African American Heritage


Martin Luther King, Jr. (January 15, 1929 - April 4, 1968)
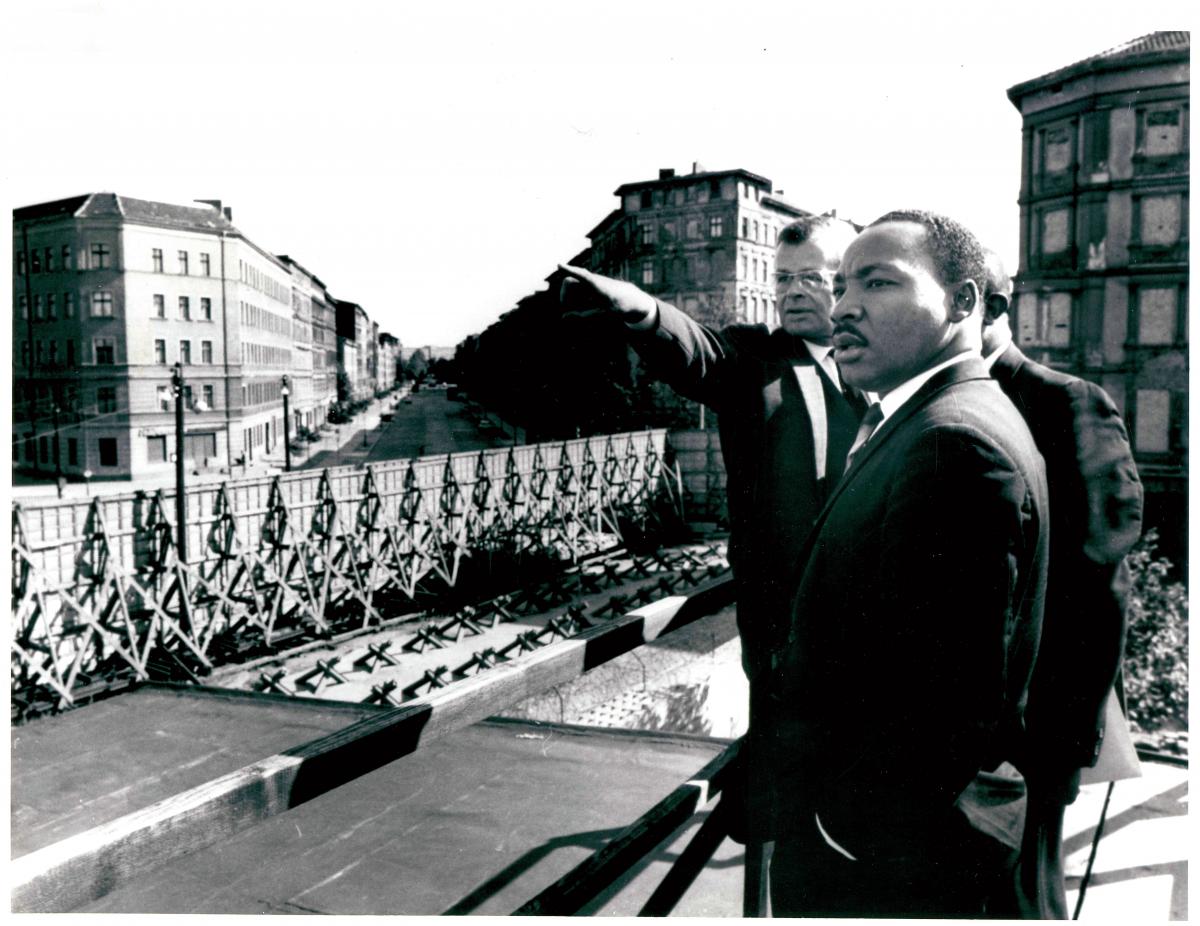

Martin Luther King, Jr. at the Soviet Border of the Berlin Wall, 1964.
View in National Archives Catalog
Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. was born in Atlanta, GA on January 15th, 1929. He was one of the most important and influential Civil Rights leaders in the 1950s and 1960s. The cornerstones of his activism were based on non-violence and civil disobedience, both of which were inspired by his Christian faith and the teachings of Mahatma Gandhi.
He rose to prominence as a leader in 1955 during the Montgomery bus boycott when he was selected to take charge to desegregate the bus services. Afterwards he was elected the president of the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC). From this position, he helped organize many Civil Rights movement actions. The most famous being the 1963 March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. It was then, on the stairs of the Lincoln Memorial, that Dr. King delivered his famous “I Have a Dream” speech. He also won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1964, and in 1965 helped organize the Selma to Montgomery marches to advocate for Black voting rights.
His influence and importance came with a heavy price. The Federal Bureau of Investigation’s Counter Intelligence Program (COINTELPRO) began surveillance of Dr. King as FBI Director J. Edgar Hoover believed him to be a threat to the nation. Part of the investigation was trying to tie Dr. King to communism. The FBI even went so far as to write him a threatening letter, anonymous at the time. Dr. King believed the letter had implied for him to commit suicide.
In the later 1960s, Martin Luther King Jr. turned his attention to poverty, capitalism, and the war in Vietnam. Dr. King wanted to occupy Washington, D.C. for his Poor People’s Campaign but he unfortunately never got the chance. On April 4th, 1968, at the age of 38, Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. was assassinated in Memphis, Tennessee.
He was posthumously awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom and the Congressional Gold Medal. In 1986 President Ronald Reagan signed legislation enacting Martin Luther King, Jr. Day, which created a national holiday on the third Monday in January to remember Dr. King on his birthday. His legacy for nonviolent action and civil disobedience still lives on.
Search the Catalog for Records relating to Martin Luther King, Jr. Social Networks and Archival Context - Martin Luther King, Jr.
Additional Resources from the National Archives
Rediscovering Black History: Blogs on Martin Luther King, Jr .
The Unwritten Record: Blogs on Martin Luther King, Jr.
Pieces of History: Blogs on Martin Luther King, Jr.
DocsTeach: Martin Luther King, Jr. and the Fight for Civil Rights
DocsTeach: The Suffrage and Civil Rights Reform Movements
Resources at the National Archives on Martin Luther King and African American History Month
Special Topics: 1968 - A Year of Turmoil and Change
Findings on the Martin Luther King Assassination

- HISTORY & CULTURE
Who was Martin Luther King, Jr.?
A civil rights legend, Dr. King fought for justice through peaceful protest—and delivered some of the 20th century's most iconic speeches.
The Reverend Martin Luther King, Jr., is a civil rights legend. In the mid-1950s, King led the movement to end segregation and counter prejudice in the United States through the means of peaceful protest. His speeches—some of the most iconic of the 20th century—had a profound effect on the national consciousness. Through his leadership, the civil rights movement opened doors to education and employment that had long been closed to Black America.
In 1983, President Ronald Reagan signed a bill creating a federal holiday to honor King for his commitment to equal rights and justice for all. Observed for the first time on January 20, 1986, it’s called Martin Luther King Jr. Day. In January 2000, Martin Luther King Jr. Day was officially observed in all 50 U.S. states . Here’s what you need to know about King’s extraordinary life.
Though King's name is known worldwide, many may not realize that he was born Michael King, Jr. in Atlanta, Georgia on January 15, 1929. His father , Michael King, was a pastor at the Ebenezer Baptist Church in Atlanta. During a trip to Germany, King, Sr. was so impressed by the history of Protestant Reformation leader Martin Luther that he changed not only his own name, but also five-year-old Michael’s.
( Read about Martin Luther King, Jr. with your kids .)
His brilliance was noted early, as he was accepted into Morehouse College , a historically Black school in Atlanta, at age 15. By the summer before his last year of college, King knew he was destined to continue the family profession of pastoral work and decided to enter the ministry. He received his Bachelor’s degree from Morehouse at age 19, and then enrolled in Crozer Theological Seminary in Chester, Pennsylvania, graduating with a Bachelor of Divinity degree in 1951. He earned a doctorate in systematic theology from Boston University in 1955.
King married Coretta Scott on June 18, 1953, on the lawn of her parents' house in her hometown of Heiberger, Alabama. They became the parents of four children : Yolanda King (1955–2007), Martin Luther King III (b. 1957), Dexter Scott King (b. 1961), and Bernice King (b. 1963).
Becoming a civil rights leader
In 1954, when he was 25 years old, Dr. King became pastor of the Dexter Avenue Baptist Church in Montgomery, Alabama. In March 1955, Claudette Colvin—a 15-year-old Black schoolgirl in Montgomery—refused to give up her bus seat to a white man, which was a violation of Jim Crow laws, local laws in the southern United States that enforced racial segregation.
( Jim Crow laws created 'slavery by another name. ')
King was on the committee from the Birmingham African-American community that looked into the case. The local chapter of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) briefly considered using Colvin's case to challenge the segregation laws, but decided that because she was so young—and had become pregnant—her case would attract too much negative attention.
Nine months later on December 1, 1955, a similar incident occurred when a seamstress named Rosa Parks was arrested for refusing to give up her seat on a city bus. The two incidents led to the Montgomery bus boycott , which was urged and planned by the President of the Alabama Chapter of the NAACP, E.D. Nixon, and led by King. The boycott lasted for 385 days.

King’s prominent and outspoken role in the boycott led to numerous threats against his life, and his house was firebombed. He was arrested during the campaign, which concluded with a United States District Court ruling in Browder v. Gayle ( in which Colvin was a plaintiff ) that ended racial segregation on all Montgomery public buses. King's role in the bus boycott transformed him into a national figure and the best-known spokesman of the civil rights movement.
Fighting for change through nonviolent protest
From the early days of the Montgomery boycott, King had often referred to India’s Mahatma Gandhi as “the guiding light of our technique of nonviolent social change.”
You May Also Like

How Martin Luther King, Jr.’s multifaceted view on human rights still inspires today

The birth of the Holy Roman Empire—and the unlikely king who ruled it

How Martin Luther Started a Religious Revolution
In 1957, King, Ralph Abernathy, Fred Shuttlesworth, Joseph Lowery, and other civil rights activists founded the Southern Christian Leadership Conference to harness the organizing power of Black churches to conduct nonviolent protests to ultimately achieve civil rights reform. The group was part of what was called “The Big Five” of civil rights organizations, which included the NAACP, the National Urban League, the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee, and the Congress on Racial Equality.
Through his connections with the Big Five civil rights groups, overwhelming support from Black America and with the support of prominent individual well-wishers, King’s skill and effectiveness grew exponentially. He organized and led marches for Blacks' right to vote, desegregation, labor rights, and other basic civil rights.
( How the U.S. Voting Rights Act was won—and why it's under fire today .)
On August 28, 1963, The March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom became the pinnacle of King’s national and international influence. Before a crowd of 250,000 people, he delivered the legendary “I Have A Dream” speech on the steps of the Lincoln Memorial. That speech, along with many others that King delivered, has had a lasting influence on world rhetoric .
In 1964, King was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for his civil rights and social justice activism. Most of the rights King organized protests around were successfully enacted into law with the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the 1965 Voting Rights Act .
Economic justice and the Vietnam War
King’s opposition to the Vietnam War became a prominent part of his public persona. On April 4, 1967—exactly one year before his death—he gave a speech called “Beyond Vietnam” in New York City, in which he proposed a stop to the bombing of Vietnam. King also suggested that the United States declare a truce with the aim of achieving peace talks, and that the U.S. set a date for withdrawal.
( King's advocacy for human rights around the world still inspires today .)
Ultimately, King was driven to focus on social and economic justice in the United States. He had traveled to Memphis, Tennessee in early April 1968 to help organize a sanitation workers’ strike, and on the night of April 3, he delivered the legendary “I've Been to the Mountaintop" speech , in which he compared the strike to the long struggle for human freedom and the battle for economic justice, using the New Testament's Parable of the Good Samaritan to stress the need for people to get involved.
Assassination
But King would not live to realize that vision. The next day, April 4, 1968, King was gunned down on the balcony of the Lorraine Motel in Memphis by James Earl Ray , a small-time criminal who had escaped the year before from a maximum-security prison. Ray was charged and convicted of the murder and sentenced to 99 years in prison on March 10, 1969. But Ray changed his mind after three days in jail, claiming he was not guilty and had been framed. He spent the rest of his life fighting unsuccessfully for a trial, despite the ultimate support of some members of the King family and the Reverend Jesse Jackson.
The turmoil that flowed from King’s assassination led many Black Americans to wonder if that dream he had spoken of so eloquently had died with him. But, today, young people around the world still learn about King's life and legacy—and his vision of equality and justice for all continue to resonate.
Related Topics
- CIVIL RIGHTS

Herod I: The controversial king who transformed the Holy Land

What was the Stonewall uprising?

