- News & Resources

Job Search Tips
The higher education job market is competitive. Put your best foot forward and increase your chances of landing your next job in academe with the useful tips, advice, and job search strategies below.
Cover Letter Advice
A well-written cover letter can be equally important as an impressive resume or CV. A cover letter should accompany each resume you send and be tailored distinctly for the position to which you are applying. You should describe your abilities, skills, and experience, and illustrate them with concrete examples to show how your knowledge and expertise is relevant to the position and will benefit the employer. Let your cover letter allow the hiring manager to see a glimpse of your personality by telling a brief story of your professional experiences that can't be seen through a list of achievements on a resume. Review the samples of cover letters and relevant articles for more information.
- The Do’s of Writing a Cover Letter
- Everything That You Say/Write Will Be Used Against You
- Is Your Cover Letter Persuasive?
- Cover Letters, A New Technique
Sample Cover Letters
- Academic Advisor Position
- Senior Recruiter Position
- Analytical Chemist Position
Resume/CV Advice
A resume is more than just a list of dates, job titles, and duties. It is your time to impress. An effective resume is a clear and concise description of your professional skills, experience, and accomplishments. It summarizes your qualifications to sell your experience and potential to an employer. It should intrigue the reader to want to learn more about your personality, skills, and potential fit within their company.
A curriculum vitae (CV) is similar to a resume in that it includes your education, skills, and experience, but it also highlights research, teaching experience, publications, grants, professional associations, licenses, and/or other awards. The CV is a more detailed synopsis, commonly used in academia by faculty.
- The Next Step Resume
- Do's and Don'ts of Submitting Through an Applicant Tracking System
- Why You Must Have Three Resumes
- The Purpose and Language of Resumes
- Crafting Your First Resume
- Are You a Reacher or a Settler?
- A Resume for Employers or a Record for You?
- Toning It Down: How and When Should You Consider Understating Your Credentials?
- Academe's Resume 2.0 in the Era of Web 2.0
- Social Media in Higher Education Careers
Sample Resumes
- Traditional Style
- Professional Style
- Modern Style
Sample CVs:
- Sciences Position
- Fine Arts Position
- Fine Arts (Professional)
- Fine Arts (Modern)
Interviewing and Job Search Strategies
In addition to writing an effective cover letter and resume, there are many other "softer" yet equally important skills that are necessary to include in your job search toolkit. See below for information and advice on preparing for and succeeding in interviews, networking, effectively using social media, marketing yourself, using references, finding the right job or institutional "fit," and other key points for building an effective strategy for job search success.
Learn More About Job Search Strategies
- Career Fitness: The Social Job Application
- How to Find a Job: Five Foundations for Success
- Limber up for that Search
- Academic Job Search: A Playbook for the Internal Candidate
- Organize Your Job Search Like an Air Traffic Controller
- Stop Applying Everywhere, Start Gathering Information
- When is the Best Time for Open Positions in Higher Ed?
- How to Appropriately Use Your Network During Your Job Search
- Search Early, Search Often
- 10 Best Practices for a Higher Education Job Search
- You Can't Get a Job By Applying For It
- Six Ways to Do Your Homework on a Potential Employer
- Talented Person...Will Work for a Job
- Finding Your Niche Market
- Internet Your Way to a New Job
- Your References: An Important Part of the Job Search Process
Learn More About Interviewing
- Is It Better to Interview First or Last?
- How to Tell Your Story Without a Self-Evaluation
- Eight Interview Mistakes You Don’t Know You’re Making
- Seven Ways to Approach Panel Interviews
- Bridging Gaps in Your Qualifications
- How to "Draft" your Message for a Second Interview
- Etiquette for a Successful Interview
Need help with your resume/CV?
Have it written by HigherEdJobs' resume writing partner,
- Certified resume/CV writers
- 100% satisfaction guaranteed
- 4-6 business day turnaround
Post Your Resume to HigherEdJobs
Upload your resume/CV to our Resume Database and let employers search for you.
Search Jobs
Advanced Search

