

Assignment and shorthand assignment operator in C
Quick links.
- Shorthand assignment
Assignment operator is used to assign value to a variable (memory location). There is a single assignment operator = in C. It evaluates expression on right side of = symbol and assigns evaluated value to left side the variable.
For example consider the below assignment table.
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| Assigns 10 to variable | |
| Evaluates expression and assign result to | |
| Evaluates and assign result to | |
| Error, you cannot re-assign a value to a constant | |
| Error, you cannot re-assign a value to a constant |
The RHS of assignment operator must be a constant, expression or variable. Whereas LHS must be a variable (valid memory location).
Shorthand assignment operator
C supports a short variant of assignment operator called compound assignment or shorthand assignment. Shorthand assignment operator combines one of the arithmetic or bitwise operators with assignment operator.
For example, consider following C statements.
The above expression a = a + 2 is equivalent to a += 2 .
Similarly, there are many shorthand assignment operators. Below is a list of shorthand assignment operators in C.
| Shorthand assignment operator | Example | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
- C Tutorials
Arithmetical Assignment Operators in C
In the realm of programming, effectiveness and clarity play pivotal roles. To streamline code and make it more concise, programmers often utilize assignment operators. Among these, arithmetical assignment operators hold a special place. They combine arithmetic operations with assignments, allowing for efficient and cleaner code. In this piece, we will delve into the realm of arithmetical assignment operators within the context of C programming. We will uncover their purpose, how to use them effectively, and the advantages they bring, all while offering simplified examples catered to beginners, ensuring a seamless learning experience.
Understanding Arithmetical Assignment Operators
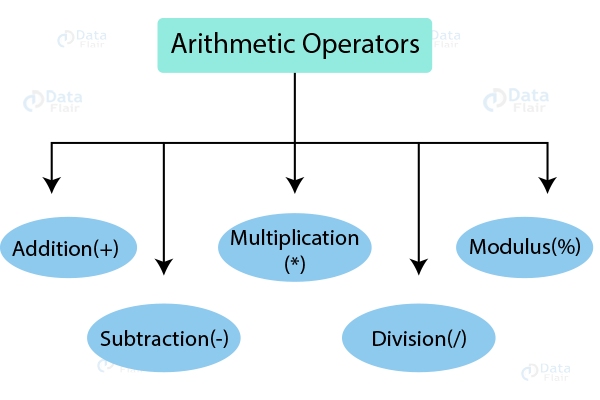
Arithmetical assignment operators are shorthand notations that perform arithmetic operations and assignments in a single step.
These operators include:
- += (Add and Assign)
- -= (Subtract and Assign)
- *= (Multiply and Assign)
- /= (Divide and Assign)
- %= (Modulus and Assign)
For instance, using +=, you can add a value to a variable without needing a separate assignment statement. Similarly, the other operators work by performing the respective operation and updating the variable’s value directly.
| Operator | Operation | Example |
| + | Addition | X + Y = 42 |
| – | Subtraction | X – Y = -18 |
| * | Multiplication | X * Y = 315 |
| / | Division | Y / X = 7 |
| % | Modulus (Remainder) | Y % X = 0 |
| ++ | Increment (Increase by One) | X++ = 8 |
| — | Decrement (Decrease by One) | X– = 6 |
| Operator name | Operator | Description | Equivalent | Example |
| Basic assignment | = | Assign the value of n to m | N/A | m = n |
| Addition assignment | += | Adds the value of n to m and assigns the result to m | m = m + n | m += n |
| Subtraction assignment | -= | Subtracts the value of n from m and assigns the result to m | m = m – n | m -= n |
| Multiplication assignment | *= | Multiplies the value of m by n and assigns the result to m | m = m * n | m *= n |
| Division assignment | /= | Divide the value of m by n and assign the result to m | m = m / n | m /= n |
| Modulo assignment | %= | Calculates the remainder of m divided by n and assigns it to m | m = m % n | m %= n |
Usage of Arithmetical Assignment Operators
The primary advantage of using arithmetical assignment operators is code simplicity. They reduce the need for separate lines of code for arithmetic operations and assignments. This improves code readability while lowering the likelihood of mistakes brought on by forgotten assignments.
Consider this example:
// Without arithmetical assignment operator x = x + 5;
// With arithmetical assignment operator x += 5;
The second approach is not only shorter but also more intuitive, as it directly communicates the intent.
Let’s explore arithmetical assignment operators through some examples:
Output: The number of apples left after eating is 13.
Subtraction:
Output: Total is now 80.
Multiplication:
Output: quantity is now 12.
Output: value is now 25.0.
Output: dividend is now 2.
Original total amount: 100 After adding incremental: 125 After subtracting incrementValue: 100 After multiplying by incrementValue: 2500 After dividing by incrementValue: 100 After getting remainder by incrementValue: 0
These examples show how, depending on the operation, the arithmetical assignment operators change the value of the variable they are applied to.
Common Mistakes and Pitfalls
While arithmetical assignment operators can simplify code, beginners should be cautious about data types. Mixing incompatible data types can lead to unexpected results. Also, remember that the order of operations still matters.
Performance Considerations
In addition to improving code readability, using arithmetical assignment operators can improve efficiency.These operators can be efficiently optimised by contemporary compilers, which lowers memory and computation overhead.
Arithmetical assignment operators are a powerful tool in a programmer’s arsenal. By combining arithmetic operations and assignments, they make code more elegant and efficient. From novice programmers to seasoned developers, anyone can benefit from incorporating these operators into their coding practices. So go ahead, simplify your code and make your programming journey smoother with arithmetical assignment operators in C.
Your 15 seconds will encourage us to work even harder Please share your happy experience on Google

Tags: arithmetic assignment operator in c arithmetic operator in c assignment operator in c operator in c
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- C – Introduction
- C – Features
- C – Pros & Cons
- C – Applications
- C – Installation
- Why C is Popular
- C – Preprocessors
- C/C++ Header Files
- C – Structure of Program
- C – Escape Sequence
- C – Structures
- C – Bit Fields
- C – Binary Tree
- C/C++ Operators
- C/C++ Strings
- C/C++ Arrays
- C/C++ Multi-dimensional Arrays
- C/C++ Variables
- C/C++ Constants & Literals
- C/C++ Data Types
- C/C++ Loops
- C/C++ Functions
- C/C++ Pointer
- C/C++ Recursion
- C/C++ typedef
- C/C++ Typecasting
- C/C++ Linked List
- C/C++ Stacks
- C/C++ Queue
- C – File Handling
- C – Standard Library Functions
- C – Command Line Arguments
- C – Error Handling
- C – Popular Programs
- C/C++ Career Opportunities
- C – Best Practices
- C Interview Que. for Freshers
- C Interview Que. for Experienced
- C Quiz Part – 1
- C Quiz Part – 2
- C Quiz Part – 3
- C++ Introduction
- C++ Features
- C++ Pros & Cons
- C++ Application
- C++ Installation
- C++ Namespace
- C++ Class & Object
- C++ Polymorphism
- C++ Data Abstraction
- C++ Encapsulation
- C++ Inheritance
- C++ Virtual Function
- C++ Inline Function
- C++ Friend Function
- C++ Interfaces
- C++ Data Strcutures
- C++ Exception Handling
- C++ Template
- C++ Overloading
- C++ Constructors & Destructor
- C++ Dynamic Memory Allocation
- C++ Interview Que. for Freshers
- C++ Interview Que. for Experienced