Harriet Tubman, the spy: uncovering her secret Civil War missions

MLK and Malcolm X only met once. Here’s the story behind an iconic image.

Meet the 5 iconic women being honored on new quarters in 2024
- Environment
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Coronavirus Coverage
- Paid Content
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
- This Day In History
- History Classics
- HISTORY Podcasts
HISTORY Vault
- Link HISTORY on facebook
- Link HISTORY on twitter
- Link HISTORY on youtube
- Link HISTORY on instagram
- Link HISTORY on tiktok
✯ ✯ ✯ Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. ✯ ✯ ✯ His Life and Legacy
Martin Luther King Jr. dedicated his life to the nonviolent struggle for civil rights in the United States. King's leadership played a pivotal role in ending entrenched segregation for African Americans and to the creation of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, considered a crowning achievement of the civil rights era. King was assassinated in 1968, but his words and legacy continue to resonate for all those seeking justice in the United States and around the world. As King said at the Washington National Cathedral on March 31, 1968, "Darkness cannot drive out darkness; only light can do that. Hate cannot drive out hate; only love can do that."

10 Things You May Not Know About Martin Luther King Jr.

An Intimate View of MLK Through the Lens of a Friend

The Fight for Martin Luther King Jr. Day

7 of Martin Luther King Jr.'s Most Notable Speeches

Martin Luther King Jr.

7 Things You May Not Know About MLK’s 'I Have a Dream' Speech
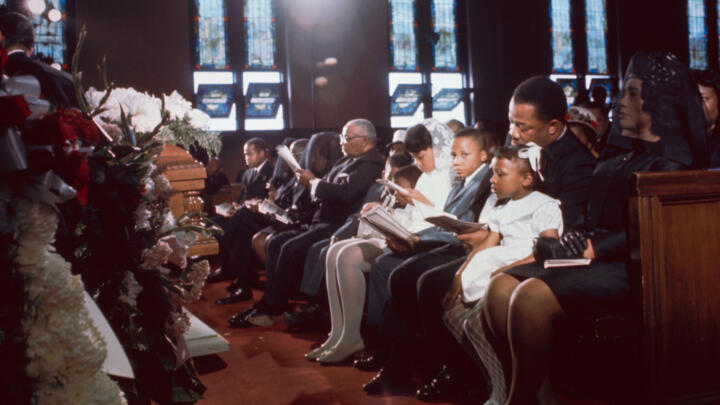

America in Mourning After MLK's Shocking Assassination: Photos

For Martin Luther King Jr., Nonviolent Protest Never Meant ‘Wait and See’
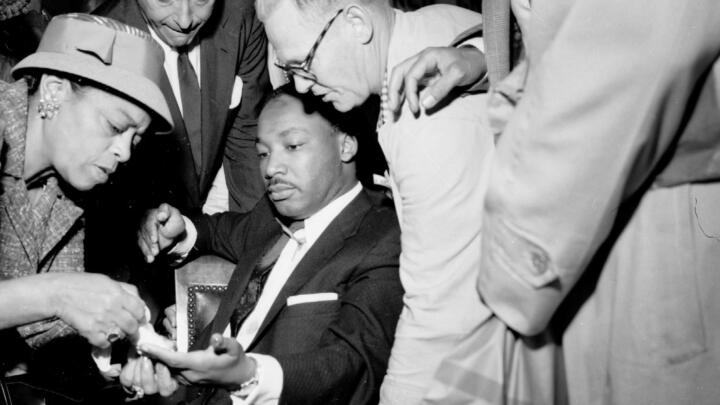

How an Assassination Attempt Affirmed MLK’s Faith in Nonviolence

Jesse Jackson on M.L.K.: One Bullet Couldn’t Kill the Movement

Martin Luther King Jr.’s Final Speech
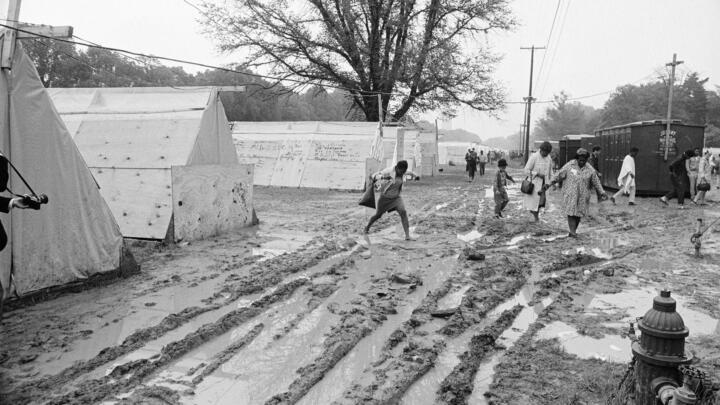

MLK's Poor People's Campaign Demanded Economic Justice
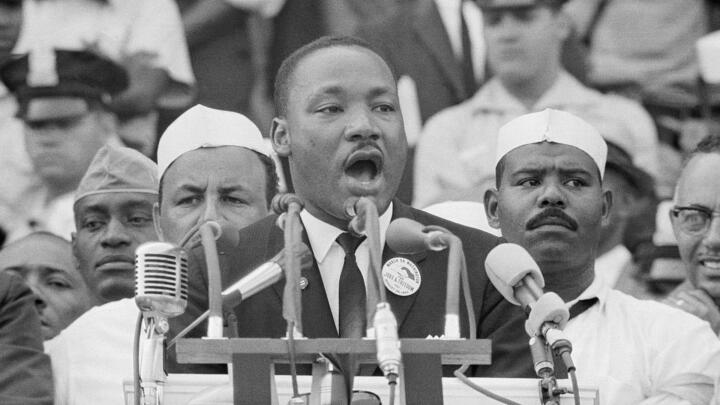

Martin Luther King Jr.’s Famous Speech Almost Didn’t Have the Phrase 'I Have a Dream'
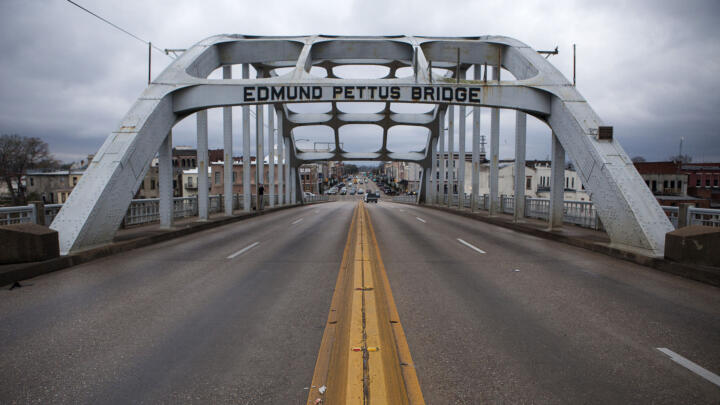

How Selma's 'Bloody Sunday' Became a Turning Point in the Civil Rights Movement

Playlist: Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.

Watch the Black History collection on HISTORY Vault to look back on the history of African American achievements.
Get instant access to free updates.
Don’t Miss Out on HISTORY news, behind the scenes content, and more.
- Privacy Notice
- Terms of Use
Need help with the site?
Create a profile to add this show to your list.
Martin Luther King Jr.
Martin Luther King Jr. was a Baptist minister and major leader of the Civil Rights Movement. After his assassination, he was memorialized by Martin Luther King Jr. Day.

We may earn commission from links on this page, but we only recommend products we back.
In Focus: Martin Luther King Jr. Day
Days after his 1968 assassination , a campaign for a holiday in King’s honor began. U.S. Representative John Conyers Jr. of Michigan first proposed a bill on April 8, 1968, but the first vote on the legislation didn’t happen until 1979. King’s widow, Coretta Scott King , led the lobbying effort to drum up public support. Fifteen years after its introduction, the bill finally became law.
In 1983, President Ronald Reagan ’s signature created Martin Luther King Jr. Day of Service as a federal holiday. It’s celebrated annually on the third Monday in January. The only national day of service, Martin Luther King Jr. Day was first celebrated in 1986. The first time all 50 states recognized the holiday was in 2000.
See Martin Luther King Jr.’s life depicted onscreen in the 2018 documentary I Am MLK Jr. or the Oscar-winning movie Selma .
Quick Facts
Where did martin luther king jr. go to school, philosophy of nonviolence, civil rights accomplishments, "i have a dream" and other famous speeches, wife and kids, fbi surveillance, later activism, assassination, who was martin luther king jr.
Martin Luther King Jr. was a Baptist minister and civil rights activist who had a seismic impact on race relations in the United States, beginning in the mid-1950s. Among his many efforts, King headed the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC). Through his nonviolent activism and inspirational speeches , he played a pivotal role in ending legal segregation of Black Americans, as well as the creation of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965 . King won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1964, among several other honors. He was assassinated by James Earl Ray and died on April 4, 1968, at age 39. King continues to be remembered as one of the most influential and inspirational Black leaders in history.
FULL NAME: Martin Luther King Jr. BIRTHDAY: January 15, 1929 DIED: April 4, 1968 BIRTHPLACE: Atlanta, Georgia SPOUSE: Coretta Scott King (1953-1968) CHILDREN: Yolanda, Martin III, Dexter, and Bernice King ASTROLOGICAL SIGN: Capricorn
Martin Luther King Jr. was born as Michael Luther King Jr. in Atlanta. His birthday was January 15, 1929.

His parents were Michael Luther King Sr. and Alberta Williams King. The Williams and King families had roots in rural Georgia. Martin’s maternal grandfather, A.D. Williams, was a rural minister for years and then moved to Atlanta in 1893. He took over the small, struggling Ebenezer Baptist Church with around 13 members and made it into a forceful congregation. He married Jennie Celeste Parks, and they had one child who survived, Alberta.
Michael Sr. came from a family of sharecroppers in a poor farming community. He married Alberta in 1926 after an eight-year courtship. The newlyweds moved to A.D.’s home in Atlanta. Michael stepped in as pastor of Ebenezer Baptist Church upon the death of his father-in-law in 1931. He, too, became a successful minister and adopted the name Martin Luther King Sr. in honor of the German Protestant religious leader Martin Luther . In due time, Michael Jr. followed his father’s lead and adopt the name himself to become Martin Luther King Jr.
A middle child, Martin Jr. had an older sister, Willie, and a younger brother, Alfred. The King children grew up in a secure and loving environment. Martin Sr. was more the disciplinarian, while Alberta’s gentleness easily balanced out their father’s strict hand.
Although they undoubtedly tried, Martin Jr.’s parents couldn’t shield him completely from racism. His father fought against racial prejudice, not just because his race suffered, but also because he considered racism and segregation to be an affront to God’s will. He strongly discouraged any sense of class superiority in his children, which left a lasting impression on Martin Jr.
Growing up in Atlanta, King entered public school at age 5. In May 1936, he was baptized, but the event made little impression on him.
In May 1941, King was 12 years old when his grandmother Jennie died of a heart attack. The event was traumatic for the boy, more so because he was out watching a parade against his parents’ wishes when she died. Distraught at the news, young King jumped from a second-story window at the family home, allegedly attempting suicide.
King attended Booker T. Washington High School, where he was said to be a precocious student. He skipped both the ninth and eleventh grades and, at age 15, entered Morehouse College in Atlanta in 1944. He was a popular student, especially with his female classmates, but largely unmotivated, floating through his first two years.
Influenced by his experiences with racism, King began planting the seeds for a future as a social activist early in his time at Morehouse. “I was at the point where I was deeply interested in political matters and social ills,” he recalled in The Autobiography of Martin Luther King, Jr . “I could envision myself playing a part in breaking down the legal barriers to Negro rights.”
The Autobiography of Martin Luther King, Jr.

At the time, King felt that the best way to serve that purpose was as a lawyer or a doctor. Although his family was deeply involved in the church and worship, King questioned religion in general and felt uncomfortable with overly emotional displays of religious worship. This discomfort had continued through much of his adolescence, initially leading him to decide against entering the ministry, much to his father’s dismay.
But in his junior year, King took a Bible class, renewed his faith, and began to envision a career in the ministry. In the fall of his senior year, he told his father of his decision, and he was ordained at Ebenezer Baptist Church in February 1948.
Later that year, King earned a sociology degree from Morehouse College and began attended the liberal Crozer Theological Seminary in Chester, Pennsylvania. He thrived in all his studies, was elected student body president, and was valedictorian of his class in 1951. He also earned a fellowship for graduate study.
Even though King was following his father’s footsteps, he rebelled against Martin Sr.’s more conservative influence by drinking beer and playing pool while at college. He became romantically involved with a white woman and went through a difficult time before he could break off the relationship.
During his last year in seminary, King came under the guidance of Morehouse College President Benjamin E. Mays, who influenced King’s spiritual development. Mays was an outspoken advocate for racial equality and encouraged King to view Christianity as a potential force for social change.

