Towards Sustainable Energy: A Systematic Review of Renewable Energy Sources, Technologies, and Public Opinions
Ieee account.
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address

Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
Renewable energy articles from across Nature Portfolio
Renewable energy is energy that comes from sources that are readily replenishable on short-timescales. Examples of these are solar radiation, wind, and biomass.
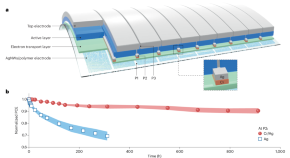
Strengthen the connections
Achieving good electrical contact without damaging underlying layers is critical to the performance of photovoltaic modules. Research now reports a silver electrode embedded into a polymer matrix and a silver/chromium protection layer, enabling over 14%-efficient flexible organic photovoltaic modules with improved stability under illumination.
- Eul-Yong Shin
- Hae Jung Son
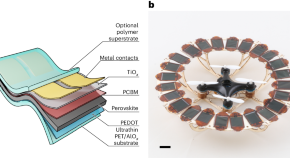
Ultralightweight perovskite solar cells for use in drones
Ultralightweight perovskite solar cells that achieve a specific power of up to 44 W g –1 and good stability are developed through engineering of the photoactive layer and substrate. These solar cells can be integrated into a drone to enable energy-autonomous flight.
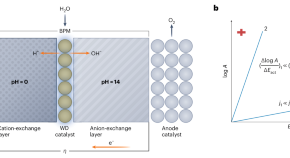
Understanding entropic barriers
The activation barriers of interfacial energy conversion reactions are key to controlling the efficiency of electrolysers. Work on the structural dynamics of water during charge transfer at electrified solid/liquid interfaces now brings greater understanding of the components of the activation barriers for water dissociation and hydrogen evolution.
- Aleksandar R. Zeradjanin
Related Subjects
- Geothermal energy
- Hydroelectricity
- Hydrogen energy
- Solar energy
- Wind energy
Latest Research and Reviews
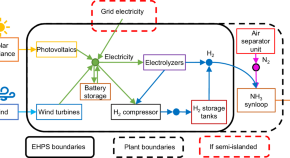
Effects of emissions caps on the costs and feasibility of low-carbon hydrogen in the European ammonia industry
Decarbonizing the European ammonia industry: Less stringent emissions caps for electrolytic hydrogen production can significantly reduce costs and land use while still achieving more than 90% reduction in emissions relative to fossil-based hydrogen.
- Stefano Mingolla
- Paolo Gabrielli
- Zhongming Lu
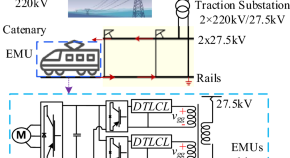
Magnetic integrated double-trap filter utilizing the mutual inductance for reducing current harmonics in high-speed railway traction inverters
- Maged Al-Barashi
- Yongjun Wang
- Muhammad Shoaib Bhutta
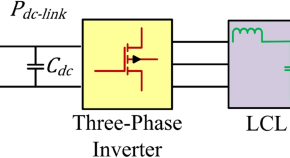
Control strategy for current limitation and maximum capacity utilization of grid connected PV inverter under unbalanced grid conditions
- Jyoti Joshi
- Vibhu Jately
- Brian Azzopardi
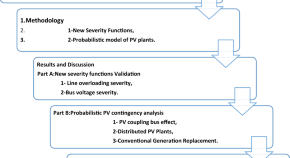
Novel risk index integrating practical operation limits enhances probabilistic contingency ranking for large-scale photovoltaic plant planning
- Rasha Elazab
- Mohamed K. El-Aser
- Adel A. El-samahy
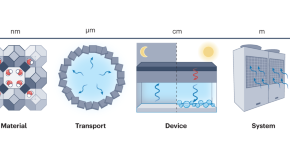
Bridging materials innovations to sorption-based atmospheric water harvesting devices
Harvesting freshwater from the air using water sorption materials is an innovative strategy to address water scarcity. This Review offers a multiscale perspective to design the next generation of sorption-based atmospheric water harvesting technology by bridging materials innovations to device realization and provides practical guidelines to understand its real-world impact.
- Lenan Zhang
- Evelyn N. Wang
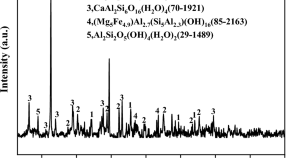
Synergistic catalytic mechanism of red mud in the co-gasification of spirit-based distillers’ grains and sewage sludge
- Junliang Wang
News and Comment
Getting a charge out of perovskites.
- Giulia Tregnago
Patterned membranes
- James Gallagher
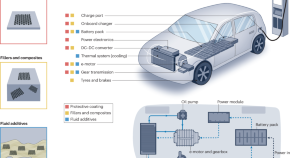
2D materials for durable and sustainable electric vehicles
The increasing popularity of electric vehicles as an alternative to internal combustion engine vehicles brings new realities, challenges and opportunities for scientists and engineers. A key element of this transition will be to develop solutions for lubrication, thermal management, electrical compatibility and corrosion inhibition. Two-dimensional materials are well poised to address these challenges and enhance the performance, efficiency, durability and, hence, sustainability of electric vehicles during this century and beyond.
- Diana Berman
- Leonardo Israel Farfan-Cabrera
- Ali Erdemir
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- Library Hours Servicios in Español Databases Research Guides Get Help My Account CCC Home myClackamas
- myClackamas
- Research Guides
- Servicios in Español
- CCC Library
- Industrial Technology + Automotive
Renewable Energy Technology
- APA (7th ed.) resources
- Course Reserves (textbooks)
- Article databases and eJournals
- eBook databases
- Streaming video databases
- CCC Library Catalog
- Search tips and strategies
APA 7th edition manual
Apa 7 citation examples, missing elements - apa 7, apa 7 paper formatting basics, apa 7 document templates, more apa 7th ed. resources.
- Job and career resources
This guide will introduce you to APA 7 citations, both for the References page of your paper and in-text citations. It is offered in multiple file formats below.
- Citation Examples - APA 7 - Word Document
- Citation Examples - APA 7 - PDF
This guide will tell you exactly what to do if your resource is missing a citation element. Can't find the author, publication date, page numbers, or something else? Use this guide to find out what to do! This guide is offered in multiple formats below.
- Missing Elements - APA 7 - Word Document
- Missing Elements - APA 7 - PDF
- Typed, double-spaced paragraphs.
- 1" margins on all sides.
- Align text to the left.
- Choose one of these fonts: 11-point Calibri, 11-points Arial, 10-point Lucida Sans Unicode, 12-point Times New Roman, 11-point Georgia, 10-point Computer Modern.
- Include a page header (also known as the "running head") at the top of every page with the page number.
- APA papers are broken up into sections. Check with your instructor for their expectations.
- In general, headings and title are centered.
APA 7th edition recognizes two kinds of paper formats - student papers (undergraduate students) and professional research papers (graduate students and professionals). At Clackamas CC, you will use the student paper formatting conventions.
You don't have to format a paper from scratch! Download this APA-formatted document template as a Word document or Google document. Save it, erase the existing text, and type your text right into the template. Learn how to format a paper in APA format by reading the contents of the template. The References page has been formatted with hanging indents.
- Download & edit: APA Word document template Microsoft Word document template to save a copy of and type into. To edit it, save a copy to your desktop or Clackamas Office 365 account. Includes tips on how to format a paper in APA. Last updated Feb. 2020.
- Download & edit: Pages document template If you need this template in Pages, email [email protected]
- View Only: Sample APA student paper (7th ed.) This sample student paper includes descriptions of indentations, margins, headers, and other formatting conventions (APA, 2020).
- APA Style (APA.org) APA's site answers all the basic questions about APA 7th edition and gives sample "student" and "professional" papers. This will help you with document format, in-text citations, the References list, and various stylistics.
- << Previous: Search tips and strategies
- Next: Job and career resources >>
- Last Updated: Apr 25, 2024 10:24 AM
- URL: https://libguides.clackamas.edu/renewable-energy


246 Energy Topics & Essay Examples
These energy topics explore the dynamic realm of energy sources, consumption, and sustainability. Here, you can find an excellent topic for your essay or project. As you go through these energy research questions, you will uncover the intricacies of energy demands, environmental concerns, and the quest for renewable energy solutions. Let’s charge up!
⚡ TOP 7 Energy Topics
🏆 best energy research topics, 🍃 renewable energy research topics, 👍 thought-provoking energy topics, ☢️ nuclear energy research topics, 🎓 interesting energy topics for project, 🌞 solar energy research topics, 💡 simple energy topics for research, ❓ energy research questions, 🌶️ hot energy ideas to write about.
- Rockstar Energy Drink Marketing Research
- The Sun as an Ultimate Source of Energy
- Helvie Energy Theory of Nursing and Health
- Analysis of Copperbelt Energy Corporation Plc.
- How Wind Turbines Convert Wind Energy into Electrical Energy?
- Activation Energy for Viscous Flow of Water, Acetone, Toluene, and o-Xylene
- Siemens Energy: Renewable Energy System
- Electricity vs. Solar Energy Compared and Contrasted Electricity and solar energy have become the most preferred energy sources for use due to their numerous advantages and sustainable development goals.
- Discussion of Renewable Energy Resources Renewable energy sources have now become a topic for continuous discussion in the contexts of environmental studies, economics, and society.
- Resolute Marine Energy: Power in Waves Resolute Marine Energy’s desalination and energy generation project is an essential step toward improving the quality of people’s lives globally.
- Extreme Scenarios: The Issue of Energy Resources Shortage Imagine that you cannot use electricity or get fuel for your car because these energy resources are no longer available.
- Adaptation of Oil and Gas Companies to a Low-Carbon Energy Industry This paper explores potential strategies through which companies operating in the O&G industry can maintain their economic and reputational resilience.
- Solving the Climate Change Crisis by Using Renewable Energy Sources Climate change has caused extreme changes in temperature and weather patterns on planet Earth, thus threatening the lives of living organisms.
- Renewable Energy Technology in Egypt Climate change has made renewable energy a global priority to replace fossil fuel which continues to impact the environment negatively.
- The Use of Renewable Energy: Advantages and Disadvantages Today’s world is dependent on electricity, which is supplied from many different sources such as fossils fuels which emit harmful gases that pollute the environment.
- GE Energy and GE Healthcare: Strategic Customer Relationships This article seeks to discuss the benefits of building strategic customer relationships for GE Energy and GE healthcare and their customers.
- Nuclear Energy: Advantages and Drawbacks This paper analyzes nuclear energy as a potential source of energy and its advantages and drawbacks. Nuclear energy is the ultimate solution to the current energy crisis.
