
The Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research (JAIR) is dedicated to the rapid dissemination of important research results to the global artificial intelligence (AI) community. The journal’s scope encompasses all areas of AI, including agents and multi-agent systems, automated reasoning, constraint processing and search, knowledge representation, machine learning, natural language, planning and scheduling, robotics and vision, and uncertainty in AI.

Current Issue
Vol. 79 (2024)
Published: 2024-01-10
Bt-GAN: Generating Fair Synthetic Healthdata via Bias-transforming Generative Adversarial Networks
Collision avoiding max-sum for mobile sensor teams, usn: a robust imitation learning method against diverse action noise, structure in deep reinforcement learning: a survey and open problems, a map of diverse synthetic stable matching instances, digcn: a dynamic interaction graph convolutional network based on learnable proposals for object detection, iterative train scheduling under disruption with maximum satisfiability, removing bias and incentivizing precision in peer-grading, cultural bias in explainable ai research: a systematic analysis, learning to resolve social dilemmas: a survey, a principled distributional approach to trajectory similarity measurement and its application to anomaly detection, multi-modal attentive prompt learning for few-shot emotion recognition in conversations, condense: conditional density estimation for time series anomaly detection, performative ethics from within the ivory tower: how cs practitioners uphold systems of oppression, learning logic specifications for policy guidance in pomdps: an inductive logic programming approach, multi-objective reinforcement learning based on decomposition: a taxonomy and framework, can fairness be automated guidelines and opportunities for fairness-aware automl, practical and parallelizable algorithms for non-monotone submodular maximization with size constraint, exploring the tradeoff between system profit and income equality among ride-hailing drivers, on mitigating the utility-loss in differentially private learning: a new perspective by a geometrically inspired kernel approach, an algorithm with improved complexity for pebble motion/multi-agent path finding on trees, weighted, circular and semi-algebraic proofs, reinforcement learning for generative ai: state of the art, opportunities and open research challenges, human-in-the-loop reinforcement learning: a survey and position on requirements, challenges, and opportunities, boolean observation games, detecting change intervals with isolation distributional kernel, query-driven qualitative constraint acquisition, visually grounded language learning: a review of language games, datasets, tasks, and models, right place, right time: proactive multi-robot task allocation under spatiotemporal uncertainty, principles and their computational consequences for argumentation frameworks with collective attacks, the ai race: why current neural network-based architectures are a poor basis for artificial general intelligence, undesirable biases in nlp: addressing challenges of measurement.
Advertisement
Artificial intelligence and machine learning research: towards digital transformation at a global scale
- Published: 17 April 2021
- Volume 13 , pages 3319–3321, ( 2022 )
Cite this article

- Akila Sarirete 1 ,
- Zain Balfagih 1 ,
- Tayeb Brahimi 1 ,
- Miltiadis D. Lytras 1 , 2 &
- Anna Visvizi 3 , 4
10k Accesses
12 Citations
Explore all metrics
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping how we live, learn, and work. Until recently, AI used to be a fanciful concept, more closely associated with science fiction rather than with anything else. However, driven by unprecedented advances in sophisticated information and communication technology (ICT), AI today is synonymous technological progress already attained and the one yet to come in all spheres of our lives (Chui et al. 2018 ; Lytras et al. 2018 , 2019 ).
Considering that Machine Learning (ML) and AI are apt to reach unforeseen levels of accuracy and efficiency, this special issue sought to promote research on AI and ML seen as functions of data-driven innovation and digital transformation. The combination of expanding ICT-driven capabilities and capacities identifiable across our socio-economic systems along with growing consumer expectations vis-a-vis technology and its value-added for our societies, requires multidisciplinary research and research agenda on AI and ML (Lytras et al. 2021 ; Visvizi et al. 2020 ; Chui et al. 2020 ). Such a research agenda should oscilate around the following five defining issues (Fig. 1 ):
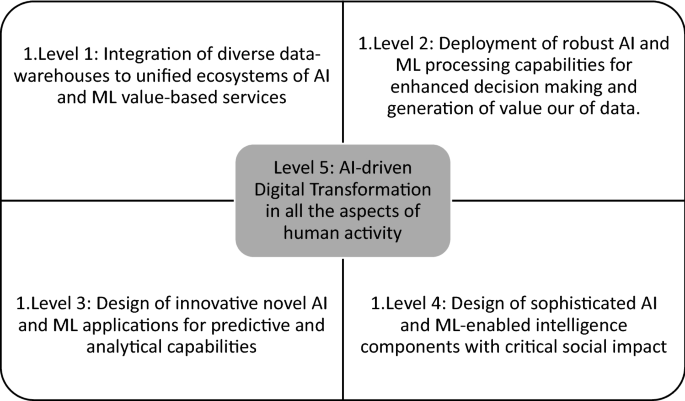
Source: The Authors
An AI-Driven Digital Transformation in all aspects of human activity/
Integration of diverse data-warehouses to unified ecosystems of AI and ML value-based services
Deployment of robust AI and ML processing capabilities for enhanced decision making and generation of value our of data.
Design of innovative novel AI and ML applications for predictive and analytical capabilities
Design of sophisticated AI and ML-enabled intelligence components with critical social impact
Promotion of the Digital Transformation in all the aspects of human activity including business, healthcare, government, commerce, social intelligence etc.
Such development will also have a critical impact on government, policies, regulations and initiatives aiming to interpret the value of the AI-driven digital transformation to the sustainable economic development of our planet. Additionally the disruptive character of AI and ML technology and research will required further research on business models and management of innovation capabilities.
This special issue is based on submissions invited from the 17th Annual Learning and Technology Conference 2019 that was held at Effat University and open call jointly. Several very good submissions were received. All of them were subjected a rigorous peer review process specific to the Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing Journal.
A variety of innovative topics are included in the agenda of the published papers in this special issue including topics such as:
Stock market Prediction using Machine learning
Detection of Apple Diseases and Pests based on Multi-Model LSTM-based Convolutional Neural Networks
ML for Searching
Machine Learning for Learning Automata
Entity recognition & Relation Extraction
Intelligent Surveillance Systems
Activity Recognition and K-Means Clustering
Distributed Mobility Management
Review Rating Prediction with Deep Learning
Cybersecurity: Botnet detection with Deep learning
Self-Training methods
Neuro-Fuzzy Inference systems
Fuzzy Controllers
Monarch Butterfly Optimized Control with Robustness Analysis
GMM methods for speaker age and gender classification
Regression methods for Permeability Prediction of Petroleum Reservoirs
Surface EMG Signal Classification
Pattern Mining
Human Activity Recognition in Smart Environments
Teaching–Learning based Optimization Algorithm
Big Data Analytics
Diagnosis based on Event-Driven Processing and Machine Learning for Mobile Healthcare
Over a decade ago, Effat University envisioned a timely platform that brings together educators, researchers and tech enthusiasts under one roof and functions as a fount for creativity and innovation. It was a dream that such platform bridges the existing gap and becomes a leading hub for innovators across disciplines to share their knowledge and exchange novel ideas. It was in 2003 that this dream was realized and the first Learning & Technology Conference was held. Up until today, the conference has covered a variety of cutting-edge themes such as Digital Literacy, Cyber Citizenship, Edutainment, Massive Open Online Courses, and many, many others. The conference has also attracted key, prominent figures in the fields of sciences and technology such as Farouq El Baz from NASA, Queen Rania Al-Abdullah of Jordan, and many others who addressed large, eager-to-learn audiences and inspired many with unique stories.
While emerging innovations, such as Artificial Intelligence technologies, are seen today as promising instruments that could pave our way to the future, these were also the focal points around which fruitful discussions have always taken place here at the L&T. The (AI) was selected for this conference due to its great impact. The Saudi government realized this impact of AI and already started actual steps to invest in AI. It is stated in the Kingdome Vision 2030: "In technology, we will increase our investments in, and lead, the digital economy." Dr. Ahmed Al Theneyan, Deputy Minister of Technology, Industry and Digital Capabilities, stated that: "The Government has invested around USD 3 billion in building the infrastructure so that the country is AI-ready and can become a leader in AI use." Vision 2030 programs also promote innovation in technologies. Another great step that our country made is establishing NEOM city (the model smart city).
Effat University realized this ambition and started working to make it a reality by offering academic programs that support the different sectors needed in such projects. For example, the master program in Energy Engineering was launched four years ago to support the energy sector. Also, the bachelor program of Computer Science has tracks in Artificial Intelligence and Cyber Security which was launched in Fall 2020 semester. Additionally, Energy & Technology and Smart Building Research Centers were established to support innovation in the technology and energy sectors. In general, Effat University works effectively in supporting the KSA to achieve its vision in this time of national transformation by graduating skilled citizen in different fields of technology.
The guest editors would like to take this opportunity to thank all the authors for the efforts they put in the preparation of their manuscripts and for their valuable contributions. We wish to express our deepest gratitude to the referees, who provided instrumental and constructive feedback to the authors. We also extend our sincere thanks and appreciation for the organizing team under the leadership of the Chair of L&T 2019 Conference Steering Committee, Dr. Haifa Jamal Al-Lail, University President, for her support and dedication.
Our sincere thanks go to the Editor-in-Chief for his kind help and support.
Chui KT, Lytras MD, Visvizi A (2018) Energy sustainability in smart cities: artificial intelligence, smart monitoring, and optimization of energy consumption. Energies 11(11):2869
Article Google Scholar
Chui KT, Fung DCL, Lytras MD, Lam TM (2020) Predicting at-risk university students in a virtual learning environment via a machine learning algorithm. Comput Human Behav 107:105584
Lytras MD, Visvizi A, Daniela L, Sarirete A, De Pablos PO (2018) Social networks research for sustainable smart education. Sustainability 10(9):2974
Lytras MD, Visvizi A, Sarirete A (2019) Clustering smart city services: perceptions, expectations, responses. Sustainability 11(6):1669
Lytras MD, Visvizi A, Chopdar PK, Sarirete A, Alhalabi W (2021) Information management in smart cities: turning end users’ views into multi-item scale development, validation, and policy-making recommendations. Int J Inf Manag 56:102146
Visvizi A, Jussila J, Lytras MD, Ijäs M (2020) Tweeting and mining OECD-related microcontent in the post-truth era: A cloud-based app. Comput Human Behav 107:105958
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Effat College of Engineering, Effat Energy and Technology Research Center, Effat University, P.O. Box 34689, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
Akila Sarirete, Zain Balfagih, Tayeb Brahimi & Miltiadis D. Lytras
King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, 21589, Saudi Arabia
Miltiadis D. Lytras
Effat College of Business, Effat University, P.O. Box 34689, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
Anna Visvizi
Institute of International Studies (ISM), SGH Warsaw School of Economics, Aleja Niepodległości 162, 02-554, Warsaw, Poland
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Akila Sarirete .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Sarirete, A., Balfagih, Z., Brahimi, T. et al. Artificial intelligence and machine learning research: towards digital transformation at a global scale. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 13 , 3319–3321 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03168-y
Download citation
Published : 17 April 2021
Issue Date : July 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03168-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Artificial Intelligence in the 21st Century
Ieee account.
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.
Help | Advanced Search
Artificial Intelligence
Authors and titles for recent submissions.
- Tue, 7 May 2024
- Mon, 6 May 2024
- Fri, 3 May 2024
- Thu, 2 May 2024
- Wed, 1 May 2024
Tue, 7 May 2024 (showing first 25 of 169 entries )
- Artificial Intelligence
- Data Science
- Hardware & Sensors
- Machine Learning
- Agriculture
- Defense & Cyber Security
- Healthcare & Sports
- Hospitality & Retail
- Logistics & Industrial
- Office & Household
- Write for Us

