Exploring the Problem Solving Cycle in Computer Science – Strategies, Techniques, and Tools
- Post author By bicycle-u
- Post date 08.12.2023
The world of computer science is built on the foundation of problem solving. Whether it’s finding a solution to a complex algorithm or analyzing data to make informed decisions, the problem solving cycle is at the core of every computer science endeavor.
At its essence, problem solving in computer science involves breaking down a complex problem into smaller, more manageable parts. This allows for a systematic approach to finding a solution by analyzing each part individually. The process typically starts with gathering and understanding the data or information related to the problem at hand.
Once the data is collected, computer scientists use various techniques and algorithms to analyze and explore possible solutions. This involves evaluating different approaches and considering factors such as efficiency, accuracy, and scalability. During this analysis phase, it is crucial to think critically and creatively to come up with innovative solutions.
After a thorough analysis, the next step in the problem solving cycle is designing and implementing a solution. This involves creating a detailed plan of action, selecting the appropriate tools and technologies, and writing the necessary code to bring the solution to life. Attention to detail and precision are key in this stage to ensure that the solution functions as intended.
The final step in the problem solving cycle is evaluating the solution and its effectiveness. This includes testing the solution against different scenarios and data sets to ensure its reliability and performance. If any issues or limitations are discovered, adjustments and optimizations are made to improve the solution.
In conclusion, the problem solving cycle is a fundamental process in computer science, involving analysis, data exploration, algorithm development, solution implementation, and evaluation. It is through this cycle that computer scientists are able to tackle complex problems and create innovative solutions that drive progress in the field of computer science.

Understanding the Importance
In computer science, problem solving is a crucial skill that is at the core of the problem solving cycle. The problem solving cycle is a systematic approach to analyzing and solving problems, involving various stages such as problem identification, analysis, algorithm design, implementation, and evaluation. Understanding the importance of this cycle is essential for any computer scientist or programmer.
Data Analysis and Algorithm Design
The first step in the problem solving cycle is problem identification, which involves recognizing and defining the issue at hand. Once the problem is identified, the next crucial step is data analysis. This involves gathering and examining relevant data to gain insights and understand the problem better. Data analysis helps in identifying patterns, trends, and potential solutions.
After data analysis, the next step is algorithm design. An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure or set of rules to solve a problem. Designing an efficient algorithm is crucial as it determines the effectiveness and efficiency of the solution. A well-designed algorithm takes into consideration the constraints, resources, and desired outcomes while implementing the solution.
Implementation and Evaluation
Once the algorithm is designed, the next step in the problem solving cycle is implementation. This involves translating the algorithm into a computer program using a programming language. The implementation phase requires coding skills and expertise in a specific programming language.
After implementation, the solution needs to be evaluated to ensure that it solves the problem effectively. Evaluation involves testing the program and verifying its correctness and efficiency. This step is critical to identify any errors or issues and to make necessary improvements or adjustments.
In conclusion, understanding the importance of the problem solving cycle in computer science is essential for any computer scientist or programmer. It provides a systematic and structured approach to analyze and solve problems, ensuring efficient and effective solutions. By following the problem solving cycle, computer scientists can develop robust algorithms, implement them in efficient programs, and evaluate their solutions to ensure their correctness and efficiency.
Identifying the Problem
In the problem solving cycle in computer science, the first step is to identify the problem that needs to be solved. This step is crucial because without a clear understanding of the problem, it is impossible to find a solution.
Identification of the problem involves a thorough analysis of the given data and understanding the goals of the task at hand. It requires careful examination of the problem statement and any constraints or limitations that may affect the solution.
During the identification phase, the problem is broken down into smaller, more manageable parts. This can involve breaking the problem down into sub-problems or identifying the different aspects or components that need to be addressed.
Identifying the problem also involves considering the resources and tools available for solving it. This may include considering the specific tools and programming languages that are best suited for the problem at hand.
By properly identifying the problem, computer scientists can ensure that they are focused on the right goals and are better equipped to find an effective and efficient solution. It sets the stage for the rest of the problem solving cycle, including the analysis, design, implementation, and evaluation phases.
Gathering the Necessary Data
Before finding a solution to a computer science problem, it is essential to gather the necessary data. Whether it’s writing a program or developing an algorithm, data serves as the backbone of any solution. Without proper data collection and analysis, the problem-solving process can become inefficient and ineffective.
The Importance of Data
In computer science, data is crucial for a variety of reasons. First and foremost, it provides the information needed to understand and define the problem at hand. By analyzing the available data, developers and programmers can gain insights into the nature of the problem and determine the most efficient approach for solving it.
Additionally, data allows for the evaluation of potential solutions. By collecting and organizing relevant data, it becomes possible to compare different algorithms or strategies and select the most suitable one. Data also helps in tracking progress and measuring the effectiveness of the chosen solution.
Data Gathering Process
The process of gathering data involves several steps. Firstly, it is necessary to identify the type of data needed for the particular problem. This may include numerical values, textual information, or other types of data. It is important to determine the sources of data and assess their reliability.
Once the required data has been identified, it needs to be collected. This can be done through various methods, such as surveys, experiments, observations, or by accessing existing data sets. The collected data should be properly organized, ensuring its accuracy and validity.
Data cleaning and preprocessing are vital steps in the data gathering process. This involves removing any irrelevant or erroneous data and transforming it into a suitable format for analysis. Properly cleaned and preprocessed data will help in generating reliable and meaningful insights.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
After gathering and preprocessing the data, the next step is data analysis and interpretation. This involves applying various statistical and analytical methods to uncover patterns, trends, and relationships within the data. By analyzing the data, programmers can gain valuable insights that can inform the development of an effective solution.
During the data analysis process, it is crucial to remain objective and unbiased. The analysis should be based on sound reasoning and logical thinking. It is also important to communicate the findings effectively, using visualizations or summaries to convey the information to stakeholders or fellow developers.
In conclusion, gathering the necessary data is a fundamental step in solving computer science problems. It provides the foundation for understanding the problem, evaluating potential solutions, and tracking progress. By following a systematic and rigorous approach to data gathering and analysis, developers can ensure that their solutions are efficient, effective, and well-informed.
Analyzing the Data
Once you have collected the necessary data, the next step in the problem-solving cycle is to analyze it. Data analysis is a crucial component of computer science, as it helps us understand the problem at hand and develop effective solutions.
To analyze the data, you need to break it down into manageable pieces and examine each piece closely. This process involves identifying patterns, trends, and outliers that may be present in the data. By doing so, you can gain insights into the problem and make informed decisions about the best course of action.
There are several techniques and tools available for data analysis in computer science. Some common methods include statistical analysis, data visualization, and machine learning algorithms. Each approach has its own strengths and limitations, so it’s essential to choose the most appropriate method for the problem you are solving.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis involves using mathematical models and techniques to analyze data. It helps in identifying correlations, distributions, and other statistical properties of the data. By applying statistical tests, you can determine the significance and validity of your findings.
Data Visualization
Data visualization is the process of presenting data in a visual format, such as charts, graphs, or maps. It allows for a better understanding of complex data sets and facilitates the communication of findings. Through data visualization, patterns and trends can become more apparent, making it easier to derive meaningful insights.
Machine Learning Algorithms
Machine learning algorithms are powerful tools for analyzing large and complex data sets. These algorithms can automatically detect patterns and relationships in the data, leading to the development of predictive models and solutions. By training the algorithm on a labeled dataset, it can learn from the data and make accurate predictions or classifications.
In conclusion, analyzing the data is a critical step in the problem-solving cycle in computer science. It helps us gain a deeper understanding of the problem and develop effective solutions. Whether through statistical analysis, data visualization, or machine learning algorithms, data analysis plays a vital role in transforming raw data into actionable insights.
Exploring Possible Solutions
Once you have gathered data and completed the analysis, the next step in the problem-solving cycle is to explore possible solutions. This is where the true power of computer science comes into play. With the use of algorithms and the application of scientific principles, computer scientists can develop innovative solutions to complex problems.
During this stage, it is important to consider a variety of potential solutions. This involves brainstorming different ideas and considering their feasibility and potential effectiveness. It may be helpful to consult with colleagues or experts in the field to gather additional insights and perspectives.
Developing an Algorithm
One key aspect of exploring possible solutions is the development of an algorithm. An algorithm is a step-by-step set of instructions that outlines a specific process or procedure. In the context of problem solving in computer science, an algorithm provides a clear roadmap for implementing a solution.
The development of an algorithm requires careful thought and consideration. It is important to break down the problem into smaller, manageable steps and clearly define the inputs and outputs of each step. This allows for the creation of a logical and efficient solution.
Evaluating the Solutions
Once you have developed potential solutions and corresponding algorithms, the next step is to evaluate them. This involves analyzing each solution to determine its strengths, weaknesses, and potential impact. Consider factors such as efficiency, scalability, and resource requirements.
It may be helpful to conduct experiments or simulations to further assess the effectiveness of each solution. This can provide valuable insights and data to support the decision-making process.
Ultimately, the goal of exploring possible solutions is to find the most effective and efficient solution to the problem at hand. By leveraging the power of data, analysis, algorithms, and scientific principles, computer scientists can develop innovative solutions that drive progress and solve complex problems in the world of technology.
Evaluating the Options
Once you have identified potential solutions and algorithms for a problem, the next step in the problem-solving cycle in computer science is to evaluate the options. This evaluation process involves analyzing the potential solutions and algorithms based on various criteria to determine the best course of action.
Consider the Problem
Before evaluating the options, it is important to take a step back and consider the problem at hand. Understand the requirements, constraints, and desired outcomes of the problem. This analysis will help guide the evaluation process.
Analyze the Options
Next, it is crucial to analyze each solution or algorithm option individually. Look at factors such as efficiency, accuracy, ease of implementation, and scalability. Consider whether the solution or algorithm meets the specific requirements of the problem, and if it can be applied to related problems in the future.
Additionally, evaluate the potential risks and drawbacks associated with each option. Consider factors such as cost, time, and resources required for implementation. Assess any potential limitations or trade-offs that may impact the overall effectiveness of the solution or algorithm.
Select the Best Option
Based on the analysis, select the best option that aligns with the specific problem-solving goals. This may involve prioritizing certain criteria or making compromises based on the limitations identified during the evaluation process.
Remember that the best option may not always be the most technically complex or advanced solution. Consider the practicality and feasibility of implementation, as well as the potential impact on the overall system or project.
In conclusion, evaluating the options is a critical step in the problem-solving cycle in computer science. By carefully analyzing the potential solutions and algorithms, considering the problem requirements, and considering the limitations and trade-offs, you can select the best option to solve the problem at hand.
Making a Decision
Decision-making is a critical component in the problem-solving process in computer science. Once you have analyzed the problem, identified the relevant data, and generated a potential solution, it is important to evaluate your options and choose the best course of action.
Consider All Factors
When making a decision, it is important to consider all relevant factors. This includes evaluating the potential benefits and drawbacks of each option, as well as understanding any constraints or limitations that may impact your choice.
In computer science, this may involve analyzing the efficiency of different algorithms or considering the scalability of a proposed solution. It is important to take into account both the short-term and long-term impacts of your decision.
Weigh the Options
Once you have considered all the factors, it is important to weigh the options and determine the best approach. This may involve assigning weights or priorities to different factors based on their importance.
Using techniques such as decision matrices or cost-benefit analysis can help you systematically compare and evaluate different options. By quantifying and assessing the potential risks and rewards, you can make a more informed decision.
Remember: Decision-making in computer science is not purely subjective or based on personal preference. It is crucial to use analytical and logical thinking to select the most optimal solution.
In conclusion, making a decision is a crucial step in the problem-solving process in computer science. By considering all relevant factors and weighing the options using logical analysis, you can choose the best possible solution to a given problem.
Implementing the Solution
Once the problem has been analyzed and a solution has been proposed, the next step in the problem-solving cycle in computer science is implementing the solution. This involves turning the proposed solution into an actual computer program or algorithm that can solve the problem.
In order to implement the solution, computer science professionals need to have a strong understanding of various programming languages and data structures. They need to be able to write code that can manipulate and process data in order to solve the problem at hand.
During the implementation phase, the proposed solution is translated into a series of steps or instructions that a computer can understand and execute. This involves breaking down the problem into smaller sub-problems and designing algorithms to solve each sub-problem.
Computer scientists also need to consider the efficiency of their solution during the implementation phase. They need to ensure that the algorithm they design is able to handle large amounts of data and solve the problem in a reasonable amount of time. This often requires optimization techniques and careful consideration of the data structures used.
Once the code has been written and the algorithm has been implemented, it is important to test and debug the solution. This involves running test cases and checking the output to ensure that the program is working correctly. If any errors or bugs are found, they need to be fixed before the solution can be considered complete.
In conclusion, implementing the solution is a crucial step in the problem-solving cycle in computer science. It requires strong programming skills and a deep understanding of algorithms and data structures. By carefully designing and implementing the solution, computer scientists can solve problems efficiently and effectively.
Testing and Debugging
In computer science, testing and debugging are critical steps in the problem-solving cycle. Testing helps ensure that a program or algorithm is functioning correctly, while debugging analyzes and resolves any issues or bugs that may arise.
Testing involves running a program with specific input data to evaluate its output. This process helps verify that the program produces the expected results and handles different scenarios correctly. It is important to test both the normal and edge cases to ensure the program’s reliability.
Debugging is the process of identifying and fixing errors or bugs in a program. When a program does not produce the expected results or crashes, it is necessary to go through the code to find and fix the problem. This can involve analyzing the program’s logic, checking for syntax errors, and using debugging tools to trace the flow of data and identify the source of the issue.
Data analysis plays a crucial role in both testing and debugging. It helps to identify patterns, anomalies, or inconsistencies in the program’s behavior. By analyzing the data, developers can gain insights into potential issues and make informed decisions on how to improve the program’s performance.
In conclusion, testing and debugging are integral parts of the problem-solving cycle in computer science. Through testing and data analysis, developers can verify the correctness of their programs and identify and resolve any issues that may arise. This ensures that the algorithms and programs developed in computer science are robust, reliable, and efficient.
Iterating for Improvement
In computer science, problem solving often involves iterating through multiple cycles of analysis, solution development, and evaluation. This iterative process allows for continuous improvement in finding the most effective solution to a given problem.
The problem solving cycle starts with problem analysis, where the specific problem is identified and its requirements are understood. This step involves examining the problem from various angles and gathering all relevant information.
Once the problem is properly understood, the next step is to develop an algorithm or a step-by-step plan to solve the problem. This algorithm is a set of instructions that, when followed correctly, will lead to the solution.
After the algorithm is developed, it is implemented in a computer program. This step involves translating the algorithm into a programming language that a computer can understand and execute.
Once the program is implemented, it is then tested and evaluated to ensure that it produces the correct solution. This evaluation step is crucial in identifying any errors or inefficiencies in the program and allows for further improvement.
If any issues or problems are found during testing, the cycle iterates, starting from problem analysis again. This iterative process allows for refinement and improvement of the solution until the desired results are achieved.
Iterating for improvement is a fundamental concept in computer science problem solving. By continually analyzing, developing, and evaluating solutions, computer scientists are able to find the most optimal and efficient approaches to solving problems.
Documenting the Process
Documenting the problem-solving process in computer science is an essential step to ensure that the cycle is repeated successfully. The process involves gathering information, analyzing the problem, and designing a solution.
During the analysis phase, it is crucial to identify the specific problem at hand and break it down into smaller components. This allows for a more targeted approach to finding the solution. Additionally, analyzing the data involved in the problem can provide valuable insights and help in designing an effective solution.
Once the analysis is complete, it is important to document the findings. This documentation can take various forms, such as written reports, diagrams, or even code comments. The goal is to create a record that captures the problem, the analysis, and the proposed solution.
Documenting the process serves several purposes. Firstly, it allows for easy communication and collaboration between team members or future developers. By documenting the problem, analysis, and solution, others can easily understand the thought process behind the solution and potentially build upon it.
Secondly, documenting the process provides an opportunity for reflection and improvement. By reviewing the documentation, developers can identify areas where the problem-solving cycle can be strengthened or optimized. This continuous improvement is crucial in the field of computer science, as new challenges and technologies emerge rapidly.
In conclusion, documenting the problem-solving process is an integral part of the computer science cycle. It allows for effective communication, collaboration, and reflection on the solutions devised. By taking the time to document the process, developers can ensure a more efficient and successful problem-solving experience.
Communicating the Solution
Once the problem solving cycle is complete, it is important to effectively communicate the solution. This involves explaining the analysis, data, and steps taken to arrive at the solution.
Analyzing the Problem
During the problem solving cycle, a thorough analysis of the problem is conducted. This includes understanding the problem statement, gathering relevant data, and identifying any constraints or limitations. It is important to clearly communicate this analysis to ensure that others understand the problem at hand.
Presenting the Solution
The next step in communicating the solution is presenting the actual solution. This should include a detailed explanation of the steps taken to solve the problem, as well as any algorithms or data structures used. It is important to provide clear and concise descriptions of the solution, so that others can understand and reproduce the results.
Overall, effective communication of the solution in computer science is essential to ensure that others can understand and replicate the problem solving process. By clearly explaining the analysis, data, and steps taken, the solution can be communicated in a way that promotes understanding and collaboration within the field of computer science.
Reflecting and Learning
Reflecting and learning are crucial steps in the problem solving cycle in computer science. Once a problem has been solved, it is essential to reflect on the entire process and learn from the experience. This allows for continuous improvement and growth in the field of computer science.
During the reflecting phase, one must analyze and evaluate the problem solving process. This involves reviewing the initial problem statement, understanding the constraints and requirements, and assessing the effectiveness of the chosen algorithm and solution. It is important to consider the efficiency and accuracy of the solution, as well as any potential limitations or areas for optimization.
By reflecting on the problem solving cycle, computer scientists can gain valuable insights into their own strengths and weaknesses. They can identify areas where they excelled and areas where improvement is needed. This self-analysis helps in honing problem solving skills and becoming a better problem solver.
Learning from Mistakes
Mistakes are an integral part of the problem solving cycle, and they provide valuable learning opportunities. When a problem is not successfully solved, it is essential to analyze the reasons behind the failure and learn from them. This involves identifying errors in the algorithm or solution, understanding the underlying concepts or principles that were misunderstood, and finding alternative approaches or strategies.
Failure should not be seen as a setback, but rather as an opportunity for growth. By learning from mistakes, computer scientists can improve their problem solving abilities and expand their knowledge and understanding of computer science. It is through these failures and the subsequent learning process that new ideas and innovations are often born.
Continuous Improvement
Reflecting and learning should not be limited to individual problem solving experiences, but should be an ongoing practice. As computer science is a rapidly evolving field, it is crucial to stay updated with new technologies, algorithms, and problem solving techniques. Continuous learning and improvement contribute to staying competitive and relevant in the field.
Computer scientists can engage in continuous improvement by seeking feedback from peers, participating in research and development activities, attending conferences and workshops, and actively seeking new challenges and problem solving opportunities. This dedication to learning and improvement ensures that one’s problem solving skills remain sharp and effective.
In conclusion, reflecting and learning are integral parts of the problem solving cycle in computer science. They enable computer scientists to refine their problem solving abilities, learn from mistakes, and continuously improve their skills and knowledge. By embracing these steps, computer scientists can stay at the forefront of the ever-changing world of computer science and contribute to its advancements.
Applying Problem Solving in Real Life
In computer science, problem solving is not limited to the realm of programming and algorithms. It is a skill that can be applied to various aspects of our daily lives, helping us to solve problems efficiently and effectively. By using the problem-solving cycle and applying the principles of analysis, data, solution, algorithm, and cycle, we can tackle real-life challenges with confidence and success.
The first step in problem-solving is to analyze the problem at hand. This involves breaking it down into smaller, more manageable parts and identifying the key issues or goals. By understanding the problem thoroughly, we can gain insights into its root causes and potential solutions.
For example, let’s say you’re facing a recurring issue in your daily commute – traffic congestion. By analyzing the problem, you may discover that the main causes are a lack of alternative routes and a lack of communication between drivers. This analysis helps you identify potential solutions such as using navigation apps to find alternate routes or promoting carpooling to reduce the number of vehicles on the road.
Gathering and Analyzing Data
Once we have identified the problem, it is important to gather relevant data to support our analysis. This may involve conducting surveys, collecting statistics, or reviewing existing research. By gathering data, we can make informed decisions and prioritize potential solutions based on their impact and feasibility.
Continuing with the traffic congestion example, you may gather data on the average commute time, the number of vehicles on the road, and the impact of carpooling on congestion levels. This data can help you analyze the problem more accurately and determine the most effective solutions.
Generating and Evaluating Solutions
After analyzing the problem and gathering data, the next step is to generate potential solutions. This can be done through brainstorming, researching best practices, or seeking input from experts. It is important to consider multiple options and think outside the box to find innovative and effective solutions.
For our traffic congestion problem, potential solutions can include implementing a smart traffic management system that optimizes traffic flow or investing in public transportation to incentivize people to leave their cars at home. By evaluating each solution’s potential impact, cost, and feasibility, you can make an informed decision on the best course of action.
Implementing and Iterating
Once a solution has been chosen, it is time to implement it in real life. This may involve developing a plan, allocating resources, and executing the solution. It is important to monitor the progress and collect feedback to learn from the implementation and make necessary adjustments.
For example, if the chosen solution to address traffic congestion is implementing a smart traffic management system, you would work with engineers and transportation authorities to develop and deploy the system. Regular evaluation and iteration of the system’s performance would ensure that it is effective and making a positive impact on reducing congestion.
By applying the problem-solving cycle derived from computer science to real-life situations, we can approach challenges with a systematic and analytical mindset. This can help us make better decisions, improve our problem-solving skills, and ultimately achieve more efficient and effective solutions.
Building Problem Solving Skills
In the field of computer science, problem-solving is a fundamental skill that is crucial for success. Whether you are a computer scientist, programmer, or student, developing strong problem-solving skills will greatly benefit your work and studies. It allows you to approach challenges with a logical and systematic approach, leading to efficient and effective problem resolution.
The Problem Solving Cycle
Problem-solving in computer science involves a cyclical process known as the problem-solving cycle. This cycle consists of several stages, including problem identification, data analysis, solution development, implementation, and evaluation. By following this cycle, computer scientists are able to tackle complex problems and arrive at optimal solutions.
Importance of Data Analysis
Data analysis is a critical step in the problem-solving cycle. It involves gathering and examining relevant data to gain insights and identify patterns that can inform the development of a solution. Without proper data analysis, computer scientists may overlook important information or make unfounded assumptions, leading to subpar solutions.
To effectively analyze data, computer scientists can employ various techniques such as data visualization, statistical analysis, and machine learning algorithms. These tools enable them to extract meaningful information from large datasets and make informed decisions during the problem-solving process.
Developing Effective Solutions
Developing effective solutions requires creativity, critical thinking, and logical reasoning. Computer scientists must evaluate multiple approaches, consider various factors, and assess the feasibility of different solutions. They should also consider potential limitations and trade-offs to ensure that the chosen solution addresses the problem effectively.
Furthermore, collaboration and communication skills are vital when building problem-solving skills. Computer scientists often work in teams and need to effectively communicate their ideas, propose solutions, and address any challenges that arise during the problem-solving process. Strong interpersonal skills facilitate collaboration and enhance problem-solving outcomes.
- Mastering programming languages and algorithms
- Staying updated with technological advancements in the field
- Practicing problem solving through coding challenges and projects
- Seeking feedback and learning from mistakes
- Continuing to learn and improve problem-solving skills
By following these strategies, individuals can strengthen their problem-solving abilities and become more effective computer scientists or programmers. Problem-solving is an essential skill in computer science and plays a central role in driving innovation and advancing the field.
Questions and answers:
What is the problem solving cycle in computer science.
The problem solving cycle in computer science refers to a systematic approach that programmers use to solve problems. It involves several steps, including problem definition, algorithm design, implementation, testing, and debugging.
How important is the problem solving cycle in computer science?
The problem solving cycle is extremely important in computer science as it allows programmers to effectively tackle complex problems and develop efficient solutions. It helps in organizing the thought process and ensures that the problem is approached in a logical and systematic manner.
What are the steps involved in the problem solving cycle?
The problem solving cycle typically consists of the following steps: problem definition and analysis, algorithm design, implementation, testing, and debugging. These steps are repeated as necessary until a satisfactory solution is achieved.
Can you explain the problem definition and analysis step in the problem solving cycle?
During the problem definition and analysis step, the programmer identifies and thoroughly understands the problem that needs to be solved. This involves analyzing the requirements, constraints, and possible inputs and outputs. It is important to have a clear understanding of the problem before proceeding to the next steps.
Why is testing and debugging an important step in the problem solving cycle?
Testing and debugging are important steps in the problem solving cycle because they ensure that the implemented solution functions as intended and is free from errors. Through testing, the programmer can identify and fix any issues or bugs in the code, thereby improving the quality and reliability of the solution.
What is the problem-solving cycle in computer science?
The problem-solving cycle in computer science refers to the systematic approach that computer scientists use to solve problems. It involves various steps, including problem analysis, algorithm design, coding, testing, and debugging.
Related posts:
- The Stages of the Problem Solving Cycle in Cognitive Psychology – Understanding, Planning, Execution, Evaluation, and Reflection
- A Comprehensive Guide to the Problem Solving Cycle in Psychology – Strategies, Techniques, and Applications
- The Step-by-Step Problem Solving Cycle for Effective Solutions
- The Importance of Implementing the Problem Solving Cycle in Education to Foster Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills in Students
- The Importance of the Problem Solving Cycle in Business Studies – Strategies for Success
- The Comprehensive Guide to the Problem Solving Cycle in PDF Format
- A Comprehensive Guide on the Problem Solving Cycle – Step-by-Step Approach with Real-Life Example
- The Seven Essential Steps of the Problem Solving Cycle
- Python Programming
- C Programming
- Numerical Methods
- Dart Language
- Computer Basics
- Deep Learning
- C Programming Examples
- Python Programming Examples
Problem Solving Using Computer (Steps)
Computer based problem solving is a systematic process of designing, implementing and using programming tools during the problem solving stage. This method enables the computer system to be more intuitive with human logic than machine logic. Final outcome of this process is software tools which is dedicated to solve the problem under consideration. Software is just a collection of computer programs and programs are a set of instructions which guides computer’s hardware. These instructions need to be well specified for solving the problem. After its creation, the software should be error free and well documented. Software development is the process of creating such software, which satisfies end user’s requirements and needs.
The following six steps must be followed to solve a problem using computer.
- Problem Analysis
- Program Design - Algorithm, Flowchart and Pseudocode
- Compilation and Execution
- Debugging and Testing
- Program Documentation
Problem-Solving Strategies
- First Online: 06 August 2020
Cite this chapter

