- I nfographics
- Show AWL words
- Subscribe to newsletter
- What is academic writing?
- Academic Style
- What is the writing process?
- Understanding the title
- Brainstorming
- Researching
- First draft
- Proofreading
- Report writing
- Compare & contrast
- Cause & effect
- Problem-solution
- Classification
- Essay structure
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Book review
- Research proposal
- Thesis/dissertation
- What is cohesion?
- Cohesion vs coherence
- Transition signals
- What are references?
- In-text citations
- Reference sections
- Reporting verbs
- Band descriptors
Show AWL words on this page.
Levels 1-5: grey Levels 6-10: orange
Show sorted lists of these words.
Any words you don't know? Look them up in the website's built-in dictionary .
Choose a dictionary . Wordnet OPTED both

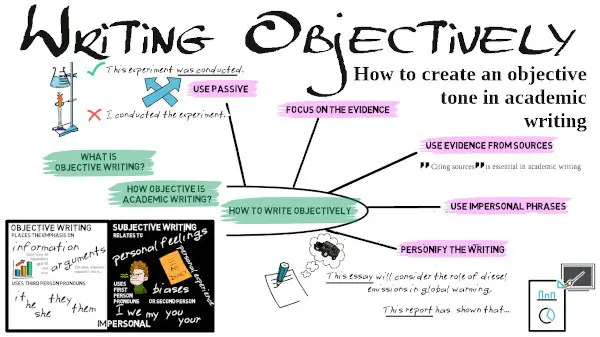
Writing objectively How and when to use an impersonal tone
For another look at the same content, check out the video on YouTube (also available on Youku ). There is a worksheet (with answers and teacher's notes) for this video.
Academic writing is generally impersonal and objective in tone. This section considers what objective writing is , how objective academic writing is , then presents several ways to make your writing more objective . There is also an academic article , to show authentic examples of objective language, and a checklist at the end, that you can use to check the objectivity of your own writing.
What is objective writing?
Objective writing places the emphasis on facts, information and arguments, and can be contrasted with subjective writing which relates to personal feelings and biases. Objective writing uses third person pronouns (it, he, she, they), in contrast to subjective writing which uses first person pronouns (I, we) or second person pronoun (you).
How objective is academic writing?
Although many academic writers believe that objectivity is an essential feature of academic writing, conventions are changing and how much this is true depends on the subject of study. An objective, impersonal tone remains essential in the natural sciences (chemistry, biology, physics), which deal with quantitative (i.e. numerical) methods and data. In such subjects, the research is written from the perspective of an impartial observer, who has no emotional connection to the research. Use of a more subjective tone is increasingly acceptable in areas such as naturalist research, business, management, literary studies, theology and philosophical writing, which tend to make greater use of qualitative rather than quantitative data. Reflective writing is increasingly used on university courses and is highly subjective in nature.
How to write objectively
There are many aspects of writing which contribute to an objective tone. The following are some of the main ones.
Use passive
Objective tone is most often connected with the use of passive, which removes the actor from the sentence. For example:
- The experiment was conducted.
- I conducted the experiment.
- The length of the string was measured using a ruler.
- I measured the length of the string with a ruler.
Most academic writers agree that passive should not be overused, and it is generally preferrable for writing to use the active instead, though this is not always possible if the tone is to remain impersonal without use of I or other pronouns. There is, however, a special group of verbs in English called ergative verbs , which are used in the active voice without the actor of the sentence. Examples are dissolve, increase, decrease, lower, and start . For example:
- The white powder dissolved in the liquid.
- I dissolved the white powder in the liquid.
- The white powder was dissolved in the liquid.
- The tax rate increased in 2010.
- We increased the tax rate in 2010.
- The tax rate was increased in 2010.
- The building work started six months ago.
- The workers started the building work six months ago.
- The building work was started six months ago.
Focus on the evidence
Another way to use active voice while remaining objective is to focus on the evidence, and make this the subject of the sentence. For example:
- The findings show...
- The data illustrate...
- The graph displays...
- The literature indicates...
Use evidence from sources
Evidence from sources is a common feature of objective academic writing. This generally uses the third person active. For example:
- Newbold (2021) shows that... He further demonstrates the relationship between...
- Greene and Atwood (2013) suggest that...
Use impersonal constructions
Impersonal constructions with It and There are common ways to write objectively. These structures are often used with hedges (to soften the information) and boosters (to strengthen it) . This kind of language allows the writer to show how strongly they feel about the information, without using emotive language, which should be avoided in academic writing.
- It is clear that... (booster)
- It appears that... (hedge)
- I believe that...
- There are three reasons for this.
- I have identified three reasons for this.
- There are several disadvantages of this approach.
- This is a terrible idea.
Personify the writing
Another way to write objectively is to personify the writing (essay, report, etc.) and make this the subject of the sentence.
- This essay considers the role of diesel emissions in global warming.
- I will discuss the role of diesel emissions in global warming.
- This report has shown that...
- I have shown that...
In short, objective writing means focusing on the information and evidence. While it remains a common feature of academic writing, especially in natural sciences, a subjective tone is increasingly acceptable in fields which make use of qualitative data, as well as in reflective writing. Objectivity in writing can be achieved by:
- using passive;
- focusing on the evidence ( The findings show... );
- referring to sources ( Newbold (2021) shows... );
- using impersonal constructions with It and There ;
- using hedges and boosters to show strength of feeling, rather than emotive language;
- personifying the writing ( This report shows... ).
Bailey, S. (2000). Academic Writing. Abingdon: RoutledgeFalmer
Bennett, K. (2009) 'English academic style manuals: A survey', Journal of English for Academic Purposes , 8 (2009) 43-54.
Cottrell, S. (2013). The Study Skills Handbook (4th ed.) , Basingstoke: Palgrave MacMillan.
Hinkel, E. (2004). Teaching Academic ESL Writing: Practical Techniques in Vocabulary and Grammar . Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc Publishers.
Hyland, K. (2006) English for Academic Purposes: An advanced resource book . Abingdon: Routledge.
Jordan, R. R. (1997) English for academic purposes: A guide and resource book for teachers . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Example article
Below is an authentic academic article. It has been abbreviated by using the abstract and extracts from the article; however, the language is unchanged from the original. Click on the different areas (in the shaded boxes) to highlight the different objective features.
Title: Obesity bias and stigma, attitudes and beliefs among entry-level physiotherapy students in the Republic of Ireland: a cross sectional study. Source: : https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031940621000353

GET FREE EBOOK
Like the website? Try the books. Enter your email to receive a free sample from Academic Writing Genres .
Below is a checklist for using objectivity in academic writing. Use it to check your writing, or as a peer to help. Note: you do not need to use all the ways given here.
Next section
Read more about writing critically in the next section.
- Critical writing
Previous section
Go back to the previous section about using complex grammar .
- Complex grammar

Author: Sheldon Smith ‖ Last modified: 05 February 2024.
Sheldon Smith is the founder and editor of EAPFoundation.com. He has been teaching English for Academic Purposes since 2004. Find out more about him in the about section and connect with him on Twitter , Facebook and LinkedIn .
Compare & contrast essays examine the similarities of two or more objects, and the differences.
Cause & effect essays consider the reasons (or causes) for something, then discuss the results (or effects).
Discussion essays require you to examine both sides of a situation and to conclude by saying which side you favour.
Problem-solution essays are a sub-type of SPSE essays (Situation, Problem, Solution, Evaluation).
Transition signals are useful in achieving good cohesion and coherence in your writing.
Reporting verbs are used to link your in-text citations to the information cited.

How to Write Objectives | A Step-to-step Guide (2023)
Astrid Tran • 31 Aug 2023 • 6 min read
Objectives are needed for every aspect of life, work and education.
Whether you are setting objectives for academic research, teaching and learning, courses and training, personal development, professional growth, a project, or more, having clear objectives like having a compass to help you stay on track.
So, how to write objectives? Check out this article to get a complete guide on writing realistic and impactful objectives.
Table of Contents
How to write objectives of a project
How to write objectives for a presentation, how to write objectives for lesson plan, how to write objectives for a research, how to write objectives for personal growth.
More tips on how to write objectives
Frequently Asked Questions
Project objectives often focus on tangible results, such as completing specific tasks, delivering products, or achieving certain milestones within a defined timeframe.
Writing project objectives should follow these principles:
Start early : It is important to set your project objectives at the beginning of your project to avoid unexpected situations and employees misunderstanding.
Changes : Project objectives can be determined to address challenges of previous projects experience and seek to minimize potential risks prior to the project begins.
Achievement : An objective of a project should mention what success is. Different success is measured by specific and measurable objectives.
OKR : OKR stands for “objectives and key results,” a managerial model that aims to set goals and identify metrics to measure progress. Objectives are your destination, while key results contribute to the path that will get you there.
Focus : Different project objectives might consist of related issues such as:
- Customer satisfaction
- Turnover and Retention
- Sales and Revenue
- Return on investment (ROI)
- Sustainability
- Productivity
For example :
- The goal of the campaign is to improve the traffic by 15% before the end of the first quarter.
- This project aims to produce 5,000 units of products in the next three months.
- Add five new methods for clients to seek the feedback form in-product within the next three months.
- Increase click through rate (CTR) engagement on email by 20% by the end of the second quarter.

Presentation objectives outline what you intend to accomplish with your presentation, which might involve informing, persuading, educating, or inspiring your audience. They guide the content creation process and shape how you engage your listeners during the presentation.
When it comes to writing presentation objectives, there are some notes to look at:
The questions “Why” : To write a good presentation objective, start with answering why questions, such as Why is this presentation important to your audience? Why should people invest time and money to attend this presentation? Why is your content important to the organization?
What do you want the audience to know, feel and do ? Another important of writing objectives for a presentation is considering the comprehensive impact your presentation has on the audience. This pertains to the informational, emotional, and actionable aspect.
Rule of three : When you write your objectives in your PPT, don’t forget to express no more than three key points per slide.
Some examples of objectives:
- Ensure the managers understand that without additional funding of $10,000, the project will fail.
- Get commitment from the director of sales to a three-tier pricing proposal for customer Prime.
- Get the audience to commit to reducing their personal plastic usage by signing a pledge to avoid single-use plastics for at least a week.
- Participants will feel empowered and confident about managing their finances, replacing financial anxiety with a sense of control and informed decision-making.