Advantages and disadvantages of wearable technologies
7 compelling reasons why competitive intelligence is a retail game, how ux design enhances human/robot collaboration, open source hardware platforms for robotics, how is digital health revolutionizing oncology, top mobile malware analysis tools, how to improve cybersecurity in the classroom, why businesses should invest in decentralized apps, a close watch: how uk businesses benefit from advanced cctv systems, empowering small businesses: the role of it support in growth and…, product marketing: leveraging photorealistic product rendering services, everything tech: how technology has evolved and how to keep up….
- Technologies
70 recent research papers in Deep Learning – Free Download

Artificial intelligence (AI) is a thriving field in this century with many practical applications. We look to AI and machine learning tools to automate routine labor, understand speech or images, make diagnoses in medicine, and support basic scientific research.
Deep Learning is a relatively new area, introduced to move machine learning closer to one of its original goals: Artificial Intelligence . It is an approach to AI or a type of machine learning that allows the computers to build complex concepts from simpler concepts and represent the world as a nested hierarchy of concepts.
Deep Learning introduces multiple levels of representation in which more abstract representations are computed with simpler representations. This helps us make sense of complex datasets such as images, videos, sound, etc. In just the past few years, deep learning has taken the world by surprise, driving rapid progress in computer vision, natural language processing (NLP), speech recognition, reinforcement learning, etc.
With these advancements, we can now build cars that drive themselves with more autonomy than ever before, smart reply systems that automatically draft the most mundane emails, and software agents that dominate humans. They already have an ever-widening impact on our lives, playing a big role in technology and sciences — from biology to astrophysics.
In this post, we list the top 70 research papers and projects in deep learning, published recently. Feel free to download. Share your own research papers with us to be added to this list.
- Person re-identification by deep learning multi-scale representations
- Classification of Diabetic Retinopathy Images by Using Deep Learning Models
- Lower jawbone data generation for deep learning tools under MeVisLab
- Theory of deep learning III: the non-overfitting puzzle
- Weblogo-2m: Scalable logo detection by deep learning from the web
- Supplementary Materials for DeepHit: A Deep Learning Approach to Survival Analysis with Competing Risks
- Symtosis: A liver ultrasound tissue characterization and risk stratification in optimized deep learning paradigm
- Discrete Deep Learning for Fast Content-Aware Recommendation
- Travel Behavior Classification: An Approach with Social Network and Deep Learning 2
- Machine Translation Using Deep Learning : A Survey
- Deep Learning for Joint Source-Channel Coding of Text
- DeepHit: A Deep Learning Approach to Survival Analysis with Competing Risks
- Learning To Share: Simultaneous Parameter Tying And Sparsification In Deep Learning
- Deep Inductive Network Representation Learning
- Exploration and Tradeoffs of Different Kernels in FPGA Deep Learning Applications
- A Deep Model with Local Surrogate Loss for General Cost-sensitive Multi-label Learning
- LSH Softmax: Sub-Linear Learning and Inference of the Softmax Layer in Deep Architectures
- Perception-Action- Learning System for Mobile Social-Service Robots using Deep Learning
- Geometry and Uncertainty in Deep Learning for Computer Vision
- Identifying RNA-binding proteins using multi-label deep learning
- A Deep Reinforcement Learning Network for Traffic Light Cycle Control
- Deep Learning for Cost-Optimal Planning: Task-Dependent Planner Selection
- Towards the quantification of uncertainty for deep learning based rainfall-runoff models
- DeepSqueak: a deep learning -based system for detection and analysis of ultrasonic vocalizations
- Investigating the Feasibility of Finger Identification on Capacitive Touchscreens using Deep Learning
- WiDeep: WiFi-based accurate and robust indoor localization system using deep learning
- The unreasonable effectiveness of deep learning in artificial intelligence
- Is Deep Learning a Game Changer for Marketing Analytics
- Robust Deep Learning as Optimal Control: Insights and Convergence Guarantees
- Deep Learning in Ultrasound Imaging
- Improving Lives of Indebted Farmers Using Deep Learning : Predicting Agricultural Produce Prices Using Convolutional Neural Networks
- Automating Cyberdeception Evaluation with Deep Learning
- When Deep Learning meets Web Measurements to infer Network Performance
- Comparison of semi-automatic and deep learning -based automatic methods for liver segmentation in living liver transplant donors
- Biomedical Imaging and Analysis In the Age of Sparsity, Big Data, and Deep Learning
- Deep Learning on the 2-Dimensional Ising Model to Extract the Crossover Region
- A Deep Learning Approach to Understanding Cloud Service Level Agreements
- Using Deep Learning to Automate Feature Modeling in Learning by Observation: A Preliminary Study
- Deep Structured Learning for Facial Expression Intensity Estimation
- Deep Learning for abnormality detection in Chest X-Ray images
- The Design and Evolution of Deep Learning Workloads
- A Systematic Literature Review on Features of Deep Learning in Big Data Analytics.
- Deep learning on CManifolds
- Plant Leaf Disease Detection using Deep Learning and Convolutional Neural Network
- Smart Library: Identifying Books on Library Shelves using Supervised Deep Learning for Scene Text Reading
- A new semantic attribute deep learning with a linguistic attribute hierarchy for spam detection
- Plant identification based on noisy web data: the amazing performance of deep learning (LifeCLEF 2017)
- Deep Learning: Shaking the Founda ons
- Fall Risk Reduction for the Elderly Using Mobile Robots Based on the Deep Reinforcement Learning
- Object Classification in Images of Neoclassical Artifacts Using Deep Learning
- Simulation based optimal control via deep learning
- Deep learning with geodesic moments for 3D shape classification
- Description of Images Related To Haze Crisis in Indonesia Using Deep Learning
- Application of deep learning neural network for classification of TB lung CT images based on patches
- Forecasting Real Time Series Data using Deep Belief Net and Reinforcement Learning
- Scaling Up Deep Learning on Clusters
- Unsupervised multi-manifold clustering by learning deep representation
- An Extensive Survey on Deep Learning Applications
- A Quick Review of Deep Learning in Facial Expression
- Query by Singing/Humming System Based on Deep Learning
- Deep Learning for Predictions in Emerging Currency Markets.
- Deep Learning Approach for Secondary Structure Protein Prediction based on First Level Features Extraction using a Latent CNN Structure
- Deep Learning for Intelligent Transportation
- Deep reinforcement learning for dynamic multichannel access
- Automated Feature Selection and Churn Prediction using Deep Learning Models
- Deep Learning for Natural Language Processing
- Development and Applications of Deep Learning Structures for Point Cloud Data
- International Workshop on Deep Learning and Music
- Deep Learning Binary Neural Network on an FPGA
- Wildcat: Weakly supervised learning of deep convnets for image classification, pointwise localization and segmentation
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
How to spot companies ai washing their products, top programming languages for building ai, history of programming languages – timeline, the historic dartmouth conference of 1956 – setting the stage for ai, thinking machines – a history of ai in chess, leveraging global talent and ai in the cpg industry – interview with drew cesario, 25 national artificial intelligence research institutes in the us, at-risk emerging technologies: balancing innovation and security.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions

- Conferences
- Last updated October 10, 2020
- In AI Mysteries
8 Open Access Resources For AI & ML Research Papers

- Published on March 19, 2019
- by Anirudh VK

Whether one is a beginner in the AI field and wishes to gain more in-depth knowledge, or an expert looking to widen his field of knowledge, here are 8 ML, DL and AI Open Access resources for research papers.
1. Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation
The NIPS Foundation blog houses research papers regarding the progress of neural networks and systems regarding them. What’s shocking is that they have been doing so since 1987, offering users the unique opportunity to look at how the fundamentals of neural networks emerged. With hundreds upon hundreds of papers available at the site, it is a great resource for learning online.
2. Academia.edu
Academia.edu functions as a platform for academicians to share research papers regarding their general field. The website uses analytics to measure impact, with over 22 million papers added to the platform as of now. The website also has hundreds of machine learning papers available for viewing or download after signing up with an email ID.
Dedicated communities of ML enthusiasts have created multiple lists of the must-reads in the machine learning and deep learning fields. These include not only curated lists of some of the influential papers published over the past few years, but also some hidden gems and a vast amount of knowledge. Some examples include terryum ‘s “Awesome – Most Cited Deep Learning Papers”, and floodsung ‘s “Deep Learning Papers Reading Roadmap” collections.
4. arXiv.org
arXiv.org is not the and top-voted great place to read research papers on a wide variety of topics, but also functions as a repository of ML and DL papers. The collection of research papers on the platform are over 1.5 million, with over 36,000 papers for machine learning alone. It is a great place for those looking to get started on reading about ML and DL. The platform will also expose individuals to a wide range of applications of AI technology due to its vast range of well-written papers.
This world famous entity was founded with a mission to advance AI research and safety and make it more human-centric. It recently turned for profit and is billed as a go-to platform for the latest research papers regarding AI development, especially in the field of Reinforcement Learning. They have contributed 16 papers to the ML community, along with open-sourcing the models and training data used.
6. Computer Vision Foundation
The Computer Vision Foundation has been a leading voice in the computer vision space, with multiple conferences starting from 2012 onwards. Starting from 2013, the research from these conventions have been archived in an open access format so as to allow further research to take place in the field of computer vision. Moreover, it also has a stance to open up the field so that individuals from across the globe can access information on it.
7. Journal of Machine Learning Research
JMLR website provides the papers published in the journal from 2000 onwards freely online, bringing high quality ML research papers to the public. Starting from October 2000, 20 volumes have been published on the website, with each containing anywhere from 50-100 research papers on Machine Learning
8. Association for Computational Linguistics
This is an association that researches the applications and science of computational linguistics, along with publishing a journal by the name of “Computational Linguistics”. The journal is also Open Access, bringing more than 30 years of research in the NLP field to the web for everyone to learn. Each year has 4 issues, offering a lot of information regarding the rise of NLP over the years.
Access all our open Survey & Awards Nomination forms in one place
Google Research Introduce PERL, a New Method to Improve RLHF

[Exclusive] Pushpak Bhattacharyya on Understanding Complex Human Emotions in LLMs

Kapur’s AlterEgo ‘Thinks’ Ahead of Musk’s Neuralink

Top 7 Hugging Face Spaces to Join

7 Must-Read Generative AI Books

2024 is the Year of AMD
LangChain, Redis Collaborate to Create a Tool to Improve Accuracy in Financial Document Analysis

Apple Smoothly Crafts ‘Mouse Traps’ for Humans

CORPORATE TRAINING PROGRAMS ON GENERATIVE AI
Generative ai skilling for enterprises, our customized corporate training program on generative ai provides a unique opportunity to empower, retain, and advance your talent., upcoming large format conference, data engineering summit 2024, may 30 and 31, 2024 | 📍 bangalore, india, download the easiest way to stay informed.