01 Career Opportunities
02 beginner, 03 intermediate, 04 advanced, 05 training programs, c programming assignment operators, free c programming online course with certificate, what is an assignment operator in c, types of assignment operators in c.
1. Simple Assignment Operator (=)
Example of simple assignment operator.
2. Compound Assignment Operators
| += | addition assignment | It adds the right operand to the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand. |
| -= | subtraction assignment | It subtracts the right operand from the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand. |
| *= | multiplication assignment | It multiplies the right operand with the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand |
| /= | division assignment | It divides the left operand with the right operand and assigns the result to the left operand. |
| %= | modulo assignment | It takes modulus using two operands and assigns the result to the left operand. |
Example of Augmented Arithmetic and Assignment Operators
| &= | bitwise AND assignment | It performs the bitwise AND operation on the variable with the value on the right |
| |= | bitwise OR assignment | It performs the bitwise OR operation on the variable with the value on the right |
| ^= | bitwise XOR assignment | It performs the bitwise XOR operation on the variable with the value on the right |
| <<= | bitwise left shift assignment | Shifts the bits of the variable to the left by the value on the right |
| >>= | bitwise right shift assignment | Shifts the bits of the variable to the right by the value on the right |
Example of Augmented Bitwise and Assignment Operators
Practice problems on assignment operators in c, 1. what will the value of "x" be after the execution of the following code, 2. after executing the following code, what is the value of the number variable, benefits of using assignment operators, best practices and tips for using the assignment operator, live classes schedule.
| Filling Fast | |
| Filling Fast | |
| Filling Fast | |
| Filling Fast | |
| Filling Fast | |
| Filling Fast | |
| Filling Fast | |
| Filling Fast | |
| Filling Fast | |
| Filling Fast | |
| Filling Fast | |
| Filling Fast |
About Author

C Programming Language: shorthand

Shorthand in C is extremely simple. Any time you are assigning a value of a variable that uses that variable in the assignment you can simplify the syntax. For example:
This line of code adds 32 to the current value of ‘myVar’. But you don’t need to type ‘myVar’ twice. Instead, move the operator (that’s the plus sign in this case) to the left side of the assignment operator (the equals sign). The portion of code originally on right side of the operator will be the only thing still remaining on the right side of the assignment operator in our shortened code snippet:
This will work for any type of operator, and for any complexity of assignment as long as you can get the variable alone on the left side of the argument.
If you want to use a bitwise operator on a variable:
It can be used by the shifting operators as well:
If you weren’t already familiar with this, it should make it much easier to read other developers’ code since shorthand is almost always used when it can be. It will also increase your coding speed, and decrease you hand and wrist pain!
Free Computer Science Tutorial
Python for class 11 Tutorial, Python for class 12 Tutorial, C language tutorial, SQL Tutorial, Tips & Tricks, sample papers class 12, C++ tutorial
Assignment Operators in C | Shorthand operators in C

Assignment/shorthand operators are used to update the value of a variable in an easy way. There are various assignment operators provided by C language.
| It is used to assign some value to a .
A=10 | |
| It is used to increment the value of a numeric by adding some value to the existing value.
A=10 | |
| It is used to decrement the existing value of a numeric by subtracting some value from the existing value.
A=10 | |
| It is used to multiply existing value of a numeric variable by another value and then store the result in it.
A=10 | |
| It is used to divide the existing value of a numeric variable by another value and then store the result in
A=10 | |
| It is used to divide the existing value of a numeric variable by another value and then storing the remainder in it.
A=10 | |
| It is used to apply bitwise AND operator on existing value of a numeric variable by another value and then storing the result in it.
A=10 | |
| It is used to apply bitwise OR operator on existing value of a numeric variable by another value and then storing the result in it.
A=10 | |
| It is used to apply bitwise XOR operator on existing value of a numeric variable by another value and then storing the result in it.
A=10 | |
| It is used to apply Bitwise LEFT SHIFT operator on existing value of a numeric variable by another value and then storing the result in it.
A=10 | |
| It is used to apply Bitwise RIGHT SHIFT operator on existing value of a numeric variable by another value and then storing the result in it.
A=10 |
| in C |
| in C. |
- Programming Language?
- Introduction
- Constants in C Language
- Data Types in C Language
- What is a variable in C Language
- Display output in C – printf() function
- Read values in C- scanf() function
- C – Unformatted Output Function
- C – Unformatted Input Function
- 4 Types of Operators in C
- Increment Decrement Operators in C (++ / –)
- Arithmetic Operators in C
- Relational Operators in C | Comparison operators in C
- Logical Operators in C | Logical AND in C | Logical Or in C | Logical NOT in C
- #8508 (no title)
- Bitwise operators in C | Bitwise Operator programs in C | Bitwise AND in C | Bitwise OR in C | Bitwise XOR in C | Bitwise complement in C | Bitwise left shift in C | Bitwise right shift in C
- Conditional operator in C | Ternary Operator in C
- sizeof() operator in C | comma operator in C | Special operators in C
- Implicit type Conversion in C | Automatic type conversion in C
- Explicit type conversion in C | Casting in C
- Precedence and Associativity of Operators in C | Expressions in C
- Simple if statement
- if else statement
- Nested if statement
- if else if ladder statement
- switch statement
- for statement
- while statement
- One dimensional array
- Two dimensional array
- Multi dimensional Array
- Introduction to characters in C
- Character functions in C
- Strings in c
- String functions
- Array of strings
- Introduction to function
- Types of function
- Call by value | Call by reference
- Scope of variable in C
- Storage classes
- Introduction to pointer
- Pointer with Array
- Pointer with Strings
- Pointer to pointer
- void type pointer in C Language | using void pointer in C
- Dynamic memory allocation
- Pointer with function
- Introduction to Structure
- Nesting of Structure in C
- Structure type Array
- Structure type arguments in C
- Function returning structure in C
- Structure with Pointers in C
- Self Referential Structure
- Introduction to Union in C Language
- Introdution to Data File Handling
- Steps to create a data file
- File Input output
- Random Access of Files
- Command Line Arguments in C
You have successfully subscribed.
There was an error while trying to send your request. Please try again.
Subscribe for Latest Updates
Assignment Operators in C
Assignment operator in c .
In C, the assignment operator is the "=" symbol. It assigns the value on the right side of the operator to the variable on the left side.
For example:
In the statement
The value 5 is assigned to the variable x .
The assignment operator can also be used to chain assignments, such as
which assigns the value 0 to the variables x, y, and z.
Below is a program that demonstrates the use of the assignment operator:
Types of Assignment operators in C
There are multiple types of assignment operators beyond the basic assignment operator ("=") described above. These include:
- Compound assignment operators
- Increment and Decrement operators
Compound assignment operators
These operators are a shorthand way of performing a specific operation on a variable and then assigning the result to the same variable.
Other common compound assignment operators include:
| Compound Assignment Operator | Equivalent Expression | Description |
|---|---|---|
| += | x = x + y | Adds the value of y to x and assigns the result to x |
| -= | x = x - y | Subtracts the value of y from x and assigns the result to x |
| *= | x = x * y | Multiplies x by y and assigns the result to x |
| /= | x = x / y | Divides x by y and assigns the result to x |
| %= | x = x % y | Assigns the remainder of x divided by y to x |
| <<= | x = x << y | Shifts the bits of x left by y positions and assigns the result to x |
| &= | x = x & y | Performs a bitwise AND operation on x and y and assigns the result to x |
| ^= | x = x ^ y | Performs a bitwise XOR operation on x and y and assigns the result to x |
| `= | x = `x |
The compound assignment operators perform the operation and assignment in one step, so it's more efficient than writing the equivalent expression.
Below is a Compound assignment operator Example in C:
Increment and Decrement operators
In C, the increment operator (++) and the decrement operator (--) are used to increase or decrease the value of a variable by 1.
They can be used as prefix or postfix.
| Operator | Equivalent Expression | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ++x | x = x + 1 | Increments the value of x by 1, then the new value is used in the expression |
| x++ | x = x + 1 | The current value of x is used in the expression, then x is incremented by 1 |
| --x | x = x - 1 | Decrements the value of x by 1, then the new value is used in the expression |
| x-- | x = x - 1 | The current value of x is used in the expression, then x is decremented by 1 |
In the above table, x is a variable, and the increment operator(++) increments the value of x by 1, and the decrement operator(--) decrements the value of x by 1.
Increment and decrement operators are not limited to integers, but it can be applied to any numeric datatype such as float, double, etc.
Also, these operators can be used in expressions and in combination with other operators. For example, x++ + y-- is a valid expression.
Prefix and Postfix Types
Prefix increment (or decrement) operator .
The prefix increment or decrement operator first increments or decriments the value of a variable, then the new value of variable is used in the expression.
In the statement y = ++x; , the value of x is first incremented by 1, and then the new value of x is assigned to y .
Postfix Increment (or Decrement) Operator
The Postfix increment or decrement operator first increments or decriments the value, then the new value is used in the expression.
The Postfix increment or decrement operator first uses the current value of variable in the expression and then increments the value of variable.
In the statement y = x++; , the current value of variable x is assigned to variable y , and then x is incremented by 1.
Explanation:
In this program,
- Three variables x , y and z are declared and initialized with the value 5.
- Then the prefix increment operator is used to increment the value of x , and the new value of x is assigned to y .
- Then the postfix increment operator is used to increment the value of x , and the current value of x is assigned to z .
- Then prefix and postfix decrement operator is used to decrement the value of x and assigned to y and z respectively.
Please note that the order of evaluation is different for prefix and postfix operators. The prefix operator increments/decrements the value of the variable first and then uses the new value, whereas the postfix operator uses the current value of the variable first and then increments/decrements the value.
- Types of Assignment operators in C
- Prefix and Postfix Types