Get your Students Engaged
Start meaningful discussion, get useful feedback and educate your students. Sign up to take free AhaSlides template
Learning objectives, often used in education and training, specify what learners are expected to gain from a learning experience. These objectives are written to guide curriculum development, instructional design, and assessment.
A guide on writing an objective for learning and lesson plan described as follows:
Learning objectives verbs : There is no better way to have learning objectives start with measurable verbs collected by Benjamin Bloom based on level of cognition.
- Knowledge level: tell, uncover, show, state, define, name, write, recall,…
- Comprehension level: indicate, illustrate, represent, formulate, explain, classify, translate,…
- Application level: perform, make a chart, put into action, build, report, employ, draw, adapt, apply,…
- Analysis Level: analyze, study, combine, separate, categorize, detect, examine,…
- Synthesis Level: integrate, conclude, adapt, compose, construct, create, design,…
- Evaluation Level: evaluate, interpret, decide, solve, rate, appraise, verify,…
Student-centered : Objectives should reflect the unique aspirations, strengths and weaknesses of each student, emphasize what students will know or be able to do, not what you will teach or cover.
Learning Objective Examples:
- To recognize the power of different types of language
- By the end of this course, students will be able to identify and develop data collection instruments and measures for planning and conducting sociological research.
- By the end of this course, students will be able to identify their own position on the political spectrum.
The purpose of research objectives is congruent with research study outcomes.They articulate the purpose of the research, what the researcher intends to investigate, and the expected outcomes.
There are severals principles to follow to ensure a well-written research objectives:
Academic language : It is important to note that research writing is strict on the use of language. It is held to a high standard of clarity, precision, and formality.
Avoid using first-person references to state the objectives. Replace “I will” with neutral phrasing that emphasizes the research’s intention. Avoid emotional language, personal opinions, or subjective judgments.
Pinpoint the Focus : Your research objectives should clearly articulate what your study aims to investigate, analyze, or uncover.
Specify the Scope : Outline the boundaries of your research by specifying the scope. Clearly delineate what aspects or variables will be examined, and what will not be addressed.
Maintain Consistency with Research Questions : Ensure your research objectives align with your research questions.
Frequently used phrases in research objectives
- …contribute to the knowledge of…
- …search for…
- Our study will also document….
- The primary objective is to integrate…
- The purposes of this research include:
- We attempt to…
- We formulated these objective based on
- This study searches for
- The second gold is to test
Objectives for personal growth often focus on individual improvement on skills, knowledge, well-being, and overall development.
Personal growth objectives encompass various aspects of life, including emotional, intellectual, physical, and interpersonal dimensions. They serve as roadmaps for continuous learning, growth, and self-awareness.
- Read one non-fiction book each month to expand knowledge in areas of personal interest.
- Incorporate regular exercise into the routine by walking or jogging for at least 30 minutes five times a week.
Tips to write objectives for personal growth from AhaSlides.
💡 Development Goals For Work: A Step-By-Step Guide For Beginners with Examples
💡 What is Personal Growth? Set Up Personal Goals For Work | Updated in 2023
💡 Work Goals Examples For Evaluation with +5 Steps To Create in 2023
How to write objectives in general? Here are common tips for setting objectives of any field.

#1. Be concise and straightforward
Keep the words as simple and straightforward as much as possible. It is much better to remove unnecessary or ambiguous words that might lead to misunderstanding.
#2. Keep your number of objectives limited
Don’t confuse your learners or readers with too many objectives. Concentrating on a few key objectives can effectively maintain focus and clarity and prevent overwhelming.
#3. Use action verbs
You can start each objective with one of the following measurable verbs: Describe, Explain, Identify, Discuss, Compare, Define, Differentiate, List, and more.
#4. Be SMART
SMART objectives framework can be defined with specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. These objectives are clearer and easier to understand and achieve.
⭐ Want more inspiration? Check out AhaSlides to explore the innovative way to get presentations and lesson engaging and fun!
What are the 3 parts of an objective?
According to Mager (1997), objective statements contain three parts: behavior (or, performance), conditions, and criteria.
What are the 4 elements of a well-written objective?
The four elements of an objective are Audience, Behavior, Condition, and Degree, called A-B-C-D method. They are used to identify what a student is expected to know and how to test them.
What are the 4 components of objective writing?
There are four components of an objective include: (1) the action verb, (2) conditions, (3) standard, and (4) the intended audience (always the students)
Ref: Indeed | Batchwood |

Astrid Tran
I've got my rhythm with words
More from AhaSlides

Go to Charlotte.edu
Prospective Students
- About UNC Charlotte
- Campus Life
- Graduate Admissions
Faculty and Staff
- Human Resources
- Auxiliary Services
- Inside UNC Charlotte
- Academic Affairs
Current Students
- Financial Aid
- Student Health
Alumni and Friends
- Alumni Association
- Advancement
- Make a Gift
Writing Measurable Course Objectives
What is a course objective.
A course objective specifies a behavior, skill, or action that a student can demonstrate if they have achieved mastery of the objective. As such, objectives need to be written in such a way that they are measurable by some sort of assessment. Course objectives form the foundation of the class. Everything in the course should work together to ensure students master the course objectives.
What do good course objectives look like?
Good course objectives will be specific , measurable , and written from the learner’s perspective . Here’s a good formula for writing objectives:
Start your course objectives with: By the end of the course, students will be able to:
Choose an action verb that corresponds to the specific action you wish students to demonstrate
Explain the knowledge students are expected to acquire or construct
[Optional]: explain the criterion or level students are expected to reach to show mastery of knowledge
You will also want to make sure that you have thought of a way to assess students’ learned knowledge when writing course objectives. For example, if you always test students’ knowledge of content matter with a multiple choice test, the course objectives cannot ask that students evaluate or create something, as multiple choice tests cannot assess those levels of learning with a high level of accuracy.
![Context for Subject Matter This fill in the blank example can help put this into context for your own subject matter: If students have learned [knowledge/subject of the course], then the should be able to [specific action students can do if they know the content] by completing [assessment/proof of knowledge]. Example: If students have learned US History since 1865, then they should be able to explain the effect of immigration on American culture by completing an essay comparing and contrasting the effect of two immigrant populations on American culture from 1865-1900.](https://teaching.charlotte.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/885/2023/11/Tf2JdTxflO75Am9ql8g-v9zjzqIMAYhTZECgo8QnlkgODcVPWBI-ELq2kWEOQ_ckEO1neoS7c4Z3TSmy7dREylxSrPco4AMvjDE92SiZ_GRDUlH2iLDhNEJTzqqf1_nUG1aqZMHG.png)
If you cannot logically fill in the last blank of this example (assessment), then the objective is not measurable. You won’t include the assessment in the text for your actual course objective that you publish on your syllabus, but you need to know if what you’re asking students to know can be assessed. Otherwise, how can you know or prove that students have learned what they’re supposed to learn in your course?
Difference between Objectives and Assessments:
One thing that can be confusing when creating course objectives is the difference between what students are being asked to know and the assessment that is used to “prove” that students know the information. In the example above, it may be tempting to write something like this: If students have learned U.S. History since 1865, then they should be able to write an essay comparing and contrasting the effect of two immigrant populations on American culture from 1865-1900.
This objective seems measurable, but it’s saying that by the end of the class “students should be able to write an essay”. That makes it sound like one of the objectives of the course is for students to write an essay. What students really need to know though is the effect of immigration on American culture. If you use the assessment in the “course objective slot,” the knowledge students need in order to complete the assessment is assumed rather than explicitly stated.
This could cause issues with the creation of materials and activities in your units because the focus may be on teaching students how to write essays rather than teaching them about the effect of immigration on American culture during a specific time period.
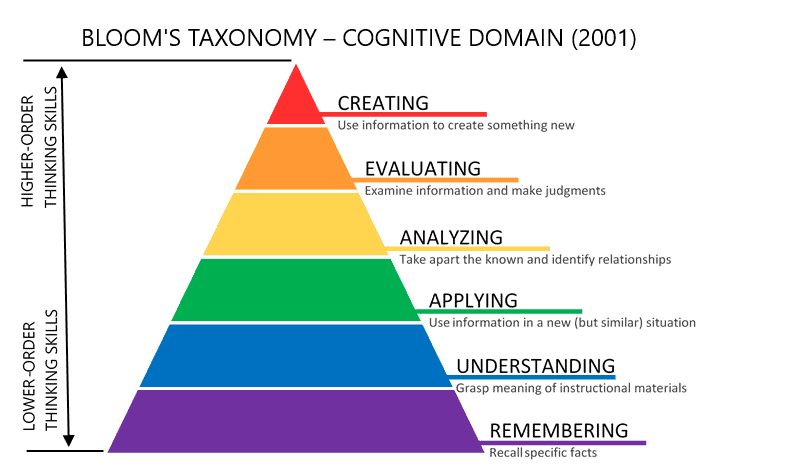
Bloom’s Taxonomy:
Using a taxonomy that explains different levels of learning can be helpful for selecting the appropriate action verbs for your course objectives. These will help prevent you from choosing lower order actions when you really want students to demonstrate higher order thinking.
Bloom’s Taxonomy is broken into six knowledge dimensions: Remembering, Understanding, Applying, Analyzing, Evaluating, and Creating and range from lower order thinking skills to higher order thinking skills.
By their very nature, higher order thinking skills are more difficult and build on the previous lower order thinking skills. An oversimplified explanation of this would be the following: A student can not be expected to create a design brief (Creating) if they can’t remember what a design brief is (Remembering).
Traditionally, entry level courses ask students to demonstrate remembering, understanding, and applying thinking skills with a few higher order thinking skills while graduate level courses ask students to demonstrate analyzing, evaluating, and creating thinking skills with a few lower order thinking skills.

How do course objectives differ from module objectives?
Course objectives are much broader in scope than module level objectives. Where module objectives break down skills and knowledge into very specific, discrete skills, course objectives point more to overarching student understanding and higher level thinking skills. In a unit, you may have 10 or more objectives explaining all of the steps/tasks involved in learning a concept. For a course, you will only want 3-6 course objectives.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write Research Objectives

