Exploring the Problem Solving Cycle in Computer Science – Strategies, Techniques, and Tools
- Post author By bicycle-u
- Post date 08.12.2023
The world of computer science is built on the foundation of problem solving. Whether it’s finding a solution to a complex algorithm or analyzing data to make informed decisions, the problem solving cycle is at the core of every computer science endeavor.
At its essence, problem solving in computer science involves breaking down a complex problem into smaller, more manageable parts. This allows for a systematic approach to finding a solution by analyzing each part individually. The process typically starts with gathering and understanding the data or information related to the problem at hand.
Once the data is collected, computer scientists use various techniques and algorithms to analyze and explore possible solutions. This involves evaluating different approaches and considering factors such as efficiency, accuracy, and scalability. During this analysis phase, it is crucial to think critically and creatively to come up with innovative solutions.
After a thorough analysis, the next step in the problem solving cycle is designing and implementing a solution. This involves creating a detailed plan of action, selecting the appropriate tools and technologies, and writing the necessary code to bring the solution to life. Attention to detail and precision are key in this stage to ensure that the solution functions as intended.
The final step in the problem solving cycle is evaluating the solution and its effectiveness. This includes testing the solution against different scenarios and data sets to ensure its reliability and performance. If any issues or limitations are discovered, adjustments and optimizations are made to improve the solution.
In conclusion, the problem solving cycle is a fundamental process in computer science, involving analysis, data exploration, algorithm development, solution implementation, and evaluation. It is through this cycle that computer scientists are able to tackle complex problems and create innovative solutions that drive progress in the field of computer science.