- Learn C Programming
Introduction
- Historical Development of C
- Importance of C
- Basic Structure of C Program
- Executing a C Program
- Compiler, Assembler, and Interpreter
Problem Solving Using Computer
- Problem Analysis
- Types of Errors
- Debugging, Testing, and Program Documentation
- Setting up C Programming Environment
C Fundamentals
- Character Set
- Identifiers and Keywords
- Data Types
- Constants and Variables
- Variable/Constant Declaration
- Pre-processor Directive
- Symbolic Constant
C Operators and Expressions
- Operators and Types
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Conditional Operator
- Increment and Decrement Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Special Operators
- Precedence and Associativity
C Input and Output
- Input and Output functions
- Unformatted I/O
- Formatted I/O
C Decision-making Statements
- Decision-making Statements in C
- Nested if else
- Else-if ladder
- Switch Case
- Loop Control Statements in C
C Functions
- Get Started
- First Program

Assignment Operators in C
Assignment operators are used to assigning the result of an expression to a variable. Up to now, we have used the shorthand assignment operator “=”, which assigns the result of a right-hand expression to the left-hand variable. For example, in the expression x = y + z, the sum of y and z is assigned to x.
Another form of assignment operator is variable operator_symbol= expression ; which is equivalent to variable = variable operator_symbol expression;
We have the following different types of assignment and assignment short-hand operators.
| Expression with an assignment operator | Detailed expression with an assignment operator |
|---|---|
| x += y; | x = x + y; |
| x -= y; | x = x – y; |
| x /= y; | x = x / y; |
| x *= y; | x = x * y; |
| x %= y; | x = x % y; |
| x &= y; | x = x & y; |
| x |= y; | x = x | y; |
| x ^= y; | x = x ^ y; |
| x >>= y; | x = x >> y; |
| x <<= y; | x = x << y; |
Expected Output:
- C Data Types
- C Operators
- C Input and Output
- C Control Flow
- C Functions
- C Preprocessors
- C File Handling
- C Cheatsheet
- C Interview Questions
Assignment Operators in C
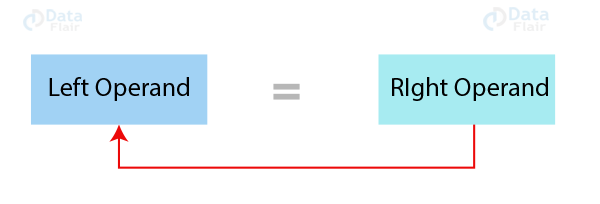
Assignment operators are used for assigning value to a variable. The left side operand of the assignment operator is a variable and right side operand of the assignment operator is a value. The value on the right side must be of the same data-type of the variable on the left side otherwise the compiler will raise an error.
Different types of assignment operators are shown below:
1. “=”: This is the simplest assignment operator. This operator is used to assign the value on the right to the variable on the left. Example:
2. “+=” : This operator is combination of ‘+’ and ‘=’ operators. This operator first adds the current value of the variable on left to the value on the right and then assigns the result to the variable on the left. Example:
If initially value stored in a is 5. Then (a += 6) = 11.
3. “-=” This operator is combination of ‘-‘ and ‘=’ operators. This operator first subtracts the value on the right from the current value of the variable on left and then assigns the result to the variable on the left. Example:
If initially value stored in a is 8. Then (a -= 6) = 2.
4. “*=” This operator is combination of ‘*’ and ‘=’ operators. This operator first multiplies the current value of the variable on left to the value on the right and then assigns the result to the variable on the left. Example:
If initially value stored in a is 5. Then (a *= 6) = 30.
5. “/=” This operator is combination of ‘/’ and ‘=’ operators. This operator first divides the current value of the variable on left by the value on the right and then assigns the result to the variable on the left. Example:
If initially value stored in a is 6. Then (a /= 2) = 3.
Below example illustrates the various Assignment Operators:
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- C-Operators
- cpp-operator
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
- Shorthand Operators
Assignment Operators are used for assigning values to the variables in the program. There are two types of Assignment operators used. The first one being the Simple Assignment Operator and the other one being Shorthand Operators or Compound Assignment Operators. Expressions or Values can be assigned to the variable using Shorthand Assignment Operators. C++ supports both types of Assignment Operators. Let us look at the Shorthand Assignment Operators and their different types in this article below.

- Shorthand Assignment Operators combines one of the arithmetic or bitwise operators with the assignment operator. They are also called as compound assignment operators.
- A Shorthand Assignment Operator is a shorter way of expressing something that is already available in the programming statements.
C++ language offers its users a few special shorthand’s that simplifies the coding of certain expressions. It also saves coding time by using these Shorthand Operators in the program. Shorthand Assignment Operators have the lowest order of precedence i.e., they are the last to be evaluated in an expression.
Shorthand Assignment Operators follow the following Syntax –
variable_name operator = expression/value ;
which is equivalent to :
variable_name = variable_name operator expression/value ;
Note: The variable data type and the value assigned to it should match. Or else the compiler will give an error while running the program.
Browse all the Topics Under Operator and Expressions: Operators
- Arithmetic Operators
- Assignment Operator s
- Unary Operator
- Increment and Decrement Operators
- Relation Operator
- Logical Operators
Types of Shorthand Assignment Operators
Shorthand Assignment Operators are Binary Operators which require 2 values or 1 variable and another value/expression. One on the left and the other on the right side.
The following are types of Shorthand Assignment Operators
This type of Operator is a combination of Arithmetic Operator ‘+’ and Assignment Operator ‘=’. This operator adds the variable on the left with the value on the right and then assigns/saves the result to the variable on the left.
These types of Shorthand Operators are used with a combination of Subtraction Arithmetic Operator ‘-‘ and Assignment operator ‘=’.
These Shorthand Operators use a combination of Multiplication type of Arithmetic Operator ‘*’ and Simple Assignment operator ‘=‘. The variable to the left is multiplied with the value or expression to the right side and then the result is stored into the variable defined to the left.
Here, a combination of Division Arithmetic operator ‘/’ and Simple Assignment Operator ‘=’ is seen. The variable is divided by the value first and then the value is stored to the left, in the variable.
This type of operator uses Modulus Operator ‘%’ and an Assignment Operator ‘=’ in its syntax. It returns the Remainder of the two operands and stores the value in the variable to the left side of the statement.
Apart from the Assignment Operators, the Shorthand Operators are also used to define the Bitwise Operators.
Some of them are:
| |= | Shorthand Bitwise Inclusive OR |
| &= | Shorthand Bitwise AND |
| ^= | Shorthand Bitwise XOR |
| <<= | Shorthand Bitwise Left Shift |
| >>= | Shorthand Bitwise Right Shift |
| ~= | Shorthand Bitwise Compliment |
| != | Shorthand Inequality |
FAQs on Shorthand Operators
Q1. Which of the following is a valid assignment operator?
- All of the Above
Answer. Option D
Q2. What does the *= assignment operator do?
- Multiplies the value twice
- Multiplies variable with value once
- Used as exponent like 2*3 = 8
- None of the Above
Answer. Option B
Q3. Do the given two equations mean the same?
count += 1 ;
count = count + 1 ;
Answer. Option A
Q4. What is the final output of variable ‘a’ in the below program?
Answer. Option C.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Operator and Expressions: Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Unary Operators
- Increment & Decrement Operators
- Relational Operators
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Operators in C
Here we will discuss operators in the C language. What are unary, binary, and ternary operators? How many types of operations are performed in the C language? We will learn these concepts in detail.
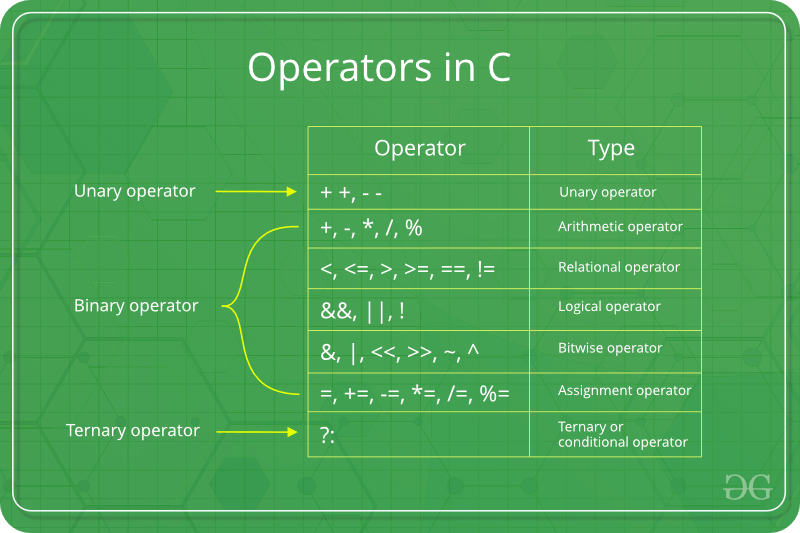
Based on the number of operands participating in the operation, operators are divided into 3 types in the C language.
Arithmetic Operators
Arithmetic operators are used to performing mathematical operations. The arithmetic operators can operate on any built-in data type.
Syntax:- operand1 operator operand2
| Addition | |
| Substraction | |
| Multiplacation | |
| Division | |
| Modulus (remainder after integer division) |
a) Integer mode arithmetic
When arithmetic operators operates on integers then it is called integer mode arithmetic. It always yields an integer value.
integer operator integer = integer
Examples:- 1+3 = 4 ‘A’ + 1 = 66 ‘a’ + ‘b’ = 195 3 * 2 = 6 8 / 2 = 4 9 % 2 = 1