- Wind Energy as an Alternative Source While energy is a must for our survival, wind energy as a seemingly perpetual source of energy is the potential answer to the energy security of our generations to come.
- Solar Energy and Its Impact on Environment The purpose of this paper is to determine the impact of solar energy on the environment. The major positive impact is the minimal emission of greenhouse gases.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Popularity and Benefits Renewable fuels are not as pollutive as fossil fuels; they can be reproduced quickly from domestic resources. They became popular because of the decreasing amount of fossil fuels.
- Energy Independence in the USA The United States is dependent on oil imports coming from politically unstable regions in the world. Energy independence is not yet possible because of several limitations.
- The Glencore Energy Firm’s Bribery Scandal Glencore Energy was convicted on the charges of bribery, related to African oil operations, which is a sensitive ethical matter in any company.
- The Power of Using Nuclear Energy The paper argues that nuclear energy is an important and powerful way of producing electricity and an option for countries to develop an independent internal energy structure.
- Renewable Energy: Why Do We Need It? Renewable sources of energy such as solar, wind, or hydropower can bring multiple environmental benefits and tackle the problems of climate change and pollution in several ways.
- Determining Enthalpy of Combustion of a High-Energy Candy The purpose of this experiment was to determine the enthalpy of combustion of Mickey Mouse Clubhouse in kilojoules using a bomb calorimeter.
- Energy Crisis and Climate Change The global community needs to adopt an energy efficient behavior and invest in the exploration of sustainable energy resources.
- AI System in Smart Energy Consumption The primary aim of the paper is to expose the significant impacts of AI integration in intelligent energy consumption methods.
- Octopus Energy’s Sociotechnical System Analysis The systems map presented in the paper shows the crucial elements within the Octopus Energy company and the external elements that may affect its business processes.
- Renewable Energy Usage: Advantages and Disadvantages This treatise attempts to support the statement that there are both advantages and disadvantages to the use of renewable energy with focus on hydroelectric power.
- Sun Power as a Promising Energy Industry Of all available options for clean energy, solar has been the most expensive, even though their increased availability has caused a decline in the process.
- Discussion of Realization of Solar Energy Company ABC is interested in creating a “solar” project which will fully install and staff solar panels to ensure the safe transformation of solar energy into electricity.
- The Future of Jamaica’s Energy Development The paper provides new strategy proposes to consider changes in energy consumption over the next 20 years in Jamaica.
- The Economic Viability of Large-Scale Wind Energy Projects.
- Advancements in Photovoltaic Solar Cell Technologies: Efficiency and Cost Considerations.
- Potential and Challenges of Biomass Energy Conversion Technologies.
- Hydroelectric Power Generation and its Environmental Impact.
- Geothermal Energy: Harnessing Earth’s Heat for Sustainable Power.
- Exploring the Potential of Oceanic Resources – Tidal and Wave Energy.
- Energy Storage Solutions for Renewable Integration: Batteries, Pumped Hydro, and Beyond.
- Smart Grids and Renewable Energy Integration.
- Scalability and Sustainability of Biofuel Production from Algae.
- The Role of Policy Incentives in Driving Renewable Energy Adoption.
- Overcoming Technical and Environmental Challenges of Offshore Wind Farms.
- Success Stories of Community-Based Renewable Energy Initiatives.
- Solar Energy in Developing Countries: Addressing Energy Poverty and Sustainability.
- Energy Independence and Reliability of Microgrid Systems for Remote Areas.
- Environmental Benefits and Trade-offs of Bioenergy from Agricultural Residues.
- Solar Energy and Urban Planning: Strategies for Efficient Integration.
- Technological Innovations in Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) Systems.
- Energy-Water Nexus: Balancing Renewable Energy Production and Water Resources.
- Comparative Analysis of Different Biomass Feedstocks for Bioenergy Production.
- Challenges and Prospects of Green Hydrogen Production from Renewable Sources.
- Unbundling Vertically Integrated Energy Companies: Benefits to Consumers This paper seeks to discuss the benefits that will accrue to the consumers as a result of the unbundling regulation.
- Energy Consumption in Architecture and Environmental Design Energy conservation can be considered as one of the fundamentals of energy consumption in architecture and environmental designs.
- International Atomic Energy Agency This report elaborates on the usage of nuclear energy in the Global International Community rather than the creation of nuclear weapons as seen in Middle East countries.
- Energy Consumption and Ecosystem Restoration Ecosystems, in general, act as filters of the environment. Cities include certain ecosystems into city planning documents since such systems act as “lungs” for the city.
- Energy Sector Challenges in Morocco The future of Morocco’s energy supply and demand faces substantial hurdles. In particular, the country is perceiving a growth in energy consumption.
- Valero Energy and Chevron Corporations’ Financial Management Valero Energy and Chevron Corporations faced a drastic decline in total revenues in 2020, mainly due to economic upheaval and uncertainty caused by COVID-19.
- Work and Energy Forms in Physics The potential energy (PE) and kinetic energy (KE) of an object increase when positive work is done on it when there is no friction present.
- Energy Conservation in the Environment There are so many undefined factors negatively affecting the environment. These are some of the things that make people to put their efforts in protecting the environment.
- Sustainability of Energy Alternatives With growing concerns and evidence of global warming and the effects of climate change, significant attention has been shifted to alternative energy sources.
- Solar Power as the Best Source of Energy The concepts of environmental conservation and sustainability have forced many countries and organizations to consider the best strategies or processes for generating electricity.
- Energy Consumption in Wireless Body Area Networks This essay seeks to present an extensive study of energy consumption technologies in WBANs. This is achieved through a concerted focus on power-efficient models.
- Biofuels and Fossil Fuels as Alternative Energy This paper compares and contrasts biofuels and fossil fuels and to evaluate whether biofuels can be considered as the alternative source of energy.
- Sunburst Renewable Energy Corporation: Business Structuring The proposed Sunburst Renewable Energy Corporation will function on a captivating value statement in product strategy and customer relationships as the core instruments of sustainable operations.
- The UAE Investment in Clean Energy The government of the UAE should focus more on strategies that promote clean energy since it is less utilized.
- The G20 Countries’ Competitiveness in Renewable Energy Resources “Assessing national renewable energy competitiveness of the G20” by Fang et al. presents an assessment of competitiveness in renewable energy resources among G20 countries.
- Biomass and Energy Crops and Technology Biomass energy is a more environmentally friendly form of energy when but the economic viability of its production still doesn’t measure up to fossil fuel production.
- Energy-Efficient Architecture and Environmental Design Energy consumption is an important aspect of architecture and environmental design, which is among the priorities when focusing on sustainability
- Household Energy Use and Poverty In many developing countries, as well as among disadvantaged populations of the industrial states, the lack or absence of energy for household use is an everyday reality.
- Energy: What Everyone Needs to Know? The book “Energy: What Everyone Needs to Know” by Jose Goldemberg – a famous Brazilian physicist, research scientist, and scientific leader of the renewable energy community.
- Green Energy and Carbon Capture Green energy is a useful strategy for providing sustainable energy for use in various economic sectors. Carbon capture and storage help to protect the environment.
- Energy Sustainability and Its Key Issues Energy sustainability is becoming the most urgent socio-environmental problem, among other aspects of energy development.
- Environmental Biology: Green Energy a precise definition of green energy is manifested in its source, which must be natural, such as the sun or geothermal sources.
- Nuclear Power Must Be a Part of Future Energy Grids Nuclear energy sources are essential and must be included in future power grids alongside renewable alternatives due to their reliability.
- The Problem of Overpopulation and Energy Scarcity The population is proliferating, and although environmental, geopolitical, and socioeconomic factors may be slowing this dynamic, growth remains evident.
- Hybrid Energy Harvesting System The hybrid energy harvesting system, its advantages, and principles of operation are described in the present paper.
- Nuclear Energy Used for Different Purposes Nuclear energy has been a very dubious concept since its very discovery and its introduction into the mass consumption environment.
- Alternative Energy Industry’s Profit Pools A profit pool is the total profits earned within an industry by all players and it extends to all players in the value chain.
- Bio-Based Materials: Alternative Energy Cultivation of bio-based materials will not only encroach on the land meant for the cultivation of crops, but that crops will also be expensive, thus resulting in looming hunger.
- Emirates Nuclear Energy Corporation’s Communication The present document will explore in detail the context of the communication plan for use by the Emirates Nuclear Energy Corporation.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Definition, Types and Stocks This research report analyzes the growing interest of the use renewable energy as an alternative to the non-renewable energy.
- Industrial Fermentation as Energy Conversion One of the most common examples of employing fermentation in the industry is producing alcoholic drinks and dairy products. This type of energy conversion refers to anaerobic.
- Usage of Alternative Energy Alternative energy is a term used to describe any source of energy that replaces the usage of fuel as the source of energy and they are deemed not to have the negative effects.
- Nuclear Reactor Safety: Analyzing Accidents and Preventive Measures.
- Generation IV and Beyond – Advanced Nuclear Reactor Designs.
- Nuclear Energy and Climate Change Mitigation: Carbon-Free Power Generation.
- Strategies for Safe Disposal of Radioactive Waste.
- Nuclear Fuel Cycle: From Mining to Reactor and Beyond.
- Prospects and Challenges of Small Modular Reactors (SMRs).
- Nuclear Fusion Research: Progress Toward Sustainable Energy Production.
- What Are the Biggest Public Misconceptions Regarding Nuclear Energy?
- Cost Analysis and Financing Models of Nuclear Power.
- Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) and Nuclear Energy: Balancing Benefits and Risks.
- Impacts Nuclear Energy Use on Water Resources Quality.
- Nuclear Energy and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- The Potential and Challenges of Thorium-Based Nuclear Fuel.
- Propulsion and Power Systems of Nuclear Energy and Space Exploration.
- Nuclear Energy and National Energy Policies: Case Studies from Different Countries.
- Radiation Exposure and Health Risks of Nuclear Energy.
- Nuclear Energy and Grid Stability: Contributions to Base Load Power.
- Nuclear Energy and Renewable Integration as Complementary Solutions.
- Public Engagement and Participation in Nuclear Energy Decision-Making.
- Nuclear Energy and Future Energy Scenarios: Role in Energy Transitions.
- Oil and Energy Companies in the US: The Windfall Profits Tax Although a windfall gains tax would not alter the demand for oil, it may make it more difficult for companies to recoup the costs of new production.
- Human Energy Consumption and Water Power Human energy use is significantly low compared to natural energy flow. Waterpower is not significant in energy flow because it is renewable energy.
- Current Energy Crisis in Beirut, Lebanon This paper supports the ideas used by the Lebanese government to reduce energy crises, such as using solar systems, alternative fuels, good governance, and cutting energy demand.
