11.4 The Business Plan
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different purposes of a business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a brief business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a full business plan
Unlike the brief or lean formats introduced so far, the business plan is a formal document used for the long-range planning of a company’s operation. It typically includes background information, financial information, and a summary of the business. Investors nearly always request a formal business plan because it is an integral part of their evaluation of whether to invest in a company. Although nothing in business is permanent, a business plan typically has components that are more “set in stone” than a business model canvas , which is more commonly used as a first step in the planning process and throughout the early stages of a nascent business. A business plan is likely to describe the business and industry, market strategies, sales potential, and competitive analysis, as well as the company’s long-term goals and objectives. An in-depth formal business plan would follow at later stages after various iterations to business model canvases. The business plan usually projects financial data over a three-year period and is typically required by banks or other investors to secure funding. The business plan is a roadmap for the company to follow over multiple years.
Some entrepreneurs prefer to use the canvas process instead of the business plan, whereas others use a shorter version of the business plan, submitting it to investors after several iterations. There are also entrepreneurs who use the business plan earlier in the entrepreneurial process, either preceding or concurrently with a canvas. For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup . 48 His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch without the detail of a full business plan. As you progress, you can also consider a brief business plan (about two pages)—if you want to support a rapid business launch—and/or a standard business plan.
As with many aspects of entrepreneurship, there are no clear hard and fast rules to achieving entrepreneurial success. You may encounter different people who want different things (canvas, summary, full business plan), and you also have flexibility in following whatever tool works best for you. Like the canvas, the various versions of the business plan are tools that will aid you in your entrepreneurial endeavor.

Business Plan Overview
Most business plans have several distinct sections ( Figure 11.16 ). The business plan can range from a few pages to twenty-five pages or more, depending on the purpose and the intended audience. For our discussion, we’ll describe a brief business plan and a standard business plan. If you are able to successfully design a business model canvas, then you will have the structure for developing a clear business plan that you can submit for financial consideration.
Both types of business plans aim at providing a picture and roadmap to follow from conception to creation. If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept.
The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, dealing with the proverbial devil in the details. Developing a full business plan will assist those of you who need a more detailed and structured roadmap, or those of you with little to no background in business. The business planning process includes the business model, a feasibility analysis, and a full business plan, which we will discuss later in this section. Next, we explore how a business plan can meet several different needs.
Purposes of a Business Plan
A business plan can serve many different purposes—some internal, others external. As we discussed previously, you can use a business plan as an internal early planning device, an extension of a napkin sketch, and as a follow-up to one of the canvas tools. A business plan can be an organizational roadmap , that is, an internal planning tool and working plan that you can apply to your business in order to reach your desired goals over the course of several years. The business plan should be written by the owners of the venture, since it forces a firsthand examination of the business operations and allows them to focus on areas that need improvement.
Refer to the business venture throughout the document. Generally speaking, a business plan should not be written in the first person.
A major external purpose for the business plan is as an investment tool that outlines financial projections, becoming a document designed to attract investors. In many instances, a business plan can complement a formal investor’s pitch. In this context, the business plan is a presentation plan, intended for an outside audience that may or may not be familiar with your industry, your business, and your competitors.
You can also use your business plan as a contingency plan by outlining some “what-if” scenarios and exploring how you might respond if these scenarios unfold. Pretty Young Professional launched in November 2010 as an online resource to guide an emerging generation of female leaders. The site focused on recent female college graduates and current students searching for professional roles and those in their first professional roles. It was founded by four friends who were coworkers at the global consultancy firm McKinsey. But after positions and equity were decided among them, fundamental differences of opinion about the direction of the business emerged between two factions, according to the cofounder and former CEO Kathryn Minshew . “I think, naively, we assumed that if we kicked the can down the road on some of those things, we’d be able to sort them out,” Minshew said. Minshew went on to found a different professional site, The Muse , and took much of the editorial team of Pretty Young Professional with her. 49 Whereas greater planning potentially could have prevented the early demise of Pretty Young Professional, a change in planning led to overnight success for Joshua Esnard and The Cut Buddy team. Esnard invented and patented the plastic hair template that he was selling online out of his Fort Lauderdale garage while working a full-time job at Broward College and running a side business. Esnard had hundreds of boxes of Cut Buddies sitting in his home when he changed his marketing plan to enlist companies specializing in making videos go viral. It worked so well that a promotional video for the product garnered 8 million views in hours. The Cut Buddy sold over 4,000 products in a few hours when Esnard only had hundreds remaining. Demand greatly exceeded his supply, so Esnard had to scramble to increase manufacturing and offered customers two-for-one deals to make up for delays. This led to selling 55,000 units, generating $700,000 in sales in 2017. 50 After appearing on Shark Tank and landing a deal with Daymond John that gave the “shark” a 20-percent equity stake in return for $300,000, The Cut Buddy has added new distribution channels to include retail sales along with online commerce. Changing one aspect of a business plan—the marketing plan—yielded success for The Cut Buddy.