b) Real mode arithmetic
real operator real = real
c) Mixed mode arithmetic
integer operator real = real real operator integer = real
Examples:- 4.0 + 5 = 9.0 9.0 – 4 = 5.0 3.0 * 2.0 = 6.0 5.0 / 2 = 2.5 5.0 % 2 = Error
C Program to see a demonstration of Arithmetic operators
Sum = 14 Substraction = 4 Multiplaction = 45 Division = 1 Modulus = 4
Some special points for arithmetic operators in c
A) subtraction operator (-).
The unary minus operator has the effect of multiplying its operand by -1. Example:- 8 x (-1) = (-8)
b) Division Operators (/)
The division operator (/) produces the quotient. The second operand should be a non-zero number. So, n using division operator (/), if exactly any one of the operand is negative then the result is negative. If both operands are -ve/+ve then result is positive.
Any integer number divided by ten removes the last digit of the number. In next coming many examples we will use this concept to solve the big problems.
c) Modulus Operators (%)
The remainder operator or modulus operator (%) produces the remainder after integer division i.e x%y = x – (x/y)*y . The operands for modulus operator (%) should be of type integer and the second operand should be a non-zero value. The modulus operator (%) does not operate on floats and doubles. On using modulus operator(%) the sign of the remainder is always same as the sign of the numerator.
Any number%10 always gives last digits of number. After some times in big problem you need to find last digit of the number the apply % operator on number.
Assignment operator
Assignment operators are used to assign the result of an expression to a variable.
Above statements are called assignment statements or assignment expressions. In an assignment statement, the right-side expression to the assignment operator is evaluated first and the obtained result is stored inside the left side variable to that assignment operator. So, we can say that it copies the value on its right side into the left side variable.
The left side operand of the assignment should be a variable. C does not allow any expression or constant to be placed to the left of the assignment operator. a+b=c; // invalid, left side operand should be a variable 10 = 20; // invalid
Compound assignment operators
C supports a set of shorthand assignment operators. Following are the advantages of using shorthand assignment operators:
| += | x+=a; | x=x+a; |
| -= | x-=a; | x=x-a; |
| *= | x*=a; | x=x*a; |
| /= | x/=a; | x=x/a; |
| %= | x%=a; | x=x%a; |
| &= | x&=a; | x=x&a; |
| |= | x|=a; | x=x|a; |
| ^= | x^=a; | x=x^a; |
| <<= | x<<=a; | x=x<<a; |
| >>= | x>>=a; | x=x>>a; |
Relational Operator
Relational operator are used to check given condition or expression is true or false. Combination of some operands and constants with relational operators is called a relational expression.
Syntax:- operand1 relational-operator operand2
If the relation is true then the value of the relational expression is 1 and if the relation is false then the value of the expression is 0. In C language (with relational operator), every non-zero value is 1 i.e. true.
| Is less than | 5<2 = 0 ; 5<10 = 1 | |
| Is less than or equal to | 5<=2 = 0; 5<=5 = 1 | |
| Is greater than | 5>2 = 1; 5>10 = 0 | |
| Is greater than equal to | 5>=2 = 1; 5>=10 = 0 | |
| Is equal to | 5==2 = 0; 5==5 = 1 | |
| Is not equal to | 5!=1 = 1; 5!=5 = 0 |
Some more examples are:- 9 == 9 result 1 9 == -9 result 0 9 == 9.0 result 1 2+3*2 == 10 result 0 (2+3)*2 == 10 result 1
0 0 1 1 0 1
Some special points for relational operators
Characters are valid operands since they are represented by numeric values (ASCII values). ‘A’ == 65 results 1 //ASCII value of ‘A’ is 65 ‘a’ > ‘A’ result 1 //ASCII value of them are 97 and 65 respectively ‘A’ == ‘A’ result 1
The relational operators should not be used for comparing strings because this will result in string addresses being compared, not string contents. “A” == “a” result 0 “Hello” < “Hi” result 0
Logical operators
| Logical AND | |
| Logical OR | |
| Logical NOT |
| | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Logical OR ( | | ) gives result 1 (true) if atleast one operand is 1 (true) otherwise it gives result 0 (false). Truth table for logical OR (| |) is given below:-
| | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 |
Q) Find the output of the below program?
Some special points on logical operators
For logical AND (&&) operator, if the left operand yields a false (0) value, then the compiler does not evaluate the right operand and directly gives result false (0). Because in logical AND operand if anyone operand is false then the expression is false. Find the output of below two programs after learning increment and decrement operators.
For logical OR ( || ) operator, if the left operand yields a true (1) value, then the compiler does not evaluate the right operand and directly gives result 1 (true). We know that for the logical OR operator if anyone operand is true than expression is also true.
Increment and Decrement operators
Increment and decrement operators are also known as unary operators’ because they operate on a single operand. The increment operator (++) adds 1 to its operand and decrement operator (–) subtracts one.
| Increment Operator | |
| Decrement Operator |
If it is pre operator, the value of the operand is incremented (or decremented) before it fetched for the computation. The altered value is used for the computation of the expression in which it occurs. If it is a post operator, the value of the operand is altered after it is fetched for the computation. The unaltered value is used in the computation of the expression in which it occurs.
Increment operator (++)
Decrement operator(- -).
1. Prefix operation (x = – -a; )
Special points for increment and decrement operator
1. It is to be noted that i++; executed faster than i=i+1; and i+=1
2. With increment and decrement operators, the operand must be a variable but not a constant or an expression.
lvalue means, that there isn’t a variable the operation is supposed to be performed on.
Conditional Operator
Syntax:- Variable = expression1? expression2 : expression3;
Here 5>2 So, Expression will be evaluated to the variable x.
Bitwise Operator
A bitwise operator operates on each bit of data. It is one of the low-level programming language features. Bitwise operator operates on integer only, not on floating-point numbers. Bitwise operations most often find application in device drivers such as modem programs, disk file routines, and printer routines.
List of bitwise operators are:-
| & | Bitwise AND |
| | | Bitwise OR |
| ^ | Bitwise Exclusive OR |
| ~ | Bitwise NOT/ Bitwise Negation |
| << | Bitwise left shift |
| >> | Bitwise right shift |
Other Operators
Except for above-discussed operators C support some other operators. Those are given below:-
| Address of Operator | |
| Value at adress operator | |
| Size operator | |
| Comma Operator | |
| Type-casting operator | |
| Array index operator | |
| Structure member access operator | |
| Structure member access operator |
We will discuss here sizeof() and the comma operator. Other operators will be discussed later on their own topics.
Address operator
There are two address operator & and *.
We will learn about these operators in more details in the pointer concept.
Sizeof() operator
The operator sizeof() is a unary compile-time operator that returns the length, in bytes, of the variable or parenthesized type-specifier that it precedes.
To compute the size of the variable or constants, parentheses are optional.
Note the difference between the 4th and 5th lines. size(a+3) gives 4 bytes but sizeof a+3 gives 7 bytes as a result.
Comma Operator
Syntax:- variable = (expression1, expression2, ......., expresionN);
If you enjoyed this post, share it with your friends. Do you want to share more information about the topic discussed above or do you find anything incorrect? Let us know in the comments. Thank you!
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Unlock the complete Logicmojo experience for FREE
Sign Up Using
Or use email
1 Million +
Strong Tech Community
Questions to Practice
Jobs Referrals
Operators In C

𝑻𝒂𝒃𝒍𝒆 𝒐𝒇 𝑪𝒐𝒏𝒕𝒆𝒏𝒕
Introduction, use of operator in c, types of operators in c, arithmetic operators in c, relational operators in c, logical operators in c.
- Bitwise Operators In C
- Assignment Operators In C
Conditional Operators In C
Misc operators in c, precedence of operators in c.

A wide range of built-in operators are supported by C. The use of an operation or collection of operations on a variable or set of variables is represented by the use of operators, which are symbols. To carry out particular mathematical and logical operations on operands, C has a collection of operators.
The operators are various symbols that provide instructions to a compiler for carrying out particular logical or mathematical operations. The operators are the building blocks of computer languages.
C operators are one of the features in C that have signs that can be applied for mathematical, relational, bitwise, conditional, or logical manipulations. There are many built-in operators in the C programming language that can be used to carry out different duties as required by the program. Operators are typically used in programs to manipulate data and variables and are included in mathematical, logical, or conditional statements.
In other terms, an operator is a symbol that instructs the compiler to carry out particular mathematical, logical, or conditional operations. It functions on a number or a variable as a symbol. For instance, the addition and subtraction operators in any C application are + and -.