Academic Cover Letters
What is this handout about.
The long list of application materials required for many academic teaching jobs can be daunting. This handout will help you tackle one of the most important components: the cover letter or letter of interest. Here you will learn about writing and revising cover letters for academic teaching jobs in the United States of America.
What is an academic cover letter?
An academic cover letter describes your experiences and interest as a candidate for a specific position. It introduces you to the hiring committee and demonstrates how your academic background fits with the description of the position.
What do cover letters for academic teaching jobs typically contain?
At their most basic level, academic cover letters accomplish three things: one, they express your interest in the job; two, they provide a brief synopsis of your research and teaching; and three, they summarize your past experiences and achievements to illustrate your competence for the job. For early-career scholars, cover letters are typically no more than two pages (up to four pages for senior scholars). Occasionally, a third page may make sense for an early-career scholar if the application does not require a separate teaching statement and/or research statement. Digital versions of cover letters often contain hyperlinks to your CV or portfolio page. For some fields, cover letters may also include examples of your work, including music, popular articles, and other multimedia related to your research, service, or teaching available online. Typically, letters appear on departmental or university letterhead and include your signature. Above all, a strong cover letter presents your accomplishments and your familiarity with the institution and with the position.
How should I prepare to write my academic cover letter?
Like all writing, composing a cover letter is a process. The process may be as short as a few hours or as long as several weeks, but at the end the letter should present you as a strong candidate for the job. The following section has tips and questions for thinking through each stage of this writing process. You don’t need to answer all of these questions to write the letter; they are meant to help you brainstorm ideas.
Before you begin writing your cover letter, consider researching the institution, the department, and the student population. Incorporating all three aspects in your letter will help convey your interest in the position.
Get to know the institution. When crafting your cover letter, be aware of the type of institution to which you are applying. Knowing how the institution presents itself can help you tailor your letter and make it more specific.
- Where is the institution located?
- Is it on a quarter-system or semester-system?
- What type of institution is it? Is it an R1? Is it an R2? Is it a liberal arts college? Is it an HBCU? Is it a community college? A private high school?
- What is the institution’s culture? Is it teaching-focused or research-focused? Does it privilege experiential learning? Does it value faculty involvement outside the classroom? Is it affiliated with a specific religious tradition?
- Does it have any specific institutional commitments?
- How does the institution advocate for involvement in its local community?
- What are the professional development opportunities for new and junior faculty?
Learn about the department. Knowing the specific culture and needs of the department can help you reach your audience: the department members who will be reading your documents and vetting you as a candidate.
- Who is on the search committee? Who is the search committee chair?
- What is the official name of the department?
- Which different subfields make up the department?
- Is it a dual appointment or a position in a dual department?
- How does the department participate in specific types of student outreach?
- Does the department have graduate students? Does it offer a terminal Master’s degree, Ph.D., or both? How large are the cohorts? How are they funded?
- Does the department encourage or engage in interdisciplinary work?
- Does the majority of the department favor certain theoretical or methodological approaches?
- Does the department have partnerships with local institutions? If so, which ones?
- Is the department attempting to fill a specific vacancy, or is it an entirely new position?
- What are the typical course offerings in the department? Which courses might you be expected to teach? What courses might you be able to provide that are not currently available?
Consider the students. The search committee will often consider how you approach instructing and mentoring the student body. Sometimes committees will even reserve a position for a student or solicit student feedback on a candidate:
- What populations constitute the majority of the undergraduate population?
- Have there been any shifts in the student population recently?
- Do students largely come from in-state or out-of-state?
- Is there an international student population? If so, from which countries?
- Is the university recruiting students from traditionally underrepresented populations?
- Are students particularly active on campus? If so, how?
Many answers to these questions can be found both in the job description and on the institution’s website. If possible, consider contacting someone you know at the institution to ask about the culture directly. You can also use the institution’s course catalog, recruitment materials, alumni magazine, and other materials to get answers to these questions. The key is to understand the sort of institution to which you are applying, its immediate needs, and its future trajectory.
Remember, there is a resource that can help you with all three aspects—people. Reach out to your advisor, committee members, faculty mentors, and other contacts for insight into the prospective department’s culture and faculty. They might even help you revise your letter based on their expertise. Think of your job search as an opportunity to cultivate these relationships.
After you have done some initial research, think about how your experiences have prepared you for the job and identify the ones that seem the most relevant. Consider your previous research, internships, graduate teaching, and summer experiences. Here are some topics and questions to get you started thinking about what you might include.
Research Experiences. Consider how your research has prepared you for an academic career. Since the letter is a relatively short document, select examples of your research that really highlight who you are as a scholar, the direction you see your work going, and how your scholarship will contribute to the institution’s research community.
- What are your current research interests?
- What topics would you like to examine in the future?
- How have you pursued those research interests?
- Have you traveled for your research?
- Have you published any of your research? Have you presented it at a conference, symposium, or elsewhere?
- Have you worked or collaborated with scholars at different institutions on projects? If so, what did these collaborations produce?
- Have you made your research accessible to your local community?
- Have you received funding or merit-based fellowships for your research?
- What other research contributions have you made? This may include opinion articles, book chapters, or participating as a journal reviewer.
- How do your research interests relate to those of other faculty in the department or fill a gap?
Teaching Experience. Think about any teaching experience you may have. Perhaps you led recitations as a teaching assistant, taught your own course, or guest lectured. Pick a few experiences to discuss in your letter that demonstrate something about your teaching style or your interest in teaching.
- What courses are you interested in teaching for the department? What courses have you taught that discussed similar topics or themes?
- What new courses can you imagine offering the department that align with their aim and mission?
- Have you used specific strategies that were helpful in your instruction?
- What sort of resources do you typically use in the classroom?
- Do you have anecdotes that demonstrate your teaching style?
- What is your teaching philosophy?
- When have you successfully navigated a difficult concept or topic in the classroom, and what did you learn?
- What other opportunities could you provide to students?
Internships/Summer/Other Experiences. Brainstorm a list of any conferences, colloquiums, and workshops you have attended, as well as any ways you have served your department, university, or local community. This section will highlight how you participate in your university and scholarly community. Here are some examples of things you might discuss:
- Professional development opportunities you may have pursued over the summer or during your studies
- International travel for research or presentations
- Any research you’ve done in a non-academic setting
- Presentations at conferences
- Participation in symposia, reading groups, working groups, etc.
- Internships in which you may have implemented your research or practical skills related to your discipline
- Participation in community engagement projects
- Participation in or leadership of any scholarly and/or university organizations
In answering these questions, create a list of the experiences that you think best reflect you as a scholar and teacher. In choosing which experiences to highlight, consider your audience and what they would find valuable or relevant. Taking the time to really think about your reader will help you present yourself as an applicant well-qualified for the position.
Writing a draft
Remember that the job letter is an opportunity to introduce yourself and your accomplishments and to communicate why you would be a good fit for the position. Typically, search committees will want to know whether you are a capable job candidate, familiar with the institution, and a great future addition to the department’s faculty. As such, be aware of how the letter’s structure and content reflect your preparedness for the position.
The structure of your cover letter should reflect the typical standards for letter writing in the country in which the position is located (the list below reflects the standards for US letter writing). This usually includes a salutation, body, and closing, as well as proper contact information. If you are affiliated with a department, institution, or organization, the letter should be on letterhead.
- Use a simple, readable font in a standard size, such as 10-12pt. Some examples of fonts that may be conventional in your field include Arial, Garamond, Times New Roman, and Verdana, among other similar fonts.
- Do not indent paragraphs.
- Separate all paragraphs by a line and justify them to the left.
- Make sure that any included hyperlinks work.
- Include your signature in the closing.
Before you send in your letter, make sure you proofread and look for formatting mistakes. You’ll read more about proofreading and revising later in this handout!
The second most important aspect of your letter is its content. Since the letter is the first chance to provide an in-depth introduction, it should expand on who you are as a scholar and possible faculty member. Below are some elements to consider including when composing your letter.
Identify the position you are applying to and introduce yourself. Traditionally, the first sentence of a job letter includes the full name of the position and where you discovered the job posting. This is also the place to introduce yourself and describe why you are applying for this position. Since the goal of a job letter is to persuade the search committee to include you on the list of candidates for further review, you may want to include an initial claim as to why you are a strong candidate for the position. Some questions you might consider:
- What is your current status (ABD, assistant professor, post-doc, etc.)?
- If you are ABD, have you defended your dissertation? If not, when will you defend?
- Why are you interested in this position?
- Why are you a strong candidate for this position?
Describe your research experience and interests. For research-centered positions, such as positions at R1 or other types of research-centered universities, include information about your research experience and current work early in the letter. For many applicants, current work will be the dissertation project. If this is the case, some suggest calling your “dissertation research” your “current project” or “work,” as this may help you present yourself as an emerging scholar rather than a graduate student. Some questions about your research that you might consider:
- What research experiences have you had?
- What does your current project investigate?
- What are some of the important methods you applied?
- Have you collaborated with others in your research?
- Have you acquired specific skills that will be useful for the future?
- Have you received special funding? If so, what kind?
- Has your research received any accolades or rewards?
- What does your current project contribute to the field?
- Where have you presented your research?
- Have you published your research? If so, where? Or are you working on publishing your work?
- How does your current project fit the job description?
Present your plans for future research. This section presents your research agenda and usually includes a description of your plans for future projects and research publications. Detailing your future research demonstrates to the search committee that you’ve thought about a research trajectory and can work independently. If you are applying to a teaching-intensive position, you may want to minimize this section and/or consider including a sentence or two on how this research connects to undergraduate and/or graduate research opportunities. Some questions to get you started:
- What is your next research project/s?
- How does this connect to your current and past work?
- What major theories/methods will you use?
- How will this project contribute to the field?
- Where do you see your specialty area or subfield going in the next ten years and how does your research contribute to or reflect this?
- Will you be collaborating with anyone? If so, with whom?
- How will this future project encourage academic discourse?
- Do you already have funding? If so, from whom? If not, what plans do you have for obtaining funding?
- How does your future research expand upon the department’s strengths while simultaneously diversifying the university’s research portfolio? (For example, does your future research involve emerging research fields, state-of-the-art technologies, or novel applications?)
Describe your teaching experience and highlight teaching strategies. This section allows you to describe your teaching philosophy and how you apply this philosophy in your classroom. Start by briefly addressing your teaching goals and values. Here, you can provide specific examples of your teaching methods by describing activities and projects you assign students. Try to link your teaching and research together. For example, if you research the rise of feminism in the 19th century, consider how you bring either the methodology or the content of your research into the classroom. For a teaching-centered institution, such as a small liberal arts college or community college, you may want to emphasize your teaching more than your research. If you do not have any teaching experience, you could describe a training, mentoring, or coaching situation that was similar to teaching and how you would apply what you learned in a classroom.
- What is your teaching philosophy? How is your philosophy a good fit for the department in which you are applying to work?
- What sort of teaching strategies do you use in the classroom?
- What is your teaching style? Do you lecture? Do you emphasize discussion? Do you use specific forms of interactive learning?
- What courses have you taught?
- What departmental courses are you prepared to teach?
- Will you be able to fill in any gaps in the departmental course offerings?
- What important teaching and/or mentoring experiences have you had?
- How would you describe yourself in the classroom?
- What type of feedback have you gotten from students?
- Have you received any awards or recognition for your teaching?
Talk about your service work. Service is often an important component of an academic job description. This can include things like serving on committees or funding panels, providing reviews, and doing community outreach. The cover letter gives you an opportunity to explain how you have involved yourself in university life outside the classroom. For instance, you could include descriptions of volunteer work, participation in initiatives, or your role in professional organizations. This section should demonstrate ways in which you have served your department, university, and/or scholarly community. Here are some additional examples you could discuss:
- Participating in graduate student or junior faculty governance
- Sitting on committees, departmental or university-wide
- Partnerships with other university offices or departments
- Participating in community-partnerships
- Participating in public scholarship initiatives
- Founding or participating in any university initiatives or programs
- Creating extra-curricular resources or presentations
Present yourself as a future faculty member. This section demonstrates who you will be as a colleague. It gives you the opportunity to explain how you will collaborate with faculty members with similar interests; take part in departmental and/or institution wide initiatives or centers; and participate in departmental service. This shows your familiarity with the role of faculty outside the classroom and your ability to add to the departmental and/or institutional strengths or fill in any gaps.
- What excites you about this job?
- What faculty would you like to collaborate with and why? (This answer may be slightly tricky. See the section on name dropping below.)
- Are there any partnerships in the university or outside of it that you wish to participate in?
- Are there any centers associated with the university or in the community that you want to be involved in?
- Are there faculty initiatives that you are passionate about?
- Do you have experience collaborating across various departments or within your own department?
- In what areas will you be able to contribute?
- Why would you make an excellent addition to the faculty at this institution?
Compose a strong closing. This short section should acknowledge that you have sent in all other application documents and include a brief thank you for the reader’s time and/or consideration. It should also state your willingness to forward additional materials and indicate what you would like to see as next steps (e.g., a statement that you look forward to speaking with the search committee). End with a professional closing such as “Sincerely” or “Kind Regards” followed by your full name.
If you are finding it difficult to write the different sections of your cover letter, consider composing the other academic job application documents (the research statement, teaching philosophy, and diversity statement) first and then summarizing them in your job letter.
Different kinds of letters may be required for different types of jobs. For example, some jobs may focus on research. In this case, emphasize your research experiences and current project/s. Other jobs may be more focused on teaching. In this case, highlight your teaching background and skills. Below are two models for how you could change your letter’s organization based on the job description and the institution. The models offer a guide for you to consider how changing the order of information and the amount of space dedicated to a particular topic changes the emphasis of the letter.
Research-Based Position Job Letter Example:
| Date: Month Day, Year Search Committee Chair’s First and Last Name, Graduate Degree Dear Dr./Mr./Ms. Search Committee Chair’s last name and/or Search Committee Members: Paragraph 1 [3-5 Sentences]: Identify the position you are applying for. Introduce yourself to the committee and your research interests. Connect your interests to the department and describe what makes you interested in becoming part of this departmental community. Paragraph 2 [3-5 Sentences]: Briefly explain your research to date. Consider mentioning your research questions, methods, key findings, as well as where and when you published and/or presented this work. Paragraph 3 [4-5 Sentences]: Elaborate on your current research project. Consider mentioning your most prestigious funding awards for this project. Explain your key findings in more detail. Paragraph 4 [3-5 Sentences]: Introduce your future research plans and goals. Point out the intellectual merit and/or broader impacts of this future work. Paragraph 5 [3-5 Sentences]: Briefly discuss your teaching experience and strategies. Provide examples of teaching strategies or an anecdote highlighting your teaching effectiveness. You may also want to introduce your philosophy on diversity in an academic setting. Paragraph 6 [2-3 Sentences]: Make a connection between your work and the department to which you are applying. Include how you will participate in the intellectual life of the department both inside and outside the classroom. Provide concrete examples of how you will be a hard-working and collaborative colleague. Paragraph 7 [1-2 Sentences]: A thank you for the search committee’s time and consideration. Sincerely, Your Name |
Teaching-Based Position Job Letter Example:
| Date: Month Day, Year Search Committee Chair’s First and Last Name, Graduate Degree Dear Dr./Mr./Ms. Search Committee Chair’s last name and/or Search Committee Members: Paragraph 1 [3-5 Sentences]: Identify the position you are applying for. Introduce yourself to the committee and your research interests. Connect your interests to the department and describe what makes you interested in becoming part of this departmental community. Paragraph 2 [3-5 Sentences]: Briefly discuss your teaching experience and pedagogical commitments. Provide examples of teaching strategies or an anecdote highlighting your teaching effectiveness. You may also want to introduce your philosophy on diversity in an academic setting. Paragraph 3 [3-4 Sentences]: Provide a discussion of how you involved yourself with students or the broader university community outside of the traditional classroom setting. Discuss how those interactions influenced your teaching. Paragraph 4 [2-3 Sentences]: Briefly explain your current research interests to date and how it relates to your teaching. State your research questions, methods, and key findings or arguments. Point out the intellectual merit and/or broader impacts of this future work. Paragraph 5 [3-5 Sentences]: Highlight when and where your research was published and/or presented this work or any forthcoming publications. Mention any prestigious funding or awards. Introduce your future research plans and goals. Paragraph 6 [2-3 Sentences]: Make a connection between your work and the department to which you are applying. Include how you will participate in the intellectual life of the department both inside and outside the classroom. Provide concrete examples of how you will be a hard-working and collaborative colleague. Paragraph 7 [1-2 Sentences]: A thank you for the search committee’s time and consideration. Sincerely, Your Name |
Remember your first draft does not have to be your last. Try to get feedback from different readers, especially if it is one of your first applications. It is not uncommon to go through several stages of revisions. Check out the Writing Center’s handout on editing and proofreading and video on proofreading to help with this last stage of writing.
Potential pitfalls
Using the word dissertation. Some search committee members may see the word “dissertation” as a red flag that an applicant is too focused on their role as a graduate student rather than as a prospective faculty member. It may be advantageous, then, to describe your dissertation as current research, a current research project, current work, or some other phrase that demonstrates you are aware that your dissertation is the beginning of a larger scholarly career.
Too much jargon. While you may be writing to a specific department, people on the search committee might be unfamiliar with the details of your subfield. In fact, many committees have at least one member from outside their department. Use terminology that can easily be understood by non-experts. If you want to use a specific term that is crucial to your research, then you should define it. Aim for clarity for your reader, which may mean simplification in lieu of complete precision.
Overselling yourself. While your job letter should sell you as a great candidate, saying so (e.g., “I’m the ideal candidate”) in your letter may come off to some search committee members as presumptuous. Remember that although you have an idea about the type of colleague a department is searching for, ultimately you do not know exactly what they want. Try to avoid phrases or sentences where you state you are the ideal or the only candidate right for the position.
Paying too much attention to the job description. Job descriptions are the result of a lot of debate and compromise. If you have skills or research interests outside the job description, consider including them in your letter. It may be that your extra research interests; your outside skills; and/or your extracurricular involvements make you an attractive candidate. For example, if you are a Latin Americanist who also happens to be well-versed in the Spanish Revolution, it could be worth mentioning the expanse of your research interests because a department might find you could fill in other gaps in the curriculum or add an additional or complementary perspective to the department.
Improper sendoff. The closing of your letter is just as important as the beginning. The end of the letter should reflect the professionalism of the document. There should be a thank-you and the word sincerely or a formal equivalent. Remember, it is the very last place in your letter where you present yourself as a capable future colleague.
Small oversights. Make sure to proofread your letter not just for grammar but also for content. For example, if you use material from another letter, make sure you do not include the names of another school, department, or unassociated faculty! Or, if the school is in Chicago, make sure you do not accidentally reference it as located in the Twin Cities.
Name dropping. You rarely know the internal politics of the department or institution to which you are applying. So be cautious about the names you insert in your cover letters. You do not want to unintentionally insert yourself into a departmental squabble or add fire to an interdepartmental conflict. Instead, focus on the actions you will undertake and the initiatives you are passionate about.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Ball, Cheryl E. 2013. “Understanding Cover Letters.” Inside Higher Ed , November 3, 2013. https://www.insidehighered.com/advice/2013/11/04/essay-cover-letter-academic-jobs .
Borchardt, John. 2014. “Writing a Winning Cover Letter.” Science Magazine , August 6, 2014. https://www.sciencemag.org/careers/2014/08/writing-winning-cover-letter# .
Helmreich, William. 2013. “Your First Academic Job.” Inside Higher Ed , June 17, 2013. https://www.insidehighered.com/advice/2013/06/17/essay-how-land-first-academic-job .
Kelsky, Karen. 2013. “How To Write a Journal Article Submission Cover Letter.” The Professor Is In (blog), April 26, 2013. https://theprofessorisin.com/2013/04/26/how-to-write-a-journal-article-submission-cover-letter/ .
Tomaska, Lubomir, and Josef Nosek. 2008. “Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Cover Letter to Accompany a Job Application for an Academic Position.” PLoS Computational Biology 14(5). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006132 .
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Sample Cover Letters for Higher Education Communications
- Cover Letters
- Skills & Keywords
- Salary & Benefits
- Letters & Emails
- Job Listings
- Job Interviews
- Career Advice
- Work-From-Home Jobs
- Internships
- What to Include in Your Cover Letter
- Tips for Writing a Cover Letter
Cover Letter Template
Cover letter examples.
Customizing your cover letter is a highly important part of an effective job application. By customizing your cover letter, you'll provide employers with all the reasons to hire you.
The end result is far more persuasive than a cookie-cutter cover letter where all you do is swap out the company name and hiring managers. When you take the time to create a customized letter, it shows—and it can lead to good results.
If you're looking for jobs in higher education communications, take a look at some advice on what to include in your letter and tips for writing it. Plus, you can review an example of a cover letter targeted for a job in the higher education industry , in the field of communications.
What to Include in Your Cover Letter
In every cover letter, regardless of industry, there are certain elements that must be included, such as:
- A salutation: Start off your letter with an appropriate greeting. Do your best to find out the name of the hiring manager, and address the letter to this person.
- Why you're writing: Traditionally, the opening paragraph of the letter will share why you're writing and where you saw the job listing. If someone referred you, mention it here!
- Your qualifications : This is the heart of a cover letter. You want to explain your work history and qualifications. But don't simply duplicate your resume. The goal is to call out elements that will be of particular interest for this specific role.
- End the letter appropriately: Include an appropriate sign-off and signature.
You'll need to format your cover letter slightly differently if it's an email, but most elements remain precisely the same.
Tips for Writing a Cover Letter
Do some research: Before you jump into writing your cover letter, you'll want to do some research. Knowing the higher education institute's values and goals will help you know which points to emphasize. Even small things, like the size of the college or university, make a difference. The communication needs of a small-town college are different than those of a world-renowned research institution.
Match your skills to the job description: You should also take a very close look at the job description in the job ad, and match it to your credentials. Pay attention to the responsibilities and skills that are called for. Then, think through your own work history, looking for examples of times when you've used these skills or done similar tasks. For example, if the job description is looking for a strong writer, you can mention that in your last role, you wrote five press releases a month, and were able to garner coverage based on 70% of the press releases that were distributed.
Call out accomplishments: In your cover letter, highlight any major achievements you've made in previous roles. This is more powerful than simply listing the day-to-day tasks you've performed in the past.
This is an example of a cover letter for a higher education position . Download the higher education cover letter template (compatible with Google Docs and Word Online) or see below for more examples.
Cover Letter Example - Higher Education / Communications (Text Version)
Alexandria Applicant 123 Main Street Anytown, CA 12345 555-555-5555 alexandria.applicant@email.com
February 15, 2021
Jon Lee Director, Human Resources University of North Florida 123 Business Rd. Business City, NY 54321
Dear Mr. Lee,
As an experienced communications professional, I'm very interested in the position of Associate Vice President of University Campaign Communications at the University of North Florida.
I have a proven track record in a majority of the competencies you're seeking, especially in strategically communicating institutional priorities. I believe I would be the ideal candidate for this role, as my experience and my skills align with the role outlined in the job description.
Here are a few highlights of my candidacy:
- Twelve years. experience developing and implementing internal and external communications for ABCD Energy/Electric and ABCD Corporation.
- Handling a wide range of creative services, collaborating with and supervising creative services staff and vendors to produce marketing and other print communications, as well as online communications and video projects.
- Exceptional writing and editing skills honed over the past 13 years in public relations and corporate communications; from press releases to newsletters to video scripts to websites and intranet publications.
- Providing communications counsel and expertise to executives and managers for issues management, benefits communications, and employee relations.
As a recent transplant to Miami, I still own a home in Tampa and would love to put my skills to work back in Tampa.
Please let me know if I can answer any questions or provide any work samples.
Signature (hard copy letter)
Alexandria Applicant
Cover Letter for a College Communications Position
Thomas Applicant 123 Main Street Anytown, CA 12345 555-555-5555 thomas.applicant@email.com
September 15, 2021
Anthony Lau Director, Human Resources Acme College 123 Business Rd. Business City, NY 54321
Dear Mr. Lau,
I am writing to indicate my interest in the position of Assistant Director of Campaign Communications. I'm a passionate supporter of our current campaign, and a fully-engaged member of the College community.
For many years, I've had a long and happy affiliation with this College, as an employee, parent (Marie 'XX), student, and Alumni Board member. My current position as Administrative Coordinator in the English Department has allowed close collaboration with my Chair, student majors, and 40-plus faculty, as well as many different offices and departments. It's been a joy to work in the English Department, though, and I'm eager to use my talents in greater contribution to the College.
The position of Director of Campaign Communications provides a wonderful opportunity for the College to engage one of its most enthusiastic community members in promotion of its important message. It is a position where my interpersonal and organizational skills, and experience with so many college constituencies, could be put to very productive and successful use.
Speaking to position qualifications, concentrations in literature and writing in both my undergraduate and graduate programs here have allowed me to become a skilled writer. I look forward to incorporating the technologies I've used in the past, and I am very excited to work with new systems. Organization is vital when balancing multiple projects and demands, and the ability to organize well has made my experience in the English Department much more rewarding.
Perhaps the greatest asset I offer is the ability to work with many personalities and groups of people, and I realize just how valuable that is when working with College constituencies, on committees, and in my work with our Alumni Board.
I can think of no better way to honor the riches of my education and work history than sharing the important message of this campaign. I appreciate your considering my application. Please review the attached resume. I look forward to hearing from you.
Thomas Applicant
Cover Letter Example - Director of Communications
Timothy Applicant 123 Main Street Anytown, CA 12345 555-555-5555 timothy.applicant@email.com
Julia Rodriguez Director, Human Resources American Organization 123 Business Rd. Business City, NY 54321
Dear Mrs. Rodriguez,
As an experienced communications professional, I'm very interested in the American Organization's Director of Communications position.
I have a proven track record in almost all of the competencies you're seeking. Here are a few highlights:
- Handled a wide range of creative services, collaborating with creative services peers, subordinates and vendors to produce marketing and other print communications, as well online communications and video projects.
- Exceptional writing and editing skills honed over the past 13 years in public relations and corporate communications; from press releases to newsletters to video scripts to websites and yes, guest columns.
- Developing and implementing communications strategies for reaching employees and other stakeholders.
In my current role at Company A, I've worked closely with nonprofits while administering our corporate marine conservation donation program. This is the most rewarding part of my job, helping connect worthy organizations with funding.
I will call in one week to follow-up and find out if I can answer any questions or provide any work samples.
Timothy Applicant
- Cover Letter Samples for Teachers
- Teacher Cover Letter Example and Writing Tips
- Write Interview Winning Resumes and Cover Letters
- Athletic Director Cover Letter and Resume Examples
- Sample Cover Letter for a Job in the Arts
- Programmer Analyst Cover Letter Example and Writing Tips
- Special Education Cover Letter: Example and Writing Tips
- Speech Pathologist Resume and Cover Letter Examples
- Sample Job Cover Letter for a College Summer Assistant Job
- Summer Sales Associate Cover Letter Example
- Sample Cover Letter for an Entry-Level Position
- Cover Letter Examples for Sales and Marketing Jobs
- Sample Cover Letter for a School Position
- Web Content Cover Letter Example
- Sample Cover Letter for a Summer Camp Job or RA Position
- Customer Service Cover Letter Samples and Writing Tips
Tips for Writing an Effective Application Essay
Find the right college for you.
Writing an essay for college admission gives you a chance to use your authentic voice and show your personality. It's an excellent opportunity to personalize your application beyond your academic credentials, and a well-written essay can have a positive influence come decision time.
Want to know how to draft an essay for your college application ? Here are some tips to keep in mind when writing.
Tips for Essay Writing
A typical college application essay, also known as a personal statement, is 400-600 words. Although that may seem short, writing about yourself can be challenging. It's not something you want to rush or put off at the last moment. Think of it as a critical piece of the application process. Follow these tips to write an impactful essay that can work in your favor.
1. Start Early.
Few people write well under pressure. Try to complete your first draft a few weeks before you have to turn it in. Many advisers recommend starting as early as the summer before your senior year in high school. That way, you have ample time to think about the prompt and craft the best personal statement possible.
You don't have to work on your essay every day, but you'll want to give yourself time to revise and edit. You may discover that you want to change your topic or think of a better way to frame it. Either way, the sooner you start, the better.
2. Understand the Prompt and Instructions.
Before you begin the writing process, take time to understand what the college wants from you. The worst thing you can do is skim through the instructions and submit a piece that doesn't even fit the bare minimum requirements or address the essay topic. Look at the prompt, consider the required word count, and note any unique details each school wants.
3. Create a Strong Opener.
Students seeking help for their application essays often have trouble getting things started. It's a challenging writing process. Finding the right words to start can be the hardest part.
Spending more time working on your opener is always a good idea. The opening sentence sets the stage for the rest of your piece. The introductory paragraph is what piques the interest of the reader, and it can immediately set your essay apart from the others.
4. Stay on Topic.
One of the most important things to remember is to keep to the essay topic. If you're applying to 10 or more colleges, it's easy to veer off course with so many application essays.
A common mistake many students make is trying to fit previously written essays into the mold of another college's requirements. This seems like a time-saving way to avoid writing new pieces entirely, but it often backfires. The result is usually a final piece that's generic, unfocused, or confusing. Always write a new essay for every application, no matter how long it takes.
5. Think About Your Response.
Don't try to guess what the admissions officials want to read. Your essay will be easier to write─and more exciting to read─if you’re genuinely enthusiastic about your subject. Here’s an example: If all your friends are writing application essays about covid-19, it may be a good idea to avoid that topic, unless during the pandemic you had a vivid, life-changing experience you're burning to share. Whatever topic you choose, avoid canned responses. Be creative.
6. Focus on You.
Essay prompts typically give you plenty of latitude, but panel members expect you to focus on a subject that is personal (although not overly intimate) and particular to you. Admissions counselors say the best essays help them learn something about the candidate that they would never know from reading the rest of the application.
7. Stay True to Your Voice.
Use your usual vocabulary. Avoid fancy language you wouldn't use in real life. Imagine yourself reading this essay aloud to a classroom full of people who have never met you. Keep a confident tone. Be wary of words and phrases that undercut that tone.
8. Be Specific and Factual.
Capitalize on real-life experiences. Your essay may give you the time and space to explain why a particular achievement meant so much to you. But resist the urge to exaggerate and embellish. Admissions counselors read thousands of essays each year. They can easily spot a fake.
9. Edit and Proofread.
When you finish the final draft, run it through the spell checker on your computer. Then don’t read your essay for a few days. You'll be more apt to spot typos and awkward grammar when you reread it. After that, ask a teacher, parent, or college student (preferably an English or communications major) to give it a quick read. While you're at it, double-check your word count.
Writing essays for college admission can be daunting, but it doesn't have to be. A well-crafted essay could be the deciding factor─in your favor. Keep these tips in mind, and you'll have no problem creating memorable pieces for every application.
What is the format of a college application essay?
Generally, essays for college admission follow a simple format that includes an opening paragraph, a lengthier body section, and a closing paragraph. You don't need to include a title, which will only take up extra space. Keep in mind that the exact format can vary from one college application to the next. Read the instructions and prompt for more guidance.
Most online applications will include a text box for your essay. If you're attaching it as a document, however, be sure to use a standard, 12-point font and use 1.5-spaced or double-spaced lines, unless the application specifies different font and spacing.
How do you start an essay?
The goal here is to use an attention grabber. Think of it as a way to reel the reader in and interest an admissions officer in what you have to say. There's no trick on how to start a college application essay. The best way you can approach this task is to flex your creative muscles and think outside the box.
You can start with openers such as relevant quotes, exciting anecdotes, or questions. Either way, the first sentence should be unique and intrigue the reader.
What should an essay include?
Every application essay you write should include details about yourself and past experiences. It's another opportunity to make yourself look like a fantastic applicant. Leverage your experiences. Tell a riveting story that fulfills the prompt.
What shouldn’t be included in an essay?
When writing a college application essay, it's usually best to avoid overly personal details and controversial topics. Although these topics might make for an intriguing essay, they can be tricky to express well. If you’re unsure if a topic is appropriate for your essay, check with your school counselor. An essay for college admission shouldn't include a list of achievements or academic accolades either. Your essay isn’t meant to be a rehashing of information the admissions panel can find elsewhere in your application.
How can you make your essay personal and interesting?
The best way to make your essay interesting is to write about something genuinely important to you. That could be an experience that changed your life or a valuable lesson that had an enormous impact on you. Whatever the case, speak from the heart, and be honest.
Is it OK to discuss mental health in an essay?
Mental health struggles can create challenges you must overcome during your education and could be an opportunity for you to show how you’ve handled challenges and overcome obstacles. If you’re considering writing your essay for college admission on this topic, consider talking to your school counselor or with an English teacher on how to frame the essay.
Related Articles
Related topics.