This YC-Backed Startup is Helping Enterprise Save Up to 30% on SaaS Expenditures with Generative AI
“A customer who spends between $1 and $2 million on SaaS applications can see 30% to 90% savings using CloudEagle”

Apple’s ‘Big AI Plans’ Coming Soon

Allstate India’s Manjula Nanjappa on How Coaching Drives Organisational Growth
Top editorial picks, ibm releases open-source granite code models, outperforms llama 3, cisco unveils ai-native cybersecurity innovations, openai joins adobe and others as c2pa committee member, sam altman says ai systems could ‘testify’ against individuals, akin to being subpoenaed in court, subscribe to the belamy: our weekly newsletter, biggest ai stories, delivered to your inbox every week., also in news.

Microsoft is Starting to Look a Lot Like OpenAI with ‘MAI-1’
The Fascinating Reason behind Silicon Valley’s Love for the Word Grok
How SuperKalam Uses OpenAI GPTs to Fuel UPSC Aspirants

Not all Indians are CEOs

Why NVIDIA GPUs are Still Not Available in India

Meet the Indian AI Startup Building a Private Perplexity for Enterprise

Fulcrum Digital’s Ryze Knocks-Down Barriers to GenAI Adoption for SMBs

The Relevance of RAG in the Era of Long-Context LLMs
Ai courses & careers.

7 Leading Data Science and AI Institutes in India

Gyan AI Unveils Smaller-Scale Maths LLM, Paramanu-Ganita, Outperforming LLama, Falcon

10 Free Online AI Courses to Learn from the Best
Become a certified generative ai engineer, industry insights.

Building a One Person $1 Bn Company is Now Possible

American Express Inaugurates Largest Global Office in Gurugram

Soket AI Labs Becomes the First Indian Startup to Build Solutions Towards Ethical AGI
Check our industry research reports.
AI Forum for India
Our discord community for ai ecosystem, in collaboration with nvidia. .
Interview with Vivek Raghvan Co-founder Sarvam AI
"> "> Flagship Events
Rising 2024 | de&i in tech summit, april 4 and 5, 2024 | 📍 hilton convention center, manyata tech park, bangalore, machinecon gcc summit 2024, june 28 2024 | 📍bangalore, india, machinecon usa 2024, 26 july 2024 | 583 park avenue, new york, cypher india 2024, september 25-27, 2024 | 📍bangalore, india, cypher usa 2024, nov 21-22 2024 | 📍santa clara convention center, california, usa, genai corner.

7 AI Startups that Featured on Shark Tank India Season 3

Top 9 Semiconductor GCCs in India

Top 6 Devin Alternatives to Automate Your Coding Tasks

10 Free AI Courses by NVIDIA

Top 6 AI/ML Hackathons to Participate in 2024

What’s Devin Up to?

10 Underrated Women in AI to Watchout For

10 AI Startups Run by Incredible Women Entrepreneurs
Data dialogues.

SAP Has Over 15,000 Customers in India
Zerodha cto warns companies to not look at ai as a solution chasing a problem.

Healthify Uses OpenAI’s GPTs to Help Indians Make Better Health Choices


Zerodha CTO Says He Stopped Googling Technical Stuff Over the Past Year

Fibe Leverages Amazon Bedrock to Increase Customer Support Efficiency by 30%

This 18-Year-Old Programmer is Creating an Open Source Alternative to Redis

Automation Anywhere Wants to Augment Humans with AI, Not Replace Them

Father of Computational Theory Wins 2023 Turing Award
Future talks.

As GitHub Begins Technical Preview of Copilot Workspace, an Engineer Answers How it Differs from Devin

T-Hub Supported MATH is Launching AI Career Finder to Create AI Jobs

Quora’s Poe Eats Google’s Lunch

Zoho Collaborates with Intel to Optimise & Accelerate Video AI Workloads

Rakuten Certified as Best Firm for Data Scientists for the 2nd Time

This Indian Logistics Company Developed an LLM to Enhance Last-Mile Delivery

Perplexity AI Reviews with Pro Access

What to Expect at the ‘Absolutely Incredible’ Apple WWDC 2024
Developer’s corner.

Software Engineering Jobs are Dying

Open-Source MS-DOS 4.0 Inspires Aspiring Developers to Embrace Retro Revolution

Japan is the Next Big Hub for Indian Tech Talent

Will TypeScript Wipe Out JavaScript?
In case you missed it.

Meta Forces Developers Cite ‘Llama 3’ in their AI Development

Why Developers Hate Jira

Which is the Most Frustrating Programming Language?

AI4Bharat Rolls Out IndicLLMSuite for Building LLMs in Indian Languages

8 Best AI Voice Generators Available for Free to Use in 2024

10 Best React Project Ideas For Beginners

8 Best AI Image Generator Apps Free for Android Users in 2024

9 Best AI Tools for Excel and Google Spread Sheet Automation

8 Best Generative AI Courses for Executives and Managers

Top 8 AI Browser Extensions for Chrome Users in 2024
Also in trends.

Microsoft Acquires 48 Acres of Lands in Hyderabad for Building Data Centres
Pure Storage and Red Hat Accelerate Modern Virtualisation Adoption
Tata Electronics Begins Exporting Semiconductor Chips

Happiest Minds Targets $1 Billion Revenue by 2031 with Generative AI

Tata Communications Announces CloudLyte, a Fully Automated Edge Computing Platform

NVIDIA is Hiring AI Engineers in India

Stack Overflow Finally Succumbs to OpenAI

Zebra Brings Generative AI to the Frontlines with Google, Android, and Qualcomm
World's biggest media & analyst firm specializing in ai, advertise with us, aim publishes every day, and we believe in quality over quantity, honesty over spin. we offer a wide variety of branding and targeting options to make it easy for you to propagate your brand., branded content, aim brand solutions, a marketing division within aim, specializes in creating diverse content such as documentaries, public artworks, podcasts, videos, articles, and more to effectively tell compelling stories., corporate upskilling, adasci corporate training program on generative ai provides a unique opportunity to empower, retain and advance your talent, with machinehack you can not only find qualified developers with hiring challenges but can also engage the developer community and your internal workforce by hosting hackathons., talent assessment, conduct customized online assessments on our powerful cloud-based platform, secured with best-in-class proctoring, research & advisory, aim research produces a series of annual reports on ai & data science covering every aspect of the industry. request customised reports & aim surveys for a study on topics of your interest., conferences & events, immerse yourself in ai and business conferences tailored to your role, designed to elevate your performance and empower you to accomplish your organization’s vital objectives., aim launches the 3rd edition of data engineering summit. may 30-31, bengaluru.
Join the forefront of data innovation at the Data Engineering Summit 2024, where industry leaders redefine technology’s future.
© Analytics India Magazine Pvt Ltd & AIM Media House LLC 2024
- Terms of use
- Privacy Policy

- Member Login
Search Filters
Research Libraries Guiding Principles for Artificial Intelligence
Articulating a set of research library guiding principles for AI is useful to influence policy and advocate for the responsible development and deployment of AI technologies, promote ethical and transparent practices, and build trust among stakeholders, within research libraries as well as across the research environment. These principles will serve as a foundational framework for the ethical and transparent use of AI and reflect the values we hold in research libraries. ARL will rely on these principles in our policy advocacy and engagement.
“Research Libraries Guiding Principles for Artificial Intelligence.” Association of Research Libraries, April 2024. https://doi.org/10.29242/principles.ai2024 .

Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Research Paper on Artificial Intelligence

