An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Inj Violence Res
- v.11(2); 2019 Jul

Causes and consequences of adolescent dating violence: a systematic review
Stella r. taquette.
a Department of Pediatrics, State University of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
Denise Leite Maia Monteiro
b Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, State University of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
Background:
Adolescent dating violence (ADV) is highly prevalent and can have serious health consequences, including homicides, and be a predictor of intimate partner violence in adulthood. This review aims to systematize the knowledge produced in recent empirical investigations in health that focus on the causes and consequences of ADV to subsidize new research and prevention programs.
Review of studies published in PubMed over the last five years through MeSH Database: “Intimate Partner Violence” AND “Adolescent” NOT “prevention and control” NOT “Adult”.
We analyzed 35 papers, of which 71.4% were developed in the USA. Some studies have shown prevalence greater than 50% in both genders, both as victims and perpetrators, with more serious consequences for females. Three main thematic cores were identified in the studies: ADV-related vulnerabilities, circularity of violence and ADV-associated health problems. Data indicate that ADV is deep-seated in the patriarchal culture and is more frequent in connection with racism, heterosexism and poverty. It occurs in a circular way and is linked to other forms of violence in different contexts (family, school, community and social media). It is associated with health problems such as depression, anxiety, low self-esteem, alcohol and drugs abuse and unprotected sex.
Conclusions:
The knowledge produced in the studies reviewed reveals the urgency and importance of implementing early preventive actions in schools, involving families and the community. These should focus on the deconstruction of current cultural gender patterns, based on their historical origin, in order to support emancipatory and liberating pedagogical approaches.
Introduction
Adolescent Dating Violence (ADV) is defined as any intentional, psychological/emotional, physical or sexual abuse that occurs between people involved in a romantic relationship. 1 It is a significant event in several parts of the world 2 and can have immediate and late health consequences, and women are the most serious and frequent injury victims. 3 , 4 ADV is often not perceived by those involved or valued by society, although it may culminate in murders, usually of women, as in abusive relationships in adulthood. 5 ADV is a predictor of marital violence in adulthood. 5 Femicide in adulthood has been addressed as an important public health problem and has been gaining prominence also concerning the health of adolescents. 6 , 7
Several population-based studies have shown health problems associated with ADV, including depression, anxiety, and alcohol and other drugs abuse. 8 Other authors point out the sexual risk behavior of STI/AIDS and the low academic performance as negative consequences of ADV. 9 In addition, there is evidence that violence in other settings, such as in the family and neighborhood may be related to ADV. 8
ADV is a health problem in different parts of the world and one of the main issues to be tackled. 7 Consequently, several policies and action programs have been implemented, especially in the school setting, the main arena for socialization and construction of adolescents’ identity. 10 , 11 However, the issue is hardly discussed in developing countries, and knowledge about the subject is still incipient, hampering sensitization of people about the problem and policy formulation to address it. 12
This bibliographic review is being proposed considering the challenges faced in addressing situations of violence involving intimate adolescents and the recognition of the need to act early to prevent this type of violence. It aims to systematize the knowledge produced in empirical investigations in the field of health focused on the causes and consequences of ADV. This review intends to subsidize new research and prevention programs that contribute to curb violence in intimate adolescent relationships.
This is a review of studies published in PubMed, the most important database of health studies. This database was chosen because it is the one that gathers the largest number of bibliographical sources from around the world in the field of health and journals of recognized quality. In general, papers published in qualified journals from other databases are also found in PubMed.
The following search strategy was followed on June 28, 2017 through MeSH Database: “Intimate Partner Violence” AND “Adolescent” NOT “prevention and control” NOT “Adult” in the last five years. Most of the articles found with this search strategy predominantly use the terminology Dating Violence.
Fifty-nine papers were made available. Then, after reading abstracts, 13 papers were excluded from the established inclusion criteria – papers with full-text in English, derived from empirical research with adolescents on ADV: 9 because they were studies with children and 4 with adults. After further reading, eleven more papers were excluded: 6 because they were not on the subject of the study, 2 because the full-texts were not available, 2 because they were review papers and 1 because they were published in German. Thus, a total of 35 papers were analyzed, as can be seen in the chart below ( Figure 1 ).

The thematic analysis of papers was carried out. First, separately by each author. Subsequently, authors showed each other’s analyses and reached the final categories through dialogue with literature. The following steps marked by Minayo13 were followed: comprehension reading and rereading to familiarize with data; identification of themes of analysis considering the objectives of the study; classification of themes and comparative dialogue with literature; and elaboration of interpretative synthesis.
In addition to papers of this review shown in Table 1 , ,2 2 and and3 3 in the results, other 19 papers included in the introduction to the text and in data discussion were read.
*TDV: Teen Dating Violence; ** IPV: Intimate Partner Violence; *** RR: Relative Risk
* TDV: Teen Dating Violence; ** IPV: Intimate Partner Violence; *** RR: Relative Risk
Results and Discussion
Most of the studies used a quantitative method, of which 25 (71.4%) were cross-sectional studies and nine (25.7%) were longitudinal cohort studies. Only one (2.8%) of the studies used a qualitative method using focal groups and participant observation. As for the location, 26 were conducted in North America (25 in the U.S. and one in Canada); four in Africa (1 in Egypt, 2 in South Africa and 1 in several countries - Egypt, South Africa, Liberia, Kenya, Malawi, Rwanda and Zambia); 4 in Europe (1 UK, 2 Spain and 1 Sweden); and 1 in Asia (Japan).
ADV prevalence rates were variable, with the highest one found at 70.7%, in a study carried out in Egypt with 400 adolescents of both genders, referring to any type of ADV, whether psychological, physical or sexual. 14 The second highest rate was 70%, shown in a research developed in the U.S. with 399 adolescents. 15 A study conducted in seven African capitals evidenced ADV prevalence ranging from 26.5% to 48%. 16 In other studies with a higher number of adolescents, rates were lower: 33.4% in a study of 14,190 secondary school students in the U.S. 17 and 27.7% in a sample of 6,390 American adolescents. 18 It is worth noting that there are different types of dating-related abuse and that, according to Reidy’s study, 19 few adolescents engage in multiple forms of violence and most young people are not perpetrators.
Considering the aim of this review to highlight the causes and consequences of ADV, three main thematic cores were identified in the studies: I– ADV-related vulnerabilities; II– circularity of violence; and III– ADV-associated health problems. We sorted papers in three tables, in a didactic way according to the main thematic core that originated them, although papers identified drew characteristics of more than one thematic core or all, as described and analyzed below. Table 1 , ,2 2 and and3 3 show the study design, location, thematic categories, objectives, sample studied and results/conclusions. They are shown at the end of each category.
I - ADV-related vulnerabilities
The concept of vulnerability applied to health emerged and gained momentum in the 1990s in the face of the HIV/AIDS epidemic. 20 It refers to a set of aspects, not only individual, but also collective and social that lead to greater susceptibility to illness. In the analysis of papers in this bibliographic review, we observed that certain vulnerabilities, similar to those observed in the HIV/AIDS epidemic, are identified as ADV-related, including gender inequality, low age, racial discrimination, homophobia and poverty.
Among these factors, what stands out the most in the reviewed works is gender inequality. This feature underpins the patriarchal culture, in which the social roles played by men and women are assigned different powers. Men are domineering and women dominated, which makes men naturally aggressive and strong, and women, in turn, fragile and helpless. Oftentimes, this domination relationship that justifies violence in certain situations is not perceived even in cases of physical abuse that are sometimes considered normal in a dating relationship. 3
The patriarchal culture favors the boys’ perpetration of violence, because when they feel their virilities threatened, they try to impose themselves by violent means and consider this violence of lesser importance. 21 Thus, gender inequality is a risk factor for violence against women in this age group. 22 , 23
The revised papers reveal that both boys and girls are ADV victims and perpetrators, with prevalence varying according to the stage of adolescence. In some phases of adolescence, women are more perpetrators of physical and psychological violence than men, 24 , 25 differing from the characteristics of intimate partner violence in adulthood. 26 However, as for sexual violence, they are the main victims. Although reciprocal involvement in violence is pointed out as the most common pattern of ADV, the consequences are always worse for girls. 14 , 27 , 28
Gender violence, such as early marriage, abusive sexual behavior, deprivation of work and inheritance and the impediment of family visits 29 is trivialized or unrecognized in certain cultures. On the other hand, in cultures where this is recognized, ADV is less frequent, just as adolescents have more conservative sexual behavior and more egalitarian relationships. 30
Racial discrimination, poverty and heterosexism are vulnerabilities found in the studies analyzed that were associated to ADV. The World Conference Against Racism held in Durban in 2001 31 stresses the importance articulating between gender discrimination, racism, homophobia and class exploitation, common oppressions in the international globalization context. Alleyne-Green et al 32 observed that ADV is particularly more likely in non-white girls.
A higher prevalence of ADV among non-whites was also found by Earnest et al 33 in a study with 75,590 students. Some papers have shown that ADV is more prevalent in poverty contexts, especially in African Americans and among couples of sexual minority. 17 , 34 , 35 The higher rate of violence in same-gender couples in some studies leads to a reflection on the weight of heterosexism and homophobia in the context of social vulnerability for the occurrence of ADV. 18 , 36 , 37
II - Circularity of Violence
Violence in other contexts, such as in the family and in the neighborhood seems to be related to ADV, 15 , 38 , 39 corroborating with the idea of circularity of violence brought by some authors. 40 , 41 It is observed that structural violence of society that denies citizenship to some social groups is also related to community, intrafamily and interpersonal violence. It occurs in circular fashion in the diverse environments of adolescents’ socialization, dating relationships, family and friends. 2 Patterns of social interaction learned throughout life may predict future violent behavior in intimate relationships. However, not all who are exposed to violence become aggressive adolescents. 19 Cultural factors influence the emergence of ADV. A study conducted in United Kingdom and Spain revealed similar ADV rates in both countries. However, severe forms are more common in Spain, since in this country, milder expressions of violence are widely accepted as a normal event. 42
Part of the studies of this review evidences an association between hostile treatment, anger and aggressive responses and ADV. 24 Other studies have shown corporal punishment in the family and at school as ADV-associated factors. 14 ADV-bullying was a frequent finding. 17 , 18
The history of ill-treatment in childhood, witnessing intrafamily violence, poor care provided by parents and feeling insecure at school are found in several studies as strongly associated with ADV. 16 , 32 - 34
Psychological distress may be the causal role in the relationship between domestic violence and victimization in adolescence dating. 43 In addition, ADV can create a relationship pattern that persists in adulthood. 44 The ADV rate is high among adolescents, estimated at 70% in a study with 299 mothers who were victims of domestic violence and their adolescent children. Adolescents reported perpetrating at least one of three dating abuse types. 15 On the other hand, adolescents with a good family relationship, in which both parents are present, engage less in ADV and are less likely to tolerate or perpetrate some kind of violence in intimate relationships. 27 , 45 ADV perpetration is also lower when adolescents have more propositional peer networks and neighborhood social control. 41 The quality of the neighborhood is itself a contextual factor that can influence the emotional well-being of individuals. The bad neighborhood objective conditions, including poverty and instability of residence cause emotional distress that can increase the probability of ADV. 38
Another context associated to ADV identified in papers was that of virtual violence. 46 The popularity of using text messages, social media and Internet among adolescents can create opportunities for dating violence through virtual media. It includes attitudes such as monitoring, control, harassment or verbal and emotional abuse of a partner through technology, cell phones, threatening text or voice messages, or online publications of insulting content.
III- ADV-associated health problems
As mentioned in previous categories, the worst consequences of ADV are endured by females, and femicideis the most serious, the murder of women committed by men, typical of patriarchal regime, in which they are subjected to their control. 5 Murder is one of the leading causes of death in young women and adolescents in the United States. 47 However, none of the papers in this review focused on this serious and relevant issue. No studies were also found to relate ADV to suicide, another severe event in which a significant gender differential is evidenced, and women and sexual minorities are the most frequent victims. 48 , 49
The consequences of ADV observed in the studies analyzed were low self-esteem, depressive symptoms, psychiatric disorders, drug abuse, risky sexual behavior and low academic performance. 18 , 32 , 50 The more intense the violence, the greater the prevalence of severe psychiatric disorders common in adolescents. The association between psychiatric disorders and ADV varies with age, and the strength of the association decreased in magnitude with age. 51 The acceptance of psychological abuse seems to mediate the association between ADV and psychiatric disorders such as depression, anxiety and hostility. 44 The heavy consumption of alcoholic beverages and other drugs is associated with an increased perpetration of physical violence in dating. 41 Copp 38 identified that symptoms of anger and depression are found in cases of intimate partner violence associated with the disadvantageous neighborhood.
ADV is related to the use of chemical substances. 52 This association is found when both partners are drug users, when only one is a drug user and with different types of drugs (alcoholic beverages, marijuana). 53 In some studies, there was an intersection between ADV and substance use as a means of dealing with the disruption of the love relationship. 54
Final Considerations
This review evidences that the phenomenon of ADV is complex since it involves multiple causes of an individual, social and cultural nature that require intersectoral actions to address it. The revised studies further clarify the potential health impairments resulting from ADV. However, it is worth highlighting the lack of research on homicides of adolescent and young women that could reveal other relevant angles of the problem to public health. The main recommendation of this review is the urgent and essential need of preventive actions that focus on the deconstruction of current cultural patterns of gender based on the revival of its history, in order to support emancipatory and liberating pedagogical approaches to be implemented early in schools, involving families and the community.
Funding: None.
Competing interests: None declared.
Ethical approval: Not required.

Push forward: 10 ways to end violence against women
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to E-mail