University Admission Application Letter (with Samples & PDFs)
I have listed sample templates to help you craft an effective and professional university admission application letter.
Also, I would like to point out that you can also download a PDF containing all the samples at the end of this post.
Successful Application Letter for University Admission
First, find the sample template for university admission application letter below.
To, The Admissions Committee, [Name of the University], [Address of the University], [City], [State], [Postal Code]
Subject: Application for Admission to [Name of the Course]
Respected Sir/Madam,
I, [Your Full Name], resident of [Your Address], am writing this letter to show my keen interest in applying for the [Name of the Course] at your esteemed university for the academic year [Year].
I have recently completed my [last educational qualification] from [Name of School/College] with an aggregate of [Your Percentage/CGPA], and I am eager to further my studies in the field of [Field of Study]. I believe that studying at [Name of the University] will provide me the right knowledge, skills, and exposure to excel in this field.
I am particularly drawn to the [Name of the Course] at [Name of the University] because of its reputation for providing high-quality education and its focus on practical learning. I am confident that this course will help me achieve my academic and career goals.
Enclosed with this letter are my mark sheets, certificates, and other required documents. I kindly request you to consider my application and provide me with an opportunity to prove my potential and contribute to the university.
I am looking forward to being a part of your esteemed institution and assure you that I will put in my best efforts in all my endeavours.
Thank you for considering my application. I am eager to hear from you soon.
[Your Full Name] [Your Contact Information] [Your Email Address]
Below I have listed 5 different sample applications for “university admission application letter” that you will certainly find useful for specific scenarios:
Crafting a Persuasive University Application Letter to Showcase Leadership Skills