1. ABSTRACT: This branch of computer science is concerned with making computers behave like humans. Artificial intelligence includes game playing, expert systems, neural networks, natural language, and robotics. Currently, no computers exhibit full artificial intelligence (that is, are able to simulate human behavior). The greatest advances have occurred in the field of games playing. The best computer chess programs are now capable of beating humans. Today, the hottest area of artificial intelligence is neural networks, which are proving successful in a number of disciplines such as voice recognition and natural-language processing. There are several programming languages that are known as AI languages because they are used almost exclusively for AI applications. The two most common are LISP and Prolog. Artificial intelligence is working a lot in decreasing human effort but with less growth. 2.
Related Papers
KAILASH N Bit
Khadijah Bahrol
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology (IJERT)
IJERT Journal
https://www.ijert.org/ai-in-computer-science-a-primer https://www.ijert.org/research/ai-in-computer-science-a-primer-IJERTV10IS020234.pdf Artificial intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science that deals with helping machines find solutions to complex problems in a more human-like fashion. AI involves the development of computer systems that can perform tasks normally requiring human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and translation between languages. It has been changing and improving the field of computer science through more advanced programming techniques. This paper examines the current and future roles of AI in computer science. Key Words: Artificial intelligence, artificial intelligence in computer science INTRODUCTION Computer science is the study of computers and computational systems. It covers the theory, design, development, and application of computer software and systems [1]. Artificial intelligence (AI) is a growing branch of computer science. Essentially, it involves borrowing characteristics from human intelligence, and applying them as algorithms in a computer friendly way. AI is the technology that is concerned with creating machine intelligence able to perform tasks heretofore only performed by human beings. Intelligence is usually regarded as the ability to collect knowledge and use it to solve complex problems. The field of artificial intelligence studies how to make machines have human thinking ability such as listening, speaking, reading, writing, thinking, and learning [2,3]. As shown in Figure 1, AI is a science and technology based on disciplines such as Computer Science, Biology, Psychology, Linguistics, Mathematics, and Engineering [4]. AI has been changing rapidly and expanding in application. Artificial intelligence has been successfully used to solve problems in diverse applications such as simulated pilots, doctor advisory system, search engines, computer games, adaptive user interfaces, personalized assistants, natural-language comprehension, and language translation. AI has played a major in computer science teaching and research since its inception, and it will keep forging its future development.
Pankaj Vashisht
ARS Publication, Chennai
P Krishna Sankar
This book "Computational Intelligence" is to understand the various characteristics of Intelligent agents and their search strategies. It contributes an impression towards representing knowledge in solving AI problems, reasoning, natural language understand, computer vision, automatic programming and machine learning. It provides a preliminary study to design and implement the different ways of software agents for problem solving. Unit I: Introduction towards future of Artificial Intelligence and characteristics of Intelligent agents. Outline towards search strategies through Uninformed, Informed and Heuristics along with optimization problems. Summary about the typical expert system and its functional models. Unit II: Introduction to Proposition logic and First order predicate logic was demonstrated with straight forward and backtracking approach. Awareness towards the ontology and reasoning based on knowledge availability. Demonstrated the Unification, Forward and Backward chaining, Ontological Engineering and Events with Prolog programming. Unit III: Brief awareness on uncertainty, non-monotonic reasoning, fuzzy, temporal and neural networks. Unit IV: Contributes a knowledge on learning with understanding towards Bayesian network and Hidden Markov Models. An Illustration on Supervised learning, Decision Tree, Regression, Neural Networks, Support vector machines and Reinforcement learning were briefed in this section. Unit V: Provides a study over Natural Language Processing and Machine Learning. It provides illustration towards Information extraction, Information retrieval, Machine Translation, Symbol-Based an Connectionist.
International Journal of Engineering Sciences & Research Technology
Ijesrt Journal
RELATED PAPERS
Naval Engineers Journal
Brij Agrawal
Benedikt Korf
suad khalifa
Future Studies Research Journal: Trends and Strategies
Kátia Lamarca
The Representation and Perception of Roman Imperial Power
Henner von Hesberg
Irena Budzanivska
Journal of Ayub Medical College, Abbottabad : JAMC
Moazzam Ali Atif
Bashir Zubair
Marcelo Machado de Luca de Oliveira Ribeiro
African Journal of Infectious Diseases
Faith P. Mabiki
Libri, atti e raccolte di saggi
stefano leale
Blanquita Pantoja
PMLA/Publications of the Modern Language Association of America
Joshua Beckelhimer
International Research Journal of Business Studies
Popong Nurhayati
Australian Journal of Earth Sciences
richard glen
Kae Reynolds
Léia Teixeira Lacerda
Revista Arbitrada Interdisciplinaria Koinonía
Adalberto Soto
The Journal of Physical Chemistry A
Nicholas Winograd
Case Reports in Anesthesiology
Nishant Kumar
Journal of Orthopaedic Science
Osamu Tanifuji
Sustainability
Jason Sawyer
hjhjgfg freghrf
Scientific Reports
Faten MAHJOUB
Yaşayan Avrupa Birliği Hukuku Blogu
Ilke Gocmen
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
This paper is in the following e-collection/theme issue:
Published on 7.5.2024 in Vol 26 (2024)
This is a member publication of National University of Singapore
Effectiveness of an Artificial Intelligence-Assisted App for Improving Eating Behaviors: Mixed Methods Evaluation
Authors of this article:

