Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format / How to Cite an Essay in MLA

How to Cite an Essay in MLA
The guidelines for citing an essay in MLA format are similar to those for citing a chapter in a book. Include the author of the essay, the title of the essay, the name of the collection if the essay belongs to one, the editor of the collection or other contributors, the publication information, and the page number(s).
Citing an Essay
Mla essay citation structure.
Last, First M. “Essay Title.” Collection Title, edited by First M. Last, Publisher, year published, page numbers. Website Title , URL (if applicable).
MLA Essay Citation Example
Gupta, Sanjay. “Balancing and Checking.” Essays on Modern Democracy, edited by Bob Towsky, Brook Stone Publishers, 1996, pp. 36-48. Essay Database, www . databaseforessays.org/modern/modern-democracy.
MLA Essay In-text Citation Structure
(Last Name Page #)
MLA Essay In-text Citation Example
Click here to cite an essay via an EasyBib citation form.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- Works Cited
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
To cite your sources in an essay in MLA style, you need to have basic information including the author’s name(s), chapter title, book title, editor(s), publication year, publisher, and page numbers. The templates for in-text citations and a works-cited-list entry for essay sources and some examples are given below:
In-text citation template and example:
For citations in prose, use the first name and surname of the author on the first occurrence. For subsequent citations, use only the surname(s). In parenthetical citations, always use only the surname of the author(s).
Citation in prose:
First mention: Annette Wheeler Cafarelli
Subsequent occurrences: Wheeler Cafarelli
Parenthetical:
….(Wheeler Cafarelli).
Works-cited-list entry template and example:
The title of the chapter is enclosed in double quotation marks and uses title case. The book or collection title is given in italics and uses title case.
Surname, First Name. “Title of the Chapter.” Title of the Book , edited by Editor(s) Name, Publisher, Publication Year, page range.
Cafarelli, Annette Wheeler. “Rousseau and British Romanticism: Women and British Romanticism.” Cultural Interactions in the Romantic Age: Critical Essays in Comparative Literature , edited by Gregory Maertz. State U of New York P, 1998, pp. 125–56.
To cite an essay in MLA style, you need to have basic information including the author(s), the essay title, the book title, editor(s), publication year, publisher, and page numbers. The templates for citations in prose, parenthetical citations, and works-cited-list entries for an essay by multiple authors, and some examples, are given below:
For citations in prose, use the first name and surname of the author (e.g., Mary Strine).
For sources with two authors, use both full author names in prose (e.g., Mary Strine and Beth Radick).
For sources with three or more authors, use the first name and surname of the first author followed by “and others” or “and colleagues” (e.g., Mary Strine and others). In subsequent citations, use only the surname of the first author followed by “and others” or “and colleagues” (e.g., Strine and others).
In parenthetical citations, use only the author’s surname. For sources with two authors, use two surnames (e.g., Strine and Radick). For sources with three or more author names, use the first author’s surname followed by “et al.”
First mention: Mary Strine…
Subsequent mention: Strine…
First mention: Mary Strine and Beth Radick…
Subsequent mention: Strine and Radick…
First mention: Mary Strine and colleagues …. or Mary Strine and others
Subsequent occurrences: Strine and colleagues …. or Strine and others
…. (Strine).
….(Strine and Radick).
….(Strine et al.).
The title of the essay is enclosed in double quotation marks and uses title case. The book or collection title is given in italics and uses title case.
Surname, First Name, et al. “Title of the Essay.” Title of the Book , edited by Editor(s) Name, Publisher, Publication Year, page range.
Strine, Mary M., et al. “Research in Interpretation and Performance Studies: Trends, Issues, Priorities.” Speech Communication: Essays to Commemorate the 75th Anniversary of the Speech Communication Association , edited by Gerald M. Phillips and Julia T. Wood, Southern Illinois UP, 1990, pp. 181–204.
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started

Chicago/Turabian Citation
- Citing a Book
Basic Chapter Citation
Example chapter of a book, example chapter of an ebook, example foreword/preface of a book.
- Citing an Article
- Citing a Webpage
- Additional Resources
Writing Center
Visit the Writing Center for help with brainstorming, organization, revising, citations, and other writing assistance!
- Every Monday: Saurwein 232
- Tuesday-Sunday in Campus Center 313: The Owen Center
Regular Writing Center Hours:
- Monday-Friday 12:00PM-7:00PM
- Sundays 12:00PM-5:00PM
Book an appointment with a Writing Center consultant.
Footnote/Endnote
Author First M. Last Name, "Chapter or Essay Title," in Book Title , ed. First M. Last Name (Place of Publication: Publisher, date), page cited.
Short version: Author Last Name, "Chapter or Essay Title (shortened if necessary)," page cited.
Bibliography
Author Last Name, First M. "Chapter or Essay Title." In Book Title , edited by First M. Last Name, page range. Place of Publication: Publisher, date.
Eric Charry, "Music and Islam in Sub-Saharan Africa," in The History of Islam in Africa , eds. Nehwmia Levtzion and Randall L. Pouwels (Athens, OH: Ohio University Press, 2000), 550.
Short version: Charry, "Music and Islam in Sub-Saharan Africa," 550.
Charry, Eric. "Music and Islam in Sub-Saharan Africa." In The History of Islam in Africa , edited by Nehwmia Levtzion and Randall L. Pouwels, 545-573. Athens, OH: Ohio University Press, 2000.
Alan Liu, "Where is Cultural Criticism in the Digital Humanities?," in Debates in the Digital Humanities , ed. Matthew K. Gold (Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 2013), accessed January 23, 2014, http://dhdebates.gc.cuny.edu/debates/text/20.
Short version: Liu, "Where is Cultural Criticism."
Liu, Alan. "Where is Cultural Criticism in the Digital Humanities?." In Debates in the Digital Humanities , edited by Matthew K. Gold. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 2013. A ccessed January 23, 2014. http://dhdebates.gc.cuny.edu/debates/text/20.
Strobe Talbott, foreword to Beyond Tianamen: The Politics of U.S.-China Relations 1989-2000 , by Robert L. Suettinger (Washington, D. C.: Brookings Institute Press, 2003), x.
Short version: Talbott, foreword, x.
Talbott, Strobe. Foreword to Beyond Tianamen: The Politics of U.S.-China Relations 1989-2000 , by Robert L. Suettinger, ix-x. Washington, D. C.: Brookings Institute Press, 2003.
- << Previous: Citing a Book
- Next: Citing an Article >>
- Last Updated: Sep 30, 2022 12:44 PM
- URL: https://libguides.heidelberg.edu/chicago
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA Works Cited Page: Books

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
When you are gathering book sources, be sure to make note of the following bibliographic items: the author name(s), other contributors such as translators or editors, the book’s title, editions of the book, the publication date, the publisher, and the pagination.
The 8 th edition of the MLA handbook highlights principles over prescriptive practices. Essentially, a writer will need to take note of primary elements in every source, such as author, title, etc. and then assort them in a general format. Thus, by using this methodology, a writer will be able to cite any source regardless of whether it’s included in this list.
Please note these changes in the new edition:
- Commas are used instead of periods between Publisher, Publication Date, and Pagination.
- Medium is no longer necessary.
- Containers are now a part of the MLA process. Commas should be used after container titles.
- DOIs should be used instead of URLS when available.
- Use the term “Accessed” instead of listing the date or the abbreviation, “n.d."
Below is the general format for any citation:
Author. Title. Title of container (do not list container for standalone books, e.g. novels), Other contributors (translators or editors), Version (edition), Number (vol. and/or no.), Publisher, Publication Date, Location (pages, paragraphs URL or DOI). 2 nd container’s title, Other contributors, Version, Number, Publisher, Publication date, Location, Date of Access (if applicable).
Basic Book Format
The author’s name or a book with a single author's name appears in last name, first name format. The basic form for a book citation is:
Last Name, First Name. Title of Book . City of Publication, Publisher, Publication Date.
* Note: the City of Publication should only be used if the book was published before 1900, if the publisher has offices in more than one country, or if the publisher is unknown in North America.
Book with One Author
Gleick, James. Chaos: Making a New Science . Penguin, 1987.
Henley, Patricia. The Hummingbird House . MacMurray, 1999.
Book with More Than One Author
When a book has two authors, order the authors in the same way they are presented in the book. Start by listing the first name that appears on the book in last name, first name format; subsequent author names appear in normal order (first name last name format).
Gillespie, Paula, and Neal Lerner. The Allyn and Bacon Guide to Peer Tutoring . Allyn and Bacon, 2000.
If there are three or more authors, list only the first author followed by the phrase et al. (Latin for "and others") in place of the subsequent authors' names. (Note that there is a period after “al” in “et al.” Also note that there is never a period after the “et” in “et al.”).
Wysocki, Anne Frances, et al. Writing New Media: Theory and Applications for Expanding the Teaching of Composition . Utah State UP, 2004.
Two or More Books by the Same Author
List works alphabetically by title. (Remember to ignore articles like A, An, and The.) Provide the author’s name in last name, first name format for the first entry only. For each subsequent entry by the same author, use three hyphens and a period.
Palmer, William J. Dickens and New Historicism . St. Martin's, 1997.
---. The Films of the Eighties: A Social History . Southern Illinois UP, 1993.
Book by a Corporate Author or Organization
A corporate author may include a commission, a committee, a government agency, or a group that does not identify individual members on the title page.
List the names of corporate authors in the place where an author’s name typically appears at the beginning of the entry.
American Allergy Association. Allergies in Children . Random House, 1998.
When the author and publisher are the same, skip the author, and list the title first. Then, list the corporate author only as the publisher.
Fair Housing—Fair Lending. Aspen Law & Business, 1985.
Book with No Author
List by title of the book. Incorporate these entries alphabetically just as you would with works that include an author name. For example, the following entry might appear between entries of works written by Dean, Shaun and Forsythe, Jonathan.
Encyclopedia of Indiana . Somerset, 1993.
Remember that for an in-text (parenthetical) citation of a book with no author, you should provide the name of the work in the signal phrase and the page number in parentheses. You may also use a shortened version of the title of the book accompanied by the page number. For more information see the In-text Citations for Print Sources with No Known Author section of In-text Citations: The Basics .
A Translated Book
If you want to emphasize the work rather than the translator, cite as you would any other book. Add “translated by” and follow with the name(s) of the translator(s).
Foucault, Michel. Madness and Civilization: A History of Insanity in the Age of Reason . Translated by Richard Howard, Vintage-Random House, 1988.
If you want to focus on the translation, list the translator as the author. In place of the author’s name, the translator’s name appears. His or her name is followed by the label, “translator.” If the author of the book does not appear in the title of the book, include the name, with a “By” after the title of the book and before the publisher. Note that this type of citation is less common and should only be used for papers or writing in which translation plays a central role.
Howard, Richard, translator. Madness and Civilization: A History of Insanity in the Age of Reason . By Michel Foucault, Vintage-Random House, 1988.
Republished Book
Books may be republished due to popularity without becoming a new edition. New editions are typically revisions of the original work. For books that originally appeared at an earlier date and that have been republished at a later one, insert the original publication date before the publication information.
For books that are new editions (i.e. different from the first or other editions of the book), see An Edition of a Book below.
Butler, Judith. Gender Trouble . 1990. Routledge, 1999.
Erdrich, Louise. Love Medicine . 1984. Perennial-Harper, 1993.
An Edition of a Book
There are two types of editions in book publishing: a book that has been published more than once in different editions and a book that is prepared by someone other than the author (typically an editor).
A Subsequent Edition
Cite the book as you normally would, but add the number of the edition after the title.
Crowley, Sharon, and Debra Hawhee. Ancient Rhetorics for Contemporary Students . 3rd ed., Pearson, 2004.
A Work Prepared by an Editor
Cite the book as you normally would, but add the editor after the title with the label "edited by."
Bronte, Charlotte. Jane Eyre, edited by Margaret Smith, Oxford UP, 1998.
Note that the format for citing sources with important contributors with editor-like roles follows the same basic template:
...adapted by John Doe...
Finally, in the event that the source features a contributor that cannot be described with a past-tense verb and the word "by" (e.g., "edited by"), you may instead use a noun followed by a comma, like so:
...guest editor, Jane Smith...
Anthology or Collection (e.g. Collection of Essays)
To cite the entire anthology or collection, list by editor(s) followed by a comma and "editor" or, for multiple editors, "editors." This sort of entry is somewhat rare. If you are citing a particular piece within an anthology or collection (more common), see A Work in an Anthology, Reference, or Collection below.
Hill, Charles A., and Marguerite Helmers, editors. Defining Visual Rhetorics . Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 2004.
Peterson, Nancy J., editor. Toni Morrison: Critical and Theoretical Approaches . Johns Hopkins UP, 1997.
A Work in an Anthology, Reference, or Collection
Works may include an essay in an edited collection or anthology, or a chapter of a book. The basic form is for this sort of citation is as follows:
Last name, First name. "Title of Essay." Title of Collection , edited by Editor's Name(s), Publisher, Year, Page range of entry.
Some examples:
Harris, Muriel. "Talk to Me: Engaging Reluctant Writers." A Tutor's Guide: Helping Writers One to One , edited by Ben Rafoth, Heinemann, 2000, pp. 24-34.
Swanson, Gunnar. "Graphic Design Education as a Liberal Art: Design and Knowledge in the University and The 'Real World.'" The Education of a Graphic Designer , edited by Steven Heller, Allworth Press, 1998, pp. 13-24.
Note on Cross-referencing Several Items from One Anthology: If you cite more than one essay from the same edited collection, MLA indicates you may cross-reference within your works cited list in order to avoid writing out the publishing information for each separate essay. You should consider this option if you have several references from a single text. To do so, include a separate entry for the entire collection listed by the editor's name as below:
Rose, Shirley K, and Irwin Weiser, editors. The Writing Program Administrator as Researcher . Heinemann, 1999.
Then, for each individual essay from the collection, list the author's name in last name, first name format, the title of the essay, the editor's last name, and the page range:
L'Eplattenier, Barbara. "Finding Ourselves in the Past: An Argument for Historical Work on WPAs." Rose and Weiser, pp. 131-40.
Peeples, Tim. "'Seeing' the WPA With/Through Postmodern Mapping." Rose and Weiser, pp. 153-67.
Please note: When cross-referencing items in the works cited list, alphabetical order should be maintained for the entire list.
Poem or Short Story Examples :
Burns, Robert. "Red, Red Rose." 100 Best-Loved Poems, edited by Philip Smith, Dover, 1995, p. 26.
Kincaid, Jamaica. "Girl." The Vintage Book of Contemporary American Short Stories , edited by Tobias Wolff, Vintage, 1994, pp. 306-07.
If the specific literary work is part of the author's own collection (all of the works have the same author), then there will be no editor to reference:
Whitman, Walt. "I Sing the Body Electric." Selected Poems, Dover, 1991, pp. 12-19.
Carter, Angela. "The Tiger's Bride." Burning Your Boats: The Collected Stories, Penguin, 1995, pp. 154-69.
Article in a Reference Book (e.g. Encyclopedias, Dictionaries)
For entries in encyclopedias, dictionaries, and other reference works, cite the entry name as you would any other work in a collection but do not include the publisher information. Also, if the reference book is organized alphabetically, as most are, do not list the volume or the page number of the article or item.
"Ideology." The American Heritage Dictionary. 3rd ed. 1997.
A Multivolume Work
When citing only one volume of a multivolume work, include the volume number after the work's title, or after the work's editor or translator.
Quintilian. Institutio Oratoria . Translated by H. E. Butler, vol. 2, Loeb-Harvard UP, 1980.
When citing more than one volume of a multivolume work, cite the total number of volumes in the work. Also, be sure in your in-text citation to provide both the volume number and page number(s) ( see "Citing Multivolume Works" on our in-text citations resource .)
Quintilian. Institutio Oratoria . Translated by H. E. Butler, Loeb-Harvard UP, 1980. 4 vols.
If the volume you are using has its own title, cite the book without referring to the other volumes as if it were an independent publication.
Churchill, Winston S. The Age of Revolution . Dodd, 1957.
An Introduction, Preface, Foreword, or Afterword
When citing an introduction, a preface, a foreword, or an afterword, write the name of the author(s) of the piece you are citing. Then give the name of the part being cited, which should not be italicized or enclosed in quotation marks; in italics, provide the name of the work and the name of the author of the introduction/preface/foreword/afterword. Finish the citation with the details of publication and page range.
Farrell, Thomas B. Introduction. Norms of Rhetorical Culture , by Farrell, Yale UP, 1993, pp. 1-13.
If the writer of the piece is different from the author of the complete work , then write the full name of the principal work's author after the word "By." For example, if you were to cite Hugh Dalziel Duncan’s introduction of Kenneth Burke’s book Permanence and Change, you would write the entry as follows:
Duncan, Hugh Dalziel. Introduction. Permanence and Change: An Anatomy of Purpose, by Kenneth Burke, 1935, 3rd ed., U of California P, 1984, pp. xiii-xliv.
Book Published Before 1900
Original copies of books published before 1900 are usually defined by their place of publication rather than the publisher. Unless you are using a newer edition, cite the city of publication where you would normally cite the publisher.
Thoreau, Henry David. Excursions . Boston, 1863.
Italicize “The Bible” and follow it with the version you are using. Remember that your in-text (parenthetical citation) should include the name of the specific edition of the Bible, followed by an abbreviation of the book, the chapter and verse(s). (See Citing the Bible at In-Text Citations: The Basics .)
The Bible. Authorized King James Version , Oxford UP, 1998.
The Bible. The New Oxford Annotated Version , 3rd ed., Oxford UP, 2001.
The New Jerusalem Bible. Edited by Susan Jones, Doubleday, 1985.
A Government Publication
Cite the author of the publication if the author is identified. Otherwise, start with the name of the national government, followed by the agency (including any subdivisions or agencies) that serves as the organizational author. For congressional documents, be sure to include the number of the Congress and the session when the hearing was held or resolution passed as well as the report number. US government documents are typically published by the Government Printing Office.
United States, Congress, Senate, Committee on Energy and Natural Resources. Hearing on the Geopolitics of Oil . Government Printing Office, 2007. 110th Congress, 1st session, Senate Report 111-8.
United States, Government Accountability Office. Climate Change: EPA and DOE Should Do More to Encourage Progress Under Two Voluntary Programs . Government Printing Office, 2006.
Cite the title and publication information for the pamphlet just as you would a book without an author. Pamphlets and promotional materials commonly feature corporate authors (commissions, committees, or other groups that does not provide individual group member names). If the pamphlet you are citing has no author, cite as directed below. If your pamphlet has an author or a corporate author, put the name of the author (last name, first name format) or corporate author in the place where the author name typically appears at the beginning of the entry. (See also Books by a Corporate Author or Organization above.)
Women's Health: Problems of the Digestive System . American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, 2006.
Your Rights Under California Welfare Programs . California Department of Social Services, 2007.
Dissertations and Master's Theses
Dissertations and master's theses may be used as sources whether published or not. Unlike previous editions, MLA 8 specifies no difference in style for published/unpublished works.
The main elements of a dissertation citation are the same as those for a book: author name(s), title (italicized) , and publication date. Conclude with an indication of the document type (e.g., "PhD dissertation"). The degree-granting institution may be included before the document type (though this is not required). If the dissertation was accessed through an online repository, include it as the second container after all the other elements.
Bishop, Karen Lynn. Documenting Institutional Identity: Strategic Writing in the IUPUI Comprehensive Campaign . 2002. Purdue University, PhD dissertation.
Bile, Jeffrey. Ecology, Feminism, and a Revised Critical Rhetoric: Toward a Dialectical Partnership . 2005. Ohio University, PhD dissertation.
Mitchell, Mark. The Impact of Product Quality Reducing Events on the Value of Brand-Name Capital: Evidence from Airline Crashes and the 1982 Tylenol Poisonings. 1987. PhD dissertation. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses.
List the names of corporate authors in the place where an author’s name typically appears at the beginning of the entry if the author and publisher are not the same.
Fair Housing—Fair Lending. Aspen Law & Business, 1985.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Cite an Essay
Last Updated: February 4, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Diya Chaudhuri, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Diya Chaudhuri holds a PhD in Creative Writing (specializing in Poetry) from Georgia State University. She has over 5 years of experience as a writing tutor and instructor for both the University of Florida and Georgia State University. There are 10 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 559,954 times.
If you're writing a research paper, whether as a student or a professional researcher, you might want to use an essay as a source. You'll typically find essays published in another source, such as an edited book or collection. When you discuss or quote from the essay in your paper, use an in-text citation to relate back to the full entry listed in your list of references at the end of your paper. While the information in the full reference entry is basically the same, the format differs depending on whether you're using the Modern Language Association (MLA), American Psychological Association (APA), or Chicago citation method.
Template and Examples