- Orit Hazzan ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8627-0997 4 ,
- Noa Ragonis ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8163-0199 5 &
- Tami Lapidot 4
1382 Accesses
Problem-solving is generally considered as one of the most important and challenging cognitive activities in everyday as well as in any professional contexts. Specifically, it is one of the central activities performed by computer scientists as well as by computer science learners. However, it is not a uniform or linear process that can be taught as an algorithm to be followed, and the understanding of this individual process is not always clear. Computer science learners often face difficulties in performing two of the main stages of a problem-solving process: problem analysis and solution construction. Therefore, it is important that computer science educators be aware of these difficulties and acquire appropriate pedagogical tools to guide and scaffold learners in learning these skills. This chapter is dedicated to such pedagogical tools. It presents several problem-solving strategies to address in the MTCS course together with appropriate activities that mediate them to the prospective computer science teachers by enabling them to experience the different strategies.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
An algorithmic problem is defined by what is given – the initial conditions of the problem and its goals – the desired state, what should be accomplished. An algorithm problem can be solved with a series of actions formulated formally either by pseudo-code or a programming language. See Sect. 12.4.1 .
In advanced computer science classes, it is relevant to mention that in computer science, in addition to the development of problem-solving strategies, special emphasis is placed also on non-solvable problems (see Sect. 12.4.3 ).
Role of Variables in Python: http://www.cs.joensuu.fi/~saja/var_roles/stud_vers/stud_Python_eng.html
Roles of Variables with examples in Scratch: https://www.sisd.net/cms/lib/TX01001452/Centricity/domain/433/cse/1.1.5%20RolesOfVariables_UsedActivity1.2.4.pptx
The Roles of Variables home page ( http://saja.kapsi.fi/var_roles/ ) is a rich resource and contains different kinds of educational resources.
See http://www.cs.joensuu.fi/~saja/var_roles/role_intro.html
See http://www.cs.joensuu.fi/~saja/var_roles/try.html
See http://cs.uef.fi/~pgerdt/RAE/
See http://www.cs.joensuu.fi/~saja/var_roles/why_roles.html
See http://www.cs.joensuu.fi/~saja/var_roles/teaching.html
See http://saja.kapsi.fi/var_roles/literature.html
Ahrendt W, Bubel R, Hahnle R (2009) Integrated and tool-supported teaching of testing, debugging, and verification. In: Gibbons J, Oliveira JN (eds) Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on teaching formal methods (TFM ’09). Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, pp 125–143
Google Scholar
Alqadi BS, Maletic JI (2017) An empirical study of debugging patterns among novices programmers. In: Proceedings of the 2017 ACM SIGCSE technical symposium on computer science education (SIGCSE ’17). ACM, New York, pp 15–20
Arshad N (2009) Teaching programming and problem solving to CS2 students using think-alouds. SIGCSE Bull 41(1):372–376
Astrachan O, Berry G, Cox L, Mitchener G (1998) Design patterns: an essential component of CS curricula. In: Proceeding of SIGCSE, pp 153–160
Batory D, Sarvela JN, Rauschmayer A (2004) Scaling stepwise refinement. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 30(6):355–371
Bauer A, Popović Z (2017) Collaborative problem solving in an open-ended scientific discovery game. In: Proceedings of the ACM Human-Computer Interaction 1, CSCW, Article 22 (December 2017)
Ben-Ari M, Sajaniemi J (2003) Roles of variables from the perspective of computer science educators. University of Joensuu, Department of Computer Science, Technical Report, Series A-2003–6
Börstler J, Hilburn TB (2016) Team projects in computing education. ACM Trans Comput Educ 16(2), Article 4 (March 2016)
Byckling P, Sajaniemi J (2006) Roles of variables and programming skills improvement. SIGCSE Bull 38(1):413–417
Carver S, McCoy (1988) Learning and transfer of debugging skills: applying task analysis to curriculum design and assessment. In Mayer RE (ed) Teaching and learning computer programming, multiple research perspectives. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc., Chapter 11
Celepkolu M, Boyer KE (2018) The importance of producing shared code through pair programming. In: Proceedings of the 49th ACM technical symposium on computer science education (SIGCSE ’18). ACM, New York, pp 765–770
Clancy MJ, Linn M C (1999) Patterns and pedagogy. In: Proceedings of the SIGCSE’99, pp 37–42
Cosmides L, Tooby J (1997) Evolutionary psychology: a primer. Retrieved 24 October 2004, from http://www.psych.ucsb.edu/research/cep/primer.html
Dijkstra EW (1976) A discipline of programming. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
MATH Google Scholar
East JP, Thomas SR, Wallingford E, Beck W, Drake J (1996) Pattern-based programming instruction. In: Proceedings of ASEE annual conference and exposition, Washington, DC
Ginat D (2003) The greedy trap and learning from mistakes. SIGCSE Bull 35(1):11–15
Ginat D (2004) Algorithmic patterns and the case of the sliding delta. SIGCSE Bull 36(2):29–33
Ginat D (2008) Learning from wrong and creative algorithm design. SIGCSE Bull 40(1):26–30
Ginat D (2009) Interleaved pattern composition and scaffolded learning. In: Proceedings of the 14th Annual ACM SIGCSE Conference on Innovation and Technology in Computer Science Education – ITiCSE ‘09, Paris, France, pp 109–113
Ginat D, Shmalo R (2013) Constructive use of errors in teaching CS1. In: Proceedings of the 44th ACM technical symposium on Computer science education (SIGCSE ’13). ACM, New York, pp 353–358
Hasni TF, Lodhi F (2011) Teaching problem solving effectively. ACM Inroads 2(3):58–62
Hazzan O, Leron U (2006) Why do we resist testing? Syst Des Front Exclus Front Cover Syst Des 3(7):20–23
Johnson DW, Johanson RT (2017) Cooperative learning. Retrieved from: https://2017.congresoinnovacion.educa.aragon.es/documents/48/David_Johnson.pdf
Jonassen DH (2000) Toward a design theory of problem solving. Educ Technol Res Dev 48(4):63–85
Kiesmüller U (2009) Diagnosing learners’ problem-solving strategies using learning environments with algorithmic problems in secondary education. Trans Comput Educ 9(3), Article 17 (September 2009), 26 pages
Laakso MJ, Malmi L, Korhonen A, Rajala T, Kaila E, Salakoski T (2008) Using roles of variables to enhance novice’s debugging work. Issues Informing Sci Inf Technol 5:281–295
Lapidot T, Hazzan O (2005) Song debugging: merging content and pedagogy in computer science education. Inroads SIGCSE Bull 37(4):79–83
Lieberman H (1997) The debugging scandal and what to do about it (special section). Comm ACM 40(4):27–29
Lishinski A, Yadav A, Enbody R, Good J (2016) The influence of problem solving abilities on Students’ performance on different assessment tasks in CS1. In: Proceedings of the 47th ACM technical symposium on computing science education (SIGCSE ’16). ACM, New York, pp 329–334
Muller O (2005) Pattern oriented instruction and the enhancement of analogical reasoning. In: Proceedings of the first International Workshop on Computer Education Research ICER ‘05, Seattle, WA, USA, pp 57–67
Muller O, Haberman B, Averbuch H (2004) (An almost) pedagogical pattern for pattern-based problem solving instruction. In: Proceedings of the 9th Annual SIGCSE Conference on Innovation and Technology in Computer Science. Education, pp 102–106
Muller O, Ginat D, Haberman B (2007) Pattern-oriented instruction and its influence on problem decomposition and solution construction. ACM SIGCSE Bull 39(3):151–155
Murphy L, Lewandowski G, McCauley R, Simon B, Thomas L, Zander C (2008) Debugging: the good, the bad, and the quirky – a qualitative analysis of novices’ strategies. SIGCSE Bull 40(1):163–167
Nagvajara P, Taskin B (2007) Design-for-debug: a vital aspect in education. In: Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE international conference on microelectronic systems education (MSE ’07). IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC, USA, pp 65–66
Papert S (1980) Mindstorms: children, computers and powerful ideas. Basic Books Inc, New York
Polya G (1957) How to solve it. Doubleday and Co., Inc, Garden City
Polya G (1981) Mathematical discovery on understanding learning and teaching problem solving. Wiley, New York
Popper KR (1992/1959) Logic of scientific discovery. Harper and Row, New York
Proulx VK (2000) Programming patterns and design patterns in the introductory computer science course. Proc SIGCSE 32(1):80–84
Ragonis N (2012) Integrating the teaching of algorithmic patterns into computer science teacher preparation programs. In: Proceedings of the 17th ACM annual conference on Innovation and technology in computer science education (ITiCSE ’12). ACM, New York, pp 339–344
Raman K, Svore KM, Gilad-Bachrach R, Burges CJC (2012) Learning from mistakes: towards a correctable learning algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 21st ACM international conference on information and knowledge management (CIKM ’12). ACM, New York, pp 1930–1934
Reed D (1999) Incorporating problem-solving patterns in CS1. J Comput Sci Edu 13(1):6–13
Reynolds RG, Maletic JI, Porvin SE (1992) Stepwise refinement and problem solving. IEEE Softw 9(5):79–88
Robins A, Rountree J, Rountree N (2003) Learning and teaching programming: a review and discussion. Comput Sci Edu 13(2):137–172
Sajaniemi J (2005) Roles of variables and learning to program. In: Jimoyiannis A (ed) Proceedings of the 3rd Panhellenic conference didactics of informatics, University of Peloponnese, Korinthos, Greece. http://cs.joensuu.fi/~saja/var_roles/abstracts/didinf05.pdf . Accessed 3 July 2010
Santos AL, Sousa J (2017) An exploratory study of how programming instructors illustrate variables and control flow. In: Proceedings of the 17th Koli calling international conference on computing education research (Koli Calling ’17). ACM, New York, pp 173–177
Schoenfeld AH (1983) Episodes and executive decisions in mathematical problem-solving. In: Lesh R, Landaue M (eds) Acquisition of mathematics concepts and processes. Academic Press Inc, New York
Schön DA (1983) The reflective practitioner. BasicBooks
Seta K, Kajino T, Umano M, Ikeda M (2006) An ontology based reflection support system to encourage learning from mistakes. In: Deved V (ed) Proceedings of the 24th IASTED international conference on artificial intelligence and applications (AIA’06). ACTA Press, Anaheim, pp 142–149
Soloway E (1986) Learning to program = learning to construct mechanisms and explanations. CACM 29(1):850–858
Spohrer JG, Soloway E (1986) Analyzing the high frequency bugs in novice programs. In: Soloway E, Iyengar S (eds) Empirical studies of programmers. Ablex, Norwood, pp 230–251
Stoeffler K, Rosen Y, von Davier A (2017) Exploring the measurement of collaborative problem solving using a human-agent educational game. In: Proceedings of the seventh international learning analytics & knowledge conference (LAK ‘17). ACM, New York, pp 570–571
Vainio V, Sajaniemi J (2007) Factors in novice programmers’ poor tracing skills. SIGCSE Bull 39(3):236–240
Vasconcelos J (2007) Basic strategy for algorithmic problem solving. http://www.cs.jhu.edu/~jorgev/cs106/ProblemSolving.html . Accessed 2 June 2010
Vírseda R d V, Orna EP, Berbis E, Guerrero S d L (2011) A logic teaching tool based on tableaux for verification and debugging of algorithms. In: Blackburn P, van Ditmarsch H, Soler-Toscano F, Manzano M (eds) Proceedings of the third international congress conference on tools for teaching logic (TICTTL’11). Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, pp 239–248
Von Davier AA, Halpin PF (2013) Collaborative problem solving and the assessment of cognitive skills: psychometric considerations. ETS Res Rep Ser 2013(2):1–36
Wallingford E (1996) Toward a first course based on object-oriented patterns. In: Proceedings of the SIGCSE, pp 27–31
Wirth N (1971) Program development by stepwise refinement. CACM 14(4):221–227. http://sunnyday.mit.edu/16.355/wirth-refinement.html . Accessed 13 Nov 2010
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Education in Science & Technology, Technion–Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa, Israel
Orit Hazzan & Tami Lapidot
Faculty of Education, Beit Berl College, Doar Beit Berl, Israel
Noa Ragonis
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Hazzan, O., Ragonis, N., Lapidot, T. (2020). Problem-Solving Strategies. In: Guide to Teaching Computer Science. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-39360-1_8
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-39360-1_8
Published : 06 August 2020
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-39359-5
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-39360-1
eBook Packages : Computer Science Computer Science (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 7, 2023 — 5 minutes to read
What Is Problem Solving?
Definition and importance.
Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a crucial skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Mastering this ability will contribute to both your personal and professional growth, leading to more successful outcomes and better decision-making.
Problem-Solving Steps
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:
- Identify the issue : Recognize the problem that needs to be solved.
- Analyze the situation : Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present.
- Generate potential solutions : Brainstorm a list of possible solutions to the issue, without immediately judging or evaluating them.
- Evaluate options : Weigh the pros and cons of each potential solution, considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and potential risks.
- Select the best solution : Choose the option that best addresses the problem and aligns with your objectives.
- Implement the solution : Put the selected solution into action and monitor the results to ensure it resolves the issue.
- Review and learn : Reflect on the problem-solving process, identify any improvements or adjustments that can be made, and apply these learnings to future situations.
Defining the Problem
To start tackling a problem, first, identify and understand it. Analyzing the issue thoroughly helps to clarify its scope and nature. Ask questions to gather information and consider the problem from various angles. Some strategies to define the problem include:
- Brainstorming with others
- Asking the 5 Ws and 1 H (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How)
- Analyzing cause and effect
- Creating a problem statement
Generating Solutions
Once the problem is clearly understood, brainstorm possible solutions. Think creatively and keep an open mind, as well as considering lessons from past experiences. Consider:
- Creating a list of potential ideas to solve the problem
- Grouping and categorizing similar solutions
- Prioritizing potential solutions based on feasibility, cost, and resources required
- Involving others to share diverse opinions and inputs
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Evaluate each potential solution, weighing its pros and cons. To facilitate decision-making, use techniques such as:
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Decision-making matrices
- Pros and cons lists
- Risk assessments
After evaluating, choose the most suitable solution based on effectiveness, cost, and time constraints.
Implementing and Monitoring the Solution
Implement the chosen solution and monitor its progress. Key actions include:
- Communicating the solution to relevant parties
- Setting timelines and milestones
- Assigning tasks and responsibilities
- Monitoring the solution and making adjustments as necessary
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the solution after implementation
Utilize feedback from stakeholders and consider potential improvements. Remember that problem-solving is an ongoing process that can always be refined and enhanced.
Problem-Solving Techniques
During each step, you may find it helpful to utilize various problem-solving techniques, such as:
- Brainstorming : A free-flowing, open-minded session where ideas are generated and listed without judgment, to encourage creativity and innovative thinking.
- Root cause analysis : A method that explores the underlying causes of a problem to find the most effective solution rather than addressing superficial symptoms.
- SWOT analysis : A tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a problem or decision, providing a comprehensive view of the situation.
- Mind mapping : A visual technique that uses diagrams to organize and connect ideas, helping to identify patterns, relationships, and possible solutions.
Brainstorming
When facing a problem, start by conducting a brainstorming session. Gather your team and encourage an open discussion where everyone contributes ideas, no matter how outlandish they may seem. This helps you:
- Generate a diverse range of solutions
- Encourage all team members to participate
- Foster creative thinking
When brainstorming, remember to:
- Reserve judgment until the session is over
- Encourage wild ideas
- Combine and improve upon ideas
Root Cause Analysis
For effective problem-solving, identifying the root cause of the issue at hand is crucial. Try these methods:
- 5 Whys : Ask “why” five times to get to the underlying cause.
- Fishbone Diagram : Create a diagram representing the problem and break it down into categories of potential causes.
- Pareto Analysis : Determine the few most significant causes underlying the majority of problems.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis helps you examine the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to your problem. To perform a SWOT analysis:
- List your problem’s strengths, such as relevant resources or strong partnerships.
- Identify its weaknesses, such as knowledge gaps or limited resources.
- Explore opportunities, like trends or new technologies, that could help solve the problem.
- Recognize potential threats, like competition or regulatory barriers.
SWOT analysis aids in understanding the internal and external factors affecting the problem, which can help guide your solution.
Mind Mapping
A mind map is a visual representation of your problem and potential solutions. It enables you to organize information in a structured and intuitive manner. To create a mind map:
- Write the problem in the center of a blank page.
- Draw branches from the central problem to related sub-problems or contributing factors.
- Add more branches to represent potential solutions or further ideas.
Mind mapping allows you to visually see connections between ideas and promotes creativity in problem-solving.
Examples of Problem Solving in Various Contexts
In the business world, you might encounter problems related to finances, operations, or communication. Applying problem-solving skills in these situations could look like:
- Identifying areas of improvement in your company’s financial performance and implementing cost-saving measures
- Resolving internal conflicts among team members by listening and understanding different perspectives, then proposing and negotiating solutions
- Streamlining a process for better productivity by removing redundancies, automating tasks, or re-allocating resources
In educational contexts, problem-solving can be seen in various aspects, such as:
- Addressing a gap in students’ understanding by employing diverse teaching methods to cater to different learning styles
- Developing a strategy for successful time management to balance academic responsibilities and extracurricular activities
- Seeking resources and support to provide equal opportunities for learners with special needs or disabilities
Everyday life is full of challenges that require problem-solving skills. Some examples include:
- Overcoming a personal obstacle, such as improving your fitness level, by establishing achievable goals, measuring progress, and adjusting your approach accordingly
- Navigating a new environment or city by researching your surroundings, asking for directions, or using technology like GPS to guide you
- Dealing with a sudden change, like a change in your work schedule, by assessing the situation, identifying potential impacts, and adapting your plans to accommodate the change.
- How to Resolve Employee Conflict at Work [Steps, Tips, Examples]
- How to Write Inspiring Core Values? 5 Steps with Examples
- 30 Employee Feedback Examples (Positive & Negative)
Browse Course Material
Course info.
- Prof. John Guttag
Departments
- Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
As Taught In
- Computer Science
Introduction to Computer Science and Programming
Lecture 3: problem solving.
- Download video
- Download transcript