Original Paper
- Han Shi Jocelyn Chew 1 , PhD ;
- Nicholas WS Chew 2 , MBBS ;
- Shaun Seh Ern Loong 3 , MBBS ;
- Su Lin Lim 4 , PhD ;
- Wai San Wilson Tam 1 , PhD ;
- Yip Han Chin 3 , MBBS ;
- Ariana M Chao 5 , PhD ;
- Georgios K Dimitriadish 6 , MBBS, MSc ;
- Yujia Gao 7 ;
- Jimmy Bok Yan So 8 , MB ChB, FRCS, MPH ;
- Asim Shabbir 8 , MBBS, MMed, FRCS ;
- Kee Yuan Ngiam 9 , MBBS, FRCS
1 Alice Lee Centre for Nursing Studies, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore
2 Department of Cardiology, National University Hospital, Singapore, Singapore
3 Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore
4 Department of Dietetics, National University Hospital, Singapore, Singapore
5 School of Nursing, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, United States
6 Department of Endocrinology ASO/EASO COM, King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, London, United Kingdom
7 Division of Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Surgery, Department of Surgery, National University Hospital, Singapore, Singapore
8 Division of General Surgery (Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery), Department of Surgery, National University Hospital, Singapore, Singapore
9 Division of Thyroid & Endocrine Surgery, Department of Surgery, National University Hospital, Singapore, Singapore
Corresponding Author:
Han Shi Jocelyn Chew, PhD
Alice Lee Centre for Nursing Studies
Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine
National University of Singapore
Level 3, Clinical Research Centre
Block MD11, 10 Medical Drive
Singapore, 117597
Phone: 65 65168687
Email: [email protected]
Background: A plethora of weight management apps are available, but many individuals, especially those living with overweight and obesity, still struggle to achieve adequate weight loss. An emerging area in weight management is the support for one’s self-regulation over momentary eating impulses.
Objective: This study aims to examine the feasibility and effectiveness of a novel artificial intelligence–assisted weight management app in improving eating behaviors in a Southeast Asian cohort.
Methods: A single-group pretest-posttest study was conducted. Participants completed the 1-week run-in period of a 12-week app-based weight management program called the Eating Trigger-Response Inhibition Program (eTRIP). This self-monitoring system was built upon 3 main components, namely, (1) chatbot-based check-ins on eating lapse triggers, (2) food-based computer vision image recognition (system built based on local food items), and (3) automated time-based nudges and meal stopwatch. At every mealtime, participants were prompted to take a picture of their food items, which were identified by a computer vision image recognition technology, thereby triggering a set of chatbot-initiated questions on eating triggers such as who the users were eating with. Paired 2-sided t tests were used to compare the differences in the psychobehavioral constructs before and after the 7-day program, including overeating habits, snacking habits, consideration of future consequences, self-regulation of eating behaviors, anxiety, depression, and physical activity. Qualitative feedback were analyzed by content analysis according to 4 steps, namely, decontextualization, recontextualization, categorization, and compilation.
Results: The mean age, self-reported BMI, and waist circumference of the participants were 31.25 (SD 9.98) years, 28.86 (SD 7.02) kg/m 2 , and 92.60 (SD 18.24) cm, respectively. There were significant improvements in all the 7 psychobehavioral constructs, except for anxiety. After adjusting for multiple comparisons, statistically significant improvements were found for overeating habits (mean –0.32, SD 1.16; P <.001), snacking habits (mean –0.22, SD 1.12; P <.002), self-regulation of eating behavior (mean 0.08, SD 0.49; P =.007), depression (mean –0.12, SD 0.74; P =.007), and physical activity (mean 1288.60, SD 3055.20 metabolic equivalent task-min/day; P <.001). Forty-one participants reported skipping at least 1 meal (ie, breakfast, lunch, or dinner), summing to 578 (67.1%) of the 862 meals skipped. Of the 230 participants, 80 (34.8%) provided textual feedback that indicated satisfactory user experience with eTRIP. Four themes emerged, namely, (1) becoming more mindful of self-monitoring, (2) personalized reminders with prompts and chatbot, (3) food logging with image recognition, and (4) engaging with a simple, easy, and appealing user interface. The attrition rate was 8.4% (21/251).
Conclusions: eTRIP is a feasible and effective weight management program to be tested in a larger population for its effectiveness and sustainability as a personalized weight management program for people with overweight and obesity.
Trial Registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04833803; https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04833803
Introduction
Overweight and obesity remain a public health concern that affects slightly more than half of the global adult population [ 1 ]. Across 52 Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, Group of Twenty, and European Union 28 countries, treating conditions related to overweight and obesity costs US $425 billion per year, based on purchasing power parity. Each US dollar used to prevent obesity results in a 6-fold return in economic benefits [ 2 ]. Strategies for maintaining a healthy weight range from policy mandates on nutritional food labeling [ 3 ] to clinical treatments focused on lifestyle modifications, pharmacotherapy, and bariatric surgery [ 4 ]. However, the effectiveness of such strategies is limited by insurance coverage [ 5 ] and challenges with weight loss maintenance [ 6 - 9 ]. Some participants have been reported to regain up to 100% of their initial weight loss within 5 years [ 9 , 10 ].
With the rapid digitalization and smartphone penetration worldwide, weight loss apps have been gaining popularity, as they help overcome the temporospatial challenges of in-person weight loss programs [ 11 ]. For instance, participants enrolled in conventional weight management programs typically attend multiple face-to-face sessions at designated facilities, which could be burdensome and inconvenient as one needs to schedule appointments and travel to the facility that may be beyond one’s usual mobility pattern. Moreover, such programs are resource-intensive, requiring a multidisciplinary team of trained health care professionals (eg, physicians, dietitians, physiotherapists, nurses), infrastructure (eg, counselling room), and equipment (eg, weighing scale, stadiometer) to maintain. Well-known apps that support weight loss in the market include MyFitnessPal [ 12 ], MyPlate Calorie Tracker [ 13 ], and Fitbit [ 14 ]. In Singapore, Healthy 365 [ 15 ] is available for the public, while nBuddy [ 16 ] is used for the clinical population. These apps mostly focus on calorie tracking, health status tracking, and progress monitoring. Increasingly, apps are enhanced with features that allow intuitive synchronization of health metrics across apps to provide a more holistic progress monitoring experience. With a fee, some apps even match users to a health coach who would provide personalized weight management plans to support weight loss. However, there is a need for apps that include monitoring and support for one’s self-regulation over momentary eating impulses, which are often triggered and influenced by dietary lapse triggers such as visual food cues, eating out, negative affect, and sleep deprivation [ 17 - 20 ]. Self-regulation of eating behaviors during weight loss treatment commonly includes portion control, increasing fruit and vegetable consumption, reducing unhealthy food (sugar-sweetened beverages and high-fat food items) consumption, and reducing overall caloric consumption [ 17 ]. Therefore, we aimed to examine the feasibility and effectiveness of a novel artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted weight management app on improving eating behaviors and to explore the mechanism by which this app influences eating behaviors, as hypothesized in our earlier work [ 21 ].
Study Design
A single-group pretest-posttest study was conducted and reported according to the TREND (Transparent Reporting of Evaluations with Nonrandomized Designs) checklist ( Multimedia Appendix 1 ) [ 22 ]. Despite the limitations of the study design, it was deemed the most appropriate and feasible experimental study design for a preliminary understanding of the usability, acceptability, and effectiveness of the app [ 23 ].
Participant Recruitment
Participants older than 21 years with BMI ≥23 kg/m 2 and not undergoing a commercial weight loss program were recruited from January 2022 to October 2022 through social media platforms and physical recruitment at a local tertiary hospital’s specialist weight management clinic in Singapore. Using G*Power (version 3.1.9.7) [ 24 ], to detect a small effect size of 0.2 at .05 significance level and 80% power while accounting for an attrition rate of 20%, 248 participants are required. To be conservative, 250 participants were recruited.
Intervention
Immediately after completing the pretest questionnaire, participants were onboarded to the Eating Trigger-Response Inhibition Program (eTRIP) app by a trained research assistant to complete the 1-week run-in of the program. During the onboarding, participants were invited to enter their anthropometric details, desired weight loss goals, and motivation. They were also encouraged to personalize certain app functions such as the timing of the check-in prompts and preferred name for interaction with a chatbot. At every mealtime (at least 3 times a day), the participants were prompted to take a picture of their food, which was immediately recognized by a food-based computer vision image recognition technology, which then triggered a set of chatbot-initiated questions on eating triggers (eg, how they are feeling). These questions were developed based on our past work on eating behaviors [ 25 - 30 ]. Participants were able to view their image-based food log and eating habits on a dashboard, reflect upon their eating habits throughout the day, and set their goals and action plans for the next day. On the 8th day, all participants’ user accounts were locked, and they were unable to make any changes but were able to still view their check-in logs. Participants could also provide feedback on the app by filling out the comments section in one of the app pages. Participants were reimbursed SGD 25 (SGD 1=US $0.74) for completing this program.
The eTRIP app was developed as a 12-week AI-assisted, app-based, self-regulation program targeted at improving weight loss through healthy eating. eTRIP was developed largely based on a modified temporal self-regulation theory [ 31 , 32 ], behavioral change taxonomy [ 33 ], and our previous work on healthy eating and weight loss [ 27 - 29 , 34 , 35 ]. This includes studies on people with overweight and obesity in the areas of personal motivators, self-regulation facilitators, and barriers [ 27 ]; the potential of AI, apps, and chatbots in improving weight loss [ 6 , 25 , 29 ]; perceptions and needs of AI to increase its adoption in weight management [ 26 ]; and the essential elements of a weight loss app [ 28 ]. The development of eTRIP was split into 2 phases: (1) development of an AI-assisted self-monitoring system and (2) development of an AI-assisted behavioral nudging system. In this paper, we report the feasibility and effectiveness of an AI-assisted self-monitoring system after a 1-week run-in. The self-monitoring system is built upon 3 main components, namely, (1) chatbot-based check-ins on eating lapse triggers, (2) food-based computer vision image recognition (system built based on local food items), and (3) automated time-based nudges and meal stopwatch.
All participants completed the same self-report questionnaire before and after the 1-week run-in of the app, which reflected their sociodemographic profile, BMI, waist circumference, intention to improve eating behaviors, habits of overeating (Self-Report Habit Index) [ 36 ], habits of snacking [ 36 ], consideration of future consequences (Consideration of Future Consequences Scale-6 items) [ 37 ], self-regulation of eating behavior (Self-Regulation of Eating Behavior Questionnaire) [ 38 ], physical activity (International Physical Activity Questionnaire-Short Form) [ 39 ], anxiety symptoms (Generalized Anxiety Disorder-2 items) [ 40 ], and depressive symptoms (Patient Health Questionnaire-2 items) [ 41 ]. Details are reported in Multimedia Appendix 2 . The primary outcomes were overeating habits, snacking habits, immediate thinking, self-regulation of eating habits, depression, anxiety, and physical activity. The secondary outcomes were their subscale scores.
Data Analysis
SPSS statistical software (version 27; IBM Corp) [ 42 ] was used for the analyses. The baseline characteristics of the participants were presented in mean (SD) and frequency (%). Paired 2-sided t tests were used to compare the differences in the psychobehavioral constructs before and after the 7-day program, including overeating habits, snacking habits, consideration of future consequences, self-regulation of eating behaviors, anxiety, depression, and physical activity. To account for the increased risk of a type 1 error due to multiple comparisons [ 43 ], the Bonferroni-corrected significant level was set to P ≤.007. Qualitative feedback were analyzed using content analysis according to 4 steps, namely, decontextualization, recontextualization, categorization, and compilation [ 44 ]. Feedback was first consolidated verbatim and read iteratively by 2 coders (Nagadarshini Nicole Rajasegaran and HSJC). The verbatim feedback was then analyzed independently by 2 reviewers into meaning units. Meaning units were then reconstituted, categorized, and reported as themes and subthemes.
Ethics Approval
This single-group pretest-posttest study was approved by the National Healthcare Group Domain Specific Review Board (ref 2020/01439), registered with the ClinicalTrials.gov (ref NCT04833803) on April 6, 2021.
Baseline Characteristics of the Participants
A total of 251 participants were enrolled in this study (Chew HSJ, unpublished data, 2023); 20 (7.9%) participants dropped out of the 1-week program due to the inability to perform check-ins every day. Among those who completed the program (n=231), 1 participant was removed from the analyses due to ineligibility. The mean age, self-reported BMI, and waist circumference of the participants was 31.25 (SD 9.98) years, 28.86 (SD 7.02) kg/m 2 , and 92.6 (SD 18.24) cm, respectively ( Table 1 ). Approximately 47.8% (111/230) of the participants were males, indicating a good mix of participants from both sexes, and most of the participants were single (169/230, 73.6%), Chinese (181/230, 78.7%), and had a university education (148/230, 64.1%).