Let us Understand by a simple example,
In the above example, "+" operator is being used which is known as addition operator for adding two operands, which are adding two integers and we get a sum of 150, after adding two integers.
In simple terms, operators act as symbols that can be applied to any number or variable. We use it to carry out a variety of tasks, including logical, mathematical, relational, and many others. For carrying out specific kinds of mathematical procedures, a programmer must use a variety of operators. As a result, the operators' main function is to carry out different logical and mathematical calculations.
Programming languages with extensive built-in functions include C, for example. These operators are frequently used. All programming languages have these operators as very strong and practical features, and without them, the usefulness of those languages would essentially be useless. These make it very simple and effective for programmers to create the code.
In the C language, various operators are useful to assist a programmer to carry out various types of operations. Using these operators, we can manage a variety of operations in a program:
Arithmetic Operators
Relational Operators
Logical Operators
Bitwise Operators
Assignment Operators
Conditional Operators
Misc Operators
Crack your next tech interview with confidence!

The arithmetic operators in C language assist a user in performing mathematical as well as arithmetic procedures in a program, such as subtraction (-), addition (+), division (/), multiplication (*), remainder of division (%), decrement (-), and increment (++).
Arithmetic operators are classified into two types:
Binary Operators :–
This operator operates with two operands such as +,-,*,/.
Unary Operators :-
This type of operator, like ++ and -, operates with a single value (operand).
The table that follows lists all of the arithmetic operators available in the C language, as well as their individual functions.
| Operator | Operator Name | Description Of Operator |
|---|---|---|
| + | addition | adds two operands |
| – | substraction | subtracts second operand from the first |
| * | Multiplication | multiplies both operands |
| / | Division | Divides numerator by de-numerator. |
| % | Modulus | operator gives the remainder of an integer after division |
| ++ | Increment | increment operator increases the integer value by 1 |
| -- | Decrement | decrement operator decreases the integer value by 1 |
There are two kinds of Decrement and Increment operators:
Prefix - A prefix operator is used when we use the operator before the accessible variable in a program as a prefix. The program first adds 1 and then gives the resultant value to the variable in a prefix increment operator. The program first subtracts 1 and then gives the resultant value to the variable when using a prefix decrement operator. For instance, we can write ++x and --x in the prefix form.
Postfix - A postfix operator is used when we use the operator after the accessible variable in a program as a postfix. The program first assigns the value to the variable, then adds 1, and finally allocates the resultant value in a postfix increment operator. In a postfix decrement operator, the program first gives the variable's value, then subtracts 1, and finally assigns the resultant value. For instance, we can write x++ and x-- in the postfix form..
Program for Arthematic Operators
The program's operators are +, -, and *, which calculate addition, subtraction, and multiplication, respectively. 25/4 equals 6.25 in standard math. In the above program, however, the result is 6. This is due to the fact that both values a and b are integers. As a result, the output must also be a number. As a result, the compiler ignores the word after the decimal point and displays 1 instead of 1.25 as the program output.
A modulus operator can only be used with integers. You can calculate the remainder of any integer using the modulus operator (%). The remainder is 1 when a=25 is split by b=4. If we want the division operator's result in decimal values, one of the operands must be a floating-point integer.
Relational operators facilitate in the formation of a connection or comparison between two operands. As a result, relational operators assist us in making programme decisions, and their end outcome is either true or false. Relationship operators include (==,!=,, >, =, >=).
The table below lists all of the relational operators that C supports. Here, we presume that variables a = 5, b = 9.
| Operator | Operator Name | Description Of Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| == | equal to | it check if two operands are equal | a==b returns 0 |
| != | not equal to | it check if two operands are not equal. | a!=b returns 1 |
| > | greater than | it check if the operand on the left is greater than operand on the right | a>b returns 0 |
| it check if the operand on the left is smaller than the right operand. | a | ||
| >= | greater than or equal to | it check if the left operand is greater than or equal to the right operand | a>=b returns 0 |
| it check if operand on left is smaller than or equal to the right operand | a |
Program for Relational Operators in C
When we need to evaluate more than one condition to make a decision in the C programming language, we have three logical operators. In C, an expression having a logical operator returns either 0 or 1, depending on whether the expression returns true or false. In C program, logical operators are commonly used to make decisions.
The table below lists all of the logical operators provided by the C programming language. We are presuming that variables a = 12 and b = 10.
| Operator | Operator Name | Description Of Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| && | logical AND | it returns true if both side operands value is true otherwise returns false | a && b returns false |
| || | logical OR | it returns true if one of the operand's value is true or both of the operand's values is true otherwise returns false | a || b returns true |
| ! | logical Not | it returns true if the condition in consideration is not satisfied Otherwise returns false | !a returns false |
Program for Logical Operators in C
(a == b) && (c > 15) calculates to 1 because both the operands (a == b) and (c > b) are 1 (true).
(a == b) && (c < b) calculates to 0 because of the operand (c < b) is 0 (false).
(a == b) || (c < b) calculates to 1 because of the operand (a = b) is 1 (true).
(a != b) || (c < b) calculates to 0 because both the operand (a != b) and (c < b) are 0 (false).
!(a != b) calculates to 1 because the operand (a != b) is 0 (false). Hence, !(a != b) is 1 (true).
!(a == b) calculates to 0 because the (a == b) is 1 (true). Hence, !(a == b) is 0 (false).
Bitwise Operator In C
In C, we use bitwise operators to execute bit-level operations on various operands. It converts the operators to bit-level first, then conducts various calculations.
Bitwise operators operate on bits and are used to conduct bit-by-bit operations. The truth table for the &, ^, and | is as follows:
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
Assume A = 45 and B = 22 in binary form, as shown below.
A = 0010 1101
B = 0001 0110
Lets see how Bitwise works,
A&B = 0000 0100
A|B = 0011 1111
A^B = 0011 1011
| Operator | Operator Name | Description Of Operator |
|---|---|---|
| & | Binary AND Operator | copies a bit to the result if it exists in both the operands |
| | | Binary OR Operator | copies a bit if and only if it exists in either operand. |
| ~ | Binary XOR Operator | copies the bit only if it is set in one operand but not both. |
| ^ | Binary One's Complement Operator | It is unary and has the effect of 'flipping' bits. |
| value of the left operands is moved left by the number of bits specified by the right operand | ||
| >> | Binary Right Shift Operator | value of the left operands is moved right by the number of bits specified by the right operand |
Program for Bitwise Operators in C
Assignment operator in c.
An assignment operator in a program is primarily responsible for giving a value to a variable. To give the result of an expression to a variable, use assignment operators. This operator is essential for giving values to variables." = " is the most commonly used assignment function.
The C language includes a set of shorthand assignment operators that can be used in C computing. The following table shows all of the assignment operators that the C language supports:
| Operator | Operator Name | Description Of Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| = | assignment | assign values from right side operands to left side operand | a = b |
| += | add assign | add the right operand to the left operand and assign the result to left | a += q is similar to a = a=b |
| -= | substract assign | subtract the right operand from the left operand and assign the result to the left operand | a -= b is similar to a = a-b |
| *= | multiply assign | multiply the left operand with the right operand and assign the result to the left operand | a *= b is similar to a = a*b |
| /= | divide assign | divide the left operand with the right operand and assign the result to the left operand | a /= b is similar tof a = a/b |
| %= | modulus assign | calculate modulus using two operands and assign the result to the left operand | a %= b is similar to a = a%b |
Program for Assignment Operators in C
The conditional statement is built using ternary or conditional operators. These are used to make decisions. A set of conditional operators "?:"
The Operator " ?: " operates like this: Expression1 is evaluated first. If it is true, the Expression2 is assessed and becomes the expression's value. If Expression1 is false, Expression3 is evaluated and its result becomes the expression's value.
Aside from the operators mentioned above, the C programming language implements a few other important operators, which include operators (such as?: and sizeof). The following table lists all of the miscellaneous operators accessible in the C language, along with their individual functions.
| Operator | Operator Name | Description Of Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| sizeof() | sizeof | returns the size of a variable | If a is an integer, then the size of(a) will return to be 4 |
| & | Address Operator | operator is used to get the address of the variable. | &a will give an address of a |
| * | pointer operator | operator is used as a pointer to a variable. | *a |
| , | comma operator | Used to link the related expressions together | value = (a=1, b=3) |
| cast | type cast | converts one datatype to another datatype | int(6.3000) would return 6 |
Program for Misc Operators in C
Operator precedence is another feature of the C computer language that determines how terms in an expression are grouped and how an expression is evaluated based on the provided expressions. Some operators have greater precedence than others, while others have lower precedence. In C, for example, the multiplication operator takes priority over the addition operator.
| Category | Operator | Associativity |
|---|---|---|
| Postfix | () [] -> . ++ - - | Left to right |
| Unary | + - ! ~ ++ - - (type)* & sizeof | Right to left |
| Multiplicative | * / % | Left to right |
| Additive | + - | Left to right |
| Shift | << >> | Left to right |
| Relational | < <= > >= | Left to right |
| Equality | == != | Left to right |
| Bitwise AND | & | Left to right |
| Bitwise XOR | ^ | Left to right |
| Bitwise OR | | | Left to right |
| Logical AND | && | Left to right |
| Logical OR | || | Left to right |
| Conditional | ?: | Right to left |
| Assignment | = += -= *= /= %=>>= <<= &= ^= |= | Right to left |
| Comma | , | Left to right |
Conclusions
The following are the things we learned about the operator in this article:
In C, operators are symbols that are used to execute various operations. It is possible for the action to be mathematical, logical, relational, bitwise, conditional, or logical. Unary operators are classified into seven types: Arithmetic operator, Relational operator, Logical operator, Bitwise operator, Assignment operator, and Conditional operator. Except for the logical and conditional operators, which yield a boolean value, all operators return a numerical value.(true or false). '=' and '==' are not the same thing because '=' gives a value whereas '==' determines whether or not two values are equal. The presence of a precedence in the operator indicates that one operator takes precedence over another.
Good luck and happy learning!
- INTERVIEW TIPS
- Customer Review

