
Welcome to the learn-c.org free interactive C tutorial.
Whether you are an experienced programmer or not, this website is intended for everyone who wishes to learn the C programming language.
There is no need to download anything - Just click on the chapter you wish to begin from, and follow the instructions. Good luck!
learn-c.org is still under construction - If you wish to contribute tutorials, please click on Contributing Tutorials down below.

Learn the Basics
- Hello, World!
- Variables and Types
- Multidimensional Arrays
- While loops
- Function arguments by reference
- Dynamic allocation
- Arrays and Pointers
- Linked lists
- Binary trees
- Pointer Arithmetics
- Function Pointers
Contributing Tutorials
Read more here: Contributing Tutorials

Coding for Kids is an online interactive tutorial that teaches your kids how to code while playing!
Receive a 50% discount code by using the promo code:
Start now and play the first chapter for free, without signing up.
C Data Types
- C Operators
- C Input and Output
- C Control Flow
- C Functions
- C Preprocessors
C File Handling
- C Cheatsheet
C Interview Questions
C programming language tutorial.
- C Language Introduction
- Features of C Programming Language
- C Programming Language Standard
- C Hello World Program
- Compiling a C Program: Behind the Scenes
- Tokens in C
- Keywords in C
C Variables and Constants
- C Variables
- Constants in C
- Const Qualifier in C
- Different ways to declare variable as constant in C
- Scope rules in C
- Internal Linkage and External Linkage in C
- Global Variables in C
- Data Types in C
- Literals in C
- Escape Sequence in C
- Integer Promotions in C
- Character Arithmetic in C
- Type Conversion in C
C Input/Output
- Basic Input and Output in C
- Format Specifiers in C
- printf in C
- Scansets in C
- Formatted and Unformatted Input/Output functions in C with Examples
- Operators in C
- Arithmetic Operators in C
- Unary operators in C
- Relational Operators in C
- Bitwise Operators in C
- C Logical Operators
- Assignment Operators in C
- Increment and Decrement Operators in C
- Conditional or Ternary Operator (?:) in C
- sizeof operator in C
- Operator Precedence and Associativity in C
C Control Statements Decision-Making
- Decision Making in C (if , if..else, Nested if, if-else-if )
- C - if Statement
- C if...else Statement
- C if else if ladder
- Switch Statement in C
- Using Range in switch Case in C
- while loop in C
- do...while Loop in C
- For Versus While
- Continue Statement in C
- Break Statement in C
- goto Statement in C
- User-Defined Function in C
- Parameter Passing Techniques in C
- Function Prototype in C
- How can I return multiple values from a function?
- main Function in C
- Implicit return type int in C
- Callbacks in C
- Nested functions in C
- Variadic functions in C
- _Noreturn function specifier in C
- Predefined Identifier __func__ in C
- C Library math.h Functions
C Arrays & Strings
- Properties of Array in C
- Multidimensional Arrays in C
- Initialization of Multidimensional Array in C
- Pass Array to Functions in C
- How to pass a 2D array as a parameter in C?
- What are the data types for which it is not possible to create an array?
- How to pass an array by value in C ?
- Strings in C
- Array of Strings in C
- What is the difference between single quoted and double quoted declaration of char array?
- C String Functions
- Pointer Arithmetics in C with Examples
- C - Pointer to Pointer (Double Pointer)
- Function Pointer in C
- How to declare a pointer to a function?
- Pointer to an Array | Array Pointer
- Difference between constant pointer, pointers to constant, and constant pointers to constants
- Pointer vs Array in C
- Dangling, Void , Null and Wild Pointers in C
- Near, Far and Huge Pointers in C
- restrict keyword in C
C User-Defined Data Types
- C Structures
- dot (.) Operator in C
- Structure Member Alignment, Padding and Data Packing
- Flexible Array Members in a structure in C
- Bit Fields in C
- Difference Between Structure and Union in C
- Anonymous Union and Structure in C
- Enumeration (or enum) in C
C Storage Classes
- Storage Classes in C
- extern Keyword in C
- Static Variables in C
- Initialization of static variables in C
- Static functions in C
- Understanding "volatile" qualifier in C | Set 2 (Examples)
- Understanding "register" keyword in C
C Memory Management
- Memory Layout of C Programs
- Dynamic Memory Allocation in C using malloc(), calloc(), free() and realloc()
- Difference Between malloc() and calloc() with Examples
- What is Memory Leak? How can we avoid?
- Dynamic Array in C
- How to dynamically allocate a 2D array in C?
- Dynamically Growing Array in C
C Preprocessor
- C Preprocessor Directives
- How a Preprocessor works in C?
- Header Files in C
- What’s difference between header files "stdio.h" and "stdlib.h" ?
- How to write your own header file in C?
- Macros and its types in C
- Interesting Facts about Macros and Preprocessors in C
- # and ## Operators in C
- How to print a variable name in C?
- Multiline macros in C
- Variable length arguments for Macros
- Branch prediction macros in GCC
- typedef versus #define in C
- Difference between #define and const in C?
- Basics of File Handling in C
- C fopen() function with Examples
- EOF, getc() and feof() in C
- fgets() and gets() in C language
- fseek() vs rewind() in C
- What is return type of getchar(), fgetc() and getc() ?
- Read/Write Structure From/to a File in C
- C Program to print contents of file
- C program to delete a file
- C Program to merge contents of two files into a third file
- What is the difference between printf, sprintf and fprintf?
- Difference between getc(), getchar(), getch() and getche()
Miscellaneous
- time.h header file in C with Examples
- Input-output system calls in C | Create, Open, Close, Read, Write
- Signals in C language
- Program error signals
- Socket Programming in C
- _Generics Keyword in C
- Multithreading in C
- C Programming Interview Questions (2024)
- Commonly Asked C Programming Interview Questions | Set 1
- Commonly Asked C Programming Interview Questions | Set 2
- Commonly Asked C Programming Interview Questions | Set 3
In this C Tutorial , you’ll learn all C programming basic to advanced concepts like variables, arrays, pointers, strings, loops, etc. This C Programming Tutorial is designed for both beginners as well as experienced professionals, who’re looking to learn and enhance their knowledge of the C programming language.
C is a general-purpose, procedural, high-level programming language used in the development of computer software and applications, system programming, games, and more.
- C language was developed by Dennis M. Ritchie at the Bell Telephone Laboratories in 1972 .
- It is a powerful and flexible language which was first developed for the programming of the UNIX operating System .
- C is one of the most widely used programming languages.
C programming language is known for its simplicity and efficiency. It is the best choice to start with programming as it gives you a foundational understanding of programming.
Print Hello World using C Programming
“Give this C code a try, and here’s a fun challenge: print ‘Hello World’ along with your name!”

Getting Started With C Programming Tutorial
Start your coding adventure with our free C Tutorial. A perfect C programming tutorial for beginners and advanced coders alike, this tutorial is your key to unlocking the magic of C programming. With clear explanations and fun examples.
C Arrays & Strings
C error handling.
- Setting Up C Development Environment
- C Identifiers
- Different Ways to Declare Variable as Constant in C
- Scope Rules in C
- Data Type Modifiers in C
C Input/Output Basic Input and Output in C Format Specifiers in C printf in C scanf in C Scansets in C Formatted and Unformatted Input and Output Functions C Operators
- Unary Operators in C
- Logical Operators in C
- size of Operator in C
- Decision-Making in C
- C if Statement
- C if…else Statement
- C if-else-if Ladder
- Using Range in switch case in C
- while looping in C
- do…while Loop in C
- for versus while Loop
- continue Statement in C
- break Statement in C
- Importance of Function Prototype in C
- Return Multiple Values From a Function
- Implicit Return Type int in C
- Nested Functions in C
- _Noreturn Function Specifier in C
- Maths Functions in C
- Initialization of Multidimensional Arrays in C
- Pass a 2D Array as a Parameter in C
- Data Types for Which Array is Not Possible
- Pass an Array by Value in C
- An Array of Strings in C
- Difference Between Single Quoted and Double Quoted Initialization
- String Functions in C
- Pointer Arithmetics in C
- Pointer to Pointer (Double Pointer) in C
- Declare Function Pointer in C
- Pointer to an Array in C
- Constant Pointer in C
- Dangling, Void, Null and Wild Pointers
- restrict Keyword in C
- Flexible Array Members in a Structure in C
- Initialization of Static Variables in C
- Static Functions in C
- Understanding “volatile” Qualifier in C
- Understanding the “register” Keyword in C
- Dynamic Memory Allocation in C
- Difference Between malloc() and calloc()
- What is a Memory Leak?
- Dynamically Allocate a 2D Array in C
- How a Preprocessor Works in C?
- Difference Between Header Files “stdio.h” and “stdlib.h”
- Write Your Own Header File in C
- Macros and their Types in C
- Interesting Facts About Macros and Preprocessors in C
- Print a Variable Name in C
- Multiline Macros in C
- Variable Length Arguments for Macros
- Branch Prediction Macros in GCC
- Difference Between #define and const in C
- C fopen() Function
- fgets() and gets() in C
- Return Type of getchar(), fgetc() and getc()
- C Program to Print Contents of File
- C Program to Delete a File
- C Program to Merge Contents of Two Files into a Third File
- Difference Between printf, sprintf and fprintf
- Difference Between getc(), getchar(), getch() and getche()
- Error Handling in C
- Using goto for Exception Handling in C
- Error Handling During File Operations in C
- C Program to Handle Divide By Zero and Multiple Exceptions
- Basic C Programs
- Control Flow Programs
- Pattern Printing Programs
- Functions Programs
- Arrays Programs
- Strings Programs
- Conversions Programs
- Pointers Programs
- Structures and Unions Programs
- File I/O Programs
- Date and Time Programs
- More C Programs
- Date and Time in C
- Input-output system calls in C
- Signals in C
- Program Error Signals in C
Top 50 C Programming Interview Questions and Answers Commonly Asked C Programming Interview Questions | Set 1 Commonly Asked C Programming Interview Questions | Set 2 Commonly Asked C Programming Interview Questions | Set 3
Why Learn C?
C programming language is one of the most popular programming language. It is a must learn for software engineering students. C is called the mother of all modern programming languages so learning C will help you to learn other languages easily like Java, C++, C#, Python, etc. C language is faster than other programming languages like Java and Python. It can handle low-level programming and we can compile the C code in a variety of computer platforms.
List of some key advantages of C language :
- Easy to learn.
- Versatile Language, which can be used in both applications and technologies.
- Mid-Level Programming Language.
- Structured Programming Language.
C compiler is a software that translates human-readable C language code into machine code or an intermediate code that can be executed by a computer’s central processing unit (CPU).
There are many C compilers available in the market, such as GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) , Microsoft Visual C++ Compiler , Clang , Intel C++ Compiler , and TinyCC (TCC) .
For this tutorial, we will be using the GNU-based online C compiler provided by GeeksforGeeks which is developed for beginners and is very easy to use compared to other compiler/IDE’s available on the web.
Features of C Language
There are some key features of C language that show the ability and power of C language:
- Simplicity and Efficiency: The simple syntax and structured approach make the C language easy to learn.
- Fast Speed: C is one of the fastest programming language because C is a static programming language, which is faster than dynamic languages like JavaScript and Python. C is also a compiler-based which is the reason for faster code compilation and execution.
- Portable: C provides the feature that you write code once and run it anywhere on any computer. It shows the machine-independent nature of the C language.
- Memory Management: C provides lower level memory management using pointers and functions like realloc(), free(), etc.
- Pointers: C comes with pointers. Through pointers, we can directly access or interact with the memory. We can initialize a pointer as an array, variables, etc.
- Structured Language: C provides the features of structural programming that allows you to code into different parts using functions which can be stored as libraries for reusability.
Applications of C Language
C was used in programs that were used in making operating systems. C was known as a system development language because the code written in C runs as fast as the code written in assembly language.
The use of C is given below:
- Operating Systems
- Language Compilers
- Text Editors
- Print Spoolers
- Network Drivers
- Modern Programs
- Language Interpreters
FAQs on C Language
Q1. how to learn c easily.
Answer:
The first steps towards learning C or any language are to write a hello world program. It gives the understanding of how to write and execute a code. After this, learn the following: Variables Operators Conditionals Loops and Errors Arrays and Strings Pointers and Memory Functions Structures Recursions
Q2. Difference between C and C++?
q3. is c easy to learn for beginners.
While C is one of the easy languages, it is still a good first language choice to start with because almost all programming languages are implemented in it. It means that once you learn C language, it’ll be easy to learn more languages like C++, Java, and C#.
Q4. Why should we learn C first rather than C++?
C is a ‘ mother of all languages .’ It provides a solid understanding of fundamental programming concepts and is considered easier to grasp. C offers versatile applications, from software development to game programming, making it an excellent choice for building a strong programming foundation.
Please Login to comment...
Related articles, improve your coding skills with practice.
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
C Functions
C structures.
C is a general-purpose programming language, developed in 1972, and still quite popular.
C is very powerful; it has been used to develop operating systems, databases, applications, etc.
Examples in Each Chapter
Our "Try it Yourself" editor makes it easy to learn C. You can edit code and view the result in your browser:
Click on the "Try it Yourself" button to see how it works.
We recommend reading this tutorial, in the sequence listed in the left menu.
C Exercises
Test yourself with exercises.
Insert the missing part of the code below to output "Hello World!".
Start the Exercise
Advertisement
Learn by taking a quiz! The quiz will give you a signal of how much you know about C.
Start C Quiz
My Learning
Track your progress with the free "My Learning" program here at W3Schools.
Log in to your account, and start earning points!
This is an optional feature. You can study at W3Schools without using My Learning.