a SGD 1=US $0.74.
Mean Baseline Scores on Each Outcome Variable
The mean baseline scores on each outcome variable of the participants who completed and who dropped out from the 1-week program were calculated ( Table 2 ). As the dropout rate was only 8.4% (20/251), statistical comparisons between those who dropped out and those who completed the program was not necessary.
a SRHI: Self-Report Habit Index.
b CFCS-6: Consideration of Future Consequences Scale-6 items.
c SREBQ: Self-Regulation of Eating Behavior Questionnaire.
d IPAQ-SF: International Physical Activity Questionnaire-Short Form.
e MET: metabolic equivalent task.
Pretest and Posttest Mean Differences
There were significant improvements in all the 7 psychobehavioral constructs, except for anxiety. After adjusting for multiple comparisons, there were only statistically significant improvements in the overeating habit, snacking habit, self-regulation of eating behavior, depression, and physical activity ( Table 3 ). Forty-one participants reported skipping at least 1 meal (ie, breakfast, lunch, or dinner), summing to a total of 578 (67.1%) of the 862 meals skipped.
b Significant at P <.007.
c CFCS-6: Consideration of Future Consequences Scale-6 items.
d Consideration of Future Consequences Scale-6 immediate subscale.
e Consideration of Future Consequences Scale-6 future subscale.
f SREBQ: Self-Regulation of Eating Behavior Questionnaire.
g IPAQ-SF: International Physical Activity Questionnaire-Short Form.
User Engagement
Among those who completed the program, 97% (46,867/48,316) chatbot-based questions were completed. As participants were given the option to add additional check-ins for snacks, the percentage of completed check-ins could not be accurately computed.
Qualitative Feedback
Of the 230 participants, 80 (34.8%) provided textual feedback that indicated satisfactory experience with eTRIP. Four themes emerged, namely, (1) becoming more mindful of self-monitoring, (2) personalized reminders with prompts and chatbot, (3) food logging with image recognition, and (4) engaging with a simple, easy, and appealing user interface.
Becoming More Mindful of Self-Monitoring
By checking in with the app for every meal, the participants mentioned being more aware of their unhealthy eating habits and more mindful of their next meal. One participant said, “It (eTRIP) incentivizes me to stick to my diet plan because I am reminded of my diet plan daily. Ticking the box that indicates ‘I did not meet my diet plan’ made me guilty and it motivates me to opt for healthier food choice the next time round” (Female, Chinese, 22 years old). Another participant said, “I really liked the eTRIP app! Has a lot of potential for further expansion and use by more people. I like how it sends prompts during selected times of the day to be careful of what we see on social media. The rating of our mood before meals also helps me know how mood can affect my eating patterns. Lastly, the stopwatch function is great because it reminds me to eat more mindfully” (Male, Chinese, 27 years old).
Personalized Reminders With Prompts and Chatbot
Some participants mentioned the appreciation for reminders to check in with themselves in terms of the triggers of overeating. One participant said, “I like that there’s a reminder to check in for every meal and users get to decide what time the app should prompt!” (Female, Indian, 27 years old). Some also suggested to develop the prompting system to prompt based on the user’s previous check-in timings to optimize the prediction of mealtimes and prompt the check-in sessions intuitively. One participant suggested, “I think what would make this better is if you could aggregate the time the meals are entered from the past few days and estimate the time the user will normally eat and auto-adjust the timing…” (Female, Chinese, 23 years old). Others suggested to include reminders of how to make their meal options healthier, “Might be good to have reminders that reminds us to eat healthy with some tips on how to choose food” (Male, Chinese, 25 years old).
Food Logging With Image Recognition
Many participants highlighted their appreciation for the image recognition-based food logging, as it was accurate and convenient for food logging. One participant said, “It is very accurate in determining the food I’ve eaten just from the picture, and this saved me a lot of time from typing out the food I’ve eaten” (Male, Chinese, 21 years old).
Engaging With a Simple, Easy, and Appealing User Interface
All the participants who commented on the user experience expressed being impressed with the user interface and structure. One participant said, “the flow was smooth, quite clear. Graphics were cute. Very easy to input my info (information) especially from the homepage, I like how there’s the ability to skip a meal” (Female, Malay, 25 years old). Another participant said, “The app is very smart, … yes it’s very easy to fill and I loss (lost) like 0.5kg?” (Female, Chinese, 25 years old).
Participants’ Suggestions
In terms of the areas for improvement, the participants preferred to have (1) more options and rating scales for each domain of eating trigger instead of typing out in the “others” field (although there was a stored text for repeated entries); (2) summary of the instances where one was able to achieve the goal of the day, which the user sets daily for the next day (based on a user preset list of goals); (3) examples of standard portions and frequency of meals; and (4) feedback on how to improve upon the unhealthy meals logged.
Real-time interventions that can effectively address eating lapse triggers and improve eating behavior self-regulation, lapse events, weight loss, and weight maintenance remain unclear [ 45 ]. OnTrack, a just-in-time adaptive intervention that has been tested, is a smartphone app that uses machine learning to predict dietary lapses based on the repeated assessments of lapse triggers (ecological momentary assessment). OnTrack is used in conjunction with existing weight loss apps such as WeightWatchers app and provides personalized recommendations to prevent dietary lapses. The compliance rate for completing the lapse trigger survey in OnTrack was 62.9% over 3 months, and the studied sample was mostly females who were Whites [ 46 ]. Evidence has shown that factors influencing obesity and overweight are population-specific, influenced by socioeconomic, cultural, and genetic factors among others [ 45 , 47 ]. Singapore is a multiethnic society with a unique food culture influenced by various racial beliefs and traditions [ 48 ]. The differences in geographical, social, environmental, and genetic characteristics could define a different set of triggers and response to such weight loss apps.
Principal Findings
In this paper, we report the effectiveness of a weeklong AI-assisted weight loss app for improving overeating habits, snacking habits, immediate thinking, self-regulation of eating habits, depression, and physical activity. Interestingly, there were no significant improvements in the anxiety symptoms before and after using eTRIP, potentially due to the already low level of anxiety in those who completed the program (ie, ceiling effect). We also report corresponding qualitative user feedback on the experience with using eTRIP, where the users appreciated the app for enabling them to become more mindful of self-monitoring; personalized reminders with prompts and chatbot; food logging with image recognition; and engaging with a simple, easy, and appealing user interface. The significant improvements observed among the participants in this study reveal the potential of this app to influence weight loss in the context of a Southeast Asian cohort with overweight and obesity. The qualitative feedback also informs future app development to enhance user engagement and reduce dropout rates.
Eating habits contribute to overweight and obesity [ 49 , 50 ]. Encouraged by an obesogenic environment, overeating is commonly triggered by situational factors such as food novelty or variety, social company (eg, eating with certain people), affect emotional states (which trigger emotional eating), and distractions (eg, concurrent tasks) [ 30 , 50 - 53 ]. Other studies have suggested that people at risk for obesity exhibit hyperresponsivity in the neural reward system to calorie-dense foods, which is associated with increased food consumption [ 54 ]. Alongside users’ feedback that the app made them more mindful of their eating patterns, the significant improvement in overeating and snacking habits could have been due to an increased awareness of one’ maladaptive eating habits and subsequently, the motivation to change. This coincides with a review that reported the effectiveness of mindful eating interventions on reducing food consumption in people with overweight and obesity [ 55 ]. Our qualitative findings showed that by self-monitoring one’s eating behavior through chatbot-initiated check-ins, one could enhance mindful eating and reduce overeating without the need for undergoing mindful eating training. This could eventually lead to a reduction in total food consumption and weight loss. However, more quantitative evidence is needed to support this point.
It is noteworthy that some participants reported skipping meals as planned, which might have led to reduced energy consumption. However, this has to be examined further, as studies have shown that the calories avoided during a skipped meal may be compensated by an increase in snacking or overeating during mealtimes [ 56 ]. One additional element that can be explored in future studies is the effectiveness of promoting healthy snacking, which includes snacking on foods rich in proteins, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, as opposed to nutrient-poor and energy-dense foods [ 57 , 58 ]. These healthier alternatives have been found not only to be associated with earlier satiety but also to be more nutritious, with their contents being more consistent with the established dietary recommendations and guidelines [ 59 , 60 ]. This strategy can be explored in conjunction with the current approach to decrease participants’ overall snacking habits.
The improvement in the self-regulation of eating habits could be attributed to several factors, including the app content focused on reminding participants of their weight loss goals and to adopt healthier eating habits of less snacking and overeating during mealtimes. In particular, in commonly stigmatized populations like those with overweight and obesity, personalization of interventions enhances one’s feeling of being taken care of, nurtured, and respected, providing them with a sense of confidence [ 61 ]. This may have improved individuals’ willingness to engage with the eTRIP content, knowing that they would be well-respected and seen as individuals through personalized chatbot conversations and reminders [ 62 ]. Other studies have shown that personalized eHealth interventions are more effective than conventional programs in enhancing weight loss maintenance, BMI, waist circumference, and various other metabolic indicators [ 63 ].
In conjunction with improvements in eating habits, participants also engaged in greater levels of physical activity by the end of this study. Increased health consciousness and self-education about the impacts and types of physical activity are factors that may explain the observed increased level of physical activity among the participants [ 64 ]. Various studies have found that a combination of diet and exercise is superior to diet-only interventions in inducing weight loss [ 65 ]. The level of physical activity is also an important factor for improving long-term weight loss [ 66 - 68 ]. Moderate amounts of physical activity were observed to prevent weight regain after weight loss [ 65 , 68 , 69 ]. In addition, the American College of Sports Medicine recommends 200-300 minutes of moderate physical activity a week to prevent similar weight regain [ 70 ]. In our study, low and moderate levels of exercise were seen to increase significantly among the participants. Although the sustainability of the increase in the exercise levels is still unknown, the preliminary data are encouraging to show the potential of the app in impacting physical activity. The amounts of high levels of exercise were, however, not impacted significantly. Additional interventions, including the provision of educational materials about the benefits of and types of exercise, along with personalized reminders for exercise can potentially further increase the success of the app in increasing moderate and high levels of exercise among its participants [ 71 , 72 ].
In addition to improvements in the eating habits and levels of physical activity, there were changes in the psychological factors among the participants. The mean depressive symptoms were significantly decreased at the end of the weeklong program. Various studies have shown that healthy living characterized by various factors such as healthy eating and sufficient levels of physical activity have the potential to positively impact psychological factors such as mood and emotions [ 73 ]. Healthy eating with adherence to dietary recommendations has been found to reduce the levels of inflammation, increase the levels of various micronutrients such as vitamins, and regulate the levels of simple sugars, all of which are protective against mental illnesses, especially depression [ 73 - 76 ]. Studies have also shown that the use of chatbots in the app may decrease depressive symptoms among some participants. Chatbots provide individuals the ability to provide self-care in an environment that is neither costly nor stigmatizing [ 77 ]. This may enable participants to be more open with their emotions, as well as to have an outlet to gain relief through their interaction with the chatbot as a proxy of human interaction [ 77 ]. Studies have shown that improvements in psychological factors such as depressive symptoms have been positively associated with weight loss and maintenance, further increasing the effectiveness of weight loss efforts among participants with overweight and obesity [ 45 ].
Strengths and Limitations
This study was the first to characterize the effectiveness of an AI-assisted weight loss app in the context of a Southeast Asian cohort. One strength of this study was the demographics of the participants, which was generally representative of the Singaporean population in terms of sex and ethnicity. The consideration of population-specific determinants of obesity and overweight during the design of the app would have also increased its applicability in this population [ 78 ], having considered the various nuances and practical needs of its target demographic. For example, the food image recognition system, which was built based on local food items, reduced the amount of time and effort required for the logging of food, improved the usability of the intervention, and enhanced user experience. The success of this app thus provides evidence that the consideration of population-specific underpinnings and practical requirements were essential toward the successful design and implementation of a weight loss intervention [ 79 ].