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 7 min read
What Is Problem Solving?
Find a solution to any problem you face..
By the Mind Tools Content Team

We all spend a lot of our time solving problems, both at work and in our personal lives.
Some problems are small, and we can quickly sort them out ourselves. But others are complex challenges that take collaboration, creativity, and a considerable amount of effort to solve.
At work, the types of problems we face depend largely on the organizations we're in and the jobs we do. A manager in a cleaning company, for example, might spend their day untangling staffing issues, resolving client complaints, and sorting out problems with equipment and supplies. An aircraft designer, on the other hand, might be grappling with a problem about aerodynamics, or trying to work out why a new safety feature isn't working. Meanwhile, a politician might be exploring solutions to racial injustice or climate change.
But whatever issues we face, there are some common ways to tackle them effectively. And we can all boost our confidence and ability to succeed by building a strong set of problem-solving skills.
Mind Tools offers a large collection of resources to help you do just that!
How Well Do You Solve Problems?
Start by taking an honest look at your existing skills. What's your current approach to solving problems, and how well is it working? Our quiz, How Good Is Your Problem Solving? lets you analyze your abilities, and signposts ways to address any areas of weakness.
Define Every Problem
The first step in solving a problem is understanding what that problem actually is. You need to be sure that you're dealing with the real problem – not its symptoms. For example, if performance in your department is substandard, you might think that the problem lies with the individuals submitting work. However, if you look a bit deeper, the real issue might be a general lack of training, or an unreasonable workload across the team.
Tools like 5 Whys , Appreciation and Root Cause Analysis get you asking the right questions, and help you to work through the layers of a problem to uncover what's really going on.
However, defining a problem doesn't mean deciding how to solve it straightaway. It's important to look at the issue from a variety of perspectives. If you commit yourself too early, you can end up with a short-sighted solution. The CATWOE checklist provides a powerful reminder to look at many elements that may contribute to the problem, keeping you open to a variety of possible solutions.
Understanding Complexity
As you define your problem, you'll often discover just how complicated it is. There are likely several interrelated issues involved. That's why it's important to have ways to visualize, simplify and make sense of this tangled mess!
Affinity Diagrams are great for organizing many different pieces of information into common themes, and for understanding the relationships between them.
Another popular tool is the Cause-and-Effect Diagram . To generate viable solutions, you need a solid understanding of what's causing the problem.
When your problem occurs within a business process, creating a Flow Chart , Swim Lane Diagram or a Systems Diagram will help you to see how various activities and inputs fit together. This may well highlight a missing element or bottleneck that's causing your problem.
Quite often, what seems to be a single problem turns out to be a whole series of problems. The Drill Down technique prompts you to split your problem into smaller, more manageable parts.
General Problem-Solving Tools
When you understand the problem in front of you, you’re ready to start solving it. With your definition to guide you, you can generate several possible solutions, choose the best one, then put it into action. That's the four-step approach at the heart of good problem solving.
There are various problem-solving styles to use. For example:
- Constructive Controversy is a way of widening perspectives and energizing discussions.
- Inductive Reasoning makes the most of people’s experiences and know-how, and can speed up solution finding.
- Means-End Analysis can bring extra clarity to your thinking, and kick-start the process of implementing solutions.
Specific Problem-Solving Systems
Some particularly complicated or important problems call for a more comprehensive process. Again, Mind Tools has a range of approaches to try, including:
- Simplex , which involves an eight-stage process: problem finding, fact finding, defining the problem, idea finding, selecting and evaluating, planning, selling the idea, and acting. These steps build upon the basic, four-step process described above, and they create a cycle of problem finding and solving that will continually improve your organization.
- Appreciative Inquiry , which is a uniquely positive way of solving problems by examining what's working well in the areas surrounding them.
- Soft Systems Methodology , which takes you through four stages to uncover more details about what's creating your problem, and then define actions that will improve the situation.
Further Problem-Solving Strategies
Good problem solving requires a number of other skills – all of which are covered by Mind Tools.
For example, we have a large section of resources to improve your Creativity , so that you come up with a range of possible solutions.
By strengthening your Decision Making , you'll be better at evaluating the options, selecting the best ones, then choosing how to implement them.
And our Project Management collection has valuable advice for strengthening the whole problem-solving process. The resources there will help you to make effective changes – and then keep them working long term.
Problems are an inescapable part of life, both in and out of work. So we can all benefit from having strong problem-solving skills.
It's important to understand your current approach to problem solving, and to know where and how to improve.
Define every problem you encounter – and understand its complexity, rather than trying to solve it too soon.
There's a range of general problem-solving approaches, helping you to generate possible answers, choose the best ones, and then implement your solution.
Some complicated or serious problems require more specific problem-solving systems, especially when they relate to business processes.
By boosting your creativity, decision-making and project-management skills, you’ll become even better at solving all the problems you face.
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
4 logical fallacies.
Avoid Common Types of Faulty Reasoning
Everyday Cybersecurity
Keep Your Data Safe
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Gain essential management and leadership skills
Busy schedule? No problem. Learn anytime, anywhere.
Subscribe to unlimited access to meticulously researched, evidence-based resources.
Join today and take advantage of our 30% offer, available until May 31st .
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Latest Updates

Winning Body Language

Business Stripped Bare
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Nine ways to get the best from x (twitter).
Growing Your Business Quickly and Safely on Social Media
Managing Your Emotions at Work
Controlling Your Feelings... Before They Control You
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
How not to develop your team infographic.
Infographic Transcript
Infographic
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Data & Visuals

Partner Center

- The Art of Effective Problem Solving: A Step-by-Step Guide

- Learn Lean Sigma
- Problem Solving
Whether we realise it or not, problem solving skills are an important part of our daily lives. From resolving a minor annoyance at home to tackling complex business challenges at work, our ability to solve problems has a significant impact on our success and happiness. However, not everyone is naturally gifted at problem-solving, and even those who are can always improve their skills. In this blog post, we will go over the art of effective problem-solving step by step.
You will learn how to define a problem, gather information, assess alternatives, and implement a solution, all while honing your critical thinking and creative problem-solving skills. Whether you’re a seasoned problem solver or just getting started, this guide will arm you with the knowledge and tools you need to face any challenge with confidence. So let’s get started!
Table of Contents
Problem solving methodologies.
Individuals and organisations can use a variety of problem-solving methodologies to address complex challenges. 8D and A3 problem solving techniques are two popular methodologies in the Lean Six Sigma framework.
Methodology of 8D (Eight Discipline) Problem Solving:
The 8D problem solving methodology is a systematic, team-based approach to problem solving. It is a method that guides a team through eight distinct steps to solve a problem in a systematic and comprehensive manner.
The 8D process consists of the following steps:

- Form a team: Assemble a group of people who have the necessary expertise to work on the problem.
- Define the issue: Clearly identify and define the problem, including the root cause and the customer impact.
- Create a temporary containment plan: Put in place a plan to lessen the impact of the problem until a permanent solution can be found.
- Identify the root cause: To identify the underlying causes of the problem, use root cause analysis techniques such as Fishbone diagrams and Pareto charts.
- Create and test long-term corrective actions: Create and test a long-term solution to eliminate the root cause of the problem.
- Implement and validate the permanent solution: Implement and validate the permanent solution’s effectiveness.
- Prevent recurrence: Put in place measures to keep the problem from recurring.
- Recognize and reward the team: Recognize and reward the team for its efforts.
Download the 8D Problem Solving Template
A3 Problem Solving Method:
The A3 problem solving technique is a visual, team-based problem-solving approach that is frequently used in Lean Six Sigma projects. The A3 report is a one-page document that clearly and concisely outlines the problem, root cause analysis, and proposed solution.
The A3 problem-solving procedure consists of the following steps:
- Determine the issue: Define the issue clearly, including its impact on the customer.
- Perform root cause analysis: Identify the underlying causes of the problem using root cause analysis techniques.
- Create and implement a solution: Create and implement a solution that addresses the problem’s root cause.
- Monitor and improve the solution: Keep an eye on the solution’s effectiveness and make any necessary changes.
Subsequently, in the Lean Six Sigma framework, the 8D and A3 problem solving methodologies are two popular approaches to problem solving. Both methodologies provide a structured, team-based problem-solving approach that guides individuals through a comprehensive and systematic process of identifying, analysing, and resolving problems in an effective and efficient manner.
Step 1 – Define the Problem
The definition of the problem is the first step in effective problem solving. This may appear to be a simple task, but it is actually quite difficult. This is because problems are frequently complex and multi-layered, making it easy to confuse symptoms with the underlying cause. To avoid this pitfall, it is critical to thoroughly understand the problem.
To begin, ask yourself some clarifying questions:
- What exactly is the issue?
- What are the problem’s symptoms or consequences?
- Who or what is impacted by the issue?
- When and where does the issue arise?
Answering these questions will assist you in determining the scope of the problem. However, simply describing the problem is not always sufficient; you must also identify the root cause. The root cause is the underlying cause of the problem and is usually the key to resolving it permanently.
Try asking “why” questions to find the root cause:
- What causes the problem?
- Why does it continue?
- Why does it have the effects that it does?
By repeatedly asking “ why ,” you’ll eventually get to the bottom of the problem. This is an important step in the problem-solving process because it ensures that you’re dealing with the root cause rather than just the symptoms.
Once you have a firm grasp on the issue, it is time to divide it into smaller, more manageable chunks. This makes tackling the problem easier and reduces the risk of becoming overwhelmed. For example, if you’re attempting to solve a complex business problem, you might divide it into smaller components like market research, product development, and sales strategies.
To summarise step 1, defining the problem is an important first step in effective problem-solving. You will be able to identify the root cause and break it down into manageable parts if you take the time to thoroughly understand the problem. This will prepare you for the next step in the problem-solving process, which is gathering information and brainstorming ideas.
Step 2 – Gather Information and Brainstorm Ideas

Gathering information and brainstorming ideas is the next step in effective problem solving. This entails researching the problem and relevant information, collaborating with others, and coming up with a variety of potential solutions. This increases your chances of finding the best solution to the problem.
Begin by researching the problem and relevant information. This could include reading articles, conducting surveys, or consulting with experts. The goal is to collect as much information as possible in order to better understand the problem and possible solutions.
Next, work with others to gather a variety of perspectives. Brainstorming with others can be an excellent way to come up with new and creative ideas. Encourage everyone to share their thoughts and ideas when working in a group, and make an effort to actively listen to what others have to say. Be open to new and unconventional ideas and resist the urge to dismiss them too quickly.
Finally, use brainstorming to generate a wide range of potential solutions. This is the place where you can let your imagination run wild. At this stage, don’t worry about the feasibility or practicality of the solutions; instead, focus on generating as many ideas as possible. Write down everything that comes to mind, no matter how ridiculous or unusual it may appear. This can be done individually or in groups.
Once you’ve compiled a list of potential solutions, it’s time to assess them and select the best one. This is the next step in the problem-solving process, which we’ll go over in greater detail in the following section.
Step 3 – Evaluate Options and Choose the Best Solution
Once you’ve compiled a list of potential solutions, it’s time to assess them and select the best one. This is the third step in effective problem solving, and it entails weighing the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, considering their feasibility and practicability, and selecting the solution that is most likely to solve the problem effectively.
To begin, weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each solution. This will assist you in determining the potential outcomes of each solution and deciding which is the best option. For example, a quick and easy solution may not be the most effective in the long run, whereas a more complex and time-consuming solution may be more effective in solving the problem in the long run.
Consider each solution’s feasibility and practicability. Consider the following:
- Can the solution be implemented within the available resources, time, and budget?
- What are the possible barriers to implementing the solution?
- Is the solution feasible in today’s political, economic, and social environment?
You’ll be able to tell which solutions are likely to succeed and which aren’t by assessing their feasibility and practicability.
Finally, choose the solution that is most likely to effectively solve the problem. This solution should be based on the criteria you’ve established, such as the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, their feasibility and practicability, and your overall goals.
It is critical to remember that there is no one-size-fits-all solution to problems. What is effective for one person or situation may not be effective for another. This is why it is critical to consider a wide range of solutions and evaluate each one based on its ability to effectively solve the problem.
Step 4 – Implement and Monitor the Solution

When you’ve decided on the best solution, it’s time to put it into action. The fourth and final step in effective problem solving is to put the solution into action, monitor its progress, and make any necessary adjustments.
To begin, implement the solution. This may entail delegating tasks, developing a strategy, and allocating resources. Ascertain that everyone involved understands their role and responsibilities in the solution’s implementation.
Next, keep an eye on the solution’s progress. This may entail scheduling regular check-ins, tracking metrics, and soliciting feedback from others. You will be able to identify any potential roadblocks and make any necessary adjustments in a timely manner if you monitor the progress of the solution.
Finally, make any necessary modifications to the solution. This could entail changing the solution, altering the plan of action, or delegating different tasks. Be willing to make changes if they will improve the solution or help it solve the problem more effectively.
It’s important to remember that problem solving is an iterative process, and there may be times when you need to start from scratch. This is especially true if the initial solution does not effectively solve the problem. In these situations, it’s critical to be adaptable and flexible and to keep trying new solutions until you find the one that works best.
To summarise, effective problem solving is a critical skill that can assist individuals and organisations in overcoming challenges and achieving their objectives. Effective problem solving consists of four key steps: defining the problem, generating potential solutions, evaluating alternatives and selecting the best solution, and implementing the solution.
You can increase your chances of success in problem solving by following these steps and considering factors such as the pros and cons of each solution, their feasibility and practicability, and making any necessary adjustments. Furthermore, keep in mind that problem solving is an iterative process, and there may be times when you need to go back to the beginning and restart. Maintain your adaptability and try new solutions until you find the one that works best for you.
- Novick, L.R. and Bassok, M., 2005. Problem Solving . Cambridge University Press.

Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is a seasoned continuous improvement manager with a Black Belt in Lean Six Sigma. With over 10 years of real-world application experience across diverse sectors, Daniel has a passion for optimizing processes and fostering a culture of efficiency. He's not just a practitioner but also an avid learner, constantly seeking to expand his knowledge. Outside of his professional life, Daniel has a keen Investing, statistics and knowledge-sharing, which led him to create the website learnleansigma.com, a platform dedicated to Lean Six Sigma and process improvement insights.

Reverse Brainstorming: A Fresh Approach to Problem Solving
Standard Work Instructions
Free lean six sigma templates.
Improve your Lean Six Sigma projects with our free templates. They're designed to make implementation and management easier, helping you achieve better results.

5S Floor Marking Best Practices
In lean manufacturing, the 5S System is a foundational tool, involving the steps: Sort, Set…
How to Measure the ROI of Continuous Improvement Initiatives
When it comes to business, knowing the value you’re getting for your money is crucial,…
8D Problem-Solving: Common Mistakes to Avoid
In today’s competitive business landscape, effective problem-solving is the cornerstone of organizational success. The 8D…
The Evolution of 8D Problem-Solving: From Basics to Excellence
In a world where efficiency and effectiveness are more than just buzzwords, the need for…
8D: Tools and Techniques
Are you grappling with recurring problems in your organization and searching for a structured way…
How to Select the Right Lean Six Sigma Projects: A Comprehensive Guide
Going on a Lean Six Sigma journey is an invigorating experience filled with opportunities for…
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support

Overview of the Problem-Solving Mental Process
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Rachel Goldman, PhD FTOS, is a licensed psychologist, clinical assistant professor, speaker, wellness expert specializing in eating behaviors, stress management, and health behavior change.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Rachel-Goldman-1000-a42451caacb6423abecbe6b74e628042.jpg)
- Identify the Problem
- Define the Problem
- Form a Strategy
- Organize Information
- Allocate Resources
- Monitor Progress
- Evaluate the Results
Frequently Asked Questions
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue.
The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything they can about the issue and then using factual knowledge to come up with a solution. In other instances, creativity and insight are the best options.
It is not necessary to follow problem-solving steps sequentially, It is common to skip steps or even go back through steps multiple times until the desired solution is reached.
In order to correctly solve a problem, it is often important to follow a series of steps. Researchers sometimes refer to this as the problem-solving cycle. While this cycle is portrayed sequentially, people rarely follow a rigid series of steps to find a solution.
The following steps include developing strategies and organizing knowledge.
1. Identifying the Problem
While it may seem like an obvious step, identifying the problem is not always as simple as it sounds. In some cases, people might mistakenly identify the wrong source of a problem, which will make attempts to solve it inefficient or even useless.
Some strategies that you might use to figure out the source of a problem include :
- Asking questions about the problem
- Breaking the problem down into smaller pieces
- Looking at the problem from different perspectives
- Conducting research to figure out what relationships exist between different variables
2. Defining the Problem
After the problem has been identified, it is important to fully define the problem so that it can be solved. You can define a problem by operationally defining each aspect of the problem and setting goals for what aspects of the problem you will address
At this point, you should focus on figuring out which aspects of the problems are facts and which are opinions. State the problem clearly and identify the scope of the solution.
3. Forming a Strategy
After the problem has been identified, it is time to start brainstorming potential solutions. This step usually involves generating as many ideas as possible without judging their quality. Once several possibilities have been generated, they can be evaluated and narrowed down.
The next step is to develop a strategy to solve the problem. The approach used will vary depending upon the situation and the individual's unique preferences. Common problem-solving strategies include heuristics and algorithms.
- Heuristics are mental shortcuts that are often based on solutions that have worked in the past. They can work well if the problem is similar to something you have encountered before and are often the best choice if you need a fast solution.
- Algorithms are step-by-step strategies that are guaranteed to produce a correct result. While this approach is great for accuracy, it can also consume time and resources.
Heuristics are often best used when time is of the essence, while algorithms are a better choice when a decision needs to be as accurate as possible.
4. Organizing Information
Before coming up with a solution, you need to first organize the available information. What do you know about the problem? What do you not know? The more information that is available the better prepared you will be to come up with an accurate solution.
When approaching a problem, it is important to make sure that you have all the data you need. Making a decision without adequate information can lead to biased or inaccurate results.
5. Allocating Resources
Of course, we don't always have unlimited money, time, and other resources to solve a problem. Before you begin to solve a problem, you need to determine how high priority it is.
If it is an important problem, it is probably worth allocating more resources to solving it. If, however, it is a fairly unimportant problem, then you do not want to spend too much of your available resources on coming up with a solution.
At this stage, it is important to consider all of the factors that might affect the problem at hand. This includes looking at the available resources, deadlines that need to be met, and any possible risks involved in each solution. After careful evaluation, a decision can be made about which solution to pursue.
6. Monitoring Progress
After selecting a problem-solving strategy, it is time to put the plan into action and see if it works. This step might involve trying out different solutions to see which one is the most effective.
It is also important to monitor the situation after implementing a solution to ensure that the problem has been solved and that no new problems have arisen as a result of the proposed solution.
Effective problem-solvers tend to monitor their progress as they work towards a solution. If they are not making good progress toward reaching their goal, they will reevaluate their approach or look for new strategies .
7. Evaluating the Results
After a solution has been reached, it is important to evaluate the results to determine if it is the best possible solution to the problem. This evaluation might be immediate, such as checking the results of a math problem to ensure the answer is correct, or it can be delayed, such as evaluating the success of a therapy program after several months of treatment.
Once a problem has been solved, it is important to take some time to reflect on the process that was used and evaluate the results. This will help you to improve your problem-solving skills and become more efficient at solving future problems.
A Word From Verywell
It is important to remember that there are many different problem-solving processes with different steps, and this is just one example. Problem-solving in real-world situations requires a great deal of resourcefulness, flexibility, resilience, and continuous interaction with the environment.
Get Advice From The Verywell Mind Podcast
Hosted by therapist Amy Morin, LCSW, this episode of The Verywell Mind Podcast shares how you can stop dwelling in a negative mindset.
Follow Now : Apple Podcasts / Spotify / Google Podcasts
You can become a better problem solving by:
- Practicing brainstorming and coming up with multiple potential solutions to problems
- Being open-minded and considering all possible options before making a decision
- Breaking down problems into smaller, more manageable pieces
- Asking for help when needed
- Researching different problem-solving techniques and trying out new ones
- Learning from mistakes and using them as opportunities to grow
It's important to communicate openly and honestly with your partner about what's going on. Try to see things from their perspective as well as your own. Work together to find a resolution that works for both of you. Be willing to compromise and accept that there may not be a perfect solution.
Take breaks if things are getting too heated, and come back to the problem when you feel calm and collected. Don't try to fix every problem on your own—consider asking a therapist or counselor for help and insight.
If you've tried everything and there doesn't seem to be a way to fix the problem, you may have to learn to accept it. This can be difficult, but try to focus on the positive aspects of your life and remember that every situation is temporary. Don't dwell on what's going wrong—instead, think about what's going right. Find support by talking to friends or family. Seek professional help if you're having trouble coping.
Davidson JE, Sternberg RJ, editors. The Psychology of Problem Solving . Cambridge University Press; 2003. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511615771
Sarathy V. Real world problem-solving . Front Hum Neurosci . 2018;12:261. Published 2018 Jun 26. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
35 problem-solving techniques and methods for solving complex problems

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation.
All teams and organizations encounter challenges as they grow. There are problems that might occur for teams when it comes to miscommunication or resolving business-critical issues . You may face challenges around growth , design , user engagement, and even team culture and happiness. In short, problem-solving techniques should be part of every team’s skillset.
Problem-solving methods are primarily designed to help a group or team through a process of first identifying problems and challenges , ideating possible solutions , and then evaluating the most suitable .
Finding effective solutions to complex problems isn’t easy, but by using the right process and techniques, you can help your team be more efficient in the process.
So how do you develop strategies that are engaging, and empower your team to solve problems effectively?
In this blog post, we share a series of problem-solving tools you can use in your next workshop or team meeting. You’ll also find some tips for facilitating the process and how to enable others to solve complex problems.
Let’s get started!
How do you identify problems?
How do you identify the right solution.
- Tips for more effective problem-solving
Complete problem-solving methods
- Problem-solving techniques to identify and analyze problems
- Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
Problem-solving warm-up activities
Closing activities for a problem-solving process.
Before you can move towards finding the right solution for a given problem, you first need to identify and define the problem you wish to solve.
Here, you want to clearly articulate what the problem is and allow your group to do the same. Remember that everyone in a group is likely to have differing perspectives and alignment is necessary in order to help the group move forward.
Identifying a problem accurately also requires that all members of a group are able to contribute their views in an open and safe manner. It can be scary for people to stand up and contribute, especially if the problems or challenges are emotive or personal in nature. Be sure to try and create a psychologically safe space for these kinds of discussions.
Remember that problem analysis and further discussion are also important. Not taking the time to fully analyze and discuss a challenge can result in the development of solutions that are not fit for purpose or do not address the underlying issue.
Successfully identifying and then analyzing a problem means facilitating a group through activities designed to help them clearly and honestly articulate their thoughts and produce usable insight.
With this data, you might then produce a problem statement that clearly describes the problem you wish to be addressed and also state the goal of any process you undertake to tackle this issue.
Finding solutions is the end goal of any process. Complex organizational challenges can only be solved with an appropriate solution but discovering them requires using the right problem-solving tool.
After you’ve explored a problem and discussed ideas, you need to help a team discuss and choose the right solution. Consensus tools and methods such as those below help a group explore possible solutions before then voting for the best. They’re a great way to tap into the collective intelligence of the group for great results!
Remember that the process is often iterative. Great problem solvers often roadtest a viable solution in a measured way to see what works too. While you might not get the right solution on your first try, the methods below help teams land on the most likely to succeed solution while also holding space for improvement.
Every effective problem solving process begins with an agenda . A well-structured workshop is one of the best methods for successfully guiding a group from exploring a problem to implementing a solution.
In SessionLab, it’s easy to go from an idea to a complete agenda . Start by dragging and dropping your core problem solving activities into place . Add timings, breaks and necessary materials before sharing your agenda with your colleagues.
The resulting agenda will be your guide to an effective and productive problem solving session that will also help you stay organized on the day!
Tips for more effective problem solving
Problem-solving activities are only one part of the puzzle. While a great method can help unlock your team’s ability to solve problems, without a thoughtful approach and strong facilitation the solutions may not be fit for purpose.
Let’s take a look at some problem-solving tips you can apply to any process to help it be a success!
Clearly define the problem
Jumping straight to solutions can be tempting, though without first clearly articulating a problem, the solution might not be the right one. Many of the problem-solving activities below include sections where the problem is explored and clearly defined before moving on.
This is a vital part of the problem-solving process and taking the time to fully define an issue can save time and effort later. A clear definition helps identify irrelevant information and it also ensures that your team sets off on the right track.
Don’t jump to conclusions
It’s easy for groups to exhibit cognitive bias or have preconceived ideas about both problems and potential solutions. Be sure to back up any problem statements or potential solutions with facts, research, and adequate forethought.
The best techniques ask participants to be methodical and challenge preconceived notions. Make sure you give the group enough time and space to collect relevant information and consider the problem in a new way. By approaching the process with a clear, rational mindset, you’ll often find that better solutions are more forthcoming.
Try different approaches
Problems come in all shapes and sizes and so too should the methods you use to solve them. If you find that one approach isn’t yielding results and your team isn’t finding different solutions, try mixing it up. You’ll be surprised at how using a new creative activity can unblock your team and generate great solutions.
Don’t take it personally
Depending on the nature of your team or organizational problems, it’s easy for conversations to get heated. While it’s good for participants to be engaged in the discussions, ensure that emotions don’t run too high and that blame isn’t thrown around while finding solutions.
You’re all in it together, and even if your team or area is seeing problems, that isn’t necessarily a disparagement of you personally. Using facilitation skills to manage group dynamics is one effective method of helping conversations be more constructive.
Get the right people in the room
Your problem-solving method is often only as effective as the group using it. Getting the right people on the job and managing the number of people present is important too!
If the group is too small, you may not get enough different perspectives to effectively solve a problem. If the group is too large, you can go round and round during the ideation stages.
Creating the right group makeup is also important in ensuring you have the necessary expertise and skillset to both identify and follow up on potential solutions. Carefully consider who to include at each stage to help ensure your problem-solving method is followed and positioned for success.
Document everything
The best solutions can take refinement, iteration, and reflection to come out. Get into a habit of documenting your process in order to keep all the learnings from the session and to allow ideas to mature and develop. Many of the methods below involve the creation of documents or shared resources. Be sure to keep and share these so everyone can benefit from the work done!
Bring a facilitator
Facilitation is all about making group processes easier. With a subject as potentially emotive and important as problem-solving, having an impartial third party in the form of a facilitator can make all the difference in finding great solutions and keeping the process moving. Consider bringing a facilitator to your problem-solving session to get better results and generate meaningful solutions!
Develop your problem-solving skills
It takes time and practice to be an effective problem solver. While some roles or participants might more naturally gravitate towards problem-solving, it can take development and planning to help everyone create better solutions.
You might develop a training program, run a problem-solving workshop or simply ask your team to practice using the techniques below. Check out our post on problem-solving skills to see how you and your group can develop the right mental process and be more resilient to issues too!
Design a great agenda
Workshops are a great format for solving problems. With the right approach, you can focus a group and help them find the solutions to their own problems. But designing a process can be time-consuming and finding the right activities can be difficult.
Check out our workshop planning guide to level-up your agenda design and start running more effective workshops. Need inspiration? Check out templates designed by expert facilitators to help you kickstart your process!
In this section, we’ll look at in-depth problem-solving methods that provide a complete end-to-end process for developing effective solutions. These will help guide your team from the discovery and definition of a problem through to delivering the right solution.
If you’re looking for an all-encompassing method or problem-solving model, these processes are a great place to start. They’ll ask your team to challenge preconceived ideas and adopt a mindset for solving problems more effectively.
- Six Thinking Hats
- Lightning Decision Jam
- Problem Definition Process
- Discovery & Action Dialogue
Design Sprint 2.0
- Open Space Technology
1. Six Thinking Hats
Individual approaches to solving a problem can be very different based on what team or role an individual holds. It can be easy for existing biases or perspectives to find their way into the mix, or for internal politics to direct a conversation.
Six Thinking Hats is a classic method for identifying the problems that need to be solved and enables your team to consider them from different angles, whether that is by focusing on facts and data, creative solutions, or by considering why a particular solution might not work.
Like all problem-solving frameworks, Six Thinking Hats is effective at helping teams remove roadblocks from a conversation or discussion and come to terms with all the aspects necessary to solve complex problems.
2. Lightning Decision Jam
Featured courtesy of Jonathan Courtney of AJ&Smart Berlin, Lightning Decision Jam is one of those strategies that should be in every facilitation toolbox. Exploring problems and finding solutions is often creative in nature, though as with any creative process, there is the potential to lose focus and get lost.
Unstructured discussions might get you there in the end, but it’s much more effective to use a method that creates a clear process and team focus.
In Lightning Decision Jam, participants are invited to begin by writing challenges, concerns, or mistakes on post-its without discussing them before then being invited by the moderator to present them to the group.
From there, the team vote on which problems to solve and are guided through steps that will allow them to reframe those problems, create solutions and then decide what to execute on.
By deciding the problems that need to be solved as a team before moving on, this group process is great for ensuring the whole team is aligned and can take ownership over the next stages.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
3. Problem Definition Process
While problems can be complex, the problem-solving methods you use to identify and solve those problems can often be simple in design.
By taking the time to truly identify and define a problem before asking the group to reframe the challenge as an opportunity, this method is a great way to enable change.
Begin by identifying a focus question and exploring the ways in which it manifests before splitting into five teams who will each consider the problem using a different method: escape, reversal, exaggeration, distortion or wishful. Teams develop a problem objective and create ideas in line with their method before then feeding them back to the group.
This method is great for enabling in-depth discussions while also creating space for finding creative solutions too!
Problem Definition #problem solving #idea generation #creativity #online #remote-friendly A problem solving technique to define a problem, challenge or opportunity and to generate ideas.
4. The 5 Whys
Sometimes, a group needs to go further with their strategies and analyze the root cause at the heart of organizational issues. An RCA or root cause analysis is the process of identifying what is at the heart of business problems or recurring challenges.
The 5 Whys is a simple and effective method of helping a group go find the root cause of any problem or challenge and conduct analysis that will deliver results.
By beginning with the creation of a problem statement and going through five stages to refine it, The 5 Whys provides everything you need to truly discover the cause of an issue.
The 5 Whys #hyperisland #innovation This simple and powerful method is useful for getting to the core of a problem or challenge. As the title suggests, the group defines a problems, then asks the question “why” five times, often using the resulting explanation as a starting point for creative problem solving.
5. World Cafe
World Cafe is a simple but powerful facilitation technique to help bigger groups to focus their energy and attention on solving complex problems.
World Cafe enables this approach by creating a relaxed atmosphere where participants are able to self-organize and explore topics relevant and important to them which are themed around a central problem-solving purpose. Create the right atmosphere by modeling your space after a cafe and after guiding the group through the method, let them take the lead!
Making problem-solving a part of your organization’s culture in the long term can be a difficult undertaking. More approachable formats like World Cafe can be especially effective in bringing people unfamiliar with workshops into the fold.
World Cafe #hyperisland #innovation #issue analysis World Café is a simple yet powerful method, originated by Juanita Brown, for enabling meaningful conversations driven completely by participants and the topics that are relevant and important to them. Facilitators create a cafe-style space and provide simple guidelines. Participants then self-organize and explore a set of relevant topics or questions for conversation.
6. Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD)
One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions.
With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so. It’s great at helping remove resistance to change and can help get buy-in at every level too!
This process of enabling frontline ownership is great in ensuring follow-through and is one of the methods you will want in your toolbox as a facilitator.
Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) #idea generation #liberating structures #action #issue analysis #remote-friendly DADs make it easy for a group or community to discover practices and behaviors that enable some individuals (without access to special resources and facing the same constraints) to find better solutions than their peers to common problems. These are called positive deviant (PD) behaviors and practices. DADs make it possible for people in the group, unit, or community to discover by themselves these PD practices. DADs also create favorable conditions for stimulating participants’ creativity in spaces where they can feel safe to invent new and more effective practices. Resistance to change evaporates as participants are unleashed to choose freely which practices they will adopt or try and which problems they will tackle. DADs make it possible to achieve frontline ownership of solutions.
7. Design Sprint 2.0
Want to see how a team can solve big problems and move forward with prototyping and testing solutions in a few days? The Design Sprint 2.0 template from Jake Knapp, author of Sprint, is a complete agenda for a with proven results.
Developing the right agenda can involve difficult but necessary planning. Ensuring all the correct steps are followed can also be stressful or time-consuming depending on your level of experience.
Use this complete 4-day workshop template if you are finding there is no obvious solution to your challenge and want to focus your team around a specific problem that might require a shortcut to launching a minimum viable product or waiting for the organization-wide implementation of a solution.
8. Open space technology
Open space technology- developed by Harrison Owen – creates a space where large groups are invited to take ownership of their problem solving and lead individual sessions. Open space technology is a great format when you have a great deal of expertise and insight in the room and want to allow for different takes and approaches on a particular theme or problem you need to be solved.
Start by bringing your participants together to align around a central theme and focus their efforts. Explain the ground rules to help guide the problem-solving process and then invite members to identify any issue connecting to the central theme that they are interested in and are prepared to take responsibility for.
Once participants have decided on their approach to the core theme, they write their issue on a piece of paper, announce it to the group, pick a session time and place, and post the paper on the wall. As the wall fills up with sessions, the group is then invited to join the sessions that interest them the most and which they can contribute to, then you’re ready to begin!
Everyone joins the problem-solving group they’ve signed up to, record the discussion and if appropriate, findings can then be shared with the rest of the group afterward.
Open Space Technology #action plan #idea generation #problem solving #issue analysis #large group #online #remote-friendly Open Space is a methodology for large groups to create their agenda discerning important topics for discussion, suitable for conferences, community gatherings and whole system facilitation
Techniques to identify and analyze problems
Using a problem-solving method to help a team identify and analyze a problem can be a quick and effective addition to any workshop or meeting.
While further actions are always necessary, you can generate momentum and alignment easily, and these activities are a great place to get started.
We’ve put together this list of techniques to help you and your team with problem identification, analysis, and discussion that sets the foundation for developing effective solutions.
Let’s take a look!
- The Creativity Dice
- Fishbone Analysis
- Problem Tree
- SWOT Analysis
- Agreement-Certainty Matrix
- The Journalistic Six
- LEGO Challenge
- What, So What, Now What?
- Journalists
Individual and group perspectives are incredibly important, but what happens if people are set in their minds and need a change of perspective in order to approach a problem more effectively?
Flip It is a method we love because it is both simple to understand and run, and allows groups to understand how their perspectives and biases are formed.
Participants in Flip It are first invited to consider concerns, issues, or problems from a perspective of fear and write them on a flip chart. Then, the group is asked to consider those same issues from a perspective of hope and flip their understanding.
No problem and solution is free from existing bias and by changing perspectives with Flip It, you can then develop a problem solving model quickly and effectively.
Flip It! #gamestorming #problem solving #action Often, a change in a problem or situation comes simply from a change in our perspectives. Flip It! is a quick game designed to show players that perspectives are made, not born.
10. The Creativity Dice
One of the most useful problem solving skills you can teach your team is of approaching challenges with creativity, flexibility, and openness. Games like The Creativity Dice allow teams to overcome the potential hurdle of too much linear thinking and approach the process with a sense of fun and speed.
In The Creativity Dice, participants are organized around a topic and roll a dice to determine what they will work on for a period of 3 minutes at a time. They might roll a 3 and work on investigating factual information on the chosen topic. They might roll a 1 and work on identifying the specific goals, standards, or criteria for the session.
Encouraging rapid work and iteration while asking participants to be flexible are great skills to cultivate. Having a stage for idea incubation in this game is also important. Moments of pause can help ensure the ideas that are put forward are the most suitable.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
11. Fishbone Analysis
Organizational or team challenges are rarely simple, and it’s important to remember that one problem can be an indication of something that goes deeper and may require further consideration to be solved.
Fishbone Analysis helps groups to dig deeper and understand the origins of a problem. It’s a great example of a root cause analysis method that is simple for everyone on a team to get their head around.
Participants in this activity are asked to annotate a diagram of a fish, first adding the problem or issue to be worked on at the head of a fish before then brainstorming the root causes of the problem and adding them as bones on the fish.
Using abstractions such as a diagram of a fish can really help a team break out of their regular thinking and develop a creative approach.
Fishbone Analysis #problem solving ##root cause analysis #decision making #online facilitation A process to help identify and understand the origins of problems, issues or observations.
12. Problem Tree
Encouraging visual thinking can be an essential part of many strategies. By simply reframing and clarifying problems, a group can move towards developing a problem solving model that works for them.
In Problem Tree, groups are asked to first brainstorm a list of problems – these can be design problems, team problems or larger business problems – and then organize them into a hierarchy. The hierarchy could be from most important to least important or abstract to practical, though the key thing with problem solving games that involve this aspect is that your group has some way of managing and sorting all the issues that are raised.
Once you have a list of problems that need to be solved and have organized them accordingly, you’re then well-positioned for the next problem solving steps.
Problem tree #define intentions #create #design #issue analysis A problem tree is a tool to clarify the hierarchy of problems addressed by the team within a design project; it represents high level problems or related sublevel problems.
13. SWOT Analysis
Chances are you’ve heard of the SWOT Analysis before. This problem-solving method focuses on identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is a tried and tested method for both individuals and teams.
Start by creating a desired end state or outcome and bare this in mind – any process solving model is made more effective by knowing what you are moving towards. Create a quadrant made up of the four categories of a SWOT analysis and ask participants to generate ideas based on each of those quadrants.
Once you have those ideas assembled in their quadrants, cluster them together based on their affinity with other ideas. These clusters are then used to facilitate group conversations and move things forward.
SWOT analysis #gamestorming #problem solving #action #meeting facilitation The SWOT Analysis is a long-standing technique of looking at what we have, with respect to the desired end state, as well as what we could improve on. It gives us an opportunity to gauge approaching opportunities and dangers, and assess the seriousness of the conditions that affect our future. When we understand those conditions, we can influence what comes next.
14. Agreement-Certainty Matrix
Not every problem-solving approach is right for every challenge, and deciding on the right method for the challenge at hand is a key part of being an effective team.
The Agreement Certainty matrix helps teams align on the nature of the challenges facing them. By sorting problems from simple to chaotic, your team can understand what methods are suitable for each problem and what they can do to ensure effective results.
If you are already using Liberating Structures techniques as part of your problem-solving strategy, the Agreement-Certainty Matrix can be an invaluable addition to your process. We’ve found it particularly if you are having issues with recurring problems in your organization and want to go deeper in understanding the root cause.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Organizing and charting a team’s progress can be important in ensuring its success. SQUID (Sequential Question and Insight Diagram) is a great model that allows a team to effectively switch between giving questions and answers and develop the skills they need to stay on track throughout the process.