Learn by Examples
Learn by examples! This tutorial supplements all explanations with clarifying examples.
See All C Examples

COLOR PICKER

Contact Sales
If you want to use W3Schools services as an educational institution, team or enterprise, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Top Tutorials
Top references, top examples, get certified.
CS2022: Introduction to C
Announcements.
This course provides a brief introduction to the C programming language and standard libraries for students with programming experience at the CS1110 level. We will cover basic syntax, programming paradigm, standard libraries, and debugging for C on the GNU/Linux platform.
Organization
- Instructor : Hussam Abu-Libdeh [first name @cs.cornell.edu]
- Wednesdays 11:10am - 12:10pm
- Location: 4139 Upson Hall
Assignments & Grading
The homework assignments will be released and submitted through the Course Management System .
As this is a S/U course, to complete it successfully you need a "pass" on all of the homework assignment s on C programming . This course follows the Cornell University Code of Academic Integrity . Each student in this course is expected to abide by the Cornell University Code of Academic Integrity. You should not discuss solutions to the assignment s with your classmates. This not only implies that you should have written them but also that you should understand them! You are free to consult books and online resources, but you will have to properly cite them. If there is enough interest, a more elaborate "final" project might be an option for completing the class, provided that it covers all features in the homeworks.
Development Environment
The class will use Linux as an environment for development and testing. Programs will be compiled with gcc and debugging will be done with gdb . You can do the homeworks on other platforms, but testing will be done on Linux and thus it is recommended to try to use Linux.
- Solutions: fact1.c , fact2.c , zipper.c
- Solutions: charfreq.c
- Solutions: iManip.c
Syllabus and Lecture Slides
- General Introduction
- examples shown in class: Hello World , Variables , Functions , Conditionals , Command Line Arguments ,
- examples shown in class: Swapping values with pointers and without
- examples shown in class: Bad stack usage . Good heap usage
- Arrays & Strings
- examples shown in class: Enums , Structs , Unions , Function pointers , typedef .
- Helpful slides from my Unix course: Moving around the filesystem , and A very quick taste of Vim . (Note: both slide sets contain more info than was covered in class, use them only as reference)
- examples used in class: Pointers vs Arrays , Tracing using fprintf , stderr vs stdout (compile this program, and then redirect its output to a file to see the effect. Example, ./stderr > output.txt ), Stepping through a program that throughs a segmentation fault
- class examples: Terminal IO (keyboard) , File IO (requires a text file called file.txt in its directory), Network Server , Network Client (run the server first then the client).
- #include : include.c , minmax.h , minmax.c Compile with gcc include.c minmax.c
- #define : define.c
- #ifdef : ifdef.c , mylib.h , mylib.c Compile with gcc -DDEBUG ifdef.c mylib.c to use the custom malloc and free. Compile without the -DDEBUG option and you will use the default malloc and free. Alternatively, you can just add a #define DEBUG at the beginning of ifdef.c to use the custom functions.
- class examples: exercise.c , iteration1.c , iteration2.c
- threads.c : compile with gcc -pthread
- counters.c : compile with gcc -pthread . This code is meant to demonstrate synchronization issues across threads. Consider taking the Operating Systems course (CS 4410) to learn more about this subject.
- Goto, Exceptions, and Assembly in C
- Course Recap
What is The C Programming Language? A Tutorial for Beginners

This tutorial will give you a broad overview of basic concepts of the C programming language.
We'll go over the history of the language, why and where it is used, the compilation process, and some very basic programming concepts that are common in most popular programming languages.
This is not a complete guide to the language, but will rather give you a high level understanding of important C concepts and ideas as an absolute beginner to coding.
Each language has its own syntax and specific ways of doing things, but the concepts covered here are common and applied to all programming languages.
Having an understanding of how things work and these universal concepts can take you a long way in your coding journey. It makes learning a new technology easier in the long run.
This tutorial takes heavy inspiration from the material covered in the first couple of weeks of the course CS50: Introduction To Computer Science which I highly recommend to anyone wanting to dive deeper into computer science and programming no matter their level of experience.
Table of Contents
- The History behind the origins of C - An Overview
- Language Characteristics and why to consider learning C
Where Is C used?
- Compilation process: Write-Compile-Run
- Header files
- Main program
- Output or printing to the console
- Declaring vs initialising a variable
- A couple rules for naming a variable
- The scope of a variable
- Format codes
- Arithmetic operators
- Assignment operator
- Logical operators
- Comparison operators
- Function arguments
- Function outputs
- Defining a method
- Calling a function
- Boolean Expressions
- Conditional Statements
- Loops 1. While loops 2. Do-While loops
- Extra Reading
The History of the C Programming Language
The history of the C programming language is closely tied to the history of the development of the Unix Operating System.
If we look back to understand what led to the development of the operating system that changed the world of computing, we'll see the steps that led to the development of C.
Simply put, C was derived from the need to initially find and eventually create a language to apply on the Unix Operating system.
Project MAC and MULTICS
It all started in 1965 when the experimental project MAC was completed at MIT – the first system of its kind. This was the beginning of the MULTICS era. It used something called CTSS, or the Compatible Time Sharing System.
This was a key innovation at that time. Up to this point, we were in the early mainframe era, where massive, powerful, and extremely costly computers used to take up entire rooms.
To get tasks done, programmers would write code by hand. Then they'd punch a deck of paper tape cards that were encoded with the program written by hand.
They did this by handing the sheets of paper the program was written on to operators who used a key punch machine that would punch the card's holes and represent the data and instructions on the card.
Then they'd feed the punched cards to a punch card reader connected to the mainframe computer. It then converted the sequences in the cards holes to digital information. Simple tasks took a long time using this method and only one person could use each machine at a time.
The idea of time sharing changed everything. Instead of using cards, it attached multiple consoles (which at the time were mechanical terminals called teletypes) to a main computer. This allowed many people to use the same computer simultaneously.
Over 100 typewriter terminals spread around MIT's campus could be attached to one main big computer. This system supported up to 30 remote users at the same time, each using one of those terminals.
The operating system of the main computer multitasked and circled around the people who wanted to perform computing tasks from their connected terminals and gave a few seconds to each one.
It provided what seemed like a continuous service, appearing to be loading and running many programs simultaneously. But in reality it just went through each user's program very quickly. This gave the illusion that one person had the whole computer to themselves.
This system proved to be extremely efficient, effective, and productive, saving time and in the long run money, since those computers were extremely expensive.
Something that might have taken days to complete now took much less time. And this started enabling greater access to computing.
Following the success of the CTSS, MIT decided it was time to build upon this system and take the next step. This next step would be to create a more advanced time sharing system.
But they imagined a more ambitious endeavor than that: they wanted to build a system that would serve as a computing utility for programers that would be capable of supporting hundreds of users accessing the mainframe at the same time. And it would share of data and resources between them.
This would require more resources, so they joined forces with General Electric and Bell Labs.
This new project was named MULTICS, which stood for 'Multiplexed Information and Computing Service' and was implemented on one of General Electric's mainframes, the GE 635.
This team worked on MULTICS for a number of years. But in 1969 Bell Labs left the project because it was taking too long and was too expensive.
Bell Labs: The Innovation Hub
Bell Labs pulling out of the MULTICS project left some employees frustrated and looking for alternatives.
While working on MULTICS, the team created an unparalleled computing environment. They were used to working with time sharing systems and had seen their effectiveness. These programmers had a vast knowledge of operating systems, and the innovations from that project made them want to expand more.
A group led mainly by Ken Thompson and Dennis Ritchie wanted to use communal computing and create a file system that they could share. It would have the innovative characteristics they liked from MULTICS but they'd implement it in a simple, smaller, and less expensive way.
They shared their ideas and started to iterate.

Bell Labs fostered an open and supportive environment that allowed creative expression and innovative ideas to bloom. It was research heavy, and they encouraged independent thinking problem solving to help them improve upon their initial solutions.
Through lots of discussion and experimentation they made the biggest breakthroughs and wrote history.
While still working on MULTICS, Ken Thompson had created a game called Space Travel. He initially wrote it on MULTICS, on the GE 635, but when Bell Labs pulled out he adapted the gamae to a Fortran program to run on the GECOS operating system that ran on the GE 635.
There were many problems with the game – it did not work as well on GECOS as it did on MULTICS and he needed a different and less expensive machine to run it on.
Ken Thompson faced rejection when asking for funding to create a different operating system, since Bell labs had pulled out from such a project already. But he did end up finding an old and little-used DEC PDP-7 minicomputer that he could try out – it was the only system available.
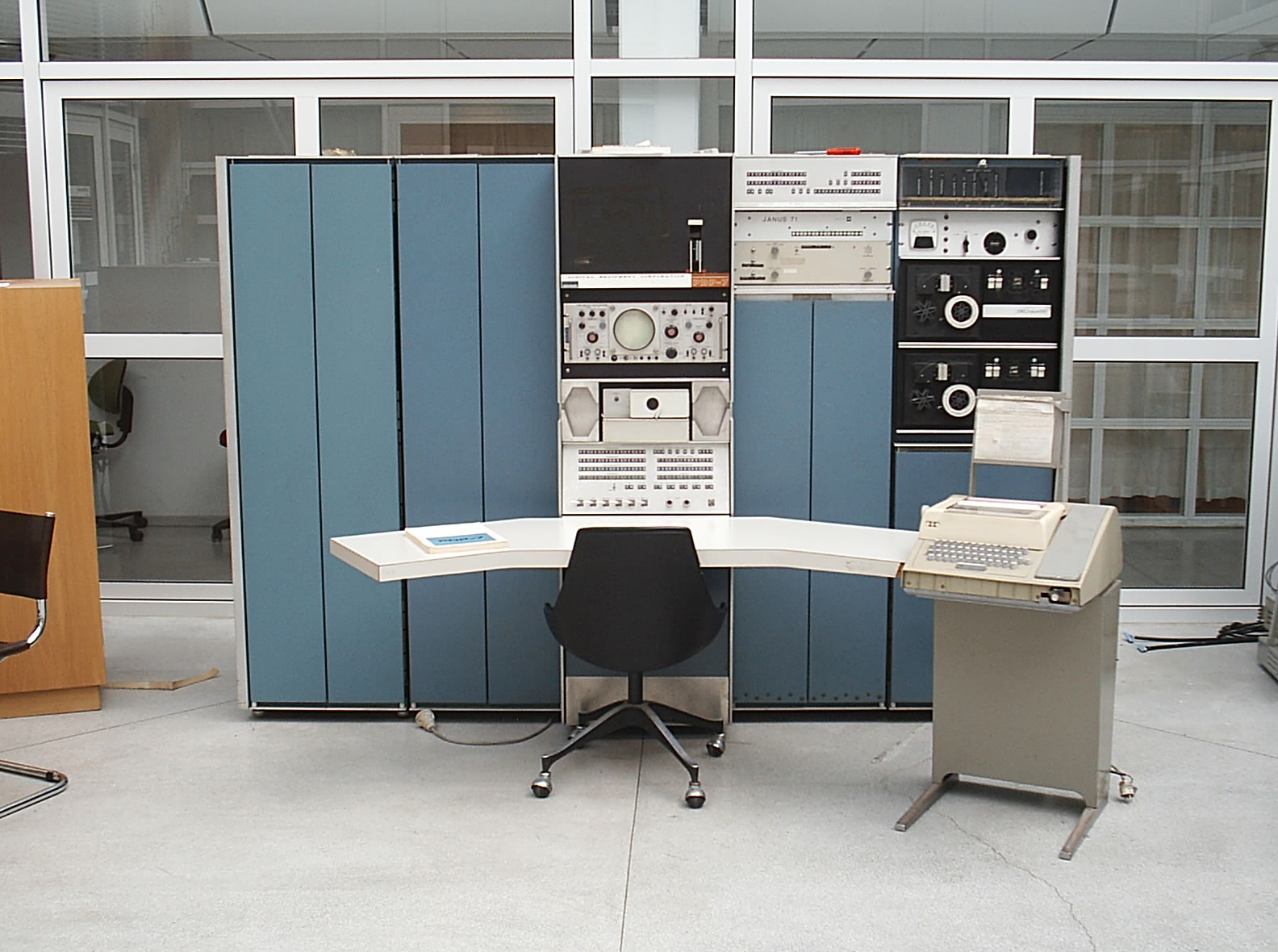

He started to write his game on that simple system but was limited by the software on the computer. So while he was working on it, he ended up implementing the bare bones of the file system his team had been envisioning.
He started with a hierarchical file system, a command line interpreter, and other utility programs. Within a month he had created an operating system with an assembler, editor, and shell. They were smaller and simpler features of MULTICS. This operating system was the first version of Unix.
The Early Days of Unix with Assembly language
At the beginning of the project, Ken Thompson could not program on the DEC PDP-7 computer. DEC PDP-7 programs had to be compiled and translated on the more powerful GE 635 mainframe and then the output was physically transferred to the PDP-7 by paper tape.
The DEC PDP-7 had very little memory, just 8KB. To deal with this restriction, the filesystem, the first version of the Unix kernel, and practically everything else in the project were coded in Assembly. Using Assembly allowed Thompson to directly manipulate and control each part of the memory on that computer.
Assembly language is a low level programming language which uses symbolic code and is close to the machine's native language, binary. The instructions in the code and each statement in the language closely corresponds to machine instructions specific to the computer's architecture.
It's machine dependent and machine specific, meaning one set of instructions has very different results from one machine to another. Programs written in Assembly language are written for a specific type of processor – so a program written in Assembly will not work on a variety of processors.
It was common to write operating systems using Assembly language back then. And when they first started working on Unix, they did not have portability in mind.
They didn't care if the operating system worked on different machine systems and architectures. That was a thought that came later. Their main priority was the efficiency of the software.
While working on MULTICS, they used high level programming languages, like PL/I in the beginning and later BCPL. Programmers had gotten used to using high level languages for writing operating system kind of software, utilities, and tools because of the advantages they offered (they were relatively easy to use and understand).
When using a higher level programming language, there is an abstraction between the computer's architecture and various obscure details. This means that it is above the level of the machine and there is no direct manipulation of the hardware's memory.
High level languages are easier to read, learn, understand, and maintain which makes them an easier choice when working on a team. Commands have an English like syntax, and terms and instructions look more familiar and human-friendly compared to the symbolic format of Assembly.
Using high level languages also means writing less code to achieve something, whereas assembly programs were extremely long.
Thompson wanted to use a higher level language for Unix from the very start, but was limited by the DEC PDP-7.
As the project progressed and as more people started working working on it, using Assembly was not ideal. Thompson decided that Unix needed a high level system programming language.
In 1970 they managed to get funding for the bigger and more powerful DEC PDP-11 that had substantially more memory.
With a fast, structured, and more efficient high level programming language that could replace Assembly, everyone could understand the code and compilers could be made available to different machines.
They started exploring different languages for writing system software that they could use to implement Unix.
From B to C: The Need for a New Language
The aim was to create utilities – programs that add functionality – to run on Unix. Thompson initially attempted to create a FORTRAN compiler but then turned to a language he used before, BCPL (Basic Combined Programming Language).
BCPL was designed and developed in the late 1960's by Martin Richards. Its main purpose was for writing compilers and system software.
This language was slow and had many restrictions, so when Thompson started using it in 1970 for the Unix project on the DEC PDP-7, he made adjustments and modifications and ended up writing his own language, called B.
B had many of the features of BCPL but it was a smaller language, with a less verbose syntax and simpler style. It was still slow and not powerful enough to support Unix utilities, however, and couldn't take advantage of the powerful features of the PDP-11.
Dennis Ritchie decided to improve upon these two previous languages, BCPL and B. He took features and characteristics from each and added additional concepts. He created a more powerful language – C – just as powerful and efficient as Assembly. This new language overcame the limitations of its predecessors and could use the power of the machine in an effective way.
So in 1972 C was born, and the first C compiler was written and implemented for the first time on the DEC PDP-11 machine.
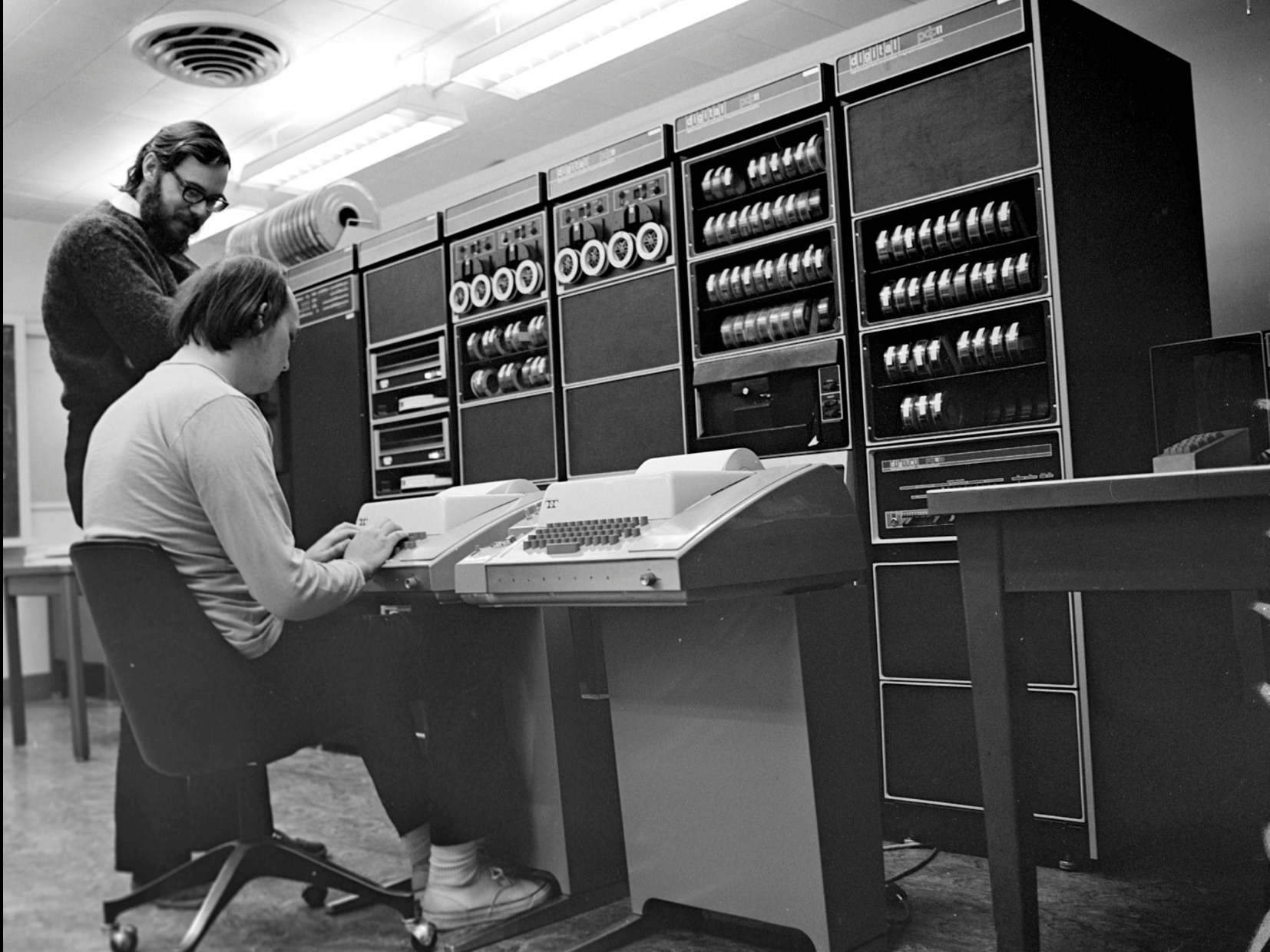

