Bicycle. Airplane. Walking on foot. Automobile (not a race car) Now, put them in order from the slowest to the fastest, when they are going at ...
Brain Teasers - A great way to stimulate thinking. Don't worry, they come complete with answer keys. Compare and Contrast - Students examine differences and similarities in a variety situations. Dictionary Practice Worksheets - Practice your dictionary skills. Fact And Opinion - Students determine the validity of a body of work.
TED-Ed lessons on the subject Critical Thinking. TED-Ed celebrates the ideas of teachers and students around the world. Discover hundreds of animated lessons, create customized lessons, and share your big ideas. ... Thinking & Learning Can you steal the most powerful wand in the wizarding world? Lesson duration 05:20 739,836 Views. 06:13 ...
Other Critical Thinking Activities. Jigsaw—Developing Community and Disseminating Knowledge: Learners take on the role of "experts" or "specialists" of a particular topic. Then a panel of experts is assembled to get the larger picture. K-W-L Charts—Assessing What We Know/What We Still Want to Learn: Charts to document "What I Know ...
100 Ready-to-Print Student Work Sheets Organized by Grade Level. Click on a grade level folder below to find a library of work sheets that you can use with your students to build a wide variety of critical thinking skills. All the work sheets in this library were provided to Education World by our partners at CriticalThinking.com .
Check out these critical thinking activities, adapted from Critical Thinking in the Classroom , a book with over 100 practical tools and strategies for teaching critical thinking in K-12 classrooms. Four Corners. In this activity, students move to a corner of the classroom based on their responses to a question with four answer choices. Once ...
Fact Families/Missing Addend/Open-Ended Worksheets These worksheets help students develop number sense and critical thinking. You can use the blank sheets to focus lessons on student needs. Both addition/subtraction and multiplication/division are included. Just let me know what I can do to help you use my materials.
Debates. This is one of those classic critical thinking activities that really prepares kids for the real world. Assign a topic (or let them choose one). Then give kids time to do some research to find good sources that support their point of view. Finally, let the debate begin!
Critical thinking, as described by Oxford Languages, is the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement. Active and skillful approach, evaluation, assessment, synthesis, and/or evaluation of information obtained from, or made by, observation, knowledge, reflection, acumen or conversation, as a guide to belief and action, requires the critical thinking process ...
Here are five critical thinking exercises that you can use to enhance your cognitive skills: 1. Explain the problem to someone else. Before you can solve any problem, it's vital to understand it completely. One of the best ways to test your understanding of a problem is to explain it to someone else. If you can make them understand, you're ...
1. Brain Teasers: Use age-appropriate puzzles to challenge students' cognitive abilities and encourage them to find creative solutions. 2. Socratic Circles: Divide the class into groups and encourage them to participate in a philosophical discussion on a given topic, asking questions that stimulate critical thinking and deeper understanding ...
52 Critical Thinking Flashcards for Problem Solving. Critical thinking activities encourage individuals to analyze, evaluate, and synthesize information to develop informed opinions and make reasoned decisions. Engaging in such exercises cultivates intellectual agility, fostering a deeper understanding of complex issues and honing problem-solving skills for navigating an increasingly intricate ...
ESL Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Activity - Speaking: Ranking, Guided Discussion, Guessing, Communicative Practice - Group Work - Upper-intermediate (B2) - 30 minutes. In this communicative critical thinking and problem-solving activity, students guess what criteria was used to put a list of ten jobs in order.
What is the theory behind 50 activities for developing a critical thinking skills worksheet? Critical thinking is the ability to solve problems, give logic and reasons, and think independently. It involves creativity, absorbing knowledge and ideas, interpreting information, and applying knowledge to solve problems.
Final Thoughts on Fun Critical Thinking Activities. There are lots of great critical thinking exercises you can partake in, whether you want to get a group of friends together or just sit down with a pen and a pencil. Developing these skills is a dynamic and valuable way of improving your ability to solve problems.
Nine: Memorize the Fallacies. One of the best critical thinking exercises is to learn the fallacies so well you know them when you see them or hear them in a conversation . There are at least two kinds of fallacies: Formal and informal. This list of fallacies is very thorough.
Incorporating critical thinking exercises within team building activities is essential for fostering creativity, collaboration, and problem-solving amongst employees. By engaging team members in activities that require them to consider multiple perspectives and work together to reach a conclusion, companies can significantly improve their team ...
Block wasting time and complete per of these 9 exercises for improving thought fast. 9 Critical Thinking Exercises That Actually Improve Your Mind - Teaching students to think critically (opinion) Ineffective kritiker thinking exercising are hard to find.
Web 2.0 tools such as blogs, wikis, social networking, podcasting etc. have received concentration in educational research over the last decade. Blogs enable students to reflect their learning experiences, disseminate ideas, and participate in analytical thinking. The Community of Inquiry (CoI) framework has been widely utilized in educational research to understand and enhance online and ...
Add to Calendar 2024-04-01 19:00:01 2024-04-01 20:15:00 Exploring your future: April 1 session Exploring your future is a five-session series designed for youth to explore and identify their personal aspirations for the future through interactive activities that encourage creativity, self-awareness, critical thinking, goal setting and self-discovery.Personalized for youth in grades 7-11 ...
Scratch Your Brain. Use addition and subtraction to figure out solutions to these brain benders. (Grades 3-5) From One Word to the Next. Change a letter in the previous word to make the word that completes each phrase. (Grades 3-5) Root Words. Complete this activity about words that have /capt/ or /tact/ as a root.
Current thinking with respect to GAMP® 5 Second Edition promotes a risk-based approach to ensure fitness of the system for its intended use3.In many instances of validation strategy, people do not apply critical thinking to ensure that the approach they are taking is customized and proportionate to the needs of the specific system they are validating: for example, when implementing the 21 CFR ...