3-minute read
- 22nd November 2021
Writing a research paper, thesis, or dissertation ? If so, you’ll want to state your research objectives in the introduction of your paper to make it clear to your readers what you’re trying to accomplish. But how do you write effective research objectives? In this post, we’ll look at two key topics to help you do this:
- How to use your research aims as a basis for developing objectives.
- How to use SMART criteria to refine your research objectives.
For more advice on how to write strong research objectives, see below.
Research Aims and Objectives
There is an important difference between research aims and research objectives:
- A research aim defines the main purpose of your research. As such, you can think of your research aim as answering the question “What are you doing?”
- Research objectives (as most studies will have more than one) are the steps you will take to fulfil your aims. As such, your objectives should answer the question “How are you conducting your research?”
For instance, an example research aim could be:
This study will investigate the link between dehydration and the incidence of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in intensive care patients in Australia.
To develop a set of research objectives, you would then break down the various steps involved in meeting said aim. For example:
This study will investigate the link between dehydration and the incidence of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in intensive care patients in Australia. To achieve this, the study objectives w ill include:
- Replicat ing a small Singaporean study into the role of dehydration in UTIs in hospital patients (Sepe, 2018) in a larger Australian cohort.
- Trialing the use of intravenous fluids for intensive care patients to prevent dehydration.
- Assessing the relationship between the age of patients and quantities of intravenous fluids needed to counter dehydration.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Note that the objectives don’t go into any great detail here. The key is to briefly summarize each component of your study. You can save details for how you will conduct the research for the methodology section of your paper.
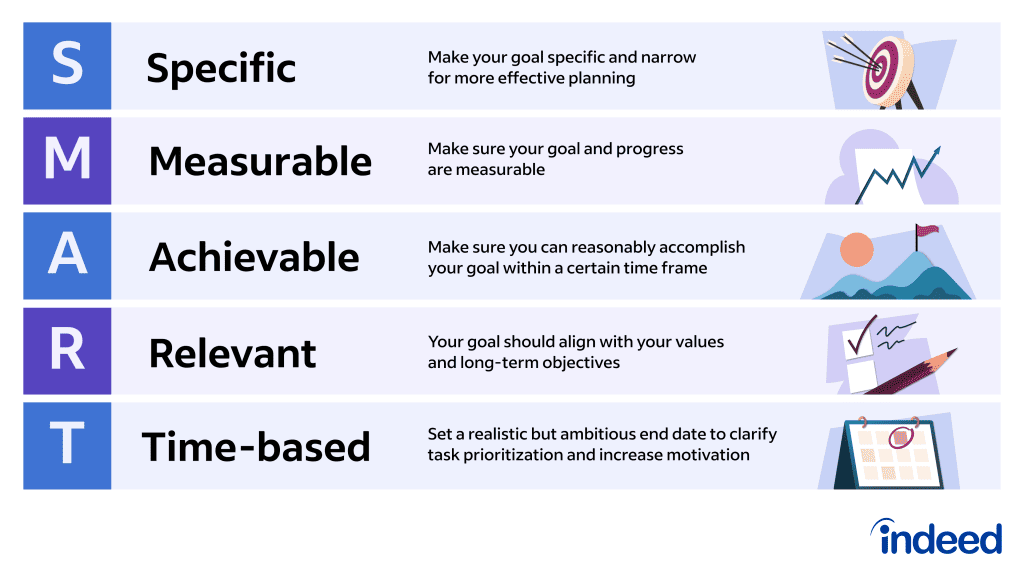
Make Your Research Objectives SMART
A great way to refine your research objectives is to use SMART criteria . Borrowed from the world of project management, there are many versions of this system. However, we’re going to focus on developing specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and timebound objectives.
In other words, a good research objective should be all of the following:
- S pecific – Is the objective clear and well-defined?
- M easurable – How will you know when the objective has been achieved? Is there a way to measure the thing you’re seeking to do?
- A chievable – Do you have the support and resources necessary to undertake this action? Are you being overly ambitious with this objective?
- R elevant – Is this objective vital for fulfilling your research aim?
- T imebound – Can this action be realistically undertaken in the time you have?
If you follow this system, your research objectives will be much stronger.
Expert Research Proofreading
Whatever your research aims and objectives, make sure to have your academic writing proofread by the experts!
Our academic editors can help you with research papers and proposals , as well as any other scholarly document you need checking. And this will help to ensure that your academic writing is always clear, concise, and precise.
Submit a free sample document today to trial our services and find out more.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
2-minute read
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...
The 5 Best Ecommerce Website Design Tools
A visually appealing and user-friendly website is essential for success in today’s competitive ecommerce landscape....

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

OASIS: Writing Center
Scholarly voice: objectivity.
Try to present your argument in as objective a way as possible. Avoid judgmental and emotive language, as this often reveals that you are presenting an opinion rather than evidence or a logical argument. Note, however, that whether a phrase or word is judgmental or emotive often depends on the context. It is best to avoid phrases like "it is right , " "I believe," or "I feel . " Often these types of statements lead the writer into bias , a mistake that academic writing avoids. Remember to back up your arguments with sources and facts in order to give you credibility and a more objective tone.
For example, take a look at this sentence:
I feel that childhood obesity is unhealthy, and children’s eating habits are not right.
Note the use of "I" and the judgmental phrase "not right." Try to think of a way to portray the same information without inserting yourself or your opinion. For example, instead of saying I feel, ask yourself, "Is this a fact?" If it is a fact, write it as a statement:
Childhood obesity is unhealthy.
With this statement, you are stating a fact and removing yourself to maintain your authorial distance. Also, rather than saying their eating habits are not right (after all, who is to judge what is right and wrong in eating?), you can use statistics and valid sources to back up your ideas:
Two major causes of childhood obesity are poor nutrition and uneducated food choices (Fredricks, 2010).
Here you are giving information rather than giving a judgment. See APA 7, Chapter 5 for more guidelines for reducing bias.
Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Search our website or email us .
Read our website accessibility and accommodation statement .
- Previous Page: Second-Person Point of View
- Next Page: Avoiding Bias
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
6 Tips on Achieving an Objective Tone in Writing

- 5-minute read
- 11th July 2021
An objective tone is standard in most formal business and academic writing. But how can you make your writing sound objective? Our top tips include:
- Try to avoid unnecessary use of the first person and first-person pronouns.
- Focus on facts and cite sources clearly to back up your claims.
- Aim for balance and consider multiple perspectives.
- Beware of emotive language that betrays a subjective opinion.
- Use a formal writing style throughout.
- Have your writing proofread to make sure it is always error-free.
For more detail on how to achieve an objective tone in writing, read on.
1. Try Not to Use the First Person
Objective writing aims for a neutral, impersonal tone. As such, you should try to minimise the use of the first person and first-person pronouns such as ‘I’, ‘me’ and ‘mine’, which put too much focus on you as the writer of the document.
One option is to use the passive voice more. For instance:
I will outline the main arguments. -> The main arguments will be outlined.
However, this can sound awkward or leave your writing unclear (e.g. the sentence above does not specify who or what will outline the arguments). As such, it is often better to stick to the active voice and use the third person instead. For example:
This paper will outline the main arguments.
Here, the meaning is clear, but we avoid using any first-person pronouns.
2. Focus on Facts and Data
Objective writing should be clear and factual. As such, you will need to:
- Research your topic extensively – Before you start writing, make sure to research the topic in detail so you are clear on the facts.
- Always cite your sources – Citing sources adds credibility to your writing by showing your reader where your information came from.
- Consider your sources – Where you get information from matters. Your sources should be unbiased, especially in academic writing. Before citing something or quoting a fact, then, make sure it is from a trustworthy source .
If you can back up your claims with well-researched facts, your writing will come across as much more objective than if you simply make unsupported claims.
3. Be Fair and Balanced
If you present only one side of an argument in your writing, it could appear biased and lose credibility. To achieve an objective tone, then, you must show balance. And this means sharing different viewpoints and perspectives.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
This is especially important if you are presenting an argument in academic writing where acknowledging potential counterarguments or competing points of view is a key part of testing the strength of your position. But it also applies to business writing, where considering multiple perspectives provides important context and shows that you have researched the issue thoroughly.
You don’t always have to give every opinion equal weight or present every possible argument, though, or you run the risk of overwhelming the reader with too much information. Instead, focus on the key perspectives in the subject area.
4. Avoid Emotive Language
Typically, objective writing should avoid emotive language or words that suggest a subjective opinion. For example:
Smith (2020) offers a brilliantly clever solution to this terrible problem.
Here, the words ‘brilliantly clever’ and ‘terrible’ don’t add anything substantive to the sentence. Rather, they signal something about the author’s opinion. And by adding this kind of emotive language, we prompt the reader to respond in a particular way (e.g. to see the solution as ‘brilliantly clever’).
This is not to say you should never offer an opinion in objective writing (e.g. you may need to weigh the benefits of certain actions and recommend the best option to meet a specific objective, which will inevitably involve an element of opinion). But you should present your opinions in a neutral tone and back them up with facts, not relying on emotive or otherwise subjective language to influence your reader.
5. Keep Your Writing Formal
As well as the subjective and emotive language discussed so far, objective writing should avoid informal and colloquial language. This includes:
- Using standard spelling and grammar throughout.
- Avoiding contractions (e.g. instead of using ‘can’t’, use ‘cannot’).
- Cutting out all slang and informal figures of speech.
- Using the correct technical language for your subject area.
This formal style is common in business and academic writing as it reduces the strength of the individual’s voice and thus contributes to an objective tone.
6. Have Your Work Proofread
Errors in writing suggest a lack of care or attention to detail (even when this isn’t true). To make sure your documents have a truly objective, authoritative tone, then, it pays to get them proofread by the writing experts.
Our editors are available 24/7, all year round, so we are always here to help. You can even try our services for free ! Get in touch today to find out more.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Get help from a language expert. Try our proofreading services for free.
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
2-minute read
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
3-minute read
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...
The 5 Best Ecommerce Website Design Tools
A visually appealing and user-friendly website is essential for success in today’s competitive ecommerce landscape....