The C Programming Language
In 1973 Dennis Ritchie rewrote the Unix source code and most Unix programs and applications using the C programming language. This made it the standard implementation language of the operating system.
He reimplemented the Unix kernel in C, and almost all of the operating system (well over 90%) is written in this high level language. It mixes both high level readability features and the low level functionality, making it the perfect choice for writing an operating system.
Towards the late 1970's, C's popularity started to rise and the language started getting more widespread support and use. Up until that point, C was still only available for Unix systems and compilers were not available outside of Bell labs.
This increase in popularity came from not only the power C gave to the machine but also to the programmer. It also helped that the Unix operating system was gaining the same popularity at an even faster rate.
Unix stood out from what came before because of its portability and its ability to run on a variety of different machines, systems, and environments.
C made that portability possible and since it was the language of the Unix system, it gained more notariety – so more and more programmers wanted to try it out.
In 1978 Brian Kernighan and Dennis Ritchie co-wrote and published the first edition of 'the C programming language' book, also known in the programming community as 'K&R'. For many years this text was the go-to for C language description, definition, and reference.

In the 1980's, C's popularity skyrocketed as different compilers were created and comercialized. Many groups and organisations that were not involved in C's design started making compilers for every operating system and computer architecture structure. C was now available on all platforms.
As these organisations created compilers of their own, they started to change characteristics of the language to adapt to each platform the compiler was being written for.
There were various versions of C that had slight differences between them. While writing the compilers, these groups came up with their own interpretations of some aspects of the language, which were based on the first edition of the book 'C programming language'.
With all the iterations and adjustments, though, this book no longer described the language as it was, and the changes to the language started to cause problems.
The world needed a common version of C, a standard for the language.
The C Standard
To make sure there was a standard, machine independent definition of the language, ANSI (the American National Standards Institute) formed a committee in 1983. This committee was named the X3J11 committee, and their mission was to provide a clear, comprehensive definition and standardization of C.
After a few years, in 1989, the committee's work was done and made official. They defined a commercial standard for the language. That version of the language is known as 'ANSI C' or C89.
C was used all around the world, so a year later in 1990 the standard was approved and adopted by ISO, the International Standards Organization. The first version, C90, was called ISO/IEC 9899:1990.
Since then, many revisions to the language have taken place.
The second version of the standard, C99, was published in 1999 called ISO/IEC 9899:1999 and introduced new language additional features. The third version, C11, was published in 2011. The most recent version is the forth, C17, and is called ISO/IEC 9899:2018.
The Continuation of C
C forged a path for the creation of many different programming languages. Many of the modern high level programming languages that we use and love today are based on C.
Many of the languages created after C wanted to solve problems that C couldn't, or overcome some of the issues that limit C. For example, the most popular child of C is its Object Oriented extension C++ – but Go, Java, and JavaScript were also inspired by C.
C Language Characteristics and Why You Should Consider Learning C
C is an old language, but it still remains popular to this day, even after all these years.
It owes its popularity to the rise and success of Unix, but nowadays it has gone far beyond just being the 'native' language of Unix. It now powers most, if not all, of the world's servers and systems.
Programming languages are tools we use to solve specific computing problems that affect us on a large scale.
You don't need to know C to create web pages and web applications. But it comes in handy when you want to write an operating system, a program that controls other programs, or a programming utility for kernel development, or when you want to program embedded devices or any systems application. C excells at all these tasks. So let's look at some reasons to learn C.
It helps you understand how your computer works
Despite the fact that C is a general purpose programming language, it is mainly used to interact with low level machine functions. Besides the practical reasons behind learning the language, knowing C can help you understand how the computer actually works, what is happening underneath the hood, and how programs actually run and execute on machines.
Since C is considered the base of other programming languages, if you can learn the concepts used in this language it will be easier to understand other languages too later on.
Writing C code lets us understand the hidden processes happening in our machines. It allows us to get closer to the underlying hardware of the computer without messing with Assembly language. It also lets us get a handle on a multitude of low level tasks while staying readable like high level languages.
C is fast and efficient
At the same time, we don't lose the functionality, efficiency, and low level control of how code executes that Assembly provides.
Rememeber that each processor in every device's hardware has its own Assembly code that is unique to that processor. It's not at all compatible with any other processor on any other device.
Using C gives us a faster, easier, and overall less cumbersome approach to interacting with the computer at its lowest level. In fact, it has a mixture of both high and low level features. And it helps us get the job done without the hassle and fuss of long incomprehensible Assembly code.
So, C is as close as you can get to the computer's underlying hardware and is a great replacement for Assembly (the old standard for writing operating systems) when you're working with and implementing system software.
C is powerful and flexible
This close proximity to the hardware means that C code is written explicitly and precisely. It gives you a clear picture and mental model of how your code is interacting with the computer.
C does not hide the complexity with which a machine operates. It gives you a lot of power and flexibility, like the ability to manually allocate, manipulate, and write directly to memory.
The programmer does a lot of the heavy work and the language lets you manage and structure memory in an efficient way for the machine delivering high performance, optimisation, and speed. C lets the programmer do what needs to get done.
C is portable, performant, and machine-independent
C is also highly portabile and machine independent. Even though it is close to the machine and has access to its low level functions, it has enough abstraction from these parts to make code portability possible.
As Assembly instructions are machine specific, programs are not portable. One program written on one machine would have to be re-written to run on another. And that is hard to maintain for every computer architecture.
C is universal and programs written in it can be compiled and run across many platforms, architectures, and a variety of machines without losing any performance. This makes C a great choice for creating systems and programs where performance really matters.
C inspired the creation of many other programming languages
Many languages that are commonly used today, like Python, Ruby, PHP and Java, were inspired by C. These modern languages rely on C to work and be efficient. Also, their libraries, compilers, and interpreters are built in C.
These languages hide most of the details about how programs actually work underneath the hood. Using these languages, you don't have to deal with memory allocation and bits and bytes since there are more levels of abstraction. And you don't need this level of granular control with higher level applications where interaction with memory is error-prone.
But when you're implementing part of an operating system or embedded device, knowing those lower-level details and direct handling can help you write cleaner code.
C is a fairly compact language
Although C can be quite cryptic and hard to learn for beginners, it is actually a fairly small and compact language with a minimal set of keywords, syntax, and built-in functions. So you can expect to learn and use all of the features of the language when exploring how it works.
Even if you're not interested in learning how to program an operating system or a systems application, knowing C basics and how it interacts with the computer will give you a good foundation of computer science concepts and principals.
Also, understanding how memory works and is laid out is a fundamental programming concept. So understanding how the computer behaves on a deeper level and the processes that are happening can really help you learn and work with any other language.
There is a lot of C code in the devices, products, and tools that billions of us use in our everyday lives. This code powers everything from the world's supercomputers to the smallest gadgets.
C code makes embedded systems and smart devices of all kinds work. Some examples are household appliances like fridges, TVs, coffee makers, DVD players, and digital cameras.
Your fitness tracker and smart watch? Powered by C. The GPS tracking system in your car, and even traffic light controllers? You guessed it – C. And there are many examples of embedded systems used in the industrial, medical, robotics, and automobile industries that run on C code.
Another area where C is widely used is Operating Systems and kernel development. Besides Unix, for which the language was created, other major and popular Operating Systems are coded to some extent in C.
The Microsoft Windows kernel is scripted mostly in C, and so is the Linux kernel. Most supercomputers are powered by Linux, and so are most Internet servers. This means that C powers a large section of the Internet.
Linux also powers Android devices, so C code not only makes supercomputers and personal computers work, but smartphones too. Even OSX is coded to some extent in C, which makes Mac computers run on C, too.
C is also popular for developing desktop applications and GUIs (Graphical User Interfaces). Most Abode Applications we use for video and photo editing and graphic design (like Photoshop, Adobe illustrator, and Adobe Premiere) are coded with C or its successor, C++.
Compilers, interpreters, and assemblers for a variety of languages are designed and built with C – in fact these are some of the most common usages of the language.
Many browsers and their extensions are built with C, like Google Chromium and the Google file system. Developers also use C often in database design (MySql and Oracle are two of the most popular database systems built in C), and it powers advanced graphics in many computer games.
From this general overview, we can see that C and it's derivative C++ run a large part of the internet and the world at large. Many of the devices and technologies we use in our daily lives are written in or depend on C.
C Compilation Process: Write-Compile-Run
What is a program in c.
A computer program written in C is a human readable and ordered set of instructions that a computer executes. It aims to provide a solution to a specific computing problem and tell the computer to perform a certain task with a sequence of instructions that it needs to follow.
Essentially all programs are just plain text files stored on your computer’s hard drive that use a special syntax which is defined by the programming language you're using.
Each language has its own rules that dictate what you can write and what's considered valid, and what is not.
A program has keywords, which are specific words that are reserved and are part of the language. It also has literal pieces of data like strings and numbers. And it has words that follow the language’s rules, which we define and introduce to the language that don’t already exist (like variables or methods).
What is a compiler?
Programs are written by us and for us. They are meant to be understood by humans.
When we write programs in human readable form, we can understand them – but the computer may not be able to. Computers don’t directly understand programming languages, they only understand binary. So programs need to be translated into this other form so the computer can actually understand our program's instructions.
Programs in high level languages can be either compiled or interpreted. They use special pieces of software called compilers and interpreters, respectively.
What's the difference between an compiler and an interpreter?
Both compilers and interpreters are programs, but they're far more complex ones, and they act as translators. They take a program that's written in a human readable form and turn it into something that computers can make sense of. And they make it possible to run and execute programs on different computer systems.
Compiled programs are first converted into machine-readable form which means they are translated into machine code before they run. Machine code is a numerical language – binary instructions composed of sequences of 0s and 1s.
This compliation produces an executable program, that is a file containing the code in the machine language that the CPU (Central Processing Unit) will be able to read, understand, and execute directly.
After this, the program can run and the computer does what the program tells it to do. Compiled programs have a stronger correspondence with the underlying hardware and can more easily manipulate the computer's CPU and memory.
Interpreted programs, on the other hand, are not directly executed by the machine nor do they need to be translated into a machine language program. Instead, they use an interpreter that automatically and directly translates and executes each statement and instruction in the code line by line during run time.
C is a compiled programming language. This means that it uses a compiler to analyse the source code written in C and then turns it into a binary file that the computer's hardware can directly execute. This will be specific for each particular machine.
How to use the GCC Compiler with examples
Unix and Unix-like systems already have a C compiler built in and installed. This means that Linux and MacOS have a popular compiler built in, called the GCC Compiler (or GNU Compiler Collection).
In the rest of this section we'll see examples using this compiler and I've based these examples on a Unix or Unix-like system. So if you have a Windows system, make sure to enable the Windows Subsystem for Linux .
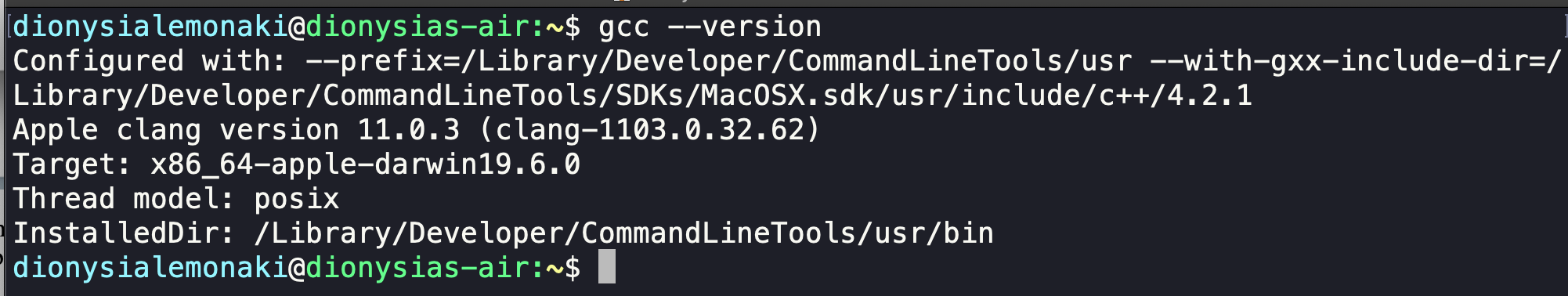
First, make sure you have the GCC compiler installed. You can check by opening your terminal and typing gcc --version in the prompt which is typically after the $ character.
If you're using MacOS and have not installed the command line developer tools, you will get a dialog box pop up asking you to install them – so if you see that, go ahead and do so.
Once you have those installed, open a new terminal session and re-type the gcc --version command. If you have already installed the command line tools, you should get the output below:
The term compiling alone is an abstraction and simplification, though, since in reality there are many steps happening behind the scenes. These are the finer lower level details that happen between us writing, compiling, and then running our C program. Most even happen automatically, without us even realising it.
How to write C source code
In order to develop C programs, we first need to have some type of text editor. A text editor is a program we can use to write our code (called our source code) in a text file.
For this you can use a command-line text editor like nano or Vim if you are comfortable with those.
You can also use an IDE (Integrated Development Environment), or text editor with IDE-like features (an integrated terminal, the ability to write, debug, run and execute our programs all in one place without leaving the editor, and much more).
One editor with these capabilities is Visual Studio Code, using the C/C++ extension . Throughout the rest of this tutorial we'll use VSCode.
Back in your terminal, go ahead and type the commands below to create a file where our C code will live.
So we have just created a plain text file, hello.c . This file will have code written in the C language meaning it will be a C program. This is indicated by the .c file extension which is a convention.
Inside it we can write any C program we like, starting from a very basic one like a program that outputs 'hello world' to the screen.