- Example: Potter, Harry.

- Example: Potter, Harry. "My Life with Voldemort."

- Example: Potter, Harry. "My Life with Voldemort." Great Thoughts from Hogwarts Alumni , by Bathilda Backshot,

- Example: Potter, Harry. "My Life with Voldemort." Great Thoughts from Hogwarts Alumni , by Bathilda Backshot, Hogwarts Press, 2019,

- Example: Potter, Harry. "My Life with Voldemort." Great Thoughts from Hogwarts Alumni , by Bathilda Backshot, Hogwarts Press, 2019, pp. 22-42.
MLA Works Cited Entry Format:
LastName, FirstName. "Title of Essay." Title of Collection , by FirstName Last Name, Publisher, Year, pp. ##-##.

- For example, you might write: While the stories may seem like great adventures, the students themselves were terribly frightened to confront Voldemort (Potter 28).
- If you include the author's name in the text of your paper, you only need the page number where the referenced material can be found in the parenthetical at the end of your sentence.
- If you have several authors with the same last name, include each author's first initial in your in-text citation to differentiate them.
- For several titles by the same author, include a shortened version of the title after the author's name (if the title isn't mentioned in your text).

- Example: Granger, H.

- Example: Granger, H. (2018).

- Example: Granger, H. (2018). Adventures in time turning.

- Example: Granger, H. (2018). Adventures in time turning. In M. McGonagall (Ed.), Reflections on my time at Hogwarts

- Example: Granger, H. (2018). Adventures in time turning. In M. McGonagall (Ed.), Reflections on my time at Hogwarts (pp. 92-130). Hogwarts Press.
APA Reference List Entry Format:
LastName, I. (Year). Title of essay. In I. LastName (Ed.), Title of larger work (pp. ##-##). Publisher.

- For example, you might write: By using a time turner, a witch or wizard can appear to others as though they are actually in two places at once (Granger, 2018).
- If you use the author's name in the text of your paper, include the parenthetical with the year immediately after the author's name. For example, you might write: Although technically against the rules, Granger (2018) maintains that her use of a time turner was sanctioned by the head of her house.
- Add page numbers if you quote directly from the source. Simply add a comma after the year, then type the page number or page range where the quoted material can be found, using the abbreviation "p." for a single page or "pp." for a range of pages.

- Example: Weasley, Ron.

- Example: Weasley, Ron. "Best Friend to a Hero."

- Example: Weasley, Ron. "Best Friend to a Hero." In Harry Potter: Wizard, Myth, Legend , edited by Xenophilius Lovegood, 80-92.

- Example: Weasley, Ron. "Best Friend to a Hero." In Harry Potter: Wizard, Myth, Legend , edited by Xenophilius Lovegood, 80-92. Ottery St. Catchpole: Quibbler Books, 2018.
' Chicago Bibliography Format:
LastName, FirstName. "Title of Essay." In Title of Book or Essay Collection , edited by FirstName LastName, ##-##. Location: Publisher, Year.

- Example: Ron Weasley, "Best Friend to a Hero," in Harry Potter: Wizard, Myth, Legend , edited by Xenophilius Lovegood, 80-92 (Ottery St. Catchpole: Quibbler Books, 2018).
- After the first footnote, use a shortened footnote format that includes only the author's last name, the title of the essay, and the page number or page range where the referenced material appears.
Tip: If you use the Chicago author-date system for in-text citation, use the same in-text citation method as APA style.
Community Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://style.mla.org/essay-in-authored-textbook/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_works_cited_page_books.html
- ↑ https://utica.libguides.com/c.php?g=703243&p=4991646
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_in_text_citations_the_basics.html
- ↑ https://guides.libraries.psu.edu/apaquickguide/intext
- ↑ https://guides.himmelfarb.gwu.edu/c.php?g=27779&p=170363
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/in_text_citations_the_basics.html
- ↑ http://libguides.heidelberg.edu/chicago/book/chapter
- ↑ https://librarybestbets.fairfield.edu/citationguides/chicagonotes-bibliography#CollectionofEssays
- ↑ https://libguides.heidelberg.edu/chicago/book/chapter
About This Article

To cite an essay using MLA format, include the name of the author and the page number of the source you’re citing in the in-text citation. For example, if you’re referencing page 123 from a book by John Smith, you would include “(Smith 123)” at the end of the sentence. Alternatively, include the information as part of the sentence, such as “Rathore and Chauhan determined that Himalayan brown bears eat both plants and animals (6652).” Then, make sure that all your in-text citations match the sources in your Works Cited list. For more advice from our Creative Writing reviewer, including how to cite an essay in APA or Chicago Style, keep reading. Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Mbarek Oukhouya
Mar 7, 2017
Did this article help you?
Sarah Sandy
May 25, 2017
Skyy DeRouge
Nov 14, 2021
Diana Ordaz
Sep 25, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
- How to Cite
- Language & Lit
- Rhyme & Rhythm
- The Rewrite
- Search Glass
How to Cite an Essay in MLA
Whether you refer to an essay from a nonfiction author in your literary paper or a work from a political figure in your history essay, you need to include citations that lead your readers to the source material. In Modern Language Association (MLA) format, these citations include the author, essay title and information about the print or online source where you found the essay, such as the editor, publisher name and publication date. MLA style also dictates the use of in-text citations to point the reader to the appropriate works cited entry.
Anthology or Collection Bibliography Citations
It is most likely that you will cite a single essay from a collection or anthology. These kinds of books often have editors, whose names you will need to add to your citation. If you refer to the entire book, which is rare, begin the citation with the editor’s names:
Strayed, Cheryl, and Robert Atwan, eds. The Best American Essays 2013 . San Diego: Mariner, 2013. Print.
In the above citation, there are two editors; the first is listed last name - first name, and the second is listed first name - last name. Most often, you need to cite a single essay found in a collection. This changes the citation format slightly because you refer to the author and essay title before the collection, as in the example :
Monson, Ander. “The Exhibit Will Be So Marked.” The Best American Essays 2013 . Ed. Cheryl Strayed and Robert Atwan. San Diego: Mariner, 2013. 245-253. Print.
All bibliographic entries in MLA need to use a hanging indent, in which the second and subsequent lines of text for each entry are indented.
Citing Books in MLA
You might need to refer to an entire collection of essays by one author; in this case, you would cite the collection as a book by an author, as follows:
Sedaris, David. Me Talk Pretty One Day . New York: Back Bay, 2001. Print.
If the book is translated, include the translator in the citation, much like you would for an editor:
de Montaigne, Michel. The Complete Essays . 1572. Trans. M. A. Screech. New York: Penguin Classics, 1993. Print.
This citation includes two dates, because the original essays were published in 1572, while the reprinted edition referred to was published in 1993. If your book source has two or three authors, follow the format of last name - first name for the first author, and use first name - last name format for the subsequent authors. If there are more than three authors, list the first author as last name - first name, followed by “et al.” for “and others.”
Essays Found Online
You might find essays online, which are likely published on a website or as part of an online journal or magazine. To cite the Web page, first list the author and essay title, followed by the name of the website and the date you accessed the site, as in the example :
Gould, Emily. “How Much My Novel Cost Me.” Medium , 2014. Web. 15 Feb. 2015.
If the essay came from a Web magazine, also include the magazine’s name and publishing information in your citation :
Comiskey, Nancy. “Dear Kate: Living With Grief.” Indianapolis Monthly . Indianapolis Monthly Publications, 2014. Web. 12 Feb. 2015.
MLA format does not require you to write the URL at the end of the citation, but you could include it after the access date.
In-Text Citations
Parenthetical and in-text citations direct your reader to the bibliographic entry in your works cited page. In MLA format, you use the author’s last name followed by the page numbers in parentheses after a sentence or group of sentences referring to the essay.
For example, “(Sedaris 25-32)” -- without the quote marks -- would finish your sentence, and you place the sentence's period after the parenthetical citation. If you mention the author within a sentence, only put the page number in parentheses at the end of the sentence. Web sources do not require page numbers in the parenthetical citations; use just the author’s last name instead.
Need help with a citation? Try our citation generator .
- Purdue Online Writing Lab: MLA Works Cited Page; Books
- Cornell University Library: MLA Citation Style
- Purdue Online Writing Lab: MLA In-Text Citations; The Basics
Cara Batema is a musician, teacher and writer who specializes in early childhood, special needs and psychology. Since 2010, Batema has been an active writer in the fields of education, parenting, science and health. She holds a bachelor's degree in music therapy and creative writing.
MLA 8 Citation Guide
- TITLE of SOURCE
- TITLE of CONTAINER
- OTHER CONTRIBUTORS
- PUBLICATION DATE
- Works Cited
- Journal Article with One Author
- Journal Article with 2 Authors
- Journal Article with 3 or more Authors
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- One Author or Editor
- Two Authors or Editors
- Three or More Authors
Article or Chapter in an Edited Book
- Article in a Reference Book
- Reference Work
- Basic Web Page
- Entry in a Reference Work
- Government or Agency Document
- YouTube Video
- Electronic Image
- Figures and Charts
- Class Lecture/Notes
- Secondary Sources
MLA Works Cited Page: Books

Ask Us 24/7

Online help is available anytime via our AskUs 24/7 chat service:
Works Cited List:
Last name, First name. "Title of Essay." Title of Collection , edited by Editor Name(s). Publisher, Year, pp Page range of entry.
Lawrence, James. A., and Alfred Dodds. "Goal-Directed Activities and Life-Span Development.” Handbook of Developmental Psychology, edited by John Valsiner and Kare Connolly. Heinemann, 2000, pp. 24-34.
In-Text Citation:
(Author Surname [of Chapter or Article] page number)
(Lawrence and Dodds 26)
Works Cited List
Jans, Nick. The Last Light Breaking: Life among Alaska's Inupiat Eskimos . Alaska Northwest Books, 1993.
Edited book
Miller, John, and Tim Smith, editors. Cape Cod Stories: Tales from Cape Cod, Nantucket, and Martha's Vineyard . Chronicle Books, 1996.
Please see the sample citation for a chapter or article in an anthology below for information on citing a component of an edited collection.
Numbered edition other than the first
Wardle, Elizabeth, and Doug Downs, editors. Writing About Writing: A College Reader . 2nd ed., Bedford/St. Martin's, 2014.
Revised edition
Culliney, John L. Islands in a Far Sea: The Fate of Nature in Hawai'i . Rev. ed., U of Hawai'i P, 2006.
Multi-volume set
Green, Constance McLaughlin. Washington . Princeton UP, 1962-63. 2 vols.
In-text citation: (Green 1: 112-14) "1" is the volume number.
- << Previous: Three or More Authors
- Next: Article in a Reference Book >>
- Last Updated: Aug 5, 2024 9:27 AM
- URL: https://utica.libguides.com/mla
How to Write an Academic Essay with References and Citations
#scribendiinc
Written by Scribendi
If you're wondering how to write an academic essay with references, look no further. In this article, we'll discuss how to use in-text citations and references, including how to cite a website, how to cite a book, and how to cite a Tweet, according to various style guides.