Understanding the Importance
In computer science, problem solving is a crucial skill that is at the core of the problem solving cycle. The problem solving cycle is a systematic approach to analyzing and solving problems, involving various stages such as problem identification, analysis, algorithm design, implementation, and evaluation. Understanding the importance of this cycle is essential for any computer scientist or programmer.
Data Analysis and Algorithm Design
The first step in the problem solving cycle is problem identification, which involves recognizing and defining the issue at hand. Once the problem is identified, the next crucial step is data analysis. This involves gathering and examining relevant data to gain insights and understand the problem better. Data analysis helps in identifying patterns, trends, and potential solutions.
After data analysis, the next step is algorithm design. An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure or set of rules to solve a problem. Designing an efficient algorithm is crucial as it determines the effectiveness and efficiency of the solution. A well-designed algorithm takes into consideration the constraints, resources, and desired outcomes while implementing the solution.
Implementation and Evaluation
Once the algorithm is designed, the next step in the problem solving cycle is implementation. This involves translating the algorithm into a computer program using a programming language. The implementation phase requires coding skills and expertise in a specific programming language.
After implementation, the solution needs to be evaluated to ensure that it solves the problem effectively. Evaluation involves testing the program and verifying its correctness and efficiency. This step is critical to identify any errors or issues and to make necessary improvements or adjustments.
In conclusion, understanding the importance of the problem solving cycle in computer science is essential for any computer scientist or programmer. It provides a systematic and structured approach to analyze and solve problems, ensuring efficient and effective solutions. By following the problem solving cycle, computer scientists can develop robust algorithms, implement them in efficient programs, and evaluate their solutions to ensure their correctness and efficiency.
Identifying the Problem
In the problem solving cycle in computer science, the first step is to identify the problem that needs to be solved. This step is crucial because without a clear understanding of the problem, it is impossible to find a solution.
Identification of the problem involves a thorough analysis of the given data and understanding the goals of the task at hand. It requires careful examination of the problem statement and any constraints or limitations that may affect the solution.
During the identification phase, the problem is broken down into smaller, more manageable parts. This can involve breaking the problem down into sub-problems or identifying the different aspects or components that need to be addressed.
Identifying the problem also involves considering the resources and tools available for solving it. This may include considering the specific tools and programming languages that are best suited for the problem at hand.
By properly identifying the problem, computer scientists can ensure that they are focused on the right goals and are better equipped to find an effective and efficient solution. It sets the stage for the rest of the problem solving cycle, including the analysis, design, implementation, and evaluation phases.
Gathering the Necessary Data
Before finding a solution to a computer science problem, it is essential to gather the necessary data. Whether it’s writing a program or developing an algorithm, data serves as the backbone of any solution. Without proper data collection and analysis, the problem-solving process can become inefficient and ineffective.
The Importance of Data
In computer science, data is crucial for a variety of reasons. First and foremost, it provides the information needed to understand and define the problem at hand. By analyzing the available data, developers and programmers can gain insights into the nature of the problem and determine the most efficient approach for solving it.
Additionally, data allows for the evaluation of potential solutions. By collecting and organizing relevant data, it becomes possible to compare different algorithms or strategies and select the most suitable one. Data also helps in tracking progress and measuring the effectiveness of the chosen solution.
Data Gathering Process
The process of gathering data involves several steps. Firstly, it is necessary to identify the type of data needed for the particular problem. This may include numerical values, textual information, or other types of data. It is important to determine the sources of data and assess their reliability.
Once the required data has been identified, it needs to be collected. This can be done through various methods, such as surveys, experiments, observations, or by accessing existing data sets. The collected data should be properly organized, ensuring its accuracy and validity.
Data cleaning and preprocessing are vital steps in the data gathering process. This involves removing any irrelevant or erroneous data and transforming it into a suitable format for analysis. Properly cleaned and preprocessed data will help in generating reliable and meaningful insights.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
After gathering and preprocessing the data, the next step is data analysis and interpretation. This involves applying various statistical and analytical methods to uncover patterns, trends, and relationships within the data. By analyzing the data, programmers can gain valuable insights that can inform the development of an effective solution.
During the data analysis process, it is crucial to remain objective and unbiased. The analysis should be based on sound reasoning and logical thinking. It is also important to communicate the findings effectively, using visualizations or summaries to convey the information to stakeholders or fellow developers.
In conclusion, gathering the necessary data is a fundamental step in solving computer science problems. It provides the foundation for understanding the problem, evaluating potential solutions, and tracking progress. By following a systematic and rigorous approach to data gathering and analysis, developers can ensure that their solutions are efficient, effective, and well-informed.
Analyzing the Data
Once you have collected the necessary data, the next step in the problem-solving cycle is to analyze it. Data analysis is a crucial component of computer science, as it helps us understand the problem at hand and develop effective solutions.
To analyze the data, you need to break it down into manageable pieces and examine each piece closely. This process involves identifying patterns, trends, and outliers that may be present in the data. By doing so, you can gain insights into the problem and make informed decisions about the best course of action.
There are several techniques and tools available for data analysis in computer science. Some common methods include statistical analysis, data visualization, and machine learning algorithms. Each approach has its own strengths and limitations, so it’s essential to choose the most appropriate method for the problem you are solving.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis involves using mathematical models and techniques to analyze data. It helps in identifying correlations, distributions, and other statistical properties of the data. By applying statistical tests, you can determine the significance and validity of your findings.
Data Visualization
Data visualization is the process of presenting data in a visual format, such as charts, graphs, or maps. It allows for a better understanding of complex data sets and facilitates the communication of findings. Through data visualization, patterns and trends can become more apparent, making it easier to derive meaningful insights.
Machine Learning Algorithms
Machine learning algorithms are powerful tools for analyzing large and complex data sets. These algorithms can automatically detect patterns and relationships in the data, leading to the development of predictive models and solutions. By training the algorithm on a labeled dataset, it can learn from the data and make accurate predictions or classifications.
In conclusion, analyzing the data is a critical step in the problem-solving cycle in computer science. It helps us gain a deeper understanding of the problem and develop effective solutions. Whether through statistical analysis, data visualization, or machine learning algorithms, data analysis plays a vital role in transforming raw data into actionable insights.
Exploring Possible Solutions
Once you have gathered data and completed the analysis, the next step in the problem-solving cycle is to explore possible solutions. This is where the true power of computer science comes into play. With the use of algorithms and the application of scientific principles, computer scientists can develop innovative solutions to complex problems.
During this stage, it is important to consider a variety of potential solutions. This involves brainstorming different ideas and considering their feasibility and potential effectiveness. It may be helpful to consult with colleagues or experts in the field to gather additional insights and perspectives.
Developing an Algorithm
One key aspect of exploring possible solutions is the development of an algorithm. An algorithm is a step-by-step set of instructions that outlines a specific process or procedure. In the context of problem solving in computer science, an algorithm provides a clear roadmap for implementing a solution.
The development of an algorithm requires careful thought and consideration. It is important to break down the problem into smaller, manageable steps and clearly define the inputs and outputs of each step. This allows for the creation of a logical and efficient solution.
Evaluating the Solutions
Once you have developed potential solutions and corresponding algorithms, the next step is to evaluate them. This involves analyzing each solution to determine its strengths, weaknesses, and potential impact. Consider factors such as efficiency, scalability, and resource requirements.
It may be helpful to conduct experiments or simulations to further assess the effectiveness of each solution. This can provide valuable insights and data to support the decision-making process.
Ultimately, the goal of exploring possible solutions is to find the most effective and efficient solution to the problem at hand. By leveraging the power of data, analysis, algorithms, and scientific principles, computer scientists can develop innovative solutions that drive progress and solve complex problems in the world of technology.
Evaluating the Options
Once you have identified potential solutions and algorithms for a problem, the next step in the problem-solving cycle in computer science is to evaluate the options. This evaluation process involves analyzing the potential solutions and algorithms based on various criteria to determine the best course of action.
Consider the Problem
Before evaluating the options, it is important to take a step back and consider the problem at hand. Understand the requirements, constraints, and desired outcomes of the problem. This analysis will help guide the evaluation process.
Analyze the Options
Next, it is crucial to analyze each solution or algorithm option individually. Look at factors such as efficiency, accuracy, ease of implementation, and scalability. Consider whether the solution or algorithm meets the specific requirements of the problem, and if it can be applied to related problems in the future.
Additionally, evaluate the potential risks and drawbacks associated with each option. Consider factors such as cost, time, and resources required for implementation. Assess any potential limitations or trade-offs that may impact the overall effectiveness of the solution or algorithm.
Select the Best Option
Based on the analysis, select the best option that aligns with the specific problem-solving goals. This may involve prioritizing certain criteria or making compromises based on the limitations identified during the evaluation process.
Remember that the best option may not always be the most technically complex or advanced solution. Consider the practicality and feasibility of implementation, as well as the potential impact on the overall system or project.
In conclusion, evaluating the options is a critical step in the problem-solving cycle in computer science. By carefully analyzing the potential solutions and algorithms, considering the problem requirements, and considering the limitations and trade-offs, you can select the best option to solve the problem at hand.
Making a Decision
Decision-making is a critical component in the problem-solving process in computer science. Once you have analyzed the problem, identified the relevant data, and generated a potential solution, it is important to evaluate your options and choose the best course of action.
Consider All Factors
When making a decision, it is important to consider all relevant factors. This includes evaluating the potential benefits and drawbacks of each option, as well as understanding any constraints or limitations that may impact your choice.
In computer science, this may involve analyzing the efficiency of different algorithms or considering the scalability of a proposed solution. It is important to take into account both the short-term and long-term impacts of your decision.
Weigh the Options
Once you have considered all the factors, it is important to weigh the options and determine the best approach. This may involve assigning weights or priorities to different factors based on their importance.
Using techniques such as decision matrices or cost-benefit analysis can help you systematically compare and evaluate different options. By quantifying and assessing the potential risks and rewards, you can make a more informed decision.
Remember: Decision-making in computer science is not purely subjective or based on personal preference. It is crucial to use analytical and logical thinking to select the most optimal solution.
In conclusion, making a decision is a crucial step in the problem-solving process in computer science. By considering all relevant factors and weighing the options using logical analysis, you can choose the best possible solution to a given problem.
Implementing the Solution
Once the problem has been analyzed and a solution has been proposed, the next step in the problem-solving cycle in computer science is implementing the solution. This involves turning the proposed solution into an actual computer program or algorithm that can solve the problem.
In order to implement the solution, computer science professionals need to have a strong understanding of various programming languages and data structures. They need to be able to write code that can manipulate and process data in order to solve the problem at hand.
During the implementation phase, the proposed solution is translated into a series of steps or instructions that a computer can understand and execute. This involves breaking down the problem into smaller sub-problems and designing algorithms to solve each sub-problem.
Computer scientists also need to consider the efficiency of their solution during the implementation phase. They need to ensure that the algorithm they design is able to handle large amounts of data and solve the problem in a reasonable amount of time. This often requires optimization techniques and careful consideration of the data structures used.
Once the code has been written and the algorithm has been implemented, it is important to test and debug the solution. This involves running test cases and checking the output to ensure that the program is working correctly. If any errors or bugs are found, they need to be fixed before the solution can be considered complete.
In conclusion, implementing the solution is a crucial step in the problem-solving cycle in computer science. It requires strong programming skills and a deep understanding of algorithms and data structures. By carefully designing and implementing the solution, computer scientists can solve problems efficiently and effectively.
Testing and Debugging
In computer science, testing and debugging are critical steps in the problem-solving cycle. Testing helps ensure that a program or algorithm is functioning correctly, while debugging analyzes and resolves any issues or bugs that may arise.
Testing involves running a program with specific input data to evaluate its output. This process helps verify that the program produces the expected results and handles different scenarios correctly. It is important to test both the normal and edge cases to ensure the program’s reliability.
Debugging is the process of identifying and fixing errors or bugs in a program. When a program does not produce the expected results or crashes, it is necessary to go through the code to find and fix the problem. This can involve analyzing the program’s logic, checking for syntax errors, and using debugging tools to trace the flow of data and identify the source of the issue.
Data analysis plays a crucial role in both testing and debugging. It helps to identify patterns, anomalies, or inconsistencies in the program’s behavior. By analyzing the data, developers can gain insights into potential issues and make informed decisions on how to improve the program’s performance.
In conclusion, testing and debugging are integral parts of the problem-solving cycle in computer science. Through testing and data analysis, developers can verify the correctness of their programs and identify and resolve any issues that may arise. This ensures that the algorithms and programs developed in computer science are robust, reliable, and efficient.
Iterating for Improvement
In computer science, problem solving often involves iterating through multiple cycles of analysis, solution development, and evaluation. This iterative process allows for continuous improvement in finding the most effective solution to a given problem.
The problem solving cycle starts with problem analysis, where the specific problem is identified and its requirements are understood. This step involves examining the problem from various angles and gathering all relevant information.
Once the problem is properly understood, the next step is to develop an algorithm or a step-by-step plan to solve the problem. This algorithm is a set of instructions that, when followed correctly, will lead to the solution.
After the algorithm is developed, it is implemented in a computer program. This step involves translating the algorithm into a programming language that a computer can understand and execute.
Once the program is implemented, it is then tested and evaluated to ensure that it produces the correct solution. This evaluation step is crucial in identifying any errors or inefficiencies in the program and allows for further improvement.
If any issues or problems are found during testing, the cycle iterates, starting from problem analysis again. This iterative process allows for refinement and improvement of the solution until the desired results are achieved.
Iterating for improvement is a fundamental concept in computer science problem solving. By continually analyzing, developing, and evaluating solutions, computer scientists are able to find the most optimal and efficient approaches to solving problems.
Documenting the Process
Documenting the problem-solving process in computer science is an essential step to ensure that the cycle is repeated successfully. The process involves gathering information, analyzing the problem, and designing a solution.
During the analysis phase, it is crucial to identify the specific problem at hand and break it down into smaller components. This allows for a more targeted approach to finding the solution. Additionally, analyzing the data involved in the problem can provide valuable insights and help in designing an effective solution.
Once the analysis is complete, it is important to document the findings. This documentation can take various forms, such as written reports, diagrams, or even code comments. The goal is to create a record that captures the problem, the analysis, and the proposed solution.
Documenting the process serves several purposes. Firstly, it allows for easy communication and collaboration between team members or future developers. By documenting the problem, analysis, and solution, others can easily understand the thought process behind the solution and potentially build upon it.
Secondly, documenting the process provides an opportunity for reflection and improvement. By reviewing the documentation, developers can identify areas where the problem-solving cycle can be strengthened or optimized. This continuous improvement is crucial in the field of computer science, as new challenges and technologies emerge rapidly.
In conclusion, documenting the problem-solving process is an integral part of the computer science cycle. It allows for effective communication, collaboration, and reflection on the solutions devised. By taking the time to document the process, developers can ensure a more efficient and successful problem-solving experience.
Communicating the Solution
Once the problem solving cycle is complete, it is important to effectively communicate the solution. This involves explaining the analysis, data, and steps taken to arrive at the solution.
Analyzing the Problem
During the problem solving cycle, a thorough analysis of the problem is conducted. This includes understanding the problem statement, gathering relevant data, and identifying any constraints or limitations. It is important to clearly communicate this analysis to ensure that others understand the problem at hand.
Presenting the Solution
The next step in communicating the solution is presenting the actual solution. This should include a detailed explanation of the steps taken to solve the problem, as well as any algorithms or data structures used. It is important to provide clear and concise descriptions of the solution, so that others can understand and reproduce the results.
Overall, effective communication of the solution in computer science is essential to ensure that others can understand and replicate the problem solving process. By clearly explaining the analysis, data, and steps taken, the solution can be communicated in a way that promotes understanding and collaboration within the field of computer science.
Reflecting and Learning
Reflecting and learning are crucial steps in the problem solving cycle in computer science. Once a problem has been solved, it is essential to reflect on the entire process and learn from the experience. This allows for continuous improvement and growth in the field of computer science.
During the reflecting phase, one must analyze and evaluate the problem solving process. This involves reviewing the initial problem statement, understanding the constraints and requirements, and assessing the effectiveness of the chosen algorithm and solution. It is important to consider the efficiency and accuracy of the solution, as well as any potential limitations or areas for optimization.
By reflecting on the problem solving cycle, computer scientists can gain valuable insights into their own strengths and weaknesses. They can identify areas where they excelled and areas where improvement is needed. This self-analysis helps in honing problem solving skills and becoming a better problem solver.
Learning from Mistakes
Mistakes are an integral part of the problem solving cycle, and they provide valuable learning opportunities. When a problem is not successfully solved, it is essential to analyze the reasons behind the failure and learn from them. This involves identifying errors in the algorithm or solution, understanding the underlying concepts or principles that were misunderstood, and finding alternative approaches or strategies.
Failure should not be seen as a setback, but rather as an opportunity for growth. By learning from mistakes, computer scientists can improve their problem solving abilities and expand their knowledge and understanding of computer science. It is through these failures and the subsequent learning process that new ideas and innovations are often born.
Continuous Improvement
Reflecting and learning should not be limited to individual problem solving experiences, but should be an ongoing practice. As computer science is a rapidly evolving field, it is crucial to stay updated with new technologies, algorithms, and problem solving techniques. Continuous learning and improvement contribute to staying competitive and relevant in the field.
Computer scientists can engage in continuous improvement by seeking feedback from peers, participating in research and development activities, attending conferences and workshops, and actively seeking new challenges and problem solving opportunities. This dedication to learning and improvement ensures that one’s problem solving skills remain sharp and effective.
In conclusion, reflecting and learning are integral parts of the problem solving cycle in computer science. They enable computer scientists to refine their problem solving abilities, learn from mistakes, and continuously improve their skills and knowledge. By embracing these steps, computer scientists can stay at the forefront of the ever-changing world of computer science and contribute to its advancements.
Applying Problem Solving in Real Life
In computer science, problem solving is not limited to the realm of programming and algorithms. It is a skill that can be applied to various aspects of our daily lives, helping us to solve problems efficiently and effectively. By using the problem-solving cycle and applying the principles of analysis, data, solution, algorithm, and cycle, we can tackle real-life challenges with confidence and success.
The first step in problem-solving is to analyze the problem at hand. This involves breaking it down into smaller, more manageable parts and identifying the key issues or goals. By understanding the problem thoroughly, we can gain insights into its root causes and potential solutions.
For example, let’s say you’re facing a recurring issue in your daily commute – traffic congestion. By analyzing the problem, you may discover that the main causes are a lack of alternative routes and a lack of communication between drivers. This analysis helps you identify potential solutions such as using navigation apps to find alternate routes or promoting carpooling to reduce the number of vehicles on the road.
Gathering and Analyzing Data
Once we have identified the problem, it is important to gather relevant data to support our analysis. This may involve conducting surveys, collecting statistics, or reviewing existing research. By gathering data, we can make informed decisions and prioritize potential solutions based on their impact and feasibility.
Continuing with the traffic congestion example, you may gather data on the average commute time, the number of vehicles on the road, and the impact of carpooling on congestion levels. This data can help you analyze the problem more accurately and determine the most effective solutions.
Generating and Evaluating Solutions
After analyzing the problem and gathering data, the next step is to generate potential solutions. This can be done through brainstorming, researching best practices, or seeking input from experts. It is important to consider multiple options and think outside the box to find innovative and effective solutions.
For our traffic congestion problem, potential solutions can include implementing a smart traffic management system that optimizes traffic flow or investing in public transportation to incentivize people to leave their cars at home. By evaluating each solution’s potential impact, cost, and feasibility, you can make an informed decision on the best course of action.
Implementing and Iterating
Once a solution has been chosen, it is time to implement it in real life. This may involve developing a plan, allocating resources, and executing the solution. It is important to monitor the progress and collect feedback to learn from the implementation and make necessary adjustments.
For example, if the chosen solution to address traffic congestion is implementing a smart traffic management system, you would work with engineers and transportation authorities to develop and deploy the system. Regular evaluation and iteration of the system’s performance would ensure that it is effective and making a positive impact on reducing congestion.
By applying the problem-solving cycle derived from computer science to real-life situations, we can approach challenges with a systematic and analytical mindset. This can help us make better decisions, improve our problem-solving skills, and ultimately achieve more efficient and effective solutions.
Building Problem Solving Skills
In the field of computer science, problem-solving is a fundamental skill that is crucial for success. Whether you are a computer scientist, programmer, or student, developing strong problem-solving skills will greatly benefit your work and studies. It allows you to approach challenges with a logical and systematic approach, leading to efficient and effective problem resolution.
The Problem Solving Cycle
Problem-solving in computer science involves a cyclical process known as the problem-solving cycle. This cycle consists of several stages, including problem identification, data analysis, solution development, implementation, and evaluation. By following this cycle, computer scientists are able to tackle complex problems and arrive at optimal solutions.
Importance of Data Analysis
Data analysis is a critical step in the problem-solving cycle. It involves gathering and examining relevant data to gain insights and identify patterns that can inform the development of a solution. Without proper data analysis, computer scientists may overlook important information or make unfounded assumptions, leading to subpar solutions.
To effectively analyze data, computer scientists can employ various techniques such as data visualization, statistical analysis, and machine learning algorithms. These tools enable them to extract meaningful information from large datasets and make informed decisions during the problem-solving process.
Developing Effective Solutions
Developing effective solutions requires creativity, critical thinking, and logical reasoning. Computer scientists must evaluate multiple approaches, consider various factors, and assess the feasibility of different solutions. They should also consider potential limitations and trade-offs to ensure that the chosen solution addresses the problem effectively.
Furthermore, collaboration and communication skills are vital when building problem-solving skills. Computer scientists often work in teams and need to effectively communicate their ideas, propose solutions, and address any challenges that arise during the problem-solving process. Strong interpersonal skills facilitate collaboration and enhance problem-solving outcomes.
- Mastering programming languages and algorithms
- Staying updated with technological advancements in the field
- Practicing problem solving through coding challenges and projects
- Seeking feedback and learning from mistakes
- Continuing to learn and improve problem-solving skills
By following these strategies, individuals can strengthen their problem-solving abilities and become more effective computer scientists or programmers. Problem-solving is an essential skill in computer science and plays a central role in driving innovation and advancing the field.
Questions and answers:
What is the problem solving cycle in computer science.
The problem solving cycle in computer science refers to a systematic approach that programmers use to solve problems. It involves several steps, including problem definition, algorithm design, implementation, testing, and debugging.
How important is the problem solving cycle in computer science?
The problem solving cycle is extremely important in computer science as it allows programmers to effectively tackle complex problems and develop efficient solutions. It helps in organizing the thought process and ensures that the problem is approached in a logical and systematic manner.
What are the steps involved in the problem solving cycle?
The problem solving cycle typically consists of the following steps: problem definition and analysis, algorithm design, implementation, testing, and debugging. These steps are repeated as necessary until a satisfactory solution is achieved.
Can you explain the problem definition and analysis step in the problem solving cycle?
During the problem definition and analysis step, the programmer identifies and thoroughly understands the problem that needs to be solved. This involves analyzing the requirements, constraints, and possible inputs and outputs. It is important to have a clear understanding of the problem before proceeding to the next steps.
Why is testing and debugging an important step in the problem solving cycle?
Testing and debugging are important steps in the problem solving cycle because they ensure that the implemented solution functions as intended and is free from errors. Through testing, the programmer can identify and fix any issues or bugs in the code, thereby improving the quality and reliability of the solution.
What is the problem-solving cycle in computer science?
The problem-solving cycle in computer science refers to the systematic approach that computer scientists use to solve problems. It involves various steps, including problem analysis, algorithm design, coding, testing, and debugging.
Related posts:
- The Stages of the Problem Solving Cycle in Cognitive Psychology – Understanding, Planning, Execution, Evaluation, and Reflection
- A Comprehensive Guide to the Problem Solving Cycle in Psychology – Strategies, Techniques, and Applications
- The Step-by-Step Problem Solving Cycle for Effective Solutions
- The Importance of Implementing the Problem Solving Cycle in Education to Foster Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills in Students
- The Importance of the Problem Solving Cycle in Business Studies – Strategies for Success
- The Comprehensive Guide to the Problem Solving Cycle in PDF Format
- A Comprehensive Guide on the Problem Solving Cycle – Step-by-Step Approach with Real-Life Example
- The Seven Essential Steps of the Problem Solving Cycle
- Python Programming
- C Programming
- Numerical Methods
- Dart Language
- Computer Basics
- Deep Learning
- C Programming Examples
- Python Programming Examples
Problem Solving Using Computer (Steps)
Computer based problem solving is a systematic process of designing, implementing and using programming tools during the problem solving stage. This method enables the computer system to be more intuitive with human logic than machine logic. Final outcome of this process is software tools which is dedicated to solve the problem under consideration. Software is just a collection of computer programs and programs are a set of instructions which guides computer’s hardware. These instructions need to be well specified for solving the problem. After its creation, the software should be error free and well documented. Software development is the process of creating such software, which satisfies end user’s requirements and needs.
The following six steps must be followed to solve a problem using computer.
- Problem Analysis
- Program Design - Algorithm, Flowchart and Pseudocode
- Compilation and Execution
- Debugging and Testing
- Program Documentation
- Trending Now
- Foundational Courses
- Data Science
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- System Design
- DevOps Tutorial
- Concept of Comments in Computer Programming
- Modular Approach in Programming
- Classification of Computers
- CBSE Class 11 | Concepts of Programming Methodology
- System Software
- Open Source, Freeware and Shareware Softwares
- Domain Specific Tools
- Cyber safety
- Difference between Algorithm, Pseudocode and Program
- CBSE Class 11 | Computer Science - C++ Syllabus
- Office Tools and Domain Specific Tools
- CBSE Class 11 | Mobile Operating Systems - Symbian, Android and iOS
- Interesting Examples of algorithms in everyday life
- ISC- Class 12 Computer Science 2017
- CBSE Class 11 C++ Sample Paper-3
- CBSE Class 11 C++ | Sample Paper -2
- Difference between fundamental data types and derived data types
- Writing First C++ Program - Hello World Example
CBSE Class 11 | Problem Solving Methodologies
Problem solving process.
The process of problem-solving is an activity which has its ingredients as the specification of the program and the served dish is a correct program. This activity comprises of four steps : 1. Understanding the problem: To solve any problem it is very crucial to understand the problem first. What is the desired output of the code and how that output can be generated? The obvious and essential need to generate the output is an input. The input may be singular or it may be a set of inputs. A proper relationship between the input and output must be drawn in order to solve the problem efficiently. The input set should be complete and sufficient enough to draw the output. It means all the necessary inputs required to compute the output should be present at the time of computation. However, it should be kept in mind that the programmer should ensure that the minimum number of inputs should be there. Any irrelevant input only increases the size of and memory overhead of the program. Thus Identifying the minimum number of inputs required for output is a crucial element for understanding the problem.
2. Devising the plan: Once a problem has been understood, a proper action plan has to be devised to solve it. This is called devising the plan. This step usually involves computing the result from the given set of inputs. It uses the relationship drawn between inputs and outputs in the previous step. The complexity of this step depends upon the complexity of the problem at hand.
3. Executing the plan: Once the plan has been defined, it should follow the trajectory of action while ensuring the plan’s integrity at various checkpoints. If any inconsistency is found in between, the plan needs to be revised.
4. Evaluation: The final result so obtained must be evaluated and verified to see if the problem has been solved satisfactorily.
Problem Solving Methodology(The solution for the problem)
The methodology to solve a problem is defined as the most efficient solution to the problem. Although, there can be multiple ways to crack a nut, but a methodology is one where the nut is cracked in the shortest time and with minimum effort. Clearly, a sledgehammer can never be used to crack a nut. Under problem-solving methodology, we will see a step by step solution for a problem. These steps closely resemble the software life cycle . A software life cycle involves several stages in a program’s life cycle. These steps can be used by any tyro programmer to solve a problem in the most efficient way ever. The several steps of this cycle are as follows :
Step by step solution for a problem (Software Life Cycle) 1. Problem Definition/Specification: A computer program is basically a machine language solution to a real-life problem. Because programs are generally made to solve the pragmatic problems of the outside world. In order to solve the problem, it is very necessary to define the problem to get its proper understanding. For example, suppose we are asked to write a code for “ Compute the average of three numbers”. In this case, a proper definition of the problem will include questions like : “What exactly does average mean?” “How to calculate the average?”
Once, questions like these are raised, it helps to formulate the solution of the problem in a better way. Once a problem has been defined, the program’s specifications are then listed. Problem specifications describe what the program for the problem must do. It should definitely include :
what is the input set of the program
What is the desired output of the program and in what form the output is desired?
2. Problem Analysis (Breaking down the solution into simple steps): This step of solving the problem follows a modular approach to crack the nut. The problem is divided into subproblems so that designing a solution to these subproblems gets easier. The solutions to all these individual parts are then merged to get the final solution of the original problem. It is like divide and merge approach.
Modular Approach for Programming :
The process of breaking a large problem into subproblems and then treating these individual parts as different functions is called modular programming. Each function behaves independent of another and there is minimal inter-functional communication. There are two methods to implement modular programming :
- Top Down Design : In this method, the original problem is divided into subparts. These subparts are further divided. The chain continues till we get the very fundamental subpart of the problem which can’t be further divided. Then we draw a solution for each of these fundamental parts.
- Bottom Up Design : In this style of programming, an application is written by using the pre-existing primitives of programming language. These primitives are then amalgamated with more complicated features, till the application is written. This style is just the reverse of the top-down design style.
3. Problem Designing: The design of a problem can be represented in either of the two forms :
The ways to execute any program are of three categories:
- Sequence Statements Here, all the instructions are executed in a sequence, that is, one after the another, till the program is executed.
- Selection Statements As it is self-clear from the name, in these type of statements the whole set of instructions is not executed. A selection has to be made. A selected number of instructions are executed based on some condition. If the condition holds true then some part of the instruction set is executed, otherwise, another part of the set is executed. Since this selection out of the instruction set has to be made, thus these type of instructions are called Selection Statements.
Identification of arithmetic and logical operations required for the solution : While writing the algorithm for a problem, the arithmetic and logical operations required for the solution are also usually identified. They help to write the code in an easier manner because the proper ordering of the arithmetic and logical symbols is necessary to determine the correct output. And when all this has been done in the algorithm writing step, it just makes the coding task a smoother one.
- Flow Chart : Flow charts are diagrammatic representation of the algorithm. It uses some symbols to illustrate the starting and ending of a program along with the flow of instructions involved in the program.
4. Coding: Once an algorithm is formed, it can’t be executed on the computer. Thus in this step, this algorithm has to be translated into the syntax of a particular programming language. This process is often termed as ‘coding’. Coding is one of the most important steps of the software life cycle. It is not only challenging to find a solution to a problem but to write optimized code for a solution is far more challenging.
Writing code for optimizing execution time and memory storage : A programmer writes code on his local computer. Now, suppose he writes a code which takes 5 hours to get executed. Now, this 5 hours of time is actually the idle time for the programmer. Not only it takes longer time, but it also uses the resources during that time. One of the most precious computing resources is memory. A large program is expected to utilize more memory. However, memory utilization is not a fault, but if a program is utilizing unnecessary time or memory, then it is a fault of coding. The optimized code can save both time and memory. For example, as has been discussed earlier, by using the minimum number of inputs to compute the output , one can save unnecessary memory utilization. All such techniques are very necessary to be deployed to write optimized code. The pragmatic world gives reverence not only to the solution of the problem but to the optimized solution. This art of writing the optimized code also called ‘competitive programming’.
5. Program Testing and Debugging: Program testing involves running each and every instruction of the code and check the validity of the output by a sample input. By testing a program one can also check if there’s an error in the program. If an error is detected, then program debugging is done. It is a process to locate the instruction which is causing an error in the program and then rectifying it. There are different types of error in a program : (i) Syntax Error Every programming language has its own set of rules and constructs which need to be followed to form a valid program in that particular language. If at any place in the entire code, this set of rule is violated, it results in a syntax error. Take an example in C Language
In the above program, the syntax error is in the first printf statement since the printf statement doesn’t end with a ‘;’. Now, until and unless this error is not rectified, the program will not get executed.
Once the error is rectified, one gets the desired output. Suppose the input is ‘good’ then the output is : Output:
(ii) Logical Error An error caused due to the implementation of a wrong logic in the program is called logical error. They are usually detected during the runtime. Take an example in C Language:
In the above code, the ‘for’ loop won’t get executed since n has been initialized with the value of 11 while ‘for’ loop can only print values smaller than or equal to 10. Such a code will result in incorrect output and thus errors like these are called logical errors. Once the error is rectified, one gets the desired output. Suppose n is initialised with the value ‘5’ then the output is : Output:
(iii) Runtime Error Any error which causes the unusual termination of the program is called runtime error. They are detected at the run time. Some common examples of runtime errors are : Example 1 :
If during the runtime, the user gives the input value for B as 0 then the program terminates abruptly resulting in a runtime error. The output thus appears is : Output:
Example 2 : If while executing a program, one attempts for opening an unexisting file, that is, a file which is not present in the hard disk, it also results in a runtime error.
6. Documentation : The program documentation involves :
- Problem Definition
- Problem Design
- Documentation of test perform
- History of program development
7. Program Maintenance: Once a program has been formed, to ensure its longevity, maintenance is a must. The maintenance of a program has its own costs associated with it, which may also exceed the development cost of the program in some cases. The maintenance of a program involves the following :
- Detection and Elimination of undetected errors in the existing program.
- Modification of current program to enhance its performance and adaptability.
- Enhancement of user interface
- Enriching the program with new capabilities.
- Updation of the documentation.
Control Structure- Conditional control and looping (finite and infinite)
There are codes which usually involve looping statements. Looping statements are statements in which instruction or a set of instructions is executed multiple times until a particular condition is satisfied. The while loop, for loop, do while loop, etc. form the basis of such looping structure. These statements are also called control structure because they determine or control the flow of instructions in a program. These looping structures are of two kinds :
In the above program, the ‘for’ loop gets executed only until the value of i is less than or equal to 10. As soon as the value of i becomes greater than 10, the while loop is terminated. Output:
In the above code, one can easily see that the value of n is not getting incremented. In such a case, the value of n will always remain 1 and hence the while loop will never get executed. Such loop is called an infinite loop. Output:
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- School Programming
- How to Use Bard for Creative Writing
- How To Get A Free Domain Name [2024]
- 10 Best Crypto Portfolio Tracker Apps in 2024
- 10 Best Free Blockchain Learning apps for Android in 2024
- Top 10 R Project Ideas for Beginners in 2024
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Browse Course Material
Course info.
- Prof. John Guttag
Departments
- Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
As Taught In
- Computer Science
Introduction to Computer Science and Programming
Lecture 3: problem solving.
- Download video
- Download transcript

