JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.

Agribusiness Planning: Providing Direction for Agricultural Firms

Introduction
Future outcomes are a function of today's decisions. Although there is a high degree of randomness and uncertainty associated with the future, you can increase the probability of a successful outcome by planning ahead. This is true in nearly every aspect of our lives, both personal and professional. For those who operate their own businesses, planning becomes increasingly important because the personal and professional aspects become more difficult to untangle. In agricultural businesses, planning may be even more vital because of the inherent uncertainty associated with agricultural production. Some important sources of uncertainty include production risk, price risk, financial (or interest rate) risk, and changes in government programs.
This publication discusses the importance of business planning for agricultural firms—from input suppliers to producers to processors—and describes the steps required to prepare a thorough business plan. The general process of business planning is the same for each type of firm. However, each may have differing individual aspects that affect its plan's contents. Regardless, we present a recommended format that should be useful for all types of agricultural firms as they develop written business plans. We use examples from the wide variety of agribusinesses to provide a broad context to the general theme of business planning.
About the Business Plan
One of the most important documents for any business is their business plan. It is common practice for consultants, lenders, potential business partners, and other business-associated individuals to request a business plan to make a more informed decision concerning their relationship with a business. However, business plans have many more direct benefits for the business owner. The planning process forces owners to systematically consider all facets of the business. In so doing, they become more knowledgeable of the business, the industry, and the market environment in which their business operates. The process also helps to define business goals and to assess the impact that uncertainty may have on future business outcomes. Perhaps most importantly, the written plan provides a well-defined direction for the business. Therefore, it can be used to keep all employees moving toward the common goals established within it.
Completing a business plan can be a time-consuming activity, but well worth the effort. Because businesses operate in an ever-changing environment, the plan should be revisited periodically to be sure that the business is headed in the proper direction or to formally alter the firm's course if circumstances dictate that this is necessary. Again, the systematic review of the business plan forces the owner, and potentially others, to look at the business as a whole and make better-informed decisions.
We provide an example format for you to use as a guide in developing your plan. Notice that there are several topics that should be addressed, corresponding to the four functional areas of management: marketing, production, finance, and human resources. By developing a section for each of these topics, the plan will be easy to follow as you revisit it or as others review it. You should take some liberty as you develop your plan; feel free to customize it in a way that will fit your specific circumstances.
SWOT Analysis
Performing a SWOT analysis , which stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, lays the foundation for the business plan. Four separate SWOT analyses should be performed, each related to one of the four functional areas of management: marketing, production/operations, finances, and human resources.
When assessing strengths and weaknesses, the focus should be internal. Opportunities and threats, on the other hand, should reflect external factors. For example, proximity to a major market, such as a large city, may provide an opportunity to market processed dairy products directly to a restaurant. Threats may take the form of new competitors or changes in agricultural production or environmental policy.
Performing SWOT analyses is relatively easy. Simply divide a piece of paper into four quarters, label the quarters appropriately, and begin to write your thoughts down.
Example Marketing SWOT Analysis for Carl's Custom Crop Scouting
- Only specialized scouting operation in the county
- 3,700 acres under contract
- No full-time sales person
Opportunities
- Expand operations to include planting and harvesting
- Partner with firm that only plants and harvests crops.
- Genetically modified corn kills insects. Scouting for those pests no longer important.
Because this is the foundation on which the planning process is based, be sure to take a broad perspective. In addition to incorporating the views of at least the owners and managers of the operation, it also might be a good idea to allow all employees, or at least a subset, to provide their perspectives. Some firms may also benefit from allowing professional advisors (such as veterinarians, bankers, nutritionists, etc.) to provide input. Although the top management should develop the plan, you should tap many sources of information. Finally, the raw results of the SWOT analyses might best be presented in an appendix, rather than in each of the four sections related to the functional areas. In the individual sections, a summarized version will suffice.
Example Business Plan Format
The format presented here represents one way to structure the business plan.
Sections of Business Plan
Marketing management, production/operations management, human resources management, financial management.
As noted, it covers the four managerial functional areas. We present the example structure and provide some ideas for what you will want to include in each section. Creating a thorough document the first time through is important. This will make follow-up revisions easier to implement.
The introductory section gives a broad overview and background of the business. Several subsections (outlined below) should be included to provide a thorough overview. However, if there's something that you feel isn't applicable to your business, feel free to omit it from your plan.
The first page should give the name of the document, the firm's name, and the names of all those involved in developing the plan. Dating the plan so that you can remember when it was developed or updated is also wise.
Executive Summary
This section, while appearing at the front of the business plan, is actually the last piece developed. Here you should present the most important information, which may include the firm's goals and objectives and associated target dates. Basically, the executive summary provides a concise overview of the business plan.
Table of Contents
The table of contents should provide the titles of all section headings in the plan and the page numbers on which the sections begin.
Vision and Mission Statements
These relatively brief statements tell the reader why the business is in operation and where the management team, or owner(s), plans to be in the future. The vision statement should tell the reader what business the firm is in, or plans to enter, and what the most important business goals are. That is, it should tell where the firm is going.
We have provided a few example vision statements for you to use as a guide when developing yours:
Example Vision Statements
Agchoice farm credit.
AgChoice Farm Credit will be the first choice for financial services that help customers succeed.
To build the world's first truly global securities market. ... A worldwide market of markets built on a worldwide network of networks ... linking pools of liquidity and connecting investors from all over the world ... assuring the best possible price for securities at the lowest possible cost.
Northwest Airlines
To build together the first choice airline and global alliance network with the best people each committed to exceeding our customers' expectations every day
Whenever dairy farmers have a need they should think first of DeLaval. We aim to always be there, always be available, always work on their behalf.
Note that some are from very different industries. Regardless, they present a common theme of what their respective companies want their firms to be.
The mission statement provides a succinct overview of the firm's operation, including its collective values, its unique circumstances or industry position, what product(s) it sells, and why it is in business. As the business evolves, the mission statement can be adapted to reflect the changing face of the firm.
The mission statement can provide more detailed information than the vision statement. We have provided some example mission statements that allow you to see how other firms— although maybe very different in nature—have defined their missions.
Example Mission Statements
Agway cooperative.
AGWAY is a farmer-owned business dedicated to improving the profitability of its members. We achieve profitability for our members by being the most effective partner on every farm we serve, by adding value to what farmers produce, and by using our capabilities to win non-farm customers.
Land O' Lakes
We are a market- and customer-driven cooperative committed to optimizing the value of our members' dairy, crop, and livestock production.
To enable people and businesses throughout the world to realize their full potential.
To help practically anyone trade practically anything on earth.
Some are more specific than others. At a minimum, the mission statement should tell the reader why you are in business.
Business Organization
Briefly describe how the business is legally organized (for example, proprietorship, partnership, or corporation). Include the names and titles of the firm's managers (or board of directors). This section should be quite short.
Overview of Current Business
In general, the business plan is concerned with the firm's future. Here, however, you should review the firm's past and fully describe its present position. Although a business start-up may not have much to reveal, documenting the present situation is important. In doing so, it will be easier to document the firm's history as you revise the plan.
An overview of the firm's past helps to set the context of how the firm has evolved into its current form. This may be particularly useful if the plan is to be used to secure financing because the past reveals something about how the firm has been managed over time. A structured chronology can serve as an outline for this subsection.
Example Firm Chronology
“Hanks' Harvesting" formed as partnership between Jerry and Ed Hanks.
Harvested 4,300 acres of corn for grain and chopped 2,200 acres of corn silage.
Purchased a new combine and a used chopper.
Harvested 8,700 acres of corn for grain and 5,300 acres of corn silage.
January 2002
Contracted for 10,500 corn grain acres and 7,800 corn silage acres for fall 2002.
Began to investigate custom planting services as a possible expansion of current operations.
The narrative in this section should also provide an overview of how the business has been financed. Furthermore, discuss how profits, equity, and other important financial measures have changed over time.
Next, describe the present situation of the firm. You should provide information related to business location (include pictures if you like), current sales, assets, inventories, geographic market area, number of employees, and any other information you feel is appropriate in describing your current business. Upon reading this section, one should have a snapshot picture of your firm's current status.
This and the three sections to follow provide the meat of the plan. These give the reader a thorough understanding of the firm's present and future. In the marketing management section, you should address several key factors, each in its own subsection.
Marketing SWOT Analysis
Provide a brief overview of the main results of the Marketing Management SWOT analysis. Let the reader know what the most important results were.
Products and/or Services Produced
Here, describe your product(s) or service(s) specifically. If you are in the custom heifer raising business, for example, your statement may be something similar to “We raise heifers for dairy producers." If you are operating a dairy farm, your statement may be much more detailed because it is recommended that you include both the products you produce and the products you sell, listed separately. For example, you may produce corn silage, but may not sell it. Remember also that you sell bull calves and cull cows. These may not be your major enterprise, but should be listed as products sold.
Remember that differentiating your product may be an important aspect of your marketing strategy. While this is difficult to do with a commodity, it's not impossible. For example, maybe you feed for high-butterfat percentage to increase the price received for your milk. It's also possible that you operate an organic turkey farm in an attempt to extract higher market prices. There are also those who market kosher meats and dairy products. These types of efforts should be included here as part of your marketing efforts.
Industry Overview and Position of Firm
Describe your industry and how you fit into it. This may not be too difficult to write if you operate under contract production because this is specified in the contract. It may also be relatively simple for anyone producing a commodity and selling it by the typical means (such as selling corn to a grain elevator or hogs to a pork processor). A custom business operator may have a more difficult time defining the industry and describing how the firm fits. However, this section is important for at least two reasons. First, it forces the planner to analyze the industry and determine the firm's relative position in terms of competitive advantages. Second, it provides important evaluative information for “outsiders" to better understand the business and its relationship with the industry.
In describing the industry, include as much information as you feel is necessary to define the firm and the market. Consider including the following: volume sold (in production units -- this may be, for example, hundredweights if describing the dairy industry, head if describing beef, or acres scouted if describing a custom crop scouting operation), total annual sales in dollars, trends in industry sales, competitors, new marketing opportunities, prevailing prices, and how prices are determined (for example, cash market, contract price, cost-plus). Also, describe the customer. Who is purchasing your product? What type of person is likely to buy your product? Again, those selling an undifferentiated commodity may have little to write. Those selling custom services or, even more importantly, those engaged in marketing agricultural products directly to the consumer may need to more thoroughly describe the customer base. This will help you better define your target market.
Managerial Expertise
Here, take stock of the total managerial expertise used by the firm. What marketing-related special knowledge do the managers possess? Is there one manager who has particular expertise in marketing? Thinking beyond the organization is wise; those in production agriculture have other sources of knowledge that may exist outside of the firm. For example, consultants may be available to provide information related to the current economic situation and outlook. Also, the Extension system and the USDA provide a great deal of information and data on agricultural prices and marketing.
Marketing Strategy
This is where you lay out your plan and future expectations, which are founded on all of the preceding information in this section. Here, you should describe any marketing opportunities you face and how you plan to take advantage of those. What advertising or promotional programs will you undertake? How will you distribute your product? How will you determine if your marketing plan is successful? For this, you should have clearly defined targets. For example, “We will market at least 2.5 million pounds of milk each year." You may also want to set targets for number of customers, market share, or any other measure(s) that you might use to determine whether your firm has been successful in marketing.
Finally, be sure to employ any appropriate risk-management tactics. In marketing, you will want to manage risks associated with input and output prices. Can you contract for some inputs to lock-in a particular price? If processing on the farm, have you contracted with a retailer or wholesaler to be sure that someone will take your product? In production agriculture, the farm owner or manager should understand and analyze futures and options markets as tools to manage price volatility. You should also understand any relevant government programs such as Loan Deficiency Payments (LDPs) that affect your price.
(We differentiate “production" and “operations" based on whether the firm's product is a good or a service. However, in many cases, we use “production" to denote either case.)
Through the production of goods and services the firm generates profits. Therefore, assessing the production/ operations process and making plans for the future is vitally important. This may be particularly important in cases where a farm is planning to expand or where a change in business enterprises is to occur.
Production SWOT Analysis
Provide a summary of the SWOT analysis for production/operations. This may be the most important area to gather input from employees, who are likely the ones most closely associated with daily production. Therefore, their insights could provide a valuable additional perspective.
Overview of Productive Assets
Outline what productive assets are necessary to make your product or provide your service. The following deserve particular attention:
- Other Facilities (particularly if on-farm processing is involved)
- Equipment and Machinery
- Materials and Supplies
Focus on what the firm currently owns, the quality of those assets, and how others will be obtained, if needed. Only discuss the resources needed. Save any discussion of financing these assets for the Financial Management section.
Here again, note the special expertise held by management in the area of production/operations. For example, is the herdsman on a dairy farm trained in dairy science? Does the crops manager have a background in agronomy, soil science, or other related field? How many years of experience in this type of position does this person have?
Production/Operations Performance
Describe your current production practices. How much do you produce? When do you produce it? You may want to develop a visual approach to help tell this story. A time line could help to describe when products are made or services are sold. The more complex the business is, the more useful a visual might be.
Regulatory Considerations
Government regulations affect production in many industries. This is particularly the case in production agriculture. If producing agricultural products, be sure that you are complying with all relevant regulations. These include, but may not be limited to:
- Manure management
- Soil conservation
- Worker Safety
- Inspections of the product and of the production facilities
You can gain information on relevant policies and regulations from business consultants, Penn State Extension, agricultural cooperatives, and government agency Web sites.
Production/Operations Strategy
Now that you have laid out your current production practices and defined some firm and industry trends as they relate to some important benchmark measures, it is time to describe your production- or operations-related plans. As you do this, be sure to set specific production goals, outline potential changes in enterprises or production practices, and describe how you plan to locate and purchase inputs. The following list of questions may be useful to you as you develop this section. Again, not all are relevant for all types of operations. Also, you may think of others that should be addressed.
- How long will your current productive assets be of use? When do leases on land and equipment expire? How soon can you expect to replace important machinery and equipment?
- Where can you find other inputs, such as feed, in the future—particularly if you are expanding your operation?
- Should you consider hiring a custom operator to perform a portion of the production tasks?
- Are there new production practices or machinery you should consider adopting?
- How many units of product do you want to sell over your planning period? Provide specific targets and a time line, if appropriate.
- Do you need to develop a nutrient management plan or update an existing one? Are there other environmental plans that should be developed?
- If expanding, how will new construction or other changes affect output? How will these changes affect your resources? Will you be able to operate in a timely manner without affecting the quality of your product(s)?
- Are there new enterprises that should be explored?
One of the most important—yet most often overlooked—inputs is labor. The competency of your human resources may dictate how successfully your business will perform. Use this section to outline your current human resource (HR) policies, how these may change over the planning period, and what you or other managers may need to do to improve HR management.
Human Resources SWOT Analysis
Provide the reader with the summarized results of the human resource management SWOT analysis. This is another point at which the insights of the employees may be particularly useful. Their perception of your HR policies could be substantially different from yours.
Organizational Chart and Related Information
Begin by providing a current organizational chart. When doing so, you should follow very distinct guidelines. However, our example chart (Figure 1) should provide enough guidance to help you if you've not yet developed one. If your organization is particularly large, you may lump several individual positions into one box, as long as the box describes those positions. In Figure 1, for example, the three parlor operators might be represented by only one box if their job descriptions are the same.