- Government Policies Lowering Energy Costs The paper summarizes a government intervention meant to lower inflation. The inflation rate has been on a steady increase for numerous reasons.
- Environmental Degradation and Renewable Energy The global community relies on the surrounding environment for food production, transport, and economic development.
- Reducing Homestead Energy Consumption in Australia This paper explores innovative methods to decrease energy consumption in Australian households, aligning with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDG).
- A New Energy Mix for the United Kingdom This paper presents an analysis of the impact of the Russia/Ukraine hostility on the UK Oil and Gas industry.
- Energy Generation as a Metabolic Process One of the metabolic processes in the organisms is the process of energy generation. Such processes should be understood as the cleavage of an organic substrate.
- Dark Energy and Its Significance for the Universe Dark energy is an energy component with negative pressure. It violates the strong energy condition and accelerates the universe.
- Cybersecurity Threats to the Energy Sector The modern era of global technologies creates a two-fold situation. On the one hand, new advanced digital technologies are emerging to automate energy production.
- Analysis of Energy Sources: Fossil Fuels and Nuclear Power Various types of fossil fuels are used for energy production. Each has different characteristics, origins, they all contain large amounts of energy that are used for various purposes.
- Utilizing Thorium in Energy Production Thorium might have elevated nuclear power production to a new level because it was affordable, safe, and produced no radioactive waste, but for some reason, it did not.
- Conducted Energy Weapon Program for Policing This work is a research paper for the Mayor of Virtual City on implementing a Conducted Energy Weapon program for the Virtual City Police Department.
- Cheerios Firm’s Diversification of Energy Sources Cheerios needs to diversify its operations and tap new environmentally friendly energy resources available in the energy sector.
- Renewable Energy in Japan: Clean Energy Transition Renewable energy in Japan became significantly important after the Fukushima Daiichi tsunami that struck Japan in 2011.
- Nuclear Technology and Radiation Energy The numerous advantages of nuclear technology exceed the disadvantages; therefore, scientists should continue making and using the technology.
- The Concept of Sustainability in Energy Plan for 2030-2040 The paper discusses the concept of sustainability takes a central role in the global discussion and presents of environment safety plan.
- The US and Canada’s Approaches to the Energy Issue The US and Canada are two of the world’s largest countries, requiring increased energy consumption and utilization as industrialized nations.
- Coal as an Energy Source and Its Impacts on Human Health Coal power generation is one of the most used energy production types in the world. The process of energy generation using coal includes the burning or combustion of solid coal.
- General Physics: Increasing Internal Energy The first law of thermodynamics deals with the state of energy and its transfer between objects. Energy is conserved in an isolated system.
- Future of 100% Renewable Energy This article explores the future of renewable green energy and a review the topical studies related to 100% renewable energy.
- The Energy Sector: Russia’s Policy This paper aims to provide a thorough and insightful analysis of Russia’s energy policy and suggest recommendations for the country to remain naturally prowess.
- Full Renewable Energy Plan Feasibility for 2030-2040 This paper argues that green energy in its current state will struggle to meet humanity’s demand and the development of better hybrid, integrated grids is required.
- Solar Energy: Advantages and Disadvantages Renewable energy sources are being supported and invested in by governments to instigate a new environment-friendly technology.
- Effects of Reducing Energy Waste Pennsylvania is a state that uses a large amount of energy each day. Most of the population utilizes natural gases energy every day in their homes and places of work.
- Biofuels and Fossil Fuels as Energy Sources The paper discusses the similarities and differences between biofuels and fossil fuels and replacing non-renewable energy sources with renewable ones.
- South Africa: The New Energy Infrastructure Policy The first stages of implementing the new energy policy in South Africa, legislative and financial ones, went smoothly without any disturbances.
- Profitability of Onshore and Offshore Wind Energy in Australia Undoubtedly, the recent increase in popularity of campaigns to decarbonize the globe proves renewable energy to be a current and future trend globally.
- Renewable Energy: The Use of Fossil Fuel The paper states that having a combination of renewable energy sources is becoming critical in the global effort to reduce the use of fossil fuels.
- Is Nuclear Power Renewable Energy? Renewable energy is obtained from the naturally-occurring elements, implying that it can be easily accessed, cheaply generated, and conveniently supplied to consumers.
- Solar Energy in China and Its Influence on Climate Change The influence of solar energy on climate change has impacted production, the advancement of solar energy has impacted climate change in the geography of China.
- Energy Crisis and Policy in the United States Currently, countries of the world face an energy crisis due to climate change, population growth, increased demand, and dependence on fossil-based fuels.
- Materials and Technologies for a Photovoltaic Solar Cell Efficiency Enhancement.
- Solar Energy Integration into Urban Design and Architecture.
- Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) Systems: Advancements and Applications.
- Prospects and Challenges of Thin-Film Solar Technologies.
- Solar Energy Storage Solutions: Batteries and Beyond.
- Solar Energy and Agriculture: Agrovoltaics and Land Use Efficiency.
- Overcoming Barriers to Adoption of Solar Energy in Developing Countries.
- Maximizing the Energy Output of Solar Tracking Systems.
- Solar Panel Recycling and Sustainability Considerations.
- Solar Thermal Collectors for Domestic Water Heating and Space Heating.
- Solar Energy and Water Desalination: Sustainable Solutions for Freshwater.
- Solar Energy Policy and Incentives: Impact on Adoption Rates.
- Decentralized Power Distribution using Solar Energy Microgrids.
- Solar-Powered Transportation: Electric Vehicles and Charging Infrastructure.
- Challenges and Benefits of Implementing Solar Energy in Remote and Off-Grid Areas.
- Solar Energy and Environmental Impacts: Life Cycle Assessment.
- Improving Grid Integration and Stability of Solar Energy Forecasting.
- Perovskite Solar Cells: Emerging Technologies and Applications.
- Solar Energy Education and Public Awareness Initiatives.
- Solar Energy Financing Models: Investment and ROI Analysis.
- Full Renewable Energy Plan Feasibility: 2030-2040 The paper argues that green energy in its current state will struggle to meet the humanity’s demand and the development of better hybrid, integrated grids is required.
- Saving Energy in a Restaurant Enterprise The paper discusses design of the restaurant is capable of appealing by its appearance to the realization of the importance of the coexistence of man and the environment.
- Energy Crisis and Methods of Countering It The standard definition of an energy crisis is a state of the economy in which the energy demand is significantly higher than the supply.
- The Energy of Future in New Jersey The U.S. economy and life quality depend on sufficient amounts of energy, most of which are obtained utilizing fossil fuels.
- Increasing Gas Price and Alternative Energy Sources Fuel demand is increasing with the increase of population, so, an alternative source of energy can be the best solution for the future demand for fuel.
- Advanced Nuclear Energy Options The report concerns advanced nuclear energy options and their implementation, adopting low-cost and safe non-emitting energy sources considering moral or ethical concerns.
- Energy and Environmental Effect of the Pipeline Bust on the US Transportation The Alaskan pipeline traverses mountain terrain, several hundreds of waterways, fault lines, frost grounds, and migratory wildlife routes over a distance of 800miles.
- The United Kingdom Energy and Emissions This paper analyses the impacts of fuel extraction and the legislations governing gas emissions in the United Kingdom (UK).
- Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Utilization This paper aims at expounding the effectiveness of renewable energy and the utilization of energy efficiency in regard to climate change.
- Regeneration of Energy in Scotland This white paper looks at a project in Scotland to replace non-renewable energy sources that increase carbon levels in the atmosphere with renewable energy sources.
- Environmental & Economic Benefit Analysis of Methane Capture for Energy Generation Methane is a natural gas that is generated through the decomposition of organic matter by bacteria. This process is successfully completed when there is an absence of oxygen.
- Utilization of Solar Energy for Thermal Desalination The following research is set to outline the prospects of utilization of solar energy for thermal desalination technologies.
- Analysis of the Energy Consumption Coefficient In the article, the author analyzes the energy consumption standards of buildings and determines their dependence on the form factor and the enclosing surface of the building.
- Engineering: Power Management Techniques for Energy Efficiency The purpose of this article is to consider various methods for reducing power consumption in digital logic systems.
- Modern Energy Technologies Introduction to Developing Countries The ultimate goal of this marketing strategy would be to make new sources of energy affordable and attractive, not only to people but also to the government and local investors.
- A World With 100% Renewable Energy Large corporations, countries, and separate states have already transferred or put a plan into action to transfer to 100% renewable energy in a couple of decades.
- Nextera Energy Culture and Reward Structure NextEra Energy’s adherence to a clan structure while rewarding rigid and numbers-based performance metrics has likely produced a pathological combination.
- Energy Crisis: The Processes of Globalization and the Unification Applying approaches in the study of economic crises, it can be concluded that the cause of an energy crisis can be not only a shortage but also an excess of energy resources.
- Change in Energy Crisis and Save of the Earth Basically, a battery is comprised of numerous electrochemical cells. In 1792, an Italian physicist by the name of Alessandro Volta came up with the first electrochemical cell.
- Renewable Energy Programs in Five Countries Energy production is vital for the drive of the economy. The world at large should diversify the sources to reduce the over-usage of fossil energy that is a threat of depletion.
- Energy Deals Derailed by Obscure Accounting Rule: Enron Case The top-level management at Enron undertook one of the largest accounting scandals to have ever hit the corporate world resulting in the bankruptcy and dissolution of this company.
- Business Models in the Alternative Energy Industry Alternative energy industry players have succeeded in developing a number of devices designed both to enhance and perpetuate in helping the public.
- Energy Innovation Evolutionary Economics and Policies The use of innovative energy technology is influenced by insights into evolutionary economics. Through such insights, better policies can be formulated.
- Wind Works Ltd.: Wind Energy Development Methodology Wind Works Ltd, as the company, which provides the alternative energy sources, and makes them available for the wide range of the population needs to resort to a particular assessment strategies.
- Energy Safety and Earthquake Hazards Program The distribution of earthquakes around the world is not uniform. Some parts experience earthquakes frequently while others do not.
- Alternative Energy Industry’s Competition Dynamics Understanding the level of competition in the industry by a company is very important as the level of profits depends to a large extent, the level of competition.
- Concept of Energy Consumption in Environmental Design Environmental concerns are not restricted to energy consumption, having other aspects to consider such as sustainability, recycling, eco-regulations.
- Alternative Energy Sources: A Collaborative Approach in Water Management With the increasingly high prices of gasoline in particular and fossil fuels in general there is a need to find an alternative source of energy.
- Energy Saving Light Bulb Manufactures Ethical Issue Whether it is ethical for companies to continue manufacturing these bulbs which have a positive effect on the environment but a negative one on people’s health.