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare
Problem Solving: Stages of problem solving
Solving problems is never easy, so you need to break them down into manageable chunks:
- 1.1 Define the problem
- 2 Define boundaries
- 3 Plan solution
- 4 Check solution
Understand the problem [ edit | edit source ]
Before we should start solving a problem, we need to understand exactly what the problem is that we are dealing with. Only then can we start to think of solutions. By doing this we can avoid spending a lot of time on unsuitable solutions that we'd then have to throw away.
Knowing the level of thinking required to solving the problem and having an idea of a solution which is relevant to the problem.
Define the problem [ edit | edit source ]
To fully understand a problem we need to think about the following:
- Given(s): the initial situation
- Goal: desired target situation
- Ownership: who does what
- Resources and constraints: tools, knowledge, skills, materials and rules, regulations, guidelines, boundaries, timing
For example:
Define boundaries [ edit | edit source ]
Understanding the limits to coming up with a solution and knowing what can and cannot be done through lateral thinking. These boundaries may also be known as a type of constraint.
It is important to define what your system is not going to do - as important as considering what it should do. Most software projects fail because of specification creep - where the code in development moves away from the requirements because someone (often the developers themselves) feels that it would be good if the application also did <this> and <why not put it in while you can> thinking. You will end up with code that you do not know how to test or fix when it goes wrong - which is a sign of poor development that markers will not be able to ignore!
Plan solution [ edit | edit source ]
Once you have defined the problem, given, goal, ownership and resources you need to start thinking about how you will implement a solution. This might involve using tools such as flow charts, pseudo code, top down design, finite state machines etc. These will allow you to get started with actually making the solution. We will meet all of these methods shortly.
Check solution [ edit | edit source ]
Once you have created a solution you need to check it against the original problem. If it solves the problem then you have a successful solution. If it doesn't then you have failed and will have to go back to the drawing board to try another solution that works.
Note that you can (and should) test your design on paper against the specification (and your test plans) before you code it. This "walk through" approach is often done in team working - which encourages the consideration of abnormal data input, or using work flows that had not been thought of.
- Book:A-level Computing
Navigation menu

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 4 min read
The Problem-Solving Process
Looking at the basic problem-solving process to help keep you on the right track.
By the Mind Tools Content Team
Problem-solving is an important part of planning and decision-making. The process has much in common with the decision-making process, and in the case of complex decisions, can form part of the process itself.
We face and solve problems every day, in a variety of guises and of differing complexity. Some, such as the resolution of a serious complaint, require a significant amount of time, thought and investigation. Others, such as a printer running out of paper, are so quickly resolved they barely register as a problem at all.

Despite the everyday occurrence of problems, many people lack confidence when it comes to solving them, and as a result may chose to stay with the status quo rather than tackle the issue. Broken down into steps, however, the problem-solving process is very simple. While there are many tools and techniques available to help us solve problems, the outline process remains the same.
The main stages of problem-solving are outlined below, though not all are required for every problem that needs to be solved.
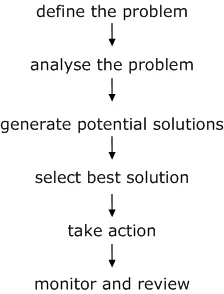
1. Define the Problem
Clarify the problem before trying to solve it. A common mistake with problem-solving is to react to what the problem appears to be, rather than what it actually is. Write down a simple statement of the problem, and then underline the key words. Be certain there are no hidden assumptions in the key words you have underlined. One way of doing this is to use a synonym to replace the key words. For example, ‘We need to encourage higher productivity ’ might become ‘We need to promote superior output ’ which has a different meaning.
2. Analyze the Problem
Ask yourself, and others, the following questions.
- Where is the problem occurring?
- When is it occurring?
- Why is it happening?
Be careful not to jump to ‘who is causing the problem?’. When stressed and faced with a problem it is all too easy to assign blame. This, however, can cause negative feeling and does not help to solve the problem. As an example, if an employee is underperforming, the root of the problem might lie in a number of areas, such as lack of training, workplace bullying or management style. To assign immediate blame to the employee would not therefore resolve the underlying issue.
Once the answers to the where, when and why have been determined, the following questions should also be asked:
- Where can further information be found?
- Is this information correct, up-to-date and unbiased?
- What does this information mean in terms of the available options?
3. Generate Potential Solutions
When generating potential solutions it can be a good idea to have a mixture of ‘right brain’ and ‘left brain’ thinkers. In other words, some people who think laterally and some who think logically. This provides a balance in terms of generating the widest possible variety of solutions while also being realistic about what can be achieved. There are many tools and techniques which can help produce solutions, including thinking about the problem from a number of different perspectives, and brainstorming, where a team or individual write as many possibilities as they can think of to encourage lateral thinking and generate a broad range of potential solutions.
4. Select Best Solution
When selecting the best solution, consider:
- Is this a long-term solution, or a ‘quick fix’?
- Is the solution achievable in terms of available resources and time?
- Are there any risks associated with the chosen solution?
- Could the solution, in itself, lead to other problems?
This stage in particular demonstrates why problem-solving and decision-making are so closely related.
5. Take Action
In order to implement the chosen solution effectively, consider the following:
- What will the situation look like when the problem is resolved?
- What needs to be done to implement the solution? Are there systems or processes that need to be adjusted?
- What will be the success indicators?
- What are the timescales for the implementation? Does the scale of the problem/implementation require a project plan?
- Who is responsible?
Once the answers to all the above questions are written down, they can form the basis of an action plan.
6. Monitor and Review
One of the most important factors in successful problem-solving is continual observation and feedback. Use the success indicators in the action plan to monitor progress on a regular basis. Is everything as expected? Is everything on schedule? Keep an eye on priorities and timelines to prevent them from slipping.
If the indicators are not being met, or if timescales are slipping, consider what can be done. Was the plan realistic? If so, are sufficient resources being made available? Are these resources targeting the correct part of the plan? Or does the plan need to be amended? Regular review and discussion of the action plan is important so small adjustments can be made on a regular basis to help keep everything on track.
Once all the indicators have been met and the problem has been resolved, consider what steps can now be taken to prevent this type of problem recurring? It may be that the chosen solution already prevents a recurrence, however if an interim or partial solution has been chosen it is important not to lose momentum.
Problems, by their very nature, will not always fit neatly into a structured problem-solving process. This process, therefore, is designed as a framework which can be adapted to individual needs and nature.
Join Mind Tools and get access to exclusive content.
This resource is only available to Mind Tools members.
Already a member? Please Login here

Team Management
Learn the key aspects of managing a team, from building and developing your team, to working with different types of teams, and troubleshooting common problems.
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

SWOT Analysis

SMART Goals
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
How to stop procrastinating.
Overcoming the Habit of Delaying Important Tasks
What Is Time Management?
Working Smarter to Enhance Productivity
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Energizing yourself infographic.
Infographic Transcript
Infographic
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast

What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 7, 2023 — 5 minutes to read
What Is Problem Solving?
Definition and importance.
Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a crucial skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Mastering this ability will contribute to both your personal and professional growth, leading to more successful outcomes and better decision-making.
Problem-Solving Steps
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:
- Identify the issue : Recognize the problem that needs to be solved.
- Analyze the situation : Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present.
- Generate potential solutions : Brainstorm a list of possible solutions to the issue, without immediately judging or evaluating them.
- Evaluate options : Weigh the pros and cons of each potential solution, considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and potential risks.
- Select the best solution : Choose the option that best addresses the problem and aligns with your objectives.
- Implement the solution : Put the selected solution into action and monitor the results to ensure it resolves the issue.
- Review and learn : Reflect on the problem-solving process, identify any improvements or adjustments that can be made, and apply these learnings to future situations.
Defining the Problem
To start tackling a problem, first, identify and understand it. Analyzing the issue thoroughly helps to clarify its scope and nature. Ask questions to gather information and consider the problem from various angles. Some strategies to define the problem include:
- Brainstorming with others
- Asking the 5 Ws and 1 H (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How)
- Analyzing cause and effect
- Creating a problem statement
Generating Solutions
Once the problem is clearly understood, brainstorm possible solutions. Think creatively and keep an open mind, as well as considering lessons from past experiences. Consider:
- Creating a list of potential ideas to solve the problem
- Grouping and categorizing similar solutions
- Prioritizing potential solutions based on feasibility, cost, and resources required
- Involving others to share diverse opinions and inputs
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Evaluate each potential solution, weighing its pros and cons. To facilitate decision-making, use techniques such as:
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Decision-making matrices
- Pros and cons lists
- Risk assessments
After evaluating, choose the most suitable solution based on effectiveness, cost, and time constraints.
Implementing and Monitoring the Solution
Implement the chosen solution and monitor its progress. Key actions include:
- Communicating the solution to relevant parties
- Setting timelines and milestones
- Assigning tasks and responsibilities
- Monitoring the solution and making adjustments as necessary
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the solution after implementation
Utilize feedback from stakeholders and consider potential improvements. Remember that problem-solving is an ongoing process that can always be refined and enhanced.
Problem-Solving Techniques
During each step, you may find it helpful to utilize various problem-solving techniques, such as:
- Brainstorming : A free-flowing, open-minded session where ideas are generated and listed without judgment, to encourage creativity and innovative thinking.
- Root cause analysis : A method that explores the underlying causes of a problem to find the most effective solution rather than addressing superficial symptoms.
- SWOT analysis : A tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a problem or decision, providing a comprehensive view of the situation.
- Mind mapping : A visual technique that uses diagrams to organize and connect ideas, helping to identify patterns, relationships, and possible solutions.
Brainstorming
When facing a problem, start by conducting a brainstorming session. Gather your team and encourage an open discussion where everyone contributes ideas, no matter how outlandish they may seem. This helps you:
- Generate a diverse range of solutions
- Encourage all team members to participate
- Foster creative thinking
When brainstorming, remember to:
- Reserve judgment until the session is over
- Encourage wild ideas
- Combine and improve upon ideas
Root Cause Analysis
For effective problem-solving, identifying the root cause of the issue at hand is crucial. Try these methods:
- 5 Whys : Ask “why” five times to get to the underlying cause.
- Fishbone Diagram : Create a diagram representing the problem and break it down into categories of potential causes.
- Pareto Analysis : Determine the few most significant causes underlying the majority of problems.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis helps you examine the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to your problem. To perform a SWOT analysis:
- List your problem’s strengths, such as relevant resources or strong partnerships.
- Identify its weaknesses, such as knowledge gaps or limited resources.
- Explore opportunities, like trends or new technologies, that could help solve the problem.
- Recognize potential threats, like competition or regulatory barriers.
SWOT analysis aids in understanding the internal and external factors affecting the problem, which can help guide your solution.
Mind Mapping
A mind map is a visual representation of your problem and potential solutions. It enables you to organize information in a structured and intuitive manner. To create a mind map:
- Write the problem in the center of a blank page.
- Draw branches from the central problem to related sub-problems or contributing factors.
- Add more branches to represent potential solutions or further ideas.
Mind mapping allows you to visually see connections between ideas and promotes creativity in problem-solving.
Examples of Problem Solving in Various Contexts
In the business world, you might encounter problems related to finances, operations, or communication. Applying problem-solving skills in these situations could look like:
- Identifying areas of improvement in your company’s financial performance and implementing cost-saving measures
- Resolving internal conflicts among team members by listening and understanding different perspectives, then proposing and negotiating solutions
- Streamlining a process for better productivity by removing redundancies, automating tasks, or re-allocating resources
In educational contexts, problem-solving can be seen in various aspects, such as:
- Addressing a gap in students’ understanding by employing diverse teaching methods to cater to different learning styles
- Developing a strategy for successful time management to balance academic responsibilities and extracurricular activities
- Seeking resources and support to provide equal opportunities for learners with special needs or disabilities
Everyday life is full of challenges that require problem-solving skills. Some examples include:
- Overcoming a personal obstacle, such as improving your fitness level, by establishing achievable goals, measuring progress, and adjusting your approach accordingly
- Navigating a new environment or city by researching your surroundings, asking for directions, or using technology like GPS to guide you
- Dealing with a sudden change, like a change in your work schedule, by assessing the situation, identifying potential impacts, and adapting your plans to accommodate the change.
- How to Resolve Employee Conflict at Work [Steps, Tips, Examples]
- How to Write Inspiring Core Values? 5 Steps with Examples
- 30 Employee Feedback Examples (Positive & Negative)
Find Study Materials for
- Business Studies
- Combined Science
- Computer Science
- Engineering
- English Literature
- Environmental Science
- Human Geography
- Macroeconomics
- Microeconomics
- Social Studies
- Browse all subjects
- Read our Magazine
Create Study Materials
Unlock the secrets of efficient coding, develop an in-depth understanding of different strategies, and learn how decision-making plays a significant role in using problem-solving techniques in Computer Science. This enlightening journey begins with an exploration into the definition of problem-solving techniques and their paramount importance in Computer Science. You further discover the basic problem-solving methods, their practical applications, and how these foundational skills apply directly to coding.

