- Business Planning

10 Types of Business Plans - Definition, Benefits, and more!

Written by Plangrowlab Team
Published Sep. 25 2024 · 17 Min Read
According to a study, businesses with plans grow 30% more quickly than those without.
But every time you sit down to plan, confusion takes over, leaving you unsure where to start, unclear on details, and fearing failure.
What adds to your fear is figuring out the type of business plan your business needs.
Frustrating, isn’t it? Not anymore!
In this blog, we’ll break down the different types of business plans and help you choose the right one for your business.
Let’s dive in.
What is a business plan?
A formal document that outlines your business strategies, target market, and financial projection to achieve your business goal is known as a business plan.
A well-crafted business plan serves as a roadmap for your business growth on how you’ll achieve your objectives over a specific period.
Remember, it’s a living document that needs updating as your business grows. Different plans, such as traditional, lean, and strategic, suit various stages of business development. Hence, understanding why these different types exist and what their purposes are is essential for selecting the right plan for your needs.
So let’s explore the next section for a better understanding.
Need A Solid Business Plan For Your Business Idea?
Get in touch with us. We’re a business plan consulting company that helps hundreds of businesses achieve their business goal with solid planning.
Connect with Our Consultant Now
Why do different types of business plans exist?
Here are reasons why there exist different business types:
Varied business goal
Businesses have diverse goals beyond just increasing sales and profit. They may focus on expanding their market reach or even enhancing brand awareness. Thus, each of these goals requires a different approach and strategies.
Different business stages
There are different types of business plans for startups and established businesses. A startup requires a business plan from scratch to outline its vision, secure funding, and validate its business idea.
Meanwhile, an established business needs a solid plan to focus on growth strategies, streamline operations, or even pivot into new markets.
Separate target audience
Business plans are tailored depending on whom you’re targeting. Whether they’re investors, partners, lenders, or internal teams.
Each audience demands a different style and focus, with changes in content and presentation to effectively communicate the business's goals and needs.
Distinct level of detail
A healthcare business requires an in-depth explanation of its operation and research hence the level of detail is high.
In contrast, a startup requires a more straightforward plan focusing on its core business idea, marketing plan, and basic startup costs and projections. Resulting in less detail.
The level of detail varies based on the industry complexity and specific business needs.
Constant evolving business growth
As market conditions change, businesses need adaptable plans that evolve with their strategies. Staying competitive requires new approaches to stay ahead in a dynamic market.
That’s about it. Now, let’s explore the different business plans.
Types of business plans
Here are the 10 types of business plans designed to address different needs and stages of business growth. Each type serves a unique purpose and provides a different level of detail.

1. Traditional business plan
Traditional business plans serve as the foundation for many entrepreneurs and growing businesses.
Its primary aim is to provide detailed insights into the business nature, market position, and competitive advantages. Such insights help businesses to craft a roadmap that offers growth, development, and prosperity to businesses.
Here are key components that are commonly included in a traditional business plan:
- A high-level overview (executive summary) of the business that includes the company’s mission, product or services, and key financial information.
- The business description provides detailed insights into the business's nature, market position, and competitive advantages.
- A market analysis that provides data on the industry landscape, target market demographics, and competitive analysis.
- Forecasts of revenue, expenses, and profitability to demonstrate financial viability.
- A description of your company's structure, management team, and key personnel.
- Your estimated income, expenses, and cash flow for the next several years.
2. Lean business plan
Unlike a traditional business plan which can be lengthy and complex, a lean business plan typically fits on one page.
It’s a simplified version of a traditional business plan that focuses on key elements like business model, target market, and essential finance.
A lean business plan is typically crafted for internal purposes or when experimenting with new products, services, or markets. The goal is to create a plan and immediately execute it to see if it succeeds.
Key features of a lean business plan are:
- Lean business plans focus on being short and to the point.
- They use bullet points and tables to share key information quickly and clearly.
- Lean business plans are designed to be easily updated as business evolves which allows for quick adjustments.
- A lean business plan focuses on practical steps like setting milestones and tracking performance to help businesses make smart decisions .
3. Internal Business Plan
The internal business plan is a strategic document that aims to bring management and employees on the same page and focuses on a common goal.
It’s designed to ensure that all team members understand their roles and stick to the roadmap to achieve the organization's vision effectively.
Additionally, the internal business plan outlines the resources available to the business. An internal business plan includes:
- Detailed plans for how to achieve those goals through day-to-day operations.
- Identification of potential challenges and strategies to mitigate them.
- Key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress and success.
- A schedule outlining when key milestones will be achieved.
- Clarification of who is responsible for each part of the plan.
- Insight into the internal market dynamics.
4. Strategic Business Plan
A strategic business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines an organization's long-term goals and the strategies to achieve them.
It acts as a roadmap for decision-making, that helps your businesses align their resources and efforts with their overall vision.
The features of a strategic business plan include:
- Specific deadlines for achieving short-term and long-term objectives.
- Defines the business vision and states the mission statement.
- In-depth study of market trends, competition, and opportunities.
- Plans for allocating financial, human, and operational resources.
- Identification of potential risks and mitigation strategies.
- Strategy for differentiating the business in the market.
- Step-by-step plan to execute strategic goals.
5. Feasibility business plan
A feasibility business plan is a document or a plan that determines the practicality of a new business idea. It's a crucial step before investing significant time and resources into a venture.
A feasibility business plan helps entrepreneurs assess whether their proposed product or service has the potential to succeed in the market.
The feasibility business plan typically includes:
- A brief overview of the business idea, target market, and key financial projections.
- Details about the proposed offering, including its unique features and benefits.
- An assessment of the target market size, customer needs, and competition.
- An outline of the resources, processes, and infrastructure required.
6. Operational business plan
An operational business plan is a detailed blueprint that outlines the specific actions and processes necessary to achieve an organization's strategic objectives.
It focuses on the internal operations of the company, including production, sales, marketing, and human resources. The purpose of operational planning is to streamline internal operations to achieve the desired goals effectively.
The operational business plan's purpose is to bring all team members on the same page and make them understand their roles and responsibilities in executing the company's goals.
Here are the key components of an operational business plan:
- Details the processes involved in producing goods or services, including equipment, materials, and staffing requirements.
- It clearly defines the roles of each team member, ensuring accountability and minimizing overlap in duties.
- Includes key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress and success.
- Explains the process of sourcing materials, managing inventory, and distributing products or services.
- Identifies potential risks and outlines strategies for mitigating them.
- Describes the technology infrastructure, systems, and software needed to support the business's operations.
- Outlines the strategies for reaching and acquiring customers, including sales channels, marketing campaigns, and pricing.
7. Growth business plan
A growth business plan outlines the necessary steps required to advance current business operations to achieve desired business goals. It serves as a roadmap for businesses looking to increase their market share, revenue, or customer base.
Importantly, a growth business plan focuses on identifying growth opportunities, developing strategies to capitalize on them, and allocating resources to support expansion.
The key components of a growth business plan include:
- Documents that examine the target market, including size, growth potential, and competition, to identify expansion opportunities.
- Blueprint that helps you identify the unique value proposition and competitive edge.
- Specific strategies for expanding the business, such as new product development, geographic expansion, or mergers and acquisitions.
- Updated financial forecasts that reflect the impact of growth.
- A clear roadmap for executing growth strategies, including timelines, resources, and key performance indicators (KPIs).
8. Startup business plan
A startup business plan is a foundational document that provides detailed information on the vision, objectives, and strategies for launching a new venture.
It serves as a roadmap for entrepreneurs, detailing everything from the business concept, techniques to deal with challenges to financial projections and growth plans.
The common components of a start up business plan include:
- Overview of business that includes your mission, product or services, target market, and financial goals.
- A detailed explanation of what the startup does, its unique value proposition, and how it solves a customer's problem.
- Detailed information on the company's structure, management team, and key personnel.
- The plan for reaching and attracting customers.
- Detailed forecasts of revenue, expenses, and profitability over a specified period
- An outline of capital needed to launch and what are the sustainable ROI.
- An explanation of the required resources, the duration for which the funds will be necessary, and how they’ll be utilized.
9. One-page business plan
A one-page business plan is a small version of the traditional plan that provides a quick overview of the business.
The purpose is to provide key information about the business clearly, which makes it easy for others to understand and make decisions quickly.
This format lets you quickly share your vision, strategies, and goals without overwhelming potential investors or stakeholders with too much detail.
The features of the one-page plan include:
- A short introduction to your business that includes mission, products or services, target market, and financial goals.
- A clear statement of the problem your business solves and the unique solution you offer.
- Overview of your target market, competitors, and industry trends.
- A brief introduction to the key members of your management team.
- If seeking funding, outline the amount requested and how the funds will be used.
10. Nonprofit business plan
Nonprofit organizations develop nonprofit business plans to achieve their social objectives. It serves as a roadmap for the organization, detailing how it intends to achieve its objectives, attract funding, and measure its impact.
The key components of a nonprofit business plan include:
- A clear and concise statement of the organization's purpose and goals.
- Detailed information about the programs and services offered.
- Identification of the specific groups or communities the organization serves.
- Plans for generating revenue, including grants, donations, memberships, and fundraising events.
- A summary of the organization's board of directors, management team, and governance policies.
- Estimated income, expenses, and cash flow for the next several years.
That said, let's see...
How to choose the right business plan type for your needs?
For a successful business plan, here's how to make an informed decision:
Understand your purpose
First, choose the right business plan to clarify your purpose. To do so, ask yourself what you want to achieve with the plan and why your business needs one.
Here are some aspects you should clear before you choose your plan:
- Is your goal to secure loans or attract investors?
- Are you aiming to expand your current business?
- Do you need a plan to guide your team and streamline operations?
- Are you exploring a new idea or project or thinking of launching a new product?
Consider your audience
Always consider to whom you’re addressing and what’s the purpose of addressing your business plan. Check out whether the business plan is for an investor, partner, lender, or internal team. Different audiences require different information and presentation styles.
Access your business scope
The complexity and scale of your business also influence the plan type you should choose. Hence, consider the following factors before choosing:
- Think about your business stage—whether you’re a startup, an established firm, or an expanding business.
- Evaluate your market size—if it's highly competitive, you'll need a detailed, analytical plan, while a smaller market may require a simpler approach.
- Look into your product and service—They dictate the plan type. Every product and services need a different plan and strategies to move in the market.
Focus on the right format
Different business plans have different formats, each serving a specific purpose. Always choose the format based on your audience.
For example, a one-page plan works for quick overviews, while a detailed plan is better suited for investors or lenders looking for in-depth insights.
However, consider the following aspects when choosing a business plan format:
- Audience you are addressing
- Font and layout choices
- Presentation style
- Length of the plan
- Presentation tone
Benefits of choosing the right type of business plan
Choosing the right business plan is crucial for success and offers several key advantages:
Provides clarity and focus
A well-chosen business plan provides clarity about your goals and strategies. It helps you define your mission and ensure that all team members are on the same page focusing on the same business objective.
Increases the chance of securing funds
Investors and lenders expect detailed plans that show a clear grasp of the market, competition, and financial forecasts. A well-tailored plan boosts your chances of securing capital by highlighting your readiness and dedication to success.
Manages risk effectively
With a solid plan, your business can prepare for unexpected challenges and remain resilient, even during tough times. Plus, with the latest technologies in your business plan, you can forecast potential risks, allowing you to be prepared in advance.
Allocates resources efficiently
Right business planning enables your business to allocate resources efficiently, leading to better returns. It ensures your time, money, and manpower are used efficiently and effectively to achieve your goal within the time and budget.
Helps you measure your progress
With a clear business plan in place, you can set specific milestones and performance metrics. Such milestones enable you to track your progress over time and make adjustments as needed.
Provides sustainable growth
A common business plan can help you reach your goals, but choosing the right plan specifically tailored to your business ensures sustainable growth. It keeps your business on track, leading to steady growth and development.
Common mistakes to avoid when choosing a business plan type
Avoiding these common mistakes can help you create an effective document that will enhance your credibility and build a solid foundation to reach your goal:

Assuming all plans are alike
Treating all business plans as interchangeable or the same can lead to selecting one that doesn’t fit your specific needs or objectives.
Ignoring your audience's needs
Failing to consider who will read the plan may result in a format or content that doesn’t resonate with stakeholders. This mistake will not convince investors and destroy your credibility.
Overlooking business stage
Not matching the plan type to your business stage (startup, growth, etc.) can lead to inappropriate detail or a lack of necessary information. A startup business plan won’t effectively support the growth of your existing business.
Underestimating the need for detail
Opting for a lean or one-page plan when more detail is necessary can hinder your ability to secure funding or support. Hence, ensure you add the required information properly to persuade investors, external and internal stakeholders, or any other reader.
Focusing solely on financials
Choosing a plan type that focuses too much on financial projections while neglecting operational plans can lead to an incomplete picture. This may raise doubts among investors and negatively affect your chances of securing funding.
Neglecting market research requirements
Choosing a plan type that doesn’t require thorough market analysis can leave you unprepared for competition. The lack of preparation can hinder your ability to adapt and respond effectively to market dynamics.
Now that you know the business plan types and how to choose the right one, you can achieve your business goals effectively.
However, if you need further assistance to craft your business plan you may get in touch with our business plan consulting company .
Our qualified business plan experts can help you create business plans, assuring you choose the right type tailored to your specific business needs.
Get your business plan ready today!
Related Article
- Eleven Reasons Why You Need a Business Plan
- Common Business Plan Mistakes to Avoid
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a traditional business plan and a lean business plan?
A traditional plan is detailed and comprehensive documents that explain each aspect of business in detail. Often 20 to 50 pages.
A lean business plan, on the contrary, is a shorter document (can be a page long) that focuses on key aspects of businesses, market opportunities, and financial viability.
When should a startup use a feasibility business plan?
Startups should use a feasibility plan to determine if their idea is viable and can generate enough revenue to witness the company’s success. It’ll help startups to gauge the potential of their business idea and identify potential challenges or obstacles they may face.
What is the purpose of a strategic business plan?
A strategic business plan aligns business resources with long-term goals and sets the direction for achieving them. It helps businesses equip resources to the right person, at the right time to achieve business objectives.
How many types of business plans are there?
There are several types of business plans however the core 7 types include traditional, startup, feasibility, one-page plan, operational or operations plan, exit strategy, and internal business plan.

PlanGrow Lab is a team of trusted business plan consultants, specializing in creating effective business plans tailored to your goals. We provide expert guidance, detailed financial forecasting, and business plans that meet the highest industry standards, turning your vision into a reality.
BUSINESS STRATEGIES
7 types of business plans every entrepreneur should know

What’s the difference between a small business that achieves breakthrough growth and one that fizzles quickly after launch? Oftentimes, it’s having a solid business plan.
Business plans provide you with a roadmap that will take you from wantrepreneur to entrepreneur. It will guide nearly every decision you make, from the people you hire and the products or services you offer, to the look and feel of the business website you create.
But did you know that there are many different types of business plans? Some types are best for new businesses looking to attract funding. Others help to define the way your company will operate day-to-day. You can even create a plan that prepares your business for the unexpected.
Read on to learn the seven most common types of business plans and determine which one fits your immediate needs.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a written document that defines your company’s goals and explains how you will achieve them. Putting this information down on paper brings valuable benefits. It gives you insight into your competitors, helps you develop a unique value proposition and lets you set metrics that will guide you to profitability. It’s also a necessity to obtain funding through banks or investors.
Keep in mind that a business plan isn’t a one-and-done exercise. It’s a living document that you should update regularly as your company evolves. But which type of plan is right for your business?
7 common types of business plans
Startup business plan
Feasibility business plan
One-page business plan
What-if business plan
Growth business plan
Operations business plan
Strategic business plan