Although the app presents significant potential in this weeklong trial, this study is limited due to its short time frame. This presents with difficulties in understanding the midterm to long-term impacts of using the app. However, it is reassuring that despite the limited time frame of this study, the various behavioral and psychological indicators were observed to be significantly improved. Through the feedback gathered from the participants, the app may be improved in specific aspects, including (1) refining choices available for the various survey fields such as the provision of a drop-down menu for the selection of weight loss goals; (2) providing additional feedback and weekly summaries to the participants for knowledge of their progress in various aspects; and (3) providing educational materials to provide participants with the means to improve, especially for what to do after eating lapses and suggestions for healthy snacking. Another limitation was the lack of feedback quotes from older individuals as opposed to those from younger individuals. This could be due to various reasons, of which decreased media literacy among older individuals might present additional obstacles for the provision of feedback [ 80 ]. Lastly, we did not collect information on the participants’ medical and pharmacological history, where certain diseases and drugs are known to influence weight gain through various metabolic and neural pathways. Weight and waist circumference were also self-reported, and thus, data from these measures should be interpreted cautiously.
This study was the first to characterize the effectiveness of an AI-assisted weight loss app in the context of a Southeast Asian cohort. The positive findings of this study show the feasibility of implementing this app and the large potential it has in impacting weight loss efforts, especially among individuals with overweight and obesity. Efforts should be made to lengthen and upscale this program for a greater understanding of the midterm to long-term effects of this app.
Conflicts of Interest
AMC has served on advisory boards to Eli Lilly and Boehringer Ingelheim and received grant support, on behalf of the University of Pennsylvania, from Eli Lilly and WW (Weight Watchers). No other authors declare conflicts of interest.
TREND (Transparent Reporting of Evaluations with Nonrandomized Designs) checklist.
Details on outcome measures.
- Abdelaal M, le Roux CW, Docherty NG. Morbidity and mortality associated with obesity. Ann Transl Med. Apr 2017;5(7):161. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- OECD. The heavy burden of obesity: the economics of prevention. OECD Health Policy Studies. Oct 10, 2019.:1-100. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hawkes C, Smith TG, Jewell J, Wardle J, Hammond RA, Friel S, et al. Smart food policies for obesity prevention. The Lancet. Jun 2015;385(9985):2410-2421. [ CrossRef ]
- Johns DJ, Hartmann-Boyce J, Jebb SA, Aveyard P, Behavioural Weight Management Review Group. Diet or exercise interventions vs combined behavioral weight management programs: a systematic review and meta-analysis of direct comparisons. J Acad Nutr Diet. Oct 2014;114(10):1557-1568. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Clarke B, Kwon J, Swinburn B, Sacks G. Understanding the dynamics of obesity prevention policy decision-making using a systems perspective: A case study of Healthy Together Victoria. PLoS One. 2021;16(1):e0245535. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Chew HSJ, Koh WL, Ng JSHY, Tan KK. Sustainability of weight loss through smartphone apps: systematic review and meta-analysis on anthropometric, metabolic, and dietary outcomes. J Med Internet Res. Sep 21, 2022;24(9):e40141. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Booth HP, Prevost TA, Wright AJ, Gulliford MC. Effectiveness of behavioural weight loss interventions delivered in a primary care setting: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Fam Pract. Dec 2014;31(6):643-653. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- LeBlanc ES, Patnode CD, Webber EM, Redmond N, Rushkin M, O'Connor EA. Behavioral and pharmacotherapy weight loss interventions to prevent obesity-related morbidity and mortality in adults: updated evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. Sep 18, 2018;320(11):1172-1191. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- MacLean PS, Wing RR, Davidson T, Epstein L, Goodpaster B, Hall KD, et al. NIH working group report: Innovative research to improve maintenance of weight loss. Obesity (Silver Spring). Jan 2015;23(1):7-15. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Daley A, Jolly K, Madigan C, et al. A brief behavioural intervention to promote regular self-weighing to prevent weight regain after weight loss: a RCT. Public Health Research. 2019.:7. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hadžiabdić MO, Mucalo I, Hrabač P, Matić T, Rahelić D, Božikov V. Factors predictive of drop-out and weight loss success in weight management of obese patients. J Hum Nutr Diet. Feb 2015;28 Suppl 2:24-32. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Evans D. MyFitnessPal. Br J Sports Med. Jan 27, 2016;51(14):1101-1102. [ CrossRef ]
- Garcia R. Utilization, Integration & Evaluation of LIVESTRONG's MyPlate Telehealth Technology. URL: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273635099_Utilization_Integration_Evaluation_of_LIVESTRONG's_MyPlate_Telehealth_Technology [accessed 2023-04-01]
- Hartman SJ, Nelson SH, Weiner LS. Patterns of Fitbit use and activity levels throughout a physical activity intervention: exploratory analysis from a randomized controlled trial. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. Feb 05, 2018;6(2):e29. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Yao J, Tan CS, Chen C, Tan J, Lim N, Müller-Riemenschneider F. Bright spots, physical activity investments that work: National Steps Challenge, Singapore: a nationwide mHealth physical activity programme. Br J Sports Med. Sep 2020;54(17):1047-1048. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Lim SL, Johal J, Ong KW, Han CY, Chan YH, Lee YM, et al. Lifestyle intervention enabled by mobile technology on weight loss in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: randomized controlled trial. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. Apr 13, 2020;8(4):e14802. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Birkett D. Disinhibition. In: The Psychiatry of Stroke. London, UK. Routledge; 2012;150-161.
- Carels RA, Hoffman J, Collins A, Raber AC, Cacciapaglia H, O'Brien WH. Ecological momentary assessment of temptation and lapse in dieting. Eat Behav. 2001;2(4):307-321. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kwasnicka D, Dombrowski SU, White M, Sniehotta FF. N-of-1 study of weight loss maintenance assessing predictors of physical activity, adherence to weight loss plan and weight change. Psychol Health. Jun 2017;32(6):686-708. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- McKee HC, Ntoumanis N, Taylor IM. An ecological momentary assessment of lapse occurrences in dieters. Ann Behav Med. Dec 2014;48(3):300-310. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Chew HSJ, Loong SSE, Lim SL, Tam WSW, Chew NWS, Chin YH, et al. Socio-demographic, behavioral and psychological factors associated with high BMI among adults in a Southeast Asian multi-ethnic society: a structural equation model. Nutrients. Apr 10, 2023;15(8):1826. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Des Jarlais DC, Lyles C, Crepaz N, TREND Group. Improving the reporting quality of nonrandomized evaluations of behavioral and public health interventions: the TREND statement. Am J Public Health. Mar 2004;94(3):361-366. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Knapp T. Why is the one-group pretest-posttest design still used? Clin Nurs Res. Oct 2016;25(5):467-472. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang AG, Buchner A. G*Power 3: a flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav Res Methods. May 2007;39(2):175-191. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Chew HSJ. The use of artificial intelligence-based conversational agents (chatbots) for weight loss: scoping review and practical recommendations. JMIR Med Inform. Apr 13, 2022;10(4):e32578. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Chew HSJ, Achananuparp P. Perceptions and needs of artificial intelligence in health care to increase adoption: scoping review. J Med Internet Res. Jan 14, 2022;24(1):e32939. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Chew HSJ, Gao Y, Shabbir A, Lim SL, Geetha K, Kim G, et al. Personal motivation, self-regulation barriers and strategies for weight loss in people with overweight and obesity: a thematic framework analysis. Public Health Nutr. Feb 22, 2022;25(9):2426-2435. [ CrossRef ]
- Chew H, Lim S, Kim G, Kayambu G, So BYJ, Shabbir A, et al. Essential elements of weight loss apps for a multi-ethnic population with high BMI: a qualitative study with practical recommendations. Transl Behav Med. Apr 03, 2023;13(3):140-148. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Chew HSJ, Ang WHD, Lau Y. The potential of artificial intelligence in enhancing adult weight loss: a scoping review. Public Health Nutr. Feb 17, 2021;24(8):1993-2020. [ CrossRef ]
- Chew HSJ, Lau ST, Lau Y. Weight-loss interventions for improving emotional eating among adults with high body mass index: A systematic review with meta-analysis and meta-regression. Eur Eat Disord Rev. Jul 2022;30(4):304-327. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Chew HSJ, Sim KLD, Choi KC, Chair SY. Effectiveness of a nurse-led temporal self-regulation theory-based program on heart failure self-care: A randomized controlled trial. Int J Nurs Stud. Mar 2021;115:103872. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hall PA, Fong GT. Temporal self-regulation theory: A model for individual health behavior. Health Psychology Review. Mar 2007;1(1):6-52. [ CrossRef ]
- Abraham C, Michie S. A taxonomy of behavior change techniques used in interventions. Health Psychol. May 2008;27(3):379-387. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Chew HSJ, Li J, Chng S. Improving adult eating behaviours by manipulating time perspective: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol Health. Jan 24, 2023.:1-17. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Chew HSJ, Rajasegaran NN, Chng S. Effectiveness of interactive technology-assisted interventions on promoting healthy food choices: a scoping review and meta-analysis. Br J Nutr. Jan 25, 2023;130(7):1250-1259. [ CrossRef ]
- Verplanken B, Orbell S. Reflections on past behavior: a self‐report index of habit strength. J Applied Social Pyschol. Jul 31, 2006;33(6):1313-1330. [ CrossRef ]
- Chng S, Chew HSJ, Joireman J. When time is of the essence: Development and validation of brief consideration of future (and immediate) consequences scales. Personality and Individual Differences. Feb 2022;186:111362. [ CrossRef ]
- Kliemann N, Beeken RJ, Wardle J, Johnson F. Development and validation of the Self-Regulation of Eating Behaviour Questionnaire for adults. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. Aug 02, 2016;13:87. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Craig CL, Marshall AL, Sjöström M, Bauman AE, et al. International Physical Activity Questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise. 2003;35(8):1381-1395. [ CrossRef ]
- Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB, Monahan PO, Löwe B. Anxiety disorders in primary care: prevalence, impairment, comorbidity, and detection. Ann Intern Med. Mar 06, 2007;146(5):317-325. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JBW. The Patient Health Questionnaire-2: validity of a two-item depression screener. Med Care. Nov 2003;41(11):1284-1292. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- IBM SPSS statistics for Windows. IBM Corp. May 21, 2021. URL: https://www.ibm.com/products/spss-statistics [accessed 2024-03-28]
- VanderWeele T, Mathur M. Some desirable properties of the Bonferroni correction: is the Bonferroni correction really so bad? Am J Epidemiol. Mar 01, 2019;188(3):617-618. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Bengtsson M. How to plan and perform a qualitative study using content analysis. NursingPlus Open. 2016;2:8-14. [ CrossRef ]
- Varkevisser RDM, van Stralen MM, Kroeze W, Ket JCF, Steenhuis IHM. Determinants of weight loss maintenance: a systematic review. Obes Rev. Feb 2019;20(2):171-211. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Forman EM, Goldstein SP, Crochiere RJ, Butryn ML, Juarascio AS, Zhang F, et al. Randomized controlled trial of OnTrack, a just-in-time adaptive intervention designed to enhance weight loss. Transl Behav Med. Nov 25, 2019;9(6):989-1001. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Qasim A, Turcotte M, de Souza RJ, Samaan MC, Champredon D, Dushoff J, et al. On the origin of obesity: identifying the biological, environmental and cultural drivers of genetic risk among human populations. Obes Rev. Feb 2018;19(2):121-149. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Executive summary on National Population Health Survey 2016/17. Singapore MoH. URL: https://www.moh.gov.sg/docs/librariesprovider5/resources-statistics/reports/executive-summary-nphs-2016_17.pdf [accessed 2023-04-01]
- McCrory MA, Suen VM, Roberts SB. Biobehavioral influences on energy intake and adult weight gain. The Journal of Nutrition. Dec 2002;132(12):3830S-3834S. [ CrossRef ]
- Davis C, Levitan RD, Muglia P, Bewell C, Kennedy JL. Decision-making deficits and overeating: a risk model for obesity. Obes Res. Jun 2004;12(6):929-935. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hetherington MM. Cues to overeat: psychological factors influencing overconsumption. Proc. Nutr. Soc. Feb 28, 2007;66(1):113-123. [ CrossRef ]
- Borer K. Understanding human physiological limitations and societal pressures in favor of overeating helps to avoid obesity. Nutrients. Jan 22, 2019;11(2):227. [ CrossRef ]
- Borer KT. Why we eat too much, have an easier time gaining than losing weight, and expend too little energy: suggestions for counteracting or mitigating these problems. Nutrients. Oct 26, 2021;13(11):3812. [ CrossRef ]
- Stice E, Burger K. Neural vulnerability factors for obesity. Clin Psychol Rev. Mar 2019;68:38-53. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Warren JM, Smith N, Ashwell M. A structured literature review on the role of mindfulness, mindful eating and intuitive eating in changing eating behaviours: effectiveness and associated potential mechanisms. Nutr. Res. Rev. Jul 18, 2017;30(2):272-283. [ CrossRef ]