Violence against women and girls remains the most pervasive human rights violation in the world, affecting more than 1 in 3 women—a figure that has remained largely unchanged over the last decade.
Global emergencies, crises and conflict have further intensified violence against women and girls and exacerbated the drivers and risk factors. Climate change is aggravating all types of gender-based violence against women and girls, an already visible pattern that will undoubtedly grow more extreme as the crisis worsens. Rapidly expanding digitalization is increasing online violence against women and girls, compounding existing forms of violence and leading to the emergence of new ones. At the same time, there has been a rise in anti-rights movements and anti-feminist groups, driving an expansion of regressive laws and policies, a backlash against women’s rights organizations and a spike in attacks against women human rights defenders and activists.
In this context, ending violence against women might seem unimaginable, but it isn’t. Large-scale reductions in violence against women can be achieved through feminist activism and advocacy coupled with coordinated action across justice, health, financial and other sectors . Recent evidence suggests that strong and autonomous feminist movements are the most critical factor in driving change .
Ending violence against women is everyone’s business. This 16 Days, show your solidarity with feminist movements and advocates around the world. Whether you’re a seasoned activist or just getting started, here are ten ways you can act now to end violence against women and girls:
1. Speak up, speak out
Violence against women is pervasive, but it’s not inevitable—unless we stay silent. In the face of rising anti-feminist movements, it’s more crucial than ever that we speak up and out.
Taboos around gender-based violence provide perpetrators with impunity and prevent women and girls from getting the help they need: less than 40 per cent of women who experience violence seek help of any sort.
Let survivors and activists know you stand with them. Amplify their voices and stories. Create spaces for dialogue, both in person and online.
Not sure where to start? Share some of the activist stories from our editorial package , and check out our social media package for more shareable assets. Or use #OrangeTheWorld, #16Days and #PushForward to start your own conversation about gender-based violence.
2. Know the issue—and the signs
Violence against women takes many forms. It can be physical, sexual or emotional. It can be public or private, online or off, perpetrated by a stranger or an intimate partner. Regardless of how, where, or why it happens, it has serious short- and long-term consequences for women and girls and serves to prevent their full and equal participation in society.
Know what to look for by familiarizing yourself with the different kinds of violence: https://www.unwomen.org/en/what-we-do/ending-violence-against-women/faqs/types-of-violence
If you think someone in your life might be suffering from abuse, there are common signs you can look for. Learn more about what abuse looks like, and how you can help: https://www.unwomen.org/en/what-we-do/ending-violence-against-women/faqs/signs-of-abuse
3. Call out sexual harassment
For many women, sexual harassment is a daily experience. Whether it’s online, on the street or in the workplace, brushing off inappropriate behavior serves to further normalize it.
Common forms of harassment like online bullying, catcalling, sexual comments and sexual jokes serve to make women and girls feel unwelcome and unsafe in public spaces. They help to reinforce biases and stereotypes that perpetuate misogyny. And they contribute to a culture of impunity, in which women can be harmed without consequence.
Create a safer environment for everyone online and offline by challenging your peers to reflect on their own behaviour and speaking up when someone crosses the line, or by enlisting the help of others if you don’t feel safe.
For more on why it’s important to report online harassment and violence against women, check out this interview with digital rights activist Marwa Azelmat: https://www.unwomen.org/en/news-stories/feature-story/2022/11/pushing-forward-preventing-violence-against-women-in-online-spaces
4. Challenge beliefs on masculinity
Toxic masculinity drives violence against women.
Evidence shows that women in relationships with men whose beliefs and behaviours reinforce male dominance and gender inequality are more likely to experience intimate partner violence.
Traditional concepts of masculinity tend to emphasize traits like aggression, strength and control—while disparaging sensitivity, empathy, vulnerability and other traits traditionally associated with femininity.
When we fail to challenge these beliefs, everyone loses. Reflect on your own ideas about masculinity and femininity, and think critically about depictions of gender in media and culture. Support the men and boys in your life to embrace caretaking, emotional expression and other traditionally non-masculine traits.
5. Fund women’s organizations
Investing in women’s movements matters.
Evidence shows that a strong and autonomous feminist movement is the most crucial factor in driving policy change on gender-based violence. But women’s rights organizations, key drivers of feminist mobilization, are increasingly being defunded, sidelined and silenced in decision-making spaces.
Increasing long-term funding to women’s rights organizations is key to finding effective solutions to prevent and respond to violence against women.
Donate to local organizations that empower women, support survivors and promote actions and policies designed to reduce and prevent violence.
UN Women works with women’s organizations around the world to end violence against women and secure equal rights for women and girls. Donate here: https://donate.unwomen.org/en .
6. Call for better responses and services
Services for women and girls experiencing violence can be the difference between life and death.
This means that shelters, hotlines, counseling and all support for survivors of gender-based violence need to be available for those in need, even during crises and emergencies.
Every year, the 16 Days of Activism campaign calls for united, global action to end all forms of violence against women and girls.
Join us in calling on governments to bridge funding gaps to address violence against women and girls, ensure essential services for survivors of violence are maintained during crisis and conflict, implement prevention measures, and invest in adapting and improving life-saving services for women and girls in diverse contexts.
Get more involved by volunteering at a local women’s shelter, donating clothes or supplies, or training to become a crisis counselor.
7. Demand more data
To effectively combat gender-based violence, we need to understand the issue.
Relevant data collection is key to implementing successful prevention measures and providing survivors with the right support. And yet the collection of sex-disaggregated and other crucial gender data remains a low priority for governments.
As gender-based violence has spiked due to COVID-19, climate change and other crises, the gaps in gender sensitive data collection have become more glaring than ever. Call on your government to invest in the collection of data on gender-based violence.
8. Push for stronger laws
We are still 21 years away from comprehensive laws banning violence against women to be in place globally.
The world needs stronger protection mechanisms to prevent and eliminate violence, harassment, threats, intimidation, and discrimination against women human rights defenders and women’s rights advocates and activists.
Find out about the laws in your country: https://evaw-global-database.unwomen.org/en . Call on your government to strengthen legal frameworks, and help raise awareness about the gaps. Start or join a protest, support a legal advocacy group, and educate yourself on the stances of political candidates and representatives.
9. Support women’s leadership
During COVID-19, women were vastly underrepresented on recovery task forces—a disparity reflected in the insufficiency of government responses to gender-specific issues like heightened domestic violence.
The same is true for climate action, peacebuilding, and a whole host of other issues: when women aren’t at the table, their voices aren’t being heard. That makes it all too easy for decision-making bodies to overlook crucial gaps in policies and financing.
Women’s representation in decision-making spaces helps to ensure that the needs of women and girls are front and center—in crisis responses, humanitarian and peace agreements and policies of all kind. At the same time, women leaders face heightened risk of violence: across 5 regions, 82 per cent of women parliamentarians reported experiencing some form of psychological violence during their terms.
Call for women’s increased representation in leadership, and for heightened protections for women in positions of power. Support women political candidates and women-led organizations and companies. Or take matters into your own hands—become the woman leader you want to see in the world.
10. Build solidarity with other movements
We’re stronger when we work together.
Violence against women and girls is inherently connected to other forms of harm and injustice, including racism, homophobia, xenophobia, ableism, poverty, and climate change.
Strengthen the fight against gender-based violence by getting involved in other social and political movements, and getting activists from those movements involved in yours.
Together, we can resist the rollback on women’s rights, amplify the demands of feminist movements across the world and push forward to end violence against women and girls once and for all.
- Anti-violence interventions
- Domestic violence/interpersonal violence
- Political violence
- Ending violence against women and girls
Related content

Documentary series shares stories of women’s survival, hope, and activism

Statement by principals of the Inter-Agency Standing Committee on the Democratic Republic of the Congo – Crushing levels of violence, displacement fuel unprecedented civilian suffering

Speech: ‘Until we make it clear there are consequences for rape—real, dire consequences—we will never turn the tide of it’
Home — Essay Samples — Social Issues — Women's Rights — Equal Rights for Women: The Ongoing Struggle for Gender Equality
Equal Rights for Women: The Ongoing Struggle for Gender Equality
- Categories: Women's Rights
About this sample

Words: 613 |
Published: Mar 6, 2024
Words: 613 | Page: 1 | 4 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Karlyna PhD
Verified writer
- Expert in: Social Issues

