
Library Services

UCL LIBRARY SERVICES
- Guides and databases
- Library skills
Thesis or dissertation
- A-Z of Harvard references
- Citing authors with Harvard
- Page numbers and punctuation
- References with missing details
- Secondary referencing
- Example reference list
- Journal article
- Magazine article
- Newspaper article
- Online video
- Radio and internet radio
- Television advertisement
- Television programme
- Ancient text
- Bibliography
- Book (printed, one author or editor)
- Book (printed, multiple authors or editors)
- Book (printed, with no author)
- Chapter in a book (print)
- Collected works
- Dictionaries and Encyclopedia entries
- Multivolume work
- Religious text
- Translated work
- Census data
- Financial report
- Mathematical equation
- Scientific dataset
- Book illustration, Figure or Diagram
- Inscription on a building
- Installation
- Painting or Drawing
- Interview (on the internet)
- Interview (newspaper)
- Interview (radio or television)
- Interview (as part of research)
- Act of the UK parliament (statute)
- Bill (House of Commons/Lords)
- Birth/Death/Marriage certificate
- British standards
- Command paper
- European Union publication
- Government/Official publication
- House of Commons/Lords paper
- Legislation from UK devolved assemblies
- Statutory instrument
- Military record
- Film/Television script
- Musical score
- Play (live performance)
- Play script
- Song lyrics
- Conference paper
- Conference proceedings
- Discussion paper
- Minutes of meeting
- Personal communication
- PowerPoint presentation
- Published report
- Student's own work
- Tutor materials for academic course
- Unpublished report
- Working paper
- Generative AI
- Referencing glossary
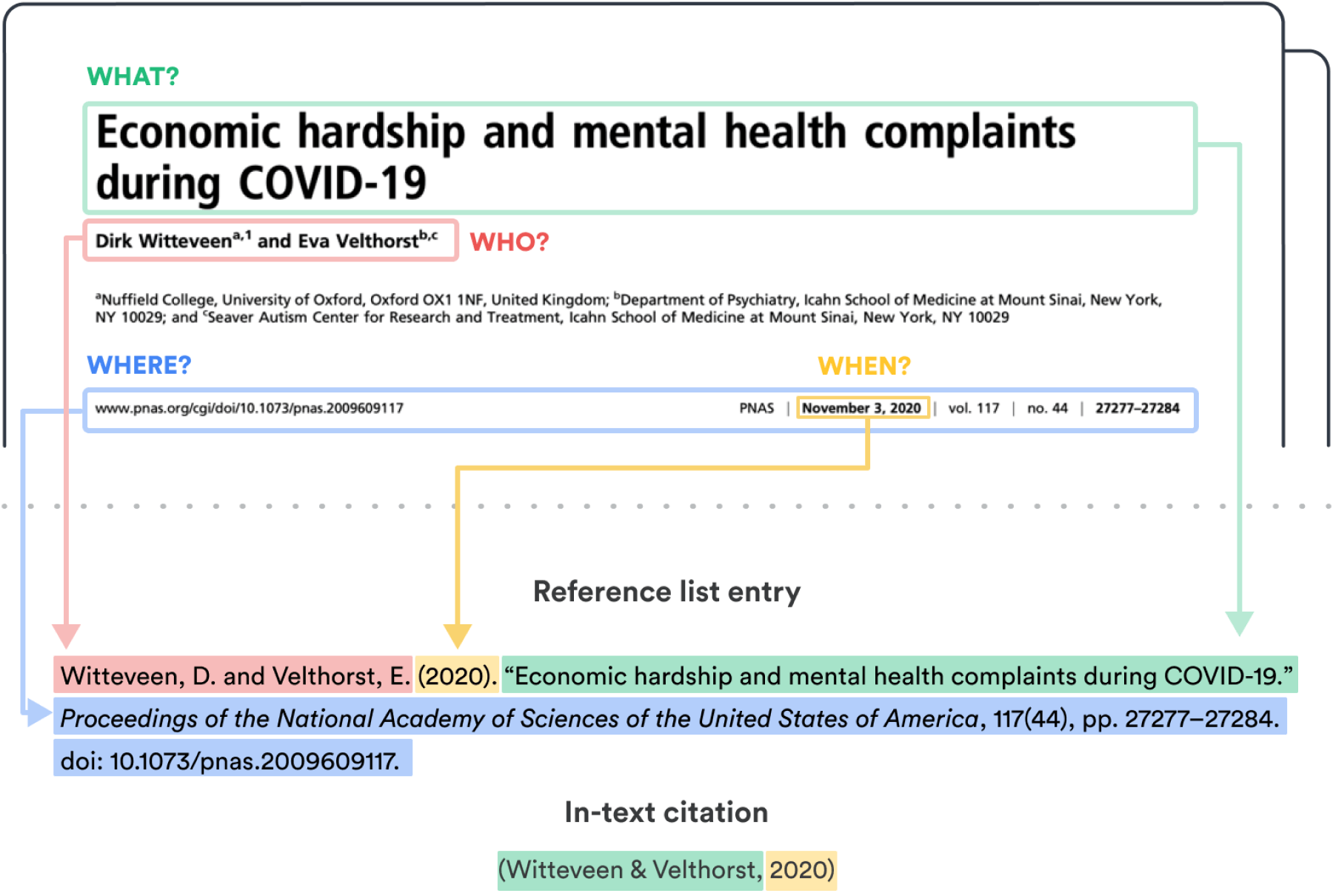
To be made up of:
- Year of submission (in round brackets).
- Title of thesis (in italics).
- Degree statement.
- Degree-awarding body.
- Available at: URL.
- (Accessed: date).
In-text citation:
(Smith, 2019)
Reference List:
Smith, E. R. C. (2019). Conduits of invasive species into the UK: the angling route? Ph. D. Thesis. University College London. Available at: https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/10072700 (Accessed: 20 May 2021).
Quick links
- Harvard references A-Z
- << Previous: Religious text
- Next: Translated work >>
- Last Updated: Oct 22, 2024 11:28 AM
- URL: https://library-guides.ucl.ac.uk/harvard
- Free Tools for Students
- Harvard Referencing Generator
Free Harvard Referencing Generator
Generate accurate Harvard reference lists quickly and for FREE, with MyBib!
🤔 What is a Harvard Referencing Generator?
A Harvard Referencing Generator is a tool that automatically generates formatted academic references in the Harvard style.
It takes in relevant details about a source -- usually critical information like author names, article titles, publish dates, and URLs -- and adds the correct punctuation and formatting required by the Harvard referencing style.
The generated references can be copied into a reference list or bibliography, and then collectively appended to the end of an academic assignment. This is the standard way to give credit to sources used in the main body of an assignment.
👩🎓 Who uses a Harvard Referencing Generator?
Harvard is the main referencing style at colleges and universities in the United Kingdom and Australia. It is also very popular in other English-speaking countries such as South Africa, Hong Kong, and New Zealand. University-level students in these countries are most likely to use a Harvard generator to aid them with their undergraduate assignments (and often post-graduate too).
🙌 Why should I use a Harvard Referencing Generator?
A Harvard Referencing Generator solves two problems:
- It provides a way to organise and keep track of the sources referenced in the content of an academic paper.
- It ensures that references are formatted correctly -- inline with the Harvard referencing style -- and it does so considerably faster than writing them out manually.
A well-formatted and broad bibliography can account for up to 20% of the total grade for an undergraduate-level project, and using a generator tool can contribute significantly towards earning them.
⚙️ How do I use MyBib's Harvard Referencing Generator?
Here's how to use our reference generator:
- If citing a book, website, journal, or video: enter the URL or title into the search bar at the top of the page and press the search button.
- Choose the most relevant results from the list of search results.
- Our generator will automatically locate the source details and format them in the correct Harvard format. You can make further changes if required.
- Then either copy the formatted reference directly into your reference list by clicking the 'copy' button, or save it to your MyBib account for later.
MyBib supports the following for Harvard style:
🍏 What other versions of Harvard referencing exist?
There isn't "one true way" to do Harvard referencing, and many universities have their own slightly different guidelines for the style. Our generator can adapt to handle the following list of different Harvard styles:
- Cite Them Right
- Manchester Metropolitan University (MMU)
- University of the West of England (UWE)

Daniel is a qualified librarian, former teacher, and citation expert. He has been contributing to MyBib since 2018.