- The Problem of Energetic Supply in State Ohio The problem of energetic supply in state Ohio is a core element for many politics in order to gain stability in rational use and afterward recycling of energy inputs or fossil fuels, on the whole.
- Peak Oil and Texas’ Energy Future The concept of peak oil refers to situations regarding the reserves of oil in the world is limited and being gradually being depleted due to excessive use.
- Chuck Plunkett “Prius Effect”: Energy Efficient Cars Harmful Effects on the Environment The main idea of the article is that energy-efficient cars made the light rail, which has harmful effects on the environment, less attractive for the passengers.
- Are Alternative Energy Sources the Answer to Ending Human Dependence on Oil?
- Does Energy Consumption Affect Economic Development?
- Can Alternative Energy Effectively Replace Fossil Fuels?
- What Are the Barriers and Incentives for Community-Owned Means of Energy Production and Use?
- Are Biofuels the Answer to the Energy Question?
- How Can Alternative Energy Be Harnessed Effectively?
- Can Wind Energy Enable the US to Become Energy Independent?
- Does Energy Consumption Contribute to Climate Change?
- Are Green Electricity Certificates the Way Forward for Renewable Energy?
- Can Nuclear Energy Contribute to the Transition Toward a Low-Carbon Economy?
- How Can Political Geography Make Sense of Energy Policy?
- Are Building Codes Effective at Saving Energy?
- Does Energy Efficiency Reduce Emissions and Peak Demand?
- Can Nuclear Energy Stimulates Economic Growth?
- What Drives the Development of Renewable Energy Technologies?
- Are Dark Energy and Dark Matter Different Aspects of the Same Physical Process?
- Does Financial Development Increase Energy Consumption?
- Are Renewable Energy Policies Climate-Friendly?
- How Important Are Current Energy Mix Choices on Future Sustainability?
- Can China’s Energy Intensity Constraint Policy Promote Total Factor Energy Efficiency?
- Should the UK Defense Strategy Support Future Energy Security?
- Are the Energy Efficiency Technologies Efficient?
- Does Green Energy Supplies Enough for Our Life?
- Who Are the Players in the Sustainable Energy Market and What Are They Doing?
- Can Declining Energy Intensity Mitigate Climate Change?
- Energy and the Economy. Oil Addiction in America In America, “addiction to oil” results in high oil prices and a unique structure of economy dependent upon crude oil.
- Energy Information Agency: Overview on Gasoline Gasoline is considered as one the most important commodity that surmised these days. It is the main ingredient in transportation, in industry and in household.
- Australian Stock Market Energy Sector: Investment Analysis The technical analysis aimed to help determine which stocks of the alternatives will give the most benefit. Analysis of five stocks under the Australian stock market energy sector.
- Energy Efficient Cars: Difficulties in Optimization The essay discusses the problem of optimizing the energy efficiency potential and reveals the universal classification of the automobile vehicles.
- Energy-Efficient Area Monitoring for Wireless Sensor Network Wireless technology is one of the upcoming technology in the market which allows portability and connectivity from anywhere.
- Energy for the Future: Discussion The peak oil theory was forwarded by Dr. M. King Herbert, who forecasted that the oil deposits of the world will start declining after reaching a maximum point of production.
- Bio-Based Materials as Alternative Energy The bio-based materials are products which main constituent consist of a substance, or substances, originally derived from living organisms.
- Quantum Energy Company’s Marketing Plan The present paper outlines a marketing plan for an up-and-coming fast-moving consumer goods company, Quantum Energy.
- Interactive Technologies in Weather and Energy Service Companies Modern weather and energy service companies significantly benefit from the wide use of digital technologies and innovative practices.
- Committee of Energy and Commerce’s Role in Healthcare Health care in the US is currently in crisis and soar the need for sustainable reform. One of the barriers on the way to meaningful changes is political polarization.
- Promoting the Use of Green Energy in Emerging Economies This paper discusses the most reliable alternative energy sources that should be promoted in different parts of the world.
- The Way Forward in the “Sustainable Energy – Without the Hot Air” by David Mackay “Sustainable Energy-Without the Hot Air” by David J. C. Mackay provides users with useful data on the way forward when it comes to sustainable energy.
- Carbon Cowboys: Environmental Protection & Energy Efficiency Climate change is real, but if you do not believe this is the case, it still makes sense to embrace clean, renewable energy sources and energy efficiency measures.
- Energy Demand and Political Will to Alternatives The study looks at alternative energy sources. The research focuses on world behavior, energy consumption demand, different theories, and political will to change to alternatives.
- Energy Demand in Pakistan The introduction of nuclear energy in Pakistan will reduce its’ reliance on its neighbors since as the energy sources become depleted, any country that will depend on its neighbors risks the lives of citizens.
- Installing Solar Panels to Reduce Energy Costs The purpose of the proposal is to request permission for research to install solar panels to reduce energy costs, which represent a huge part of the company’s expenses.
- Energy Infrastructure Management in the United States Energy assets in the US are predisposed to various vulnerabilities. Threats facing energy assets include natural disasters, danger related to industrial and technological issues.
- Renewable Energy Sources for Saudi Arabia This paper will provide background information on the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, its energy resources, and how it may become more modern and efficient.
- Energy Management: Key Components The news about data centers’ possible switching to solar power relates to all the major components of energy management.
- Renewable Energy: Economic and Health Benefits The US should consider the adoption of renewable sources of energy, because of the high cost of using fossil fuels and expenses related to health problems due to pollution.
- Energy Drinks Effects and Changes in Heart Rate The increased consumption of energy drinks by young people makes health care practitioners and researchers focus on studying the effects of these beverages on the people’s health.
- Renewable and Alternative Energy Sources in Hawaii Nowadays, people all over the world consume energy and, that is why the industry which produces it is one of the most important ones in the modern world.
- Meteorology for Future Commodity and Energy Markets This paper discusses what meteorological trading opportunities will become more important in future commodity and energy markets.
- Renewable Energy Systems Group and Toyota Company The application of the Lean Six Sigma to the key company processes, creates prerequisites for stellar success, as the examples of Toyota and the Renewable Energy Systems Group have shown.
- Energy Efficiency and Economic Approaches This paper analyzes some of the economic approaches that can be applied to generate suitable models for efficient energy resource use.
- Sustainability and Energy Politics by G. Curran The paper analyzes the book “Sustainability and Energy Politics: Ecological Modernization and Corporate Social Responsibility” by Giorel Curran.
- The Future of Energy in California This essay describes the major sources of energy in California. A powerful energy conservation strategy is also identified in the paper.
- Iran’s Nuclear Energy and Relations with Israel The fact that Iran has questioned the existence of Israel as Jews homeland and threatened to annihilate it has further complicated the issue.
- Mega Energy Projects: China’s Solar Generator The China’s solar power mega project, which will be implemented in phases, is set to make a remarkable supplement in China total national energy production.
- Sustainable Energy: Without the Hot Air by MacKay In the book Sustainable Energy: Without the Hot Air, MacKay renders a range of topics related to the issue of energy source and the concept of renewable resources.
- US Energy Policy: Vulnerabilities and Challenges As the world’s need for energy continues to grow, the US government has to formulate a comprehensive strategy to secure energy resources.
- Managing Energy Demand in Abu Dhabi: Toward Sustainable City This paper seeks to carry out a comprehensive analysis of the Abu Dhabi energy needs situation, including making comparison with other international cities.
- Gas Price Increasing and Alternative Energy Sources The alternatives source of energy can be the best solution of energy demand. The energy, which are considering as an alternative to gas, are solar power, wind power, and biomass or bio-fuel etc.
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2021, September 9). 246 Energy Topics & Essay Examples. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/energy-essay-topics/
"246 Energy Topics & Essay Examples." StudyCorgi , 9 Sept. 2021, studycorgi.com/ideas/energy-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2021) '246 Energy Topics & Essay Examples'. 9 September.
1. StudyCorgi . "246 Energy Topics & Essay Examples." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/energy-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "246 Energy Topics & Essay Examples." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/energy-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2021. "246 Energy Topics & Essay Examples." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/energy-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Energy were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on January 22, 2024 .
Energy Research Paper

View sample energy research paper. Browse other research paper examples and check the list of history research paper topics for more inspiration. If you need a history research paper written according to all the academic standards, you can always turn to our experienced writers for help. This is how your paper can get an A! Feel free to contact our custom writing service for professional assistance. We offer high-quality assignments for reasonable rates.
From simple mechanical muscle energy to the energy derived from radioactive materials, energy use has ebbed and flowed throughout history. The economic, social, and political consequences of these changes are great, correlating with the rise and fall of empires and eras. Energy use continues to evolve in tandem with humanity and will dictate which choices are available for future development.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
When seen from the most fundamental physical point of view, all processes—natural or social, geological or historical, gradual or sudden—are just conversions of energy that must conform to the laws of thermodynamics as such conversions increase the overall entropy (the degree of disorder or uncertainty) of the universe. This perspective would make the possession and mastery of energy resources and their ingenious use the critical factor shaping human affairs. Also, given the progressively higher use of energy in major civilizations, this perspective would lead logically to a notion of linear advances with history reduced to a quest for increased complexity that is made possible by higher energy flows. People who could command—and societies and civilizations who could use large or high-quality energy resources with superior intensities or efficiencies—would be obvious thermodynamic winners; those converting less with lower efficiencies would be fundamentally disadvantaged.
Such a deterministic interpretation of energy’s role in world history may be a flawless proposition in terms of fundamental physics, but it amounts to a historically untenable reductionism (explanation of complex life-science processes and phenomena in terms of the laws of physics and chemistry) of vastly more complex realities. Energy sources and their conversions do not determine a society’s aspirations, its ethos (distinguishing character, sentiment, moral nature, or guiding beliefs) and cohesion, its fundamental cultural accomplishments, its long-term resilience or fragility.
Nicholas Georgescu-Roegen, a pioneer of thermodynamic studies of economy and the environment, made a similar point in 1980 by emphasizing that such physical fundamentals are akin to geometric constraints on the size of the diagonals in a square—but they do not determine its color and tell us nothing whatsoever about how that color came about. Analogically, all societies have their overall scope of action, their technical and economic capacities, and their social achievements constrained by the kinds of energy sources and by varieties and efficiencies of prime movers that they rely on—but these constraints cannot explain such critical cultural factors as creative brilliance or religious fervor, and they offer little predictive guidance regarding a society’s form and efficiency of governance or its dedication to the welfare of its citizens. The best explanation of energy’s role in history thus calls for a difficult task of balancing these two realities, of striving for explanations that take account of these opposites.