The organizational chart allows the employees to see their position in the firm. Also, the chart should show that each person has only one immediate supervisor. We cannot stress this point enough. Defining the managerial structure so that employees directly answer to only one person is very important. Often the partners who own the farm tend to supervise employees together. This results in a situation in which the employee may get conflicting directions. If the employee has only one direct supervisor, this situation can be avoided.
Overview of Current Policies
Whether formalized or not, your firm has HR policies. While we encourage you to formalize those if they are not already, you should complete this section with the most accurate information you have at your disposal. Think about the following individual points as you consider what you would like to include in this section. Also, remember to include information regarding all employees of the business, including the management team.
- Compensation and Benefits (Incorporation of this information may dictate that a portion of the plan be labeled as confidential. Thus, only certain members of the ownership or management team would have rights to view this type of information. you are trying to hide information.)—How much do you pay your employees? At what intervals are they paid (for example, weekly or monthly)? What sort of benefits package is offered? Does the package differ by type of employee? Do you have an incentive plan for employees? Are owner/ operators paid a salary or do they capture retained earnings?
- Job Descriptions and Recruiting — Does each position have a written job description? Are these used to assess the suitability of potential employees? How do you recruit new workers/managers? Provide written copies of job announcements and descriptions in an appendix.
- Training and Standard Operating Procedures —What training is provided for new employees? What training is provided when employees assume new responsibilities? Are common task sequences documented with written standard operating procedures (SOPs)?
- Performance Evaluation and Performance Feedback —Is there a formal mechanism for evaluating workers' performances? If so, how frequently is performance assessed? How does the employee receive the manager's assessment? Are salaries or wages based at least partially on these evaluations?
Penn State Extension provides materials to help develop job descriptions, SOPs, and other important HR documents. Business consultants with expertise in HR management should also be used in many instances to help the business owner develop the best HR policies possible for that particular business.
Human Resource Strategy
Once you have outlined your production and marketing plans, you must evaluate the ramifications of those plans for the firm's human resources. Will the plan require any shift in HR policy? If so, how? For example, an expanding custom heifer grower may need to hire a full-time nutritionist to be sure that the heifers are receiving a properly balanced ration as they develop. The best way to reflect these changes may be to provide one or more additional organizational charts showing how the organization is expected to change over time. In the text, be specific as to what changes are to be made and when.
Also, be sure to describe any changes you plan to make in your HR management. If you don't have formal job descriptions, standard operating procedures, or evaluations, for example, you should consider putting those in writing. Also indicate if the plan will require additional training of existing and new employees. Finally, if expanding, describe where you might find potential employees.
This section is the most crucial from a potential lender's perspective. Here, you should tie together the details in the rest of the plan in terms of how they affect the firm's financial performance. Ultimately, operating a business is about making money. Therefore, this section needs to allow the reader to assess where the firm is and where it intends to go over the planning horizon. Although you should provide current and projected future (“pro forma") financial statements with the plan, they might be best presented in an appendix. This section should be mostly a verbal explanation of the business's finances, with perhaps a few tables to highlight important information.
Because this section is so important, especially if financing is being pursued, we highly recommend that you work with a business consultant, accountant, or other financial advisor to develop it.
Financial SWOT Analysis
Perform a SWOT analysis of the firm's financial position. Unlike some other areas, your frontline workers may not have as much to provide in this analysis. However, depending on the firm's “culture," (the accepted values and norms under which it operates. Some firms may be quite “laid back," allowing employees a good bit of decision-making authority. Others might be more “straightlaced" following a well-established set of rules, whether written or unwritten) you may still want to invite their input.
Review of Current Financial Situation
Here you should highlight the important points of your financial statements (income statement, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows). Focus on the positive aspects, while not ignoring the negative. You do not want to provide a potential lender with an impression that you are trying to hide information. It might help if you work with a financial advisor to develop this narrative.
Provide a table of current outstanding debt. Include the terms of the debt, the lender(s), the principle amount(s), your payment amount(s), how frequently you make payments, and how many payments remain. Furthermore, a table of financial ratios would be useful in providing a snapshot view of the firm. You will want to provide measures of profitability, financial efficiency, liquidity, and solvency. Although your financial advisor may have some specific advice, we provide a few commonly used measures, which are defined in the glossary:
Commonly Used Financial Measures
Profitability.
- Rate of return on assets
- Rate of return on equity
- Profit margin
Financial Efficiency
- Asset turnover ratio
- Operating expense ratio
- Current ratio
- Working capital to value of production ratio
- Leverage ratio
- Debt to asset ratio
Provide other sources of managerial decision-making input. For many farm owners, this is the most difficult facet to monitor. Using a business consultant, a CPA, or some other financial advisor may increase farm profits as you allow some of these individuals to help analyze financial data and make recommendations for you to review.
Financial Strategy
At this point, you need to set forth your plan for financing the firm's operations over the planning period. Where will you get money when you need to purchase a new truck or replace your barn, for example? Present the highlights of the pro forma financial statements as discussed earlier. Also, you should relate your financial plan to your production, marketing, and human resources plans. A time line relating events planned in the other sections to financing may help to clarify this section's message for the reader.
In your discussion, be sure to let the reader know how you will assess financial performance. As in other sections, be specific. Will you require that net income grow at 8 percent per year, for example? Set goals for the measures you have used previously to describe the health of the business. Therefore, you should aim for specific values for your selected measures of profitability, financial efficiency, solvency, and liquidity. Also, do not forget that an information management system should be in place so that the financial data you gather is accurate. (An information management system (IMS) is any system that you can use to track important information regarding financial performance, in this case. Actually, you should have a system of information management that provides high-quality information for each of the four facets of management. This might include a production record-keeping system (DHIA for dairy farms), an accounting system, an inventory list, employee time sheets, and so forth.)
You should be realistic with your plans, yet push yourself. Stated differently, you should plan to succeed, not just survive. If your business is to be viable over the long term, then you should generate returns to grow the business, grow equity, improve your credit-worthiness, and otherwise improve the odds of operating this business well into the future. If the plan covers a major shift in the business's operations, such as a large expansion, then special care is needed to discuss how cost overruns might be handled, when production will begin in a new facility, when debt repayment will commence, and so forth. Although the planning process should reduce the amount of uncertainty associated with such a change, it can never eliminate uncertainty. Therefore, it should be noted that insurance may be used to protect the firm against financial losses that may be associated with operating a business. Be sure to define your insurance needs in this section of the business plan.
Uncertainty should also be accounted for in your financial forecasts. Let the reader know what assumptions you have made when developing the proforma statements. Also, some sensitivity analyses would be useful to show how your statements would change if output or input prices were different from your projections. If appropriate, set forth some contingency plans to be enacted if certain undesired outcomes are realized. For example, if milk production suffers from a hot, dry summer, you should have a contingency plan in place to help cash flow the business until production increases. For example, such a plan might include a revolving line of credit with the local bank.
The body of your business plan should have a final section in which you again tell the reader the highlights of the plan. Highlight the most important features of your plan. Restate your most important goals and briefly mention how you will achieve them. Here again, a time line might help to state what your goals are and when your firm expects to reach them. Remember, you have already provided many details, so keep this section relatively brief, referring the reader to earlier material where necessary.
In this section, draw focus on what your plan means for future profitability, efficiency, liquidity, and solvency. That is, all of your plans will likely affect the farm's financial status. Because this is a business plan, and businesses continue to operate only when profitable, this should be the major thrust. However, remind the reader of what may happen if your assumptions, particularly those related to input and output prices and quantities produced, are not realized. Refer to your contingency plans and sensitivity analyses.
If the business is a family-run operation, as many farms and other small agricultural businesses are, then you may want to include some family goals in your plan. Although you should try to separate family issues from business issues to the extent possible, completely divorcing the two is not always possible. Highlight where business success coincides with success in meeting the family's goals.
Finally, a concluding paragraph should draw the plan together and reinforce for the reader that your firm is committed to working collectively toward the plan's goals. Leave no doubt in the reader's mind that, barring detrimental outside influences, the goals of the plan will be reached.
Throughout this publication, we have pointed out some things that you may want to include in appendices. For example, one appendix might contain your financial statements, both actual and proforma, to which you refer in the Financial Management section. You may also want to include the formal job descriptions you have prepared. Use appendices as you feel appropriate. If you would like to include something that may not be relevant for the body of the manuscript to further describe your operation, then include it as an appendix. To differentiate them, give each new appendix a unique name such as, “Financial Statements" or “SWOT Analysis Results."
One of the most important things you can do to ensure success is to plan for the future. The planning process may take many hours to complete, especially if it is to provide a thorough representation of the firm. However, it will be a valuable asset as it forces a review of the firm and the industry, unites the collective labor force of the firm to work toward a set of common goals, and allows outsiders to gain a detailed understanding of the firm's past, present, and future.
Business planning is not applicable only to large firms. Smaller agricultural businesses, which are often family owned, stand to benefit at least as much from planning as do larger firms. In agriculture, especially agricultural production, the small compete directly with the large. Business planning will help firms of all sizes to better understand their relative positions in the agricultural industry. It will also help the owner to set goals and devise strategies for reaching those goals.
Asset Turnover Ratio
The percentage of total assets earned as gross income. A higher number is generally associated with higher profits. Mathematically, this equals gross income divided by average total productive assets.
Balance Sheet
A financial statement that shows total assets, total liabilities, and owners' equity at a specific point in time. The liabilities and owners' equity represent claims on the firm's assets.
Business Planning
The process of analyzing the firm's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, using that information to develop organizational goals, and crafting strategies to reach those goals.
Competitive Advantages
Refers to particular strengths of the firm relative to those of other firms. Some examples are being the first firm in an area to provide custom heifer raising, having a manager with strong direct-marketing skills, or having superior land for growing crops.
Contingency Plans
These are strategies for dealing with potential outcomes that differ from those assumed in the initial planning process. These are most frequently associated with unfavorable outcomes.
Contract Production
Refers to any situation in which the farmer grows crops or livestock for a specific firm under terms negotiated in a contract.
The system of offices located around individual states that provides information and education to farm managers and other individuals. In Pennsylvania, this is Penn State Extension.
Current Ratio
Measures the ability of the firm to pay its current liabilities with its current assets. A ratio greater than one indicates that the firm is liquid and able to cover its current liabilities. Mathematically, this is equal to current assets divided by current liabilities. Current assets include cash and other assets that will be converted to cash or used up within one year. Current liabilities are those that are payable within one year.
Custom Business
Any firm offering to perform services for a farm that would replace those already provided by the farm's labor. Some examples include crop scouting services, custom planting and harvesting, or custom heifer growing.
Debt to Asset Ratio
Indicates the percentage of total assets owned by creditors. For example, a debt to asset ratio of 0.5 means creditors own 50 percent of the farm's assets. Mathematically, this is total debt divided by total assets.
Income Statement
Provides a review of revenues and expenses over a given period of time, often a year. This may also be referred to as a profit and loss statement, earnings statement, or an operating statement.
Leverage Ratio
This represents total farm debt as a percentage of equity. If this ratio is greater than one, for example, then the business is financed by debt more than by equity. Mathematically, this is total debt divided by equity.
Mission Statement
Provides a summary of why the business is in operation. This may include the firm's common values, an overview of products or services, target markets, or other information to provide a clear picture of the firm's purpose.
Represents the difference between gross income and total expenses. Mathematically, this equals gross income minus total expenses. A positive number means that the business is making enough to cover expenses and either reinvest in the company, pay debt more quickly, or increase owner incomes.
Operating Expense Ratio
Represents the percentage of gross income used in operating expenses (those expenses on inputs used in the current period). Mathematically, subtract interest expenses from operating expenses and divide the result by gross income.
Organizational Chart
A graphical representation of the formal chain of command for a firm. It shows who the supervisors are and over whom these have authority.
This indicates that the financial statement is a projection of the future. These should be based on the best possible estimates at the time they are put together.
Profit Margin
This shows the percentage of gross income resulting in profits for the firm. Mathematically, find the value of net income plus interest expense minus the value of operator and unpaid operator labor and divide that value by gross income. Interest expense is added back to net income because it represents a return to the debt-financed assets. Removing the value of operator and unpaid operator labor shows that returns must be enough to cover this value.
Rate of Return on Assets
This shows the return to all assets employed in the business as a percentage of the total assets employed. Mathematically, it is found by dividing the numerator of net income plus interest expense minus the value of operator and unpaid operator labor by the denominator of average total farm assets. Interest expense is added back to net income because it represents a return to the debt-financed assets. Removing the value of operator and unpaid operator labor shows that returns must be enough to cover this value.
Rate of Return on Equity
This shows the returns to equity assets employed in the business as a percentage of the equity assets. Mathematically, it is found by dividing the numerator of net income minus the value of operator and unpaid operator labor by the denominator of average total equity assets. Removing the value of operator and unpaid operator labor shows that returns must be enough to cover this value.
Revolving Line of Credit
A type of credit account in which the borrower has a given credit limit which can be borrowed at any time. A credit card or standing account with an equipment dealer are examples of revolving credit lines.
Risk Management
Refers to any attempt to avoid the possibility of unfavorable outcomes under uncertainty. Insurance and buying on futures and options markets to lock in input or output prices are good examples of tools used in risk management.
Sensitivity Analyses
Refers to using alternative assumptions to determine what the outcome of a financial analysis will be if different outcomes are realized. For example, if developing a proforma income statement, using a range of assumptions associated with output prices helps to show how projected net income will change if prices differ from the base assumption.
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
These are written sequences of steps required to perform a specific task. Milking a cow, for example, requires many steps. A written SOP allows the milker to perform this task in the same way every time the cow is milked.
Statement of Cash Flows
This shows cash income and cash expenses over a specified period of time, often a year. These receipts and payments are typically broken into three categories associated with operations, investments, and financing.
A systematic review of the firm's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This is used to draw focus on what the firm does well and what it may be able to do to take advantage of emerging market opportunities.
Vision Statement
Provides a summary of the firm's most important goals. Firms differ with respect to how specific they state these goals in their business plans. We recommend being as specific as you can comfortably be.
Working Capital to Value of Production Ratio
This represents working capital as a percentage of gross income. Working capital is equal to current assets minus current liabilities. Current assets include cash and other assets that will be converted to cash or used up within one year. Current liabilities are those that are payable within one year.
Additional Resources
See the Penn State Farm Management website for other resources that may be useful as you develop your agribusiness plan.
Prepared by Jeffrey Hyde, assistant professor of agricultural economics, and Sarah Cornelisse, extension associate.
The authors would like to thank Todd D. Davis, extension economist at Clemson University, and Richard Stup, senior extension associate with Penn State Dairy Alliance, for their helpful reviews of an earlier draft of this publication.

- Value-added agriculture
- Agricultural entrepreneurship
- Value-added dairy entrepreneurship
- Value-added dairy foods marketing
- Online marketing and sales
- Social media
- Direct marketing
- Farm and ag business management
- Business planning
You may also be interested in ...

Milk Production Records for Management Control

Pennsylvania Farm Account Book
Starting at $15.00

Pennsylvania Farm Account Book, Part 1

Using Quickbooks to Manage Your Farm Business

Farm Accrual Adjustments to a Cash-basis Income Statement

Onion Production

The Build-a-Budget Book

Estate Planning for Pennsylvania Farm Families

Beef Background Production
Personalize your experience with penn state extension and stay informed of the latest in agriculture..
Agricultural Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Agricultural Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your Agricultural business plan.
We have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their Agricultural companies.
Below is a template to help you create each section of your Agricultural business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
Schrute’s Roots is a startup agricultural business that produces crops for Scranton, Pennsylvania and the surrounding area. Schrute’s Roots will specifically grow root vegetables, including potatoes, onions, and beets. The company’s mission statement is to work hard to grow these vegetables organically and without any chemicals. We will sell our produce at local farmer’s markets as well as to local restaurants and other establishments that would like to use or sell our produce.
Schrute’s Roots is owned and led by Dwight Schrute. Dwight has been a farm operations manager for the past twenty years, bringing a plethora of knowledge and skills that will prove to be invaluable to all aspects of the business. After working as a farm operations manager, Dwight desired to run his own agricultural farm business that grows organic produce and benefits the local community. He will utilize his prior knowledge and experience to manage crop production, operations, and other aspects of the business.
Product Offering
Schrute’s Roots grows a variety of root vegetables for Scranton, Pennsylvania and the local community. All produce will be organically grown. We alternate our crops, so the exact crops that are grown will be dependent on the season and current crop cycle. Some crops that we plan to grow include the following:
Customer Focus
Schrute’s Roots will primarily serve the residents and businesses of Scranton, Pennsylvania and the surrounding areas. Any individual or establishment that is interested in purchasing our crops is welcome to partner with us. We will sell our crops to individuals at local farmer’s markets and directly to wholesalers, grocery stores, and restaurants.
Management Team
Schrute’s Roots’ most valuable asset is the expertise and experience of its founder, Dwight Schrute. Dwight has been a farm operations manager for the past twenty years, bringing a plethora of knowledge and skills that will prove to be invaluable to all aspects of the business. After working as a farm operations manager, Dwight desired to run his own agricultural business that grows organic produce and benefits the local community. He will utilize his prior knowledge and experience to manage crop production, operations, and other aspects of the business.
Success Factors
Schrute’s Roots will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Management: Schrute’s Roots’ management team has years of experience in agricultural operations, which will prove invaluable to all aspects of the business.
- Relationships: Having lived in the community for twenty years, Dwight Schrute knows all of the local leaders, media, and other influencers. As such, it will be relatively easy for Schrute’s Roots to build brand awareness and an initial customer base.
- Quality products at affordable pricing: Schrute’s Roots will provide quality products at affordable pricing, as it has high-quality equipment and uses the latest techniques.
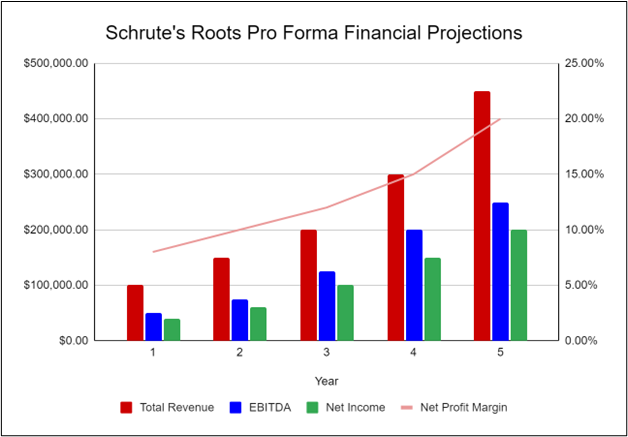
Financial Highlights
Schrute’s Roots is currently seeking $750,000 to start the company. The funding will be dedicated towards securing the land and purchasing equipment and supplies. Funding will also be dedicated towards three months of overhead costs and marketing costs. Specifically, these funds will be used as follows:
- Land: $200,000
- Equipment: $200,000
- Three Months of Overhead Expenses (payroll, utilities): $150,000
- Marketing Costs: $100,000
- Working Capital: $100,000
The following graph below outlines the pro forma financial projections for Schrute’s Roots.
Company Overview
Who is schrute’s roots.
Schrute’s Roots is a startup agricultural business that produces crops for Scranton, Pennsylvania and the surrounding area. Schrute’s Roots will specifically grow root vegetables, including potatoes, onions, and beets. The company’s mission is to grow vegetables organically and without any chemicals. We will sell our produce at local farmer’s markets as well as to local restaurants and other establishments that would like to use or sell our produce.
Schrute’s Roots is owned and led by Dwight Schrute. Dwight has been a farm operations manager for the past twenty years, bringing a plethora of knowledge and skills that will prove to be invaluable to all aspects of the business. After working as a farm operations manager, Dwight desired to run his own agricultural business that grows organic produce and benefits the local community. He will utilize his prior knowledge and experience to manage crop production, operations, and other aspects of the business.
Schrute’s Roots’ History
Dwight Schrute incorporated Schrute’s Roots as an S-corporation on May 1st, 2023. The operations aspects of the business will be run from Dwight’s home, while the agricultural aspects will be run from the land purchased for crop production.
Since incorporation, the company has achieved the following milestones:
- Found land to grow the crops and wrote a letter of intent to purchase it
- Developed the company’s name, logo, and website
- Determined agricultural equipment and inventory requirements
- Began recruiting key employees
Schrute’s Roots’ Services
Industry analysis.
The agricultural industry is vital to all communities. The crops and products grown by local farmers and crop production companies are essential to the health of local communities. They provide jobs to the locals and result in locally grown food that the nearby residents can purchase. Larger agriculture businesses do not offer these benefits to smaller communities. Because of this, there has been a greater demand and emphasis on the sustainability of local agricultural companies that can directly benefit the local community.
Furthermore, market research shows that local communities are demanding that crop production and other agricultural companies grow their products organically. Organic foods are much healthier for individuals to eat because they provide more nutrition and aren’t laced with chemicals. Improved technology and research into organic methods are making this form of crop production more profitable and sustainable.
Therefore, with the increasing demand for local organic farms, we are confident that Schrute’s Roots will succeed in the local market and benefit the residents of the Scranton area.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
Schrute’s Roots will serve the industries and community residents of Scranton, Pennsylvania and its surrounding areas. We will sell our produce at farmer’s markets to individuals and directly to establishments that wish to partner with us.
The demographics of Scranton, Pennsylvania are as follows:
Customer Segmentation
Schrute’s target audience segments include:
- Individuals
- Restaurants
- Grocery Stores
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
Schrute’s Roots will face competition from other agriculture businesses. A description of each competitor company is below.
AgraFarm is one of the largest raw food manufacturers in the U.S., owning a 15,000-acre farm for agriculture. It has well-established connections with big FMCG companies and has been thriving in the agricultural industry for 12 years. It also has automated equipment and machines, which helps in improving its operations and reducing costs. AgraFarm is also known for delivering large orders at the right time without delay.
BDA Farms was established in 1998. BDA Farms is a very well-known company that provides good quality organic produce to companies. It also has a very good brand value, and its product packaging is second to none. BDA Farms is located in Scranton, Pennsylvania, and it has a very effective distribution and supply chain network.
BeetFarms was initially a beets producer company and then branched out to other vegetables. BeetFarms is now one of the ten largest vegetable producers in the state. The Company’s packaging and processing units are located in Scranton, Pennsylvania. It has recently acquired other local vegetable producers, expanding its operations as well as limiting the variety of farms producing vegetables for the community.
Competitive Advantage
Schrute’s Roots will be able to offer the following advantages over their competition:
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
Schrute’s Roots will offer the unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Production of high-quality organic produce
- Affordable pricing
- Providing excellent customer service and customer experiences
Promotions Strategy
The promotions strategy for Schrute’s Roots is as follows:
Social Media Marketing
Social media is one of the most cost-effective and practical marketing methods for improving brand visibility. The company will use social media to develop engaging content in terms of various forms and technologies of commercial cultivation and post customer reviews that will increase audience awareness and loyalty.
Website/SEO
Schrute’s Roots will develop a professional website that showcases pictures of the farm and the products we will grow. It will also invest in SEO so that the company’s website will appear at the top of search engine results.
Industry Events
By attending regional farming conferences, association meetings, and symposia, Schrute’s Roots will network with agricultural industry leaders and seek referrals to potential customers.
Direct Mail
The company will use a direct mail campaign to promote its brand and draw customers, as well. The campaign will blanket specific neighborhoods with simple, effective mail advertisements that highlight the credentials and credibility of Schrute’s Roots as a high-quality crop production agriculture business.
Schrute’s Roots’ pricing will be competitive. Pricing will be about 50% lower than retail prices to allow wholesalers and retailers to earn their margins.
Operations Plan
Operation Functions: The following will be the operations plan for Schrute’s Roots.
- Dwight Schrute will be the Owner and President of the company. He will oversee all staff and manage client relations. He will help with the produce cultivation until he has hired a full staff of farmhands. Dwight has spent the past year recruiting the following staff:
- Meredith Grant – will oversee all administrative aspects of running the farm. This will include bookkeeping, tax payments, and payroll of the staff.
- Kevin Baird – Head Farmhand who will oversee the farming staff and day to day operations.
- Oscar Smith– Assistant Farmhand who will assist Kevin.
Milestones:
Schrute’s Roots will have the following milestones completed in the next six months.
- 07/202X Finalize land purchase
- 08/202X Design and build out Schrute’s Roots
- 09/202X Hire and train initial staff
- 10/202X Kickoff of promotional campaign
- 11/202X Launch Schrute’s Roots
- 12/202X Reach break-even
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
Schrute’s Roots’ revenues will come from the sales of root vegetables to its customers and local food establishments.
The major cost drivers for Schrute’s Roots will be labor expenses, land purchase, equipment purchases and maintenance, and marketing plan expenses.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
- Three months of overhead expenses (payroll, utilities): $150,000
- Marketing costs: $100,000
- Working capital: $100,000
Key Assumptions
The following outlines the key assumptions required in order to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and pay off the startup business loan.
- Number of customers per month:
- Annual equipment maintenance costs: $20,000
Financial Projections
Income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, agricultural business plan faqs, what is an agricultural business plan.
An agricultural business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your agricultural business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your Agricultural business plan using our Agricultural Business Plan Template here .
What are the Main Types of Agricultural Businesses?
There are a number of different kinds of agricultural businesses , some examples include: Animal feed manufacturing, Agrichemical and seed manufacturing, Agricultural engineering, Biofuel manufacturing, and Crop production.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Agricultural Business Plan?
Agricultural businesses are often funded through small business loans. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are also popular forms of funding.
What are the Steps To Start an Agricultural Business?
Starting an agricultural business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop An Agricultural Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed agricultural business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your agricultural business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your agricultural business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Agricultural Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your agricultural business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your agricultural business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Agricultural Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your agricultural business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your agricultural business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.

