new offer

Root Cause Analysis and the 8D Problem Solving Bootcamp

Four RCA approaches for permanent and effective corrective actions | Includes FMEA, VSM and Seven Basic Quality Tools
No contents are available in this lesson!
No lessons available , lesson contents locked.
Enroll to unlock this lesson.

- Tất cả Ngoại ngữ.
- Tiếng Trung
- Tất cả Marketing.
- Facebook Marketing
- Zalo Marketing
- Email Marketing
- Youtube Marketing
- Content Marketing
- Video marketing
- Affiliate Marketing
- Marketing Online
- Tin học văn phòng
- Tất cả Tin học văn phòng.
- Google Sheets
- Kinh doanh và khởi nghiệp
- Tất cả Kinh doanh và khởi nghiệp.
- Quản trị doanh nghiệp
- Nhân sự - Tuyển dụng
- Kinh doanh Online
- Bất động sản
- Dropshipping
- Tài chính & Kế toán
- Tất cả Tài chính & Kế toán.
- Chứng khoán
- Sales Bán hàng
- Tất cả Sales Bán hàng.
- Bán hàng Online
- Bán hàng livestream
- Chăm sóc khách hàng
- Chiến lược bán hàng
- Thiết kế & Xây dựng
- Tất cả Thiết kế & Xây dựng.
- Thiết kế quảng cáo
- Thiết kế Web
- Dự án - Xây dựng
- Kiến Trúc, Nội Thất
- Tất cả Kỹ năng.
- Kỹ năng lãnh đạo
- Kỹ năng mềm
- Phát triển bản thân
- Tất cả Công nghệ.
- Công nghệ thông tin
- Sửa chữa, chế tạo
- Sức khoẻ & Làm đẹp
- Tất cả Sức khoẻ & Làm đẹp.
- Yoga - Thiền
- Giảm stress
- Massage - Trị liệu
- Fitness - Gym
- Phong cách sống
- Tất cả Phong cách sống.
- Ẩm thực - Nấu ăn
- Nhiếp ảnh, dựng phim
- Tình yêu - Hôn nhân & gia đình
- Tất cả Tình yêu - Hôn nhân & gia đình.
- Nuôi dạy con
- Chăm sóc trẻ
- Hạnh phúc gia đình
- Đời sống vợ chồng
- Phân tích dữ liệu
- Hành chính nhân sự
- Kỹ năng quản lý
- Udemy Business
- Mua dung lượng Google Drive
- Tất cả bài viết

Root Cause Analysis and the 8D Problem Solving Bootcamp
Loại khoá học: Management
Four RCA approaches for permanent and effective corrective actions | Includes FMEA, VSM and Seven Basic Quality Tools

Nội dung khoá học
Note: Students who complete this course have an option to apply for the certification exam by Quality Gurus Inc. and can achieve the Verified Certification from Quality Gurus Inc. It is optional and there is no separate fee for that.
In this course I will cover four broad strategies or approaches for Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and problem-solving:
1. Five Why's
2. Cause and Effect Diagram
3. A3 Problem Solving Approach
4. Eight Disciplines or 8D Problem Solving Approach
Depending upon the complexity of the problem you can choose one of these approaches.
While taking these approaches, there are many tools and techniques which could be applied. I will cover many such tools, for example:
1. Seven Basic Quality Tools (Cause and Effect Analysis, Flow Chart, Check Sheet, Pareto Chart, Scatter Plot, Control Charts and Histograms)
2. Descriptive Statistics (Mean, Mode, Median, Range and Standard Deviation)
3. Graphs and Charts (Box and Whisker Plot, Individual Value Plot, Bar Chart, Pie Chart, Bubble Chart, Matrix Plot, and Time Series)
4. Value Stream Mapping
5. Tools for D1 (Establish the Team): Team Roles, Team Stages, Conflict Management and Negative Team Behaviours
6. Tools for D2 (Describe the Problem): 5W2H, SIPOC, Gemba Walk and Stakeholder Analysis
7. Tools for D3 (Interim Containment): Identification and Traceability
8. Tools for D4 (Root Cause Analysis): Brainstorming, Nominal Group Technique and Affinity Diagram
9. Tools for D5 (Develop CA): Poka-yoke, Force Field Analysis, Control Plan and Benefit-Cost Analysis
10. Tools for D6 (Implement CA): Gantt Chart, RACI Matrix, Reports and Dashboard
11. Tools for D7 (Prevent Recurrence): FMEA
Bạn sẽ học được gì
Perform the root cause analysis to eliminate the problem permanently
Choose the right tool for the root cause analysis
Learn about more than 40 tools that can be used for problem solving
Proven problem solving approaches
Taking permanent corrective actions, so that the problem does not come back again.
Templates are included in the course.
- Some basic understanding of the quality management concepts
Introduction
Technique #1: five whys, technique #2: cause and effect analysis, technique #3: a3 problem solving approach, technique #4: 8d problem solving approach, bonus section, đánh giá của học viên, bình luận khách hàng, viết bình luận, bạn đánh giá khoá học này thế nào, khoá học liên quan.

Developing Professional Gantt Charts with Excel & MS Project

Start A T-Shirt Business | Redbubble, Merch by Amazon & More

The Complete Shopify Aliexpress Dropship course

The Complete Shopify Dropshipping Masterclass 2024

Etsy Shop SetUp, SEO & Ads - Beginner To Advanced 2024

How to Franchise Your Business
Process Capability Analysis

Wedding planner MBA: the complete how to start 4-in-1 course

Đánh Thức Năng Lực Giao Tiếp Trong Bạn

Probability and Statistics - Practice Tests and Solutions

Business Analyst (BA) for Practitioners (BA thực chiến)

HR Strategy - Xây dựng chiến lược Nhân sự

HR Reports - Xây dựng hệ thống báo cáo Quản trị Nhân sự

89 ngày thành tài với amazon dropshipping

Market Research: Strategies for Business Decision-Making

Franchise Your Business Accelerator Program

Đăng ký get khoá học Udemy - Unica - Gitiho giá chỉ 50k!
Get khoá học giá rẻ ngay trước khi bị fix.
Lean Six Sigma Training Certification
- Facebook Instagram Twitter LinkedIn YouTube
- (877) 497-4462