- Harvard Library
- Research Guides
- Harvard Graduate School of Design - Frances Loeb Library
Write and Cite
- Theses and Dissertations
- Academic Integrity
- Using Sources and AI
- Academic Writing
- From Research to Writing
- GSD Writing Services
- Grants and Fellowships
- Reading, Notetaking, and Time Management
What is a thesis?
What is a dissertation, getting started, staying on track, thesis abstract, lit(erature) review.
A thesis is a long-term project that you work on over the course of a semester or a year. Theses have a very wide variety of styles and content, so we encourage you to look at prior examples and work closely with faculty to develop yours.
Before you begin, make sure that you are familiar with the dissertation genre—what it is for and what it looks like.
Generally speaking, a dissertation’s purpose is to prove that you have the expertise necessary to fulfill your doctoral-degree requirements by showing depth of knowledge and independent thinking.
The form of a dissertation may vary by discipline. Be sure to follow the specific guidelines of your department.
- PhD This site directs candidates to the GSAS website about dissertations , with links to checklists, planning, formatting, acknowledgments, submission, and publishing options. There is also a link to guidelines for the prospectus . Consult with your committee chair about specific requirements and standards for your dissertation.
- DDES This document covers planning, patent filing, submission guidelines, publishing options, formatting guidelines, sample pages, citation guidelines, and a list of common errors to avoid. There is also a link to guidelines for the prospectus .
- Scholarly Pursuits (GSAS) This searchable booklet from Harvard GSAS is a comprehensive guide to writing dissertations, dissertation-fellowship applications, academic journal articles, and academic job documents.
Finding an original topic can be a daunting and overwhelming task. These key concepts can help you focus and save time.
Finding a topic for your thesis or dissertation should start with a research question that excites or at least interests you. A rigorous, engaging, and original project will require continuous curiosity about your topic, about your own thoughts on the topic, and about what other scholars have said on your topic. Avoid getting boxed in by thinking you know what you want to say from the beginning; let your research and your writing evolve as you explore and fine-tune your focus through constant questioning and exploration.
Get a sense of the broader picture before you narrow your focus and attempt to frame an argument. Read, skim, and otherwise familiarize yourself with what other scholars have done in areas related to your proposed topic. Briefly explore topics tangentially related to yours to broaden your perspective and increase your chance of finding a unique angle to pursue.
Critical Reading
Critical reading is the opposite of passive reading. Instead of merely reading for information to absorb, critical reading also involves careful, sustained thinking about what you are reading. This process may include analyzing the author’s motives and assumptions, asking what might be left out of the discussion, considering what you agree with or disagree with in the author’s statements and why you agree or disagree, and exploring connections or contradictions between scholarly arguments. Here is a resource to help hone your critical-reading skills:
https://guides.library.harvard.edu/sixreadinghabits
https://youtu.be/BcV64lowMIA
Conversation
Your thesis or dissertation will incorporate some ideas from other scholars whose work you researched. By reading critically and following your curiosity, you will develop your own ideas and claims, and these contributions are the core of your project. You will also acknowledge the work of scholars who came before you, and you must accurately and fairly attribute this work and define your place within the larger discussion. Make sure that you know how to quote, summarize, paraphrase , integrate , and cite sources to avoid plagiarism and to show the depth and breadth of your knowledge.
A thesis is a long-term, large project that involves both research and writing; it is easy to lose focus, motivation, and momentum. Here are suggestions for achieving the result you want in the time you have.
The dissertation is probably the largest project you have undertaken, and a lot of the work is self-directed. The project can feel daunting or even overwhelming unless you break it down into manageable pieces and create a timeline for completing each smaller task. Be realistic but also challenge yourself, and be forgiving of yourself if you miss a self-imposed deadline here and there.
Your program will also have specific deadlines for different requirements, including establishing a committee, submitting a prospectus, completing the dissertation, defending the dissertation, and submitting your work. Consult your department’s website for these dates and incorporate them into the timeline for your work.
Accountability
Sometimes self-imposed deadlines do not feel urgent unless there is accountability to someone beyond yourself. To increase your motivation to complete tasks on schedule, set dates with your committee chair to submit pre-determined pieces of a chapter. You can also arrange with a fellow doctoral student to check on each other’s progress. Research and writing can be lonely, so it is also nice to share that journey with someone and support each other through the process.
Common Pitfalls
The most common challenges for students writing a dissertation are writer’s block, information-overload, and the compulsion to keep researching forever.
There are many strategies for avoiding writer’s block, such as freewriting, outlining, taking a walk, starting in the middle, and creating an ideal work environment for your particular learning style. Pay attention to what helps you and try different things until you find what works.
Efficient researching techniques are essential to avoiding information-overload. Here are a couple of resources about strategies for finding sources and quickly obtaining essential information from them.
https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/subject_specific_writing/writing_in_literature/writing_in_literature_detailed_discussion/reading_criticism.html
https://students.dartmouth.edu/academic-skills/learning-resources/learning-strategies/reading-techniques
Finally, remember that there is always more to learn and your dissertation cannot incorporate everything. Follow your curiosity but also set limits on the scope of your work. It helps to create a folder entitled “future projects” for topics and sources that interest you but that do not fit neatly into the dissertation. Also remember that future scholars will build off of your work, so leave something for them to do.
An abstract is a short (approximately 200-word) summary or overview of your research project. It provides enough information for a reader to know what they will find within the larger document, such as your purpose, methodology, and results or conclusion. It may also include a list of keywords. An abstract is an original document, not an excerpt, and its contents and organization may vary by discipline.
A literature review establishes a set of themes and contexts drawn from foundational research and materials that relate to your project. It is an acknowledgment that your scholarship doesn’t exist in a vacuum. With the review, you identify patterns and trends in the literature to situate your contribution within the existing scholarly conversation.
What is a literature review? A literature review (or lit review, for short) is a critical analysis of published scholarly research (the "literature") related to a specific topic. Literature here means body of work, which traditionally was done in written form and may include journal articles, books, book chapters, dissertations and thesis, or conference proceedings. In the case of design, however, literature has an expanded breadth since the body of work is oftentimes not represented by words. A design review may include plans, sections, photographs, and any type of media that portrays the work.
A literature review may stand on its own or may be inside a larger work, usually in the introductory sections. It is thorough but not exhaustive--there will always be more information than you can reasonably locate and include. Be mindful of your scope and time constraints and select your reviewed materials with care. A literature review
- summarizes the themes and findings of works in an area
- compares and contrasts relevant aspects of literature on a topic
- critically assesses the strengths and omissions of the source material
- elaborates on the implications of their findings for one's own research topic
What does a literature review look like? Each discipline has its own style for writing a literature review; urban planning and design lit reviews may look different than those from architecture, and design lit reviews will look significantly different than reviews from the biological sciences or engineering. Look at published journal articles within your field and note how they present the information.
- Introduction: most scholarly articles and books will have a literature review within the introductory sections. Its precise location may vary, but it is most often in the first few paragraphs or pages.
Dedicated literature reviews: these are stand-alone resources unto themselves. You can search for "literature review" and a topic, and you may find that one already exists. These literature reviews are useful as models within your field, for finding additional sources to explore, and for beginning to map the general relationships within the scholarly conversation around your topic. Be mindful not to plagiarize the source material.
Database search tip : Add the phrase "literature review" to your search to find published literature reviews.
Browsing through theses and dissertations of the past can help to get a sense of your options and gain inspiration but be careful to use current guidelines and refer to your committee instead of relying on these examples for form or formatting.
Theses at the Frances Loeb Library is a research guide to finding p ast GSD theses.
DASH Digital Access to Scholarship at Harvard.
HOLLIS Harvard Library’s catalog provides access to ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global .
MIT Architecture has a list of their graduates’ dissertations and theses.
Rhode Island School of Design has a list of their graduates’ dissertations and theses.
University of South Florida has a list of their graduates’ dissertations and theses.
Harvard GSD has a list of projects, including theses and professors’ research.
- << Previous: Reading, Notetaking, and Time Management
- Next: Publishing >>
- Last Updated: Oct 8, 2024 3:11 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.harvard.edu/gsd/write
Harvard University Digital Accessibility Policy
- How it works
"Christmas Offer"
Terms & conditions.
As the Christmas season is upon us, we find ourselves reflecting on the past year and those who we have helped to shape their future. It’s been quite a year for us all! The end of the year brings no greater joy than the opportunity to express to you Christmas greetings and good wishes.
At this special time of year, Research Prospect brings joyful discount of 10% on all its services. May your Christmas and New Year be filled with joy.
We are looking back with appreciation for your loyalty and looking forward to moving into the New Year together.
"Claim this offer"
In unfamiliar and hard times, we have stuck by you. This Christmas, Research Prospect brings you all the joy with exciting discount of 10% on all its services.
Offer valid till 5-1-2024
We love being your partner in success. We know you have been working hard lately, take a break this holiday season to spend time with your loved ones while we make sure you succeed in your academics
Discount code: RP0996Y

How to Cite a Dissertation in Harvard Style
Published by Alaxendra Bets at August 27th, 2021 , Revised On September 25, 2023
What is a Dissertation?
In the UK, countries of Western Europe, as well as New Zealand and Australia, the term ‘ dissertation ’ is used instead of a ‘thesis.’ The majority of the remaining countries in the world prefer to use ‘thesis’ instead of ‘dissertation.’
Both represent the same thing, though: a full-length, academic piece of writing that students must submit after their undergraduate, post-graduate (Master), or PhD studies.
More specifically, a dissertation can refer to:
- Large-scale research as part of a degree.
- An article based on a small-scale study as part of a degree.
- A review of another study, research or an accumulation of both.
- Other full-length body texts are a requirement of the student’s degree program, no matter which level it is.
1. Basic Format
In Harvard, the following in-text citation format is used for the dissertation:
(Author Surname, Year Published)
For example, ‘Occasionally the talent for drawing passes beyond mere picture-copying and shows the presence of a real artistic capacity of no mean order. (Darius, 2014)’
In Harvard, the following reference list entry format is used for the dissertation:
Author Surname, Author Initials. (Year Published). Title of the dissertation in italics. Level. Institution Name.
For example, reference list entry for the above source would be:
Darius, H. (2014). Running head: SAVANT SYNDROME – THEORIES AND EMPIRICAL FINDINGS . University of Skövde, University of Turku.
However, a slightly different format is also used in some institutions. According to that, in-text citations are done in the following way:
Author surname Year, p.#
For instance, Exelby (1997, p. 3) described the process … OR … processing gold (Exelby 1997, p. 3).
But in the case of reference list entries, these ‘other’ institutions recommend naming the dissertation title not in italics but in single quotation marks. The format would then be:
Author Surname, Initials Year of Publication, ‘Title of thesis in single quotation marks’, Award, Institution issuing degree, Location of the institution.
So, according to this format, the above example’s reference list entry would be:
Exelby, HRA 1997, ‘Aspects of Gold and Mineral Liberation’, PhD thesis, University of Queensland, Brisbane, Qld.
Whichever format is followed largely depends on one’s institutional guidelines. The format specified by the university is the one that should be followed. Furthermore, it should be followed consistently throughout a manuscript.
2. Citing a Dissertation Published Online
The format for both in-text and reference list entries is the same for online and print dissertations. For example:
- In-text citation: (Ram 2012) OR (Ram 2011, p. 130)
- Reference list entry: Ram, R 2012, ‘Development of the International Financial Reporting Standard for Small and Medium-sized Entities’, PhD thesis, The University of Sydney, viewed 23 May 2014, <http://hdl.handle.net/2123/8208>.
An important point to note: While referencing dissertations published online, the URL may or may not be enclosed within < > symbols. Whichever format is chosen, it should be used consistently throughout the text.
3. Citing an Unpublished Dissertation
This type of dissertation also uses the same formatting for in-text and reference list entries in Harvard style. For example:
- In-text citation: (Sakunasingha 2006) OR (Sakunasingha 2006, p. 36)
- Reference list entry: Sakunasingha, B 2006, ‘An empirical study into factors influencing the use of value-based management tools’, DBA thesis, Southern Cross University, Lismore, NSW.
Hire an Expert Writer
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in an academic style
- Free Amendments and 100% Plagiarism Free – or your money back!
- 100% Confidential and Timely Delivery!
- Free anti-plagiarism report
- Appreciated by thousands of clients. Check client reviews

Frequently Asked Questions
How do i cite my dissertation.
To cite your dissertation, follow your chosen citation style (e.g., APA, MLA). Generally, include author name, year, title, and source details. For APA: Author. (Year). Title. Source. For MLA: Author. “Title.” Degree, University, Year.
You May Also Like
Surname, (or Newspaper/Magazine Title,) Year. Title of article. Newspaper/Magazine Title [online], Day Month Year or Volume (Issue), URL [Accessed date].
In academia, you may need to cite a patent. This article shows you how to do this in Harvard Referencing,
Find the easiest ways to cite the images in our “how to cite images in Harvard Style” guide
As Featured On

USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

Splash Sol LLC
- How It Works
- TutorHome |
- IntranetHome |
- Contact the OU Contact the OU Contact the OU |
- Accessibility hub Accessibility hub
- StudentHome
- Help Centre
You are here
Help and support.
- Referencing and plagiarism
Quick guide to Harvard referencing (Cite Them Right)

Print this page
There are different versions of the Harvard referencing style. This guide is a quick introduction to the commonly-used Cite Them Right version. You will find further guidance available through the OU Library on the Cite Them Right Database .
For help and support with referencing and the full Cite Them Right guide, have a look at the Library’s page on referencing and plagiarism . If you need guidance referencing OU module material you can check out which sections of Cite Them Right are recommended when referencing physical and online module material .
This guide does not apply to OU Law undergraduate students . If you are studying a module beginning with W1xx, W2xx or W3xx, you should refer to the Quick guide to Cite Them Right referencing for Law modules .
Table of contents
In-text citations and full references.
- Secondary referencing
- Page numbers
- Citing multiple sources published in the same year by the same author
Full reference examples
Referencing consists of two elements:
- in-text citations, which are inserted in the body of your text and are included in the word count. An in-text citation gives the author(s) and publication date of a source you are referring to. If the publication date is not given, the phrase 'no date' is used instead of a date. If using direct quotations or if you paraphrase a specific section in the source you also need the page number/s if available, or paragraph number for web pages.
- full references, which are given in alphabetical order in a reference list at the end of your work and are not included in the word count. Full references give full bibliographical information for all the sources you have referred to in the body of your text.
To see a reference list and intext citations check out this example assignment on Cite Them Right .
Difference between reference list and bibliography
a reference list only includes sources you have referred to in the body of your text.
a bibliography includes sources you have referred to in the body of your text AND sources that were part of your background reading that you did not use in your assignment.
Back to top
Examples of in-text citations
You need to include an in-text citation wherever you quote from, summarise, or paraphrase from a source. An in-text citation consists of the last name of the author(s), the year of publication, and a page number if relevant. There are a number of ways of incorporating in-text citations into your work - some examples are provided below. You should include page numbers in your citation if you are quoting directly from, paraphrasing , or using ideas from a specific page or set of pages. You do not need to include page numbers if you are summarising (providing a brief overview of the main topics or points) a complete source, e.g. a whole book. You can see further examples of setting out in-text citations in Cite Them Right .
Example with one author:
Almeroth-Williams, T. (2019) City of Beasts: How Animals Shaped Georgian London . Manchester: Manchester University Press.
RSPCA (2024) Caring for cats and kittens . Available at: https://www.rspca.org.uk/adviceandwelfare/pets/cats (Accessed: 1 August 2024).
Example with two or three authors:
Grayling, A. and Ball, B. (2024) ' Philosophy is crucial in the age of AI', The Conversation , 1 August. Available at: https://theconversation.com/philosophy-is-crucial-in-the-age-of-ai-235907 (Accessed: 1 August 2024).
Chu, M., Leonard, P. and Stevenson, F. (2012) ' Growing the Base for Citizen Science: Recruiting and Engaging Participants', in J.L. Dickinson and R. Bonney (eds.) Citizen Science: Public Participation in Environmental Research . Ithaca: Cornell University Press, pp. 69-81.
Example with four or more authors:
Young, H.D. et al. (2015) Sears and Zemansky's university physics . San Francisco, CA: Addison-Wesley.
Note: You can choose one or other method to reference four or more authors (unless your School requires you to name all authors in your reference list) and your approach should be consistent.
Online module materials
(Includes written online module activities, audio-visual material such as online tutorials, recordings or videos).
When referencing material from module websites, the date of publication is the year you started studying the module.
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication/presentation) 'Title of item'. Module code: Module title . Available at: URL of VLE (Accessed: date).
OR, if there is no named author:
The Open University (Year of publication/presentation) 'Title of item'. Module code: Module title . Available at: URL of VLE (Accessed: date).
Rietdorf, K. and Bootman, M. (2022) 'Topic 3: Rare diseases'. S290: Investigating human health and disease . Available at: https://learn2.open.ac.uk/mod/oucontent/view.php?id=1967195 (Accessed: 24 January 2023).
The Open University (2022) ‘3.1 The purposes of childhood and youth research’. EK313: Issues in research with children and young people . Available at: https://learn2.open.ac.uk/mod/oucontent/view.php?id=1949633§ion=1.3 (Accessed: 24 January 2023).
You can also use this template to reference videos and audio that are hosted on your module website:
The Open University (2022) ‘Video 2.7 An example of a Frith-Happé animation’. SK298: Brain, mind and mental health . Available at: https://learn2.open.ac.uk/mod/oucontent/view.php?id=2013014§ion=4.9.6 (Accessed: 22 November 2022).
The Open University (2022) ‘Audio 2 Interview with Richard Sorabji (Part 2)’. A113: Revolutions . Available at: https://learn2.open.ac.uk/mod/oucontent/view.php?id=1960941§ion=5.6 (Accessed: 22 November 2022).
Note: if a complete journal article has been uploaded to a module website, or if you have seen an article referred to on the website and then accessed the original version, reference the original journal article, and do not mention the module materials. If only an extract from an article is included in your module materials that you want to reference, you should use secondary referencing, with the module materials as the 'cited in' source, as described above.
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) 'Title of message', Title of discussion board , in Module code: Module title . Available at: URL of VLE (Accessed: date).
Fitzpatrick, M. (2022) ‘A215 - presentation of TMAs', Tutor group discussion & Workbook activities , in A215: Creative writing . Available at: https://learn2.open.ac.uk/mod/forumng/discuss.php?d=4209566 (Accessed: 24 January 2022).
Note: When an ebook looks like a printed book, with publication details and pagination, reference as a printed book.
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) Title . Edition if later than first. Place of publication: publisher. Series and volume number if relevant.
For ebooks that do not contain print publication details
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) Title of book . Available at: DOI or URL (Accessed: date).
Bell, J. (2014) Doing your research project . Maidenhead: Open University Press.
Adams, D. (1979) The hitchhiker's guide to the galaxy . Available at: http://www.amazon.co.uk/kindle-ebooks (Accessed: 23 June 2021).
Note: Books that have an editor, or editors, where each chapter is written by a different author or authors.
Surname of chapter author, Initial. (Year of publication) 'Title of chapter or section', in Initial. Surname of book editor (ed.) Title of book . Place of publication: publisher, Page reference.
Franklin, A.W. (2012) 'Management of the problem', in S.M. Smith (ed.) The maltreatment of children . Lancaster: MTP, pp. 83–95.
Note: When referencing a chapter of an edited book, your in-text citation should give the author(s) of the chapter.
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) 'Title of article', Title of Journal , volume number (issue number), page reference.
If accessed online:
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) 'Title of article', Title of Journal , volume number (issue number), page reference. Available at: DOI or URL (if required) (Accessed: date).
Shirazi, T. (2010) 'Successful teaching placements in secondary schools: achieving QTS practical handbooks', European Journal of Teacher Education , 33(3), pp. 323–326.
Shirazi, T. (2010) 'Successful teaching placements in secondary schools: achieving QTS practical handbooks', European Journal of Teacher Education , 33(3), pp. 323–326. Available at: https://libezproxy.open.ac.uk/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/log... (Accessed: 27 January 2023).
Barke, M. and Mowl, G. (2016) 'Málaga – a failed resort of the early twentieth century?', Journal of Tourism History , 2(3), pp. 187–212. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1080/1755182X.2010.523145
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) 'Title of article', Title of Newspaper , Day and month, Page reference.
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) 'Title of article', Title of Newspaper , Day and month, Page reference if available. Available at: URL (Accessed: date).
Mansell, W. and Bloom, A. (2012) ‘£10,000 carrot to tempt physics experts’, The Guardian , 20 June, p. 5.
Roberts, D. and Ackerman, S. (2013) 'US draft resolution allows Obama 90 days for military action against Syria', The Guardian , 4 September. Available at: http://www.theguardian.com/world/2013/sep/04/syria-strikes-draft-resolut... (Accessed: 9 September 2015).
Surname, Initial. (Year that the site was published/last updated) Title of web page . Available at: URL (Accessed: date).
Organisation (Year that the page was last updated) Title of web page . Available at: URL (Accessed: date).
Robinson, J. (2007) Social variation across the UK . Available at: https://www.bl.uk/british-accents-and-dialects/articles/social-variation... (Accessed: 21 November 2021).
The British Psychological Society (2018) Code of Ethics and Conduct . Available at: https://www.bps.org.uk/news-and-policy/bps-code-ethics-and-conduct (Accessed: 22 March 2019).
Note: Cite Them Right Online offers guidance for referencing webpages that do not include authors' names and dates. However, be extra vigilant about the suitability of such webpages.
Surname, Initial. (Year) Title of photograph . Available at: URL (Accessed: date).
Kitton, J. (2013) Golden sunset . Available at: https://www.jameskittophotography.co.uk/photo_8692150.html (Accessed: 21 November 2021).
stanitsa_dance (2021) Cossack dance ensemble . Available at: https://www.instagram.com/p/COI_slphWJ_/ (Accessed: 13 June 2023).
Note: If no title can be found then replace it with a short description.
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Getting started with the online library
- Disabled user support
- Finding resources for your assignment
- Finding ejournals and articles
- Access eresources using Google Scholar
- Help with online resources
- Finding and using books and theses
- Finding information on your research topic
- Canllaw Cyflym i Gyfeirnodi Harvard (Cite Them Right)
- Quick guide to Cite Them Right referencing for Law modules
- The Classical Studies guide to referencing
- Bibliographic management
- What if I cannot find the reference type I need in my referencing guide?
- I have found a web page with no author, date or publisher - how do I reference it?
- Identifying a source
- Training and skills
- Study materials
- Using other libraries and SCONUL Access
- Borrowing at the Walton Hall Library
- OU Glossary
- Contacting the helpdesk
Smarter searching with library databases
Wednesday, 6 November, 2024 - 19:30
Learn how to access library databases, take advantage of the functionality they offer, and devise a proper search technique.

Library Helpdesk
Chat to a Librarian - Available 24/7
Other ways to contact the Library Helpdesk
The Open University
- Study with us
- Work with us
- Supported distance learning
- Funding your studies
- International students
- Global reputation
- Sustainability
- Apprenticeships
- Develop your workforce
- News & media
- Contact the OU
Undergraduate
- Arts and Humanities
- Art History
- Business and Management
- Combined Studies
- Computing and IT
- Counselling
- Creative Arts
- Creative Writing
- Criminology
- Early Years
- Electronic Engineering
- Engineering
- Environment
- Film and Media
- Health and Social Care
- Health and Wellbeing
- Health Sciences
- International Studies
- Mathematics
- Mental Health
- Nursing and Healthcare
- Religious Studies
- Social Sciences
- Social Work
- Software Engineering
- Sport and Fitness
Postgraduate
- Postgraduate study
- Research degrees
- Masters in Social Work (MA)
- Masters in Economics (MSc)
- Masters in Creative Writing (MA)
- Masters in Education (MA/MEd)
- Masters in Engineering (MSc)
- Masters in English Literature (MA)
- Masters in History (MA)
- Masters in International Relations (MA)
- Masters in Finance (MSc)
- Masters in Cyber Security (MSc)
- Masters in Psychology (MSc)
- A to Z of Masters degrees
- OU Accessibility statement
- Conditions of use
- Privacy policy
- Cookie policy
- Manage cookie preferences
- Modern slavery act (pdf 149kb)
Follow us on Social media
- Student Policies and Regulations
- Student Charter
- System Status
- Contact the OU Contact the OU
- Modern Slavery Act (pdf 149kb)
© . . .
Harvard referencing style
- In-text citations and reference list
- Conference papers
- Video, film, television
- Figures and tables
- Standards and patents
- Generative artificial intelligence (AI)
- Computer software and mobile applications
- Legal sources
Thesis or dissertation
- Personal communications
- << Previous: Legal sources
- Next: Personal communications >>
- Last Updated: Jun 5, 2024 9:35 AM
- URL: https://aut.ac.nz.libguides.com/Harvard
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
- Exhibitions
- Visit and Contact
- UCD Library
- Current Students
- News & Opinion
- Staff Directory
- UCD Connect
Harvard Style Guide: Theses
- Introduction
- Harvard Tutorial
- In-text citations
- Book with one author
- Book with two or three authors
- Book with four or more authors
- Book with a corporate author
- Book with editor
- Chapter in an edited book
- Translated book
- Translated ancient texts
- Print journal article, one author
- Print journal article, two or three authors
- Print journal article, four or more authors
- eJournal article
- Journal article ePublication (ahead of print)
- Secondary sources
- Generative AI
- Images or photographs
- Lectures/ presentations
- Film/ television
- YouTube Film or Talk
- Music/ audio
- Encyclopaedia and dictionaries
- Email communication
- Conferences
- Official publications
- Book reviews
- Case studies
- Group or individual assignments
- Legal Cases (Law Reports)
- No date of publication
- Personal communications
- Repository item
- Citing same author, multiple works, same year
Back to Academic Integrity guide
Reference : Author, Initial. (Year of submission) Title of thesis . Degree statement. Degree-awarding body.
Example : Allen, S. J. (2009) The social and moral fibre of Celtic Tiger Ireland . Unpublished PhD thesis. University College Dublin.
In-Text-Citation :
- Author Last name (Year)
- (Author Last name, Year)
- Allen (2009) disagrees with this…..
- As argued elsewhere (Allen, 2009)….
Still unsure what in-text citation and referencing mean? Check here .
Still unsure why you need to reference all this information? Check here .

- << Previous: Email communication
- Next: Conferences >>
- Last Updated: Jul 9, 2024 3:12 PM
- URL: https://libguides.ucd.ie/harvardstyle
- For educators
- Go to my projects
- Português (PT)
- Português (BR)
BibGuru Harvard Referencing Generator
Cite websites, books, articles, ...
What is Harvard referencing?
How do i reference in harvard, harvard referencing examples, helpful resources on harvard style, the ultimate guide to citing in harvard.
When you reference a work, you are acknowledging other people's contributions to your research. References can provide key background information, support or dispute your thesis, or offer important definitions and data. Referencing also shows that you have personally read the work.
When using the Harvard referencing style, you identify the sources you have used by citing them in text, enclosing partial citations within parentheses embedded in the text, either within or after a sentence. This referencing system is called the author-date system.
The in-text citations are followed by a full, alphabetised list of references in an end section. We will explain this in further detail below with plenty of examples.
Citing can be very complex, which is why we have created the BibGuru Harvard reference generator to help you focus on the content of your work instead of worrying about how to get your reference list done correctly.
Learn everything you need to know about Harvard citations on this page and in our Harvard citation guide . This guide is based on the 11th edition of Cite Them Right .

I want to cite a ...
The Harvard style is one of the most widely used referencing styles in the world. This is most likely due to its simplicity and ease of use. There is no official manual, but many institutions offer their own Harvard reference style guides, which of course leads to slight nuances when it comes to punctuation and formatting rules.
The Harvard referencing style uses the author-date system for in-text citations, which means the author's surname and the year of publication in round brackets are placed within the text. If there is no discernible author, the title and date are used.
The reference list outlines all the sources directly cited in your work. It should be ordered alphabetically by the surname of the first author of each work. References with no author are ordered alphabetically by the first significant word of the title. Only the initials of the authors' given name are used, with no full stop and space between the initials.
Here is an example:
EXAMPLE In-text citation
There are five strategies to implement Diversity Management in companies (Cox, 2001).
EXAMPLE Reference list
Cox, T. (2001). Creating the multicultural organization. 1st ed. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass, p.50.
When you cite you are referring to someone else's work or ideas in your text. In-text references give brief details of the work that you are quoting from, or which you are referring to, in your text. These references will then link to the full reference in the reference list at the end of your work. Footnotes or Endnotes are not used in the Harvard or other author-date citation styles.
When citing in-text, provide the author's surname and date of publication in brackets right after the borrowed information or at the end of the sentence. If you have already mentioned the author's name in the text, you only need to place the date of publication in brackets directly after where the author's surname is mentioned.
If you are only quoting a particular section of the source, instead of the whole book, you should also include a page number or range after the publication date. If the book has more than four authors, you do not need to write out all of their surnames. Use the first author’s surname followed by the abbreviation ‘et al.’, which means 'and others'.
The reference list at the end of your work should start on a new page and be arranged in alphabetical order. Italicise the titles of books, reports, etc. Beware that for journal articles, the name of the journal should be italicised instead of the title of the article you are citing. Make sure to capitalise the first letter of the publication title, the first letters of all main words in the title of a journal, and all first letters of a publication place and publisher.

How to use Bibguru for Harvard citations

- Printed books
- Journals and Magazines
- Webpages and Websites
- United Kingdom Legal Sources
The general referencing order for a book in Harvard for your reference list is:
- Author/editor
- Year of publication (in round brackets)
- Title (in italics)
- Place of publication: Publisher
- Series and volume number (where relevant)
EXAMPLE Book with one author
All of those factors contribute to climate change (See, 2012).
Reference list
See, M. (2012) Greenhouse gas emissions: Global business aspects . Berlin, Germany: Springer.
EXAMPLE Book with two authors
Auerbach and Kotlikoff (1998) explain that a higher level of labor productivity means more output per person.
Auerbach, A. J. and Kotlikoff, L. J. (1998) Macroeconomics: An integrated approach. 2nd ed. London, England: MIT Press.
EXAMPLE Book with an editor and multiple authors
.. as claimed by the authors (Raab et al., 2015).
Raab, M. et al. (eds.) (2015) Performance psychology: Perception, action, cognition, and emotion . San Diego, CA: Academic Press.
EXAMPLE Ebook
.. as claimed by the authors (Christian and Griffiths, 2016).
Christian, B. and Griffiths, T. (2016) Algorithms to live by: The computer science of human decisions. London, England: William Collins. Available at: http://a.co/7qGBZAk.
Many journals have print and online equivalents, or they may just be available in print or in online editions. You should reference the version that you are using. As long as the journal reference provides enough bibliographic information for the article to be located by the reader, other elements - e.g. database title or URL - don't need to be included. However, if the article you are citing is only available online, you have to include the DOI or URL.
The general referencing order for a journal article in Harvard is:
- Author (surname followed by initials)
- Title of article (in single quotation marks)
- Title of journal (in italics - capitalise first letter of each word in title, except for linking words)
- Issue information (volume (unbracketed), and, where applicable, part number, month or season)
- Page reference (if available)
- If accessed online: DOI or Available at: URL (Accessed: date)
EXAMPLE Journal article
In their review of the literature (Norrie et al. , 2012)..
Norrie, C. et al. (2012) 'Doing it differently?' A review of literature on teaching reflective practice across health and social care professions', Reflective Practice , 13(4), pp. 565-578.
EXAMPLE Journal article with DOI
(McCauley and Christiansen, 2019)
McCauley, S. M. and Christiansen, M. H. (2019) “Language learning as language use: A cross-linguistic model of child language development,” Psychological review , 126(1), pp. 1–51. doi: 10.1037/rev0000126.
Magazine articles
To cite a magazine article in Harvard, follow this citation order:
- Title of magazine (in italics - capitalise first letter of each word in title, except for linking words)
EXAMPLE Electronic magazine article
The southern part of Kalahari has characteristics of a dry savanna ecosystem (Joubert, 2021).
Joubert, L. (2021) 'Rising heat puts the Kalahari’s ecosystem on the edge of survival', National Geographic, 27 July. Available at: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/magazine/article/rising-heat-puts-the-kalaharis-ecosystem-on-the-edge-of-survival-feature (Accessed: 28 July 2021).
The citation order for theses is the following:
- Year of submission (in round brackets)
- Title of thesis (in italics)
- Degree statement
- Degree-awarding body
EXAMPLE Doctoral thesis
Pradhan, S. (2021) Impacts of road construction on landsliding in Nepal. Doctoral thesis. Durham University. Available at: http://etheses.dur.ac.uk/14069/ (Accessed: 28 July 2021).
When referencing information from the internet, make sure to distinguish what you are referring to. The internet is made up of a broad range of material - from journal articles to government publications, blogs, and images. This section shows you how to reference internet sites or web pages produced by individuals or organisations.
As always, the information you provide should be just enough for the reader to find the source. As material on the internet can be removed or changed, also note the date when you have accessed the information.
The defining element in referencing a website is the URL. It should be included in your reference list, but not in your in-text citation.
Citation order of a website with individual authors:
- Year that the site was published/last updated (in round brackets)
- Title of web page (in italics)
- Available at: URL (Accessed: date)
EXAMPLE Websites with individual authors
McCarthy (2021) also says that wasted food significantly impacts climate change.
McCarthy, S. (2021) Over 1 Billion Tonnes More Food Being Wasted Than Previously Estimated, Contributing 10% of All Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Available at: https://www.worldwildlife.org/press-releases/over-1-billion-tonnes-more-food-being-wasted-than-previously-estimated-contributing-10-of-all-greenhouse-gas-emissions (Accessed: 27 July 2021).
EXAMPLE Websites with organisations as authors
After identifying symptoms (National Health Service, 2018)...
National Health Service (2018) Check your symptoms . Available at: http://www.nhsdirect.nhs.uk/checkyoursymptoms (Accessed: 17 October 2018).
EXAMPLE Websites with no authors
.. and is considered a virtue (Altruism, 2021).
Altruism (2021) Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia . Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Altruism (Accessed: August 24, 2021).
Blogs and Vlogs
Beware that blogs and vlogs are someone's opinion, and therefore might not provide objective, reasoned discussion of an issue. Use them together with reputable sources. This is the citation order for blogs:
- Title of message (in single quotation marks)
- Title of internet site (in italics)
- Day/month of posted message
EXAMPLE Blog
Social channels help us share common interests (Liegl, 2021)
Liegl, J. (2021) 'Communicating with humanity', Several People Are Typing , 2 July. Available at: https://slack.com/intl/en-at/blog (Accessed: 28 July 2021).
Social Media
This would be the citation order for an Instagram post, but other social media websites follow the same order:
- Author (Instagram account holder/poster)
- Year posted (in round brackets)
- Title of post (in single quotation marks)
- [Instagram]
EXAMPLE Instagram post
.. by painting a sea horse (VeganArtShare, 2021).
VeganArtShare (2021) 'Tiny dancer of the sea.' [Instagram]. 25 June. Available at: https://www.instagram.com/p/CQjWYSWJDqT/ (Accessed: 24 August 2021).
Photographs
To reference a photograph from the internet, follow this citation order:
- Photographer
- Title of photograph (in italics)
EXAMPLE Photograph from the internet
His beautiful photograph (Kitto, 2013)...
Kitto, J. (2013) Golden Sunset. Available at: http://www.jameskitto.co.uk/photo_1827786.html (Accessed: 14 June 2018).
Television programmes
When viewing a television programme through a streaming service (e.g. Netflix), use the following citation order:
- Title of programme (in italics)
- Year of original broadcast (in round brackets)
- Name of transmitting channel
- Date and time of transmission (if available)
- Available at: Name of streaming service (Accessed: date)
EXAMPLE Programme on Netflix
While this show is set in the Cold war era ( The Queen's Gambit , 2020),..
The Queen's Gambit (2020) Netflix Original, 12 January, 20:00. Available at: Netflix (Accessed: 24 August 2021).
There is a multitude of different legal sources in the UK that we can use to explain referencing in Harvard. The safest way to get the correct reference is to use the BibGuru Harvard reference generator .
This is the citation order for papers from the House of Commons and House of Lords:
- Parliament. House of ...
- Year of Publication (in round brackets)
- Paper number (in round brackets) - for House of Lords papers, the paper number is also in round brackets to distinguish it from identical House if Commons paper numbers
EXAMPLE Papers from the House of Commons and House of Lords
Parliamentary reports for the year included the criminal justice system (Parliament. House of Commons, 1999) and renewable energy (Parliament. House of Lords, 1999).
Parliament. House of Commons (1999) Criminal Justice: working together, Session 1999-2000 . (HC 1999-2000 29). London: The Stationery Office.
Parliament. House of Lords (1999) Electricity from renewables: first report from the Select Committee on the European Union . (HL 1999-2000 (18)). London: The Stationery Office.
While there is a multitude of details and specific rules on how to cite various publications or works in Harvard (magazines, online books, the internet, social media, legal sources, movies, etc.), you do not need to worry about getting your citations wrong with BibGuru. Use our BibGuru Harvard reference generator to create the fastest and most accurate Harvard citations possible.
Ditch the frustrations for stress-free citations
From our blog.

More Bibguru Harvard guides
General Guides (UK)
- Dundalk Institute of Technology Library
- Anglia Ruskin University Library
- University of York Library
- Birmingham City University Library
- University College, London Library
- Imperial College, London Library
- University of Bolton
General Guides (Australia)
- Macquarie University Library
- Monash University Library
- University of New South Wales
Cite Them Right Specific Guides
- Open University Library
- University of Sheffield Library
- University of St. Andrews Library
- University of Sussex Library
The APA style is a variant of the Harvard style. Both styles use author-date references in brackets right after the borrowed information or at the end of the sentence, and full references in the reference list. There are a few differences between APA and Harvard, you can learn more about them here .
Your Harvard paper should be double-spaced with smooth left margins. The Harvard Reference list is double-spaced too.
The Reference list is alphabetised by the author's surname and is double-spaced with a hanging indent, meaning that all but the first line have an indent. The margin can vary depending on your institution, but in general is 0.5.
In general, numbers below 101 should be spelled out. The same goes for large round numbers like "one thousand" or "twenty thousand", although 250,000 would be too long to spell out. Very large numbers, like 4.3 billion, should be expressed in figures. What is most important though is consistency. However, you choose to express numbers, be consistent with them throughout your paper. You can read more about this here .
The Harvard citation style uses the author-date system for in-text references, which means the author's surname and the year of publication in round brackets are placed within the text, not in footnotes. Only use footnotes within a Harvard formatted paper for explanatory notes that would not detract from the text, if necessary.
Citation generators
Citation guides, alternative to.
- NoodleTools
- Getting started
- 📚 How to write a book report
- 📝 APA Running Head
- 📑 How to study for a test
Harvard Citation Generator
Powered by chegg.
- Select style:
- Archive material
- Chapter of an edited book
- Conference proceedings
- Dictionary entry
- Dissertation
- DVD, video, or film
- E-book or PDF
- Edited book
- Encyclopedia article
- Government publication
- Music or recording
- Online image or video
- Presentation
- Press release
- Religious text
What is the Harvard Referencing System?
The Harvard citation style is a system that students, writers and researchers can use to incorporate other people’s quotes, findings and ideas into their work in order to support and validate their conclusions without breaching any intellectual property laws. The popular format is typically used in assignments and publications for humanities as well as natural, social and behavioural sciences.
It is a parenthetical referencing system that is made up of two main components:
- In-text citations including the author’s surname and the year of publication should be shown in brackets wherever another source has contributed to your work
- A reference list outlining all of the sources directly cited in your work
Whilst in-text citations are used to briefly indicate where you have directly quoted or paraphrased a source, your reference list is an alphabetized list of complete Harvard citations that enables your reader to locate each source with ease. Each entry should be keyed to a corresponding parenthetical citation in the main body of your work, so that a reader can take an in-text citation and quickly retrieve the source from your reference list.
Note that some universities, and certain disciplines, may also require you to provide a bibliography. This is a detailed list of all of the material you have consulted throughout your research and preparation, and it will demonstrate the lengths you have gone to in researching your chosen topic.
‘Harvard referencing’ is an umbrella term for any referencing style that uses the author name and year of publication within the text to indicate where you have inserted a source. This author-date system appeals to both authors and readers of academic work. Scholars find the format an economical way of writing, and it is generally more accessible to the reader as there are no footnotes crowding the page. Only the name of the author, the publication date of the source and, if necessary, the page numbers are included in the parenthetical citations, for example: (Joyce, 2008).
Use Cite This For Me’s Harvard style referencing generator to create your fully-formatted in-text references and reference list in the blink of an eye. Stop giving yourself extra pain and work for no reason and sign up to Cite This For Me today – your only regret will be that you didn’t use our open-generator sooner!
Popular Harvard Referencing Examples
- Chapter of a book
- Conference proceedings
- Court case
- Dissertation
- Encyclopedia article
- Image online or video
- Presentation or lecture
- Video, film, or DVD
Cite This For Me’s Harvard Referencing Guide
The following guide provides you with everything you need to know to do justice to all your hard work and get a mark that reflects those sleepless nights. If you’re not sure how to format your Harvard style citations, what citations are, or are simply curious about Cite This For Me citation generator, our guide will answer all of your questions whilst offering you a comprehensive introduction to the style. Keep reading to find out why you need to use a referencing system, how to add citations in the body of your assignment, and how to compile a reference list.
Sometimes, students do not encounter citing until they embark onto degree-level studies, yet it is a crucial academic skill that will propel you towards establishing yourself in the academic community. It’s a common mistake to leave citing and creating a complete and accurate bibliography until the very last minute, but with Cite This For Me’s Harvard referencing generator you can cite-as-you-go.
So, if you need a helping hand with your referencing then why not try Cite This For Me’s automated citation generator ? The generator accesses knowledge from across the web, assembling all of the relevant information into a fully-formatted reference list that clearly presents all of the sources that have contributed to your work. Using this Harvard reference generator to cite your sources enables you to cross the finishing line in style.
It is important to bear in mind that there is a plethora of different citation styles out there – the use of any particular one depends on the preference of your college, subject, professor or the publication you are submitting the work to. If you’re unsure which style you should be using, consult your tutor and follow their guidelines. If your lecturer or department does not ask you to use a particular style, we recommend using the Harvard referencing system because it is simple to use and easy to learn.
The powerful open-access generator above can auto-generate citations in 1,000+ styles. So, whether your professor prefers that you use the MLA format , or your discipline requires you to adopt the APA citation or Chicago citation style , we have the style you need. Cite This For Me also provides open generators and handy style guides for styles such as ASA , AMA or IEEE . To accurately create citations in a specific format, simply sign up to Cite This For Me for free and select your chosen style.
Are you struggling with citing an unfamiliar source type? Or feeling confused about whether to cite a piece of common knowledge? This guide will tell you everything you need to know to get both your parenthetical Harvard citations and reference list completed quickly and accurately.
Why do I Need to Cite?
Harvard referencing can be a confusing task, especially if you are new to the concept, but it’s absolutely essential. In fact, accurate and complete referencing can mean the difference between reaching your academic goals and damaging your reputation amongst scholars. Simply put – referencing is the citing of sources you have utilised to support your essay, research, conference or article etc.
Even if you are using our Harvard style citation generator, understanding why you need to cite will go a long way in helping you to naturally integrate the process into your research and writing routine.
Firstly, whenever another source contributes to your work you must give the original author the appropriate credit in order to avoid plagiarism, even when you have completely reworded the information. The only exception to this rule is common knowledge – e.g. Barack Obama is President of the United States. Whilst plagiarism is not always intentional, it is easy to accidentally plagiarize your work when you are under pressure from imminent deadlines, you have managed your time ineffectively, or if you lack confidence when putting ideas into your own words. The consequences can be severe; deduction of marks at best, expulsion from college or legal action from the original author at worst. Find out more here.
This may sound overwhelming, but plagiarism can be easily avoided by using our Harvard citation generator and carrying out your research and written work thoughtfully and responsibly. We have compiled a handy checklist to follow whilst you are working on an assignment.
How to avoid plagiarism:
- Formulate a detailed plan – carefully outline both the relevant content you need to include, as well as how you plan on structuring your work
- Keep track of your sources – record all of the relevant publication information as you go (e.g. If you are citing a book you should note the author or editor’s name(s), year of publication, title, edition number, city of publication and name of publisher). Carefully save each quote, word-for-word, and place it in inverted commas to differentiate it from your own words. Tired of interrupting your workflow to cite? Use our Harvard referencing generator to automate the process
- Manage your time effectively – make use of time plans and targets, and give yourself enough time to read, write and proofread
- When you are paraphrasing information, make sure that you use only your own words and a sentence structure that differs from the original text
- Save all of your research and citations in a safe place – organise and manage your Harvard style citations.
If you carefully check your college or publisher’s advice and guidelines on citing and stick to this checklist, you should be confident that you will not be accused of plagiarism.
Secondly, proving that your writing is informed by appropriate academic reading will enhance your work’s authenticity. Academic writing values original thought that analyzes and builds upon the ideas of other scholars. It is therefore important to use Harvard style referencing to accurately signpost where you have used someone else’s ideas in order to show that your writing is based on knowledge and informed by appropriate academic reading. Citing your sources will demonstrate to your reader that you have delved deeply into your chosen topic and supported your thesis with expert opinions.
Here at Cite This For Me we understand how precious your time is, which is why we created our Harvard citation generator and guide to help relieve the unnecessary stress of citing. Escape assignment-hell and give yourself more time to focus on the content of your work by using Cite This For Me citation management tool.
Harvard Referencing Guidelines by School
- Anglia University Harvard Referencing
- Bournemouth University Harvard Referencing
- Cardiff University Harvard Referencing
- Coventry University Harvard Referencing
- DMU Harvard Referencing
- Edge Hill University Harvard Referencing
- Imperial College University Harvard Referencing
- Leeds University Harvard Referencing
- LSBU Harvard Referencing
- MMU Harvard Referencing
- SHU Harvard Referencing
- Staffordshire University Harvard Referencing
- UCA Harvard Referencing
- UWE Harvard Referencing
- UWS Harvard Referencing
- Wolverhampton University Harvard Referencing
How do I Create and Format In-text Harvard Style Citations?
In-text citations are the perfect way to seamlessly integrate sources into your work, allowing you to strengthen the connection between your own ideas, and the source material that you have found, with ease. It is worth noting that in-text citations must be included in your assignment’s final word count.
When adopting Harvard style referencing in your work, if you are inserting a quote, statement, statistic or any other kind of source information into the main body of your essay you should:
- Provide the author’s surname and date of publication in brackets right after the taken information or at the end of the sentence
There are many assumptions when it comes to the information processing approach to cognition… (Lutz and Huitt, 2004).
- If you have already mentioned the author in the sentence, Harvard referencing guidelines require you to only enter the year of publication in parentheses, directly after where the author’s surname is mentioned
In the overview of these developmental theories, Lutz and Huitt (2004) suggest that…
- If you are quoting a particular section of the source (rather than the entire work), you should also include a page number, or page range, after the date, within the parenthetical Harvard citation
“…the development of meaning is more important than the acquisition of a large set of knowledge or skills …” (Lutz and Huitt, 2004, p.8), which means that …
- Note that if the source has four or more authors, you do not need to write out all of their surnames; simply use the first author’s surname followed by the abbreviation ‘et al.’ (meaning ‘and others’) in italics
Why use a Harvard referencing tool? As well as saving you valuable time, Cite This For Me generator will enable you to easily avoid common errors when formatting your in-text citations. So, if you’re looking for an easy and free way to credit your source material, simply login to your Cite This For Me account, select ‘Cite Them Right 10th Edition – Harvard’, then ‘Create reference’, to copy, save and export each in-text Harvard citation instantly.
How do I Format My Reference List?
Utilizing and building on a wide range of relevant sources is a guaranteed way of impressing your reader, and a comprehensive list of the source material you have used is the perfect platform to exhibit your research efforts. The brief in-text Harvard style citations in your work should directly link to your reference list.
As a general rule a reference list includes every source that you have cited in your work, whilst a bibliography also contains any relevant background reading which you have consulted (even those sources that are never mentioned in the narrative). Your bibliography should start on its own page, with the same formatting as the rest of the paper and aligned to the left with the sources listed alphabetically. Many people use the terms ‘reference list’ and ‘bibliography’ interchangeably, and if you are using the Harvard reference style you may be required to provide a bibliography as well as a reference list, so be sure to check this with your tutor.
Follow these guidelines when compiling your reference list:
- Start your reference list on a new page at the end of your document
- General formatting should be in keeping with the rest of your work
- Use ‘Reference List’ as the heading
- Copy each of your full-length Harvard citations into a list
- Arrange the list in alphabetical order by the author’s last name (titles with no author are alphabetized by the work’s title, and if you are citing two or more sources by the same author they should be listed in chronological order of the year of publication)
- When there are several works from one author or source, they should be listed together but in date order – with the earliest work listed first
- Italicize titles of books, reports, conference proceedings etc. For journal articles, the title of the journal should be printed in italics, rather than the title of the journal article
- Capitalize the first letter of the publication title, the first letters of all main words in the title of a journal, and all first letters of a place name and publisher
Creating and managing your reference list with Cite This For Me’s Harvard referencing generator will transform and improve the way you reference and conduct research.
Reference list / bibliography examples:
- Book, one author:
Bell, J. (2010) Doing your research project. 5th edn. Maidenhead: Open University Press.
- One author, book, multiple editions:
Hawking, S.W. (1998) A brief history of time: From the big bang to black holes. 10th edn. New York: Bantam Doubleday Dell Publishing Group.
If all information resembles a book, use the template for a book reference.
If a page number is unavailable, use chapter number. URL links are not necessary, but can be useful. When including a URL, include the date the book was downloaded at the end of the Harvard citation:
Available at: URL (Downloaded: DD Month YYYY)
- More than three authors, journal article*:
Shakoor, S., et al. (2011) ‘A prospective longitudinal study of children’s theory of mind and adolescent involvement in bullying’, Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 53(3), pp. 254–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2011.02488.x.
- Conference papers:
Drogen, E. (2014) ‘Changing how we think about war: The role of psychology’, The British Psychological Society 2014 Annual Conference. The ICC, Birmingham British Psychological Society, 07-09 May 2014.
Are you struggling to find all of the publication information to complete a reference? Did you know that our Harvard citation generator can do it for you?
Time is of the essence when you’re finishing a paper, but there’s no need to panic because you can compile your reference list in a matter of seconds using Cite This For Me’s Harvard style citation generator.
Harvard Referencing Formatting Guidelines
Accurate referencing doesn’t only protect your work from plagiarism – presenting your source material in a consistent and clear way also enhances the readability of your work. Closely follow the style’s formatting rules on font type, font size, text-alignment and line spacing to ensure that your work is easily legible. Before submitting your work check that you have formatted your whole paper – including your reference list – according to the style’s formatting guidelines.
How to format in Harvard referencing:
- Margins: 2.5cm on all sides
- Shortened title followed by the page number in the header, aligned to the right
- Double-space the entirety of the paper
- ½ inch indentation for every new paragraph (press tab bar)
- Suggested fonts: Times New Roman, Arial and Courier New for Windows; Times New Roman, Helvetica and Courier for Mac, 12pt size. Ensure that all Harvard citations are in the same font as the rest of the work
- Reference list titled ‘Bibliography’ on a separate page at the end of the body of your work
Even when using a Harvard citation generator, always check with your professor for specified guidelines – there is no unified style for the formatting of a paper. Make sure that you apply the recommended formatting rules consistently throughout your work.
A Brief History of the Harvard Reference Style
The author-date system is attributed to eminent zoologist Edward Laurens Mark (1847-1946), Hersey professor of anatomy and director of Harvard’s zoological laboratory. It is widely agreed that the first evidences of Harvard referencing can be traced back to Mark’s landmark cytological paper (Chernin, 1988). The paper breaks away from previous uses of inconsistent and makeshift footnotes through its use of a parenthetical author-date citation accompanied by an explanatory footnote.
- Parenthetic author-year citation, page 194 of Mark’s 1881 paper:
[…] The appearance may be due solely to reflection from the body itself. (Comp. Flemming, ‘78b, p. 310.*)
- Mark’s rationale for his Harvard citational scheme:
*The numbers immediately following an author’s name serve the double purpose of referring the reader to the list (p. 591) where the titles of papers are given, and of informing him at once of the approximate date of the paper in question.
A tribute dedicated to Mark in 1903 by 140 students credits Mark’s paper with having ‘introduced into zoology a proper fullness and accuracy of citation and a convenient and uniform method of referring from text to bibliography’ (Parker, 1903). Today Harvard referencing is widely considered one of the most accessible styles and, although it originated in biology, these days it is used across most subjects – particularly in the humanities, history and social science.
The Evolution of the Harvard Referencing Style
Due to its simplicity and ease of use, the format has become one of the most widely used citation styles in the world. Unlike many citing styles there is no official manual, but institutions such as colleges offer their own unique Harvard reference style guide, and each has its own nuances when it comes to punctuation, order of information and formatting rules. Simply go to the Cite This For Me website to login to your Cite This For Me account and search for the version you need. Make sure you apply consistency throughout your work.
It is increasingly easy for writers to access information and knowledge via the internet, and in turn both the style’s guidelines and our open-generator are continually updated to include developments in electronic publishing. Cite This For Me’s Harvard style citation generator currently uses the Cite Them Right 10th Edition, which has evolved in recent years to match the rapidly advancing digital age. In order to avoid plagiarism, you must be cautious about pulling information from the internet, and ensure that you accurately cite all source material used in your written work – including all online sources that have contributed to your research.
Key differences from previous Cite Them Right editions:
- Previous editions required printed books and eBooks to be referenced differently – in the 10th edition, both are now referenced using the same template (if all the necessary information is available). An Ebook is considered to be the digital format of a published book (or a book that is only published in digital format) that is meant for reading on an electronic device
- URLs are no longer a requirement for digital media if the information provided in the Harvard citation is sufficient to find the source without it. They should be included if the source is difficult to find, or pieces of source information – such as an author name – are missing
- If you have more than 3 authors for a source, you are now encouraged to use the abbreviation “et al.” instead of listing each author.
These days students draw on a diverse range of digital sources to support their written work. The Cite This For Me generator will take care of all your Harvard citations, regardless of the type of source you want to cite. So don’t be held back by sources that are difficult to cite – locating unusual source material will help your work to stand out from the crowd.
How do I Create Accurate Harvard Citations?
Creating complete and correctly formatted citations can be a challenge for many writers, especially when documenting multiple source types. Our primary goal at Cite This For Me is to offer support to students and researchers across the globe by transforming the way in which they perceive citing. We hope that after using our open-generator and reading this Harvard referencing guide, what was once considered an arduous process, will be viewed as a highly valued skill that enhances the quality of your work.
Disheartened by the stressful process of citing? Got a fast-approaching deadline? Using Cite This For Me’s fast, accessible and free generator makes creating accurate citations easier than ever, leaving more time for you to focus on achieving your academic goals.
Create a free account to add and edit each Harvard citation on the spot, import and export full projects or individual entries, utilise our add-ons and save your work in the cloud.
Cite on-the-go with your mobile phone or tablet – when you scan the barcode of your book with the mobile app, the generator will automatically add the fully-formatted citation to your chosen project.
Cite This For Me’s citation management tool is here to help you, so what are you waiting for? Accurate Harvard citations are just a click away!
Reference List
Chernin, E. (1988) The ‘Harvard System’: A mystery dispelled. Available at: http://www.uefap.com/writing/referenc/harvard.pdf (Accessed: 4 July 2016).
Parker, G. (ed.) (1903) Mark anniversary volume. New York: Henry Holt.
Manage all your citations in one place
Create projects, add notes, cite directly from the browser and scan books’ barcodes with a mobile app.
Sign up to Cite This For Me – the ultimate citation management tool.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Referencing
- Harvard In-Text Citation | A Complete Guide & Examples
Harvard In-Text Citation | A Complete Guide & Examples
Published on 30 April 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on 5 May 2022.
An in-text citation should appear wherever you quote or paraphrase a source in your writing, pointing your reader to the full reference .
In Harvard style , citations appear in brackets in the text. An in-text citation consists of the last name of the author, the year of publication, and a page number if relevant.
Up to three authors are included in Harvard in-text citations. If there are four or more authors, the citation is shortened with et al .
Make your writing flawless in 1 upload
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Including page numbers in citations, where to place harvard in-text citations, citing sources with missing information, frequently asked questions about harvard in-text citations.
When you quote directly from a source or paraphrase a specific passage, your in-text citation must include a page number to specify where the relevant passage is located.
Use ‘p.’ for a single page and ‘pp.’ for a page range:
- Meanwhile, another commentator asserts that the economy is ‘on the downturn’ (Singh, 2015, p. 13 ).
- Wilson (2015, pp. 12–14 ) makes an argument for the efficacy of the technique.
If you are summarising the general argument of a source or paraphrasing ideas that recur throughout the text, no page number is needed.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
When incorporating citations into your text, you can either name the author directly in the text or only include the author’s name in brackets.
Naming the author in the text
When you name the author in the sentence itself, the year and (if relevant) page number are typically given in brackets straight after the name:
Naming the author directly in your sentence is the best approach when you want to critique or comment on the source.
Naming the author in brackets
When you you haven’t mentioned the author’s name in your sentence, include it inside the brackets. The citation is generally placed after the relevant quote or paraphrase, or at the end of the sentence, before the full stop:
Multiple citations can be included in one place, listed in order of publication year and separated by semicolons:
This type of citation is useful when you want to support a claim or summarise the overall findings of sources.
Common mistakes with in-text citations
In-text citations in brackets should not appear as the subject of your sentences. Anything that’s essential to the meaning of a sentence should be written outside the brackets:
- (Smith, 2019) argues that…
- Smith (2019) argues that…
Similarly, don’t repeat the author’s name in the bracketed citation and in the sentence itself:
- As Caulfield (Caulfield, 2020) writes…
- As Caulfield (2020) writes…
Sometimes you won’t have access to all the source information you need for an in-text citation. Here’s what to do if you’re missing the publication date, author’s name, or page numbers for a source.
If a source doesn’t list a clear publication date, as is sometimes the case with online sources or historical documents, replace the date with the words ‘no date’:
When it’s not clear who the author of a source is, you’ll sometimes be able to substitute a corporate author – the group or organisation responsible for the publication:
When there’s no corporate author to cite, you can use the title of the source in place of the author’s name:
No page numbers
If you quote from a source without page numbers, such as a website, you can just omit this information if it’s a short text – it should be easy enough to find the quote without it.
If you quote from a longer source without page numbers, it’s best to find an alternate location marker, such as a paragraph number or subheading, and include that:
A Harvard in-text citation should appear in brackets every time you quote, paraphrase, or refer to information from a source.
The citation can appear immediately after the quotation or paraphrase, or at the end of the sentence. If you’re quoting, place the citation outside of the quotation marks but before any other punctuation like a comma or full stop.
In Harvard referencing, up to three author names are included in an in-text citation or reference list entry. When there are four or more authors, include only the first, followed by ‘ et al. ’
In Harvard style , when you quote directly from a source that includes page numbers, your in-text citation must include a page number. For example: (Smith, 2014, p. 33).
You can also include page numbers to point the reader towards a passage that you paraphrased . If you refer to the general ideas or findings of the source as a whole, you don’t need to include a page number.
When you want to use a quote but can’t access the original source, you can cite it indirectly. In the in-text citation , first mention the source you want to refer to, and then the source in which you found it. For example:
It’s advisable to avoid indirect citations wherever possible, because they suggest you don’t have full knowledge of the sources you’re citing. Only use an indirect citation if you can’t reasonably gain access to the original source.
In Harvard style referencing , to distinguish between two sources by the same author that were published in the same year, you add a different letter after the year for each source:
- (Smith, 2019a)
- (Smith, 2019b)
Add ‘a’ to the first one you cite, ‘b’ to the second, and so on. Do the same in your bibliography or reference list .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, May 05). Harvard In-Text Citation | A Complete Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 October 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/referencing/harvard-in-text-citation/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, a quick guide to harvard referencing | citation examples, harvard style bibliography | format & examples, referencing books in harvard style | templates & examples, scribbr apa citation checker.
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!

- Bibliography
- More Referencing guides Blog Automated transliteration Relevant bibliographies by topics
- Automated transliteration
- Relevant bibliographies by topics
- Referencing guides
Dissertation (thesis): how to cite in Harvard style?
Create a spot-on reference in harvard, general rules.
According to the Harvard citation style, the same template is used for referencing a master's thesis and a doctoral dissertation in a list of bibliographic references:
Author , ( year ). Title . Work type , University .
NB: Fill in the 'Work type' field the type of work and the academic grade, for instance, 'Ph.D. thesis'.
If the text of the work can be accessed online, use the following template for your reference:
Author , ( year ). Title . Work type , University . [Viewed date viewed ]. Available from: URL
NB: The text '[online]' is not given after the title of the work, in contrast to the references to a book , a journal article , etc.
Examples in a list of references
Middleton, H. J., (2020). *ABA syncretism patterns in pronominal morphology . Ph.D. thesis, University College London. [Viewed 12 January 2021]. Available from: https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/10105591/
Reed, B. H., (1992). The genetic analysis of endoreduplication in Drosophila melanogaster. Ph.D. thesis, University of Cambridge.
Other citation styles:
- What is APA Style (7th ed.)?
- Examples of bibliographic references in APA (7th ed.)
- APA 7 vs APA 6: key differences
- How to cite authors?
- How to format the references page with APA (7th ed.)?
- In-text citations
- Archival document
- Book chapter
- Conference paper
- Dictionary/encyclopedia/dictionary entry/encyclopedia article
- Dissertation (thesis)
- Journal article
- Newspaper article
- Press release
- Religious text
- Social media post
- Software / mobile app
- Video (online)
- Video game / computer game
- What is MLA Style (8th ed.)?
- Examples of references in works cited in MLA (8th ed.)
- How to format the works cited page in MLA (8th ed.)?
- What is Chicago Style?
- Examples of bibliographic references in Chicago Style – notes and bibliography (17th ed.)
- How to format the bibliography page?
- Notes and in-text citations
- Examples of bibliographic references in Chicago Style – author-date (17th ed.)
- What is Harvard referencing style?
- Examples of bibliographic references in Harvard style
- Online video
- What is IEEE Style?
- Examples of bibliographic references in IEEE Style
- How to format the references pages in IEEE Style?
- What is Vancouver Style?
- Examples of bibliographic references in Vancouver Style

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This guide introduces the Harvard referencing style and includes examples of citations. Welcome Toggle Dropdown. A-Z of Harvard references ; Citing authors with Harvard ; ... Title of thesis (in italics). Degree statement. Degree-awarding body. Available at: URL. (Accessed: date). In-text citation: (Smith, 2019)
To cite a master's thesis in a reference entry in Harvard style include the following elements:. Author(s) of the master's thesis: Give the last name and initials (e. g. Watson, J.) of up to three authors with the last name preceded by 'and'. For four authors or more include the first name followed by et al., unless your institution requires referencing of all named authors.
A Harvard Referencing Generator is a tool that automatically generates formatted academic references in the Harvard style. It takes in relevant details about a source -- usually critical information like author names, article titles, publish dates, and URLs -- and adds the correct punctuation and formatting required by the Harvard referencing style.
When you cite a source with up to three authors, cite all authors' names. For four or more authors, list only the first name, followed by ' et al. ': Number of authors. In-text citation example. 1 author. (Davis, 2019) 2 authors. (Davis and Barrett, 2019) 3 authors.
To cite a PhD thesis in a reference entry in Harvard style include the following elements:. Author(s) of the PhD thesis: Give the last name and initials (e. g. Watson, J.) of up to three authors with the last name preceded by 'and'. For four authors or more include the first name followed by et al., unless your institution requires referencing of all named authors.
A thesis is a long-term, large project that involves both research and writing; it is easy to lose focus, motivation, and momentum. Here are suggestions for achieving the result you want in the time you have. The dissertation is probably the largest project you have undertaken, and a lot of the work is self-directed.
Citing a Secondary Source: In this case, state the reference you used first followed by 'cited in' and the original author: Smith 2000 (cited in Mitchell, 2017, p. 189) or (Smith, 2000, cited in Mitchell, 2017, p. 189) 3. How to Cite Different Source Types. Reference list references vary quite a lot between sources.
There are many versions of Harvard referencing style. Our guidance reflects the rules laid out in Cite Them Right: The Essential Referencing Guide (12th edition) by Richard Pears and Graham Shields. Scribbr's free reference generator can create flawless Harvard style references for a wide variety of sources. Cite a webpage.
Harvard Style Bibliography | Format & Examples. Published on 1 May 2020 by Jack Caulfield.Revised on 7 November 2022. In Harvard style, the bibliography or reference list provides full references for the sources you used in your writing.. A reference list consists of entries corresponding to your in-text citations.; A bibliography sometimes also lists sources that you consulted for background ...
In Harvard, the following reference list entry format is used for the dissertation: Author Surname, Author Initials. (Year Published). Title of the dissertation in italics. Level. Institution Name. For example, reference list entry for the above source would be: Darius, H. (2014).
There are different versions of the Harvard referencing style. This guide is a quick introduction to the commonly-used Cite Them Right version. You will find further guidance available through the OU Library on the Cite Them Right Database. For help and support with referencing and the full Cite Them Right guide, have a look at the Library's ...
To cite an undergraduate thesis in a reference entry in Harvard style include the following elements:. Author(s) of the undergraduate thesis: Give the last name and initials (e. g. Watson, J.) of up to three authors with the last name preceded by 'and'. For four authors or more include the first name followed by et al., unless your institution requires referencing of all named authors.
Harvard; In-text citations and reference list; Articles; Books; Conference papers; Webpages; Reports; Video, film, television; Figures and tables; Standards and patents; Generative artificial intelligence (AI) Computer software and mobile applications; Legal sources; Thesis or dissertation. Thesis or dissertation; Personal communications
Theses. Reference: Author, Initial. (Year of submission) Title of thesis. Degree statement. Degree-awarding body. Example: Allen, S. J. (2009) The social and moral fibre of Celtic Tiger Ireland. Unpublished PhD thesis. University College Dublin. In-Text-Citation:
Cite A Dissertation in Harvard style. Use the following template or our Harvard Referencing Generator to cite a dissertation. For help with other source types, like books, PDFs, or websites, check out our other guides. To have your reference list or bibliography automatically made for you, try our free citation generator.
Use our FREE Harvard referencing generator to quickly generate citations from websites, books, and journals in the Harvard reference format. ... References can provide key background information, support or dispute your thesis, or offer important definitions and data. Referencing also shows that you have personally read the work.
Creating and managing your reference list with Cite This For Me's Harvard referencing generator will transform and improve the way you reference and conduct research. Reference list / bibliography examples: Book, one author: Bell, J. (2010) Doing your research project. 5th edn. Maidenhead: Open University Press. One author, book, multiple ...
In Harvard style, citations appear in brackets in the text. An in-text citation consists of the last name of the author, the year of publication, and a page number if relevant. Up to three authors are included in Harvard in-text citations. If there are four or more authors, the citation is shortened with et al. Harvard in-text citation examples.
According to the Harvard citation style, the same template is used for referencing a master's thesis and a doctoral dissertation in a list of bibliographic references: Author, (year). Title. Work type, University. NB: Fill in the 'Work type' field the type of work and the academic grade, for instance, 'Ph.D. thesis'.