Subject: Application for Admission to [Desired Course Name]
I have consistently excelled in my studies, but more importantly, I have taken the initiative to lead and guide my peers through various activities. As the Head Boy/Girl of my school, I’ve learned to inspire and motivate my fellow students, organize events, and address issues efficiently. These experiences have honed my leadership abilities and have taught me how to balance my academic commitments with extracurricular responsibilities.
I played a pivotal role in initiating a ‘Clean Campus Drive’ in my school, where I led a team of students to maintain cleanliness and fostered a sense of responsibility among them. This initiative not only improved the school environment but also instilled a sense of community and teamwork among the students.
If given the opportunity to join [University Name], I assure you that I will bring these leadership qualities to contribute positively to the university community. I am eager to leverage my experiences to participate actively in student-led initiatives and further develop my leadership skills.
I am confident that [University Name] is the perfect platform for me to grow not just acadically but also as a leader. I humbly request you to consider my application favorably. I look forward to the opportunity to be a part of your esteemed institution.
Yours Sincerely, [Your Full Name], [Your Contact Information].
Writing a Compelling University Application Letter Highlighting Athletic Achievements

Subject: Application for Admission and Highlighting Athletic Achievements
I hope this letter finds you in the best of health and spirits. I am [Your Name], a student from [Your School Name], [Your City], intending to apply for the [Course Name] at your esteemed university.
Academically, I have consistently performed well, securing a GPA of [Your GPA] in the previous year. However, I am not just a diligent student in the classroom, but also a passionate sportsperson. I believe my athletic achievements will contribute to the vibrant sports culture at your university.
My commitment to sports has not only honed my physical abilities but has also helped me develop leadership skills, team spirit, and resilience. I believe that these qualities will not only aid me in my academic pursuit but also contribute to the overall diversity and vitality of your university’s student community.
I am enthusiastic about bringing the same dedication and spirit to your esteemed university and contributing to its athletic teams. I am certain that the comprehensive education and diverse opportunities provided by your university will help me grow, both acadically and athletically.
I am hopeful that you will consider my application favourably. Thank you for considering my application. I am looking forward to the possibility of becoming a part of your prestigious university.