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 775 words
2 pages / 755 words
6 pages / 2671 words
4 pages / 1750 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Women's Rights
Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie's essay "We Should All Be Feminist" is a powerful and thought-provoking call to action that explores the importance of feminism in today's society. Through a skillful use of rhetorical devices, Adichie [...]
Judy Brady's essay, "Why I Want a Wife," is a thought-provoking piece that challenges societal norms and gender roles. Originally published in Ms. Magazine in 1972, Brady's essay is a satirical take on the expectations placed on [...]
The waves of feminism represent distinct phases in the ongoing struggle for gender equality and women's rights. These waves, characterized by their goals, strategies, and socio-political contexts, have shaped the trajectory of [...]
In the tapestry of human rights and gender equality, the freedom to choose one's attire emerges as a crucial thread. This essay delves into the importance of women's autonomy over their clothing choices, asserting the [...]
Munro, A. (1968). Dance of the Happy Shades. McClelland and Stewart.Munro, A. (1978). The Beggar Maid. McClelland and Stewart.Munro, A. (1994). Open Secrets. McClelland and Stewart.Munro, A. (2001). Hateship, Friendship, [...]
Feminism is the “belief that women should have economic, political, and social equality with men”(Gustafson). Many inspirational feminists have “challenged the traditional gender roles and demanded more opportunities for women [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Open access
- Published: 01 November 2022
A qualitative study on gender inequality and gender-based violence in Nepal
- Pranab Dahal 1 ,
- Sunil Kumar Joshi 2 &
- Katarina Swahnberg 1
BMC Public Health volume 22 , Article number: 2005 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
80k Accesses
16 Citations
Metrics details
Gender inequality and violence are not mutually exclusive phenomena but complex loops affecting each other. Women in Nepal face several inequalities and violence. The causes are diverse, but most of these results are due to socially assigned lower positioning of women. The hierarchies based on power make women face subordination and violence in Nepal. The study aims to explore participants' understanding and experience to identify the status of inequality for women and how violence emerges as one of its consequences. Furthermore, it explores the causes of sex trafficking as an example of an outcome of inequality and violence.
The study formulated separate male and female groups using a purposive sampling method. The study used a multistage focus group discussion, where the same groups met at different intervals. Six focus group discussions, three times each with male and female groups, were conducted in a year. Thirty-six individuals, including sixteen males and twenty females, were involved in the discussions. The study used constructivist grounded theory for the data analysis.
The study participants identify that a power play between men and women reinforce inequality and increases the likelihood of violence for women. The findings suggest that the subjugation of women occurs due to practices based on gender differences, constricted life opportunities, and internalization of constructed differences among women. The study identifies that interpersonal and socio-cultural violence can result due to established differences between men and women. Sex trafficking, as an example of the outcome of inequality and violence, occurs due to the disadvantageous position of women compounded by poverty and illiteracy. The study has developed a concept of power-play which is identified as a cause and consequence of women's subordination and violence. This power play is found operative at various levels with social approval for men to use violence and maintain/produce inequality.
The theoretical concept of power play shows that there are inequitable power relations between men and women. The male-centric socio-cultural norms and practices have endowed men with privilege, power, and an opportunity to exploit women. This lowers the status of women and the power-play help to produce and sustain inequality. The power-play exposes women to violence and manifests itself as one of the worst expressions used by men.
Peer Review reports
Violence against women is identified as an attempt by men to maintain power and control over women [ 1 ] and is manifested as a form of structural inequality. This structural inequality is apparent with greater agency among men [ 2 ]. The differences between sexes are exhibited in the attainment of education and professional jobs, ownership of assets, the feminization of poverty, etc., and these differences increase the risk of violence towards women [ 3 ]. The global estimate identifies that thirty percent of women experience physical and/or sexual violence during their lifetime, illustrating the enormity of this problem [ 4 ]. From a feminist perspective, lending ideas of patriarchy [ 5 ] and gender performativity [ 6 ], the understanding of gender roles prescribed by male-dominated social structures and processes helps further explore the violence and abuse faced by women [ 7 ]. According to Heise [ 8 ], men who adhere to traditional, rigid, and misogynistic views on gender norms, attitudes, and behaviors are more likely to use violence towards women. The individual and collective attitudes of men toward different established gender norms, and their reproduction explain men’s use of violence toward women [ 9 ]. It is known that gender norms influence violence, but at the same time violence also directs and dictates gender performance with fear, sanction, and corrective measures for enacting respective prescribed gender functions [ 10 ].
It is difficult for women subjected to violence to enjoy legitimate rights, as most of the infringement of their rights and violence takes place inside a private sphere of the home [ 11 , 12 ]. Violence against women is the major cause of death and disability for women [ 13 ] and globally a major public health concern [ 14 ]. Establishing gender equality is fundamental for fostering justice and attaining sustainable development [ 15 ]; moreover, violence against women has to be acknowledged as a fundamental abuse of human rights [ 16 ]. A report on global violence has identified that violence against women exists at all levels of the family, community, and state. The report recommended the development of frameworks for respecting, protecting, and fulfilling women’s rights [ 17 ]. Fifteen years later, a review of the same identifies that violence continues with impunity, reaffirming violence as a major obstacle to the attainment of justice [ 18 ].
The inclusion of the gender lens to violence against women has provided more contextual evidence to explore these processes of violence. This requires the identification of unequal power relationships and an inquiry into the differences-producing various gender stereotypes [ 19 ]. This analysis of violence requires an understanding of behaviors that promote women’s subordination and factors that favor men to sustain these malpractices [ 8 ]. A closer look at the male-centric structural arrangements embedded in the social, political, and economic organization of life reveals that these structures provide lesser access and lower accountability toward women, promote systemic subordination, and create hierarchies, resulting in the increase of violence against women [ 20 ]. This unequal gender power relationship reinforced and manifested by social approval of men’s authority over women is found operative at multiple levels and helps to produce diversities of inequalities and violence [ 21 , 22 ].
The inequalities faced by women in Nepal majorly stem from socio-cultural, economic, and religious factors and influencers that define traditional roles and responsibilities between men and women [ 23 ]. The inequalities are more evident and pronounced in settings exhibiting prominent patriarchal norms restricting advantages and opportunities for the majority of women [ 24 ]. Women in Nepal are restricted inside their homes, have lesser access to life opportunities, and have limited or no involvement in decision-making on important issues directly affecting their lives [ 25 , 26 ]. Figures indicative of women’s inequalities in Nepal suggest that one-third of women have no education, fifty-two percent of women are involved in non-paid jobs, and women are less likely than men to own a home or land [ 27 ]. The men in Nepalese society are positioned higher and are expected to be the breadwinner and protectors of their families. Most of these men intend to earn respect and obedience from women and are socially expected to discipline women to achieve it [ 28 ]. Many societies across the world including Nepal, recognizes violence as a private affair requiring discussion only within a family. This has led to a serious underreporting of violence committed toward women in Nepal [ 29 ]. The national gender data in Nepal is scarce, the available Nepal Demographic Health Survey 2016 identifies that since the age of fifteen, twenty-two percent of women and seven percent of women experience physical and sexual violence, respectively in the past twelve months [ 27 ].
The contributing factors for violence against women in Nepal include the lower social status of women, illiteracy, economic dependency, patriarchal society, sex trafficking, alcohol-related abuse, dowry-related violence, infidelity, extramarital affairs of husband, unemployment, and denial of sex with husband [ 30 , 31 , 32 ]. Nepalese women have been repressing violence with silence due to the fear of breaking relationships, receiving less love and affection from family, fear of social norms by going against men, lack of faith in the justice system, and the threat of increased violence [ 33 ]. Women and girls in Nepal are sex trafficked to various countries. Sex trafficking in Nepal is prevalent due to persistent gender inequality, violence, stigma, and discriminatory socio-cultural structures; however, the actual extent of sex trafficking is still undetermined [ 17 , 34 , 35 ].
The recent trends in Nepal with the increasing number of out-migration of men for employment have provided women with temporary autonomy, and a shift in the gender roles. Earlier research has identified that migration of male spouses has provided a resistance to the power dynamics for women on the other hand it has limited their mobility, required them to share decision-making with household structures, face continued social vigilance on the money received from remittance, and get central attention with their personal sexual lives [ 36 , 37 ].
Morang district lies in the eastern region of Nepal. A district profile report based on a census survey [ 38 ] identifies that the place is inhabited by a close to a million population, out of which ethnic groups ( close to forty percent) live in the district with a majority (seventy-eight percent) of its population living in the rural areas. Tharu an ethnic group is one of the dominant population in the study area and all study participants for this study were from same Tharu population. A close to thirty-six percent of women in the district are illiterate and the average age of marriage is eighteen years. The report identifies that only twenty-three percent of women engage in economic activities apart from agricultural work and less than fourteen percent of women head the household. Almost eighty percent of the population in the district practice Hinduism.
This study is a part of a large intervention project and it was focused to establish a qualitative baseline of the gender status in the study area. This study aimed to explore participants’ experiences and understanding of gender inequality, violence against women, and information on sex trafficking in the Morang district of eastern Nepal. The selection of sex trafficking topic was motivated to assess the respondents’ general understanding of one of the consequences of inequality and violence faced by women. The study focused to explore factors that help to produce and sustain the practice of gender inequality and violence against women in the local community.
Participants
This study was part of a larger control-comparison project that used Forum Theatre interventions to promote gender equality, reduce violence against women, and increase awareness of sex trafficking [ 39 , 40 ]. The participants for the focus group discussion included the intervention population from one of the randomly sampled intervention sites. A multistage focus group discussion [ 41 ] was used involving the same participants discussing various emerging topics at different periods. The participants were recruited voluntarily during an earlier quantitative data collection for the project. The study used a purposive sampling method for the selection of participants. The local field staff at the study site facilitated the recruitment of the participants. The study formulated separate male and female groups. A total of six focus groups, three each with male and female groups were conducted over twelve months. Two inclusion criteria were set for participation. First, the participants had to be part of the population of the larger study. Secondly, they had to witness and/or participate in the Forum Theatre interventions conducted in between the study. The set inclusion criteria served a dual purpose of understanding the causes of inequality and violence and further helped to develop and determine the efficacy of participatory Forum Theater intervention for awareness-raising among the study intervention groups [ 39 ].
A total of thirty-six participants consisting of sixteen males and twenty females joined the discussions. The first discussion consisted of eight participants each from groups while the second and the third discussion missed two female and four male participants respectively. The majority of the participants were 20–29 years old. Tharu, an ethnic community of Nepal, is a dominant population in the study area, and all the participants belonged to the same Tharu community. Only one female participant was unmarried, and a single married male participated in the discussions. All participants were literate, with four males completing a bachelor's level of education. Seven female participants had education below the high school level. The nuclear family with parents and their children was the major family type identified in both male and female groups. Table 1 provides the detail of the participants.
The focus group discussions were conducted in January 2017, April–May 2017, and January 2018. The discussions were conducted in a place recommended by the participants. An isolated place in an open setting at the premise of a local temple was used for conducting all discussions. The participants were briefed about the objectives of the discussion and written consent was obtained for their participation. Verbal consent was taken for the audio recording of the discussions. Each participant was assigned a unique numerical code before the discussions to ensure anonymity during recording, note-taking, and analysis. The discussions averaged ninety minutes during each session. The discussions were conducted with the same participants and no new participants were added during the follow-ups. A single male and female participant were missing in the second follow up and two male participants missed the final follow-up. The reason for missing participants was due to their unavailability as they were out of the village due to personal reasons.
The discussions were conducted in the Nepali language. The first author moderated all six discussions, a support field staff member took the notes, and the last author observed the discussions. The audio recordings were translated into English, and the transcriptions were checked with the recordings to verify accuracy. The field and the discussion notes were used during various stages of data analysis. The notes provided information on the discussion setting, as well as the verbal and nonverbal expressions of the participants. The notes helped to assess the impressions, emphasis, and feelings of the participants during the discussions.
The discussions used pre-formulated discussion guides with open-ended questions on inequalities, gender practices, violence, and sex trafficking. The guiding questions were based on the theoretical premise of discrimination, patriarchy, oppression, hegemony, and participation of women. Three separate discussion guides were developed for each of discussions. The guides were developed by the first and last authors. Probing was done on several occasions during the discussion to gain more clarity on the issue. Cross-checking among the participants and between the groups was done to triangulate received information. Any topic deemed appropriate for discussions and/or any unclear issues identified during the initial data analysis came up subsequently in the discussion guide during the follow-ups.
Data analysis
This study used the constructivist grounded theory method. This method adheres to a constructivist philosophical approach wherein both researchers and participants mutually co-construct the meaning of a phenomenon [ 42 ]. This interaction is important since it helps to impart the meaning of shared experiences [ 42 ]. The constructivist grounded theory made it possible to (re) discover gender issues, important for both the researcher and the study participants. This method allowed the study to progress with responsiveness to emerging issues with an in-depth exploration of the identified issues. This clarity was achieved through repeated interactive discussions, analysis of explanations, and sharing of emergent findings with the study participants.
The audio recordings were translated and transcribed into English. Six transcripts from discussions were initially analyzed using a line-by-line coding process. The coding process helped with the fragmentation of data through interactive comparisons. Fifty-two initial codes such as gender differences, restricting women, alcohol-related violence, underreporting of sexual violence, coping, etc. were identified. The later stage of focused coding helped to achieve categorized data, providing logical sense to the developed initial codes. Three focused codes, namely, the subjugation of women, violence, and chasing dreams were formulated during the analysis. The abductive reasoning from the codes, memos, and discussion notes helped to develop the theoretical concept. The development of conceptual abstraction involved an iterative comparison of the data, codes, categories, memos, and discussion notes.
The constant communication between the authors during the stages of data analysis such as the formulation of codes, explanations of concepts, and categories helped to refine the analysis. The shared experiences of the participants and the description of the data collection and analysis included substantial details, enabling comparisons for future research and application to other similar contexts. The reliability of the study is warranted by the theoretical saturation [ 42 ] achieved by this study. This is supported by prolonged engagement with the study participants with communication on the emerging findings, and triangulation.
Reflexivity has a greater significance for the constructivist approach. The first and the second author of Nepalese origin were aware of the socio-cultural norms, stereotypes, values, and stigmas associated with gender in the local context. This helped the study to ascertain the depth of inquiry within the acceptable local normative limits. The non-Nepalese author, familiar with the study participants and Nepalese contexts, witnessed the discussions as an observer. The prior knowledge of the authors helped to critically assess different schemas, perspectives, and explanations shared by the participants. The universality of gender inequality and violence against women and its re-examination in the local context helped the authors to build upon existing knowledge by providing contextual explanations. The diversities among the authors and research participants established a basis for co-creating the perceived and observed realities.
The section below describes the participants’ perceptions and understanding of inequality and violence. The section contains subheadings that were derived as themes in the data analysis. The first theme subjugation of women; discusses how norms, beliefs, and practices produce inferior status and positions for women. The second theme domestic and gender violence; provides a narrative of interpersonal and socio-cultural violence present in the study area. The theme of chasing dreams; discusses the process of sex trafficking as an outcome of violence. The theoretically abstracted concept of power-play identifies the cause for the generation of power imbalance producing inequality and the use of violence by men.
Subjugation of women
The subjugation of women reflected practices and beliefs imparting positional differences for women and their social situation compared to men. The participants shared a common understanding that belief systems adhering to male supremacy have positioned women in a lower status. They provided examples of social practices of male supremacy such as males being considered as the carrier of a family name, legacy, and heritage, while women were referred to as someone else’s property. The socialization of the idea that girls will be married off to a husband and relocate themselves to their homes was identified as the major reason for instilling and perpetuating early gender differences. The participants mentioned that discriminatory practices and seclusion have situated women at the bottom rung of the gender hierarchy, establishing them as socially incompetent individuals or groups. Moreover, they inferred that selective preferences provided preparatory grounds for inequalities, and they remain attached to women throughout their lives. The participants provided examples of unequal access to education and life opportunities as a practice of selective preferences occurring in the community. They mentioned that socialization with these discriminatory beliefs and their practice helped to develop specialized gender roles from an early age. The participants provided an example of how gender intersected with mobility and resource generation in the community, it was clear from the discussions that this has restricted women inside homes but provided freedom and opportunities for men. A female participant expressed,
A woman from a poor family is more than willing to work and support her family. But she is not allowed by the men in the family to work outside of the home.
The participants informed that differences between the sexes were visible for women from a young age. Sharing practical examples from the community, the participants from both groups stated that girls received education mostly in low-cost government and community schools, while boys were enrolled in expensive private schools. They raised concerns that this selective investment for education, cited as the ‘building block of life’ by the participants, installed lesser capacity, and negotiating abilities in girls. A female participant stated,
There are differences in educational opportunities for boys and girls in our community. Family provides more support for a boy’s education by enrolling him in private schools, while a girl mostly gets her education in a community school together with engagement in household work.
The discussions revealed that women required several male anchors for their survival during their various stages of life. The participants provided examples of the shift of anchors for women which traversed from a father to a husband during marriage and later to the male child during her old age. They believed that this tradition of transferring women’s identity established men as a higher social category and stripped women of their individuality and identity. A male participant added,
Women have to remain dependent on men throughout their lives, first with their fathers and later with their husbands. They remain completely dependent as they are not economically active. This makes men believe that they have higher authority.
The female participants provided an example of marriage to illustrate how someone else’s decision-making had been affecting women’s lives. A participant explained that women were held responsible for household activities after marriage and any support for career progression or education was restricted despite her desire for its continuation. It was inferred that women had to drop their hopes and aspirations as the husband and his family made decisions for them. The female participants agreed that this continuous exposure to the ideas of male supremacy makes them start to believe and internalize the idea that women have lesser cognitive abilities and intelligence compared to men. A female participant stated,
Men and women certainly have different mental abilities. Men think and act differently often in a smart way compared to women.
The participants from both groups expressed that youth in the community were developing flexible attitudes and beliefs towards gender roles and responsibilities. They agreed that both young men and women were observed altering their roles and responsibilities shifting from traditional gender ideologies. The participants expressed that instilling these fluidity and flexible approaches in the older generation was impossible as they strictly followed traditional beliefs and practices. Few of the female participants admitted that at times young women also fail to accommodate the situation and reap benefits from available opportunities. The discussions revealed that a few of the women in the community received opportunities for independence and economic empowerment. These women had received entrepreneurial training and various skill development activities for sustaining livelihoods with practical skill-based training in tailoring, beautician, and doll-making. The female participants expressed that opportunities for independence and growth slipped away from them due to a lack of family support, financial constraints, and self-passivity. They explained that starting a business required approval from a family which was difficult to obtain. Moreover, if women made a self-decision to start up on their own, they lacked the initial capital and had to rely on men for obtaining resources. The participants further explained that the denial of men to support women were majorly due to the fear that norms of staying indoors for women will be breached and economic independence may enable women to have a similar financial footing as men. The participants stated that self-passivity in women emerged due to their engagement in household multiple roles, dependency upon males, and lack of decision-making power and abilities. A female participant summed it up by stating,
Some of us women in the community have received entrepreneurial skills training, but we have not been able to use our skills for our growth and development. Once the training finishes, we get back to our household chores and taking care of the children.
The female participants admitted that acceptance of belief systems requiring women to be docile, unseen, and unheard were the reasons for this self-passivity. The female participants resonated that the external controlling and unfavorable environment influenced by practices of discriminatory norms and beliefs developed self-passivity for women. A female participant expressed the cause and consequence of self-passivity as,
Women have inhibitions to speaking their minds; something stops us from making our position clear, making us lose all the time.
The discussions identified that gender norms were deeply engraved in various social interactions and daily life, and any deviance received strict criticism. The participants shared common examples of sanctions for women based on rigid norms like restrictive movements for women, social gossiping when women communicated with outsider men, prohibition for opinion giving in public, and lesser involvement during key decision-making at home. The participants shared that norms dictating gender roles were in place for both men and women with social sanctions and approval for their performance. A male discussion participant who occasionally got involved with cooking which was a so-called “women’s job” faced outright disapproval from his female relatives and neighbors. The male participant stated,
If I cook or get engaged in any household jobs, it is mostly females from the home and neighborhood who make fun of me and remind me that I am a man and that I should not be doing a woman’s job.
The foreign migration of youth looking for job opportunities has affected the Tharu community. It was known that a large number of men were absent from the community. The participants stated that women in such households with absent men had gained authority and control over resources, moreover, these women have been taking some of the men’s roles. The participants disclosed that these women had greater access and control over resources and were involved in the key decision-making positioning them in a relatively higher position compared to other women. It was known that this higher position for women came with a price, they were under higher social vigilance and at higher risk of abuse and violence due to the absence of ‘protective men’. It was known that women's foreign employment was associated with myths and sexist remarks. The participants shared that women had to face strict social criticisms and that their plans for livelihood and independence were related to an issue of sexual immorality and chastity. The participants from both groups strictly opposed the norms that associated women with sexual immorality but lamented that it continues. A male participant provided an insight into the social remarks received by women if she dares to go for foreign employment,
If a woman wants to go for a foreign job, she is considered to be of loose character. The idea that she is corrupt and will get involved in bad work will be her first impression of anyone.
Although the participant did not explicitly describe what bad work referred to as but it was inferred that he was relating it to sex work.
Domestic and gender violence
The participants identified violence as control, coercion, and use of force against someone will occurring due to unequal status. They primarily identified men as the perpetrators and women as the victims of violence. They explained that two types of violence were observed in the community. The first type occurred in an interpersonal relationship identified as physical, emotional, and sexual violence. The second type, as explained by the participants had its roots in socio-cultural belief systems. They provided examples of dowry exchange and witchcraft accusations for the latter type. The participants identified women as primary victims and listed both men and women as the perpetrators of both types of violence. They reported that physical violence against women by men under the influence of alcohol was the most commonly occurring violence in the community. The participants from both groups confirmed that wife-beating, verbal abuse, and quarrel frequently occurred in the community. It was known from discussions that alcohol consumption among men was widespread, and its cultural acceptance was also increasing episodes of violence. One of the female participants clarified further,
The most common violence occurring in our society is wife-beating by a husband under the influence of alcohol. We see it every day.
The participants reported the occurrence of sexual violence in the community but also pointed out that people refrained from discussing it considering it a taboo and private affair. The participants had hesitation to discuss freely on sexual violence. During the discussions, participants from both groups informed only of rape and attempted rape of women by men as sexual violence present in the community. Despite repeated probing, on several occasions, none of the participants from either group brought up issues and discussions about any other forms of sexual violence. Participants from both groups confirmed that stories about incidents of rape or attempted rape emerged only after cases were registered with the local police. The participants presumed that incidents of rape and attempted rape were not known to the wider community. A female participant stated,
Sexual violence does occur in our community, but people mostly do not report or disclose it, but they tend to keep it amongst themselves and their families.
The participants explained the identity of the rape perpetrator and victim. They identified the perpetrator as a rich, influential, and relatively powerful man from the community. The victim was portrayed as a poor and isolated woman which lesser social ties. It was known from the discussions that most of the rape cases in the community were settled with financial negotiations and monetary compensations for the victim rather than finding legal remedies. It can be inferred that the victimization of women intersects with gender, wealth, social stature, and affluence. The participants feared that this practice of settlement of rape with money could make rape a commodity available for the powerful, rich, and affluent men to exploit and victimize women. A male participant clarifies,
Recently, a man in his sixties raped a young girl near our village. The victim's family was ready to settle with monetary compensation offered by the rapist, but the involvement of the community stopped it and the rapist was handed over to the police.
The participants shared available coping mechanisms against violence practiced in the community by women. It was learned that the victim of household violence mostly used community consultation and police reporting to evade further violence. They divulged that community consultation and police reporting resulted in decisions in favor of victim women, directing abusive husbands to show decency and stop committing violence. The fear of legal repercussions such as spending time in police custody and getting charged under domestic violence cases was understood as the reasons for husbands to stop abuse and violence. The discussions revealed that women who file a formal complaint about their husband’s violent behavior could face an increased risk of violence. The participants disclosed that sharing such incidents publicly brought shame to some of the men and increased their anger, and often backlashed with increased violence. The participants in both groups stated that not all women in the community reported violence. They identified that women tend to be quiet despite facing continuous violence due to the fear of encountering more violence and to keeping their families together. A female participant clarifies,
Lodging public complaints against the abusive husband can sometimes escalate the violence. The husband’s anger for being humiliated in public must be faced by the woman inside the closed doors of the house with more violence and the men’s threat of abandoning the relationship.
The participants stated that socio-cultural violence against women in dowry-related cases was widespread and increasing. The dowry exchange was explained as a traditional practice with the family of the bride paying cash and kind to the groom's family. The participants clarified that the practice of dowry in the earlier days must have been an emergency fund for the newly wedded bride in a newer setting. According to the participants, the system of dowry has now developed and evolved as a practice of forced involuntary transfer of goods and cash demanded by the groom’s family. The discussions disclosed that the demands for dowry were increasing with time and failing to provide as promised immediately resulted in violence for the newly wedded bride. The participants described that dowry-related violence starts with taunts and progresses to withholding of food, verbal abuse, and finally, physical violence. They added that perpetrators of such violence were both men and women from the groom’s family. They stated that due to poverty not all bride families in the community were able to supply all demanded dowry which has exposed a large number of women to face dowry-related abuse and violence. The discussions also informed of a newer trend among girls by demanding goods during their wedding. It was shared that this new emerging trend had increased a two-fold financial burden on the bride’s family with heavy marriage debts. The male participants when questioned about the dowry demands cunningly shifted the responsibilities towards family and stated that it was not the groom but their families who were making such dowry demands. The discussions verified that dowry practice was so engraved in the community that it was impossible to even imagine a marriage without any dowry. A male participant reflected,
If I marry without any dowry, my family, neighbors, and all whom I know would consider that I am insane.
The participants also discussed and identified harmful traditional practices present in the community. The participants informed a common practice of accusing women of as witches existed in the community. It was mentioned that women faced witchcraft allegations in different situations. They provided examples of witchcraft allegations in common situations such as when someone’s cow stops producing milk when a child has a sore eye, when someone is bedridden due to sickness for days, or when a woman undergoes a miscarriage, etc. The participants stated that women accused of witch were always elderly/single women living in seclusion, poverty, and with fewer social ties. They also shared that the witch doctors, who ascertain whether a woman is a witch or not, were surprisingly mostly always men and hold higher status, respect, and social recognition. The consequences of being labeled as a witch, as explained by the participants, haunted victim women with torture, name-calling, social boycott, and extremes of physical violence. The participants informed that inhumane practices such as forceful feeding of human excreta prevailed during the witch cleansing sessions. A female participant explaining the witchcraft situation stated,
Witchcraft accusation is very real in our community; I know someone who has tortured his mother, citing reasons for his wife being childless. The old woman was called names, beaten, and later thrown out of the home.
The participants felt that men’s use of violence and its legitimization primarily existed due to gender hierarchy and internalization of the belief that violence was the best method to resolve any conflict. They inferred that men’s use of violence was further reinforced by women's acceptance and belief that violence had occurred due to their faults and carelessness. The female participants shared examples of common household situations that could result in an episode of violence such as women cooking distasteful food, failing to provide timely care to children and the elderly due to workload, and forgetting to clean rooms. These incidents make women believe that violence majorly occurred due to their mistakes. Furthermore, the participants believed that this self-blaming of the victim resulted due to constant exposure to violence and a non-negotiable social positioning of women for raising questions. The participants stated that beliefs instilled by religion increased the likelihood of victimization for women. They explained that religious practices and ideologies required women to refer to their husbands as godly figures, and a religious belief that anything said or done against husbands was a disgrace bringing sin upon her and family positioned women in an inferior position. A male participant added,
We belong to a culture where females worship their husbands as a god, and this might be an important reason for men to feel powerful as a god to exploit and abuse women.
The discussions put forward the idea that the existence of discriminatory beliefs, reinforcement of such beliefs, and a blind following of such practices produced differences and violence. The male participants acknowledged that the idea of male supremacy not only produced violence but also established a belief system that considered violence as an indispensable way to treat deviated women. One male participant stated this idea of male supremacy and privilege as,
The language of the feet is essential when words fail.
The participants also discussed violence committed toward men by women. The male participants burst into laughter when they stated that some men were beaten by their wives when they were drunk. The male participants admitted that intoxication reduced their strength and they got beaten. The female participants, on the other hand, assumed that women hit intoxicated men due to frustration and helplessness. They further clarified that the act of husband beating was a situational reaction towards men who had spent all of their daily earnings on alcohol. They stated that women with the responsibility to cook and feed family find themselves in an utterly helpless situation by the irresponsible drinking behavior of men. The male participants shared incidences of violence against men due to foreign migration. It was revealed in the discussions that some of the migrating men’s wives had run away with remitted money, abandoning marriage, and breaking up the family. The male participants identified this as a form of victimization of men, furthermore, the spreading of rumors and gossip caused emotional instability in those men. The female participants confirmed that some returning men failed to find their homes, property, money, and/or their wives. The discussion participants in both groups identified that this practice was on the rise in the community. It became apparent from the discussions that this increasing trend of women running away with the money and breaking away from family was a personal issue requiring social remedies.
Chasing dreams
The participants referred to sex trafficking as the exploitation of women, arising from poverty, illiteracy, and deceit. Explaining the causes of trafficking, the participants stated that women living in poverty, having dreams of prosperity and abundance were tricked by the traffickers making them victims of sex trafficking. The participants mentioned that women who had dreams larger than life and yearned for a comfortable and luxurious life in a short time were at a greater risk for sex trafficking. The participants from both groups resonated that the traffickers had been manipulating the dreams of poor women and deceiving them into trafficking. A female participant elaborated,
Women in poverty can be fooled easily with dreams. She can be tricked by a trafficker by saying I will find you employment with good pay abroad, and she gets into the trap easily.
A male participant further clarified,
Women readily fall into fraud and trickery shown by the traffickers who assure of luxurious life with foreign employment and this bait often leads to sex trafficking.
They identified that false hopes for foreign jobs were primarily used as an entry point by the traffickers to trap potential victims. Besides, they stated that some traffickers tricked women with false romantic relationships and marriages to win over their trust enabling traffickers to maneuver women as they wished.
It was identified that traffickers were not always strangers but known and familiar faces from the community, allowing the traffickers to gain the victim’s trust. The discussions divulged that traffickers strategically chose women who were less educated and poor. The participants explained that sex trafficking mostly occurred among women from a lower caste (the caste system is hierarchy-based in Hindu society which is determined by birth and unchangeable). They further explained that if one of these lower caste women went missing, it seldom raised any serious concerns in society, making these women easy targets for the traffickers. The discussions revealed that life for the survivors of sex trafficking was difficult. They identified that the survivor had to face strong stigmas and stereotypes which further increased their risk for re-victimization. The participants explained that the social acceptance of the trafficking survivors was minimal and finding a job for survival was very difficult. It was reported that social beliefs, norms, and practices were rigid for sex trafficking survivors and provided lesser opportunities for complete social integration. A female participant stated,
The story of a sex-trafficked woman does not end after her rescue. It is difficult for her to live in society, and this increases her chances of being a further victim.
The discussions in both groups highlighted that education and awareness were important for reducing sex trafficking. The participants felt that securing a livelihood for women was essential, but they identified it as a major challenge. The female participants recommended the use of education and awareness for reducing sex trafficking. They demanded effective legal actions and stringent enforcement of the law with maximum punishment for offending sex traffickers. They mentioned that the fear of law with maximum punishment for culprits could help decrease cases of trafficking.
The theoretical concept of power play
The discussions identified that gender inequality and violence against women occurred as men possessed and exercised greater authority. The participants explained that the authority emerging from male-centric beliefs was reinforced through established socio-cultural institutions. It was known that oppressive practices toward women in both public and private life have led to the domination and devaluation of women. The differences between men and women were known to be instilled by evoking discriminatory beliefs and due to internalization of them as fundamental truths by women which further helps to sustain these created differences.
The concept of power-play developed from the study has its roots in the belief systems and was found constantly used by men to maintain created differences. The power-play rise due to patriarchy, guiding discriminatory norms and unequal gender practices. These norms and practices in the canopy of patriarchy positions women inferior to men and impose control and restrictions. The power play possessed multi-dimensional effects on women such as creating further barriers, restricted life opportunities, the need for men-centered anchoring systems, and exclusion from the public arena. The power play gains its strength from the strict enforcement of stereotypical practices and committed adherence to gender performances. This leads to internalization of subordination as a natural occurrence by women. These further isolate women putting them into several non-negotiating positions. The power play at an individual level provides restrictive movement for women, barring them from quality education and other life opportunities, and is exhibited in alcohol-related assault and sexual violence. At the structural level, this power play limits women from economic opportunities, access to resources, and decision-making, and induces socio-cultural inequality exhibited in dowry and cases of witchcraft. The socio-cultural acceptance of power-play allows men to use violence as a misuse of power and use it as an effort to maintain authority. The use of power-play for committing violence was identified as the worst display of exercised power play.
Figure 1 describes the concept of power-play developed from the study. The power-play model is based on discussions and inferences made from data analysis. The model provides a description and explanation of how women are subjected to inequality and face violence. The concept of power play derives its strength from the subjugated status of women which are based on selective treatment, self-embodiment of inferiority, imposed restrictions and due to lesser life opportunities. The power play gain legitimacy through social approval of the status differences between men and women and through social systems and institutions majorly developed and favoring men. The status difference between men and women and its approval by developed social institutions and processes give rise to the concept of powerplay. It identifies that status differences allow men to gain and (mis)use power play not only to maintain differences but also enable men to use violence. The use of power-play exists at both interpersonal and cultural levels. Further, the model elaborates on influencers causing subjugation of women, display of power-play, and violence. The model identified that lodging public complaints and seeking legal remedies are the influencers that suppress violence against women. The influence of Forum Theater was perceived to have greater influence for victim, perpetrator, and bystanders. The influencers that aggravate violence are fear of further violence, the nature of the interpersonal relationship, alcohol-related abuse, and remaining silent especially on sexual violence. The cultural violence mentioned in the model refers to dowry and witchcraft-related violence and stands as systemic subordination. In the model, sex trafficking is depicted as one of the outcomes of inequality and violence faced by women majorly occurring due to deceit and fraud.
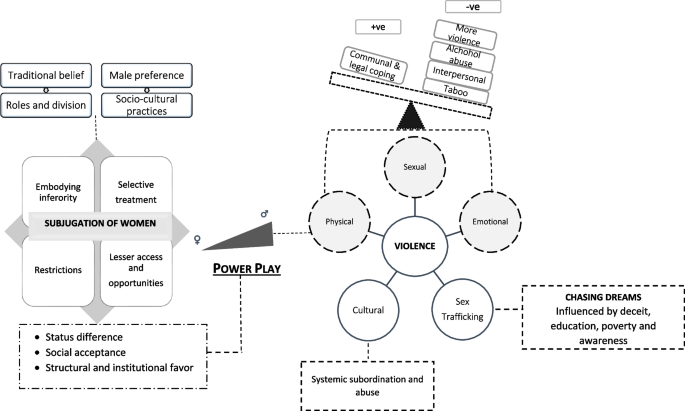
The theoretical concept of power-play developed in this study identifies that inequality produces violence and violence further reinforces inequality, creating a vicious circle. The power play situates hierarchy based on gender as the primary cause and identifies violence as an outcome of this power asymmetry. The authority to use power by men is received by social approval from embedded structures and institutions. The functioning of associated structures and norms is designed and run by men helping to perpetuate the dominance and subjugation of women. The study identifies that both interpersonal and socio-cultural violence emerges due to the positional differences and use of power. The study found that an element of control exists in interpersonal violence. The findings show that few victim women in the community took advantage of consultations and rely on the law to evade and /or cope during the occurrence of interpersonal violence. A large number of victims women however suffer silently as they are unable and unwilling to take a stand on violence due to their perceived positional differences and strict norms following. The study finds that violence originating from socio-cultural systems is widely accepted and no established means of control exists. The practice of heinous acts against a fellow human during witchcraft allegations and dowry exchanges is prohibited by the law of Nepal but is widespread. This situates that practices which are based on belief systems are more effective than prevailing national laws which try to stop them. Sex trafficking as a form of sexual violence use deceit and fraud against women. Poverty and illiteracy compel women to search for alternatives, and they become easy victims of sex trafficking when their dreams of a better life are manipulated by the traffickers. The false promise of a better life and highly paid job put women in a non-negotiating position with traffickers. The cherished dream of escaping the prevailing status-quo of oppression, subordination, violence, and poverty mesmerizes women to take risky decisions, falling into the risk and trap of sex trafficking.
The socio-cultural norms are the unwritten script of social operatives and functioning. These social norms function as codes of operation and are a major determinant for behavior and interactions between people [ 43 ]. The study has found that these norms were skewed, and most favored men, giving rise to status differences and producing inequalities for women. This is observed with lesser life opportunities, lower participation in decision-making, and a constant need to anchor women. This further helps men to maintain their hierarchical positional status and use violence. The subjugation of women does not occur in a linear process, it is influenced by the internalization of discrimination resulting in lower self-esteem, suppression, and domination of women based on norms and unequal practices. Earlier research has identified that norms and beliefs encourage men to control women, and direct them to use force to discipline women which increases the risk of violence occurrence [ 44 , 45 ]. An earlier study shows that traits of masculinity require men to become controlling, aggressive, and dominant over women to maintain status differences [ 46 ]. The study confirms that men upon receiving both normative and social approval for using violence against women can do so without hesitation.
Violence against women in Nepal mostly occurs inside the home and is only reported when it reaches higher levels of severity. The acceptance of violence as a private affair has restricted women from seeking support and discourages them from communicating their problems with outsiders [ 47 ] this increases more likelihood for men to use violence. The study finds issues related to sex and sexual violence is a taboo and are seldom reported. The study could only identify cases of sexual assault registered with the police and other cases known to the wider community as sexual violence. A community with known incidents of rape may have other cases of abuse, harassment, incest, forceful sexual contact, etc. Failure to report incidents of sexual violence infer that a large number of women could be suffering in silence. Earlier research identifies that increased stigmatization associated with sexual violence, and fear of seclusion cause reluctance in victims to report or seek support [ 48 ]. This silencing of victims provides men with greater sexual control over women [ 49 ] increasing more likelihood of use of violence. Gender-based inequality and violence intersect structures, institutions, and socio-cultural processes, making inequality and violence visible at all levels. The dowry-related violence and witchcraft allegation intersect interpersonal and structural violence. This cultural violence forces women to be a victim of lifelong abuse and trauma. The intersecting relationship between gender norms, social structures, and individual is so closely knitted that it produces varieties of inequality and violence at all levels [ 50 ]. Emotional violence in this study only emerged as a type of violence, during discussions in both groups. It did not emerge as a major concern for the participants except for dowry-related violence and violence against men. The intertwined nature of emotional violence and its occurrence with each abusive, exploitative, and violent situation may have influenced the participants understand it as a result, rather than as a specific type of violence.
The power play between sexes was found in synchronicity with the established norms and prevailing stereotypes, helping to perpetuate gender power imbalance. The gender system is influenced and governed by norms and the social arena becomes the site of its reproduction through the interaction and engagement of people. This interaction provides approval to the institutions and processes that are based on constructed differences between men and women [ 51 ]. The power, as identified by Fricker [ 52 ], controls a social group and operates and operates through the agent or established social structures. A man can actively use the vested power to either patronize and/or abuse women while passively women’s internalization of social settings and embedded norms can put them docile. The social controls as reported by Foucault [ 53 ] work with the embedded systems of internalization, discipline, and social monitoring and uses coercion rather than inflicting pain. The internalization of status differences among women as indicated by the study confirms this schema of social control. The dominance of men over women with patriarchal beliefs establishes the significance of male-centered kinship. This requires women to constantly anchor with men providing grounds for inequalities to perpetuate further. This idealizes men and reinforces the belief that women are non-existent without their presence. The requirement for male anchorage has an attachment to prevailing structural inequality. The family property and resources are mostly controlled by men and it usually transfers from father to son limiting inheritance to women [ 51 ]. These glorified idealizations of men's competence as described by Ridgeway [ 54 ] idealize men as individuals with abilities, status, power, and influences. The need for women to rely on men as anchors, fear of going against the norms and social sanctions explains the positional difference and show that men possess greater competencies. The internalization of men-centric superior beliefs by women occurs due to self-passivity and devalues women creating false impressions of their abilities. The gender roles and responsibilities were strict for both sexes but provided greater flexibility, privilege, and opportunity for men. Earlier studies in congruence with this study find that socio-cultural expectations limit women from deviation, and strictly adhere to their prescribed role and expectations [ 55 , 56 ] providing an upper hand to the men. The unequal social positioning of women, as defined by a few of the participants, can help define men's use of violence. As inferred by Kaufman [ 57 ], the disadvantageous position of women and support from the established structures enable men to use aggression and violence with considerable ease. The concept of power-play derived from this study also reflects that inequalities not only create hierarchies, putting women into a subordinating position but also legitimize norms of harmful masculinity and violence [ 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 ] creating a vicious cycle of inequality and violence. The concept of power-play developed by this study requires further exploration of gender relations, injustice, and patriarchy to identify multiple operatives of power with an outcome of inequality and violence.
Strengths and limitations of the study
The study followed the same participants over a period, which helped the study to achieve clarity on the topics through constant engagement. The data collection and the initial data analysis of the study were conducted by the same person, which reduced the risk of misrepresented findings. The study used follow-up discussions, which provided an opportunity to meet the participants again to resolve any ambiguities. The constant engagement with the participants helped to develop rapport and trust, which is essential to enable meaningful discussions. The study gathered rich data for developing the theory of power play in the Nepalese context. The study has attempted to explain the interplay of men’s use of power play, gender inequality, and violence against women, which, in itself, is a complex, but important issue. The study helped to develop a platform by identifying a level of awareness and needs for a Forum Theatre intervention study, a first of its kind in Nepal.
The major limitation of the study is that it was conducted with only one of the ethnic populations of Nepal; thus, the findings from this study cannot be generalized to a completely different setting. However, the transferability of the study is possible in a similar setting. The incidences of inequality and violence shared by the participants were self-reported, and no other means of verification were available to crosscheck those claims. The differences among the participants both in and between groups based on education and marital status might have influenced the study participants to understand, observe, and experience the phenomenon. The possibility of social desirability bias remains with the study, as a constant engagement with the study participants might have influenced them to answer differently. Furthermore, the discussions were conducted in groups, and participants might have had hesitation to bring up any opposing views. The study relied on collecting information on social norms and individual experiences and the perceptions of the study participants. It cannot be claimed that the study is devoid of any data rigidity as participants were free to choose what they wanted to share and express.
Study implications
The study explains gender practices, norms, violence against women, and sex trafficking in Nepal. The study helps to increase the understanding of how gender systems are operative in the daily lives of the Tharu community in the Morang district of Nepal. Future studies can explore the established linkages of interpersonal and socio-cultural violence. Like the complex link existing between gender inequality and violence against women, interpersonal violence and socio-cultural violence cannot be studied in isolation. The study provides an opportunity for future research on exploring how changing norms have been altering the position and victimization of women. The study finds that changing gender norms and responsibilities have, on the one hand, provided agency and empowerment for women, but on the other hand, they have also increased their risk of being a victim, an area that requires further exploration. The study has identified that constant engagement with the study participants through follow-up studies ensures the richness of data, which can be useful information for a future research study design. The study can be helpful for policy development, social activists, leaders, and researchers as it discusses prevalent gender oppressions and victimization, which need to be addressed. The findings from the study can be helpful for dialogue imitation and for designing intervention projects aimed at providing justice and equality to women.
The study identifies the presence of gender inequalities and violence against women in the study area. The positional differences based on norms, institutions, and practices have assigned greater privileges to men. The concept of power-play devised by the study ascertains the maintenance of gender hierarchy to produce inequality further and victimization of women. The subjugation of women based on the social-cultural process, embedded belief systems, and norms prevent women from life opportunities and dignified life. It situates men at the highest rung of the gender and social ladder providing a comparative advantage for men to use power. Violence emerges as men’s use of power play and as a strategy for the continued subjugation of women. Sex trafficking as a consequence of inequality and violence has its origins in illiteracy and poverty with women falling prey to the deceit of traffickers. It is important that dreams for progression provide motivation for women to develop further but at the same time, dreams should not be exchanged with trickery and fraud offered by the traffickers. Awareness and attitudinal changes are imperative to challenge unequal norms, and practices, and reduce the risks of sex trafficking. This can help to develop negotiations for power-sharing which helps to reduce inequality, violence, and preparedness in chasing dreams. Changes at both individual and societal levels are necessary to develop a collective action for establishing belief systems and practices providing women with an equal position and reducing the risk of violence.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to privacy but are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Felson RB, Outlaw MC. The control motive and marital violence. Violence Vict. 2007;22:387–407.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Wamala S, Ågren G. Gender inequity and public health: Getting down to real issues. European Journal of Public Health. 2002.
World Health Organization. Promoting gender equality to prevent violence against women. World Health Organization. 2009.
Devries K, Maki J, Garcia-Moreno C, Petzold M, Child J, Falder G, et al. The Global Prevalence of Intimate Partner Violence Against Women. Science (80- ). 2013;340(6140):1527–38.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Walby S. Theorising patriarchy. Sociology. 1989;
Butler J. Undoing gender. Routledge. 2004.
Yllo K. Through a Feminist Lens: Gender, Diversity, and Violence: Extending the Feminist Framework In Current Controversies on Family Violence. California: Sage Publication; 2005.
Google Scholar
Heise L. Violence against women: An integrated, ecological framework. Violence Against Women. 1998;4:262–90.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Pulerwitz J, Barker G. Measuring attitudes toward gender norms among young men in Brazil: Development and psychometric evaluation of the GEM Scale. Men Masculinities. 2008;10:322–38.
Article Google Scholar
Jakobsen H. What’s Gendered about Gender-Based Violence?: An Empirically Grounded Theoretical Exploration from Tanzania. Gend Soc [Internet]. 2014;28(4):537–61. Available from: ( http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/0891243214532311 ).
Cook RJ. Gender, Health and Human Rights. Heal Hum Rights Quart. 1995;350–68.
Freeman MA. Reservations to CEDAW: An Analysis for UNICEF. Discussion Pper [Internet]. UNICEF; 2009. Available from: http://www.unicef.org/gender/files/Reservations_to_CEDAW-an_Analysis_for_UNICEF.pdf
UNIFEM. Facts and figures: Violence against women [Internet]. 2007. Available from: https://asiapacific.unwomen.org/en/focus-areas/end-violence-against-women/evaw-facts-and-figures .
WHO. Multi-country study on women’s health and violence against women [Internet]. World Health Organization: Geneva; 2005. Available from: http://www.who.int/gender/violence/whomulticountry-study/en/ .
UN Women. World Survey on the Role of Women in Development. Gender Equality and Sustainable Development. New York: United Nations; 2014.
Thomas D, Beasley M. Domestic Violence as a Human Rights Issue. Albany Law Rev. 1995;58:1119–47.
Coomaraswamy R. Special Rapporteur on Violence against Women, its Causes and Consequences, Integration of the Human Rights of Women and the Gender Perspective: Violence U.N. Doc. E/CN.4/1999/68 Against Women: Violence against women in the family [Internet]. Geneva, Switzerland; 2002. Available from: https://digitallibrary.un.org/record/459009?ln=en
OHCHR. 15 Years of the United Nations Special Rapporteur on Violence against Women (1994–2009)-A Critical Review [Internet]. Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR); 2009. Available from: https://www.ohchr.org/Documents/Issues/Women/15YearReviewofVAWMandate.pdf
Stephanie Rose M. The role of structural and interpersonal violence in the lives of women: a conceptual shift in prevention of gender-based violence. BMC Women Heal. 2015;15:93.
Farmer PE, Nizeye B, Stulac S, Keshavjee S. Structural violence and clinical medicine. Plos Med. 2006;3(10):e449.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
WHO. World Report on Violence and Health. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2002.
Connell RW. Hegemonic Masculinity. Jackson S, Scott S, editors. Gender: A Sociological Reader. London: Routledge; 1987.
UNFPA. Overcoming violence against women through an integrated and community-based approach Vol. 2, Programming to Address Violence Against Women. 8 Case Studies. 2008.
Pigg S. Inventing Social Categories through Place: Social Representations and Development in Nepal. Comp Stud Soc Hist. 1992;34(3):491–513.
Lamichhane P, Puri M, Tamang J, Dulal B. Women’s Status and Violence against Young Married Women in Rural Nepal. BMC Womens Health. 2011;11:19.
Atteraya MS, Gnawali S, Song IH. Factors Associated With Intimate Partner Violence Against Married Women in Nepal. J Interpers Violence. 2015;30(7):1226–46.
Ministry of Health N, New Era. Nepal Demographic and Health Survey 2016 [Internet]. Kathmandu, Nepal: MOH/Nepal, New ERA, and ICF; 2017. Available from: http://dhsprogram.com/pubs/pdf/FR336/FR336.pdf
Ghimire DJ, Axinn WG, Smith-Greenaway E. Impact of the spread of mass education on married women’s experience with domestic violence. Soc Sci Res. 2015;
Joshi S, Kharel J. Violence against Women in Nepal -- An Overview. Free Libr. 2008;
Government of Nepal. A study on gender based violence conducted in selected rural districts of Nepal. Kathmandu, Nepal: Office of the Prime Minister and Council of Ministers; 2012.
Deuba K, Mainali A, Alvesson HM, Karki DK. Experience ofintimate partner violence among young pregnant women in urban slums of Kathmandu Valley, Nepal: a qualitative study. BMC Women’s Heal. 2016;16:11.
Sharma S, SRIF/SNV. Domestic violence in Nepali society: root cause and consequences a research report. Social Inclusion Research Fund; 2007.
Joshi SK. Violence Against Women (VAW) in Nepal: Role of Health Care Workers. Kathmandu Univ Med J. 2009;7(2):89–91.
Dahal P, Kumar Joshi S, Swahnberg K. “We are looked down upon and rejected socially”: A qualitative study on the experiences of trafficking survivors in nepal. Glob Health Action. 2015;8:29267.
Huda S. Sex trafficking in South Asia. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2006;94(3):374–81.
Hendrickson ZM, Owczarzak J, Lohani S, Thapaliya Shrestha B, Underwood CR. The (re)productive work of labour migration: the reproductive lives of women with an absent spouse in the central hill region of Nepal. Cult Heal Sex. 2019;21(6):684–700.
Hendrickson ZM, Lohani S, Thapaliya Shrestha B, Underwood CR. Talking about reproduction with a migrating spouse: Women’s experiences in Dhading. Nepal Health Care Women Int. 2018;39(11):1234–58.
DDC. District Profile Morang 2070 [Internet]. Biratnagar, Morang; 2013. Available from: http://ddcmorang.gov.np/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/District-profile-2070.pdf
Dahal P, Joshi SK, Swahnberg K. Does Forum Theater Help Reduce Gender Inequalities and Violence? Findings From Nepal. J Interpers Violence [Internet]. 2021 Mar 4;0886260521997457. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1177/0886260521997457
Dahal P, Joshi SK, Swahnberg K. The Prevalence of gender inequalities and gender based violence in eastern Nepal. Kathmandu Univ Med J. 2019;17(4 [ISSUE 68|OCT.-DEC).
Hummelvol JK. The Multistage Focus Group Interview A Relevant and Fruitful Method in Action Research Based on a Co-operative Inquiry Perspective. Nor Tidsskr Sykepl. 2008;10.
Chamraz K. Constructing Grounded Theory A Practical Guide Through Qualitative Analysis. London, Thousand Oaks, New Delhi: SAGE Publications; 2010.
Darlauf SN, Blume LE. New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics. Second. London: Macmillan; 2008.
Book Google Scholar
Ilika AL. Women’s Perception of Partner Violence in a Rural Igbo Community. Afr J Reprod Health. 2005;9:77–88.
Mitra A, Singh P. Human Capital Attainment and Gender Empowerment: The Kerela Paradox. Soc Sci Q. 2007;88:1227–42.
Niaz U. Violence against women in South Asian countries. Arch Women’s Ment Heal. 2003;6(3):173–84.
Khan H. Women’s perceptions and experiences of sexual violence in marital relationships and its effect on reproductive health. Health Care Women Int. 2008;29:468–83.
Sable M, Danis F, Mauzy D, Gallagher SK. Barriers to reporting sexual assault for women and men: perspectives of college students. J Am Coll Heal. 2006;55:157–62.
Flood M, Pease B. Factors Influencing Attitudes To Violence Against Women. Trauma Violence Abuse. 2009;10(2):125–42.
Jewkes R, Penn KL, Rose JH. ‘‘If they rape me, I can’t blame them”: Reflections on gender in the social context of child rape in South Africa and Namibia. Soc Sci Med. 2005;61:1809–20.
Cislaghi B, Heise L. Using social norms theory for health promotion in low-income countries. Heal Promot Int. 2019;34(3):616–23.
Fricker M. Epistemic Injustice: Power and the Ethics of Knowing. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2007.
Foucault M. Discipline and Punish: The Birth of the Prison. New York: Vintage Books; 1995.
Ridgeway CL. Framed Before We Know It: How Gender Shapes Social Relations. Gend Soc. 2009;23(2):145–60.
Hollander J. Demand More of People: Accountability, Interaction, and Gender Change. Gend Soc. 2013;27(1):5–29.
West C, Zimmerman D. Doing Gender. Gend Soc. 1987;1(2):125–51.
Kaufman M. The Construction of Masculinity and the Triad of Men’s Violence. Beyond Patriarchy: Essays by Men on Pleasure, Power, and Change. Canada: Oxford University Press; 1987.
Connell R. Masculinities. Berkeley: University of California Press; 1995.
Courtenay WH. Constructions of masculinity and their influence on men’s well-being: a theory of gender and health. Soc Sci Med [Internet]. 2000;50(10):1385–401. Available from: ( http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0277953699003901 ).
Jakobsen H. What’s Gendered about Gender-Based Violence? Gend Soc. 2014;28(4):537–61.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to all the focus group discussion participants. The authors are indebted to Bhojraj Sharma, Deekshya Chaudhary, Subham Chaudhary, and Dev Kala Dhungana for their coordination and facilitation in reaching the discussion participants.
Open access funding provided by Linnaeus University.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Health and Caring Science, Linnaeus University, 391 82, Kalmar, Sweden
Pranab Dahal & Katarina Swahnberg
Department of Community Medicine, Kathmandu Medical College, 446 00, Kathmandu, Nepal
Sunil Kumar Joshi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
PD, SKJ, and KS were involved in the study design. PD and KS developed the discussion guides. PD was responsible for the data collection and the data analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Pranab Dahal .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The ethical clearance for this study was obtained from the Institutional Review Committee, Kathmandu Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu. All protocols were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants for the study and verbal consent was sought for the audio recording of the discussions.
Consent for publication
All the participants provided Informed consent for the publication of their data.

Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Dahal, P., Joshi, S.K. & Swahnberg, K. A qualitative study on gender inequality and gender-based violence in Nepal. BMC Public Health 22 , 2005 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-14389-x
Download citation
Received : 18 February 2021
Accepted : 19 October 2022
Published : 01 November 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-14389-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Constructivist grounded theory
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
153 Domestic Violence Topics & Essay Examples
A domestic violence essay can deal with society, gender, family, and youth. To help you decide which aspect to research, our team provided this list of 153 topics .
📑 Aspects to Cover in a Domestic Violence Essay
🏆 best domestic violence titles & essay examples, ⭐ interesting domestic violence topics for an essay, 🎓 good research topics about domestic violence, ❓ research questions on domestic violence.
Domestic violence is a significant problem and one of the acute topics of today’s society. It affects people of all genders and sexualities.
Domestic violence involves many types of abuse, including sexual and emotional one. Essays on domestic violence can enhance students’ awareness of the issue and its causes. Our tips will be useful for those wanting to write outstanding domestic violence essays.
Start with choosing a topic for your paper. Here are some examples of domestic violence essay titles:
- Causes of domestic violence and the ways to eliminate them
- The consequences of domestic violence
- The importance of public domestic violence speech
- Ways to reduce domestic violence
- The prevalence of domestic violence in the United States (or other countries)
- The link between domestic violence and mental health problems among children
Now that you have selected one of the titles for your essay, you can start working on the paper. We have prepared some tips on the aspects you should cover in your work:
- Start with researching the issue you have selected. Analyze its causes, consequences, and effects. Remember that you should include some of the findings in the paper using in-text citations.
- Develop a domestic violence essay outline. The structure of your paper will depend on the problem you have selected. In general, there should be an introductory and a concluding paragraph, as well as three (or more) body paragraphs. Hint: Keep in mind the purpose of your essay while developing its structure.
- Present your domestic violence essay thesis clearly. The last sentence of your introductory paragraph should be the thesis statement. Here are some examples of a thesis statement:
Domestic violence has a crucial impact on children’s mental health. / Domestic violence affects women more than men.
- Present a definition of domestic violence. What actions does the term involve? Include several possible perspectives on domestic violence.
- Discuss the victims of domestic violence and the impact it has on them too. Provide statistical data, if possible.
- Help your audience to understand the issue better by discussing the consequences of domestic violence, even if it is not the primary purpose of your paper. The essay should show why it is necessary to eliminate this problem.
- You can include some relevant quotes on domestic violence to make your arguments more persuasive. Remember to use citations from relevant sources only. Such sources include peer-reviewed articles and scholarly publications. If you are not sure whether you can use a piece of literature, consult your professor to avoid possible mistakes.
- Support your claims with evidence. Ask your professor in advance about the sources you can use in your paper. Avoid utilizing Wikipedia, as this website is not reliable.
- Stick to a formal language. Although you may want to criticize domestic violence, do not use offensive terms. Your paper should look professional.
- Pay attention to the type of paper you should write. If it is an argumentative essay, discuss opposing views on domestic violence and prove that they are unreliable.
- Remember that you should include a domestic violence essay conclusion in your paper too. This section of the paper should present your main ideas and findings. Remember not to present any new information or citations in the concluding paragraph.
There are some free samples we have prepared for you, too. Check them out!
- Domestic Violence and Conflict Theory in Society The Conflict Theory explains remarkable events in history and the changing patterns of race and gender relations and also emphasizes the struggles to explain the impact of technological development on society and the changes to […]
- Break the Silence: Domestic Violence Case The campaign in question aimed to instruct victims of domestic violence on how to cope with the problem and where to address to get assistance.
- Domestic Violence against Women Domestic violence against women refers to “any act of gender-based violence that results in or is likely to result in physical, sexual, and mental harm or suffering to women, including threats of such acts as […]
- Supporting Female Victims of Domestic Violence and Abuse: NGO Establishment The presence of such a model continues to transform lives and make it easier for more women to support and provide basic education to their children.
- Domestic Violence and Honor Killing Analysis Justice and gender equality are important aspects of the totality of mankind that measure social and economic development in the world. The cultural justification is to maintain the dignity and seniority framework of the family.
- Domestic Violence: Reason, Forms and Measures The main aim of this paper is to determine the reason behind the rapid increase of domestic violence, forms of domestic violence and measures that should be taken to reduce its effects.
- Annotated Bibliography on Domestic Violence Against Women They evaluate 134 studies from various countries that provide enough evidence of the prevalence of domestic violence against women and the adverse effects the vice has had for a decade.
- Behind Closed Doors: Domestic Violence The term “domestic violence” is used to denote the physical or emotional abuse that occurs in the homes. Therefore, it has contributed to the spread of domestic violence in the country.
- Guilty until Proven Otherwise: Domestic Violence Cases The presumption of the guilt of a man in domestic violence cases is further proven by the decision of the court in which the man is required to post a bond despite the fact that […]
- Domestic Violence Ethical Dilemmas in Criminal Justice Various ethical issues such as the code of silence, the mental status of the offender, and limited evidence play a vital role in challenging the discretion of police officers in arresting the DV perpetrators.
- Ambivalence on Part of the Police in Response to Domestic Violence The police have been accused of ambivalence by their dismissive attitudes and through sexism and empathy towards perpetrators of violence against women.
- Domestic Violence: Qualitative & Quantitative Research This research seeks to determine the impacts of domestic violence orders in reducing the escalating cases of family brutality in most households. N1: There is a significant relationship between domestic violence orders and the occurrence […]
- What Causes Domestic Violence? Domestic abuse, which is also known as domestic violence, is a dominance of one family member over another or the other. As a result, the probability of them becoming abusers later in life is considerably […]
- National Coalition Against Domestic Violence In addition, NCADV hopes to make the public know that the symbol of the purple ribbon represents the mission of the organization, which is to bring peace to all American households.
- Effects of Domestic Violence on Children’s Social and Emotional Development In the case of wife-husband violence, always, one parent will be the offender and the other one the victim; in an ideal situation, a child needs the love of a both parents. When brought up […]
- The Impact of COVID-19 on Domestic Violence in the US Anurudran et al.argue that the new measures taken to fight COVID-19 infections heightened the risk of domestic abuse. The pandemic paradox: The consequences of COVID 19 on domestic violence.
- Domestic Violence Restraining Orders: Renewals and Legal Recourse Since upon the expiry of a restraining order, a victim can file a renewal petition the current task is to determine whether the original DVRO of our client has expired, the burden of obtaining a […]
- Sociological Imagination: Domestic Violence and Suicide Risk Hence, considering these facts, it is necessary to put the notion of suicide risk in perspective when related to the issue of domestic violence.
- Domestic Violence: The Impact of Law Enforcement Home Visits As the study concludes, despite the increase in general awareness concerning domestic violence cases, it is still a significant threat to the victims and their children.
- Domestic Violence Factors Among Police Officers The objective of this research is to establish the level of domestic violence among police officers and relative the behavior to stress, divorce, police subculture, and child mistreatment.
- Domestic Violence and Drug-Related Offenders in Australia The article is very informative since outlines a couple of the reasons behind the rampant increase in cases of negligence and lack of concern, especially from the government.
- Domestic Violence in Women’s Experiences Worldwide Despite the fact the author of the article discusses a controversial problem of domestic violence against women based on the data from recent researches and focusing on such causes for violence as the problematic economic […]
- Addressing Domestic Violence in the US: A Scientific Approach The implementation of sound research can help in addressing the problem and decreasing the incidence of domestic violence, which will contribute to the development of American society.
- Millennium Development Goals and Domestic Violence: A Bilateral Link As a result, a review of the potential of MDGs for resolving the issue needs to analyze the contribution of the goals to the resolution of the instances, consequences, and causes of DV.
- Domestic Violence and Family Dynamics: A Dual Perspective There are different types and causes of domestic violence, but the desire to take control over relationships is the most common cause.
- Reporting Decisions in Child Maltreatment: A Mixed Methodology Approach The present research aims to address both the general population and social workers to examine the overall attitudes to the reporting of child maltreatment.
- Domestic Violence in Australia: Budget Allocation and Victim Support On the other hand, the allocation of financial resources with the focus on awareness campaigns has also led to a lack of financial support for centres that provide the frontline services to victims of domestic […]
- Domestic and Family Violence: Case Studies and Impacts This paper highlights some of the recent cases of the violence, the forms of abuse involved, and their overall impacts on the victims.
- Legal Recourse for Victims of Child Abuse and Domestic Violence Victims of child abuse and domestic violence have the right to seek legal recourse in case of violation of their rights.
- The Impact of Domestic Violence Laws: Social Norms and Legal Consequences I also suppose that some of these people may start lifting their voices against the law, paying particular attention to the idea that it is theoretically allowable that the law can punish people for other […]
- Affordable, Effective Legal Assistance for Victims of Domestic Violence Legal assistance significantly increases the chances for domestic abuse victims to obtain restraining orders, divorce, and custody of their children. Helping victims of domestic violence with inexpensive legal aid is a critical step in assisting […]
- Domestic Violence: Far-Right Conspiracy Theory in Australia’s Culture Wars The phenomenon of violence is directly related to the violation of human rights and requires legal punishment for the perpetrators and support for the victims.
- Domestic Violence and Black Women’s Experiences Overall, the story’s exploration of the reality of life for an African American married woman in a patriarchal society, and the challenges faced by black women, is relevant to the broader reality of domestic violence […]
- Domestic Violence: Criminal Justice In addition, the usage of illegal substances such as bhang, cocaine, and other drugs contributes to the increasing DV in society.
- Witnessed Domestic Violence and Juvenile Detention Research The primary purpose of this study is to examine the relationship between witnessed domestic violence and juvenile detention. Research has pointed to a relationship between witnessed violence and juvenile delinquency, and this study holds that […]
- Domestic Violence Against Women in Melbourne Thus, it is possible to introduce the hypothesis that unemployment and related financial struggles determined by pandemic restrictions lead to increased rates of domestic violence against women in Melbourne.
- Domestic Violence and Its Main Signs In general, the providers should be able to identify the markers of abuse by paying closer attention to the people they serve, treat, teach, or work with.
- Intersectionality in Domestic Violence Another way an organization that serves racial minorities may address the unique needs of domestic violence victims is to offer additional educational and consultancy activities for women of color.
- Domestic Violence and Primordial Prevention In addition, the promotion of social norms against violence and increased penalties for domestic and sexual abuse need to be supported at the legislative level.
- Healthcare Testing of a Domestic Violence Victim Accordingly, the negative aspects of this exam include difficulties in identifying and predicting the further outcome of events and the course of side effects.
- Financial Insecurity: Impact on Domestic Violence Therefore, this problem is global and widespread, and it would be wrong to assume that spousal abuse only exists when couples are poor.
- Domestic Violence, Child Abuse, or Elder Abuse In every health facility, a nurse who notices the signs of abuse and domestic violence must report them to the relevant authorities.
- Educational Services for Children in Domestic Violence Shelters In order to meet the objectives of the research, Chanmugam et al.needed to reach out to the representatives of emergency domestic violence shelters located in the state of Texas well-aware of the shelters’ and schools’ […]
- The Domestic Violence Arrest Laws According to the National Institute of Justice, mandatory arrest laws are the most prevalent in US states, indicating a widespread agreement on their effectiveness.
- Environmental Scan for Hart City Domestic Violence Resource Center In particular, it identifies the target population, outlines the key resources, and provides an overview of data sources for assessing key factors and trends that may affect the Resource Center in the future.
- Domestic Violence Investigation Procedure If they claim guilty, the case is proceeded to the hearing to estimate the sentencing based on the defendant’s criminal record and the scope of assault. The issue of domestic abuse in households is terrifyingly […]
- Educational Group Session on Domestic Violence This will be the first counseling activity where the counselor assists the women to appreciate the concepts of domestic violence and the ways of identifying the various kinds of violence.
- Domestic Violence and COVID-19: Literature Review The “stay safe, stay at home” mantra used by the governments and public health organizations was the opposite of safety for the victims of domestic violence.
- Rachel Louise Snyder’s Research on Domestic Violence Language and framing play a significant role in manipulating people’s understanding of domestic violence and the nature of the problem. However, it is challenging to gather precise data on the affected people and keep track […]
- Alcoholism, Domestic Violence and Drug Abuse Kaur and Ajinkya researched to investigate the “psychological impact of adult alcoholism on spouses and children”. The work of Kaur and Ajinkya, reveals a link between chronic alcoholism and emotional problems on the spouse and […]
- Domestic Violence Counselling Program Evaluation The evaluation will be based upon the mission of the program and the objectives it states for the participants. The counselors arrange treatment for both sides of the conflict: the victims and offenders, and special […]
- The Roles of Domestic Violence Advocates Domestic conflict advocates assist victims in getting the help needed to cope and move forward. Moreover, these advocates help the survivors in communicating to employers, family members, and lawyers.
- Domestic Violence: How Is It Adressed? At this stage, when the family members of the battered women do this to them, it becomes the responsibility of the people to do something about this.
- Victimology and Domestic Violence In this situation there are many victims; Anne is a victim of domestic violence and the children are also victims of the same as well as the tragic death of their father.
- “The Minneapolis Domestic Violence Experiment” by Sherman and Berk The experiment conducted by the authors throws light on the three stages of the research circle. This is one of the arguments that can be advanced.
- An Investigation on Domestic Violence This particular experiment aimed to evaluate the nature of relationship and the magnitude of domestic violence meted on either of the partners.
- Educational Program on Domestic Violence The reason why I have chosen this as the topic for my educational program is that victims of domestic violence often feel that they do not have any rights and hence are compelled to live […]
- Family and Domestic Violence: Enhancing Protective Factors Current partner Previous partner Percentage of children When children are exposed to violence, they encounter numerous difficulties in their various levels of development.
- Parenting in Battered Women: The Effects of Domestic Violence In this study, ‘Parenting in Battered Women: The Effects of Domestic Violence on Women and their Children,’ Alytia A. It is commendable that at this stage in stating the problem the journalists seek to conclude […]
- Domestic Violence Types and Causes This is acknowledged by the law in most countries of the world as one of the most brutal symbols of inequality.
- Alcohol and Domestic Violence in Day-To-Day Social Life My paper will have a comprehensive literature review that will seek to analyze the above topic in order to assist the reader understand the alcohol contributions in the domestic and social violence in our society.
- Power and Control: Domestic Violence in America The abusive spouse wants to feel powerful and in control of the family so he, usually the abusive spouse is the man, beats his wife and children to assert his superiority.
- Domestic or Intimate Partner Violence Intervention Purpose of the study: The safety promoting behavior of the abused women is to be increased using a telephone intervention. They were allocated to either of the groups by virtue of the week of enrolment […]
- Federal and State Legislative Action on Domestic Violence In 2004, the state of New York decided to look into some of the ways of preventing this form of domestic violence by forming an Office for the Prevention of Domestic Violence in 2005, employers […]
- Substance Abuse and Domestic Violence: Comprehensive Discussion Substance abuse refers to the misuse of a drug or any other chemical resulting in its dependence, leading to harmful mental and physical effects to the individual and the wellbeing of the society.
- Environmental Trends and Conditions: Domestic Violence in the Workplace Despite the fact that on average the literacy rate and the rate of civilization in the world have been increasing in the past few decades, the statistics for domestic violence have been increasing on an […]
- Domestic Violence in the Organizations Despite the fact that on average the literacy rate and the rate of civilization in the world has been increasing in the past few decades, the statistics for domestic violence have been increasing on an […]
- Facts About Domestic Violence All aspects of the society – which starts from the smallest unit, that is the family, to the church and even to the government sectors are all keen on finding solutions on how to eliminate, […]
- Domestic Violence in Marriage and Family While there are enormous reports of intimate partner homicides, murders, rapes, and assaults, it is important to note that victims of all this violence find it very difficult to explain the matter and incidents to […]
- Domestic Violence and Repeat Victimisation Theory Domestic violence is a crime which often happens because of a bad relationship between a man and woman and usually continues to be repeated until one of the parties leaves the relationship; hence victims of […]
- One-Group Posttest-Only Design in the Context of Domestic Violence Problem This application must unveil the risks and their solutions by researching the variables and the threats to the validity of the research.
- Help-Seeking Amongst Women Survivors of Domestic Violence First, the article explains the necessity of the research conduction, which includes the relevance of the abuse problem and the drawbacks of solving and studying it.
- Domestic Violence as a Social Issue It is one of the main factors which stimulate the study’s conduction, and among the rest, one can also mention the number of unexplored violence questions yet to be answered.
- Reflections on Domestic Violence in the Case of Dr. Mile Crawford Nevertheless, the only way out of this situation is to escape and seek help from the legal system. From a personal standpoint, to help her would be the right thing to do.
- Gender Studies: Combating Domestic Violence The purpose of this paper is to provide a detailed description of domestic violence, as well as the development of an action plan that can help in this situation.
- Domestic Violence Funding and Impact on Society The number of domestic violence cases in the US, both reported and unreported, is significant. The recent decision of Trump’s administration to reduce the expenses for domestic violence victims from $480,000,000 to $40,000,000 in the […]
- Campaign against Domestic Violence: Program Plan In addition, men who used to witness aggressive behavior at home or in the family as children, or learned about it from stories, are two times more disposed to practice violence against their partners than […]
- Domestic Violence and Bullying in Schools It also states the major variables related to bullying in schools. They will confirm that social-economic status, gender, and race can contribute to bullying in schools.
- Domestic Violence Within the US Military In most of the recorded domestic violence cases, females are mostly the victims of the dispute while the males are the aggressors of the violence.
- Family and Domestic Violence Legislation in the US In fact, this law is a landmark pointing to the recognition of the concept of domestic violence at the legal level and acknowledging that it is a key problem of the society.
- Domestic Violence and Social Interventions In conclusion, social learning theory supports the idea that children have a high likelihood of learning and simulating domestic violence through experiences at home.
- Domestic Violence and Child’s Brain Development The video “First Impressions: Exposure to Violence and a Child’s Developing Brain” answers some questions of the dependence of exposure to domestic violence and the development of brain structures of children. At the beginning of […]
- Local Domestic Violence Victim Resources in Kent The focus of this paper is to document the local domestic violence victim resources found within a community in Kent County, Delaware, and also to discuss the importance of these resources to the community.
- Domestic Violence Abuse: Laws in Maryland The Peace and Protective Orders-Burden of Proof regulation in Maryland and the Violence against Women Act are some of the laws that have been created to deal with domestic violence.
- Theories of Domestic Violence It is important to point out that women have received the short end of the stick in regards to domestic violence. A third reason why people commit domestic violence according to the Family Violence Theory […]
- Domestic Violence in Australia: Policy Issue In this paper, DV in Australia will be regarded as a problem that requires policy decision-making, and the related terminology and theory will be used to gain insights into the reasons for the persistence of […]
- Nondiscriminatory Education Against Domestic Violence The recent event that prompted the proposed advocacy is the criticism of a banner that depicts a man as the victim of abuse.
- Domestic Violence in International Criminal Justice The United Nations organization is deeply concerned with the high level of violence experienced by women in the family, the number of women killed, and the latency of sexual violence.
- Project Reset and the Domestic Violence Court The majority of the decisions in courts are aimed to mitigate the effects of the strict criminal justice system of the United States.
- Same-Sex Domestic Violence Problem Domestic violence in gay or lesbian relationships is a serious matter since the rates of domestic violence in such relationships are almost equivalent to domestic violence in heterosexual relationships. There are a number of misconceptions […]
- Domestic, Dating and Sexual Violence Dating violence is the sexual or physical violence in a relationship which includes verbal and emotional violence. The rate of sexual violence in other nations like Japan and Ethiopia, range from 15 to 71 percent.
- Anger Management Counseling and Treatment of Domestic Violence by the Capital Area Michigan Works These aspects include: the problem that the program intends to solve, the results produced by the program, the activities of the program, and the resources that are used to achieve the overall goal.
- Understanding Women’s Responses to Domestic Violence The author’s research orientation is a mix of interpretive, positivism and critical science – interpretive in informing social workers or practitioners on how to enhance their effectiveness as they deal with cases related to violence […]
- Poverty and Domestic Violence It is based on this that in the next section, I have utilized my educational experience in order to create a method to address the issue of domestic violence from the perspective of a social […]
- Teenage Dating and Domestic Violence That is why it is important to report about the violence to the police and support groups in order to be safe and start a new life.
- Evaluation of the Partnership Against Domestic Violence According to the official mission statement of the organization, PADV is aimed at improving the overall wellbeing of families all over the world and helping those that suffer from domestic violence The organization’s primary goal […]
- Cross-Cultural Aspects of Domestic Violence This is one of the limitations that should be taken account. This is one of the problems that should not be overlooked.
- Domestic Violence in the Lives of Women She gives particular focus on the social and traditional aspects of the community that heavily contribute to the eruption and sustenance of violence against women in households. In the part 1 of the book, Renzetti […]
- Financial Planning and Management for Domestic Violence Victims Acquisition of resources used in criminal justice require financial resources hence the need to manage the same so as to provide the best machines and equipments.
- Violence against Women: Domestic, National, and Global Rape as a weapon for the enemy Majority of cultures in war zones still accept and regard rape to be a weapon of war that an enemy should be punished with.
- Effects of Domestic Violence on Children Development In cases where children are exposed to such violence, then they become emotionally troubled: In the above, case them the dependent variable is children emotions while the independent variable is domestic violence: Emotions = f […]
- Evaluation of Anger Management Counseling and Treatment of Domestic Violence by the Capital Area Michigan Works These aspects include: the problem that the program intends to solve, the results produced by the program, the activities of the program, and the resources that are used to achieve the overall goal.
- Knowledge and Attitudes of Nurses Regarding Domestic Violence and Their Effect on the Identification of Battered Women In conducting this research, the authors sought the consent of the prospective participants where the purpose of the study was explained to participants and confidentiality of information to be collected was reassured.
- Domestic Violence Dangers Mount With Economic, Seasonal Pressures These variables are believed to be able to prompt the family to explore the experiences and meanings of stress and stress management.
- Impact of the Economic Status on Domestic Violence This article investigates the possible factors that may help in explaining the status of women who are homeless and their capacity to experience domestic violence.
- Dominance and “Power Plays” in Relationships to Assist Clients to Leave Domestic Violence According to psychologists, the problem of domestic violence is based on the fact that one partner needs to be in control of the other.
- Social Marketing Campaign on Domestic Violence In this marketing campaign strategy the focus would be centered on violence against women, as a form of domestic violence that is currently experience in many countries across the globe.
- Art Therapy With Women Who Have Suffered Domestic Violence One of the most significant benefits of art therapy is the fact the patients get to understand and interpret their own situations which puts them in a better position to creatively participate in own healing […]
- Collaborative Crisis Intervention at a Domestic Violence Shelter The first visit is meant to collect the information that the professional in domestic violence deem crucial concerning the precipitating incidence and history of violence.
- Domestic Violence Exposure in Colombian Adolescents In this topic, the authors intend to discover the extent of association of drug abuse to domestic violence exposure, violent and prosocial behavior among adolescents.
- Domestic Violence and Its Classification Sexual abuse is the other common form of maltreatment which is on the rise and refers to any circumstance in which force is utilized to get involvement in undesired intimate action. Emotional maltreatment entails inconsistent […]
- Domestic Violence and Social Initiatives in Solving the Problem The absence of the correct social programs at schools and the lack of desire of government and police to pay more attention to the prevention of the problem while it is not too late are […]
- Domestic Violence in the African American Community Previous research has suggested this due to the many causes and effects that are experienced by the members and especially the male members of the African American community.
- Domestic Violence: Predicting and Solutions There are several factors which predict the state of domestic violence in the future and this will help in preventing domestic violence.
- Domestic Violence: Signs of Abuse and Abusive Relationships The unprecedented rejuvenation of such a vile act, prompted the formation of factions within society, that are sensitive to the plight of women, and fight for the cognizance of their rights in society.
- Domestic Violence against South Asian Women Again, this strategy is premised on the idea that domestic violence can be explained by the financial dependence of women in these communities.
- The Effects of Domestic Violence According to statistics and research provided in the handout, women are at a higher risk of being victims of domestic violence.
- Effect of Domestic Violence on Children This is done with the aim of ensuring that the child is disciplined and is meant as a legitimate punishment. Most of our children have been neglected and this has contributed to the increase in […]
- Domestic Violence and Elderly Abuse- A Policy Statement Though this figure has been changing with the change in the method of survey that was conducted and the nature of samples that were taken during the research process, it is widely accepted fact that […]
- Domestic Violence as a Social and Public Health Problem The article, authored by Lisa Simpson Strange, discusses the extent of domestic violence especially in women and the dangers it exposes the victims to, insisting that severe actions should be taken against those who commit […]
- Community and Domestic Violence: Elder Abuse In addition, the fact the elderly people cannot defend themselves because of the physical frailty that they encounter, they will experience most of the elderly abuse.
- Community and Domestic Violence; Gang Violence Solitude, peer pressure, need to belong, esteem, and the excitement of the odds of arrest entice adolescents to join these youth gangs.
- Fighting Domestic Violence in Pocatello, Idaho Having realized the need to involve the family unit in dealing with this vice, Walmart has organized a sensitization program that will involve the education of whole family to increase awareness on the issue. The […]
- What Is the Purpose of Studying Domestic Violence?
- What Does Theory Explain Domestic Violence?
- What Is the Difference Between IPV and Domestic Violence?
- What Age Group Does Domestic Violence Affect Most?
- When Domestic Violence Becomes the Norm?
- How Are Domestic Violence Problems Solved in American and Other Cultures?
- What Are the 3 Phases in the Domestic Violence Cycle?
- How Can Domestic Violence Be Explained?
- How Many Deaths Are Caused by Domestic Violence?
- When Was Domestic Violence First Defined?
- How Is a Domestic Violence Prevention?
- How Race, Class, and Gender Influences Domestic Violence?
- Why Do Victims of Abuse Sometimes Stay Silent?
- How Does Domestic Violence Affect the Brain?
- Is Mental Illness Often Associated With Domestic Violence?
- How Does Domestic Violence Affect a Person Emotionally?
- How Does Domestic Violence Affect Children’s Cognitive Development?
- Why Should Employers Pay Attention to Domestic Violence?
- What Are the Causes of Domestic Violence?
- What Country Has the Highest Rate of Domestic Violence?
- How Does Domestic Violence Affect the Lives of Its Victims?
- What Are the Possible Causes and Signs of Domestic Violence?
- How Does Socioeconomic Status Affect Domestic Violence?
- How Does the Australian Criminal Justice System Respond to Domestic Violence?
- How Does Culture Affect Domestic Violence in the UK?
- What Is the Psychology of an Abuser?
- What Is Police Doing About Domestic Violence?
- How Does the Government Define Domestic Violence?
- What Profession Has the Highest Rate of Domestic Violence?
- What Percent of Domestic Violence Is Alcohol-Related?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 26). 153 Domestic Violence Topics & Essay Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/domestic-violence-essay-examples/
"153 Domestic Violence Topics & Essay Examples." IvyPanda , 26 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/domestic-violence-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '153 Domestic Violence Topics & Essay Examples'. 26 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "153 Domestic Violence Topics & Essay Examples." February 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/domestic-violence-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "153 Domestic Violence Topics & Essay Examples." February 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/domestic-violence-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "153 Domestic Violence Topics & Essay Examples." February 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/domestic-violence-essay-examples/.
- Family Relationships Research Ideas
- Alcohol Abuse Paper Topics
- Drug Abuse Research Topics
- Child Welfare Essay Ideas
- Childhood Essay Topics
- Sexual Abuse Essay Titles
- Divorce Research Ideas
- Gender Stereotypes Essay Titles
I Used to Judge Women in Abusive Relationships — Until I Became One
When your self esteem is chipped away and you're terrified of being alone, you may not even realize it's abuse.