Link to Learning
Watch this video of Cut Buddy’s founder, Joshua Esnard, telling his company’s story to learn more.
If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept. This version is used to interest potential investors, employees, and other stakeholders, and will include a financial summary “box,” but it must have a disclaimer, and the founder/entrepreneur may need to have the people who receive it sign a nondisclosure agreement (NDA) . The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, providing supporting details, and would be required by financial institutions and others as they formally become stakeholders in the venture. Both are aimed at providing a picture and roadmap to go from conception to creation.
Types of Business Plans
The brief business plan is similar to an extended executive summary from the full business plan. This concise document provides a broad overview of your entrepreneurial concept, your team members, how and why you will execute on your plans, and why you are the ones to do so. You can think of a brief business plan as a scene setter or—since we began this chapter with a film reference—as a trailer to the full movie. The brief business plan is the commercial equivalent to a trailer for Field of Dreams , whereas the full plan is the full-length movie equivalent.
Brief Business Plan or Executive Summary
As the name implies, the brief business plan or executive summary summarizes key elements of the entire business plan, such as the business concept, financial features, and current business position. The executive summary version of the business plan is your opportunity to broadly articulate the overall concept and vision of the company for yourself, for prospective investors, and for current and future employees.
A typical executive summary is generally no longer than a page, but because the brief business plan is essentially an extended executive summary, the executive summary section is vital. This is the “ask” to an investor. You should begin by clearly stating what you are asking for in the summary.
In the business concept phase, you’ll describe the business, its product, and its markets. Describe the customer segment it serves and why your company will hold a competitive advantage. This section may align roughly with the customer segments and value-proposition segments of a canvas.
Next, highlight the important financial features, including sales, profits, cash flows, and return on investment. Like the financial portion of a feasibility analysis, the financial analysis component of a business plan may typically include items like a twelve-month profit and loss projection, a three- or four-year profit and loss projection, a cash-flow projection, a projected balance sheet, and a breakeven calculation. You can explore a feasibility study and financial projections in more depth in the formal business plan. Here, you want to focus on the big picture of your numbers and what they mean.
The current business position section can furnish relevant information about you and your team members and the company at large. This is your opportunity to tell the story of how you formed the company, to describe its legal status (form of operation), and to list the principal players. In one part of the extended executive summary, you can cover your reasons for starting the business: Here is an opportunity to clearly define the needs you think you can meet and perhaps get into the pains and gains of customers. You also can provide a summary of the overall strategic direction in which you intend to take the company. Describe the company’s mission, vision, goals and objectives, overall business model, and value proposition.
Rice University’s Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions (see Telling Your Entrepreneurial Story and Pitching the Idea ), requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. 51 , 52 Its suggested sections are shown in Table 11.2 .
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Company summary | Brief overview (one to two paragraphs) of the problem, solution, and potential customers |
| Customer analysis | Description of potential customers and evidence they would purchase product |
| Market analysis | Size of market, target market, and share of market |
| Product or service | Current state of product in development and evidence it is feasible |
| Intellectual property | If applicable, information on patents, licenses, or other IP items |
| Competitive differentiation | Describe the competition and your competitive advantage |
| Company founders, management team, and/or advisor | Bios of key people showcasing their expertise and relevant experience |
| Financials | Projections of revenue, profit, and cash flow for three to five years |
| Amount of investment | Funding request and how funds will be used |
Are You Ready?