In order to see what our code does, we have to run the program we have just written. Before running it, though, we have to first compile it by typing some commands in the terminal.
We can continue using the command line on our computer or we can use the integrated terminal in VSCode (by holding the control ~ keys at the same time a new terminal window opens).
So far we can see on the left panel that there is only one file in our cprogram directory, hello.c , which contains our C code.
The term 'compiling our C code' doesn't just happen in one step. It also involves some smaller actions that occur automatically for us.
As a reminder, when we refer to compiling, we typically mean that the compiler takes our source code as input (the code we wrote in C which has English like syntax), and translates it to produce machine code statements as output.
This machine code corresponds directly to our source code instructions, but it's written in a way the CPU can understand so it can carry out the instructions and execute them.
How C source code gets transformed into binary code
This is the general idea – but there are 4 smaller steps involved that happen in between. When we compile our code we are actually preprocessing, compiling, assembling, and linking it.
These steps start happening when we type the command gcc hello.c in the terminal which is the name of the compiler and the source code file, respectively.
If we wanted, we could alternate and customise that command by typing a more specific one like gcc -o hello hello.c , where:
- -o stands for 'output this file'
- hello is the name we ourselves specify for the executable program file we want to output that will be created, and
- hello.c is the file the gcc compiler will take as input (which is the file where our source code lives and we want to compile).
Preprocessing in C
Another program that is part of the compiler conducts this first step – the preprocessor. The preprocessor does many things – for example, it acts as a ‘find and replace tool’ as it scans through our source code looking for special statements and searches for lines starting with a # .
Lines starting with a # ,like #include , are called preprocessor directives. Any line starting with a # indicates to the preprocessor that it must do something. In particular, it tells that it should substitute that line with something else automatically. We don't see this process, but it's happening behind the scenes.
For example, when the preprocessor finds the line #include <stdio.h> in our hello world program from earlier, the #include literally tells the preprocessor to include, by copying and pasting, all the code from that header file (which is an external library, stdio.h ) in the place of that statement in our own source code. So it replaces the #include <stdio.h> line with the actual contents of the stdio.h file.
Inside the <stdio.h> library there are function prototypes and definitions or hints. This way all the functions are defined so the computer recognizes them during compilation time, and we can use them in our program.
For example, the function printf(); is defined as int printf(const char *format,…); inside <stdio.h> . The same steps happen for other header files, that is files with a .h extension.
During the preprocessing step, our comments in our code are also removed and macros are expanded and replaced with their values. A macro is a fragment of code which has been given a name.
At this stage if there are no errors in our code, there should be no output in the terminal, which is a good sign.
We see no output, but a new file has been created with a .i extension which is still C source code. This file includes the output from the preprocessing, so it is called preprocessed source code. In this case a new file, hello.i , is generated but it won't be visible in our editor.
If we run the command gcc -E hello.c :

We will be able to see all the contents of this file (which is a lot) and the ending looks something like this:
If there are any mistakes with the correctness of our code or we're not following the semantics of the language, we'll see some errors and the compilation will end. We would have to correct the mistakes and start the process from the beginning.
Compiling in C
After the preprocessing step which produces preprocessed C source code, next we have to compile the code. This involves taking the code that is still source code and changing it into another intermediate form. We use a compiler for this step.
To review, a compiler is a program which takes as input the source code and translates it into something closer to the native language of computers.
When we refer to compiling we can either mean the entire process of translating source code to object code (machine code) or just a specific step in the whole compilation process.
The step we're discussing now is when compiling converts every statement of the preprocessed C source code program to a more computer friendly language. This language is closer to binary which the computer can actually directly understand.
This intermediate language is assembly code, a low level programming language used to control the CPU and manipulate it to perform specific tasks and get close access to the computer's memory. Remember assembly code from the history section?
Every CPU – the brains of the computer – has its own set of instructions. Assembly code uses specific statements and commands that directly correlate to those instructions and low level operations that a CPU performs and carries out.
So in this step of the compilation process, each statement in the preprocessed C source code in the file hello.i is translated by the compiler to the equivalent statement in assembly language at a lower level.
The output of this action creates a file ending in .s (so hello.s behind the scenes) that contains instructions in assembly.
By typing the command gcc -S hello.c we can view the contents and the somewhat incomprehensible assembly commands of the hello.s file that the compiler created (but that was not visible to us when we typed gcc hello.c alone).
If we look closely we'll see a couple familiar keywords and statements used in our C source code like main and printf :
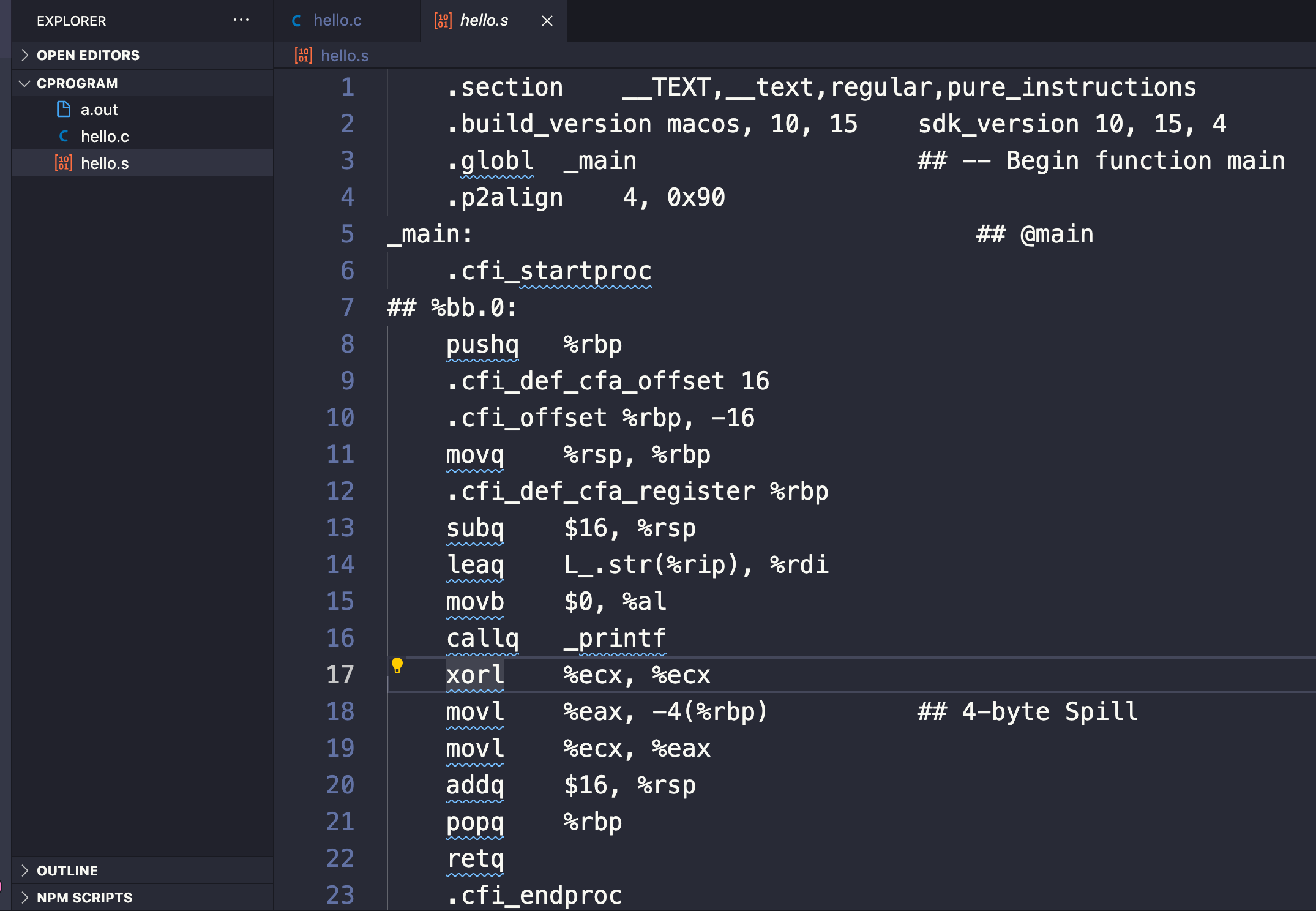
Assembling in C
Assembling means taking the hello.s file containing assembly code statements as input and, with the help of another program that is executed automatically in the compilation process, assembling it to machine code instructions. This means it will have as output actual 0s and 1s, or binary format statements.
This step also happens behind the scenes, and it results in the final language the instructions in our source code are translated to. And now the computer can finally understand those instructions.
Each of the commands we wrote in our C source code were transformed to assembly language statements and finally into the equivalent binary instructions. All this happened just with the command gcc . Whew!
The code we wrote is now called object code, which a specific computer's CPU can understand. The language is incomprehensible to us humans.
People used to code in machine language, but it was a very tedious process. Any symbols that are non-machine code symbols (that is, anything that's not 0s and 1s) are hard to make sense of. Coding in such a language directly is extremely error-prone.
At this stage, another file is created with a .o extension (for object) – so in our case it'll be hello.o .
We can see the actual contents of the object file containing the machine level instructions with the command gcc -c hello.c . If we do this, we'll see the not human readable contents of hello.o :
Linking in C
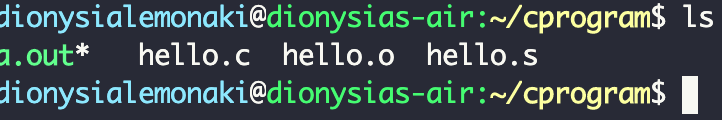
In the images above, you might have noticed an a.out file in our directory.
This is the default step and file that gets created when we type the compiler command and our filename, gcc hello.c in our case.
If we had used the command gcc -o hello hello.c mentioned earlier, we would have seen a custom named hello executable program in place of a.out .
The a.out stands for assembly output . If we type ls in the terminal to list the files in our directory, we see that a.out even looks different from the rest:
Linking is the final stage of the compilation process where the final binary file hello.o is linked with all the other object code in our project.
So if there are other files containing C source code (like files included in our program that implement C libraries which are already processed and compiled, or another file we have written named, for example, filename.c besides hello.c ), this is when the object file filename.o will be combined with hello.o and the other object codes, linking them all together.
This forms one big executable file with the combined machine code, a.out or hello , which represents our program.
Since we're finally done compiling, the program is in its final form. And now we can execute and run the file on our machine by typing ./a.out . This means 'run the a.out file that is in the current directory', since ./ represents the folder we are in. We then see the output of our program in the terminal:

Whenever we make changes to our source code file, we have to repeat the process of compiling from the beginning in order to see the changes when we run the code again.
How to Write Hello World in C
A hello world program is a very simple one, but it's a tradition that also acts as a test message when you're first starting to learn how to code in a new programming language.
If you execute your "Hello World" program successfully, this lets you know that your system is correctly configured.
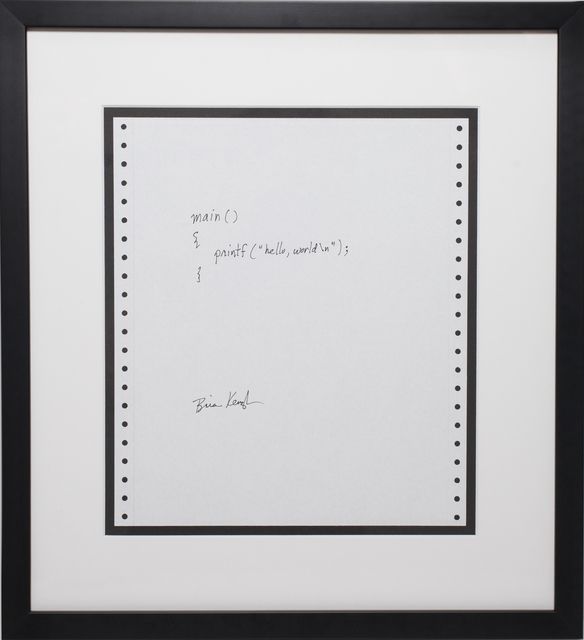

A 'hello world' program contains the basic syntax for the language and we can break it down into smaller parts:
Header files in C
Header files are external libraries. This means they are a set of code already written by some developers for other developers to use.
They provide features that are not included at the core of the C language. By adding header files to our code, we in return get additional functionality that we can use in our programs.
Header files like include <stdio.h> end in the extension .h . In particular, a header file like stdio.h comes already built into the compiler.
The line include <stdio.h> is an instruction for the pre-written functions in the stdio.h library file which tells the computer to access and include them in our program.
stdio.h gives us the functionality standard input and standard output , which means we'll be able to get input and output from the user. We therefore get to use input/output functions like printf .
If you don't include the stdio.h file at the top of your code, the computer will not understand what the printf function is.
The main program in C
Here's the code:
This is the main starting function of a C program. The curly braces ( {} ) are the body which wraps all the code that should be in our program.
This line acts as a boilerplate and starting point for all C programs. It lets the computer know where to begin reading the code when it executes our programs.
Comments in C
Whatever we write after the // will not affect how our code runs and the computer will not take it into account during compilation and execution time.
Those two lines indicate that you're adding comments, which are notes to our future selves and to our coworkers. Comments can help us remember and remind others what a certain line of code does or why we wrote that code in the first place. It also reminds us what exactly is the purpose of that code when we come back to it the next day of even months later.
Output or printing to the console in C
printf("Hello world/n"); prints the phrase 'Hello world' to the console. We use printf when we want to say something and to see the output on the screen. The characters we want to output need to be surrounded by double quotes "" and parentheses () .
The /n is an escape character, which means that it creates a newline and tells the cursor to move to the next line when it sees it.
The ; indicates the end of of sentence and the end of that line of code.
Variables in C
Here's how we define a variable in C:
A data item that may take on more than one value during the runtime of a program.
In the simplest terms, you can think of variables as a named box. A box that acts as a storage place and location for holding different information that can vary in content.
Each box has a unique name which acts like a label put on the outside that is a unique identifier, and the information/content lives on the inside. The content is the variable's value.
Variables hold and point to a value, to some useful data. They act as a reference or abstraction to literal data. That data is stored in the computer's memory, and takes up an certain amount of space. It lives there so we can retrieve it later and use it in our programs when we need to.
As the name suggests, what variables point to can vary. They are able to take different values over time as information changes during the life of the program.
Variable Assignment in C
The process of naming a variable is called assignment. You set a specific value that is on the right, to a specific variable name that is on the left. You use the = or the assignment operator to do this.
As I mentioned, you can change a variable's value, so you can assign and reassign variables. When you reassign a value, the new value points to the variable name. So the value can be a new one, but the variable name stays the same.
How to declare vs initialise a variable in C
The C programming language is a strongly statically typed language, unlike many other modern programming languages.
In statically typed languages, you need to explicitly declare your variables to be of a certain data type. That way the compiler knows during compilation time if the variable is able to perform the actions it was set out and requested to do.
In dynamically typed languages, a variable can change between different data types without the need to explicitly define that data type.
So, when declaring a new variable in the C language, you need to define and specify what type it is, and what type of data its value holds.
A variable's type is the type of the value it holds. This lets the program and later the compiler know what kind of information it's storing.
To declare a variable, you specify the data type, and give a name to the variable . An optional step is to set an initial value. Do not forget the semicolon at the end, which ends the statement!
What is the difference between initialising and declaring a variable?
In summary:
int n; is declaring a variable. Declaring means we define a name for the variable and specify its type.
We don't necessarily need to specify a value for the variable just yet. This is enough, as declaring a variable tells the computer we want a variable to exist and we need to allocate some space in memory for it. The value can and will be stored at a later time.
When we do assign the variable a value later, there is no need to specify the data type again. We can also declare multiple variables at once.
If we declare a variable and assign it a value at once, this is called initialising the variable.
int n = 27; is initialising the variable. It refers to assigning an initial value which we can change later.
If the new value is the same data type, we don't need to include the data type, just the new value. If the data type is different, we will get an error.
Rules for naming variables in C
- Variable names must begin either with a letter or an underscore, for example age and _age are valid.
- A variable name can contain letters (uppercase or lowercase), numbers, or an underscore.
- There can be no other special symbols besides an underscore.
- Variable names are case sensitive , for example age is different from Age .