Articulating Academic Excellence in a University Admission Application Letter

The Dean of Admissions, [University Name], [University Address], [City], [State], [Pin Code]
Subject: Application for Admission
I have always been passionate about [subject(s) related to the course], and I am confident that my academic achievements reflect this. I have consistently maintained a high academic standing in my schooling years, ranking in the top [percentage/rank] of my class. My teachers have commended me for my dedication and commitment to learning, which is evident from my grades and participation in various academic competitions.
Moreover, I have been an active participant in various extracurricular activities that have helped me develop a holistic understanding of the world. I have led [mention some leadership roles], worked on [mention any projects or initiatives], and engaged in [mention any community service or volunteer work]. These experiences have taught me the importance of teamwork, leadership, and responsibility, and have fuelled my desire to further my learning.
Your institution, with its exemplary faculty and state-of-the-art facilities, stands as the ideal platform for me to deepen my knowledge and broaden my horizon. I am particularly drawn to the [mention specific aspects of the course or university that attract you], and I am confident that these will provide the right environment to nurture my academic and personal growth.
I am committed to maintaining my academic excellence and contributing positively to the university community. I am hopeful that I will be given the opportunity to bring my passion, dedication, and academic prowess to your esteemed institution.
Thank you for considering my application. I look forward to the possibility of contributing to and learning from the [University Name] community.
Yours Sincerely, [Your Name] [Your Address] [City, State, Pin Code] [Email Address] [Phone Number]
Tailoring a University Application Letter to Highlight Community Service Experiences

Dear Sir/Madam,
I hope this letter finds you in good health. I am [Your Name], a student of [Your School Name], seeking admission to your esteemed university for the upcoming academic year.
I am writing this letter to express my keen interest in the [Course Name] program at your prestigious institution. I have always been intrigued by [Subject Name], and I am eager to explore this field under the guidance of the accomplished faculty at [University Name].
In addition, I volunteered in the ‘Joy of Giving’ initiative, aimed at providing essential supplies to underprivileged children. This experience truly humbled me and made me realize the value of giving back to society. I believe these experiences have shaped me as an individual and have taught me the importance of empathy, teamwork, and leadership.
I am certain that these experiences will enable me to contribute to the diverse community at [University Name]. I am eager to bring my commitment to service and dedication to learning to your campus, and I look forward to the possibility of contributing my skills and experiences to your distinguished institution.
[Your Name] [Your Contact Information]
Penning a University Application Letter Expressing a Deep Passion for a Specific Field of Study

Subject: Application for Admission in [Specific Field of Study]
I, [Your Full Name], a resident of [Your City Name], am writing this letter to express my deep interest in applying for the [Specific Field of Study] program at your esteemed university for the academic year [Year of Admission].
My passion for [Specific Field of Study] was kindled during my school years, when I found myself fascinated by [Mention something specific about the field that fascinated you]. Since then, my curiosity and interest in this field have only grown. I have spent countless hours learning and honing my skills, and now I aspire to take this passion forward and delve deeper into this field at a university level.
I have consistently excelled in this field during my school years [mention any achievements, awards, or recognition received]. I am confident that my dedication, coupled with the guidance of the exceptional faculty at [University Name], will equip me with the necessary skills and knowledge to contribute positively to this field.
I assure you of my utmost commitment and dedication towards my studies, and I am eager to make the most of the opportunities offered at your prestigious institution. I am hopeful that you will consider my application favorably.
[Your Full Name] [Your Contact Information]
How to Write University Admission Application Letter
Related Topics:
I am sure you will get some insights from here on how to write “university admission application letter”. And to help further, you can also download all the above application samples as PDFs by clicking here .
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to secondary sidebar
- Skip to footer
career-advice.jobs.ac.uk
How to Write a Cover Letter for Academic Jobs

The purpose of your cover letter
The power of the cover letter in making an effective job application should never be underestimated. A good cover letter will grab the employer’s attention and make them want to read your CV. The purpose of your cover letter and CV together is to whet the employer’s appetite, to establish you as a serious contender for the post and to persuade the recruiter that you are worth an interview.
The cover letter exists to:
- Demonstrate your enthusiasm for the post, based on the research you have done about the role and the institution
- Explain your rationale for applying and how the role fits with your career plans
- Answer the question “Why should we hire you?” by demonstrating how you meet the key criteria for the post and what sets you apart from other candidates
- Provide evidence of your written communication and language skills, including the ability to be clear, succinct and articulate. This is especially important for teaching roles as the ability to communicate the nature and impact of your academic work to a non-academic audience is crucial.
This article focuses on cover letters for roles in Academia and addresses:
When to send a cover letter
- What format to use
- How to tailor it to a particular role
- Marketing yourself in the cover letter
- The dos and don’ts of cover letter writing
- An example ‘before’ and ‘after’ cover letter with detailed explanations of the improvements made
- A checklist for you to ensure your cover letter is as effective as possible.
You should always send a cover letter with your CV unless you are expressly asked not to. The only exception is if you are posting your CV on a database/with an agency where it will be seen by numerous employers, in which case a Profile on the CV itself is helpful.
Even if you have explained your motivation for applying on the application form, it is still worth sending a separate cover letter. This is because the cover letter gives you another opportunity to market yourself and can strengthen your chances.
The format of a cover letter
For jobs in academia, the length of the cover letter will depend on the seniority of the post. In any event, you should ensure the letter is no longer than two pages; one and a half pages is better still. In order to make an impact, and to prove that you can explain ideas fluently and clearly, the letter needs to be succinct. This is not the place to give in-depth detail about your research and academic interests; remember that the letter may be read by non-academics too, such as staff from Human Resources. You can always give further details of your academic and research activities on your CV or in an Appendix to your CV.
Keep paragraphs short and your typeface clear (a font size of 11 or 12 is recommended) as the employer’s attention span will be brief.
It is traditional to write the cover letter in paragraph format, and this is the format we have used for our example letter, although some candidates choose to use bullet points and/or bold to highlight key points.
The order of paragraphs is not critical, but the following is recommended:
- Address and salutation: Address the letter to a named person i.e. the Head of Department.
- First paragraph: An introduction, explaining which post you are applying for, how you heard about it, and some brief background on who you are e.g. in terms of your research interests and academic background.
- Middle section: Evidence of your academic career in terms of your research interests and achievements as well as teaching and administrative experience. Also mention your future research plans. The balance between research, teaching and administration will depend on the nature of the institution and department’s work.
- Final section: Explain what attracts you to this role in this institution and department and how the role fits in to your career plans.
- Concluding paragraph: A conclusion summarising what makes you suitable for the job and a statement expressing interest in an interview.
Tailoring your letter
The best way to tailor your letter effectively is to:
Do your research
Your cover letter needs to show what a great match you are for the job. The job and person specification will only give you so much. In order to understand the job context, how your own research interests will fit into the department’s academic offering, what the recruiters are really looking for and how the department and job might develop in future you need to make your own enquiries.
This could include:
Online research
For example: into the University and Department’s academic programmes, it’s research and student profile, the research interests of key staff and so on. There is much information available publicly (for example, the institution’s and department’s external websites, the department’s latest research ranking, academic forums and even Good University Guides). For external appointments, you may be limited to what is available publicly so do use your networks to access these.
Discussion with the Head of Department
Most recruiters are only too happy to answer questions about the job from potential applicants beforehand. This can also help you get your ‘name in the frame’ early. Just ensure that your questions are well researched and be warned that the conversation might turn into an informal interview. You should reflect on why the department should hire you, and refine your ‘elevator pitch’ before arranging the call.
Conversations with other academics in the department and institution
You can also speak to people who previously worked there, who have worked with key staff in the department at some point in their career, as well as support staff. This will give you a better idea of the culture of the institution and the work of the department. For internal roles, you can use your internal networks to find these people. For external roles, you might ask the Head of Department to put you in touch with other staff – or use your networks to see who knows someone in the right department and institution.
The depth of your research will show in your application and can really distinguish serious applicants from the rest of the pack. It’s also great preparation for the interview stage.
Be selective
The best way to tailor your letter is to pick out only the top three or four criteria for the post and focus your evidence on these. If the employer is convinced you have the right credentials, experience and skills for the areas that matter most, the chances are that they will invite you to interview. Your CV and your interview can cover the rest.
Remember to include your skills outside research
Whilst the focus of your cover letter may be about communicating the relevance and depth of your academic experience, don’t forget to give evidence of those softer skills which may also be relevant to the job. These are likely to be outlined in the person specification and may include supervising PhD students, writing funding bids, managing other staff and project planning.
Marketing yourself effectively
Before you write your letter, you need to be clear on what your Unique Selling Points are for the role in relation to the key job criteria.
Think about what will differentiate you from the competition. Consider who else might apply, internally and externally, and what they might offer. Consider what makes you stand out from them. This might include:
- Greater depth of expertise in this field or a higher research profile than other likely applicants
- A particular blend of experiences which give you a unique perspective (e.g. international experience, having worked in both academia and industry, or having held posts in more than one academic discipline)
- Specific achievements in your current and previous roles
- A passion for and commitment to this area of research or working for this institution (e.g. perhaps you completed your PhD there)
- Well developed research or funding networks which could prove helpful in the job
- Or anything else you think might make the stand out in a way which is relevant to the role.
Tips for success
- Put your most convincing evidence first. You need to make an impact in the first few sentences. Talk about your current or most relevant job first
- Focus on achievements in your current and previous roles rather than merely your responsibilities (publications, new courses developed, funding awards won and so on). Quantify these wherever possible
- Illustrate your achievements with brief but specific examples, explaining why these are relevant to this role. You can refer the employer to the CV for more detail
- Concentrate on the areas which differentiate you from the competition rather than the basic job criteria
- Demonstrate how well you have researched the role and the job context when explaining your career motivation
- Explain your rationale if you are seeking a career change or sideways move
- Be succinct. Ask someone to go through it with you and edit out any wordy sentences and redundant words. Some academic institutions offer a confidential careers advice service to staff members through their University Careers Service
- End on a note of enthusiasm and anticipation.
- Try to summarise your CV or give too much detail – you need to be selective about the points that you highlight
- Make unsubstantiated statements about relevant skills and experience without giving examples
- Send the same or a similar letter to more than one employer. Never ‘cut and paste’ as employers will suspect a lack of research and career focus
- Make generalised statements about why you want to work for the institution (e.g. referring to ‘a top 50 global institution’ or ‘a department with a high reputation’)
- Use jargon specific to your employer or profession which the employer might not understand
- Focus on what the employer can do for you – it’s more about what you can do for the employer.
Example cover letter – with comments