Periodization based on the dominant uses of primary energy cleaves world history into just two highly asymmetrical spans: the renewable fuel era and the nonrenewable fuel era. All premodern societies relied overwhelmingly on solar, that is, perpetually (when measured on civilizational time scales) renewable energies. They derived their heat and light from biomass (the amount of living matter) that is produced by photosynthetic conversion of sunlight and harvested mostly as wood and crop residues, above all straws and stalks; plant and animal fats were also used in lighting. Their kinetic energy came from human and animal metabolism (energized, obviously, by eating the biomass) and, to a much lesser extent, from wind and flowing water, the two forms of converted solar radiation (after it is absorbed by the Earth’s biosphere) that power the global water cycle and atmospheric circulation.
Fossil fuels, too, had their origin in photosynthesis, but the constituent biomass was subsequently transformed into qualitatively new materials over a period of 1 million to 100 million years by high temperatures and pressures in the uppermost layers of the Earth’s crust. Consequently, fossil fuels—ranging, in the ascending order of quality, from peats through various coals (lignites to anthracites) to hydrocarbons (crude oils and natural gases)—are not renewable on historic time scales. This means that premodern, solar societies had an energy basis whose potential longevity coincided with the remaining duration of the biosphere (the part of the world in which life can exist) itself (i.e., still hundreds of millions of years to go). On the other hand, modern societies will have to change their energy base if they are to survive for more than a few hundred years.
Energy Sources: Biomass Fuels
Biomass fuels had two inherent disadvantages: low power density (expressed in watts per square meter—W/m2) and low energy density (expressed in joules per kilogram—J/kg). Even in rich forests biomass was harvested with densities not surpassing 1 W/m2, but most people did not have tools to cut mature tree trunks and had to rely on smaller trees, branches, and leaves gathered with much lower density. Similarly, the collection of crop residues, needed also as feed and as a raw material, rarely yielded more than 0.1 W/m2. Consequently, extensive forested areas were needed in order to supply the energy needs of larger settlements. A large preindustrial city in a temperate climate would have required at least 20 to 30 watts (W) per square meter of its built-up area for heating, cooking, and manufacturing, and, depending on the kind fuel it used, it would have needed a nearby area of up to three hundred times its size to supply its fuel. The constraint is clear: no temperate-climate megacities of 10 million people or more could have existed during the era when wood was the main source of energy.
These power density limitations became even more acute after charcoal became used on a relatively large scale. Conversion from wood to charcoal was done to increase wood’s low energy density: in its air-dried form (about 20 percent moisture) the fuel had about 18 MJ/kg, whereas charcoal rates about 60 percent higher at 29 MJ/kg. The obvious advantages of the better fuel include smaller mass to be transported and stored, smaller furnaces (or braziers), less frequent stoking, and less air pollution. But traditional charcoaling was inefficient, wasting about 80 percent of the initially used wood in the process. This waste would put a great strain on wood resources even if charcoal’s use was limited to space heating and cooking, but its expanded use in various manufactures and in metallurgy made it an acutely limiting factor. For example, in 1810 the metallurgical charcoal needs of the United States prorated annually to a forested area of roughly 50 by 50 kilometers (2,500 square kilometers), and a century later they would have amounted to an area of 170,000 square kilometers, equal to a square whose side is the distance between Philadelphia and Boston. The constraint is clear: no global steel-dominated civilization based on charcoal could exist, and coal-derived coke took over.
Energy Sources: Human and Animal Muscles
Similarly, the limited power of human and animal muscles constrained productive capacities as well as aggressive forays of all traditional societies. Healthy adults can sustain work at 40–50 percent of their maximum aerobic capacity, and for men (assuming muscle efficiencies of 20 percent) this translates to 70–100 W of useful work. Small bovines (cattle and water buffalo) can sustain about 300 W, lighter horses around 500 W, and heavier animals 800–900 W (one horsepower is equal to 745 W). These rates give common equivalences of at least four men for an ox and eight to ten men for a horse. No less importantly, heavier draft animals can develop briefly maximum power well in excess of 3 kilowatts (kW) and can thus perform tasks unattainable by men (plowing heavy soils, pulling out tree stumps). Larger numbers of stronger draft animals thus greatly improved the productivity of traditional farming: even slow plowing was three to five times faster than hoeing.
These gains, however, had to be paid for by devoting more time to caring for these animals and devoting increasing amounts of land to their feeding. For example, feeding the peak number of U.S. farm horses and mules in 1919 (approximately 25 million) required about 20 percent of the country’s farmland. Obviously, only countries endowed with extensive farmland could afford this burden: the option was foreclosed for Japan, China, or India. Heavier draft animals and better implements eventually cut the time that was spent in producing staple crops. For example, all fieldwork on a hectare of wheat required 180 hours in medieval England, 120 hours in early nineteenth-century Holland, and 60 hours on the U.S. Great Plains in 1900. But in any society where food production was energized solely by human and animal muscles, most of the labor force had to be employed in agriculture. The rates ranged from more than 90 percent in imperial China to more than 66 percent in the post–Civil War United States, and in all traditional agricultures children commonly helped adults.
Limits were also obvious in warfare because even trained muscles could impart relatively restrained destructive force to the tools of war, a reality made clear by comparing kinetic energies of common preindustrial weapons. The kinetic energy of a single stone ball shot from a medieval cannon equaled that of five hundred arrows discharged from heavy crossbows or one thousand thrusts delivered with heavy swords. Pre-gunpowder battles thus consisted of limited expenditures of muscular energy, a reality that explains frequent preference for either sieges or stealthy maneuvers. Wars became much more destructive only with the introduction of gunpowder—in China during the tenth century and in Europe at the beginning of the fourteenth century.
Speed of travel was another obvious constraint imposed by animate metabolism and by inefficient conversion of wind. Speedy running and horse riding were used only for urgent messaging, and impressive distances could be covered in a single day: the maximum on Roman roads was up to 380 kilometers. Speeds of normal travel, however, were restricted to 10–15 kilometers a day for men with wheelbarrows (a common means of transport in imperial China), not much more for wagons drawn by oxen, 30–40 kilometers for wagons pulled by heavy horses, and 50–70 kilometers for passenger horse carts on relatively good roads. The prohibitive costs of animate land transport are perfectly illustrated by prices noted in the Roman emperor Diocletian’s famous edictum de pretiis (price edict): in 301 CE moving grain just 120 kilometers by road cost more than shipping it from Egypt to Ostia, Rome’s harbor.
Energy Sources: Preindustrial Inanimate Prime Movers
Most preindustrial Old World societies eventually introduced simple mechanical devices to convert two indirect solar energy flows—flowing water and wind—to rotary power, and they also used sails to propel their ships. The evolution of sails shows slow progress from inefficient square sails of ancient Egypt and classical Mediterranean cultures to triangular sails of the Muslim world, batten sails of medieval China, and finally complex rigging (flying jibs, fore, main, mizzen, topgallant, and spanker sails) of large ships that early modern Europe sent on its global conquests during the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. Although seaborne transport was by far the cheapest alternative, it was both unpredictable and unreliable.
The best sailing ships—British and U.S. China clippers of the second half of the nineteenth century—could average more than 30 kilometers per hour for hours and came close to 20 kilometers per hour for entire intercontinental journeys, whereas the best Roman cargo vessels could not surpass 10 kilometers per hour. But all sailing ships had to resort to extensive tacking when sailing into the wind or could be becalmed by lack of winds. Consequently, grain ships sailing between Ostia and Egypt could take as little as a week or as long as three months or more, and two thousand years later homeward-bound English ships had to wait sometimes up to three months for the right wind to take them into Plymouth Sound.
The origins of waterwheels remain uncertain, but, notwithstanding such impressive examples as a cascade of Roman watermills in Barbegal in southern France, they were of limited importance in all classical societies where slave labor provided cheap energy for grain milling and manufacturing tasks. Waterwheels did become particularly important in some medieval societies where their power was used above all for food processing, wood sawing, and metallurgical processing. However, eight hundred years passed before the capacities of the largest wheels increased tenfold, and by the beginning of the eighteenth century, when they were the largest available prime movers, their European ratings averaged less than 4 kW, an equivalent of just five heavy horses. Windmills appeared only toward the end of the first millennium CE and, much as waterwheels, became eventually important in some Middle Eastern and Mediterranean countries and in parts of the coastal Atlantic Europe. Again, however, even the relatively advanced Dutch machines averaged less than 5 kW during the eighteenth century.
As a result, societies that derived their kinetic energy almost exclusively or overwhelmingly from animate power that was supplemented locally and regionally by small waterwheels and windmills could not guarantee either an adequate food supply or a modicum of material comforts for most of their inhabitants. Nutrition remained barely sufficient even after good harvests (yields remained static for centuries), famines were recurrent, small-scale artisanal manufactures (except for a limited luxury trade) were inefficient and limited to a narrow range of crude products, typical personal possessions were meager, illiteracy was the norm, and leisure and travel were uncommon.
Energy Sources: Fossil Fuels, Prime Movers, Electricity
All of those circumstances changed with the introduction of fossil fuels. Although people had used coal in parts of Europe and Asia in limited ways for centuries, the Western transition from biomass to coal took place (obviously with the exception of England) only during the nineteenth century (for example, in the United States wood supplied more than half of all primary energy until the early 1880s), and in the most populous Asian countries the transition was accomplished only during the second half of the twentieth century. The oldest fossil fuels (anthracites) go back 100 million years, the youngest ones (peats) go back just 1,000 years. Both solid fuels (different kinds of coal) and hydrocarbons (crude oils and natural gases) are found in often highly concentrated deposits from which they can be extracted with extraordinarily high-power densities: coal mines with multiple seams and rich oil and gas fields can produce between 1,000 and 10,000 W/m2, densities 10,000–100,000 higher than those for biomass fuels.
Moreover, fossil fuels, with the exception of marginal kinds such as low-quality lignites and peat, also have much higher energy densities: steam coal, now used largely for electricity generation, rates 22–26 MJ/kg, and crude oil and refined products rate 42–44 MJ/kg. Extraction and distribution of fossil fuels thus create energy systems that are the opposite of biomass-based societies: high-energy-density fuels are produced from a limited number of highly concentrated deposits and then distributed not just regionally or nationally but increasingly also globally. The distribution task is particularly easy with liquid hydrocarbons that are shipped by large tankers or sent through large-diameter pipelines. Not surprisingly, liquid fuels became the world’s leading energy sources during the latter half of the twentieth century.