01. Startup business plan
The startup business plan is a comprehensive document that will set the foundation for your company’s success. It covers all aspects of a business, including a situation analysis, detailed financial information and a strategic marketing plan.
Startup plans serve two purposes: internally, they provide a step-by-step guide that you and your team can use to start a business and generate results on day one. Externally, they prove the validity of your business concept to banks and investors, whose capital you’ll likely need to make your entrepreneurial dreams a reality.
Elements of a startup business plan should include the following steps:
Executive summary : Write a brief synopsis of your company’s concept, potential audience, product or services, and the amount of funding required.
Company overview: Go into detail about your company’s location and its business goals. Be sure to include your company’s mission statement , which explains the “why” behind your business idea.
Products or services: Explain exactly what your business will offer to its customers. Include detailed descriptions and pricing.
Situation analysis: Use market research to explain the competitive landscape, key demographics and the current status of your industry.
Marketing plan: Discuss the strategies you’ll use to build awareness for your business and attract new customers or clients.
Management bios: Introduce the people who will lead your company. Include bios that detail their industry-specific background.
Financial projections: Be transparent about startup costs, cash flow projections and profit expectations.
Don’t be afraid to go into too much detail—a startup business plan can often run multiple pages long. Investors will expect and appreciate your thoroughness. However, if you have a hot new product idea and need to move fast, you can consider a lean business plan. It’s a popular type of business plan in the tech industry that focuses on creating a minimum viable product first, then scaling the business from there.
02. Feasibility business plan
Let’s say you started a boat rental company five years ago. You’ve steadily grown your business. Now, you want to explore expanding your inventory by renting out jet skis, kayaks and other water sports equipment. Will it be profitable? A feasibility business plan will let you know.
Often called a decision-making plan, a feasibility business plan will help you understand the viability of offering a new product or launching into a new market. These business plans are typically internal and focus on answering two questions: Does the market exist, and will you make a profit from it? You might use a feasibility plan externally, too, if you need funding to support your new product or service.
Because you don’t need to include high-level, strategic information about your company, your feasibility business plan will be much shorter and more focused than a startup business plan. Feasibility plans typically include:
A description of the new product or service you wish to launch
A market analysis using third-party data
The target market , or your ideal customer profile
Any additional technology or personnel needs required
Required capital or funding sources
Predicted return on investment
Standards to objectively measure feasibility
A conclusion that includes recommendations on whether or not to move forward
03. One-page business plan
Imagine you’re a software developer looking to launch a tech startup around an app that you created from scratch. You’ve already written a detailed business plan, but you’re not sure if your strategy is 100% right. How can you get feedback from potential partners, customers or friends without making them slog through all 32 pages of the complete plan?
That’s where a one-page business plan comes in handy. It compresses your full business plan into a brief summary. Think of it as a cross between a business plan and an elevator pitch—an ideal format if you’re still fine-tuning your business plan. It’s also a great way to test whether investors will embrace your company, its mission or its goals.
Ideally, a one-page business plan should give someone a snapshot of your company in just a few minutes. But while brevity is important, your plan should still hit all the high points from your startup business plan. To accomplish this, structure a one-page plan similar to an outline. Consider including:
A short situation analysis that shows the need for your product or service
Your unique value proposition
Your mission statement and vision statement
Your target market
Your management team
The funding you’ll need
Financial projections
Expected results
Because a one-page plan is primarily used to gather feedback, make sure the format you choose is easy to update. That way, you can keep it fresh for new audiences.
04. What-if business plan
Pretend that you’re an accountant who started their own financial consulting business. You’re rapidly signing clients and growing your business when, 18 months into your new venture, you’re given the opportunity to buy another established firm in a nearby town. Is it a risk worth taking?
The what-if business plan will help you find an answer. It’s perfect for entrepreneurs who are looking to take big risks, such as acquiring or merging with another company, testing a new pricing model or adding an influx of new staff.
A what-if plan is additionally a great way to test out a worst-case scenario. For example, if you’re in the restaurant business, you can create a plan that explores the potential business repercussions of a public health emergency (like the COVID-19 pandemic), and then develop strategies to mitigate its effects.
You can share your what-if plan internally to prepare your leadership team and staff. You can also share it externally with bankers and partners so that they know your business is built to withstand any hard times. Include in your plan:
A detailed description of the business risk or other scenario
The impact it will have on your business
Specific actions you’ll take in a worst-case scenario
Risk management strategies you’ll employ
05. Growth business plan
Let’s say you’re operating a hair salon (see how to create a hair salon business plan ). You see an opportunity to expand your business and make it a full-fledged beauty bar by adding skin care, massage and other sought-after services. By creating a growth business plan, you’ll have a blueprint that will take you from your current state to your future state.
Sometimes called an expansion plan, a growth business plan is something like a crystal ball. It will help you see one to two years into the future. Creating a growth plan lets you see how far—and how fast—you can scale your business. It lets you know what you’ll need to get there, whether it’s funding, materials, people or property.
The audience for your growth plan will depend on your expected sources of capital. If you’re funding your expansion from within, then the audience is internal. If you need to attract the attention of outside investors, then the audience is external.
Much like a startup plan, your growth business plan should be rather comprehensive, especially if the people reviewing it aren’t familiar with your company. Include items specific to your potential new venture, including:
A brief assessment of your business’s current state
Information about your management team
A thorough analysis of the growth opportunity you’re seeking
The target audience for your new venture
The current competitive landscape
Resources you’ll need to achieve growth
Detailed financial forecasts
A funding request
Specific action steps your company will take
A timeline for completing those action steps
Another helpful thing to include in a growth business plan is a SWOT analysis . SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. A SWOT analysis will help you evaluate your performance, and that of your competitors. Including this type of in-depth review will show your investors that you’re making an objective, data-driven decision to expand your business, helping to build confidence and trust.
06. Operations business plan
You’ve always had a knack for accessories and have chosen to start your own online jewelry store. Even better, you already have your eCommerce business plan written. Now, it’s time to create a plan for how your company will implement its business model on a day-to-day basis.
An operations business plan will help you do just that. This internal-focused document will explain how your leadership team and your employees will propel your company forward. It should include specific responsibilities for each department, such as human resources, finance and marketing.
When you sit down to write an operations plan, you should use your company’s overall goals as your guide. Then, consider how each area of your business will contribute to those goals. Be sure to include:
A high-level overview of your business and its goals
A clear layout of key employees, departments and reporting lines
Processes you’ll use (i.e., how you’ll source products and fulfill orders)
Facilities and equipment you’ll need to conduct business effectively
Departmental budgets required
Risk management strategies that will ensure business continuity
Compliance and legal considerations
Clear metrics for each department to achieve
Timelines to help you reach those metrics
A measurement process to keep your teams on track
07. Strategic business plan
Say you open a coffee shop, but you know that one store is just the start. Eventually, you want to open multiple locations throughout your region. A strategic business plan will serve as your guide, helping define your company’s direction and decision-making over the next three to five years.
You should use a strategic business plan to align all of your internal stakeholders and employees around your company’s mission, vision and future goals. Your strategic plan should be high-level enough to create a clear vision of future success, yet also detailed enough to ensure you reach your eventual destination.
Be sure to include:
An executive summary
A company overview
Your mission and vision statements
Market research
A SWOT analysis
Specific, measurable goals you wish to achieve
Strategies to meet those goals
Financial projections based on those goals
Timelines for goal attainment
Related Posts
What is a target market and how to define yours
21 powerful mission statement examples that stand out
How to write a business plan in 7 easy to follow steps
Was this article helpful?
Starting a Business | Listicle
Types of Business Plans: Ultimate Guide for Business Owners
Published October 2, 2024
Published Oct 2, 2024
WRITTEN BY: Mary King
This article is part of a larger series on Starting a Business .
1. One-page Business Plan
2. traditional business plan, 3. business model canvas, 4. startup plan, 5. lean canvas, 6. strategic plan, 7. feasibility plan, 8. operations plan.
- 9. Contingency Plan
10. Expansion Plan
11. nonprofit business plan, business plan writing services, bottom line.
Starting or growing your small business requires careful planning. A business plan is a detailed document outlining the goals, strategies, operational plans, and risks associated with starting or running a business. Various types of business plans will be your roadmaps to securing funding, planning for growth, or making big decisions through your business’s lifespan.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through different types of business plans, discussing their format and ideal use cases so you can make the best moves for your business.
Key Takeaways:
- Business plans are not a one-time project when you start your business.
- You may use one or more types of plans in business to make major changes throughout its lifespan.
- The type of business plan you need varies by your industry, business size, and goals.
The one-page business plan is for very small businesses like side hustles. A one-page business plan is a great way to get your ideas on paper and work out the fundamentals of the business without doing a bunch of high-level calculations that aren’t relevant to your micro-business.
With this plan, you’ll write a couple of sentences for a few important business sections. Your one-page business plan should include information on your business model (how will your business make money?) and competitive advantage (what will your business do better than competitors?).
You should plan on spending around an hour to write out a one-page business plan. The simplified financial projections will be the most challenging and time-consuming. Most likely, you will need to do research online to get accurate income and expense estimates.
Key Sections
To create a one-page business plan, you’ll need to write one to two sentences to answer the following questions:
- Problem: What problem will your business solve?
- Solution: What will your business provide to solve that problem?
- Business model: How will your business make money?
- Target customers: What type of people will buy your product or service?
- Promotion: How will your target customers learn about your business?
- Competitive advantage: What will your business do better than the competitors?
- Financial projections: How much money do you need to start? How much will you earn every month? And how much will you spend every month?
- Funding required: How much money do you need to start the business?
A one-page business plan is a great fit for side hustles like dog walking, small handicrafts, and cottage food businesses. If you are helping your child start a business, a one-page business plan is a good exercise to help prepare your child for thinking through their business plans.
Get started writing a one-page business plan by downloading our free template.
FILE TO DOWNLOAD OR INTEGRATE
One Page Business Plan Template