Example cover letter – improved version

Cover letter checklist
Before you send off your letter, use our final checklist to ensure your letter is as strong as possible.
- Done your homework so that you are clear about what the employer wants?
- Given clear evidence of how you meet the most important criteria of the job?
- Kept it to two pages or less?
- Put your most important evidence in the first half of the letter?
- Explained your academic interests clearly in a way that non-academics could understand?
- Asked a friend to proof read it and ensure the language is succinct and clear?
- Addressed it to the right person?
- Given a convincing explanation of why you want the job?
- Ended with a summary of why you would be perfect for this role?
What did you think of our article? - please rate
Share this article
Lisa Carr is a careers consultant and coach who works with a range of public and private organisations including the University of Warwick and Warwick Business School, where she coaches Executive MBAs. She began her career as an HR manager in the energy industry and spent a number of years lecturing for the Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development. After qualifying as a Careers Guidance practitioner she has worked with a wide range of clients from undergraduates through to senior academics and company directors.
Reader Interactions
You may also like:, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Please enter an answer in digits: five × three =
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Home » Letters » Approval Letters » Letter Seeking Approval for Higher Studies from Employer – Sample Letter Requesting Approval for Higher Studies from Employer
Letter Seeking Approval for Higher Studies from Employer – Sample Letter Requesting Approval for Higher Studies from Employer
Table of Contents:
- Sample Letter
Live Editing Assistance
How to use live assistant, additional template options, download options, share via email, share via whatsapp, copy to clipboard, print letter, sample letter seeking approval for higher studies from employer.
To, The HR Manager, _________, (Company’s name) _________ (Company’s Address)
Date: __/__/_____ (date)
Subject: Requesting approval for higher education
Sir/ Madam,
Most respectfully, I am ___________ (name), _____________ (Designation) having employee ID number ____________ (mention your employee ID number).
Through this letter, I would like to inform you that I am willing to pursue higher education along with my job. I am looking forward to managing the profile better as a specialist. I want to pursue the ________ (mention course name – Masters/Online Course/Other). The duration of the said course would be _________ (mention duration – 6 months/ 1 year) and the mode of study will be __________ (Full-time/Part-time/Online/evening/other).
Therefore, I need your kind approval in this regard. I shall be obliged if you could provide me with ___________ (type of leave) for the _________ (admission/study/entrance exam/other) for ____ (no.of days) – if applicable. This is to request you kindly approve my request and issue the letter of recommendation (LOR) in my name.
Thanking you, Yours sincerely, __________ (Signature), __________ (Your name), __________ (Employee ID number)
Live Preview
The Live Assistant feature is represented by a real-time preview functionality. Here’s how to use it:
- Start Typing: Enter your letter content in the "Letter Input" textarea.
- Live Preview: As you type, the content of your letter will be displayed in the "Live Preview" section below the textarea. This feature converts newline characters in the textarea into <br> tags in HTML for better readability.
The letter writing editor allows you to start with predefined templates for drafting your letters:
- Choose a Template: Click one of the template buttons ("Start with Sample Template 1", "Start with Sample Template 2", or "Start with Sample Template 3").
- Auto-Fill Textarea: The chosen template's content will automatically fill the textarea, which you can then modify or use as is.
Click the "Download Letter" button after composing your letter. This triggers a download of a file containing the content of your letter.
Click the "Share via Email" button after composing your letter. Your default email client will open a new message window with the subject "Sharing My Draft Letter" and the content of your letter in the body.
Click the "Share via WhatsApp" button after you've composed your letter. Your default browser will open a new tab prompting you to send the letter as a message to a contact on WhatsApp.
If you want to copy the text of your letter to the clipboard:
- Copy to Clipboard: Click the "Copy to Clipboard" button after composing your letter.
- Paste Anywhere: You can then paste the copied text anywhere you need, such as into another application or document.
For printing the letter directly from the browser:
- Print Letter: Click the "Print Letter" button after composing your letter.
- Print Preview: A new browser window will open showing your letter formatted for printing.
- Print: Use the print dialog in the browser to complete printing.
- Clearly state your intention to pursue higher education alongside your job, including details such as the course name, duration, and mode of study. Request any necessary leave and ask for a letter of recommendation if needed.
- Ensure your letter is polite, clear, and includes all necessary details. Highlight how your continued education will benefit both you and the company, and be open to discussing any concerns your employer may have.
- Yes, including your employee ID number helps the HR department identify you quickly and process your request efficiently.
- Yes, providing these details gives your employer a clear understanding of the commitment required and demonstrates your preparedness and planning.
- Yes, it's common to request a letter of recommendation from your employer, especially if the course you're pursuing is relevant to your job role or career advancement.
Incoming Search Terms:
- letter seeking permission approval for studying while job
- higher education approval letter sample template to the HR Manager
By letterskadmin
Related post, request letter for issuance of approval letter for delivery – sample letter for delivery approval, request letter for extension of time to deliver goods – sample letter requesting for extension of timeto deliver goods, request letter for annual leave approval – sample letter requesting annual leave approval.
Request Letter to Principal for Organizing Science Fair – Sample Letter Requesting for Organization of Science Fair
Request letter for participation in cultural event – sample letter requesting for participation in cultural event, request letter for changing optional subject – sample letter to school principal requesting for change of optional subject, request letter for permission to start a new club – sample letter requesting to start a new club in school, privacy overview.
Internship and Career Center
Cover letter template for academic faculty and teaching positions.
Below is a general template for use when crafting a cover letter for academic teaching positions. Before getting started, you will also want to review the academic cover letter samples .
Optional – include header (similar to your resume and other supporting documents)
[Mailing date] [Search committee mailing info, including department and address] [Dear Professor _____________________, or Dear Search Committee Chair and Members:] [Paragraph 1: simple introduction.]
I am writing to apply for the position of [official title] announced in the XXX [e.g., Chronicle of Higher Education]. I am completing a Ph.D. in XX from the [department name] at the University of California, Davis. I will defend my dissertation, "[dissertation title]” and expect to graduate in [month]. OR: I am finishing the first year of my postdoc with XX [your PI's name or in the lab of XX], where I am working on X, Y, and Z [briefly describe, but leave the bulk of the research description for the below sections]. [Paragraph 2: principal research area(s) and dissertation - this paragraph along with paragraph 3 would follow the introduction when applying for a faculty or teaching position within a R1 university emphasizing the research over the teaching. For Liberal Arts Colleges and State Universities, research and teaching paragraphs should be somewhat balanced in length. For teaching-only Community Colleges, a research statement might be included towards the bottom of the cover letter, but only in the context of staying on top of the discipline in order to perform more effectively as a teacher. ]
My principal research area is X [area here], with a focus on [focus area(s)]. [3-4 sentence summary of dissertation here]. I've used X method/technique/approach to explore W and Z. [Paragraph 3: other research areas, contributions, and future directions - this paragraph would be included for R1, Liberal Arts College or State University.]
My immediate research priority is to expand this manuscript into a book. I will direct future research toward [1-2 sentences on next project]. [Add additional sentences on your broader research agenda, how you would apply this to your new institution]. [Paragraph 4: teaching experience and interests - this paragraph would follow the 1st paragraph when applying to a State University.]
During my [number] years at X [campus], I have taught [identify what you have taught, particularly as it relates to the institution you are applying]. [Add 2 or so sentences on any pedagogical training, innovative approaches you have taken in the classroom, technology you've used, areas you are particularly interested in exploring, and/or specific new class or seminars you would like to teach at their institution]. [Paragraph 5: closing.]
I have enclosed my CV, a writing sample, and a teaching philosophy state [or whatever they ask for…]. Three faculty recommendations will be mailed under separate cover [or by Interfolio , a dossier service]. I will attend the XX conference in [city] this year, and I can always be reached by phone or email. Thank you for your consideration, and I look forward to hearing from you. Sincerely, [your signature] [your email] – include if you don’t use a header [your phone number] – include if you don’t use a header
A couple of notes:
- The tone of the cover letter should be that of a potential colleague. It should showcase your knowledge, contribution to the discipline. The cover letter should be used to outline your academic accomplishments and to share a five year vision for where you are heading into the future.
- You want to present the perspective of an independent researcher and teacher, not simply a list the coursework and tasks you've completed as a graduate student or postdoc.
- Note that you do not have to separate your dissertation and other research interests (i.e. paragraphs 2 and 3).
- Understand the different missions of the institutions for which you are applying.
Adapted from a template provided by Robert P. Newcomb, Ph.D., Department of Spanish & Portuguese, UC Davis
- Career Advice
- Carpe Careers
Uncovering the Secrets of the Cover Letter
By Joseph Barber
You have / 5 articles left. Sign up for a free account or log in.

Istockphoto.com/cnythzl
While specific styles of résumés can reflect different career fields and industries, the cover letter offers a much less structured document, and so often leads to much more confusion among job seekers. You will no doubt get different advice from everyone you ask about cover letters for jobs beyond faculty roles, and what I discuss here will certainly add to that cacophony of recommendations.
But having read a frighteningly enormous number of cover letters in my role as a career adviser, my advice comes from a certain amount of experience. That experience can be divided into positive situations, where the letters were interesting to read, and neutral-to-negative ones, where the letters were readable but not very engaging. When you are thinking of your cover letters, the description of “readable” should be the absolute minimum outcome that you aim to achieve. Ideally, your letter will be interesting, engaging, unique, positive, energetic, relevant and optimistic. That’s a lot to achieve in one page!
The first question to ask yourself is what is the purpose of a cover letter? If you have already created a customized résumé for the job you are applying to (and this is essential), then you have already highlighted your relevant skills. You don’t just want to provide exactly the same information again in your cover letter. Reading such information twice doesn’t make it any more impactful but can definitely make it less interesting. Used strategically, the cover letter gives you an opportunity to highlight some of the best parts of your résumé in a slightly different way, and with the goal of explaining why you’re the right person for the job, why your experiences are relevant, and why you want to use your skills and knowledge in this new role at this new organization.
The answers to these questions are not punchy bullet points. Instead, they need to be slightly more narrative in their form. When you use more narrative formats, you can start taking some storytelling approaches to engage the reader. The benefit of telling stories is that you don’t just have to state empirically what happened -- which is what the bullet point in the résumé does -- but you can also talk about the broader impacts of the experience. That includes what you learned from it, how it made you feel, why you sought it out, what was so surprising about it, why is was challenging and so on. Those perspectives are distinctly yours, which makes them interesting to the reader, who won’t have read them in 100 other cover letters. And they can help make your letter more energetic by bringing in action-based emotional states. People remember stories more than they remember generic statements that you have important skills.
Let’s cover the basic structure of a one-page cover letter that I tend to recommend. To make it easier to consider, we can break it down into three separate sections.
First paragraph/opening. Make a clear statement of intent at the start to help the reader put the letter into context. That means avoiding statements such as: “I am writing to possibly explore the opportunity to be so honored to be interested in applying for the position of …” Instead, a more direct approach might be: “I am applying for the position of X that was advertised on your website.”
You can add to that, of course, but be direct. The rest of the first paragraph should be present a takeaway conclusion about yourself. Yes, you can start your letter with a conclusion. That means that the reader immediately knows you have something that they want and makes them more likely to read the rest of the letter to find out more. If you are going to start off with a conclusion, though, make sure that it is relevant to your reader by summarizing what they are likely to care about the most. Take a look at this introduction sentence and see if you can identify what some of the key takeaways are -- and thus what some of the job requirements might have been:
With eight years of experience managing multistep data collection projects in academic and industry settings, and an ability to establish and maintain relationships with clients, stakeholders and international collaborators, I am excited to bring my creativity and structured approach to this data analyst role.
Middle paragraphs. Once you have made a conclusion statement in the introduction (I know, it sounds a little weird!), the main part of the letter should expand on those themes. You don’t have to go through all of your experiences from the résumé; rather, you will want to highlight the best parts. Everything in your cover letter should be echoed by something in your résumé, but not everything in your résumé needs to be mentioned in your cover letter. And if you are wondering why you can’t just customize your cover letter and send a standard résumé as part of your application, just remember that not everyone will read a cover letter. You want them to, but you cannot make them!
The main body of your letter will contain good illustrations of your relevant skills in action, all wrapped up in a narrative form that includes just a sprinkling of drama. Here is an example of a story without much drama:
As a project leader in the student health-care consulting group, I oversaw a team of three students and completed an extensive market analysis of the medical device field to determine a suitable pricing model for a wearable device developed by the client.
None of this is bad information; it is just not that engaging. It would be much better as a bullet point in a résumé. And if it were already a bullet in the résumé, it should not just be repeated in the cover letter. Here is an alternative version with a little more drama.
When I was serving as a project leader in the student consulting group, my team had engaged with a client seeking market access information for a new wearable device. We faced two immediate challenges with this work: the device was unique with few comparable products, and this was the first consulting experience for half of our four-member team. In thinking about the project, I saw their lack of experience as a possible advantage and took the opportunity to encourage the two new team members to think creatively about comparable products in the medical space and beyond. In two brainstorming sessions, we successfully generated sufficient data for our market analysis. I found it really satisfying to see how well the new members complemented and then learned from our more practiced approach.
This is not just a statement of what was done; it illustrates how you approached the assignment. Every project you have been involved with has presented its own distinct challenges. If you can state what those were, and talk about how you have used skills and abilities relevant to the job to which you’re applying to overcome them, then you have the basis for good examples. Concepts that you can touch on in a cover letter that are hard to highlight in a résumé include:
- learning from an experience that went well or badly;
- combining experiences from two separate roles you have had (that might be separated by years on a résumé) to show how you solved a problem;
- explaining why you did something, not just that you did it; and
- demonstrating passion, or enjoying or being excited about something.
Final paragraph. Once you have given some examples to illustrate the themes highlighted in the first paragraph, you can move to the final one. Here you might want to answer the questions “Why do you want this job?” and “Why do you want to work here?” The answers to those questions should flow nicely from the examples you have been giving.
In all these projects, I have found myself most engaged when I have been able to bridge disciplines and draw upon my relationship-building skills to establish productive collaborations. I would enjoy the opportunity to liaise between the marketing and science teams in this project coordinator role, and that would make exceptional use of my lab research skills and creative mind-set. I have spoken with three alumni from my university who work at your institution, and each has highlighted the mentoring program for junior staff as wonderfully helpful for their own professional development. I have been fortunate to have strong mentors in my current lab, which has certainly helped me progress in my research, and I am very excited about learning from the experience of senior staff through this program.
The more you know about an organization, and the role itself, the easier it will be to come up with an authentic answer to the “why this job?” and “why this company?” questions.
There is no perfect cover letter, and different approaches can be just as effective. After all, different people will read each letter, and they have their own ideas about good and bad ones. But I hope you can apply some of these suggestions when composing your next cover letter -- and uncover just a hint of drama as you successfully describe your exceptional skills, knowledge and experiences.