You might need to cite sources when writing a paper that references other sources. For example, when writing an essay, you may use information from other works, such as books, articles, or websites. You must then inform readers where this information came from. Failure to do so, even accidentally, is plagiarism—passing off another person's work as your own.
You can avoid plagiarism and show readers where to find information by using citations and references.
Citations tell readers where a piece of information came from. They take the form of footnotes, endnotes, or parenthetical elements, depending on your style guide. In-text citations are usually placed at the end of a sentence containing the relevant information.
A reference list , bibliography, or works cited list at the end of a text provides additional details about these cited sources. This list includes enough publication information allowing readers to look up these sources themselves.
Referencing is important for more than simply avoiding plagiarism. Referring to a trustworthy source shows that the information is reliable. Referring to reliable information can also support your major points and back up your argument.
Learning how to write an academic essay with references and how to use in-text citations will allow you to cite authors who have made similar arguments. This helps show that your argument is objective and not entirely based on personal biases.
How Do You Determine Which Style Guide to Use?

Often, a professor will assign a style guide. The purpose of a style guide is to provide writers with formatting instructions. If your professor has not assigned a style guide, they should still be able to recommend one.
If you are entirely free to choose, pick one that aligns with your field (for example, APA is frequently used for scientific writing).
Some of the most common style guides are as follows:
AP style for journalism
Chicago style for publishing
APA style for scholarly writing (commonly used in scientific fields)
MLA style for scholarly citations (commonly used in English literature fields)
Some journals have their own style guides, so if you plan to publish, check which guide your target journal uses. You can do this by locating your target journal's website and searching for author guidelines.
How Do You Pick Your Sources?
When learning how to write an academic essay with references, you must identify reliable sources that support your argument.
As you read, think critically and evaluate sources for:
Objectivity
Keep detailed notes on the sources so that you can easily find them again, if needed.
Tip: Record these notes in the format of your style guide—your reference list will then be ready to go.
How to Use In-Text Citations in MLA
An in-text citation in MLA includes the author's last name and the relevant page number:
(Author 123)
How to Cite a Website in MLA

Here's how to cite a website in MLA:
Author's last name, First name. "Title of page."
Website. Website Publisher, date. Web. Date
retrieved. <URL>
With information from a real website, this looks like:
Morris, Nancy. "How to Cite a Tweet in APA,
Chicago, and MLA." Scribendi. Scribendi
Inc., n.d. Web. 22 Dec. 2021.
<https://www.scribendi.com/academy/articles/how_to_cite_a_website.en.html>
How Do You Cite a Tweet in MLA ?
MLA uses the full text of a short Tweet (under 140 characters) as its title. Longer Tweets can be shortened using ellipses.
MLA Tweet references should be formatted as follows:
@twitterhandle (Author Name). "Text of Tweet." Twitter, Date Month, Year, time of
publication, URL.
With information from an actual Tweet, this looks like:
@neiltyson (Neil deGrasse Tyson). "You can't use reason to convince anyone out of an
argument that they didn't use reason to get into." Twitter, 29 Sept. 2020, 10:15 p.m.,
https://twitter.com/neiltyson/status/1311127369785192449 .
How to Cite a Book in MLA
Here's how to cite a book in MLA:
Author's last name, First name. Book Title. Publisher, Year.
With publication information from a real book, this looks like:
Montgomery, L.M. Rainbow Valley. Frederick A. Stokes Company, 1919.
How to Cite a Chapter in a Book in MLA
Author's last name, First name. "Title of Chapter." Book Title , edited by Editor Name,
Publisher, Year, pp. page range.
With publication information from an actual book, this looks like:
Ezell, Margaret J.M. "The Social Author: Manuscript Culture, Writers, and Readers." The
Broadview Reader in Book History , edited by Michelle Levy and Tom Mole, Broadview
Press, 2015,pp. 375–394.
How to Cite a Paraphrase in MLA
You can cite a paraphrase in MLA exactly the same way as you would cite a direct quotation.
Make sure to include the author's name (either in the text or in the parenthetical citation) and the relevant page number.
How to Use In-Text Citations in APA
In APA, in-text citations include the author's last name and the year of publication; a page number is included only if a direct quotation is used:
(Author, 2021, p. 123)
How to Cite a Website in APA
Here's how to cite a website in APA:
Author, A. A., & Author, B. B. (Year, Month. date of publication). Title of page. https://URL
Morris, N. (n.d.). How to cite a Tweet in APA, Chicago, and MLA.
https://www.scribendi.com/academy/articles/how_to_cite_a_website.en.html
Tip: Learn more about how to write an academic essay with references to websites .
How Do You Cite a Tweet in APA ?
APA refers to Tweets using their first 20 words.
Tweet references should be formatted as follows:
Author, A. A. [@twitterhandle). (Year, Month. date of publication). First 20 words of the
Tweet. [Tweet] Twitter. URL
When we input information from a real Tweet, this looks like:
deGrasse Tyson, N. [@neiltyson]. (2020, Sept. 29). You can't use reason to convince anyone
out of an argument that they didn't use reason to get into. [Tweet] Twitter.
https://twitter.com/neiltyson/status/1311127369785192449

How to Cite a Book in APA
Here's how to cite a book in APA:
Author, A. A. (Year). Book title. Publisher.
For a real book, this looks like:
Montgomery, L. M. (1919). Rainbow valley.
Frederick A. Stokes Company.
How to Cite a Chapter in a Book in APA
Author, A. A. (Year). Chapter title. In Editor Name (Ed.), Book Title (pp. page range).
With information from a real book, this looks like:
Ezell, M. J. M. (2014). The social author: Manuscript culture, writers, and readers. In
Michelle Levy and Tom Mole (Eds.), The Broadview Reader in Book History (pp. 375–
394). Broadview Press.
Knowing how to cite a book and how to cite a chapter in a book correctly will take you a long way in creating an effective reference list.

How to Cite a Paraphrase in APA
You can cite a paraphrase in APA the same way as you would cite a direct quotation, including the author's name and year of publication.
In APA, you may also choose to pinpoint the page from which the information is taken.
Referencing is an essential part of academic integrity. Learning how to write an academic essay with references and how to use in-text citations shows readers that you did your research and helps them locate your sources.
Learning how to cite a website, how to cite a book, and how to cite a paraphrase can also help you avoid plagiarism —an academic offense with serious consequences for your education or professional reputation.
Scribendi can help format your citations or review your whole paper with our Academic Editing services .
Take Your Essay from Good to Great
Hire an expert academic editor , or get a free sample, about the author.

Scribendi's in-house editors work with writers from all over the globe to perfect their writing. They know that no piece of writing is complete without a professional edit, and they love to see a good piece of writing transformed into a great one. Scribendi's in-house editors are unrivaled in both experience and education, having collectively edited millions of words and obtained numerous degrees. They love consuming caffeinated beverages, reading books of various genres, and relaxing in quiet, dimly lit spaces.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

APA Style and APA Formatting

How to Research a Term Paper

MLA Formatting and MLA Style: An Introduction
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
| File | Word Count | Include in Price? |
|---|
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

MLA 9 Citation Style: Work in an Anthology or Edited Book
- Textbook With One Author
- Textbook With Two Authors
- Textbook With Three or More Authors
- Textbook as an Anthology or Edited Book
- Textbook Work Within an Anthology or Edited Book
- Textbook Two or More from an Anthology or Edited Book
- Textbook with One Author (Mobile)
- Textbook with Two Authors (Mobile)
- Textbook with Three or More Authors (Mobile)
- Textbook as an Anthology or Edited Book (Mobile)
- Textbook Work Within an Anthology or Edited Book (Mobile)
- Textbook Two or More from an Anthology or Edited Book (Mobile)
- Two Authors
- Three or More Authors
- Anthology or Edited Book
- Work in an Anthology or Edited Book
- Two or More Selections from the Same Anthology or Edited Book
- Journal Article (Print)
- Journal Article (Online)
- Newspaper Articles (Print)
- Newspaper Articles (Online)
- Database Article with One Author
- Database Article with Two Authors
- Database Article with More Than Three Authors
- Database Previously Published Scholarly Article (Blooms, MasterPlots, Literary Reference Center)
- Online Government Publication
- Website with an Author’s/Contributor’s Name
- Website with No Author’s/Contributor’s Name
- Web Page with Author
- Web Page with No Author’s/Contributor’s Name
- Art – From a Book
- Art – From a Web Page
- Picture/Photo Online -- General
- Motion Picture -- DVD
- Motion Picture -- Streaming
- Video -- Online (YouTube, etc.)
- An Interview You Conducted
- Lecture Notes, PowerPoints, or Handouts from Class
- In-Text Citations
- Works Cited Page
- Popular vs. Scholarly Sources
- Direct Quotes, Paraphrasing, Summarizing
MLA Citation -- Work in an Anthology or Edited Book
Works Cited Format
Last name of author, First name of author. “Title of the Part of the Book Being Cited.” Title of Anthology .
Edited by First and Last Names, edition * (if any), Publisher, Date, Page(s).
In-Text Citation Format
(Editor’s Last Name p. # * )
* Please note, the in-text citation should be just the number itself and should not include the p., as in the example below.
Works Cited Example
Gilman, Charlotte Perkins. “The Yellow Wallpaper.” Literature: Reading, Reacting, Writing . Edited by Laurie G.
Kirszner and Stephen R. Mandell, Compact 9 th ed. * , Cengage Learning, 2017, pp. 379-391.
In-Text Citation Example
(Gilman 381)
*Sometimes the edition may include a qualifier, such as shorter edition or portable edition . When citing an anthology itself, you should include the qualifier before the edition number. For example: Compact 9 th ed.
A Word About Punctuation
The punctuation in your citations does matter. Make sure you pay attention to where the periods and commas are in the examples.
- << Previous: Anthology or Edited Book
- Next: Two or More Selections from the Same Anthology or Edited Book >>
- Last Updated: Jul 15, 2024 12:20 PM
- URL: https://warren.libguides.com/MLA9
Warren County Community College Haytaian & Maier Library 475 Route 57 West Washington, New Jersey 07882 Text: 908-652-4445 [email protected]
APA In-Text Citations and Sample Essay 7th Edition
This handout focuses on how to format in-text citations in APA.
Proper citation of sources is a two-part process . You must first cite each source in the body of your essay; these citations within the essay are called in-text citations . You MUST cite all quoted, paraphrased, or summarized words, ideas, and facts from sources. Without in-text citations, you are technically in danger of plagiarism, even if you have listed your sources at the end of the essay.
In-text citations point the reader to the sources’ information on the references page. The in-text citation typically includes the author's last name and the year of publication. If you use a direct quote, the page number is also provided.
More information can be found on p. 253 of the 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association.
Citation Rules
Direct quotation with the author named in the text.
Heinze and Lu (2017) stated, “The NFL shifted its responses to institutional change around concussions significantly as the field itself evolved” (p. 509).
Note: The year of publication is listed in parenthesis after the names of the authors, and the page number is listed in parenthesis at the end of the quote.
Direct Quotation without the Author Named in the Text
As the NFL developed as an organization, it “shifted its responses to institutional change around concussions significantly” (Heinze & Lu, 2017, p. 509).
Note: At the end of the quote, the names of the authors, year of publication, and page number are listed in parenthesis.
Paraphrase with 1-2 Authors
As the NFL developed as an organization, its reactions toward concussions also transformed (Heinze & Lu, 2017).
Note: For paraphrases, page numbers are encouraged but not required.
Paraphrase with 3 or More Authors
To work toward solving the issue of violence in prisons begins with determining aspects that might connect with prisoners' violent conduct (Thomson et al., 2019).
Direct Quotation without an Author
The findings were astonishing "in a recent study of parent and adult child relationships" ("Parents and Their Children," 2007, p. 2).
Note: Since the author of the text is not stated, a shortened version of the title is used instead.
Secondary Sources
When using secondary sources, use the phrase "as cited in" and cite the secondary source on the References page.
In 1936, Keynes said, “governments should run deficits when the economy is slow to avoid unemployment” (as cited in Richardson, 2008, p. 257).
Long (Block) Quotations
When using direct quotations of 40 or more words, indent five spaces from the left margin without using quotation marks. The final period should come before the parenthetical citation.
At Meramec, an English department policy states:
To honor and protect their own work and that of others, all students must give credit to proprietary sources that are used for course work. It is assumed that any information that is not documented is either common knowledge in that field or the original work of that student. (St. Louis Community College, 2001, p. 1)
Website Citations
If citing a specific web document without a page number, include the name of the author, date, title of the section, and paragraph number in parentheses:
In America, “Two out of five deaths among U.S. teens are the result of a motor vehicle crash” (National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, 2004, Overview section, para. 1).
Here is a print-friendly version of this content.
Learn more about the APA References page by reviewing this handout .
For information on STLCC's academic integrity policy, check out this webpage .
For additional information on APA, check out STLCC's LibGuide on APA .
Sample Essay
A sample APA essay is available at this link .

- Citation Generator
- Style Guides
- Chicago/Turabian Format
Citing an Anthology in MLA Works Cited Pages
Anthologies are collections of writings published in a book or journal. The writings center around a similar theme, time, or subject matter. Oftentimes, this involves various authors. However, collections of poems or short stories by the same author are also anthologies. How you cite an anthology in MLA style depends on whether you are referencing the whole anthology or a single entry in it. Learn how to create an MLA anthology citation through examples.

Types of Anthologies
Using works from anthologies gives you a way to find related research sources. An anthology is a collection of related works. Often poetry and short stories are collected into a single book. MLA 8 anthology examples use the nine core elements within the container system in the works cited. To cite one essay out of a collection of works, use this MLA citation format. Short stories are collected in an anthology. For example, consider this book on Chicano/Latino writings:
The Chicano/Latino Literary Prize: An Anthology of Prize-Winning Fiction, Poetry, and Drama Paperback – May 31, 2008
By Stephanie Fetta. (Editor) This landmark collection of prize-winning fiction, poetry, and drama paints a historical and aesthetic panorama of Chicana/o and Latina/o letters over a twenty-five-year period beginning in 1974 and ending in 1999.
Works by a single author are often collected in an anthology too.
The Complete Tales and Poems of Edgar Allan Poe Paperback – September 12, 1975
by Edgar Allan Poe (Author).

How to Cite a Whole Anthology in MLA
If you’re citing the whole anthology in MLA, use the editor(s) name in place of the author. When this is the case, also indicate they are an editor by adding ed. after the name.
Last, First Name, ed. Title of Anthology. Edition number, Publisher, Year.
How to Cite an Anthology in MLA – Works Cited
Carretta, Vincent, ed. Unchained Voices: An Anthology of Black Authors in the English-Speaking World of the Eighteenth Century . University Press of Kentucky, 2013.
Mazer, Anne, ed. America Street: A Multicultural Anthology of Stories . Turtleback Books, 1993.
How to Cite an Anthology MLA In-Text
If you’re paraphrasing or summarizing a work, place the author’s last name or editor in parentheses. For a direct quotation, include the page number.
MLA Anthology Citation Examples – Single Selection
Typically, you’ll be citing one selection out of the collection rather than the whole anthology. Format those citations as follows:
Last name, First name. “Title of Essay.” Title of Collection , edited by Editor’s Name(s), Publisher, Year, Page range of entry.
How to Cite an Anthology Selection MLA Example – Works Cited
Hughes, Langston. “The All-American Slurp.” America Street: A Multicultural Anthology of Stories, edited by Anne Mazer, Turtleback Books. 1993. pp. 18-25.
How to Cite an Anthology Single Author Example
There may not be an editor if the anthology consists of a single author’s works. So, use the author’s name as you normally would for other books.
Angelou, Maya. “Amazing Peace.” Maya Angelou: The Complete Poetry . Random House, 2015. Google Books. pp. 283-285
Online MLA Anthology Citation Examples
Often, you’ll find good books, including anthologies, available online . Cite these sources using MLA’s nine core elements and include the URL or DOI at the end of the citation.
Last, First Name, ed. Title of Anthology. Publisher, Year, URL.
Online MLA Anthology Citation Example – Works Cited
Begbie, Harold, ed. The Bed Book of Happiness. Gutenberg, 2004, www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/13457.
Online MLA Anthology Citation Example – In-Text Citation
(Begbie 48)
- If your source has a DOI, use that instead of the URL.
- Follow the MLA book format for citing anthologies.
Nesting MLA Containers
If the work you are citing in your MLA paper was previously published on its own, you need to add that publication information too. You do this by nesting the containers. There are nine core elements to a citation. Elements 3 to 9 are considered a container.
The first two elements stay the same:
- Title of source
The remaining 7 elements can be repeated at the end of the first container. This is how you account for additional publication information.

Container One Example
- Title of container,
- Other contributors,
- Publication date,
How to Cite an Anthology
Creating citations for anthologies in MLA works cited pages follows the same basic format as books. Use the container system with its core elements. This gives you an easy way to place the data in the correct order. Also, don’t forget to punctuate as noted! Use MLA anthology citation examples to make sure your citations are perfect.
Works Cited Page Example
FAQ Citing an Anthology in MLA Works Cited Pages
How do you cite an anthology.
To cite a whole anthology in any writing style, you typically include the anthology editor rather than the author of a specific work. However, if you are citing an excerpt from an anthology, you use the author's name that created the excerpt. How you format your citations varies depending on the specific style. For example, MLA uses the 9 core elements and container system.
How do you cite an anthology in MLA?
To cite a whole anthology in MLA style, you include the work's editor rather than the author. You will then use all the containers that fit into the work. An example of an MLA anthology: Duben, Anne, ed. Stories Around the World. New York Publishing, 2010.
How do you cite an excerpt from an anthology?
To cite an anthology in MLA of works by the same author, you include the author of the work, title, collection title, editor's name, publisher, year, and page range. An example of an MLA anthology citation includes: Frost, Robert. "A Road Not Taken." The Poetry of Robert Frost, edited by Edward Lethem, Turtleback Books. 2010. pp. 18-25.
How do you cite a single work in an anthology MLA?
To cite a single work in an anthology in MLA, you use the author's name of the work you are citing. For example, if you were citing a poem by Maya Angelou in an anthology about African American poems, you would use Maya Angelou and the poem's title as the first two elements. You'd then follow the container system to add the rest of the elements.
How do you in text cite an excerpt?
To in-text cite an excerpt from an anthology in MLA, you include the author's last name and page number of the excerpt. An example of an MLA anthology excerpt looks like: (Maya 76)
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 4.2 / 5. Vote count: 35
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Arranging Numbers in Works Cited List
How to cite a picture in mla, using note cards for mla research papers, mla format basics.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
MLA Referencing – Citing a Chapter from an Edited Book
- 3-minute read
- 3rd October 2017
You might know how to cite a book with MLA referencing , but what about citing only part of a book? For example, you might need to reference a chapter from a collection of essays . If so, you need to know how to cite an edited book.

In-Text Citations
When citing an edited book, you need to name the author of the chapter or section in question (not the editor of the book as a whole). As with any MLA citation , you should also give a page number:
One approach to art history is known as the ‘technological theory’ (Wollheim 527).
If the author is named in the text, just give the page number in brackets:
According to Richard Wollheim (527), art history mirrors technological advances in representation.
When quoting a source , moreover, the page numbers should come after the quoted passage (even if the author is named in the text):
Wollheim argues that we appreciate naturalistic art because it bears a ‘very lifelike’ (536) resemblance to a real object.
The only time you need to cite the editor of a book is when citing an edited book as a whole. But this is fairly unusual, so typically you’ll need to cite the author of the relevant chapter.
The ‘Works Cited’ Page
In the ‘Works Cited’ list , a chapter from an edited book is referenced as follows:
Surname, First name. ‘Title of Chapter’. Title of Collection , edited by Editor’s Name(s), Publisher, Year, Page range.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
The essay cited in the examples above, for instance, would be listed like this:
Wollheim, Richard. ‘Reflections on Art and Illusion’. Aesthetics: A Critical Anthology , edited by George Dickie, Richard Sclafani, and Ronald Roblin, St. Martin’s Press, 1989, pp. 525-543.
Cross-Referencing Chapters
Finally, MLA has special rules for referencing more than one essay from the same collection. In the ‘Works Cited’ list, you can cross-reference chapters with the container volume.
To do this, simply give one entry for the edited book, then list each chapter separately by referring to the book it comes from. To cite several chapters from Aesthetics: A Critical Anthology , for example, we’d list them like this:
Danto, Arthur. ‘The Artistic Enfranchisement of Real Objects: The Artworld’. Dickie, Sclafani, and Roblin, pp. 171-182.
Dickie, George, Richard Sclafani, and Ronald Roblin, editors. Aesthetics: A Critical Anthology . St. Martin’s Press, 1989.
Goodman, Nelson. ‘How Buildings Mean’. Dickie, Sclafani, and Roblin, pp. 544-555.
Wollheim, Richard. ‘Reflections on Art and Illusion’. Dickie, Sclafani, and Roblin, pp. 525-543.
As with any source in MLA referencing, chapters and edited books should be listed alphabetically by the surname of the first-listed editor/author in the entry.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Get help from a language expert. Try our proofreading services for free.
5-minute read
Free Email Newsletter Template (2024)
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
6-minute read
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- Back to AC Library Home
Library FAQs: Answer
- Library FAQs
- SLC FAQ Home
- 1 Accessibility Services
- 14 Articles & Journals
- 1 Audio-Visual Materials
- 25 Borrowing and Circulation
- 2 Catalogue
- 4 Community & Alumni
- 6 Contact Us
- 2 Copyright
- 28 Digital Resource Collections
- 5 Digital Resources Log In Problems
- 5 Faculty Services
- 3 Laptop Loans
- 9 Library Account/Card
- 1 Library Services
- 6 Off-campus access (online library resources)
- 2 Printing-Photocopying-Scanning
- 35 Research Help
- 28 Search Strategies
- 4 Study Space
- 19 Technical Help
- 33 Types of Digital Resources
- 23 Writing your paper
Anthologies in APA: Citing an anthology, compilation, or multi-authored textbook Last Updated: Aug 28, 2020 Views: 6117
Anthologies are collections of multiple works either by the same author or organized around the same theme. How you cite an anthology in the seventh edition of the American Psychological Association (APA) style depends on whether you are citing the entire anthology or a specific work within it.
An entire anthology/edited book
Treat the editor of the anthology as its author, i.e. Editor's Last Name, First Initials. (Eds.). (Year of Publication). Title of book. Publisher.
Example Citation
Potter, P. A., Perry, A. G., Kerr, J. C., & Wood, M. J. (Eds.). (2009). Canadian fundamentals of nursing. Mosby/Elsevier Canada.
A single work included in the anthology/edited book
Place the author of the work first, and include information about the editor of the anthology later in the citation, i.e. Author’s Last Name, First Initials. (Year of anthology’s publication). Title of work in anthology. In First Initial. Last Name of the anthology editor (Ed.), Title of anthology (page numbers). Publisher.
Blake, W. (1990). The Tyger. In R. Scholes, N. R. Comley, C. H. Klaus, & D. Staines (Eds.), Elements of literature (pp 487-488). Oxford University Press.
Pen and the Pad has a good explanation of these citations.
Related FAQs
Related topics.
- Writing your paper
Ask The Library
Need more help.
Do you need to talk to library staff? All campus libraries offer brief research consultation and search help during business hours. Contact us in one of the following ways and we will answer within 24 hours during the business work week:
By Online Form
By live chat.
- Monday to Friday: 9am - 5pm
By One-on-One Appointments
- Students: research support in the form of advice or assistance. Please have a copy of your assignment or research notes with you to share with the reference staff.
- Faculty: Curate resources for your online teaching from Library subscribed content. Learn how to use Open Educational Resources (OER) to find, share and adapt material for your online courses or receive guidance with copyright.
Book Your Appointment
Citing Special Collections materials in Chicago/Turabian style: Citing Primary Materials in Special Collections
Citing primary sources.
This guide contains the following sections (click to link directly to the section you need)
Citing Primary Sources - Overview
Citing manuscript collections in print and online, citing oral histories in special collections, citing maps, citing photographs, citing previously published magazine and newspaper articles found in manuscript collections.
This page includes citation examples for different kinds of primary sources using the Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) , 16th edition, and Kate Turabian's A Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations , 8th edition. This guide shows how to create an initial citation, a subsequent note, and a bibliography entry for primary sources.
Materials covered include:
- Manuscript & Document Collections
- Oral Histories
- Maps and Illustrations
- Photographs
- Digitized materials from our website
A word about "Preferred Citation" and "Citation" information in Special Collections' finding aids:
Nearly all Special Collections finding aids include basic citation information. Sometimes it's labeled "Preferred Citation," and other times it's labeled "Citation." This information typically includes the following information:
- the name of the collection (such as "Ernest A. Mills Family Collection")
- the name of the repository - D. H. Ramsey Library Special Collections
- the location of the repository - University of North Carolina at Asheville, Asheville, NC 28804
The other details needed for a citation (such as the name of the item, the author of the item, and the box and folder number) will emerge during your research.
If you have any questions about citing materials from Special Collections, ask one of the Special Collections staff or your professor .
From the finding aid for the Frank Coxe Papers:
Preferred Citation
[Identification of item],Frank Coxe Papers, D.H. Ramsey Library, Special Collections, University of North Carolina at Asheville 28804
From the finding aid for the Carolina Mountain Club Archives:
Carolina Mountain Club Archive , D.H. Ramsey Library, Special Collections, University of North Carolina at Asheville 28804.
Example 1: Citing a document from a manuscript collection
Look at the citation information from the Carolina Mountain Club finding aid above. This has basic information about the collection, repository, and location of repository that you will need for your citation, but you will also add more information as you conduct your research .
For instance, you might be working with the Carolina Mountain Club Archives, and you want to cite a specific document, the "Certificate of Incorporation of the Carolina Mountain Club" which is dated September 2, 1924. You found this document in Folder 19 in Box 15. There is a corporate author, the Carolina Mountain Club. (For more detailed information on citing manuscript collections, see the "Manuscript Collections" section of the Chicago Manual of Style , 16th edition, sections 14.232-14.242, pp. 749-752.)
So you have your document and you want to cite it. Now what? Let's take a look at how this would work:
Note (First mention, full reference):
1. Carolina Mountain Club , " Certificate of Incorporation of the Carolina Mountain Club," 2 September 1924, Box 15, Folder 19, Carolina Mountain Club Archives, D. H. Ramsey Library Special Collections, University of North Carolina at Asheville, Asheville, NC.
- Note that this is a full reference. The first line is indented.
- If the author is an individual, their name should be listed with the first name then last name (Frank Coxe).
- Sometimes you will not have an author. In this case, start the note with the name or title of the item.
- If the item has a specific title, as this one does, then that title is in quotation marks. If the item does not have a title but only a description it does not go in quotation marks.
- If the item does not have a date use the phrase n.d. (for no date)
- Use a comma after all the elments in the note and a period at the end of the note.
Note (Subsequent mentions, shortened reference):
7. Carolina Mountain Club , " Certificate of Incorporation."
- The shortened reference refers to a work that has already been cited in full form but not in a note immediately preceding it (which takes the ibid form ).
- The first line is indented, but the note only requires the author's name and the title of the document (which is sometimes shortened).
Bibliography:
- The first line is not indented, but the second line and all following lines are indented.
- Use a period after the collection name, after the repository name, and at the end of the bibliography entry.
- While the note included the item or document being cited, the bibliography does not include specific items -- unless only one item from a collection is cited. Then you would list the individual item in addition to the collection, repository, and repository location.
- For instance, if you cited two or more items from this collection, then you would use the bibliography entry as listed above.
- If you cited only one item from this collection then your bibliography entry would look like this:
Example 2: Citing a personal letter from a manuscript collection
Look at the citation information from the Frank Coxe Papers finding aid above. This has basic information about the collection, repository, and location of repository that you will need for your citation, but you will also add more information as you conduct your research .
Let's say you're working with the Frank Coxe Papers and you find a letter you want to cite. The letter is from A. B. Harris to Frank Coxe, and it was written on March 25, 1889. You found this letter in Folder 6 in Box 2. While this is similar to the Carolina Mountain Club example above it varies in how you cite the names of individuals and how you cite the actual letter.
1. A. B. Harris to Frank Coxe, 25 March 1889, Box 2, Folder 6, Frank Coxe Papers, D. H. Ramsey Library Special Collections, University of North Carolina at Asheville, Asheville, NC.
- Since the author is an individual rather than a corporate author, his name should be listed with the first name then last name (A.B. Harris). The same holds true for the recipient of the letter (Frank Coxe).
- Sometimes you will not have a date. In this case, use the phrase n.d.
- Use a comma after every element of the note and a period at the end of the note.
- After you’ve listed one full reference, any other footnote/endnote citing this specific source will use a shortened reference or ibid.
Note (Subsequent mentions, shortened reference):
7. A. B. Harris to Frank Coxe , 25 March 1889, Coxe Papers.
Bibliography:
Coxe, Frank., Papers . D. H. Ramsey Library Special Collections. University of North Carolina at Asheville, Asheville, NC.
- Because this collection contains the papers of an individual, the collection name is listed with the person's last name first, followed by a comma, then the first name, then a comma, then "Papers," then a period: Coxe, Frank., Papers .
- While the note cites an individual item or document, the bibliography entry does not list specific items -- unless only one item from a collection is cited . In that case the bibliography will include the individual item in addition to the collection, repository, and repository location.
- In other words, if you cited two or more items from the Frank Coxe Paper, then you would use the bibliography entry as listed above.
- If you cited only one item from the Frank Coxe Papers in your paper, then your bibliography entry would look like this:
Harris, A. B., and Frank Coxe. Letter of 25 March 1889. Frank Coxe Papers. D. H. Ramsey Library Special Collections. University of North Carolina at Asheville, Asheville, NC.
Example 3: Citing an online document from a manuscript collection
The Chicago Manual of Style states that "It should be noted that citations of collections consulted online... will usually be the same as citations of physical collections, aside from the addition of a URL or DOI." (14.232, p 749)
How does this work?
Let's say you are researching the building of the Battery Park Hotel and using the Frank Coxe Papers. You find this doucment in the Western North Carolina Heritage website (which is part of Special Collections at UNC Asheville): "Specificiations for Standard Hydraulic Passenger Elevator to be manufactured by Otis Brothers & Co." The document is dated February 24, 1886, and is a digitized document from the Frank Coxe Papers. The corporate author is Otis Brothers & Co. The URL is http://cdm15733.contentdm.oclc.org/cdm/ref/collection/p15733coll5/id/13.
Here's how you would cite this:
- Use a comma after every element in the note and a period at the end of the note.
7. Otis Brothers, Coxe Papers.
- It does not include the URL.
- Use a period after each element in the bibliography.
Special Collections contains over 600 Oral Histories. Often an oral history may have a tape recording or CD of the actual interview. Sometimes it may have a transcript of the interview as well.
In Chicago style, the kinds of oral histories we have in Special Collections are treated as unpublished interviews. (For more detailed information, see section 14.218-14.223 of the Chicago Manual of Style, 16th ed., pp 744-746)
Citing an oral history
Look at this oral history in Special Collections: Hugh Creasman Oral History. Looking at the information about the oral history, you'll note that the oral history is with Hugh Creasman, he was interviewed by Louis D. Sliveri on August 16, 1976, and that the oral history is part of the Louis D. Silveri Oral History Collection.
According to the Chicago Manual of Style, "unpublished interviews are best cited in text or in notes, although they may occasionally appear in bibliographies." (14.219, p. 744). Check with your professor about whether you should include a bibliography entry for an oral history. This example will show both a note and an bibliography entry.
| | |||
8. Hugh Creasman , interview by Louis Silveri, 16 August 1976, transcript, Louis Silveri Oral History Collection, Ramsey Library Special Collections, University of North Carolina at Asheville, Asheville, NC.
- Use commas after all elements and a period at the end of the note.
- Many oral histories are not part of a collection. If so, omit the collection part of the citation.
- There may either be a transcript or recording. Cite whichever you used.
Note (Subsequent Mentions):
Shortened reference:
10. Creasman, interview .
- The first line is indented, and the note only requires the interviewee's last name, the title of the article (sometimes shortened), and a specific page reference.
Bibliography (As noted above, check with your professor before making a biblography entry for an oral history. )
Creasman, Hugh . Interview by Louis Silveri. 16 August 1976 . T ranscript. Louis Silveri Oral History Collection. Ramsey Library Special Collections. University of North Carolina at Asheville, Asheville, NC.
- The first line is not indented, but the second line and all following lines are indented.
- The interviewee's last name is listed first, unlike the note, where it is First Name Last Name.
- Use periods after all parts of the bibliography (except the comma between "University of North Carolina at Asheville" and "Asheville, NC.")
Sometimes your research will involve using maps that you will need to cite. In terms of citations, the library has two different types of maps that require different different citations.
- One type of map is a published map , such as the topographical maps in the map case on the second floor.
- The second type are unpublished maps that are part of manuscript collections in Special Collections.
- This section will show you how to cite both published and unpublished maps.
Citing a published map
Suppose you are writing a paper about the history of the exploration of Mt. Mitchell and you are using a topographic map from the map case on the second floor of the library. You look at the map and note that it's a US Geological Survey map that was published by the Tennessee Valley Authority. Further inspection of the map shows the following information:
- U.S. Geological Survey (author - who created/authored the map)
- Mt. Mitchell Quadrangle, North Carolina, 200-SE (the title of the map)
- 1946 (the publication date)
- Scale 1:24,000
- Tennessee Valley Authority, Maps and Surveys Division, Knoxville, TN (the publisher and place)
The format for citing published maps and illustrations is the same (see Chicago Manual of Style,16th ed. , 14-165, p. 726)
| | ||||
1. U.S. Geological Survey, Mt. Mitchell Quadrangle, North Carolina [map], (Knoxville, TN: Tennessee Valley Authority, 1946)
- Use a comma after the author's name, a comma after the map title, and the format in brackets with a comma after it. The next section is in parentheses, and includes the place of publication followed by a colon, the publisher followed by a comma, and the publication date.
7. U.S. Geological Survey , Mt. Mitchell Quadrangle.
- Use period after all elements except the place of publication, which takes a colon between it and the publisher.
Citing a unpublished map from a manuscript collection
Special Collections contains hundreds of unpublished maps that can only be found in manuscript collections. Citing a map is like citing a document in a manuscript collection, and follows the same guidelines as above for "Citing a document in a manuscript collection." Here's an example:
For instance, you are using the Carolina Mountain Club Archives to research a paper about Linville Gorge. You find a hand-drawn map of a hike to Shortoff Mountain. While this map has no actual title written on it, it is important to describe the item so it can be easily identified. There is no date on it and you found it in Folder 9 in Box 8. There is a corporate author, the Carolina Mountain Club. Let's take a look at how this would work:
1. Carolina Mountain Club , Hiking map to Shortoff Mountain, n.d., Box 8, Folder 9, Carolina Mountain Club Archives, D. H. Ramsey Library Special Collections, University of North Carolina at Asheville, Asheville, NC.
- Because this is part of the Carolina Mountain Club archives and no specific author is noted on the map, use the "Carolina Mountan
- Note that because Hiking map to Shortoff Mountain is a description of the item rather than a title, is not in quotation marks. If the map actually had the title " Hiking map to Shortoff Mountain" on it, then you would put it in quotation marks as a title.
- The map does not have a date. In this case, use the phrase n.d.
- Use a comma after the author's name, a comma after the document title, and a comma after the date, a comma after the box and file number, a comma after the collection name, a comma after the repository name, and a period at the end of the note.
7. Carolina Mountain Club , Hiking map to Shortoff Mountain.
- Use a period after the collection name, after the respository name, and after the author's name, and at the end of the bibliography entry.
- While the note included the item or document being cited, the bibliography does not include specific items -- unless only one item from a collection is cited. Then you would list the individual item in addition to the collection, respository, and repository location. For instance, if you cited two or more items from the Carolina Mountain Club Archives, then you would use the bibliography entry as listed above. If you cited only the one document listed in the bibliography above and no more documents, then your bibliograhy entry would look like this:
Photographs are a bit different in Chicago/Turabian style because they are cited in notes only and not in the bibliography.
You will need to use the following elements in your citation (Turabian, 8th ed., 17.8.1.1)
- Name of the photographer (if known)
- Title of the photograph in italics
- Date of photograph (preceded by ca. [ circa ] in italics if approximate, or n.d. if unknown)
- Name of the repository that houses the photograph
How to cite a photograph
| | |||
Suppose you are researching the history of Tryon, NC. You find a photograph of a Catholic Church in Tryon, NC, in the R. Henry Scadin Collection that you want to use in your paper. You find this information about the photograph:
The photographer is R. Henry Scadin, and the photograph is labeled "Catholic Church, Tryon, NC," it's photograph number 958, and it's in Box 33. There is no date on the photograph. Here's how you would do the citation:
- The title and photograph number are in italics. If it does not have a title, use "untitled" and describe the photograph in your narrative.
- The photograph does not have a date. In this case, use the phrase n.d.
- Use a comma after the photographer's name, a comma after the photograph title, a comma after the date, a comma after the box and file number, a comma after the collection name, a comma after the repository name, and a period at the end of the note.
7. R. Henry Scadin, Catholic Church.
- The first line is indented, but the note only requires the photographer's name and the title of the photograph (which is sometimes shortened).
There is no bibliography entry for a photograph.
How to cite a photograph in an online collection
Citing a photograph from an online, digitized collection is the same as citing a regular photograph, with the addition of adding the URL and an access date.
| | |||
- Name of the online collection
- Date accessed
You are writing a paper about Asheville in the early 20th century, and you want to use a photograph of President Theodore Roosevelt when he spoke at Pack Square in 1902. You find a photograph of Roosevelt's talk in the Western North Carolina Heritage website, and you have this information:
The photographer is H. W. Pelton, the photograph is titled "Pack Square Crowds greet President Theodore Roosevelt." It's from the E. M. Ball Collection. The date is 1902, and the URL is http://cdm15733.contentdm.oclc.org/cdm/ref/collection/Photographs/id/639. You accessed it on November 5, 2014.
4. H. W. Pelton, Pack Square Crowds Greet President Theodore Roosevelt , 1902, E. M. Ball Collection, accessed November 5, 2014, http://cdm15733.contentdm.oclc.org/cdm/ref/collection/Photographs/id/639
- The photograph title is in italics. If it does not have a title, use "untitled" and describe the photograph in your narrative.
- Use a comma after the photographer's name, a comma after the photograph title, a comma after the date, a comma after the accession date, and a period at the end of the note.
Sometimes you will find newspaper clippings, magazine articles, or academic journal articles in a manuscript collection. How do you cite these? When citing a newspaper, magazine, or journal in a manuscript collection, it's good to also provide information about the article, such as the title of the article, the name of the newspaper, the author of the article, and the date it was published. Sometime you might not have all this information, especially if the article was clipped out of the newspaper, but you can use what information you do have to describe the article as completely as possible. Let's take a look at a few examples of how this would work.
Example 1: Citing a newspaper article or clipping from a manuscript collection
Look at the citation information from the Carolina Mountain Club Archives finding aid above. This has basic information about the collection, repository, and location of repository that you will need for your citation, but you will also add more information about the newspaper article.
Let's say you're working with the Carolina Mountain Club Archives and you find a newspaper article that you need for your research. You find an article that you want to cite, and you are able to identify a lot of information about it. The article is "Are Dogwoods Doomed?" by Clarke Morrison. It was published in The Asheville Citizen on September 14, 1990. It was in Box 9, Folder 3 of the Carolina Mountain Club Archives. To cite this, what you end up doing is using the citation style for a newspaper article and adding it to the manuscript citation - thereby providing information about both the original article and the manuscript collection where you found it.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Clarke Morrison , "Are Dogwoods Doomed?," The Asheville Citizen , September 14, 1990, Box 9, Folder 3, Carolina Mountain Club Archives , D. H. Ramsey Library Special Collections, University of North Carolina at Asheville, Asheville, NC.
- Note that this describes the information about the newspaper article, then describes the collection information.
7. Morrison , "Dogwoods," Carolina Mountain Club Archives .
Carolina Mountain Club Archives. D. H. Ramsey Library Special Collections. University of North Carolina at Asheville, Asheville, NC.
- In other words, if you cited two or more items from the Carolina Mountain Club Archives, then you would use the bibliography entry as listed above.
- If you cited only one item from the Carolina Mountain Club Archives in your paper, then your bibliography entry would look like this:
Morrison, Clarke . "Are Dogwoods Doomed? . " The Asheville Citizen. September 14, 1990. Carolina Mountain Club Archives. D. H. Ramsey Library Special Collections. University of North Carolina at Asheville, Asheville, NC.
Example 2: Citing a newspaper article with missing information
Sometimes you will find a newspaper or magazine article that has been clipped from the original paper or magazine. All you have is an article - you don't have the author, publication date, or even what newspaper published the article. If you add no information at all the reader may wonder who wrote the article, what paper it was in, and when it was published. However, Chicago style allows for comments in footnotes and endnotes (CMOS, 14.32) that you can use to explain this, and the commentary is inserted at the end of the note.
Let's assume you're working with the Carlina Mountain Club Archives. You find a clipping of a newspaper article titled "Hiking the Appalachian Trail" in Box 9, Folder 3, but it does not list an author or publication date, and you can't tell what paper it was published in. Your citation would look like this:
Note (First mention, full reference) :
1. "Hiking the Appalachian Trail," Box 9, Folder 3, Carolina Mountain Club Archives, D. H. Ramsey Library Special Collections, University of North Carolina at Asheville, Asheville, NC. Newspaper clipping missing author, publication date, and name of newspaper.
- Note that this describes the information about the newspaper article, then describes the collection information. The additional phrase at the end clarifies why the information about the artilce is incomplete.
- Use a comma after every element of the note and a period after the repository location. Use a period after the commentary phrase.
7 . " Hiking the Appalachian Trail," Carolina Mountain Club Archives.
Bibliography:
Carolina Mountain Club Archives. D. H. Ramsey Library Special Collections. University of North Carolina at Asheville, Asheville, NC .
- If you cited only one item from the Carolina Mountain Club Archives in your paper, then your bibliography entry would look like this:
"Hiking the Appalachian Trail." Carolina Mountain Club Archives. D. H. Ramsey Library Special Collections. University of North Carolina at Asheville, Asheville, NC
Head of Special Collections & University Archivist