- Savige G, Macfarlane A, Ball K, Worsley A, Crawford D. Snacking behaviours of adolescents and their association with skipping meals. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. Sep 17, 2007;4:36. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Njike VY, Smith TM, Shuval O, Shuval K, Edshteyn I, Kalantari V, et al. Snack food, satiety, and weight. Adv Nutr. Sep 2016;7(5):866-878. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Larson N, Story M. A review of snacking patterns among children and adolescents: what are the implications of snacking for weight status? Child Obes. Apr 2013;9(2):104-115. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Lucan SC, Karpyn A, Sherman S. Storing empty calories and chronic disease risk: snack-food products, nutritive content, and manufacturers in Philadelphia corner stores. J Urban Health. May 2010;87(3):394-409. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hess J, Jonnalagadda S, Slavin J. What is a snack, why do we snack, and how can we choose better snacks? The definitions of snacking, motivations to snack, contributions to dietary intake, and recommendations for improvement. The FASEB Journal. Apr 2016;30(S1):466-475. [ CrossRef ]
- Coulter A, Entwistle V, Eccles A, Ryan S, Shepperd S, Perera R. Personalised care planning for adults with chronic or long-term health conditions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;2015(3):1-117. [ CrossRef ]
- Elwyn G, Frosch D, Thomson R, Joseph-Williams N, Lloyd A, Kinnersley P, et al. Shared decision making: a model for clinical practice. J Gen Intern Med. Oct 2012;27(10):1361-1367. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Lau Y, Chee DGH, Chow XP, Cheng LJ, Wong SN. Personalised eHealth interventions in adults with overweight and obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Prev Med. Mar 2020;132:106001. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Wang Q, Egelandsdal B, Amdam GV, Almli VL, Oostindjer M. Diet and physical activity apps: perceived effectiveness by app users. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. Apr 07, 2016;4(2):e33. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kim B, Choi D, Jung C, Kang S, Mok J, Kim C. Obesity and physical activity. J Obes Metab Syndr. Mar 2017;26(1):15-22. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Anderson JW, Konz EC, Frederich RC, Wood CL. Long-term weight-loss maintenance: a meta-analysis of US studies. Am J Clin Nutr. Nov 2001;74(5):579-584. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Fogelholm M, Kukkonen-Harjula K. Does physical activity prevent weight gain--a systematic review. Obes Rev. Oct 2000;1(2):95-111. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Thomas DM, Bouchard C, Church T, Slentz C, Kraus WE, Redman LM, et al. Why do individuals not lose more weight from an exercise intervention at a defined dose? An energy balance analysis. Obesity Reviews. Jun 11, 2012;13(10):835-847. [ CrossRef ]
- Saris WHM, Blair SN, van Baak MA, Eaton SB, Davies PSW, Di Pietro L, et al. How much physical activity is enough to prevent unhealthy weight gain? Outcome of the IASO 1st Stock Conference and consensus statement. Obes Rev. May 2003;4(2):101-114. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Haskell W, Lee I, Pate R, Powell K, Blair S, Franklin B. Physical activity and public health: updated recommendation for adults from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007;39(8):1423-1434. [ CrossRef ]
- Fredriksson SV, Alley SJ, Rebar AL, Hayman M, Vandelanotte C, Schoeppe S. How are different levels of knowledge about physical activity associated with physical activity behaviour in Australian adults? PLoS One. 2018;13(11):e0207003. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Muntaner-Mas A, Sanchez-Azanza VA, Ortega FB, Vidal-Conti J, Borràs PA, Cantallops J, et al. The effects of a physical activity intervention based on a fatness and fitness smartphone app for University students. Health Informatics J. 2021;27(1):1460458220987275. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hautekiet P, Saenen ND, Martens DS, Debay M, Van der Heyden J, Nawrot TS, et al. A healthy lifestyle is positively associated with mental health and well-being and core markers in ageing. BMC Med. Sep 29, 2022;20(1):328. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Lassale C, Batty GD, Baghdadli A, Jacka F, Sánchez-Villegas A, Kivimäki M, et al. Healthy dietary indices and risk of depressive outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Mol Psychiatry. Jul 2019;24(7):965-986. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Petridou ET, Kousoulis AA, Michelakos T, Papathoma P, Dessypris N, Papadopoulos FC, et al. Folate and B12 serum levels in association with depression in the aged: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging Ment Health. Sep 2016;20(9):965-973. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Wang C, Yang T, Wang G, Zhao Y, Yang L, Bi B. Association between dietary patterns and depressive symptoms among middle-aged adults in China in 2016-2017. Psychiatry Res. Feb 2018;260:123-129. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Vaidyam AN, Wisniewski H, Halamka JD, Kashavan MS, Torous JB. Chatbots and conversational agents in mental health: a review of the psychiatric landscape. Can J Psychiatry. Jul 2019;64(7):456-464. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Population in brief. National Population and Talent Division SG. 2022. URL: https://www.strategygroup.gov.sg/files/media-centre/publications/population-in-brief-2022.pdf [accessed 2023-04-01]
- Hebden L, Cook A, van der Ploeg HP, King L, Bauman A, Allman-Farinelli M. A mobile health intervention for weight management among young adults: a pilot randomised controlled trial. J Hum Nutr Diet. Aug 2014;27(4):322-332. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Rasi P, Vuojärvi H, Rivinen S. Promoting media literacy among older people: a systematic review. Adult Education Quarterly. May 25, 2020;71(1):37-54. [ CrossRef ]
Abbreviations
Edited by A Mavragani; submitted 26.01.23; peer-reviewed by YC Liu, V Jennings; comments to author 07.12.23; revised version received 12.12.23; accepted 12.03.24; published 07.05.24.
©Han Shi Jocelyn Chew, Nicholas WS Chew, Shaun Seh Ern Loong, Su Lin Lim, Wai San Wilson Tam, Yip Han Chin, Ariana M Chao, Georgios K Dimitriadish, Yujia Gao, Jimmy Bok Yan So, Asim Shabbir, Kee Yuan Ngiam. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (https://www.jmir.org), 07.05.2024.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work, first published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, is properly cited. The complete bibliographic information, a link to the original publication on https://www.jmir.org/, as well as this copyright and license information must be included.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Download full-text PDF Download full-text PDF ... Join for free. Public Full ... 2020 with our research paper Artificial intelligence in the context of digitalization and internationalization of ...
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Innovation Iain M. Cockburn, Rebecca Henderson, and Scott Stern NBER Working Paper No. 24449 March 2018 JEL No. L1 ABSTRACT Artificial intelligence may greatly increase the efficiency of the existing economy. But it may have an even larger impact by serving as a new general-purpose "method of invention ...
The Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research (JAIR) is dedicated to the rapid dissemination of important research results to the global artificial intelligence (AI) community. The journal's scope encompasses all areas of AI, including agents and multi-agent systems, automated reasoning, constraint processing and search, knowledge ...
Artificial intelligence and machine learning research: towards digital transformation at a global scale ... Download references. Author information. Authors and Affiliations. ... Brahimi, T. et al. Artificial intelligence and machine learning research: towards digital transformation at a global scale. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 13, 3319 ...
The Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research (www.jair.org) covers all areas of artificial intelligence, publishing refereed research articles, survey articles, and technical notes. JAIR was established in 1993 as one of the very first open access scientific journals on the Web. Since it began publication in 1993, JAIR has had a major impact on the field, and has been continuously ranked as ...
The field of artificial intelligence (AI) has shown an upward trend of growth in the 21st century (from 2000 to 2015). The evolution in AI has advanced the development of human society in our own time, with dramatic revolutions shaped by both theories and techniques. However, the multidisciplinary and fast-growing features make AI a field in which it is difficult to be well understood. In this ...
The journal of Artificial Intelligence (AIJ) welcomes papers on broad aspects of AI that constitute advances in the overall field including, but not limited to, cognition and AI, automated reasoning and inference, case-based reasoning, commonsense reasoning, computer vision, constraint processing, ethical AI, heuristic search, human interfaces, intelligent robotics, knowledge representation ...
Artificial Intelligence Volume 7 Aims and Scope of the Series Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a rapidly developing multidisciplinary research area that aims to solve increasingly complex problems. In today's highly integrated world, AI promises to become a robust and powerful means for obtaining solutions to previously unsolvable problems.
Subjects: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV) [19] arXiv:2405.01472 (cross-list from cs.RO) [ pdf , other ] Title: IntervenGen: Interventional Data Generation for Robust and Data-Efficient Robot Imitation Learning
In this post, we list the top 70 research papers and projects in deep learning, published recently. Feel free to download. Share your own research papers with us to be added to this list. Person re-identification by deep learning multi-scale representations. Classification of Diabetic Retinopathy Images by Using Deep Learning Models.
Artificial neural networks (ANNs) are inspired by the functionality of the brain. Inputs are translated into signals which are passed through a network of artificial neurons to generate outputs that are interpreted as responses to the inputs. Adding more neurons and layers allow ANNs to tackle more complex problems.
Although artificial intelligence is the product of science-fiction literature, it currently represents a significant branch of computer science dealing with intelligent behavior, machine learning, and machine adaptation. It has become a... more. Download. by István Hegedűs. 10.
These papers provide a breadth of information about Artificial intelligence (AI − the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems) that is generally useful and interesting from a computer science perspective. ... Download Free PDF. 10 Important AI Research Papers. ... Artificial Intelligence Research ...
4. arXiv.org. arXiv.org is not the and top-voted great place to read research papers on a wide variety of topics, but also functions as a repository of ML and DL papers. The collection of research papers on the platform are over 1.5 million, with over 36,000 papers for machine learning alone. It is a great place for those looking to get started ...
music theory, sound processing are some of the major areas on which research in Music and Artificial Intelligence are focusing on. Eg:chucks, Orchextra, smartmusic etc. 7. Antivirus: Artificial intelligence (AI) techniques have played increasingly important role in antivirus detection. At present,
Articulating a set of research library guiding principles for AI is useful to influence policy and advocate for the responsible development and deployment of AI technologies, promote ethical and transparent practices, and build trust among stakeholders, within research libraries as well as across the research environment.
6 Conclusion. Considering AI as a general purpose technology that improves productivity growth, our analysis has shown that AI adoption raises aggregate output, consumption and invest-ment. The impact on inflation depends on households' and firms' anticipation of future income growth from AI.
Download Free PDF. View PDF. [CASE STUDIES JOURNAL VOL-2, ISSUE 6 ISSN (2305-509X)] July 1, 2013 Research Paper on Artificial Intelligence 1) Pooja Agarwal 2) Pooja Yadav 3) Neelam Sharma 4) Ruchika Uniyal 5) Swati Sharma (Student, Department of Computer Science & Engg.
Background: Falls and their consequences are a serious public health problem worldwide. Each year, 37.3 million falls requiring medical attention occur. Therefore, the analysis of fall risk is of great importance for prevention. Artificial intelligence (AI) represents an innovative tool for creating predictive statistical models of fall risk through data analysis.
9. "Advancements in NLP: Contextual Understanding in Language Models" by Prof. N. Rodriguez. This paper discusses the latest strides in natural language processing, highlighting the evolution of contextual language models for nuanced text understanding and generation. 10. "Human-Robot Collaboration: AI's Role in Robotics" by Dr. S. Khan.
A research paper on artificial intelligence - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
Background: A plethora of weight management apps are available, but many individuals, especially those living with overweight and obesity, still struggle to achieve adequate weight loss. An emerging area in weight management is the support for one's self-regulation over momentary eating impulses. Objective: This study aims to examine the feasibility and effectiveness of a novel artificial ...
25654. Research Paper on Artificial I ntelligence. Rajiv Gupta. Chandigarh University, Chandigarh, Haryana. Abstract: This branch of computer science is concerned with making computers behave like ...
This paper discusses the dispute resolution procedure that innovative digital commerce has adopted for the future for sustainable business. As digital trade becomes increasingly important for economic growth, trade-related disputes must be settled in both business and consumer situations. This study examines the advantages of using digital technology to resolve disputes involving digital trade ...
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force in healthcare, offering a. plethora of applications that promise to revolutionize the industry. This paper explores the. diverse ...