Thank you for downloading!
The traditional business plan is more thorough than the one-pager. A traditional plan may contain over 40 pages of info about your business. Typically, you’ll use this plan to get funding, such as a larger loan from a bank. You may also use a traditional business plan to attract investors.
You should plan on spending at least 30 hours creating a well-researched business plan. In addition to writing the plan, you will also spend time doing market research and creating financial projections.
Most small business owners can easily do the research and write a traditional business plan. Where most have difficulty is financial projections, which require creating several financial documents. If you don’t have a financial analysis background or interest, it’s a wise strategy to purchase a business plan software that walks you step-by-step through the financial projection process or hire an accountant to assist.
A traditional business plan has many sections and can be 30 to 40 pages (or more) in length. The length of your traditional business plan will vary depending on your business type, industry, and the amount of information you include in your appendix.
- Opening organizational and legal pages: The opening pages of your business plan need to be a cover page, a non-disclosure agreement, and a table of contents.
- Executive summary: This one- to two-page section is a summary of the whole plan, highlighting the key details to encourage potential investors, business partners, or banks to read the full business plan.
- Company summary: Discuss the basics of the company such as its history, location, facilities, ownership, and competitive advantage.
- Products and services: Talk about how your business makes money (business model), its products or services, and future products or services.
- Market and industry analysis: This section analyzes your potential customers and industry. Include any data here about your current (or ideal) customers, business industry, and competitors.
- Marketing strategy and implementation summary: How will you reach your customers? Discuss your marketing, sales, and pricing strategy.
- Management and organization summary: Who will own and operate the business? If your business isn’t open yet, give a compelling reason why your background will make it a success. Include information on any managers in the business as well.
- Financial data and analysis: Here you want to show in charts and graphs how your business will be a success. You will include financial projections such as a profit & loss statement, projected cash flow, and business ratios.
- Appendix: Any documents or information that doesn’t fit in the above categories goes in the appendix. You may want to include documents such as a floor plan, trademark, or marketing materials.
Small to medium-sized businesses that may need investors, grants, or business loans to get started can benefit from a traditional business plan. Beyond ensuring you get the funds you need, going through the process of writing a traditional business plan will help you refine your idea and answer questions you may not have considered.
A business model canvas is a visually dynamic one-page business plan. This business plan model was developed in the early 2000s as a collaborative tool to help fast-moving, customer-focused businesses quickly collaborate on a business plan. The Business Model Canvas (BMC) is a strategic tool that lets you visualize your business model.
Many business owners prefer to use the BMC because it can be done as a visual exercise with the leadership team. Together, the team can go through each section and provide high-level input. Once you create the basics of the BMC, it’s easy to share with others. The contents can be summed up on one page, whereas the traditional plan above will likely be at least 40 pages.
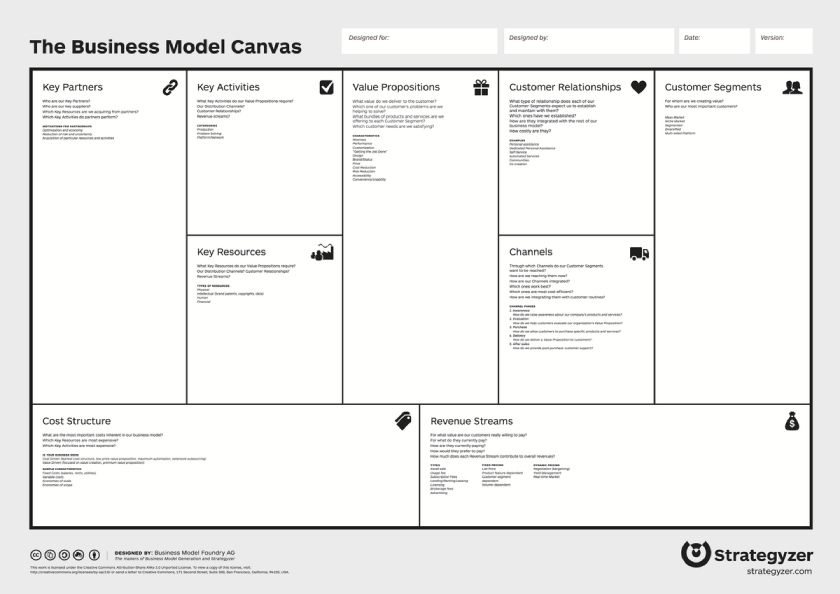
Source: Strategyzer
- Key partners: What people or organizations (outside of the business) help your business operate such as suppliers or referral sources?
- Key activities: What crucial activities need to be done in the business so that you can serve your customers?
- Key resources: Who are the key people (inside the business), and what are the patents, places, and machines that the business couldn’t operate without?
- Value proposition: What value will you be delivering to customers? What customer problems are you trying to solve?
- Customer relationships: How will you maintain relationships with your customers?
- Channels: What channels will you use to reach customers and maintain relationships?
- Customer segments: Who are the most important types of customers or businesses that will be buying your products or services?
- Cost structure: What are the largest expenses in your business? List at least seven.
- Revenue streams: In what ways will your business earn money? If possible, list specific numbers such as the average earned per product or service performed.
The Business Model Canvas is great for team collaboration. It is a great business plan for startups and businesses that need agility. If you need to raise funds for your business, you’ll need to supplement your BMC with financial projections.
A startup plan is similar to a traditional business plan. However, startups tend to be larger, more complex businesses than the typical small to midsize business. A startup business plan will have many of the same sections as a traditional business plan, but the financial projections for a startup plan will typically include many more dynamic visualizations to dramatically illustrate the idea. Startups are characterized by fast growth and a need for large initial investments, so startup business plans tend to focus a lot of energy on finding funding.
You’ll see a lot of the same sections in a startup business plan as in a traditional business plan, though the key sections may have a different focus.
- Opening organizational and legal pages: A non-disclosure agreement is standard for a startup business plan. This section also includes business information like the addresses and contact information of key owners and partners.
- Executive summary: This is a high-level summary of the entire business plan that enables potential investors and business partners to quickly understand the key elements of your proposed business.
- Company description: This section covers your business mission, vision, and goals. It should also list your legal structure (i.e. sole proprietorship, LLC, corporation), and briefly describe what sets your company apart from competitors.
- Market research and analysis: Demonstrate your understanding of the market size, trends, competition, and customer demographics. Potential investors want to feel confident that you know the industry you are entering.
- Organization and management: Introduce key team members, including a brief description of their roles, responsibilities, and qualifications. If you have an advisory board (not uncommon for startups) list those key stakeholders, too.
- Products or services: Explain how your product or service solves a problem or meets a market need. Include specific mention of any intellectual property or proprietary technology you have or will develop.
- Marketing and sales strategy: Outline your plan for attracting and retaining customers. Include details about your pricing strategy, sales tactics, and distribution channels.
- Financial projections: It can be tricky to generate accurate financial projections if you are proposing a new business model or developing a disruptive technology. Financial projections in a startup business plan are generally more speculative than in a traditional business plan and are based on hypotheses about customer acquisition, market penetration, and growth. Startup plans may only include one-, three-, and five-year projections and leave off longer-term 10-year projections.
- Funding request: Detail how much money you need and what you’ll use it for. Startups tend to have multiple funding “rounds,” so list the timeline and requested funds for each funding round here.
- Appendix: As with a traditional business plan, any documents—like design plans, licenses, or patents—that don’t fit in the categories above, add them to your appendix.
A startup business plan is the right fit for technology-based and industry-disrupting businesses. If your product or service is novel and expected to grow quickly, a startup business plan can also work for you. Any business with a focus on quickly raising lots of initial capital from investors or banks can benefit from following this business plan format.
The Lean Canvas combines the Business Model Canvas template with the focus of a lean business plan. A Lean Canvas is ideal for startups that want a more focused, streamlined business plan. The Lean Canvas is great for quickly recording a business idea based on a gut feeling or instinct.
A Lean Canvas plan focuses on the customers’ problems and the solution your business will provide. Unlike a traditional business model, a Lean Canvas is not heavy on financial projections. Like all canvas-based business plans, the Lean Canvas is also great for collaborating with other stakeholders or business partners to create a business plan.
These are the major sections of a Lean Canvas business plan. As with a Business Model Canvas, these sections are all laid out in a tile formation on a single page.
- Problem: This section lists the one to three major problems your business will solve. It also typically includes a short list of one to three businesses that already exist to solve this problem.
- Solution: These are the top features of your product or service that will solve the problems you listed in the first section. It should provide a clear vision of how your solutions directly solve the problems.
- Key metrics: This is a short bulleted list of the key performance indicators you’ll track to measure your business’s growth and success. Customer acquisition cost, customer lifetime value, customer retention, and sales per customer are all common KPIs.
- Unique value proposition (UVP): Describe what makes your business unique compared to your competitors.
- Unfair advantage: This goes beyond your UVP to list exactly what your business can provide that other competitors cannot replicate. Many people think of this as the “moat” around your business.
- Channels: These are the pathways you will use to reach your customer segments. Depending on your business type, you might list direct sales, social media, partnerships, government contracts, ecommerce platforms, or more.
- Customer segments: Define the specific customer types or groups that will benefit from your business. Include a brief description of the likely “early adopters.”
- Cost structure: List the major fixed and variable costs required to get your business started (permits, licenses, rent, etc.) and keep it running (marketing, salaries, etc.).
- Revenue streams: List the ways your business will make money—subscriptions, direct sales, consulting fees, licensing, ecommerce sales, etc.
The Lean Canvas emphasizes agility and a customer-centered approach. It is great for startups that focus on experimentation and direct problem-solving for customers, like software-as-a-service (SaaS) companies. It’s not the greatest fit for a brick-and-mortar business like a retail or restaurant operation.
A strategic plan is a business plan that you write after your business is already operational. These plans are designed to help your business plan for growth in a specific area while staying aligned with your mission and core values.
A strategic plan will focus on long-term goals and objectives, laying out your path to achieving strategic milestones. Depending on your business type, those milestones might be growing sales in a specific region or obtaining a business certification, like a B Corp designation. Medium to large businesses commonly write strategic plans. But it can also be a good fit for small businesses that operate in challenging or quickly changing industries.
Your strategic plan needs to be clear, concise, and easy to understand. It should simplify your decision-making process, not complicate it. If you need support writing a strategic plan, contact a small business advisor at your local Small Business Development Center (SBDC), or book some time with a business consultant in your industry to get additional guidance.
- Vision and mission statements: Starting with your vision statement or mission statement ensures you keep your strategic plan focused and design solutions that demonstrate your business values.
- Organizational goals: Write down where you hope to see your business in three, five, and ten years. If you foresee changes on the horizon for your industry, include a brief description of the challenge and how you plan to react to it. Mention how you will grow your business and reach new customers at each milestone.
- SWOT analysis: A SWOT analysis is a list of your business’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- PESTEL analysis: This is typically a table that illustrates the external forces that influence your business. To create your table follow the acronym and list the political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal influences.
- Current state: This is a description of the current state of your business performance and business operation. This section provides a baseline to compare your future business states, so you can more easily see your business growth.
- Future state: This is a detailed description of the future state you see for your business, or where you hope the business will go.
- Key objectives: This is a list of your major projects, initiatives, or goals; whatever activities you’ll need to undertake to get your business where you want it to be.
- Strategies: Describe what needs to happen for your business to meet your stated goals. List what resources you will need (and when) to get there. This section should include a one-page action plan that summarizes each key action you plan to take and the planned timeline for each shift.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): List the KPIs or metrics you will use to measure your business’s progress toward your long-term goals. What will you measure, and how will you measure it?
Strategic plans are a great fit for established businesses that need to grow or refine operations and for businesses pivoting due to disruption from third parties or market forces (like supply chain disruption or inflation).
A feasibility study is like a rough draft of a business plan; it’s a “business plan lite.” A feasibility plan focuses on answering a single question: is this business idea viable? A feasibility plan or feasibility study helps you determine if a business idea will be profitable before you expend too much time or money to get the business off the ground.
- Executive summary: As with other business plan types, the feasibility plan starts with a one-page executive summary. This lists the key takeaways from your whole plan, so you and other stakeholders can get the main information quickly.
- Business idea: Clearly and succinctly detail your business idea. This is the foundation for the rest of the document, so make sure it is clear how your business will make money.
- Demand analysis: This section is a summary of how many people, and what specific types of customers are likely to purchase your proposed product or service. List who they are, where they are located relative to your business, and other defining characteristics.
- Market research: This section lists competitors in your market and looks at how your proposed business idea compares.
- Risk analysis: This section should include foreseeable legal concerns (like any permits or licenses you’ll need to obtain), logistics issues (like supply chain logistics), and technical challenges (like needing to design an app).
- Financial feasibility: This section includes costs like marketing, required staff, rent, and other costs as compared to your projected profits. These
- Recommendations: This section is the “TL;DR” section of this feasibility plan. After considering all the information in the plan document, does the business idea get a thumbs up or a thumbs down? If the recommendation is that the business idea is not feasible, you should offer alternative ideas that may work instead.
Feasibility plans are a great first step before committing to writing a full, traditional business plan. Feasibility plans, or feasibility studies, are ideal for startups and any business that is offering novel products or services.
A lot of these business plans have focused on big questions like your business vision, the big problems your product will solve, and your projections for the future. An operations plan is focused on the day-to-day logistics and workflows that keep your business running. If other business plans focus on the “why” and the “what,” your operations plan is all about the “how.”
An operations plan is much shorter than a typical business plan. Key sections of an operational plan include:
- Product (or service) delivery: This section describes how you deliver your product or service to customers. It covers every step of the process, from sourcing raw materials to final delivery. Service-based businesses should detail how services are scheduled and managed. Product-based businesses should include details about their manufacturing, inventory management, and distribution processes.
- Supply chain management: This section focuses on the source of your raw materials. It lists your key suppliers, explains your purchasing strategy, and details how these materials arrive at your location.
- Facilities and equipment: Provide information about your physical business spaces, along with the equipment and technology that you use to run your business. Depending on your business type, you might list office space, warehouses, retail locations, or manufacturing facilities. If you plan to schedule upgrades or additional equipment when you reach key milestones, mention that here.
- Staffing and organizational structure: List your business’s personnel needs and management structure. Explain the key employee roles, the number of each employee you need, and how you plan to recruit, train, and manage these team members.
- Operating model: Describe your typical work tasks and their workflows. How do customers place orders or book appointments? How are those orders communicated internally amongst your staff? How do you handle customer inquiries or complaints?
- Quality control: Explain how you’ll monitor the quality of your products or services. Will you inspect and test products? Will you use secret shoppers?
- Risk management: Identify common risks you encounter and your plans for mitigating those risks. Risks might include supply chain disruption, employee workplace injuries, customer injuries, equipment failure, or natural disasters.
- Key metrics: List the major performance indicators you will track to measure your operational performance.
An operations plan is a great tool for businesses in complex industries and those with complicated supply chains. If your business combines any configuration of manufacturing, distribution, sales, and services, an operations plan will help you identify bottlenecks and keep you organized.
9. Contingency Plan (What-if Plan)
A contingency plan (also called a “What-if Plan”) helps your business prepare for unexpected events like changes in customer demand or market downturns. You can write a contingency plan at any stage in your business journey, whether you are a new or existing business. A contingency plan can help your business weather crises from natural disasters to cyberattacks.
- Risk assessment: Identify the potential risks that can impact your business. Cyberattacks, data breaches, supply chain disruptions, and equipment failures are common small business risks.
- Impact assessment: Evaluate the potential impact of each risk you identified. Consider revenue, employee, customer, and safety impacts. Prepare for both short- and long-term impacts.
- Response strategy: Outline the specific steps your business will take to respond to each risk you listed. Be detailed and include alternatives to ensure your business is prepared for all variables. List the resources you’ll need for each strategy to ensure they are easily accessible if the worst happens.
- Chain of command: Clearly articulate who should take responsibility for key tasks in your business in the event that you need to implement any of your response strategies.
- Communication strategy: Describe how information about your business response to crises will be communicated to your team, your suppliers, customers, and the general public.
- Training plan: Include a schedule and training details for how you plan to get your whole team on the same page for each response strategy.
- Monitoring and updating: How will you monitor risk development? How often will you update your contingency plan?
Businesses in volatile industries (like ecommerce or technology) or those with complex supply chains (like manufacturers) have long created contingency plans. In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic and multiple armed conflicts around the world, though, it’s clear that even small businesses can benefit from creating contingency plans.
An expansion plan will guide your business as it grows, laying out a strategic plan for expanding your existing operation. Whether you are opening a new location, launching new products, or expanding your services, an expansion plan will keep you focused and keep your costs in line.
An expansion plan is shorter than a traditional business plan, but it still has some key elements to include.
- Executive summary: Like all the other business plan types, your expansion plan should start with an executive summary to highlight the key points of the complete plan.
- Market analysis: This is a detailed analysis of the market for the new audience you hope to attract or the new competitors your business will encounter by expanding.
- Expansion strategy: Outline the specific steps you need to take to complete your expansion, from locating additional storage or operational space, obtaining or creating new products or services, entering new markets, or building new locations. Include a timeline for each phase in your expansion plan.
- Operational adjustments: Will you need to hire additional staff or retrain existing ones? Will you need to secure additional suppliers, forge relationships with new vendors, or improve your customer service bandwidth to meet increased demand?
- Marketing and sales strategy: How will you draw new customers or inform existing ones of your expansion? Include plans for advertising, partnerships, and other promotional efforts.
- Risk assessment: Include a clear assessment of the risks of expanding your business, including your plan for mitigating those risks.
- Financial projections: As an existing business, you should have some historical data to draw from to create future projections for this expansion. Use this information, along with your expectations of the expansion, to generate projections of your expected costs, cash flow, and how much capital you will need to fund your expansion. This is particularly important if you need to seek funding in the form of loans or investments to fund your expansion.
- Metrics and KPIs: Define the metrics you’ll use to measure the success of your expansion, from revenue growth to customer ratings and retention.
An expansion plan is a great idea for any growing business to strategically plan to grow their business and measure impacts. Even the smallest businesses should comprise an expansion plan to ensure they maintain profitability as they grow.
A nonprofit business plan is different from a traditional business plan because it focuses more on mission and longevity than profit. Unlike for-profit businesses that create plans to appeal to investors, nonprofit business plans need to appeal to donors and grant-awarding agencies. A nonprofit business plan needs to show how a nonprofit organization will achieve its mission while remaining financially stable.
A nonprofit business plan may be 12 to 30 pages long, depending on the organization’s mission, the number of staff, and the impact it hopes to have on the community.
- Executive summary: Like traditional business plans, a nonprofit business plan should include a summary at the beginning that lists the key points of the business plan.
- Mission statement: This is the foundation of the whole nonprofit organization. This should describe the specific social, environmental, or community issues your organization will address.
- Needs analysis: This is similar to the market research section of a traditional business plan. Research and include detailed information about the community your nonprofit will serve, other organizations that work on similar issues, and any specific gaps your organization will fill.
- Programs and services: This section describes all the programs and services the nonprofit will offer and mentions how they align with the nonprofit’s mission. For each program or service you outline, include the population the program serves and how you will measure its success.
- Fundraising strategy: How will your nonprofit generate the financial resources needed to support its mission? Include details about fundraising campaigns, grant applications, corporate partnerships, and other donor strategies.
- Organizational structure and management: List the nonprofit’s key team members. This may include the leadership team and staff, as well as a full list of the board of directors. If you rely on volunteers, include information about how you recruit, train, and manage them.
- Operations and administrative plan: Describe all the processes that keep your organization running from day to day. This might include administrative tasks, tasks associated with legal and regulatory requirements in the industry you serve, and fundraising. Mention internal communication and reporting procedures, as well.
- Marketing and outreach strategy: Describe how you will promote your programs and raise awareness of your cause. Include strategies for reaching donors, volunteers, and the beneficiaries of your services. This might include printed materials, social media campaigns, community events, and media outreach.
- Impact measurement: Outline the methods and metrics you will use to measure the impact of your nonprofit’s efforts. Include how you will evaluate the success of individual programs and services as well as how you will track progress toward long-term goals.
- Financial plan: Nonprofit organizations have an obligation to demonstrate fiscal responsibility. This section should include your projected operating budget, along with any income statements, cash flow projections, and contingency plans for financial difficulties.
Nonprofit organizations of all sizes—from grassroots community groups to large, charitable foundations—benefit from the structure and planning that composing a nonprofit business plan provides. A nonprofit business plan helps organizations that rely on donors, grants, or corporate partnerships attract funding. Newly formed nonprofits can use a nonprofit business plan to establish credibility and articulate their vision.
If you need a business plan, but don’t want to write it yourself, you have two major options; use business plan writing software or pay a professional to create your plan. Several companies provide business plan writing services with experts who do market research and create custom-designed plans. Many of these companies also offer other writing services such as a pitch deck, feasibility study, or franchise-specific plans.
How to Choose a Biz Plan Writing Service
When choosing a business plan writing service, you first want to review the background of the writers. Some companies provide writers with MBAs (Master of Business Administration).
You also want to review samples of the business plans created. The company likely provided their best-designed business plans in their portfolio, so make sure to ask how much a particular well-designed business plan will cost; it may be out of your budget.
Cost of a Business Plan Writing Service
A basic business plan writing service will typically charge you a minimum of $2,000. If your plan requires extensive research, custom graphics, and enhanced overall design, that cost can go up to over $10,000.
Contact Your Local SBDC for a Review
If you have your business plan and are looking for someone to review it for feedback, your local SBDC (Small Business Development Center) may be able to help. The SBDC provides no-cost consulting and is funded in part by the SBA (Small Business Administration). There are over 1,000 SBDC locations across the US, most of them housed in or near state colleges and universities. Visit the SBDC website to find your local SBDC.
One of the SBDC’s core services is to provide detailed reviews of business plans. Depending on the expertise of your local SBDC Consultants, you may get lucky and have a business plan expert at your local center. Inquire if he or she can review your biz plan and provide feedback.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
These are the most common questions I hear about business plan types.
How many types of business plans are there?
There are dozens of business plan types that you might use to create a roadmap for various business strategies. Most small businesses benefit from a traditional or a one-page business plan. Existing businesses can benefit from targeted business plans like an expansion plan, contingency plan, or feasibility plan.