The scope of a variable in C
The scope of a variable refers to where the variable can be referenced and accessed from. It is essentially where the variable lives and is valid and how visible it is to the rest of the program.
Local scope
If a variable is declared within a set of culry braces, {} , like for example a specific function, that will be its scope and we can't access it and use it outside those braces in the rest of the program. The rest of the program won't know it exists.
Therefore it is not a good idea to declare variables that way since their scope and use is so limited which can lead to errors. This scope is called local scope.
Global scope
If variables are declared outside of functions, they have global scope. Having a global scope means they are visible within the whole program and can be accessed from anywhere.
But keep in mind that it can be difficult to keep track of them. Also, any changes we make to them along the way can get confusing since they can happen in any part and location of the program.
Data Types in C
Data types specify in what form we can represent and store information in our C programs. They let us know how that information will be used and what operations can be performed on it.
Data types also determine what type of data our variables can hold, as each variable in C needs to declare what data type it represents.
There are 6 data types built into the language. But you can convert between different types which makes it not as strongly typed.
Each of the data types requires a different allocation of memory and each data type can have different ranges up to which they can store values.
Adding keywords in front of a type name modifies and makes changes to the type. These keywords can be either unsigned or signed .
An unsigned keyword means that the type can only be positive and not negative, so the range of numbers start from 0. A signed keyword lets you make a number negative or positive.
Let's look at these data types in more detail.
The char data type in C
The most basic data type in C is char . You use it to store a single character such as letters of the ASCII chart like 'a', 'Z', or '!". (Notice how I used single quotation marks surrounding the single character – you can't use double quotes in this case.)
char also lets you store numbers ranging from [-128 to 127] and in both cases uses 1 byte of memory.
An unsigned char can take a range of numbers form [0-255]
The int data type in C
int is a an integer, a whole number, that can hold a positive or negative value or 0 but that has no decimal.
It is a value up to a certain number of bits. When you declare an int , it the computer allocates 4 bytes of memory for it. More specifically it uses at least 2 bytes but usually 4. 4 bytes of memory means it allocates 32 bits (since 1 byte = 8 bits). So an int has 2 32 possible values – more than 4 billion possible integers.
The range is of a -2 31 to 2 31 -1,specifically from [-2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647].
- An unsigned int has still the same size as an int (4 bytes) but that doesn't include the negative numbers in the range of possible values. So the range is from 0 to 2 32 -1, more specifically [0 to 4,294,969,295]
- A short int has smaller values than an int and allocates 2 bytes of memory. It allows for numbers in a range of [-32,768 to 32,767]
- An unsigned short int uses again 2 bytes of memory and has a range of numbers from [0 to 65,535]
- A long int is for when we need to use a larger number. It uses at least 4 bytes of memory, but usually 8 bytes with values from [-2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647]
- An unsigned long int has at least 4 bytes of memory with a range from [0 to 4,294,967,295]
- A long long int is an integer with more bits that's able to count to higher and larger numbers compared to ints and long ints. They use 8 bytes instead of 4 and so use 64 bits. This allows for a range from -2 63 to 2 63 -1 ,so for numbers from [-9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807]
- An unsigned long long uses 8 bytes and has a range of numbers from [0 to 18,446,744,073,709,551,615]
The float data type in C
Floats are a floating point value which is a number with a decimal (also called a real number), with single precision. It allocates 4 bytes of memory.
The double data type in C
A double is a floating point value which has bigger values than that of a float. It can hold more memory – 8 bytes – compared to a float, and is double precision.
- A long double is the largest size compared to floats and doubles, holding at least 10 bytes of memory, but can even hold up to 12 or 16 bytes.
And lastly, the void type essentially means nothing or no value.
Format Codes in C
Format codes or format specifiers are used for input and output in C.
These are a way to tell the compiler what type of data it takes in as input with a variable, and what type of data it produces as output when using the printf() function. The f in printf() stands for formated .
They act as a format code placeholder and substitute for variables. They let the compiler know in advance what type they are when the value of the standard output (that is, what we want to print) is not already known.
The syntax we use is % format specifier for data type :
There are different format specifiers for each data type we discussed earlier. Here are some of them:
Operators in C
Arithmetic operators in c.
Arithmetic operators are mathematical operators that perform mathematical functions on numbers. Operations can include addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
The most commonly used operators are:
- + for addition
- - for subtraction
- * for multiplication
- / for division
- % for modulo division (calculating the remainder of the division)
Assignment operator in C
The assignment operator, = , assigns a value to a variable. It 'puts' a value into a variable.
In other words, it sets whatever is on the right side of the = to be the value of the variable on the left side of the = .
There are specific assignment operators for updating a variable by modifying the value.
In C, there are various ways we can update the values of variables. For example, if we want to increment the variable by 1 there are three possible ways to do so.
It is worth mentioning first that incrementing means to take the existing value of a variable, whatever value is on the right, and add 1 to it. The new value is then stored back to the variable and automatically updated.
The simplest way to increment or update is to have a variable called x with an initial value of 5 , so:
To add 1 to the variable x , we do x = x + 1 which means x = 5 + 1 .
The new value of x is now 6 , x=6 .
There is a shorthand for this operation, using a special syntax that increments variables.
Instead of writing x = x +1 we can write x += 1 .
An even shorter way is to use the increment operator, which looks like variable_name ++ , so in our case x++ .
The same goes for decreasing, that is decrementing, a variable by 1.
The three ways to do so are:
x = x-1 , x -= 1 , x -- (using the decrement operator) respectively.
Those are the ways to increment and decrement a variable by 1 in C. We are able to update a variable by taking its value and adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing that value by any other number and setting the result of that operation as the new value. Those operations would be += , -= , *= , and /= respectively.
So x = x * 5 or the shorthand x *= 5 will take the value of the variable x and multiply it by 5 and store it back to x .
Logical Operators in C
We use logical operators to make decisions in C. The result of an operation can be either true or false.
There is the logical AND operator, && . Operands on both the left and right sides of && need to be true for the condition to be true.
There is also the logical OR operator, || . At least one or both of the operands on the right and left sides of || need to be true for the condition to be true.
Lastly, there is the logical NOT . This inverts the value of the operand. If an operand is true, then the NOT operator makes the condition false and vice versa.
Comparison operators in C
Comparison operators are:
- Greater than >
- Greater than or equal to >=
- Less than <
- Less than or equal to =<
There is also an equality comparisson operator, == . Don't confuse this with = , the assignment operator.
We use the == to compare two values and test to see if they are equal or not. This operator asks the question 'Are these two equal?', whereas = assigns a value to a variable.
When using the equality comparisson operator and asking the above question, there is always a return value that can either be true or false , otherwsie knokn as a Boolean value in the context of computer programming.
Lastly, there is the inequality operator, != , that we use to test whether two values are NOT equal.
Functions in C
Functions are verbs, that is, small actions. They do something. They perform a particular, specific task.
They encapsulate a piece of behaviour that is meant to be used again and again. The purpose of functions is to have that behaviour written out just once somewhere so you can reuse it whenever you need to, at different times and in different places throughout a program. This makes your code simpler and better organised.
Functions exist to perform one task, serve a particular purpose, and be reused. And they can take in inputs and produce outputs.
Function arguments in C
The inputs that functions take in are called arguments. A function can have one or more arguments.
A common function in the C programming language is printf(); . This prints something to the screen. It's a function used to say something.
The parentheses () are the inputs to the function, where the arguments go in – that is, what we actually want to say and print to the screen. What is between the parentheses gets printed out.
In printf("Hello world!"); , Hello world! is the input to the printf function. Here, we are calling a function called printf and we are giving it an argument that is a string. This says literally, print 'Hello world! 'to the screen.
Function outputs in C
There are two types of function output:
First, outputs can just be something visual, an immediate visual effect, something quickly printed to the screen.
You can't do anything more with that output after the effect. Like in the case of printf("Hello world!"); , the output is the string "Hello world!" printed to the screen, and that's it. You can't use that string in some other way, because printf has no return value.
These types of functions are known as side effects , meaning they have an immediate observable effect without returning a value.
Also, a function like printf is a function invocation and in the stdio library is defined as int printf(const char *format,...); .
Second, the output can be reusable, and has a return value. A return value is a value passed back to the programmer and stored in a variable for later use.
In such cases, there is no immediate effect – nothing gets printed to the screen. The output is instead return to us, stored as information and saved in a variable.
How to Define a Method in C
There are three things you need to have in the first line, the decelerating line, when defining a function.
- The return type
This is the very first keyword used, and how a function starts indicates the return value.
For example in a function like: void say_something(void) , the first void means that the function has no return value.
In another example with a different function, int main(void) , we specify and define its return data type, in this case an int . The function's output will be an int data type and will be returned to where the function is called.
- The function name
The name can be anything we want, although it is best practice to name the methods after what they intend to do.
- None or one or more arguments
These are the function's inputs, and the data type of those inputs.
In void say_something(void) , the void inside the parentheses is a keyword for the argument and a placeholder for 'nothing'. It means it takes In no inputs. In cases like this, the argument is also called a parameter.
Parameters are essentially variables declared in the function, inside the parentheses like the void keyword. They act as a placeholder to access the function input data, the arguments.
Parameters refer to the value being passed in to the method. This means that when we later call the function, we pass the actual values to it, the arguments to the function.
How to Call a Function in C
We can call a function like:
By writing the function's name, followed by any arguments in parentheses and a semicolon like say_hi(); . The say_hi function takes in no inputs and has no return value. When called it just prints 'hello' to the screen.
Another function like:
is called in the same way as the previous example. In this case, the square function take in an input and has a return value (both are int s). The input it takes in is the parameter called n , that returns an int when the function is called.
The word return specifies that what will get returned, the input n multiplied by itself.
For example, when the function is called square(3); , n acts as a variable that points to the parameter that has been passed in to the function, like 3 . It is like we have set n = 3 . The value that gets returned is 9 .
Functions are meant to be reused, so we can use it anytime we wish to square a number:
How to Use Boolean Expressions in C
A boolean expression is an expression that evaluates to one of two values, true or false. They get their name after the mathematician, philosopher, and logician George Boole.
We use boolean expressions to compare two values and they are particularly helpful in control flow.
Every non-zero value is true and 0 is false .
We can combine boolean expressions with the use of the different logical operators, like && (and), || (or) and ! (not) mentioned earlier in the article.
Different combinations of values and operators lead to different output results, which can be expressed in a truth table , a mathematical table used to represent logical equations wich result to 1 or 0 or their equivalent true or false .
When comparing two boolean values using the && (and) operator, both values have to equate to true for the combined experssion to be true.
For example if someone asks us "Do you want a pizza and a salad?", the only way for the expression to be true is for us to want both a pizza and a salad (so our answer is yes to both). If the answer to one of them is not true then the whole expression is false.
Truth Table for &&
Unlike && , the || operator lets us take action if one or both values are true. So this operator is not exclusive, either one of the comparissons has to be true for the experssion to evaluate to true or even both.
This is quite unique to computing, since in our example question used earlier, if instead of AND we changed it to OR, the statement 'Do you want pizza or a salad?' does not mean that you want both. You want one or the other, not necessarily both together.
Truth table for ||
Lastly, the ! (not) operator is used for negation, meaning it turns true to false and false to true .
How to Use Conditional Statements in C
Conditional statements take a specific action based on the result of a comparisson that takes place. The act of doing one thing if a particular condition is true and possibly a different thing if that particular condition turns out to be false is called control flow .
Certain parts of the program may not run depending on the results or depending on certain user input. The user can go down different paths depending on the various forks in the road that come up during a program's life.
Programs with conditional statements use if blocks primaraly. The if blocks use boolean expressions that can only be true or false and they make decisions depending on those resulting values. We denote an if block statement by using curly braces, {} , and indendation of the code that follows.
An if statement on its own is not that helpful especially as the programs grow larger and larger. So in that case the if statement is accompanied by an else statement.
These mean that ' if this condition is true do the following, else do this instead'. The else keyword is the solution for when the if condition is false and therefore doesn't run.
If we wish to chose between more than just two options and want to have a greater variety in statement and actions, then we can introduce an else if condition.
This means that 'If this condition is true, do this. If it is not, do this thing instead. However, if none of the above is true, finally do this instead.'
How to Use Loops in C
A loop is an isolated behavior or a specific set of instructions that are repeated a certain number of times, over and over again, until a condition is met. It is the same action, the same code, being repeated again and again.
While loops in C
Before they run any code, while loops have to check a condition. If it is met, the code runs. If not, the code doesn't take any action. So, code is not guaranteed to run even at least one time if a condition is not met.
There are different types of while loops. One of them is an infinite loop.
The while keyword is used along with a required boolean expression, true in this case (which always stays true ).
After printing the line of code inside the curly braces, it continuously checks wether it should run the code again. As the answer is always yes (since the condition it needs to check is always true each and every time), it runs the code again and again and again.
In this example the only way to stop the program and escape from the endless loop is running Ctrl + C in the terminal.
If the condition was false , it would never run the code inside the curly braces.
Another loop, is a loop that repeats something a certain number of times.
Do-while loops
Compared to the while loop, the do- while loop is guaranteed to run at least once and execute the code inside the curly braces at least one time.
It first does something and then checks a condition. This is useful when we want to repeat something at least once but for an unknown number of times.
In our example, the code will run at least one time and the statement will be printed at least once. Next, the value is incremented. It then checks if the value is less than 20, and if so, it runs the code again. It will stop running the code once the value being incremented each time is no longer less than 20.
Resources to continue learning C
This marks the end of this intoduction to the C programming language! Nice work for making it through to the end.
I hope this gave you an insight into the 'whys' and the 'hows' of the language and the fundamentals you need to know to start writing basic programs in C.
If you want to go more in depth, build some projects, and problem solve using C, give CS50 Introduction To Computer Science a go.
If you enjoy learning by reading books, I recommend the ones below:
- C programming absolute beginners guide
- Programming in C
If you enjoy learning by watching videos and coding along,check out the C Programming Tutorial for Beginners video on freeCodeCamp's YouTube channel.
Thanks for reading and happy coding!
Read more posts .
If this article was helpful, share it .
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp's open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
Browse Course Material
Course info, instructors.
- Daniel Weller
- Sharat Chikkerur
Departments
- Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
As Taught In
- Programming Languages
- Software Design and Engineering
Learning Resource Types
Practical programming in c, problem set 1.
Problem set on writing, compiling, and debugging C programs, preprocessor macros, the C file structure, variables, functions and program statements, and returning from functions.

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare
- [email protected]

What’s New ?
The Top 10 favtutor Features You Might Have Overlooked

- Don’t have an account Yet? Sign Up
Remember me Forgot your password?
- Already have an Account? Sign In
Lost your password? Please enter your email address. You will receive a link to create a new password.
Back to log-in
By Signing up for Favtutor, you agree to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy.
24/7 C Programming Assignment Help (Chat Now)
Chat with experts to get instant C programming assignment help or homework help now.