Agriculture Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide to Start Agri-Business
- May 24, 2023
- Business Loan , Finance

Agriculture has long been the foundation of economies all across the world, supplying communities with food, resources, and income. With the agricultural sector employing more than 80% of the world’s labour force, it is obvious that this sector is crucial to the prosperity of any nation’s economy.
For an entrepreneur, there are numerous opportunities in this sector. Whether you want to start a successful farm business, or you are looking for government assistance in the form of loans and subsidies. In this article, we’ll cover all the topics.
Let’s understand what are different factors to consider in Agriculture business plans.
The Importance of Agriculture in India

- Over 60% to 70% of the Indian population relies on agriculture and related industries.
- Almost 52% of the labour force in the nation is employed in the agriculture industry.
- About 18.3% of India’s GDP (2022-23) (Gross Domestic Product) is attributed to agriculture. ( PIB )
- India’s GDP from agriculture increased to 6934.75 INR billion in the 4th quarter of 2022 from 4297.55 INR billion in the 3rd quarter.
- The Indian agriculture industry is projected to grow by 3.5% during the fiscal year 2022-2023.[ Source ]
Agriculture Business Plan
A solid plan may make your agriculture business successful. Therefore when writing one, consider all the elements that constitute an excellent agriculture business plan. Also, take inspiration and incorporate key elements from already existing businesses.
Purpose of Agriculture Business Plan
- A strong agriculture business plan helps you understand the teams and make key business decisions to accomplish desired goals.
- It also helps you get investors for your business. Investors could be bankers or any other venture capitalists who would be willing to raise funds for your agribusiness.
- It helps determine if you can get the business going in a set direction and also allows you to estimate the costs required for founding the business.
- A good business plan clearly defines your corporate objectives.
Elements of an Agriculture Business Plan

While creating a strategy for your agriculture business, use a step-by-step procedure and include a comprehensive list of all the necessary components. Of course, your business strategy will determine whether you are a startup or an established firm. In any case, you must ensure that your business plan is inclusive, succinct, detailed, and grounded in reality.
Planning to create an Agriculture Business plan? Here’s what you should include:
1. Purpose and Objectives
The goal of the company is expressed in its objective statement. It dictates why you want to start the business and what you hope to achieve. Also, it identifies the other companies or entities your business will work with.
Thus, your company’s mission statement must incorporate information about your brand and core values.
2. Business Details
Illustrate every important component of your business, including its location, the size of its property, the date it began operations, its current status, and the sector it operates in. This section could also address other subjects, like marketing and sustainability.
3. Market Analysis
The majority of businesses begin by researching their industry. So, it would be great to implement the same idea in your agricultural business.
You can start by learning about the needs and compiling as much data as possible on supply and demand, market trends, rivals, and customers.
4. SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis is a way to determine your agribusiness’s internal strengths and weaknesses. The outside world may teach you about your possibilities, threats, skills, and shortcomings. For example, new markets, competitors, governmental limits, laws, and current economic conditions could all be opportunities or dangers.
By conducting a SWOT analysis, you can know the strengths and weaknesses of your agribusiness on the inside. Besides strengths and weaknesses, you can also learn about opportunities and threats from the outside. Opportunities and threats could include new markets and competitors, government regulations and restrictions, and prevailing economic conditions.
5. Business Strategy
Create a marketing plan corresponding to your mission statement and goals, the products and services you want to sell. The information you gathered during the research and analysis phases can provide ideas for this.
While creating a marketing plan, be sure to take into account all aspects, including pricing, location, and promotion. Consider how your products or services could help your clientele as well. Customers should be made aware of your product’s benefits. Then and only then will your business thrive in today’s competitive marketplace.
6. Finances
One of the most important sections of any agriculture business plan is the financing portion. You should assess your current financial condition and future prospects.
Depending on your financial status, you can decide whether a business loan is necessary for your agribusiness. Determine your current financial status and the money required to build your agriculture business.
7. Management Summary
The management summary, which comes last in your agricultural business plan, is where you highlight your successes and showcase them to potential investors.
Show them your financial projections and reassure them that investing in your business is a smart move. Doing this can bring in more potential investors for your agricultural business.
Steps to Draft an Agriculture Business Plan
- Step 1: Before getting started you need to first make up your mind about the type of agriculture business you want to start.
- Step 2: Narrow down land and secure the boundaries of it. Make sure you close the lease agreement.
- Step 3: Do deep research on the market to identify the requirements you need to cater to.
- Step 4: Do a calculation of different aspects of your agribusiness. This could include the economic viability of the business, commodities you are going to trade or what role you need to take up in order to tap into future opportunities.
- Step 5: When you are done with the above steps, now is the time to identify the resources you need to for the production.
- Step 6: Register your business
- Step 7: Make a strategy to secure the credit for your business. Unless you have a strong foundation of credit, it is very difficult to kickstart an agribusiness.
Agriculture loans in India
An agribusiness loan is a type of overdraft that can be used for farming and other agriculturally related operations that require working capital.
Farmers in India can typically apply for low-interest agricultural loans. Repayment conditions for agricultural loans vary from lender to lender. The loan can be repaid in monthly, yearly, or biannual payments.
Uses of Agribusiness loans
- Purchasing agricultural and irrigation machinery
- Buying cattle and livestock
- Purchase of agricultural land
- Storage and warehousing expenses
- Marketing expenses
- Transportation costs
- Managing day-to-day operations
Eligibility Criteria for an Agriculture Business Loan
- The primary applicant must be aged between 18 – 70 years old.
- Applicant should use the loan credit for the cultivation of the farmland.
Documents required to avail of an Agriculture Loan
- ID proof – PAN card/ Aadhar card/ Ration card/ Driving license/ Voter ID
- Address proof – Bank statement/ 3 months utility bill/ Ration card/ Driving license/ Passport
- Land ownership proof.
Let’s see what are the different components of an Agriculture Business Plan.
Closing Words
It should go without saying that planning your farm business is a major task. But, don’t let it deter you.
When drafting the plan, your mission statement and goals should come first. After that, go on to strategy creation and market research. You can then describe how you’ll carry out your plan after that. You will market your products to your customers in this manner. You must identify your target customers at this point in your agriculture business strategy.
Hence, when creating a plan for your farm business, go step by step. And ensure that you don’t miss anything. Just follow the steps mentioned in this article. Happy Farming!
What business can I start with agriculture?
Every business in agriculture holds a key to profits. If you are not sure which business to start with then, here’s a list of businesses you can consider: 1. Organic Farming 2. Organic Fertilizer 3. Poultry Farming 4. Dairy Farming 5. Garlic Farming 6. Lavender Farming 7. Gourmet Mushrooms Farming 8. Flower Business 9. Fertilizer Distribution 10. Mushroom Farming 11. Sunflower Farming 12. Hydroponic Retail Store Business 13. Bamboo Farming 14. Willows Farming
Which agriculture business plan example is most profitable?
When we talk about profitability, Dairy farming has an exceptional potential to become most profitable. Its not just the milk but other products like manure are in high demand.
How to start an agriculture loan application process?
You can start your agriculture loan application process by duly filling out all the details and submitting the application form to the bank while attaching all the necessary documentation.
What is the online application procedure for agriculture loans?
When applying for a loan online, you must fill out the application form and upload it along with the required documents on the bank’s website.
Who can be categorized as small and marginal farmers?
Any farmer who owns less than 2.5 acres of irrigated land or 5 acres of non-irrigated land falls under the small and marginal farmer category.
Can women avail of agriculture loans in India?
The Indian government encourages women to avail of agriculture loans by offering special schemes for women borrowers.
Who is eligible to apply for an agriculture loan in India?
All categories of farmers, including small and marginal farmers, tenant farmers and sharecroppers, are all eligible to apply for agriculture loans.
How do you write an agricultural business plan?
You just need the follow the below-mentioned steps to make an agricultural business plan
Step 1: Business statement
Start with a mission statement. The why should be clear. This includes what your business is all about and what it will do. Include the business identity and values.
Step 2. Details of your business
Highlight all important details of your business. Everything right from the location to the date when you’ll start operations.
Step 3: Competition Analysis
Analyse the market. It will help you to strategize better. Gather information about your competitors. Do a SWOT analysis.
Step 4: Business Strategy
Create a marketing strategy, that aligns with your business statement and values.
Step 5: Finances
Assess your financial standing and project future. Based on that apply for a loan
Step 6: Management Summary
Highlight your business achievements.
How do I start my own agricultural startup?
It’s pretty straightforward to start an agricultural startup in India. Follow the below-mentioned steps:
Step 1: Competition Analysis
Do a proper competition analysis. This will help you to make a good business plan.
Step 2: Arranging the Funds
Consider taking a loan or arrange the funds to kickstart the business.
Step 3: Register your Business
It is the first and foremost step that you should take. Registering your business will help you to take advantage of various government initiatives or schemes.
Step 4: Marketing your Business
Mow market your business. Make a marketing strategy and stick to it. It will reap results for you.
Suggested Reads:
- Best 30+ Business Ideas for Women Entrepreneurs in India
- What is SSI? Small-Scale Industries Explained
- What is Loan Resource App: Benefits, Comparison & How to Apply
- 70+ Best RBI Approved Loan Apps In India [2023]
- Fake loan app list: 500+ apps you should avoid at any cost
- MSME Advantages and Disadvantages: Unlocking the potential of MSMEs in India
Check your eligibility
Related post.

Home Loan Top Up vs Home Loan Balance Transfer | All you Need to Know

9 Different Types of Business Loans and How to Choose the Right Business Loan for Your Needs

How to setup EV charging station in India? Costing, Government Guidelines and Initiatives

50+ Small Business Ideas with Low Investment

NBFC Business Loan

5 Different Ways That Can Help You Reduce Home Loan EMI Amidst RBI’s Hawkish Policy Stance

How to get loan from bank for business?

How to check active loan on my name using Pan card?

Top High demand Indian goods that World wants from India

How to Start an Export Business in India: A Comprehensive Guide
Latest news.

RBI Mandates Banks To Provide Key Facts Statement (KFS) To Loan Seekers

Property Market in India Witnesses Significant Growth Despite Higher Mortgage Rates and Rising Prices: Report

Ram Navami Bank Holiday: Will Banks Remain Closed On April 17?