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- How to Cite
- Language & Lit
- Rhyme & Rhythm
- The Rewrite
- Search Glass
How to Write an Objective Essay
Objectivity in essay writing is important in order for the writer to clearly state both sides of an argument without displaying a bias toward one side or the other. When students are given essay titles to complete, not all titles call for objectivity, but the main question will always point to a pro-and-con situation. Personal opinions in essays are not usually accepted unless they are written with objectivity and backed up by references and proof.
Begin your essay with an introductory paragraph that presents the purpose of the essay. If there is a hypothesis involved, state how you intend to prove or disprove the hypothesis and broadly explain how you intend to do so. Details at this point are not necessary, as they will be covered in the main body of your essay.
State one side of the argument and report the evidence and findings that support the statement you are making. Leave out how you personally feel about the issue but do bring in supporting evidence that you find compelling. Remain objective when you compose an essay by keeping your arguments balanced in support or for rebuttal of the hypothesis.
Read back over the essay as you write and remain focused on your objectivity. To be objective is the opposite of being subjective. Being objective is being able to remove yourself from the personal emotions and thoughts you may have about the subject, while being able to examine fairly and critique both sides of the argument you are discussing.
State the opposing argument in your next paragraph or chapter. Use words and phrases that express the change of direction within the essay, such as “however,” “although” and “on the other hand.” Include comments that contrast the preceding paragraphs. For example, you may be writing about Freud, and your contrasting statement would include something like “While Freud argued that ... Jung disagreed with this by stating ...” Your goal in the rebuttal argument is to compel readers to see both sides and draw their own conclusions.
Conclude your essay by summing up the arguments both for and against the position. Again, remaining objective means reiterating your argument in a simplified form to remind readers what they have heard and, hopefully, learned from your statements. Your aim is to gear the readers up for a short evaluation of the topic of discussion. State the facts you have laid out and remind the readers of your own objectivity by using an equal number of references and arguments from both sides. If your essay requires you to conclude with an opinion, then you should compose and add one. If the essay simply requests an argumentative approach, then lay out the two sides and state the conclusion as the recap of the elements of the essay.
Jackie Michael has been a freelance writer since 2007. Her work has appeared on various websites, including Autos.com and CarsDirect. She holds a Bachelor of Arts in psychology and sociology from East London University.
- Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning
- Instructional Guide
Writing Goals and Objectives
“If you’re not sure where you are going, you’re liable to end up some place else.” ~ Robert Mager, 1997
Instructional goals and objectives are the heart of instruction. When well- written, goals and objectives will help identify course content, structure the lecture, and guide the selection of meaningful and relevant activities and assessments. In addition, by stating clear instructional goals and objectives, you help students understand what they should learn and exactly what they need to do.
Course Goals
A course goal may be defined as a broad statement of intent or desired accomplishment. Goals do not specify exactly each step, component, or method to accomplish the task, but they help pave the way to writing effective learning objectives. Typical course goals include a number of subordinate skills, which are further identified and clarified as learning objectives.
A course goal may be defined as a broad statement of intent or desired accomplishment.
For example, an English 102 goal might be to prepare students for English 103. The goal “prepare students” specifies the big picture or general direction or purpose of the course. Course goals often do not specify student outcomes or how outcomes will be assessed. If you have difficulty defining a course goal, brainstorm reasons your course exists and why students should enroll in it. Your ideas can then generate course-related goals. Course goals often originate in the course description and should be written before developing learning objectives. You should also discuss course goals with your colleagues who teach the same class so that you can align your goals to provide students with a somewhat consistent experience of the course.
Course Goal Examples
Marketing course .
Students will learn about personal and professional development, interpersonal skills, verbal and written presentation skills, sales and buying processes, and customer satisfaction development and maintenance.
Physical Geography course
Students will understand the processes involved in the interactions between, spatial variations of, and interrelationships between hydrology, vegetation, landforms, and soils and humankind.
Theatre/Dance course
Students will investigate period style from pre-Egyptian through the Renaissance as it relates to theatrical production. Exploration of period clothing, manners, décor, and architecture with projects from dramatic literature.
General Goal Examples
- Students will know how to communicate in oral and written formats.
- Students will understand the effect of global warming.
- Students’ perspective on civil rights will improve .
- Students will learn key elements and models used in education.
- Students will grasp basic math skills.
- Students will understand the laws of gravity.
Learning Objectives
We cannot stop at course goals; we need to develop measurable objectives. Once you have written your course goals, you should develop learning objectives. Learning Objectives are different from goals in that objectives are narrow, discrete intentions of student performance, whereas goals articulate a global statement of intent. Objectives are measurable and observable, while goals are not.
Comparison of Goals and Objectives
- Broad, generalized statements about what is to be learned
- General intentions
- Cannot be validated
- Defined before analysis
- Written before objectives
Objectives are
- Narrow, specific statements about what is to be learned and performed
- Precise intentions
- Can be validated or measured
- Written after analysis
- Prepared before instruction is designed
Objectives should be written from the student’s point of view
Well-stated objectives clearly tell the student what they must do by following a specified degree or standard of acceptable performance and under what conditions the performance will take place. In other words, when properly written, objectives will tell your learners exactly what you expect them to do and how you will be able to recognize when they have accomplished the task. Generally, each section/week/unit will have several objectives (Penn State University, n.p.). Section/week/unit objectives must also align with overall course objectives.
Well-stated objectives clearly tell the student what they must do ... and under what conditions the performance will take place.
Educators from a wide range of disciplines follow a common learning objective model developed by Heinich (as cited by Smaldino, Mims, Lowther, & Russell, 2019). This guide will follow the ABCD model as a starting point when learning how to craft effective learning objectives.
ABCD Model of Learning Objectives
- A udience: Who will be doing the behavior?
- B ehavior: What should the learner be able to do? What is the performance?
- C ondition: Under what conditions do you want the learner to be able to do it?
- D egree: How well must the behavior be done? What is the degree of mastery?
Writing a learning objective for each behavior you wish to measure is good instructional practice. By using the model as illustrated in Table 2, you will be able to fill in the characteristics to the right of each letter. This practice will allow you to break down more complex objectives (ones with more than one behavior) into smaller, more discrete objectives.
Writing a learning objective for each behavior you wish to measure is good instructional practice.
Behavioral Verbs
The key to writing learning objectives is using an action verb to describe the behavior you intend for students to perform. You can use action verbs such as calculate, read, identify, match, explain, translate, and prepare to describe the behavior further. On the other hand, words such as understand, appreciate, internalize, and value are not appropriate when writing learning objectives because they are not measurable or observable. Use these words in your course goals but not when writing learning objectives. See Verbs to Use in Creating Educational Objectives (based on Bloom’s Taxonomy) at the end of this guide.
Overt behavior: If the behavior is covert or not typically visible when observed, such as the word discriminate, include an indicator behavior to clarify to the student what she or he must be able to do to meet your expectations. For example, if you want your learners to be able to discriminate between good and bad apples, add the indicator behavior “sort” to the objective: Be able to discriminate (sort) the good apples from the bad apples.
Some instructors tend to forget to write learning objectives from the students’ perspective. Mager (1997) contends that when you write objectives, you should indicate what the learner is supposed to be able to do and not what you, the instructor, want to accomplish. Also, avoid using fuzzy phrases such as “to understand,” “to appreciate,” “to internalize,” and “to know,” which are not measurable or observable. These types of words can lead to student misinterpretation and misunderstanding of what you want them to do.
…avoid using fuzzy phrases such as “to understand,” “to appreciate,” “to internalize,” and “to know,” which are not measurable or observable.
The Link Between Learning Objectives and Course Activities and Assessment
After you have crafted your course goals and learning objectives, it is time to design course activities and assessments that will tell you if learning has occurred. Matching objectives with activities and assessments will also demonstrate whether you are teaching what you intended. These strategies and activities should motivate students to gain knowledge and skills useful for success in your course, future courses, and real-world applications. The table below illustrates objective behaviors with related student activities and assessments.
Examples of Linked Instructional Goals, Objectives, and Assessments
Instructional goal .
Students will know the conditions of free Blacks during antebellum south.
Learning Objective
In at least 2 paragraphs, students will describe the conditions of free Blacks in pre-Civil War America, including 3 of 5 major points that were discussed in class.
A traditional essay or essay exam.

Instructional Goal
Students will know how to analyze blood counts.
Given a sample of blood and two glass slides, students will demonstrate the prescribed method of obtaining a blood smear for microscopic analysis.
Instructor observation of student demonstration in a lab using a criterion checklist of critical steps for objective scoring.
Students will understand how to interpret classic literature.
Learning Objective
Students will compare/contrast Shakespeare’s Merchant of Venice and Marlowe’s Jaw of Malta in terms of plot, character, and social-political themes.
Assessment
Instructional goals and learning objectives are the heart of your role as a learning facilitator. When written well, goals and objectives will assist you in identifying course content, help you structure your lecture, and allow you to select activities and assessments that are relevant and meaningful for learning. Make sure that you check with your department to determine whether they require certain learning objectives for a course, for example to align courses with Illinois Articulation Initiative (IAI) requirements for transferrable general education courses (see the current NIU Undergraduate Catalog section on “Illinois Articulation Initiative Core Curriculum).
Several sources are available that you can use to check the accuracy and efficacy of your learning objectives. The sources below provide checklists and other instruments to help you design effective and meaningful objectives.
Mager, R. F. (1997). Measuring instructional results: How to find out if your learning objectives have been achieved. (3 rd ed.). Atlanta, GA: CEP Press.
Mager, R. F. (1997). Preparing learning objectives: A critical tool in the development of effective instruction. (3 rd ed.). Atlanta, GA: CEP Press.
Penn State University, Schreyer Institute (n.p.). Learning outcomes assessment tutorial. https://sites.psu.edu/loatutorial/
Smaldino, S. E., Lowther, D. L., Mims, C., & Russell, J. D. (2019). Instructional technology and media for learning (12 th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson.
Selected Resources
Gronlund, N. E., & Brookhart, S. M. (2009). Gronlund’s writing instructional objectives (8 th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson.

Suggested citation
Northern Illinois University Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. (2020). Writing goals and objectives. In Instructional guide for university faculty and teaching assistants. Retrieved from https://www.niu.edu/citl/resources/guides/instructional-guide
Phone: 815-753-0595 Email: [email protected]
Connect with us on
Facebook page Twitter page YouTube page Instagram page LinkedIn page
Subjective vs. Objective Essay: Examples, Writing Guides, & Topics
Subjective or objective essay writing is a common task students have to deal with. On the initial stage of completing the assignment, you should learn how to differentiate these two types of papers. Their goals, methods, as well as language, tone, and voice, are different.
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
A subjective essay focuses on the writer’s personal opinion, while an objective one represents valid facts. So, be careful when composing an objective paragraph or paper. Don’t let your beliefs take over real arguments supported by substantial evidence.
In short, differences between these styles concern the following:
- The ground for objective essays is facts; for subjective essays – personal opinions and beliefs.
- Objective papers report the findings from scientific sources, while subjective ones describe the writer’s thoughts.
- The objective essay’s goal is to help the reader make a decision. Subjective writing aims to reflect the author’s vision of the issue.
So, if you face this task for the first time, you may need some explanations. Custom-writing.org experts prepared a list of tips on how to write objective and subjective essays. Some topics, as well as objective and subjective writing examples, will also be useful.
- 🆚 Subjective vs. Objective
🔗 References
🆚 subjective vs. objective essays.
First and foremost, let’s find out the critical differences between the writing styles. Take a look at the following table and shed light on this issue.
An objective essay is a presentation of the material with no independent opinion involved. Only facts matter in this paper, and only facts can back up some assertions. Writing subjective essays implies introducing your standpoint on a particular problem.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
📋 How to Write an Objective Essay
Writing any essay consists of three parts: preparation, the actual writing, and revision. During the first one, you need to decide on your topic and do a little research. You can see how it looks in a real example.
Objective Essay Example: The Portrayal of Odysseus
In Odyssey, Homer portrays Odysseus, the king of Ithaca, as the true epic hero. The depiction of Odysseus is thoughtfully knitted together with the themes of love and loyalty that further magnify it, painting a holistic picture of a long 10-year journey home. Although it can be argued that some of Odysseus’s personality traits he displays cannot be applied to a true hero, he is still depicted following a very specific heroic archetype.
Now, let’s get into more detail!
Objective Essay Topics
If you’ve decided to write an objective essay, you need to come up with a topic. The topic gives a reader a brief overview of what will be covered in the paper.
Here are ten great examples:
- While the differences between Italy and Spain are evident, the resemblances are striking.
- There are several similarities between the movies “Deep Impact” and “Armageddon.”
- Compare and contrast the capitals of two English-speaking countries.
- Somatic symptoms in people with PTSD can be influenced by age, gender, and avoidance.
- Some might argue, but being overweight carries a social stigma.
- Environmental factors contribute to the phenotypic expression of psychological disorders.
- Although the exact reason remains unclear, depression is affected by sex, gender, hormonal changes, and age.
- When comparing and contrasting the Bible and Quran, it seems that they have more similarities than differences.
- Musical ability is the result of influence on the person from outside.
- In comparison to extroverts, introverts draw power from within themselves to use it in future activities.
Objective Essay Structure
We shall continue with exploring an essay structure. Note that the parts described below are essential for any essay.
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 20% off your first order!
- Introduction . The introduction is usually the part that broadly describes the topic and gets the interest of the reader. This part of the paper should cover some background information and present the purpose.
- Hypothesis . In case your essay has one, state it in your introduction. A hypothesis includes information about how you intend to prove or refute the claim. It briefly describes the way you intend to do so.
- Arguments . Present one side of the argument. In the next paragraph, present the opposing one, using such words as “however,” “nevertheless,” and “although.” The task is to provide the readers with two sides of the argument.
- Evidence . Provide the evidence for all of your points. Keep the balance in providing proof and refutal. Omit your personal opinion, rather than include the evidence you find informative and convincing.
- Conclusion . Summarize the arguments both for and against the position. While remaining objective, shortly go over the information you presented as evidence. If the instructions require a personal opinion, in conclusion, you might write one. In other cases, briefly recap the parts of the essay. Shorten sentence generator would be greatly beneficial in such endeavor.
📜 How to Write a Subjective Essay
As we’ve mentioned earlier, a subjective essay represents the author’s vision of a particular issue. You have an opportunity to introduce your point of view without supporting your ideas with evidence from the primary sources. However, make sure your arguments are still logical and adequate.
Now see how to write a subjective essay in the sections below.
Subjective Writing Example
A well-chosen topic is the vital determinant of a successful essay. Yet, the process of selecting an idea for your paper might be challenging. That’s why you may find our example helpful.
The rapid pace of development of modern technologies increases the demand for oil and gas every year. A considerable amount of these resources is necessary to maintain both industrial enterprises and private equipment. Despite active production, there are still many unexplored places on Earth, potentially rich in oil and gas deposits. However, while making them public would help solve the existing problem, I’m afraid I disagree with this proposal.
Subjective Essay Topics
Check our list of subjective essay topics, choose the one you like the most, or inspire and come up with your idea!
- The fake and too glamorous life presented in social media leads to the development of an inferiority complex among teenagers.
- The information flows within the country should not be controlled by the governments.
- Since developed nations provoked the climate crisis, they should take full responsibility for their past actions and reduce carbon emissions in the atmosphere.
- Cyberbullying should be a matter of the same importance as physical abuse.
- Remote learning opens more opportunities and expands the students’ horizons.
- Instead of catching up with fashion trends, it is better to develop your unique style.
- People should have enough rest to reduce the levels of anxiety and decrease the chances of depression.
- Studying abroad is an experience worth trying.
- Planning and scheduling are perfect strategies to deal with procrastination.
- While applying for a job position, work experience is more significant than having a degree.
📝 Subjective Essay Structure
When you deal with this task, you have full freedom of choice. You can decide for yourself what idea to support and what arguments to present. Still, you have to structure even a subjective essay properly.
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
Here are the elements you have to include in your paper:
- grab the readers’ attention;
- introduce your subject;
- state your position in the thesis statement.
Important note: your thesis should be clear and straightforward. Let your audience understand your opinion.
- Description . Dive deeper into your topic and describe your issue in detail. However, don’t go too far. Avoid including irrelevant facts and unnecessary information. Follow the principle “quality over quantity” to keep your reader engaged.
- Opinion . After describing your issue, move to the most crucial part of your essay—opinion. State it clearly and concisely. Although you don’t need to provide any evidence from scholarly sources, your ideas should be supported by substantial arguments or examples from your personal life.
- Conclusion . In the last paragraph of your subjective essay, restate your thesis statement. Don’t introduce any other ideas here. To make your paper more dynamic, ask a provocative question at the end. It may motivate your reader for further investigation of your subject.
A helpful tip:
Before submitting your work, make sure it is coherent. Check if all of your ideas follow the logical flow. To avoid redundancy and wordiness, mix shorter sentences with longer ones and apply transitional phrases. Polish your essay, turn it in, and wait for your perfect grade.
Thanks for reading the page! Share it with your peers who may need some guidance as well. Our writers are ready to explain any other essay type , not only objective or subjective ones.
Learn more on this topic:
- How to Write an Expository Essay in Simple Steps
- Nursing Reflective Essay Example and Guidelines for Students
- Essay on Dengue Fever: How to Write + Free Examples
- French Essay Writing: How-to Guide and Examples
- How to Write a Rebuttal Essay: Jackie Michael, Pen and the Pad
- Writing Objectively: OWLL, Massey University
- Subjective vs Objective: Difference and Comparison, Diffen
- Objective and Subjective Claims: TIP Sheet, Butte College
- Evidence: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- Organizing Your Argument: Purdue Online Writing Lab, College of Liberal Arts, University of Purdue
- Argumentative Paper Format: Courtesy the Odegaard Writing & Research Center, University of Washington
- How Do I Write an Intro, Conclusion, & Body Paragraph: LSA Sweetland Center for Writing, the University of Michigan
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Writing All About Me paragraph is probably one of the most usual assignments. For example, students might write it when entering an academic institution. Such work gives an opportunity to introduce yourself, your skills, and goals. However, it is not the only possible situation.

Coral reefs can be called one of the most amazing things created by nature. These structures can be found in tropical and temperate waters. Like many other unique natural phenomena, coral reefs are influenced by human activity these days. This negative impact is one of the significant issues to consider when...

An ambition essay focuses on one’s strong desire to achieve success in one or several areas. It might be one’s career, finance, family, art, health, or all at once. Writing an ambition essay, you might want to consider your own life or examples from the world literature. You can describe...
![how to write a objectives essay Essay for Primary School: Simple Guide for Kids [with Samples]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/pupils-raising-hand-classroom-284x153.jpg)
The age of primary school students ranges from 5 to 11 years. At this stage of education, children start developing their writing skills. They make their first steps to analyzing and proving their points of view. Besides, they study how to write an essay for elementary school. Correctly preparing all...

Canadian identity is something that has become really important for many Canadians in the past fifty years. Canada is a big, multinational country with its own traditions, culture, and history. However, because of quite a large number of foreigners and even Americans, its culture and people are associated with the...

Let’s say you received a task to write an essay about cars. The topic might be interesting for you, but you may still have no idea how to organize your paper. Well, this article is for you.

Smoking can be viewed as one of the trendy habits. Numerous teenagers try it since they think that it is cool or can help them socialize. Often students start smoking due to stress or mental illnesses. But is it okay? Educators tend to give different written assignments, which may disclose...
![how to write a objectives essay Child Labor Essay: Thesis, Examples, & Writing Guide [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/child-working-in-cambodia-e1565628499749-284x153.jpg)
Children have always been apprentices and servants all over human history. However, the Industrial Revolution increased the use of child labor in the world. It became a global problem that is relevant even today when such employment is illegal.

Dissertation critique writing develops the students’ critical and logical thinking abilities. When composing, the students learn to analyze the works conducted by other researchers. To critique a dissertation, you should: Thoroughly read the paper.Take notes and summarize the text (you can even try and use auto summarizer for that).Interpret and...

An opinion essay is a formal piece of writing which presents the author’s point of view on a particular subject supported by reasoning and examples. The opposing viewpoint is also suggested, but it is followed by arguments that show its inconsistency. Take a look at the guide prepared by Custom-writing experts to...

So, you need to accomplish your discursive essay writing. The typical questions most students ask are: How do you write it? What is discursive essay? A discursive essay is an academic paper that involves a discussion on a particular topic. It is usually assigned to college students. You may be...

How to write a narrative essay? To do that, you need to know what a narrative essay is. It is an academic text usually written as a story and containing all the usual elements of a story. Narrative essays are often personal, experiential, and creative. Still, they should be made...
Very helpful to make my assignment. Thank you so much!

Glad to know that. Thank you very much, Farhana!
Subjective and reflective.
That’s right, Raj 🙂
Thank you for this information. I submitted my subjective essay, which was rejected by my teacher for lack of an attractive hook. After reading your info on writing subjective essays, I know what I should change in my paper to get a good grade.
Thank you so sweet for these wonderful tips for objective essays! I love your blog, and it’s really helpful one online! Keep it up!
This is what I need to complete my paper. Your subjective essay writing secrets are appropriate for students who can’t cope with their essays themselves. Even those who write a paper for the first time will complete their subjective essays without any problems.
I really appreciate your help in posting all this information for students — this time you’ve taught me how to write an objective essay. You’re real specialists in writing all types of papers!
- If you are writing in a new discipline, you should always make sure to ask about conventions and expectations for introductions, just as you would for any other aspect of the essay. For example, while it may be acceptable to write a two-paragraph (or longer) introduction for your papers in some courses, instructors in other disciplines, such as those in some Government courses, may expect a shorter introduction that includes a preview of the argument that will follow.
- In some disciplines (Government, Economics, and others), it’s common to offer an overview in the introduction of what points you will make in your essay. In other disciplines, you will not be expected to provide this overview in your introduction.
- Avoid writing a very general opening sentence. While it may be true that “Since the dawn of time, people have been telling love stories,” it won’t help you explain what’s interesting about your topic.
- Avoid writing a “funnel” introduction in which you begin with a very broad statement about a topic and move to a narrow statement about that topic. Broad generalizations about a topic will not add to your readers’ understanding of your specific essay topic.
- Avoid beginning with a dictionary definition of a term or concept you will be writing about. If the concept is complicated or unfamiliar to your readers, you will need to define it in detail later in your essay. If it’s not complicated, you can assume your readers already know the definition.
- Avoid offering too much detail in your introduction that a reader could better understand later in the paper.
- picture_as_pdf Introductions
Objective Writing
6 July 2023
last updated
The purpose of higher learning is to communicate ideas effectively through writing. Basically, teachers expect learners to present accurate findings, concerning a specific matter. In this case, students use verifiable evidence. Also, the method is unique because it allows one to gather, calculate, or evaluate information. In turn, objective writing enables people to present irrefutable facts, apply critical thinking styles, maintain a neutral tone, and use formal and explicit language.
Presenting Facts
Objective writing is a factual process that enhances knowledge. For instance, learners gather facts that support the selected topic. In this case, one must support arguments with evidence from credible sources . Besides, students address both sides of an opinion. Then, being objective makes essays appear professional and reliable. In turn, people avoid making judgments. Also, they remain fair in their work. Thus, empirical writing allows individuals to present accurate information that addresses existing knowledge gaps.

Critical Thinking in Objective Writing
Objective writing is unique because it enhances critical thinking. For instance, learners evaluate, calculate, and verify the information. In this case, students must gather relevant details and determine their significance to the subject. Besides, people must ensure that the audience attains a deeper understanding of the topic. Therefore, learners must appraise information to achieve the desired goals during factual writing.
Maintaining a Neutral Tone
Objective writing is essential because it allows students to use a neutral tone. For instance, one should not use opinionated, biased, or exclusive language. Basically, learners must submit unbiased information to an audience. Instead, scholars allow readers to determine their opinions. However, imbalanced information does not persuade people to accept a narrow way of thinking. In this case, the approach helps writers to present relevant facts about a subject. Thus, scholars should learn factual writing since the method allows them to be less judgmental.
Following a Formal Style in Objective Writing
Objective writing is an essential skill because it helps learners to follow formal style. Basically, academic papers must use the official language. In this case, students avoid personal pronouns. Also, the extensive use of the third person enhances the clarity of an assignment. Then, empirical writing helps scholars to avoid intensifiers that exaggerate their arguments. For example, people should avoid words, like “very” and “really,” since they make information vague. Finally, scholarly papers require the proper use of punctuation marks. In turn, successful learners proofread their works to ensure that they use commas and full stops effectively. Besides, the approach prevents all forms of miscommunication. Therefore, writers should follow the rules of factual writing because it trains them to maintain a formal tone in their papers.
Expressing Ideas
Objective writing allows students to express ideas explicitly. For example, learners develop precise sentences to express their thoughts. In this case, they make their work comprehensible. Besides, the approach helps essays to stand out. Therefore, people should learn objective writing because it allows them to communicate clearly.
Summing Up on Objective Writing
In conclusion, objective writing requires people to cover irrefutable facts. Basically, the process is unique because it enables learners to develop critical thinking skills when completing assignments. Also, scholars should learn to empirical writing because they gain the ability to follow a neutral tone. In turn, they learn to write by using a formal and specific style. Thus, objective writing improves the quality of academic papers.
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles
Essay on education, proper mla format.
Tips for Writing an Effective Application Essay