Desirable qualities of fossil fuels were greatly augmented by two fundamental technical revolutions: the invention and rapid commercial adoption of new mechanical prime movers, and by the creation of an entirely new energy system that produced and distributed electricity. Chronologically, the new inanimate prime movers were steam engines, internal combustion engines, steam turbines, and gas turbines, and their evolution has brought increased overall capacities and higher conversion efficiencies. The English inventor Thomas Newcomen’s steam engines (after 1700) were extraordinarily wasteful, converting no more than 0.5 percent of energy in coal into reciprocating motion; the Scottish inventor James Watt’s radical redesign (separate condenser) raised the performance to 5 percent by 1800, and his machines averaged about 20 kW, equivalent to two dozen good horses. Before the end of the nineteenth century gradual improvements increased the power of the largest steam engines to the equivalent of four thousand horses and their efficiency to more than 10 percent.
These machines powered the main phase of nineteenth- century industrialization by mechanizing many industrial processes, expanding productive capacities, and putting the cost of an increasing range of basic consumer products within the reach of average families. Their impact was particularly critical in coal mining, the iron and steel industry, and machine construction. They also offered unprecedented power for both landborne and waterborne transportation. By 1900 railways offered scheduled services at speeds an order of magnitude faster than those of horse-drawn carriages, and large steamships cut the transatlantic crossing to less than six days, compared to the pre-1830s mean of nearly four weeks.
Their peak was short-lived however: during the last two decades of the nineteenth century small steam engines began to be replaced by internal combustion machines and the large ones by steam turbines. Internal combustion engines of the German engineer Nicolaus Otto’s motorcycle (commercialized as stationary machines after 1866 and as wheeled transport by the German engineers Gottlieb Daimler, Karl Benz, and Wilhelm Maybach starting in the 1880s) eventually reached efficiencies in excess of 20 percent. Inherently more efficient engines of the German engineer Rudolf Diesel (introduced after 1900) reached more than 30 percent. Inventions of the 1880s, the most innovation-packed decade in history, also laid lasting foundations for the development of the electric industry with the U.S. inventor Thomas Edison’s development of an entirely new energy system (a contribution more important than his tenacious work on incandescent light), the U.S. inventor Nikola Tesla’s electric motor, and the Irish engineer Charles Parsons’s steam turbine.
Electricity provided the superlative form of energy: clean at the point of use, convenient, flexible to use (as light, heat, motion), and amenable to precise control. The latter fact revolutionized industrial production as electric motors (eventually more than 90 percent efficient) replaced unwieldy and wasteful steam-driven shafts and belts. The last of the modern prime movers, the gas turbine, was introduced for aircraft jet propulsion during the 1930s, and later it also became a common choice for generation of electricity. All of these machines were much lighter per unit of installed power than were steam engines—and hence more compact and (with the exception of large steam turbogenerators) suitable for mobile applications.
On the destructive side the Swedish manufacturer Alfred Nobel’s invention of dynamite introduced an explosive whose detonation velocity was nearly four times that of gunpowder, and even more powerful compounds followed soon. By 1945 destructiveness was raised to an entirely new level by the development of nuclear-fission weapons, with fusion bombs following just a few years later. By the time the Cold War ended in 1990 with the demise of the USSR, the two superpowers had diverted significant shares of their total energy consumption to the assembly of an incredibly destructive arsenal that amounted to nearly twenty-five thousand strategic nuclear warheads whose aggregate capacity was equivalent to nearly half a million Hiroshima bombs.
Modern Energy Systems
Every component of fossil-fueled energy systems experienced impressive gains in capacity and efficiency, the combination that resulted in large increases in per capita consumption of energy. Although the world’s population nearly quadrupled between 1900 and 2000 (from 1.6 billion to 6.1 billion), the average annual per capita supply of commercial energy more than quadrupled, and higher efficiencies meant that in the year 2000 the world had at its disposal about twenty-five times more useful commercial energy than it did in 1900. As a result, today’s affluent economies have experienced eightfold to tenfold increases in the per capita supply of useful energy services (heat, light, motion), and the corresponding multiples have exceeded twenty-, or even thirtyfold, in such industrializing countries as China or Brazil: never before in history had an even remotely comparable gain translated into enormous improvements in the quality of life.
Gains in energy flows that are controlled directly, and casually, by individuals were equally stunning. In 1900 even a well-off U.S. farmer holding the reins of six large horses controlled sustained delivery of no more than 5 kW of animate power; a century later his great-grandson driving a large tractor controlled more than 250 kW from the air-conditioned comfort of his cabin. In 1900 a stoker on a transcontinental train traveling at 100 kilometers per hour worked hard to sustain about 1 megawatt (MW) of steam power; in 2000 a pilot of a Boeing 747 retracing the same route 11 kilometers above the Earth’s surface merely supervised computerized discharge of up to 60 MW at a cruising speed of 900 kilometers per hour.
In 2000, however, the benefits of those spectacular energy flows remained unevenly divided. When measured in metric tons of oil equivalent (toe), annual per capita energy consumption in the year 2000 ranged from about 8 in the United States and Canada to 4 in Germany and Japan, less than 3 in South Africa, 1 in Brazil, about 0.75 in China, and less than 0.25 in many countries of sub-Saharan Africa. Yet a closer look at the rewards of high energy consumption shows that all of the quality-of-life variables (life expectancy, food supply, personal income, literacy, political freedom) relate to average per capita energy use in a distinctly nonlinear manner: clear diminishing returns set in for all of these variables as the energy use increases beyond 1–2 toe/capita, and there are hardly any additional gains attached to levels above roughly 2.5 toe. This reality becomes obvious when one asks a simple question: have the lives of U.S. citizens of the last two generations been twice as good (twice as long, healthy, productive, literate, informed, or free) as those of people in western Europe or Japan?
What does a rich energy endowment do for a country? In the United States it has obviously contributed to the country’s emergence as an economic, military, and technical superpower—but it could not prevent the collapse of the USSR, which was in 1989 the world’s largest producer of fossil fuels. Other prominent examples of the failure to use rich energy resources to build modern, prosperous societies include such different societies as Iran, Nigeria, Sudan, and Indonesia: none of them secured vibrant economies and prosperous lives for its citizens. In contrast, three energy-poor countries of eastern Asia (Japan, South Korea, Taiwan) became the paragons of rapid economic growth and impressive improvements in average quality of life.
Finally, energy use cannot explain the rise and fall of major civilizations and powerful societies. Such notable consolidations and expansions as the rise of Egypt’s Old Kingdom, maturation of the Roman republic, unification of Han China (206 BCE–220 CE), the spread of Islam, the Mongolian conquests in Eurasia, and the enormous eastward extension of the Russian Empire cannot be linked to any new prime movers or to new, or more efficient, fuel uses. As for the declines, no drastic change of fuel base and delivery (wood, charcoal) or prime movers (slaves, oxen, horses, sailing ships, waterwheels) took place during the long decline of the western Roman Empire (the eastern part managed to survive with the identical infrastructure for another millennium), and none of the great breaks of the early modern and modern world—the French Revolution, the collapse of the czarist Russian Empire, the fall of Nationalist China, the collapse of the USSR— could be given convincing (or indeed any) energy explanations.
Energy resources and uses are, undeniably, among the critical variables whose specific and unpredictable combinations determine the fortunes of societies. They promote, restrict, or complicate many economic and individual options, and once in place they are critical for setting the tempo of life and the levels of general welfare. Immutable dictates of thermodynamics also mean that higher socioeconomic complexity requires higher energy flows. This undeniable relationship is not a matter of continuous linear progress, however, but rather one of a relatively early saturation. Moreover, possession of abundant energy sources or their high consumption cannot guarantee well-functioning economies, decent quality of life, personal happiness, or a nation’s security. Energy sources and uses constrain our actions but do not dictate our choices, do not assure economic success, and do not condemn civilizations to failure. In the modern world the only inescapable consequences of higher energy use are greater impacts on the Earth’s biosphere: the fate of modern civilization may be ultimately decided by our capacity to deal with this challenge.
Bibliography:
- Adams, R. N. (1982). Paradoxical harvest. Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press.
- Basalla, G. (1988). The evolution of technology. Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press.
- Chaisson, E. (2001). Cosmic Evolution: The Rise of Complexity in Nature. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Cleveland, C. (Ed.). (2004). Encyclopedia of energy. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
- Finniston, M., Williams, T., & Biseell, C. (Eds.). (1992). Oxford illustrated encyclopedia: Vol. 6. Invention and technology. Oxford, U.K.: Oxford University Press.
- Jones, H. M. (1970). The age of energy. New York: Viking.
- MacKay, D. J. C. (2009.) Sustainable energy—without the hot air. Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press.
- Smil, V. (1991). General energetics. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Smil, V. (1994). Energy in world history. Boulder, CO: Westview.
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essay Examples >
- Essays Topics >
- Essay on Wind
Renewable Energy Research Paper Examples
Type of paper: Research Paper
Topic: Wind , Environment , Solar Energy , Water , Energy , World , Renewable Energy , Products
Words: 1500
Published: 01/22/2020
ORDER PAPER LIKE THIS
Introduction
Renewable energy is a kind of energy whose origin is a resource that can be recycled or replenished. Examples of renewable energy include; rain, wind, geothermal heat, waves and tides.With the increasing technological progress, many companies, households and even governments are embracing renewable energy. Currently, 16 per cent of the energy used across the world renewable. The share of renewable energy is rising rapidly. For instance, energy derived from wind power is increasing at an annual rate of 20 per cent. Renewable energy is not only cheap but also environmentally friendly. This is why many organizations and governments are resorting to clean energy. However, renewable energy is also being exploited because of the exhaustion of other energy sources that are not renewable. For example, the use of wood as fuel in households has contributed to the decline of forests all over the world. Crude oil consumption has also exceeded the supply hence; forcing people to resort to renewable energy. Renewable energy is increasingly becoming a global trend. Energy is a necessity if human beings are to lead a quality life socially and economically. This paper discusses why renewable sources of energy are increasing becoming popular, the uses of renewable sources of energy, and various examples of renewable sources of energy.
Preference for renewable energy
Over the last decade, the use of renewable energy has increased significantly. The sudden increase in the number of renewable energy users can be attributed to several factors.Because of political instability in northern African countries and in most Middle East nations, the oil prices have shot up in the last few years. This has discouraged people from using oil and has resorted to cheap energy sources such as the sun, wind, water and other renewable energy resources. Another reason why people resorted to renewable energy is climate changes. The exploitation of conventional energy sources such as forests has led to climate changes. Climate change comes with many detrimental impacts on human beings and the environment. Governments and environmental organizations are also responsible for the increasing use of renewable energy. Many governments all over the globe and international environmental organizations are encouraging citizens to use renewable energy because of its benefits to man and the environment. For instance, the Kyoto Protocol which was designed by the United Nations seeks to encourage the use of renewable energy sources that are eco-friendly. Some governments have made policies to ensure that renewable energy is exploited by as many people as possible.