What are the components of a business plan?
Every business plan starts with an executive summary that highlights the key takeaways from the entire business plan. You’ll also typically need to include the following sections:
- Opening organizational and legal pages
- Company summary
- Products and services
- Market and industry analysis
- Marketing strategy and implementation summary
- Management and organization summary
- Financial data and analysis
Various business plan types can help you plan your business strategy, attract business partners, or qualify for small business loans and grants. Your next steps after writing your business plan depends on your business type and the business plan type.
About the Author

Find Mary On LinkedIn Twitter
Mary King is an expert restaurant and small business contributor at Fit Small Business. With more than a decade of small business experience, Mary has worked with some of the best restaurants in the world, and some of the most forward-thinking hospitality programs in the country. Mary’s firsthand operational experience ranges from independent food trucks to the grand scale of Michelin-starred restaurants, from small trades-based businesses to cutting-edge co-working spaces.
By downloading, you’ll automatically subscribe to our weekly newsletter.
Join Fit Small Business
Sign up to receive more well-researched small business articles and topics in your inbox, personalized for you. Select the newsletters you’re interested in below.
AI ASSISTANTS
Upmetrics AI Your go-to AI-powered business assistant
AI Writing Assist Write, translate, and refine your text with AI
AI Financial Assist Automated forecasts and AI recommendations
AI Research Assist Your go-to AI-powered research assistant
TOP FEATURES
AI Business Plan Generator Create business plans faster with AI
Financial Forecasting Make accurate financial forecasts faster
INTEGRATIONS
QuickBooks Sync and compare with your QuickBooks data
Strategic Planning Develop actionable strategic plans on-the-go
AI Pitch Deck Generator Use AI to generate your investor deck
Xero Sync and compare with your Xero data
See how easy it is to plan your business with Upmetrics: Take a Tour →
AI-powered business planning software
Very useful business plan software connected to AI. Saved a lot of time, money and energy. Their team is highly skilled and always here to help.
- Julien López
BY USE CASE
Secure Funding, Loans, Grants Create plans that get you funded
Starting & Launching a Business Plan your business for launch and success
Validate Your Business Idea Discover the potential of your business idea
E2 Visa Business Plan Create a business plan to support your E2 - Visa
Business Consultant & Advisors Plan with your team members and clients
Incubators & Accelerators Empowering startups for growth
Business Schools & Educators Simplify business plan education for students
Students & Learners Your e-tutor for business planning
- Sample Plans
Plan Writing & Consulting We create a business plan for you
Business Plan Review Get constructive feedback on your plan
Financial Forecasting We create financial projections for you
SBA Lending Assistance We help secure SBA loans for your business
WHY UPMETRICS?
Reviews See why customers love Upmetrics
Blogs Latest business planning tips and strategies
Strategic Planning Templates Ready-to-use strategic plan templates
Business Plan Course A step-by-step business planning course
Customer Success Stories Read our customer success stories
Help Center Help & guides to plan your business
Ebooks & Guides A free resource hub on business planning
Business Tools Free business tools to help you grow
The Different Types of Business Plans