How to Write an Effective Essay
Writing an essay for college admission gives you a chance to use your authentic voice and show your personality. It's an excellent opportunity to personalize your application beyond your academic credentials, and a well-written essay can have a positive influence come decision time.
Want to know how to draft an essay for your college application ? Here are some tips to keep in mind when writing.
Tips for Essay Writing
A typical college application essay, also known as a personal statement, is 400-600 words. Although that may seem short, writing about yourself can be challenging. It's not something you want to rush or put off at the last moment. Think of it as a critical piece of the application process. Follow these tips to write an impactful essay that can work in your favor.
1. Start Early.
Few people write well under pressure. Try to complete your first draft a few weeks before you have to turn it in. Many advisers recommend starting as early as the summer before your senior year in high school. That way, you have ample time to think about the prompt and craft the best personal statement possible.
You don't have to work on your essay every day, but you'll want to give yourself time to revise and edit. You may discover that you want to change your topic or think of a better way to frame it. Either way, the sooner you start, the better.
2. Understand the Prompt and Instructions.
Before you begin the writing process, take time to understand what the college wants from you. The worst thing you can do is skim through the instructions and submit a piece that doesn't even fit the bare minimum requirements or address the essay topic. Look at the prompt, consider the required word count, and note any unique details each school wants.
3. Create a Strong Opener.
Students seeking help for their application essays often have trouble getting things started. It's a challenging writing process. Finding the right words to start can be the hardest part.
Spending more time working on your opener is always a good idea. The opening sentence sets the stage for the rest of your piece. The introductory paragraph is what piques the interest of the reader, and it can immediately set your essay apart from the others.
4. Stay on Topic.
One of the most important things to remember is to keep to the essay topic. If you're applying to 10 or more colleges, it's easy to veer off course with so many application essays.
A common mistake many students make is trying to fit previously written essays into the mold of another college's requirements. This seems like a time-saving way to avoid writing new pieces entirely, but it often backfires. The result is usually a final piece that's generic, unfocused, or confusing. Always write a new essay for every application, no matter how long it takes.
5. Think About Your Response.
Don't try to guess what the admissions officials want to read. Your essay will be easier to write─and more exciting to read─if you’re genuinely enthusiastic about your subject. Here’s an example: If all your friends are writing application essays about covid-19, it may be a good idea to avoid that topic, unless during the pandemic you had a vivid, life-changing experience you're burning to share. Whatever topic you choose, avoid canned responses. Be creative.
6. Focus on You.
Essay prompts typically give you plenty of latitude, but panel members expect you to focus on a subject that is personal (although not overly intimate) and particular to you. Admissions counselors say the best essays help them learn something about the candidate that they would never know from reading the rest of the application.
7. Stay True to Your Voice.
Use your usual vocabulary. Avoid fancy language you wouldn't use in real life. Imagine yourself reading this essay aloud to a classroom full of people who have never met you. Keep a confident tone. Be wary of words and phrases that undercut that tone.
8. Be Specific and Factual.
Capitalize on real-life experiences. Your essay may give you the time and space to explain why a particular achievement meant so much to you. But resist the urge to exaggerate and embellish. Admissions counselors read thousands of essays each year. They can easily spot a fake.
9. Edit and Proofread.
When you finish the final draft, run it through the spell checker on your computer. Then don’t read your essay for a few days. You'll be more apt to spot typos and awkward grammar when you reread it. After that, ask a teacher, parent, or college student (preferably an English or communications major) to give it a quick read. While you're at it, double-check your word count.
Writing essays for college admission can be daunting, but it doesn't have to be. A well-crafted essay could be the deciding factor─in your favor. Keep these tips in mind, and you'll have no problem creating memorable pieces for every application.
What is the format of a college application essay?
Generally, essays for college admission follow a simple format that includes an opening paragraph, a lengthier body section, and a closing paragraph. You don't need to include a title, which will only take up extra space. Keep in mind that the exact format can vary from one college application to the next. Read the instructions and prompt for more guidance.
Most online applications will include a text box for your essay. If you're attaching it as a document, however, be sure to use a standard, 12-point font and use 1.5-spaced or double-spaced lines, unless the application specifies different font and spacing.
How do you start an essay?
The goal here is to use an attention grabber. Think of it as a way to reel the reader in and interest an admissions officer in what you have to say. There's no trick on how to start a college application essay. The best way you can approach this task is to flex your creative muscles and think outside the box.
You can start with openers such as relevant quotes, exciting anecdotes, or questions. Either way, the first sentence should be unique and intrigue the reader.
What should an essay include?
Every application essay you write should include details about yourself and past experiences. It's another opportunity to make yourself look like a fantastic applicant. Leverage your experiences. Tell a riveting story that fulfills the prompt.
What shouldn’t be included in an essay?
When writing a college application essay, it's usually best to avoid overly personal details and controversial topics. Although these topics might make for an intriguing essay, they can be tricky to express well. If you’re unsure if a topic is appropriate for your essay, check with your school counselor. An essay for college admission shouldn't include a list of achievements or academic accolades either. Your essay isn’t meant to be a rehashing of information the admissions panel can find elsewhere in your application.
How can you make your essay personal and interesting?
The best way to make your essay interesting is to write about something genuinely important to you. That could be an experience that changed your life or a valuable lesson that had an enormous impact on you. Whatever the case, speak from the heart, and be honest.
Is it OK to discuss mental health in an essay?
Mental health struggles can create challenges you must overcome during your education and could be an opportunity for you to show how you’ve handled challenges and overcome obstacles. If you’re considering writing your essay for college admission on this topic, consider talking to your school counselor or with an English teacher on how to frame the essay.
Related Articles
How To Write A Research Paper
Find Sources For A Research Paper

How to Find Sources For a Research Paper | A Guide
10 min read
Published on: Mar 26, 2024
Last updated on: Mar 25, 2024

People also read
How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step
How to Write a Proposal For a Research Paper in 10 Steps
A Comprehensive Guide to Creating a Research Paper Outline
Types of Research - Methodologies and Characteristics
300+ Engaging Research Paper Topics to Get You Started
Interesting Psychology Research Topics & Ideas
Qualitative Research - Types, Methods & Examples
Understanding Quantitative Research - Definition, Types, Examples, And More
Research Paper Example - Examples for Different Formats
How To Start A Research Paper - Steps With Examples
How to Write an Abstract That Captivates Your Readers
How To Write a Literature Review for a Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Types of Qualitative Research Methods - An Overview
Understanding Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research - A Complete Guide
How to Cite a Research Paper in Different Citation Styles
Easy Sociology Research Topics for Your Next Project
200+ Outstanding History Research Paper Topics With Expert Tips
How To Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper | Steps & Examples
How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Write a Good Research Paper Title
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper in 3 Simple Steps
How to Write an Abstract For a Research Paper with Examples
How To Write a Thesis For a Research Paper Step by Step
How to Write a Discussion For a Research Paper | Objectives, Steps & Examples
How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper - Structure and Tips
How to Write a Problem Statement for a Research Paper in 6 Steps
How To Write The Methods Section of a Research Paper Step-by-Step
Share this article
Research papers are an essential part of academic life, but one of the most challenging aspects can be finding credible sources to support your arguments.
With the vast amount of information available online, it's easy to feel overwhelmed. However, by following some simple steps, you can streamline the process of finding reliable sources for your research paper .
In this guide, we'll break down the process into easy-to-follow steps to help you find the best sources for your paper.
On This Page On This Page -->
Step 1: Define Your Topic and Research Questions
Before you venture into your quest for sources, it's essential to have a clear understanding of your research topic and the specific questions you aim to address. Define the scope of your paper and identify keywords and key concepts that will guide your search for relevant sources.
Step 2: Utilize Academic Databases
Academic databases are treasure troves of scholarly articles, research papers, and academic journals covering a wide range of subjects. Institutions often provide access to these databases through their libraries. Some popular academic databases include:
- IEEE Xplore
- Google Scholar
These databases allow you to search for peer-reviewed articles and academic papers related to your topic.
Use advanced search features to narrow down your results based on publication date, author, and keywords .
Academic Resources Classified by Discipline
Here's a breakdown of prominent databases categorized by academic discipline:
Step 3: Explore Library Catalogs
Your university or local library's catalog is another valuable resource for finding sources. Library catalogs contain books, periodicals, and other materials that may not be available online.
Use the catalog's search function to locate relevant books, journals, and other materials that can contribute to your research.
Step 4: Consult Bibliographies and References
When you find a relevant source, take note of its bibliography or make a list of sources for the research paper. These lists often contain citations to other works that may be useful for your research.
By exploring the references cited in a particular source, you can uncover additional resources and expand your understanding of the topic.
Step 5: Boolean Operators for Effective Searches
Boolean operators are words or symbols used to refine search queries by defining the relationships between search terms. The three primary operators include "AND," which narrows searches by requiring all terms to be present; "OR," which broadens searches by including either term or both; and "NOT," which excludes specific terms to refine results further.
Most databases provide advanced search features for seamless application of Boolean logic.
Step 6: Consider Primary Sources
Depending on your research topic, primary sources such as interviews, surveys, archival documents, and original data sets can provide valuable insights and support for your arguments.
Primary sources offer firsthand accounts and original perspectives on historical events, social phenomena, and scientific discoveries.
Step 7: Evaluate the Credibility of Sources
Not all sources are created equal, and it's crucial to evaluate the credibility and reliability of the information you encounter.
Consider the author's credentials, the publication venue, and whether the source is peer-reviewed. Look for evidence of bias or conflicts of interest that may undermine the source's credibility.
Step 8: Keep Track of Your Sources
As you gather sources for your research paper, maintain a systematic record of the materials you consult. Keep track of bibliographic information, including author names, publication dates, titles, and page numbers . This information will be invaluable when citing your sources and creating a bibliography or works cited page.
Other Online Sources
In addition to academic databases and library catalogs, exploring popular online sources can provide valuable insights and perspectives on your research topic. Here are some types of online sources you can consider:
Websites hosted by reputable organizations, institutions, and experts (such as the New York Times) can offer valuable information and analysis on a wide range of topics. Look for websites belonging to universities, research institutions, government agencies, and established non-profit organizations.
Crowdsourced Encyclopedias like Wikipedia
While Wikipedia can provide a broad overview of a topic and lead you to other sources, it's essential to verify the information found there with more authoritative sources.
Use Wikipedia as a starting point for your research, but rely on peer-reviewed journal articles and academic sources for in-depth analysis and evidence.
Tips for Assessing the Credibility of Online Sources
When using online sources, it's important to exercise caution and critically evaluate the credibility and reliability of the information you find. Here are some tips for assessing the credibility of online sources:
- Check the Domain Extension: Look for websites with domain extensions that indicate credibility. URLs ending in .edu are educational resources, while URLs ending in .gov are government-related resources. These sites often provide reliable and authoritative information.
- Look for DOIs (Digital Object Identifiers): DOIs are unique alphanumeric strings assigned to scholarly articles and indicate that the article has been published in a peer-reviewed, scientific journal. Finding a DOI can help you assess the scholarly rigor of the source.
- Evaluate the Authorship and Credentials: Consider the qualifications and expertise of the author or organization behind the website or blog. Look for information about the author's credentials, affiliations, and expertise in the subject matter.
- Consider the Currency and Relevance: Assess how up-to-date the information is and whether it aligns with the scope and focus of your research. Look for recent publications and timely analyses that reflect current trends and developments in the field.
Wrapping it up!
Finding sources for your research paper may seem like a challenge, but by following these steps, you can locate credible sources to support your arguments and enhance the quality of your paper.
By approaching the research process systematically and critically evaluating the information you encounter, you can produce a well-researched and compelling research paper.
If you are struggling with finding credible sources or have time constraints, do not hesitate to seek writing help for your research papers . CollegeEssay.org has professional writers ready to assist you.
Connect with our essay writing service now and receive expert guidance and support to elevate your research paper to the next level.
Cathy A. (Law)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips
Published on July 24, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
An argumentative essay expresses an extended argument for a particular thesis statement . The author takes a clearly defined stance on their subject and builds up an evidence-based case for it.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When do you write an argumentative essay, approaches to argumentative essays, introducing your argument, the body: developing your argument, concluding your argument, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about argumentative essays.
You might be assigned an argumentative essay as a writing exercise in high school or in a composition class. The prompt will often ask you to argue for one of two positions, and may include terms like “argue” or “argument.” It will frequently take the form of a question.
The prompt may also be more open-ended in terms of the possible arguments you could make.
Argumentative writing at college level
At university, the vast majority of essays or papers you write will involve some form of argumentation. For example, both rhetorical analysis and literary analysis essays involve making arguments about texts.
In this context, you won’t necessarily be told to write an argumentative essay—but making an evidence-based argument is an essential goal of most academic writing, and this should be your default approach unless you’re told otherwise.
Examples of argumentative essay prompts
At a university level, all the prompts below imply an argumentative essay as the appropriate response.
Your research should lead you to develop a specific position on the topic. The essay then argues for that position and aims to convince the reader by presenting your evidence, evaluation and analysis.
- Don’t just list all the effects you can think of.
- Do develop a focused argument about the overall effect and why it matters, backed up by evidence from sources.
- Don’t just provide a selection of data on the measures’ effectiveness.
- Do build up your own argument about which kinds of measures have been most or least effective, and why.
- Don’t just analyze a random selection of doppelgänger characters.
- Do form an argument about specific texts, comparing and contrasting how they express their thematic concerns through doppelgänger characters.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