Explore our app and discover over 50 million learning materials for free.
Problem Solving Techniques
Want to get better grades, get free, full access to:.
- Explanations
- Study Planner
- Textbook solutions
- StudySmarter AI
- Textbook Solutions
- Algorithms in Computer Science
- Computer Network
- Computer Organisation and Architecture
- Computer Programming
- Computer Systems
- Data Representation in Computer Science
- Data Structures
- Functional Programming
- Issues in Computer Science
- Abstraction Computer Science
- Agile Methodology
- Agile Scrum
- Breakpoints
- Computational Thinking
- Decomposition Computer Science
- Integration Testing
- Kanban Boards
- Pattern Recognition
- Software Development Life Cycle
- Step Into Debugging
- Step Over Debugging
- System Testing
- Unit Testing
- Watch Variable
- Waterfall Model
- Theory of Computation
Lerne mit deinen Freunden und bleibe auf dem richtigen Kurs mit deinen persönlichen Lernstatistiken
Nie wieder prokastinieren mit unseren Lernerinnerungen.
Unlock the secrets of efficient coding, develop an in-depth understanding of different strategies, and learn how decision-making plays a significant role in using problem-solving techniques in Computer Science. This enlightening journey begins with an exploration into the definition of problem-solving techniques and their paramount importance in Computer Science. You further discover the basic problem-solving methods, their practical applications, and how these foundational skills apply directly to coding.
Going deeper, you explore seven pivotal problem-solving techniques, understanding their concepts and their indispensable uses in Computer Science. Finally, learn the nuances involved in contrasting problem-solving and decision-making techniques, the subtleties that set them apart, and ways in which they can be combined for the most effective results, in terms of both efficiency and creativity.
Understanding Problem-Solving Techniques
Problem-solving techniques in computer science are the protocols, procedures, or methods employed to identify the root cause of a problem and construct an efficient solution.
Definition of problem-solving techniques in Computer Science
Problem-solving techniques in computer science refer to the methods used to find solutions to complex issues using algorithmic or heuristic approaches. These techniques can be systematic, analytical, or intuitive, encompassing traditional programming, machine learning, or artificial intelligence methods.
These techniques are used in various domains within computer science, including data analysis, software development, network troubleshooting, and cybersecurity. For example, in software development, problem-solving may involve debugging an application. Here, the issue could be a broken functionality within the application, and the solution might be modifying a specific segment of code.
At a software development company, the team notices that their mobile application crashes whenever a user tries to upload a profile picture. By employing problem-solving techniques such as testing , the team identifies that the crash occurs due to a buffer overflow when processing large images. Once identified, they solve this problem by modifying the code to handle large image sizes better.
Importance of problem-solving techniques in Computer Science
Problem-solving techniques are the cornerstone of computer science. From designing efficient algorithms for a given task to optimising or guaranteeing certain performance metrics, these techniques are used daily. Here's why they're important:
- Mitigating runtime errors and system crashes: By identifying and rectifying coding mistakes effectively.
- Optimizing software: Problem-solving techniques can help improve the efficiency of software, leading to enhanced user experience and reduced resource consumption.
- Data analysis: They help in organizing, evaluating, and interpreting complex datasets to derive meaningful insights.
- Cybersecurity: By identifying potential vulnerabilities and patching them before they can be exploited, thereby safeguarding digital assets.
In the domain of machine learning, problem-solving techniques are even more paramount. Here, problems can include determining the best machine learning model for a specific task, tuning the hyperparameters of a model, or dealing with issues like data imbalance or overfitting. These techniques can guide computer scientists in their quest to develop robust, accurate machine-learning models that can make sense of vast, complex data.
Given the rapidly evolving nature of computer science, mastering various problem-solving techniques is essential to stay ahead in this field. It helps you adapt to new advancements and tackle a wide range of challenges that come your way.
Basic Problem-Solving Techniques
Before diving into advanced, specialized techniques for solving problems, it is essential to become proficient in the fundamentals, which transcend specific problem domains and provide a solid foundation for exploring more complex areas within computer science.
Introduction to basic problem-solving techniques
There are several standard problem-solving techniques that you can employ irrespective of the field of study in computer science. The first step, however, is always understanding the problem, then you can choose the right strategy to solve it. Here are some of the basic problem-solving methods that are particularly useful:
Divide and Conquer: This technique involves breaking a larger problem into smaller, more manageable parts, solving each of them individually, and finally combining their solutions to get the overall answer.
Consider an example in the context of sorting a list of numbers. Using a divide-and-conquer algorithm like Merge Sort , the list is continually split in half, until you reach lists of size one. These lists are inherently sorted, and then you recursively merge these sorted lists, resulting in a fully sorted list.
Algorithm Design: This technique involves formalizing a series of organized steps into an algorithm to solve a specific problem. Common approaches include greedy algorithms, dynamic programming, and brute force .
Heuristics: These are rules of thumb or educated guesses that can help you find an acceptable, if not the perfect, solution when the problem is too complex for a direct mathematical approach, or when computational resources are limited.
Heuristics are not guaranteed to yield the optimal solution but are often good enough for practical purposes and can dramatically reduce the time and resources needed to find a solution.
Recursive Thinking: Recursion is predicated on solving a problem by breaking it down into smaller instances of the same problem. The idea is that, eventually, you will get to a problem that is small enough to solve directly.
Even though these techniques might sound simple, they form a cornerstone and are often cloaked within complex problem-solving techniques used in higher-level computer science.
Practical application of basic problem-solving techniques
The practical application of basic problem-solving techniques in computer science is broad and varied, depending on the specific domain. However, some applications cut across most sectors of computer science:
Each technique has its strengths and weaknesses, and the key is knowing which technique (or combination of techniques) to use for a particular problem. Remember, the goal is not just to find any solution, but to find the most efficient one possible.
Other fields, too, benefit from these problem-solving techniques. For example, bioinformatics implements algorithm design to match genetic sequences, while digital forensics employs divide-and-conquer techniques to sift through large amounts of data during an investigation. Moreover, heuristics play a significant role in the burgeoning field of AI, proving that these problem-solving techniques not only provide a solid foundation for computer science but also have real-world applications.
Coding Problem-Solving Techniques
Delving into the more specific realm of coding within computer science, the arsenal of problem-solving techniques takes on facets best suited for resolving issues related to programming and development.
Importance of coding problem-solving techniques in Computer Science
Coding problem-solving techniques are the tools that software developers use to create, optimise, and manage software applications effectively. These techniques play an instrumental role in many aspects:
- Enhancing code efficiency: Efficient code is faster to execute, consumes less memory, and results in responsive, user-friendly applications. For instance, choosing an optimal sorting algorithm based on the size of the list can markedly improve runtime.
- Mitigating errors: Through structured debugging and systematic thinking, developers can track and rectify logic errors, syntax errors , or runtime exceptions, leading to robust, error-free code.
- Facilitating code readability and maintenance: Good coding practices, such as following a consistent naming scheme and using descriptive comments, make code easier to understand, troubleshoot, and maintain – essential when working in a team.
- Implementing complex functionalities: Many modern applications require intricate algorithms, use elaborate data structures , and handle large volumes of data. Mastery of coding problem-solving techniques enables developers to tackle these challenges effectively.
Examples of coding problem-solving techniques
There's a myriad of coding problem-solving techniques at a developer's disposal. These methods typically supplement basic problem-solving techniques with practices tailored for the coding environment. Let's delve into a few:
Debugging: Debugging is the process of identifying and rectifying coding errors. It often involves using built-in tools or software debuggers to step through the code line-by-line, track variable values, and uncover where things go awry. A systematic debugging approach is essential for problem-solving in coding.
Suppose you are developing a JavaScript web application, and some functionality isn't working as expected. By using the browser's debugging tools, you can step through your JavaScript code, watch the values assigned to variables, and identify the line creating the issue.
Code Refactoring: Refactoring implies rearranging and improving the structure of existing code without changing its functionality. Refactoring techniques, such as extracting repeated code into functions or simplifying conditional expressions, are integral problem-solving tools aimed at improving code readability and efficiency.
Using Data Structures & Algorithms: Effective use of data structures ( Arrays , LinkedList, Stack, Queue, Tree, Hashtable, etc.) and algorithms (Sorting, Searching, etc.) is fundamental in coding problem-solving. The correct choice and application of such tools can have a dramatic impact on a program’s performance.
Version Control: While writing code, you often need to try out different solutions or collaborate with other team members. Using version control systems , like Git, helps manage changes, track history, and merge code from different branches. This aids in solving and managing complex coding problems.
Apart from these fundamental techniques, advanced paradigms, such as Test-Driven Development (TDD), Behaviour Driven Development (BDD), etc., also exist. In TDD, the developer writes tests for a function before writing the actual function. In BDD, the behaviour of an application from the end user's perspective is the guiding force behind development. These paradigms incorporate problem-solving in their methodologies and guide the development process to create effective, robust applications.
Indeed, coding problem-solving techniques enrich a developer's toolkit and provide avenues to tackle the myriad of challenges that arise in programming. Whether it's minimising bugs, improving code efficiency, or implementing complex functionalities, these techniques are indispensable in daily coding endeavours.
In-depth study of 7 Problem-Solving Techniques
Problem-solving takes centre stage in the realm of computer science, where challenges need methodical approaches for efficient resolution. Let's delve into an in-depth exploration of seven such techniques, with each offering a unique perspective on how to tackle and solve issues effectively.
Conceptual understanding of the 7 problem-solving techniques
Within the realm of computer science, efficient problem-solving techniques can be the key to unlocking streamlined workflows, effective data handling, and improved coding management. These problem-solving methods include:
- Divide and Conquer: This technique splits larger problems into smaller, more manageable sub-problems, solves the sub-problems individually and combines the solutions to get a complete resolution. This technique is pertinent to a wide range of algorithms in computer science , including sorting and searching algorithms.
- Greedy Algorithms: Greedy algorithms solve problems by making the best choice at each step, with the hope that these local optimal solutions will lead to a globally optimal solution. They are often used in scenarios where the optimal solution has a 'greedy property', such as in the famous 'travelling salesman' problem.
- Backtracking : This technique incrementally builds candidates for the solutions and abandons a candidate as soon as it determines that this candidate cannot possibly be extended to a valid solution.
- Dynamic Programming: This method solves complex problems by breaking them down into simpler sub-problems, but unlike divide and conquer, these sub-problems are not solved independently. Instead, the results of sub-problems are stored and utilised to build up solutions to larger problems.
- Brute Force : This straightforward approach tries every possible solution until it finds the best one. The simplicity of this method often makes it a practical and easy-to-implement fallback plan, although it may not be the most efficient.
- Randomised Algorithms: For certain problems, deterministic algorithms may be too slow or complex, and the solution space too large to navigate exhaustively. In such cases, randomised algorithms offer an option where random choices drive the solution process. These algorithms have proven extremely efficient in problems like QuickSort and the Monte Carlo method.
- Heuristic Methods: Heuristics are problem-solving approaches that are not always guaranteed to provide the perfect solution but will produce a good solution in a reasonable time. Various AI and machine learning techniques, such as genetic algorithms or neural networks, heavily use heuristic methods.
A Greedy Algorithm is one where, at each step, the choice that looks the best at that moment is selected with the belief that this choice will lead to an optimal global solution.
Understanding the foundations of these techniques provides a comprehensive toolset to approach a wide array of problems in computer science. It's important to remember that a technique's effectiveness largely depends on the nature of the problem.
Uses of the 7 problem-solving techniques in Computer Science
Each problem-solving method can be coupled with different facets within computer science. For example, encryption techniques, compression algorithms, network routing strategies, and database searches all rely on precise problem-solving methodologies. Here are just a few of the potential uses for each method:
The flexibility and variety of these problem-solving techniques enable a far-reaching applicability across the vast landscape of computer science. By understanding and mastering these techniques, you can tackle a wide array of complex problems more efficiently.
Brainstorming Problem-Solving Techniques
In the context of problem-solving techniques, brainstorming is an invaluable tool. Brainstorming offers a creative, open-ended approach well-suited for troubleshooting challenges, stimulating new ideas, and tackling issues from fresh angles.
Role of brainstorming in problem-solving techniques
Brainstorming's emphasis on exploratory thinking and collaborative problem-solving makes it an excellent tool in computer science. This interactive technique encourages you to think outside the box, ushering a wealth of ideas and potential problem-solving approaches. Here's why brainstorming plays a pivotal role in problem-solving techniques:
- Encourages Creative Thinking: Brainstorming breaks down the barriers of conventional thought, promoting imaginative solutions that may not be immediately evident. This out-of-the-box thinking can generate unique problem-solving methods for complex computer science problems.
- Fosters Collaboration: Brainstorming is fundamentally a collective effort. By combining the expertise and viewpoints of multiple individuals, it can foster innovative problem-solving approaches that would not surface in isolated thinking.
- Aids in Problem Understanding: In the process of brainstorming, not only are solutions discussed, but the problem itself is dissected from different angles. This aids in gaining a deeper understanding of the problem, essential to uncover the most effective solutions.
Consider a team of developers brainstorming to develop a feature for a software application. One developer might suggest a direct approach that, although simple, may not be the most efficient. Another team member could propose a more complex, but efficient, algorithm for the feature. A third might contribute an innovative approach that balances both performance and simplicity.
Through this collective brainstorming, the team converges on the most well-rounded approach, emphasising the critical role that brainstorming plays in problem-solving methodologies.
Applying brainstorming in problem-solving techniques
Brainstorming is not just about generating as many ideas as possible; it's also about creating an organized framework for synthesizing and evaluating those ideas.
For effective brainstorming in problem-solving and decision-making techniques, you can follow the steps below:
- Define the Problem: Clearly understand and define the problem that needs solving. The more accurately the problem is described, the more targeted the brainstorming will be.
- Set Guidelines: Establish rules for the brainstorming session to keep it focused and productive. These might include encouraging free thinking, postponing judgment, welcoming wild ideas, building on other ideas, and setting a time limit.
- Idea Generation: Begin brainstorming, inviting everyone involved to share their ideas. The key is to promote creativity and diversity of thought. No idea is too outlandish; often, the most unconventional suggestions lead to the most innovative solutions.
- Categorise and Consolidate: Once all the ideas are documented, start to group related ideas together and consolidate overlapping ideas.
- Analyse and Evaluate: It's time to analyse each idea based on its feasibility, potential impact, and resource requirement. Ideas that might not appear effective initially can be valuable when combined with other ideas.
- Select and Implement: After thorough analysis and discussion, decide on the best solution(s) to implement, based on the resources and time available, instantly making the brainstorming session instrumental in decision making as well.
Remember: Brainstorming is not just a one-time activity. It can and should be done iteratively. Often, implementation of an idea will bring forward new challenges, requiring another round of brainstorming. The strength of brainstorming lies in its fluid nature, allowing it to adapt and iterate until the problem at hand is fully resolved.
All in all, brainstorming is a powerful problem-solving and decision-making technique in computer science. By cultivating creativity, encouraging collaboration, and fostering a deeper understanding of problems, it holds the potential to tackle complex issues effectively.
Problem Solving and Decision Making Techniques
In computer science, problem-solving and decision-making form the core techniques widely employed in managing software development, debugging, data analysis, network operations, and more. Incorporating these methodologies in a concerted, structured manner can significantly enhance the outcomes in various fields of technology.