Free Business Plan Template
- June 29, 2023
Different situations call for different business plans.
Whether you want to acquire funds, analyze market risks, introduce a new product, or simply need a roadmap for business operations— a specifically tailored business plan is essential for different business purposes.
Identifying the type of business plan you require is quintessential so that you create a document fit for your business needs.
In this blog post, we will introduce you to the 7 different types of business plans and help you understand which suits your business needs the best.
Ready to get started? Let’s dive right in.
Types of business plans
Businesses in different business situations call for different business plans.
To understand different types of business plans, we will categorize them based on audience, scope, and purpose to instill better clarity in your minds.
Let us understand these in detail to help you choose your ideal business plan.
Based on audience
Business plans are broadly categorized into two types based on the type of audience they cater to.
1. Internal business plans
As the name suggests, an internal business plan is solely for the people inside the company. These can be specific to certain departments such as marketing, HR, production, etc.
Internal business plans focus primarily on the company’s goals, operations, finances, and personnel and define the strategies to achieve their goals.
2. External business plans
On the contrary, external business plans are intended for people outside the company, such as investors, banks, partners, etc.
These plans usually contain detailed information about the company’s background, finances, market share, and business strategies.
Based on scope
Similarly, business plans are classified into two types based on their size and the depth of information they encompass.
1. Standard business plan
A standard plan or traditional business plan is a professional document offering a comprehensive understanding of your business idea. It serves as a step-by-step guide to launching your business and offers a roadmap to operate it efficiently.
A standard plan follows a structured format and usually includes components such as
- Executive summary
- Company description
- Market analysis
- Products and services
- Marketing and sales plan
- Operations plan
- Financial plan
- Funding demand
Most entrepreneurs follow this structure to write a business plan and add depth to the sections that hold significant value to them.
Best for: Startups and businesses that require a detailed roadmap or operate in highly volatile markets. These plans are also used for getting funding approvals.
2. Lean business plans
A lean plan, also known as a startup business plan, is a condensed version of the standard business plan including highlights and summaries of all its sections.
Such plans empower entrepreneurs to kickstart their business endeavors with a minimum viable product and build it gradually by gathering real market feedback.
Lean business plans are crafted with brevity and outline your strategies, revenue model, tactics, and timeline.
- Strategies: How will you reach your goals
- Tactics: What are the KPIs to evaluate your performance
- Revenue model: How will you make money
- Timeline: Who will accomplish the tasks
Drafting such plans is not only easier, it is considered to be more efficient compared to a standard plan.
Best for: Entrepreneurs who want to quickly launch their business in a hot-moving market.
Based on purpose
Every business plan tends to solve a specific purpose. Let’s understand 7 different types of business plans based on different purposes.
1. One-page business plan
One-page business plans offer a snapshot of your entire business idea in one page. Such plans follow the same structure as traditional plans, however, they are much more concise and crisp.
One-page plans are simplified versions of detailed business plans and can be placed together in less than 10 minutes.
They are quite useful when you want to convey essential information in a brief document without missing out on important points.
Best for: One-page business plan is best suited for startups and small businesses that require rapid adjustments and quick implementation.
2. Growth business plan
A growth business plan combines the crispness of one-page business plans and the detailing of financial forecasts to enable prompt decision-making.
Such plans are quite handy when you want to upscale or grow your business without writing a full-fledged detailed business plan.
Businesses can compare their forecasts with the actuals, identify the discrepancies in the current strategy, and adjust it to ensure maximum growth when they have a clear demonstration of financials.
To prepare your growth business plan, outline the target market, business strategies, and a business model as you do in your one-page plans. And additionally, also include detailed financial projections for sales, cash flow, and revenue to help individuals make data-driven decisions.
Best for: A growth plan is best for businesses entering new markets, launching new products, scaling operations, or practicing a growth planning process.
3. Strategic business plan
Strategic business plans highlight your strategic objectives, define your business strategies, and outline a roadmap to take you there. It covers the nitty-gritty about your company’s goals, mission objectives, and long-term vision.
Such plans are extremely efficient in communicating your goals to internal teams and stakeholders, while ensuring everyone is on the same page as you.
Best for: Businesses and startups planning long-term growth and nonprofits aiming to increase their impact.
4. Feasibility business plan
A feasibility business plan is specifically designed to test the viability of a new product or business expansion in a new market. As opposed to a detailed business plan, such plans focus on two primary matters:
- Determining the existence of a market
- Determining the profits of the initiative
This type of business plan usually excludes all the other sections included in usual business plans. Instead, it concentrates mainly on the scope of a new initiative, its profitability, market analysis, competition, and associated financial implications.
It is mostly crafted for internal management and ends with recommendations on whether the decision to enter a new market or introduce a new product or service is viable or not.
Best for: Established businesses and early-stage startups to assess the viability of a specific product, market, or business idea before allocating significant resources.
5. Operational business plan
Operational plans are specific documents outlining processes and procedures of day-to-day business activities. Such plans focus on operational aspects of the business such as logistics, inventory, supply chain, production, and resource allocation.
A well-mapped operational plan serves as a guidebook for internal team and management. It streamlines the workflow, establishes SOPs, and offers a clear understanding of who will perform what tasks and what resources will be required.
There is no strict format outlining the contents of such a plan. The plan just needs to be clear, communicative, and viable enough to implement practically.
Best for: Established businesses to manage operations and resource allocation and startups to establish standard clear processes.
6. Nonprofit business plan
Nonprofit business plans are suited for businesses that operate for a charitable or social cause. Such plans are quite similar to traditional plans, however, they include an additional section where you explain the impact your non-profit organization will make in society.
Like a traditional plan, you will highlight the business concept, outline the market research, set the business goals, determine your business and promotional strategies, and demonstrate your team.
Additionally, you will include a section demonstrating the financial sustainability of the nonprofit venture. This is essential to attract donors, grants, and investors for your nonprofit business.
Best for: Nonprofit startups planning to secure funding and grants from financial institutions.
7. What-If business plan
What-if business plans are contingency plans used to draft strategies for the worst-case scenarios. This plan is usually less formal unless a funding request is included.
Such planning allows you to test and study the impact of different hypothetical situations related to the market, environment, competition, and legal regulations on your business.
Best for: Businesses in highly volatile markets and companies practicing crisis management. Also suited when considering mergers, price hikes, or undertaking any major business decision.
And those are some of the many different types of business plans you can have for your business. Wondering which one your business needs? Let us make your choice easier.
Choosing the right type of business plan
Here are the 2 criteria that will help in determining the right plan for your business.
The first step to choosing a business plan is to understand the purpose and objective of writing a business plan. For instance, your objective could be to acquire funds, guide an internal team, create a strategic roadmap, expand into a new geographic market, or prepare for contingencies.
Align your objective with the purpose of specific business plans and see which one suits you the best.
2. Scope of business
The scope and complexity of your business play a crucial role in determining the type of business plan you require. Take into account factors like products and service offerings, the scale of the business, and the business complexity to make a choice.
Even the stage of your business, depending on whether it is a startup or an established business, will influence this decision.
Start preparing your business plan with Upmetrics
You now have a proper understanding of the different types of business. If you’re not sure which one to pick, let us help you.
Our business planning software helps create stellar business plans and saves you the pain of writing one from scratch.
You can either choose a business plan sample and follow its step-by-step instructions to prepare your functional and actionable business plan.
Don’t have enough time to write the entire thing from scratch? Go ahead with our AI business plan generator ; it will quickly generate the entire plan for you..
Simply enter your business details, answer a few questions, and see your plan coming together in front of your eyes in less than 15 minutes.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 8 most common sections of a business plan.
The 8 common components of a successful business plan include
- Management team
Which type of business plan is right for me?
The answer entirely depends upon what you want to achieve with your business plan. Apart from that the scope, nature, and complexity of your business will determine the type of business plan you need.
Do I need a business plan to start a business?
A business plan is highly recommended before you kickstart your business endeavor. It builds a solid foundation for your business idea and offers a roadmap to achieve your strategic and business objectives. A well-drafted business proposal increases the chances of your business venture succeeding.
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Get started with Upmetrics Al
- 400+ sample business plans
- Al-powered financial planning
- Collaborative workspace
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning

- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Tips White Papers
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- United Kingdom
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
The 4 Types of Business Plans Learn which of these four business plan formats best fits your needs.
By Teresa Ciulla Dec 4, 2014
Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own.
In their book Write Your Business Plan , the staff of Entrepreneur Media offer an in-depth understanding of what's essential to any business plan, what's appropriate for your venture, and what it takes to ensure success. In this edited excerpt, the authors describe four different types of plans you could write and what you'd use each one for.
Business plans can be divided roughly into four distinct types. There are very short plans, or miniplans, presentation plans or decks, working plans, and what-if plans. They each require very different amounts of labor and not always with proportionately different results. That is to say, a more elaborate plan isn't guaranteed to be superior to an abbreviated one. Success depends on various factors and whether the right plan is used in the right setting. For example, a new hire may not want to read the same, elaborate version of your plan that might be important to a potential investor.
The Miniplan
The miniplan is preferred by many recipients because they can read it or download it quickly to read later on their iPhone or tablet. You include most of the same ingredients that you would in a longer plan, but you cut to the highlights while telling the same story. For a small-business venture, it's typically all that you need. For a more complex business, you may need the longer version.
The Presentation Plan
The advent of PowerPoint presentations changed the way many, if not most, plans are presented. And while the plan is shorter than its predecessors, it's not necessarily easier to present. Many people lose sleep over an upcoming presentation, especially one that can play a vital role in the future of their business. But presenting your plan as a deck can be very powerful. Readers of a plan can't always capture your passion for the business nor can they ask questions when you finish. But in 20 minutes, you can cover all the key points and tell your story from concept and mission statement through financial forecasts.
Remember to keep your graphics uncluttered and to make comments to accentuate your ideas rather than simply reading what's in front of your audience.
While a presentation plan is concise, don't be fooled: It takes plenty of planning. The pertinent questions who, what, where, why, when and how all need to be answered.
The Working Plan
A working plan is a tool to be used to operate your business. It has to be long on detail but may be short on presentation. As with a miniplan, you can probably can afford a somewhat higher degree of candor and informality when preparing a working plan. In a plan you intend to present to a bank loan committee, you might describe a rival as "competing primarily on a price basis." In a working plan, your comment about the same competitor might be "When is Jones ever going to stop this insane price-cutting?"
A plan intended strictly for internal use may also omit some elements that you need not explain to yourself. Likewise, you probably don't need to include an appendix with resumes of key executives. Nor would a working plan especially benefit from product photos.
Internal policy considerations may guide the decision about whether to include or exclude certain information in a working plan. Many entrepreneurs are sensitive about employees knowing the precise salary the owner takes home from the business. To the extent such information can be left out of a working plan without compromising its utility, you can feel free to protect your privacy.
This document is like an old pair of khakis you wear to the office on Saturdays or that one ancient delivery truck that never seems to break down. It's there to be used, not admired.
The What-If Plan
When you face unusual circumstances, you need a variant on the working plan. For example, you might want to prepare a contingency plan when you're seeking bank financing. A contingency plan is a plan based on the worst-case scenario that you can imagine your business surviving—loss of market share, heavy price competition, defection of a key member of your management team. A contingency plan can soothe the fears of a banker or investor by demonstrating that you have indeed considered more than a rosy scenario.
Your business may be considering an acquisition, in which case a pro forma business plan (some call this a what-if plan) can help you understand what the acquisition is worth and how it might affect your core business. What if you raise prices, invest in staff training and reduce duplicative efforts? Such what-if planning doesn't have to be as formal as a presentation plan. Perhaps you want to mull over the chances of a major expansion. A what-if plan can help you spot the increased needs for space, equipment, personnel and other variables so you can make good decisions.
What sets these kinds of plans apart from the working and presentation plans is that they aren't necessarily describing how you'll run the business. They're essentially more like an addendum to your actual business plan. If you decide to acquire that competitor or grow dramatically, you'll want to incorporate some of the thinking already invested in these special purpose plans into your primary business plan.
Freelance Editor
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- Businesses Are Reviving This 1800s Holiday Tradition With a 'Surprise and Delight' Factor That Drives Sales — Here's How One Buzzy Brand Is Making It Work
- Lock I Was Fired From My Job at a Bank — Then Started a Multimillion-Dollar Company. Here's How I Turned Failure Into Success.
- Lock This Couple Started a Side Hustle Out of Their Volkswagen. It Made $1 Million a Month Last Year and Is 'So Fulfilling.'
- She Became CEO of Her Whole Company By Raising Her Hand and Saying This
- Over a Million People Have Recently Joined Bluesky, the Ad-Free X Alternative and Threads Competitor
- Lock This Might Be the Worst Type of Person to Hire, According to an Elite Special Operations Leader — Look for These Red Flags Before It's Too Late
Most Popular Red Arrow
Looking for a remote job here are the most in-demand skills to have on your resume, according to employers..
Employers are looking for interpersonal skills like teamwork as well as specific coding skills.
After Curing Her Debilitating Pain With Traditional Chinese Medicine, She Started a Business to Deliver Ancient Treatments With Modern Tech: 'You Saved My Life.'
Founder and CEO Camilla Sievers shares the inspiration and growth story of Qi Health, a digital health platform focused on providing women access to TCM treatments.
'I Don't Believe in Work-Life Balance': Infosys' 78-Year-Old Co-Founder Says He Worked 14 Hours a Day, 6.5 Days a Week
He kept the schedule up until he retired.
63 Small Business Ideas to Start in 2024
We put together a list of the best, most profitable small business ideas for entrepreneurs to pursue in 2024.
5 Links You Need to Be Successful As a Day Trader
Mastering drive, computer skills, emotional regulation, situational awareness and discipline are essential for day trading success.
Video: SpaceX Is Launching Starship's Sixth Test Flight—Watch the Lift Off and Catch Attempt Live
President-elect Donald Trump is expected to attend SpaceX's sixth test flight of its Starship rocket on Tuesday.
Successfully copied link

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

What is a business plan? Definition, Purpose, and Types
Table of Contents
What is a business plan?
Looking for someone to write a business plan, purposes of a business plan, what are the essential components of a business plan, executive summary, business description or overview, product and price, competitive analysis, target market, marketing plan, financial plan, funding requirements, types of business plan, lean startup business plans, traditional business plans, need guidance with your business plan, how often should a business plan be reviewed and revised, what are the key elements of a lean startup business plan, what are some of the reasons why business plans don't succeed.
In the world of business, a well-thought-out plan is often the key to success. This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies , and financial projections. Whether you’re starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a business plan is an essential tool.
As a business plan writer and consultant , I’ve crafted over 15,000 plans for a diverse range of businesses. In this article, I’ll be sharing my wealth of experience about what a business plan is, its purpose, and the step-by-step process of creating one. By the end, you’ll have a thorough understanding of how to develop a robust business plan that can drive your business to success.
A business plan is a roadmap for your business. It outlines your goals, strategies, and how you plan to achieve them. It’s a living document that you can update as your business grows and changes.
Find professional business plan writers for your business success.
These are the following purpose of business plan:
- Attract investors and lenders: If you’re seeking funding for your business , a business plan is a must-have. Investors and lenders want to see that you have a clear plan for how you’ll use their money to grow your business and generate revenue.
- Get organized and stay on track: Writing a business plan forces you to think through all aspects of your business, from your target market to your marketing strategy. This can help you identify any potential challenges and opportunities early on, so you can develop a plan to address them.
- Make better decisions: A business plan can help you make better decisions about your business by providing you with a framework to evaluate different options. For example, if you’re considering launching a new product, your business plan can help you assess the potential market demand, costs, and profitability.

The executive summary is the most important part of your business plan, even though it’s the last one you’ll write. It’s the first section that potential investors or lenders will read, and it may be the only one they read. The executive summary sets the stage for the rest of the document by introducing your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
The business description section of your business plan should introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way. It should include your business name, years in operation, key offerings, positioning statement, and core values (if applicable). You may also want to include a short history of your company.
In this section, the company should describe its products or services , including pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other relevant information could include production and manufacturing processes, patents, and proprietary technology.
Every industry has competitors, even if your business is the first of its kind or has the majority of the market share. In the competitive analysis section of your business plan, you’ll objectively assess the industry landscape to understand your business’s competitive position. A SWOT analysis is a structured way to organize this section.
Your target market section explains the core customers of your business and why they are your ideal customers. It should include demographic, psychographic, behavioral, and geographic information about your target market.
Marketing plan describes how the company will attract and retain customers, including any planned advertising and marketing campaigns . It also describes how the company will distribute its products or services to consumers.
After outlining your goals, validating your business opportunity, and assessing the industry landscape, the team section of your business plan identifies who will be responsible for achieving your goals. Even if you don’t have your full team in place yet, investors will be impressed by your clear understanding of the roles that need to be filled.
In the financial plan section,established businesses should provide financial statements , balance sheets , and other financial data. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years, and may also request funding.
Since one goal of a business plan is to secure funding from investors , you should include the amount of funding you need, why you need it, and how long you need it for.
- Tip: Use bullet points and numbered lists to make your plan easy to read and scannable.
Access specialized business plan writing service now!
Business plans can come in many different formats, but they are often divided into two main types: traditional and lean startup. The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) says that the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
Lean startup business plans are short (as short as one page) and focus on the most important elements. They are easy to create, but companies may need to provide more information if requested by investors or lenders.
Traditional business plans are longer and more detailed than lean startup business plans, which makes them more time-consuming to create but more persuasive to potential investors. Lean startup business plans are shorter and less detailed, but companies should be prepared to provide more information if requested.
Access 14 free business plan samples!
A business plan should be reviewed and revised at least annually, or more often if the business is experiencing significant changes. This is because the business landscape is constantly changing, and your business plan needs to reflect those changes in order to remain relevant and effective.
Here are some specific situations in which you should review and revise your business plan:
- You have launched a new product or service line.
- You have entered a new market.
- You have experienced significant changes in your customer base or competitive landscape.
- You have made changes to your management team or organizational structure.
- You have raised new funding.
A lean startup business plan is a short and simple way for a company to explain its business, especially if it is new and does not have a lot of information yet. It can include sections on the company’s value proposition, major activities and advantages, resources, partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.

- Unrealistic assumptions: Business plans are often based on assumptions about the market, the competition, and the company’s own capabilities. If these assumptions are unrealistic, the plan is doomed to fail.
- Lack of focus: A good business plan should be focused on a specific goal and how the company will achieve it. If the plan is too broad or tries to do too much, it is unlikely to be successful.
- Poor execution: Even the best business plan is useless if it is not executed properly. This means having the right team in place, the necessary resources, and the ability to adapt to changing circumstances.
- Unforeseen challenges: Every business faces challenges that could not be predicted or planned for. These challenges can be anything from a natural disaster to a new competitor to a change in government regulations.
What are the benefits of having a business plan?
- It helps you to clarify your business goals and strategies.
- It can help you to attract investors and lenders.
- It can serve as a roadmap for your business as it grows and changes.
- It can help you to make better business decisions.
How to write a business plan?
There are many different ways to write a business plan, but most follow the same basic structure. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Executive summary.
- Company description.
- Management and organization description.
- Financial projections.
How to write a business plan step by step?
Start with an executive summary, then describe your business, analyze the market, outline your products or services, detail your marketing and sales strategies, introduce your team, and provide financial projections.
Why do I need a business plan for my startup?
A business plan helps define your startup’s direction, attract investors, secure funding, and make informed decisions crucial for success.
What are the key components of a business plan?
Key components include an executive summary, business description, market analysis, products or services, marketing and sales strategy, management and team, financial projections, and funding requirements.
Can a business plan help secure funding for my business?
Yes, a well-crafted business plan demonstrates your business’s viability, the use of investment, and potential returns, making it a valuable tool for attracting investors and lenders.
Related Posts

Why Experienced Legal Consultation is Crucial for New Businesses

Creating a ‘Second Brain’ to Manage Information Overload and Enhance Focus

What Are Mobile App Development Services? Guide for Businesses and Startups
Quick links.

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- Business Credit Cards
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- A Comprehensive Guide to Venture Capitalists
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077

🎧 Real entrepreneurs. Real stories.
Subscribe to The Hurdle podcast today!
What is a Business Plan? Definition and Resources

9 min. read
Updated July 29, 2024

If you’ve ever jotted down a business idea on a napkin with a few tasks you need to accomplish, you’ve written a business plan — or at least the very basic components of one.
The origin of formal business plans is murky. But they certainly go back centuries. And when you consider that 20% of new businesses fail in year 1 , and half fail within 5 years, the importance of thorough planning and research should be clear.
But just what is a business plan? And what’s required to move from a series of ideas to a formal plan? Here we’ll answer that question and explain why you need one to be a successful business owner.
- What is a business plan?