Begin with two different colored sticky notes – one for questions and one for answers – and with your central topic (the head of the squid) on the board. Ask the group to first come up with a series of questions connected to their best guess of how to approach the topic. Ask the group to come up with answers to those questions, fix them to the board and connect them with a line. After some discussion, go back to question mode by responding to the generated answers or other points on the board.
It’s rewarding to see a diagram grow throughout the exercise, and a completed SQUID can provide a visual resource for future effort and as an example for other teams.
SQUID #gamestorming #project planning #issue analysis #problem solving When exploring an information space, it’s important for a group to know where they are at any given time. By using SQUID, a group charts out the territory as they go and can navigate accordingly. SQUID stands for Sequential Question and Insight Diagram.
16. Speed Boat
To continue with our nautical theme, Speed Boat is a short and sweet activity that can help a team quickly identify what employees, clients or service users might have a problem with and analyze what might be standing in the way of achieving a solution.
Methods that allow for a group to make observations, have insights and obtain those eureka moments quickly are invaluable when trying to solve complex problems.
In Speed Boat, the approach is to first consider what anchors and challenges might be holding an organization (or boat) back. Bonus points if you are able to identify any sharks in the water and develop ideas that can also deal with competitors!
Speed Boat #gamestorming #problem solving #action Speedboat is a short and sweet way to identify what your employees or clients don’t like about your product/service or what’s standing in the way of a desired goal.
17. The Journalistic Six
Some of the most effective ways of solving problems is by encouraging teams to be more inclusive and diverse in their thinking.
Based on the six key questions journalism students are taught to answer in articles and news stories, The Journalistic Six helps create teams to see the whole picture. By using who, what, when, where, why, and how to facilitate the conversation and encourage creative thinking, your team can make sure that the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the are covered exhaustively and thoughtfully. Reporter’s notebook and dictaphone optional.
The Journalistic Six – Who What When Where Why How #idea generation #issue analysis #problem solving #online #creative thinking #remote-friendly A questioning method for generating, explaining, investigating ideas.
18. LEGO Challenge
Now for an activity that is a little out of the (toy) box. LEGO Serious Play is a facilitation methodology that can be used to improve creative thinking and problem-solving skills.
The LEGO Challenge includes giving each member of the team an assignment that is hidden from the rest of the group while they create a structure without speaking.
What the LEGO challenge brings to the table is a fun working example of working with stakeholders who might not be on the same page to solve problems. Also, it’s LEGO! Who doesn’t love LEGO!
LEGO Challenge #hyperisland #team A team-building activity in which groups must work together to build a structure out of LEGO, but each individual has a secret “assignment” which makes the collaborative process more challenging. It emphasizes group communication, leadership dynamics, conflict, cooperation, patience and problem solving strategy.
19. What, So What, Now What?
If not carefully managed, the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the problem-solving process can actually create more problems and misunderstandings.
The What, So What, Now What? problem-solving activity is designed to help collect insights and move forward while also eliminating the possibility of disagreement when it comes to identifying, clarifying, and analyzing organizational or work problems.
Facilitation is all about bringing groups together so that might work on a shared goal and the best problem-solving strategies ensure that teams are aligned in purpose, if not initially in opinion or insight.
Throughout the three steps of this game, you give everyone on a team to reflect on a problem by asking what happened, why it is important, and what actions should then be taken.
This can be a great activity for bringing our individual perceptions about a problem or challenge and contextualizing it in a larger group setting. This is one of the most important problem-solving skills you can bring to your organization.
W³ – What, So What, Now What? #issue analysis #innovation #liberating structures You can help groups reflect on a shared experience in a way that builds understanding and spurs coordinated action while avoiding unproductive conflict. It is possible for every voice to be heard while simultaneously sifting for insights and shaping new direction. Progressing in stages makes this practical—from collecting facts about What Happened to making sense of these facts with So What and finally to what actions logically follow with Now What . The shared progression eliminates most of the misunderstandings that otherwise fuel disagreements about what to do. Voila!
20. Journalists
Problem analysis can be one of the most important and decisive stages of all problem-solving tools. Sometimes, a team can become bogged down in the details and are unable to move forward.
Journalists is an activity that can avoid a group from getting stuck in the problem identification or problem analysis stages of the process.
In Journalists, the group is invited to draft the front page of a fictional newspaper and figure out what stories deserve to be on the cover and what headlines those stories will have. By reframing how your problems and challenges are approached, you can help a team move productively through the process and be better prepared for the steps to follow.
Journalists #vision #big picture #issue analysis #remote-friendly This is an exercise to use when the group gets stuck in details and struggles to see the big picture. Also good for defining a vision.
Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
The success of any problem-solving process can be measured by the solutions it produces. After you’ve defined the issue, explored existing ideas, and ideated, it’s time to narrow down to the correct solution.
Use these problem-solving techniques when you want to help your team find consensus, compare possible solutions, and move towards taking action on a particular problem.
- Improved Solutions
- Four-Step Sketch
- 15% Solutions
- How-Now-Wow matrix
- Impact Effort Matrix
21. Mindspin
Brainstorming is part of the bread and butter of the problem-solving process and all problem-solving strategies benefit from getting ideas out and challenging a team to generate solutions quickly.
With Mindspin, participants are encouraged not only to generate ideas but to do so under time constraints and by slamming down cards and passing them on. By doing multiple rounds, your team can begin with a free generation of possible solutions before moving on to developing those solutions and encouraging further ideation.
This is one of our favorite problem-solving activities and can be great for keeping the energy up throughout the workshop. Remember the importance of helping people become engaged in the process – energizing problem-solving techniques like Mindspin can help ensure your team stays engaged and happy, even when the problems they’re coming together to solve are complex.
MindSpin #teampedia #idea generation #problem solving #action A fast and loud method to enhance brainstorming within a team. Since this activity has more than round ideas that are repetitive can be ruled out leaving more creative and innovative answers to the challenge.
22. Improved Solutions
After a team has successfully identified a problem and come up with a few solutions, it can be tempting to call the work of the problem-solving process complete. That said, the first solution is not necessarily the best, and by including a further review and reflection activity into your problem-solving model, you can ensure your group reaches the best possible result.
One of a number of problem-solving games from Thiagi Group, Improved Solutions helps you go the extra mile and develop suggested solutions with close consideration and peer review. By supporting the discussion of several problems at once and by shifting team roles throughout, this problem-solving technique is a dynamic way of finding the best solution.
Improved Solutions #creativity #thiagi #problem solving #action #team You can improve any solution by objectively reviewing its strengths and weaknesses and making suitable adjustments. In this creativity framegame, you improve the solutions to several problems. To maintain objective detachment, you deal with a different problem during each of six rounds and assume different roles (problem owner, consultant, basher, booster, enhancer, and evaluator) during each round. At the conclusion of the activity, each player ends up with two solutions to her problem.
23. Four Step Sketch
Creative thinking and visual ideation does not need to be confined to the opening stages of your problem-solving strategies. Exercises that include sketching and prototyping on paper can be effective at the solution finding and development stage of the process, and can be great for keeping a team engaged.
By going from simple notes to a crazy 8s round that involves rapidly sketching 8 variations on their ideas before then producing a final solution sketch, the group is able to iterate quickly and visually. Problem-solving techniques like Four-Step Sketch are great if you have a group of different thinkers and want to change things up from a more textual or discussion-based approach.
Four-Step Sketch #design sprint #innovation #idea generation #remote-friendly The four-step sketch is an exercise that helps people to create well-formed concepts through a structured process that includes: Review key information Start design work on paper, Consider multiple variations , Create a detailed solution . This exercise is preceded by a set of other activities allowing the group to clarify the challenge they want to solve. See how the Four Step Sketch exercise fits into a Design Sprint
24. 15% Solutions
Some problems are simpler than others and with the right problem-solving activities, you can empower people to take immediate actions that can help create organizational change.
Part of the liberating structures toolkit, 15% solutions is a problem-solving technique that focuses on finding and implementing solutions quickly. A process of iterating and making small changes quickly can help generate momentum and an appetite for solving complex problems.
Problem-solving strategies can live and die on whether people are onboard. Getting some quick wins is a great way of getting people behind the process.
It can be extremely empowering for a team to realize that problem-solving techniques can be deployed quickly and easily and delineate between things they can positively impact and those things they cannot change.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
25. How-Now-Wow Matrix
The problem-solving process is often creative, as complex problems usually require a change of thinking and creative response in order to find the best solutions. While it’s common for the first stages to encourage creative thinking, groups can often gravitate to familiar solutions when it comes to the end of the process.
When selecting solutions, you don’t want to lose your creative energy! The How-Now-Wow Matrix from Gamestorming is a great problem-solving activity that enables a group to stay creative and think out of the box when it comes to selecting the right solution for a given problem.
Problem-solving techniques that encourage creative thinking and the ideation and selection of new solutions can be the most effective in organisational change. Give the How-Now-Wow Matrix a go, and not just for how pleasant it is to say out loud.
How-Now-Wow Matrix #gamestorming #idea generation #remote-friendly When people want to develop new ideas, they most often think out of the box in the brainstorming or divergent phase. However, when it comes to convergence, people often end up picking ideas that are most familiar to them. This is called a ‘creative paradox’ or a ‘creadox’. The How-Now-Wow matrix is an idea selection tool that breaks the creadox by forcing people to weigh each idea on 2 parameters.
26. Impact and Effort Matrix
All problem-solving techniques hope to not only find solutions to a given problem or challenge but to find the best solution. When it comes to finding a solution, groups are invited to put on their decision-making hats and really think about how a proposed idea would work in practice.
The Impact and Effort Matrix is one of the problem-solving techniques that fall into this camp, empowering participants to first generate ideas and then categorize them into a 2×2 matrix based on impact and effort.
Activities that invite critical thinking while remaining simple are invaluable. Use the Impact and Effort Matrix to move from ideation and towards evaluating potential solutions before then committing to them.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
27. Dotmocracy
If you’ve followed each of the problem-solving steps with your group successfully, you should move towards the end of your process with heaps of possible solutions developed with a specific problem in mind. But how do you help a group go from ideation to putting a solution into action?
Dotmocracy – or Dot Voting -is a tried and tested method of helping a team in the problem-solving process make decisions and put actions in place with a degree of oversight and consensus.
One of the problem-solving techniques that should be in every facilitator’s toolbox, Dot Voting is fast and effective and can help identify the most popular and best solutions and help bring a group to a decision effectively.
Dotmocracy #action #decision making #group prioritization #hyperisland #remote-friendly Dotmocracy is a simple method for group prioritization or decision-making. It is not an activity on its own, but a method to use in processes where prioritization or decision-making is the aim. The method supports a group to quickly see which options are most popular or relevant. The options or ideas are written on post-its and stuck up on a wall for the whole group to see. Each person votes for the options they think are the strongest, and that information is used to inform a decision.
All facilitators know that warm-ups and icebreakers are useful for any workshop or group process. Problem-solving workshops are no different.
Use these problem-solving techniques to warm up a group and prepare them for the rest of the process. Activating your group by tapping into some of the top problem-solving skills can be one of the best ways to see great outcomes from your session.
- Check-in/Check-out
- Doodling Together
- Show and Tell
- Constellations
- Draw a Tree
28. Check-in / Check-out
Solid processes are planned from beginning to end, and the best facilitators know that setting the tone and establishing a safe, open environment can be integral to a successful problem-solving process.
Check-in / Check-out is a great way to begin and/or bookend a problem-solving workshop. Checking in to a session emphasizes that everyone will be seen, heard, and expected to contribute.
If you are running a series of meetings, setting a consistent pattern of checking in and checking out can really help your team get into a groove. We recommend this opening-closing activity for small to medium-sized groups though it can work with large groups if they’re disciplined!
Check-in / Check-out #team #opening #closing #hyperisland #remote-friendly Either checking-in or checking-out is a simple way for a team to open or close a process, symbolically and in a collaborative way. Checking-in/out invites each member in a group to be present, seen and heard, and to express a reflection or a feeling. Checking-in emphasizes presence, focus and group commitment; checking-out emphasizes reflection and symbolic closure.
29. Doodling Together
Thinking creatively and not being afraid to make suggestions are important problem-solving skills for any group or team, and warming up by encouraging these behaviors is a great way to start.
Doodling Together is one of our favorite creative ice breaker games – it’s quick, effective, and fun and can make all following problem-solving steps easier by encouraging a group to collaborate visually. By passing cards and adding additional items as they go, the workshop group gets into a groove of co-creation and idea development that is crucial to finding solutions to problems.
Doodling Together #collaboration #creativity #teamwork #fun #team #visual methods #energiser #icebreaker #remote-friendly Create wild, weird and often funny postcards together & establish a group’s creative confidence.
30. Show and Tell
You might remember some version of Show and Tell from being a kid in school and it’s a great problem-solving activity to kick off a session.
Asking participants to prepare a little something before a workshop by bringing an object for show and tell can help them warm up before the session has even begun! Games that include a physical object can also help encourage early engagement before moving onto more big-picture thinking.
By asking your participants to tell stories about why they chose to bring a particular item to the group, you can help teams see things from new perspectives and see both differences and similarities in the way they approach a topic. Great groundwork for approaching a problem-solving process as a team!
Show and Tell #gamestorming #action #opening #meeting facilitation Show and Tell taps into the power of metaphors to reveal players’ underlying assumptions and associations around a topic The aim of the game is to get a deeper understanding of stakeholders’ perspectives on anything—a new project, an organizational restructuring, a shift in the company’s vision or team dynamic.
31. Constellations
Who doesn’t love stars? Constellations is a great warm-up activity for any workshop as it gets people up off their feet, energized, and ready to engage in new ways with established topics. It’s also great for showing existing beliefs, biases, and patterns that can come into play as part of your session.
Using warm-up games that help build trust and connection while also allowing for non-verbal responses can be great for easing people into the problem-solving process and encouraging engagement from everyone in the group. Constellations is great in large spaces that allow for movement and is definitely a practical exercise to allow the group to see patterns that are otherwise invisible.
Constellations #trust #connection #opening #coaching #patterns #system Individuals express their response to a statement or idea by standing closer or further from a central object. Used with teams to reveal system, hidden patterns, perspectives.
32. Draw a Tree
Problem-solving games that help raise group awareness through a central, unifying metaphor can be effective ways to warm-up a group in any problem-solving model.
Draw a Tree is a simple warm-up activity you can use in any group and which can provide a quick jolt of energy. Start by asking your participants to draw a tree in just 45 seconds – they can choose whether it will be abstract or realistic.
Once the timer is up, ask the group how many people included the roots of the tree and use this as a means to discuss how we can ignore important parts of any system simply because they are not visible.
All problem-solving strategies are made more effective by thinking of problems critically and by exposing things that may not normally come to light. Warm-up games like Draw a Tree are great in that they quickly demonstrate some key problem-solving skills in an accessible and effective way.
Draw a Tree #thiagi #opening #perspectives #remote-friendly With this game you can raise awarness about being more mindful, and aware of the environment we live in.
Each step of the problem-solving workshop benefits from an intelligent deployment of activities, games, and techniques. Bringing your session to an effective close helps ensure that solutions are followed through on and that you also celebrate what has been achieved.
Here are some problem-solving activities you can use to effectively close a workshop or meeting and ensure the great work you’ve done can continue afterward.
- One Breath Feedback
- Who What When Matrix
- Response Cards
How do I conclude a problem-solving process?
All good things must come to an end. With the bulk of the work done, it can be tempting to conclude your workshop swiftly and without a moment to debrief and align. This can be problematic in that it doesn’t allow your team to fully process the results or reflect on the process.
At the end of an effective session, your team will have gone through a process that, while productive, can be exhausting. It’s important to give your group a moment to take a breath, ensure that they are clear on future actions, and provide short feedback before leaving the space.
The primary purpose of any problem-solving method is to generate solutions and then implement them. Be sure to take the opportunity to ensure everyone is aligned and ready to effectively implement the solutions you produced in the workshop.
Remember that every process can be improved and by giving a short moment to collect feedback in the session, you can further refine your problem-solving methods and see further success in the future too.
33. One Breath Feedback
Maintaining attention and focus during the closing stages of a problem-solving workshop can be tricky and so being concise when giving feedback can be important. It’s easy to incur “death by feedback” should some team members go on for too long sharing their perspectives in a quick feedback round.
One Breath Feedback is a great closing activity for workshops. You give everyone an opportunity to provide feedback on what they’ve done but only in the space of a single breath. This keeps feedback short and to the point and means that everyone is encouraged to provide the most important piece of feedback to them.
One breath feedback #closing #feedback #action This is a feedback round in just one breath that excels in maintaining attention: each participants is able to speak during just one breath … for most people that’s around 20 to 25 seconds … unless of course you’ve been a deep sea diver in which case you’ll be able to do it for longer.
34. Who What When Matrix
Matrices feature as part of many effective problem-solving strategies and with good reason. They are easily recognizable, simple to use, and generate results.
The Who What When Matrix is a great tool to use when closing your problem-solving session by attributing a who, what and when to the actions and solutions you have decided upon. The resulting matrix is a simple, easy-to-follow way of ensuring your team can move forward.
Great solutions can’t be enacted without action and ownership. Your problem-solving process should include a stage for allocating tasks to individuals or teams and creating a realistic timeframe for those solutions to be implemented or checked out. Use this method to keep the solution implementation process clear and simple for all involved.
Who/What/When Matrix #gamestorming #action #project planning With Who/What/When matrix, you can connect people with clear actions they have defined and have committed to.
35. Response cards
Group discussion can comprise the bulk of most problem-solving activities and by the end of the process, you might find that your team is talked out!
Providing a means for your team to give feedback with short written notes can ensure everyone is head and can contribute without the need to stand up and talk. Depending on the needs of the group, giving an alternative can help ensure everyone can contribute to your problem-solving model in the way that makes the most sense for them.
Response Cards is a great way to close a workshop if you are looking for a gentle warm-down and want to get some swift discussion around some of the feedback that is raised.
Response Cards #debriefing #closing #structured sharing #questions and answers #thiagi #action It can be hard to involve everyone during a closing of a session. Some might stay in the background or get unheard because of louder participants. However, with the use of Response Cards, everyone will be involved in providing feedback or clarify questions at the end of a session.
Save time and effort discovering the right solutions
A structured problem solving process is a surefire way of solving tough problems, discovering creative solutions and driving organizational change. But how can you design for successful outcomes?
With SessionLab, it’s easy to design engaging workshops that deliver results. Drag, drop and reorder blocks to build your agenda. When you make changes or update your agenda, your session timing adjusts automatically , saving you time on manual adjustments.
Collaborating with stakeholders or clients? Share your agenda with a single click and collaborate in real-time. No more sending documents back and forth over email.
Explore how to use SessionLab to design effective problem solving workshops or watch this five minute video to see the planner in action!