Create a brief business plan.
Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business. See if you can find a version of the company’s actual executive summary, business plan, or canvas. Compare and contrast your vision with what the company has articulated.
- These companies are well established but is there a component of what you charted that you would advise the company to change to ensure future viability?
- Map out a contingency plan for a “what-if” scenario if one key aspect of the company or the environment it operates in were drastically is altered?
Full Business Plan
Even full business plans can vary in length, scale, and scope. Rice University sets a ten-page cap on business plans submitted for the full competition. The IndUS Entrepreneurs , one of the largest global networks of entrepreneurs, also holds business plan competitions for students through its Tie Young Entrepreneurs program. In contrast, business plans submitted for that competition can usually be up to twenty-five pages. These are just two examples. Some components may differ slightly; common elements are typically found in a formal business plan outline. The next section will provide sample components of a full business plan for a fictional business.
Executive Summary
The executive summary should provide an overview of your business with key points and issues. Because the summary is intended to summarize the entire document, it is most helpful to write this section last, even though it comes first in sequence. The writing in this section should be especially concise. Readers should be able to understand your needs and capabilities at first glance. The section should tell the reader what you want and your “ask” should be explicitly stated in the summary.
Describe your business, its product or service, and the intended customers. Explain what will be sold, who it will be sold to, and what competitive advantages the business has. Table 11.3 shows a sample executive summary for the fictional company La Vida Lola.
Executive Summary Component | Content |
|---|---|
The Concept | La Vida Lola is a food truck serving the best Latin American and Caribbean cuisine in the Atlanta region, particularly Puerto Rican and Cuban dishes, with a festive flair. La Vida Lola offers freshly prepared dishes from the mobile kitchen of the founding chef and namesake Lola González, a Duluth, Georgia, native who has returned home to launch her first venture after working under some of the world’s top chefs. La Vida Lola will cater to festivals, parks, offices, community and sporting events, and breweries throughout the region. |
Market Advantage | Latin food packed with flavor and flair is the main attraction of La Vida Lola. Flavors steeped in Latin American and Caribbean culture can be enjoyed from a menu featuring street foods, sandwiches, and authentic dishes from the González family’s Puerto Rican and Cuban roots. craving ethnic food experiences and are the primary customers, but anyone with a taste for delicious homemade meals in Atlanta can order. Having a native Atlanta-area resident returning to her hometown after working in restaurants around the world to share food with area communities offers a competitive advantage for La Vida Lola in the form of founding chef Lola González. |
Marketing | The venture will adopt a concentrated marketing strategy. The company’s promotion mix will comprise a mix of advertising, sales promotion, public relations, and personal selling. Much of the promotion mix will center around dual-language social media. |
Venture Team | The two founding members of the management team have almost four decades of combined experience in the restaurant and hospitality industries. Their background includes experience in food and beverage, hospitality and tourism, accounting, finance, and business creation. |
Capital Requirements | La Vida Lola is seeking startup capital of $50,000 to establish its food truck in the Atlanta area. An additional $20,000 will be raised through a donations-driven crowdfunding campaign. The venture can be up and running within six months to a year. |
Business Description
This section describes the industry, your product, and the business and success factors. It should provide a current outlook as well as future trends and developments. You also should address your company’s mission, vision, goals, and objectives. Summarize your overall strategic direction, your reasons for starting the business, a description of your products and services, your business model, and your company’s value proposition. Consider including the Standard Industrial Classification/North American Industry Classification System (SIC/NAICS) code to specify the industry and insure correct identification. The industry extends beyond where the business is located and operates, and should include national and global dynamics. Table 11.4 shows a sample business description for La Vida Lola.
Business Description | La Vida Lola will operate in the mobile food services industry, which is identified by SIC code 5812 Eating Places and NAICS code 722330 Mobile Food Services, which consist of establishments primarily engaged in preparing and serving meals and snacks for immediate consumption from motorized vehicles or nonmotorized carts. Ethnically inspired to serve a consumer base that craves more spiced Latin foods, La Vida Lola is an Atlanta-area food truck specializing in Latin cuisine, particularly Puerto Rican and Cuban dishes native to the roots of the founding chef and namesake, Lola González. La Vida Lola aims to spread a passion for Latin cuisine within local communities through flavorful food freshly prepared in a region that has embraced international eats. Through its mobile food kitchen, La Vida Lola plans to roll into parks, festivals, office buildings, breweries, and sporting and community events throughout the greater Atlanta metropolitan region. Future growth possibilities lie in expanding the number of food trucks, integrating food delivery on demand, and adding a food stall at an area food market. After working in noted restaurants for a decade, most recently under the famed chef José Andrés, chef Lola González returned to her hometown of Duluth, Georgia, to start her own venture. Although classically trained by top world chefs, it was González’s grandparents’ cooking of authentic Puerto Rican and Cuban dishes in their kitchen that influenced her profoundly. The freshest ingredients from the local market, the island spices, and her attention to detail were the spark that ignited Lola’s passion for cooking. To that end, she brings flavors steeped in Latin American and Caribbean culture to a flavorful menu packed full of street foods, sandwiches, and authentic dishes. Through reasonably priced menu items, La Vida Lola offers food that appeals to a wide range of customers, from millennial foodies to Latin natives and other locals with Latin roots. |
Industry Analysis and Market Strategies
Here you should define your market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. You’ll want to include your TAM and forecast the SAM . (Both these terms are discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis .) This is a place to address market segmentation strategies by geography, customer attributes, or product orientation. Describe your positioning relative to your competitors’ in terms of pricing, distribution, promotion plan, and sales potential. Table 11.5 shows an example industry analysis and market strategy for La Vida Lola.
Industry Analysis and Market Strategy | According to ’ first annual report from the San Francisco-based Off The Grid, a company that facilitates food markets nationwide, the US food truck industry alone is projected to grow by nearly 20 percent from $800 million in 2017 to $985 million in 2019. Meanwhile, an report shows the street vendors’ industry with a 4.2 percent annual growth rate to reach $3.2 billion in 2018. Food truck and street food vendors are increasingly investing in specialty, authentic ethnic, and fusion food, according to the report. Although the report projects demand to slow down over the next five years, it notes there are still opportunities for sustained growth in major metropolitan areas. The street vendors industry has been a particular bright spot within the larger food service sector. The industry is in a growth phase of its life cycle. The low overhead cost to set up a new establishment has enabled many individuals, especially specialty chefs looking to start their own businesses, to own a food truck in lieu of opening an entire restaurant. Off the Grid’s annual report indicates the average typical initial investment ranges from $55,000 to $75,000 to open a mobile food truck. The restaurant industry accounts for $800 billion in sales nationwide, according to data from the National Restaurant Association. Georgia restaurants brought in a total of $19.6 billion in 2017, according to figures from the Georgia Restaurant Association. There are approximately 12,000 restaurants in the metro Atlanta region. The Atlanta region accounts for almost 60 percent of the Georgia restaurant industry. The SAM is estimated to be approximately $360 million. The mobile food/street vendor industry can be segmented by types of customers, types of cuisine (American, desserts, Central and South American, Asian, mixed ethnicity, Greek Mediterranean, seafood), geographic location and types (mobile food stands, mobile refreshment stands, mobile snack stands, street vendors of food, mobile food concession stands). Secondary competing industries include chain restaurants, single location full-service restaurants, food service contractors, caterers, fast food restaurants, and coffee and snack shops. The top food truck competitors according to the , the daily newspaper in La Vida Lola’s market, are Bento Bus, Mix’d Up Burgers, Mac the Cheese, The Fry Guy, and The Blaxican. Bento Bus positions itself as a Japanese-inspired food truck using organic ingredients and dispensing in eco-friendly ware. The Blaxican positions itself as serving what it dubs “Mexican soul food,” a fusion mashup of Mexican food with Southern comfort food. After years of operating a food truck, The Blaxican also recently opened its first brick-and-mortar restaurant. The Fry Guy specializes in