An argumentative essay should be objective in its approach; your arguments should rely on logic and evidence, not on exaggeration or appeals to emotion.
There are many possible approaches to argumentative essays, but there are two common models that can help you start outlining your arguments: The Toulmin model and the Rogerian model.
Toulmin arguments
The Toulmin model consists of four steps, which may be repeated as many times as necessary for the argument:
- Make a claim
- Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim
- Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim)
- Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives
The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays. You don’t have to use these specific terms (grounds, warrants, rebuttals), but establishing a clear connection between your claims and the evidence supporting them is crucial in an argumentative essay.
Say you’re making an argument about the effectiveness of workplace anti-discrimination measures. You might:
- Claim that unconscious bias training does not have the desired results, and resources would be better spent on other approaches
- Cite data to support your claim
- Explain how the data indicates that the method is ineffective
- Anticipate objections to your claim based on other data, indicating whether these objections are valid, and if not, why not.
Rogerian arguments
The Rogerian model also consists of four steps you might repeat throughout your essay:
- Discuss what the opposing position gets right and why people might hold this position
- Highlight the problems with this position
- Present your own position , showing how it addresses these problems
- Suggest a possible compromise —what elements of your position would proponents of the opposing position benefit from adopting?
This model builds up a clear picture of both sides of an argument and seeks a compromise. It is particularly useful when people tend to disagree strongly on the issue discussed, allowing you to approach opposing arguments in good faith.
Say you want to argue that the internet has had a positive impact on education. You might:
- Acknowledge that students rely too much on websites like Wikipedia
- Argue that teachers view Wikipedia as more unreliable than it really is
- Suggest that Wikipedia’s system of citations can actually teach students about referencing
- Suggest critical engagement with Wikipedia as a possible assignment for teachers who are skeptical of its usefulness.
You don’t necessarily have to pick one of these models—you may even use elements of both in different parts of your essay—but it’s worth considering them if you struggle to structure your arguments.
Regardless of which approach you take, your essay should always be structured using an introduction , a body , and a conclusion .
Like other academic essays, an argumentative essay begins with an introduction . The introduction serves to capture the reader’s interest, provide background information, present your thesis statement , and (in longer essays) to summarize the structure of the body.
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how a typical introduction works.
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts is on the rise, and its role in learning is hotly debated. For many teachers who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its critical benefits for students and educators—as a uniquely comprehensive and accessible information source; a means of exposure to and engagement with different perspectives; and a highly flexible learning environment.
The body of an argumentative essay is where you develop your arguments in detail. Here you’ll present evidence, analysis, and reasoning to convince the reader that your thesis statement is true.
In the standard five-paragraph format for short essays, the body takes up three of your five paragraphs. In longer essays, it will be more paragraphs, and might be divided into sections with headings.
Each paragraph covers its own topic, introduced with a topic sentence . Each of these topics must contribute to your overall argument; don’t include irrelevant information.
This example paragraph takes a Rogerian approach: It first acknowledges the merits of the opposing position and then highlights problems with that position.
Hover over different parts of the example to see how a body paragraph is constructed.
A common frustration for teachers is students’ use of Wikipedia as a source in their writing. Its prevalence among students is not exaggerated; a survey found that the vast majority of the students surveyed used Wikipedia (Head & Eisenberg, 2010). An article in The Guardian stresses a common objection to its use: “a reliance on Wikipedia can discourage students from engaging with genuine academic writing” (Coomer, 2013). Teachers are clearly not mistaken in viewing Wikipedia usage as ubiquitous among their students; but the claim that it discourages engagement with academic sources requires further investigation. This point is treated as self-evident by many teachers, but Wikipedia itself explicitly encourages students to look into other sources. Its articles often provide references to academic publications and include warning notes where citations are missing; the site’s own guidelines for research make clear that it should be used as a starting point, emphasizing that users should always “read the references and check whether they really do support what the article says” (“Wikipedia:Researching with Wikipedia,” 2020). Indeed, for many students, Wikipedia is their first encounter with the concepts of citation and referencing. The use of Wikipedia therefore has a positive side that merits deeper consideration than it often receives.
An argumentative essay ends with a conclusion that summarizes and reflects on the arguments made in the body.
No new arguments or evidence appear here, but in longer essays you may discuss the strengths and weaknesses of your argument and suggest topics for future research. In all conclusions, you should stress the relevance and importance of your argument.
Hover over the following example to see the typical elements of a conclusion.
The internet has had a major positive impact on the world of education; occasional pitfalls aside, its value is evident in numerous applications. The future of teaching lies in the possibilities the internet opens up for communication, research, and interactivity. As the popularity of distance learning shows, students value the flexibility and accessibility offered by digital education, and educators should fully embrace these advantages. The internet’s dangers, real and imaginary, have been documented exhaustively by skeptics, but the internet is here to stay; it is time to focus seriously on its potential for good.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
The majority of the essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Unless otherwise specified, you can assume that the goal of any essay you’re asked to write is argumentative: To convince the reader of your position using evidence and reasoning.
In composition classes you might be given assignments that specifically test your ability to write an argumentative essay. Look out for prompts including instructions like “argue,” “assess,” or “discuss” to see if this is the goal.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved March 25, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/argumentative-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, how to write an expository essay, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

Should college essays touch on race? Some feel the affirmative action ruling leaves them no choice
The Associated Press
March 27, 2024, 2:51 PM
- Share This:
- share on facebook
- share on threads
- share on linkedin
- share on email