Why are we best to help you?
Qualified & professional experts to help you
24x7 support to resolve your queries
Top rated tutoring service specializing in international education
Affordable pricing to go easy on your pocket
C homework or assignment help.
Our qualified tutors are ready to provide their expertise and assist you with all your assignments and queries. We are available 24x7! Reach us at any time to get your queries solved.

Instant C programming Assignment help
Looking for C programming assignment help online? Most college students are burdened with academic pressure, exams, and internal seminars. Some students also take up part-time jobs, and it gets difficult for them to complete their assignments within the given deadline. If you are looking for a C programming assignment help, whether it is a simple demonstration of your code or writing a templated data structure- you have come to the right place. At FavTutor, we have expert tutors in C programming who help you accomplish impeccable quality assignments well within the required deadline. Moreover, you can also connect with our tutors 24/7 through chat or email.
About C Programming
C is a general programming language that's very common, simple, and versatile to use. It's a structured programming language that's machine-independent and extensively accustomed to writing varied applications, in operation Systems like Windows, and plenty of alternative advanced programs like Oracle information, Git, Python interpreter, and more. It was initially developed by Dennis Ritchie in the year 1972. The main features of the C language embrace low-level access to memory, an easy set of keywords, and clean style, these options create C language appropriate for system programming like associate degree package or compiler development.
There are many important topics in the C programming language. Some of these are quite difficult for someone who is familiar more with C++ or Java, so C programming help becomes a necessity for them. These topics help to work with the C language and make it simple and easier to work with. Let us study some of them below:
The C program consists of preprocessor commands, functions, variables, statements that are to be executed, and comments if required. This program is then compiled and executed according to the output we require from the program.
Data sorts in c are an intensive system used for declaring variables or functions of various types. The type of a variable determines what quantity of space it occupies in storage and the way the bit pattern considers it.
Operators are special symbols that help the compiler to perform some specific mathematical and logical operators. Some of the operators are arithmetic operator, relational operator, logical operator, bitwise operator, assignment operator, etc.
The functions can be defined as a group of the statement in a program performs a specific task. It is the reusable code used to perform a single related task.
How we provide C programming help?
Solving a C programming assignment involves extensive study and research and is not feasible for students to write their homework without adequate knowledge and information. FavTutor provides online C programming help to students with original quality and professional competency. You can receive instant C programming homework help or assignment help right now. Our experts follow extensive research and help in completing your assignments from scratch. If completing your C assignment is a challenging task for you, our experts offer live one-on-one sessions to share the hacks of the assignment and get a knack of the subject.

Reasons to choose FavTutor
- Expert Tutors- We pride in our tutors who are experts in various subjects and provide excellent help to students for all their assignments, and help them secure better grades.
- Specialize in International education- We have tutors across the world who deal with students in USA and Canada, and understand the details of international education.
- Prompt delivery of assignments- With an extensive research, FavTutor aims to provide a timely delivery of your assignments. You will get adequate time to check your homework before submitting them.
- Student-friendly pricing- We follow an affordable pricing structure, so that students can easily afford it with their pocket money and get value for each penny they spend.
- Round the clock support- Our experts provide uninterrupted support to the students at any time of the day, and help them advance in their career.
3 Steps to Connect-
Get help in your assignment within minutes with these three easy steps:

Click on the Signup button below & register your query or assignment.

You will be notified when we have assigned the best expert for your query.

Voila! You can start chatting with your tutor and get started with your learning.

Pointer programming exercises and solutions in C
Pointer is a variable that stores memory addresses. Unlike normal variables it does not store user given or processed value, instead it stores valid computer memory address.
Pointer allows various magical things to be performed in C.
- Pointers are more efficient in handling arrays and structures.
- Pointers are used to return multiple values from a function.
- Pointer allows dynamic memory allocation and deallocation (creation and deletion of variables at runtime) in C. Which undoubtedly is the biggest advantage of pointers.
- Pointer allows to refer and pass a function as a parameter to functions.
and many more…
For beginners pointers can be a bad dream if not practiced well. However, once mastered you can do anything you want to do in C programming language.
In this exercise I will cover most of the pointer related topics from a beginner level. Always feel free to drop your queries and suggestion down below in the comments section .
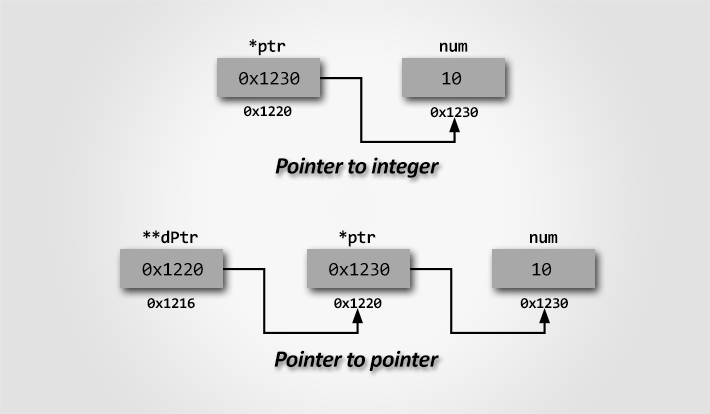
Required knowledge
Pointers , Pointer Arithmetic , Pointer to Pointer , Pointer and Arrays , Function Pointer
Please go through above tutorials to get a good grasp of following examples.
List of pointer programming exercises
- Write a C program to create, initialize and use pointers .
- Write a C program to add two numbers using pointers .
- Write a C program to swap two numbers using pointers .
- Write a C program to input and print array elements using pointer .
- Write a C program to copy one array to another using pointers .
- Write a C program to swap two arrays using pointers .
- Write a C program to reverse an array using pointers .
- Write a C program to search an element in array using pointers .
- Write a C program to access two dimensional array using pointers .
- Write a C program to add two matrix using pointers .
- Write a C program to multiply two matrix using pointers .
- Write a C program to find length of string using pointers .
- Write a C program to copy one string to another using pointers .
- Write a C program to concatenate two strings using pointers .
- Write a C program to compare two strings using pointers .
- Write a C program to find reverse of a string using pointers .
- Write a C program to sort array using pointers .
- Write a C program to return multiple value from function using pointers .
C Online Compiler
Code With C
The Way to Programming
- C Tutorials
- Java Tutorials
- Python Tutorials
- PHP Tutorials
- Java Projects
50+ C/C++ Projects with Source Code
Your search for complete and error-free projects in C and C++ ends here! Here, we’ve enlisted all the mini-projects, projects, games, software and applications built using C and C++ programming language — these are the projects published in our site or available with us at the moment. You can download all these projects (with source code) for free; make sure to check their individual post description as well.
First thing, most students learn C and C++ as their first programming language. They quickly become able to write programs that include functions, arrays and pointers, file handling and data structure, etc. But, when it comes to building a mini-game, an application, or a small project, incorporating all these features in one compact program becomes difficult.
In such case, reference projects always come in handy. The C and C++ projects published in our site will teach you how to get started, give you ideas and topics regarding your project, and sharpen your programming skills in C and C++. Here, you’ll find short and simple as well as long and complicated projects.
C Projects:

The C projects softwares enlisted below are mini projects, mini games, and small applications. Most of these projects utilize functions, file handling, and data structure effectively. Try to analyze and understand the source code of these projects, and you’ll learn how to add, modify, view, search and delete data using file to create a similar project.
In some large and somewhat complicated projects, comments are provided in the multiple lines of the source code to help you understand the project better.
- Bank Management System
- Calendar Application
- Contact Management System
- Cricket Score Sheet
- Customer Billing System
- Cyber Management System
- Department Store Management System
- Employee Record System
- Hangman Game
- Hospital Management System
- Library Management System
- Medical Store Management System
- Modern Periodic Table
- Pacman Game
- Personal Diary Management System
- Phonebook Application
- School Billing System
- Student Record System
- Telecom Billing System
- Tic-Tac-Toe Game
- Typing Tutor
C++ Projects:
Just like the C projects, the C++ projects enlisted below are mini projects – small games and applications. They are good for starters who are looking for reference projects to create a C++ mini-project of their own.
- Banking Record System
- Bookshop Management System
- Bus Reservation System
- Hotel Management System
- Payroll Management System
- Phonebook Management System
- Railway Reservation System
- Sales Management System
- Student Database Management System
- Student Report Card System
- Supermarket Billing System
- Telephone Directory System
- Live Cricket Score C Program: Dive into Real-time Data Fetching
Some Advanced Projects in C and C++:
These are some projects with wider scope, utilizing the advanced aspects and graphics of C and C++ programming.
- Snakes and Ladders Game in C
- Bike Race Game (using SDL) in C++
- Database Management System (using wxWidgets) in C++
- Fortune Teller (Predict Future) in C++
- Helicopter Game (using SDL) in C++
- Search Engine in C++
- Tank Game in C++
- Traffic Control Management System in C++
- University Management System in C++
- 3D Bounce Ball Game in OpenGL
More C and C++ Projects:
More projects for you! We haven’t had the time to publish these projects, so we’ll just provide a download link to the ones mentioned below.
- Copter Game (using Allegro) in C
- Balloon Shooting Game in C++
- Canteen Management System in C++
- Casino Game in C++
- Digital Clock in C++
- Memory Game in C++
- Music Store Management System in C++
- School Fee Inquiry Management System in C++
- Shuffle Game in C++
- Snakes and Ladders Game in C++
- Sudoku Game in C++
- Telephone Billing System in C++
- Travel Agency Management System in C++
Note : The C/C++ projects mentioned in this listing have not been checked and debugged for errors. So, it’s up to you to find and remove those errors (if present)!
C and C++ Mini Project Ideas:
If you’re going to build a mini-project of your own in C or C++ language, here are some nice project topics and ideas:
- Airlines Reservation System
- ATM Banking System
- Cafeteria Order Management System
- Car Insurance System
- Car Rental System
- Clothing Store Management System
- College Management System
- Gym Management System
- Hostel Accommodation System
- Human Resource Management System
- Mess Management System
- Movie Ticket Booking System
- Pharmacy Management System
- Student Attendance Management System
- Supermarket Management System
The projects/software are divided into different headings just for the sake of clarity. So, if you’re a beginner in making a project, try understanding and analyzing a mini project, before moving on to developing a project of wider scope and application.
Most of the mini projects/software here are compiled in Code::Blocks IDE , so running the programs in other compiling platforms such as Turbo C/C++ may produce errors (unless mentioned otherwise in the post descriptions for respective projects).
If you are thinking of submitting these projects as your college mini project, we’d like to advise you to make some modifications to the project source code before sending them. There are always some rooms to add new features, and make the project a even better one.
We are always adding more and more projects, so bookmark this page to keep updated with the latest C and C++ projects published on this site. We hope these projects will serve you as reference projects and guide you more than enough to help you build a C/C++ project of your own.
Note : If you have developed a project in C or C++ and want to share it, Code with C is the right place! Just send us the source code and a brief abstract of your project at [email protected] , and we’ll publish it with your name. Also, if you have a project request, you can mail us or mention your queries in the comments below.
Conclusion : C and C++ are two of the most popular programming languages in the world. They are versatile, powerful and relatively easy to learn. If you’re looking for a comprehensive list of projects that you can use as a resource for learning or to simply get ideas, you’ve come to the right place. We have over 50 C/C++ projects with source code available for download, and we will be adding more soon. So whatever your level of expertise, we have something here for you!
You Might Also Like
Cutting-edge artificial intelligence project unveiled in machine learning world, enhancing exams with image processing: e-assessment project, cutting-edge blockchain projects for cryptocurrency enthusiasts – project, artificial intelligence marvel: cutting-edge machine learning project, personalized affective feedback project: deep learning solutions for student frustration in it.