A business plan lays out a strategic roadmap for any new or growing business.
Any entrepreneur with a great idea for a business needs to conduct market research , analyze their competitors , validate their idea by talking to potential customers, and define their unique value proposition .
The business plan captures that opportunity you see for your company: it describes your product or service and business model , and the target market you’ll serve.
It also includes details on how you’ll execute your plan: how you’ll price and market your solution and your financial projections .
Reasons for writing a business plan
If you’re asking yourself, ‘Do I really need to write a business plan?’ consider this fact:
Companies that commit to planning grow 30% faster than those that don’t.
Creating a business plan is crucial for businesses of any size or stage. It helps you develop a working business and avoid consequences that could stop you before you ever start.
If you plan to raise funds for your business through a traditional bank loan or SBA loan , none of them will want to move forward without seeing your business plan. Venture capital firms may or may not ask for one, but you’ll still need to do thorough planning to create a pitch that makes them want to invest.
But it’s more than just a means of getting your business funded . The plan is also your roadmap to identify and address potential risks.
It’s not a one-time document. Your business plan is a living guide to ensure your business stays on course.
Related: 14 of the top reasons why you need a business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
What research shows about business plans
Numerous studies have established that planning improves business performance:
- 71% of fast-growing companies have business plans that include budgets, sales goals, and marketing and sales strategies.
- Companies that clearly define their value proposition are more successful than those that can’t.
- Companies or startups with a business plan are more likely to get funding than those without one.
- Starting the business planning process before investing in marketing reduces the likelihood of business failure.
The planning process significantly impacts business growth for existing companies and startups alike.
Read More: Research-backed reasons why writing a business plan matters
When should you write a business plan?
No two business plans are alike.
Yet there are similar questions for anyone considering writing a plan to answer. One basic but important question is when to start writing it.
A Harvard Business Review study found that the ideal time to write a business plan is between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business.
But the reality can be more nuanced – it depends on the stage a business is in, or the type of business plan being written.
Ideal times to write a business plan include:
- When you have an idea for a business
- When you’re starting a business
- When you’re preparing to buy (or sell)
- When you’re trying to get funding
- When business conditions change
- When you’re growing or scaling your business
Read More: The best times to write or update your business plan
How often should you update your business plan?
As is often the case, how often a business plan should be updated depends on your circumstances.
A business plan isn’t a homework assignment to complete and forget about. At the same time, no one wants to get so bogged down in the details that they lose sight of day-to-day goals.
But it should cover new opportunities and threats that a business owner surfaces, and incorporate feedback they get from customers. So it can’t be a static document.
Related Reading: 5 fundamental principles of business planning
For an entrepreneur at the ideation stage, writing and checking back on their business plan will help them determine if they can turn that idea into a profitable business .
And for owners of up-and-running businesses, updating the plan (or rewriting it) will help them respond to market shifts they wouldn’t be prepared for otherwise.
It also lets them compare their forecasts and budgets to actual financial results. This invaluable process surfaces where a business might be out-performing expectations and where weak performance may require a prompt strategy change.
The planning process is what uncovers those insights.
Related Reading: 10 prompts to help you write a business plan with AI
- How long should your business plan be?
Thinking about a business plan strictly in terms of page length can risk overlooking more important factors, like the level of detail or clarity in the plan.
Not all of the plan consists of writing – there are also financial tables, graphs, and product illustrations to include.
But there are a few general rules to consider about a plan’s length:
- Your business plan shouldn’t take more than 15 minutes to skim.
- Business plans for internal use (not for a bank loan or outside investment) can be as short as 5 to 10 pages.
A good practice is to write your business plan to match the expectations of your audience.
If you’re walking into a bank looking for a loan, your plan should match the formal, professional style that a loan officer would expect . But if you’re writing it for stakeholders on your own team—shorter and less formal (even just a few pages) could be the better way to go.
The length of your plan may also depend on the stage your business is in.
For instance, a startup plan won’t have nearly as much financial information to include as a plan written for an established company will.
Read More: How long should your business plan be?
What information is included in a business plan?
The contents of a plan business plan will vary depending on the industry the business is in.
After all, someone opening a new restaurant will have different customers, inventory needs, and marketing tactics to consider than someone bringing a new medical device to the market.
But there are some common elements that most business plans include:
- Executive summary: An overview of the business operation, strategy, and goals. The executive summary should be written last, despite being the first thing anyone will read.
- Products and services: A description of the solution that a business is bringing to the market, emphasizing how it solves the problem customers are facing.
- Market analysis: An examination of the demographic and psychographic attributes of likely customers, resulting in the profile of an ideal customer for the business.
- Competitive analysis: Documenting the competitors a business will face in the market, and their strengths and weaknesses relative to those competitors.
- Marketing and sales plan: Summarizing a business’s tactics to position their product or service favorably in the market, attract customers, and generate revenue.
- Operational plan: Detailing the requirements to run the business day-to-day, including staffing, equipment, inventory, and facility needs.
- Organization and management structure: A listing of the departments and position breakdown of the business, as well as descriptions of the backgrounds and qualifications of the leadership team.
- Key milestones: Laying out the key dates that a business is projected to reach certain milestones , such as revenue, break-even, or customer acquisition goals.
- Financial plan: Balance sheets, cash flow forecast , and sales and expense forecasts with forward-looking financial projections, listing assumptions and potential risks that could affect the accuracy of the plan.
- Appendix: All of the supporting information that doesn’t fit into specific sections of the business plan, such as data and charts.
Read More: Use this business plan outline to organize your plan
- Different types of business plans
A business plan isn’t a one-size-fits-all document. There are numerous ways to create an effective business plan that fits entrepreneurs’ or established business owners’ needs.
Here are a few of the most common types of business plans for small businesses:
- One-page plan : Outlining all of the most important information about a business into an adaptable one-page plan.
- Growth plan : An ongoing business management plan that ensures business tactics and strategies are aligned as a business scales up.
- Internal plan : A shorter version of a full business plan to be shared with internal stakeholders – ideal for established companies considering strategic shifts.
Business plan vs. operational plan vs. strategic plan
- What questions are you trying to answer?
- Are you trying to lay out a plan for the actual running of your business?
- Is your focus on how you will meet short or long-term goals?
Since your objective will ultimately inform your plan, you need to know what you’re trying to accomplish before you start writing.
While a business plan provides the foundation for a business, other types of plans support this guiding document.
An operational plan sets short-term goals for the business by laying out where it plans to focus energy and investments and when it plans to hit key milestones.
Then there is the strategic plan , which examines longer-range opportunities for the business, and how to meet those larger goals over time.
Read More: How to use a business plan for strategic development and operations
- Business plan vs. business model
If a business plan describes the tactics an entrepreneur will use to succeed in the market, then the business model represents how they will make money.
The difference may seem subtle, but it’s important.
Think of a business plan as the roadmap for how to exploit market opportunities and reach a state of sustainable growth. By contrast, the business model lays out how a business will operate and what it will look like once it has reached that growth phase.
Learn More: The differences between a business model and business plan
- Moving from idea to business plan
Now that you understand what a business plan is, the next step is to start writing your business plan .
The best way to start is by reviewing examples and downloading a business plan template . These resources will provide you with guidance and inspiration to help you write a plan.
We recommend starting with a simple one-page plan ; it streamlines the planning process and helps you organize your ideas. However, if one page doesn’t fit your needs, there are plenty of other great templates available that will put you well on your way to writing a useful business plan.
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
- Reasons to write a business plan
- Business planning research
- When to write a business plan
- When to update a business plan
- Information to include
- Business vs. operational vs. strategic plans
Related Articles

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix

4 Min. Read
How to Define Your Target Market

10 Min. Read
How to Write a Small Restaurant Business Plan + Free Sample Plan PDF

15 Min. Read
How to Write a Business Plan for an Outpatient Medical Practice
The LivePlan Newsletter
Become a smarter, more strategic entrepreneur.
Your first monthly newsetter will be delivered soon..
Unsubscribe anytime. Privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
7 Different Types of Business Plans Explained. Business plans go by many names: Strategic plans, traditional plans, operational plans, feasibility plans, internal plans, growth plans, and more. Different situations call for different types of plans. But what makes each type of plan unique?
Value proposition. Strategic marketing plan. Market evaluations. Projected startup costs. Cash flow projections and income and profit expectations. Within the financial section, a business also needs to explain the exit strategy for investors and how specifically the company plans to use investor money.
Here are the 10 types of business plans designed to address different needs and stages of business growth. Each type serves a unique purpose and provides a different level of detail. 1. Traditional business plan. When Needed. Starting a new business, seeking investment, or applying for a loan. Typical Spanning Length.
Feasibility Plan. • Audience: Generally internal. • Depth: Generally lean. • Purpose: Explore the viability of offering a new product or service. Sometimes called a "feasibility study ...
Operations business plan. Strategic business plan. 01. Startup business plan. The startup business plan is a comprehensive document that will set the foundation for your company's success. It covers all aspects of a business, including a situation analysis, detailed financial information and a strategic marketing plan.
You may use one or more types of plans in business to make major changes throughout its lifespan. The type of business plan you need varies by your industry, business size, and goals. 1. One-page Business Plan. The one-page business plan is for very small businesses like side hustles. A one-page business plan is a great way to get your ideas on ...
These can be specific to certain departments such as marketing, HR, production, etc. Internal business plans focus primarily on the company's goals, operations, finances, and personnel and define the strategies to achieve their goals. 2. External business plans. On the contrary, external business plans are intended for people outside the ...
Business plans can be divided roughly into four distinct types. There are very short plans, or miniplans, presentation plans or decks, working plans, and what-if plans. They each require very ...
In the world of business, a well-thought-out plan is often the key to success. This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company's goals, strategies, and financial projections.Whether you're starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a business plan is an essential tool.. As a business plan writer and consultant, I've crafted over ...
Different types of business plans. A business plan isn't a one-size-fits-all document. There are numerous ways to create an effective business plan that fits entrepreneurs' or established business owners' needs. Here are a few of the most common types of business plans for small businesses: