Essay Papers Writing Online
Mastering the art of essay writing – a comprehensive guide.

Essay writing is a fundamental skill that every student needs to master. Whether you’re in high school, college, or beyond, the ability to write a strong, coherent essay is essential for academic success. However, many students find the process of writing an essay daunting and overwhelming.
This comprehensive guide is here to help you navigate the intricate world of essay writing. From understanding the basics of essay structure to mastering the art of crafting a compelling thesis statement, we’ve got you covered. By the end of this guide, you’ll have the tools and knowledge you need to write an outstanding essay that will impress your teachers and classmates alike.
So, grab your pen and paper (or fire up your laptop) and let’s dive into the ultimate guide to writing an essay. Follow our tips and tricks, and you’ll be well on your way to becoming a skilled and confident essay writer!

The Art of Essay Writing: A Comprehensive Guide
Essay writing is a skill that requires practice, patience, and attention to detail. Whether you’re a student working on an assignment or a professional writing for publication, mastering the art of essay writing can help you communicate your ideas effectively and persuasively.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the key elements of a successful essay, including how to choose a topic, structure your essay, and craft a compelling thesis statement. We’ll also discuss the importance of research, editing, and proofreading, and provide tips for improving your writing style and grammar.
By following the advice in this guide, you can become a more confident and skilled essay writer, capable of producing high-quality, engaging essays that will impress your readers and achieve your goals.
Understanding the Essay Structure
When it comes to writing an essay, understanding the structure is key to producing a cohesive and well-organized piece of writing. An essay typically consists of three main parts: an introduction, the body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Introduction: The introduction is where you introduce your topic and provide some background information. It should also include your thesis statement, which is the main idea or argument that you will be discussing in the essay.
Body paragraphs: The body of the essay is where you present your supporting evidence and arguments. Each paragraph should focus on a separate point and include evidence to back up your claims. Remember to use transition words to link your ideas together cohesively.
Conclusion: The conclusion is where you wrap up your essay by summarizing your main points and restating your thesis. It is also a good place to make any final thoughts or reflections on the topic.
Understanding the structure of an essay will help you write more effectively and communicate your ideas clearly to your readers.
Choosing the Right Topic for Your Essay

One of the most crucial steps in writing a successful essay is selecting the right topic. The topic you choose will determine the direction and focus of your writing, so it’s important to choose wisely. Here are some tips to help you select the perfect topic for your essay:
| Choose a topic that you are passionate about or interested in. Writing about something you enjoy will make the process more enjoyable and your enthusiasm will come through in your writing. | |
| Do some preliminary research to see what topics are available and what resources are out there. This will help you narrow down your choices and find a topic that is both interesting and manageable. | |
| Think about who will be reading your essay and choose a topic that will resonate with them. Consider their interests, knowledge level, and any biases they may have when selecting a topic. | |
| Take some time to brainstorm different topic ideas. Write down all the potential topics that come to mind, and then evaluate each one based on relevance, interest, and feasibility. | |
| Try to choose a topic that offers a unique perspective or angle. Avoid overly broad topics that have been extensively covered unless you have a fresh take to offer. |
By following these tips and considering your interests, audience, and research, you can choose a topic that will inspire you to write an engaging and compelling essay.
Research and Gathering Information
When writing an essay, conducting thorough research and gathering relevant information is crucial. Here are some tips to help you with your research:
| Make sure to use reliable sources such as academic journals, books, and reputable websites. Avoid using sources that are not credible or biased. | |
| As you research, take notes on important information that you can use in your essay. Organize your notes so that you can easily reference them later. | |
| Don’t rely solely on one type of source. Utilize a variety of sources to provide a well-rounded perspective on your topic. | |
| Before using a source in your essay, make sure to evaluate its credibility and relevance to your topic. Consider the author’s credentials, publication date, and biases. | |
| Make sure to keep a record of the sources you use in your research. This will help you properly cite them in your essay and avoid plagiarism. |
Crafting a Compelling Thesis Statement
When writing an essay, one of the most crucial elements is the thesis statement. This statement serves as the main point of your essay, summarizing the argument or position you will be taking. Crafting a compelling thesis statement is essential for a strong and cohesive essay. Here are some tips to help you create an effective thesis statement:
- Be specific: Your thesis statement should clearly state the main idea of your essay. Avoid vague or general statements.
- Make it arguable: A strong thesis statement is debatable and presents a clear position that can be supported with evidence.
- Avoid clichés: Stay away from overused phrases or clichés in your thesis statement. Instead, strive for originality and clarity.
- Keep it concise: Your thesis statement should be concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary words or phrases.
- Take a stand: Your thesis statement should express a clear stance on the topic. Don’t be afraid to assert your position.
By following these guidelines, you can craft a compelling thesis statement that sets the tone for your essay and guides your reader through your argument.
Writing the Body of Your Essay
Once you have your introduction in place, it’s time to dive into the body of your essay. The body paragraphs are where you will present your main arguments or points to support your thesis statement.
Here are some tips for writing the body of your essay:
- Stick to One Main Idea: Each paragraph should focus on one main idea or argument. This will help keep your essay organized and easy to follow.
- Use Topic Sentences: Start each paragraph with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea of the paragraph.
- Provide Evidence: Support your main points with evidence such as facts, statistics, examples, or quotes from experts.
- Explain Your Points: Don’t just state your points; also explain how they support your thesis and why they are important.
- Use Transition Words: Use transition words and phrases to connect your ideas and create a smooth flow between paragraphs.
Remember to refer back to your thesis statement and make sure that each paragraph contributes to your overall argument. The body of your essay is where you can really showcase your critical thinking and analytical skills, so take the time to craft well-developed and coherent paragraphs.
Perfecting Your Essay with Editing and Proofreading

Editing and proofreading are essential steps in the essay writing process to ensure your work is polished and error-free. Here are some tips to help you perfect your essay:
- Take a Break: After writing your essay, take a break before starting the editing process. This will help you look at your work with fresh eyes.
- Focus on Structure: Check the overall structure of your essay, including the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Make sure your ideas flow logically and cohesively.
- Check for Clarity: Ensure that your arguments are clear and easy to follow. Eliminate any jargon or confusing language that might obscure your message.
- Grammar and Punctuation: Review your essay for grammar and punctuation errors. Pay attention to subject-verb agreement, verb tense consistency, and proper punctuation usage.
- Use a Spell Checker: Run a spell check on your essay to catch any spelling mistakes. However, don’t rely solely on spell checkers as they may miss certain errors.
- Read Aloud: Read your essay aloud to yourself or have someone else read it to you. This can help you identify awkward phrasing or unclear sentences.
- Get Feedback: Consider getting feedback from a peer, teacher, or writing tutor. They can offer valuable insights and suggestions for improving your essay.
By following these editing and proofreading tips, you can ensure that your essay is well-crafted, organized, and free of errors, helping you make a strong impression on your readers.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, unlock success with a comprehensive business research paper example guide, unlock your writing potential with writers college – transform your passion into profession, “unlocking the secrets of academic success – navigating the world of research papers in college”, master the art of sociological expression – elevate your writing skills in sociology.
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How to Write an Essay — A Comprehensive Guide

Table of Contents
Writing an essay can be a daunting task, especially if you are new to academic writing. However, with the right approach and a clear understanding of the essay structure, you can tackle this challenge seamlessly. In this article, we will guide you through the process of essay writing in a detailed manner. By following these guidelines, you will be able to gather your materials, develop a strong argument, and craft a well-structured essay that will leave your readers hooked.
Getting Started — Gather Your Materials and Research
Before you start writing your essay, it is important to gather all the necessary materials and conduct thorough research on your topic. This includes finding relevant books, articles, and online sources that will provide you with the information needed to support your argument. The more well-informed you are on the subject, the stronger your essay will be.
When gathering your materials, it is essential to consider the credibility and reliability of your sources. Look for reputable publications, academic journals, bibliography databases , and expert opinions to ensure that the information you include in your essay is accurate and trustworthy. Remember, the quality of your research will greatly influence the overall quality of your essay.
Additionally, conducting thorough research will not only provide you with the necessary information but also help you gain a deeper understanding of your topic. As you delve into different sources, you may come across various perspectives and arguments that will enrich your own analysis. This exploration will allow you to develop a well-rounded and comprehensive essay that considers different viewpoints.
While conducting your research, it is crucial to take organized and detailed notes. Jot down key points, quotes, and any thoughts or ideas that come to mind. This will not only help you remember important information but also assist you in organizing your thoughts and structuring your essay effectively. By keeping track of your sources, you will also avoid any issues with plagiarism and ensure that you can properly cite your references.
Furthermore, the research process provides an opportunity for you to engage critically with the topic. As you read and analyze different sources, you may encounter conflicting information or gaps in the existing literature. This presents a chance for you to contribute to the academic discourse by addressing these discrepancies or proposing new insights. Your essay can become a platform for advancing knowledge and sparking further discussions.
Lastly, remember that research is an ongoing process. Even after you have gathered your initial materials, it is important to remain open to new information and perspectives. Embrace this continuous learning and be willing to revise and refine your arguments as you progress.
Create an Outline
Once you have gathered your research materials, it is time to create an outline for your essay. An outline will serve as a roadmap for your writing, helping you organize your thoughts and ensure that your essay flows logically. Start by identifying the main points you want to cover in your essay. Then, arrange these points in a logical order, considering the overall structure of your essay.
When creating an outline, it is important to consider the overall structure of your essay. Think about how you want to introduce your topic and engage your readers. Consider what information is essential to include in each section of your essay and how you want to transition between different ideas.
Understand the Essay Structure
Before diving into the essay writing process, it is important to understand the basic structure of an essay. Most essays follow a standard format, consisting of an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. The introduction should grab the reader's attention and provide a clear thesis statement that reflects your main argument. The body paragraphs should expand on your argument, providing evidence and examples to support your claims. Finally, the conclusion should summarize your essay and restate your main points.
Write the Introduction
The introduction is the first impression your essay makes on the reader, so it is essential to make it engaging and captivating. Start with a hook that grabs the reader's attention and introduces the topic. Then, provide some background information and context to set the stage for your argument. Finally, end your introduction with a clear and concise thesis statement that reflects the main point you will be discussing throughout your essay.
Develop Your Argument
Once you have established your thesis statement, it is time to develop your argument in the body paragraphs of your essay. Each body paragraph should focus on a specific point that supports your thesis. Commence with each paragraph by presenting a topic sentence that serves to introduce the main idea to the reader. Subsequently, provide evidence and illustrations to support your argument. Be sure to use clear and concise language and vary your sentence structure to keep the reader engaged.
Use Evidence to Support Your Argument
To strengthen your argument and validate your claims, it is crucial to use evidence and examples throughout your essay. This can include research findings, statistics, quotes from authoritative sources, or real-life examples. Make sure to cite your sources properly and provide enough context for the reader to understand the significance of the evidence you are presenting.
Write the Body Paragraphs
With your argument and evidence in place, it is time to write the body paragraphs of your essay. Each body paragraph should focus on a separate point that contributes to your overall argument. Start with a topic that introduces the main concept of the paragraph. Then, provide supporting details and evidence to expand on your point. Use transition words and phrases to ensure a smooth flow between the paragraphs.
Craft the Conclusion
The conclusion is the final opportunity to leave a lasting impression on your reader. In this section, you should summarize your main points and restate your thesis statement. Do not introduce new information or arguments in the conclusion section. Instead, focus on wrapping up your essay and leaving the reader with a thought-provoking closing statement. Make sure to leave a lasting impact and reinforce the significance of your argument.
Edit and Proofread
Once you have finished writing your essay, it is crucial to edit and proofread it thoroughly. Check for grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and awkward phrasing. Ensure that your sentences flow smoothly and that your ideas are clearly expressed. Trim any unnecessary information and make sure that your essay is concise and focused. Consider seeking feedback from your peer or teacher to get a fresh perspective on your work.
Final Touches and Submission
Before submitting your essay, take some time to add the final touches. This includes formatting your essay according to the guidelines provided by your instructor or educational institution. Make sure that your essay is properly formatted, with consistent font, spacing, and citation style . Double-check that all your sources are properly cited, both within the text and in the bibliography or reference list. Finally, read your essay once more to ensure that it is polished and ready for submission.
Wrapping up
By following these guidelines, you can approach essay writing with confidence. Remember to gather your materials and conduct thorough research, create a well-structured outline, and develop a strong argument supported by evidence. Craft an engaging introduction, write clear and concise body paragraphs, and wrap up your essay with a thought-provoking conclusion. Finally, edit and proofread your essay, ensuring that it is well-written and free of errors. By following these steps, you can write an essay that will ingrain your readers and showcase your skills as an academic writer.
You might also like

5 Tools zur Literaturrecherche für die optimale Recherche (+2 Bonustools)

5 outils de revue de littérature pour réussir vos recherches (+2 outils bonus)

人工智能在系统文献综述中的作用
Would you like to explore a topic?
- LEARNING OUTSIDE OF SCHOOL
Or read some of our popular articles?
Free downloadable english gcse past papers with mark scheme.
- 19 May 2022
How Will GCSE Grade Boundaries Affect My Child’s Results?
- Akshat Biyani
- 13 December 2021
The Best Free Homeschooling Resources UK Parents Need to Start Using Today
- Joseph McCrossan
- 18 February 2022
How to Write the Perfect Essay: A Step-By-Step Guide for Students
- June 2, 2022

- What is an essay?
What makes a good essay?
Typical essay structure, 7 steps to writing a good essay, a step-by-step guide to writing a good essay.
Whether you are gearing up for your GCSE coursework submissions or looking to brush up on your A-level writing skills, we have the perfect essay-writing guide for you. 💯
Staring at a blank page before writing an essay can feel a little daunting . Where do you start? What should your introduction say? And how should you structure your arguments? They are all fair questions and we have the answers! Take the stress out of essay writing with this step-by-step guide – you’ll be typing away in no time. 👩💻

What is an essay?
Generally speaking, an essay designates a literary work in which the author defends a point of view or a personal conviction, using logical arguments and literary devices in order to inform and convince the reader.
So – although essays can be broadly split into four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive – an essay can simply be described as a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. 🤔
The purpose of an essay is to present a coherent argument in response to a stimulus or question and to persuade the reader that your position is credible, believable and reasonable. 👌
So, a ‘good’ essay relies on a confident writing style – it’s clear, well-substantiated, focussed, explanatory and descriptive . The structure follows a logical progression and above all, the body of the essay clearly correlates to the tile – answering the question where one has been posed.
But, how do you go about making sure that you tick all these boxes and keep within a specified word count? Read on for the answer as well as an example essay structure to follow and a handy step-by-step guide to writing the perfect essay – hooray. 🙌
Sometimes, it is helpful to think about your essay like it is a well-balanced argument or a speech – it needs to have a logical structure, with all your points coming together to answer the question in a coherent manner. ⚖️
Of course, essays can vary significantly in length but besides that, they all follow a fairly strict pattern or structure made up of three sections. Lean into this predictability because it will keep you on track and help you make your point clearly. Let’s take a look at the typical essay structure:
#1 Introduction
Start your introduction with the central claim of your essay. Let the reader know exactly what you intend to say with this essay. Communicate what you’re going to argue, and in what order. The final part of your introduction should also say what conclusions you’re going to draw – it sounds counter-intuitive but it’s not – more on that below. 1️⃣
Make your point, evidence it and explain it. This part of the essay – generally made up of three or more paragraphs depending on the length of your essay – is where you present your argument. The first sentence of each paragraph – much like an introduction to an essay – should summarise what your paragraph intends to explain in more detail. 2️⃣
#3 Conclusion
This is where you affirm your argument – remind the reader what you just proved in your essay and how you did it. This section will sound quite similar to your introduction but – having written the essay – you’ll be summarising rather than setting out your stall. 3️⃣
No essay is the same but your approach to writing them can be. As well as some best practice tips, we have gathered our favourite advice from expert essay-writers and compiled the following 7-step guide to writing a good essay every time. 👍
#1 Make sure you understand the question
#2 complete background reading.
#3 Make a detailed plan
#4 Write your opening sentences
#5 flesh out your essay in a rough draft, #6 evidence your opinion, #7 final proofread and edit.
Now that you have familiarised yourself with the 7 steps standing between you and the perfect essay, let’s take a closer look at each of those stages so that you can get on with crafting your written arguments with confidence .
This is the most crucial stage in essay writing – r ead the essay prompt carefully and understand the question. Highlight the keywords – like ‘compare,’ ‘contrast’ ‘discuss,’ ‘explain’ or ‘evaluate’ – and let it sink in before your mind starts racing . There is nothing worse than writing 500 words before realising you have entirely missed the brief . 🧐
Unless you are writing under exam conditions , you will most likely have been working towards this essay for some time, by doing thorough background reading. Re-read relevant chapters and sections, highlight pertinent material and maybe even stray outside the designated reading list, this shows genuine interest and extended knowledge. 📚
#3 Make a detailed plan
Following the handy structure we shared with you above, now is the time to create the ‘skeleton structure’ or essay plan. Working from your essay title, plot out what you want your paragraphs to cover and how that information is going to flow. You don’t need to start writing any full sentences yet but it might be useful to think about the various quotes you plan to use to substantiate each section. 📝
Having mapped out the overall trajectory of your essay, you can start to drill down into the detail. First, write the opening sentence for each of the paragraphs in the body section of your essay. Remember – each paragraph is like a mini-essay – the opening sentence should summarise what the paragraph will then go on to explain in more detail. 🖊️
Next, it's time to write the bulk of your words and flesh out your arguments. Follow the ‘point, evidence, explain’ method. The opening sentences – already written – should introduce your ‘points’, so now you need to ‘evidence’ them with corroborating research and ‘explain’ how the evidence you’ve presented proves the point you’re trying to make. ✍️
With a rough draft in front of you, you can take a moment to read what you have written so far. Are there any sections that require further substantiation? Have you managed to include the most relevant material you originally highlighted in your background reading? Now is the time to make sure you have evidenced all your opinions and claims with the strongest quotes, citations and material. 📗
This is your final chance to re-read your essay and go over it with a fine-toothed comb before pressing ‘submit’. We highly recommend leaving a day or two between finishing your essay and the final proofread if possible – you’ll be amazed at the difference this makes, allowing you to return with a fresh pair of eyes and a more discerning judgment. 🤓
If you are looking for advice and support with your own essay-writing adventures, why not t ry a free trial lesson with GoStudent? Our tutors are experts at boosting academic success and having fun along the way. Get in touch and see how it can work for you today. 🎒

Popular posts

- By Guy Doza

- By Akshat Biyani

- By Joseph McCrossan
- In LEARNING TRENDS

What are the Hardest GCSEs? Should You Avoid or Embrace Them?
- By Clarissa Joshua

4 Surprising Disadvantages of Homeschooling
- By Andrea Butler
Want to try tutoring? Request a free trial session with a top tutor.
More great reads:.

Benefits of Reading: Positive Impacts for All Ages Everyday
- May 26, 2023

15 of the Best Children's Books That Every Young Person Should Read
- By Sharlene Matharu
- March 2, 2023

Ultimate School Library Tips and Hacks
- By Natalie Lever
- March 1, 2023
Book a free trial session
Sign up for your free tutoring lesson..
Academic Editing and Proofreading
- Tips to Self-Edit Your Dissertation
- Guide to Essay Editing: Methods, Tips, & Examples
- Journal Article Proofreading: Process, Cost, & Checklist
- The A–Z of Dissertation Editing: Standard Rates & Involved Steps
- Research Paper Editing | Guide to a Perfect Research Paper
- Dissertation Proofreading | Definition & Standard Rates
- Thesis Proofreading | Definition, Importance & Standard Pricing
- Research Paper Proofreading | Definition, Significance & Standard Rates
- Essay Proofreading | Options, Cost & Checklist
- Top 10 Paper Editing Services of 2024 (Costs & Features)
- Top 10 Essay Checkers in 2024 (Free & Paid)
- Top 10 AI Proofreaders to Perfect Your Writing in 2024
- Top 10 English Correctors to Perfect Your Text in 2024
- 10 Advanced AI Text Editors to Transform Writing in 2024
- Personal Statement Editing Services: Craft a Winning Essay
- Top 10 Academic Proofreading Services & How They Help
- College Essay Review: A Step-by-Step Guide (With Examples)
- 10 Best Proofreading Services Online for All in 2024
- Top 10 College Essay Review Services: Pricing and Benefits
- How to Edit a College Admission Essay (8-Step Guide)
Academic Research
- Research Paper Outline: Free Templates & Examples to Guide You
- How to Write a Research Paper: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Write a Lab Report: Examples from Academic Editors
- Research Methodology Guide: Writing Tips, Types, & Examples
- The 10 Best Essential Resources for Academic Research
- 100+ Useful ChatGPT Prompts for Thesis Writing in 2024
- Best ChatGPT Prompts for Academic Writing (100+ Prompts!)
- Sampling Methods Guide: Types, Strategies, and Examples
- Independent vs. Dependent Variables | Meaning & Examples
- Top 10 AI Tools for Research in 2024 (Fast & Efficient!)
Academic Writing & Publishing
- Difference Between Paper Editing and Peer Review
- What are the different types of peer review?
- How to Handle Journal Rejection: Essential Tips
- Editing and Proofreading Academic Papers: A Short Guide
- How to Carry Out Secondary Research
- The Results Section of a Dissertation
- Final Checklist: Is My Article Ready for Submitting to Journals?
- Types of Research Articles to Boost Your Research Profile
- 8 Types of Peer Review Processes You Should Know
- The Ethics of Academic Research
- How does LaTeX based proofreading work?
- How to Improve Your Scientific Writing: A Short Guide
- Chicago Title, Cover Page & Body | Paper Format Guidelines
- How to Write a Thesis Statement: Examples & Tips
- Chicago Style Citation: Quick Guide & Examples
- The A-Z Of Publishing Your Article in A Journal
- What is Journal Article Editing? 3 Reasons You Need It
- 5 Effective Personal Statement Examples & Templates
- Complete Guide to MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Book in APA Style | Format & Examples
- How to Start a Research Paper | Step-by-step Guide
- APA Citations Made Easy with Our Concise Guide for 2024
- A Step-by-Step Guide to APA Formatting Style (7th Edition)
- Top 10 Online Dissertation Editing Services of 2024
- Academic Writing in 2024: 5 Key Dos & Don’ts + Examples
- What Are the Standard Book Sizes for Publishing Your Book?
- MLA Works Cited Page: Quick Tips & Examples
- 2024’s Top 10 Thesis Statement Generators (Free Included!)
- Top 10 Title Page Generators for Students in 2024
- What Is an Open Access Journal? 10 Myths Busted!
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources: Definition, Types & Examples
- How To Write a College Admissions Essay That Stands Out
- How to Write a Dissertation & Thesis Conclusion (+ Examples)
- APA Journal Citation: 7 Types, In-Text Rules, & Examples
- What Is Predatory Publishing and How to Avoid It!
- What Is Plagiarism? Meaning, Types & Examples
- How to Write a Strong Dissertation & Thesis Introduction
- How to Cite a Book in MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Website in MLA Format | 9th Edition Rules
- 10 Best AI Conclusion Generators (Features & Pricing)
- Top 10 Academic Editing Services of 2024 [with Pricing]
- 100+ Writing Prompts for College Students (10+ Categories!)
- How to Create the Perfect Thesis Title Page in 2024
- What Is Accidental Plagiarism & 9 Prevention Strategies
- What Is Self-Plagiarism? (+ 7 Prevention Strategies!)
- Additional Resources
- Preventing Plagiarism in Your Thesis: Tips & Best Practices
- Final Submission Checklist | Dissertation & Thesis
- 7 Useful MS Word Formatting Tips for Dissertation Writing
- How to Write a MEAL Paragraph: Writing Plan Explained in Detail
- Em Dash vs. En Dash vs. Hyphen: When to Use Which
- The 10 Best Citation Generators in 2024 | Free & Paid Plans!
- 2024’s Top 10 Self-Help Books for Better Living
- The 10 Best Free Character and Word Counters of 2024
- Know Everything About How to Make an Audiobook
- Mastering Metaphors: Definition, Types, and Examples
- Citation and Referencing
- Citing References: APA, MLA, and Chicago
- How to Cite Sources in the MLA Format
- MLA Citation Examples: Cite Essays, Websites, Movies & More
- Citations and References: What Are They and Why They Matter
- APA Headings & Subheadings | Formatting Guidelines & Examples
- Formatting an APA Reference Page | Template & Examples
- Research Paper Format: APA, MLA, & Chicago Style
- How to Create an MLA Title Page | Format, Steps, & Examples
- How to Create an MLA Header | Format Guidelines & Examples
- MLA Annotated Bibliography | Guidelines and Examples
- APA Website Citation (7th Edition) Guide | Format & Examples
- APA Citation Examples: The Bible, TED Talk, PPT & More
- APA Header Format: 5 Steps & Running Head Examples
- APA Title Page Format Simplified | Examples + Free Template
- How to Write an Abstract in MLA Format: Tips & Examples
- 10 Best Free Plagiarism Checkers | Accurate & Reliable Tools
- 5 Reasons to Cite Your Sources Properly | Avoid Plagiarism!
- Dissertation Writing Guide
- Writing a Dissertation Proposal
- The Acknowledgments Section of a Dissertation
- The Table of Contents Page of a Dissertation
- The Introduction Chapter of a Dissertation
- The Literature Review of a Dissertation
- The Only Dissertation Toolkit You’ll Ever Need!
- 5 Thesis Writing Tips for Master Procrastinators
- A Beginner’s Guide to How to Write a Dissertation in 2024
- The 5 Things to Look for in a Dissertation Editing Service
- Top 10 Dissertation Editing & Proofreading Services
- Why is it important to add references to your thesis?
- Thesis Editing | Definition, Scope & Standard Rates
- Expert Formatting Tips on MS Word for Dissertations
- A 7-Step Guide on How to Choose a Dissertation Topic
- 350 Best Dissertation Topic Ideas for All Streams in 2024
- A Guide on How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- Dissertation Defense: What to Expect and How to Prepare
- Creating a Dissertation Title Page (Examples & Templates)
- Essay Writing Guide
- Essential Research Tips for Essay Writing
- What Is a Mind Map? Free Mind Map Templates & Examples
- How to Write an Essay Outline: Free Template & Examples
- How to Write an Essay Header: MLA and APA Essay Headers
- What Is an Essay? A Comprehensive Guide to Structure and Types
How to Write an Essay: 8 Simple Steps with Examples
- The Four Main Types of Essay | Quick Summary with Examples
- Expository Essay: Structure, Tips, and Examples
- Narrative Essays: Structure, Tips, and Examples
- How to Write an Argumentative Essay (Examples Included)
- How to Write a Descriptive Essay | Examples and Structure
- How to Write an Essay Introduction | 4 Examples & Steps
- How to Write a Conclusion for an Essay (Examples Included!)
- How to Write an Impactful Personal Statement (Examples Included)
- Literary Analysis Essay: 5 Steps to a Perfect Assignment
- How to Write a Compare and Contrast Essay: Tips & Examples
- 100 Best College Essay Topics & How to Pick the Perfect One!
- College Essay Format: Tips, Examples, and Free Template
- Structure of an Essay: 5 Tips to Write an Outstanding Essay
- 10 Best AI Essay Outline Generators of 2024
- The Best Essay Graders of 2024 That You Can Use for Free!
- Top 10 Free Essay Writing Tools for Students in 2024
- Top 10 Best AI Essay Writing Tools in 2024
- Top 10 Essay Editing Services of 2024
Still have questions? Leave a comment
Add Comment
Checklist: Dissertation Proposal
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!
Examples: Edited Papers
Need editing and proofreading services.
- Tags: Academic Writing , Essay , Essay Writing
Knowing how to write an essay can help you out significantly in both, your academic and professional life. An essay is a highly versatile nonfiction piece of writing that not only tests your knowledge of a topic but also your literary and argumentative skills.
Each essay requires the same basic process of planning, writing, and editing. Naturally, we’ve used these stages to group our steps on how to write an essay. So w ithout further ado, let’s get into it! Here are the eight steps to write an essay:
Stage 1: Planning
1. Pick an appropriate research topic
In certain cases, your teacher or professor may assign you a topic. However, in many cases, students have the freedom to select a topic of their choice. Make sure you choose a topic that you’re well versed in and have significant knowledge of.
Having prior knowledge of the topic will help you determine the subsequent steps to write an essay. It will also make your research process considerably easier.
2. Form an appropriate thesis statement
A thesis statement is the central idea or premise your essay is based on. It is usually a sentence or two long and is included in the introduction of the essay. The scope of your thesis statement depends on the type of your essay and its length.
For instance, the scope of the thesis statement for a 500–1000 word school essay will be narrower than a 1000–5000 word college essay. A rule of thumb is that your essay topic should be broad enough to gather enough information, but narrow enough to address specific points and not be vague. Here’s an example:
The invention of the airplane by the Wright Brothers in 1903 revolutionized transportation and paved the way for modern aviation. It represents a monumental achievement in human history that forever changed the course of human civilization.
3. Create an essay outline
Creating a well-organized essay outline not only gives structure and flow to your essay but also makes it more impactful and easy to understand. The idea is to collect the main points of information that support or elaborate on your thesis statement. You can also include references or examples under these main points.
For example, if your thesis statement revolves around the invention of the airplane, your main points will include travel before the invention of the airplane, how it was invented, and its effects on modern-day travel. Take a look:
The Wright Brothers’ invention had a massive impact on modern-day travel. The subsequent growth of the aviation industry led to increased accessibility of air travel to the general public.
Stage 2: Writing
4. Write a comprehensive introduction
After creating the basic outline, it is important to know how to write an essay. Begin your essay by introducing your voice and point of view to the reader. An introduction is usually a paragraph or two long and consists of three main parts:
- Background information
- Thesis statement
Let’s better understand this with the help of an example:
The Wright Brothers’ invention of the airplane in 1903 revolutionized the way humans travel and explore the world. Prior to this invention, transportation relied on trains, boats, and cars, which limited the distance and speed of travel. However, the airplane made air travel a reality, allowing people to reach far-off destinations in mere hours. This breakthrough paved the way for modern-day air travel, transforming the world into a smaller, more connected place. In this essay, we will explore the impact of the Wright Brothers’ invention on modern-day travel, including the growth of the aviation industry, increased accessibility of air travel to the general public, and the economic and cultural benefits of air travel.
Let’s understand how to construct each of these sections in more detail.
A. Construct an attractive hook
The opening sentence of an essay, also known as the hook, should include a powerful or startling statement that captures the reader’s attention. Depending on the type of your essay, it can be an interesting fact, a surprising statistic, or an engaging anecdote.
B. Provide relevant background information
While writing the introduction, it’s important to provide context or background information before including the thesis statement. The background information may include the time before a groundbreaking invention, the pros and cons of a significant discovery, or the short- and long-term effects of an event.
C. Edit the thesis statement
If you’ve constructed your thesis statement during the outlining stage, it’s time to edit it based on the background information you’ve provided. Observe the slight changes we’ve made to the scope of the thesis statement in the example above. This accommodates the bits of information we’ve provided in the background history.
5. Form relevant body paragraphs
Body paragraphs play a crucial role in supporting and expanding the central argument presented in the thesis statement. The number of body paragraphs depends on the type of essay as well as the scope of the thesis statement.
Most school-level essays contain three body paragraphs while college-level essays can vary in length depending on the assignment.
A well-crafted body paragraph consists of the following parts:
- A topic sentence
- Supporting information
- An analysis of the information
- A smooth transition to the next paragraph
Let’s understand this with the help of an example.
The Wright Brothers’ invention of the airplane revolutionized air travel. They achieved the first-ever successful powered flight with the Wright Flyer in 1903, after years of conducting experiments and studying flight principles. Despite their first flight lasting only 12 seconds, it was a significant milestone that paved the way for modern aviation. The Wright Brothers’ success can be attributed to their systematic approach to problem-solving, which included numerous experiments with gliders, the development of a wind tunnel to test their designs, and meticulous analysis and recording of their results. Their dedication and ingenuity forever changed the way we travel, making modern aviation possible.
Here’s a detailed overview of how to construct each of these sections.
A. Construct appropriate topic sentences
A topic sentence is the title of the body paragraph that elaborates on the thesis statement. It is the main idea on which the body paragraph is developed. Ensure that each topic sentence is relevant to the thesis statement and makes the essay flow seamlessly.
The order of topic sentences is key in creating an impactful essay. This order varies depending on the type of essay you choose to write. These sentences may be arranged chronologically, in the order of importance, or in a cause-and-effect format.
B. Provide supporting information
It is necessary to provide relevant supporting information and evidence to validate your topic statement. This may include examples, relevant statistics, history, or even personal anecdotes.
You should also remember to cite your sources wherever you use them to substantiate your arguments. Always give researchers and authors credit for their work!
C. Analyze the supporting information
After presenting the appropriate evidence, the next step is to conduct an in-depth analysis. Establish connections and provide additional details to strengthen the link between your topic sentence and the supporting information.
Depending on the type of essay, this step may also involve sharing your subjective opinions and key takeaways.
D. Create a smooth transition
In case you plan to create multiple body paragraphs, it is crucial to create a seamless transition between them. Transitional statements not only make the essay less jarring to read but also guide the reader in the right direction.
However, these statements need not be too lengthy and complicated. Use words such as “however”, “in addition to”, and “therefore” to convey transitions.
6. Construct an impactful conclusion
An impactful conclusion creates a lasting impression on the mind of the reader. Although it varies in length depending on the specific essay, the conclusion is typically a paragraph long.
It consists of
- A restated thesis statement
- Summary of the main points
- The broader implications of the thesis statement
Here’s an example of a well-structured conclusion:
The Wright Brothers’ invention of the airplane forever changed history by paving the way for modern aviation and countless aerospace advancements. Their persistence, innovation, and dedication to problem-solving led to the first successful powered flight in 1903, sparking a revolution in transportation that transformed the world. Today, air travel remains an integral part of our globalized society, highlighting the undeniable impact of the Wright Brothers’ contribution to human civilization.
Let’s take a closer look at how to construct each of these sections.
A. Restate the thesis statement
Your conclusion should call back to your original argument or thesis statement.
However, this does not mean repeating the thesis statement as is. The essence of your argument should remain the same, but it should also be modified and evolved as per the information presented in your essay.
B. Summarize important points
A powerful conclusion not only lingers in the reader’s mind but also provokes thought. You can create a strong impression on the reader by highlighting the most impactful points of your essay.
C. State the greater implications
End your essay with the most powerful and impactful part: the larger perspective. This can include a question you’d like to leave the reader with, the broader implications and impact of your thesis statement, or the long-term, lingering effects of your experience.
Make sure to include no new evidence or arguments, or to undermine your findings in any way.
Stage 3: Editing
7. Review your essay
Knowing how to write an essay is just one part of essay writing. Properly reviewing and editing your essay is just as important. Make sure to spend enough time going over your essay and adding any bits of information that you’ve missed.
This is also a good time to make minor structural changes in your essay.
8. Thoroughly proofread your essay
After making the necessary structural changes, recheck your essay word by word. It is important to not only correct major grammatical and spelling errors but also minor errors regarding the phrasing or tone of voice.
You can either choose to do this by yourself, ask a friend for assistance, or hire an essay proofreading service to go over your writing. To construct a fool-proof, error-free essay, it is helpful to have a trained pair of eyes go over it. Professional proofreaders can spot errors that are not visible to most people and set the right tone for your essay.
Now that you know the basics of how to write an essay, it’s time to learn about the specifics. Feel free to dig into the articles below and keep reading!
- What Is an Essay? Structure, Parts, and Types
- How to Write an Essay Header in 4 Steps
- How to Write an Essay Outline
- 8 Types of Essays | Quick Summary with Examples
- What is an Expository Essay?
- How to Start an Essay
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the steps to write an essay, what is the best essay writing style, how do i start an essay introduction, what are the tips for effective essay writing, what makes a good essay.
Found this article helpful?

2 comments on “ How to Write an Essay: 8 Simple Steps with Examples ”
This is really help ful
Great insights on essay writing! In our time, artificial intelligence can significantly ease the writing process.
Leave a Comment: Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Your vs. You’re: Learn the Differences with Easy Examples
Your organization needs a technical editor: here’s why, your guide to the best ebook readers in 2024, writing for the web: 7 expert tips for web content writing.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Get carefully curated resources about writing, editing, and publishing in the comfort of your inbox.
How to Copyright Your Book?
If you’ve thought about copyrighting your book, you’re on the right path.
© 2024 All rights reserved
- Terms of service
- Privacy policy
- Self Publishing Guide
- Pre-Publishing Steps
- Fiction Writing Tips
- Traditional Publishing
- Academic Writing and Publishing
- Partner with us
- Annual report
- Website content
- Marketing material
- Job Applicant
- Cover letter
- Resource Center
- Case studies
How to Write the Perfect Essay
06 Feb, 2024 | Blog Articles , English Language Articles , Get the Edge , Humanities Articles , Writing Articles

You can keep adding to this plan, crossing bits out and linking the different bubbles when you spot connections between them. Even though you won’t have time to make a detailed plan under exam conditions, it can be helpful to draft a brief one, including a few key words, so that you don’t panic and go off topic when writing your essay.
If you don’t like the mind map format, there are plenty of others to choose from: you could make a table, a flowchart, or simply a list of bullet points.
Discover More
Thanks for signing up, step 2: have a clear structure.
Think about this while you’re planning: your essay is like an argument or a speech. It needs to have a logical structure, with all your points coming together to answer the question.
Start with the basics! It’s best to choose a few major points which will become your main paragraphs. Three main paragraphs is a good number for an exam essay, since you’ll be under time pressure.
If you agree with the question overall, it can be helpful to organise your points in the following pattern:
- YES (agreement with the question)
- AND (another YES point)
- BUT (disagreement or complication)
If you disagree with the question overall, try:
- AND (another BUT point)
For example, you could structure the Of Mice and Men sample question, “To what extent is Curley’s wife portrayed as a victim in Of Mice and Men ?”, as follows:
- YES (descriptions of her appearance)
- AND (other people’s attitudes towards her)
- BUT (her position as the only woman on the ranch gives her power as she uses her femininity to her advantage)
If you wanted to write a longer essay, you could include additional paragraphs under the YES/AND categories, perhaps discussing the ways in which Curley’s wife reveals her vulnerability and insecurities, and shares her dreams with the other characters. Alternatively, you could also lengthen your essay by including another BUT paragraph about her cruel and manipulative streak.
Of course, this is not necessarily the only right way to answer this essay question – as long as you back up your points with evidence from the text, you can take any standpoint that makes sense.

Step 3: Back up your points with well-analysed quotations
You wouldn’t write a scientific report without including evidence to support your findings, so why should it be any different with an essay? Even though you aren’t strictly required to substantiate every single point you make with a quotation, there’s no harm in trying.
A close reading of your quotations can enrich your appreciation of the question and will be sure to impress examiners. When selecting the best quotations to use in your essay, keep an eye out for specific literary techniques. For example, you could highlight Curley’s wife’s use of a rhetorical question when she says, a”n’ what am I doin’? Standin’ here talking to a bunch of bindle stiffs.” This might look like:
The rhetorical question “an’ what am I doin’?” signifies that Curley’s wife is very insecure; she seems to be questioning her own life choices. Moreover, she does not expect anyone to respond to her question, highlighting her loneliness and isolation on the ranch.
Other literary techniques to look out for include:
- Tricolon – a group of three words or phrases placed close together for emphasis
- Tautology – using different words that mean the same thing: e.g. “frightening” and “terrifying”
- Parallelism – ABAB structure, often signifying movement from one concept to another
- Chiasmus – ABBA structure, drawing attention to a phrase
- Polysyndeton – many conjunctions in a sentence
- Asyndeton – lack of conjunctions, which can speed up the pace of a sentence
- Polyptoton – using the same word in different forms for emphasis: e.g. “done” and “doing”
- Alliteration – repetition of the same sound, including assonance (similar vowel sounds), plosive alliteration (“b”, “d” and “p” sounds) and sibilance (“s” sounds)
- Anaphora – repetition of words, often used to emphasise a particular point
Don’t worry if you can’t locate all of these literary devices in the work you’re analysing. You can also discuss more obvious techniques, like metaphor, simile and onomatopoeia. It’s not a problem if you can’t remember all the long names; it’s far more important to be able to confidently explain the effects of each technique and highlight its relevance to the question.

Step 4: Be creative and original throughout
Anyone can write an essay using the tips above, but the thing that really makes it “perfect” is your own unique take on the topic. If you’ve noticed something intriguing or unusual in your reading, point it out – if you find it interesting, chances are the examiner will too!
Creative writing and essay writing are more closely linked than you might imagine. Keep the idea that you’re writing a speech or argument in mind, and you’re guaranteed to grab your reader’s attention.
It’s important to set out your line of argument in your introduction, introducing your main points and the general direction your essay will take, but don’t forget to keep something back for the conclusion, too. Yes, you need to summarise your main points, but if you’re just repeating the things you said in your introduction, the body of the essay is rendered pointless.
Think of your conclusion as the climax of your speech, the bit everything else has been leading up to, rather than the boring plenary at the end of the interesting stuff.
To return to Of Mice and Men once more, here’s an example of the ideal difference between an introduction and a conclusion:
Introduction
In John Steinbeck’s Of Mice and Men , Curley’s wife is portrayed as an ambiguous character. She could be viewed either as a cruel, seductive temptress or a lonely woman who is a victim of her society’s attitudes. Though she does seem to wield a form of sexual power, it is clear that Curley’s wife is largely a victim. This interpretation is supported by Steinbeck’s description of her appearance, other people’s attitudes, her dreams, and her evident loneliness and insecurity.
Overall, it is clear that Curley’s wife is a victim and is portrayed as such throughout the novel in the descriptions of her appearance, her dreams, other people’s judgemental attitudes, and her loneliness and insecurities. However, a character who was a victim and nothing else would be one-dimensional and Curley’s wife is not. Although she suffers in many ways, she is shown to assert herself through the manipulation of her femininity – a small rebellion against the victimisation she experiences.
Both refer back consistently to the question and summarise the essay’s main points. However, the conclusion adds something new which has been established in the main body of the essay and complicates the simple summary which is found in the introduction.

Hannah is an undergraduate English student at Somerville College, University of Oxford, and has a particular interest in postcolonial literature and the Gothic. She thinks literature is a crucial way of developing empathy and learning about the wider world. When she isn’t writing about 17th-century court masques, she enjoys acting, travelling and creative writing.
Recommended articles
Best Universities to Study Medicine in the World
A degree in Medicine spans many years, so it’s important to make a good choice when committing yourself to your studies. This guide is designed to help you figure out where you'd like to study and practise medicine. For those interested in getting a head start, the...

What Is A Year Abroad?
One of the great opportunities offered to UK university students is taking a year abroad. But what does this involve? Who can do it? What are some of the pros and cons? In our year abroad guide, we’ll explain some of the things to bear in mind when considering this...

The Ultimate Guide To Summer Internships
Are you eager to make the most of your summer break and jumpstart your career? There are so many productive things students can do in the summer or with their school holidays, and an internship is one of the most valuable! A summer internship could be the perfect...
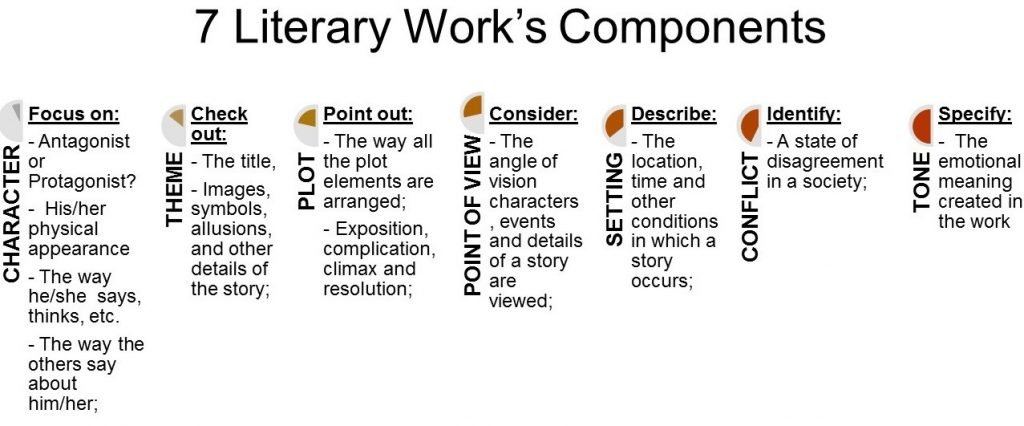
How to Write a Literary Essay Step by Step
Let’s start with a quick literary essay definition. Literary essay writing is a type of formal writing that students may encounter at different levels of education – school, college, and university. It is possible to face this task even if your main area of expertise isn’t Literary Studies at all. Adore literature? Look at what careers in Literature are available to you today. But still, let’s get back to the point – essay writing. Effectively-written essays have become an inextricable component of the academic curriculum. Essays are an important part of school assignments, standardized tests, and a form and requirement for a school application. But how does it belong to literature? If you want to know more about literary essay writing, literary essay structure, or how to start a literary essay, this article is for you. You’ll know what a literary essay is and what specifics it has. Proceed with reading it to the end to find out what tips it is worth following! And write a good literary essay!
What is a Good Literary Essay?
In general, a literary essay is defined as a piece of writing that offers the author’s point of view based on his/her strong arguments retrieved from a literary work. In other words, it is an academic assignment given to a student to measure a work of literature from various perspectives – its structure, form, and content, plot and subplot, theme, characters, images, and so on. The main essence of writing a literary essay is to analyze a specific literary piece of work. Know what belongs to it? Indeed, if you think that literary works are limited to works of literature only, you are wrong. Besides Stephen King and Joanne Rowling, you can evaluate all works expressed in print or writing. As a result, all dramatic, musical, and poetic works can be evaluated by you in a literary essay.
Let’s take an example: you’re analyzing a musical drama, Lerner and Loewe’s My Fair Lady. You know that it is based on play Pygmalion by George Bernard Shaw. It’s a highly popular book with many reviews all over the Internet. If you read those reviews, you’ll notice they are all about the way it is perceived by readers. Nobody rejects the fact the originality of writing is considered a matter of priority. You’re allowed to share your own impressions in a literary analysis based both on a book and a play. Remember your literary essay should be written in a structured format with a detailed analysis of all components every literary work has:
How Does a Literary Essay Introduction Look?
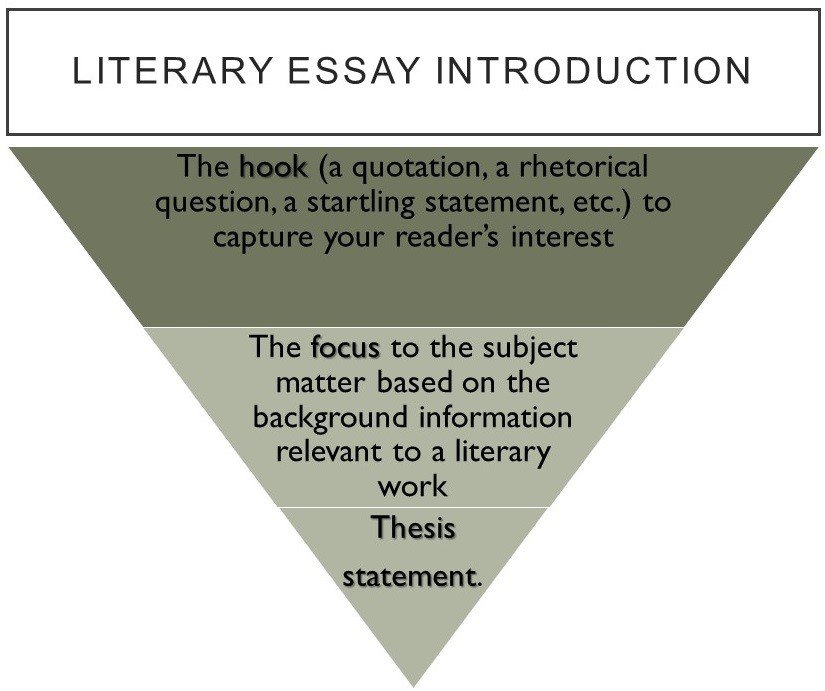
What Does a Literary Essay Body Paragraph Contain?
After you introduce the main idea that is related to your literary essay, it is logical to develop it from various angles of a literary analysis regarding the question words – what, who, how, and why. The part dealing with developing the central idea of a literary analysis essay is called the body. The term regularly used for developing the central idea of a literary analysis essay is the body with at least 3 physical paragraphs.
Each of the paragraphs you’re writing must have:
- Topic sentence , i.e., the first sentence stating the subpoint of the thesis statement which you have mentioned. So you need to tie all the details of the paragraph together tight so that it will be logically complete;
- Textual evidence , i.e., the supporting detail relevant to the main point and subpoint you state in the topic sentence. It can be either a paraphrase of content or a direct quotation from a book. The latter plays a greater role in assessing your ability to analyze a literary work. Just remember it!
- Closing sentence , i.e., the last sentence of a paragraph to have it logically completed. It’s up to you what way of closing to choose, but don’t forget to use transitions . The simplest way is to count your main points with the help of “Firstly”, “Secondly”, “Thirdly”, and so on. But you can use many other transitional expressions in your literary essay.
How to Draw a Conclusion for a Literary Essay?
Eventually, your essay is coming to an end when all the final words are being written. What are these final words in your literary essay? Firstly, you remind your readers of the essay question. Secondly, you provide the main essay argument(s) briefly. Thirdly, make a relevant comment about the literary work you are analyzing – it can be a comment on liking or disliking it or the work’s value or disvalue. Indeed, there are many ways to make a conclusion – ask any qualified literary essay writer to write a paper for you. Just look them through. Going to switch off your computer or other electronic devices you work on immediately after putting in a full point? Stop, stop, stop! Reread a written essay to make sure that everything corresponds to the requirements given to you. Make all the necessary revisions before submitting any of your papers. Remember this once and for all!
3 Literary Essay Writing Challenges to Overcome Beforehand
At any stage of writing, a student may encounter some challenges. So writing a literary essay is no exception. Let’s look at 3 possible issues you may experience with the most effective ways of dealing with each of them:
#1 Reading and Analyzing Processes
Without any doubt, you realize that before writing a well-analyzed literary essay, you need to read a piece of literature. Agree that reading and analyzing is better done with a short story, for example, The Gift of the Magi by O. Henry, than with a novel, War and Peace by Lev Tolstoy, for example? So, find enough time to accomplish these stages effectively. It’s up to you what way of reading to choose, but remember, how to read a book impacts your final literary essay writing. It is found that you are more likely to remember content if you read it out loud. Besides it, you can try out:
- Color marking of the main ideas in the text;
- Using sticky notes with the main points of content;
- Charting character development, etc.
#2 Gathering All the Details Essential for the Literary Analysis
When you are asked to do a literary analysis in essays, you should think about how and why a poem, short story, novel, or play was written. Therefore, you should collect all the necessary information about a specific literary work. Pay attention to the arrangement of ideas and/or incidents that make up a story, setting, characters, figurative language, imagery, symbolism, etc. How to gather all that? While reading a literary piece of work, it is better to have a pen or several highlighters at hand for:
- Underlining or copy-pasting direct quotations from a book or any other literary work;
- Marking each point with the help of corresponding colors on paper;
- Drawing graphic organizers to show the content illustratively. For example, this graphic organizer shows the main steps in writing a literary essay and its results:

#3 Writing a Literary Essay Analysis Itself
It would seem as if every obstacle in the path of dealing with a literary essay was overcome. But it isn’t worth forgetting that after reading a book and gathering all the essential information to do an in-depth analysis, you have to think of words that could make your essay informative, easy to follow, and remember. Moreover, all the information in your literary essay must be well-structured and properly formatted. Here, besides the question, “How to write my literary essay?” or “Maybe someone else can write my literary essay for me?” the question becomes, in turn, “How to structure and format my literary essay?” Know what comes to help? Before you rush to buy a literary essay, take into account what is below:
- Outlining or mapping all the main ideas of an essay;
- Following the ‘Introduction + Body + Conclusion’ structure;
- The guide on how to write a literary analysis essay , the guide on writing essays in the English Language and Literature, or the guide to an academic writing style ;
- Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , 6th edition;
- MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers , 7th edition;
- The Chicago Manual of Style , 16th edition;
- The Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations , 8th edition.
- Some literary essays are written as good examples of formatting in APA, MLA, Harvard, Turabian, or Chicago.
We’ve just mentioned three main challenges you may face after being assigned a literary essay. However, there are many other obstacles appearing in your way no matter what task is in front of you – procrastination, the lack of time, poor time management, and writing skills. The list goes on, and so on indefinitely… Stop putting off the moment when you start getting inspired by the art of your own writing!
What is a literary essay?
A literary essay is a piece of academic work that is focused on exploring and analyzing a poem, a novel, a play, or any other work of literature. In addition to summarizing the plot, the literary essay examines the symbols, characters, themes, and various techniques that the author employed to convey their message.
How to start a literary essay?
To start a literary essay, start with a hooking introduction introducing the literary work about to be discussed. Begin with a thought-provoking sentence, captivating stats, or any relevant quote. It is recommended to include some background info about the author of the literary work and write a solid and concise thesis statement. The latter should contain the core argument you will make in a project. Your thesis statement must be focused, clear, and debatable.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
What our customers say
Our website uses secure cookies. More details
Get professional help from best writers right from your phone

How to Write a 1500 Word Essay & How Many Pages Is It? + Examples
Writing a 1500 word essay can seem daunting at first, but with the right approach, it’s a manageable and rewarding task.
This comprehensive guide on How to Write a 1500 Word Essay will walk you through the process of crafting a well-structured 1500 word essay, provide insights on its typical length in pages, and offer examples to help you succeed.

What You'll Learn
Understanding the 1500 Word Essay
Before diving into the writing process, it’s essential to understand what a 1500 word essay entails. A 1500 word essay is a common assignment in academic settings, striking a balance between brevity and depth. It allows you to explore a topic in detail without the expansiveness of a longer research paper.
When tackling a 1500 word essay, keep in mind that it’s not just about reaching the word count. The quality of your content, the strength of your arguments, and the clarity of your writing are equally important. A well-written 1500 word essay demonstrates your ability to research, analyze, and articulate your thoughts concisely.
Planning Your 1500 Word Essay
The key to writing a successful 1500 word essay lies in careful planning. Here’s a step-by-step approach to get you started:
- Understand the prompt: Carefully read and analyze the essay question or prompt.
- Research: Gather relevant information from credible sources.
- Outline: Create a detailed outline to structure your thoughts.
- Allocate words: Divide your word count among different sections.
Remember, a 1500 word essay typically consists of an introduction, 3-4 body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Allocate roughly 10% of your words to the introduction and conclusion each, leaving about 80% for the body.
Writing Your 1500 Word Essay
Now that you’ve planned your essay, it’s time to start writing. Here’s how to approach each section of your 1500 word essay:
Introduction (150-200 words)
Your introduction should:
- Hook the reader with an interesting opening
- Provide background information on the topic
- Present your thesis statement
Body Paragraphs (1000-1100 words)
Each body paragraph should:
- Start with a clear topic sentence
- Present evidence to support your arguments
- Analyze the evidence and link it back to your thesis
- Transition smoothly to the next paragraph
Conclusion (150-200 words)
Your conclusion should:
- Summarize your main points
- Restate your thesis in light of the evidence presented
- Provide final thoughts or a call to action
Revising and Editing Your 1500 Word Essay
After completing your first draft, take time to revise and edit your 1500 word essay. Here are some tips:
- Check for clarity and coherence
- Ensure your arguments flow logically
- Eliminate unnecessary words or repetitive phrases
- Verify that you’ve met the 1500 word count requirement
- Proofread for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors
Examples of 1500 Word Essays
To help you visualize what a 1500 word essay looks like, here are a few example topics with brief outlines:
- “The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health”
- Introduction: Define social media and its prevalence
- Body: Discuss positive impacts, negative impacts, and research findings
- Conclusion: Summarize findings and suggest healthy social media habits
- “Climate Change: Causes, Effects, and Solutions”
- Introduction: Define climate change and its importance
- Body: Explore major causes, discuss current and future effects, propose solutions
- Conclusion: Emphasize urgency and call for action
- “The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence”
- Introduction: Define AI and its significance
- Body: Trace historical development, discuss current applications, explore future possibilities
- Conclusion: Reflect on the implications of AI advancement
Remember, these are just outlines. A full 1500 word essay would delve much deeper into each topic, providing detailed analysis and supporting evidence.
How Many Pages Is a 1500 Word Essay?
The number of pages a 1500 word essay occupies depends on several factors, including font size, line spacing, and margins. However, as a general guideline:
- With single spacing, a 1500 word essay is typically about 3 pages.
- With 1.5 spacing, it’s usually around 4-5 pages.
- With double spacing, it’s approximately 6 pages.
Keep in mind that these are estimates. The actual page count may vary slightly depending on the specific formatting requirements of your assignment.
Tips for Success in Writing a 1500 Word Essay
- Start early: Give yourself plenty of time to research, write, and revise.
- Break it down: Tackle your 1500 word essay in smaller, manageable chunks.
- Stay focused: Keep your thesis in mind throughout the writing process.
- Use transitions: Ensure smooth flow between paragraphs and ideas.
- Cite sources: Properly attribute any information from external sources.
- Read aloud: This can help you catch errors and improve flow.
- Seek feedback: Have someone else read your essay for a fresh perspective.
Related Article; How to Write a 1500 Word Essay: Structure, Length, & Examples
How many pages is a 1500 word essay? A 1500 word essay is typically 3 pages single-spaced, 4-5 pages with 1.5 spacing, or 6 pages double-spaced.
How long is a 1500 word essay example? A 1500 word essay is about 5-6 pages double-spaced or 3 pages single-spaced, depending on formatting.
How to structure a 1500 word essay? Structure a 1500 word essay with an introduction (150-200 words), 3-4 body paragraphs (1000-1100 words total), and a conclusion (150-200 words).
How long does it take to type a 1500 word paper? Typing time varies, but it typically takes 3-5 hours to research, write, and edit a 1500 word essay.
Start by filling this short order form order.studyinghq.com
And then follow the progressive flow.
Having an issue, chat with us here
Cathy, CS.
New Concept ? Let a subject expert write your paper for You
Post navigation
Previous post.
📕 Studying HQ
Typically replies within minutes
Hey! 👋 Need help with an assignment?
🟢 Online | Privacy policy
WhatsApp us

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
My Favourite Author Essay: 100, 150, 250, and 300 Words

- Updated on
- Oct 21, 2024

My favourite author essay: Books are magical, taking us to places we’ve never been and introducing us to characters we’ll never forget. Behind every great book is an author who breathes life into the pages. Everyone has that one writer whose works inspire, entertain, or leave a lasting impact. In this essay, we’ll explore various samples of “My Favourite Author” in 100, 150, 250, and 300 words. Each sample shares the love and admiration readers hold for their chosen authors, from classic literary figures to contemporary storytellers.
My Favourite Author Essay 100 Words
My favourite author is J.K. Rowling, the brilliant mind behind the Harry Potter series. Her magical world of wizards, friendship, and bravery has captured my heart since I first read the books. Rowling’s storytelling transports readers into a universe full of imagination, where characters grow, learn, and face challenges with courage. Her writing teaches valuable life lessons about love, loyalty, and perseverance. Through her books, she has inspired millions of readers to believe in themselves and the magic within. For these reasons, J.K. Rowling remains my all-time favourite author.
My Favourite Author Essay 150 Words
My favourite author is Enid Blyton, known for her captivating children’s books, including the Famous Five and Secret Seven series. Her stories are filled with adventure, friendship, and a sense of wonder that has always fascinated me. As a child, I would lose myself in the exciting worlds she created, imagining myself as part of the daring group of friends who solve mysteries and explore hidden treasures.
What I love most about Blyton’s writing is her ability to make ordinary life feel extraordinary. Her characters are relatable, brave, and full of curiosity, encouraging readers to embrace adventure and problem-solving. The moral lessons of teamwork, honesty, and courage in her books still resonate with me today. Enid Blyton’s stories have not only entertained but also shaped my imagination and love for reading, making her my favourite author of all time.
My Favourite Author Essay 250 Words
My favourite author is Ruskin Bond, a master storyteller known for his heartwarming tales set in the hills of India. His simple yet captivating style of writing makes everyday life seem magical. I particularly love his stories about nature, childhood, and the small joys of life. Whether it’s a quiet afternoon in the mountains or an adventurous trek through the forest, Bond’s descriptions make me feel like I’m right there in the scene.
What makes Ruskin Bond my favourite author is his deep understanding of human emotions and his ability to connect with readers of all ages. His stories are often about ordinary people, but they teach powerful lessons about kindness, resilience, and love. Books like The Room on the Roof and The Blue Umbrella have stayed with me long after I finished reading them, as they beautifully capture the innocence of childhood and the beauty of life’s simple pleasures.
Bond’s love for nature and his gentle way of portraying relationships make his books truly special. His writing has sparked my imagination and made me appreciate the small details around me, whether it’s the rustling of leaves or the sound of rain. He has inspired me to look for beauty in everyday life. For his unique storytelling and the comfort his books bring, Ruskin Bond will always be my favourite author. His stories have left a lasting impact on me and my love for reading.
My Favourite Author Essay Rabindranath Tagore 300 Words
Rabindranath Tagore, the great Indian poet, philosopher, and writer, is my favourite author. His works are a perfect blend of beauty, emotion, and profound thought. Tagore’s contributions to literature, particularly his poems, songs, and short stories, have left an indelible mark on me and millions of readers worldwide. He was the first non-European to win the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1913, an achievement that speaks volumes about his literary genius.
What I love most about Tagore is the depth of his writing. His poetry, especially in Gitanjali (Song Offerings), touches the soul with its spiritual themes and exploration of life, nature, and human emotions. The simplicity and clarity of his verses allow readers to connect deeply with the profound messages he conveys, often about love, freedom, and the divine presence in everyday life. His poems invite us to reflect on our existence and the beauty of the world around us.
Apart from poetry, Tagore’s short stories, like “Kabuliwala” and “The Postmaster,” are heartwarming and full of life lessons. His characters are drawn from everyday life, yet they embody universal truths about human relationships, struggles, and aspirations. Through his writing, Tagore has championed themes of education, social justice, and unity, which remain relevant even today.
Tagore’s ability to weave emotion, philosophy, and social issues into his work makes him an extraordinary author. His legacy as a writer and thinker continues to inspire readers, artists, and scholars around the world. For his timeless wisdom, artistic mastery, and the way his words resonate with both heart and mind, Rabindranath Tagore is my favourite author. His works have enriched my understanding of life and continue to be a source of inspiration.
My Favourite Author Essay J. K. Rowling 300 Words
J.K. Rowling, the mastermind behind the Harry Potter series, is my favourite author. Her ability to create a magical world filled with wizards, mythical creatures, and unforgettable characters has enchanted millions of readers around the globe, including me. Rowling’s writing takes us on a journey into the enchanting world of Hogwarts, where friendship, bravery, and love triumph over darkness.
One of the reasons I admire Rowling is her incredible imagination. The world she created is rich with detail, from the enchanted spells to the complex characters like Harry, Hermione, and Ron. Her storytelling weaves magic with real-life emotions and struggles, allowing readers to connect with the characters on a deep, personal level. Even though the Harry Potter series is a fantasy, it deals with universal themes like loyalty, self-discovery, courage, and the fight between good and evil, which makes the books both entertaining and meaningful.
What I love most about Rowling’s writing is the way she has inspired readers of all ages to embrace their imagination and believe in themselves. Her characters face adversity but overcome it with perseverance, friendship, and kindness. Rowling’s message of hope and resilience is a constant theme throughout her books, and it encourages readers to confront challenges with courage.
Beyond Harry Potter , Rowling’s own personal journey of overcoming hardships and achieving success is truly inspirational. She has shown that with determination and creativity, we can rise above our circumstances and achieve greatness. J.K. Rowling’s ability to blend magic, emotion, and life lessons into her stories has made her an unforgettable author and my personal favourite. Her books have not only ignited my imagination but also taught me valuable lessons that will stay with me forever.
To write about your favourite author, start by introducing who they are and why you admire them. Highlight key aspects of their work, such as their storytelling style, themes, or characters that have impacted you. Mention specific books or pieces of writing you love and explain how their writing has influenced your thoughts, emotions, or imagination. You can also include how the author’s life story or achievements inspire you. Keep your response personal and focused on what makes the author special to you.
To write like your favourite author, start by studying their writing style closely. Pay attention to how they develop characters, structure plots, and use language. Practice writing with similar themes or techniques, such as their approach to dialogue, pacing, or tone. Focus on incorporating their storytelling methods while still adding your unique voice. Reading their works often and experimenting with what inspires you will help you blend their influence with your own creativity.
The most favourite author varies depending on personal preferences, but globally, some of the most beloved authors include J.K. Rowling for the Harry Potter series, William Shakespeare for his timeless plays, and Agatha Christie for her mystery novels. These authors have influenced millions of readers and left a lasting legacy in literature.
Popular Essay Topics
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu.
Mohit Rajak
Mohit Rajak, a soul entwined with the rhythm of words, finds solace in crafting verses that dance between the lines of poetry. With a pen as his wand, he weaves intricate tales and musings, breathing life into the blank canvas of pages. Through the art of blogging, Mohit embraces the world, sharing his thoughts, emotions, and unique perspective with those who venture into the realm of his written expressions. Each word, a brushstroke painting the canvas of his literary journey.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2025
September 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
- International
- Education Jobs
- Schools directory
- Resources Education Jobs Schools directory News Search

GCSE English Language: Write a personal essay about a time when you felt misunderstood ~ Sample
Subject: English
Age range: 14-16
Resource type: Other
Last updated
21 October 2024
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

This sample answer provides a thoughtful and engaging personal essay on the theme of feeling misunderstood. It tells the story of a student’s experience with a passion for photography, exploring the emotional journey of being dismissed by peers and family. The essay delves into themes of individuality, self-expression and resilience, making it relatable and inspiring for teenage readers.
Language Techniques Highlighted The essay uses a variety of effective language techniques, including:
- Descriptive Language : Vivid imagery, particularly in describing the emotions and the environment, helps bring the reader into the narrative.
- Metaphor and Simile : The essay incorporates figurative language, such as comparing the experience to “standing on the fringes of understanding.”
- First-Person Narrative : The personal tone creates an intimate and engaging connection with the reader.
- Emotive Language : The author skillfully conveys feelings of rejection and eventual empowerment, making the emotional journey clear and impactful.
- Reflection : The reflective conclusion offers insight and personal growth, which adds depth to the narrative.
Why This Digital File is Essential for Exam Preparation This sample is an invaluable resource for GCSE English students. It demonstrates how to structure a personal essay, use language techniques effectively, and engage readers with personal experiences. Observing this example can help students understand how to approach similar tasks with clarity, emotion, and sophistication. This file serves as an ideal model for mastering personal writing, making it a must-have for exam preparation. It not only teaches essential writing skills but also boosts confidence in handling similar prompts.
Click the download button to have the full file at your fingertips!
CONTAINS: 10 PAGES
Thanks a million for visiting Sweet Success Supplies! May your endeavors be as sweet as our deals!
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips
Published on July 24, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
An argumentative essay expresses an extended argument for a particular thesis statement . The author takes a clearly defined stance on their subject and builds up an evidence-based case for it.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When do you write an argumentative essay, approaches to argumentative essays, introducing your argument, the body: developing your argument, concluding your argument, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about argumentative essays.
You might be assigned an argumentative essay as a writing exercise in high school or in a composition class. The prompt will often ask you to argue for one of two positions, and may include terms like “argue” or “argument.” It will frequently take the form of a question.
The prompt may also be more open-ended in terms of the possible arguments you could make.
Argumentative writing at college level
At university, the vast majority of essays or papers you write will involve some form of argumentation. For example, both rhetorical analysis and literary analysis essays involve making arguments about texts.
In this context, you won’t necessarily be told to write an argumentative essay—but making an evidence-based argument is an essential goal of most academic writing, and this should be your default approach unless you’re told otherwise.
Examples of argumentative essay prompts
At a university level, all the prompts below imply an argumentative essay as the appropriate response.
Your research should lead you to develop a specific position on the topic. The essay then argues for that position and aims to convince the reader by presenting your evidence, evaluation and analysis.
- Don’t just list all the effects you can think of.
- Do develop a focused argument about the overall effect and why it matters, backed up by evidence from sources.
- Don’t just provide a selection of data on the measures’ effectiveness.
- Do build up your own argument about which kinds of measures have been most or least effective, and why.
- Don’t just analyze a random selection of doppelgänger characters.
- Do form an argument about specific texts, comparing and contrasting how they express their thematic concerns through doppelgänger characters.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
An argumentative essay should be objective in its approach; your arguments should rely on logic and evidence, not on exaggeration or appeals to emotion.
There are many possible approaches to argumentative essays, but there are two common models that can help you start outlining your arguments: The Toulmin model and the Rogerian model.
Toulmin arguments
The Toulmin model consists of four steps, which may be repeated as many times as necessary for the argument:
- Make a claim
- Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim
- Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim)
- Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives
The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays. You don’t have to use these specific terms (grounds, warrants, rebuttals), but establishing a clear connection between your claims and the evidence supporting them is crucial in an argumentative essay.
Say you’re making an argument about the effectiveness of workplace anti-discrimination measures. You might:
- Claim that unconscious bias training does not have the desired results, and resources would be better spent on other approaches
- Cite data to support your claim
- Explain how the data indicates that the method is ineffective
- Anticipate objections to your claim based on other data, indicating whether these objections are valid, and if not, why not.
Rogerian arguments
The Rogerian model also consists of four steps you might repeat throughout your essay:
- Discuss what the opposing position gets right and why people might hold this position
- Highlight the problems with this position
- Present your own position , showing how it addresses these problems
- Suggest a possible compromise —what elements of your position would proponents of the opposing position benefit from adopting?
This model builds up a clear picture of both sides of an argument and seeks a compromise. It is particularly useful when people tend to disagree strongly on the issue discussed, allowing you to approach opposing arguments in good faith.
Say you want to argue that the internet has had a positive impact on education. You might:
- Acknowledge that students rely too much on websites like Wikipedia
- Argue that teachers view Wikipedia as more unreliable than it really is
- Suggest that Wikipedia’s system of citations can actually teach students about referencing
- Suggest critical engagement with Wikipedia as a possible assignment for teachers who are skeptical of its usefulness.
You don’t necessarily have to pick one of these models—you may even use elements of both in different parts of your essay—but it’s worth considering them if you struggle to structure your arguments.
Regardless of which approach you take, your essay should always be structured using an introduction , a body , and a conclusion .
Like other academic essays, an argumentative essay begins with an introduction . The introduction serves to capture the reader’s interest, provide background information, present your thesis statement , and (in longer essays) to summarize the structure of the body.
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how a typical introduction works.
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts is on the rise, and its role in learning is hotly debated. For many teachers who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its critical benefits for students and educators—as a uniquely comprehensive and accessible information source; a means of exposure to and engagement with different perspectives; and a highly flexible learning environment.
The body of an argumentative essay is where you develop your arguments in detail. Here you’ll present evidence, analysis, and reasoning to convince the reader that your thesis statement is true.
In the standard five-paragraph format for short essays, the body takes up three of your five paragraphs. In longer essays, it will be more paragraphs, and might be divided into sections with headings.
Each paragraph covers its own topic, introduced with a topic sentence . Each of these topics must contribute to your overall argument; don’t include irrelevant information.
This example paragraph takes a Rogerian approach: It first acknowledges the merits of the opposing position and then highlights problems with that position.
Hover over different parts of the example to see how a body paragraph is constructed.
A common frustration for teachers is students’ use of Wikipedia as a source in their writing. Its prevalence among students is not exaggerated; a survey found that the vast majority of the students surveyed used Wikipedia (Head & Eisenberg, 2010). An article in The Guardian stresses a common objection to its use: “a reliance on Wikipedia can discourage students from engaging with genuine academic writing” (Coomer, 2013). Teachers are clearly not mistaken in viewing Wikipedia usage as ubiquitous among their students; but the claim that it discourages engagement with academic sources requires further investigation. This point is treated as self-evident by many teachers, but Wikipedia itself explicitly encourages students to look into other sources. Its articles often provide references to academic publications and include warning notes where citations are missing; the site’s own guidelines for research make clear that it should be used as a starting point, emphasizing that users should always “read the references and check whether they really do support what the article says” (“Wikipedia:Researching with Wikipedia,” 2020). Indeed, for many students, Wikipedia is their first encounter with the concepts of citation and referencing. The use of Wikipedia therefore has a positive side that merits deeper consideration than it often receives.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

An argumentative essay ends with a conclusion that summarizes and reflects on the arguments made in the body.
No new arguments or evidence appear here, but in longer essays you may discuss the strengths and weaknesses of your argument and suggest topics for future research. In all conclusions, you should stress the relevance and importance of your argument.
Hover over the following example to see the typical elements of a conclusion.
The internet has had a major positive impact on the world of education; occasional pitfalls aside, its value is evident in numerous applications. The future of teaching lies in the possibilities the internet opens up for communication, research, and interactivity. As the popularity of distance learning shows, students value the flexibility and accessibility offered by digital education, and educators should fully embrace these advantages. The internet’s dangers, real and imaginary, have been documented exhaustively by skeptics, but the internet is here to stay; it is time to focus seriously on its potential for good.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
The majority of the essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Unless otherwise specified, you can assume that the goal of any essay you’re asked to write is argumentative: To convince the reader of your position using evidence and reasoning.
In composition classes you might be given assignments that specifically test your ability to write an argumentative essay. Look out for prompts including instructions like “argue,” “assess,” or “discuss” to see if this is the goal.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved October 21, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/argumentative-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, how to write an expository essay, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
4. Organize Your Ideas: Create an outline to organize your thoughts and ensure a logical flow of ideas in your essay. 5. Write Clearly and Concisely: Use clear, concise language and avoid unnecessary jargon or complex sentences. Be direct and to the point. 6. Revise and Edit: Always proofread your essay for grammar and spelling errors. Revise ...
Essay writing is a fundamental skill that every student needs to master. Whether you're in high school, college, or beyond, the ability to write a strong, coherent essay is essential for academic success. However, many students find the process of writing an essay daunting and overwhelming.
In that sense, college essays are a bizarre bait-and-switch—in high school, you're taught a few different ways to write (e.g., maybe some historical analysis, or how to analyze literature, or creative writing), and then to apply to college, you're asked to write something fairly different (or maybe completely different) from any of the ...
6 types of essays. Essay writing tips. How to write an essay. The basic steps for how to write an essay are: Generate ideas and pick a type of essay to write. Outline your essay paragraph by paragraph. Write a rough first draft without worrying about details like word choice or grammar. Edit your rough draft, and revise and fix the details.
Essay writing process. The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay.. For example, if you've been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you'll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay, on the ...
The second principle is that background information should appear towards the beginning of your essay. General background is presented in the introduction. If you have additional background to present, this information will usually come at the start of the body. The third principle is that everything in your essay should be relevant to the ...
For this reason, it's often a good idea to wait until later in the writing process before you write the introduction paragraph—it can even be the very last thing you write. When you've finished writing the essay body and conclusion , you should return to the introduction and check that it matches the content of the essay.
Sometimes your assignment will be open-ended ("write a paper about anything in the course that interests you"). But more often, the instructor will be asking you to do something specific that allows you to make sense of what you've been learning in the course. You may be asked to put new ideas in context, to analyze course texts, or to do
Finally, read your essay once more to ensure that it is polished and ready for submission. Wrapping up. By following these guidelines, you can approach essay writing with confidence. Remember to gather your materials and conduct thorough research, create a well-structured outline, and develop a strong argument supported by evidence.
There are three main stages to writing an essay: preparation, writing and revision. In just 4 minutes, this video will walk you through each stage of an acad...
In high school, you were probably taught to write five-paragraph essays. This is a solid essay structure to work with, but in college, you generally have more flexibility with assignment lengths and formats. Now, consider five the minimum—not the standard—number of paragraphs you should include in your essays. Essay structure examples
Intriguing ways to start an essay. There are many different ways to write an essay introduction. Each has its benefits and potential drawbacks, and each is best suited for certain kinds of essays.Although these essay introductions use different rhetorical devices and prime the reader in different ways, they all achieve the same goal: hooking the reader and enticing them to keep reading.
As well as some best practice tips, we have gathered our favourite advice from expert essay-writers and compiled the following 7-step guide to writing a good essay every time. 👍 #1 Make sure you understand the question #2 Complete background reading #3 Make a detailed plan #4 Write your opening sentences #5 Flesh out your essay in a rough draft
In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills. Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative: you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence, analysis and interpretation.
Create an essay outline. Creating a well-organized essay outline not only gives structure and flow to your essay but also makes it more impactful and easy to understand. The idea is to collect the main points of information that support or elaborate on your thesis statement. You can also include references or examples under these main points.
If you wanted to write a longer essay, you could include additional paragraphs under the YES/AND categories, perhaps discussing the ways in which Curley's wife reveals her vulnerability and insecurities, and shares her dreams with the other characters. Alternatively, you could also lengthen your essay by including another BUT paragraph about ...
One way to write an argumentative essay is to do so in 6 paragraphs: 1. Introduction, including thesis statement. 2. First supporting argument, including evidence. 3. Second supporting argument, including evidence. 4. Third supporting argument, including evidence. 5. Counterargument or opposing viewpoints. 6. Conclusion, reinforces your thesis
The guide on how to write a literary analysis essay, the guide on writing essays in the English Language and Literature, or the guide to an academic writing style; The citation guidelines according to the last editions of the style manuals:
Create an essay tracker sheet. If you're applying to multiple schools, you will have to juggle writing several essays for each one. We recommend using an essay tracker spreadsheet to help you visualize and organize the following: Deadlines and number of essays needed; Prompt overlap, allowing you to write one essay for similar prompts
Writing a 1500 word essay can seem daunting at first, but with the right approach, it's a manageable and rewarding task. This comprehensive guide on How to Write a 1500 Word Essay will walk you through the process of crafting a well-structured 1500 word essay, provide insights on its typical length in pages, and offer examples to help you succeed.
How do I write like my favourite author? To write like your favourite author, start by studying their writing style closely. Pay attention to how they develop characters, structure plots, and use language. Practice writing with similar themes or techniques, such as their approach to dialogue, pacing, or tone.
How to Write an Essay Outline | Guidelines & Examples. Published on August 14, 2020 by Jack Caulfield.Revised on July 23, 2023. An essay outline is a way of planning the structure of your essay before you start writing. It involves writing quick summary sentences or phrases for every point you will cover in each paragraph, giving you a picture of how your argument will unfold.
Metaphor and Simile: The essay incorporates figurative language, such as comparing the experience to "standing on the fringes of understanding." First-Person Narrative: The personal tone creates an intimate and engaging connection with the reader.
At university, the vast majority of essays or papers you write will involve some form of argumentation. For example, both rhetorical analysis and literary analysis essays involve making arguments about texts. In this context, you won't necessarily be told to write an argumentative essay—but making an evidence-based argument is an essential ...