8D Corrective Action: Mastering Problem-Solving for Continuous Improvement
May 13th, 2024
Businesses constantly refine products, services, and workflows to stay ahead. But issues can still pop up, angering customers and jacking costs while hurting a company’s image. This is where the 8D corrective action problem-solving method earns its stripes.
It was developed by Ford in the 80s and has since spread widely across manufacturing, healthcare, aerospace, and more.
The 8D approach is a methodical process combining pros from different parts of the company, analytical tools, and fact-based decision-making.
By following its eight systematic steps, organizations can expertly handle thorny problems. They uncover root causes and implement lasting fixes addressing immediate concerns while fueling constant upgrades to prevent repeat issues.
Key Highlights
- Understanding the origins and history of the 8D corrective action methodology, its benefits, and when to apply it for optimal results.
- Exploring the eight disciplined steps of the 8D corrective action process.
- Integrating the 8D methodology with quality management systems, leveraging Enterprise Quality Management Software (EQMS) to streamline workflows.
- Examining case studies and examples from various industries, including manufacturing, service, healthcare, and the automotive sector.
Understanding the 8D Corrective Action Problem-Solving Methodology
The Eight Disciplines (8D) methodology is a structured, team-based approach to problem-solving that aims to identify the root causes of issues and implement effective corrective actions.
It is a comprehensive framework that combines analytical tools, cross-functional collaboration, and a disciplined mindset to tackle complex problems systematically.
The 8D process establishes a step-by-step approach that guides organizations through eight distinct disciplines, each building upon the previous one.
Origins and History of 8D Corrective Action
The origins of the 8D methodology can be traced back to the 1980s when it was developed and pioneered by Ford Motor Company.
Initially referred to as “ Team Oriented Problem Solving ” (TOPS), this approach was designed to address the recurring quality issues that plagued the automotive industry at the time.
Recognizing the limitations of traditional problem-solving techniques, Ford sought to establish a more robust and effective framework that would not only resolve immediate concerns but also drive continuous improvement and prevent future issues.
The 8D methodology quickly gained traction within Ford and was subsequently adopted as the company’s primary approach for documenting and addressing problem-solving efforts.
As the benefits of the 8D corrective action process became evident, it rapidly gained popularity among other manufacturers and industries, transcending its automotive roots.
Today, the 8D methodology is widely employed across various sectors, including manufacturing, healthcare, aerospace, and service industries, among others.
Benefits of Using 8D Corrective Action
Implementing the 8D problem-solving methodology offers numerous benefits to organizations, including:
1. Systematic Approach : The structured nature of the 8D process ensures a consistent and comprehensive approach to problem-solving, reducing the risk of overlooking critical factors or jumping to premature conclusions.
2. Root Cause Identification : By emphasizing root cause analysis , the 8D methodology goes beyond addressing surface-level symptoms and focuses on identifying and eliminating the underlying causes of problems.
3. Cross-Functional Collaboration : The team-based approach fosters cross-functional collaboration, leveraging diverse perspectives and expertise from various departments, leading to more robust and well-rounded solutions.
4. Preventive Measures : The 8D corrective action process incorporates preventive actions to mitigate the recurrence of similar issues, promoting a culture of continuous improvement and proactive problem-solving.
5. Improved Quality and Reliability : By addressing root causes and implementing corrective actions, organizations can enhance the quality and reliability of their products, services, and processes, leading to increased customer satisfaction and cost savings.
6. Knowledge Sharing and Organizational Learning : The documentation and archiving of 8D processes facilitate knowledge sharing and organizational learning, enabling teams to build upon past experiences and lessons learned.
When to Apply 8D Corrective Action
The 8D problem-solving methodology is particularly valuable in situations where:
- Root Cause Analysis is Required: When issues persist despite initial troubleshooting efforts, or when the underlying causes are not immediately apparent, the 8D process can provide a structured approach to root cause analysis.
- Recurring Problems: If an organization experiences recurring problems or quality issues, the 8D methodology can help identify and eliminate the root causes, preventing future occurrences.
- Quality Issues with Significant Impact: When quality issues have a substantial impact on customer satisfaction, safety, regulatory compliance, or financial performance, the rigorous 8D approach can be employed to address the problem comprehensively.
- Complex Problems: For intricate problems involving multiple factors, processes, or departments, the cross-functional nature of the 8D team and the systematic approach can facilitate a thorough investigation and effective solution development.
By understanding the core principles, benefits, and appropriate application scenarios of the 8D problem-solving methodology, organizations can leverage this powerful framework to drive continuous improvement , enhance quality, and maintain a competitive edge in their respective industries.
The Eight Disciplines (8D) Process
At the heart of the 8D corrective action methodology lies a structured, step-by-step approach that guides organizations through eight distinct disciplines.
Each discipline builds upon the previous one, ensuring a thorough investigation, analysis, and resolution of the problem at hand.
The eight disciplines of the 8D process are designed to facilitate a systematic and disciplined approach to problem-solving, leveraging cross-functional collaboration, analytical tools, and data-driven decision-making.
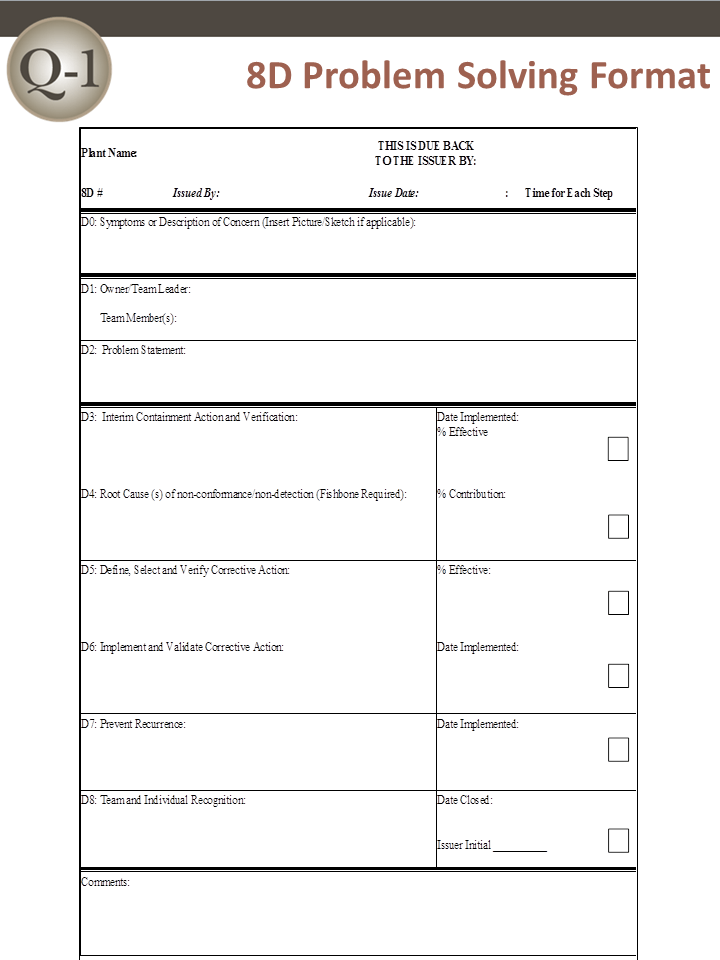
D0: Planning and Preparation
Before embarking on the 8D corrective action journey, proper planning and preparation are crucial. This initial step, often referred to as Discipline Zero (D0), lays the foundation for a successful problem-solving effort.
During D0, the team gathers relevant information about the problem, assesses the need for interim containment actions, and establishes the prerequisites for forming an effective cross-functional team.
This stage involves collecting data on symptoms, identifying potential risks, and ensuring that the necessary resources and support are in place to execute the 8D process effectively.
D1: Team Formation
The first formal discipline of the 8D process focuses on assembling a cross-functional team with the collective knowledge, skills, and expertise required to tackle the problem at hand.
Effective team formation is critical to the success of the 8D corrective action effort, as it ensures diverse perspectives and a comprehensive understanding of the issue.
During D1, team members are carefully selected from various departments or functions, such as product engineering, process engineering, quality assurance, and data analysis.
Best practices in team formation involve considering factors such as technical expertise, problem-solving skills, interpersonal abilities, and the availability and commitment of potential team members.
Establishing ground rules, communication protocols, and team-building exercises can further enhance collaboration and effective teamwork.
D2: Problem Description
In Discipline 2, the team focuses on accurately describing the problem, utilizing quantitative data and evidence-based approaches.
This step is crucial, as it establishes a shared understanding of the issue and guides the subsequent steps of the 8D process.
The problem description involves defining the problem statement in specific, measurable terms, identifying the affected product or process, and quantifying the impact on operations, quality, customer satisfaction, and costs.
Tools such as the “ 5 Whys ” technique, Ishikawa (fishbone) diagrams , and “ Is/Is Not ” analysis can aid in this process, helping to capture relevant details and categorize information.
D3: Interim Containment Actions
While the team works towards identifying and implementing permanent solutions, Discipline 3 focuses on implementing interim containment actions to mitigate the immediate impact of the problem and protect customers from further exposure.
Interim containment actions are temporary measures designed to isolate the problem and prevent it from causing further harm or spreading to other areas, processes, or products.
These actions may include segregating defective products, implementing additional inspections or checks, or introducing manual oversight until permanent corrective actions are in place.
It is essential to verify the effectiveness of interim containment actions and monitor their implementation to ensure that they are successful in containing the problem and minimizing its impact on operations and customers.
D4: Root Cause Analysis
At the core of the 8D corrective action process lies Discipline 4, which focuses on identifying the root causes of the problem through rigorous analysis and data-driven investigation.
This step is crucial, as it lays the foundation for developing effective and sustainable corrective actions.
During root cause analysis, the team employs various analytical tools and techniques, such as comparative analysis , fault tree analysis , and root cause verification experiments.
These methods help to isolate and verify the underlying causes of the problem, separating symptoms from true root causes.
Thorough documentation and verification of root causes are essential in this discipline, ensuring that the team has a solid foundation for developing effective corrective actions.
D5: Permanent Corrective Actions (PCAs)
Building upon the insights gained from root cause analysis , Discipline 5 focuses on selecting and verifying permanent corrective actions (PCAs) that address the identified root causes and mitigate the risk of future occurrences.
During this stage, the team evaluates potential corrective actions based on their effectiveness in addressing the root causes, as well as their feasibility, cost, and potential impact on other processes or systems.
Risk assessment tools, such as Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), can aid in this evaluation process.
Once the most appropriate corrective actions have been selected, the team verifies their effectiveness through pilot testing , simulations, or other validation methods.
This step ensures that the proposed solutions will indeed resolve the problem and prevent its recurrence without introducing unintended consequences.
Detailed planning and documentation of the corrective actions, including acceptance criteria, implementation timelines, and responsibilities, are critical components of Discipline 5.
D6: Implementation and Validation
In Discipline 6, the team focuses on implementing the selected permanent corrective actions and validating their effectiveness in resolving the problem and preventing future occurrences.