Uses of renewable energy
Renewable energy can be used in the same manner conventional energy is used. Therefore, it can be used in place of conventional energy in four main categories; heating, power generation and transport fuels. The development of solar panels has revolutionized heating. Households and firms can now install water solar heaters in their buildings. Currently about 70 million people harness solar energy for heating purposes. Renewable energy can also be converted to electricity. To generate power, renewable power generators are used to harness wind power, solar energy, geothermal heat and water. Renewable energy also comes in the form of transport fuels. Biofuels are responsible for the massive reduction in oil consumption in most developed countries. For instance, Brazil and USA have successfully managed to develop biofuels such as ethanol fuel from corn and sugar cane. These fuels are used in motor vehicles and in industrial machinery. United Nations records indicate that in 2009, 93 billion liters of biofuels were produced. The biofuel replaces 68 billion liters of gasoline.
Wind is one of the most common sources of renewable energy. Wind is a natural resource that can be easily harnessed into different forms of energy. From harnessing wind power, one can get electricity. Usually, windmills are set up in an open area where strong winds blow often such as off shores or high altitude locations. The windmills have wind turbines, which are turned by airflows. Countries such as Iran have set up large scale windmill energy production plants for commercial use. The advantage of harnessing wind energy is that it produces clean energy at a significantly cheap cost. The potential of wind generated energy is reported to be five times the amount of energy consumes today. However, this would require that windmills are set up over a very large area to tap maximum wind power.
Geothermal energy
This is another form of renewable energy that has not yet been fully exploited. This is a form of energy obtained from the thermal resources from beneath the earth’s surface. Some sites on the earth’s surface have hot springs where very hot water comes from beneath the earth at very high pressure. The hot springs may be in the form of steam or just hot water. Springs come about as a result of endogenic activities of the earth. The heat generated from the geothermal springs is used to turn turbines that generate electricity. The amount of electricity generated is usually high depending on the amount of pressure steam or water comes from beneath the earth’s surface.
Solar energy
Solar energy is one of the most common forms of renewable energy. It is derived from the sun through devices called solar panels. The solar panels are able to convert solar radiations into electric power. Other devices that can be used to harness solar energy include photovoltaic, day lighting, solar architecture, solar cooking and water heating. The mode of harnessing solar energy could be active or passive basing on the manner the sun rays are captured, changed and distributed as solar energy. Active techniques include the solar thermal collectors and photovoltaic panels. Passive techniques are those that do not involve direct harnessing of solar energy.
These are organic products derived from affordable products and bi-products such as corn, sugar cane and cane wastes. The products from which bio fuels are obtained are called biomass. Bio fuels can be in liquid, solid or gas form. Examples of bio fuels include bio ethanol, bio diesel, bio gas, synthetic gas and landfill gas. In most cases, bio fuels are obtained by fermenting organic products such as plant materials such as sugarcane to obtain bio ethanol. Advanced technology is used to when converting biomass such as grass and trees to produce bio ethanol. This form of renewable energy has been successful implemented in Brazil and USA. This has helped save the government and households vast sums of money on conventional fuel, which is usually more expensive that biofuels. However, it has been discovered that biofuels still contribute to environmental problems such as global warming. 3 per cent of the fuel used for transport in the world is in the form of bio fuels.
These are plant material used as a source of renewable energy since plants contain energy derived from the sun. Through photosynthesis, plants convert the sun’s energy and store it. When burnt, the energy contained in the plant is released. Therefore, plants can be used as a natural storage of solar energy. Therefore, a sustainable production of biomass can be beneficial in production of renewable energy. Plants that are cut for energy use should be replaced immediately they are cut. However, with the increasing world population, the use of biomass as a source of renewable energy is risky. This is because forest cover has reduced as people settle in what used to be forests.
The only way to ensure that energy sources are efficiently exploited and conserved equally is to ensure that the public understand the concept of renewable energy. Renewable energy is the best and probably the only alternative source of energy to conventional energy sources. Industrialization and the world’s expanding population mean that conventional sources are becoming scarce, expensive, and there is also the environmental problems resulting from these forms of energy. Therefore, households, firms and governments should embrace the concept of renewable energy. Solar energy, wind power, hydroelectricity, geothermal power and biofuels are some of the renewable energy sources that should be exploited. However, with the increasing world population, the use of biomass as a source of renewable energy is risky. Some of these sources such as wind have so much potential that they can produce surplus energy if fully exploited. To attain economic viability, environmental conservation and social progress, the world must embrace renewable energy for prosperity today and in future.
Works Cited
Boyle, Godfrey. Renewable Energy: Power for a Sustainable Future. 3, illustrated. New York: OUP Oxford, 2012. Johansson, Thomas B. Renewable Energy: Sources for Fuels and Electricity. 2 revised. New York: Island Press, 1993. Twidell, John and Tony Weir. Renewable Energy Resources ED2. 2, illustrated, revised. New York: Taylor & Francis, 2012. Wengenmayr, Roland and Thomas B?hrke. Renewable Energy: Sustainable Energy Concepts for the Future. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2011.

Cite this page
Share with friends using:
Removal Request

Finished papers: 2270
This paper is created by writer with
ID 270930807
If you want your paper to be:
Well-researched, fact-checked, and accurate
Original, fresh, based on current data
Eloquently written and immaculately formatted
275 words = 1 page double-spaced

Get your papers done by pros!
Other Pages
Christians thesis proposals, prison thesis proposals, religion thesis proposals, wellness thesis proposals, wireless technology thesis proposals, police thesis proposals, kinship thesis proposals, olympics thesis proposals, engrossed college essays, north haven essays, simon wiesenthal essays, fajardo essays, handwash essays, ing group essays, warsaw ghetto essays, panamax essays, target behavior essays, the university of idaho essays, a review of evidence based therapeutic interventions for bipolar disorder term paper example, example of the devastating consequences of the black death can be examined from several horizons research paper, free statistics for managers case study example, free research paper about the need for customization platforms 3, good research paper on how can californias workers compensation policies be changed to reduce fraud, good social marketing and childhood obesity essay example, good book review about graham greenes the confidential agent 1939, good example of research paper on hantavirus, a leadership case study, free essay on education in nursing, essay on employee relations, social ethical and economics prospective of solar energy essay example, free childhood obesity literature review sample, example of the english patient essay, good example of essay on functional silos, good movie review about theatre studies, good example of operant conditioning application course work, the rejection of the gospel course work examples, co occuring disorders course work examples, essay on social media and google examples of hegemony, example of essay on minimum wage, in a letter to president william mckinley explain whether you support or oppose essays examples, example of course work on umuc hair cuts case study, aligning curriculum essay example, free research paper on cultures and websites.
Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline
96 Wind Energy Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best wind energy topic ideas & essay examples, 📌 most interesting wind energy topics to write about, 👍 good research topics about wind energy, ❓ wind energy research questions.
- Wind Power: Process, Advantages and Disadvantages Wind power involves the use of turbines, the modern equivalent of windmills, to convert wind energy into a more useful form of energy.
- Wind Energy as Forms of Sustainable Energy Sources T he only costs to be met in producing wind energy is the cost of equipment for harnessing wind, wind turbines for converting the energy and photovoltaic panels for storing energy. We will write a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts 808 writers online Learn More
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Wind Energy Another advantage is the fact that most of the turbines that are used in the generation of wind power are located in ranches, and on farms.
- Wind Power as an Alternative Energy Source Wind energy is a renewable source of energy that is an alternative to fossil fuel use, which is necessary for the conservation of the environment.
- Technology and Wind Energy Efforts by the elite members of the society enlightened the global countries about the benefits of renewable energy sources in conserving the environment prompting the need to consider wind energy.
- Investing in an Offshore Wind Power Plant in Greece The purpose of the research is to minimize the risk by collecting information and examining the attractiveness of this investment opportunity.
- Possibility of Investing in an Offshore Wind Power Plant in Greece Greece is one of the countries in the world that enjoys a substantial amount of wind resources, especially in the Aegean Sea Islands and on the mountain ridges on the mainland.
- Electrical Engineering Building Uses Wind Energy The purpose of this fact-finding mission was to determine an appropriate type and rating of the wind turbine based on three factors: the average wind data at UNSW; the peak power demand for the EE […]
- Solar and Wind Energy in the Empty Quarter Desert However, the main bulk of the report focuses on the proposal to build a stand alone renewable energy source, a combination of a solar power wind turbine system that will provide a stable energy source […]
- Wind Energy for the Citizens of Shikalabuna, Sri Lanka The citizens of Shikalabuna are shot of the possibility to implement the required wind turbines and get a chance to pay less using the natural source available.
- Wind Power in West Texas and Its Effects The main cause of introducing and developing wind power in West Texas is the need to generate more electricity with fewer costs and environmental friendliness.
- “Wind Power Fills Our Sails” Poster Visual Argument As a result, the audience is expected to think about the effectiveness of using wind power to develop the future with a lot of green energy and jobs.
- Saudi Arabian Wind Power Plants: Status and Future In the globalized society, the issue of climate change prompts stakeholders to take part in the establishment and implementation of strategies that enhance the sustainability of the environment.
- Wind Energy Feasibility in Russia In Russia, feasibility studies have been conducted to establish the viability of wind turbine projects. In conjunction with the problem statement above, the following aims have been formulated: To use the available and relevant data […]
- Wind Power Exploitation to Generate Electricity The most basic way that a wind turbine works is by using the kinetic energy of the wind and turning it into electricity that can be used by humans.
- Is wind power “green”? The aim of this paper is to determine whether wind turbine is a feasible power source option in terms of “green”, economic friendliness, and its aptitude to produce considerable quantity of power.”Green” power, as any […]
- Is wind power considered green? This paper aims to analyze whether wind energy is green and the impacts of contemporary issues of environment to the sustainable world.
- Abu Dhabi Wind Energy The report covers energy crisis in Abu Dhabi, wind energy as a potential source of renewable energy for Abu Dhabi, and recommendations.
- Wind Energy for Environmental Sustainability Production of this energy is important to the survival and enhancement of lives of people in a society. It refers to the role of that business or a corporate towards the society.
- Wind Energy, Its Advantages and Disadvantages Reliable sources of energy need to be renewable; they include wind energy, solar energy and hydro-energy; wind energy is a dependable source of energy although it remains the least used among the available renewable sources […]
- Wind Energy: The Use of Wind Turbines One of the most promising is wind energy, specifically the use of wind turbines to produce clean and renewable energy. The only problem is that it is more expensive to build large wind turbines.