Bank of Baroda Hikes Lending Rate By 5 Basis Points For Select Tenures; Check Details Here

Another Bank In Trouble: What Should You Do As Depositors If Your Bank Fails?
Join our newsletter.
Expert insights, and industry updates to grow the financial health for your business.
Hit enter to search or ESC to close

How to Create an Agricultural Business Plan
Blog > how to create an agricultural business plan, table of content, introduction, executive summary, company description, market analysis, product/service description, marketing and sales strategies, operational plan, swot analysis, financial projections, funding and investment, risk management, sustainability and environmental impact, legal and regulatory compliance, timeline and milestones, our other categories.
- Company Valuation
- Pitch Deck Essentials
- Raising Capital
- Startup Guide
- Uncategorized
Reading Time : 16 Min
Business plan 101.
Starting an agricultural venture is an exciting and rewarding journey, but it requires careful planning and a well-crafted agricultural business plan. This document serves as a roadmap for your agricultural business, outlining your goals, strategies, and financial projections. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through each step of creating a robust agricultural business plan to set your venture up for success. Whether you’re planning to start a small family farm or a large-scale agricultural operation, this guide will help you make informed decisions and navigate the challenges of the agricultural industry.
The executive summary is the first section of your agricultural business plan, but it is typically written last. This section provides a concise overview of your entire plan and should capture the reader’s attention. Include the following elements in your executive summary:
- Example: ABC Farms is a sustainable agriculture venture committed to providing organic, locally sourced produce to health-conscious consumers in the region. Our mission is to promote eco-friendly farming practices and support local communities while delivering premium-quality products.
Stellar Business Tips: Keep your executive summary clear, compelling, and focused. Highlight the unique selling points of your agricultural business and how it addresses market demands.
In this section, provide a comprehensive description of your agricultural business. Include the following details:
- Example: ABC Farms was founded in 2010 by John and Jane Smith, who have a combined experience of over 20 years in sustainable agriculture. The business started as a small family farm and has since expanded to a 50-acre organic farm with a diverse range of crops, including vegetables, fruits, and herbs.
Stellar Business Tips: Share your business’s background, founders’ expertise, and growth trajectory. Emphasize your passion for agriculture and commitment to environmental and social responsibility.
Conduct a thorough market analysis to gain insights into the agricultural industry, market trends, and potential opportunities. Consider the following factors:
- Example: The organic produce market has been steadily growing at a rate of 10% per year, driven by increasing consumer awareness of health benefits and environmental concerns. Local restaurants and grocery stores are eager to source fresh, organic produce from nearby farms.
Stellar Business Tips: Use data and statistics to support your market analysis. Identify target customers and potential gaps in the market that your agricultural business can address.
Detail the agricultural products or services your business offers. If you are into crop farming, describe the crops you plan to grow, their varieties, and their uses. If you are into livestock rearing, specify the types of animals and breeds you’ll raise. If you offer agricultural services, describe them in detail.
- Example: ABC Farms specializes in heirloom vegetables, such as tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers, renowned for their exceptional flavor and nutritional value. We also raise heritage-breed livestock, including free-range chickens and pasture-raised pigs, to provide ethically sourced meat products.
Stellar Business Tips: Highlight the uniqueness and quality of your agricultural products or services. Emphasize your commitment to sustainability and responsible animal husbandry if applicable.
Outline your marketing and sales strategies to reach and attract your target customers. Consider the following aspects:
- Example: ABC Farms utilizes social media platforms to showcase our farm-to-table journey and engage with customers. We actively participate in farmers’ markets and local food events to promote our brand and build personal connections with consumers.
Stellar Business Tips: Utilize digital marketing tools, such as social media and email marketing, to create brand awareness and engage with customers directly. Explore partnerships with local businesses to expand your reach.
The operational plan outlines how your agricultural business will function on a day-to-day basis. It includes the following details:
- Example: ABC Farms employs a team of experienced farmers who follow sustainable farming practices, including crop rotation and integrated pest management, to ensure soil health and minimize environmental impact. We have invested in modern irrigation systems and machinery to optimize productivity and reduce labor costs.
Stellar Business Tips: Detail the specific practices and technologies you’ll use to enhance efficiency and sustainability. Showcase your commitment to ethical and responsible farm management.
Conduct a SWOT analysis to evaluate your agricultural business’s internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats. Use this analysis to make informed decisions and develop effective strategies.
- Example: Strengths: ABC Farms has established a strong reputation for premium-quality produce, garnering repeat customers and positive reviews. Weaknesses: We currently face limited storage facilities for harvested crops, which may affect our ability to meet peak demands.
Stellar Business Tips: Be honest about your agricultural business’s strengths and weaknesses. Address how you plan to capitalize on opportunities and mitigate potential risks.
The financial projections section provides a detailed forecast of your agricultural business’s financial performance over the next 3-5 years. Include the following financial statements:
- Example: Sales Forecast: We anticipate steady growth in sales, with a projected increase of 15% annually due to expanding customer base and diversified product offerings.
Stellar Business Tips: Use realistic and data-driven estimates for your financial projections. Include contingency plans for unforeseen financial challenges.
If your agricultural business requires funding or investment, outline your funding requirements and sources of financing. This section should include:
- Example: Funding Requirements: ABC Farms seeks a capital investment of $200,000 to expand farmland, install greenhouses, and upgrade equipment to meet the growing demand for our organic products.
Stellar Business Tips: Clearly explain how the investment will be used to drive the growth and success of your agricultural business.
Identify potential risks and challenges that your agricultural business may face and develop risk management strategies to mitigate their impact. Consider the following risk categories:
- Example: Market Risks: Fluctuations in commodity prices and changes in consumer preferences may impact our sales revenue. To address this, we will diversify our product offerings and explore new markets.
Stellar Business Tips: Demonstrate your proactive approach to risk management. Provide solutions for handling potential challenges to reassure stakeholders.
As the importance of sustainable farming practices grows, customers and investors increasingly value agricultural businesses that prioritize environmental stewardship and social responsibility. In this section, highlight your commitment to sustainability:
- Example: ABC Farms is committed to regenerative agriculture practices, including cover cropping and no-till farming, to enhance soil health and sequester carbon. We actively participate in local conservation programs to protect natural habitats and biodiversity.
Stellar Business Tips: Showcase your efforts to contribute positively to the environment and local community. Share success stories of how your sustainable practices have made a difference.
The agricultural industry is subject to various laws and regulations, such as agricultural zoning laws, environmental regulations, labor laws, and food safety standards. In this section, address the legal and regulatory aspects of your agricultural business:
- Example: ABC Farms complies with all local, state, and federal regulations for organic certification and food safety. We conduct regular inspections and maintain accurate records to ensure full compliance.
Stellar Business Tips: Emphasize your commitment to adhering to legal requirements and ensuring transparency in your agricultural operations.
Develop a timeline for your agricultural business’s key milestones and achievements. This section should include:
- Example: Milestone Timeline: Year 1 – Acquire additional farmland; Year 2 – Expand greenhouse production; Year 3 – Launch an online farm-to-table store.
Stellar Business Tips: Set realistic timelines for achieving your milestones. This will help you track progress and stay on course.
In conclusion, creating a well-structured and comprehensive agricultural business plan is crucial for your venture’s success. It provides a roadmap to guide your agricultural business towards its goals, while also attracting investors and other stakeholders. Remember that the agricultural industry is dynamic and continually evolving, so your business plan should be flexible enough to adapt to changing market conditions and opportunities.
By following the steps outlined in this guide and incorporating sustainable practices, your agricultural business can thrive in an increasingly competitive landscape. At Stellar Business Plans , we are dedicated to supporting the success of agricultural entrepreneurs like you. Our team of experts can assist you in crafting a tailored business plan that aligns with your vision and values. Let’s cultivate growth together and create a sustainable future for agriculture!
Remember, agricultural business success is not only about financial gains but also about nurturing the land, supporting local communities, and providing consumers with nutritious and ethically sourced products. Let your passion for agriculture and dedication to sustainability shine through every aspect of your business. Together, we can sow the seeds of a thriving agricultural future.
Start Your Journey With Us
To know us more.
Updated On : September 2, 2023
Total shares:, average rating :, related posts.
How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
How to create an airline business plan, how to create an effective amazon fba business plan, how to create an advertising agency business plan, how to create an accounting business plan, how to create 3d printing business plan, how to create mcdonalds restaurant business plan, how to create a bbq restaurant business plan, how to create airbnb business plan, how to create a gym business plan: complete guide.

How to Write a Strong Executive Summary?


13 Reasons why you need a Solid Business Plan
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 4.2 / 5. Vote count: 33
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
WhatsApp us

Farm Business Planning
Farm Business Planning is key to beginning farmer success.
It helps beginning farmers :
- Plan for the economic sustainability of a new farm enterprise.
- Obtain funding to purchase land, equipment and other resources from lending institutions, investors and/or grant making agencies.
- Articulate what their farm will look like.
On this page, we compiled free farm business planning resources to help you understand what a formal business plan is, and how to start planning your farm business. Sections include:
- Developing a Farm Business Plan
- Enterprise Budgeting
Enterprise budget resources are included on the farm business planning page because such tools are usually essential in helping you to develop your business plan.
Planning your farm business involves more than is outlined on this page alone. You’ll probably also be interested in funding (loans/grants) , farm incorporation , and risk management . Our starting a farm page is worth visiting first. Also, you might find the following article helpful, because it touches on many farm business planning topics: Farm Products, What to Charge: Marketing, Price, Calculating Costs, Strategy and Much More .

1. Developing a Farm Business Plan
A business plan is a decision making tool that takes the form of a formal document. It states your business goals, why you think you can achieve them, and lays out your plan for doing so. Farm business planning is also a process, not an end product. A business plan is a work in progress, which farm business owners or operators will want to revisit regularly.
Planning and Funding Your Farm Business from the Cornell University Small Farms Project has lots of important and useful farm business planning resources.
Rural Businesses is a web and print publication from the Minnesota institute for Sustainable Agriculture (MISA).
Building a Business Plan for Your Farm: Important First Steps is a 20 page farm business planning publication that discusses the initial steps to help you move toward writing a formal business plan.
The Center for Agroecology has a Small Farm Business Planning publication that goes over many of the basics in a step by step format.
Building a Sustainable Business: A Guide to Developing a Business Plan for Farms and Rural Businesses is a farm business planning publication available from SARE.
Do I need a Business Plan for my Farm? is a web resource from the New England Small Farm Institute. It’s a great place to get started.
AgPlan from the University of Minnesota helps rural business owners develop a business plan for free, while also offering sample business plans for ideas, and a way to print or download your plan.
Developing a Farm Business Plan includes several helpful resources from the USDA National Agricultural Library’s Rural Information Center.
Organic Farm Business Planning Page from North Carolina State University features a number of publications and links related to financial planing for organic farmers.
Agricultural Business Planning Templates and Resources is an ATTRA publication most relevant to smaller-scale or alternative agricultural entrepreneurs.
Beginning Farmer and Rancher Resources offers comprehensive resources on Bookkeeping and Other Basics ; Cash Flow Budgeting and Managing Debt ; Small Farm and Ranch Income Taxes , and more.
Purdue University’s Center for Food and Agricultural Business has educational resources to explore, such as the New Ventures in Food and Agriculture in Indiana , which offers business planning assistance.
Purdue University Cooperative Extension offers strategic farm business planning tools for commercial farm producers.
Penn State University College of Agricultural Sciences has many Business Planning tools and information. Penn State Cooperative Extension has a Developing a Business Plan page. Penn State also has a Farm Business Plan Template that allows you to plug in your information and create a basic business plan.
The U.S. Small Business Administration works with local partners to counsel, mentor and train small businesses. It is worth getting to know their programs and connect with your local office.
The Martindale Center Reference Desk has an extensive compilation of links to calculators, applets, spreadsheets, courses, manuals, handbooks, simulations, animations, videos and more. Martindale’s Agriculture Center can be of great use to farmers making business plans.

2. Enterprise Budgets
Enterprise budgets project costs and returns for a particular farm production practice. You can use enterprise budgets to make smart business management decisions, and to help you develop a viable business plan.
Enterprise Budgeting Tools of all sorts from the Agricultural Marketing Resource Center, including organic crop budgeting tools, many vegetable budgeting tools, the crop conversion tool for side-by-side crop comparisons, specialty crop and livestock budgets, hydroponics budgets, wind calculators, composting calculators, manure calculators, distillers grain budgets, biomass calculators and specialty foods calculators.
Introduction to Farm Planning Budgets for New and Beginning Farmers (Virginia Tech)
Importance and Use of Enterprise Budgets in Agriculture (University of Nevada)
Enterprise Budgeting (Kerr Center)
Organic Specific Enterprise Budgets
- Enterprise Budgets and Production Costs for Organic Production (ATTRA)
- Organic Crop Production Enterprise Budgets and Information (Iowa State)
- Organic Enterprise Budget (Kansas Rural Center)
More Enterprise Budget Pages and Information
- Enterprise Budgets List (Virginia Cooperative Extension)
- Dairy Sheep Enterprise Budget (Center for Integrated Ag Systems, UW-Madison)
- Crop Budgets (University of Maryland)
- Farm Management Enterprise Budgets (Ohio State)
- Alabama Enterprise Budget Summaries (Alabama A&M and Auburn)
- Start developing your business plan with the resources at https://www.beginningfarmers.org/farm-business-planning/
- You can find more gr eat farming resources at https://www.beginningfarmers.org/additional-farming-resources/

An official website of the United States government Here’s how you know
- Translations |
- Service Centers |
- Local Dashboard
Farmers.gov is not optimized for this browser. Please use the latest versions of Chrome, Edge, or Safari for the best experience. Dismiss
Find your state/county's agriculture data and USDA resources on your farmers.gov Local Dashboard !
How to Start a Farm: Plan Your Operation
Think about your operation from the ground up and start planning for your business. A good farm business plan is your roadmap to start-up, profitability, and growth, and provides the foundation for your conversation with USDA about how our programs can complement your operation.
Keep reading about planning your business below, get an overview of the beginning farmer's journey , or jump to a different section of the farmer's journey.
On This Page
Why you need a farm business plan.
A comprehensive business plan is an important first step for any size business, no matter how simple or complex. You should create a strong business plan because it:
- Will help you get organized . It will help you to remember all of the details and make sure you are taking all of the necessary steps.
- Will act as your guide . It will help you to think carefully about why you want to farm or ranch and what you want to achieve in the future. Over time, you can look back at your business plan and determine whether you are achieving your goals.
- Is required to get a loan . In order to get an FSA loan, a guarantee on a loan made by a commercial lender, or a land contract, you need to create a detailed business plan . Lenders look closely at business plans to determine if you can afford to repay the loan.
How USDA Can Help
Whether you need a good get-started guide, have a plan that you would like to verify, or have a plan you’re looking to update for your next growth phase, USDA can help connect you to resources to help your decisions.
Your state's beginning farmer and rancher coordinator can connect you to local resources in your community to help you establish a successful business plan. Reach out to your state's coordinator for one-on-one technical assistance and guidance. They can also connect you with organizations that specifically serve beginning farmers and ranchers.
It is important to know that no single solution fits everyone, and you should research, seek guidance, and make the best decision for your operation according to your own individual priorities.
Build a Farm Business Plan
There are many different styles of business plans. Some are written documents; others may be a set of worksheets that you complete. No matter what format you choose, several key aspects of your operation are important to consider.
Use the guidelines below to draft your business plan. Answering these kinds of questions in detail will help you create and develop your final business plan. Once you have a business plan for your operation, prepare for your visit to a USDA service center. During your visit, we can help you with the necessary steps to register your business and get access to key USDA programs.
Business History
Are you starting a new farm or ranch, or are you already in business? If you are already in business:
- What products do you produce?
- What is the size of your operation?
- What agricultural production and financial management training or experience do you, your family members, or your business partners have?
- How long have you been in business?
Mission, Vision, and Goals
This is your business. Defining your mission, vision and goals is crucial to the success of your business. These questions will help provide a basis for developing other aspects of your business plan.
- What values are important to you and the operation as a whole?
- What short- and long-term goals do you have for your operation?
- How do you plan to start, expand, or change your operation?
- What plans do you have to make your operation efficient or more profitable ?
- What type of farm or ranch model (conventional, sustainable, organic, or alternative agricultural practices) do you plan to use?
Organization and Management
Starting your own business is no small feat. You will need to determine how your business will be structured and organized, and who will manage (or help manage) your business. You will need to be able to convey this to others who are involved as well.
- What is the legal structure of your business? Will it be a sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, trust, limited liability company, or other type of entity?
- What help will you need in operating and managing your farm or ranch?
- What other resources, such as a mentor or community-based organization , do you plan to use?
Marketing is a valuable tool for businesses. It can help your businesses increase brand awareness, engagement and sales. It is important to narrow down your target audience and think about what you are providing that others cannot.
- What are you going to produce ?
- Who is your target consumer ?
- Is there demand for what you are planning to produce?
- What is the cost of production?
- How much will you sell it for and when do you expect to see profit ?
- How will you get your product to consumers ? What are the transportation costs and requirements?
- How will you market your products?
- Do you know the relevant federal, state, and local food safety regulations? What licensing do you need for your operation?
Today there are many types of land, tools, and resources to choose from. You will need to think about what you currently have and what you will need to obtain to achieve your goals.
- What resources do you have or will you need for your business?
- Do you already have access to farmland ? If not, do you plan to lease, rent, or purchase land?
- What equipment do you need?
- Is the equipment and real estate that you own or rent adequate to conduct your operation? If not, how do you plan to address those needs?
- Will you be implementing any conservation practices to sustain your operation?
- What types of workers will you need to operate the farm?
- What additional resources do you need?
Now that you have an idea of what you are going to provide and what you will need to run your operation you will need to consider the finances of your operation.
- How will you finance the business?
- What are your current assets (property or investments you own) and liabilities (debts, loans, or payments you owe)?
- Will the income you generate be sufficient to pay your operating expenses, living expenses, and loan payments?
- What other sources of income are available to supplement your business income?
- What business expenses will you incur?
- What family living expenses do you pay?
- What are some potential risks or challenges you foresee for your operation? How will you manage those risks?
- How will you measure the success of your business?
Farm Business Plan Worksheets
The Farm Business Plan Balance Sheet can help gather information for the financial and operational aspects of your plan.
Form FSA-2037 is a template that gathers information on your assets and liabilities like farm equipment, vehicles and existing loans.
- FSA-2037 - Farm Business Plan - Balance Sheet
- FSA-2037 Instructions
Planning for Conservation and Risk Management
Another key tool is a conservation plan, which determines how you want to improve the health of your land. A conservation plan can help you lay out your plan to address resource needs, costs and schedules.
USDA’s Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) staff are available at your local USDA Service Center to help you develop a conservation plan for your land based on your goals. NRCS staff can also help you explore conservation programs and initiatives, such as the Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP) .
Conservation in Agriculture
Crop insurance, whole farm revenue protection and other resources can help you prepare for unforeseen challenges like natural disasters.
Disaster Recovery

Special Considerations
Special considerations for businesses.
There are different types of farm businesses each with their own unique considerations. Determine what applies to your operation.
- Organic Farming has unique considerations. Learn about organic agriculture , organic certification , and the Organic Certification Cost Share Program to see if an organic business is an option for you. NRCS also has resources for organic producers and offers assistance to develop a conservation plan.
- Urban Farming has special opportunities and restrictions. Learn how USDA can help farmers in urban spaces .
- Value-Added Products . The Agricultural Marketing Resource Center (AgMRC) is a national virtual resource center for value-added agricultural groups.
- Cooperative. If you are interested in starting a cooperative, USDA’s Rural Development Agency (RD) has helpful resources to help you begin . State-based Cooperative Development Centers , partially funded by RD, provide technical assistance and education on starting a cooperative.
Special Considerations for Individuals
Historically Underserved Farmers and Ranchers: We offer help for the unique concerns of producers who meet the USDA definition of "historically underserved," which includes farmers who are:
- socially disadvantaged
- limited resource
- military veterans
Women: Learn about specific incentives, priorities, and set asides for women in agriculture within USDA programs.
Heirs' Property Landowners: If you inherited land without a clear title or documented legal ownership, learn how USDA can help Heirs’ Property Landowners gain access to a variety of programs and services
Business Planning
Creating a good business plan takes time and effort. The following are some key resources for planning your business.
- Farm Answers from the University of Minnesota features a library of how-to resources and guidance, a directory of beginning farmer training programs, and other sources of information in agriculture. The library includes business planning guides such as a Guide to Developing a Business Plan for Farms and Rural Businesses and an Example Business Plan .
- The Small Business Administration (SBA) offers information about starting, managing, and transitioning a business.
SCORE is a nonprofit organization with a network of volunteers who have experience in running and managing businesses. The Score Mentorship Program partners with USDA to provide:
- Free, local support and resources, including business planning help, financial guidance, growth strategies.
- Mentorship through one-on-one business coaching -- in-person, online, and by phone.
- Training from subject matter experts with agribusiness experience.
- Online resources and step-by-step outlines for business strategies.
- Learn more about the program through the Score FAQ .
Training Opportunities
Attend field days, workshops, courses, or formal education programs to build necessary skills to ensure you can successfully produce your selected farm products and/or services. Many local and regional agricultural organizations, including USDA and Cooperative Extension, offer training to beginning farmers.
- Cooperative Extension offices address common issues faced by agricultural producers, and conduct workshops and educational events for the agricultural community.
- extension.org is an online community for the Cooperative Extension program where you can find publications and ask experts for advice.
Now that you have a basic plan for your farm operation, prepare for your visit to a USDA service center.
2. Visit Your USDA Service Center
How to Start a Farm with USDA
Get an overview of the beginning farmer's journey or jump to a specific page below.
Find Your Local Service Center
USDA Service Centers are locations where you can connect with Farm Service Agency, Natural Resources Conservation Service, or Rural Development employees for your business needs. Enter your state and county below to find your local service center and agency offices. If this locator does not work in your browser, please visit offices.usda.gov.
Learn more about our Urban Service Centers . Visit the Risk Management Agency website to find a regional or compliance office or to find an insurance agent near you.
Business Plan for Investors
- Bank/SBA Business Plan
- Operational/Strategic Planning Services
- L1 Visa Business Plan
- E1 Treaty Trader Visa Business Plan
- E2 Treaty Investor Visa Business Plan
- EB-1 Business Plan
- EB-2 NIW Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- Innovator Founder Visa Business Plan
- Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- Expansion Worker Visa Business Plan
- Manitoba MPNP Visa Business Plan
- Nova Scotia NSNP Visa Business Plan
- British Columbia BC PNP Visa Business Plan
- Self-Employed Visa Business Plan
- OINP Entrepreneur Stream Business Plan
- LMIA Owner Operator Business Plan
- ICT Work Permit Business Plan
- LMIA Mobility Program – C11 Entrepreneur Business Plan
- USMCA (ex-NAFTA) Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Landlord business plan
- Nonprofit Start-Up Business Plan
- USDA Business Plan
- Cannabis business plan
- Ecommerce business plan
- Online boutique business plan
- Mobile application business plan
- Daycare business plan
- Restaurant business plan
- Food delivery business plan
- Real estate business plan
- Business Continuity Plan
- Pitch Deck Consulting Services
- Financial Due Diligence Services
- ICO whitepaper
- ICO consulting services
- Confidential Information Memorandum
- Private Placement Memorandum
- Feasibility study
- Fractional CFO
- How it works
- Business Plan Examples
Agriculture Farm Business Plan Example
JUL.25, 2013

Agriculture business plan for starting your own business
Farming and agriculture business is not as easy as it seems. An even difficult step is to plan how to write a business plan for agriculture. Whether it is a Christmas tree farm business plan or an organic fertilizer business plan , you need to put real effort into planning each and every aspect of your agriculture business plan . To become successful, you should know the ways to operate your enterprise efficiently. You should know your revenue and cash position. You also need to forecast your crop rotations.
We have here provided a detailed business plan so that you can avoid any inconvenience in making a plan for yourself. No matter if you want to make a fish farm business plan or fountain pepper farm business plan , hydroponics farm business plan , or even an aquaponics farm business plan , this sample business plan agriculture template will help you.
A well-formed business plan of agriculture will help your agriculture business plan grow and generate the revenue that you dream of. It will help in managing your business in hard times and will also improve the chances of getting loans from the government for your business. So, if are thinking of creating a business for a bank loan , check out this template.
Executive Summary
2.1 the business.
The Old Maple Way will be a registered farm in New York, US. The business will aim to provide fresh fruits and vegetables to its customers. Along with it, we provide high-quality dairy products. Instead of competing with other farms in town, we will mainly focus on the quality and pricing of our products.
In any business plan agriculture project, the aims and goals should be clear. Instead of looking for an online business plan expert , you can write your business plan exact like agriculture business plan examples available online.
2.2 Management of Agriculture
The Old Maple Way Farm will be managed by James Celery. He will look into all the operations going on the farm. For his assistance, three managers will work with him. These managers will be trained for a month before starting their jobs. As per this agriculture business plan pdf, James will hire some highly experienced farmers who will look after the growth and management of fruits and vegetables. James will ensure the quality of production himself.
2.3 Customers of Agriculture
Customers are the backbone of every business. If you know the right audience for your agriculture business , you will be able to achieve your target. You will get the idea of how to run your agriculture business plan if you understand your customers. The main customers for the agriculture business will be the following:
- Export to Foreign Markets
- Domestic Hotels and Restaurants
- Domestic Food Companies
2.4 Business Target
The main goal of Old Maple Way Farm is to produce high-quality products for the people. We do not compromise on the hygiene and our team takes care of it. The most important thing matter to us is our customers’ satisfaction.
Here are our targets:
- Our primary target is to become the most loved farm by people within the next 3 years of our launch.
- Our secondary target is to increase the net profit every month.

Company Summary
3.1 company owner.
The owner of the Old Maple Way will be James Celery. James had a dream of starting his own agriculture business plan since he was a teenager. He wanted to produce high-quality products that do not contain harmful chemicals.
3.2 Why the farm is being started?
When James was asked why he is interested in starting a farm, he said he wanted to produce chemical-free and organic products for the people. He says that nowadays, it is difficult to find something that is purely organic and chemical-free.
Companies and farms are using harmful chemicals to increase their production. Due to it, they have ignored the quality and only focus on the quantity of production. To produce pure products, he planned to start a farm of his own. He further added that he wants to produce products that are affordable and easy to buy.
3.3 How the Farm will be started?
In a business plan for agriculture, you should mention the steps to start a farm. When you know how to make a business plan for agriculture, your agriculture business will be successful. The agriculture export business plan includes all the necessary steps needed to start an agriculture business. To start a farm, you need the right techniques and ideas. Before starting a farm, you need to consider these essential steps:
Know your Niche
The first and most important step before starting the agriculture business is to identify your niche. Without deciding the niche, you cannot start a healthy business.
Research Market
Once you have decided on your niche, you need to do market research. For instance, you have planned to grow a specific fruit, so to make the business successful, you should know who will buy your product. Making research on the market will let you know about your competitors and how will you sell your product.
If you are interested in particular fruit, vegetable or product, first learn more about the local market.
Find the Right Land
Once you have decided what product you are going to plant, you need to take the next step, i.e, deciding the land.
If you are starting at a low budget, you can take land on lease. But if you have sufficient investment to start, you can buy your land. If you start the farm on your land, you will have complete control of your farm. But at the same time, there will be more risk factors of financial loss.
In the sample of an agricultural business plan, you will find more detailed steps on how to start an agriculture business depending upon the type of farm you want to start.

In agriculture service business plan, you should mention all the services and products that your farm will produce. In the business plan agriculture pdf and business plan for agriculture available online. You will find the services that farms offer. Our products include the following:
We will produce fruits that are chemical-free and pure. We believe in producing organic products. Unlike other farms, we do not use any chemical that increases the quantity.
We will produce 100% organic vegetables. Our main focus is on quality and our customer satisfaction.
Cereals & Grains
We will also produce export-quality cereals and grains.
Dairy Products
We will also be offering two dairy products (milk and butter) to further supplement our sales.
20 Highly Profitable Agricultural Farm Business Ideas
If you are an entrepreneur willing to start an agriculture farm business, the following 20 agriculture farm business ideas can come in handy for your business venture.
Growing Mushrooms
Mushroom is a very popular Unlike various other crops, mushrooms can grow in less than a month. It is ready to be harvested in just about 21 days. This is the reason mushrooms have a high profit margin. Often new entrepreneurs are restless to harvest and sell their crops. So, if you too are one such impatient entrepreneur then mushrooms won’t make your wait too long to be ready. You can sell them in 3 weeks time from d date of cultivation.
- Mushroom farming comprises of 6 stages- first you need to compost; next spawn; case; pin and finally crop it.
- The soil of your farming land must be suitable for growing mushrooms. If this suits your soil then this is the best crop to grow. Some soils only support specific mushroom cultivation. The environment also plays a significant factor.
- You can aim to sell the produce in the local markets and also trade them. There are various countries that use mushrooms in their everyday meals. If your land in near such countries, where mushrooms are a favorite among the masses, then this is the best crop to cultivate in your farming land. Also, the convenience of export can take your mushroom business to far off markets as well.
Potato Farming
This is a very common vegetable. Yet, you should consider this as potato cultivation is greatly rewarding in many ways. Potato is consumed in meals almost daily by people both at home as well as in canteens. It is yummy, simple and very nutritious. The demand for potato is so high that even if there are other near-by farming areas growing potatoes, you still can produce it and benefit largely.
- There are a large variety of potatoes, so check the soil and the market, in order to decide which potato you should cultivate in your land. You can opt for the sweet potatoes or Irish potato farming. They are quite popular across the globe. Furthermore, they can be sold as vegetables directly and can also be sold in the processed form.
- You can choose bulk potato farming and process them if you have the capital and equipment. Potato chips and French fries are savory snacks loved by all. You can never go wrong with potato business as it ensures a high profit margin.
- You can also choose to sell potato seeds. This is an excellent money-spinning business idea. Get in touch with local, national and international potato cultivators to sell potato seed tubes and make a flourishing agriculture business out of it.
Spice Production
With the widespread knowledge about the health benefits hidden in various spices, household cooking as well as commercial restaurants have started using spices in their food in daily basis around the world. Furthermore, the boost in flavor and the pleasant aroma that come from adding spices to cuisines has made spices a favorite ingredient in the kitchen. The high demand and being a very costly product, spices are a great option for agriculture farm business plan. Spice cultivation can churn a lot of money making farming a flourishing business opportunity.
- There are a large variety of spices available such as cardamom, black pepper, nutmeg, cumin, etc. You have a lot of agriculture farming options when it comes to spices.
- You can choose to start farming the spice as per the popularity in your locality.
- Spices can be used in food either whole, sun dried, powdered, paste or even in liquid form. You can sell the whole spice. You can also extract the oils from the spices and sell it in bottles.
- You can plan to grow either a single type of spice or multiple ones depending on your soil. There are different spices that grow in different seasons. You can also opt to grow a spice rarely cultivated in your state and reap huge profits.
Cashew nut agriculture production
Cashew nuts a type of dry fruit that is widely popular across the globe. It is consumed mostly as a savory snack with salt and other spices. You can sell them raw, as well as in processed form. Cashew nut processing entails 4 simple stages. It starts with cleaning the nuts, they roasting them, followed by drying and finally removing the peel.
- Cashew nuts are highly nutritious, boosts energy and fiber in the body. Hence, demand for cashew nuts is quite high globally. You can earn huge capital by producing cashew nuts in your farm land.
- Processed cashew nut sale can get you high profits if you can ally with wholesalers near your land and draw in a fixed cashew nut supply. Wholesalers will sell you the raw cashew nuts at a low cost. You can process the cashew and make profit.
- The medicinal value of cashew nuts has made cashew nut farming a highly lucrative business.
Poultry farming
Chicken is the particular poultry bird raised to the highest number. Gone are the days when households had a few chickens in their backyard to serve their need for eggs and meet. Currently, poultry farming is a huge money-making business that has made its mark internationally. Poultry farming being a lucrative venture has led to the birds being injected with harmful chemicals and are reared in large number without proper hygiene. This has resulted in the rise in demand for good quality poultry farms. This can be your opportunity to grab. Strategize to start an excellently well-maintained poultry farm business to give the masses the best quality eggs and meat.
- Eggs and meat being a high source of protein have notched a vital place in the dietary charts for good health. This has made people from all walks of life add eggs to their breakfast and consume a portion of meat regularly. Hence, a magnificent rise in the sales of poultry farms.
- Another way of making gains through poultry farming is selling frozen chicken. You would needs some additional tools and storage facilities incorporated in your farm for this sort of business. Get in touch with the local eateries, fast-food joints, restaurants and hotels to deliver them- frozen chicken. This can be a profitable venture when you have some good contacts established.
Bee-Keeping and Honey-Making Business:
Producing honey by keeping bees in the garden was a personal choice earlier. People passionate about making honey who had a little space in their backyard kept bees. But now, it has turned out to become a huge farming industry that a large number of entrepreneurs take interest in pursuing as an agriculture endeavor. With the heightened honey consumption worldwide, the sales margin has also increased drastically. This has drawn more entrepreneurs in bee farming. The reason for such rise in the demand for honey is because people are switching to honey intake instead of sugar. Honey has been proved very healthy, helps in losing weight and is also used in beauty products. If you desire to start agriculture farm business plan, then this is one of the best choices. Bee-keeping does not require a large farming land nor do you need to invest huge capital. All you require is- some knowledge and training on the basics of keeping bees for agriculture business. There are training schools and experts who teach how to start a honey producing business and also how bees should be monitored. Furnished with such skillful training you can conveniently start farming and run a bee-keeping and honey making business. If you produce honey in your farming area, you can have several prospective clients to sell, such as –
- Sell it to high net-worth person,
- There are hard-working people, fitness conscious people who prefer honey to sugar
- You can buy low-priced top quality honey from dealers, bottle it up and sell it in the market, both in the local as well as global arena.
Herb and Flower Plantation
The best part about herbs and flower plantation is that they can be grown in small quantities. You do not need any skills or expertise to grow them. They can be grown indoors as well as outdoors. Moreover, both hers and flower plants have multiple usages. You can even do a profitable business with dry herbs and flowers. Both are easy to grow, high in demand and lucrative ventures. Furthermore, you can grow both herbs and flowers in the same farming land. Yes, you will need some appropriate apparatus for good quality plantation results. Adequate water supply, proper sunshine, manure and right method must be followed too. Herbs have a wide range of usages-
- They are a central ingredient in flavoring food
- Used for making beautiful fragrances
- Is majorly bought by the Pharma company
- Are also used in healing centers to help people relax and loose there stress
Flowers too have multiple usages-
- There are edible flowers used in cakes and various cuisines
- They are used in beauty products, to make lipsticks, nail-polish, hair color and so on
- Several fragrances and extracted from flowers, rose, lavender, orchid being popular blooms. In fact, dry flowers are majorly bought by the fragrance company.
- Extensively used for decorating venues
- Flower bouquets, for weddings as well as gifting item is always in trend
Aloe Vera Plantation
Aloe Vera is basically a tropical plant but the good thing about this plant is that, it can be cultivated in dry farming lands as well. Aloe Vera is a profitable agriculture business idea because its medicinal value makes it a highly saleable agriculture product. It can be consumed as well as applied externally. It has lots of vitamins and minerals that are good for heart, immune system, digestion, skin ailments and many more.
Aloe Vera crop is most suitable if your farming land is in a dry area where the climate is mostly warm and humid. This plant doesn’t require much rainfall and doesn’t grow is cold regions. Light sandy type of soil is absolutely befitting for the plantation of aloe Vera agriculture crops.
Aloe Vera plants are best suited for selling globally to the-
- Herbal industry
- Pharma companies
Bamboo Plantation
Bamboos mostly grow in the hilly areas. This is why we most often see bamboo farming in the mountains. The immense uses of bamboos plants have made it a successful agriculture business plan choice for several entrepreneurs. There is no way you can fail with bamboo farming plan as there are always buyers inclined to purchase the raw product and process it to use in various form.
Some of the uses of bamboo plants may be listed as follows-
- Bamboos are strong and flexible. Thus, a very useful construction product. Be it to build roofs, floors, fences etc.
- They are utilized to build various interior decoration items
- Furniture made from bamboo plants are a modern trend
- Best writing papers are made from bamboo fiber
- Various types of musical instruments are also made using bamboos
- Tender Bamboo tips are used in cooking
- Several infectious diseases can be cured through the medicine made from bamboo plants
- In Asia, the chopsticks being used, are mostly made of bamboo
The huge number of uses makes bamboo plantation a very rewarding business.
Coffee & Tea Plantation
Tea and coffee are two drinks that are very popular globally. So, with coffee and tea plantation you can extend your agriculture business plan and earn huge benefits through export. Coffee and tea plantation requires a suitable soil and good amount of rainfall. The rains and dry season must be well defined so that there can be a growing season and a maturing season. You can plan to directly sell the tea leafs and coffee beans or choose to sell the processed product. With the basic plantation and harvesting techniques learnt, and equipped with the processing tools, machinery and staff, you can make flourishing business out of tea and coffee farming. Get in touch with the tea manufacturing industries, restaurants and cafeterias where there is a constant demand for tea leaves and coffee beans.
Cocoa Farming
Take your love for chocolates a step further! Plan on beginning a cocoa agriculture business. It can prove to be a flourishing enterprise. Chocolate is a favorite not only among kids but among all age groups. Relished across the globe, cocoa farming can be hugely profitable agriculture prospect. You can earn huge capital income by exporting the produced cocoa from your farming area. Cocoa is grown mostly in humid tropical region. Its beans are extracted for cocoa solids and cocoa butter. So, in order to begin farming cocoa trees in your land, you first must ensure you have an agriculture land in a humid area, or plan to buy some area. Once you have the suitable soil you can begin with your cocoa plantation business.
- To satisfy chocolate lovers delight, cocoa is added in all sorts of foods, beverages and even fragrances.
- Dark chocolates, chocolate ice-cream, cakes, muffin, cookies, various sweets, deserts, etc., are found everywhere.
- Spas & beauty parlors too use cocoa in their beauty therapies as it’s very good for skin.
- Chocolate consumption is a very delicious and easy way to counter bouts of stress & depression.
So, you have a farming soil and climate suitable for growing cocoa; prepare yourself to turn your passion into a agriculture business venture. Cocoa crops can land for hundreds of years. So follow the proper methods of farming and you can be very rich soon.
Lettuce Plantation
Lettuce has become a very popular farming vegetable for its fresh flavor. Restaurants add it to their salads, burgers, sides, etc. as consumers enjoy the crunchy fresh texture of this leafy vegetable.Additionally, the health benefits in lettuce have also made it a favorite among those fit and active person who are always on the look-out to incorporate healthy greens to their daily meal. Lettuce can be grown in several types of farming soils. Mostly, it is suitable to grow in soils rich in organic matter. The best soils for lettuce are those that can contain good quality of water and also have well made drainage system. As far as the temperature goes, lettuce grows well in fairly cool weather, about 15 degree Celsius. If your agriculture farm business plan space is in a slightly warmer land, you can grow lettuce crops by building a shade. You can go for a soil test before beginning to work on the farming area.
Lettuce crops cannot be stored for a longer period. So, keep connected with nearest markets and eateries. After harvesting the lettuce, you must sell them fresh. Lettuce farming is a rewarding business idea for start-ups.
Fruit Plantation
Various types of fruits are consumed around the globe. You may opt to begin farming any type of fruit that suits the land and climate of your particular region. When the soil is befitting only then you will get a productive yield out of which you can gain revenue.
Peaches, exotic fruits, papaya, berries, mangoes, apples, jackfruit, oranges etc., are some fruit types. You can grow any of these fruits or any other for your agriculture business endeavor depending on your soil suitability. Most fruits are used for making juices, added to cuisines, incorporated in meals as fruit salads, and beauty treatments. Since fruits can be consumed raw you may plan to market and export them immediately after you harvest the produce. You may build processing equipments to make fruit juices and pack them to sell them anywhere in the world.
Fruits contain various healthy & healing ingredients. Hence, maximum nutritionists & doctors suggest children, adults and the elderly; to consume fruits regularly. The fruit agriculture business is an opportunity you must definitely try out.
Palm Tree Cultivation
This is the crop that gives the most quantity of oil. Due to it high yielding capacity palm tree farming is considered a money-spinning business idea. If you intend to earn on a monthly basis through agriculture business then palm tree cultivation is the best choice for your start-up venture.
Deep, moist and well-drained soils are best suited for farming palm trees. This particular crop requires a humid tropical climate. Throughout the year an even amount of rainfall is essential. When every aspect is satisfactory for palm tree farming then you should start off with it at the earliest.
Palm tree plantation and selling of the palm oils, can aid you to cut down the sale of other oils , in turn enhancing the sale of your business. Those oils that are imported are costly for the local market, thus your palm oil will sell more. It is a win-win situation for both you as well as your buyers. Thus, your business will flourish.
Cotton & Wool Production
Textile firms need wool and cotton at all times. They need it constantly for manufacturing various types of cloths. Therefore, it’s a lucrative business idea for any entrepreneur.
Cotton flower and sheep give cotton and wool respectively. So for cotton crop cultivation you need a suitable land. There may be some basic agriculture methods to be followed, certain tools and apparatus required. Of course you have to invest at the onset but after harvest you can make high business gains from your sales. You can also opt to rear sheep and get wool from them.
An advantageous factor of cotton flower and wool is that you can export them easily. There is not much critical process attached to attain the cotton from flowers and the wool is just shaved off the sheep. Furthermore, unlike fruits and vegetable, cotton and wool can be stored for as longer time span and exported to far-off countries as they do not get damaged. Thus you can plan to earn good capital by national and global export of your cotton and wool.
Rubber Production
Rubber, a stretchy materiel, is in huge demand in the market. This crop plantation can prove to be very rewarding. The innumerable items made from rubber makes it a very suitable farming product as it is sale-able in the worldwide market. For instance- Tires, Bags, etc are made from rubber.
Rubber plants cannot grow in extremely windy and freezing temperature. It needs 5-7 hrs of sunlight per day and adequate rainfall. Porous farming soil which is somewhat acidic having well-drainage is best suited for rubber plantation.
Rubber trees when taken proper care can survive for generations. So, this is a good agriculture business investment indeed.
Cattle Ranch
A very common and popular livestock raising business that includes animals such as cows, calves, ox, donkeys, bulls, etc., are known as a cattle ranch. You can choose to breed a single type of animal or several ones depending on the capital and land you have. It is best to start off with a single type of animal and slowly progress to rearing more types in your farming area. Actually, each type of animal needs to be well taken care of, with the proper food and hygiene maintained in your farming space.
Cattles are reared for multiple purposes, milk, manure, skin, as well as meat. Having a cattle ranch can instantly place you in the international business market if the quality of milk, meat and manure supplied by you if of good quality. With high sales and recognition in the global market you can easily gain huge profits and grow your agriculture business.
Shrimp Business
If you plan to own a land near the coastal region, or rent a riverside area, you can earn cash through shrimp farming. Earlier shrimp was farmed in a smaller quantity, but the rapid growth of consumption worldwide has turned it into a large scale global industry.
Shrimp is high in protein and contains anti-oxidants. A favorite among a large group of people, this is marketed in bulk in several countries. Japan, US, Thailand and China are some countries where shrimp farming is done is large quantity. You can definitely give shrimp farming a shot as success is guaranteed.
Saffron Cultivation
This costly spice is actually very easy to grow in any type of farming area. The reason for saffron being so pricey is the extensive toil that goes into harvesting the crop. Only a few strands of saffron are acquired from a flower.
Saffron is mostly used in cooking, creating beautiful fragrances and in cosmetic products. If you have a fertile agriculture soil suitable for saffron cultivation and reside in a sub-tropical warm region then saffron is the spice you must opt to cultivate in your farming area.
You can market it across the whole world. This expensive spice can churn huge money.
Rosemary Cultivation
Rosemary shrub can be cultivated across the world. It is best suited for region with cool temperatures. It can also handle frost. You can harvest rosemary 2 times per year. It depends on whether you want to harvest it for the leaves or the oil.
Rosemary is most famous for its oils. It has high commercial value for its medicinal and herbal properties. This is a lucrative business idea and if you reside in a cold region then get a soil test done and you can start off your rosemary cultivation.
Marketing Analysis of agriculture
To make your agriculture business successful, you need to keep an eye on the market trends as well. If you run a complete analysis of the market, you will get an idea about many things. Understanding the trends and variables will help you in making decisions for your business. The goal of this market research is to understand and get a general idea of the overall market around your farm and how you can adjust to that ecosystem. The marketing plan for agriculture business includes market trends and market segmentation.
5.1 Market Trends
The agriculture industry is a kind of industry that never goes into loss. It continues to evolve with time. Over the past five years, the agricultural industry has grown at an incredible rate. People are now more attracted to buy organic products that are chemical-free and hygienic.
5.2 Marketing Segmentation
In agricultural business ideas and agricultural business proposal, the market segmentation is clearly defined. Besides knowing how to start an agricultural business, you need to make a complete analysis of market segmentation for it.
The most important part of a farm business plan is to have an idea of the expected marketing segmentation. In agriculture start up, you should know about the market segmentation. Here is the market segmentation that will be facing our farm:

5.2.1 Foreign Markets
The products that we manufacture will be exported. It will generate the largest part of our revenue.
5.2.2 Domestic Hotels and Restaurants
We will offer our products to restaurants and hotels. Along with fruits and vegetables, we will provide dairy products such as milk and butter to the restaurants in town.
5.2.3 Domestic Food Companies
We will also sell our products to food companies in the domestic markets.
5.3 Business Target
In a community sustained agriculture business plan, the following are our business target
- Building a trustworthy relationship among customers
- Providing high-quality products to customers
- Making an excellent customer care service for our loyal customers
- Recovering the initial investment within two years of launch
- Increase the revenue every year by at least 20%.
5.4 Product Pricing
The prices of the products that Old Maple Way provide are comparable to other farms. We will try to provide better products and customer care to our clients. We will satisfy our customers by providing exceptional services to make as much profit as possible.
Marketing Strategy
When you are starting an agricultural business, you should also know the marketing strategy. No business can grow and become successful without a marketing strategy. No matter how many excellent services you offer, if you do not have customers, it is all in vain. The more people know about your farm and its products, the more they reach out to you.
Nowadays, the best way of marketing is social media marketing. Social platforms are strong, and they are accessible to everyone. A good thing about social media marketing is its low cost. You can reach out to millions of people with online marketing. All the business ideas in agriculture explain the importance of social media marketing and how you can use them to reach out to people.
Along with that, you need a competitive analysis to make a strategy that will make your agriculture business plan successful. You also need some agro processing business ideas as well as a perfect understanding of what is an agricultural business.
6.1 Competitive Analysis
- People are not satisfied with the products manufactured by other farms because of the chemicals they use to increase their quantity.
- The products that other farms sell are expensive and everyone cannot afford them.
6.2 Our Strategy
- We will use social media platforms to advertise our products.
- We will make our online presence so that we can reach out to more and more people.
- We will use the advertisements channels in the area to reach out to the people.
6.3 Sales Monthly

6.4 Sales Yearly

6.5 Sales Forecast

Personnel plan
To make your business best agricultural business, you need to make sure that the staff should work as a team. In the agriculture business model, you will find out that the environment of the farm depends on the number and type of staff which should be determined in the initial stages.
7.1 Company Staff
James Celery will be the owner and CEO of the Old Maple Way farm business. The following people will be hired to run the farm:
- 1 Operations Manager
- 2 Deputy Managers
- 8 Farm Workers
- 2 Packaging Helpers
- 1 Accountant
7.2 Average Salary of Employees
Financial plan.
Proper planning and execution of the finance help you to maintain a stable budget for the upcoming entire year. To execute farming ideas for profit, you need to manage the finances wisely. In agricultural business plans, all the finances are mentioned.
- Money to buy a land or take it on lease
- The cost of buying and maintaining animals
- The salary of employees
- The cost of buying fruits and vegetables seeds
8.1 Important Assumptions
8.2 break-even analysis.

8.3 Projected Profit and Loss
8.3.1 profit monthly.

8.3.2 Profit Yearly

8.3.3 Gross Margin Monthly

8.3.4 Gross Margin Yearly

8.4 Projected Cash Flow

8.5 Projected Balance Sheet
8.6 business ratios.
- How do I make an agricultural business plan? When you look out to sample business plan agriculture farm, you will see the steps to write a business plan. Business plan for agriculture company may not necessarily be long but it should be written in an easily understandable way.
- What is an agriculture farm business plan? It is the farming production, creating a plan for marketing and management of crops and livestock in a profitable way is an agriculture farm business plan. It includes everything such as a detailed business plan for agriculture and an agriculture equipment business plan.
- Which agriculture is most profitable? One of the most profitable agriculture is an agricultural farm. You can start this business by investing a small amount of money. According to the demand of the local public, you can produce the items and sell them.
- Is agriculture farming profitable? Agriculture farming is profitable as it offers a stable revenue. It is one of the fastest-growing agricultural businesses all over the world.
Download example agriculture farming business plan pdf
OGSCapital’s team has assisted thousands of entrepreneurs with top-rate business plan development, consultancy and analysis. They’ve helped thousands of SME owners secure more than $1.5 billion in funding, and they can do the same for you.

Add comment
E-mail is already registered on the site. Please use the Login form or enter another .
You entered an incorrect username or password
Comments (0)
mentioned in the press:
Search the site:
OGScapital website is not supported for your current browser. Please use:

Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai Pitch Deck Generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customers Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Small Business Tools
Strategic Canvas Templates
E-books, Guides & More
- Sample Business Plans
Agriculture, Farm & Food Production Business Plans
- IT, Staffing & Customer Service
- Construction, Architecture & Engineering
- Food, Beverage & Restaurant
- Real Estate & Rentals
- Mobile Apps & Software
- Education & Training
- Beauty Salon & Fitness
- Medical & Health Care
- Retail, Consumers & E-commerce
- Entertainment & Media
- Transportation, Logistics & Travel
- Agriculture, Farm & Food Production
- Nonprofit & Community
- Manufacturing & Wholesale
- Clothing & Fashion
- Children & Pets
- Fine Art & Crafts
- Cleaning, Maintenance & Repair
- Hotel & Lodging
- Finance & Investing
- Consulting, Advertising & Marketing
- Accounting, Insurance & Compliance
Agritourism Business Plan
Beekeeping Business Plan
Farming Business Plan
Hydroponics Business Plan
Fishing Farming Business Plan
Food Distribution Business Plan
Dairy Farm Business Plan
Small Farming Business Plan
Cannabis Cultivation Business Plan
Organic Farm Business Plan
How to Write a Cannabis Business Plan + Free Template
Cattle Farm Business Plan
Poultry Farming Business Plan
Lawn Care Business Plan
Horse Boarding Business plan
Solar Farm Business Plan
Plant Nursery Business Plan
Microgreens Business Plan Template & Guide [Updated]
Did you find what you are looking for.
Agriculture or farming is the only industry consistently performing well, regardless of economic climate changes.
Whether you plan to start farming, cannabis cultivation, a cattle farm, or nursery business, you’ll do great as long as you do things right and have a solid business plan.
This library of farm business plan examples here can inspire and guide you as you begin to plan your business. So, don’t worry; we got you covered on that part.
Let’s learn more about these agriculture business plan samples, starting with their benefits.
Benefits of using an industry-specific business plan example
Believe it or not, using an industry-specific business plan example is the best and probably the quickest way of writing a business plan.
Doubt it? Hold, this may change your perception; an extended list of the benefits of using an industry-specific business plan template.
- Inspiration : Reading a business-specific template can be incredibly helpful in getting content inspiration. Furthermore, it helps you gain insights into how to present your business idea, products, vision, and mission.
- Risk-free method : You are taking a reference from a real-life, let’s say, plant nursery business plan—so you know this plan has worked in the past or uses a method subscribed by experts.
- Deep market understanding : Analyzing and reading such examples can provide clarity and develop a deeper market understanding of complex industry trends and issues you may not know but relate directly to the realities of your business landscape.
- Increased credibility : A business plan developed using an example follows a standard business plan format, wisely presents your business, and provides invaluable insights into your business. There’s no question it establishes you as a credible business owner, demonstrating your deep business and market understanding.
- Realistic financial projections : Financial forecasting being a critical aspect of your plan, this real-life example can help you better understand how they project their financials—ultimately helping you set realistic projections for your business.
These were the benefits; let’s briefly discuss choosing an agriculture or food production plan example that best suits your business niche.
Choosing an Agriculture or Farming Business Plan
This category has business plan templates for various farming or agricultural businesses. With many similar business types and templates, you may not find the most suitable one through manual scrolling.
Here are the steps to consider while choosing the most suitable business plan template.
Identify your business type
Are you planning to start cannabis cultivation? Or thinking of doing organic farming? Thinking of taking care of horses through horse boarding?
Asking yourself these questions will help you identify your business type, which will help in choosing a niche-specific business plan template.
Once you identify your business type, you can choose between templates for different business segments.
Search for the template
We have an in-built search feature, so you can easily search for a business-specific template using your business type as a key term. Once you have the search results, choose the most suitable one. Simple as that.
Review the example
Look closely at the content of the sample business plan you are considering. Analyze its sections and components to identify relevant as well as unnecessary areas.
Since all the Upmetrics templates are tailored to specific business needs, there won’t be many fundamental customizations. However, a hybrid business model targeting multiple customer segments may require adjustments.
For instance, if you plan to start a cannabis cultivation business and also produce and sell CBD, you may need to adjust some of your business plan sections accordingly.
No big deal—you can view and copy sections from other business plan examples or write using AI while customizing a template.
That’s how you find and select the most suitable business plan for your farming business. Still haven’t found the perfect business plan example? Here’s the next step for you.
Explore 400+ business plan examples
Check out Upmetrics’ library of 400+ sample plans and get your free business plan template now. Upmetrics is a modern and intuitive business planning software that streamlines business planning with its free templates and AI-powered features. So what are you waiting for? Download your example and draft a perfect business plan.
From simple template to full finished business plan
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates
Details of a Small Farm Business Plan
- Swarthmore College
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Betsy-Petrick-4x5-70cf94b5a1934c9199bddce1f2457f37.jpg)
- Ohio Wesleyan University
- Brandeis University
- Northeastern University
- Urban Farms
- Planting Guides
- Indoor Gardening
Writing a farm business plan can be a tool for you to plan your farming business. It can also be a requirement of securing grants and loans for your farm business. The process of writing a farm business plan may seem overwhelming and intimidating at first, but if you break it down into its component steps, it becomes much more manageable.
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a roadmap for your small farm . It is both process and product. During the writing of a farm business plan, you'll develop an overall vision and mission for your business. You will think about your short- and long-term goals. You'll define the steps needed to achieve those goals. You'll set the direction for your business to develop over the next five years.
If you're already an established business, your new business plan will show where you're going next. A good business plan should be:
Mission Statement
Your farm’s mission statement is your overarching purpose for your business:
- Why does your farm exist?
- What purpose does your farm serve?
- Where is your farm headed?
This is beyond “make money.” This mission statement is based on your values and your core identity as a small farm.
The goals in your business plan are the specific, measurable “things” you will achieve with your small farm. Short-term goals are defined as those that you will complete within one year. Long-term goals are those that take longer than one year to complete.
SMART Goals are:
- Rewarding, and have a
Background Information
In this section of your business plan, take inventory of what you have right now:
- Where are you located?
- How many acres of land are you farming?
- When did you begin farming?
- How are you currently operating?
- What general practices do you use for such things as conservation, tillage, environmental impact, and marketing?
Farm Strategy
This is where your business plan gets to looking forward. You are going to formulate your farm strategy from now into the next five years or so.
- Gather information and research markets. Make sure that your farm plan fits into the general market in terms of supply and demand. Investigate and analyze industry trends, identify competitors, and define buyers.
- SWOT Analysis. This is an analytical tool that can be used in making decisions. SWOT stands for: strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. As a business, analyze your internal strengths and weaknesses. Then look externally at what opportunities and threats exist - competitors, new markets, government regulations, economic conditions, and so forth.
- Create alternative strategies. Looking at the information you've gleaned and the analysis you just did, think through options for your farm strategy. Don't rely on price alone; economies of scale are challenging on the small farm level.
- Don't jump to one conclusion immediately. Really spend some time fleshing out the specifics of some of the strategies and looking at their advantages and disadvantages. Try to find options that combine your internal strengths with opportunities in the external environment.
- Look at all your strategies, then reread your mission statement. The ideal farm plan will fit your mission best.
- Write an implementation plan. This is where you write a plan that will make your new strategy happen.
Marketing Strategy and Plan
In the next part of your farm business plan, you develop and outline a marketing strategy for your products and services. This can build on the research you did in the previous step. For each product, include the price, placement, and promotion ideas. Consider how you will convey real and perceived value to your customers.
Management Summary
This part of your business plan details your farm business’ structure. Everyone who is involved in the management of the business should be listed here. External resources are listed here as well.
Financial Analysis
In this section, you will need to detail the financial aspect of your farming operation. List your current finances in detail, including all income and operating expenses. Referring to your new strategy, you will forecast what is needed for future growth and to meet the goals you have outlined in terms of capital. Include what your future operating expenses will be.
Pulling It All Together
Writing a farm business plan is a big project. Don’t let that put you off. Your plan can be as simple as it needs to be for right now. Begin with your mission statement and goals. Do your homework by analyzing markets and researching competitors and trends. Have fun brainstorming alternative strategies and let them marinate a while. Take it one step at a time.
- How to Start a Small Farm Business
- How to Start a Small Farm
- Starting Your Small Farm from Scratch
- Best of Green Awards 2021: Eco Tech
- Best Urban Farming Certifications
- Tips for Converting Small Farms to Organic Production
- Small Farm Grants and Financial Assistance
- How to Grow More in Your Garden With Less Work
- What Is Ecotourism? Definition, Examples, and Pros and Cons
- Make Your Garden Passion Project a Reality
- Rescuer Saves and Rehabs Hundreds of Wild Animals in Peru
- Why It's Crucial to Establish Goals for Your Garden
- Frozen Potato Giant McCain Commits to 'Regenerative' Agriculture
- New Resource Outlines Nature-Based Solutions for Dealing with Flooding
- How to Create a Better Microclimate in Your Garden
- How 'Gleaning' Can Help Prevent Food Loss

12: Business Plans
What is a business plan.
A business plan is a document that helps you to organize and succinctly summarize the vision you have for your business. The plan contains the operational and financial objectives of a business, the detailed plans and budgets showing how the objectives are to be realized.
A good business plan will contain the following:
- Your business vision, mission statement, key values, and goals
- Description of the product(s) you intend to produce
- Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats the business may experience are described
- Production plans
- Marketing plans
- Estimated start-up costs
- Information on your legal structure and management team
- Current financial statements or projected financial statements.
- Resume or brief explanation of your background and relevant experience
- Less than 10 total pages so that people actually read it
Helpful Publications for Writing a Business Plan
General Business Resource Publications:
- Starting an Ag-Business? A Pre-Planning Guide http://publications.dyson.cornell.edu/outreach/extensionpdf/2004/Cornell_AEM_eb0408.pdf
- Business Transfer Guide: Junior Generation http://publications.dyson.cornell.edu/outreach/extensionpdf/2016/Cornell-Dyson-eb1605.pdf
- Producing a Business Plan for Value-Added Agriculture http://publications.dyson.cornell.edu/outreach/extensionpdf/2007/Cornell_AEM_eb0708.pdf
- Business Planning for the Agriculture Sector: A Guide to Business Plan Development for Start-up to Mid-size Operations http://publications.dyson.cornell.edu/outreach/extensionpdf/2010/Cornell_ pdf
- Building a Sustainable Business (Sustainable Agricultural Research Education (SARE)Publications) sare.org/publications/business.htm 280 pages of education and practical exercises to guide you through the financial, management, and interpersonal skills needed to start a successful farm business. Order hard copy for $17 or download PDF online for free.
Cornell Cooperative Extension Publications for Specific Commodities:
- Landscape Business Planning Guide http://publications.dyson.cornell.edu/outreach/extensionpdf/2003/Cornell_AEM_eb0313.pdf
- Writing a Business Plan: A Guide for Small Premium Wineries http://publications.dyson.cornell.edu/outreach/extensionpdf/2002/Cornell_AEM_eb0206.pdf
- Writing a Business Plan: An Example for a Small Premium Winery https://ageconsearch.umn.edu/bitstream/122203/2/Cornell_AEM_eb0207.pdf
Getting Help Writing a Business Plan

How To Write a Business Plan for Agriculture Consulting Firm in 9 Steps: Checklist
By henry sheykin, resources on agriculture consulting firm.
- Financial Model
- Business Plan
- Value Proposition
- One-Page Business Plan
- SWOT Analysis
- Business Model
- Marketing Plan
If you're looking to start an agricultural consulting firm, it's essential to have a solid business plan in place. According to recent data, the global agricultural consulting market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.2% from 2020 to 2027, with increased demand for efficient and sustainable food production practices driving growth.
The following nine steps will help you create a comprehensive business plan for your agriculture consulting firm, starting with market research . Conducting thorough research on your target market and competitors is essential to understanding your industry and identifying potential opportunities.
Next, identify your target market based on factors such as location, crop type, and business size. Once you've determined your target market, define the scope of services you will offer, which may include crop and livestock management, pest control, food safety regulations, and specialized training seminars.
When analyzing your competition , consider factors such as pricing, service quality, and unique offerings. Use this information to develop a pricing strategy that is both competitive and reflective of your firm's value.
Determine necessary resources , such as personnel, equipment, and technology, to effectively deliver your services. Establish a marketing plan to reach your target market, utilizing both traditional and digital marketing tactics.
Create an organizational chart outlining the management structure and responsibilities of your firm's employees. Finally, develop financial projections to understand the potential profitability of your business and to secure funding from investors or lenders.
By following these nine steps, you'll be well on your way to creating a successful business plan for your agriculture consulting firm.
Conduct Market Research
Market research is a crucial step in creating a successful Agriculture Consulting Firm . This step involves identifying your target market and understanding their needs, preferences, and behaviors. Market research helps you assess the market's potential demand for your services and helps you identify your competition.
At the first stage of market research, start by identifying the geographic location and size of your market. You can use data from sources such as government census reports, trade associations, and online research tools like Google. Once you have identified your market, you can then study their needs by conducting surveys, focus groups, and gathering data about their purchasing habits through online analytics tools.
It is important to research your competition. Study their services, pricing, and marketing strategy. Determine the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors and identify key areas of differentiation that will help you stand out in the market. This knowledge will help you identify gaps in the market and adjust your services accordingly.
- Use multiple data sources: Rely on more than one source for market data to avoid biased research.
- Identify your niche market: Consider specializing in a specific area like organic farming or greenhouse production to differentiate yourself from competitors.
- Asses the market demand: Evaluate the market size and growth potential to forecast your potential growth and risk.
Conducting market research is an integral part of creating a successful business plan for your Agriculture Consulting Firm. Through acquiring market knowledge, you can identify opportunities, capitalize on trends, and set realistic goals.
Identify Target Market
Identifying your target market is a crucial step when starting any business, and it's no different for an agriculture consulting firm. Clearly defining your target market will help you tailor your services and marketing efforts to the needs and wants of your potential clients, allowing you to focus your resources on the areas where there is the most demand.
The first step in identifying your target market is to determine who has a need for your services. In the case of an agriculture consulting firm, your potential clients could be farmers, agricultural businesses, food processors, and other organizations involved in the industry. It's important to note that your target market may vary depending on the types of services you offer, the size of your firm, and your expertise in different areas of agricultural production.
Once you have a general idea of who your potential clients could be, the next step is to identify their specific needs. For example, a small family-run farm may need guidance on how to increase crop yields, while a large food processing plant may require assistance with regulatory compliance. This information can be gathered through market research, surveys, and speaking with potential clients to better understand their pain points and challenges.
Tips for Identifying Your Target Market:
- Research your local market to identify potential clients and look for trends in the agriculture industry.
- Speak with industry experts and potential clients to understand the challenges they faced and the services they need most.
- Consider the size of your firm and your expertise in different areas of agriculture production when defining your target market.
By identifying your target market and their specific needs, you can develop services and marketing strategies that will resonate with potential clients and set your agriculture consulting firm apart from the competition.
Define Scope Of Services
Defining the scope of services is an essential step in creating a comprehensive business plan for your agriculture consulting firm. This step requires you to outline the services that your firm will offer to clients in order to meet their agricultural production needs. Here are some important aspects to consider when defining your scope of services:
- Identify the key agricultural services that your firm will offer to clients. This may include advisory services, technical support, and training
- Determine the agricultural sectors that your firm will focus on. Your firm may specialize in crop management, livestock management, or pest control, among other areas
- Identify the geographic area that your firm will serve. Is it a local or regional audience?
- Define the expected outcomes for clients who use your services. This may include reducing costs, increasing yields, improving quality, or complying with food safety regulations
- Determine the level of support that your firm will offer to clients. Will it be ongoing support or on-demand assistance?
- Conduct market research to identify the needs of your target market when defining your scope of services
- Be specific and clear when describing the services you offer in your business plan
- Keep in mind that your scope of services can evolve over time as your business grows and your clients' needs change
Once you have defined your scope of services, it is important to communicate it clearly in your business plan and marketing materials. This will help potential clients understand what your firm offers and how it can benefit them.
Analyze Competition
As an agriculture consulting firm, understanding your competition is essential to creating a successful business plan. Competition analysis allows you to identify potential threats and opportunities within your market, enabling you to refine your services and develop a unique selling proposition.
First, identify your primary competitors within the market. These competitors can come in many forms, including individual or group consultancies, large and small agricultural businesses, and other consulting firms outside of the industry.
Next, analyze the strengths and weaknesses of their services. Look at their pricing, what specific services they offer, and how they meet the needs of their clients. This information will help you understand how to differentiate your services from their offerings.
Additionally, research their marketing strategies and branding efforts. How are they reaching their target audience, and what messaging do they use to differentiate themselves from their competitors? Take note of what seems to be working and what needs improvement.
- Use tools like Google Alerts and social media monitoring to stay up-to-date on your competitors’ activities.
- Consider conducting a SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis to help you better understand your competitors.
- After analyzing your competition, brainstorm ways to differentiate yourself and your services from them.
By conducting a thorough analysis of your competition, you can position your agriculture consulting firm for success in a crowded market. This process will help you refine your services, pricing, and marketing strategies to create a unique and compelling offering for potential clients.
Determine Pricing Strategy
Pricing strategy is one of the most important elements of business planning. For agriculture consulting firms, the pricing strategy must be fair, competitive, and in line with the level of expertise that the firm provides. Determining the pricing strategy must take into account the cost of services, the profit margin, and the needs and budgets of the target market.
Different pricing strategies for agriculture consulting firm include:
- Hourly rate: This strategy is based on the amount of time that the consultant spends on each project. The hourly rate varies depending on the level of expertise and experience of the consultant.
- Project-based pricing: This strategy involves setting a fixed price for a specific project or service. This pricing model is suitable for specialized services such as pest control or food safety regulation compliance.
- Retainer-based pricing: This pricing strategy involves a monthly or annual fee for the firm's services. It is suitable for long-term consulting projects in which the client requires ongoing support and regular updates.
- Conduct market research on the pricing models used by other agriculture consulting firms in your area.
- Consider the level of expertise and experience that your consultants bring to the table when setting your prices.
- Be transparent about your pricing strategy and explain to clients the value of your services.
Other factors that can influence pricing strategy include location and the level of competition in the target market. Prices of agriculture consulting firms in urban areas may be relatively higher than those in rural areas. In addition, the competition from other consulting firms can also affect the pricing strategy.
The profit margin is another important factor to consider when determining the pricing strategy. The profit margin should be fair and reasonable while also ensuring the sustainability of the business. Proper financial analysis can help determine the minimum pricing required to cover operating costs and produce profits.
The pricing strategy must be flexible enough to accommodate changes in the market, while also being competitive and sustainable. Once the pricing strategy is defined, it is essential to continually monitor and adjust the prices whenever necessary.
In conclusion, determining the pricing strategy for an agriculture consulting firm is a critical step in business planning. Pricing strategy should be based on the cost of services, profit margin, target market, location, and competition. It is also essential to be transparent about pricing and periodically evaluate and adjust the prices accordingly.
Determine Necessary Resources
After you have determined your pricing strategy and analyzed the competition, it is time to evaluate the resources you will need to start and operate your agriculture consulting firm. Resources can include anything from equipment and office space to employees and software.
Here are some essential resources to consider:
- Equipment: Will you need specialized equipment to conduct on-farm assessments or soil analyses? Ensure that you have the necessary equipment and tools to provide your clients with the best service possible.
- Office Space: Do you need an office to run your operations? Consider the space requirements for your staff, as well as the necessary equipment such as computers, printers, and internet access.
- Employees: How many employees will you need to start and run your consulting firm? Define the roles and responsibilities of each employee and their salary requirements.
- Software: What software will you need to manage your finances, generate reports, and provide your clients with customized services? Consider investing in industry-specific software to streamline your operations and improve overall efficiency.
- Insurance: What insurance policies will you need to protect your business and employees? Consider insurance policies for general liability, professional liability, and workers' compensation.
- Legal Services: Will you need legal support to draft contracts and agreements with clients? Consider working with a legal professional to ensure that your business is protected from legal disputes.
- Before purchasing any equipment or software, research your options to find the best deal. Look for discounts or promotions to save on costs.
- Consider renting equipment or outsourcing services to reduce overhead costs.
- When hiring employees, consider their experience and expertise in the agricultural industry. Look for individuals who have worked in the field and understand the challenges farmers face.
- Consult with an insurance agent and legal professional to ensure that you have the necessary coverage and legal documentation to protect your business.
By determining the necessary resources upfront, you can better prepare for the initial costs associated with starting an agriculture consulting firm. Additionally, having the proper resources in place can help improve the quality of your services and set your business up for long-term success.
Establish A Marketing Plan
Marketing is an essential aspect of running any business, and an agriculture consulting firm is not an exception. Even the best services will remain unknown without effective branding and promoting. Therefore, it is crucial to establish a marketing plan for your agriculture consulting firm right from the start. Here are the key steps to follow for setting up a comprehensive marketing plan:
- Identify your target audience: Before implementing any marketing strategy, you should define your target market. Identifying the target audience will help you tailor your services to meet their specific needs, thereby increasing your chances of success.
- Create a branding strategy: Creating a unique and memorable brand is critical for standing out in a competitive market. Develop a brand strategy that includes your company's mission, values, logo, and messaging. Ensure that the branding aligns with your target market, goals, and services you provide.
- Develop a content strategy: Develop a content strategy that is consistent with your branding and target audience. Ensure that your content is informative, engaging, and optimized for search engines and social media. This can include blog posts, social media posts, infographics, testimonials, and case studies.
- Utilize social media: Social media is an effective marketing tool that allows you to connect with your target audience, increase brand awareness, and promote your services. Create social media profiles for your company and post regular updates, photos, and videos that showcase your expertise. Participate in social media groups related to agriculture and share your expertise with potential clients.
- Network with industry professionals: Attend industry conferences and networking events to meet other professionals in the agriculture industry. This will provide an opportunity to showcase your expertise and make connections with potential clients. Networking can also lead to partnerships and collaborations with other businesses.
- Ensure that your marketing plan aligns with your company goals and mission
- Plan and budget your marketing efforts accordingly
- Measure your marketing efforts to track performance and make adjustments as needed
- Keep your marketing strategies up-to-date and evolve with changes in the industry and technology.
Create An Organizational Chart
Creating an organizational chart is an essential step for starting any business, including an agriculture consulting firm. An organizational chart provides a visual representation of your company's structure and helps to define employee roles and responsibilities. Here's how to create one for your agriculture consulting firm:
Step 1: Define Your Company's Structure
The first step in creating an organizational chart is to define your company's structure. Consider the number of employees you need, the type of roles that are required to fulfill your business objectives, and potential growth opportunities.
- Start with a basic structure and add or remove roles as needed.
- Consider delegating tasks based on skill level and expertise.
- Define clear lines of communication and decision-making.
Step 2: Identify the Key Positions
The next step is to identify the key positions that will be required to operate your agriculture consulting firm successfully. This may include administrative staff, consultants, marketing personnel, and trainers.
- Identify essential roles before hiring staff members.
- Ensure each position has defined responsibilities and objectives.
- Consider hiring staff members with diverse backgrounds that complement the company's overall objectives.
Step 3: Create the Chart
Now you're ready to create the organizational chart. There are various tools available online to help you design your chart, including Microsoft Word, Excel, and PowerPoint. Additionally, you can consider using organizational chart software to make the process easier.
- Ensure the chart is clear and easy to read.
- Include job titles and employee names, if applicable.
- Consider using colors, shapes, or icons to differentiate job roles.
Step 4: Review and Modify
Once you've created your chart, it's crucial to review it periodically and make any necessary modifications based on ongoing operations and growth opportunities.
- Ensure each role is appropriately defined and updated as required.
- Consider modifying the structure based on business objectives or challenges.
- Communicate changes in the organizational chart to employees and stakeholders.
Creating an organizational chart for your agriculture consulting firm is an important step that can help you effectively manage your staff, define responsibilities, and establish clear lines of communication. Follow these steps to create an organizational chart that can drive success and growth in your business.
Develop Financial Projections
Developing accurate financial projections is a crucial step to launch and sustain a successful agriculture consulting firm. This step requires estimating the realistic revenue and expenses the firm will earn over a certain period, usually for the next three to five years. These projections will help determine the startup costs, funding requirements, cash flow management, and the expected return on investment.
There are several factors to consider when developing financial projections for an agriculture consulting firm. Here are the essential elements you need to include:
- Revenue Forecast: Project and analyze your revenue streams, which may include consulting fees, training seminars, workshops, and other services you offer.
- Cost of Goods Sold: Estimate the costs associated with delivering your services and products, such as wages, salaries, advertising, travel, and other miscellaneous expenses.
- Operating Expenses: Determine overhead costs such as rent, utilities, insurance, and general administration costs.
- Profit and Loss: Calculate your earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and determine your profitability.
- Cash Flow: Create a cash flow statement that shows the money coming in and going out of your business. This will help you understand when your expenses are due, and when your revenue is coming in.
- Capital Requirements: Determine the amount of funding you need to launch and sustain your business, which may include loans, investments, or grants.
Tips for Developing Financial Projections
- Use realistic assumptions and credible data when developing your projections. Base them on available research, industry benchmarks and trends, and your experience in the field.
- Consult with a financial advisor, accountant, or other professional experts to ensure your projections are accurate and feasible.
- Review and update your projections regularly to reflect changes in the market, your competition, and your business operations.
- Use your projections as a tool to make informed decisions about your business strategy, such as identifying potential gaps in your funding or adjusting your pricing strategy to maximize profitability.
Developing financial projections can be a challenging but critical step in creating a successful agriculture consulting firm. By considering the factors above and seeking expert advice, you can create projections that will provide an accurate picture of your business's financial health and help you make informed decisions about your strategy going forward.
Conclusion:
Writing a business plan is an essential step in starting any business, including an agriculture consulting firm. It helps you determine your target market, analyze competition, develop financial projections, and establish a marketing plan. By following these nine steps, you will have a detailed checklist to guide you through the process of creating a comprehensive business plan. With a well-crafted plan, you can persuade potential investors or lenders that your agriculture consulting firm is a valuable investment opportunity.

$169.00 $99.00 Get Template
Related Blogs
- Starting a Business
- KPI Metrics
- Running Expenses
- Startup Costs
- Pitch Deck Example
- Increasing Profitability
- Sales Strategy
- Rising Capital
- Valuing a Business
- How Much Makes
- Sell a Business
- Business Idea
- How To Avoid Mistakes
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Please note, comments must be approved before they are published

Poultry Farm Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Poultry Farm Business Plan
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their poultry farms. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning. We will then go through a poultry farm business plan template step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What is a Poultry Farm Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your poultry farm as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategy for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan for a Poultry Farm
If you’re looking to start a poultry farm, or grow your existing poultry farm, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your poultry farm in order to improve your chances of success. Your poultry farming business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for Poultry Farms
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for a poultry farm are personal savings, credit cards, USDA Farm Service Agency (FSA) loans, bank loans, and angel investors. With regards to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to confirm that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business. Personal savings and USDA FSA loans are the most common funding paths for poultry farm.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to write a business plan for a chicken farm.
If you want to start a poultry farm or expand your current one, you need a business plan. We detail each section of a traditional business plan for a poultry farming business.
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of poultry farm you are operating and its status. For example, are you a startup, do you have a poultry farm business that you would like to grow, or are you operating poultry farm businesses in multiple locations?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan. For example, give a brief overview of the poultry farm industry. Discuss the type of poultry farm you are operating. Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target customers. Provide a snapshot of your marketing plan. Identify the key members of your team. And offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Analysis
In your company analysis, you will detail the type of poultry farm you are operating.
For example, you might operate one of the following types of poultry farms:
- Breeder Farms : this type of poultry farm produces hatching eggs for delivery to the hatchery. After the 21 day incubation period, the hatchery then delivers the baby chicks to the broiler houses.
- Broiler Farms: this type of farm produces a 2.5 lb. to 8 lb. bird in 4 to 8 weeks which is processed for various types of retail sale to consumers, grocery stores or fast food chains as whole birds, cut-up breast, wings, thigh, drumsticks, deboned breast meat, or further processed pieces.
- Pullet Farms: this type of poultry farm produces pullets and roosters to be delivered to a breeder hen house at 20-22 weeks old when they are sexually mature to breed and lay eggs.
In addition to explaining the type of poultry farming business you will operate, the Company Analysis section of your business plan needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to question such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include the number of chickens and/or turkeys produced, number of production contracts, etc.
- Your legal structure. Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry analysis, you need to provide an overview of the poultry farm industry.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the poultry farm industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your strategy, particularly if your research identifies market trends.
The third reason for market research is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section of your poultry farming business plan:
- How big is the poultry farm industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential market for your poultry farm business? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your target market.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section of your poultry farming business plan must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments: processors, grocery stores, and restaurants.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of poultry farm business you operate. Clearly, processors would respond to different marketing promotions than restaurants, for example.
Try to break out your target customers in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, include a discussion of the ages, genders, locations and income levels of the customers you seek to serve. Because most poultry farm businesses primarily serve customers living in their same region, such demographic information is easy to find on government websites.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can understand and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your Poultry Farm Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other poultry farm businesses.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t direct competitors. This includes producers of other meat such as beef, pork, or fish, as well as producers of meat alternatives. You need to mention such competition as well.
With regards to direct competition, you want to describe the other poultry farms with which you compete. Most likely, your direct competitors will be poultry farms located very close to your location.
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their businesses and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as:
- What types of customers do they serve?
- What kinds of poultry do they produce (breeders, broilers, pullets)?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you use superior production methods?
- Will you provide services that your competitors don’t offer?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a poultry farm business plan, your marketing plan should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type of poultry farm company that you documented in your Company Analysis. Then, detail the specific products you will be offering. For example, in addition to traditional poultry, will you provide organic or cage-free poultry?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of your marketing plan, you are presenting the products and services you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the location of your poultry farm company. Document your location and mention how the location will impact your success. For example, is your poultry farm located near a processing facility, near a transportation hub, etc. Discuss how your location might be the ideal location for your customers.
Promotions : The final part of your poultry farm marketing plan is the promotions section. Here you will document how you will drive customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertising in trade papers and magazines
- Reaching out to local agriculture extension offices
- Social media marketing
- Local radio advertising
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your poultry farm, including animal care / feeding, flock supervision, animal transportation, sourcing feed, etc.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to sign your 20th production contract, or when you hope to reach $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your poultry farm to a new location.
Management Team
To demonstrate your poultry farm’s ability to succeed, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally you and/or your team members have direct experience in managing poultry farms. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act like mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in managing farms or successfully running small businesses.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statements.
Income Statement
An income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenues and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will you supply 50 restaurants, or produce 2,000 birds for processing each month? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets
Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your poultry farming business, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a bank writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement
Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and make sure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
In developing your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a poultry farm business:
- Location build-out including design fees, construction, etc.
- Cost of equipment and supplies
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Taxes and permits
- Legal expenses
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your farm title or lease, or blueprints of the production facility.
Putting together a business plan for your poultry farm is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert. You will really understand the poultry farm industry, your competition, and your customers. You will have developed a marketing plan and will really understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful poultry farming business.
Poultry Farm Business Plan FAQs
What is the easiest way to complete my poultry farm business plan.
Growthink's Ultimate Business Plan Template allows you to quickly and easily complete your Poultry Farm Business Plan.
What is the Goal of a Business Plan's Executive Summary?
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of poultry farm business you are operating and the status; for example, are you a startup, do you have a poultry farm business that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of poultry farm businesses?
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your Poultry Farm business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. Click here to see how Growthink’s professional business plan consulting services can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates


SUBSCRIBE TODAY!
- Taxes and Finance
Prepare Your Farm With a Business Continuity Plan

Business continuity planning
Having a business continuity program in place is key to maintaining minimum operations and reduce recovery time during a business disruption.
What is Business Continuity Management?
Business Continuity Management (BCM) is about preparing your organization to respond to potential threats of business disruption. It can also help create resilience to withstand negative impacts and continue operations when a disruption occurs. It’s about protecting your business and the stakeholders who rely on it – the customers who purchase your products or services, the owners and shareholders with a financial stake in the success of the company and the employees who make their livelihood serving your business and its customers.
The primary goals of planning are:
- Maintain a minimum level of operations during disruption
- Reduce recovery time
Having a business continuity program in place, along with associated contingency plans, is key to helping an organization achieve these goals.
Disaster recovery, crisis response, emergency response and incident response The terminology used by business continuity professionals can be confusing. For example, the term disaster recovery may be used to describe business continuity, but its typically reserved to reference strategic plans for recovery and resumption of only critical information technology (IT) and telecommunications assets during a disaster.
Crisis response, emergency response and incident response are terms that refer to the immediate actions taken during an incident to preserve life, prevent injury and prevent further damage to property.
Contingency planning (or plans) refers to specific tactics or actions taken during a disruption. Each of these are among the elements included in a broader overall business continuity management plan.
The International Standards Organization (ISO), in May of 2012, published the first edition standard ISO 22301, Societal security – Business continuity management systems – Requirements. This document serves as a consensus standard specifying the requirements for setting up and managing an effective Business Continuity Management System (BCMS).
In summary, a Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) can be considered a suite of documented policies, organizational structure, analyses, assessments, plans, procedures and responsibilities to help ensure an organization does not experience an unacceptable interruption in the event of a disruption to its business operations.
At the core of Business Continuity Management (BCM) are four main elements:
- Crisis response and communications
- Risk management
- IT disaster recovery
- Business contingency or resumption planning and recovery
Is your business prepared for an unexpected disruption or disaster? The risk of disruptive incidents to businesses and organizations is increasing. Recent increases in frequency and severity of weather-related disasters, rains associated with landslides and flooding, severe windstorms, and even drought conditions that can lead to increased exposure to wildfires.
Additional disruption examples include:
- Manufacturers relying on just-in-time supplies and inventory
- Suppliers with an increased risk of supply chain disruptions
- Livestock producers face increased risk for disease outbreaks that can wipe out poultry, swine or other animals
- Computer hackers create increased risk of security breach and denial-of-service (DNS) attacks
- Food manufacturers and retail restaurants face the risk of food contamination and associated customer illness, often leading to bad publicity and risks to their reputation.
How vulnerable is your business to threats of disruption? How safe are your resources? What is your tolerance for downtime?
These are all things to consider when developing a business continuity plan. Identifying key operations and dependencies, completing a business impact analysis (BIA) and conducting a risk assessment are some of the components of business continuity planning that will help you answer these questions. The results can help guide your determination for appropriate risk management techniques to employ and the specific business contingency plans to develop as a part of your overall business continuity management plan.
What keeps many businesses from developing and implementing a continuity plan? Many business leaders and managers are aware of the concept of business continuity and the importance to their organizations. In many cases they consider potential incidents that could disrupt business and the possible actions to take in response. However, few small to medium-sized companies have formally analyzed their risk or developed business continuity plans. Why?
One reason may be that major interruption of business is relatively infrequent. This may lead to a sense of apathy about the probability of an incident impacting business operations and reduces the significance.
Another reason is the belief that disruptions can be addressed at point of impact, therefore rendering the effort and resources to develop and implement a business continuity plan low priority. The result? Many businesses will find themselves unprepared in the event of a major disruption.
Furthermore, many businesses rely on business income insurance coverage to indemnify and compensate for lost income due to interruptions of their operations. While this is one effective risk management strategy, this coverage is normally limited and tied to direct physical damage or loss to covered property due to a covered peril. Many potential threats (or perils) that can lead to a disruption of your business are not covered by your property policy. And perhaps most importantly, it will not cover the potential permanent loss of customers. Where will your customers go if your business cannot provide its products or service following a loss? Will they return?
And finally, developing a formal business continuity plan may not be a top management priority or commitment because of lack of time, budget or funding. But when you consider the risks of loss and the potential impacts to your business from a disruption, can you afford NOT to plan for business continuity?
Make Business Continuity Management part of your corporate risk management program Nationwide encourages all businesses to make Business Continuity Management (BCM) a part of their company’s overall corporate risk management program. To help you get started, we've developed Business Contingency Planning – A Seven-Step Guide to help develop business contingency plans to address potential risks that could impact your businesses.
Click to learn more
Sponsored by Nationwide
Latest news.
AgMarket.Net's Matt Bennett says the grain markets are suffering from a lack of buying enthusiasm due to the bearish supplies.
The RSC proposals include shutting off crop subsidies to farmers with more than $500,000 a year in adjusted gross income, requiring growers to pay a larger share of the premium for subsidized crop insurance...
At farm bill listening session in South Dakota members of the Senate Ag Committee expressed optimism about getting a farm bill done yet in 2024 and putting more farm in the farm bill.
Many of the largest Brazilian mills have already been certified to make feedstock for sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) that meets official international and domestic standards.
Row crops fall on weather and planting progress. Funds are still short ahead of the growing season. When will that change? Matt Bennett, AgMarket.Net, has the answer on that and if the cattle market is bottoming.
Marc and Meagan Kaiser are building their future — finding a way to be part of their families' corn and soybean operation and soil testing lab while starting a precision ag business and being active in farm groups.
Agriculture Consulting Business Plans
Agricultural consultants business plan.
O'Connor & Partners offers management consulting to industrial-biotechnology, chemical,utility, and agricultural companies producing chemicals and energy from annually renewable feedstocks.
Consulting isn’t just limited to marketing and finances. In fact, almost every industry, including agriculture, has new businesses looking for seasoned professionals to assist them. Kick-start your career as a consultant by building your agriculture consulting firm using our library of sample business plans.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Agricultural Business Plan. Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 500 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their agricultural companies. If you're unfamiliar with creating an agricultural business plan, you may think creating one will be a time-consuming and frustrating process.
You'll probably want to include each of these sections: 1. Executive summary. An overview of your agriculture business, with a brief description of your products or services, your legal structure, and a snapshot of your future plans. While it's the first part of the plan, it's often easier to write your executive summary last. 2.
This publication discusses the importance of business planning for agricultural firms—from input suppliers to producers to processors—and describes the steps required to prepare a thorough business plan. The general process of business planning is the same for each type of firm.
Specifically, these funds will be used as follows: Land: $200,000. Equipment: $200,000. Three months of overhead expenses (payroll, utilities): $150,000. Marketing costs: $100,000. Working capital: $100,000. Easily complete your Agricultural business plan! Download the Agricultural business plan template (including a customizable financial ...
Five-year plan. Year One: 20XX. Create a legal business entity. Apply for necessary licenses and permits. Finalize farm layout. Procure additional equipment. Establish social media profiles. Build a small farm stand. Attend farmer's markets.
Writing a farming business plan is a crucial step toward the success of your business. Here are the key steps to consider when writing a business plan: 1. Executive Summary. An executive summary is the first section of the business plan intended to provide an overview of the whole business plan. Generally, it is written after the entire ...
Step 1: Before getting started you need to first make up your mind about the type of agriculture business you want to start. Step 2: Narrow down land and secure the boundaries of it. Make sure you close the lease agreement. Step 3: Do deep research on the market to identify the requirements you need to cater to.
The operational plan outlines how your agricultural business will function on a day-to-day basis. It includes the following details: Example: ABC Farms employs a team of experienced farmers who follow sustainable farming practices, including crop rotation and integrated pest management, to ensure soil health and minimize environmental impact.
Follow these tips to quickly develop a working business plan from this sample. 1. Don't worry about finding an exact match. We have over 550 sample business plan templates. So, make sure the plan is a close match, but don't get hung up on the details. Your business is unique and will differ from any example or template you come across.
A business plan is a decision making tool that takes the form of a formal document. It states your business goals, why you think you can achieve them, and lays out your plan for doing so. Farm business planning is also a process, not an end product. A business plan is a work in progress, which farm business owners or operators will want to ...
Farm Machinery Manufacturer Business Plan. Farming and agriculture are complicated businesses. To be successful, you need more than a green thumb and the willingness to get your hands dirty. You need to know how to operate your agricultural enterprise efficiently and not just forecast your crop rotations, but your cash position and revenue.
The Farm Business Plan Balance Sheet can help gather information for the financial and operational aspects of your plan. Form FSA-2037 is a template that gathers information on your assets and liabilities like farm equipment, vehicles and existing loans. FSA-2037 - Farm Business Plan - Balance Sheet. FSA-2037 Instructions.
A well-formed business plan of agriculture will help your agriculture business plan grow and generate the revenue that you dream of. It will help in managing your business in hard times and will also improve the chances of getting loans from the government for your business. So, if are thinking of creating a business for a bank loan, check out ...
Agriculture or farming is the only industry consistently performing well, regardless of economic climate changes. Whether you plan to start farming, cannabis cultivation, a cattle farm, or nursery business, you'll do great as long as you do things right and have a solid business plan. This library of farm business plan examples here can ...
A business plan is a roadmap for your small farm. It is both process and product. During the writing of a farm business plan, you'll develop an overall vision and mission for your business. You ...
The plan contains the operational and financial objectives of a business, the detailed plans and budgets showing how the objectives are to be realized. A good business plan will contain the following: Your business vision, mission statement, key values, and goals. Description of the product (s) you intend to produce.
Establish a marketing plan to reach your target market, utilizing both traditional and digital marketing tactics. Create an organizational chart outlining the management structure and responsibilities of your firm's employees. Finally, develop financial projections to understand the potential profitability of your business and to secure funding ...
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P's: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a poultry farm business plan, your marketing plan should include the following: Product: In the product section, you should reiterate the type of poultry farm company that you documented in your Company Analysis.
Cash at End of Period. $24,463. $29,034. $87,541. Download This Plan. Explore a real-world agriculture farm business plan example and download a free template with this information to start writing your own business plan.
List what this plan covers and the goals for business continuity. (Example: This plan includes key production activities, financial, employee, and technical operations of the farm.) Farm Risk and Prevention • Farm Production activities - biosecurity, alarms, security systems, suppliers, supplies, customers, crop and animal protection
The primary goals of planning are: Maintain a minimum level of operations during disruption. Reduce recovery time. Having a business continuity program in place, along with associated contingency ...
Agricultural Consultants Business Plan. O'Connor & Partners offers management consulting to industrial-biotechnology, chemical,utility, and agricultural companies producing chemicals and energy from annually renewable feedstocks. Consulting isn't just limited to marketing and finances. In fact, almost every industry, including agriculture ...