This stage involves developing a comprehensive project plan that outlines the steps, timelines, and resources required for successful implementation.
Effective communication and coordination with all relevant stakeholders, including cross-functional teams and management, are essential to ensure a smooth transition and minimize disruptions.
During implementation, the team closely monitors the progress and performance of the corrective actions, gathering data and feedback to validate their effectiveness.
This validation process may involve conducting simulations, inspections, or collecting performance metrics to assess the impact of the implemented solutions.
If the validation process reveals any shortcomings or unintended consequences, the team may need to revisit the corrective actions, make adjustments, or conduct further root cause analysis to address any remaining issues.
D7: Preventive Actions
Discipline 7 of the 8D process focuses on taking preventive measures to ensure that the lessons learned and improvements made during the problem-solving journey are embedded into the organization’s processes, systems, and culture.
In this stage, the team reviews similar products, processes, or areas that could be affected by the same or similar root causes, identifying opportunities to apply preventive actions more broadly.
This proactive approach helps to mitigate the risk of future occurrences and promotes a culture of continuous improvement .
Effective implementation of preventive actions requires cross-functional collaboration, clear communication, and ongoing monitoring to ensure their sustained effectiveness.
D8: Closure and Celebration
The final discipline of the 8D process, D8, serves as a critical step in recognizing the team’s efforts, sharing lessons learned, and celebrating the successful resolution of the problem.
During this stage, the team conducts a final review of the problem-solving journey, documenting key lessons and insights that can be applied to future projects.
This documentation not only preserves institutional knowledge but also facilitates continuous improvement by enabling the organization to build upon past experiences.
Equally important is the recognition and celebration of the team’s achievements. By acknowledging the collective efforts, dedication, and collaboration of team members, organizations can foster a positive and supportive culture that values problem-solving and continuous improvement.
Formal recognition events, such as team presentations or awards ceremonies, can be organized to showcase the team’s accomplishments and highlight the impact of their work on the organization’s quality, customer satisfaction, and overall performance.
By completing the eight disciplines of the 8D process, organizations can effectively navigate complex problems, identify root causes, implement sustainable solutions, and establish a foundation for continuous improvement and organizational learning.
Integrating 8D Corrective Action with Quality Management Systems
While the 8D problem-solving methodology offers a robust framework for addressing quality issues and driving continuous improvement, its effectiveness can be further amplified by integrating it with an organization’s quality management systems .
Leveraging enterprise-level software solutions can streamline the 8D process, enhance collaboration, and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
The Role of EQMS in 8D Corrective Action
Enterprise Quality Management Software (EQMS) plays a pivotal role in supporting the successful implementation of the 8D corrective action methodology.
By utilizing an EQMS, teams can benefit from features such as:
- Standardized 8D Workflows: Pre-configured 8D workflows and templates ensure consistency and adherence to best practices, guiding teams through each discipline with clearly defined tasks, responsibilities, and timelines.
- Collaboration and Communication: EQMS platforms facilitate cross-functional collaboration by providing secure document sharing, real-time updates, and centralized communication channels, ensuring that all stakeholders remain informed and engaged throughout the 8D process.
- Data Management and Reporting: Comprehensive data management capabilities within an EQMS enable teams to easily capture, analyze, and report on quality data, facilitating data-driven decision-making and root cause analysis during the 8D process.
- Integration with Quality Systems: EQMS solutions often integrate with other quality management systems, such as corrective and preventive action (CAPA) systems, enabling seamless information sharing and ensuring that the insights gained from the 8D process are incorporated into broader quality improvement initiatives.
Automating 8D Corrective Action Workflows
One of the key advantages of leveraging an EQMS is the ability to automate 8D workflows, streamlining the process and reducing the administrative burden on teams.
Automated workflows also facilitate consistent documentation and record-keeping, which is essential for maintaining compliance with industry regulations and standards, as well as enabling knowledge sharing and organizational learning.
Data-Driven Decision-making
The 8D corrective action methodology heavily relies on data-driven decision-making, particularly during the root cause analysis and corrective action selection phases.
An EQMS provides teams with powerful data analysis and reporting capabilities, enabling them to quickly identify trends, patterns, and correlations that can inform their decision-making process.
Continuous Improvement Culture
Ultimately, the integration of the 8D methodology with an EQMS fosters a culture of continuous improvement within an organization.
The insights gained from the 8D process, coupled with the robust reporting and analytics capabilities of an EQMS, provide organizations with a wealth of data and knowledge that can be leveraged to drive ongoing process optimization and quality enhancement initiatives.
Case Studies and Examples of 8D Corrective Action
To illustrate the practical application and impact of the 8D problem-solving methodology, let us explore a few real-world case studies and examples from various industries.
These examples will showcase how organizations have successfully leveraged the 8D approach to address quality issues, resolve complex problems, and drive continuous improvement.
Manufacturing Quality Issues
In the manufacturing sector, where quality and reliability are paramount, the 8D methodology has proven invaluable in addressing a wide range of issues.
One notable example is a leading automotive parts manufacturer that faced recurring quality issues with a critical component, resulting in costly rework and customer dissatisfaction.
By implementing the 8D process, a cross-functional team was assembled to investigate the problem. Through root cause analysis , they identified a flaw in the supplier’s raw material handling processes, leading to inconsistencies in the component’s material properties.
The team implemented interim containment actions to segregate and inspect incoming materials, while also working with the supplier to implement permanent corrective actions, such as upgrading their material handling equipment and revising their quality control procedures.
Service Industry Applications of 8D Corrective Action
While the 8D corrective action approach is often associated with manufacturing, it has also proven valuable in the service industry, where quality and process excellence are equally critical.
A prominent financial institution faced challenges with excessive customer complaints related to billing errors and account discrepancies.
By implementing the 8D methodology, a cross-functional team analyzed the problem, identifying root causes such as outdated software systems, inadequate training for customer service representatives, and inefficient data entry processes.
The team implemented interim containment actions, including manual account audits and increased customer communication, while also developing permanent corrective actions, such as upgrading their billing software, revising training programs, and streamlining data entry procedures.
Healthcare and Life Sciences
In the healthcare and life sciences industries, where patient safety and regulatory compliance are paramount, the 8D methodology has proven invaluable in addressing quality issues and mitigating risks.
A prominent pharmaceutical company faced a recurring issue with contamination in one of its drug products, posing potential health risks and regulatory concerns.
By implementing the 8D corrective action process, a cross-functional team investigated the issue, identifying root causes related to inadequate environmental controls in the manufacturing facility and inconsistencies in the cleaning and sterilization procedures.
Interim containment actions included quarantining and recalling affected product batches, while permanent corrective actions focused on upgrading the facility’s HVAC systems, revising cleaning and sterilization protocols, and implementing enhanced environmental monitoring.
Automotive Industry (origin of 8D Corrective Action)
It is fitting to revisit the automotive industry, where the 8D methodology originated. In a recent case study, a major automaker faced recurring issues with engine failures in one of their popular vehicle models, leading to costly warranty claims and customer dissatisfaction.
By implementing the 8D process, a cross-functional team investigated the issue, identifying root causes related to a design flaw in the engine’s cooling system and inadequate testing procedures during the product development phase.
Interim containment actions included issuing technical service bulletins and providing temporary cooling system modifications for affected vehicles.
Permanent corrective actions focused on redesigning the engine’s cooling system, implementing more rigorous testing protocols, and enhancing communication between the engineering and manufacturing teams.
Through the 8D process and integration with their quality management practices, the automaker successfully resolved the engine failure issue, regained customer trust, and enhanced their overall product quality and reliability.
The 8D corrective action problem-solving method has proven extremely useful for handling thorny quality issues, continuously upgrading workflows, and cultivating an excellence culture in businesses.
By pairing its structured team approach with analytical tools and fact-based choices, the 8D process empowers companies to uncover root causes. It also helps implement lasting fixes and prevent repeating mistakes through establishing protective measures.
As the case studies and examples show, it’s been put to great use across many industries from manufacturing to healthcare where it originated in automotive.
Its flexibility and power have made 8D valued for boosting quality, improving customer satisfaction and staying ahead competitively no matter the market.
The Eight Disciplines methodology remains a strong tool for companies serious about excellence, innovation, and customer focus.
By wholeheartedly embracing this robust framework and blending it with modern quality practices, businesses can expertly handle complex problems. They can also unlock fresh opportunities and build the foundation for sustainable success.
In other words, don’t sleep on 8D corrective action problem-solving. Its fact-based, team-centric transformation approach strengthens any organization now and into the future.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs
SixSigma.us Accreditation & Affiliations