Over to you
The problem-solving process can often be as complicated and multifaceted as the problems they are set-up to solve. With the right problem-solving techniques and a mix of creative exercises designed to guide discussion and generate purposeful ideas, we hope we’ve given you the tools to find the best solutions as simply and easily as possible.
Is there a problem-solving technique that you are missing here? Do you have a favorite activity or method you use when facilitating? Let us know in the comments below, we’d love to hear from you!
thank you very much for these excellent techniques
Certainly wonderful article, very detailed. Shared!
Your list of techniques for problem solving can be helpfully extended by adding TRIZ to the list of techniques. TRIZ has 40 problem solving techniques derived from methods inventros and patent holders used to get new patents. About 10-12 are general approaches. many organization sponsor classes in TRIZ that are used to solve business problems or general organiztational problems. You can take a look at TRIZ and dwonload a free internet booklet to see if you feel it shound be included per your selection process.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of online tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your job as a facilitator easier. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting facilitation software you can…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free

- INTERPERSONAL SKILLS
- Problem Solving and Decision Making
Identifying and Structuring Problems
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Interpersonal Skills:
- A - Z List of Interpersonal Skills
- Interpersonal Skills Self-Assessment
- Communication Skills
- Emotional Intelligence
- Conflict Resolution and Mediation Skills
- Customer Service Skills
- Team-Working, Groups and Meetings
- Decision-Making and Problem-Solving
- Effective Decision Making
- Decision-Making Framework
- Introduction to Problem Solving
- Investigating Ideas and Solutions
- Implementing a Solution and Feedback
- Creative Problem-Solving
- Social Problem-Solving
- Negotiation and Persuasion Skills
- Personal and Romantic Relationship Skills
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
This page continues from Problem Solving an Introduction that introduces problem solving as a concept and outlines the stages used to successfully solve problems.
This page covers the first two stages in the problem solving process: Identifying the Problem and Structuring the Problem .
Stage One: Identifying the Problem
Before being able to confront a problem its existence needs to be identified. This might seem an obvious statement but, quite often, problems will have an impact for some time before they are recognised or brought to the attention of someone who can do anything about them.
In many organisations it is possible to set up formal systems of communication so that problems are reported early on, but inevitably these systems do not always work. Once a problem has been identified, its exact nature needs to be determined: what are the goal and barrier components of the problem? Some of the main elements of the problem can be outlined, and a first attempt at defining the problem should be made. This definition should be clear enough for you to be able to easily explain the nature of the problem to others.
Looking at the problem in terms of goals and barriers can offer an effective way of defining many problems and splitting bigger problems into more manageable sub-problems.
Sometimes it will become apparent that what seems to be a single problem, is more accurately a series of sub-problems. For example, in the problem:
“I have been offered a job that I want, but I don't have the transport to get there and I don't have enough money to buy a car.”
“ I want to take a job ” (main problem)
“ But I don't have transport to get there ” (sub-problem 1)
“ And I don't have enough money to buy a car ” (sub-problem 2)
Useful ways of describing more complex problems are shown in the section, ' Structuring the Problem' , below.
During this first stage of problem solving, it is important to get an initial working definition of the problem. Although it may need to be adapted at a later stage, a good working definition makes it possible to describe the problem to others who may become involved in the problem solving process. For example:
Stage Two: Structuring the Problem
The second stage of the problem solving process involves gaining a deeper understanding of the problem. Firstly, facts need to be checked.
The questions have to be asked, is the stated goal the real goal? Are the barriers actual barriers and what other barriers are there? In this example, the problem at first seems to be:
This is also a good opportunity to look at the relationships between the key elements of the problem . For example, in the 'Job-Transport-Money' problem, there are strong connections between all the elements.
By looking at all the relationships between the key elements, it appears that the problem is more about how to achieve any one of three things, i.e. job, transport or money, because solving one of these sub-problems will, in turn, solve the others.
This example shows how useful it is to have a representation of a problem.
Problems can be represented in the following ways:
- Visually: using pictures, models or diagrams.
- Verbally: describing the problem in words.
Visual and verbal representations include:
- Chain diagrams
- Flow charts
- Tree diagrams
Chain Diagrams
Chain diagrams are powerful and simple ways of representing problems using a combination of diagrams and words. The elements of the problem are set out in words, usually placed in boxes, and positioned in different places on a sheet of paper, using lines to represent the relationship between them.
Chain Diagrams are the simplest type, where all the elements are presented in an ordered list, each element being connected only with the elements immediately before and after it. Chain diagrams usually represent a sequence of events needed for a solution. A simple example of a chain diagram illustrates the job-transport-money example as as follows:
Flow Charts
Flow charts allow for inclusion of branches, folds, loops, decision points and many other relationships between the elements. In practice, flow charts can be quite complicated and there are many conventions as to how they are drawn but, generally, simple diagrams are easier to understand and aid in 'seeing' the problem more readily.
Tree Diagrams
Tree diagrams and their close relative, the Decision Tree , are ways of representing situations where there are a number of choices or different possible events to be considered. These types of diagram are particularly useful for considering all the possible consequences of solutions.
Remember that the aim of a visualisation is to make the problem clearer. Over-complicated diagrams will just confuse and make the problem harder to understand.
Listing the elements of a problem can also help to represent priorities, order and sequences in the problem. Goals can be listed in order of importance and barriers in order of difficulty. Separate lists could be made of related goals or barriers. The barriers could be listed in the order in which they need to be solved, or elements of the problem classified in a number of different ways. There are many possibilities, but the aim is to provide a clearer picture of the problem.
A visual representation and a working definition together makes it far easier to describe a problem to others. Many problems will be far more complex than the example used here.
Continue to: Investigating Ideas and Possible Solutions
See also: Social Problem Solving Project Management Risk Management

The 5 Steps of Problem Solving

Problem solving is a critical skill for success in business – in fact it’s often what you are hired and paid to do. This article explains the five problem solving steps and provides strategies on how to execute each one.
Defining Problem Solving
Before we talk about the stages of problem solving, it’s important to have a definition of what it is. Let’s look at the two roots of problem solving — problems and solutions.
Problem – a state of desire for reaching a definite goal from a present condition [1] Solution – the management of a problem in a way that successfully meets the goals set for treating it
[1] Problem solving on Wikipedia
One important call-out is the importance of having a goal. As defined above, the solution may not completely solve problem, but it does meet the goals you establish for treating it–you may not be able to completely resolve the problem (end world hunger), but you can have a goal to help it (reduce the number of starving children by 10%).
The Five Steps of Problem Solving
With that understanding of problem solving, let’s talk about the steps that can get you there. The five problem solving steps are shown in the chart below:
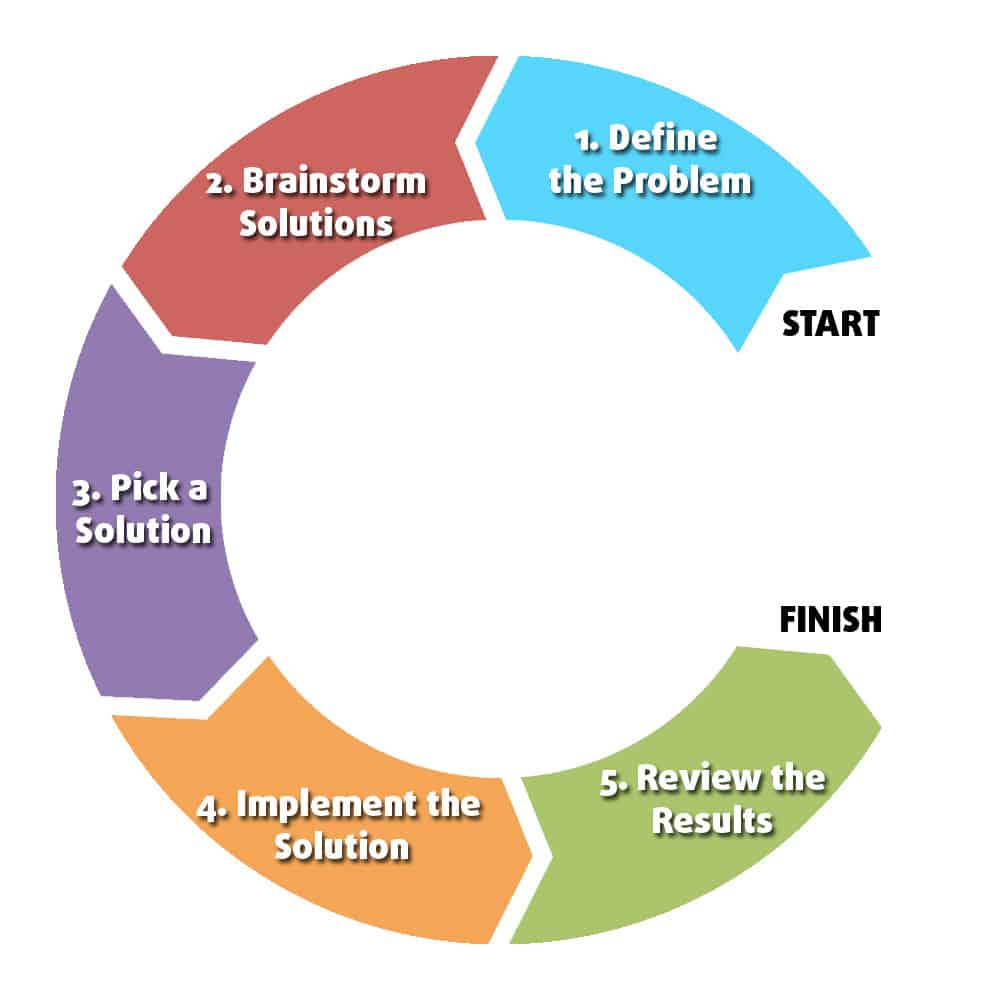
However this chart as is a little misleading. Not all problems follow these steps linearly, especially for very challenging problems. Instead, you’ll likely move back and forth between the steps as you continue to work on the problem, as shown below:
Let’s explore of these steps in more detail, understanding what it is and the inputs and outputs of each phase.
1. Define the Problem
aka What are you trying to solve? In addition to getting clear on what the problem is, defining the problem also establishes a goal for what you want to achieve.
Input: something is wrong or something could be improved. Output: a clear definition of the opportunity and a goal for fixing it.
2. Brainstorm Ideas
aka What are some ways to solve the problem? The goal is to create a list of possible solutions to choose from. The harder the problem, the more solutions you may need.
Input: a goal; research of the problem and possible solutions; imagination. Output: pick-list of possible solutions that would achieve the stated goal.
3. Decide on a Solution
aka What are you going to do? The ideal solution is effective (it will meet the goal), efficient (is affordable), and has the fewest side effects (limited consequences from implementation).
Input: pick-list of possible solutions; decision-making criteria. Output: decision of what solution you will implement.
4. Implement the Solution
aka What are you doing? The implementation of a solution requires planning and execution. It’s often iterative, where the focus should be on short implementation cycles with testing and feedback, not trying to get it “perfect” the first time.
Input: decision; planning; hard work. Output: resolution to the problem.
5. Review the Results
aka What did you do? To know you successfully solved the problem, it’s important to review what worked, what didn’t and what impact the solution had. It also helps you improve long-term problem solving skills and keeps you from re-inventing the wheel.
Input: resolutions; results of the implementation. Output: insights; case-studies; bullets on your resume.
Improving Problem Solving Skills
Once you understand the five steps of problem solving, you can build your skill level in each one. Often we’re naturally good at a couple of the phases and not as naturally good at others. Some people are great at generating ideas but struggle implementing them. Other people have great execution skills but can’t make decisions on which solutions to use. Knowing the different problem solving steps allows you to work on your weak areas, or team-up with someone who’s strengths complement yours.
Want to improve your problem solving skills? Want to perfect the art of problem solving? Check out our training programs or try these 20 problem solving activities to improve creativity .
THIS FREE 129 SECOND QUIZ WILL SHOW YOU
what is your humor persona?
Humor is a skill that can be learned. And when used correctly, it is a superpower that can be your greatest asset for building a happier, healthier and more productive life. See for yourself...
you might also be interested in...
Want to Be Funnier? Here’s The #1 Tip From Comedians
There are a few things that just about every comedian does, regardless of comedic stylings or background. We talked about […]
Infographic on Humor at Work
A great infographic on the value of humor at work.

Nominations open for Corporate Humor Awards
Nominations are still open for the 2020 Corporate Humor Awards! Nominate an individual or organization that is helping to keep […]
22 thoughts on “The 5 Steps of Problem Solving”
very helpful and informative training
Thank you for the information
YOU ARE AFOOL
I’m writing my 7th edition of Effective Security Management. I would like to use your circular graphic illustration in a new chapter on problem solving. You’re welcome to phone me at — with attribution.
Sure thing, shoot us an email at [email protected] .
i love your presentation. It’s very clear. I think I would use it in teaching my class problem solving procedures. Thank you
It is well defined steps, thank you.
these step can you email them to me so I can print them out these steps are very helpful
I like the content of this article, it is really helpful. I would like to know much on how PAID process (i.e. Problem statement, Analyze the problem, Identify likely causes, and Define the actual causes) works in Problem Solving.
very useful information on problem solving process.Thank you for the update.
Pingback: Let’s Look at Work Is Working with the Environment | #EnviroSociety
It makes sense that a business would want to have an effective problem solving strategy. Things could get bad if they can’t find solutions! I think one of the most important things about problem solving is communication.
Well in our school teacher teach us –
1) problem ldentification 2) structuring the problem 3) looking for possible solutions 4) lmplementation 5) monitoring or seeking feedback 6) decision making
Pleace write about it …
I teach Professional communication (Speech) and I find the 5 steps to problem solving as described here the best method. Your teacher actually uses 4 steps. The Feedback and decision making are follow up to the actual implementation and solving of the problem.
i know the steps of doing some guideline for problem solving
steps are very useful to solve my problem
The steps given are very effective. Thank you for the wonderful presentation of the cycle/steps/procedure and their connections.
I like the steps for problem solving
It is very useful for solving difficult problem i would reccomend it to a friend
this is very interesting because once u have learned you will always differentiate the right from the wrong.
I like the contents of the problem solving steps. informative.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Humor Persona - Template B2B
I make an effort to appreciate the humor of everyday life....
This question helps us further the advancement of humor research to make it more equitable.
Humor Persona - Main B2C
News, Views & Insights
- Best of Blog (70)
- Astronomy (28)
- Computational Thinking (64)
- Current Events (36)
- Data Analysis and Visualization (138)
- Data Repository (11)
- Design (24)
- Developer Insights (76)
- Digital Humanities (7)
- Education (194)
- Events (44)
- Finance (24)
- Function Repository (12)
- Geosciences (12)
- High-Performance Computing (12)
- History (18)
- Image Processing (48)
- Machine Learning (16)
- Mathematica News (112)
- Mathematica Q&A (13)
- Mathematics (129)
- New Technology (41)
- Other Application Areas (136)
- Raspberry Pi (18)
- Recreational Computation (163)
- Software Development (35)
- System Modeler (49)
- Uncategorized (1)
- Wolfram Cloud (24)
- Wolfram Community (19)
- Wolfram Demonstrations Project (31)
- Wolfram Language (297)
- Wolfram News (278)
- Wolfram Notebooks (37)
- Wolfram U (29)
- Wolfram|Alpha (48)
- Wolfram|One (7)
Marking a Milestone: Four Years of Daily Study Groups
From data to discovery: studying computational biology with wolfram, navigating quantum computing: accelerating next-generation innovation, unlock innovative problem-solving skills with creative computation.

As computers continue to perform an increasing number of tasks for us, it’s never been more important to learn how to use computers in creative ways. Creative computing, an interdisciplinary subject combining coding with artistic expression, allows us to blend technology with human experiences. Learning to create in this way can help you unlock your innovative problem-solving skills. By mastering creative computation, you can create interactive artwork, design immersive experiences and develop creative solutions to real-world challenges.
Wolfram U ’s new Creative Computation course combines an introduction to Wolfram Language coding with a project-based exploration of various art forms, like visual art, poetry, audio and video game design. If you’ve never coded in Wolfram Language before, this course is a fantastic introduction to applied computing and will help you learn the language for any project. If you’ve already mastered the basics of coding, this course will help you apply your skills to fascinating new problems and projects.
We would love for you to join us in this interactive course as we explore what it means to work creatively with coding.