Shorthand Operators
Things to do first.
- Download the notes for this session.
- Read Chapter 2.13 and 2.14 of your textbook, and do all the CheckPoint, Self-Check, and Exercises in those sections.
Things To Do Later
- What are the different kinds of assignment operators in Java?
- What are the unary operators in Java? Why are they referred to as "unary"?
- How is a post-fix unary operator different from a pre-fix unary operator?
- Explain the following assignment statement: result = x / y++;
- How is the assignment statement double result = x / y++; different from the previous one?
- Assignment Operators
- Unary Operators
Shorthand Assignment Operators
There are some special assignment operators you can use as shortcuts to certain kinds of assignment statements. To understand how these can be used, look at the program listing below. What is the output of this program? What is the value of the variable "sum" during execution of this program?
This small program demonstrates a situation where you can use the special += assignment operator. This operator, the "plus-equals" operator, adds the operand on the right to the operand on the left. If you rewrote the program using the += operator, you'd have:
There are also similar operators to perform subtraction, division, and modulus. You can see them in Table 2.4 in section 2.13 of your text.
Determine, without coding a program, the output of the following code segment:
[ solutions ]
In addition to the assignment operators, there are also some unary operators. Recall that regular operators, such as +, * and += are binary operators - they require two operands, one on each side. Unary operators require only 1 operand. You can see the unary operators listed in Table 2.5 in Chapter 2.14 of your textbook.
The code listing below demonstrates how the increment operator works:
The output for this program:
Unary operators in Java can go on the left or the right of the operand. The difference is in when the increment actually takes place. Some of the exercises below demonstrate this.
For each of the examples above, type the code into a Java program and print/display the value of "result". Do you get the output you expected? Why or why not?
When the ++ or -- operator is to the left of the operand, we refer to it as a pre-fix operator . When the ++ or -- operator is to the right of the operand, we call it the post-fix operator .
The pre-fix operator has higher precedence than the post-fix operator. In a statement with multiple types of operators, the pre-fix operator will execute before most other operators. The post-fix operator will usually execute after the other operators. See your Operator Precedence chart in Appendix C of your textbook for more information.
When you compile, you'll get the error message
This error message is telling you that the variable x was declared, but was not initialized with a value. Unary operators and the special assignment operators (such as +=) do not work on variables that have not yet been initialized!
1. Examine the code listing below. What do you think the output should be? Write this down. Then run the program and see if you're correct.
- Stack Overflow for Teams Where developers & technologists share private knowledge with coworkers
- Advertising & Talent Reach devs & technologists worldwide about your product, service or employer brand
- OverflowAI GenAI features for Teams
- OverflowAPI Train & fine-tune LLMs
- Labs The future of collective knowledge sharing
- About the company Visit the blog
Collectives™ on Stack Overflow
Find centralized, trusted content and collaborate around the technologies you use most.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Get early access and see previews of new features.
Is there an "and assignment operator" for && and || for shorthand?
To add a value and assign it back to itself, I would do this:
For making that shorthand, I can use the add assignment operator like this:
Is there a shorthand like this for the && and || operator for this?:
I tried the below, the results is not the same as above:
- The result is not the same because x &&= y would not evaluate y if x was false, I assume. There is no short-circuiting compound operator. – Eric Lippert Commented Nov 20, 2015 at 4:51
- 1 Is this question just for knowledge or out of curiosity etc? Because x = x && y; itself is so short to write! – Nikhil Vartak Commented Nov 20, 2015 at 5:05
- how the result is not same? – M.kazem Akhgary Commented Nov 20, 2015 at 6:31
2 Answers 2
You can see the list of C# operators here .
x &= y – AND assignment. AND the value of y with the value of x, store the result in x, and return the new value. x |= y – OR assignment. OR the value of y with the value of x, store the result in x, and return the new value.
When you say "the results is not the same," can you provide example values of x and y that you're testing? I think what you're observing is the difference between logical/bitwise AND/OR (&/|) and conditional AND/OR (&&/||). The latter will not evaluate y if it doesn't need to in order to figure out the value of the expression. If the evaluation of y has side effects, you would notice a difference between the bitwise and conditional operators.
No, there is not as it doesn't make too much sense.
According to MSDN , there are only the following shortand operators in C#:
Your Answer
Reminder: Answers generated by artificial intelligence tools are not allowed on Stack Overflow. Learn more
Sign up or log in
Post as a guest.
Required, but never shown
By clicking “Post Your Answer”, you agree to our terms of service and acknowledge you have read our privacy policy .
Not the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged c# c#-4.0 or ask your own question .
- The Overflow Blog
- Navigating cities of code with Norris Numbers
- Featured on Meta
- We've made changes to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy - July 2024
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
- Feedback requested: How do you use tag hover descriptions for curating and do...
Hot Network Questions
- What is the legal status of the Avengers before Civil War and after Winter Soldier?
- Why was I was allowed to bring 1.5 liters of liquid through security at Frankfurt Airport?
- What are these commands in the code?
- Why isn't openvpn picking up my new .conf file?
- Stargate "instructional" videos
- Advice needed: Team needs developers, but company isn't posting jobs
- How predictable are the voting records of members of the US legislative branch?
- Difference between "backpedal" and "change your tune"
- Where exactly was this picture taken?
- Prove that there's a consecutive sequence of days during which I took exactly 11 pills
- Has anybody replaced a LM723 for a ua723 and experienced problems with drift and oscillations
- Would donations count as revenue from a free software?
- Who became an oligarch after the collapse of the USSR
- Does the Ghost achievement require no kills?
- Do "Whenever X becomes the target of a spell" abilities get triggered by counterspell?
- How to satisfy the invitation letter requirement for Spain when the final destination is not Spain
- What is a transition of point man in French?
- Does H3PO exist?
- Unexpected behaviour during implicit conversion in C
- Enigmatic Puzzle 4: Three Leaf Clover
- What does it mean to have a truth value of a 'nothing' type instance?
- Non-linear recurrence for rational sequences with generating function with radicals?
- What majority age is taken into consideration when travelling from country to country?
- Can I use the Chi-square statistic to evaluate theoretical PDFs against an empirical dataset of 60,000 values?