He threw the car into park, and turned to face me with a look of pure rage. His fist connected with the left side of my jaw, the right side of my head hit the passenger-side window, and I heard a loud crack .
He wasn't finished, though. He grabbed my hair and pinched my arm, bruising it instantly, and then he reached over and squeezed my throat. I somehow croaked out, "You loved me once!" and he let go, disgust on his face. It was after midnight, and I got out of the car, numb and overwhelmingly ashamed, and walked a mile back to my friend's house as he squealed the tires and raced away from me.
Two days later, I drove myself to an urgent care facility when I couldn't move my neck.
"How did you sustain the injury?" the young doctor asked me.
"I was at a Super Bowl party and playing on the floor with some kids, and one of them jumped on my neck," I lied. It was the first of many lies I would tell about my relationship. The thought of telling the truth was humiliating. Plus, I thought, It's my fault anyway .
The doctor glanced at the fading finger imprints around my throat and the angry green and black bruises on my arm. I could feel his gaze on me as he wrote a prescription for a painkiller and muscle relaxers.
"You have a severe sprain," he told me. "You're lucky you didn't break it."
Later that week, I was in a golf cart with a colleague at a client event, wearing a short-sleeved shirt with a collar. I reached over to grab a water bottle, and the bruises on my upper arm were exposed.
My colleague took my hand and looked me in the eye. "Please don't tell me it's like that, Kristin," he said quietly. I looked away.
A Slippery Slope
It didn't start like this when I met my live-in boyfriend six years earlier. At first, he was loving and sweet and attentive. I was already in love with him by the first time he called me a worthless piece of s*** in an alcohol-infused fury; I was in shock. I thought about leaving him that night, but I was frozen with indecision. I loved him, after all. And my mind had started to believe what he said about me.
The next morning, he was sober again and rushed to apologize, holding me in his arms while I cried. The cycle began.
.css-107b7z2{font-family:MajestiBanner,MajestiBanner-weightbold-roboto,MajestiBanner-weightbold-local,Georgia,Times,Serif;font-size:1.625rem;font-weight:bold;letter-spacing:0.03rem;line-height:1.2;margin:0rem;}@media(max-width: 64rem){.css-107b7z2{font-size:2.5rem;line-height:1;}}@media(min-width: 48rem){.css-107b7z2{font-size:2.8125rem;line-height:1;}}@media(min-width: 64rem){.css-107b7z2{font-size:3.125rem;line-height:1;}}.css-107b7z2 b,.css-107b7z2 strong{font-family:inherit;font-weight:bold;}.css-107b7z2 em,.css-107b7z2 i{font-style:italic;font-family:inherit;} Over the course of several years, I had learned to see myself through his eyes: unattractive, unlovable, and stupid.
The first time he kicked me, I was walking down the stairs to our apartment, and he told me it was my fault. I "pushed his buttons" and made him do it. Soon, I started taking all the blame for his rages, walking on eggshells every moment we were together.
Over the course of several years, I had learned to see myself through his eyes: unattractive, unlovable, and stupid. I believed him when he told me that he was the best I would ever find and that I was not sexy or desirable. I wish I could go back in time and tell myself that he was talking about himself — not about me.