Monthly Management Tips
- Be the first one to receive the latest updates and information from 6Sigma
- Get curated resources from industry-experts
- Gain an edge with complete guides and other exclusive materials
- Become a part of one of the largest Six Sigma community
- Unlock your path to become a Six Sigma professional
" * " indicates required fields

Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
– Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving –
⇓ Introduction to 8D
⇓ What is 8D
⇓ Why Apply 8D
⇓ When to Apply 8D
⇓ How to Apply 8D

Introduction to Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D) is a problem solving methodology designed to find the root cause of a problem, devise a short-term fix and implement a long-term solution to prevent recurring problems. When it’s clear that your product is defective or isn’t satisfying your customers, an 8D is an excellent first step to improving Quality and Reliability.
Ford Motor Company developed this problem solving methodology, then known as Team Oriented Problem Solving (TOPS), in the 1980s. The early usage of 8D proved so effective that it was adopted by Ford as the primary method of documenting problem solving efforts, and the company continues to use 8D today.
8D has become very popular among manufacturers because it is effective and reasonably easy to teach. Below you’ll find the benefits of an 8D, when it is appropriate to perform and how it is performed.
What is Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D problem solving process is a detailed, team oriented approach to solving critical problems in the production process. The goals of this method are to find the root cause of a problem, develop containment actions to protect customers and take corrective action to prevent similar problems in the future.
The strength of the 8D process lies in its structure, discipline and methodology. 8D uses a composite methodology, utilizing best practices from various existing approaches. It is a problem solving method that drives systemic change, improving an entire process in order to avoid not only the problem at hand but also other issues that may stem from a systemic failure.
8D has grown to be one of the most popular problem solving methodologies used for Manufacturing, Assembly and Services around the globe. Read on to learn about the reasons why the Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving may be a good fit for your company.
Why Apply Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D methodology is so popular in part because it offers your engineering team a consistent, easy-to-learn and thorough approach to solving whatever problems might arise at various stages in your production process. When properly applied, you can expect the following benefits:
- Improved team oriented problem solving skills rather than reliance on the individual
- Increased familiarity with a structure for problem solving
- Creation and expansion of a database of past failures and lessons learned to prevent problems in the future
- Better understanding of how to use basic statistical tools required for problem solving
- Improved effectiveness and efficiency at problem solving
- A practical understanding of Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
- Problem solving effort may be adopted into the processes and methods of the organization
- Improved skills for implementing corrective action
- Better ability to identify necessary systemic changes and subsequent inputs for change
- More candid and open communication in problem solving discussion, increasing effectiveness
- An improvement in management’s understanding of problems and problem resolution
8D was created to represent the best practices in problem solving. When performed correctly, this methodology not only improves the Quality and Reliability of your products but also prepares your engineering team for future problems.
When to Apply Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D problem solving process is typically required when:
- Safety or Regulatory issues has been discovered
- Customer complaints are received
- Warranty Concerns have indicated greater-than-expected failure rates
- Internal rejects, waste, scrap, poor performance or test failures are present at unacceptable levels
How to Apply Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D process alternates inductive and deductive problem solving tools to relentlessly move forward toward a solution. The Quality-One approach uses a core team of three individuals for inductive activities with data driven tools and then a larger Subject Matter Expert (SME) group for the deductive activities through brainstorming, data-gathering and experimentation.
D0: Prepare and Plan for the 8D
Proper planning will always translate to a better start. Thus, before 8D analysis begins, it is always a good idea to ask an expert first for their impressions. After receiving feedback, the following criterion should be applied prior to forming a team:
Collect information on the symptoms
Use a Symptoms Checklist to ask the correct questions
Identify the need for an Emergency Response Action (ERA), which protects the customer from further exposure to the undesired symptoms
D1: Form a Team
A Cross Functional Team (CFT) is made up of members from many disciplines. Quality-One takes this principle one step further by having two levels of CFT:
- The Core Team Structure should involve three people on the respective subjects: product, process and data
- Additional Subject Matter Experts are brought in at various times to assist with brainstorming, data collection and analysis
Teams require proper preparation. Setting the ground rules is paramount. Implementation of disciplines like checklists, forms and techniques will ensure steady progress. 8D must always have two key members: a Leader and a Champion / Sponsor:
- The Leader is the person who knows the 8D process and can lead the team through it (although not always the most knowledgeable about the problem being studied)
- The Champion or Sponsor is the one person who can affect change by agreeing with the findings and can provide final approval on such changes
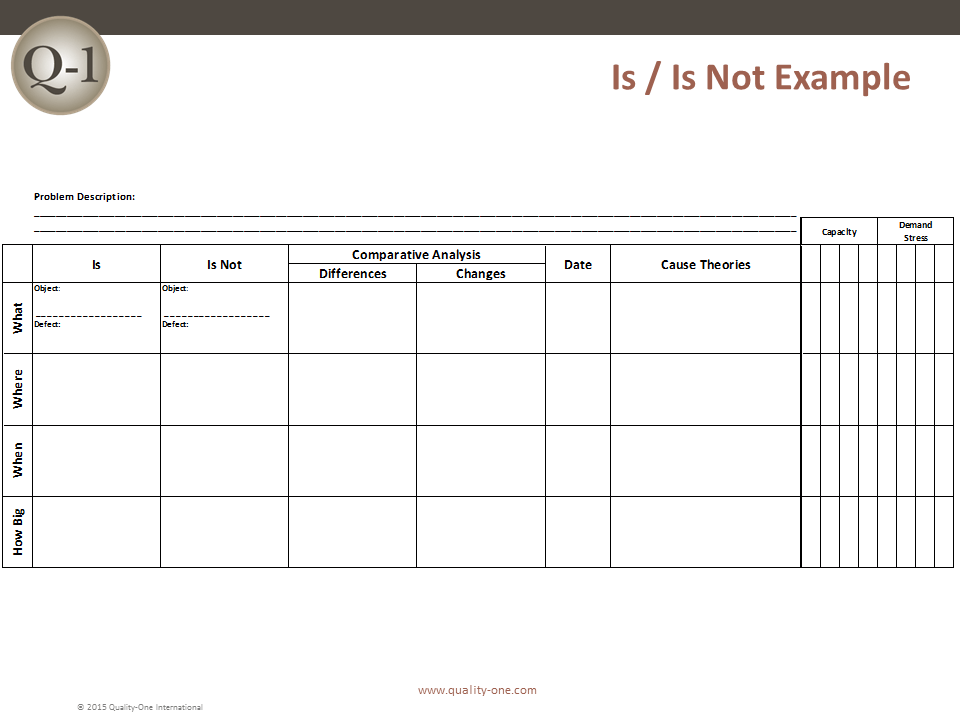
D2: Describe the Problem
The 8D method’s initial focus is to properly describe the problem utilizing the known data and placing it into specific categories for future comparisons. The “Is” data supports the facts whereas the “Is Not” data does not. As the “Is Not” data is collected, many possible reasons for failure are able to be eliminated. This approach utilizes the following tools:
- Problem Statement
- Affinity Diagram (Deductive tool)
- Fishbone/Ishikawa Diagram (Deductive tool)
- Problem Description
D3: Interim Containment Action
In the interim, before the permanent corrective action has been determined, an action to protect the customer can be taken. The Interim Containment Action (ICA) is temporary and is typically removed after the Permanent Correct Action (PCA) is taken.
- Verification of effectiveness of the ICA is always recommended to prevent any additional customer dissatisfaction calls
D4: Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and Escape Point
The root cause must be identified to take permanent action to eliminate it. The root cause definition requires that it can be turned on or off, at will. Activities in D4 include:
- Comparative Analysis listing differences and changes between “Is” and “Is Not”
- Development of Root Cause Theories based on remaining items
- Verification of the Root Cause through data collection
- Review Process Flow Diagram for location of the root cause
- Determine Escape Point, which is the closest point in the process where the root cause could have been found but was not
D5: Permanent Corrective Action (PCA)
The PCA is directed toward the root cause and removes / changes the conditions of the product or process that was responsible for the problem. Activities in D5 include:
- Establish the Acceptance Criteria which include Mandatory Requirements and Wants
- Perform a Risk Assessment / Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) on the PCA choices
- Based on risk assessment, make a balanced choice for PCA
- Select control-point improvement for the Escape Point
- Verification of Effectiveness for both the PCA and the Escape Point are required
D6: Implement and Validate the Permanent Corrective Action
To successfully implement a permanent change, proper planning is essential. A project plan should encompass: communication, steps to complete, measurement of success and lessons learned. Activities in D6 include:
- Develop Project Plan for Implementation
- Communicate the plan to all stakeholders
- Validation of improvements using measurement
D7: Prevent Recurrence
D7 affords the opportunity to preserve and share the knowledge, preventing problems on similar products, processes, locations or families. Updating documents and procedures / work instructions are expected at this step to improve future use. Activities in D7 include:
- Review Similar Products and Processes for problem prevention
- Develop / Update Procedures and Work Instructions for Systems Prevention
- Capture Standard Work / Practice and reuse
- Assure FMEA updates have been completed
- Assure Control Plans have been updated
D8: Closure and Team Celebration
Teams require feedback to allow for satisfactory closure. Recognizing both team and individual efforts and allowing the team to see the previous and new state solidifies the value of the 8D process. Activities in D8 include:
- Archive the 8D Documents for future reference
- Document Lessons Learned on how to make problem solving better
- Before and After Comparison of issue
- Celebrate Successful Completion
8D and Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
The 8D process has Root Cause Analysis (RCA) imbedded within it. All problem solving techniques include RCA within their structure. The steps and techniques within 8D which correspond to Root Cause Analysis are as follows:
- Problem Symptom is quantified and converted to “Object and Defect”
- Problem Symptom is converted to Problem Statement using Repeated Whys
- Possible and Potential Causes are collected using deductive tools (i.e. Fishbone or Affinity Diagram)
- Problem Statement is converted into Problem Description using Is / Is Not
- Problem Description reduces the number of items on the deductive tool (from step 3)
- Comparative Analysis between the Is and Is Not items (note changes and time)
- Root Cause theories are developed from remaining possible causes on deductive tool and coupled with changes from Is / Is Not
- Compare theories with current data and develop experiments for Root Cause Verification
- Test and confirm the Root Causes

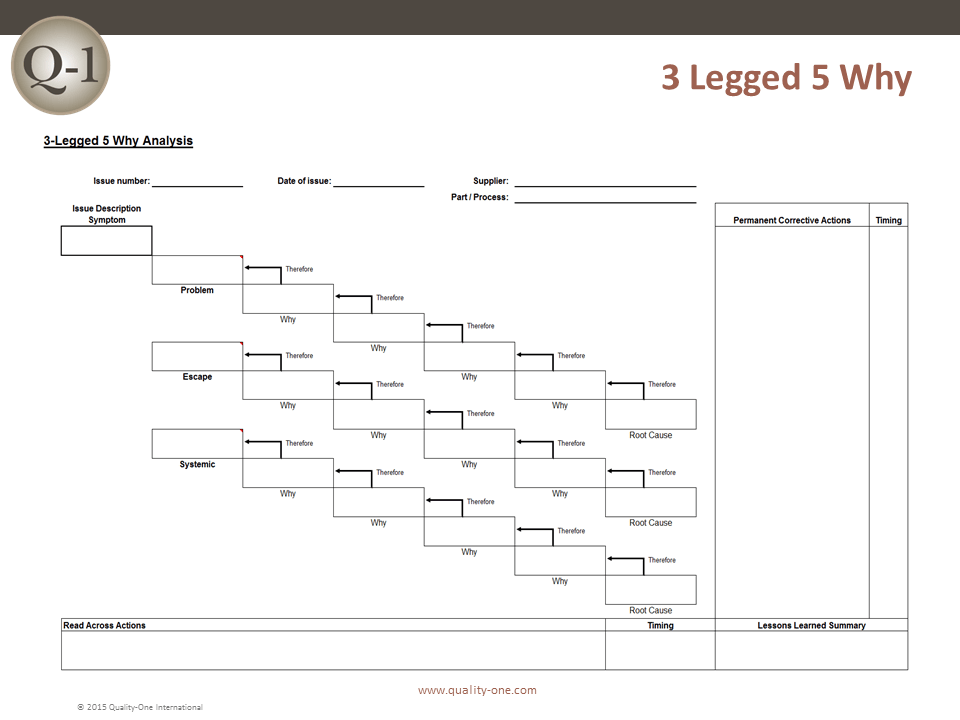
Example: Multiple Why Technique
The Multiple / Repeated Why (Similar to 5 Why) is an inductive tool, which means facts are required to proceed to a more detailed level. The steps required to determine problem statement are:
- Problem Symptom is defined as an Object and Defect i.e. “Passenger Injury”
- Why? In every case “SUV’s Roll Over”
- Why? In every case, it was preceded by a “Blown Tire”
- Why? Many explanations may be applied, therefore the team cannot continue with another repeated why past “Blown Tire”
- Therefore, the Problem Statement is “Blown Tire”
- Why? Low (Air) Pressure, Tire Defect (Degradation of an Interface) and High (Ambient) Temperature
- Counter measures assigned to low pressure and tire defect
This example uses only 4 of the 5 Whys to determine the root causes without going further into the systemic reasons that supported the failure. The Repeated Why is one way to depict this failure chain. Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) could also be used.
Learn More About Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
Quality-One offers Quality and Reliability Support for Product and Process Development through Consulting, Training and Project Support. Quality-One provides Knowledge, Guidance and Direction in Quality and Reliability activities, tailored to your unique wants, needs and desires. Let us help you Discover the Value of 8D Consulting , 8D Training or 8D Project Support .
Contact Us | Discover the Value!
(248) 280-4800 | [email protected]
Remember Me
- Don't have an account? Register
- Lost your password? Click here
- Already have an account? Log in

The 8D of Root Cause Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Addressing Non-Conformances Effectively
- Ossian Muscad
- November 23, 2023
- No Comments