Most College Students Aren’t Hostile Toward Jews or Israel
A new study from Brandeis found that about one-third of college students surveyed agreed with at least one negative s
Share This Article
More from carpe careers.

Rethinking Professional Development for Grad Students
Laura Kuizin describes how to create opportunities that go beyond the classroom and prepare students for the dynamic

Helping Humanities Ph.D.s Thrive Beyond Academia
Amy Braun describes how honing existing skillsets through experiential learning transforms such students into industr

Breaking the Bamboo Ceiling
Nana Lee describes some of the challenges that Asian women in STEM experience and what they and others can do to help
- Become a Member
- Sign up for Newsletters
- Learning & Assessment
- Diversity & Equity
- Career Development
- Labor & Unionization
- Shared Governance
- Academic Freedom
- Books & Publishing
- Financial Aid
- Residential Life
- Free Speech
- Physical & Mental Health
- Race & Ethnicity
- Sex & Gender
- Socioeconomics
- Traditional-Age
- Adult & Post-Traditional
- Teaching & Learning
- Artificial Intelligence
- Digital Publishing
- Data Analytics
- Administrative Tech
- Alternative Credentials
- Financial Health
- Cost-Cutting
- Revenue Strategies
- Academic Programs
- Physical Campuses
- Mergers & Collaboration
- Fundraising
- Research Universities
- Regional Public Universities
- Community Colleges
- Private Nonprofit Colleges
- Minority-Serving Institutions
- Religious Colleges
- Women's Colleges
- Specialized Colleges
- For-Profit Colleges
- Executive Leadership
- Trustees & Regents
- State Oversight
- Accreditation
- Politics & Elections
- Supreme Court
- Student Aid Policy
- Science & Research Policy
- State Policy
- Colleges & Localities
- Employee Satisfaction
- Remote & Flexible Work
- Staff Issues
- Study Abroad
- International Students in U.S.
- U.S. Colleges in the World
- Intellectual Affairs
- Seeking a Faculty Job
- Advancing in the Faculty
- Seeking an Administrative Job
- Advancing as an Administrator
- Beyond Transfer
- Call to Action
- Confessions of a Community College Dean
- Higher Ed Gamma
- Higher Ed Policy
- Just Explain It to Me!
- Just Visiting
- Law, Policy—and IT?
- Leadership & StratEDgy
- Leadership in Higher Education
- Learning Innovation
- Online: Trending Now
- Resident Scholar
- University of Venus
- Student Voice
- Academic Life
- Health & Wellness
- The College Experience
- Life After College
- Academic Minute
- Weekly Wisdom
- Reports & Data
- Quick Takes
- Advertising & Marketing
- Consulting Services
- Data & Insights
- Hiring & Jobs
- Event Partnerships
4 /5 Articles remaining this month.
Sign up for a free account or log in.
- Sign Up, It’s FREE
CV for University Application example
Getting into university and getting a degree will give you a huge head-start in your career, but getting into university isn’t easy
This guide contains an example University Applicant CV and plenty of tips on how to create your own winning CV, so you can stand out amongst the other candidates and get into the university of your dreams.
Guide contents
CV for University Application example 1
Cv for university application example 2.
- Structuring and formatting your CV
- Writing your CV profile
- Detailing work experience
- Your education
CV templates

Unsure of what your University Applicant CV should look like?
Have a look at the CV example above to get familiar with the structure, layout and format of a professional CV.
As you can see, it provides plenty of relevant information about the applicant but is still very easy to read, and brief – which will please busy university recruiters.
University Applicant CV structure and format
The format and structure of your CV is important because it will determine how easy it is for recruiters and employers to read your CV.
If they can find the information they need quickly, they’ll be happy; but if they struggle, your application could be overlooked.
A simple and logical structure will always create a better reading experience than a complex structure, and with a few simple formatting tricks, you’ll be good to go.

Formatting Tips
- Length: Recruiters will be immediately put off by lengthy CVs – with hundreds of applications to read through, they simply don’t have the time! Grabbing their attention with a short, snappy and highly relevant CV is far more likely to lead to success. Aim for two sides of A4 or less.
- Readability : Make sure your CV is easy to read and looks professional by applying some simple formatting tricks. Bullet points are great for making large paragraphs more digestible, while formatting your headings with bold or coloured text will help the reader to find the information they need, with speed.
- Design: It’s generally best to stick to a simple CV design, as funky or elaborate designs rarely add any value to your application. A clear, modern font and a subtle colour scheme work perfectly and allow your skills, experience and achievements to speak for themselves.
- Avoid photos: Logos, profile photos or other images aren’t necessary and rarely add any value – save the space for written content, instead!

Build your CV now
Structuring your CV
As you write your CV , work to the simple but effective structure below:
- Name and contact details – Pop them at the top of your CV, so it’s easy for recruiters to contact you.
- CV profile – Write a snappy overview of what makes you a good fit for the role; discussing your key experience, skills and accomplishments.
- Core skills section – Add a short but snappy list of your relevant skills and knowledge.
- Work experience – A list of your relevant work experience, starting with your current role.
- Education – A summary of your relevant qualifications and professional/vocational training.
- Hobbies and interests – An optional sections, which you could use to write a short description of any relevant hobbies or interests.
Now I’ll guide you through exactly what you should include in each CV section.
CV Contact Details