- Water Pollution and Wind Energy Chemical pollution of water is one of the leading causes of death of aquatic life. It is thus evident that chemical pollution of water not only has negative effects on health, but it also substantially […]
- Wind Energy Saves The World
- Impact Of Science And Technology On Society Wind Energy
- Improvement of Wind Energy Production through HVDC Systems
- Investigation of Wind Energy Potential Evaluation in Kerman, Iran
- The Use of Wind Energy, Wind Turbines and Wind Spins in Making Electricity
- The Wind Energy Improves The Energy Security
- The Market Developments of Wind Energy – Accessibility, Availability and Acceptability
- The German Wind Energy Lobby: How to Successfully Promote Costly Technological Change
- The European and Romanian Wind Energy Investments Dynamics Analysis
- Optimal Control of a Dispatchable Energy Source for Wind Energy Management
- Renewable Forms of Energy: Wind Energy
- The Effect Of Wind Energy On Fossil Fuels
- The Galician Wind Energy Policy. An Analysis Of Its Development
- The Potential Benefits of Using Wind Energy
- Renewable Energy As Solar And Wind Energy
- The On Wind Energy And Its Effect On Our Society
- Pros And Cons Of Wind Energy
- How Sustainable Is A Wind Energy System Environmental Sciences
- The Repercussions of Using Wind Energy
- Navigating Contested Winds: Development Visions and Anti-Politics of Wind Energy in Northern Kenya
- The Job-Creating Potential of Wind Energy and How Global Warming Affects
- Small Wind Energy Alternative Energy Solutions
- Should the Use of Wind Energy Be Encouraged
- Renewable Energy Project Wind Energy
- Human Development and the Importance of Wind Energy Conversion
- Joint Planning of Energy Storage and Transmission for Wind Energy Generation
- Wind Energy And Hydroelectric Energy Environmental Sciences
- Wind Energy Contribution to a Low-Carbon Grid
- The Pros And Cons Of Wind Energy
- The Resilience of Clusters in the Context of Increasing Globalization: The Basque Wind Energy Value Chain
- The Effects Of Wind Energy On Fossil Fuels
- The Wind Energy Industry in North America
- Optimization Model for Economic Evaluation of Wind Farms – How to Optimize a Wind Energy Project Economically and Technically
- The Past, Present, And Future Of Wind Energy
- The Wind Energy Is The Fastest Growing Power Source
- Synchronous Generator Based Wind Energy Conversion System Engineering
- Learning to Grow A Comparative Analysis of the Wind Energy Sector in Denmark and India
- Wind Energy Is A Viable Option For Urban Areas
- Solar and Wind Energy to Ashton Island
- Wind Energy The Positive Effects On The United States
- Wind Energy Facilities and Residential Properties: The Effect of Proximity and View on Sales Prices
- Wind Energy As A Replacement For Fossil Fuels
- Switching to Wind Energy Supports the Common Good for Mankind
- The Wind Energy Industry: R&D Funding and International Technological Diffusion
- What Are Some Innovations in Wind Energy?
- What Are the Down Sides to Wind Energy?
- How Far Can Wind Energy Be Piped?
- What Is the Future Use of Wind Energy?
- Which Is More Scalable, Nuclear Energy or Wind Energy?
- Is Wind Energy Expensive?
- What Future Does Wind Energy Have in India?
- Why Do People Say Wind Energy Doesn’t Work?
- Where Is Wind Energy Used the Most?
- Could Wind Energy Provide All the World’s Energy Needs?
- Which Country Is the Leader in Wind Energy?
- Is All of the Earth’s Wind Energy Generated by Solar Radiation?
- Why Is Wind Energy the Energy of the Future?
- Can I Use Wind Energy in Car?
- What Is the Contribution of Wind Energy in Combatting Climate Change?
- Is Wind Energy Competitive Without Subsidies?
- the Hottest Wind Energy Startups in the US?
- How Can One Start a Solar or Wind Energy Startup?
- What Are the Some Good Books on Wind Energy Engineering?
- Why India Has Developed More Wind Energy Than Solar Energy?
- Is Wind Energy Practical? Should the US Spend More Money on Wind Energy?
- How Is Wind Energy Exported?
- Is Wind Energy What It Was Forecasted to Be?
- Can Wind Energy Be Efficient in Nigeria?
- Can Wind Energy Replace Fossil Fuels?
- Are Solar and Wind Energy Replacing Nuclear Energy?
- Could Wind Energy Become the Main Energy Source for the Planet?
- Which Are the Best Universities or Institutes for Wind Energy Research?
- How Could Wind Energy Power the Earth?
- Why Is Japan So Reluctant to Invest in Wind Energy?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, October 26). 96 Wind Energy Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/wind-energy-essay-topics/
"96 Wind Energy Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 26 Oct. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/wind-energy-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2023) '96 Wind Energy Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 26 October.
IvyPanda . 2023. "96 Wind Energy Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." October 26, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/wind-energy-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "96 Wind Energy Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." October 26, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/wind-energy-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "96 Wind Energy Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." October 26, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/wind-energy-essay-topics/.
- Alternative Energy Paper Topics
- Energy Essay Ideas
- Nuclear Energy Essay Titles
- Solar Energy Essay Ideas
- Government Regulation Titles
- Biodiversity Research Topics
- Aerospace Research Topics
- Ecosystem Essay Topics
- Climate Change Titles
- Electronics Engineering Paper Topics
- Global Warming Essay Titles
- Environmental Protection Titles
- Green Building Questions
- Nuclear Power Questions
- Renewable Energy Essay Titles

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The aim of the paper is to ascertain if renewable energy sources are sustainable and examine how a shift from fossil fuel-based energy sources to renewable energy sources would help reduce climate change and its impact. A qualitative research was employed by reviewing peer-reviewed papers in the area of study.
This review paper focuses on the connection between academic solar energy research and its practical real-world implications. It examines the current state of solar power and related academic solar energy research in different countries, aiming to provide valuable guidance for researchers, designers, and policymakers interested in incorporating ...
The use of renewable energy resources, such as solar, wind, and biomass will not diminish their availability. Sunlight being a constant source of energy is used to meet the ever-increasing energy need. This review discusses the world's energy needs, renewable energy technologies for domestic use, and highlights public opinions on renewable energy. A systematic review of the literature was ...
This paper aims to assess the situation of the energy system throughout the European Union member states (EU28), with a focus set on renewable energy and energy efficiency programs.
fuel and two-third of the global energy demand is fulfilled by renewable energy sources. According to a report by Bloomberg New Energy Finance, b y 2050 about 50% of the. global energy demand is ...
Intermediate research papers like the documents published between 2016 and 2019 are more cited and favorable among authors than the newer articles. ... (energy usage per unit of GDP), for example, smart cities, digital technologies, and more circular production systems" (Díaz-López et al., 2019; Dincer and Acar, 2018). However, advancement ...
Energy is a linchpin for most of the SDGs, and research that merges climate, energy and the SDGs underscores this 1. For example, the agriculture and food-transport sectors still depend on fossil ...
Impact of global heterogeneity of renewable energy supply on heavy industrial production and green value chains. A new study of low-carbon value chains of basic materials (steel and chemicals ...
The major sources of renewable. energy include solar, wind, biomass, geothermal, hydropower. and tidal energy. Non renewable energy, such as coal, natural. gas and oil, require costly explorations ...
About International Journal of Energy Research. The International Journal of Energy Research is dedicated to providing a multidisciplinary platform for the discussion of issues arising in energy research without the constraints imposed by aiming at a restricted audience. It aims to reach all researchers, scientists, engineers, technology ...
A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications. Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the ...
Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.) by APA. Call Number: BF76.7 .P83 2020. Publication Date: 2020. Parts of the APA Manual are reproduced for free on APA's Style Blog. Scroll down to the "Popular Style Guidelines" section for basic APA 7th edition guidance and sample "student" and "professional" papers.
The purpose of this paper is to determine the impact of solar energy on the environment. The major positive impact is the minimal emission of greenhouse gases. Renewable Energy Sources: Popularity and Benefits. Renewable fuels are not as pollutive as fossil fuels; they can be reproduced quickly from domestic resources.
The results of the one-sample t-test revealed that the respondents positively opined that renewable energy initiatives by corporations influence sustainable development. ... Within the context of a research paper, ... G., Alex, J., Zhang, T., & Ma, C. (2020). Research progress of energy utilization of agricultural waste in China: Bibliometric ...
The Benefits of Renewable and Non-Renewable Energy. This research paper seeks to describe renewable and non renewable energy sources, their effects on the environment and economic benefits."Fossils fuels are one of the most widely used sources of energy". Renewable Energy Sources: Existence, Impacts and Trends.
246 Energy Topics & Essay Examples. These energy topics explore the dynamic realm of energy sources, consumption, and sustainability. Here, you can find an excellent topic for your essay or project. As you go through these energy research questions, you will uncover the intricacies of energy demands, environmental concerns, and the quest for ...
1 hour! Figure 1 demonstrates that only wind and solar energy can provide adequate power to meet global energy demands. For example, wind in developable regions can satisfy global energy demands up to about 4 times over while areas with solar energy potential can meet global demands by over 18 times over (Jacobson & Delucchi, 2011, p.1159).
67. JRTE-2020. Solar Energy Technology. Sumedha R.G. Weliwaththage, Udara S.P.R. Arach chige. Faculty of Technology, University of Sri Jayewardenepura, Sri Lanka. Abstract Energy resources can ...
Sample Energy Economics Research Paper. Browse other research paper examples and check the list of research paper topics for more inspiration. If you need a research paper written according to all the academic standards, you can always turn to our experienced writers for help. This is how your paper can get an A!
461 Energy Essay Topics to Write about & Examples. Welcome to our ultimate list of topics related to energy! Here, you will find solar energy essay topics, interesting titles for energy projects, writing ideas about environmentally friendly and renewable energy sources, research titles on trending issues, and more.
7. In contrast to nonrenewable, renewable energy sources produce little or no pollution or hazardous wastes, pose few risks to public safety, and are entirely domestic resources. Explain why you agree or disagree with this statement. 8. Energy sources are used mainly to produce electricity--a more useful energy source. Choose any energy
View sample energy research paper. Browse other research paper examples and check the list of history research paper topics for more inspiration. If you need a history research paper written according to all the academic standards, you can always turn to our experienced writers for help. This is how your paper can get an A!
Renewable energy is a kind of energy whose origin is a resource that can be recycled or replenished. Examples of renewable energy include; rain, wind, geothermal heat, waves and tides.With the increasing technological progress, many companies, households and even governments are embracing renewable energy. Currently, 16 per cent of the energy ...
Wind Power as an Alternative Energy Source. Wind energy is a renewable source of energy that is an alternative to fossil fuel use, which is necessary for the conservation of the environment. We will write. a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts. 809 writers online.