CHICAGO (AP) — When she started writing her college essay, Hillary Amofa told the story she thought admissions offices wanted to hear. About being the daughter of immigrants from Ghana and growing up in a small apartment in Chicago. About hardship and struggle.
Then she deleted it all.
“I would just find myself kind of trauma-dumping,” said the 18-year-old senior at Lincoln Park High School in Chicago. “And I’m just like, this doesn’t really say anything about me as a person.”
When the Supreme Court ended affirmative action in higher education, it left the college essay as one of few places where race can play a role in admissions decisions. For many students of color, instantly more was riding on the already high-stakes writing assignment. Some say they felt pressure to exploit their hardships as they competed for a spot on campus.
Amofa was just starting to think about her essay when the court issued its decision, and it left her with a wave of questions. Could she still write about her race? Could she be penalized for it? She wanted to tell colleges about her heritage but she didn’t want to be defined by it.
In English class, Amofa and her classmates read sample essays that all seemed to focus on some trauma or hardship. It left her with the impression she had to write about her life’s hardest moments to show how far she’d come. But she and some of her classmates wondered if their lives had been hard enough to catch the attention of admissions offices.
“For a lot of students, there’s a feeling of, like, having to go through something so horrible to feel worthy of going to school, which is kind of sad,” said Amofa, the daughter of a hospital technician and an Uber driver.
This year’s senior class is the first in decades to navigate college admissions without affirmative action . The Supreme Court upheld the practice in decisions going back to the 1970s, but this court’s conservative supermajority found it is unconstitutional for colleges to give students extra weight because of their race alone.
Still, the decision left room for race to play an indirect role: Chief Justice John Roberts wrote universities can still consider how an applicant’s life was shaped by their race, “so long as that discussion is concretely tied to a quality of character or unique ability.”
“A benefit to a student who overcame racial discrimination, for example, must be tied to that student’s courage and determination,” he wrote.
Scores of colleges responded with new essay prompts asking about students’ backgrounds. Brown University asked applicants how “an aspect of your growing up has inspired or challenged you.” Rice University asked students how their perspectives were shaped by their “background, experiences, upbringing, and/or racial identity.”
WONDERING IF SCHOOLS ‘EXPECT A SOB STORY’
When Darrian Merritt started writing his essay, he knew the stakes were higher than ever because of the court’s decision. His first instinct was to write about events that led to him going to live with his grandmother as a child.
Those were painful memories, but he thought they might play well at schools like Yale, Stanford and Vanderbilt.
“I feel like the admissions committee might expect a sob story or a tragic story,” said Merritt, a senior in Cleveland. “And if you don’t provide that, then maybe they’re not going to feel like you went through enough to deserve having a spot at the university. I wrestled with that a lot.”
He wrote drafts focusing on his childhood, but it never amounted to more than a collection of memories. Eventually he abandoned the idea and aimed for an essay that would stand out for its positivity.
Merritt wrote about a summer camp where he started to feel more comfortable in his own skin. He described embracing his personality and defying his tendency to please others. The essay had humor — it centered on a water gun fight where he had victory in sight but, in a comedic twist, slipped and fell. But the essay also reflects on his feelings of not being “Black enough” and getting made fun of for listening to “white people music.”
“I was like, ‘OK, I’m going to write this for me, and we’re just going to see how it goes,’” he said. “It just felt real, and it felt like an honest story.”
The essay describes a breakthrough as he learned “to take ownership of myself and my future by sharing my true personality with the people I encounter. … I realized that the first chapter of my own story had just been written.”
A RULING PROMPTS PIVOTS ON ESSAY TOPICS
Like many students, Max Decker of Portland, Oregon, had drafted a college essay on one topic, only to change direction after the Supreme Court ruling in June.
Decker initially wrote about his love for video games. In a childhood surrounded by constant change, navigating his parents’ divorce, the games he took from place to place on his Nintendo DS were a source of comfort.
But the essay he submitted to colleges focused on the community he found through Word is Bond, a leadership group for young Black men in Portland.
As the only biracial, Jewish kid with divorced parents in a predominantly white, Christian community, Decker wrote he constantly felt like the odd one out. On a trip with Word is Bond to Capitol Hill, he and friends who looked just like him shook hands with lawmakers. The experience, he wrote, changed how he saw himself.
“It’s because I’m different that I provide something precious to the world, not the other way around,” he wrote.
As a first-generation college student, Decker thought about the subtle ways his peers seemed to know more about navigating the admissions process . They made sure to get into advanced classes at the start of high school, and they knew how to secure glowing letters of recommendation.
If writing about race would give him a slight edge and show admissions officers a fuller picture of his achievements, he wanted to take that small advantage.
His first memory about race, Decker said, was when he went to get a haircut in elementary school and the barber made rude comments about his curly hair. Until recently, the insecurity that moment created led him to keep his hair buzzed short.
Through Word is Bond, Decker said he found a space to explore his identity as a Black man. It was one of the first times he was surrounded by Black peers and saw Black role models. It filled him with a sense of pride in his identity. No more buzzcut.
The pressure to write about race involved a tradeoff with other important things in his life, Decker said. That included his passion for journalism, like the piece he wrote on efforts to revive a once-thriving Black neighborhood in Portland. In the end, he squeezed in 100 characters about his journalism under the application’s activities section.
“My final essay, it felt true to myself. But the difference between that and my other essay was the fact that it wasn’t the truth that I necessarily wanted to share,” said Decker, whose top college choice is Tulane, in New Orleans, because of the region’s diversity. “It felt like I just had to limit the truth I was sharing to what I feel like the world is expecting of me.”
SPELLING OUT THE IMPACT OF RACE
Before the Supreme Court ruling, it seemed a given to Imani Laird that colleges would consider the ways that race had touched her life. But now, she felt like she had to spell it out.
As she started her essay, she reflected on how she had faced bias or felt overlooked as a Black student in predominantly white spaces.
There was the year in math class when the teacher kept calling her by the name of another Black student. There were the comments that she’d have an easier time getting into college because she was Black .
“I didn’t have it easier because of my race,” said Laird, a senior at Newton South High School in the Boston suburbs who was accepted at Wellesley and Howard University, and is waiting to hear from several Ivy League colleges. “I had stuff I had to overcome.”
In her final essays, she wrote about her grandfather, who served in the military but was denied access to GI Bill benefits because of his race.
She described how discrimination fueled her ambition to excel and pursue a career in public policy.
“So, I never settled for mediocrity,” she wrote. “Regardless of the subject, my goal in class was not just to participate but to excel. Beyond academics, I wanted to excel while remembering what started this motivation in the first place.”
WILL SCHOOLS LOSE RACIAL DIVERSITY?
Amofa used to think affirmative action was only a factor at schools like Harvard and Yale. After the court’s ruling, she was surprised to find that race was taken into account even at some public universities she was applying to.
Now, without affirmative action, she wondered if mostly white schools will become even whiter.
It’s been on her mind as she chooses between Indiana University and the University of Dayton, both of which have relatively few Black students. When she was one of the only Black students in her grade school, she could fall back on her family and Ghanaian friends at church. At college, she worries about loneliness.
“That’s what I’m nervous about,” she said. “Going and just feeling so isolated, even though I’m constantly around people.”
The first drafts of her essay focused on growing up in a low-income family, sharing a bedroom with her brother and grandmother. But it didn’t tell colleges about who she is now, she said.
Her final essay tells how she came to embrace her natural hair . She wrote about going to a mostly white grade school where classmates made jokes about her afro. When her grandmother sent her back with braids or cornrows, they made fun of those too.
Over time, she ignored their insults and found beauty in the styles worn by women in her life. She now runs a business doing braids and other hairstyles in her neighborhood.
“I stopped seeing myself through the lens of the European traditional beauty standards and started seeing myself through the lens that I created,” Amofa wrote.
“Criticism will persist, but it loses its power when you know there’s a crown on your head!”
Ma reported from Portland, Oregon.
The Associated Press’ education coverage receives financial support from multiple private foundations. AP is solely responsible for all content. Find AP’s standards for working with philanthropies, a list of supporters and funded coverage areas at AP.org .
Copyright © 2024 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, written or redistributed.
Related News

Looking at a solar eclipse can be dangerous without eclipse glasses. Here’s what to know

The British royal family learns that if you don’t fill an information vacuum, someone else will
Recommended.

'All hands on deck': Divers plunge in search of 6 workers feared dead after Baltimore bridge collapse

'It was like a knife in my heart': WTOP speaks with the company that captured the Key Bridge collapse

MLB owners unanimously approve sale of Baltimore Orioles to a group headed by David Rubenstein
Related categories:.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Objective writing places the emphasis on facts, information and arguments, and can be contrasted with subjective writing which relates to personal feelings and biases. ... Another way to write objectively is to personify the writing (essay, report, etc.) and make this the subject of the sentence. This essay considers the role of diesel ...
Here are common tips for setting objectives of any field. Best tips on how to write objectives. #1. Be concise and straightforward. Keep the words as simple and straightforward as much as possible. It is much better to remove unnecessary or ambiguous words that might lead to misunderstanding. #2.
For example, personal essays and opinion papers are examples of texts that contain subjective writing, because they contain subjective language. Subjective language includes words that indicate a ...
This objective seems measurable, but it's saying that by the end of the class "students should be able to write an essay". That makes it sound like one of the objectives of the course is for students to write an essay. What students really need to know though is the effect of immigration on American culture.
Essay writing objectives apply to expository and persuasive essays on a variety of topics. Thesis Development. Every essay should clearly state a thesis -- the main idea of the essay. A mere overview of a topic that does not take a stand one way or the other is not a thesis. The main idea of the essay should be obvious to the reader.
To develop a set of research objectives, you would then break down the various steps involved in meeting said aim. For example: This study will investigate the link between dehydration and the incidence of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in intensive care patients in Australia. To achieve this, the study objectives w ill include:
Try to present your argument in as objective a way as possible. Avoid judgmental and emotive language, as this often reveals that you are presenting an opinion rather than evidence or a logical argument. Note, however, that whether a phrase or word is judgmental or emotive often depends on the context. It is best to avoid phrases like "it is ...
1. Try Not to Use the First Person. Objective writing aims for a neutral, impersonal tone. As such, you should try to minimise the use of the first person and first-person pronouns such as 'I', 'me' and 'mine', which put too much focus on you as the writer of the document. One option is to use the passive voice more. For instance:
Step 2. State one side of the argument and report the evidence and findings that support the statement you are making. Leave out how you personally feel about the issue but do bring in supporting evidence that you find compelling. Remain objective when you compose an essay by keeping your arguments balanced in support or for rebuttal of the ...
The essay writing process consists of three main stages: Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline. Writing: Set out your argument in the introduction, develop it with evidence in the main body, and wrap it up with a conclusion. Revision: Check your essay on the content, organization, grammar, spelling ...
Behavioral Verbs. The key to writing learning objectives is using an action verb to describe the behavior you intend for students to perform. You can use action verbs such as calculate, read, identify, match, explain, translate, and prepare to describe the behavior further. On the other hand, words such as understand, appreciate, internalize, and value are not appropriate when writing learning ...
Research objectives describe what your research project intends to accomplish. They should guide every step of the research process, including how you collect data, build your argument, and develop your conclusions. Your research objectives may evolve slightly as your research progresses, but they should always line up with the research carried ...
In short, differences between these styles concern the following: The ground for objective essays is facts; for subjective essays - personal opinions and beliefs. Objective papers report the findings from scientific sources, while subjective ones describe the writer's thoughts. The objective essay's goal is to help the reader make a decision.
How to write objectives for learning. Here are some steps you could follow to develop clear and concise learning objectives: 1. Reflect on important skills for students to develop. Learning objectives typically discuss the abilities learners gain from taking your workshop or course.
The chronological approach (sometimes called the cause-and-effect approach) is probably the simplest way to structure an essay. It just means discussing events in the order in which they occurred, discussing how they are related (i.e. the cause and effect involved) as you go. A chronological approach can be useful when your essay is about a ...
In general, your introductions should contain the following elements: When you're writing an essay, it's helpful to think about what your reader needs to know in order to follow your argument. Your introduction should include enough information so that readers can understand the context for your thesis. For example, if you are analyzing ...
Objective writing is a factual process that enhances knowledge. For instance, learners gather facts that support the selected topic. In this case, one must support arguments with evidence from credible sources. Besides, students address both sides of an opinion. Then, being objective makes essays appear professional and reliable.
Follow these tips to set the right career goals: 1. Understand the concept of career goals. Before you write your career goals essay, you must first identify your career ambitions. Career goals are a form of personal development. Focus on the professional or educational goals you would like to achieve aside from a high salary.
Knowing how to be objective in writing can help you make use of the technique. Here are some ways you can achieve this: 1. Use facts and data. One of the primary distinguishing factors between objective and subjective writing is how much you rely on facts and data. Objective writing seeks to present facts and information so that readers can ...
In 100 words, tell us about your career goals. 100-word essays, while short, can take careful planning and thought. With so little space to communicate your ideas, it's important to ensure you maximize the strength of every sentence. Scholarship teams might give you this prompt to assess your future goals quickly or to supplement some of the ...
When writing college essays, consider the point you want to make and develop a fleshed-out response that fits the prompt. Avoid force-fitting prewritten pieces. Approach every personal essay prompt as if it's your first. 4. Stick to Your Style. Writing college essays isn't about using flowery or verbose prose.
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Follow these tips to write an impactful essay that can work in your favor. 1. Start Early. Few people write well under pressure. Try to complete your first draft a few weeks before you have to turn it in. Many advisers recommend starting as early as the summer before your senior year in high school.
Step 1: Define Your Topic and Research Questions. Before you venture into your quest for sources, it's essential to have a clear understanding of your research topic and the specific questions you aim to address. Define the scope of your paper and identify keywords and key concepts that will guide your search for relevant sources.
A new tool called Writable, which uses ChatGPT to help grade student writing assignments, is being offered widely to teachers in grades 3-12. Why it matters: Teachers have quietly used ChatGPT to grade papers since it first came out — but now schools are sanctioning and encouraging its use. Driving the news: Writable, which is billed as a ...
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
A RULING PROMPTS PIVOTS ON ESSAY TOPICS . Like many students, Max Decker of Portland, Oregon, had drafted a college essay on one topic, only to change direction after the Supreme Court ruling in June.