I thought I knew all about abusive relationships before I found myself in the middle of one. I thought I was too smart to get involved with someone who would hurt me physically and mentally. I thought I knew what to look for and that it would be so obvious that I needed to walk away. I thought I didn't fit into the "stereotypical" mold of what a domestic violence survivor looks like. I'm sure that once upon a time, I looked down on women who were in abusive relationships and found them weak.
Breaking the Silence
In the end, I didn't walk away from him. And I didn't tell my closest friends and family for years about what happened — most of them not until after he left me to move in with another woman four years into our marriage. Now, I tell my story without (most of) the shame; I believe it's important to share it to show others that someone can come through this and survive. And perhaps thrive. Maybe it will help someone you know. Maybe it will help you . I tell the story to help my nieces, my friends, my colleagues, myself.
People are often baffled by how beautiful, intelligent women fall in love with (and even marry) abusers. The truth is that it happens very gradually. It begins with a sarcastic putdown, and is followed up quickly by an apology. It may escalate to a kick or a slap, with more apologies and promises that it will never happen again. By the time I realized that I was in a bad relationship, I had invested so much of myself and my self-esteem had been chipped away so drastically, I was terrified to be alone.
You may know someone who has been abused, and you can't understand why she doesn't leave. She may be afraid that no one else will love her. Perhaps she has kids and doesn't know how to provide for them on her own. He may have threatened to kill her. She may be so ashamed that no one knows the extent of the abuse and suffers in silence. He may be someone powerful or well-liked in the community, and she is afraid no one would believe her.
This post is part of a Good Housekeeping series of stories about domestic violence and abuse . If you or someone you know is at risk, reach the National Domestic Violence Hotline at 1-800-799-7233 . If you are in danger, call 911. More information and resources are available at the National Resource Center on Domestic Violence or the National Online Resource Center for Violence Against Women .