Last Updated on November 23, 2023 by Ossian Muscad
The 8D Root Cause Analysis is a robust, team-oriented problem-solving methodology initially developed by Ford in the late 1980s. It is an invaluable tool for addressing nonconformances within an organization, offering systematic steps to identify, correct, and eliminate recurring problems. This comprehensive guide is designed to provide an in-depth understanding of the method, its application, and its benefits.
Addressing nonconformances efficiently and effectively is critical in today’s fast-paced manufacturing environment. Failing to do so could lead to decreased product quality, increased production costs, and potential reputational damage. The 8D Root Cause Analysis assists in pinpointing the underlying issues, enabling organizations to implement corrective actions that mitigate risks, enhance product quality, and improve overall operational efficiency.
This guide is your roadmap to mastering the 8D Root Cause Analysis. We delve into its nuances, reveal best practices, and highlight common pitfalls to avoid. Whether you’re a novice looking to get started or a seasoned professional seeking to refine your problem-solving skills, this guide offers a comprehensive overview of using the 8D method to resolve nonconformances effectively.
Understanding 8D Root Cause Analysis
The 8D Root Cause Analysis is a step-by-step problem-solving methodology designed to find the root cause of a problem, devise a short-term fix, and implement a long-term solution to prevent recurring issues. The 8D process involves eight disciplines that promote root cause analysis and preventive action.
Ford first introduced the 8D methodology in its 1987 Team-Oriented Problem Solving manual. The idea was to create a systemic approach to problem-solving that was efficient, effective, and adaptable. The 8D tool has since evolved and is now regarded as Ford’s primary problem-solving method, Global 8D.
There are several key principles and components of the 8D process:
- Team Establishment: Assemble a team of people with product/process knowledge, allocate roles, and define the problem.
- Problem Description: Describe the problem accurately and in measurable terms.
- Immediate Containment Actions: Define and implement containment actions to isolate the problem from any customer.
- Root Cause Identification: Identify all potential causes that could explain why the problem occurred. Then, evaluate each potential cause in light of the problem description and available facts.
- Choose and Verify Corrective Actions: Confirm that the selected corrective actions will resolve the problem for the customer and will not cause undesirable side effects.
- Implement and Validate Corrective Actions: Develop and execute optimal corrective measures for effective resolution.
- Prevent Recurrence: To prevent the recurrence of this and similar issues, it is crucial to enhance the management systems, operation systems, practices, and procedures. This will ensure improved efficiency, effectiveness, and problem-solving capabilities.
- Congratulations: Recognize the collective efforts of the team. The organization must extend a formal expression of gratitude to the team for their invaluable contributions.
The Eight Disciplines Explained
The Eight Disciplines of the 8D Root Cause Analysis act as a comprehensive roadmap to navigate problem-solving in a structured and systematic manner. Each discipline is designed to address a specific part of the process, starting from team formation, problem identification, and immediate action and culminating in the full implementation of long-term corrective measures.
This section delves into each of these disciplines, providing a detailed understanding of their function, implementation, and significance in the overall 8D methodology:
D1: Form a Team
The first discipline of the 8D Root Cause Analysis underscores the importance of assembling a competent team. A well-rounded team with diverse skills and comprehensive product/process knowledge is the backbone of successful problem-solving. Team formation should not be taken lightly, as the team’s collective expertise will be the driving force behind identifying the root cause and formulating effective corrective measures.
Roles and responsibilities should be distinctly defined for each team member to ensure smooth collaboration and efficient task management. Each member’s role should align with their expertise, enabling them to contribute effectively to the problem-solving process.
Responsibilities might include leading the team, facilitating communication, managing resources, performing data analysis, or developing corrective measures. By clearly defining roles and responsibilities, organizations can streamline problem-solving, mitigate conflicts, and ensure productive collaboration.
D2: Define the Problem
The second discipline, “Define the Problem,” is a critical step that directs the entire problem-solving process. Firmly rooted in evidence and data, it thoroughly examines the nonconformance to create a clear, concise, and measurable problem statement.
This discipline emphasizes the importance of distinguishing between symptoms and the actual problem. Techniques such as the ‘5 Whys’ and ‘Is/Is Not’ analysis can be used to clarify the problem’s nature and scope.
For instance, consider a scenario in a manufacturing company where a noticeable increase in product defects has been observed. A simple problem statement might be, “Product defect rates have increased by 20% over the last three months.”
However, the team might discover that the issue is more specific through rigorous problem definition techniques like the ‘5 Whys’—”Machine XYZ’s calibration settings are off by 0.05 units, causing a 20% increase in product defects over the last three months.”
Defining the problem accurately is crucial as it paves the way for subsequent steps in the 8D Root Cause Analysis process. It enables teams to focus on addressing the actual problem and not just the symptoms, thereby increasing the effectiveness of the corrective actions implemented.
D3: Containment Actions
The third discipline, “Containment Actions,” centers on implementing quick, temporary solutions to prevent further problem escalation. During this stage, the team should prioritize immediate actions that can effectively isolate the issue, preventing it from affecting customers or other parts of the production process.
While these actions are not meant to address the root cause of the problem, they serve as vital stopgap measures, minimizing negative impacts. At the same time, the team works on identifying the root cause and devising long-term corrective measures. This stage emphasizes the need for swift action, as delays can worsen the problem or branch out into other areas.
Temporary containment actions could include rerouting production, increasing quality checks, or informing customers about potential delays. By swiftly implementing containment actions, teams can minimize the issue’s impact on the overall operation and customer satisfaction until a permanent solution is put in place.
D4: Root Cause Analysis
The fourth discipline, “Root Cause Analysis,” is arguably the heart of the 8D methodology. This stage involves uncovering the problem’s underlying cause, moving beyond the symptoms to identify what is truly driving the issue. A thorough root cause analysis lays the foundation for effective corrective actions that address the problem at its source. Several techniques can be employed to identify root causes accurately:
- 5 Whys: A simple yet powerful tool, the 5 Whys technique involves asking ‘why?’ repeatedly (usually five times) until the root cause is identified. Every answer serves as the foundation for the subsequent question.
- Fishbone Diagram: Also known as Ishikawa or cause-and-effect diagrams, these help teams brainstorm and categorize root causes. The ‘head’ of the fish represents the problem, and the ‘bones’ are potential root causes.
- Fault Tree Analysis: This is a top-down, deductive failure analysis in which an undesired state of a system is analyzed using Boolean logic to combine a series of lower-level events.
- Pareto Analysis: Named after economist Vilfredo Pareto, this method uses the principle that 80% of problems come from 20% of causes. It helps prioritize the potential root causes.
It’s essential to be aware of common pitfalls that can compromise the effectiveness of root cause analysis. This includes:
- Rushing the process: It’s crucial to take the time to identify the root cause accurately and not jump to conclusions too quickly.
- Overlooking systemic issues: Often, problems are not isolated incidents but symptoms of larger, systemic issues. Failing to identify these can lead to recurring problems.
- Lack of team involvement: All team members should actively participate in the root cause analysis to ensure diverse perspectives and insights.
- Focus on blame: The goal is to find the problem’s cause, not assign blame. A blame-oriented approach can stifle open discussion and prevent identifying the true root cause.
The Root Cause Analysis phase of the 8D methodology is vital in preventing the recurrence of the same or similar issues. It demands a systematic approach, active team involvement, and a focus on factual evidence over assumptions. Steering clear of common pitfalls and using proven techniques can greatly enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of this process.
D5: Permanent Corrective Actions
After identifying the root cause of the problem in the previous step, the fifth discipline, “Permanent Corrective Actions,” revolves around developing and implementing long-term solutions that effectively address the identified root cause.
The goal is to enact changes that will prevent the recurrence of the problem in the future, going beyond temporary fixes to create sustainable improvements. To achieve this, teams should follow a strategic approach to implementing permanent corrective actions:
- Develop an Action Plan: Begin by outlining a detailed plan that includes the steps to be taken, the resources needed, and a timeline for implementation. This ensures everyone involved understands their roles and responsibilities.
- Test the Solution: Before full implementation, test the proposed solution under controlled conditions to evaluate its effectiveness. This helps identify potential issues and make necessary adjustments.
- Implement the Solution: Once the solution has proven effective, it’s time to implement it fully. This should be done in accordance with the action plan, with careful monitoring to ensure proper execution.
- Document Everything: Keep detailed records of the actions taken, their effects, and any challenges encountered. This aids in future problem-solving efforts and ensures accountability.
The final part of this stage is “Monitoring Progress,” which is crucial for assessing the effectiveness of the corrective actions over time. Regular monitoring allows teams to determine whether the actions have successfully resolved the problem and to evaluate their impact on overall operations.
If the problem persists or new issues arise, the team may need to revise their approach and consider alternative solutions. This stage reinforces the principle of continuous improvement at the heart of the 8D methodology, encouraging teams to constantly review and refine their practices in pursuit of operational excellence.
D6: Preventive Measures
The sixth discipline, “Preventive Measures,” underscores the proactive approach of the 8D methodology, focusing on taking steps to prevent the recurrence of similar issues in the future. It’s not enough to correct a problem; teams should also implement preventive measures to ensure the same or similar issues do not occur again.
This proactive approach can save time and resources and enhance overall operational efficiency. The following key steps should be taken to establish effective preventative measures:
- System Walk-throughs and Audits: Periodically review processes and systems to identify potential areas of concern before they become a problem.
- FMEA (Failure Mode and Effect Analysis): This is a step-by-step approach for identifying all possible failures in a design, a manufacturing or assembly process, or a product or service.
- Preventive Maintenance: Regular maintenance can catch and address issues before they develop into larger problems.
- Staff Training and Development: Ensure all team members are adequately trained in procedures, protocols, and problem-solving methods.
- Update Documentation: Update procedures and protocols based on lessons learned from the problem-solving process, ensuring they reflect any changes made.
The importance of preventive measures is well illustrated in various industry case studies. For instance, a renowned automobile manufacturer used the 8D methodology to identify a recurring problem in their assembly line, causing significant production delays.
Through a thorough root cause analysis, the team identified the problem and successfully implemented permanent corrective actions. However, the preventive measures, including regular system audits and staff training, ensured the issue did not recur, saving the company significant time and resources in the future.
Another example is a pharmaceutical company that faced a quality assurance issue. The company rectified the problem and took preventive measures, such as updating their documentation and procedures, conducting regular preventive maintenance, and carrying out systematic FMEA.
These steps helped them maintain the high-quality standards of their products and significantly reduce the risk of similar issues in the future.
D7: Verification of Effectiveness