Motivation from History
Creative computing is a relatively new subject, but people have been using technology to make art for centuries. From the loom to the printing press or Walkman to Atari, technology has been part of art for as long as both have existed.
We now have a variety of exciting and creative ways to engage with computers, from AI-generated images to immersive virtual realities.
In this course, you will learn how to use Wolfram Language to create various forms of art. There are four main sections to the course: Computational Art, Computational Strings, Sound and Game Development. In each section, there are lessons teaching Wolfram Language skills, with associated exercises, and at the end of each section, there is a larger project. The projects are designed for you to stretch your creative muscles and use your new coding skills to create art. You’ll learn how to create visual art using images, how to write poetry using string manipulation, how to visualize audio and how to make text-based and graphics-based video games, all while learning how to code in Wolfram Language.
Here is a sneak peek at some of the topics in the course (shown in the left-hand column):

With 16 lessons, five quizzes and four projects, this course should take around five hours to complete. We recommend doing all the activities and projects to maximize your understanding and explore your new skills.
There is no background required to participate in this course. We will teach you all the coding skills you need to make the projects, so all that is required is your excitement and creativity.
Let’s explore what’s in the course.
There are 16 lessons in this course spread out over the five total sections (Computational Thinking and Coding, Computational Art, Computational Strings, Sound and Game Development). In each lesson, you will explore a different aspect of coding through a short video. You’ll start off by exploring the concept of computational thinking: how to translate your thoughts and your creativity into something the computer can understand and how to work with a computer to build creative artifacts. Here is a short excerpt from the video for this lesson:
Each lesson teaches a specific coding skill, with lots of examples and exploration of key concepts. In the Computational Art section, the goal is to use images and graphics to create a piece of art. In order to do that, we need to learn skills like variables, functions, lists, the Table and Map functions, colors, graphics and randomness, and image manipulation. Each skill is taught with an interactive video lesson in conjunction with exercises, before you use the project to test your knowledge.
The video lessons range from 5–13 minutes in length, and each video is accompanied by a transcript notebook displayed on the right-hand side of the screen. You can copy and paste Wolfram Language input directly from the transcript notebook to the embedded scratch notebook to try the examples for yourself.
Each lesson has a set of exercises to review the concepts covered during the lesson. Since this course is designed for independent study, a detailed solution is given for all exercises. Each exercise will help you practice a specific skill you’ve learned so that you are ready to use that skill in the project. Here is an example of an exercise from lesson 6 on image manipulation:

The exercise notebooks are interactive, so you can try variations of each problem in the Wolfram Cloud . You’re encouraged to blend skills together as you learn them. For example, for the aforementioned exercise, you could use the skills you just learned about randomness to replace the dominant colors in the image of the wolf with random colors, or you could import images to do the same exercise with a different image. When you’ve gotten further in the course, you could come back and build your own function that can do this to any two images.
Each section of the course includes a short project, and the Game Development section has two longer projects. In each case, you’ll use the skills you learned in that section to build something creative. In the first three sections, we provide detailed solutions and walk you though our processes, but in the Game Development section, we encourage you to build something unique.
In the Computational Art section, you’ll make art using images and shapes. In Computational Strings, you’ll write a Mad Libs haiku. In Sound, you’ll make an audio visualizer. In Game Development, you’ll make a text adventure game and a graphics-based Pac-Man –style game.
These projects will allow you to celebrate your successes and practice your new coding skills while cementing your understanding of creative computation.
Each section of the course ends with a short quiz, which allows you to demonstrate your understanding:

You will get instant feedback on your solutions, and you’re encouraged to try out the code.
Course Certificate
You are encouraged to watch all the lessons and attempt the projects and quizzes in the recommended sequence, since each topic in the course relies on earlier concepts and techniques. When you watch all 16 lesson videos and pass the five course quizzes, you will earn a certificate of course completion. The Track My Progress status bar in the course helps you to chart your progress, showing you where you left off from your previous course session. While you don’t have to submit projects to earn a certificate, they are a fundamental part of gaining computational skills, and we look forward to connecting with course users about their projects on Wolfram Community . Your course certificate represents completion of the basic course requirements, demonstrates your interest in exploring the latest technology and in building new computational skills, and it will add value to your resume or social media profile.

You are also encouraged to use the skills you learn in this course to go on to earn Level 1 certification for Wolfram Language proficiency . While the course does not require the same level of mathematics as the Level 1 certification exam, it will prepare you well for accomplishing the range of computational tasks that are required for Level 1 certification.
A Building Block for Success
A mastery of the fundamental concepts of creative computing will prepare you for working with computers to innovatively solve problems. Whether you’re interested in creating art or you’re interested in developing your coding skills, this course will provide a detailed foundation in both. Learning Wolfram Language is a valuable pursuit regardless of your career aspirations, as you can use the skills you learn in this course in any field.
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank my coauthor Eryn Gillam for their major contributions to the development of this course, as well as others who helped this course come together, including (but not limited to) Anisha Basil, Abrita Chakravarty, Cassidy Hinkle, Joyce Tracewell, Arben Kalziqi, Isabel Skidmore, Zach Shelton, Simeon Buttery, Ryan Domier and Eder Ordonez.
! Please enter your comment (at least 5 characters).
! Please enter your name.
! Please enter a valid email address.
Related Posts

Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Computation and Language
Title: self-reflection in llm agents: effects on problem-solving performance.
Abstract: In this study, we investigated the effects of self-reflection in large language models (LLMs) on problem-solving performance. We instructed nine popular LLMs to answer a series of multiple-choice questions to provide a performance baseline. For each incorrectly answered question, we instructed eight types of self-reflecting LLM agents to reflect on their mistakes and provide themselves with guidance to improve problem-solving. Then, using this guidance, each self-reflecting agent attempted to re-answer the same questions. Our results indicate that LLM agents are able to significantly improve their problem-solving performance through self-reflection ($p < 0.001$). In addition, we compared the various types of self-reflection to determine their individual contribution to performance. All code and data are available on GitHub at this https URL
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
Wavefunction matching for solving quantum many-body problems
Strongly interacting systems play an important role in quantum physics and quantum chemistry. Stochastic methods such as Monte Carlo simulations are a proven method for investigating such systems. However, these methods reach their limits when so-called sign oscillations occur. This problem has now been solved by an international team of researchers from Germany, Turkey, the USA, China, South Korea and France using the new method of wavefunction matching. As an example, the masses and radii of all nuclei up to mass number 50 were calculated using this method. The results agree with the measurements, the researchers now report in the journal " Nature ."
All matter on Earth consists of tiny particles known as atoms. Each atom contains even smaller particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. Each of these particles follows the rules of quantum mechanics. Quantum mechanics forms the basis of quantum many-body theory, which describes systems with many particles, such as atomic nuclei.
One class of methods used by nuclear physicists to study atomic nuclei is the ab initio approach. It describes complex systems by starting from a description of their elementary components and their interactions. In the case of nuclear physics, the elementary components are protons and neutrons. Some key questions that ab initio calculations can help answer are the binding energies and properties of atomic nuclei and the link between nuclear structure and the underlying interactions between protons and neutrons.
However, these ab initio methods have difficulties in performing reliable calculations for systems with complex interactions. One of these methods is quantum Monte Carlo simulations. Here, quantities are calculated using random or stochastic processes. Although quantum Monte Carlo simulations can be efficient and powerful, they have a significant weakness: the sign problem. It arises in processes with positive and negative weights, which cancel each other. This cancellation leads to inaccurate final predictions.
A new approach, known as wavefunction matching, is intended to help solve such calculation problems for ab initio methods. "This problem is solved by the new method of wavefunction matching by mapping the complicated problem in a first approximation to a simple model system that does not have such sign oscillations and then treating the differences in perturbation theory," says Prof. Ulf-G. Meißner from the Helmholtz Institute for Radiation and Nuclear Physics at the University of Bonn and from the Institute of Nuclear Physics and the Center for Advanced Simulation and Analytics at Forschungszentrum Jülich. "As an example, the masses and radii of all nuclei up to mass number 50 were calculated -- and the results agree with the measurements," reports Meißner, who is also a member of the Transdisciplinary Research Areas "Modeling" and "Matter" at the University of Bonn.
"In quantum many-body theory, we are often faced with the situation that we can perform calculations using a simple approximate interaction, but realistic high-fidelity interactions cause severe computational problems," says Dean Lee, Professor of Physics from the Facility for Rare Istope Beams and Department of Physics and Astronomy (FRIB) at Michigan State University and head of the Department of Theoretical Nuclear Sciences.
Wavefunction matching solves this problem by removing the short-distance part of the high-fidelity interaction and replacing it with the short-distance part of an easily calculable interaction. This transformation is done in a way that preserves all the important properties of the original realistic interaction. Since the new wavefunctions are similar to those of the easily computable interaction, the researchers can now perform calculations with the easily computable interaction and apply a standard procedure for handling small corrections -- called perturbation theory.
The research team applied this new method to lattice quantum Monte Carlo simulations for light nuclei, medium-mass nuclei, neutron matter and nuclear matter. Using precise ab initio calculations, the results closely matched real-world data on nuclear properties such as size, structure and binding energy. Calculations that were once impossible due to the sign problem can now be performed with wavefunction matching.
While the research team focused exclusively on quantum Monte Carlo simulations, wavefunction matching should be useful for many different ab initio approaches. "This method can be used in both classical computing and quantum computing, for example to better predict the properties of so-called topological materials, which are important for quantum computing," says Meißner.
The first author is Prof. Dr. Serdar Elhatisari, who worked for two years as a Fellow in Prof. Meißner's ERC Advanced Grant EXOTIC. According to Meißner, a large part of the work was carried out during this time. Part of the computing time on supercomputers at Forschungszentrum Jülich was provided by the IAS-4 institute, which Meißner heads.
- Quantum Computers
- Computers and Internet
- Computer Modeling
- Spintronics Research
- Mathematics
- Quantum mechanics
- Quantum entanglement
- Introduction to quantum mechanics
- Computer simulation
- Quantum computer
- Quantum dot
- Quantum tunnelling
- Security engineering
Story Source:
Materials provided by University of Bonn . Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference :
- Serdar Elhatisari, Lukas Bovermann, Yuan-Zhuo Ma, Evgeny Epelbaum, Dillon Frame, Fabian Hildenbrand, Myungkuk Kim, Youngman Kim, Hermann Krebs, Timo A. Lähde, Dean Lee, Ning Li, Bing-Nan Lu, Ulf-G. Meißner, Gautam Rupak, Shihang Shen, Young-Ho Song, Gianluca Stellin. Wavefunction matching for solving quantum many-body problems . Nature , 2024; DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07422-z
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- Toward a Successful Vaccine for HIV
- Highly Efficient Thermoelectric Materials
- Toward Human Brain Gene Therapy
- Whale Families Learn Each Other's Vocal Style
- AI Can Answer Complex Physics Questions
- Otters Use Tools to Survive a Changing World
- Monogamy in Mice: Newly Evolved Type of Cell
- Sustainable Electronics, Doped With Air
- Male Vs Female Brain Structure
- Breeding 'Carbon Gobbling' Plants
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.

COMMENTS
The problem solving cycle is a systematic approach to analyzing and solving problems, involving various stages such as problem identification, analysis, algorithm design, implementation, and evaluation. Understanding the importance of this cycle is essential for any computer scientist or programmer.
Problem Solving Using Computer (Steps) Computer based problem solving is a systematic process of designing, implementing and using programming tools during the problem solving stage. This method enables the computer system to be more intuitive with human logic than machine logic. Final outcome of this process is software tools which is ...
Computer science learners often face difficulties in performing two of the main stages of a problem-solving process: problem analysis and solution construction. Therefore, it is important that computer science educators be aware of these difficulties and acquire appropriate pedagogical tools to guide and scaffold learners in learning these skills.
Here is the CompTIA troubleshooting methodology: Identify the problem. Establish a theory of probable cause. Test the theory to determine the cause. Establish a plan of action to resolve the problem and identify potential effects. Implement the solution or escalate as necessary. Verify full system functionality and, if applicable, implement ...
Finding a suitable solution for issues can be accomplished by following the basic four-step problem-solving process and methodology outlined below. Step. Characteristics. 1. Define the problem. Differentiate fact from opinion. Specify underlying causes. Consult each faction involved for information. State the problem specifically.
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps: Identify the issue: Recognize the problem that needs to be solved. Analyze the situation: Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present. Generate potential solutions: Brainstorm a list of possible ...
Example problem: Step 1 - Identify the problem that must be solved. The first step is to identify the problem that needs to be solved. In this example, the largest number in the list must be found and displayed. Step 2 - Understand what the problem presents. The problem presents a list of numbers.
The good thing is that the system translates nicely to computer problems, which is very useful, since the focus of the book is to solve problems on a computer. The six steps in this system are: What is the problem. Make a model. Analyze the model. Find the solution.
The Problem-Solving Process. Problem-solving is an important part of planning and decision-making. The process has much in common with the decision-making process, and in the case of complex decisions, can form part of the process itself. We face and solve problems every day, in a variety of guises and of differing complexity.
MIT OpenCourseWare is a web based publication of virtually all MIT course content. OCW is open and available to the world and is a permanent MIT activity
The first step in solving a problem is understanding what that problem actually is. You need to be sure that you're dealing with the real problem - not its symptoms. For example, if performance in your department is substandard, you might think that the problem lies with the individuals submitting work. However, if you look a bit deeper, the ...
The several steps of this cycle are as follows : Step by step solution for a problem (Software Life Cycle) 1. Problem Definition/Specification: A computer program is basically a machine language solution to a real-life problem. Because programs are generally made to solve the pragmatic problems of the outside world.
Problem solving is the process of achieving a goal by overcoming obstacles, a frequent part of most activities. Problems in need of solutions range from simple personal tasks (e.g. how to turn on an appliance) to complex issues in business and technical fields. The former is an example of simple problem solving (SPS) addressing one issue ...
From Why Groups Struggle to Solve Problems Together , Nov 07, 2019. Find new ideas and classic advice on strategy, innovation and leadership, for global leaders from the world's best business and ...
Step 1 - Define the Problem. The definition of the problem is the first step in effective problem solving. This may appear to be a simple task, but it is actually quite difficult. This is because problems are frequently complex and multi-layered, making it easy to confuse symptoms with the underlying cause.
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue. The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything ...
Problem analysis can be one of the most important and decisive stages of all problem-solving tools. Sometimes, a team can become bogged down in the details and are unable to move forward. Journalists is an activity that can avoid a group from getting stuck in the problem identification or problem analysis stages of the process.
This page continues from Problem Solving an Introduction that introduces problem solving as a concept and outlines the stages used to successfully solve problems.. This page covers the first two stages in the problem solving process: Identifying the Problem and Structuring the Problem. Stage One: Identifying the Problem. Before being able to confront a problem its existence needs to be identified.
Structure diagrams show hierarchical top-down design in a visual form. Each problem is divided into sub-problems and each sub-problem divided into further sub-problems. At each level the problem is broken down into more detailed tasks that can be implemented using a single subroutine; Figure 1: A structure diagram
There are basically three types of problem in artificial intelligence: 1. Ignorable: In which solution steps can be ignored. 2. Recoverable: In which solution steps can be undone. 3. Irrecoverable: Solution steps cannot be undo. Steps problem-solving in AI: The problem of AI is directly associated with the nature of humans and their activities.
In insight problem-solving, the cognitive processes that help you solve a problem happen outside your conscious awareness. 4. Working backward. Working backward is a problem-solving approach often ...
The implementation of a solution requires planning and execution. It's often iterative, where the focus should be on short implementation cycles with testing and feedback, not trying to get it "perfect" the first time. Input: decision; planning; hard work. Output: resolution to the problem. 5.
Learning to create in this way can help you unlock your innovative problem-solving skills. By mastering creative computation, you can create interactive artwork, design immersive experiences and develop creative solutions to real-world challenges. Wolfram U 's new Creative Computation course combines an introduction to Wolfram Language coding ...
Problem-solving is often an ongoing process, and feedback from the implementation and evaluation stages may lead to adjustments in the chosen solution or the identification of new issues that need to be addressed. Problem-Solving Example in Education. Certainly: Let's consider a problem-solving example in the context of education.
This guide is perfect for computer science students, programmers, and anyone interested in mastering tree traversal techniques and detecting duplicate structures within data. In this tutorial, you'll learn: Understanding the Problem: Gain a foundational understanding of the task, which involves identifying if a binary tree contains any subtrees ...
In this study, we investigated the effects of self-reflection in large language models (LLMs) on problem-solving performance. We instructed nine popular LLMs to answer a series of multiple-choice questions to provide a performance baseline. For each incorrectly answered question, we instructed eight types of self-reflecting LLM agents to reflect on their mistakes and provide themselves with ...
University of Bonn. (2024, May 15). Wavefunction matching for solving quantum many-body problems. ScienceDaily. Retrieved May 16, 2024 from www.sciencedaily.com / releases / 2024 / 05 ...