- Last Updated: Apr 19, 2023 10:44 AM
- URL: https://library.unca.edu/CMOSSpecialCollections
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Citing sources
How to Cite Sources | Citation Generator & Quick Guide
Citing your sources is essential in academic writing . Whenever you quote or paraphrase a source (such as a book, article, or webpage), you have to include a citation crediting the original author.
Failing to properly cite your sources counts as plagiarism , since you’re presenting someone else’s ideas as if they were your own.
The most commonly used citation styles are APA and MLA. The free Scribbr Citation Generator is the quickest way to cite sources in these styles. Simply enter the URL, DOI, or title, and we’ll generate an accurate, correctly formatted citation.
Generate accurate citations with Scribbr
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text.
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When do you need to cite sources, which citation style should you use, in-text citations, reference lists and bibliographies.
Scribbr Citation Generator
Other useful citation tools
Citation examples and full guides, frequently asked questions about citing sources.
Citations are required in all types of academic texts. They are needed for several reasons:
- To avoid plagiarism by indicating when you’re taking information from another source
- To give proper credit to the author of that source
- To allow the reader to consult your sources for themselves
A citation is needed whenever you integrate a source into your writing. This usually means quoting or paraphrasing:
- To quote a source , copy a short piece of text word for word and put it inside quotation marks .
- To paraphrase a source , put the text into your own words. It’s important that the paraphrase is not too close to the original wording. You can use the paraphrasing tool if you don’t want to do this manually.
Citations are needed whether you quote or paraphrase, and whatever type of source you use. As well as citing scholarly sources like books and journal articles, don’t forget to include citations for any other sources you use for ideas, examples, or evidence. That includes websites, YouTube videos , and lectures .
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Usually, your institution (or the journal you’re submitting to) will require you to follow a specific citation style, so check your guidelines or ask your instructor.
In some cases, you may have to choose a citation style for yourself. Make sure to pick one style and use it consistently:
- APA Style is widely used in the social sciences and beyond.
- MLA style is common in the humanities.
- Chicago notes and bibliography , common in the humanities
- Chicago author-date , used in the (social) sciences
- There are many other citation styles for different disciplines.
If in doubt, check with your instructor or read other papers from your field of study to see what style they follow.
In most styles, your citations consist of:
- Brief in-text citations at the relevant points in the text
- A reference list or bibliography containing full information on all the sources you’ve cited
In-text citations most commonly take the form of parenthetical citations featuring the last name of the source’s author and its year of publication (aka author-date citations).
An alternative to this type of in-text citation is the system used in numerical citation styles , where a number is inserted into the text, corresponding to an entry in a numbered reference list.
There are also note citation styles , where you place your citations in either footnotes or endnotes . Since they’re not embedded in the text itself, these citations can provide more detail and sometimes aren’t accompanied by a full reference list or bibliography.
| (London: John Murray, 1859), 510. |
A reference list (aka “Bibliography” or “Works Cited,” depending on the style) is where you provide full information on each of the sources you’ve cited in the text. It appears at the end of your paper, usually with a hanging indent applied to each entry.
The information included in reference entries is broadly similar, whatever citation style you’re using. For each source, you’ll typically include the:
- Author name
- Publication date
- Container (e.g., the book an essay was published in, the journal an article appeared in)
- Location (e.g., a URL or DOI , or sometimes a physical location)
The exact information included varies depending on the source type and the citation style. The order in which the information appears, and how you format it (e.g., capitalization, use of italics) also varies.
Most commonly, the entries in your reference list are alphabetized by author name. This allows the reader to easily find the relevant entry based on the author name in your in-text citation.
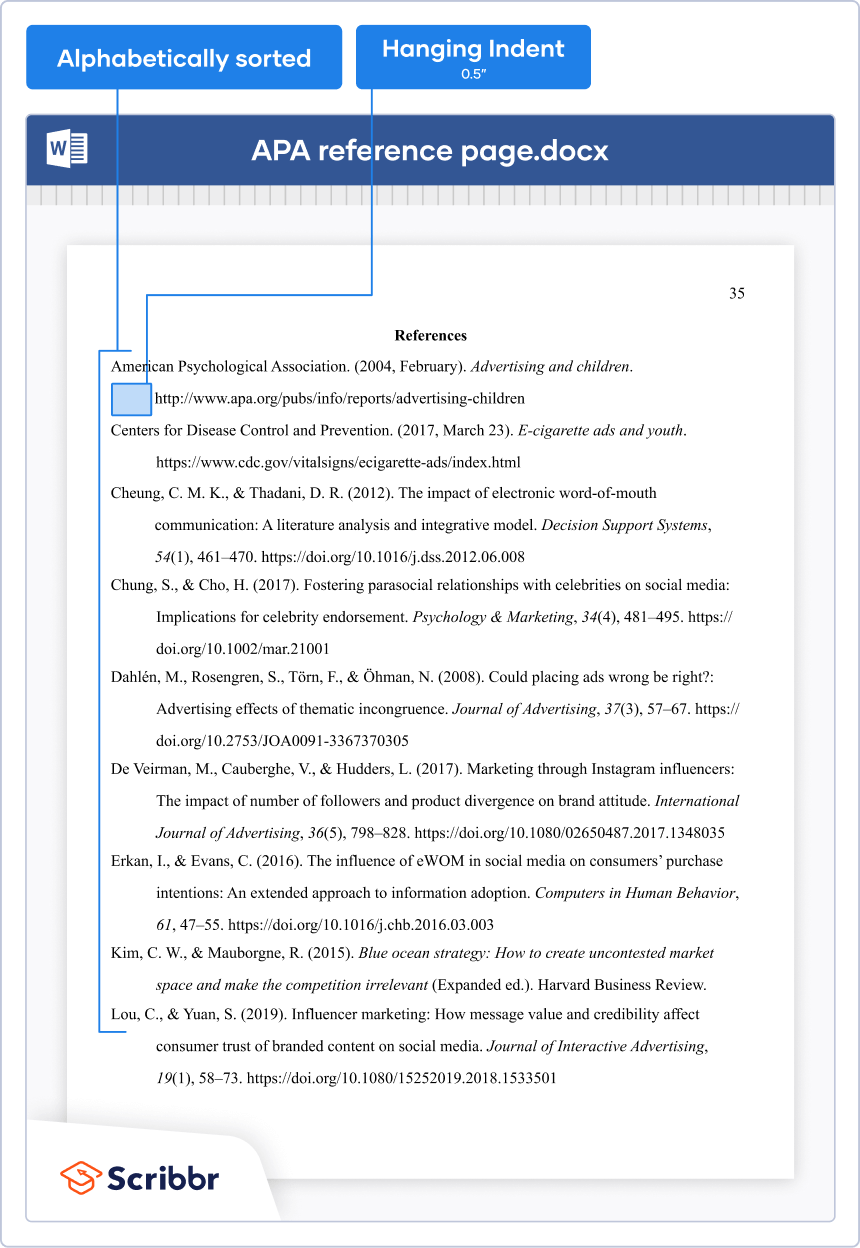
In numerical citation styles, the entries in your reference list are numbered, usually based on the order in which you cite them. The reader finds the right entry based on the number that appears in the text.
Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
Because each style has many small differences regarding things like italicization, capitalization , and punctuation , it can be difficult to get every detail right. Using a citation generator can save you a lot of time and effort.
Scribbr offers citation generators for both APA and MLA style. Both are quick, easy to use, and 100% free, with no ads and no registration required.
Just input a URL or DOI or add the source details manually, and the generator will automatically produce an in-text citation and reference entry in the correct format. You can save your reference list as you go and download it when you’re done, and even add annotations for an annotated bibliography .
Once you’ve prepared your citations, you might still be unsure if they’re correct and if you’ve used them appropriately in your text. This is where Scribbr’s other citation tools and services may come in handy:
Plagiarism Checker
Citation Checker
Citation Editing
Plagiarism means passing off someone else’s words or ideas as your own. It’s a serious offense in academia. Universities use plagiarism checking software to scan your paper and identify any similarities to other texts.
When you’re dealing with a lot of sources, it’s easy to make mistakes that could constitute accidental plagiarism. For example, you might forget to add a citation after a quote, or paraphrase a source in a way that’s too close to the original text.
Using a plagiarism checker yourself before you submit your work can help you spot these mistakes before they get you in trouble. Based on the results, you can add any missing citations and rephrase your text where necessary.
Try out the Scribbr Plagiarism Checker for free, or check out our detailed comparison of the best plagiarism checkers available online.
Scribbr Plagiarism Checker
Scribbr’s Citation Checker is a unique AI-powered tool that automatically detects stylistic errors and inconsistencies in your in-text citations. It also suggests a correction for every mistake.
Currently available for APA Style, this is the fastest and easiest way to make sure you’ve formatted your citations correctly. You can try out the tool for free below.
If you need extra help with your reference list, we also offer a more in-depth Citation Editing Service.
Our experts cross-check your in-text citations and reference entries, make sure you’ve included the correct information for each source, and improve the formatting of your reference page.
If you want to handle your citations yourself, Scribbr’s free Knowledge Base provides clear, accurate guidance on every aspect of citation. You can see citation examples for a variety of common source types below:
And you can check out our comprehensive guides to the most popular citation styles:
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
The abbreviation “ et al. ” (Latin for “and others”) is used to shorten citations of sources with multiple authors.
“Et al.” is used in APA in-text citations of sources with 3+ authors, e.g. (Smith et al., 2019). It is not used in APA reference entries .
Use “et al.” for 3+ authors in MLA in-text citations and Works Cited entries.
Use “et al.” for 4+ authors in a Chicago in-text citation , and for 10+ authors in a Chicago bibliography entry.
The Scribbr Citation Generator is developed using the open-source Citation Style Language (CSL) project and Frank Bennett’s citeproc-js . It’s the same technology used by dozens of other popular citation tools, including Mendeley and Zotero.
You can find all the citation styles and locales used in the Scribbr Citation Generator in our publicly accessible repository on Github .
APA format is widely used by professionals, researchers, and students in the social and behavioral sciences, including fields like education, psychology, and business.
Be sure to check the guidelines of your university or the journal you want to be published in to double-check which style you should be using.
MLA Style is the second most used citation style (after APA ). It is mainly used by students and researchers in humanities fields such as literature, languages, and philosophy.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- Citation Styles Guide | Examples for All Major Styles
- APA vs. MLA | The Key Differences in Format & Citation
- The Basics of In-Text Citation | APA & MLA Examples
More interesting articles
- Citation examples for common sources types
- Et Al. | Meaning & Use in APA, MLA & Chicago
- Hanging Indent | Word & Google Docs Instructions
- How to Cite a Book | APA, MLA, & Chicago Examples
- How to Cite a Journal Article | APA, MLA, & Chicago Examples
- How to Cite a Lecture | APA, MLA & Chicago Examples
- How to Cite a Newspaper Article | MLA, APA & Chicago
- How to Cite a Website | MLA, APA & Chicago Examples
- How to Cite a Wikipedia Article | APA, MLA & Chicago
- How to Cite a YouTube Video | MLA, APA & Chicago
- How to Cite an Image | Photographs, Figures, Diagrams
- How to Cite an Interview | APA, MLA & Chicago Style
- Parenthetical Citation | APA, MLA & Chicago Examples
- What Are Endnotes? | Guide with Examples
- What Are Footnotes? | Guide with Word Instructions
- What Does Ibid. Mean? | Definition & Examples
- What is a DOI? | Finding and Using Digital Object Identifiers
- What Is an Annotated Bibliography? | Examples & Format
Scribbr APA Citation Checker
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!