Difference between problem-solving and decision-making techniques
While it might appear that problem-solving and decision-making are interchangeable terms, they signify distinct aspects of addressing challenges in computer science.
- Problem-solving: Within a computer science context, problem-solving involves identifying an issue within a system, application, or theory and resolving it effectively. This process often includes defining the problem, identifying root causes, generating alternative solutions, selecting a solution, and implementing it. Problem-solving often utilises techniques like debugging, algorithmic design, divide and conquer, dynamic programming, recursive thinking, heuristic methods, and more.
- Decision-making: Decision-making, on the other hand, is a process of choosing between different alternatives. It often follows problem-solving whereby, after identifying potential solutions to a problem, the best option needs to be chosen. Decision-making techniques might include tools like decision matrices, cost-benefit analyses, or simple pros-and-cons lists. In computer science, decision-making can involve choosing the right data structure, deciding which algorithm to use, or selecting a coding methodology.
For instance, problem-solving might involve identifying a bottleneck in a software's performance and brainstorming different ways to enhance the efficiency. However, decision-making comes into play when you need to choose one of the generated solutions based on various factors like resource availability, time constraints, the impact of the solution, etc. Thus, while both techniques cater to overcoming challenges, problem-solving is more focused on creating solutions, whereas decision-making prioritises choosing the most optimal one from these solutions.
Combining problem-solving and decision-making for effective results
Effective results in computer science often stem from an amalgamation of both problem-solving and decision-making techniques. Combining these approaches ensures a comprehensive solution to challenges, complete with a thorough understanding of the problem, an array of possible solutions, and a well-thought-out decision on implementing the best solution.
Consider a situation where a computer system is repeatedly encountering a fatal error. Here's how problem-solving and decision-making techniques can be combined for effective results:
- Identification: Firstly, identify the issue affecting the system. This could be established through system monitoring tools or error logs. Once the problem is identified, it sets the base for problem-solving.
- Problem-Solving: Now, brainstorm for possible solutions to rectify the error. This could involve debugging the system or reviewing the code to find potential bugs. Perhaps the issue might be a memory leak that needs addressing or a race condition in multi-threaded operations. These solutions emanate from problem-solving techniques.
- Decision-Making: Once a list of possible solutions is generated, use decision-making techniques to select the best course of action. You could create a pros-and-cons list for each solution or use a more formal decision matrix to evaluate effectiveness, resources required, impact on system performance, etc. Finally, implement the solution.
- Review: After implementation, monitor the system to ensure the solution is working as intended. If the problem persists, the process returns to the problem-solving stage to revisit the issue and generate new solutions.
It's important to keep in mind that real-word scenarios seldom follow a tidy linear sequence. More commonly, problem-solving and decision-making are iterative, cyclical processes that overlap and interrelate. It's a dynamic environment where a bottleneck can stimulate new decision-making criteria, or an unforeseen decisional deadlock might call for fresh problem-solving ideas.
Combining problem-solving with decision-making offers a structured, strategic approach to tackle challenges commonly found in computer science. This conjunction of techniques provides a robust, versatile methodology to drive effective results across the diverse landscape of technology.
Problem Solving Techniques - Key takeaways
- Problem-solving techniques in Computer Science are techniques which typically use algorithmic or heuristic approaches to resolve complex issues.
- Problem-solving techniques can be systematic, analytical, or intuitive, and involve traditional programming, machine learning, or artificial intelligence methods. Applied in domains such as data analysis, software development, network troubleshooting, and cybersecurity.
- Basic problem-solving techniques comprises of methods like divide and conquer, algorithm design, heuristics, and recursive thinking, all aimed at understanding and tackling problems.
- Practical applications of basic problem-solving techniques include applications spanning across various sectors of computer science, including sorting and searching algorithms, routing protocols for networks, AI game playing, and parsing syntax trees in compilers.
- Examples of coding problem-solving techniques include Debugging which is essential in identifying and rectifying coding errors, Code Refactoring to improve the structure of existing code without changing its functionality, Using Data Structures & Algorithms to have a dramatic impact on a program’s performance, and Version Control System like Git for managing changes, tracking history and merging code from different branches.
Frequently Asked Questions about Problem Solving Techniques
--> what are some problem-solving techniques.
Some common problem solving techniques include brainstorming, the five whys technique, root cause analysis, lateral thinking, striving for simplicity, the 6 thinking hats and using flow charts or diagrams. Additionally, techniques such as SWOT analysis, Trial and Error, and Decision Trees can also be effective tools in problem-solving. Each technique is employed based on the nature and context of the problem to be solved. It's crucial to understand the problem fully before choosing a technique to apply.
--> What are the four problem-solving techniques?
The four problem solving techniques are:
1) Defining the problem clearly to understand its nature and scope
2) Generating a range of potential solutions through brainstorming or creative thinking
3) Evaluating and selecting the most feasible solutions by analysing their pros and cons
4) Implementing the chosen solution and monitoring its effectiveness.
--> How to apply problem-solving techniques?
To apply problem solving techniques, you first need to clearly identify and define the problem. Next, gather as much information as you can related to the problem. Once you have all the details, generate a range of potential solutions and evaluate each for its merits and downsides. Finally, implement the best solution and review its effectiveness, making adjustments as necessary.
--> What are the different problem solving techniques?
Different problem solving techniques include brainstorming, lateral thinking, root cause analysis, the five whys technique, mind mapping, SWOT analysis, "divide and conquer" technique and use of algorithms or heuristics. Additionally, the use of decision trees, fishbone diagrams, and PEST & STEEPLE analysis are also widely used in strategic problem solving. All these techniques help in breaking down complex problems into manageable parts and finding effective solutions. The choice of technique may vary depending on the nature and complexity of the problem.
--> How to choose problem-solving techniques?
Choosing problem-solving techniques involves understanding the nature and scope of the problem, identifying all potential methods for resolution, and then carefully evaluating each one in terms of its appropriateness, feasibility, and probable effectiveness, selecting the most promising one. Take into consideration multidisciplinary insights, and factor in resources available, time constraints, and potential risks. It can also be useful to bring in outside perspectives or utilise brainstorming techniques. The chosen method should ideally be both effective and efficient in resolving the problem at hand.
Test your knowledge with multiple choice flashcards
What are problem-solving techniques in computer science?
Why are problem-solving techniques important in computer science?
What is the 'Divide and Conquer' problem-solving technique in computer science?
Your score:

Join the StudySmarter App and learn efficiently with millions of flashcards and more!
Learn with 404 problem solving techniques flashcards in the free studysmarter app.
Already have an account? Log in
Problem-solving techniques in computer science refer to the methods used to find solutions to complex issues using algorithmic or heuristic approaches, which can be systematic, analytical, or intuitive. They encompass traditional programming, machine learning, or artificial intelligence methods.
Problem-solving techniques in computer science are important for mitigating runtime errors and system crashes, optimizing software, organizing, evaluating, and interpreting complex datasets, and identifying potential cybersecurity vulnerabilities and patching them.
What is the 'Divide and Conquer' problem-solving technique in computer science?
The 'Divide and Conquer' technique involves breaking a larger problem into smaller, more manageable parts, solving each individually, and combining their solutions to get the overall answer. This is often used in sorting algorithms like Merge Sort.
What is the purpose of the 'Heuristics' problem-solving technique?
'Heuristics' are educated guesses that can help find an acceptable solution when the problem is too complex for a direct mathematical approach, or when computational resources are limited. They are often used in AI and language translations.
What are some of the important functions of coding problem-solving techniques in computer science?
Coding problem-solving techniques aid in enhancing code efficiency, mitigating errors, facilitating code readability and maintenance, and implementing complex functionalities.
What are some examples of coding problem-solving techniques?
Examples include debugging, code refactoring, using appropriate data structures and algorithms, and implementing version control.

of the users don't pass the Problem Solving Techniques quiz! Will you pass the quiz?
How would you like to learn this content?
Free computer-science cheat sheet!
Everything you need to know on . A perfect summary so you can easily remember everything.
Join over 22 million students in learning with our StudySmarter App
The first learning app that truly has everything you need to ace your exams in one place
- Flashcards & Quizzes
- AI Study Assistant
- Smart Note-Taking

Sign up to highlight and take notes. It’s 100% free.
This is still free to read, it's not a paywall.
You need to register to keep reading, create a free account to save this explanation..
Save explanations to your personalised space and access them anytime, anywhere!
By signing up, you agree to the Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy of StudySmarter.
Entdecke Lernmaterial in der StudySmarter-App

Privacy Overview
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Overview of the Problem-Solving Mental Process
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Rachel Goldman, PhD FTOS, is a licensed psychologist, clinical assistant professor, speaker, wellness expert specializing in eating behaviors, stress management, and health behavior change.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Rachel-Goldman-1000-a42451caacb6423abecbe6b74e628042.jpg)
- Identify the Problem
- Define the Problem
- Form a Strategy
- Organize Information
- Allocate Resources
- Monitor Progress
- Evaluate the Results
Frequently Asked Questions
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue.
The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything they can about the issue and then using factual knowledge to come up with a solution. In other instances, creativity and insight are the best options.
It is not necessary to follow problem-solving steps sequentially, It is common to skip steps or even go back through steps multiple times until the desired solution is reached.
In order to correctly solve a problem, it is often important to follow a series of steps. Researchers sometimes refer to this as the problem-solving cycle. While this cycle is portrayed sequentially, people rarely follow a rigid series of steps to find a solution.
The following steps include developing strategies and organizing knowledge.
1. Identifying the Problem
While it may seem like an obvious step, identifying the problem is not always as simple as it sounds. In some cases, people might mistakenly identify the wrong source of a problem, which will make attempts to solve it inefficient or even useless.
Some strategies that you might use to figure out the source of a problem include :
- Asking questions about the problem
- Breaking the problem down into smaller pieces
- Looking at the problem from different perspectives
- Conducting research to figure out what relationships exist between different variables
2. Defining the Problem
After the problem has been identified, it is important to fully define the problem so that it can be solved. You can define a problem by operationally defining each aspect of the problem and setting goals for what aspects of the problem you will address
At this point, you should focus on figuring out which aspects of the problems are facts and which are opinions. State the problem clearly and identify the scope of the solution.
3. Forming a Strategy
After the problem has been identified, it is time to start brainstorming potential solutions. This step usually involves generating as many ideas as possible without judging their quality. Once several possibilities have been generated, they can be evaluated and narrowed down.
The next step is to develop a strategy to solve the problem. The approach used will vary depending upon the situation and the individual's unique preferences. Common problem-solving strategies include heuristics and algorithms.
- Heuristics are mental shortcuts that are often based on solutions that have worked in the past. They can work well if the problem is similar to something you have encountered before and are often the best choice if you need a fast solution.
- Algorithms are step-by-step strategies that are guaranteed to produce a correct result. While this approach is great for accuracy, it can also consume time and resources.
Heuristics are often best used when time is of the essence, while algorithms are a better choice when a decision needs to be as accurate as possible.
4. Organizing Information
Before coming up with a solution, you need to first organize the available information. What do you know about the problem? What do you not know? The more information that is available the better prepared you will be to come up with an accurate solution.
When approaching a problem, it is important to make sure that you have all the data you need. Making a decision without adequate information can lead to biased or inaccurate results.
5. Allocating Resources
Of course, we don't always have unlimited money, time, and other resources to solve a problem. Before you begin to solve a problem, you need to determine how high priority it is.
If it is an important problem, it is probably worth allocating more resources to solving it. If, however, it is a fairly unimportant problem, then you do not want to spend too much of your available resources on coming up with a solution.
At this stage, it is important to consider all of the factors that might affect the problem at hand. This includes looking at the available resources, deadlines that need to be met, and any possible risks involved in each solution. After careful evaluation, a decision can be made about which solution to pursue.
6. Monitoring Progress
After selecting a problem-solving strategy, it is time to put the plan into action and see if it works. This step might involve trying out different solutions to see which one is the most effective.
It is also important to monitor the situation after implementing a solution to ensure that the problem has been solved and that no new problems have arisen as a result of the proposed solution.
Effective problem-solvers tend to monitor their progress as they work towards a solution. If they are not making good progress toward reaching their goal, they will reevaluate their approach or look for new strategies .
7. Evaluating the Results
After a solution has been reached, it is important to evaluate the results to determine if it is the best possible solution to the problem. This evaluation might be immediate, such as checking the results of a math problem to ensure the answer is correct, or it can be delayed, such as evaluating the success of a therapy program after several months of treatment.
Once a problem has been solved, it is important to take some time to reflect on the process that was used and evaluate the results. This will help you to improve your problem-solving skills and become more efficient at solving future problems.
A Word From Verywell
It is important to remember that there are many different problem-solving processes with different steps, and this is just one example. Problem-solving in real-world situations requires a great deal of resourcefulness, flexibility, resilience, and continuous interaction with the environment.
Get Advice From The Verywell Mind Podcast
Hosted by therapist Amy Morin, LCSW, this episode of The Verywell Mind Podcast shares how you can stop dwelling in a negative mindset.
Follow Now : Apple Podcasts / Spotify / Google Podcasts
You can become a better problem solving by:
- Practicing brainstorming and coming up with multiple potential solutions to problems
- Being open-minded and considering all possible options before making a decision
- Breaking down problems into smaller, more manageable pieces
- Asking for help when needed
- Researching different problem-solving techniques and trying out new ones
- Learning from mistakes and using them as opportunities to grow
It's important to communicate openly and honestly with your partner about what's going on. Try to see things from their perspective as well as your own. Work together to find a resolution that works for both of you. Be willing to compromise and accept that there may not be a perfect solution.
Take breaks if things are getting too heated, and come back to the problem when you feel calm and collected. Don't try to fix every problem on your own—consider asking a therapist or counselor for help and insight.
If you've tried everything and there doesn't seem to be a way to fix the problem, you may have to learn to accept it. This can be difficult, but try to focus on the positive aspects of your life and remember that every situation is temporary. Don't dwell on what's going wrong—instead, think about what's going right. Find support by talking to friends or family. Seek professional help if you're having trouble coping.
Davidson JE, Sternberg RJ, editors. The Psychology of Problem Solving . Cambridge University Press; 2003. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511615771
Sarathy V. Real world problem-solving . Front Hum Neurosci . 2018;12:261. Published 2018 Jun 26. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
35 problem-solving techniques and methods for solving complex problems

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation.
All teams and organizations encounter challenges as they grow. There are problems that might occur for teams when it comes to miscommunication or resolving business-critical issues . You may face challenges around growth , design , user engagement, and even team culture and happiness. In short, problem-solving techniques should be part of every team’s skillset.
Problem-solving methods are primarily designed to help a group or team through a process of first identifying problems and challenges , ideating possible solutions , and then evaluating the most suitable .
Finding effective solutions to complex problems isn’t easy, but by using the right process and techniques, you can help your team be more efficient in the process.
So how do you develop strategies that are engaging, and empower your team to solve problems effectively?
In this blog post, we share a series of problem-solving tools you can use in your next workshop or team meeting. You’ll also find some tips for facilitating the process and how to enable others to solve complex problems.
Let’s get started!
How do you identify problems?
How do you identify the right solution.
- Tips for more effective problem-solving
Complete problem-solving methods
- Problem-solving techniques to identify and analyze problems
- Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
Problem-solving warm-up activities
Closing activities for a problem-solving process.
Before you can move towards finding the right solution for a given problem, you first need to identify and define the problem you wish to solve.
Here, you want to clearly articulate what the problem is and allow your group to do the same. Remember that everyone in a group is likely to have differing perspectives and alignment is necessary in order to help the group move forward.
Identifying a problem accurately also requires that all members of a group are able to contribute their views in an open and safe manner. It can be scary for people to stand up and contribute, especially if the problems or challenges are emotive or personal in nature. Be sure to try and create a psychologically safe space for these kinds of discussions.
Remember that problem analysis and further discussion are also important. Not taking the time to fully analyze and discuss a challenge can result in the development of solutions that are not fit for purpose or do not address the underlying issue.
Successfully identifying and then analyzing a problem means facilitating a group through activities designed to help them clearly and honestly articulate their thoughts and produce usable insight.
With this data, you might then produce a problem statement that clearly describes the problem you wish to be addressed and also state the goal of any process you undertake to tackle this issue.
Finding solutions is the end goal of any process. Complex organizational challenges can only be solved with an appropriate solution but discovering them requires using the right problem-solving tool.
After you’ve explored a problem and discussed ideas, you need to help a team discuss and choose the right solution. Consensus tools and methods such as those below help a group explore possible solutions before then voting for the best. They’re a great way to tap into the collective intelligence of the group for great results!
Remember that the process is often iterative. Great problem solvers often roadtest a viable solution in a measured way to see what works too. While you might not get the right solution on your first try, the methods below help teams land on the most likely to succeed solution while also holding space for improvement.
Every effective problem solving process begins with an agenda . A well-structured workshop is one of the best methods for successfully guiding a group from exploring a problem to implementing a solution.
In SessionLab, it’s easy to go from an idea to a complete agenda . Start by dragging and dropping your core problem solving activities into place . Add timings, breaks and necessary materials before sharing your agenda with your colleagues.
The resulting agenda will be your guide to an effective and productive problem solving session that will also help you stay organized on the day!
Tips for more effective problem solving
Problem-solving activities are only one part of the puzzle. While a great method can help unlock your team’s ability to solve problems, without a thoughtful approach and strong facilitation the solutions may not be fit for purpose.
Let’s take a look at some problem-solving tips you can apply to any process to help it be a success!
Clearly define the problem
Jumping straight to solutions can be tempting, though without first clearly articulating a problem, the solution might not be the right one. Many of the problem-solving activities below include sections where the problem is explored and clearly defined before moving on.
This is a vital part of the problem-solving process and taking the time to fully define an issue can save time and effort later. A clear definition helps identify irrelevant information and it also ensures that your team sets off on the right track.
Don’t jump to conclusions
It’s easy for groups to exhibit cognitive bias or have preconceived ideas about both problems and potential solutions. Be sure to back up any problem statements or potential solutions with facts, research, and adequate forethought.
The best techniques ask participants to be methodical and challenge preconceived notions. Make sure you give the group enough time and space to collect relevant information and consider the problem in a new way. By approaching the process with a clear, rational mindset, you’ll often find that better solutions are more forthcoming.
Try different approaches
Problems come in all shapes and sizes and so too should the methods you use to solve them. If you find that one approach isn’t yielding results and your team isn’t finding different solutions, try mixing it up. You’ll be surprised at how using a new creative activity can unblock your team and generate great solutions.
Don’t take it personally
Depending on the nature of your team or organizational problems, it’s easy for conversations to get heated. While it’s good for participants to be engaged in the discussions, ensure that emotions don’t run too high and that blame isn’t thrown around while finding solutions.
You’re all in it together, and even if your team or area is seeing problems, that isn’t necessarily a disparagement of you personally. Using facilitation skills to manage group dynamics is one effective method of helping conversations be more constructive.
Get the right people in the room
Your problem-solving method is often only as effective as the group using it. Getting the right people on the job and managing the number of people present is important too!
If the group is too small, you may not get enough different perspectives to effectively solve a problem. If the group is too large, you can go round and round during the ideation stages.
Creating the right group makeup is also important in ensuring you have the necessary expertise and skillset to both identify and follow up on potential solutions. Carefully consider who to include at each stage to help ensure your problem-solving method is followed and positioned for success.
Document everything
The best solutions can take refinement, iteration, and reflection to come out. Get into a habit of documenting your process in order to keep all the learnings from the session and to allow ideas to mature and develop. Many of the methods below involve the creation of documents or shared resources. Be sure to keep and share these so everyone can benefit from the work done!
Bring a facilitator
Facilitation is all about making group processes easier. With a subject as potentially emotive and important as problem-solving, having an impartial third party in the form of a facilitator can make all the difference in finding great solutions and keeping the process moving. Consider bringing a facilitator to your problem-solving session to get better results and generate meaningful solutions!
Develop your problem-solving skills
It takes time and practice to be an effective problem solver. While some roles or participants might more naturally gravitate towards problem-solving, it can take development and planning to help everyone create better solutions.
You might develop a training program, run a problem-solving workshop or simply ask your team to practice using the techniques below. Check out our post on problem-solving skills to see how you and your group can develop the right mental process and be more resilient to issues too!
Design a great agenda
Workshops are a great format for solving problems. With the right approach, you can focus a group and help them find the solutions to their own problems. But designing a process can be time-consuming and finding the right activities can be difficult.
Check out our workshop planning guide to level-up your agenda design and start running more effective workshops. Need inspiration? Check out templates designed by expert facilitators to help you kickstart your process!
In this section, we’ll look at in-depth problem-solving methods that provide a complete end-to-end process for developing effective solutions. These will help guide your team from the discovery and definition of a problem through to delivering the right solution.
If you’re looking for an all-encompassing method or problem-solving model, these processes are a great place to start. They’ll ask your team to challenge preconceived ideas and adopt a mindset for solving problems more effectively.
- Six Thinking Hats
- Lightning Decision Jam
- Problem Definition Process
- Discovery & Action Dialogue
Design Sprint 2.0
- Open Space Technology
1. Six Thinking Hats
Individual approaches to solving a problem can be very different based on what team or role an individual holds. It can be easy for existing biases or perspectives to find their way into the mix, or for internal politics to direct a conversation.
Six Thinking Hats is a classic method for identifying the problems that need to be solved and enables your team to consider them from different angles, whether that is by focusing on facts and data, creative solutions, or by considering why a particular solution might not work.
Like all problem-solving frameworks, Six Thinking Hats is effective at helping teams remove roadblocks from a conversation or discussion and come to terms with all the aspects necessary to solve complex problems.
2. Lightning Decision Jam
Featured courtesy of Jonathan Courtney of AJ&Smart Berlin, Lightning Decision Jam is one of those strategies that should be in every facilitation toolbox. Exploring problems and finding solutions is often creative in nature, though as with any creative process, there is the potential to lose focus and get lost.
Unstructured discussions might get you there in the end, but it’s much more effective to use a method that creates a clear process and team focus.
In Lightning Decision Jam, participants are invited to begin by writing challenges, concerns, or mistakes on post-its without discussing them before then being invited by the moderator to present them to the group.
From there, the team vote on which problems to solve and are guided through steps that will allow them to reframe those problems, create solutions and then decide what to execute on.
By deciding the problems that need to be solved as a team before moving on, this group process is great for ensuring the whole team is aligned and can take ownership over the next stages.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
3. Problem Definition Process
While problems can be complex, the problem-solving methods you use to identify and solve those problems can often be simple in design.
By taking the time to truly identify and define a problem before asking the group to reframe the challenge as an opportunity, this method is a great way to enable change.
Begin by identifying a focus question and exploring the ways in which it manifests before splitting into five teams who will each consider the problem using a different method: escape, reversal, exaggeration, distortion or wishful. Teams develop a problem objective and create ideas in line with their method before then feeding them back to the group.
This method is great for enabling in-depth discussions while also creating space for finding creative solutions too!
Problem Definition #problem solving #idea generation #creativity #online #remote-friendly A problem solving technique to define a problem, challenge or opportunity and to generate ideas.
4. The 5 Whys
Sometimes, a group needs to go further with their strategies and analyze the root cause at the heart of organizational issues. An RCA or root cause analysis is the process of identifying what is at the heart of business problems or recurring challenges.
The 5 Whys is a simple and effective method of helping a group go find the root cause of any problem or challenge and conduct analysis that will deliver results.
By beginning with the creation of a problem statement and going through five stages to refine it, The 5 Whys provides everything you need to truly discover the cause of an issue.
The 5 Whys #hyperisland #innovation This simple and powerful method is useful for getting to the core of a problem or challenge. As the title suggests, the group defines a problems, then asks the question “why” five times, often using the resulting explanation as a starting point for creative problem solving.
5. World Cafe
World Cafe is a simple but powerful facilitation technique to help bigger groups to focus their energy and attention on solving complex problems.
World Cafe enables this approach by creating a relaxed atmosphere where participants are able to self-organize and explore topics relevant and important to them which are themed around a central problem-solving purpose. Create the right atmosphere by modeling your space after a cafe and after guiding the group through the method, let them take the lead!
Making problem-solving a part of your organization’s culture in the long term can be a difficult undertaking. More approachable formats like World Cafe can be especially effective in bringing people unfamiliar with workshops into the fold.
World Cafe #hyperisland #innovation #issue analysis World Café is a simple yet powerful method, originated by Juanita Brown, for enabling meaningful conversations driven completely by participants and the topics that are relevant and important to them. Facilitators create a cafe-style space and provide simple guidelines. Participants then self-organize and explore a set of relevant topics or questions for conversation.
6. Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD)
One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions.
With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so. It’s great at helping remove resistance to change and can help get buy-in at every level too!
This process of enabling frontline ownership is great in ensuring follow-through and is one of the methods you will want in your toolbox as a facilitator.
Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) #idea generation #liberating structures #action #issue analysis #remote-friendly DADs make it easy for a group or community to discover practices and behaviors that enable some individuals (without access to special resources and facing the same constraints) to find better solutions than their peers to common problems. These are called positive deviant (PD) behaviors and practices. DADs make it possible for people in the group, unit, or community to discover by themselves these PD practices. DADs also create favorable conditions for stimulating participants’ creativity in spaces where they can feel safe to invent new and more effective practices. Resistance to change evaporates as participants are unleashed to choose freely which practices they will adopt or try and which problems they will tackle. DADs make it possible to achieve frontline ownership of solutions.
7. Design Sprint 2.0
Want to see how a team can solve big problems and move forward with prototyping and testing solutions in a few days? The Design Sprint 2.0 template from Jake Knapp, author of Sprint, is a complete agenda for a with proven results.
Developing the right agenda can involve difficult but necessary planning. Ensuring all the correct steps are followed can also be stressful or time-consuming depending on your level of experience.
Use this complete 4-day workshop template if you are finding there is no obvious solution to your challenge and want to focus your team around a specific problem that might require a shortcut to launching a minimum viable product or waiting for the organization-wide implementation of a solution.
8. Open space technology
Open space technology- developed by Harrison Owen – creates a space where large groups are invited to take ownership of their problem solving and lead individual sessions. Open space technology is a great format when you have a great deal of expertise and insight in the room and want to allow for different takes and approaches on a particular theme or problem you need to be solved.
Start by bringing your participants together to align around a central theme and focus their efforts. Explain the ground rules to help guide the problem-solving process and then invite members to identify any issue connecting to the central theme that they are interested in and are prepared to take responsibility for.
Once participants have decided on their approach to the core theme, they write their issue on a piece of paper, announce it to the group, pick a session time and place, and post the paper on the wall. As the wall fills up with sessions, the group is then invited to join the sessions that interest them the most and which they can contribute to, then you’re ready to begin!
Everyone joins the problem-solving group they’ve signed up to, record the discussion and if appropriate, findings can then be shared with the rest of the group afterward.
Open Space Technology #action plan #idea generation #problem solving #issue analysis #large group #online #remote-friendly Open Space is a methodology for large groups to create their agenda discerning important topics for discussion, suitable for conferences, community gatherings and whole system facilitation
Techniques to identify and analyze problems
Using a problem-solving method to help a team identify and analyze a problem can be a quick and effective addition to any workshop or meeting.
While further actions are always necessary, you can generate momentum and alignment easily, and these activities are a great place to get started.
We’ve put together this list of techniques to help you and your team with problem identification, analysis, and discussion that sets the foundation for developing effective solutions.
Let’s take a look!
- The Creativity Dice
- Fishbone Analysis
- Problem Tree
- SWOT Analysis
- Agreement-Certainty Matrix
- The Journalistic Six
- LEGO Challenge
- What, So What, Now What?
- Journalists
Individual and group perspectives are incredibly important, but what happens if people are set in their minds and need a change of perspective in order to approach a problem more effectively?
Flip It is a method we love because it is both simple to understand and run, and allows groups to understand how their perspectives and biases are formed.
Participants in Flip It are first invited to consider concerns, issues, or problems from a perspective of fear and write them on a flip chart. Then, the group is asked to consider those same issues from a perspective of hope and flip their understanding.
No problem and solution is free from existing bias and by changing perspectives with Flip It, you can then develop a problem solving model quickly and effectively.
Flip It! #gamestorming #problem solving #action Often, a change in a problem or situation comes simply from a change in our perspectives. Flip It! is a quick game designed to show players that perspectives are made, not born.
10. The Creativity Dice
One of the most useful problem solving skills you can teach your team is of approaching challenges with creativity, flexibility, and openness. Games like The Creativity Dice allow teams to overcome the potential hurdle of too much linear thinking and approach the process with a sense of fun and speed.
In The Creativity Dice, participants are organized around a topic and roll a dice to determine what they will work on for a period of 3 minutes at a time. They might roll a 3 and work on investigating factual information on the chosen topic. They might roll a 1 and work on identifying the specific goals, standards, or criteria for the session.
Encouraging rapid work and iteration while asking participants to be flexible are great skills to cultivate. Having a stage for idea incubation in this game is also important. Moments of pause can help ensure the ideas that are put forward are the most suitable.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
11. Fishbone Analysis
Organizational or team challenges are rarely simple, and it’s important to remember that one problem can be an indication of something that goes deeper and may require further consideration to be solved.
Fishbone Analysis helps groups to dig deeper and understand the origins of a problem. It’s a great example of a root cause analysis method that is simple for everyone on a team to get their head around.
Participants in this activity are asked to annotate a diagram of a fish, first adding the problem or issue to be worked on at the head of a fish before then brainstorming the root causes of the problem and adding them as bones on the fish.
Using abstractions such as a diagram of a fish can really help a team break out of their regular thinking and develop a creative approach.
Fishbone Analysis #problem solving ##root cause analysis #decision making #online facilitation A process to help identify and understand the origins of problems, issues or observations.
12. Problem Tree
Encouraging visual thinking can be an essential part of many strategies. By simply reframing and clarifying problems, a group can move towards developing a problem solving model that works for them.
In Problem Tree, groups are asked to first brainstorm a list of problems – these can be design problems, team problems or larger business problems – and then organize them into a hierarchy. The hierarchy could be from most important to least important or abstract to practical, though the key thing with problem solving games that involve this aspect is that your group has some way of managing and sorting all the issues that are raised.
Once you have a list of problems that need to be solved and have organized them accordingly, you’re then well-positioned for the next problem solving steps.
Problem tree #define intentions #create #design #issue analysis A problem tree is a tool to clarify the hierarchy of problems addressed by the team within a design project; it represents high level problems or related sublevel problems.
13. SWOT Analysis
Chances are you’ve heard of the SWOT Analysis before. This problem-solving method focuses on identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is a tried and tested method for both individuals and teams.
Start by creating a desired end state or outcome and bare this in mind – any process solving model is made more effective by knowing what you are moving towards. Create a quadrant made up of the four categories of a SWOT analysis and ask participants to generate ideas based on each of those quadrants.
Once you have those ideas assembled in their quadrants, cluster them together based on their affinity with other ideas. These clusters are then used to facilitate group conversations and move things forward.
SWOT analysis #gamestorming #problem solving #action #meeting facilitation The SWOT Analysis is a long-standing technique of looking at what we have, with respect to the desired end state, as well as what we could improve on. It gives us an opportunity to gauge approaching opportunities and dangers, and assess the seriousness of the conditions that affect our future. When we understand those conditions, we can influence what comes next.
14. Agreement-Certainty Matrix
Not every problem-solving approach is right for every challenge, and deciding on the right method for the challenge at hand is a key part of being an effective team.
The Agreement Certainty matrix helps teams align on the nature of the challenges facing them. By sorting problems from simple to chaotic, your team can understand what methods are suitable for each problem and what they can do to ensure effective results.
If you are already using Liberating Structures techniques as part of your problem-solving strategy, the Agreement-Certainty Matrix can be an invaluable addition to your process. We’ve found it particularly if you are having issues with recurring problems in your organization and want to go deeper in understanding the root cause.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Organizing and charting a team’s progress can be important in ensuring its success. SQUID (Sequential Question and Insight Diagram) is a great model that allows a team to effectively switch between giving questions and answers and develop the skills they need to stay on track throughout the process.
Begin with two different colored sticky notes – one for questions and one for answers – and with your central topic (the head of the squid) on the board. Ask the group to first come up with a series of questions connected to their best guess of how to approach the topic. Ask the group to come up with answers to those questions, fix them to the board and connect them with a line. After some discussion, go back to question mode by responding to the generated answers or other points on the board.
It’s rewarding to see a diagram grow throughout the exercise, and a completed SQUID can provide a visual resource for future effort and as an example for other teams.
SQUID #gamestorming #project planning #issue analysis #problem solving When exploring an information space, it’s important for a group to know where they are at any given time. By using SQUID, a group charts out the territory as they go and can navigate accordingly. SQUID stands for Sequential Question and Insight Diagram.
16. Speed Boat
To continue with our nautical theme, Speed Boat is a short and sweet activity that can help a team quickly identify what employees, clients or service users might have a problem with and analyze what might be standing in the way of achieving a solution.
Methods that allow for a group to make observations, have insights and obtain those eureka moments quickly are invaluable when trying to solve complex problems.
In Speed Boat, the approach is to first consider what anchors and challenges might be holding an organization (or boat) back. Bonus points if you are able to identify any sharks in the water and develop ideas that can also deal with competitors!
Speed Boat #gamestorming #problem solving #action Speedboat is a short and sweet way to identify what your employees or clients don’t like about your product/service or what’s standing in the way of a desired goal.
17. The Journalistic Six
Some of the most effective ways of solving problems is by encouraging teams to be more inclusive and diverse in their thinking.
Based on the six key questions journalism students are taught to answer in articles and news stories, The Journalistic Six helps create teams to see the whole picture. By using who, what, when, where, why, and how to facilitate the conversation and encourage creative thinking, your team can make sure that the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the are covered exhaustively and thoughtfully. Reporter’s notebook and dictaphone optional.
The Journalistic Six – Who What When Where Why How #idea generation #issue analysis #problem solving #online #creative thinking #remote-friendly A questioning method for generating, explaining, investigating ideas.
18. LEGO Challenge
Now for an activity that is a little out of the (toy) box. LEGO Serious Play is a facilitation methodology that can be used to improve creative thinking and problem-solving skills.
The LEGO Challenge includes giving each member of the team an assignment that is hidden from the rest of the group while they create a structure without speaking.
What the LEGO challenge brings to the table is a fun working example of working with stakeholders who might not be on the same page to solve problems. Also, it’s LEGO! Who doesn’t love LEGO!
LEGO Challenge #hyperisland #team A team-building activity in which groups must work together to build a structure out of LEGO, but each individual has a secret “assignment” which makes the collaborative process more challenging. It emphasizes group communication, leadership dynamics, conflict, cooperation, patience and problem solving strategy.
19. What, So What, Now What?
If not carefully managed, the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the problem-solving process can actually create more problems and misunderstandings.
The What, So What, Now What? problem-solving activity is designed to help collect insights and move forward while also eliminating the possibility of disagreement when it comes to identifying, clarifying, and analyzing organizational or work problems.
Facilitation is all about bringing groups together so that might work on a shared goal and the best problem-solving strategies ensure that teams are aligned in purpose, if not initially in opinion or insight.
Throughout the three steps of this game, you give everyone on a team to reflect on a problem by asking what happened, why it is important, and what actions should then be taken.
This can be a great activity for bringing our individual perceptions about a problem or challenge and contextualizing it in a larger group setting. This is one of the most important problem-solving skills you can bring to your organization.
W³ – What, So What, Now What? #issue analysis #innovation #liberating structures You can help groups reflect on a shared experience in a way that builds understanding and spurs coordinated action while avoiding unproductive conflict. It is possible for every voice to be heard while simultaneously sifting for insights and shaping new direction. Progressing in stages makes this practical—from collecting facts about What Happened to making sense of these facts with So What and finally to what actions logically follow with Now What . The shared progression eliminates most of the misunderstandings that otherwise fuel disagreements about what to do. Voila!
20. Journalists
Problem analysis can be one of the most important and decisive stages of all problem-solving tools. Sometimes, a team can become bogged down in the details and are unable to move forward.
Journalists is an activity that can avoid a group from getting stuck in the problem identification or problem analysis stages of the process.
In Journalists, the group is invited to draft the front page of a fictional newspaper and figure out what stories deserve to be on the cover and what headlines those stories will have. By reframing how your problems and challenges are approached, you can help a team move productively through the process and be better prepared for the steps to follow.
Journalists #vision #big picture #issue analysis #remote-friendly This is an exercise to use when the group gets stuck in details and struggles to see the big picture. Also good for defining a vision.
Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
The success of any problem-solving process can be measured by the solutions it produces. After you’ve defined the issue, explored existing ideas, and ideated, it’s time to narrow down to the correct solution.
Use these problem-solving techniques when you want to help your team find consensus, compare possible solutions, and move towards taking action on a particular problem.
- Improved Solutions
- Four-Step Sketch
- 15% Solutions
- How-Now-Wow matrix
- Impact Effort Matrix
21. Mindspin
Brainstorming is part of the bread and butter of the problem-solving process and all problem-solving strategies benefit from getting ideas out and challenging a team to generate solutions quickly.
With Mindspin, participants are encouraged not only to generate ideas but to do so under time constraints and by slamming down cards and passing them on. By doing multiple rounds, your team can begin with a free generation of possible solutions before moving on to developing those solutions and encouraging further ideation.
This is one of our favorite problem-solving activities and can be great for keeping the energy up throughout the workshop. Remember the importance of helping people become engaged in the process – energizing problem-solving techniques like Mindspin can help ensure your team stays engaged and happy, even when the problems they’re coming together to solve are complex.
MindSpin #teampedia #idea generation #problem solving #action A fast and loud method to enhance brainstorming within a team. Since this activity has more than round ideas that are repetitive can be ruled out leaving more creative and innovative answers to the challenge.
22. Improved Solutions
After a team has successfully identified a problem and come up with a few solutions, it can be tempting to call the work of the problem-solving process complete. That said, the first solution is not necessarily the best, and by including a further review and reflection activity into your problem-solving model, you can ensure your group reaches the best possible result.
One of a number of problem-solving games from Thiagi Group, Improved Solutions helps you go the extra mile and develop suggested solutions with close consideration and peer review. By supporting the discussion of several problems at once and by shifting team roles throughout, this problem-solving technique is a dynamic way of finding the best solution.
Improved Solutions #creativity #thiagi #problem solving #action #team You can improve any solution by objectively reviewing its strengths and weaknesses and making suitable adjustments. In this creativity framegame, you improve the solutions to several problems. To maintain objective detachment, you deal with a different problem during each of six rounds and assume different roles (problem owner, consultant, basher, booster, enhancer, and evaluator) during each round. At the conclusion of the activity, each player ends up with two solutions to her problem.
23. Four Step Sketch
Creative thinking and visual ideation does not need to be confined to the opening stages of your problem-solving strategies. Exercises that include sketching and prototyping on paper can be effective at the solution finding and development stage of the process, and can be great for keeping a team engaged.
By going from simple notes to a crazy 8s round that involves rapidly sketching 8 variations on their ideas before then producing a final solution sketch, the group is able to iterate quickly and visually. Problem-solving techniques like Four-Step Sketch are great if you have a group of different thinkers and want to change things up from a more textual or discussion-based approach.
Four-Step Sketch #design sprint #innovation #idea generation #remote-friendly The four-step sketch is an exercise that helps people to create well-formed concepts through a structured process that includes: Review key information Start design work on paper, Consider multiple variations , Create a detailed solution . This exercise is preceded by a set of other activities allowing the group to clarify the challenge they want to solve. See how the Four Step Sketch exercise fits into a Design Sprint
24. 15% Solutions
Some problems are simpler than others and with the right problem-solving activities, you can empower people to take immediate actions that can help create organizational change.
Part of the liberating structures toolkit, 15% solutions is a problem-solving technique that focuses on finding and implementing solutions quickly. A process of iterating and making small changes quickly can help generate momentum and an appetite for solving complex problems.
Problem-solving strategies can live and die on whether people are onboard. Getting some quick wins is a great way of getting people behind the process.
It can be extremely empowering for a team to realize that problem-solving techniques can be deployed quickly and easily and delineate between things they can positively impact and those things they cannot change.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
25. How-Now-Wow Matrix
The problem-solving process is often creative, as complex problems usually require a change of thinking and creative response in order to find the best solutions. While it’s common for the first stages to encourage creative thinking, groups can often gravitate to familiar solutions when it comes to the end of the process.
When selecting solutions, you don’t want to lose your creative energy! The How-Now-Wow Matrix from Gamestorming is a great problem-solving activity that enables a group to stay creative and think out of the box when it comes to selecting the right solution for a given problem.
Problem-solving techniques that encourage creative thinking and the ideation and selection of new solutions can be the most effective in organisational change. Give the How-Now-Wow Matrix a go, and not just for how pleasant it is to say out loud.
How-Now-Wow Matrix #gamestorming #idea generation #remote-friendly When people want to develop new ideas, they most often think out of the box in the brainstorming or divergent phase. However, when it comes to convergence, people often end up picking ideas that are most familiar to them. This is called a ‘creative paradox’ or a ‘creadox’. The How-Now-Wow matrix is an idea selection tool that breaks the creadox by forcing people to weigh each idea on 2 parameters.
26. Impact and Effort Matrix
All problem-solving techniques hope to not only find solutions to a given problem or challenge but to find the best solution. When it comes to finding a solution, groups are invited to put on their decision-making hats and really think about how a proposed idea would work in practice.
The Impact and Effort Matrix is one of the problem-solving techniques that fall into this camp, empowering participants to first generate ideas and then categorize them into a 2×2 matrix based on impact and effort.
Activities that invite critical thinking while remaining simple are invaluable. Use the Impact and Effort Matrix to move from ideation and towards evaluating potential solutions before then committing to them.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
27. Dotmocracy
If you’ve followed each of the problem-solving steps with your group successfully, you should move towards the end of your process with heaps of possible solutions developed with a specific problem in mind. But how do you help a group go from ideation to putting a solution into action?
Dotmocracy – or Dot Voting -is a tried and tested method of helping a team in the problem-solving process make decisions and put actions in place with a degree of oversight and consensus.
One of the problem-solving techniques that should be in every facilitator’s toolbox, Dot Voting is fast and effective and can help identify the most popular and best solutions and help bring a group to a decision effectively.
Dotmocracy #action #decision making #group prioritization #hyperisland #remote-friendly Dotmocracy is a simple method for group prioritization or decision-making. It is not an activity on its own, but a method to use in processes where prioritization or decision-making is the aim. The method supports a group to quickly see which options are most popular or relevant. The options or ideas are written on post-its and stuck up on a wall for the whole group to see. Each person votes for the options they think are the strongest, and that information is used to inform a decision.
All facilitators know that warm-ups and icebreakers are useful for any workshop or group process. Problem-solving workshops are no different.
Use these problem-solving techniques to warm up a group and prepare them for the rest of the process. Activating your group by tapping into some of the top problem-solving skills can be one of the best ways to see great outcomes from your session.
- Check-in/Check-out
- Doodling Together
- Show and Tell
- Constellations
- Draw a Tree
28. Check-in / Check-out
Solid processes are planned from beginning to end, and the best facilitators know that setting the tone and establishing a safe, open environment can be integral to a successful problem-solving process.
Check-in / Check-out is a great way to begin and/or bookend a problem-solving workshop. Checking in to a session emphasizes that everyone will be seen, heard, and expected to contribute.
If you are running a series of meetings, setting a consistent pattern of checking in and checking out can really help your team get into a groove. We recommend this opening-closing activity for small to medium-sized groups though it can work with large groups if they’re disciplined!
Check-in / Check-out #team #opening #closing #hyperisland #remote-friendly Either checking-in or checking-out is a simple way for a team to open or close a process, symbolically and in a collaborative way. Checking-in/out invites each member in a group to be present, seen and heard, and to express a reflection or a feeling. Checking-in emphasizes presence, focus and group commitment; checking-out emphasizes reflection and symbolic closure.
29. Doodling Together
Thinking creatively and not being afraid to make suggestions are important problem-solving skills for any group or team, and warming up by encouraging these behaviors is a great way to start.
Doodling Together is one of our favorite creative ice breaker games – it’s quick, effective, and fun and can make all following problem-solving steps easier by encouraging a group to collaborate visually. By passing cards and adding additional items as they go, the workshop group gets into a groove of co-creation and idea development that is crucial to finding solutions to problems.
Doodling Together #collaboration #creativity #teamwork #fun #team #visual methods #energiser #icebreaker #remote-friendly Create wild, weird and often funny postcards together & establish a group’s creative confidence.
30. Show and Tell
You might remember some version of Show and Tell from being a kid in school and it’s a great problem-solving activity to kick off a session.
Asking participants to prepare a little something before a workshop by bringing an object for show and tell can help them warm up before the session has even begun! Games that include a physical object can also help encourage early engagement before moving onto more big-picture thinking.
By asking your participants to tell stories about why they chose to bring a particular item to the group, you can help teams see things from new perspectives and see both differences and similarities in the way they approach a topic. Great groundwork for approaching a problem-solving process as a team!
Show and Tell #gamestorming #action #opening #meeting facilitation Show and Tell taps into the power of metaphors to reveal players’ underlying assumptions and associations around a topic The aim of the game is to get a deeper understanding of stakeholders’ perspectives on anything—a new project, an organizational restructuring, a shift in the company’s vision or team dynamic.
31. Constellations
Who doesn’t love stars? Constellations is a great warm-up activity for any workshop as it gets people up off their feet, energized, and ready to engage in new ways with established topics. It’s also great for showing existing beliefs, biases, and patterns that can come into play as part of your session.
Using warm-up games that help build trust and connection while also allowing for non-verbal responses can be great for easing people into the problem-solving process and encouraging engagement from everyone in the group. Constellations is great in large spaces that allow for movement and is definitely a practical exercise to allow the group to see patterns that are otherwise invisible.
Constellations #trust #connection #opening #coaching #patterns #system Individuals express their response to a statement or idea by standing closer or further from a central object. Used with teams to reveal system, hidden patterns, perspectives.
32. Draw a Tree
Problem-solving games that help raise group awareness through a central, unifying metaphor can be effective ways to warm-up a group in any problem-solving model.
Draw a Tree is a simple warm-up activity you can use in any group and which can provide a quick jolt of energy. Start by asking your participants to draw a tree in just 45 seconds – they can choose whether it will be abstract or realistic.
Once the timer is up, ask the group how many people included the roots of the tree and use this as a means to discuss how we can ignore important parts of any system simply because they are not visible.
All problem-solving strategies are made more effective by thinking of problems critically and by exposing things that may not normally come to light. Warm-up games like Draw a Tree are great in that they quickly demonstrate some key problem-solving skills in an accessible and effective way.
Draw a Tree #thiagi #opening #perspectives #remote-friendly With this game you can raise awarness about being more mindful, and aware of the environment we live in.
Each step of the problem-solving workshop benefits from an intelligent deployment of activities, games, and techniques. Bringing your session to an effective close helps ensure that solutions are followed through on and that you also celebrate what has been achieved.
Here are some problem-solving activities you can use to effectively close a workshop or meeting and ensure the great work you’ve done can continue afterward.
- One Breath Feedback
- Who What When Matrix
- Response Cards
How do I conclude a problem-solving process?
All good things must come to an end. With the bulk of the work done, it can be tempting to conclude your workshop swiftly and without a moment to debrief and align. This can be problematic in that it doesn’t allow your team to fully process the results or reflect on the process.
At the end of an effective session, your team will have gone through a process that, while productive, can be exhausting. It’s important to give your group a moment to take a breath, ensure that they are clear on future actions, and provide short feedback before leaving the space.
The primary purpose of any problem-solving method is to generate solutions and then implement them. Be sure to take the opportunity to ensure everyone is aligned and ready to effectively implement the solutions you produced in the workshop.
Remember that every process can be improved and by giving a short moment to collect feedback in the session, you can further refine your problem-solving methods and see further success in the future too.
33. One Breath Feedback
Maintaining attention and focus during the closing stages of a problem-solving workshop can be tricky and so being concise when giving feedback can be important. It’s easy to incur “death by feedback” should some team members go on for too long sharing their perspectives in a quick feedback round.
One Breath Feedback is a great closing activity for workshops. You give everyone an opportunity to provide feedback on what they’ve done but only in the space of a single breath. This keeps feedback short and to the point and means that everyone is encouraged to provide the most important piece of feedback to them.
One breath feedback #closing #feedback #action This is a feedback round in just one breath that excels in maintaining attention: each participants is able to speak during just one breath … for most people that’s around 20 to 25 seconds … unless of course you’ve been a deep sea diver in which case you’ll be able to do it for longer.
34. Who What When Matrix
Matrices feature as part of many effective problem-solving strategies and with good reason. They are easily recognizable, simple to use, and generate results.
The Who What When Matrix is a great tool to use when closing your problem-solving session by attributing a who, what and when to the actions and solutions you have decided upon. The resulting matrix is a simple, easy-to-follow way of ensuring your team can move forward.
Great solutions can’t be enacted without action and ownership. Your problem-solving process should include a stage for allocating tasks to individuals or teams and creating a realistic timeframe for those solutions to be implemented or checked out. Use this method to keep the solution implementation process clear and simple for all involved.
Who/What/When Matrix #gamestorming #action #project planning With Who/What/When matrix, you can connect people with clear actions they have defined and have committed to.
35. Response cards
Group discussion can comprise the bulk of most problem-solving activities and by the end of the process, you might find that your team is talked out!
Providing a means for your team to give feedback with short written notes can ensure everyone is head and can contribute without the need to stand up and talk. Depending on the needs of the group, giving an alternative can help ensure everyone can contribute to your problem-solving model in the way that makes the most sense for them.
Response Cards is a great way to close a workshop if you are looking for a gentle warm-down and want to get some swift discussion around some of the feedback that is raised.
Response Cards #debriefing #closing #structured sharing #questions and answers #thiagi #action It can be hard to involve everyone during a closing of a session. Some might stay in the background or get unheard because of louder participants. However, with the use of Response Cards, everyone will be involved in providing feedback or clarify questions at the end of a session.
Save time and effort discovering the right solutions
A structured problem solving process is a surefire way of solving tough problems, discovering creative solutions and driving organizational change. But how can you design for successful outcomes?
With SessionLab, it’s easy to design engaging workshops that deliver results. Drag, drop and reorder blocks to build your agenda. When you make changes or update your agenda, your session timing adjusts automatically , saving you time on manual adjustments.
Collaborating with stakeholders or clients? Share your agenda with a single click and collaborate in real-time. No more sending documents back and forth over email.
Explore how to use SessionLab to design effective problem solving workshops or watch this five minute video to see the planner in action!

Over to you
The problem-solving process can often be as complicated and multifaceted as the problems they are set-up to solve. With the right problem-solving techniques and a mix of creative exercises designed to guide discussion and generate purposeful ideas, we hope we’ve given you the tools to find the best solutions as simply and easily as possible.
Is there a problem-solving technique that you are missing here? Do you have a favorite activity or method you use when facilitating? Let us know in the comments below, we’d love to hear from you!
thank you very much for these excellent techniques
Certainly wonderful article, very detailed. Shared!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of online tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your job as a facilitator easier. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting facilitation software you can…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free
Table of Contents
The problem-solving process, how to solve problems: 5 steps, train to solve problems with lean today, what is problem solving steps, techniques, & best practices explained.

Problem solving is the art of identifying problems and implementing the best possible solutions. Revisiting your problem-solving skills may be the missing piece to leveraging the performance of your business, achieving Lean success, or unlocking your professional potential.
Ask any colleague if they’re an effective problem-solver and their likely answer will be, “Of course! I solve problems every day.”
Problem solving is part of most job descriptions, sure. But not everyone can do it consistently.
Problem solving is the process of defining a problem, identifying its root cause, prioritizing and selecting potential solutions, and implementing the chosen solution.
There’s no one-size-fits-all problem-solving process. Often, it’s a unique methodology that aligns your short- and long-term objectives with the resources at your disposal. Nonetheless, many paradigms center problem solving as a pathway for achieving one’s goals faster and smarter.
One example is the Six Sigma framework , which emphasizes eliminating errors and refining the customer experience, thereby improving business outcomes. Developed originally by Motorola, the Six Sigma process identifies problems from the perspective of customer satisfaction and improving product delivery.
Lean management, a similar method, is about streamlining company processes over time so they become “leaner” while producing better outcomes.
Trendy business management lingo aside, both of these frameworks teach us that investing in your problem solving process for personal and professional arenas will bring better productivity.
1. Precisely Identify Problems
As obvious as it seems, identifying the problem is the first step in the problem-solving process. Pinpointing a problem at the beginning of the process will guide your research, collaboration, and solutions in the right direction.
At this stage, your task is to identify the scope and substance of the problem. Ask yourself a series of questions:
- What’s the problem?
- How many subsets of issues are underneath this problem?
- What subject areas, departments of work, or functions of business can best define this problem?
Although some problems are naturally large in scope, precision is key. Write out the problems as statements in planning sheets . Should information or feedback during a later step alter the scope of your problem, revise the statements.
Framing the problem at this stage will help you stay focused if distractions come up in later stages. Furthermore, how you frame a problem will aid your search for a solution. A strategy of building Lean success, for instance, will emphasize identifying and improving upon inefficient systems.
2. Collect Information and Plan
The second step is to collect information and plan the brainstorming process. This is another foundational step to road mapping your problem-solving process. Data, after all, is useful in identifying the scope and substance of your problems.
Collecting information on the exact details of the problem, however, is done to narrow the brainstorming portion to help you evaluate the outcomes later. Don’t overwhelm yourself with unnecessary information — use the problem statements that you identified in step one as a north star in your research process.
This stage should also include some planning. Ask yourself:
- What parties will ultimately decide a solution?
- Whose voices and ideas should be heard in the brainstorming process?
- What resources are at your disposal for implementing a solution?
Establish a plan and timeline for steps 3-5.
3. Brainstorm Solutions
Brainstorming solutions is the bread and butter of the problem-solving process. At this stage, focus on generating creative ideas. As long as the solution directly addresses the problem statements and achieves your goals, don’t immediately rule it out.
Moreover, solutions are rarely a one-step answer and are more like a roadmap with a set of actions. As you brainstorm ideas, map out these solutions visually and include any relevant factors such as costs involved, action steps, and involved parties.
With Lean success in mind, stay focused on solutions that minimize waste and improve the flow of business ecosystems.
Become a Quality Management Professional
- 10% Growth In Jobs Of Quality Managers Profiles By 2025
- 11% Revenue Growth For Organisations Improving Quality
Certified Lean Six Sigma Green Belt
- 4 hands-on projects to perfect the skills learnt
- 4 simulation test papers for self-assessment
Lean Six Sigma Expert
- IASSC® Lean Six Sigma Green Belt and Black Belt certification
- 13 Projects, 12 Simulation exams, 18 Case Studies & 114 PDUs
Here's what learners are saying regarding our programs:
Xueting Liu
Mechanical engineer student at sargents pty. ltd. ,.
A great training and proper exercise with step-by-step guide! I'll give a rating of 10 out of 10 for this training.
Abdus Salam
I have completed the Lean Six Sigma Expert Master’s Program from Simplilearn. And after the course, I could take up new projects and perform better. My average pay rate for a research position increased by 21%.
4. Decide and Implement
The most critical stage is selecting a solution. Easier said than done. Consider the criteria that has arisen in previous steps as you decide on a solution that meets your needs.
Once you select a course of action, implement it.
Practicing due diligence in earlier stages of the process will ensure that your chosen course of action has been evaluated from all angles. Often, efficient implementation requires us to act correctly and successfully the first time, rather than being hurried and sloppy. Further compilations will create more problems, bringing you back to step 1.
5. Evaluate
Exercise humility and evaluate your solution honestly. Did you achieve the results you hoped for? What would you do differently next time?
As some experts note, formulating feedback channels into your evaluation helps solidify future success. A framework like Lean success, for example, will use certain key performance indicators (KPIs) like quality, delivery success, reducing errors, and more. Establish metrics aligned with company goals to assess your solutions.
Master skills like measurement system analysis, lean principles, hypothesis testing, process analysis and DFSS tools with our Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Training Course . Sign-up today!
Become a quality expert with Simplilearn’s Lean Six Sigma Green Belt . This Lean Six Sigma certification program will help you gain key skills to excel in digital transformation projects while improving quality and ultimate business results.
In this course, you will learn about two critical operations management methodologies – Lean practices and Six Sigma to accelerate business improvement.
Our Quality Management Courses Duration And Fees
Explore our top Quality Management Courses and take the first step towards career success
Get Free Certifications with free video courses
Quality Management
Lean Management
Project Management
Learn from industry experts with free masterclasses, digital marketing.
The Top 10 AI Tools You Need to Master Marketing in 2024
Unlock Digital Marketing Career Success Secrets for 2024 with Purdue University
Your Gateway to Game-changing Digital Marketing Careers in 2024 with Purdue University
Recommended Reads
Introduction to Machine Learning: A Beginner's Guide
Webinar Wrap-up: Mastering Problem Solving: Career Tips for Digital Transformation Jobs
An Ultimate Guide That Helps You to Develop and Improve Problem Solving in Programming
Free eBook: 21 Resources to Find the Data You Need
ITIL Problem Workaround – A Leader’s Guide to Manage Problems
Your One-Stop Solution to Understand Coin Change Problem
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.

Encyclopedia of Personality and Individual Differences pp 4042–4045 Cite as
Problem-Solving
- Jon C. Willford 3
- Reference work entry
- First Online: 01 January 2020
42 Accesses
Problem solving refers to the process of identifying a gap between a desired goal state and a present state, and proposing and performing a set of operations or solutions in order to move toward the goal state. Generally, the solution to the problem is not immediately known and the process can involve multiple solutions and attempts to reach the intended goal. Problem solving involves a set of cognitive processes associated with problem definition, information gathering, analyzing, planning, and execution. An individual’s capacity to problem solve is influenced by a number of factors including cognitive ability, disposition, knowledge, and background.
Introduction
Problem solving involves a set of complex cognitive processes that require thinking and reasoning. A problem occurs when there is a goal that needs to be reached and there is not a clear path to achieving the goal (Mayer 2013 ). Problems can range in terms of type, complexity, strategy use, domain, and other...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Ackerman, P. L. (1996). A theory of adult intellectual development: Process, personality, interests, and knowledge. Intelligence, 22 (2), 227–257.
Google Scholar
Carroll, J. B. (1993). Human cognitive abilities: A survey of factor-analytic studies . Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Elliott, T. R., Herrick, S. M., MacNair, R. R., & Harkins, S. W. (1994). Personality correlates of self-appraised problem solving ability: Problem orientation and trait affectivity. Journal of Personality Assessment, 63 (3), 489–505.
Article Google Scholar
Greiff, S., & Neubert, J. C. (2014). On the relation of complex problem solving, personality, fluid intelligence, and academic achievement. Learning and Individual Differences, 36 , 37–48.
Mayer, R. E. (2013). Problem solving. In D. Reisberg (Ed.), The Oxford Handbook of Cognitive Psychology . Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
Neubert, J. C., Mainert, J., Kretzschmar, A., & Greiff, S. (2015). The assessment of 21st century skills in industrial and organizational psychology: Complex and collaborative problem solving. Industrial and Organizational Psychology, 8 (02), 238–268.
Pretz, J. E., Naples, A. J., & Sternberg, R. J. (2003). Recognizing, defining, and representing problems. In J. E. Davidson & R. J. Sternberg (Eds.), The psychology of problem solving (pp. 3–30). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Chapter Google Scholar
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
The George Washington University, Washington, DC, USA
Jon C. Willford
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jon C. Willford .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Oakland University, Rochester, MI, USA
Virgil Zeigler-Hill
Todd K. Shackelford
Section Editor information
University of North Carolina-Charlotte, Charlotte, NC, USA
Charlie Reeve
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Willford, J.C. (2020). Problem-Solving. In: Zeigler-Hill, V., Shackelford, T.K. (eds) Encyclopedia of Personality and Individual Differences. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24612-3_993
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24612-3_993
Published : 22 April 2020
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-24610-9
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-24612-3
eBook Packages : Behavioral Science and Psychology Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The problem solving cycle is a systematic approach to analyzing and solving problems, involving various stages such as problem identification, analysis, algorithm design, implementation, and evaluation. Understanding the importance of this cycle is essential for any computer scientist or programmer.
Problem Solving Using Computer (Steps) Computer based problem solving is a systematic process of designing, implementing and using programming tools during the problem solving stage. This method enables the computer system to be more intuitive with human logic than machine logic. Final outcome of this process is software tools which is ...
The several steps of this cycle are as follows : Step by step solution for a problem (Software Life Cycle) 1. Problem Definition/Specification: A computer program is basically a machine language solution to a real-life problem. Because programs are generally made to solve the pragmatic problems of the outside world.
Computer science learners often face difficulties in performing two of the main stages of a problem-solving process: problem analysis and solution construction. Therefore, it is important that computer science educators be aware of these difficulties and acquire appropriate pedagogical tools to guide and scaffold learners in learning these skills.
Example problem: Step 1 - Identify the problem that must be solved. The first step is to identify the problem that needs to be solved. In this example, the largest number in the list must be found and displayed. Step 2 - Understand what the problem presents. The problem presents a list of numbers.
MIT OpenCourseWare is a web based publication of virtually all MIT course content. OCW is open and available to the world and is a permanent MIT activity
Computational thinking is a problem-solving process in which the last step is expressing the solution so that it can be executed on a computer. However, before we are able to write a program to implement an algorithm, we must understand what the computer is capable of doing -- in particular, how it executes instructions and how it uses data.
Computer Scientists classify problems by how hard they are. One measure of how hard a problem is, is based on the behavior of the worst case runtime as a function of the input length. For example, if for every length x the worst input of size x takes time x then this problem has linear runtime. Every program you've written so far for ...
Computational Thinking allows us to take complex problems, understand what the problem is, and develop solutions. We can present these solutions in a way that both computers and people can understand. The course includes an introduction to computational thinking and a broad definition of each concept, a series of real-world cases that ...
Knowing the level of thinking required to solving the problem and having an idea of a solution which is relevant to the problem. Define the problem [edit | edit source] To fully understand a problem we need to think about the following: Given(s): the initial situation; Goal: desired target situation; Ownership: who does what
The good thing is that the system translates nicely to computer problems, which is very useful, since the focus of the book is to solve problems on a computer. The six steps in this system are: What is the problem. Make a model. Analyze the model. Find the solution.
Abstract. Solving problems is the core of computer science. Programmers must first understand how a human solves a problem, then understand how to translate this "algorithm" into something a ...
The Problem-Solving Process. Problem-solving is an important part of planning and decision-making. The process has much in common with the decision-making process, and in the case of complex decisions, can form part of the process itself. We face and solve problems every day, in a variety of guises and of differing complexity.
Finding a suitable solution for issues can be accomplished by following the basic four-step problem-solving process and methodology outlined below. Step. Characteristics. 1. Define the problem. Differentiate fact from opinion. Specify underlying causes. Consult each faction involved for information. State the problem specifically.
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps: Identify the issue: Recognize the problem that needs to be solved. Analyze the situation: Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present. Generate potential solutions: Brainstorm a list of possible ...
Problem-solving takes centre stage in the realm of computer science, where challenges need methodical approaches for efficient resolution. ... Problem-solving techniques in computer science are important for mitigating runtime errors and system crashes, optimizing software, organizing, evaluating, and interpreting complex datasets, and ...
The 5 Stages of Problem-solving: 1. Define the problem 2. Ideate on the solution 3. Choose the best strategy 4. ... often referred to as a breakthrough handheld computer. During its time, this new ...
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue. The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything ...
Explore the 5 critical stages of problem-solving in our comprehensive guide. Learn to identify, analyze, brainstorm, evaluate, and implement solutions effectively for personal and professional growth.
Problem analysis can be one of the most important and decisive stages of all problem-solving tools. Sometimes, a team can become bogged down in the details and are unable to move forward. Journalists is an activity that can avoid a group from getting stuck in the problem identification or problem analysis stages of the process.
How to Solve Problems: 5 Steps. 1. Precisely Identify Problems. As obvious as it seems, identifying the problem is the first step in the problem-solving process. Pinpointing a problem at the beginning of the process will guide your research, collaboration, and solutions in the right direction. At this stage, your task is to identify the scope ...
Stages of Problem Solving. Because problem solving is set of processes, many researchers have described the process of problem solving as a set of actions, cycles, or stages that an individual or group of individuals typically go through when solving problems (Pretz et al. 2003).Though a number of stages or steps have been identified, most can be organized around the following:
Computer log trace data provides a wealth of information about learner behaviors that can be captured and monitored for the purposes of detecting learning trajectories ... Participants' in-game problem-solving behaviors were coded based on three problem-solving stages: generating initial hypothesis, generate-and-differential provisional ...