The seventh discipline of the 8D methodology, “Verification of Effectiveness,” confirms the success of the implemented corrective actions. It provides the opportunity to reflect on the changes made and assess their impact on the problem faced. This discipline reinforces the importance of implementing solutions and validating their effectiveness in resolving the problem and improving operations.
This systematic evaluation involves determining whether the corrective actions have met the set objectives, solved the problem, and prevented its recurrence. If the corrective actions have been effective, they should result in noticeable improvements in the processes impacted and overall operations.
It’s essential to remember that verification of effectiveness isn’t an immediate step—it often necessitates a waiting period post-implementation to monitor changes and accurately assess impact. To objectively measure the effectiveness of the corrective actions, it’s crucial to rely on metrics and KPIs. These could include:
- Problem Recurrence Rate: A decrease in the recurrence of the same or similar problems is a strong indicator of effective corrective actions.
- Process Performance Metrics: These include metrics related to quality, efficiency, or productivity, depending on the specific problem addressed.
- Overall Operational Performance: Broader operational metrics like customer satisfaction, cost savings, or reduced waste can also indicate the effectiveness of the corrective actions.
- Employee Feedback: While not a quantitative metric, feedback from team members involved in the process can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of the changes.
Remember, the chosen metrics and KPIs should be clearly defined, measurable, and directly related to the problem at hand and the objectives of the corrective actions. Regular monitoring and reviewing of these indicators will contribute to a more objective and accurate evaluation of the effectiveness of the implemented corrective actions.
D8: Documentation and Closure
The eighth and final discipline highlights the importance of thoroughly documenting the 8D process and its outcomes. Detailed documentation of the problem, the investigation process, the root cause analysis, the implemented corrective actions, and their effectiveness provides valuable insights for future reference. It aids in knowledge transfer within the organization and can be used as a reference to tackle similar problems in the future, enhancing problem-solving efficiency.
Finalizing the 8D process involves:
- Reviewing the entire process.
- Validating the implemented corrective actions.
- Formally recognizing the efforts of everyone involved in the problem-solving process.
This step underscores the importance of team recognition and closure, reinforcing a sense of achievement and encouraging continued commitment to operational excellence. After all, the goal of the 8D methodology is not just to solve individual problems but to foster an environment of continuous learning and improvement.
Documenting the 8D process and achieving closure is not just an administrative task; it’s an integral part of the problem-solving process. It ensures that the lessons learned and best practices adopted remain confined to one problem and institutionalized within the organization, contributing to its long-term success and resilience.
Benefits of Implementing 8D Root Cause Analysis
Implementing the 8D root cause analysis in an organization brings along numerous advantages. These benefits range from enhanced product quality and customer satisfaction to cost savings and efficiency, and they ultimately contribute to fostering a culture of continuous improvement. Let’s delve deeper into these benefits.
Improved Quality and Customer Satisfaction
When organizations use the 8D root cause analysis, they invest in a systematic approach that addresses the root causes of problems rather than just their symptoms. This results in improved product or service quality, as issues are temporarily fixed and eliminated from the process.
Consequently, improvement in quality leads to increased customer satisfaction. Customers are likely to remain loyal to a brand that consistently meets or exceeds their expectations, enhancing the organization’s reputation and market share.
Cost Reduction and Efficiency
The 8D root cause analysis is also instrumental in reducing costs and enhancing efficiency. Addressing problems at their root cause extends beyond immediate cost savings from problem resolution. It also prevents the recurrence of the problem, which could lead to additional costs in the future. Moreover, by streamlining processes and eliminating nonconformances, organizations can significantly improve their efficiency, using their resources better and optimizing productivity.
Building a Culture of Continuous Improvement
One of the most profound advantages of the 8D methodology is its contribution to cultivating a culture of continuous improvement within an organization. The 8D root cause analysis emphasizes learning from mistakes, making necessary changes, and consistently looking for ways to improve.
This approach encourages team members to take ownership of problems, collaborate on solutions, and continually strive to enhance their performance. It fosters a proactive rather than reactive mindset, driving ongoing improvement and innovation.
Challenges and Best Practices
Implementing the 8D root cause analysis in an organization can pose some challenges, particularly for those new to the process. Recognizing potential obstacles in advance can help teams prepare and navigate these hurdles more effectively. Some common challenges include:
- Lack of Training: Without proper training and understanding of the 8D methodology, teams might find it difficult to apply the method correctly.
- Inadequate Resources: Undertaking a thorough root cause analysis and implementing corrective actions often require time, money, and manpower, which can be lacking in some organizations.
- Resistance to Change: Like any new process, the 8D method can meet resistance from team members who are comfortable with existing processes and cautious of change.
- Insufficient Data Collection and Analysis: Gathering and analyzing data is critical to identifying the root cause and evaluating the success of corrective actions but is often overlooked or inadequately done.
- Failure to Follow Through: The final steps of the 8D process—verification of effectiveness and documentation—can sometimes be neglected, undermining the success and sustainability of the corrective actions.
Best Practices for a Successful 8D Process
Organizations should adhere to certain best practices to successfully implement the 8D root cause analysis. These include:
- Training and Education: Provide team members with comprehensive training on the 8D methodology to ensure they understand how to effectively apply it.
- Resource Allocation: Dedicate the necessary resources—time, budget, and personnel—to ensure a thorough and effective problem-solving process.
- Open Communication: Foster a culture of open communication, encouraging team members to voice concerns, share ideas, and collaborate on solutions.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: The 8D process should be guided by accurate and comprehensive data. Invest in data collection and analysis tools and make decisions based on clear, relevant metrics.
- Commitment to Follow-through: It’s crucial to fully commit to each step of the process, especially the often-neglected final steps of verification and documentation. This ensures the sustainability of corrective actions and provides a reference for future problem-solving activities.
Tools and Software for 8D Root Cause Analysis
There are a myriad of tools and software available that can facilitate the 8D root cause analysis process. These tools have been designed to streamline the process, improve accuracy, and increase efficiency, making it easier for teams to identify nonconformities, determine their root cause, and implement effective corrective actions.
Overview of Available Tools
Some of the tools available for 8D root cause analysis stand out due to their comprehensive features and user-friendly interfaces. The options below provide an overview of some of the top tools and software to consider:
- Problem-Solving Software: These are comprehensive programs designed to guide teams through the entire 8D process, from problem identification to resolution and documentation.
- Data Analysis Tools: These tools allow teams to collect, organize, analyze, and visualize data, aiding in identifying root causes.
- Project Management Tools: These platforms help track the progress of corrective actions, assign tasks, and ensure accountability.
- Low-Code Platforms: Low-code platforms provide the means to build custom applications for root cause analysis, allowing organizations to tailor their tools to their specific needs. These platforms are user-friendly and require minimal coding knowledge, making them accessible to all team members.
- Collaboration Tools: Collaboration tools facilitate teamwork and communication, making it easier for team members to work together on a problem-solving project.
Choosing the Right Software for Your Organization
Selecting the right software for 8D root cause analysis is critical to ensure effectiveness and efficiency. Here are some important tips to guide your selection process:
- Understand Your Needs: Consider the unique needs of your organization and the specific problems you’re trying to solve.
- Evaluate Features: Look for software with features that align with your needs. This may include data analysis capabilities, collaboration features, documentation tools, etc.
- Consider User-Friendliness: The software should be intuitive and easy to use. It will be difficult for your team to adopt if it’s overly complicated.
- Check Compatibility: The software should easily integrate with your existing systems.
- Assess Support and Training: Good software providers offer robust support and training to help users make the most of their tools.
- Consider Cost: While cost should not be the only factor, finding a solution that fits within your budget without compromising on essential features is important.
By carefully evaluating available tools and making an informed choice, organizations can ensure they have the right resources to effectively carry out 8D root cause analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: what is the significance of the ‘d’ in the 8d method.
The ‘D’ in the 8D Method stands for ‘Disciplines,’ referring to the eight disciplined steps that the method involves. This systematic approach helps to ensure that no aspect of the problem-solving process is overlooked, improving the likelihood of finding a genuine root cause and effective corrective actions.
Q2: Is the 8D Root Cause Analysis Method applicable to all industries?
Yes, the 8D method is applicable across a wide range of industries. While initially developed within the automotive industry, systematic problem investigation, root cause identification, and corrective action implementation principles are universally relevant. However, the specific application of the method may vary depending on industry regulations, standards, and specific operational contexts.
Q3: What role does the team play in the 8D Root Cause Analysis Method?
The role of a diverse and cross-functional team is vital in the 8D method. Such a team offers a broader perspective, enabling a more extensive understanding of the problem and potential solutions. The collaborative nature of the method allows for a more thorough analysis of the problem, fosters creativity in finding solutions, and ensures shared ownership and accountability in implementing and sustaining corrective actions.
Streamline 8D Root Cause Analysis with DATAMYTE
DATAMYTE is a quality management platform with low-code capabilities. Our Digital Clipboard , in particular, is a low-code workflow automation software that features a workflow, checklist, and smart form builder. This tool lets you create custom applications for 8D root cause analysis, making capturing data, identifying nonconformities, and implementing effective corrective actions easier.
DATAMYTE also lets you conduct layered process audits, a high-frequency evaluation of critical process steps, focusing on areas with the highest failure risk or non-compliance. Conducting LPA with DATAMYTE lets you effectively identify and correct potential defects before they become major quality issues.
With DATAMYTE , you have an all-in-one solution for your 8D root cause analysis, helping you streamline and improve your problem-solving process. Book a demo now to learn more.
The 8D root cause analysis continues to be a reliable and effective method for identifying, resolving, and preventing nonconformities. It leverages a disciplined, team-oriented approach to problem-solving, ensuring a thorough investigation, accurate identification of root causes, and the implementation of effective corrective actions.
Choosing the right software tools can significantly enhance the effectiveness of your 8D process, improving your ability to analyze data, manage projects, and collaborate with your team. As we move forward, the future of root cause analysis lies in integrating advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning.
These technologies promise to enhance the data analysis capabilities of root cause analysis tools, enabling more precise identification of root causes and prediction of potential nonconformities. Implementing the 8D method can elevate your organization’s problem-solving capabilities, reduce risk, and improve overall productivity.
Don’t hesitate to adopt this proven approach and harness the power of technology to streamline and enhance your 8D process. Invest in your future by investing in the right tools and methodologies today.
Related Articles:
- Decoding BIQS: Essential Insights for Auto Suppliers on GM’s Latest Benchmarking Tool
- A Comprehensive Guide to Torque Testing and its Methodologies

- Implementation
- Case-Studies
- White Papers
- Knowledge Base
Experts in the Connected Factory

- 1-800-455-4359
- (763) 553-0455 ext. 1
- [email protected]
Root Cause Analysis and the 8D Problem Solving Bootcamp
Course comparison
See Better Alternatives
Skills related
People often say.
Good and logic Introduction
Knowledge and Experience Teaching
Recommended, Engaging and Informative
Insightful, valuable and clear Teaching
Applied fundamentals and worthy instructor
This course covers four Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and problem-solving approaches. Depending upon the complexity of the problem, you may choose one of these approaches. While taking these approaches, there are many tools and techniques which could be applied. The course also includes Descriptive Statistics (means, modes, median, ranges and standard deviation), Graphs and Charts (box and Whisker Plot, individual value plot, bar chart, pie chart, bubble chart, Matrix Plot, and time series), value stream mapping (team roles, team stages, conflict management and negative team behaviour), and tools for D1 (establish the team: team roles, team stages, conflict management and negative team behaviour), and tools for D2 (describe the problem: 5W2H, SIPOC, Gemba walk and stakeholder analysis).
Introduction
Technique #1: Five Whys
Technique #2: Cause and Effect Analysis
AI review summary
Most favorable.
Students appreciate the course for its focus on tools commonly used for quick root cause analysis and reporting. The concepts are explained in a simple way with relevant examples. The instructor's knowledge and high-quality delivery are highly valued. Despite covering difficult topics, the instructor effectively simplifies them for easy understanding. The course also provides clear examples for easy follow-through.
Related content for you
No items found.
This course includes
SkillMapper rating :
Start date :
Amount of students :
Downloadable resources :
Certificate of completion :
© SkillMapper SAS
Privacy Policy
Terms and use
Root Cause Analysis and the 8D Problem Solving Bootcamp

Share this page
Rating 4.6 out of 5 (540 ratings in Udemy)
- Perform the root cause analysis to eliminate the problem permanently
- Choose the right tool for the root cause analysis
- Learn about more than 40 tools that can be used for problem solving
- Proven problem solving approaches
- Taking permanent corrective actions, so that the problem does not come back again.
- Templates are included in the course.
Note: Students who complete this course have an option to apply for the …
Note: Students who complete this course have an option to apply for the certification exam by Quality Gurus Inc. and can achieve the Verified Certification from Quality Gurus Inc. It is optional and there is no separate fee for that.
In this course I will cover four broad strategies or approaches for Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and problem-solving:
1. Five Why's
2. Cause and Effect Diagram
3. A3 Problem Solving Approach
4. Eight Disciplines or 8D Problem Solving Approach
Depending upon the complexity of the problem you can choose one of these approaches.
While taking these approaches, there are many tools and techniques which could be applied. I will cover many such tools, for example:
1. Seven Basic Quality Tools (Cause and Effect Analysis, Flow Chart, Check Sheet, Pareto Chart, Scatter Plot, Control Charts and Histograms)
2. Descriptive Statistics (Mean, Mode, Median, Range and Standard Deviation)
3. Graphs and Charts (Box and Whisker Plot, Individual Value Plot, Bar Chart, Pie Chart, Bubble Chart, Matrix Plot, and Time Series)
4. Value Stream Mapping
5. Tools for D1 (Establish the Team): Team Roles, Team Stages, Conflict Management and Negative Team Behaviours
6. Tools for D2 (Describe the Problem): 5W2H, SIPOC, Gemba Walk and Stakeholder Analysis
7. Tools for D3 (Interim Containment): Identification and Traceability
8. Tools for D4 (Root Cause Analysis): Brainstorming, Nominal Group Technique and Affinity Diagram
9. Tools for D5 (Develop CA): Poka-yoke, Force Field Analysis, Control Plan and Benefit-Cost Analysis
10. Tools for D6 (Implement CA): Gantt Chart, RACI Matrix, Reports and Dashboard
11. Tools for D7 (Prevent Recurrence): FMEA
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Marketing strategic planning
- Request tracking
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Project management |
- What is 8D? A template for efficient pr ...
What is 8D? A template for efficient problem-solving
How you respond when problems arise is one of the most defining qualities of a manager. Luckily, there are tools you can use to master problem-solving. The 8D method of problem-solving combines teamwork and basic statistics to help you reach a logical solution and prevent new issues from arising.
You’ve spent months overseeing the development of your company's newest project. From initiation, planning, and execution, you’re confident this may be your best work yet.
Until the feedback starts rolling in.
There’s no sugar-coating it—things don’t always go as planned. But production or process issues are hardly a signal to throw in the towel. Instead, focus on honing your problem-solving skills to find a solution that keeps it from happening again.
The 8D method of problem solving emphasizes the importance of teamwork to not only solve your process woes but prevent new ones from occurring. In this guide, we’ll break down what 8D is, how to use this methodology, and the benefits it can give to you and your team. Plus, get an 8D template to make solving your issue easier.
What is 8D?
The eight disciplines (8D) method is a problem-solving approach that identifies, corrects, and eliminates recurring problems. By determining the root causes of a problem, managers can use this method to establish a permanent corrective action and prevent recurring issues.
How do you use the 8D method?
The 8D method is a proven strategy for avoiding long-term damage from recurring problems. If you’re noticing issues in your workflow or processes, then it’s a good time to give this problem-solving method a try.
To complete an 8D analysis, follow “the eight disciplines” to construct a statistical analysis of the problem and determine the best solution.
The eight disciplines of problem-solving
8D stands for the eight disciplines you will use to establish an 8D report. As you may notice, this outline starts with zero, which makes nine total disciplines. The “zero stage” was developed later as an initial planning stage.
To illustrate these steps, imagine your organization experienced a decline in team innovation and productivity this past year. Your stakeholders have noticed and want to see changes implemented within the next six months. Below, we’ll use the 8D process to uncover a morale-boosting solution.
![root cause analysis and the 8d problem solving bootcamp [inline illustration] D8 problem solving approach (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/6ab7c188-3258-4d2e-afe6-9a4a084cc09f/inline-productivity-8d-template-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
D0: Prepare and plan
Before starting the problem-solving process, evaluate the problem you want to solve. Understanding the background of the problem will help you identify the root cause in later steps.
Collect information about how the problem has affected a process or product and what the most severe consequences may be. Planning can include:
Gathering data
Determining the prerequisites for solving the problem
Collecting feedback from others involved
![root cause analysis and the 8d problem solving bootcamp [inline illustration] D0 Planning (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/abc3621d-e1ae-47ff-b731-0ee38cff99e9/inline-productivity-8d-template-2-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
If we look back at our example, you may want to figure out whether this decline in morale is organization-wide or only applies to a few departments. Consider interviewing a few employees from different departments and levels of management to gain some perspective. Next, determine what knowledge and skills you will need to solve this lapse in productivity.
D1: Form your team
Create a cross-functional team made up of people who have knowledge of the various products and workflows involved. These team members should have the skills needed to solve the problem and put corrective actions in place.
Steps in this discipline may include:
Appointing a team leader
Developing and implementing team guidelines
Determining team goals and priorities
Assigning individual roles
Arranging team-building activities
![root cause analysis and the 8d problem solving bootcamp [inline illustration] D1 Team members (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/51986017-5150-4dd4-940c-252cd0eb8ba5/inline-productivity-8d-template-3-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
From our example, a solid team would consist of people with first-hand experience with the issues—like representatives from all departments and key people close to workshop-level work. You may also want to pull someone in from your HR department to help design and implement a solution. Most importantly, make sure the people you choose want to be involved and contribute to the solution.
D2: Identify the problem
You may have a good understanding of your problem by now, but this phase aims to break it down into clear and quantifiable terms by identifying the five W’s a and two H’s (5W2H):
Who first reported the problem?
What is the problem about?
When did it occur and how often?
Where did it occur (relating to the sector, supplier, machine, or production line involved)?
Why is solving the problem important?
How was the problem first detected?
How many parts/units/customers are affected?
![root cause analysis and the 8d problem solving bootcamp [inline illustration] D2 Problem statement & description (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/9825ecd6-2bd3-4559-a68c-b1ae8aca2e52/inline-productivity-8d-template-4-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Use your team’s insights to answer these questions. From our example, your team may conclude that:
Employees feel overwhelmed with their current workload.
There is no real structure or opportunity to share new ideas.
Managers have had no training for meetings or innovation settings.
Disgruntled employees know they can achieve more—and want to achieve more—even if they seem disengaged.
Once you answer these questions, record an official problem statement to describe the issue. If possible, include photos, videos, and diagrams to ensure all parties have a clear understanding of the problem. It may also help to create a flowchart of the process that includes various steps related to the problem description.
D3: Develop an interim containment plan
Much like we can expect speedy first aid after an accident, your team should take immediate actions to ensure you contain the problem—especially if the problem is related to customer safety.
An interim containment plan will provide a temporary solution to isolate the problem from customers and clients while your team works to develop a permanent corrective action. This band-aid will help keep your customers informed and safe—and your reputation intact.
![root cause analysis and the 8d problem solving bootcamp [inline illustration] D3 Interim containment action (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/d6279c36-ccc6-4de3-89d2-f221632a1059/inline-productivity-8d-template-5-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Because your findings revealed workers were overworked and managers lacked training, your team suggests scheduling a few mandatory training sessions for leaders of each department covering time and stress management and combating burnout . You may also want to have a presentation outlining the topics of this training to get key managers and stakeholders interested and primed for positive upcoming changes.
D4: Verify root causes and escape points
Refer back to your findings and consult with your team about how the problem may have occurred. The root cause analysis involves mapping each potential root cause against the problem statement and its related test data. Make sure to test all potential causes—fuzzy brainstorming and sloppy analyses may cause you to overlook vital information.
![root cause analysis and the 8d problem solving bootcamp [inline illustration] D4 Root cause & escape points (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/301717c6-0434-4c88-addf-d500dc23ae87/inline-productivity-8d-template-6-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
In our example, focus on the “why” portion of the 5W2H. You and your team identify six root causes:
Managers have never had any training
There is a lack of trust and psychological safety
Employees don’t understand the objectives and goals
Communication is poor
Time management is poor
Employees lack confidence
In addition to identifying the root causes, try to pinpoint where you first detected the problem in the process, and why it went unnoticed. This is called the escape point, and there may be more than one.
D5: Choose permanent corrective actions
Work with your team to determine the most likely solution to remove the root cause of the problem and address the issues with the escape points. Quantitatively confirm that the selected permanent corrective action(s) (PCA) will resolve the problem for the customer.
Steps to choosing a PCA may include:
Determining if you require further expertise
Ensuring the 5W2Hs are defined correctly
Carrying out a decision analysis and risk assessment
Considering alternative measures
Collecting evidence to prove the PCA will be effective
![root cause analysis and the 8d problem solving bootcamp [inline illustration] D5 Permanent corrective action (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/53509966-18dd-4bb4-88a1-c7ca940fde3f/inline-productivity-8d-template-7-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Your team decides to roll out the training used in the interim plan to all employees, with monthly company-wide workshops on improving well-being. You also plan to implement meetings, innovation sessions, and team-coaching training for managers. Lastly, you suggest adopting software to improve communication and collaboration.
D6: Implement your corrective actions
Once all parties have agreed on a solution, the next step is to create an action plan to remove the root causes and escape points. Once the solution is in effect, you can remove your interim containment actions.
After seeing success with the training in the interim phase, your stakeholders approve all of your team’s proposed PCAs. Your representative from HR also plans to implement periodic employee wellness checks to track employee morale .
![root cause analysis and the 8d problem solving bootcamp [inline illustration] D6 PCA implementation plan (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/ca68af4a-afa7-4be4-93cb-8a8321eb5172/inline-productivity-8d-template-8-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
To ensure your corrective action was a success, monitor the results, customer, or employee feedback over a long period of time and take note of any negative effects. Setting up “controls” like employee wellness checks will help you validate whether your solution is working or more needs to be done.
D7: Take preventive measures
One of the main benefits of using the 8D method is the improved ability to identify necessary systematic changes to prevent future issues from occurring. Look for ways to improve your management systems, operating methods, and procedures to not only eliminate your current problem, but stop similar problems from developing later on.
![root cause analysis and the 8d problem solving bootcamp [inline illustration] D7 Preventive measure (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/cdd7b133-fb80-4db7-8935-1285a6b62b69/inline-productivity-8d-template-9-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Based on our example, the training your team suggested is now adopted in the new manager onboarding curriculum. Every manager now has a “meeting system” that all meetings must be guided by, and workloads and projects are managed as a team within your new collaboration software . Innovation is improving, and morale is at an all-time high!
D8: Celebrate with your team
The 8D method of problem-solving is impossible to accomplish without dedicated team members and first-class collaboration. Once notes, lessons, research, and test data are documented and saved, congratulate your teammates on a job well done! Make an effort to recognize each individual for their contribution to uncovering a successful solution.
![root cause analysis and the 8d problem solving bootcamp [inline illustration] 8D Team congratulations & reward (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/d2055965-bf3d-4bf4-a1ea-a0a7c4bf8a32/inline-productivity-8d-template-10-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
8D report template and example
Check out our 8D report template below to help you record your findings as you navigate through the eight disciplines of problem solving. This is a formal report that can be used as a means of communication within companies, which makes for transparent problem-solving that you can apply to the entire production or process chain.
Benefits of using the 8D method
The 8D method is one of the most popular problem-solving strategies for good reason. Its strength lies in teamwork and fact-based analyses to create a culture of continuous improvement —making it one of the most effective tools for quality managers. The benefits of using the 8D method include:
Improved team-oriented problem-solving skills rather than relying on an individual to provide a solution
Increased familiarity with a problem-solving structure
A better understanding of how to use basic statistical tools for problem-solving
Open and honest communication in problem-solving discussions
Prevent future problems from occurring by identifying system weaknesses and solutions
Improved effectiveness and efficiency at problem-solving
Better collaboration = better problem solving
No matter how good a manager you are, production and process issues are inevitable. It’s how you solve them that separates the good from the great. The 8D method of problem solving allows you to not only solve the problem at hand but improve team collaboration, improve processes, and prevent future issues from arising.
Try Asana’s project management tool to break communication barriers and keep your team on track.
Related resources