- RRU Writing Centre
- WriteAnswers
Q. How do I cite and reference a work from an anthology or an edited collection of works?
- 3 Academic Integrity
- 48 Academic writing
- 42 APA Style
- 33 APA Style: Formatting
- 109 APA Style: In-text citations
- 107 APA Style: References
- 3 Generative AI
- 19 Legal citations
- 16 Paraphrasing
- 10 Punctuation
- 25 Quotations
- 17 Writing Centre information
- 65 Writing Centre resources
Answered By: Jonathan Faerber (he/him/his) Last Updated: Nov 02, 2021 Views: 25935
APA Style (7th ed.)
Since each work in an anthology or an edited collection is typically written and published as a single resource, cite and reference the individual work you read rather than the entire anthology or collection. For example, instead of citing and referencing the editors of the following collection (Milkoreit, Martinez, and Eschrich), an individual work in the collection is cited and referenced as follows:
- Narrative citation : Davenport (2016) writes that "quoted text" (p. 108).
- Parenthetical citation : (Davenport, 2016. p. 108)
- Reference entry : Davenport, S. (2016). Masks. In M. Milkoreit, M. Martinez, and J. Eschrich (Eds.) Everything change: An anthology of climate fiction (pp. 107-126). Arizona State University. https://www.kobo.com/ca/en/ebook/everything-change-an-anthology-of-climate-fiction
Include the original publication date at the end of the reference entry and within in-text citations when applicable. See the following example for the format of republished work in a printed anthology or collection:
- In-text citation : (Author, 1989/2019)
- Reference entry : Author, A. (2019). Title of original work. In E. Editor (Ed.). Title of anthology or collection in sentence case and italics (pp. xx-xxx). Publisher. (Original work published 1989).
Please see How do I reference a chapter of a book in APA Style? and How do I cite or reference non-English or translated sources in APA Style? for similar information as well as examples of non-English works that have been republished in English.
- Share on Facebook
Was this helpful? Yes 0 No 0

Citing part of collection of essays.
- adamsmith December 11, 2018 No there isn't -- it's not clear how this would be conceptualized (and it's quite rare). It's also not commonly done nor particularly necessary for citation practices. The Webster essay is widely cited just by its title, without referring to the entire collection; I'd recommend doing that. If you use a citation style without quotation markes, you can in principle add both title and essay collection title in the title field, but as soon as the style adds quotation marks, those will also include the "in" which you presumably don't want.
- alexhem December 11, 2018 Thank you for the feedback @adamsmith - I'll just cite Webster's title. It should be sufficient. A
Upload image file with the file dialog or by dragging and dropping images onto the dashed region
- Essay Editor
10 Practical Ways to Improve Your Essay Writing Skills

What makes a great essay stand out from an average one? It's all about finding the right mix between what you say and how you say it. Even the best ideas can fall flat if they're not written well. At the same time, good writing can't make up for weak content.
A really good essay needs to do many things at once. It should teach the reader something new and keep them interested. It should also be fun to read. On top of that, it needs to have perfect grammar, sentence structure, and punctuation. If you're having trouble getting the grades you want and don't know why, this article will show you ten ways to improve your essay writing skills. We'll also touch on a tool that can make writing essays easier and more enjoyable.
1. Read Often
To get better at writing essays, it's important to read lots of different types of writing. Try reading different kinds of books and articles to learn new words and ideas. Pay special attention to published essays and academic journals. These can show you how good writers make their points and keep their ideas flowing smoothly.
For example, if you're writing about climate change, don't just read science papers. Read opinion pieces, stories about environmental movements from the past, and even stories that talk about nature and how people affect it. This will help you improve your essays by giving you a bigger picture of the topic.
2. Understand Your Essay Topic
Before you start writing, take time to really understand what your essay is supposed to be about. Read the instructions carefully and gather information. Don't rush this part. Instead, take your time to build a strong base for your arguments. Look at different viewpoints to make sure your main idea is correct and well-thought-out. This step is very important if you want to improve your essay and do high-quality work.
3. Create a Solid Essay Structure
Even the best writers start with an outline. Making a plan is really important for organizing your thoughts and making sure your essay makes sense from start to finish. As you research more, your topic might change in ways you didn't expect. A flexible outline can help you manage these new ideas and fit them into your essay in a way that makes sense.
You could try using the basic five-paragraph essay structure to start:
- Introduction (with your main idea)
- First main point
- Second main point
- Third main point
But don't feel like you have to stick to this exactly. As you improve your essay writing skills, you can try different structures that fit your topic and argument better.
4. Polish Your Writing Fundamentals
Knowing how to correctly use grammar, sentence structure, and punctuation is important for writing a good essay. A few small mistakes might not hurt your grade too much, but lots of mistakes can make your reader think less of your work.
Tools like the Aithor essay writer can improve your essays, but learning these rules yourself will help you use these tools better and improve your essay writing skills in the long run.
5. Write a Compelling Introduction
The introduction sets the mood for your whole essay and is your chance to get the reader interested. A good intro should start with something that grabs attention, like an interesting fact or question that leads into your main idea.
For example, instead of starting with a boring sentence like "This essay will talk about what caused the French Revolution", you could start with something more interesting: "What if a loaf of bread costs as much as you make in a week? For many French people in 1789, this was real life, and it helped start a revolution." This way of starting can really improve your essay's impact from the beginning.
6. Use Active Voice in Your Writing
Most of the time, using active voice makes your writing easier to read and more interesting. It keeps readers engaged and makes your points clearer. Look at these two sentences:
Passive: "The experiment was conducted by the scientist."
Active: "The scientist conducted the experiment."
The active voice clearly shows who is doing the action, making your writing stronger and easier to understand. But sometimes, passive voice is okay, like in science writing or when we don't know or don't need to say who did the action. As you improve your essays, you'll learn when to use each type of voice to make your writing better.
7. Don't Repeat Things
It's important not to use the same words or ideas over and over in your essay. Try to use different words and sentence types to keep your reader interested and make your writing sound nice.
Instead of always saying "In conclusion" or "Furthermore", try using words like "Moreover", "Additionally", or "Given these facts". Using different words not only makes your essay flow better but also shows you know how to use language well, helping you improve your essay writing skills.
8. Seek Constructive Criticism
One of the best ways to improve your essay is by asking others what they think. Your teacher's comments are very important, but getting feedback before you turn in your final essay is also good. Classmates, tutors, or people at the writing center can give you new ideas about your work.
When you get feedback, try not to feel bad about criticism. Instead, think of it as a chance to make your writing better. Ask specific questions about things you're not sure about, like whether your argument is strong or if your explanations are clear.
9. Use Your Sources Correctly
When you mention information from other places, make sure you're using the right format that your teacher asked for (like APA, MLA, or Chicago). Using sources correctly not only avoids copying others' work without permission but also makes your arguments stronger by showing you've read reliable information. Paying attention to these details is a key part of how to improve your essays.
10. Edit and Refine Your Work
The best way to improve essays is by carefully checking and fixing them. Try to finish your first draft well before it's due so you can let it sit for a while. When you come back to it with fresh eyes, you'll often see ways to make it better that you didn't notice before.
Try reading your essay out loud during this process. This can help you find awkward phrases or parts that repeat too much that you might not notice when reading silently. Tools like the Aithor essay writer can also help you make your essay better.
Key Takeaways to Improve Essays
Improving your essay writing skills takes time and practice. By using these tips, you'll be on your way to writing better, more convincing, and more interesting essays. Remember, the goal isn't to be perfect, but to keep getting better.
If you want more help on how to improve your essay, think about using tools like the Aithor essay writer . It can give you guidance and suggestions as you work on your essays, helping you improve your essay writing skills over time.
Related articles
Can plagiarism be detected on pdf.
Plagiarism has been a challenge for a long time in writing. It's easy to find information online, which might make some people use it without saying where it came from. But plagiarism isn't just taking someone else's words. Sometimes, we might do it by accident or even use our own old work without mentioning it. When people plagiarize, they can get into serious trouble. They might lose others' trust or even face legal problems. Luckily, we now have tools to detect plagiarism. But what about PDF ...
Plagiarism: 7 Types in Detail
Your professor says that it is necessary to avoid plagiarism when writing a research paper, essay, or any project based on the works of other people, so to say, any reference source. But what does plagiarism mean? What types of it exist? And how to formulate the material to get rid of potential bad consequences while rendering original texts? Today we try to answer these very questions. Plagiarism: Aspect in Brief Plagiarism is considered to be a serious breach, able to spoil your successful ...
How To Write Essays Faster Using AI?
Creating various topical texts is an obligatory assignment during studies. For a majority of students, it seems like a real headache. It is quite difficult to write a smooth and complex work, meeting all the professors' requirements. However, thanks to modern technologies there appeared a good way of getting a decent project – using AI to write essays. We'd like to acquaint you with Aithor, an effective tool of this kind, able to perform fine and elaborated texts, and, of course, inspiration, i ...
How to Write a Dialogue in an Essay: Useful Tips
A correct usage of dialogues in essays may seem quite difficult at first sight. Still there are special issues, for instance, narrative or descriptive papers, where this literary technique will be a good helper in depicting anyone's character. How to add dialogues to the work? How to format them correctly? Let's discuss all relevant matters to master putting conversation episodes into academic essays. Essay Dialogue: Definition & Purpose A dialogue is a literary technique for presenting a con ...
What is Citation and Why Should You Cite the Sources When Writing Content
When we write something for school, work, or just for fun, we often use ideas and facts from other places. This makes us ask: what is a citation in writing? Let's find out what this means and why it's really important when we write. What is Citation? Citation in research refers to the practice of telling your readers where you got your information, ideas, or exact words from. It's like showing them the path to the original information you used in your writing. When you cite something, you us ...
Paraphrasing vs Plagiarism: Do They Really Differ?
Academic assignments require much knowledge and skill. One of the most important points is rendering and interpreting material one has ever studied. A person should avoid presenting word-for-word plagiarism but express his or her thoughts and ideas as much as possible. However, every fine research is certain to be based on the previous issues, data given, or concepts suggested. And here it's high time to differentiate plagiarism and paraphrasing, to realize its peculiarities and cases of usage. ...
Top 10 Use Cases for AI Writers
Writing is changing a lot because of AI. But don't worry — AI won't take human writers' jobs. It's a tool that can make our work easier and help us write better. When we use AI along with our own skills, we can create good content faster and better. AI can help with many parts of writing, from coming up with ideas to fixing the final version. Let's look at the top 10 ways how to use AI for content creation and how it can make your writing better. What Is AI Content Writing? AI content writin ...
What Is Self-Plagiarism & How To Avoid It
Have you ever thought about whether using your own work again could be seen as copying? It might seem strange, but self-plagiarism is a real issue in school and work writing. Let's look at what this means and learn how to avoid self-plagiarism so your work stays original and ethical. What is self-plagiarism? Self-plagiarism, also called auto-plagiarism or duplicate plagiarism, happens when a writer uses parts of their old work without saying where it came from. This isn't just about copying w ...
Skip to Content
Other ways to search:
- Events Calendar
Want to write a college essay that sets you apart? Three tips to give you a head start