advantages of shorthand operator
What is the efficient way ???
Eric Sosman
-- Eric Sosman [email protected]
John B. Matthews
-- John B. Matthews trashgod at gmail dot com home dot woh dot rr dot com slash jbmatthews
Roedy Green
Roedy Green Canadian Mind Products The Java Glossary http://mindprod.com
Arne Vajhøj
see http://mindprod.com/jgloss/assignmentoperator.html

IMAGES
COMMENTS
C supports a short variant of assignment operator called compound assignment or shorthand assignment. Shorthand assignment operator combines one of the arithmetic or bitwise operators with assignment operator. For example, consider following C statements. The above expression a = a + 2 is equivalent to a += 2.
Arithmetical assignment operators are shorthand notations that perform arithmetic operations and assignments in a single step. These operators include: For instance, using +=, you can add a value to a variable without needing a separate assignment statement. Similarly, the other operators work by performing the respective operation and updating ...
Assignment Operators in C are used to assign values to the variables. They come under the category of binary operators as they require two operands to operate upon. The left side operand is called a variable and the right side operand is the value. The value on the right side of the "=" is assigned to the variable on the left side of "=".
Assignment operators are used in programming to assign values to variables. We use an assignment operator to store and update data within a program. They enable programmers to store data in variables and manipulate that data. The most common assignment operator is the equals sign (=), which assigns the value on the right side of the operator to ...
Shorthand in C is extremely simple. Any time you are assigning a value of a variable that uses that variable in the assignment you can simplify the syntax. For example: myVar = myVar + 32; This line of code adds 32 to the current value of 'myVar'. But you don't need to type 'myVar' twice. Instead, move the operator (that's the plus ...
These operators allow you to write concise and easy t... In this video, we'll teach you how to use the shorthand assignment operators in C programming language.
An example of thee shorthand Java Arithmetic operator is a += 4; for a=a+4; In The Complete Reference, Java 2, Herbert Schildt mentions "they are implemented more efficiently by the Java run-time system than are their equivalent" What makes its implementation more efficient than a=a+4;
A=15. ^=. It is used to apply bitwise XOR operator on existing value of a numeric variable by another value and then storing the result in it. Example: A=10. A^=7 //A=A^7. A=13. <<=. It is used to apply Bitwise LEFT SHIFT operator on existing value of a numeric variable by another value and then storing the result in it.
There are multiple types of assignment operators beyond the basic assignment operator ("=") described above. These include: Compound assignment operators; Increment and Decrement operators; Compound assignment operators These operators are a shorthand way of performing a specific operation on a variable and then assigning the result to the same ...
Topics Covered in this lecture:1. Shorthand Assignment OperatorsPython Programming Classes by Arvind Kharwalhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uXcHsZtOfik&list=...
C also has some shorthand assignment operators. For Example: x=x+y+1 can be written in shorthand form x+=y+1. The shorthand operator += means "add y+1 to x' or 'increment x by y+1'. If y=2 and x=1, then x after execution would become 5. The advantages of using shorthand are: No repetition of left-hand side and thus the readability is good
Assignment operators are used to assigning the result of an expression to a variable. Up to now, we have used the shorthand assignment operator "=", which assigns the result of a right-hand expression to the left-hand variable. For example, in the expression x = y + z, the sum of y and z is assigned to x.
C Programming & Data Structures: Assignment Operators in CTopics discussed:1. Introduction to Assignment Operators in C language.2. Types of Shorthand Assign...
1. "=": This is the simplest assignment operator. This operator is used to assign the value on the right to the variable on the left. Example: a = 10; b = 20; ch = 'y'; 2. "+=": This operator is combination of '+' and '=' operators.This operator first adds the current value of the variable on left to the value on the right and then assigns the result to the variable on the left.
Relational Operators. Shorthand Operators are operators that combine one of the arithmetic or bitwise operators with the assignment operator. Shorthand Operators are a shorter way of expressing something that is already available in the programming statements. Expressions or Values can be assigned to the variable using Shorthand Operators.
C supports a set of shorthand assignment operators. Following are the advantages of using shorthand assignment operators: Shorthand expression is easier to write as the expression on the left side need not be repeated. The statement involving shorthand operators are easier to read as they are more concise.
To give the result of an expression to a variable, use assignment operators. This operator is essential for giving values to variables." = " is the most commonly used assignment function. The C language includes a set of shorthand assignment operators that can be used in C computing.
This small program demonstrates a situation where you can use the special += assignment operator. This operator, the "plus-equals" operator, adds the operand on the right to the operand on the left. If you rewrote the program using the += operator, you'd have: public class AssignOps {.
Instead you use this (*ptr).kg and you force compiler to 1st dereference the pointer and enable acess to the chunk of data and 2nd you add an offset (designator) to choose the member. Check this image I made: But if you would have nested members this syntax would become unreadable and therefore -> was introduced.
a = a+2; can be written as: a += 2; The operator += tells the compiler that a is assigned the value of a + 2; This shorthand works for all binary operators in C. The general form is variable operator = variable / constant / expression. These operators are listed below: C Shorthand Operators. Operators. Example.
You can see the list of C# operators here. x &= y - AND assignment. AND the value of y with the value of x, store the result in x, and return the new value. x |= y - OR assignment. OR the value of y with the value of x, store the result in x, and return the new value.
A guess: by "shorthand assignment operator" you probably mean operators like `+=' and `*='. (If you mean something else, ignore the rest of this message