How to choose project management software for your team

7 steps to complete a social media audit (with template)
3 visual project management layouts (and how to use them)
Grant management: A nonprofit’s guide

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In this course I will cover four broad strategies or approaches for Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and problem-solving: 1. Five Why's. 2. Cause and Effect Diagram. 3. A3 Problem Solving Approach. 4. Eight Disciplines or 8D Problem Solving Approach.
2. Cause and Effect Diagram 3. A3 Problem Solving Approach 4. Eight Disciplines or 8D Problem Solving Approach Depending upon the complexity of the problem you can choose one of these approaches. While taking these approaches, there are many tools and techniques which could be applied. I will cover many such tools, for example: 1. Seven Basic ...
Root Cause Analysis and the 8D Problem Solving Bootcamp Four RCA approaches for permanent and effective corrective actions | Includes FMEA, VSM and Seven Basic Quality Tools Discount Link
Root Cause Analysis and the 8D Problem Solving Bootcamp. Skip to main content. We will keep fighting for all libraries - stand with us! ... root-cause-analysis-and-the-8-d-problem-solving-bootcamp Ocr tesseract 4.1.1 Ocr_autonomous true Ocr_detected_lang en Ocr_detected_lang_conf ...
Technique #1: Five Whys. Download Section 2 Slides and Templates. 2a Five Whys Intro. 2b Five Whys. 2c Five Whys Demo Preview. Quiz - Five Whys. Technique #2: Cause and Effect Analysis. Technique #3: A3 Problem Solving Approach. Technique #4: 8D Problem Solving Approach.
2. Cause and Effect Diagram. 3. A3 Problem Solving Approach. 4. Eight Disciplines or 8D Problem Solving Approach. Depending upon the complexity of the problem you can choose one of these approaches. While taking these approaches, there are many tools and techniques which could be applied.
D4: Root Cause Analysis. At the core of the 8D corrective action process lies Discipline 4, which focuses on identifying the root causes of the problem through rigorous analysis and data-driven investigation. This step is crucial, as it lays the foundation for developing effective and sustainable corrective actions.
The 8D problem solving process is a detailed, team oriented approach to solving critical problems in the production process. The goals of this method are to find the root cause of a problem, develop containment actions to protect customers and take corrective action to prevent similar problems in the future. The strength of the 8D process lies ...
The 8D Root Cause Analysis is a step-by-step problem-solving methodology designed to find the root cause of a problem, devise a short-term fix, and implement a long-term solution to prevent recurring issues. The 8D process involves eight disciplines that promote root cause analysis and preventive action. Ford first introduced the 8D methodology ...
The 8D problem solving model establishes a permanent corrective action based on statistical analysis of the problem and focuses on the origin of the problem by determining its root causes. Although it originally comprised eight stages, or disciplines, the eight disciplines system was later augmented by an initial planning stage.
This course covers four Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and problem-solving approaches. Depending upon the complexity of the problem, you may choose one of these approaches. While taking these approaches, there are many tools and techniques which could be applied.
This course covers four Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and problem-solving approaches. Depending upon the complexity of the problem, you may choose one of these Root Cause Analysis and the 8D Problem Solving Bootcamp by Sandeep Kumar, Quality Gurus Inc. (Udemy)
Perform the root cause analysis to eliminate the problem permanently; Choose the right tool for the root cause analysis; Learn about more than 40 tools that can be used for problem solving; Proven problem solving approaches; Taking permanent corrective actions, so that the problem does not come back again. Templates are included in the course.
8D (Eight Disciplines) Root Cause Analysis is a part of the bigger theme: "Problem Solving" Problem Solving Two ways to solve a problem: Reactive -Act once the problem happens and focus on removing the symptoms. Proactive -Focus on removing the cause of the problem so that problem does not happen again.
Investigate root causes with cause-and-effect analysis, 5 Whys, FMEA, and other analytical tools. Assess and work with various data collection plans and methods, as well as data charts and control charts. Define problem-solving models used for root cause analysis, including 8D, PDCA, and DMAIC.
The eight disciplines (8D) method is a problem-solving approach that identifies, corrects, and eliminates recurring problems. By determining the root causes of a problem, managers can use this method to establish a permanent corrective action and prevent recurring issues. First introduced by Ford, the 8D method offers a consistent way of ...
Powered by AI and the LinkedIn community. 1. Step 3: Root Cause Analysis. Be the first to add your personal experience. 2. Step 4: Choose and Verify Corrective Actions. Be the first to add your ...
Avoid causes such as: human error, lack of attention or blaming a person. As far as possible avoid "lack of resources", "lack of manpower" etc. As these could be the root cause of any and every problem you may have. You need to identify proposed actions as well. Finding the root cause is not enough.
The 8D problem-solving process is best known as the 8 Disciplines and used to solve major, critical, chronic, and recurring problems. This short course introduces the 8D approach which provides a better understanding of Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and how to use basic tools required for problem-solving in a health care setting. Need