1. Keep it real. It’s normal to want to make a good impression on the school of your choice, but it’s also important to show who you really are. So just be yourself! Compelling stories might not be perfectly linear or have a happy ending, and that’s OK. It’s best to be authentic instead of telling schools what you think they want to hear.
2. Be reflective . Think about how you’ve changed during high school. How have you grown and improved? What makes you feel ready for college, and how do you hope to contribute to the campus community and society at large?
3. Look to the future. Consider your reasons for attending college. What do you hope to gain from your education? What about college excites you the most, and what would you like to do after you graduate? Answering these questions will not only give colleges insight into the kind of student you’ll be, but it will also give you the personal insight you’ll need to choose the school that’s right for you.
Have questions about college prep? We're here to help.
Written by CU Boulder Office of Admissions
- College-Prep
The University of Colorado does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, sex, age, pregnancy, disability, creed, religion, sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression, veteran status, political affiliation, or political philosophy. All qualified individuals are encouraged to apply. You may view the list of ADA and Title IX coordinators and review the Regent policy .
As a student or prospective student at CU Boulder, you have a right to certain information pertaining to financial aid programs, the Clery Act, crime and safety, graduation rates, athletics and other general information such as the costs associated with attending CU Boulder. To view this information visit colorado.edu/your-right-know .
Apply for Admission
Visit Campus
Support CU Boulder
- Safety & Health Services
- COVID-19 Information
- Campus Communications
- Emergency Alert System
- New Student & Family Programs
Getting Around
- Campus Events
- Parking & Transportation
- Visit Information
Information for
- Faculty & Staff
- Journalists
Initiatives
- Business & Industry Collaborations
- Diversity, Equity & Inclusion
- Free Speech
- Innovation & Entrepreneurship
- Public & Outreach Programs
- Sustainability
- Understanding Your Cost of Attendance

How to cite ChatGPT

Use discount code STYLEBLOG15 for 15% off APA Style print products with free shipping in the United States.
We, the APA Style team, are not robots. We can all pass a CAPTCHA test , and we know our roles in a Turing test . And, like so many nonrobot human beings this year, we’ve spent a fair amount of time reading, learning, and thinking about issues related to large language models, artificial intelligence (AI), AI-generated text, and specifically ChatGPT . We’ve also been gathering opinions and feedback about the use and citation of ChatGPT. Thank you to everyone who has contributed and shared ideas, opinions, research, and feedback.
In this post, I discuss situations where students and researchers use ChatGPT to create text and to facilitate their research, not to write the full text of their paper or manuscript. We know instructors have differing opinions about how or even whether students should use ChatGPT, and we’ll be continuing to collect feedback about instructor and student questions. As always, defer to instructor guidelines when writing student papers. For more about guidelines and policies about student and author use of ChatGPT, see the last section of this post.
Quoting or reproducing the text created by ChatGPT in your paper
If you’ve used ChatGPT or other AI tools in your research, describe how you used the tool in your Method section or in a comparable section of your paper. For literature reviews or other types of essays or response or reaction papers, you might describe how you used the tool in your introduction. In your text, provide the prompt you used and then any portion of the relevant text that was generated in response.
Unfortunately, the results of a ChatGPT “chat” are not retrievable by other readers, and although nonretrievable data or quotations in APA Style papers are usually cited as personal communications , with ChatGPT-generated text there is no person communicating. Quoting ChatGPT’s text from a chat session is therefore more like sharing an algorithm’s output; thus, credit the author of the algorithm with a reference list entry and the corresponding in-text citation.
When prompted with “Is the left brain right brain divide real or a metaphor?” the ChatGPT-generated text indicated that although the two brain hemispheres are somewhat specialized, “the notation that people can be characterized as ‘left-brained’ or ‘right-brained’ is considered to be an oversimplification and a popular myth” (OpenAI, 2023).
OpenAI. (2023). ChatGPT (Mar 14 version) [Large language model]. https://chat.openai.com/chat
You may also put the full text of long responses from ChatGPT in an appendix of your paper or in online supplemental materials, so readers have access to the exact text that was generated. It is particularly important to document the exact text created because ChatGPT will generate a unique response in each chat session, even if given the same prompt. If you create appendices or supplemental materials, remember that each should be called out at least once in the body of your APA Style paper.
When given a follow-up prompt of “What is a more accurate representation?” the ChatGPT-generated text indicated that “different brain regions work together to support various cognitive processes” and “the functional specialization of different regions can change in response to experience and environmental factors” (OpenAI, 2023; see Appendix A for the full transcript).
Creating a reference to ChatGPT or other AI models and software
The in-text citations and references above are adapted from the reference template for software in Section 10.10 of the Publication Manual (American Psychological Association, 2020, Chapter 10). Although here we focus on ChatGPT, because these guidelines are based on the software template, they can be adapted to note the use of other large language models (e.g., Bard), algorithms, and similar software.
The reference and in-text citations for ChatGPT are formatted as follows:
- Parenthetical citation: (OpenAI, 2023)
- Narrative citation: OpenAI (2023)
Let’s break that reference down and look at the four elements (author, date, title, and source):
Author: The author of the model is OpenAI.
Date: The date is the year of the version you used. Following the template in Section 10.10, you need to include only the year, not the exact date. The version number provides the specific date information a reader might need.
Title: The name of the model is “ChatGPT,” so that serves as the title and is italicized in your reference, as shown in the template. Although OpenAI labels unique iterations (i.e., ChatGPT-3, ChatGPT-4), they are using “ChatGPT” as the general name of the model, with updates identified with version numbers.
The version number is included after the title in parentheses. The format for the version number in ChatGPT references includes the date because that is how OpenAI is labeling the versions. Different large language models or software might use different version numbering; use the version number in the format the author or publisher provides, which may be a numbering system (e.g., Version 2.0) or other methods.
Bracketed text is used in references for additional descriptions when they are needed to help a reader understand what’s being cited. References for a number of common sources, such as journal articles and books, do not include bracketed descriptions, but things outside of the typical peer-reviewed system often do. In the case of a reference for ChatGPT, provide the descriptor “Large language model” in square brackets. OpenAI describes ChatGPT-4 as a “large multimodal model,” so that description may be provided instead if you are using ChatGPT-4. Later versions and software or models from other companies may need different descriptions, based on how the publishers describe the model. The goal of the bracketed text is to briefly describe the kind of model to your reader.
Source: When the publisher name and the author name are the same, do not repeat the publisher name in the source element of the reference, and move directly to the URL. This is the case for ChatGPT. The URL for ChatGPT is https://chat.openai.com/chat . For other models or products for which you may create a reference, use the URL that links as directly as possible to the source (i.e., the page where you can access the model, not the publisher’s homepage).
Other questions about citing ChatGPT
You may have noticed the confidence with which ChatGPT described the ideas of brain lateralization and how the brain operates, without citing any sources. I asked for a list of sources to support those claims and ChatGPT provided five references—four of which I was able to find online. The fifth does not seem to be a real article; the digital object identifier given for that reference belongs to a different article, and I was not able to find any article with the authors, date, title, and source details that ChatGPT provided. Authors using ChatGPT or similar AI tools for research should consider making this scrutiny of the primary sources a standard process. If the sources are real, accurate, and relevant, it may be better to read those original sources to learn from that research and paraphrase or quote from those articles, as applicable, than to use the model’s interpretation of them.
We’ve also received a number of other questions about ChatGPT. Should students be allowed to use it? What guidelines should instructors create for students using AI? Does using AI-generated text constitute plagiarism? Should authors who use ChatGPT credit ChatGPT or OpenAI in their byline? What are the copyright implications ?
On these questions, researchers, editors, instructors, and others are actively debating and creating parameters and guidelines. Many of you have sent us feedback, and we encourage you to continue to do so in the comments below. We will also study the policies and procedures being established by instructors, publishers, and academic institutions, with a goal of creating guidelines that reflect the many real-world applications of AI-generated text.
For questions about manuscript byline credit, plagiarism, and related ChatGPT and AI topics, the APA Style team is seeking the recommendations of APA Journals editors. APA Style guidelines based on those recommendations will be posted on this blog and on the APA Style site later this year.
Update: APA Journals has published policies on the use of generative AI in scholarly materials .
We, the APA Style team humans, appreciate your patience as we navigate these unique challenges and new ways of thinking about how authors, researchers, and students learn, write, and work with new technologies.
American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). https://doi.org/10.1037/0000165-000
Related and recent
Comments are disabled due to your privacy settings. To re-enable, please adjust your cookie preferences.
APA Style Monthly
Subscribe to the APA Style Monthly newsletter to get tips, updates, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Welcome! Thank you for subscribing.
APA Style Guidelines
Browse APA Style writing guidelines by category
- Abbreviations
- Bias-Free Language
- Capitalization
- In-Text Citations
- Italics and Quotation Marks
- Paper Format
- Punctuation
- Research and Publication
- Spelling and Hyphenation
- Tables and Figures
Full index of topics
- Also available in:
- Home-Entertainment
- Miscellaneous
- Deal Of The Day
- Tips and Tricks
- Mobile Feature
- Wearable Feature
- Social Media Feature
- Apps Feature
- Internet Features
- Computer Features
- Laptop Features
- Tablet Features
- First Impression
New Devices
- Latest Mobiles
- Upcoming Mobiles
- Compare Mobiles
- Top 10 Mobiles

The Best AI Tools for Students & Researchers in 2024 (Top Recommendations)

There is no doubt that AI tools have not only made writing easier but have also helped many students and researchers improve the quality of their work. However, finding a good tool might be difficult, especially with the recent increase in AI tools online.
In this blog, we have mentioned a few incredible AI writing tools that have proven to be helpful not only with writing and research but also with other factors. These factors include citation generation, grammar checking, image generation, etc.
Let's have a look!
Interesting Topic Selection to Get Started
Choosing a good topic is important for writing engaging academic work. Many students struggle with finding ideas that match their interests or assignment requirements.
AI tools use advanced technology to suggest topics and refine ideas based on what students need. Here are some suggested tools to help you generate ideas:
ChatGPT - Get Ideas for Your Research
ChatGPT uses smart technology to have conversations and suggest interesting topics. It helps students overcome writer's block by offering different perspectives and ideas that fit their assignments.
EssayService.ai - Generate Research Specific Topics
EssayService.ai helps students by generating essay topics based on what students need. It analyzes prompts and suggests topics that are relevant and interesting, helping students start their essays with clarity.
Generate Content to Overcome Writer's Block
It is not uncommon for students to face writer's block from time to time. AI can boost creativity by suggesting new ideas and ways to write. This can make writing more interesting and help explore new ideas.
Take a look at these AI tools that can help students write creatively:
MyEssayWriter.ai - Helps You Write Clear Essays Since 2021
MyEssayWriter.ai assists students in writing essays by generating ideas and improving the clarity of their writing. It helps structure essays so they are easier to read and understand. This essay writer also helps with organizing thoughts and making sure the writing flows well.
CollegeEssay.org's AI Essay Writer - Expert College-Level Essays
CollegeEssay.org's AI Essay Writer specializes in writing college-level essays on various subjects. This essay maker helps students create well-written essays that follow academic guidelines. This tool also ensures sources are cited correctly and helps students develop their ideas effectively.
MyPerfectWord.com's EssayBot - Comprehensive Essay Assistance
MyPerfectWord.com's EssayBot covers a wide range of essay topics and assists with essay structure and originality. This essay writer tool helps students brainstorm ideas, organize their writing logically, and ensure their essays are unique and well-structured. This tool is useful for improving writing skills across different subjects.
MyPerfectPaper.net's AI Essay Writer - Original, Plagiarism-Free Essays
MyPerfectPaper.net's AI Essay Writer generates essays that are original and free from plagiarism. It conducts thorough research and ensures the essays meet academic rigor. This paper writer helps students produce high-quality essays that meet specific academic requirements.
Citation Generation: Keeping Your References in Order
When working on any academic assignment, it is important to cite the information. Using the right citations is important in academic writing to give credit to sources and avoid plagiarism.
However, with so many rules to follow, citing accurately might be a problem.
AI citation tools make this easier by automatically formatting references in different styles, saving time and ensuring accuracy.
Here are some of the suggested tools that might be helpful:
MyBib - Generate Citations Fast
MyBib is easy to use to generate citations in APA, MLA, Chicago, and other formats. Students can input details about their sources, and MyBib formats the citations correctly for their research papers.
PerfectEssayWriter.ai - Get Accurate Citations in 20+ Styles
PerfectEssayWriter.ai handles citations in over 20 styles, including APA and MLA. It helps students accurately cite sources from books, journals, and websites. This tool makes citing sources easier, so students can focus more on their writing and ensure their papers meet academic standards.
Writing and Editing Tools: Enhancing Clarity and Coherence
Clear and well-structured writing is important in academic work. Many students face challenges with grammar, style, and making their writing flow smoothly.
AI writing tools provide helpful support by checking grammar, suggesting improvements, and even rewriting sentences to make them clearer. Take a look at these tools to help you:
Grammarly - Improve the Content
Grammarly is a popular tool for checking grammar and improving writing style. It helps students correct mistakes in punctuation, spelling, and word choice, making their writing more polished and professional.
PerfectEssayWriter.ai - Enhancing Clarity and Quality
PerfectEssayWriter.ai offers advanced grammar checking and rewriting suggestions. It helps students improve sentence structure and clarity in their essays and research papers, ensuring their writing meets high academic standards. Moreover, its style and tone suggestion can also help students understand whether the tone is suitable or not.
Image Generation: Enhance Visuals & Presentations
Visuals play a key role in presenting complex ideas in academic work. AI tools for image generation empower students to create compelling visuals without needing design skills, enhancing the impact of their presentations.
Here are some of the best tools for image generation:
Leonardo - High Quality Images
Leonardo uses AI to create high-quality images from descriptions. It's useful for illustrating concepts and data trends in academic presentations, making ideas clearer and more engaging.
Canva - Let Your Creativity Flow
Canva is an easy-to-use tool with AI-powered design features. It offers templates for creating presentations, infographics, and posters, helping students create professional-looking visuals that enhance their academic projects.
Free to Use AI Tool for Students
The tools mentioned above all offer something great. However, they might not be a good fit for students on a budget. Though their prices are low, they still might not be feasible for students. Here is a free AI tool that can help with all of the functions mentioned above and perhaps more:
5StarEssays.com - AI Essay Writer - Budget-Friendly Option
5StarEssays.com - AI Essay Writer tool is free to use and helps with writing well-written drafts. This free AI essay writer is good for students who need help with their work but don't want to pay money. This tool helps students improve their writing and do well in school without needing to worry about money.
To Wrap it Up!
AI tools are changing how essays are written by making them faster, more creative, and better for students' needs. AI makes writing easier and helps students learn more about different things.
Using these AI tools can greatly improve productivity, research quality, and the overall presentation of academic work. Whether you're a student working on assignments or a researcher advancing in your field, these tools help with various tasks and ensure your work meets high academic standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best ai text writer.
PerfectEssayWriter.ai is considered one of the best AI text writers. It creates customized drafts, generates citations, and checks grammar, ensuring your writing is clear and accurate. It's especially useful for students and professionals who need to produce high-quality drafts quickly and efficiently.
Which AI tool is the most advanced for writers?
MyEssayWriter.ai is one of the most advanced AI tools for writers. It offers a range of features such as idea generation, paraphrasing, summarizing, and the Humanizer tool, which makes writing sound more natural and human-like. This tool is ideal for those looking to enhance their writing quality and creativity.
Can AI writing tools help with all types of writing?
Yes, AI writing tools can help with many types of writing, including essays, research papers, creative writing, and more. Different tools have different strengths, so it's good to choose one that fits your needs.

- Best Cameras
- Best Selling

Vivo T3 Pro 5G Set to Launch Soon in India; Flipkart Microsite Goes Live

Apple Rumored to Be Building a 360-Degree Rotating Tabletop Robot

OnePlus Buds Pro 3 TWS Set to Launch on August 20 in India; Here's What to Expect?
- Don't Block
- Block for 8 hours
- Block for 12 hours
- Block for 24 hours
- Dont send alerts during 1 am 2 am 3 am 4 am 5 am 6 am 7 am 8 am 9 am 10 am 11 am 12 pm 1 pm 2 pm 3 pm 4 pm 5 pm 6 pm 7 pm 8 pm 9 pm 10 pm 11 pm 12 am to 1 am 2 am 3 am 4 am 5 am 6 am 7 am 8 am 9 am 10 am 11 am 12 pm 1 pm 2 pm 3 pm 4 pm 5 pm 6 pm 7 pm 8 pm 9 pm 10 pm 11 pm 12 am
Announcing the Visiting Writers Series, Fall 2024
DATE: August 16, 2024
Immediate Release
Contact: Ryan Mihaly, @email
413-545-8724
UMass MFA for Poets & Writers Presents Fall ‘24 Visiting Writers Series
Celebrating 61 years of free public readings
Amherst, MA – The UMass MFA for Poets and Writers is pleased to announce the Fall ‘24 Visiting Writers Series. This year’s series features Hanif Abdurraqib, Rae Armantrout, Tongo Eisen-Martin, and Yuri Herrera with translator Lisa Dillman . Readings are free, open to the public and will be held in the Old Chapel’s Great Hall. All events begin at 6PM.
Celebrating its sixty-first year, the nationally renowned Visiting Writers Series at UMass Amherst presents emerging and established writers of poetry, fiction and nonfiction. The series is sponsored by the MFA for Poets and Writers and the Juniper Initiative for Literary Arts and Action, and is made possible with support from the Massachusetts Cultural Council, the University of Massachusetts Arts Council, the Massachusetts Review, and the English Department. In addition, funding for the December 6 reading featuring Yuri Herrera and Lisa Dillman is underwritten, in part, by the Chancellor’s Community, Democracy, and Dialogue working group.
Tongo Eisen-Martin | September 19, 2024, 6pm
Tongo Eisen-Martin is the Poet Laureate of San Francisco, California. He is the author of Heaven Is All Goodbyes (City Lights Books, 2017), which was shortlisted for the Griffin International Poetry Prize, received the California Book Award for Poetry, an American Book Award, and a PEN Oakland Book Award. He is also the author of someone's dead already (Bootstrap Press, 2015). Blood on the Fog , his newest collection of poems, was published as volume 62 in the City Lights Pocket Poets Series in September 2021.
In their citation, the judges for the Griffin Prize wrote that Eisen-Martin’s work “moves between trenchant political critique and dreamlike association, demonstrating how, in the right hands, one mode might energize the other—keeping alternative orders of meaning alive in the face of radical injustice ... His poems are places where discourses and vernaculars collide and recombine into new configurations capable of expressing outrage and sorrow and love.”
Eisen-Martin is also an educator and organizer whose work centers on issues of mass incarceration, extrajudicial killings of Black people, and human rights. He has taught at detention centers around the country and at the Institute for Research in African-American Studies at Columbia University. He lives in San Francisco.
Hanif Abdurraqib | October 24, 2024, 6pm
Hanif Abdurraqib is a poet, essayist, and cultural critic from Columbus, Ohio. His poetry has been published in Muzzle , Vinyl , PEN American , and other journals. His essays and music criticism have been published in The FADER , Pitchfork , The New Yorker , and The New York Times . His first full length poetry collection, The Crown Ain't Worth Much , was released in June 2016 from Button Poetry. It was named a finalist for the Eric Hoffer Book Prize, and was nominated for a Hurston-Wright Legacy Award. With Big Lucks, he released a limited edition chapbook, Vintage Sadness , in summer 2017 (you cannot get it anymore and he is very sorry.) His first collection of essays, They Can't Kill Us Until They Kill Us , was released in winter 2017 by Two Dollar Radio and was named a book of the year by Buzzfeed, Esquire, NPR, Oprah Magazine, Paste, CBC, The Los Angeles Review, Pitchfork , and The Chicago Tribune , among others. He released Go Ahead In The Rain: Notes To A Tribe Called Quest with University of Texas press in February 2019. The book became a New York Times Bestseller, was a finalist for the Kirkus Prize, and was long-listed for the National Book Award. His second collection of poems, A Fortune For Your Disaster , was released in 2019 by Tin House, and won the 2020 Lenore Marshall Prize. In 2021, he released the book A Little Devil In America with Random House, which was a finalist for the National Book Award, the National Book Critics Circle Award, and the The PEN/Diamonstein-Spielvogel Award for the Art of the Essay. The book won the 2022 Andrew Carnegie Medal for Excellence in Nonfiction and the Gordon Burn Prize. His newest book is There's Always This Year: On Basketball and Ascension with Random House. Hanif is a graduate of Beechcroft High School.
Rae Armantrout | November 14, 2024, 6pm
Rae Armantrout has fifteen previous books including Versed, which received a Pulitzer Prize, a National Book Award, and a National Book Critics Circle Award; Finalists ; Conjure ; Wobble (finalist for a National Book Award); Partly: New and Selected Poems ; Itself ; Just Saying ; and Money Shot . Armantrout is Professor Emerita of Writing at the University of California at San Diego. She has been published in many anthologies, including, The Oxford Book of American Poetry , and Scribner's Best American Poetry , and in such magazines as, Harpers, The New Yorker, American Poetry Review, Boston Review, Scientific American, Chicago Review, and the Los Angeles Times Book Review.
Yuri Herrera & Lisa Dillman | December 5, 2024
Born in Actopan, Mexico, Yuri Herrera is the author of three novels, including Signs Preceding the End of the World , as well as the collection Ten Planets , which was a finalist for the Ursula K. Le Guin Prize. His first novel Trabajos del reino (in English: Kingdom Cons ) won the Premio Binacional de Novela Joven 2003 and received the “Otras voces, otros ámbitos” prize for the best novel published in Spain in 2008. His second novel, Señales que precederán al fin del mundo ( Signs Preceding the End of the World ) was a finalist of the Rómulo Gallegos Prize. His third novel is La transmigración de los cuerpos ( Transmigration of Bodies ). All of these novels have been translated into English by Lisa Dillman for British publisher And Other Stories. In 2016, he and Dillman shared the Best Translated Book Award for Signs Preceding the End of the World. Herrera teaches at Tulane University in New Orleans.
Lisa Dillman has translated a number of Spanish and Latin American writers. Some of her recent translations include Rain Over Madrid , Such Small Hands and The Right Intention by Andrés Barba and Yuri Herrera’s novels. She won the 2016 Best Translated Book Award for Herrera’s Signs Preceding the End of the World . She teaches in the Department of Spanish and Portuguese at Emory University in Atlanta, Georgia.
The Visiting Writers Series is an annual event by the UMass MFA for Poets and Writers bringing literary artists from around the world to western Massachusetts with free and public programming. The voice of the writer brings ideas and rhythms of language to life, inspiring listeners through intellectual engagement, imagination, and possibility. By showcasing a variety of aesthetics, perspectives, genres, forms, and performance styles the series provides audience members with unique opportunities to experience contemporary literary art.
Author/translator photos are available here: VWS Photos 2024
For more information: Ryan Mihaly, @email
E445 South College 150 Hicks Way Amherst, MA 01003 (413) 545-5456

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Only capitalize the first letter in the first word of the title. Starting with the word "In" write the editor's name followed by " (Ed.)," a comma and the title of the anthology. Italicize or underline the anthology's title and end with a period. Place the page numbers of the essay in parentheses followed with a period.
Include the author of the essay, the title of the essay, the name of the collection if the essay belongs to one, the editor of the collection or other contributors, the publication information, and the page number(s). Citing an Essay MLA Essay Citation Structure. Last, First M. "Essay Title." Collection Title, edited by First M. Last ...
When you cite a work that appears inside a larger source (for instance, an article in a periodical or an essay in a collection), cite the author of the internal source (i.e., the article or essay). For example, to cite Albert Einstein's article "A Brief Outline of the Theory of Relativity," which was published in Nature in 1921, you might write ...
Author First M. Last Name, "Chapter or Essay Title," in Book Title, ed. First M. Last Name (Place of Publication: Publisher, date), page cited. Short version: Author Last Name, "Chapter or Essay Title (shortened if necessary)," page cited. Bibliography. Author Last Name, First M. "Chapter or Essay Title." In Book Title, edited by First M. Last ...
Anthology or Collection (e.g. Collection of Essays) To cite the entire anthology or collection, list by editor(s) followed by a comma and "editor" or, for multiple editors, "editors." This sort of entry is somewhat rare. ... If you cite more than one essay from the same edited collection, MLA indicates you may cross-reference within your works ...
3. Include the title of the essay. Type the title of the essay in sentence case, capitalizing only the first word and any proper nouns in the title. If the essay has a subtitle, type a colon at the end of the title and then type the subtitle, also in sentence case. Place a period at the end.
Next write "In" (without the quotation marks) and give the editor, first initial followed by last name. Use "&" (without the quotation marks) between them if you have more than one. Put (Ed.) and a comma to indicate this is an editor, and then give the title of the book, italicized. The page numbers for the essay appear next, in parentheses ...
In-Text Citations. Parenthetical and in-text citations direct your reader to the bibliographic entry in your works cited page. In MLA format, you use the author's last name followed by the page numbers in parentheses after a sentence or group of sentences referring to the essay. For example, " (Sedaris 25-32)" -- without the quote marks ...
Please see the sample citation for a chapter or article in an anthology below for information on citing a component of an edited collection. Numbered edition other than the first. Wardle, Elizabeth, and Doug Downs, editors. Writing About Writing: A College Reader. 2nd ed., Bedford/St. Martin's, 2014. Revised edition
When learning how to write an academic essay with references, you must identify reliable sources that support your argument. As you read, think critically and evaluate sources for: Accuracy. Objectivity. Currency. Authority. Keep detailed notes on the sources so that you can easily find them again, if needed.
In-Text Citation Format (Editor's Last Name p. # *) * Please note, the in-text citation should be just the number itself and should not include the p., as in the example below. Works Cited Example . Gilman, Charlotte Perkins. "The Yellow Wallpaper." Literature: Reading, Reacting, Writing. Edited by Laurie G.
In-text citations point the reader to the sources' information on the references page. The in-text citation typically includes the author's last name and the year of publication. If you use a direct quote, the page number is also provided. More information can be found on p. 253 of the 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American ...
An anthology is a collection of related works. Often poetry and short stories are collected into a single book. MLA 8 anthology examples use the nine core elements within the container system in the works cited. To cite one essay out of a collection of works, use this MLA citation format. Short stories are collected in an anthology.
To cite an essay with an author in a textbook with authors rather than editors, follow the MLA format template and list the authors of the textbook in the "Other contributors" slot: Graff, Gerald. "Disliking Books." From Inquiry to Academic Writing: A Practical Guide, by Stuart Greene and April Lidinsky, 2nd ed., Bedford / St. Martin's, 2012, pp. …
by Chelsea Lee. An anthology is a collection of works, organized around a central theme, that has been assembled by an editor or publisher. One type of anthology is often called a collected works or complete works, in which all the writings of a particular author are published in one volume (or set of volumes) for easy reference.Other anthologies contain works by many different authors all of ...
To cite a book chapter, first give the author and title (in quotation marks) of the chapter cited, then information about the book as a whole and the page range of the specific chapter. The in-text citation lists the author of the chapter and the page number of the relevant passage. MLA format. Author last name, First name.
For example, you might need to reference a chapter from a collection of essays. If so, you need to know how to cite an edited book. In-Text Citations. When citing an edited book, you need to name the author of the chapter or section in question (not the editor of the book as a whole). As with any MLA citation, you should also give a page number:
How you cite an anthology in the seventh edition of the American Psychological Association (APA) style depends on whether you are citing the entire anthology or a specific work within it. An entire anthology/edited book. Treat the editor of the anthology as its author, i.e. Editor's Last Name, First Initials. (Eds.).
This page includes citation examples for different kinds of primary sources using the Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS), 16th edition, and Kate Turabian's A Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations, 8th edition.This guide shows how to create an initial citation, a subsequent note, and a bibliography entry for primary sources.
To quote a source, copy a short piece of text word for word and put it inside quotation marks. To paraphrase a source, put the text into your own words. It's important that the paraphrase is not too close to the original wording. You can use the paraphrasing tool if you don't want to do this manually.
See the following example for the format of republished work in a printed anthology or collection: In-text citation: (Author, 1989/2019) Reference entry: Author, A. (2019). Title of original work. In E. Editor (Ed.). Title of anthology or collection in sentence case and italics (pp. xx-xxx). Publisher. (Original work published 1989).
Is there a way for Zotero to cite a specific chapter (essay or article) within a multi-author book (collection of essays, etc.)? Perhaps there are sources that would feed the necessary information or Zotero to create the citation. Thanks, José . bwiernik. December 28, 2019. You would enter such items as "Book Section" and enter both the ...
The Webster essay is widely cited just by its title, without referring to the entire collection; I'd recommend doing that. If you use a citation style without quotation markes, you can in principle add both title and essay collection title in the title field, but as soon as the style adds quotation marks, those will also include the "in" which ...
Unlike an edited book, where each chapter has unique authors, usually you expect an authored book to have the same author(s) throughout. Thus, citing a chapter of an edited book is common, but as a general rule, citing chapters from authored books is not. For authored books, the whole book is referenced, with specific chapters included in the in-text citation as needed.
Tools like the Aithor essay writer can improve your essays, but learning these rules yourself will help you use these tools better and improve your essay writing skills in the long run. 5. Write a Compelling Introduction. The introduction sets the mood for your whole essay and is your chance to get the reader interested.
Writing the personal essay for your college application can be tough, but we're here to help. Sometimes the hardest part is just getting started, but the sooner you begin, the more time and thought you can put into an essay that stands out. Check out some tips: 1. Keep it real.
For literature reviews or other types of essays or response or reaction papers, you might describe how you used the tool in your introduction. In your text, provide the prompt you used and then any portion of the relevant text that was generated in response. ... Narrative citation: OpenAI (2023) Let's break that reference down and look at the ...
CollegeEssay.org's AI Essay Writer specializes in writing college-level essays on various subjects. This essay maker helps students create well-written essays that follow academic guidelines.
His essays and music criticism have been published in The FADER, Pitchfork, The New Yorker, and The New York Times. His first full length poetry collection, The Crown Ain't Worth Much, was released in June 2016 from Button Poetry. It was named a finalist for the Eric Hoffer Book Prize, and was nominated for a Hurston-Wright Legacy Award.
This essay is a review of Raymond Geuss's book, Seeing Double.The review discusses the seven essays that comprise the book, which is concerned with the implications of the fact that the world never makes complete sense to us and that there are only fragments of meaning without any higher order or authority to make sense of the world.