After being accepted at several colleges for his doctoral study, King enrolled at Boston University. In 1954, while still working on his dissertation, King became pastor of the Dexter Avenue Baptist Church of Montgomery, Alabama. He completed his doctorate and earned his degree in 1955 at age 25.
Decades after King’s death, in the late 1980s, researchers at Stanford University’s King Papers Project began to note similarities between passages of King’s doctoral dissertation and those of another student’s work. A committee of scholars appointed by Boston University determined that King was guilty of plagiarism in 1991, though it also recommended against the revocation of his degree.

First exposed to the concept of nonviolent resistance while reading Henry David Thoreau ’s On Civil Disobedience at Morehouse, King later discovered a powerful exemplar of the method’s possibilities through his research into the life of Mahatma Gandhi . Fellow civil rights activist Bayard Rustin , who had also studied Gandhi’s teachings, became one of King’s associates in the 1950s and counseled him to dedicate himself to the principles of nonviolence.
As explained in his autobiography , King previously felt that the peaceful teachings of Jesus applied mainly to individual relationships, not large-scale confrontations. But he came to realize: “Love for Gandhi was a potent instrument for social and collective transformation. It was in this Gandhian emphasis on love and nonviolence that I discovered the method for social reform that I had been seeking.”
It led to the formation of King’s six principles of nonviolence :
- Nonviolence is a way of life for courageous people.
- Nonviolence seeks to win friendship and understanding.
- Nonviolence seeks to defeat injustice, not people.
- Nonviolence holds that suffering for a just cause can educate and transform.
- Nonviolence chooses love instead of hate.
- Nonviolence believes that the universe is on the side of justice.
In the years to come, King also frequently cited the “ Beloved Community ”—a world in which a shared spirit of compassion brings an end to the evils of racism, poverty, inequality, and violence—as the end goal of his activist efforts.

Led by his religious convictions and philosophy of nonviolence, King became one of the most prominent figures of the Civil Rights Movement . He was a founding member of the Southern Christian Leadership Conference and played key roles in several major demonstrations that transformed society. This included the Montgomery Bus Boycott that integrated Alabama’s public transit, the Greensboro Sit-In movement that desegregated lunch counters across the South, the March on Washington that led to the passage of the 1964 Civil Rights Act, and the Selma-to-Montgomery marches in Alabama that culminated in the 1965 Voting Rights Act.
King’s efforts earned him the Nobel Peace Prize in 1964 when he was 35.
Montgomery Bus Boycott
King’s first leadership role within the Civil Rights Movement was during the Montgomery Bus Boycott of 1955–1956. The 381-day protest integrated the Alabama city’s public transit in one of the largest and most successful mass movements against racial segregation in history.
The effort began on December 1, 1955, when 42-year-old Rosa Parks boarded the Cleveland Avenue bus to go home after an exhausting day at work. She sat in the first row of the “colored” section in the middle of the bus. As the bus traveled its route, all the seats in the white section filled up, then several more white passengers boarded the bus.
The bus driver noted that there were several white men standing and demanded that Parks and several other African Americans give up their seats. Three other Black passengers reluctantly gave up their places, but Parks remained seated.
The driver asked her again to give up her seat, and again she refused. Parks was arrested and booked for violating the Montgomery City Code. At her trial a week later, in a 30-minute hearing, Parks was found guilty and fined $10 and assessed $4 court fee.
The local NAACP chapter had been looking to challenge Montgomery’s segregated bus policy and had almost made 15-year-old Claudette Colvin the face of the campaign months earlier. She similarly refused to give up her bus seat to a white man on March 2, 1955, but after organizers learned Colvin was pregnant, they feared it would scandalize the deeply religious Black community and make Colvin, along with the group’s efforts, less credible in the eyes of sympathetic white people. Parks’ experience of discrimination provided another opportunity.
On the night Parks was arrested, E.D. Nixon , head of the local NAACP chapter, met with King and other local civil rights leaders to plan a Montgomery Bus Boycott. King was elected to lead the boycott because he was young, well-trained, and had solid family connections and professional standing. He was also new to the community and had few enemies, so organizers felt he would have strong credibility with the Black community.
In his first speech as the group’s president, King declared:
“We have no alternative but to protest. For many years, we have shown an amazing patience. We have sometimes given our white brothers the feeling that we liked the way we were being treated. But we come here tonight to be saved from that patience that makes us patient with anything less than freedom and justice.”
King’s skillful rhetoric put new energy into the civil rights struggle in Alabama. The Montgomery Bus Boycott began December 5, 1955, and for more than a year, the local Black community walked to work, coordinated ride sharing, and faced harassment, violence, and intimidation. Both King’s and Nixon’s homes were attacked.
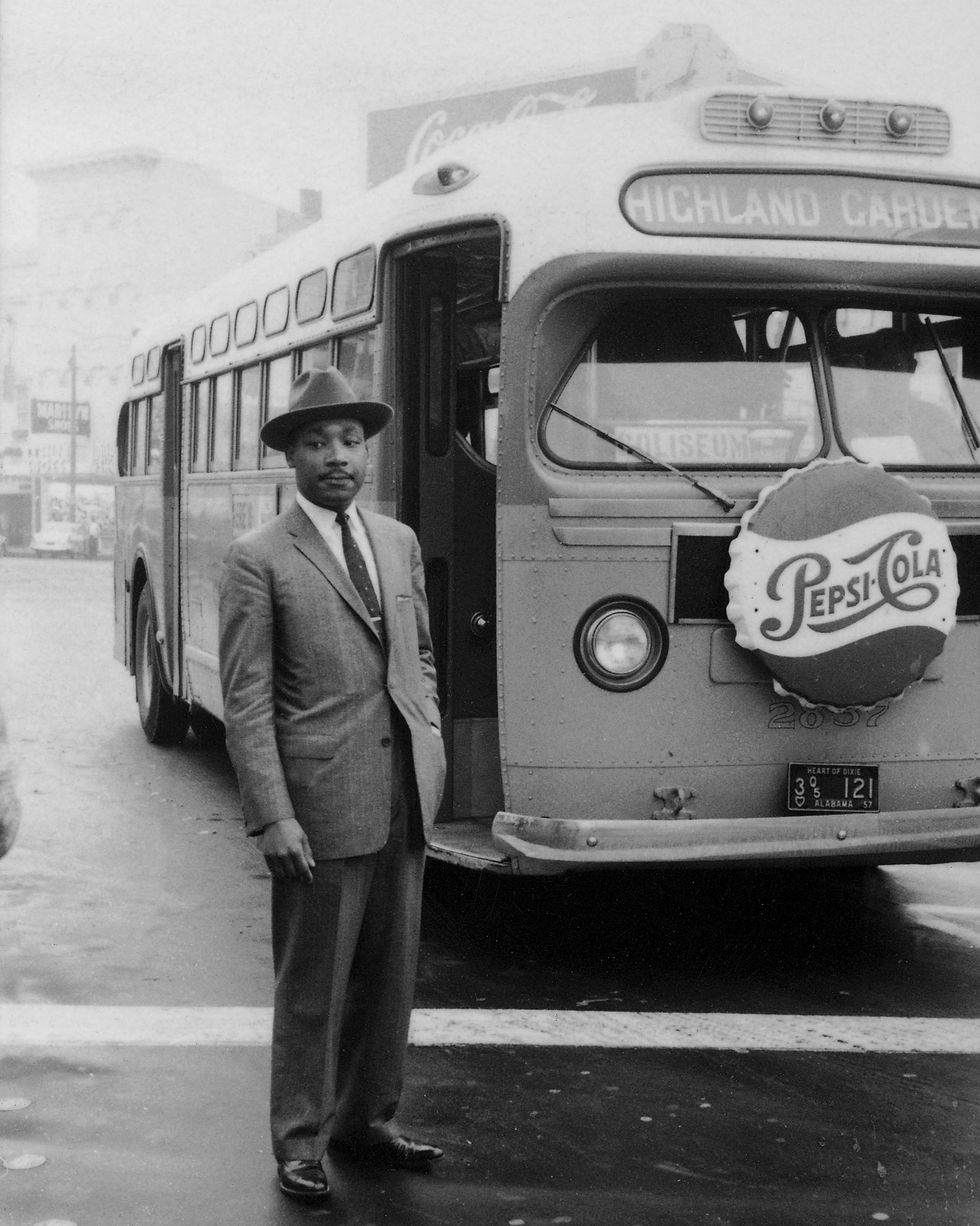
In addition to the boycott, members of the Black community took legal action against the city ordinance that outlined the segregated transit system. They argued it was unconstitutional based on the U.S. Supreme Court ’s “separate is never equal” decision in Brown v. Board of Education (1954). Several lower courts agreed, and the nation’s Supreme Court upheld the ruling in a November 13, 1956, decision that also ruled the state of Alabama’s bus segregation laws were unconstitutional.
After the legal defeats and large financial losses, the city of Montgomery lifted the law that mandated segregated public transportation. The boycott ended on December 20, 1956.
Southern Christian Leadership Conference
Flush with victory, African American civil rights leaders recognized the need for a national organization to help coordinate their efforts. In January 1957, King, Ralph Abernathy , and 60 ministers and civil rights activists founded the Southern Christian Leadership Conference to harness the moral authority and organizing power of Black churches. The SCLC helped conduct nonviolent protests to promote civil rights reform.
King’s participation in the organization gave him a base of operation throughout the South, as well as a national platform. The SCLC felt the best place to start to give African Americans a voice was to enfranchise them in the voting process. In February 1958, the SCLC sponsored more than 20 mass meetings in key southern cities to register Black voters. King met with religious and civil rights leaders and lectured all over the country on race-related issues.
Stride Toward Freedom: The Montgomery Story

That September, King survived an attempt on his life when a woman with mental illness stabbed him in the chest as he signed copies of his book Stride Toward Freedom in a New York City department store. Saved by quick medical attention, King expressed sympathy for his assailant’s condition in the aftermath .
In 1959, with the help of the American Friends Service Committee, King visited Gandhi ’s birthplace in India. The trip affected him in a profound way, increasing his commitment to America’s civil rights struggle.
Greensboro Sit-In
By 1960, King was gaining national exposure. He returned to Atlanta to become co-pastor with his father at Ebenezer Baptist Church but also continued his civil rights efforts. His next activist campaign was the student-led Greensboro Sit-In movement.
In February 1960, a group of Black students in Greensboro, North Carolina , began sitting at racially segregated lunch counters in the city’s stores. When asked to leave or sit in the “colored” section, they just remained seated, subjecting themselves to verbal and sometimes physical abuse.
The movement quickly gained traction in several other cities. That April, the SCLC held a conference at Shaw University in Raleigh, North Carolina, with local sit-in leaders. King encouraged students to continue to use nonviolent methods during their protests. Out of this meeting, the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC) formed and, for a time, worked closely with the SCLC. By August 1960, the sit-ins had successfully ended segregation at lunch counters in 27 southern cities. But the movement wasn’t done yet.
On October 19, 1960, King and 75 students entered a local department store and requested lunch-counter service but were denied. When they refused to leave the counter area, King and 36 others were arrested. Realizing the incident would hurt the city’s reputation, Atlanta’s mayor negotiated a truce, and charges were eventually dropped.
Soon after, King was imprisoned for violating his probation on a traffic conviction. The news of his imprisonment entered the 1960 presidential campaign when candidate John F. Kennedy made a phone call to Martin’s wife, Coretta Scott King . Kennedy expressed his concern over the harsh treatment Martin received for the traffic ticket, and political pressure was quickly set in motion. King was soon released.
Letter from Birmingham Jail
In the spring of 1963, King organized a demonstration in downtown Birmingham, Alabama. With entire families in attendance, city police turned dogs and fire hoses on demonstrators. King was jailed, along with large numbers of his supporters.
The event drew nationwide attention. However, King was personally criticized by Black and white clergy alike for taking risks and endangering the children who attended the demonstration.
In his famous Letter from Birmingham Jail , King eloquently spelled out his theory of nonviolence: “Nonviolent direct action seeks to create such a crisis and foster such a tension that a community, which has constantly refused to negotiate, is forced to confront the issue.”
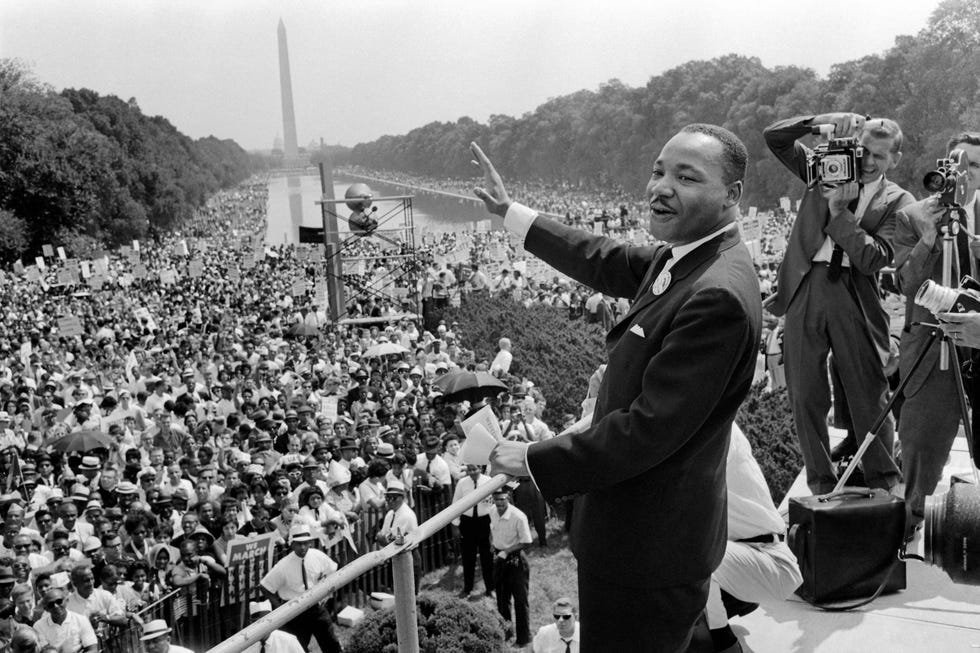
1963 March on Washington
By the end of the Birmingham campaign, King and his supporters were making plans for a massive demonstration on the nation’s capital composed of multiple organizations, all asking for peaceful change. The demonstration was the brainchild of labor leader A. Philip Randolph and King’s one-time mentor Bayard Rustin .
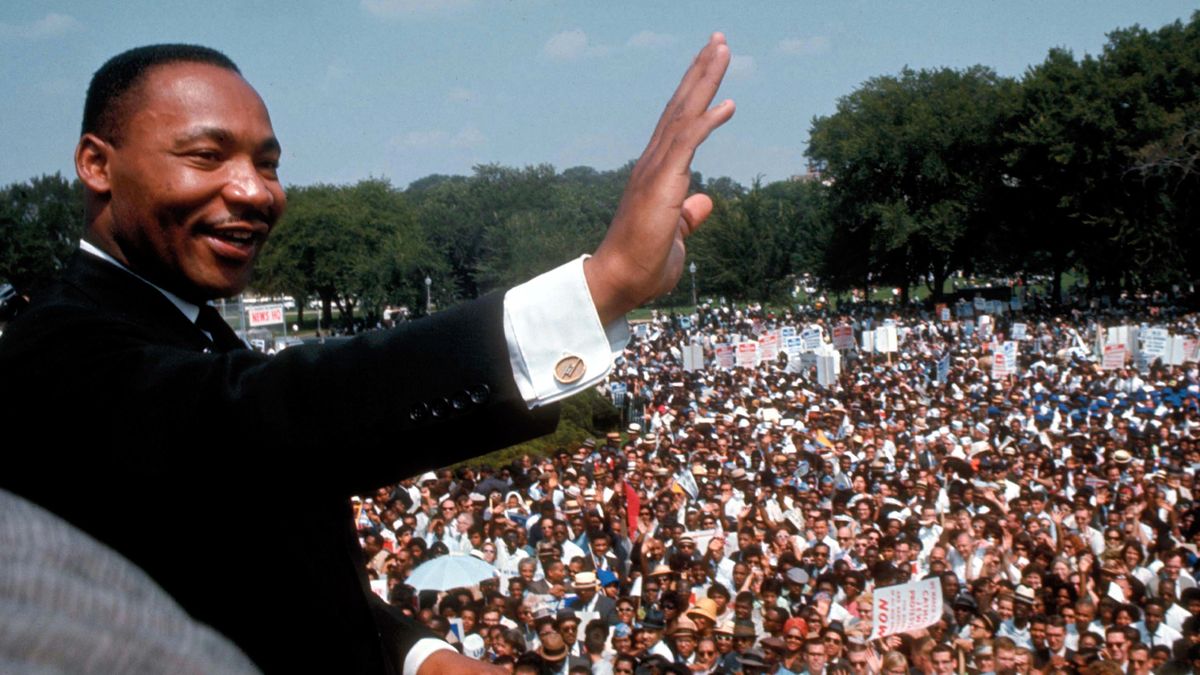
On August 28, 1963, the historic March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom drew an estimated 250,000 people in the shadow of the Lincoln Memorial. It remains one of the largest peaceful demonstrations in American history. During the demonstration, King delivered his famed “I Have a Dream” speech .
The rising tide of civil rights agitation that had culminated in the March on Washington produced a strong effect on public opinion. Many people in cities not experiencing racial tension began to question the nation’s Jim Crow laws and the near-century of second-class treatment of African American citizens since the end of slavery. This resulted in the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 , authorizing the federal government to enforce desegregation of public accommodations and outlawing discrimination in publicly owned facilities.
Selma March
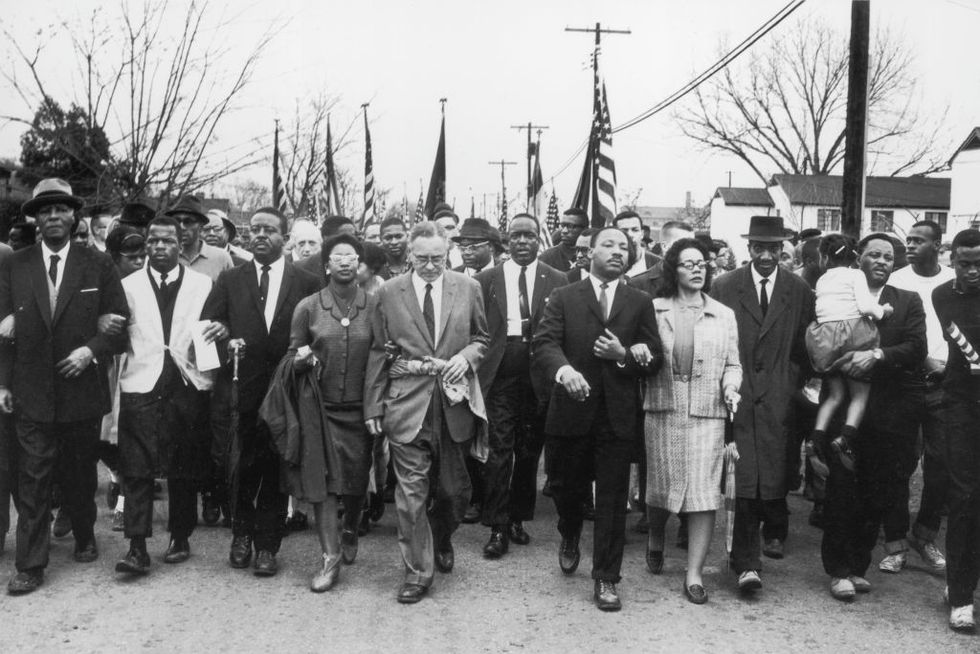

Continuing to focus on voting rights, King, the SCLC, SNCC, and local organizers planned to march peacefully from Selma, Alabama, to the state’s capital, Montgomery.
Led by John Lewis and Hosea Williams , demonstrators set out on March 7, 1965. But the Selma march quickly turned violent as police with nightsticks and tear gas met the demonstrators as they tried to cross the Edmund Pettus Bridge in Selma. The attack was televised, broadcasting the horrifying images of marchers being bloodied and severely injured to a wide audience. Of the 600 demonstrators, 58 were hospitalized in a day that became known as “ Bloody Sunday .” King, however, was spared because he was in Atlanta.
Not to be deterred, activists attempted the Selma-to-Montgomery march again. This time, King made sure he was part of it. Because a federal judge had issued a temporary restraining order on another march, a different approach was taken.
On March 9, 1965, a procession of 2,500 marchers, both Black and white, set out once again to cross the Pettus Bridge and confronted barricades and state troopers. Instead of forcing a confrontation, King led his followers to kneel in prayer, then they turned back. This became known as “Turnaround Tuesday.”
Alabama Governor George Wallace continued to try to prevent another march until President Lyndon B. Johnson pledged his support and ordered U.S. Army troops and the Alabama National Guard to protect the protestors.
On March 21, 1965, approximately 2,000 people began a march from Selma to Montgomery. On March 25, the number of marchers, which had grown to an estimated 25,000 gathered in front of the state capitol where King delivered a televised speech. Five months after the historic peaceful protest, President Johnson signed the 1965 Voting Rights Act .

Along with his “I Have a Dream” and “I’ve Been to the Mountaintop” speeches, King delivered several acclaimed addresses over the course of his life in the public eye.
“I Have A Dream” Speech
Date: august 28, 1963.
King gave his famous “I Have a Dream” speech during the 1963 March on Washington. Standing at the Lincoln Memorial, he emphasized his belief that someday all men could be brothers to the 250,000-strong crowd.
Notable Quote: “I have a dream that my four children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character.”
“Give Us the Ballot” Speech
Date: may 17, 1957.
Six years before he told the world of his dream, King stood at the same Lincoln Memorial steps as the final speaker of the Prayer Pilgrimage for Freedom. Dismayed by the ongoing obstacles to registering Black voters, King urged leaders from various backgrounds—Republican and Democrat, Black and white—to work together in the name of justice.
Notable Quote: “Give us the ballot, and we will no longer have to worry the federal government about our basic rights. Give us the ballot, and we will no longer plead to the federal government for passage of an anti-lynching law... Give us the ballot, and we will transform the salient misdeeds of bloodthirsty mobs into the calculated good deeds of orderly citizens.”

Nobel Peace Prize Acceptance Speech
Date: december 10, 1964.
Speaking at the University of Oslo in Norway, King pondered why he was receiving the Nobel Prize when the battle for racial justice was far from over, before acknowledging that it was in recognition of the power of nonviolent resistance. He then compared the foot soldiers of the Civil Rights Movement to the ground crew at an airport who do the unheralded-yet-necessary work to keep planes running on schedule.
Notable Quote: “I think Alfred Nobel would know what I mean when I say that I accept this award in the spirit of a curator of some precious heirloom which he holds in trust for its true owners—all those to whom beauty is truth and truth, beauty—and in whose eyes the beauty of genuine brotherhood and peace is more precious than diamonds or silver or gold.”
“Our God is Marching On (How Long? Not Long)” Speech
Date: march 25, 1965.
At the end of the bitterly fought Selma-to-Montgomery march, King addressed a crowd of 25,000 supporters from the Alabama State Capitol. Offering a brief history lesson on the roots of segregation, King emphasized that there would be no stopping the effort to secure full voting rights, while suggesting a more expansive agenda to come with a call to march on poverty.
Notable Quote: “I come to say to you this afternoon, however difficult the moment, however frustrating the hour, it will not be long, because ‘truth crushed to earth will rise again.’ How long? Not long, because ‘no lie can live forever.’... How long? Not long, because the arc of the moral universe is long, but it bends toward justice.”
“Beyond Vietnam: A Time to Break Silence” Speech
Date: april 4, 1967.
One year before his assassination, King delivered a controversial sermon at New York City’s Riverside Church in which he condemned the Vietnam War. Explaining why his conscience had forced him to speak up, King expressed concern for the poor American soldiers pressed into conflict thousands of miles from home, while pointedly faulting the U.S. government’s role in escalating the war.
Notable Quote: “We still have a choice today: nonviolent coexistence or violent co-annihilation. We must move past indecision to action. We must find new ways to speak for peace in Vietnam and justice throughout the developing world, a world that borders on our doors. If we do not act, we shall surely be dragged down the long, dark, and shameful corridors of time reserved for those who possess power without compassion, might without morality, and strength without sight.”
“I’ve Been to the Mountaintop” Speech
Date: april 3, 1968.
The well-known orator delivered his final speech the day before he died at the Mason Temple in Memphis, Tennessee. King reflected on major moments of progress in history and his own life, in addition to encouraging the city’s striking sanitation workers.
Notable Quote: “I’ve seen the promised land. I may not get there with you. But I want you to know tonight that we, as a people, will get to the promised land.”
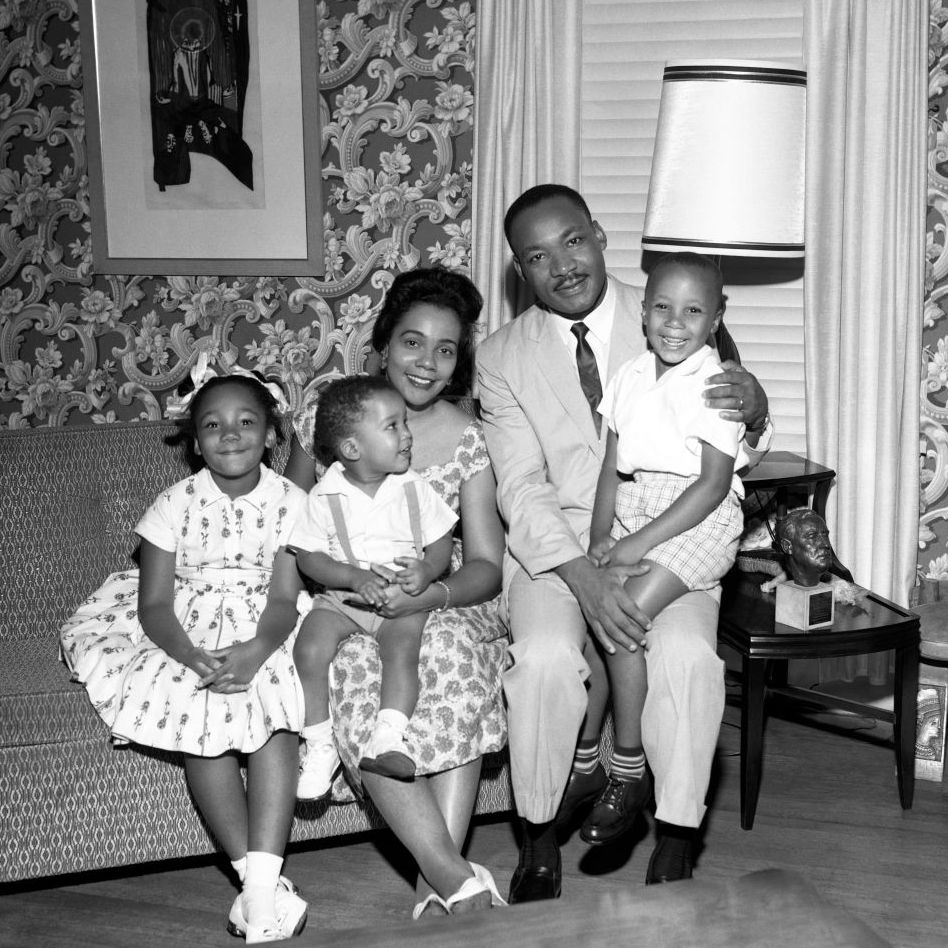
While working on his doctorate at Boston University, King met Coretta Scott , an aspiring singer and musician at the New England Conservatory school in Boston. They were married on June 18, 1953, and had four children—two daughters and two sons—over the next decade. Their oldest, Yolanda, was born in 1955, followed by sons Martin Luther King III in 1957 and Dexter in 1961. The couple welcomed Bernice King in 1963.
Although she accepted the responsibility to raise the children while King travelled the country, Coretta opened their home to organizational meetings and served as an advisor and sounding board for her husband. “I am convinced that if I had not had a wife with the fortitude, strength, and calmness of Corrie, I could not have withstood the ordeals and tensions surrounding the movement,” King wrote in his autobiography.
His lengthy absences became a way of life for their children, but Martin III remembered his father returning from the road to join the kids playing in the yard or bring them to the local YMCA for swimming. King also fostered discussions at mealtimes to make sure everyone understood the important issues he was seeking to resolve.
Leery of accumulating wealth as a high-profile figure, King insisted his family live off his salary as a pastor. However, he was known to splurge on good suits and fine dining, while contrasting his serious public image with a lively sense of humor among friends and family.
Due to his relationships with alleged Communists, King became a target of FBI surveillance and, from late 1963 until his death, a campaign to discredit the civil rights activist. While FBI wiretaps failed to produce evidence of Communist sympathies, they captured the civil rights leader’s engagement in extramarital dalliances. This led to the infamous “suicide letter” of 1964, later confirmed to be from the FBI and authorized by then-Director J. Edgar Hoover , which urged King to kill himself if he wanted to prevent news of his affairs from going public.
In 2019, historian David Garrow wrote of explosive new allegations against King following his review of recently released FBI documents. Among the discoveries was a memo suggesting that King had encouraged the rape of a parishioner in a hotel room, as well as evidence that he might have fathered a daughter with a mistress. Other historians questioned the veracity of the documentation, especially given the FBI’s known attempts to damage King’s reputation. The original surveillance tapes regarding these allegations are under judicial seal until 2027.
From late 1965 through 1967, King expanded his civil rights efforts into other larger American cities, including Chicago and Los Angeles. But he met with increasing criticism and public challenges from young Black power leaders. King’s patient, non-violent approach and appeal to white middle-class citizens alienated many Black militants who considered his methods too weak, too late, and ineffective.
To address this criticism, King began making a link between discrimination and poverty, and he began to speak out against the Vietnam War . He felt America’s involvement in Vietnam was politically untenable and the government’s conduct in the war was discriminatory to the poor. He sought to broaden his base by forming a multiracial coalition to address the economic and unemployment problems of all disadvantaged people. To that end, plans were in the works for another march on Washington to highlight the Poor People’s Campaign, a movement intended to pressure the government into improving living and working conditions for the economically disadvantaged.
By 1968, the years of demonstrations and confrontations were beginning to wear on King. He had grown tired of marches, going to jail, and living under the constant threat of death. He was becoming discouraged at the slow progress of civil rights in America and the increasing criticism from other African American leaders.
In the spring of 1968, a labor strike by Memphis, Tennessee, sanitation workers drew King to one last crusade. On April 3, 1968, he gave his final and what proved to be an eerily prophetic speech, “I’ve Been to the Mountaintop,” in which he told supporters, “Like anybody, I would like to live a long life. Longevity has its place. But I’m not concerned about that now… I’m not worried about anything. I’m not fearing any man. Mine eyes have seen the glory of the coming of the Lord.”

While standing on a balcony outside his room at the Lorraine Motel in Memphis, Tennessee, Martin Luther King Jr. was killed by a sniper’s bullet on April 4, 1968. King died at age 39. The shocking assassination sparked riots and demonstrations in more than 100 cities across the country.
The shooter was James Earl Ray , a malcontent drifter and former convict. He initially escaped authorities but was apprehended after a two-month international manhunt. In 1969, Ray pleaded guilty to assassinating King and was sentenced to 99 years in prison.
The identity of King’s assassin has been the source of some controversy. Ray recanted his confession shortly after he was sentenced, and King’s son Dexter publicly defended Ray’s innocence after meeting with the convicted gunman in 1997. Another complicating factor is the 1993 confession of tavern owner Loyd Jowers, who said he contracted a different hit man to kill King. In June 2000, the U.S. Justice Department released a report that dismissed the alternative theories of King’s death. Ray died in prison on April 23, 1998.

King’s life had a seismic impact on race relations in the United States. Years after his death, he is the most widely known Black leader of his era.
His life and work have been honored with a national holiday, schools and public buildings named after him, and a memorial on Independence Mall in Washington, D.C.
Over the years, extensive archival studies have led to a more balanced and comprehensive assessment of his life, portraying him as a complex figure: flawed, fallible, and limited in his control over the mass movements with which he was associated, yet a visionary leader who was deeply committed to achieving social justice through nonviolent means.
- But we come here tonight to be saved from that patience that makes us patient with anything less than freedom and justice.
- There comes a time when the cup of endurance runs over and men are no longer willing to be plunged into an abyss of injustice where they experience the bleakness of corroding despair.
- Any law that uplifts human personality is just. Any law that degrades human personality is unjust.
- The whirlwinds of revolt will continue to shake the foundations of our nation until the bright day of justice emerges.
- Let us not seek to satisfy our thirst for freedom by drinking from the cup of bitterness and hatred.
- Darkness cannot drive out darkness: only light can do that. Hate cannot drive out hate: only love can do that.
- The ultimate measure of a man is not where he stands in moments of comfort and convenience, but where he stands at times of challenge and controversy. The true neighbor will risk his position, his prestige, and even his life for the welfare of others.
- We must all learn to live together as brothers, or we will all perish together as fools.
- Forgiveness is not an occasional act; it is a permanent attitude.
- I have a dream that my four children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character.
- The function of education, therefore, is to teach one to think intensively and to think critically. But education which stops with efficiency may prove the greatest menace to society. The most dangerous criminal may be the man gifted with reason but with no morals.
- I’ve seen the promised land. I may not get there with you. But I want you to know tonight that we, as a people, will get to the promised land.
- Power at its best is love implementing the demands of justice. Justice at its best is love correcting everything that stands against love.
- A man who won’t die for something is not fit to live.
- At the center of non-violence stands the principle of love.
- Right, temporarily defeated, is stronger than evil triumphant.
- In the end, we will remember not the words of our enemies, but the silence of our friends.
- Injustice anywhere is a threat to justice everywhere.
- Our lives begin to end the day we become silent about things that matter.
Fact Check: We strive for accuracy and fairness. If you see something that doesn’t look right, contact us !
The Biography.com staff is a team of people-obsessed and news-hungry editors with decades of collective experience. We have worked as daily newspaper reporters, major national magazine editors, and as editors-in-chief of regional media publications. Among our ranks are book authors and award-winning journalists. Our staff also works with freelance writers, researchers, and other contributors to produce the smart, compelling profiles and articles you see on our site. To meet the team, visit our About Us page: https://www.biography.com/about/a43602329/about-us
Civil Rights Activists

30 Civil Rights Leaders of the Past and Present

Benjamin Banneker

Marcus Garvey

Madam C.J. Walker

Maya Angelou

17 Inspiring Martin Luther King Quotes

Bayard Rustin

Colin Kaepernick

W.E.B. Du Bois and Booker T. Washington’s Clash
Featured Topics
Featured series.
A series of random questions answered by Harvard experts.
Explore the Gazette
Read the latest.

Cease-fire will fail as long as Hamas exists, journalist says

Imagining a different Russia

Remember Eric Garner? George Floyd?
The Harvard Crimson’s April 8, 1968, edition.
Stephanie Mitchell/Harvard Staff Photographer
Losing King: Shock, sorrow, anger, and a voice time hasn’t silenced
Five decades after assassination, views from Gates, Gordon-Reed, others on the nation then and now
Colleen Walsh
Harvard Staff Writer
Fifty years ago the murder of a Baptist minister turned Civil Rights giant shook the nation. Just after 6 p.m. on April 4, 1968, Martin Luther King Jr. was gunned down on the second-floor balcony of the Lorraine Motel in Memphis, Tenn. There to support the city’s striking sanitation workers, King was about to head to dinner when he was struck in the jaw by a single bullet. In a country already roiled by racial violence and civil unrest, the killing set off a wave of deadly riots from coast to coast.
We asked a group of Harvard scholars to reflect on King’s life, death, and legacy. Historians Annette Gordon-Reed and Henry Louis Gates Jr . recalled where they were when they heard about the assassination. Philosopher Tommie Shelby remembered his earliest impressions of King’s language and rhetoric. All three shared thoughts on how the Civil Rights leader would view today’s America. Political theorist Danielle Allen , set to deliver the keynote at a King-focused conference on Friday, said that 50 years on, his work remains unfinished.
Annette Gordon-Reed (from left), Danielle Allen, Henry Louis Gates Jr., and Tommie Shelby.
File photos by Stephanie Mitchell and Rose Lincoln/Harvard Staff
‘It’s a shock that I’ve never gotten over’
A senior in high school, Gates was at home in Piedmont, Va., watching TV when an announcement interrupted the news.
“I had three best friends that were black and they came over and we were just shocked — we were stunned,” said Gates, the Alphonse Fletcher Jr. University Professor and director of the Hutchins Center . “There was nothing that we could do.
“Basically it’s a shock that I’ve never gotten over, really. I mean, I still can’t believe it when I watch the footage.”
The shock lingered in Gates’ voice as he considered King’s relative youth.
“He seemed like such an old man but he was 39 years old. He did all of that when he was 39, and I definitely believe — I am one of the black people who thinks there was some kind of conspiracy to kill him. I think he could have been the first black president and I don’t think America was ready for that.”
King, Gates added, was “moving toward an amalgamation of race and class and that was threatening to the system.”
What would he think of the U.S. today?
Gates said King would be surprised by how much the country has moved the dial, and stunned by the numbers of upper- and middle-class African-Americans. “But he would be equally shocked that the percentage of black children living at or beneath the poverty line is roughly the same as it was in 1970, roughly the same as it was when he died.”
And while King would be pleased by the progress made since 1968, and “astonished and delighted” that the country was led by an African-American president for eight years, he would also be dismayed “at mass incarceration” and at “deindustrialization which interrupted the cycle of moving from the working class to the middle class and the middle class to the upper-middle class.”
‘ It was clear that he was making lots of people angry ’
More like this.

When King came to Harvard

Beyond ‘I Have a Dream’
Gordon-Reed, 9 years old in 1968, was with her mother at the home of one her friends “when her son came into the room and told us that King had been assassinated.”
Her Texas community’s reaction was one of “great sadness,” said Gordon-Reed, Harvard Law School ’s Charles Warren Professor of American Legal History, a professor of history in the Faculty of Arts and Sciences , and a Pulitzer Prize winner for “The Hemingses of Monticello: An American Family.”
“But this was a small town with a small black population,” she said. “More open anger was expressed in urban communities.”
Gordon-Reed said her mother and father “were not surprised” by King’s murder. “It was clear that he was making lots of people angry. The possibility of violence was always present given all that was at stake.”
Her parents’ reaction was likely shared by countless Americans. King had endured repeated physical attacks during his years of nonviolent protests, and death threats against him were common. In his last public address, delivered at Memphis’ Mason Temple the day before his death, King alluded to his own mortality.
“Like anybody, I would like to live a long life. Longevity has its place. But I’m not concerned about that now. I just want to do God’s will. And He’s allowed me to go up to the mountain. And I’ve looked over. And I’ve seen the Promised Land. I may not get there with you. But I want you to know tonight, that we, as a people, will get to the Promised Land.”
Turning to today, Gordon-Reed said King would have been amazed by the Obama presidency, though unsurprised by the backlash against it.
“I would imagine he may also be surprised at how he has been embraced by so many different segments of society, for their own purposes,” she added, and “by the pace of social changes — the women’s movement, the movement for LGBTQ rights. And [that] the issue of race is not just a matter of black and white anymore.”
While much has changed for the better, Gordon-Reed said the economic advances King pressed for at the end of this life “have not come to fruition.”
“All available evidence indicates that communities of color still lag behind in terms of wealth,” she said. “The legacies of slavery, segregation, and the commitment to white supremacy have not yet been overcome. In fact, the issue of inequality is not just about race. The situation of organized labor — the weakening of unions overall — would have surprised him, I think. He thought that unions, along with working-class people of all colors, could cooperate to strike a blow on behalf of all marginalized people. That does not seem to be on the horizon.”
‘Leaders should not seek riches, fame, or even recognition for their efforts’
One of Shelby’s most powerful King moments was the first time he read “Letter from a Birmingham Jail.”
“It has so many important ethical lessons,” said the Caldwell Titcomb Professor of African and African American Studies and of Philosophy. “For instance, King argued that it is wrong to counsel the oppressed not to fight for their rights because this might provoke others to engage in violence or might create social strife. ‘Law and order’ and civil peace are not ends in themselves. They are means for establishing and maintaining just social conditions.”
Which of King’s beliefs would most surprise people today? Reparations are high on Shelby’s list.
In “Why We Can’t Wait” (1964), King wrote that while the cost made it “impossible to fully pay reparations to blacks for all the wrongs of slavery … compensation was due to the descendants of slaves for the unpaid toil of their ancestors.”
And King’s life still contains crucial lessons for those in charge today, said Shelby, co-editor of “To Shape a New World: Essays on the Political Philosophy of Martin Luther King Jr.”
“Leaders should not seek riches, fame, or even recognition for their efforts,” Shelby said. “They should see their vocation as one of service and sacrifice and should lead by example. This kind of leadership requires integrity, resilience, a willingness to speak hard truths in public, and most of all hope — the conviction that, through our determined efforts, we can make our world more peaceful and just.”
‘C ourage, endurance, moral clarity, and love’
With Harvard students on spring break the week of the assassination, King was remembered on Palm Sunday at Memorial Church. The Harvard Crimson’s Monday, April 8, edition ran a picture of the slain icon accompanied by an article headlined “Funeral, Sympathy March Draw Thousands to South.” The following day, President Nathan M. Pusey canceled morning and early afternoon classes to allow students to attend a special service in Memorial Church. The Harvard leader addressed the crowd during the somber ceremony.
“I do not know when the death of a private citizen has quickened such a universal response of grief and deprivation — nationwide and worldwide,” said Pusey. “Our grief is for the man and for the many unaccomplished things for which he worked and died.”
The impact of King’s death rippled through Commencement events. In March 1968, students had broken from tradition and directly invited the Class Day speaker. They selected King, whose speech, set for June 12, was expected to address the Vietnam War .
A year earlier King had registered his opposition to the conflict in a blistering New York speech that connected war, racism, and poverty. Congressman John Lewis of Georgia was in the audience that day. “I heard him speak so many times,” Lewis told The New Yorker in 2017 . “I still think this is probably the best.” (In a fitting turn, Lewis will be the principal speaker at the Afternoon Program of Harvard’s 367th Commencement on May 24. )
Her husband’s death still raw, Coretta Scott King agreed to speak in his place on Class Day. By then the nation was mourning another loss. Six days earlier Civil Rights advocate and presidential candidate Robert F. Kennedy had been shot to death in Los Angeles.
“These two men addressed themselves to the burning issues of our times: They spoke out against great evils in our society: racism, poverty, and war,” King told seniors at Sanders Theatre. “They were great and effective actors on the stage of history. They played their parts exceedingly well, thus inspiring millions. They are a part of that creative minority which helped to move society forward.
“As young people, as students, your lives have been greatly affected by the loss of these champions of freedom, of justice, of human dignity and peace. In a power-drunk world, where means become ends, and violence becomes a favorite pastime, we are swiftly moving toward self-annihilation. Your generation must speak out with righteous indignation against the forces which are seeking to destroy us.”
Five decades removed from the grieving widow’s show of courage and resolve, Allen, the James Bryant Conant University Professor, will focus her address at Friday’s symposium on urging the same qualities upon a nation still struggling to live up to Martin Luther King Jr.’s highest hopes.
“The Civil Rights movement is far from done; the onward march of freedom still requires courage, endurance, moral clarity, and love,” Allen said. “I think we can best memorialize the men and women who worked with King, and King himself, by finding the courage to insist, over and over again and lovingly, on the ethical demands of full integration.”
Share this article
You might like.
Times opinion writer Bret Stephens also weighs in on campus unrest in final Middle East Dialogues event

Former ambassador sees two tragedies: Ukraine war and the damage Putin has inflicted on his own country

Mother, uncle of two whose deaths at hands of police officers ignited movement talk about turning pain into activism, keeping hope alive
How old is too old to run?
No such thing, specialist says — but when your body is trying to tell you something, listen
Alcohol is dangerous. So is ‘alcoholic.’
Researcher explains the human toll of language that makes addiction feel worse
- Louisiana State University
- Research Guides
- LSU Libraries
Martin Luther King, Jr.
- Biographical Sketch
- Honorary Degrees
- Selected Resources at LSU Libraries
Birth & Family, Education, Speeches, and Death

Birth and Family Martin Luther King, Jr. was born at noon Tuesday, January 15, 1929, at the family home, 501 Auburn Avenue, N.E., Atlanta, Georgia. Dr. Charles Johnson was the attending physician. Martin Luther King, Jr., was the first son and second child born to the Reverend Martin Luther King, Sr., and Alberta Williams King. Other children born to the Kings were Christine King Farris and the late Reverend Alfred Daniel Williams King. Martin Luther King's maternal grandparents were the Reverend Adam Daniel Williams, second pastor of Ebenezer Baptist, and Jenny Parks Williams. His paternal grandparents, James Albert and Delia King, were sharecroppers on a farm in Stockbridge, Georgia. He married the former Coretta Scott, younger daughter of Obadiah, and Bernice McMurray Scott of Marion, Alabama on June 18, 1953. The marriage ceremony took place on the lawn of the Scotts' home in Marion. The Reverend King, Sr., performed the service, with Mrs. Edythe Bagley, the sister of Mrs. King, maid of honor, and the Reverend A.D. King, the brother of Martin Luther King, Jr., best man. Four children were born to Dr. and Mrs. King:
- Yolanda Denise (November 17, 1955 Montgomery, Alabama);
- Martin Luther III (October 23, 1957 Montgomery, Alabama);
- Dexter Scott (January 30, 1961 Atlanta, Georgia); and
- Bernice Albertine (March 28, 1963 Atlanta, Georgia)
Education Martin Luther King, Jr. began his education at the Yonge Street Elementary School in Atlanta, Georgia. Following Yonge School, he was enrolled in David T. Howard Elementary School. He also attended the Atlanta University Laboratory School and Booker T. Washington High School. Because of his high score on the college entrance examinations in his junior year of high school, he advanced to Morehouse College without formal graduation from Booker T. Washington. Having skipped both the ninth and twelfth grades, Dr. King entered Morehouse at the age of fifteen. In 1948, he graduated from Morehouse College with a B.A. degree in Sociology. That fall, he enrolled in Crozer Theological Seminary in Chester, Pennsylvania where he was: elected president of the senior class and delivered the valedictory address; won the Pearl Plafker Award for the most outstanding student; and received the J. Lewis Crozer fellowship for graduate study at a university of his choice. He was awarded a Bachelor of Divinity degree from Crozer in 1951. While attending Crozer, he also studied at the University of Pennsylvania In September of 1951, Martin Luther King began doctoral studies in Systematic Theology at Boston University. He also studied at Harvard University. His dissertation, A Comparison of God in the Thinking of Paul Tillich and Henry Wieman , was completed in 1955, and the Ph.D. degree from Boston, a Doctorate of Philosophy in Systematic Theology, was awarded on June 5, 1955. Martin Luther King entered the Christian ministry and was ordained in February 1948 at the age of nineteen at Ebenezer Baptist Church, Atlanta, Georgia. Following his ordination, he became Assistant Pastor of Ebenezer. Upon completion of his studies at Boston University, he accepted the call of Dexter Avenue Baptist Church, Montgomery, Alabama. He was the pastor of Dexter Avenue from September 1954 to November 1959, when he resigned to move to Atlanta to direct the activities of the Southern Christian Leadership Conference. From 1960 until his death in 1968, he was co-pastor with his father at Ebenezer Baptist Church and President of the Southern Christian Leadership Conference. Dr. King was a pivotal figure in the Civil Rights Movement. He was elected president of the Montgomery Improvement Association, the organization which was responsible for the successful Montgomery Bus Boycott from 1955 to 1956 (381 days). He was arrested thirty times for his participation in civil rights activities. He was a founder and president of Southern Christian Leadership Conference from 1957 to 1968. He was also vice president of the national Sunday School and Baptist Teaching Union Congress of the National Baptist Convention. He was a member of several national and local boards of directors and served on the boards of trustees of several institutions and agencies. Dr. King was elected to membership in several learned societies including the prestigious American Academy of Arts and Sciences.
Speeches Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. was a vital personality of the modern era. His lectures and remarks stirred the concern and sparked the conscience of a generation; the movements and marches he led brought significant changes in the fabric of American life; his courageous and selfless devotion gave direction to thirteen years of civil rights activities; his charismatic leadership inspired men and women, young and old, in the nation and abroad.
Dr. King's concept of somebodiness gave black and poor people a new sense of worth and dignity. His philosophy of nonviolent direct action, and his strategies for rational and non-destructive social change, galvanized the conscience of this nation and reordered its priorities. The Voting Rights Act of 1965, for example, went to Congress as a result of the Selma to Montgomery march. His wisdom, his words, his actions, his commitment, and his dreams for a new cast of life, are intertwined with the American experience. Dr. King's speech at the march on Washington in 1963, his acceptance speech of the Nobel Peace Prize, his last sermon at Ebenezer Baptist Church, and his final speech in Memphis ( I've Been to the Mountaintop )are among his most famous. The Letter from Birmingham Jail ranks among the most important American documents.
Death Dr. King was shot while standing on the balcony of the Lorraine Motel in Memphis, Tennessee on April 4, 1968, by James Earl Ray. James Earl Ray was arrested in London, England on June 8, 1968, and returned to Memphis, Tennessee to stand trial for the assassination of Dr. King. On March 9, 1969, before coming to trial, he entered a guilty plea and was sentenced to ninety-nine years in the Tennessee State Penitentiary. Dr. King had been in Memphis to help lead sanitation workers in a protest against low wages and intolerable conditions. His funeral services were held on April 9, 1968, in Atlanta at Ebenezer Church and on the campus of Morehouse College, with the President of the United States proclaiming a day of mourning and flags being flown at half-staff. The area where Dr. King was entombed is located on Freedom Plaza and surrounded by the Freedom Hall Complex of the Martin Luther King, Jr. Center for Nonviolent Social Change, Inc. The Martin Luther King, Jr. Historic Site, a 23-acre area was listed as a National Historic Landmark on May 5, 1977, and was made a National Historic Site on October 10, 1980 by the U.S. Department of the Interior.
- Next: Timeline >>
- Last Updated: Jun 6, 2023 8:54 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.lsu.edu/mlk
Provide Website Feedback Accessibility Statement
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
- Martin Luther King Jr.’s Legacy 60 Years After the March on Washington
1. How Americans see the legacy of Martin Luther King Jr.
Table of contents.
- King’s impact on the country
- King’s impact on personal views on racial equality
- Familiarity with King’s ‘I Have a Dream’ speech
- The country’s progress on racial equality in the last 60 years
- Efforts to ensure equal rights for all, regardless of race or ethnicity
- The future of racial equality
- 3. Achieving racial equality
- Acknowledgments
- The American Trends Panel survey methodology
Most U.S. adults (81%) say Martin Luther King Jr. has had a positive impact on the country, with 47% saying King has had a very positive impact. Some 38% say their own views on racial equality have been influenced by King’s legacy a great deal or a fair amount.
By race and ethnicity
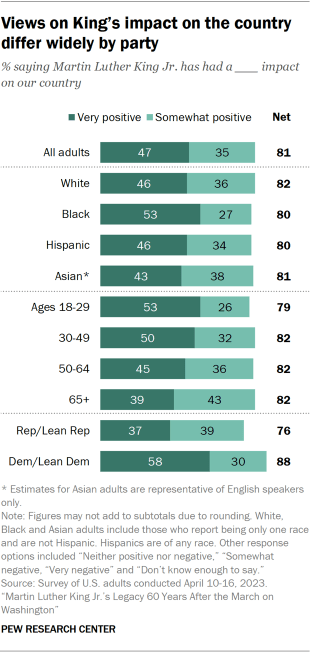
Some 53% of Black adults say Martin Luther King Jr. has had a very positive impact on the country, compared with 46% each among White and Hispanic adults and 43% of Asian adults.
Asian (10%), White (6%) and Hispanic (6%) adults are all more likely than Black adults (2%) to say they don’t know enough about King’s impact to answer.
Adults younger than 50 are more likely than those who are older to say King has had a very positive impact on the country. This overall variance is mostly due to the differing views of older and younger White Americans.
Some 54% of White Americans younger than 50 say King’s impact has been very positive, compared with 40% of White Americans ages 50 and older. The opposite is true among Black Americans: 60% of those 50 and older say King has had a very positive impact, compared with 49% of Black Americans younger than 50.
There are no differences by age among Hispanic Americans, and the sample of Asian Americans is too small to analyze by age group.
By partisanship
A majority of Democrats and Democratic leaners (58%) say King has had a very positive impact on the country, compared with 37% of Republicans and those who lean to the GOP.
Ideological differences among Democrats
Liberal Democrats (68%) are far more likely than moderate and conservative Democrats (50%) to say King has had a very positive impact on the country.
There is no difference on this question between conservative Republicans and moderate and liberal Republicans.
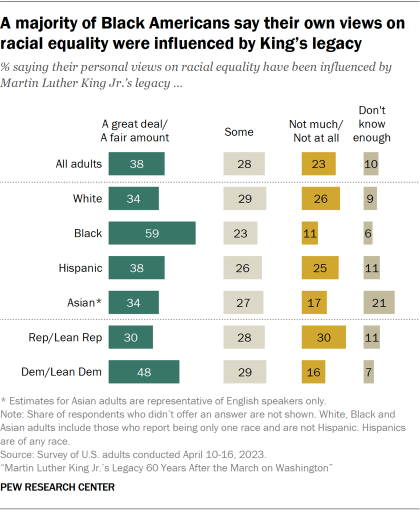
A majority of Black Americans (59%) say Martin Luther King Jr.’s legacy has influenced their own views on racial equality a great deal or a fair amount. Far smaller shares of Hispanic (38%), White (34%) and Asian (34%) Americans say the same.
About one-in-five Asian adults (21%) say they don’t know enough about King’s legacy to say how it’s impacted their own views. This is larger than the shares of Hispanic (11%), White (9%) and Black (6%) adults who say they don’t know enough to answer.
About half of Democrats (48%) say King’s legacy has influenced their own views on racial equality a great deal or a fair amount; 29% say King’s legacy has influenced their views some; and 16% say it hasn’t influenced their views much or at all.
Republicans are more mixed: 30% say King’s legacy has influenced their own views on racial equality a great deal or a fair amount; 28% say it has influenced their views some; and 30% say it hasn’t had much influence or hasn’t influenced their views at all.
Racial and ethnic differences among Democrats
A majority of Black Democrats (63%) say King’s legacy has had a great deal or a fair amount of influence on their views on racial equality. Far smaller shares of White (46%), Hispanic (41%) and Asian (40%) Democrats say the same.
In their own words: What Americans say about Martin Luther King Jr.’s legacy
(Selected written responses to an open-ended question)
“He wanted equality for all people, not just for blacks. He wanted all poor people to have a better life in this country. He was against the war in Vietnam. He fought for voters’ rights. He loved all people in this country.” – Black Democrat
“At the time he was a radical, hated by a majority of white folks. He advocated for equality not just in racial acceptance but by changing the economic system to lift up the poor.” – White Democrat
“MLK, Jr. pushed for equality among all people, regardless of skin color, not because of skin color. He did not intend for the outcome of his fight to be an emphasis on race, as we are seeing today, but rather, he sought a world in which race is irrelevant.” – White Republican
“MLK Jr was remembered for civil disobedience and peaceful protests, but people often forget he was a radical and was not some quiet pastor. He was a man of the people and he was killed for advocating for human rights.” – Asian Democrat
“He didn’t only want equality for black people; he advocated for all. He also didn’t tear down white people to make his point; he knew and said that it took their involvement for change as well.” – Black Republican
“MLK believed in a meritocracy rather than affirmative action, or worse, reparations.” – White Republican
“The popular conception of MLK was that he was someone who cared solely about racial equality. In fact, King viewed economic injustice and racial injustice as interlinked and inseparable. King supported radical redistribution of wealth, strengthening the safety net and, yes, reparations for black Americans.” – White Democrat
“His legacy, which was far more radical in his day than is recognized now, has largely been whitewashed to one carrying a ‘love everyone but don’t change anything systemic’ message. His views on economic equality, the ones he espoused shortly before his death, are still radical today.” – Black Democrat
“He believed true equality is colorblind and that the goal is equal opportunity, not equal outcomes. He would very much disagree with the ‘Black Lives Matter’ movement. He believed ALL LIVES MATTER, and that it is not racist to say so.” – White Republican
“He tried to get both black and white people (and other colors) to get along because we’re not different races, rather one race, the Human Race. Sadly, I think only some people understand that and live it, others try to use race as a tool to divide us.” – Hispanic Republican
“I think about how much he’s been whitewashed and how many people quoting him today would have hated him back then. I think of how he wanted equality for all, most notably for Black people, but also for all marginalized people.” – White Democrat
“When I think of what MLK taught, the first things that come to mind are ideas rooted in finding commonality in each other, uniting people on the principle of being equal, and fostering mutual respect and appreciation for one another.” – White Republican
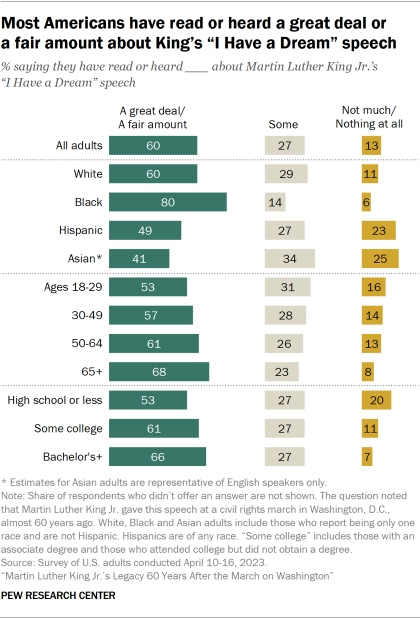
Most U.S. adults (60%) say they have heard or read a great deal or a fair amount about Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech . About a quarter (27%) have heard or read some, and 13% haven’t heard or read much or anything at all about the speech.
Eight-in-ten Black adults say they’ve heard or read a great deal or a fair amount about the speech, followed by 60% of White adults, 49% of Hispanic adults and 41% of Asian adults.
About a quarter of Asian (25%) and Hispanic (23%) adults say they haven’t heard much or anything at all about King’s “I Have a Dream” speech.
Adults ages 65 and older – all of whom were at least 5 years old when King gave the speech in 1963 – are the most likely to say they’ve heard or read a great deal or a fair amount about it: 68% say this, compared with shares ranging from 53% to 61% among younger groups.
By education
About two-thirds (66%) of adults with a bachelor’s degree or more education say they’ve heard or read a great deal or a fair amount about the speech. Smaller shares of those with some college (61%) or with a high school diploma or less education (53%) say the same.
Differences by education are evident among White and Hispanic adults, but not among Black adults. Eight-in-ten Black Americans with at least a bachelor’s degree say they’ve heard or read a great deal or a fair amount about the speech, as do 83% of those with some college and 77% of Black Americans with a high school diploma or less education. There aren’t enough Asian adults in the sample to analyze by education.
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Black Americans
- Discrimination & Prejudice
- Partisanship & Issues
- Racial Bias & Discrimination
A look at Black-owned businesses in the U.S.
8 facts about black americans and the news, black americans’ views on success in the u.s., among black adults, those with higher incomes are most likely to say they are happy, fewer than half of black americans say the news often covers the issues that are important to them, most popular, report materials.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
- African American Heroes
Hero for All: Martin Luther King, Jr.
Civil Rights leader Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr., never backed down in his stand against racism. Learn more about the life of this courageous hero who inspired millions of people to right a historical wrong.
A hero is born
Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr., was born in Atlanta, Georgia , in 1929. At the time in that part of the country, segregation—or the separation of races in places like schools, buses, and restaurants—was the law. He experienced racial predjudice from the time he was very young, which inspired him to dedicate his life to achieving equality and justice for Americans of all colors. King believed that peaceful refusal to obey unjust law was the best way to bring about social change.
Marching Forward
King and his wife, Coretta Scott King, lead demonstrators on the fourth day of a historic five-day march in 1965. Starting in Selma, Alabama , where local African Americans had been campaigning for the right to vote, King led thousands of nonviolent demonstrators 54 miles to the state capitol of Montgomery.
Brave sacrifices
King was arrested several times during his lifetime. In 1960, he joined Black college students in a sit-in at a segregated lunch counter. Presidential candidate John F. Kennedy interceded to have King released from jail, an action that is credited with helping Kennedy win the presidency.
speaking out
King inspires a large crowd with one of his many speeches. Raised in a family of preachers, he's considered one of the greatest speakers in U.S. history.
INSPIRING OTHERS
King waves to supporters from the steps of the Lincoln Memorial in Washington, D.C. during the March on Washington . There, he delivered the "I Have a Dream" speech, which boosted public support for civil rights.
making history
President Lyndon B. Johnson shakes King's hand at the signing of the landmark 1964 Civil Rights Act, which outlawed racial segregation in publicly owned facilities.
FAMILY LIFE
King his wife, Coretta Scott King, sit with three of their four children in their Atlanta, Georgia, home in 1963. His wife shared the same commitment to ending the racist system they had both grown up under.
A win for peace
King receives the Nobel Prize for Peace from Gunnar Jahn, president of the Nobel Prize Committee, in Oslo, Norway , on December 10, 1964.
Remembering a hero
A crowd of mourners follows the casket of King through the streets of Atlanta, Georgia, after his assassination in April 4, 1968. King was shot by James Earl Ray on the balcony of the Lorraine Motel. Americans honor the civil rights activist on the third Monday of January each year, Martin Luther King Day.
Learn more at National Geographic.
PHOTOGRAPHS BY: COURTESY THE LIBRARY OF CONGRESS; BEN MARTIN, TIME LIFE PICTURES / GETTY IMAGES; HORACE CORT; JULIAN WASSER, TIME LIFE PICTURES / GETTY IMAGES; AFP, GETTY IMAGES; HULTON ARCHIVE / GETTY IMAGES; COURTESY ASSOCIATED PRESS; COURTESY KEYSTONE / GETTY IMAGES; COURTESY HULTON ARCHIVE / GETTY IMAGES
Explore more
African american pioneers of science, black history month, 1963 march on washington.
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your California Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell My Info
- National Geographic
- National Geographic Education
- Shop Nat Geo
- Customer Service
- Manage Your Subscription
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
Search Online King Records Access (OKRA)
- Advanced Search
- Browse Topics
- Browse Names
- Browse Places
- Browse Genres
- Browse Archival Locations
Quick Start
Select one of these links to begin exploring our collection.
Volume I (January 1929–June 1951)
Volume II (July 1951–November 1955)
Volume III (December 1955–December 1956)
Volume IV (January 1957–December 1958)
Volume V (January 1959–December 1960)
Volume VI (September 1948–March 1963)
Volume VII (January 1961–August 1962)
King Speeches
King Sermons
This searchable database gives you access to thousands of King documents through the year 1968. It is a joint project of the Howard Gotlieb Archival Research Center at Boston University, the Martin Luther King, Jr., Research and Education Institute at Stanford University, and the Robert W. Woodruff Library at Atlanta University Center. Funded by the Andrew W. Mellon Foundation.

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .

Money Talks News
5 Facts About Martin Luther King Jr.
Posted: May 3, 2024 | Last updated: May 3, 2024
Martin Luther King Jr. was born Michael King Jr. He earned a doctorate in theology and went to jail 30 times during the civil rights movement. King won a Grammy award posthumously and was a fan of Star Trek.
More for You
Anna Nicole Smith's daughter Dannielynn Birkhead steps out in a bold red gown at Kentucky Derby
Top RNC lawyer resigns after less than 2 months
I study people with high emotional intelligence for a living—8 things they never ever do when talking to others
11 Facts You Should Know About Hard-Boiled Eggs
Report: Former Bears quarterback died from cancer
17 Phrases Older People Use That No One Else Gets
Apple Unveils AI Enhanced iPhone 16 with Advanced Features

Photo finish at 150th Kentucky Derby marred by controversy
The Best 27 Red Carpet Moments of the '70s
Stephen A. Smith snaps back at former MLB pitcher who called him 'racist' for blasting Mike Trout after injury
25 Healthy Fast-Food Orders That You Can Grab and Go
17 Polite Habits Most People Secretly Dislike
17 Well-Paid Remote Jobs You Can Do at Night
Blue Screen of Death: What it means and what to do if you get one
This Social Security Spousal Rule Is Officially Finished in 2024 — But These 3 Strategies Remain
Five exercises that are better than tricep pushdowns for building serious arm size
Donald Trump Gets Worrying Sign From New Poll Amid Manhattan Trial
Arby’s Just Launched 3 New Menu Items and Brought Back a Fan Fave
17 Phrases Confident People Use When They Want to Be Assertive But Not Rude
MLB umpire ridiculed after brutal strike-three call ends game after 3-hour rain delay
Ebenezer Baptist Church (Atlanta, Georgia)
January 1, 1886 to December 31, 1886

In the fall of 1947, Martin Luther King delivered his first sermon at the pulpit of Ebenezer Baptist Church in Atlanta. Ebenezer’s congregation voted to license King as a minister soon afterward, and he was ordained in February 1948. King went on to serve as Ebenezer’s associate minister during his breaks from Crozer Theological Seminary and from his doctoral studies at Boston University through early 1954. He returned as co-pastor with his father, Martin Luther King, Sr. , serving from 1960 until his assassination in 1968.
The church was founded in 1886 by its first minister, John Andrew Parker. In 1894 Adam Daniel Williams , King, Jr.’s maternal grandfather, became Ebenezer’s second pastor. Under Williams the church grew from 13 members to nearly 750 members by 1913. Williams moved the church twice before purchasing a lot on the corner of Auburn Avenue and Jackson Street and announced plans to raise $25,000 for a new building that would include an auditorium and gallery seating for 1,250 people. In March 1914 the Ebenezer congregation celebrated the groundbreaking for its new building. After the death of Williams in 1931, King, Sr., who had married Williams’ daughter Alberta in 1926, became pastor.
With King, Sr., as pastor and his wife, Alberta Williams King , serving as musical director, the King family spent much of their time at Ebenezer. King, Jr., later described how his earliest relationships were formed at church: “My best friends were in Sunday School, and it was the Sunday School that helped me to build the capacity for getting along with people” ( Papers 1:359 ). While in seminary, King often preached at Ebenezer. He delivered some of his most enduring sermons for the first time at Ebenezer, including “The Dimensions of a Complete Life,” “What Is Man?” and “Loving Your Enemies.”
After King accepted the pastorate at Dexter Avenue Baptist Church in Montgomery, members of Ebenezer’s congregation attended his October 1954 installation service, prompting King to express his gratitude: “Your prayers and words of encouragement have meant a great deal to me in my ministry; and you can never know what your presence in such large numbers meant to me at the beginning of my pastorate. I want you to know Ebenezer, that I feel greatly indebted to you; and that whatever success I might achieve in my life’s work you will have helped to make it possible” ( Papers 2:314 ).
In November 1959, King accepted Ebenezer’s call to join his father as co-pastor, a move that brought him closer to the headquarters of the Southern Christian Leadership Conference . His first sermon as co-pastor at Ebenezer was “The Three Dimensions of a Complete Life.” After King’s assassination in 1968, his brother, A. D. Williams King , was installed as Ebenezer’s co-pastor. King, Sr., continued as pastor until 1975, and Coretta Scott King continued to attend services at Ebenezer until her death.
Introduction, in Papers 1:6–7, 13 , 25–26, 28 .
King, “An Autobiography of Religious Development,” 12 September 1950–22 November 1950, in Papers 1:359–363 .
King to The Ebenezer Baptist Church Members, 6 November 1954, in Papers 2:313–314 .
King, Sr., with Riley, Daddy King , 1980.
Lillian D. Watkins, Certification of Minister’s License for Martin Luther King, Jr., 4 February 1948, in Papers 1:150 .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Martin Luther King, Jr. (born January 15, 1929, Atlanta, Georgia, U.S.—died April 4, 1968, Memphis, Tennessee) was a Baptist minister and social activist who led the civil rights movement in the United States from the mid-1950s until his death by assassination in 1968. His leadership was fundamental to that movement's success in ending the ...
The Institute cannot give permission to use or reproduce any of the writings, statements, or images of Martin Luther King, Jr. Please contact Intellectual Properties Management (IPM), the exclusive licensor of the Estate of Martin Luther King, Jr., Inc. at [email protected] or 404 526-8968. Screenshots are considered by the King Estate a ...
Stephen F. Somerstein/Getty Images. Martin Luther King Jr. was a social activist and Baptist minister who played a key role in the American civil rights movement from the mid-1950s until his ...
Introduction. Martin Luther King, Jr., made history, but he was also transformed by his deep family roots in the African-American Baptist church, his formative experiences in his hometown of Atlanta, his theological studies, his varied models of religious and political leadership, and his extensive network of contacts in the peace and social ...
Welcome to the Martin Luther King, Jr. Encyclopedia! The Encyclopedia, based on the extensive historical research originally conducted for The Papers, has over 280 articles on civil rights movement figures, events, and organizations.It also offers a detailed day-to-day chronology of King's life, drawn from the volumes.
Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. was born in Atlanta, GA on January 15th, 1929. He was one of the most important and influential Civil Rights leaders in the 1950s and 1960s. The cornerstones of his activism were based on non-violence and civil disobedience, both of which were inspired by his Christian faith and the teachings of Mahatma Gandhi.
Martin Luther King Jr. (born Michael King Jr.; January 15, 1929 - April 4, 1968) was an American Christian minister, activist, and political philosopher who was one of the most prominent leaders in the civil rights movement from 1955 until his assassination in 1968. A black church leader and a son of early civil rights activist and minister Martin Luther King Sr., King advanced civil rights ...
January 12, 2023. • 9 min read. The Reverend Martin Luther King, Jr., is a civil rights legend. In the mid-1950s, King led the movement to end segregation and counter prejudice in the United ...
During the less than 13 years of Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr.'s leadership of the modern American Civil Rights Movement, from December 1955 until April 4, 1968, African Americans achieved more genuine progress toward racial equality in America than the previous 350 years had produced. Dr. King is widely regarded as America's pre-eminent advocate of nonviolence and one of the greatest ...
Martin Luther King Jr. was a social activist and Baptist minister who played a key role in the American civil rights movement from the mid-1950s until his assassination in 1968. Explore his life ...
Martin Luther King Jr. was a Baptist minister and civil rights activist who had a seismic impact on race relations in the United States, beginning in the mid-1950s. Among his many efforts, King ...
Just after 6 p.m. on April 4, 1968, Martin Luther King Jr. was gunned down on the second-floor balcony of the Lorraine Motel in Memphis, Tenn. There to support the city's striking sanitation workers, King was about to head to dinner when he was struck in the jaw by a single bullet.
Terminology. On Aug. 28, 1963, about 250,000 people gathered at the Lincoln Memorial in Washington, D.C., for the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom, where Martin Luther King Jr. gave his historic "I Have a Dream" speech advocating for economic and civil rights for Black Americans. As the 60th anniversary of the March on Washington ...
The Institute cannot give permission to use or reproduce any of the writings, statements, or images of Martin Luther King, Jr. Please contact Intellectual Properties Management (IPM), the exclusive licensor of the Estate of Martin Luther King, Jr., Inc. at [email protected] or 404 526-8968. Screenshots are considered by the King Estate a ...
The area where Dr. King was entombed is located on Freedom Plaza and surrounded by the Freedom Hall Complex of the Martin Luther King, Jr. Center for Nonviolent Social Change, Inc. The Martin Luther King, Jr. Historic Site, a 23-acre area was listed as a National Historic Landmark on May 5, 1977, and was made a National Historic Site on October ...
The "Stone of Hope" statue is seen at the Martin Luther King Jr. Memorial in Washington, D.C. (Mandel Ngan/AFP via Getty Images) About eight-in-ten American adults (81%) say civil rights leader Martin Luther King Jr. has had a positive impact on the United States, according to a Pew Research Center report that comes ahead of the 60th anniversary of the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom.
Title The Martin Luther King, Jr. Research and Education Institute; Summary Founded in 2005, the Martin Luther King, Jr. Research and Education Institute provides an institutional home for a broad range of activities illuminating the Nobel Peace laureate's life and the movements he inspired.
A majority of Black Americans (59%) say Martin Luther King Jr.'s legacy has influenced their own views on racial equality a great deal or a fair amount. Far smaller shares of Hispanic (38%), White (34%) and Asian (34%) Americans say the same. About one-in-five Asian adults (21%) say they don't know enough about King's legacy to say how it ...
A hero is born. Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr., was born in Atlanta, Georgia, in 1929. At the time in that part of the country, segregation—or the separation of races in places like schools, buses, and restaurants—was the law. He experienced racial predjudice from the time he was very young, which inspired him to dedicate his life to achieving ...
The Martin Luther King, Jr. Research and Education Institute. Web Login Address. Cypress Hall D 466 Via Ortega Stanford, CA 94305-4146 United States. Facebook; Twitter; P: (650) 723-2092 F: (650) 723-2093 [email protected] Campus Map.
About OKRA. This searchable database gives you access to thousands of King documents through the year 1968. It is a joint project of the Howard Gotlieb Archival Research Center at Boston University, the Martin Luther King, Jr., Research and Education Institute at Stanford University, and the Robert W. Woodruff Library at Atlanta University Center.
As a theologian, Martin Luther King reflected often on his understanding of nonviolence. He described his own "pilgrimage to nonviolence" in his first book, Stride Toward Freedom, and in subsequent books and articles."True pacifism," or "nonviolent resistance," King wrote, is "a courageous confrontation of evil by the power of love" (King, Stride, 80).
Martin Luther King Jr. was born Michael King Jr. He earned a doctorate in theology and went to jail 30 times during the civil rights movement. King won a Grammy award posthumously and was a fan of ...
Martin Luther King, Jr., described the student sit-ins as an "electrifying movement of Negro students [that] shattered the placid surface of campuses and communities across the South," and he expressed pride in the new activism for being "initiated, fed and sustained by students" ( Papers 5:447 ; 368 ). The sit-ins started on 1 February ...
The Martin Luther King, Jr. Research and Education Institute. Web Login Address. Cypress Hall D 466 Via Ortega Stanford, CA 94305-4146 United States. Facebook; Twitter; P: (650) 723-2092 F: (650) 723-2093 [email protected] Campus Map.