Really good useful projects
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1g7UHjidkWsIIfB2dMdsA2uJMpDHUpBNp?usp=sharing link for student record management-file structures mini project in c++
Sir please give me source code for car rental system using c code
thanks for sharing Value able knowledge
i am in class 12 cbse plz give me a suggestion for my project in c++
can u please put the program of scholorship of any university in c++
Very very thanks for help.
sir can i get the source code for time table management system using c programming.I need college time table based on some constraints like number of teachers etc.please help me out sir,I am not getting any idea.
Hey.. I am in electricalengineering and we have to make a project using c++ programming. So can u plz give some ideas?
sir can you mail me project on binary search in c language
Do you have project on student project allocation management system in c language?
sir send me the source codes of some applications based on data structures
I want a project about drawing logic Gates using C++? Thanks.
Kindly can you send me Email Client System mini project in c language
please write a program for admission criteria in a university in c++
do you have source code of budget tracking system???? in c++
i want a project on electronic movie ticketing system in c++
Can u do me a progrm for school fee management system please
sir. can you make helpdesk system
can u mail a project on “daily dairy reaminder”
may i get a C code for BAR management project.? it must include stacks or queue compulsorily…
please could you help me in doing this project, I have finished with the coding and it has left with the algorithm and flowchart. here is the question: Pay as you study in VVU charges $100 for each semester hour of credit, $ 150 for regular room and $ 200 for air condition and $ 50 for the use of academic facilities. All student pay $30 for graduation and $20 for matriculation. write and develop an algorithm and flowchart that computes the total fees paid by each students. A warning message should be displayed if a student is taking more than 21 credits hours and less than 15 credit hours. the inputs are student id, room, credit hours and graduating student
hi sir can you plz tell me the source code of cricket management system project.
can u please post me cultural programmes and management system program in java
i will need the c++ code for online exam registration system immediately.
Source code already added after first pera in above post you need to unlock it by sharing on facebook
Comment:actually it z v difficult to implement online exam project in c++… you can try JavaScript, php for this implementation….
sir i need Dispensary Management System Project In c++ Language Please Inbox me .and anyone who has this project plz forward me at [email protected]
sir can you send me bug tracking system in c ,c++
sir can you tell me what to do after downloading the link given above ? really don`t have any idea 🙁 you can mail me here : [email protected] thanks in advance
can anyone post how to open the source code after downloading it ?? please need help thanks in advance..!
sir can you plz send the timetable management c mini project for B.tech students.
sir can u send me cinema ticket system in c program…
sir.. do you have learning abc for kid project in c++
No, sorry. That’s a totally new project you mentioned. Sounds interesting! 🙂
Sir, could u plz mail me project on the car showroom management system. my mail id is [email protected]
Sorry, we don’t have that project. All the project available with us can be searched for and found in the site.
Can You please give me a dictionary code using file handling? it should Search a word and show its meaning from file
I don’t have such a project, but if we ever publish such project (in C/C++ language) on the site, it’ll appear in this page’s listing.
i want alot of things in project management system
sir, pls pls…send me your mini project of college management system or student attendence record system or anything in c programming….pls sir i have to submit for internals in 2 days..
hi sir can u plz send me project of car parking managment system
Sorry, we currently don’t have a project by that name. But you can refer Bus Reservation System Project .
sir…..pls send any c mini project sir….i really not need too many pages sir…..can u please send me some project in c which is small in size please
Try projects like Quiz Game, Phonebook, and Contact Management System. These are the most simple and easy projects we developed.
sir, do you have a project on timetable of an engineering college?
Currently, I don’t. But if I come across one, I’ll notify you.
need a project in which inheritence is used??
sir i want c program for car rental system . if have the program means please send to my mail address sir this is my request sir. mail: [email protected]
Hey, I don’t have such program, sorry!
do you have coding for power supply failiure alarm? Is there any website are available?reply me..
Hmm, I don’t have the coding and don’t know any websites related to this thing. Sorry! Please, Google it; you may find something useful.
Sir.can you help to get a c++ mini project on Air ticket reservation
sir,you have any environmental related project source code in c++…………. if yes than please give me tha reply
hye sir .. did u hv a spa management system ?
Sorry, I don’t have such project.
sir do you have c++ project about science and engineering application.. more then 100 code…
Hey, I don’t have such project, sorry. And, what do you mean by a project about “science and engineering”. Please be more specific.
Sir can you give me mastermind game code or any other like that and any social networking code in C++
Hey, if you’re looking for gaming C++ projects, these might help you: Helicopter Game Biking Game Tank Game
data structure together with function void non-void with/without parameter array and for loop
creating payroll
please help me
can you help me for my project?
What is your project? I can’t help you by developing the project for you; what I can do is provide a reference project that may help you.
Sir can u please help us about payroll system in c++, codes of students… please??
You can download that code from here .
Hey Pramesh, please I need two(2) short and simple projects in C
Try Quiz Game and Phonebook Application; these two are very simple and easy to understand.
Sir the passcode for the hospital management project I downloaded. thanks
Sir can you make a C++ Chat Sytem ? with Bot or AI
make file .txt 1. check file size 2. find total number of words replace words uper to lower,,,,lower to uper number of lines number of specific words like find ‘f’ in whole string total number of characters
plz mail me a java program code on “Mobile Postpaid Billing Management System”. It is my project . plz
I don’t have this project now, sorry.
waah!! :'( this project is kinda difficult… can someone help me make it?? i really need a hand to help me.. 🙁 i dont have any idea in making this project.
What project are you talking about?
Can u mail me the project on Cruise management system in c/c++.
I don’t have this project, sorry!
Can you message me a project on Hospital billing System in c++. Thankyou in advance! Godbless 🙂
I don’t have the exact project, but there’s hospital management system project in C . Use this as a reference project.
44. Emailing System: Design a simple email messaging system. A message has a recipient, sender, time and message. A mail box can store message. Supply number of mail boxes for different users. Provide following user interfaces a. Login b. Send message to other users c. Read their own message d. Log out
Please give me the answer sir
hey .. plzzzz help me out i need a soccer leauge management project on c programming .. i am not getting the logic of fixtures .. plzz help me
Please Help me out!.. i want a school timetable system project based on file handling in c++ language for class12th project submission
I don’t have that project in C++, sorry.
can u hav the same project i.e school time table system in JAVA
Sorry, I don’t have that exact project in Java.
sir also i need c code for railway management system with linked list please send me my email address
You can download Railway Management System Source Code from here .
hello Can you tell me how to get the lost data in hard drive or removable drive using c++. could you send me sample code
textcolor(5+143);
Which colour will the above statement produce?
Sorry for the previous comments
Sir can u please mail the tic tac toe game source code. There is some error while downloading.
What error did it show? The download link is working here.
Tic Tac Toe Source Code
Plz tell me some site to download Turbo C++ the one with blue working environment. You can contact me on: [email protected]
Please Please Please reply to this. Waiting for your mails and posts.
Type “download Turbo C++” in Google 😀
guys pls!!!!!help me!!!!!!!!!my question is ticketing system c++ program using structure………………………………….. 1.add customers information 2.search customers information 3.inventory of sales per daily and weekly 4.customers payment will be depend on the place 5.provide destinations 6.provide ur own fare and also 7.the system should be secured……………………..plssssssssssssssssss help meeeeeeeeeeeeeeee!!!!!!! inbox the answer to me at:::[email protected]
could i get a c++ code on Customer booking for cruises 1. Enquire for routes and tariffs 2. Enquire Ship schedules 3. Customer bookings 4. Generate customer bookings Ship schedule wise
I don’t have this project, sorry.
Verrrrrrrrrrrry nice tnx
sir, may u email me the mini project on homestay booking system using php or c++?
Need c++ program to :
1. Maintain details related to Cultural events related Judges
2. Maintain details related to Technical events related
3. Maintain details related to Project completions related
4. Maintain details related to Fine arts related Judges
I don’t have such a project, sorry.
Sir, can you please send me a project in C++ on cruise travel management.The project should be made up using concepts of data file handling for class XII. It should include grahics. Also please provide it’s output. Please reply soon. In urgent need.
Sir, can you please tell me how to include graphics and change the background color in c++. It always comes up as an error. Also if you can tell me all the codes for the colors. Thanks! 🙂
Are you using Turbo C++ or CodeBlocks? By how to include graphics, do you mean how to include graphics.h? And, about the background color, go to this category ; there are three posts there on how to change background and text color. Those may help you.
Here are the color codes:
BLACK 0 BLUE 1 GREEN 2 CYAN 3 RED 4 MAGENTA 5 BROWN 6 LIGHTGRAY 7 DARKGRAY 8 LIGHTBLUE 9 LIGHTGREEN 10 LIGHTCYAN 11 LIGHTRED 12 LIGHTMAGENTA 13 YELLOW 14 WHITE 15
I have both C++ and Code Blocks in my system but the programs which have been copied from the net aren’t working. But rest of the programs which I have written are running successfully. Please help! If you can send me a link to download C++ it would be really helpful. Mail id – [email protected]
Thanks! for the codes.
What do you mean by – “If you can send me a link to download C++”. What are you trying to download? Turbo C++?
And you say that you have copied programs from the net and they aren’t working. Maybe these programs show errors or they have header files not included in your compiler.
Most of the projects here at Code with C are to be compiled in CodeBlocks. So, our programs run well; I don’t know about the programs elsewhere on the web.
Sir, I have send you an email having my file as attachment. Please see to it. Many Thanks once again.
hey can you pls mail me the project on event management system…….
Sorry, I don’t have that project right now in any language.
i need advanced hospital management system project in cpp
We have Hospital Management System in C only at the moment.
sir, can u mail me the project of marks management system using file operations. In this project we have to register student,to update his marks ,and to look for his grade,to check whether he passed or not.
I don’t have a very exact project for the features you mentioned. You can use this Student Report Card System in C++ as a reference project. Hope this helps.
sir can u send cultural and technical event management system program for me to my gmail module is 1)maintain master schedule for cultural events 2)maintain master schedule for annual events
Many people asked for this project, but I couldn’t find it anywhere. Sorry, I don’t have it.
sir ,can you please send me alumni information system project ????
I don’t have a project with that title, sorry!
can u mail me c++ program for cultural and technical maagement system
I don’ have this project, sorry. I’ve searched this project in many other sites, but couldn’t find it. What are the main objectives of “Cultural and Technical Management System”? Please, elaborate the project abstract. The project title sounds ambiguous!
code for advanced cultural&technical events plzzzzzzz………..
I don’ have this project, sorry.
cultural and technical management systam in c++ language
Sorry, I don’t have this project; if I find it, I will let you know.
can u mail me c++ program for cultural and technical maagement system/////
i need c++ program for cultural and technical management system..
Sir can u mail the c++ project on class timetable schedule
Sorry, I don’t have this project; this project sounds good though. I’ll let you know if I find this project.
can u mail me the project on advanced school fee billing system in c++ @[email protected]
Sorry, I have only School Billing System Mini Project in C.
cultural and technical program mangement system
Sorry, I don’t have this project.
can u send me a project on advanced hospital managment system in c++ language.. Thanks
I don’t have Advanced Hospital Management System in C++. If I find that project, I’ll let you know. (There’s Hospital Management System in C in the post above.)
can u mail me the project on online exam management system in c++ .Thanks
Sorry, I have Online Exam Management System in Java only. If I find one built in C++, I’ll let you know.
Sir if you have source code for “Home automation by using bluetooth mobile” please forward me… mail id: [email protected]
Sorry, I don’t have that project at the moment.
You have send me new projects name in C++.
Hi, I didn’t understand what you just said there 😀
can u mail me the project onCollege Admission Management System inc++ to [email protected]
Sorry Aishwarya, I don’t have that project at the moment.
can u mail me the project on house budget management system in c @ [email protected]
Hey Subham, I don’t have that project at the moment, sorry.
hi ,i am having error in medical store management ,windows.h has error ,and some error is their ,pls reply me ,my mail id is [email protected]
That project should be compiled on Code::Blocks, and there are no errors in that project.
pramesh, why do i get a error in the for statement? im using turbo c, im quite new to this as im a first year student of computerscience , i would like to see how your program runs , but theres an error shown on line 59 , thank you.
Could you be more specific? In what project’s line 59 did you find the error? Most of the projects here need to be run on Code::Blocks.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Latest Posts

Privacy Overview
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
- Social Sciences
CS50: Introduction to Computer Science
An introduction to the intellectual enterprises of computer science and the art of programming.
Navigation Menu
Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests..., provide feedback.
We read every piece of feedback, and take your input very seriously.
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly.
To see all available qualifiers, see our documentation .
- Notifications
CSE341: Homework and Study Note for Programming Languages on Coursera
Weiting-Zhang/Programming-Languages
Folders and files, repository files navigation, programming languages on coursera.
This course is an introduction to the basic concepts of programming languages, with a strong emphasis on functional programming . The course uses the languages ML (in Part A ), Racket (in Part B ), and Ruby (in Part C ) as vehicles for teaching the concepts, but the real intent is to teach enough about how any language “fits together” to make you more effective programming in any language -- and in learning new ones.
Introduction
This repo contains all my work for this course. All the code base, quiz questions, screenshot, and images, are taken from, unless specified, Programming Languages on Coursera . The course is also avilable on washington.edu .
What I want to say
VERBOSE CONTENT WARNING: YOU CAN JUMP TO THE NEXT SECTION IF YOU WANT
Here I released these solutions, which are only for your reference purpose . It may help you to save some time. And I hope you don't copy any part of the code (the programming assignments are fairly easy if you read the instructions carefully), see the quiz solutions before you start your own adventure.
Currently, this repo has 3 major parts you may be interested in and I will give a list here.
Homework Assignments and Exams
Part A: ML and Functional Pragramming
- Week 2 - Homework 1 - ML Functions, Tuples, Lists, and More : 104/100
- Week 3 - Homework 2 - Datatypes, Pattern Matching, Tail Recursion, and More : 104/100
- Week 4 - Homework 3 - First-Class Functions and Closures : 100/100
- Week 5 - Part A - Exam
Part B: Racket and Dynamically Typed Language
- Week 1 - Homework 4 - Racket, Delaying Evaluation, Memoization, Macros
- Week 2 - Homework 5 - Structs, Implementing Languages, Static vs. Dynamic Typing
- Week 3 - Section Quiz
Part C: Ruby and Object-Oriented Language
- Week 1 - Homework 6 - Ruby, Object-Oriented Programming, Subclassing
- Week 2 - Homework 7 - Program Decomposition, Mixins, Subtyping, and More
- Week 3 - Final Exam
- Standard ML 100.0%
C Programming Assignment Help |Programming Assignment Helper

- Adobe Flash Assignment Help
- AJAX Assignment Help
- Algorithm assignment help
- Arduino Assignment Help
- Assembly Language Assignment Help
- C Programming Assignment Help
- C++ Programming Assignment Help
- C-Sharp Assignment Help
- Coding Assignment Help
- CoffeeScript Assignment Help
- Data Analysis Assignment Help
- Data Structure Assignment Help
- Data Visualization Assignment Help
- Database Assignment Help
- Flask Assignment Help
- Game Development Assignment Help
- HTML Assignment Help
- Java Assignment Help
- JavaFx Assignment Help
- JavaScript Assignment Help
- JQuery Assignment Help
- Kotlin Assignment Help
- Linux Assignment Help
- Map Reduce Assignment Help
- MySQL Assignment Help
- Neo4j Assignment Help
- Network Design in MATLAB Assignment Help
- Neural Network Assignment Help
- Objective-C Assignment Help
- Perl Assignment Help
- PHP Assignment Help
- Programming Coursework Help
- Python Assignment Help
- Python GUI Assignment Help
- R Markdown Assignment Help
- R Programming Assignment Help
- R Studio Assignment Help
- Raspberry Pi Assignment Help
- React Native Assignment Help
- Redux Assignment Help
- Ruby Assignment Help
- Rust Assignment Help
- Scala Assignment Help
- Scikit Learn Assignment Help
- Smalltalk Assignment Help
- Spring Boot Assignment Help
- SQL Assignment Help
- Standard ML Assignment Help
- TensorFlow Assignment Help
- TypeScript Assignment Help
- UML Diagram Assignment Help
- Urgent Programming Assignment Help
- Visual Basic Assignment Help
- Vue.Js Assignment Help
- WordPress Assignment Help
- Analog Assignment Help
- Animation assignment help
- Apache Spark assignment help
- AWS Assignment Help
- Computer Architecture Assignment Help
- Computer Graphics Assignment Help
- Computer Networks Assignment Help
- Computer Science Assignment Help
- Computer Security Assignment Help
- ERP Assignment Help
- Firebase Assignment Help
- Go Programming Assignment Help
- Google Cloud Platform Assignment Help
- Information Technology Assignment Help
- Internet Security Assignment Help
- Ionic Mobile App Assignment Help
- IOS Assignment Help
- Laravel Assignment Help
- Mechatronics Assignment Help
- Mobile App Development Assignment Help
- Mobile Operating Systems Assignment Help
- Network and Systems Assignment Help
- Object Oriented Design Assignment Help
- Object-Oriented Programming Assignment Help
- Operating Systems Assignment Help
- Oracle Assignment Help
- PowerBI Assignment Help
- Python Tkinter Assignment Help
- ReactJS Assignment Help
- Software Engineering Assignment Help
- Swift Assignment Help
- Tableau Assignment Help
- Visual Studio Assignment Help
- Web App Development Assignment Help
- Web Programming Assignment Help
- Xcode Assignment Help
- .NET Assignment Help Online
- Android Programming Assignment Help
- Angular Assignment Help Online
- Artificial Intelligence Assignment Help
- Big Data Assignment Help
- Biotechnology assignment help
- Blockchain Technology Assignment Help
- Cloud Computing Assignment Help
- Control Systems using MATLAB Assignment Help
- Cryptography Assignment Help
- Cyber Security Assignment Help
- Data Analytics Assignment Help
- Data Mining Assignment Help
- Data Science Assignment Help
- Deep Learning Assignment Help
- Digital Signal Processing in MATLAB Assignment Help
- Gaming and Simulation Assignment Help
- Graphic Design Assignment Help
- GUI Assignment Help
- Hadoop assignment help
- Image Processing in MATLAB Assignment Help
- Iphone Application Development Assignment
- Machine Learning Assignment Help
- MATLAB Assignment Help
- MATLAB GUI Assignment Help
- MATLAB in Computing Assignment Help
- MongoDB Assignment Help Online
- Neuroscience assignment help
- NLP Assignment Help
- NodeJs Assignment Help Online
- Numerical methods in MATLAB Assignment Help
- Programming Assignment Help
- Programming Project Help
- Reinforcement Learning Assignment Help
- Robotics Assignment Help
- Statistics Assignment Experts
- Supervised Learning Assignment Help
- Trending Topics in Programming
- Unity 3D Assignment Help
- Unsupervised Learning Assignment Help
- Visual Computing Assignment Help
- Web API Assignment Help
- Cheap Programming Assignment Help
- Computer Science Exam Help
- Engineering Exam Help
- MyMathlab Quiz Help
- MyStatLab Quiz Help
- Online Computer Engineering Exam Help
- Pay Someone To Take Programming Exam
- Proctored Exam Help
- Programming - Take My Online Exam
- Programming Assignment Experts
- Programming Assignment Help Australia
- Programming Assignment Help Canada
- Programming Assignment Help Hong Kong
- Programming Assignment Help Ireland
- Programming Assignment Help Qatar
- Programming Assignment Help Saudi Arabia
- Programming Assignment Help Singapore
- Programming Assignment Help UK
- Programming Assignment Help USA
- Programming Exam Helper
- Python Assignment Help Australia
- Python Assignment Help Canada
- Python Assignment Help UK
- Python Assignment Help USA
- Python Exam Help
- Take My C Programming Exam
- Take My C++ Exam
- Take My GED Test Online
- Take My Java Exam
- Take My Programming Exam
- Take my Programming Quiz
- Take my Programming Test
- Take My R Programming Exam

Can't read the image? click here to refresh.
Why Choose The Programming Assignment Help?
On Time Delivery
Plagiarism Free Service
24/7 Support
Affordable Pricing
PhD Holder Experts
100% Confidentiality

My C programming assignment on memory management and algorithms was done within 24 hours. Thank you guys for urgent delivery at such cheap prices
My C programming project on high-performance computing and efficient data manipulation was done by a PhD expert from their team. Amazon work guys. You are truely professional
Thank you for the 5 C Programming classes given by your expert. I scored 100/100 on my Exam. The exam preparation service has been very helpful
I got 5 C Programming assignments solved last semester on topics like Multi-dimensional arrays in C, Data Flow Analysis, Dynamic arrays in C and more. I got A grade in all. Thank you
My professors are totally impressed with the error-free well-commented code that I submitted for my C Programming Gaming Assignment. Thank you expert for your help.
I had a big C programming project which was related to game designing in C. Got A grade thanks to the programming project experts who guided me through online tutoring and helped me complete the project
Do My C Programming Assignment
C is one of the most widely used programming languages for academics. Due to its syntax, many students find it challenging to complete C assignments on their own. We at The Programming Assignment Help aim to cater to such needs. We have a large team of experts who hold Masters' and PhDs in Computer Science/ Programming to assist students and help them secure A+ grades. For years, we have been offering C assignment help to students across the globe. With a team of 900+ dedicated programmers, we have established ourselves as the leading C programming assignment help provider.
If you are looking for online C Homework Help , then you can rely on us! You just have to tell our experts - Do my C Programming Assignment & a well-commented executable code will be sent to your inbox along with a screenshot of outputs.
C programming in the latest coursework is less about mastering the language itself and more about harnessing its power to tackle the challenges shaping the technology future. The foundational concepts like memory management and algorithms remain firmly rooted in the programming coursework. Embedded systems, fueled by the Internet of Things (IoT) revolution, are demanding mastery of low-level programming and real-time constraints. Security is prompting deep dives into secure coding practices and vulnerability analysis. The burgeoning field of data science finds C playing a crucial role in high-performance computing and efficient data manipulation, particularly for resource-constrained systems. The C programming coursework is changing with technology and hence students come to us with C programming assignment help , homework help, and tutoring services.
Who Buys C Programming Assignment Help Solutions? Is it Legit?
C Programming Assignment Help is a legit service provided by The Programming Assignment Help Company. We have been providing C programming assignments, homework & tutoring to Global students for more than a decade. Our team of 120+ Ph.D. programming experts ensures that all students get well-commented executable codes within a given deadline. To ensure reliability, we share a screenshot of the executable code & the output before taking the complete payment from the student.
We have a global customer base with a majority of our customers from countries like the USA, UK, Australia, Canada, India, Singapore & many more.
Online C Programming Assignment Helper
Students who are new to C language would find it tough to complete the assignments given by their Professors. Even before a student starts writing a simple C Programming code, one should be aware of the basic concepts of the programming language. Key concepts in C programming include program syntax, input/output, operators, conditional & iteration statements, functions (standard library, user-defined, call-by-reference, scope), arrays (single and two-dimensional), data types, storage classes, structures, strings, etc.
- C language comprises a wide range of data types and powerful operators
- Programs that are coded in C language are quick, efficient, and simple to understand
- C programs are portable and can be easily used on systems
- C programming supports system programming and graphics
Operators used in C Programming are listed below:
C Programming Tutors and Coursework Help
It is very important to use these operators correctly to ensure your C program provides the desired output.
Many times, students ask us - Is It Worth Paying for Help with C Programming ? - Yes, it is! If you are stuck & are not getting the desired output after trying hard, that means you are doing something wrong & you need help.
C programming is the favorite language of many programmers, as it allows you to execute programs quickly compared to the other assembly languages . C programming is used in the operating system, language interpreters, network drivers, text editors, utilities, and program assemblers. With our 24*7 availability of tutors, we offer instant online C homework help for all your assignments.
Advantages of C Programming language include:
- C language acts as a building block for other assembly languages
C Programming Concepts Used in Solving Assignment and Homework
We have been offering C Programming homework Help for the last 10 years. Some of the important concepts that programmers use while working on a C Program include:
- Creating libraries in C :
For students to get hold of the libraries concept in C programming, they have to spend a lot of time practicing this concept. It is challenging for them to complete a C assignment without having knowledge of libraries. If you are one of them, then you can hire our C Programming Assignment Help experts who deliver top-notch quality assignments in a short time period. We review, debug, and document the code precisely.
- Multi-dimensional arrays in C :
A multi-dimensional array comprises two or more arrays. Programmers will use multiple arrays to perform software operations consecutively in a series of items. This approach is far better compared to the parallel array approach since you can execute tasks quickly and efficiently. It is highly recommended to use a multi-dimensional array when you are working on huge data tables.
- Searching algorithms in C :
An algorithm is a set of instructions that are carried out to execute a specific task. There are different functions that are executed to provide the right commands. Our C homework help experts have in-depth knowledge and experience in completing assignments on this topic. We also have an editing team to review the completed assignment multiple times prior to delivering it.
- Dynamic arrays in C :
Dynamic arrays will allow software developers to modify information by adding or deleting key elements. It is easy to expand the capacity of a dynamic array with the help of geometric expansion sequences to give more space to elements that are otherwise impossible in a static array. Dynamic structures will allow you to run programs with less memory. We help students in completing the assignment on this topic. All you need is to reach out to us and ask for help with the C Programming Assignment.
- Debugging in C :
This is the process of detecting bugs in the program and fixing them to make the program run smoothly. There are many reasons for the bugs encountered in the program. For instance, poor coding, leak of memory, or malware infection. Our programmers can debug the code by going through the code line by line and identifying the error.
- Functions and problem statements in C Programming :
There are functions required to execute certain tasks. Functions will allow developers to group the code and debug it easily. Students who are still in the learning phase find it hard to create an accurate function and problem statement if they lack knowledge of C programming. In such cases, avail the trusted C homework help from us!
- C file structure :
There are many inputs and outputs a C program comprises. If you are moving computer programming from one language to another, it is challenging to change the file structure rules for a student. File structuring is the most critical concept in C programming. We provide well-researched and well-structured documents on this concept for students at pocket-friendly prices.
Why Students Avail Our C Programming Assignment Help?
Our quality services are what make us stand out from others. In addition, we also offer the following benefits to students
- Concepts Clarification - For many students, C programming can be a challenging language with its own set of syntax and logic. If students fail to grasp fundamental concepts then we can help you in solving assignments and homework. We can also provide online tutoring to give 1-on-1 tutoring to students.
- Better Grades - Students seek help to improve their grades. They work along with C Programming tutors to solve assignments and homework. This ensures that students have their concepts clear to focus on C programming exams and get good grades and the tutors can solve assignments and homework so that students submit all the C programming coursework on time.
- Good Service - We are available 24 Hours. We ensure privacy and confidentiality. We share the C programming assignment solution within the agreed deadline with the screenshot of the code running successfully.
Order C programming Assignment Help now and get a 10% discount!
We at The Programming Assignment Help understand your requirements and then complete your C program or assignment. If you come across any compiling error in the program after the delivery, you can get in touch with us at any time to clarify your doubts. So, email us your assignment/homework and de-stress yourself from the worries of solving it on your own.
Example of A Simple C Programming Code Written By Our Expert
Code for: Building and using Functions in Programming using a Real-World Example.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you do a quality check to provide a plagiarism-free c programming assignment.
When a student asks for a c programming assignment help from us it’s our duty to provide a clean and authentic code. The code should be plagiarism-free so that students can submit it without any hesitation. Our experts use original variables names, check the code with programming plagiarism tool, write original functions and comment on the code to make sure that the code is authentic.
Can We Ask Any Questions For a C Programming Assignment Directly To Experts?
Yes, you can ask questions and clarify your doubts regarding your programming assignment. You can email us all your queries/doubts regarding the solution provided by our experts, we will treat it as a priority and resolve all your doubts. Our experts will help you to understand the concepts thoroughly.
What will be the cost of my C language program?
The price quote of a C language depends upon many factors like complexity of the project, length, and detailing of your assignment. If the project is more complex then the charges will be higher than the normal assignments. If you want your assignment on an urgent basis then it will cost you more.
How does C Programming Homework Help work?
The C Programming Homework Help process is simple:
- Submit Details: Share your C Programming homework requirements.
- Payment: Make a secure payment to kickstart the assistance process.
- Work Progress: Track the progress as our experts handle your C Programming homework.
- Final Delivery: Receive your completed C Programming homework, complete with explanations and guidance.
Is C Programming Assignment Help Legit?
Yes, our C Programming Assignment Help is entirely legitimate. You can trust our service to provide authentic assistance for your C Programming assignments. We prioritize your academic success and offer reliable support to help you excel in your C Programming coursework.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
So, Keep it Up! Solve topic-wise C exercise questions to strengthen your weak topics. C Programming Exercises. The following are the top 30 programming exercises with solutions to help you practice online and improve your coding efficiency in the C language.
The C programming language was first released in 1972, making it one of the oldest still used today. All modern operating systems are implemented with C code, which means that the C language powers almost every technological experience we have. Python's interpreter is also written in C. Get started learning C fundamentals to become a better ...
Welcome. Welcome to the learn-c.org free interactive C tutorial. Whether you are an experienced programmer or not, this website is intended for everyone who wishes to learn the C programming language. There is no need to download anything - Just click on the chapter you wish to begin from, and follow the instructions. Good luck!
Whether C is the right choice depends on what you want to accomplish and your career goals. C from a Learning Perspective. If you are new to coding, learning C can help you build a strong programming foundation. However, when we compare the code of C with other modern languages like Python, C might seem a bit complex.
Program. C Program to Print an Integer (Entered by the User) C Program to Add Two Integers. C Program to Multiply Two Floating-Point Numbers. C Program to Find ASCII Value of a Character. C Program to Compute Quotient and Remainder. C Program to Find the Size of int, float, double and char. C Program to Demonstrate the Working of Keyword long.
C is a general-purpose, procedural, high-level programming language used in the development of computer software and applications, system programming, games, and more. C language was developed by Dennis M. Ritchie at the Bell Telephone Laboratories in 1972. It is a powerful and flexible language which was first developed for the programming of ...
C is a general-purpose, imperative computer programming language, supporting structured programming, lexical variable scope and recursion, while a static type system prevents many unintended operations. C was originally developed by Dennis Ritchie between 1969 and 1973 at Bell Labs.
C is a general-purpose programming language, developed in 1972, and still quite popular. C is very powerful; it has been used to develop operating systems, databases, applications, etc. Start learning C now ».
(This ZIP file contains: 1 .txt file and 2 .c files.) 4 Pointers, arrays, strings, searching and sorting algorithms 5 Linked lists, trees 6a Pointers to pointers, multidimensional arrays, stacks and queues (This ZIP file contains: 1 .txt file and 2 .c files.) 6b Function pointers, hash table
A Brief History of the C Programming Language. C was developed in the early 1970s by Dennis Ritchie at AT&T Bell Laboratories. The development of C was closely tied to the development of the Unix operating system at Bell Labs. Historically, operating systems were typically written in Assembly language and without portability in mind.
PRACTICE. With this section CodeChef works on improving your programming skills by providing solutions in 35+ programming languages that includes Java, C++, PERL, Ruby, PASCAL, C# and C Programming Language. For each successful submission you will receive a point and move up the CodeChef rank.
Overview. This course provides a brief introduction to the C programming language and standard libraries for students with programming experience at the CS1110 level. We will cover basic syntax, programming paradigm, standard libraries, and debugging for C on the GNU/Linux platform.
Specialization - 4 course series. This specialization develops strong programming fundamentals for learners who want to solve complex problems by writing computer programs. Through four courses, you will learn to develop algorithms in a systematic way and read and write the C code to implement them. This will prepare you to pursue a career in ...
A Tutorial for Beginners. Dionysia Lemonaki. This tutorial will give you a broad overview of basic concepts of the C programming language. We'll go over the history of the language, why and where it is used, the compilation process, and some very basic programming concepts that are common in most popular programming languages.
Problem set on writing, compiling, and debugging C programs, preprocessor macros, the C file structure, variables, functions and program statements, and returning from functions. ... Programming Languages; Software Design and Engineering; Learning Resource Types notes Lecture Notes. group_work Projects.
Once your C programming assignment help is ready for review, we'll notify you by message on the StudyGate platform and email. You then review the work and either approve it or ask for edits. We have 1000+ qualified C Programming homework help experts available 24/7, with an 80%+ grade guarantee. Ready to pass that class now.
FavTutor provides online C programming help to students with original quality and professional competency. You can receive instant C programming homework help or assignment help right now. Our experts follow extensive research and help in completing your assignments from scratch. If completing your C assignment is a challenging task for you ...
List of pointer programming exercises. Write a C program to create, initialize and use pointers. Write a C program to add two numbers using pointers. Write a C program to swap two numbers using pointers. Write a C program to input and print array elements using pointer. Write a C program to copy one array to another using pointers.
Get ready to learn a fresh and beautiful way to look at software and how to have fun building it. The course assumes some prior experience with programming, as described in more detail in the first module of Part A. Part B assumes successful completion of Part A. The course is divided into three Coursera courses: Part A, Part B, and Part C.
The user friendly C online compiler that allows you to Write C code and run it online. The C text editor also supports taking input from the user and standard libraries. It uses the GCC C compiler to compile code.
Some Advanced Projects in C and C++: These are some projects with wider scope, utilizing the advanced aspects and graphics of C and C++ programming. Snakes and Ladders Game in C. Bike Race Game (using SDL) in C++. Database Management System (using wxWidgets) in C++. Fortune Teller (Predict Future) in C++. Helicopter Game (using SDL) in C++.
Jay Jaganath@ApnaCollegeOfficial Apna College C Programming One Shot - https://youtu.be/irqbmMNs2BoLink To My GitHub Account - https://github.com/TheCoderAdi...
CS50: Introduction to Computer Science. An introduction to the intellectual enterprises of computer science and the art of programming. Free *. 11 weeks long. Available now. Browse the latest C courses from Harvard University.
This course is an introduction to the basic concepts of programming languages, with a strong emphasis on functional programming. The course uses the languages ML (in Part A ), Racket (in Part B ), and Ruby (in Part C ) as vehicles for teaching the concepts, but the real intent is to teach enough about how any language "fits together" to ...
C programming is the favorite language of many programmers, as it allows you to execute programs quickly compared to the other assembly languages. C programming is used in the operating system, language interpreters, network drivers, text editors, utilities, and program assemblers. With our 24*7 availability of tutors, we offer instant online C ...
Understanding C Programming Language homework has never been easier than with Chegg Study. Why is Chegg Study better than downloaded C Programming Language PDF solution manuals? It's easier to figure out tough problems faster using Chegg Study. Unlike static PDF C Programming Language solution manuals or printed answer keys, our experts show ...