Tuck your contact details into the corner of your CV, so that they don’t take up too much space. Stick to the basic details, such as:
- Mobile number
- Email address – It should sound professional, such as your full name.
- Location -Just write your rough location, rather than your full address.
- LinkedIn profile or portfolio URL – If you include these, ensure they’re sleek, professional and up-to-date.
University Applicant CV Profile
Recruiters read through countless applications every day.
If they don’t find what they’re looking for quickly, they’ll simply move onto the next one.
That’s what makes your CV profile (or personal statement , if you’re an entry-level/graduate candidate) so important.
This short and snappy summary sits at the top of your CV, and should give a high-level overview of why you’re a good match for the university.
This way, you can ensure that busy recruiters see your suitability from the outset, and so, feel your CV is worth their time.
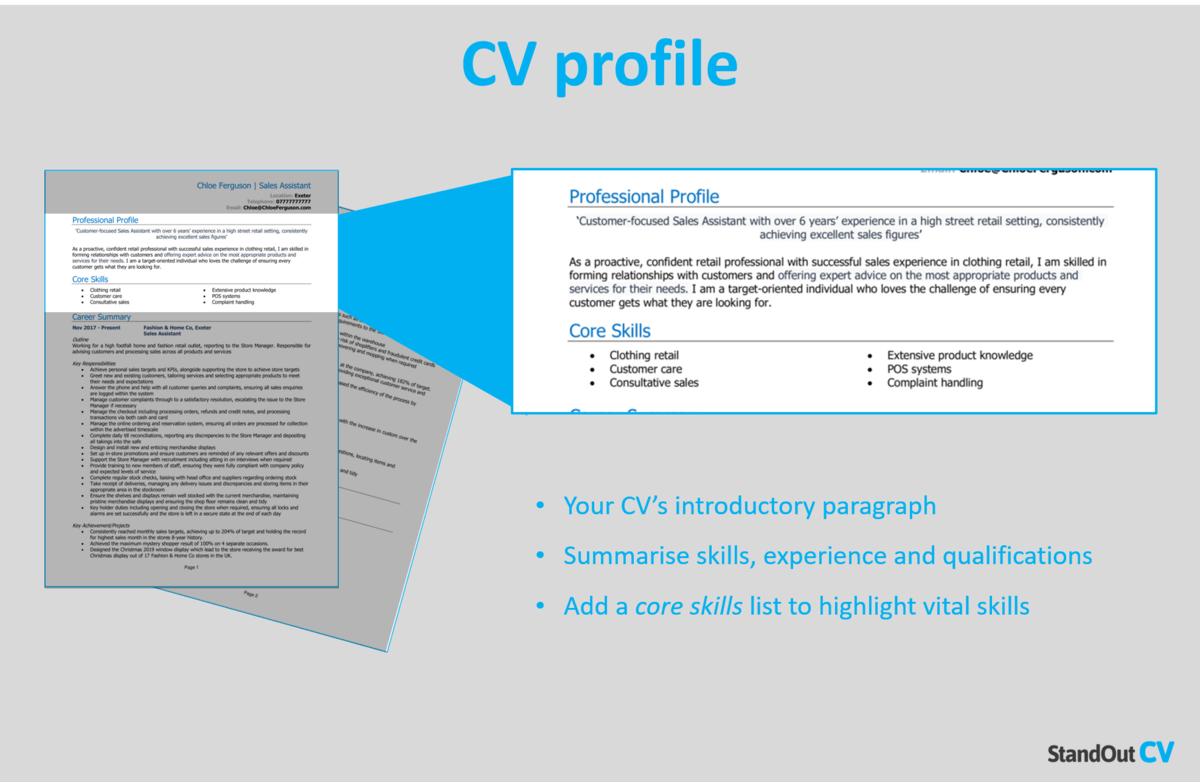
Tips for creating an impactful CV profile:
- Keep it brief: It might be tempting to submit a page-long CV profile, but recruiters won’t have the time to read it. To ensure every word gets read, it’s best to include high-level information only; sticking to a length of 3-5 lines.
- Tailor it: Before writing your CV, make sure to do some research. Figure out exactly what your desired employers are looking for and make sure that you are making those requirements prominent in your CV profile, and throughout.
- Don’t add an objective: Leave your career objectives or goals out of your profile. You only have limited space to work with, so they’re best suited to your cover letter .
- Avoid cliches: “Determined team player who always gives 110%” might seem like a good way to fill up your CV profile, but generic phrases like this won’t land you an interview. Recruiters hear them time and time again and have no real reason to believe them. Instead, pack your profile with your hard skills and tangible achievements.
What to include in your University Applicant CV profile?
- Summary of experience: Recruiters will want to know what type of companies you’ve worked for, industries you have knowledge of, and the type of work you’ve carried out in the past, so give them a summary of this in your profile.
- Relevant skills: Highlight your skills which are most relevant, to ensure that recruiters see your most in-demand skills as soon as they open your CV.
- Essential qualifications: Be sure to outline your relevant qualifications, so that anyone reading the CV can instantly see you are qualified for the universities you are applying to.
Quick tip: Your CV is your first impression on recruiters, so it’s vital to avoid spelling and grammar mistakes if you want to appear professional. Use our quick-and-easy CV Builder to add pre-written content that has been crafted by recruitment experts.
Core skills section
In addition to your CV profile, your core skills section provides an easily digestible snapshot of your skills – perfect for grabbing the attention of busy hiring managers.
As University places might receive a huge pile of applications, this is a great way to stand out and show off your suitability for the role.
It should be made up of 2-3 columns of bullet points and be made up of skills that are highly relevant to the universities you are targeting.

Work experience/Career history
Next up is your work experience section, which is normally the longest part of your CV.
Start with your current (or most recent) job and work your way backwards through your experience.
Can’t fit all your roles? Allow more space for your recent career history and shorten down descriptions for your older roles.

Structuring your roles
If you don’t pay attention to the structure of your career history section, it could quickly become bulky and overwhelming.
Get in recruiters’ good books by creating a pleasant reading experience, using the 3-step structure below:

Begin with a summary of your role, detailing what the purpose of your job was, who you reported to and what size of team you were part of (or led).
Key responsibilities
Next, write up a punchy list of your daily duties and responsibilities, using bullet points.
Wherever you can, point out how you put your hard skills and knowledge to use – especially skills which are applicable to your target role.
Key achievements
Finish off by showcasing 1-3 key achievements made within the role.
This could be anything that had a positive effect on your company, clients or customers, such as saving time or money, receiving exemplary feedback or receiving an award.
At the bottom of your CV is your full education section. You can list your formal academic qualifications, such as:
- GCSE’s
As well as any specific qualifications that are essential to the jobs you are applying for. Note down the name of the qualification, the organisation at which you studied, and the date of completion.
Interests and hobbies
This section is entirely optional, so you’ll have to use your own judgement to figure out if it’s worth including.
If your hobbies and interests could make you appear more suitable for your dream job, then they are definitely worth adding.
Interests which are related to the industry, or hobbies like sports teams or volunteering, which display valuable transferable skills might be worth including.
Writing your University Applicant CV
An interview-winning CV for a University Application needs to be both visually pleasing and packed with targeted content.
Whilst it needs to detail your experience, accomplishments and relevant skills, it also needs to be as clear and easy to read as possible.
Remember to research the role and review the university before applying, so you’re able to match yourself up to the requirements.
If you follow these guidelines and keep motivated in your university search, you should land an interview in no time.
Best of luck with your next application!

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Use a proper salutation. Begin your college application letter with a formal salutation. The standard, in this case, is "Dear". Be sure to avoid informal salutations such as "Hey", "Hi", and "Hello". 💡 Tip: Do your best to personalize your university application letter in every way that you can.
Be clear and concise. Write short, declarative sentences. Do not write long, complicated sentences, as your point may get lost in the details. Here are a few things to avoid when writing a cover letter. Excessive detail. Don't try to describe each and every paper you've written in the cover letter.
2. Format the page. As with most other documents, your academic cover letter contains a heading with your name, contact information and location at the top, followed by the date and the organization's name. Set your page margins to one inch, and use a professional font like Times New Roman, Calibri or Garamond.
Cover Letter Advice. A well-written cover letter can be equally important as an impressive resume or CV. A cover letter should accompany each resume you send and be tailored distinctly for the position to which you are applying. You should describe your abilities, skills, and experience, and illustrate them with concrete examples to show how ...
over Letters for Academic PositionsThe purpose of a cover letter is to introduce yourself and to demonstrate the fit between your ba. advertised position. THE BASICS cover letter must accompany and be ta. lored to any application you submit. STE. letters should not exceed one page. Humanities and social science.
At their most basic level, academic cover letters accomplish three things: one, they express your interest in the job; two, they provide a brief synopsis of your research and teaching; and three, they summarize your past experiences and achievements to illustrate your competence for the job. For early-career scholars, cover letters are ...
Cover Letter for a College Communications Position. September 15, 2021. Dear Mr. Lau, I am writing to indicate my interest in the position of Assistant Director of Campaign Communications. I'm a passionate supporter of our current campaign, and a fully-engaged member of the College community.
These are some steps you can follow to write an effective education cover letter: 1. Format your document. A well-formatted cover letter is easier for the hiring manager to review. To format your cover letter, you can use a word processing system and choose a font like Times New Roman, Georgia, Arial or Calibri.
Follow these tips to write an impactful essay that can work in your favor. 1. Start Early. Few people write well under pressure. Try to complete your first draft a few weeks before you have to turn it in. Many advisers recommend starting as early as the summer before your senior year in high school.
First Paragraph - the Introduction - WHY you are writing GET THEM TO KEEP READING • Clearly state who you are and why you are writing. • Give any compelling reasons why you are applying to the position. e.g., "I was excited to see XYZ posting on STARS as it speaks to my background in X and my passion in Y."
First, find the sample template for university admission application letter below. Subject: Application for Admission to [Name of the Course] Respected Sir/Madam, I, [Your Full Name], resident of [Your Address], am writing this letter to show my keen interest in applying for the [Name of the Course] at your esteemed university for the academic ...
Address and salutation: Address the letter to a named person i.e. the Head of Department. First paragraph: An introduction, explaining which post you are applying for, how you heard about it, and some brief background on who you are e.g. in terms of your research interests and academic background. Middle section: Evidence of your academic ...
include are your contact information, education, research experience, teaching experience, publications, presentations, honors and awards, and contact information for your references, or those people willing to speak or write on your behalf. Some formatting pointers: There is no single best format.
The job application letter, or the cover letter, is the most important part of your application. It's the first thing a search committee member sees. Typically, a search committee member will read your materials in the following order: cover letter, C.V., letters of recommendation, writing sample or other additional materials.
How to Use Live Assistant. The Live Assistant feature is represented by a real-time preview functionality. Here's how to use it: Start Typing: Enter your letter content in the "Letter Input" textarea. Live Preview: As you type, the content of your letter will be displayed in the "Live Preview" section below the textarea. This feature converts newline characters in the textarea into <br> tags ...
Below is a general template for use when crafting a cover letter for academic teaching positions. Before getting started, you will also want to review the academic cover letter samples. Optional - include header (similar to your resume and other supporting documents) [Mailing date] [Search committee mailing info, including department and address]
Make a clear statement of intent at the start to help the reader put the letter into context. That means avoiding statements such as: "I am writing to possibly explore the opportunity to be so honored to be interested in applying for the position of …". Instead, a more direct approach might be: "I am applying for the position of X that ...
Include the following information to help ensure your academic recommendation letter sets your student apart from other applicants: Address the letter. Include a brief introduction. Outline the student's qualifications. Describe a time that the student impressed you. End the letter with a particular endorsement.
Build your CV now Structuring your CV. As you write your CV, work to the simple but effective structure below:. Name and contact details - Pop them at the top of your CV, so it's easy for recruiters to contact you.; CV profile - Write a snappy overview of what makes you a good fit for the role; discussing your key experience, skills and accomplishments.
College Application Resume Example Refer to this example when writing your own college application resume: Monika Paul Pune, Maharashtra | (91) 92544-59888 | [email protected] Summary I am a determined worker and a team player looking for opportunities to work in the domain of customer support. I am interested in fine-tuning my diverse skill-sets on the job before I apply for higher ...
The International Admissions Office is looking for volunteers! We are involved in attracting international students to our 5 campuses and invite you to join us and contribute to the growth of our international community! Community ideas & experience students international students Invitation to participate HSE Development Programme up to 2030.
Start of application submission, review of applications by educational programmes. April 30, 2024 ... Management in Higher Education (Russian-taught) Management in Creative Industries (Russian-taught) Science, Technology and Innovation Management and Policy ... Creative Writing (Russian-taught) Russian and Comparative Literature (Russian-taught
Deadline for accepting applications for Russian government scholarship place. August 11, 2024 Deadline for applications. August 18, 2024 Deadline for participation in qualifying events ... HSE Education & Training Advisory Centre. Email. [email protected]. Phone +7 (495) 531 0059. WhatsApp +7 (916) 311 8521. Telegram +7 (916) 311 8521.
Come to Dubosekovskaya str., 4, MAI, Main Academic Building (GUK), admissions hall, room 15. If you are lost, call +7 499 158-00-27 , we will help you to find the way. 3. Take a seat in room 15 and admissions manager will answer all your questions and make you a cup of coffee.