@media(max-width: 64rem){.css-o9j0dn:before{margin-bottom:0.5rem;margin-right:0.625rem;color:#ffffff;width:1.25rem;bottom:-0.2rem;height:1.25rem;content:'_';display:inline-block;position:relative;line-height:1;background-repeat:no-repeat;}.loaded .css-o9j0dn:before{background-image:url(/_assets/design-tokens/goodhousekeeping/static/images/Clover.5c7a1a0.svg);}}@media(min-width: 48rem){.loaded .css-o9j0dn:before{background-image:url(/_assets/design-tokens/goodhousekeeping/static/images/Clover.5c7a1a0.svg);}} Relationships

100 Best Birthday Wishes for Friends

The Best Love Messages

Thoughtful "Thank You" Messages for Any Occasion

Sweet "Good Morning" Messages to Send
How Strangers Helped Me Fix My Love Life

Beautiful Quotes All About Friendship

11 Best Lesbian Dating Apps to Try in 2024

120 Best Birthday Wishes for Brothers

Our Favorite Pride Month Quotes

25 Great Long-Distance Date Ideas

Here's What to Write in a Wedding Card
University of Notre Dame
Notre Dame Philosophical Reviews
- Home ›
- Reviews ›
The Equal Society: Essays in Theory and Practice

George Hull (ed.), The Equal Society: Essays in Theory and Practice , Rowman and Littlefield, 2015, 354pp., $100.00 (hbk), ISBN 9781498515719.
Reviewed by Valentin Beck, Freie Universität Berlin
What would be the central characteristics of a society in which its citizens are truly treated as equals? While egalitarian thinkers are united in their affirmation of the value of equality, they notoriously have -- for centuries -- disagreed about its interpretation. Egalitarianism now is a dominant current within Western moral and political philosophy, but it is also very broad and multifaceted. There is a wide range of mutually inconsistent egalitarian conceptions, ranging from libertarian and meritocratic positions to social liberal, communitarian and socialist ones. Therefore, the decisive question is not whether one should be an egalitarian, but what kind of egalitarian one should be, and how to interpret the central tenet of equal treatment more concretely in political theory and practice.
The anthology under review sheds light on this question. It offers a fascinatingly rich collection of original essays from a diverse group of scholars, some of whom have been shaping egalitarian discourse for decades. An introduction by George Hull and a helpful index complete a collection that will surely be indispensable for those wishing to take stock of recent developments in egalitarian thought. The book's more theoretical first part is dedicated to expansions and revisions of the concept of equality. It focuses on theoretical innovations concerning, among other topics, the interpretation of "social" or "relational" equality, and methodological issues such as the relation of non-ideal to ideal theory. The second part contains contributions on more applied issues, namely equality in higher education (Ann E. Cudd), the challenges to equality posed by the gendered division of labour (Gina Schouten), workplace democracy (Pierre-Yves Néron), modern constitutionalism (David Bilchitz) and historical redress claims (Daryl Glaser). The division of the book into two parts should not be misinterpreted, however. All of the contributions in one way or the other address the theoretical challenge of fleshing out the tenet of equal treatment. And while the articles in the second part have a more specific focus, those in the first also contain more concrete references to what the tenet of equal treatment implies in practice.
The volume does not take stock of the entire range of egalitarian theories, but rather assembles a variety of innovative positions and perspectives. At least six such areas receive in-depth treatment in the volume: first, the idea of "social" or "relational equality", as opposed to "distributional equality" (Jonathan Wolff, Miranda Fricker, Tom P. S. Angier, Lucy Allais, Néron and Daniel Putnam); second, the focus on race as a neglected category in egalitarian thinking (Charles W. Mills and Glaser); third, reflection on capabilities as metric of justice and wellbeing (Fricker, Bekka Williams and Hull); fourth, the importance of rectificatory justice for establishing more equal societies (Mills and Glaser); fifth, African-communitarianism as a distinct egalitarian current (Thaddeus Metz); and sixth, a negativist methodology, according to which specific inequalities or injustices should be the starting point of egalitarian theorizing, rather than the affirmation of an abstract ideal (particularly Wolff, Mills and Fricker). The treatment of this array of topics is generally very stimulating and deserves to be studied in detail. Without wishing to neglect any of these areas or essays in particular, I will limit my more extensive comments to the essays of Mills, Fricker and Wolff, in which several of the above-mentioned innovative concepts are concerned. At the end of this review, I will briefly reflect on why the present volume, which is up-to-date on an impressive number of issues, excludes any treatment of international and global economic inequalities as well as intergenerational environmental inequalities.
In "Racial Equality" Mills addresses race as a neglected category as well as the issues of methodological negativism (see Hull's introduction, p. 3, for this term) and corrective justice, which are interlinked. Mills has gained prominence by arguing that contemporary political philosophy, and particularly its contractualist strand, does not adequately address racial inequalities in liberal societies. In this essay, he argues that race is an essential category and shows the extent to which it has been neglected in what he calls "mainstream social justice theory, particularly Rawlsianism" (p. 44). Beyond this deconstructive concern, however, Mills also demonstrates how egalitarian theorizing can better incorporate issues of racial inequalities. He points to different positions on the metaphysics of race, ranging from simple eliminativism, according to which race does not exist in any sense, to variants of anti-eliminativism, including the constructivist variant to which Mills himself subscribes. Anti-eliminativist constructivism holds that races do not exist biologically, but as "socio-political constructs brought into existence through discriminatory socio-political processes" (p. 44).
From this angle, Mills analyses different forms of racism in "racist societies", which are distinguished from "overtly racist regimes" such as the U.S. under Jim Crow, Nazi Germany or South Africa under apartheid, because they lack features such as an "overtly racist ideology" or de jure discriminations (see p. 49). What matters is that racist societies still structurally advantage whites to a very significant extent, even in the absence of formal discrimination. Mills sets aside racism of the interpersonal kind, embodied in individual actions, since it is deemed "not relevant for racial inequality as a broad social phenomenon" (p. 45). Alternatively, one might argue that individual racist behaviour is relevant and could be integrated into the structural analysis that Mills is championing, since structural injustices likely influence the forms that interpersonal racism takes. Be that as it may, Mills focuses on "socio-institutional" racism (see p. 45) as the more fundamental phenomenon and which can exist even in the absence of interpersonal racism. He holds that racially unequal societies possess a "racialized basic structure" (p. 54), which discriminates against black people even while they possess formal equality with white people. These distinctions allow for the observation that ideal theory of the Rawlsian kind, which justifies principles for societies that are at least approximately just, cannot address racial discriminations of the kind that are typical for Western societies, since they simply do not exist in this framework.
This is where methodological negativism comes into play. Mills states that, instead of focusing on scenarios of roughly full compliance, theorists should start by designing principles of non-ideal theory with the aim of establishing transitional justice. This will lead to substantially different principles and priority rules, compared for example to the well-known principles that are discussed by Rawls under the notion of justice as fairness. Ideal theory does not become altogether obsolete in this variant of methodological negativism, however. Its proper function is to illustrate the ideal of a just society, which could one day be realized if principles of non-ideal theory are implemented. So despite his harsh criticism of Rawlsian ideal theory, Mills acknowledges a need for ideal theory next to non-ideal theorizing. Within his framework of "modified Rawlsianism" (p. 66), his use of the distinction between ideal and non-ideal theory is also broadly in line with Rawls' usage.
Fricker, too, is renowned for addressing a category that has hitherto been neglected in egalitarian thought, namely that of epistemic injustice (2007). In "Epistemic Contribution as a Central Human Capability", Fricker builds on central themes of her groundbreaking monograph. Her goal is to show that any society dedicated to furthering human well-being has to take seriously the ways in which it enables or constrains the capacities of its members to contribute to commonly shared knowledge. In order to enhance the well-being of their members, societies must realize their capability of epistemic contribution, understood as a "combined capability" in the sense coined by Martha Nussbaum (that is, as both an internally developed and an externally enabled capability). Fricker affirms and significantly extends the capabilities metric developed by Sen and Nussbaum. Her work is more closely aligned with Nussbaum than with Sen, since she emphasizes her sympathies for the project of formulating a "list of capabilities that might at least roughly capture workable universal characterisation of human well-being" (p. 77). However, Nussbaum's list is incomplete according to Fricker, because it displays a bias towards capabilities of practical as opposed to theoretical reason (see p. 75). In going back to Wolff and Avner de-Shalit (2007, p. 45), Fricker defends a "two-directional conception of human well-being" (p. 76), reminding us that "while it is good to receive it is also good to give " (p. 75). Fricker posits that the capability of epistemic contribution consists in being able to "contribute to the pool of shared epistemic materials -- materials for knowledge, understanding, and very often for practical deliberation" (p. 76).
It is not Fricker's aim to show that we can sometimes be morally obliged not to withhold knowledge from others, which would be a relatively easy and straightforward task depending on the concrete type and context of concealment in question. She instead aims to show that it is good and even essential for their wellbeing for individuals to contribute knowledge to society. Individuals' capabilities of epistemic contribution can be constrained or enabled by certain types of interpersonal behaviour as well as by societal structures. To justify why the protection of this capability of theoretical reason is important, Fricker draws on the value of non-domination in the sense of liberty from arbitrary interference made famous by Philip Pettit. Pettit argues that freedom from arbitrary interference can only be secured through public institutions which allow members of society to publicly contest such interferences. For such contestation, however, the capability of epistemic contribution must in turn be realized (see p. 86).
Beyond introducing a concept that deserves the concern of egalitarians in theory and practice, Fricker sheds light on a number of other hotly debated issues, such as the critique of recipient-oriented approaches to equality and the conceptualization of relational equality. Fricker also has interesting things to say on what she calls a "failure-first methodology" (p. 74), which informs her account of epistemic injustice and her concept of epistemic contribution. Her methodology is similar to Mills', in that it places an emphasis on starting with the negative. But it diverges at least in one respect: for Fricker, starting with the negative is not necessarily tied to non-ideal theorizing, since the concepts of "justice" and "equality" need to be comprehensively interpreted by taking into account the "endemic pressures for collapse into injustice and inequality" (p. 73). Fricker therefore emphasizes that a failure-first-methodology is conceptually distinct from the dichotomy of ideal and non-ideal theorizing and can yield fruitful results within either framework.
In "Social Equality, Relative Poverty and Marginalised Groups", Wolff answers these methodological questions differently. Wolff's aim is to analyze how absolute and relative poverty prevent the achievement of a (truly) equal society, which he defines as one that is free from asymmetrical relations and from relations of estrangement and alienation. His methodology for this enterprise is set out at the start of the essay. Like Mills and Fricker, Wolff emphasizes the importance of "starting from problems with the actual world rather than a depiction of an ideal world" (p. 24). But unlike Mills and Fricker, who each acknowledge the significance of ideal theory when appropriately combined with non-ideal theory, Wolff completely rejects ideal theory. He holds that "an ideal theory of social equality is hard to sustain, because it is very difficult to give precise and unique content to an ideal of social equality" (p. 22). Instead, there are "many different ways in which a society could count as a 'society of equals' . . . . Quaker Society, a Kibbutz, and a 1960s Californian Hippy community may all, if things go well, count as small-scale societies of equals" (p. 23). In place of the term of non-ideal theory Wolff suggests that of "real-world political philosophy" (p. 22), because it avoids any connotation of dependence on ideal theorizing.
Looking at the work of Mills, Fricker, and Wolff, we can distinguish three variants of methodological negativism. Mills' variant is placed within the classical Rawlsian understanding of ideal and non-ideal theory, but displays a much greater emphasis on the latter as opposed to the former. Fricker's approach underlines the distinctness and complementarity of the negativist methodology by stating that it can be applied to either non-ideal or ideal theorizing. Wolff's methodological negativism transcends the classic distinction of ideal and non-ideal theory by rejecting the focus on ideals for political theory altogether. Mills' and Fricker's approaches to methodological negativism are in principle compatible, but Wolff's approach cannot be reconciled with them, due to his complete rejection of ideal theory.
Methodological concerns are not the only focus in Wolff's article. His two main themes are providing an account of different forms of poverty, and reflecting on how to tackle them from a perspective that values the idea of "social equality" (widely treated as synonymous with "relational equality"). This idea has gained steam in recent years since being affirmed in the writings of thinkers such as Elizabeth Anderson, Samuel Scheffler and Tim Scanlon, and it is also treated in a number of other contributions to the volume (compare the third paragraph above; see also Fourie/Schuppert/Wallimann-Helmer 2015). Wolff dedicates particular attention to the notion of relative poverty and how it is connected with that of social (in)equality. Poverty is dependent on what is customary in a given society, Adam Smith noted when he wrote that "in the present times, through the greater part of Europe, a creditable day-labourer would be ashamed to appear in public without a linen shirt" (Smith 1776, book 5, ch. 2). According to Wolff, "one is in relative poverty if one lacks the consumption and household goods customary in one's society, or lacks resources sufficient to allow a social life, or is unable to purchase what is needed to avoid shame" (p. 26). While this tripartite notion of relative poverty has material implications, it is preferable to purely monetary definitions (e.g. defining poverty as receiving an income below 60 percent of the median income). Numerical definitions of poverty scratch only at the surface of what it means to be poor, and fail to distinguish between material inequalities, as problematic as they may otherwise be, and poverty. Wolff's definition shows how relative poverty and social inequality are connected yet distinct phenomena. They are not identical because there can be other forms of inequality that are not reflected in a lack of resources to participate in customary social practices -- such as asymmetric race or gender relations. Wolff analyses different constellations of deprivation that result from the desire to "fit in", such as when people spend resources on status goods such as mobile phones despite lacking the resources for basic necessities (see p. 29). Fighting poverty effectively might also be complicated by the fact that "fitting in" to a local community might require different resources or efforts than fitting in to society more broadly.
Wolff's account of poverty is illuminating. It shows how relative poverty may be interpreted from a social egalitarian perspective, according to which equal distributions of specific goods are not of ultimate, but only derivative egalitarian concern. His essay should be of interest not only for normative and empirical theorists, but also for policy-makers and others who deal with the goal of poverty-alleviation in practice.
The articles by Mills, Fricker and Wolff are representative of a collection that embodies the state of the art of contemporary egalitarian theory in many respects. Two important subjects, however, are missing from the otherwise multifaceted picture. There is no engagement with economic inequalities beyond the nation state. Neither does this work treat intergenerational environmental inequalities resulting from environmental degradation and man-made climate change. These two concerns give egalitarians reason to question the fairness and legitimacy of the international order. To start with, the distribution of income and capital across nation states remains highly unequal, which increases incentives for those who find themselves in less fortunate circumstances to seek better living conditions abroad. Furthermore, while trade with resources, goods and services has never been more global and interdependent than today, it may be argued that the current system has primarily benefitted the world's wealthy and powerful, and that it rests on practices that are highly environmentally destructive and which violate the basic human rights of labourers and affected populations. Finally, past and present generations have contributed to environmental degradation and fossil fuel consumption to a much larger degree than future generations will, assuming they act in such a way as to avoid the most catastrophic outcomes.
What should we make of the absence of these topics in an anthology that seeks to shed light on contemporary egalitarian theorizing? An uncharitable reading may trace it back to an unexpressed particularism. It would be hard to argue that demands of equal treatment stop at national or communal borders or generational confines -- at least not in a highly interdependent world like ours. Neither could the widely shared social (or relational) egalitarian perspective plausibly attach any such categorical constraints to egalitarian demands. New technologies now allow an increasing number of the world's least well-off individuals to compare themselves to more privileged individuals across national boundaries, which in turn affects what they seek to achieve in life and what they will regard as justified or unjustified inequalities. A more charitable interpretation is that a single anthology simply cannot cover all of the issues that are currently at the forefront of egalitarian theory. However, it should be clear that while it remains important and rewarding to reflect on the conditions of "The Equal Society", an egalitarian should certainly not stop there. Instead, she should also ask what it would mean to transform transnational and transgenerational relations in a way so that all humans are (truly) treated as equals.
Carina Fourie, Fabian Schuppert, Ivo Wallimann-Helmer (eds.), Social Equality: On What It Means to Be Equals , Oxford University Press 2015.
Miranda Fricker, Epistemic Injustice: Power & the Ethics of Knowing , Oxford University Press 2007.
Adam Smith, An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations [1776], edited by R. H. Campbell and A. S. Skinner, Clarendon Press/Oxford University Press 1976.
Jonathan Wolff/Avner De-Shalit, Disadvantage , Oxford University Press 2007.
We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essay Examples >
- Essays Topics >
- Essay on Discrimination
Example of essay on violence in relationships
Type of paper: Essay
Topic: Discrimination , Relationships , Education , Violence , Criminal Justice , Experience , Bullying , Study
Published: 12/09/2019
ORDER PAPER LIKE THIS
Violence in relationships has been long acknowledged as a serious problem all over the world. I am interested in learning what age of person is most likely to be in a violent relationship, either as a victim or as a perpetrator. Violence in relationships can involve physical abuse, sexual abuse or emotional abuse (Chebucto). All can be equally as harmful. I plan to conduct a study into which age of person is more likely to experience violence in a relationship. My hypothesis is that more violence occurs in relationships where one or both people are between the ages of 25 and 35.
In order to conduct this study, a random sample of people needs to be interviewed. There will be five different age brackets: 18-25, 25-35, 35-45, 45-55, 50 and upwards. Ten participants from each age bracket must be asked a series of questions exploring whether they have experienced violence in relationships and at what age. Furthermore, it should be ascertained whether the participant was the perpetrator or the victim of violence, and what type of violence was experienced (physical, sexual or emotional). It is vital that the interviews are carried out in private and confidential settings. Violence is a sensitive subject for many people, especially those who have experienced it, and the setting of the study needs to be appropriate for such sensitivity. Clearly, it has to be acknowledged that some people may not be honest with their answers due to the delicate nature of the subject matter. The independent variable for this study is range of different age brackets that the participants fall into. The dependent variable is which age group contains the most experience of violence in relationships.
Works Cited
Chebucto. “Understanding Violence in Relationships.” 2011. Web. 18 Feb 2012. http://www.chebucto.ns.ca/CommunitySupport/Men4Change/violencerelate.html

Cite this page
Share with friends using:
Removal Request

Finished papers: 437
This paper is created by writer with
ID 286968421
If you want your paper to be:
Well-researched, fact-checked, and accurate
Original, fresh, based on current data
Eloquently written and immaculately formatted
275 words = 1 page double-spaced

Get your papers done by pros!
Other Pages
Dilemma research papers, demille essays, angling essays, legal philosophy essays, hilo essays, holdout essays, kerensky essays, dipsomaniac essays, flagellation essays, dollhouse essays, heming essays, branches of government essays, crespo essays, democratization essays, damping essays, geologist essays, alkali metal essays, nims essays, vending essays, oppositions essays, vitals essays, vanzetti essays, piston engines essays, fuchs essays, example of essay on basic management decision making model, example of report on communication, media article review example, article review on does media violence cause aggression, classical and contemporary sociological essay examples, crossing and dwelling a theory of religion by tomas a tweed essay, media representations of pregnancy article review examples, example of critical thinking on toni morrison paradise, example of meaningful event experience or accomplishment admission essay, free essay on u s before 1865, argumentative essay on symbols and interpretations of the africans in heart of darkness, literature review on nietzsches master morality and slave morality, example of quantitative methods and analysis research paper, chinese in america 1860s creative writing sample, trinity law school re admission essay admission essay examples, review of the movie the gray essay example, good example of following the guidelines of the course id guidelinesstudents nameuniversity case study, example of product essay.
Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline
Home / Essay Samples / Social Issues / Violence Against Women / Breaking the Silence: Shedding Light on Violence Against Women
Breaking the Silence: Shedding Light on Violence Against Women
- Category: Social Issues
- Topic: Domestic Violence , Sexual Abuse , Violence Against Women
Pages: 2 (761 words)
Views: 2280
- Downloads: -->
--> ⚠️ Remember: This essay was written and uploaded by an--> click here.
Found a great essay sample but want a unique one?
are ready to help you with your essay
You won’t be charged yet!
2Nd Amendment Essays
Censorship Essays
Civil Rights Essays
Discrimination Essays
Gender Inequality Essays
Related Essays
We are glad that you like it, but you cannot copy from our website. Just insert your email and this sample will be sent to you.
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Your essay sample has been sent.
In fact, there is a way to get an original essay! Turn to our writers and order a plagiarism-free paper.
samplius.com uses cookies to offer you the best service possible.By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .--> -->