
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
How to enforce office 365 custom "role assignment policy" applied default to all new emails to be created?
I have created a RoleAssignmentPolicy called "DisabledForwardingRoleAssignmentPolicy" via Exchange admin center --permissions-- user roles .

I would like to apply "DisabledForwardingRoleAssignmentPolicy" default to all new emails accounts to be created.
In gui of Exchange admin center, there seems to be no way to do this. So I did this by longing to office 365 in powershell.
The command successfully executed. and when I verify it via Get-RoleAssignmentPolicy it says DisabledForwardingRoleAssignmentPolicy is default .
But when I create a new email and when i go to recipients --mailboxes-- select user and mailbox features--- Role assignment policy , still the default policy is applied.

I have to change it manually to DisabledForwardingRoleAssignmentPolicy
What I'm missing here? Please shade a light.
- email-server
- microsoft-office
You need to run "Set-MailboxPlan" cmdlet to change the default role assignment policy to the customize one.
First, run "get-mailboxplan" to confirm which plan your license is used, as below:
Then, run "Set-MailboxPlan" to change the RoleAssignmentPolciy to the customize one:

- You are truly a great resource to serverfault. thanks a lot for your time testing it before posting. I was googling and no correct path was found. It worked. – user879 May 30, 2018 at 5:21
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged email exchange email-server microsoft-office mailbox ..
- The Overflow Blog
- Upcoming research at Stack Overflow
- The reverse mullett model of software engineering
- Featured on Meta
- Testing a new version of Stack Overflow Jobs
Hot Network Questions
- Bootstrapped confidence interval overestimates variance in difference of means
- What is the difference between roots and zeroes?
- Would hear the 90Hz and 150Hz signals when tuned to ILS frequencies with a basic handheld radio?
- No output for a "who am i" command
- Does the top of a wheel really move at twice the velocity of the center?
- How to read the result of quantum shor circuit for N=15
- According to Newton's Third Law why is there a difference in movements between collisions of different mass (please read description)?
- What if a vampire is charmed into entering a residence
- Implementing a simple byte manipulation encryption
- Significant external pressure in non-SCF calculation results
- In Fallout: the role-playing game, is the gauss rifles supposed to use the "small guns" or "energy weapons" skill?
- how to draw circle touching two other circles near intersection
- Write a Swift-function, which computes the Digital Root
- Why aren’t there Seaplane AWACS?
- Is the “civil shield” for employees a real thing?
- Celebrating Shushan Purim in cities outside the Land of Israel
- Why wouldn't the world have advanced warning of a significant asteroid/comet strike?
- What can be learned from viewing the sun on earth during a total eclipse that cannot be studied by spacecraft in orbit?
- Double slit experiment with polychromatic light
- For community property that is to be divided equally during divorce, can I pay my spouse the equal amount instead of selling my house?
- A particular morphism being zero in the singularity category
- Can the word "christen" be used in an entirely non-religious context to describe the naming of something like a building?
- How many people can China geographically support?
- How to make gas bbq ready for cooking after a long non use
Stefanos Cloud
How to manage Microsoft 365 user role assignments and administrative units
- Role assignments
- Administrative Units
This article provides guidance on how to manage Microsoft 365 user role assignments and administrative units. The article is also available on my podcast and Youtube channel .
View this article as a how-to video on Youtube.
You need to manage existing user roles, create new custom user roles and assign users and groups to existing roles in Microsoft 365 . You need to also manage Microsoft 365 administrative units.
In this how-to article, we will show you how to manage Microsoft 365 user role assignments and administrative units.
Role assignments #
From within the Microsoft 365 Admin Center portal, you can assign Azure AD built-in roles to users who need access to other admin centers and resources in Azure Active Directory, such as users, groups, and apps which use Microsoft Graph API. The following groups of user role assignments can be made from the Admin Center portal.
- Azure AD role assignments
- Exchange Online role assignments
- Intune role assignments
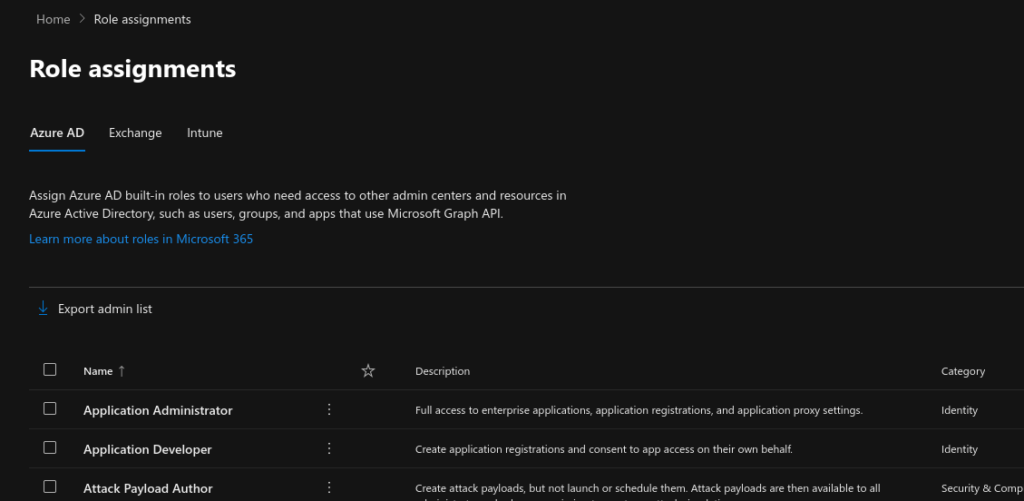
In the next steps, we will show you how to assign the Global Administrator Azure AD role to a user and group. Follow the steps below to assign the Global Administrator role to a user or group.
- Navigate to https://admin.microsoft.com and authenticate as a global admin user.
- On the left pane, expand the "Roles" section and click on "Role assignments". On the main section click on the "Global Administrator" role. On the popup form on the right, you should be able to review the general properties of the role in question. On the permissions tab, the system lists details of the permissions which are assigned with the role in question.
- On the "Assigned" tab, you can assign users or groups to the role in question. Click on "Add Users" and then "Add Groups" to add a user and group respectively to the specific role.
- To run the Azure portal as a specific Azure AD user role, tick on the checkbox next to the role and click "Run As". This will show you the view of the Azure portal as if you had logged in via a user with the role in question.
- To compare permissions of user roles, tick on two or more roles and then click on "Compare Roles". In the next screen, you should see a tabular comparison of the permissions assigned to each of the compared roles. You can also click on "Export comparison" to export the comparison matrix of the selected roles.
In the next steps, we will show you how to assign the Organization Management Exchange Online role to a user and group, as well as how to create a new custom Exchange Online role. Follow the steps below.
- Navigate to the "Exchange" tab under the "Role Assignments" section.
- Click on the "Organization Management" role. On the popup form on the right, you can review the general settings of the role under the "general" tab. Under the "Permissions" tab, you can review in detail the available permissions of the role in question.
- Under the "Assigned" tab, you can assign a user or group to the role in question. Click "Add" and choose the user or group to assign to the role.
- You can also create a custom Exchange Online role by ticking the checkbox next to the role which will be used as the template for the new role. Then click on "Copy role group". This will take you to a wizard to create your new custom role. On the "Set up the basics" page, fill-in the name, description and write scope of the new role and click Next.
- Select the roles to add to the new custom role group. Roles define the scope of the tasks that the members assigned to this role group have permission to manage.
- Select the users to assign to this role group. They'll have permissions to manage the roles that you assigned in the previous step.
- Review your selections and click Finish.
In the next steps, we will show you how to assign Intune roles. Assign Intune roles to specialists who need to view or manage Intune data, devices, or services. These roles can only be assigned to users who have a license that includes Intune. Follow the steps below.
- Under the "Role assignments" section, navigate to the "Intune" tab. If you need to export existing assignments, click on the "Export assignments" button.
- Click on the Intune role you wish to edit assignments of. On the "General tab" you can review the general settings of the role in question. On the "Permissions" tab you can see in detail all permissions of the role in question.
- To assign users to the Intune role, under the "Assigned" tab click on "Add". This will take you to the "Set up the basics" wizard. Fill-in a name and description and click Next.
- Select the security groups that contain the users you want to become admins for the role. Click Next.
- Select a built-in security group like 'All users', or search for and select security groups which contain the users and devices that the Intune role can manage.
- You can optionally add tabs which limit the specific Intune policies, apps and devices that the admins can see. Click "Next".
- Review all your assignment settings and click "Finish".
Administrative Units #
Now we will move on to show you how to create and manage Microsoft 365 Administrative Units. Units let you sub-divide your organization into any unit that you want, and then assign specific administrators that can only manage that unit. For example, you can assign the Helpdesk Administrator role to a regional support specialist, so they can manage users only in that region.
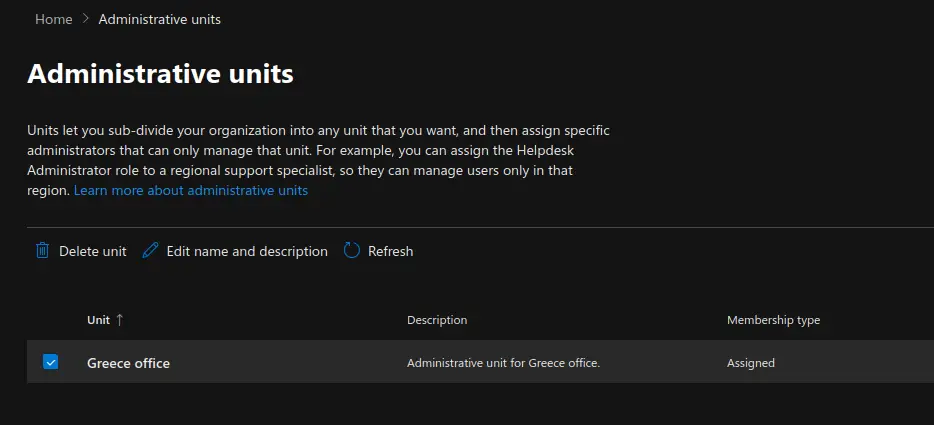
Carry out the following steps:
- Under the "Roles" section, click on "Administrative Units". Click on "Add Unit" to add a new administrative unit.
- Provide a name and Description of the new administrative unit and click "Next". Administrative units let you limit admins to manage users for a specific department, region, or any segment that your organization defines. Start by giving the administrative unit a name and description that will let other admins know its purpose.
- Choose "Add up to 20 users and groups" or "Upload users" if you need to bulk upload a large number of users to be linked to the new administrative unit. If you choose "Add up to 20 users and groups", then click on "Add Users" or "Add Groups" to add the desired users to the administrative unit and click Next. The administrators assigned to this unit will manage the settings for these users and groups. Adding groups doesn't add users to the unit, it lets the assigned admins manage group settings. You can only add up to 20 members individually or you can bulk upload up to 200 users. If you need to add more, you can edit this unit to add them.
- Assign admins to scoped roles. The following roles are the only roles that support administrative units. Authentication Administrator Cloud Device Administrator Groups Administrator Helpdesk Administrator License Administrator Password Administrator SharePoint Administrator Teams Administrator Teams Device Administrator User Administrator.
Select a role and then assign admins to it. The admins that you assign to roles in this step will manage the members of this administrative unit.
- Review your selections and click "Finish". The new administrative unit has been created. You can always edit its properties by clicking on the Administrative Unit name. From that page you can edit the administrative unit's members and role assignments.
- You can also edit the name and description of an administrative unit by ticking the checkbox next to the administrative unit name and clicking on "Edit name and description".
What are your Feelings
Share this article :, how can we help.
Powered by BetterDocs
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Role assignment policies in Exchange Online
- 15 contributors
A role assignment policy is a collection of one or more end-user roles that enable users to manage their mailbox settings and distribution groups in Exchange Online. End-users roles are part of the role based access control (RBAC) permissions model in Exchange Online. You can assign different role assignment policies to different users to allow or prevent specific self-management features in Exchange Online. For more information, see Role assignment policies .
In Exchange Online, a default role assignment policy named Default Role Assignment Policy is specified by the mailbox plan that's assigned to users when their account is licensed. For more information about mailbox plans, see Mailbox plans in Exchange Online .
User roles and Outlook Web App policies are now available in Exchange admin center.
Role assignment policies are how end-user roles (as opposed to management roles) are assigned to users in Exchange Online. There are several ways you can use role assignment policies to assign permissions to users:
New users :
Change the end-user roles that are assigned to the default role assignment policy.
Create a custom role assignment policy and set it as the default. Note that this method only affects mailboxes that you create without specifying a role assignment policy or assigning a license (the license specifies the mailbox plan, which specifies the role assignment policy).
Specify a custom role assignment policy in the mailbox plan. For more information, see Use Exchange Online PowerShell to modify mailbox plans .
Existing users :
Assign a different license to the user. This will apply the settings of the different mailbox plan, which specifies the role assignment policy to apply.
Manually assign a custom role assignment policy to mailboxes.
The available end-user roles that you can assign to mailbox plans are described in the following table:
* This feature isn't available in all regions or organizations.
What do you need to know before you begin?
Estimated time to complete each procedure: less than 5 minutes.
The procedures in this topic require the Role Management RBAC role in Exchange Online. Typically, you get this permission via membership in the Organization Management role group (the Microsoft 365 or Office 365 Global administrator role). For more information, see Manage role groups in Exchange Online .
To open the Exchange admin center (EAC), see Exchange admin center in Exchange Online . To connect to Exchange Online PowerShell, see Connect to Exchange Online PowerShell .
Changes to permissions take effect after the user logs out and logs in again.
View roles assigned to a role assignment policy
Use the eac to view roles assigned to a role assignment policy.
In the EAC, click Roles > Admin roles . All of the role groups in your organization are listed here.
Select a role group. The details pane shows the Name , Description , and add the Permissions of the role group.
Use Exchange Online PowerShell to view roles assigned to a role assignment policy
To view the roles assigned to a role assignment policy, use the following syntax:
This example returns the roles that are assigned to the policy named Default Role Assignment Policy.
For detailed syntax and parameter information, see Get-ManagementRoleAssignment .
Note : To return a list of all available end-user roles, run the following command:
Add or remove roles from a role assignment policy
Use the eac to add or remove roles from a role assignment policy.
In the policy properties window that opens, do one of the following steps:
To add a role, select the check box next to the role.
To remove a role that's already assigned, clear the check box.
If you select a check box for a role that has child roles, the check boxes for the child roles are also selected. If you clear the check box of the parent role, the check boxes for the child roles are also cleared. You can select a child role by clearing the check box of the parent role and then selecting the individual child role.
When you're finished, click Save .
Use Exchange Online PowerShell to add roles to a role assignment policy
Adding a role to a role assignment policy creates a new role assignment with a unique name that's a combination of the names of the role and the role assignment policy.
To add roles to a role assignment policy, use the following syntax:
This example adds the role MyMailboxDelegation to the role assignment policy named Default Role Assignment Policy.
For detailed syntax and parameter information, see New-ManagementRoleAssignment .
Use Exchange Online PowerShell to remove roles from a role assignment policy
Use the procedure from the Use Exchange Online PowerShell to view roles assigned to a role assignment policy section earlier in this topic to find the name of the role assignment for the role that you want to remove (it's a combination of the names of the role and the role assignment policy).
To remove the role from the role assignment policy, use this syntax:
This example removes the MyDistributionGroups role from the role assignment policy named Default Role Assignment Policy.
For detailed syntax and parameter information, see Remove-ManagementRoleAssignment .
Create role assignment policies
Use the eac to create role assignment policies.
In the EAC, go to Roles > Admin roles and then click Add role group .
In the Add role group window, click Set up the basics section, configure the following settings and click Next :
Name : Enter a unique name for the role group.
Description : Enter an optional description for the role group.
Select the roles that you want to assign to the policy.
In the Add permissions section, select the roles and click Next . Roles define the scope of the tasks that the members assigned to this role group have permission to manage.
In the Assign admins section, select the users to assign to this role group and click Next . They'll have permissions to manage the roles that you assigned.
In the Review role group and finish section, verify all the details, and then click Add role group .
Click Done .
Use Exchange Online PowerShell to create role assignment policies
To create a role assignment policy, use the following syntax:
This example creates a new role assignment policy named Contoso Contractors that include the specified end-user roles.
For detailed syntax and parameter information, see New-RoleAssignmentPolicy .
Modify role assignment policies
You can use the EAC or Exchange PowerShell to Add or remove roles from a role assignment policy .
You can only use Exchange Online PowerShell to specify the default role assignment policy that's applied to new mailboxes that aren't assigned a license or a role assignment policy when they're created.
Otherwise, all you can do in the EAC or Exchange Online PowerShell is modify the name and description of the role assignment policy.
Use Exchange Online PowerShell to specify the default role assignment policy
To specify the default role assignment policy, use the following syntax:
This example configures Contoso Users as the default role assignment policy.
Note : The IsDefault switch is also available on the New-RoleAssignmentPolicy cmdlets.
For detailed syntax and parameter information, see Set-RoleAssignmentPolicy .
Remove role assignment policies
You can't remove the role assignment policy that's currently specified as the default. You first need to specify another role assignment policy as the default before you can delete the policy.
You can't remove a role assignment policy that's assigned to mailboxes. Use the procedures described in the Use Exchange Online PowerShell to modify role assignment policy assignments on mailboxes section to replace the role assignment policy that's assigned to mailboxes.
Use the EAC to remove role assignment policies
In the EAC, go to Roles > Admin roles .
Select the role group and click Delete .
Click Confirm in the confirmation window.
Use Exchange Online PowerShell to remove role assignment policies
To remove a role assignment policy, use the following syntax:
This example removes the role assignment policy named Contoso Managers.
For detailed syntax and parameter information, see Remove-RoleAssignmentPolicy .
View role assignment policy assignments on mailboxes
Use the eac to view role assignment policy assignments on mailboxes.
In the mailbox properties window that opens, click Mailbox features . The role assignment policy is shown in the Role assignment policy field.
Use Exchange Online PowerShell to view role assignment policy assignments on mailboxes
To see the role assignment policy assignment on a specific mailbox, use the following syntax:
This example returns the role assignment policy for the mailbox named Pedro Pizarro.
To return all mailboxes that have a specific role assignment policy assigned, use the following syntax:
This example returns all mailboxes that have the role assignment policy named Contoso Managers assigned.
Modify role assignment policy assignments on mailboxes
A mailbox can have only one role assignment policy assigned. The role assignment policy that you assign to the mailbox will replace the existing role assignment policy that's assigned.
Use the EAC to modify role assignment policy assignments on mailboxes
In the EAC, click Recipients > Mailboxes , and do one of the following steps:
Multiple mailboxes : Select multiple mailboxes of the same type (for example, User ) by selecting a mailbox, holding down the Shift key, and select another mailbox farther down in the list or by holding down the Ctrl key as you select each mailbox. In the details pane (that's now titled Bulk Edit ): click More options > click Update . In the Role Assignment Policy section, select the role assignment policy in the window that appears > click Save .
Use Exchange Online PowerShell to modify role assignment policy assignments on mailboxes
To change the role assignment policy assignment on a specific mailbox, use this syntax:
This example applies the role assignment policy named Contoso Managers to the mailbox named Pedro Pizarro.
To change the assignment for all mailboxes that have a specific role assignment policy assigned, use the following syntax:
This example changes the role assignment policy from Default Role Assignment Policy to Contoso Staff for all mailboxes that currently have Default Role Assignment Policy assigned.
Additional resources
Subscribe for Practical 365 updates
Please turn off your ad blocker and refresh the page to subscribe.
You may withdraw your consent at any time. Please visit our Privacy Statement for additional information
Exchange Server
Exchange server role based access control in action: using management roles.

Exchange Server uses a permissions model called Role Based Access Control (RBAC) to manage the delegation of permissions for Exchange administrative tasks. RBAC was first introduced in Exchange 2010 and continues to be used in Exchange Server and Exchange Online today. It’s important to understand how RBAC works because it is the mechanism that you use to apply a least-privilege approach to Exchange administrative permissions. RBAC is also how end users are granted permissions to perform tasks such as managing their own distribution groups.
In this tutorial we’ll look at:
- How RBAC works by examining the pre-defined RBAC management roles
- How to configure custom management roles
The Basics of Role Based Access Control
Whether you understand the inner workings of RBAC or not, you’re still making use of it every day when you perform Exchange administrative tasks. That’s because RBAC has a series of pre-defined management role groups, management roles, and management role assignments for a variety of common administrative scenarios.
Management role groups are the security groups in Active Directory. You can see the management role groups that Exchange creates during setup in the Microsoft Exchange Security Groups OU in Active Directory.

Some of those groups should already look familiar to you, such as Organization Management and Recipient Management. Some of the groups in that OU are for other purposes, such as the Exchange Trusted Subsystem group which contains computer accounts for Exchange servers. So if you want to see just the role groups, you can switch to the Exchange Management Shell instead and run the Get-RoleGroup cmdlet.
Notice how each role group has one or more assigned roles, which refer to management roles. An example of a management role is Mail Recipients.
Management roles are collections of management role entries. Management role entries are specific tasks that can be performed by users who are assigned with that particular role. Continuing with the example of the Mail Recipients role, the management role entries can be summarized by looking at the description of the management role.
So the Mail Recipients role contains a whole bunch of role entries to make that possible. Role entries have a naming convention of “RoleEntry”, so all of the role entries for the Mail Recipients role will be named “Mail RecipientsEntry”. This means that you can see the list of role entries for the Mail Recipients role by running the following command:
On my system there’s 125 role entries for the Mail Recipients role, so I won’t list them all here. But they basically include all the cmdlets you’d need for that purpose, such as Get-Mailbox, Set-Mailbox, and Enable-Mailbox (for mail-enabling an existing user). However, it is a separate management role called “Mail Recipient Creation” that has the role entries that permit creating entirely new recipients, such as New-Mailbox, New-MailUser, and New-MailContact.
Both the Mail Recipients and Mail Recipient Creation roles, along with others, are assigned to the role group named Recipient Management. You can see the role assignments for the Recipient Management role group by running the Get-RoleGroup cmdlet.
The Recipient Management role group is one of the Active Directory security groups that exists in the Microsoft Exchange Security Groups OU. Therefore, if you add a user account to the Recipient Management group, they are granted the ability to perform those administration tasks such as managing mail recipients, distribution groups, and performing message tracking. When that user opens the Exchange Management Shell, only the cmdlets that are included in the role entries for the management roles assigned to the role groups they are a member of will be available. For example, a Recipient Management role group member won’t have access to the New-AcceptedDomain or Set-AcceptedDomain cmdlets, but they do have access to the Get-AcceptedDomain cmdlet.
When the user logs into the Exchange Admin Center, they will also see only the sections that they have access to through their role group membership. For example in the screenshot below, the web browser on the left shows the sections visible to a Recipient Management role group member, and the browser on the right shows the sections visible to an Organization Management role group member.

Some of the differences are obvious, for example the Recipient Management role group member can’t see the compliance management section of the Exchange Admin Center. Others are not so obvious at first. Both users can see the mail flow section where things like Accepted Domains are managed. The Recipient Management role group holder can still see that section, because they need to be able to “see” the list of accepted domains in the organization when assigning SMTP addresses to recipients. But they can’t edit any of the accepted domains, nor can they add new ones.
As the final piece of the RBAC picture, there’s also the concept of management role scope. The management roles (such as Mail Recipients) assigned to the pre-canned role groups (such as Recipient Management) have a scope of “Organization”, which effectively means they apply to the entire organization. Management roles can be scoped to more specific area, such as to a single organizational unit in Active Directory.
So to summarize what’s been covered so far, RBAC is made up of:
- Management role entries, which are specific tasks that a user can perform, such as running the Set-Mailbox cmdlet.
- Management roles, which are collections of role entries, such as the Mail Recipients role.
- Management role scope, which defines where in the organization a management role is applicable to, such as the entire organization, a specific server, or a specific organizational unit.
- Management role assignments, which link management roles to role groups.
- Management role groups, which are security groups that users can be added to as members to grant them the permissions to perform administrative tasks.
Once you are comfortable with those basics, you can start looking at creating custom roles.

Creating a Custom RBAC Role
Let’s say that you have a user in the organization who is responsible for managing mail contacts. To provide them with the permissions to perform that task, without any additional effort on your part, you would need to add them to the Recipient Management role group. However, that role group permits them to do much more than just manage the mail contacts they are responsible for, so it doesn’t align with the least privilege approach to security.
The more sensible approach is to create a custom RBAC role and assign it to that user, or to a role group that the user can be made a member of.
The easiest way to create a custom role is by using the Exchange Admin Center. In the permissions section under admin roles , click the icon to create a new role group.

Give the role group a meaningful name, and set the organizational unit that you want to limit the role group to.

Next, click the icon to add a role. In scanning through the list of existing roles (remember, these are collections of role entries), there doesn’t appear to be one already created for managing mail contacts. So a custom role (or two) with the role entries for managing contacts needs to be created. Creating custom roles is easiest when you create the custom role based on an existing role, and then customize it for your needs. In this case, Mail Recipients and Mail Recipient Creation are the two roles to base the new custom roles on.
The next step is to remove the unwanted role entries from each of the custom roles, so that they’re only left with the capability to manage mail contacts.
So now we’re left with two custom roles called “Custom Role – Mail Contacts” and “Custom Role – Mail Contacts Creation”, each containing only the role entries required for managing contacts.
Back to the Exchange Admin Center, the two custom roles are now visible in the picker to add to the new role group we’re creating. Add the two custom roles, and also add the View-Only Recipients role.

Finally, add the users who will be performing the administrative tasks to the role group as members, and save the new role group.

When the members of the new “Mail Contact Managers” role group log in to the Exchange Admin Center, they’ll be able to see the recipients in the organization (just as they can see them in the global address list via Outlook), and in the Contacts area will be able to create new Mail Contacts. If the role group member shown above tries to create a contact in an OU other than the one their role has been scoped to, they’ll receive an error.

But if they choose the correct OU when creating the contact, they’ll be successful. The same OU restrictions also apply to modifying or deleting contacts.
In this tutorial I’ve demonstrated how to use pre-defined management roles in Exchange Server to assign RBAC permissions for administrative tasks. I’ve also demonstrated how to create custom roles and role groups to assign limited permissions to users for specific tasks.

About the Author

Paul Cunningham
Is an Exchange mailbox required on a domain account to add it to the Organization Management Role ? We are using Exchange 2016
It seems I can add domain user accounts and universal security groups to a role. But I’m wondering if there are any limitations in any of the permissions when there is no mailbox assigned to the account?
Thank, Bill
Yor admin account will need a mailbox to sign in to the ECP console on Exchange 2016.
You do not need to use the mailbox for mail . You can set the mailbox to reject all mail under: Mailbox features – Message Delivery Restrictions.
I am trying to create exactly this same thing in Office 365 Exchange and run into an issue with running the second removal command. One user posted the same issue but never got a response.
When running
Get-ManagementRoleEntry “Custom Role – Mail Contacts Creation\*” | Where {$_.Name -notlike “*MailContact”} | Remove-ManagementRoleEntry
Cannot process argument transformation on parameter ‘Identity’. Cannot convert value “Custom Role – Mail Contacts Creation” to type “Microsoft.Exchange.Configuration.Tasks.RoleEntryIdParameter”. Error: “The format of the value you specified in the Microsoft.Exchange.Configuration.Tasks.RoleEntryIdParameter parameter isn’t valid. Check the value, and then try again. Parameter name: identity” + CategoryInfo : InvalidData: (Custom Role – Mail Contacts Creation:PSObject) [Remove-ManagementRoleEntry ], ParameterBindin…mationException + FullyQualifiedErrorId : ParameterArgumentTransformationError,Remove-ManagementRoleEntry + PSComputerName : outlook.office365.com
For some reason when running
Get-ManagementRoleEntry “Custom Role – Mail Contacts\*” | Where {$_.Name -notlike “*MailContact”} | Remove-ManagementRoleEntry
It works fine but only leaves 2 cmdlets in there instead of the 4 you are showing. I basically need working script that enables a user to add and remove mail contacts in the ECP, that’s it.
Excellent article and thank you for posting this. I’m having trouble with the following: Get-ManagementRoleEntry “CustomBNSKMailContacts\*” | Where {$_.Name -notlike “MailContact”} | Remove-ManagementRoleEntry
The error I get multiple times is: Cannot process argument transformation on parameter ‘Identity’. Cannot convert value “CustomBNSKMailContacts” to type “Microsoft.Exchange.Configuration.Tasks.RoleEntryIdParameter”. Error: “The format of the value you specified in the Microsoft.Exchange.Configuration.Tasks.RoleEntryIdParameter parameter isn’t valid. Check the value, and then try again. Parameter name: identity” + CategoryInfo : InvalidData: (CustomBNSKMailContacts:PSObject) [Remove-ManagementRoleEntry], ParameterBi ndin…mationException + FullyQualifiedErrorId : ParameterArgumentTransformationError,Remove-ManagementRoleEntry + PSComputerName : outlook.office365.com
Any ideas? Thanks in advance – John
I know I’m a year late, but just in case anyone else comes across this same problem.
The syntax for that command needs to look like the below (using your example):
Get-ManagementRoleEntry “CustomBNSKMailContacts\*” | Where {$_.Name -notlike “MailContact”} | %{Remove-ManagementRoleEntry -Identity “$($_.id)\$($_.name)”}
Not sure if this was an error in the article or an Exchange vs EOL thing, or just something Microsoft have changed since, but hey.
Slight error in your script. Missing an *.
Get-ManagementRoleEntry “CustomBNSKMailContacts\*” | Where {$_.Name -notlike “*MailContact”} | %{Remove-ManagementRoleEntry -Identity “$($_.id)\$($_.name)”}
thx for your post !
Hi Paul, I am a great fan of your articles – you save my a.. many times :). I try to find something, hope can help me with this. I need to understand what rights or group in RBAC – Exchange 2010 – give rights to user to change user account photo. Thumbnail photo I think is name of attribute.
Is I can see it, it’s possible to possible to limit 2: nd level support to only create/change users is specific OU, is it also possible to limit them to a specified DB? – we have all our users in site-specific databases.
Did this, and works great for write scopes, but why on god’s green earth can’t I seem to find a way to limit read scopes?
Does view only permission group members actually need a account with license on office 365 ?
Thanks Paul,
Very helpful article.
One question – is it possible to create a custom group from blank and only add the permissions you require, or is modification by removal from an existing group the only way?
Is there any role only can change user mailbox quota?
You can create a custom role for that.
Great writeup,
I’m looking to delegate ONLY certain functions to a specific group at my organization; We want them to be able to modify quotas, mailbox delegates, and e-mail addresses, but you don’t appear to be able to do that without a high level of control (or at least it doesn’t appear in the limited ECP).
Is there a way to give the same “view” as full admins for mailbox objects only?
I don’t understand your question. RBAC lets you control granular admin access all the way down to specific cmdlets and parameters of cmdlets. You can create custom roles to allow as much or as little admin access as necessary.
Dear Paul Cunningham, There are three OU into exchange 2016. When I user of any OU login in CEP, he can see all recipients of all OU but I want that “A user will only see his own OU recipients login exchange 2016 ecp” is it possible ?
i want to remove “wipe mobile device” permission from role My test role doesn’t contains clear-mobiledevice command but i can choose this option. Which role entry related with wipe mobile device?
My test role entries:
Set-CASMailbox Get-MobileDevice New-PartnerApplication Test-ClientAccessRule Set-ClientAccessRule New-ClientAccessRule Get-CASMailboxPlan Set-PartnerApplication Export-AutoDiscoverConfig Get-ActiveSyncDeviceAccessRule Get-ActiveSyncDeviceClass Get-ActiveSyncOrganizationSettings Get-ClientAccessArray Get-DomainController Get-OutlookProvider Get-RpcClientAccess New-ActiveSyncDeviceAccessRule New-OutlookProvider New-RpcClientAccess Remove-ClientAccessArray Remove-OutlookProvider Remove-RpcClientAccess Set-ActiveSyncDeviceAccessRule Set-RpcClientAccess Write-AdminAuditLog New-AuthRedirect Set-AuthRedirect Remove-AuthRedirect Get-AuthRedirect New-ClientAccessArray New-AuthServer Remove-AuthServer Set-AuthServer Get-PartnerApplication Set-AuthConfig Set-ClientAccessArray Get-ClientAccessRule Get-CASMailbox Get-AuthServer Get-AuthConfig Set-OutlookProvider Remove-ClientAccessRule Get-ActiveSyncDevice Remove-PartnerApplication Start-AuditAssistant Set-UnifiedAuditSetting Set-SweepRule Set-MailboxLocation Remove-SweepRule Remove-MailboxUserConfiguration Remove-MailboxLocation New-SweepRule Import-RecipientDataProperty Get-UnifiedAuditSetting Get-SweepRule Get-RbacDiagnosticInfo Get-OnlineMeetingConfiguration Get-MobileDeviceStatistics Get-MailboxUserConfiguration Get-MailboxPreferredLocation Get-MailboxLocation Enable-SweepRule Disable-SweepRule Add-MailboxLocation SetUserPhoto
i have a little bit extra for you excellent blog post. Thank you so much. Why this? When you use the role View-Only Recipients, you see to much of ecp functions from exchange. We reduce the view to the most necessary.
New-ManagementRole -Parent “View-Only Recipients” -Name “Custom Role – View-Only Recipients”
Get-ManagementRoleEntry “Custom Role – View-Only Recipients\*” | Where {$_.Name -notlike “*MailContact”} | Remove-ManagementRoleEntry
I have not found a option to add more than one role to the custom view
Add-ManagementRoleEntry “Custom Role – View-Only Recipients\Get-OrganizationalUnit” Add-ManagementRoleEntry “Custom Role – View-Only Recipients\Get-Recipient” Add-ManagementRoleEntry “Custom Role – View-Only Recipients\Get-Contact”
Now you have only 4 roles
Get-Contact Get-OrganizationalUnit Get-Recipient Get-MailContact
that is all!
Can you help with my above problem running Exchange 2016? I am unable to set the Write Scope to a specific OU. Please see above comments from me.
Problem was sorted out by upgrading from CU7 to CU8
Not working in Exchange 2016. Getting error when applying the role group to the Contacts OU as write scrope:
“Object class organizationalUnit is not recognized as a valid object class for E-mail recipient objects.”
Can you help?
What command are you running?
I am doing from the ECP. According to your guide, I set the Write Scope to a specific OU where we have got the contacts, and then the ECP throws above error.
The corresponding command would be something like:
New-RoleGroup -Name “Mail Contacts Manager” -RecipientOrganizationalUnitScope Contacts -Roles “Custom – Mail Contacts”, “Custom – Mail Contacts Creation” -Members contactadmin
Are you using the full path to the OU?
Yes. Using the Full path in ECP, it sees the OU, otherwise it would say it does not exist.
Ok. I haven’t seen the issue. Maybe there’s an ambiguous OU name causing problems or something like that. Perhaps running the command in the shell will work better.
I know it has been a while, but I just came across this same error:
“Object class organizationalUnit is not recognized as a valid object class for E-mail recipient objects.”
What I had to do was create it with the Write Scope set to Default, save it, then I could come back and change the write scope to an Organizational Unit.
Hope this helps someone in the future.
Thank you. This worked for me.
Perfect! Worked for me too
Awesome! Worked for me.
From ECP Create the Role with Default Scope. After it is created in 2nd Step Add the required OU. Worked for me .
Hey Poul, wonderfull article and really nicely written.
I have tried deploying this setup in our test/QA enviroments but i run into a error when the user needs to select the ou upon contact creation. I looks to me like there is some role/permission needed, if a user should be granted access to navigate the AD (so they can select the right ou which they are allowed to write to)
When the user tries to browse the AD, they are informed that they do not have permission to browse the ad, and the progress circle just keeps spinning.
Have you seen this problem before?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Latest articles.
Report SharePoint Online Files Using the Microsoft Graph PowerShell SDK
This article describes creating a SharePoint Online files report using the Microsoft Graph PowerShell SDK. While keeping digital debris online might have been unimportant in the past, it's something that can wreak havoc in the era of generative AI when tools like Copilot for Microsoft 365 are happy to consume obsolete and inaccurate material.

Microsoft on Protecting Identity – The Core of Your Digital Ecosystem: The Practical 365 Podcast S4 E18
On this week's episode of the Practical 365 podcast, Steve, Rich, and Paul are joined by Alex Weinert, Director of Identity Security at Microsoft, to discuss the critical topic of identity threat detection and response (ITDR).
Practical Sentinel: Setting the Scene
Welcome to Practical Sentinel! In the introductory blog of this series, we review how Microsoft positions Sentinel, what capabilities the product includes, and what it does well.

Contribute to the Microsoft 365 and Office forum! Click here to learn more 💡
April 9, 2024
Contribute to the Microsoft 365 and Office forum!
Click here to learn more 💡
- Search the community and support articles
- Microsoft 365 and Office
- Subscription, account, billing
- Search Community member
Ask a new question
Exchange online users unable to change personal info
I have double checked that the default role assignment policy (All users have the default role assignment policy.) is set correctly to allow users to update their contact info, profile info, etc... however the users can't do any of this.
They go under my account\personal info, but nothing is editable.
I have seen other articles referencing that they need to go into office 365 OWA and click on settings\options, but there is NO 'options' showing under the settings button in OWA.
What is going on? How do I get this working correctly?
Report abuse
Reported content has been submitted
- Microsoft Agent |
Hi Kegerreis,
The personal information of users just can be edited by Office 365 Admins under Settings > Office 365 > Personal info in OWA. However, users can edit their own information under Settings > Mail ( Options ) > General > My account .

Let us know if you have any concern.
1 person found this reply helpful
Was this reply helpful? Yes No
Sorry this didn't help.
Great! Thanks for your feedback.
How satisfied are you with this reply?
Thanks for your feedback, it helps us improve the site.
Thanks for your feedback.
Replies (2)
Question info.
- Norsk Bokmål
- Ελληνικά
- Русский
- עברית
- العربية
- ไทย
- 한국어
- 中文(简体)
- 中文(繁體)
- 日本語
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Manage role assignment policies
- 6 contributors
Applies to: Exchange Server 2013
If you want to customize the permissions that you assign to a group of end users, create a new custom management role assignment policy. The assignment policy you create can be customized to suit your end user's specific requirements. For more information about assignment policies in Microsoft Exchange Server 2013, see Understanding management role assignment policies .
Looking for other management tasks related to managing permissions? Check out Permissions .
What do you need to know before you begin?
Estimated time to complete each procedure: 5 minutes
You need to be assigned permissions before you can perform this procedure or procedures. To see what permissions you need, see the "Assignment policies" entry in the Role management permissions topic.
For information about keyboard shortcuts that may apply to the procedures in this topic, see Keyboard shortcuts in the Exchange admin center .
Having problems? Ask for help in the Exchange forums. Visit the forums at Exchange Server .
Add an assignment policy
After you've created the new assignment policy, you assign users to it. For more information, see Change the assignment policy on a mailbox .
Use the EAC to create a new assignment policy
You can only create explicit assignment policies using the Exchange admin center (EAC). If you want to create a new default assignment policy, you must use the Exchange Management Shell. For more information, see the "Use the Shell to create a default assignment policy" section later in this topic.
In the role assignment policy window, provide a name for the new assignment policy.
Select the check box next to the role or roles you want to add to the assignment policy. You can select multiple roles, including end-user roles you've added. If you select a role that has child roles, the child roles are automatically selected.
Click Save to save the changes to the assignment policy.
Use the Shell to create an explicit assignment policy
To create an explicit assignment policy that can be manually assigned to mailboxes, use the following syntax.
This example creates the explicit assignment policy Limited Mailbox Configuration and assigns the MyBaseOptions , MyAddressInformation , and MyDisplayName roles to it.
For detailed syntax and parameter information, see New-RoleAssignmentPolicy .
Use the Shell to create a default assignment policy
To create a default assignment policy assigned to new mailboxes, use the following syntax.
This example creates the default assignment policy Limited Mailbox Configuration and assigns the MyBaseOptions , MyAddressInformation , and MyDisplayName roles to it.
Remove an assignment policy
If you no longer need a management role assignment policy, you can remove it.
All users assigned the assignment policy must be changed to another assignment policy. For more information about how to change an assignment policy on a mailbox, see Change the assignment policy on a mailbox .
All the management role assignments between the assignment policy and the assigned management roles must be removed. For more information about how to remove a role assignment from an assignment policy, see the Use the Shell to remove a role from an assignment policy section later in this topic.
If you want to remove a default assignment policy, it must be the last assignment policy in the Exchange 2013 organization.
Use the EAC to remove an assignment policy
In the EAC, navigate to Permissions > User Roles .
Use the Shell to remove an assignment policy
To remove an assignment policy, use the following syntax.
This example removes the New York Temporary Users assignment policy.
For detailed syntax and parameter information, see Remove-RoleAssignmentPolicy .
View a list of assignment policies or assignment policy details
You can view management role assignment policies in a variety of ways, depending on the information you want and whether you're using the EAC or the Shell.
In the EAC, you can view the list of assignment policies and the roles assigned to them. In the Shell, you can view all the assignment policies in your organization, list the mailboxes assigned a specific policy, and more.
Use the EAC to view a list of assignment policies
In the EAC, navigate to Permissions > User Roles . All of the assignment policies in the organization are listed here.
To view the details of a specific assignment policy, select the assignment policy you want to view. The description and the roles assigned to the assignment policy are displayed in the details pane.
Use the Shell to view a list of assignment policies
You can view a list of all the assignment policies in your organization by not specifying any assignment policies when you run the Get-RoleAssignmentPolicy cmdlet.
This procedure makes use of pipelining and the Format-Table cmdlet. For more information about these concepts, see the following topics:
about_Pipelines
Working with command output
To return a list of all assignment policies in your organization, use the following command.
To return a list of specific properties for all the assignment policies in your organization, you can pipe the results to the Format-Table cmdlet and specify the properties you want in the list of results. Use the following syntax.
This example returns a list of all the assignment policies in your organization and includes the Name and IsDefault properties.
For detailed syntax and parameter information, see Get-Mailbox or Get-RoleAssignmentPolicy .
Use the Shell to view the details of a single assignment policy
You can view the details of a specific assignment policy by using the Get-RoleAssignmentPolicy cmdlet and piping the output to the Format-List cmdlet.
This procedure makes use of pipelining and the Format-List cmdlet. For more information about these concepts, see the following topics:
To view the details of a specific assignment policy, use the following syntax.
This example views the details about the Redmond Users - no Text Messaging assignment policy.
Use the Shell to find the default assignment policy
You can find the default assignment policy by piping the output of the Get-RoleAssignmentPolicy cmdlet to the Where cmdlet. With the Where cmdlet, filter the data returned to display only the assignment policy that has its IsDefault property set to $True .
This procedure makes use of pipelining and the Where cmdlet. For more information about these concepts, see the following topics:
This example returns the default assignment policy.
Use the Shell to view mailboxes that are assigned a specific policy
You can find all the mailboxes assigned a specific assignment policy by piping the output of the Get-Mailbox cmdlet to the Where cmdlet. With the Where cmdlet, filter the data returned to display only the mailboxes that have their RoleAssignmentPolicy property set to the assignment policy name you specify.
Use the following syntax.
This example finds all the mailboxes assigned the policy Vancouver End Users.
Change the default assignment policy
You can change the management role assignment policy assigned to new mailboxes that are created. Changing the default role assignment policy doesn't change the assignment policy assigned to existing mailboxes. To change the assignment policy assigned to existing mailboxes, see Change the assignment policy on a mailbox .
You can't use the EAC to change the default assignment policy. You need to use the Shell.
Use the Shell to change the default assignment policy
To change the default assignment policy, use the following syntax.
This example sets the Vancouver End Users assignment policy as the default assignment policy.
New mailboxes are assigned the default assignment policy even if the policy hasn't been assigned management roles. Mailboxes assigned assignment policies with no assigned management roles can't access any mailbox configuration features in Microsoft Outlook Web App.
For detailed syntax and parameter information, see Set-RoleAssignmentPolicy .
Add a role to an assignment policy
Use the eac to add a role to an assignment policy, use the shell to add a role to an assignment policy.
To create a management role assignment between a role and an assignment policy, use the following syntax.
This example creates the role assignment Seattle Users - Voicemail between the MyVoicemail role and the Seattle Users assignment policy.
For detailed syntax and parameter information, see New-ManagementRoleAssignment .
Remove a role from an assignment policy
If you don't want end users to have permissions to manage certain features of their mailbox or distribution group, you can remove the management role that grants the permissions from the management role assignment policy to which the user is assigned. If other users are assigned the same assignment policy, they also lose the ability to manage that feature.
Use the EAC to remove a role from an assignment policy
Clear the check box next to the role or roles you want to remove from the assignment policy. If you clear the check box for a role that has child roles, the check boxes for the child roles are also cleared.
Use the Shell to remove a role from an assignment policy
You can remove roles from assignment policies by retrieving the associated management role assignment using the Get-ManagementRoleAssignment cmdlet and then piping the role assignment returned to the Remove-ManagementRoleAssignment cmdlet.
For more information about regular and delegating role assignments, see Understanding management role assignments .
This procedure uses pipelining. For more information about pipelining, see about_Pipelines .
To remove a role from an assignment policy, use the following syntax.
This example removes the MyVoicemail management role, which enables users to manage their voice mail options, from the Seattle Users assignment policy.
For detailed syntax and parameter information, see Remove-ManagementRoleAssignment .
Additional resources

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Use the EAC to create role assignment policies. In the EAC, go to Roles > Admin roles and then click Add role group. In the Add role group window, click Set up the basics section, configure the following settings and click Next: Name: Enter a unique name for the role group.
The "Default Role Assignment Policy" is assigned to every mailbox and " grants end users the permission to set their options in Outlook on the web and perform other self-administration tasks ". You'll find the policy in the Exchange Admin Center under "Permissions" and "User Roles".
Now let's check the Role Assignments for these roles: The figure above shows the expected output; unless you have custom RBAC configured or you have customized the Exchange default management role groups, you need to pay attention to the value RoleAssignmentDelegationType, which could be Regular or DelegatingOrgWide.
You need to run "Set-MailboxPlan" cmdlet to change the default role assignment policy to the customize one. First, run "get-mailboxplan" to confirm which plan your license is used, as below: Get-MailboxPlan |fl identity,RoleAssignmentPolicy Then, run "Set-MailboxPlan" to change the RoleAssignmentPolciy to the customize one:
Creating a new user role assignment policy. If your organization does decide to limit the self-management permissions of your users in Exchange Online, you have a couple of options. You can either modify the default role assignment policy, or you can create a new role assignment policy. Modifying the default role assignment policy is very easy.
The Default Role Assignment Policy role assignment policy is included with Exchange Online. As the name implies, it's the default role assignment policy. If you want to change the permissions provided by this role assignment policy, or if you want to create role assignment policies, see Work with role assignment policies later in this topic.
To replace the built-in default role assignment policy with your own default role assignment policy, you can use the Set-RoleAssignmentPolicy cmdlet to select a new default. When you do this, any new mailboxes are assigned the role assignment policy you specified by default if you don't explicitly specify a role assignment policy. More ...
The Exchange Online Role-Based Access Control model consists of several different components: Roles, Role Groups, Role Entries and Role Assignments. To begin exploring, run the Get-ManagementRole cmdlet to see what management roles exist in the environment. The Get-ManagementRole cmdlet lists the management roles in the organization.
1.What role assignment policy is assigned to all our mailboxes in Office 365. "Default Role Assignment Policy" is assigned to existing and new mailboxes that aren't explicitly assigned a specific role assignment policy when they're created. The policy contains 13 roles for "commonly used permissions" as defined by Microsoft.
Add or remove roles from a role assignment policy. Step 1: Sign in to Office 365 admin center. Step 2: Navigate to the Exchange admin center. Step 3: Go to Permissions > User roles, select the role assignment policy, and then click Edit. Step 4: Select the check box next to the role. Step 5: Click Save. Need Support?
Microsoft Exchange 2019 Beginners Video Tutorials Series:This is a step by step guide on How to Create and Manage User Role Assignment Policy in Exchange Ser...
The MyDistributionGroups and MyDistributionGroupMembership in the user role assignment policy will not affect the contact groups or distribution lists end users created in their own contact lists. They will applies to the Office 365 groups and the distribution groups that admins created in Office 365 EAC ( Exchange Admin Center ). Regards,
Follow the steps below to assign the Global Administrator role to a user or group. Navigate to https://admin.microsoft.com and authenticate as a global admin user. On the left pane, expand the "Roles" section and click on "Role assignments". On the main section click on the "Global Administrator" role.
Admins can learn about role assignment policies, and how to view, create, modify, remove, and assign them in Exchange Online. Skip to main content. This browser is no longer supported. Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support. ... Role assignment policies in Exchange Online ...
For more information about assignment policies, see Understanding management role assignment policies. You need to be assigned permissions before you can run this cmdlet. Although this topic lists all parameters for the cmdlet, you may not have access to some parameters if they're not included in the permissions assigned to you. To find the permissions required to run any cmdlet or parameter ...
The easiest way to create a custom role is by using the Exchange Admin Center. In the permissions section under admin roles, click the icon to create a new role group. Give the role group a meaningful name, and set the organizational unit that you want to limit the role group to. Next, click the icon to add a role.
Exchange online users unable to change personal info I have double checked that the default role assignment policy (All users have the default role assignment policy.) is set correctly to allow users to update their contact info, profile info, etc... however the users can't do any of this. ...
In the EAC, navigate to Permissions > User Roles and then click Add . In the role assignment policy window, provide a name for the new assignment policy. Select the check box next to the role or roles you want to add to the assignment policy. You can select multiple roles, including end-user roles you've added.