Belgian-style street fries with a variety of homemade dipping sauces. These three food trucks would be the primary competition to La Vida Lola, since they are in the “ethnic food” space, while the other two offer traditional American food. All five have established brand identities and loyal followers/customers since they are among the industry leaders as established by “best of” lists from area publications like the . Most dishes from competitors are in the $10–$13 price range for entrees. La Vida Lola dishes will range from $6 to $13. One key finding from Off the Grid’s report is that mobile food has “proven to be a powerful vehicle for catalyzing diverse entrepreneurship” as 30 percent of mobile food businesses are immigrant owned, 30 percent are women owned, and 8 percent are LGBTQ owned. In many instances, the owner-operator plays a vital role to the brand identity of the business as is the case with La Vida Lola. Atlanta has also tapped into the nationwide trend of food hall-style dining. These food halls are increasingly popular in urban centers like Atlanta. On one hand, these community-driven areas where food vendors and retailers sell products side by side are secondary competitors to food trucks. But they also offer growth opportunities for future expansion as brands solidify customer support in the region. The most popular food halls in Atlanta are Ponce City Market in Midtown, Krog Street Market along the BeltLine trail in the Inman Park area, and Sweet Auburn Municipal Market downtown Atlanta. In addition to these trends, Atlanta has long been supportive of international cuisine as Buford Highway (nicknamed “BuHi”) has a reputation for being an eclectic food corridor with an abundance of renowned Asian and Hispanic restaurants in particular. The Atlanta region is home to a thriving Hispanic and Latinx population, with nearly half of the region’s foreign-born population hailing from Latin America. There are over half a million Hispanic and Latin residents living in metro Atlanta, with a 150 percent population increase predicted through 2040. The median age of metro Atlanta Latinos is twenty-six. La Vida Lola will offer authentic cuisine that will appeal to this primary customer segment. La Vida Lola must contend with regulations from towns concerning operations of mobile food ventures and health regulations, but the Atlanta region is generally supportive of such operations. There are many parks and festivals that include food truck vendors on a weekly basis. |
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis is a statement of the business strategy as it relates to the competition. You want to be able to identify who are your major competitors and assess what are their market shares, markets served, strategies employed, and expected response to entry? You likely want to conduct a classic SWOT analysis (Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats) and complete a competitive-strength grid or competitive matrix. Outline your company’s competitive strengths relative to those of the competition in regard to product, distribution, pricing, promotion, and advertising. What are your company’s competitive advantages and their likely impacts on its success? The key is to construct it properly for the relevant features/benefits (by weight, according to customers) and how the startup compares to incumbents. The competitive matrix should show clearly how and why the startup has a clear (if not currently measurable) competitive advantage. Some common features in the example include price, benefits, quality, type of features, locations, and distribution/sales. Sample templates are shown in Figure 11.17 and Figure 11.18 . A competitive analysis helps you create a marketing strategy that will identify assets or skills that your competitors are lacking so you can plan to fill those gaps, giving you a distinct competitive advantage. When creating a competitor analysis, it is important to focus on the key features and elements that matter to customers, rather than focusing too heavily on the entrepreneur’s idea and desires.
Operations and Management Plan
In this section, outline how you will manage your company. Describe its organizational structure. Here you can address the form of ownership and, if warranted, include an organizational chart/structure. Highlight the backgrounds, experiences, qualifications, areas of expertise, and roles of members of the management team. This is also the place to mention any other stakeholders, such as a board of directors or advisory board(s), and their relevant relationship to the founder, experience and value to help make the venture successful, and professional service firms providing management support, such as accounting services and legal counsel.
Table 11.6 shows a sample operations and management plan for La Vida Lola.
| Operations and Management Plan Category | Content |
|---|---|
Key Management Personnel | The key management personnel consist of Lola González and Cameron Hamilton, who are longtime acquaintances since college. The management team will be responsible for funding the venture as well as securing loans to start the venture. The following is a summary of the key personnel backgrounds. Chef Lola González has worked directly in the food service industry for fifteen years. While food has been a lifelong passion learned in her grandparents’ kitchen, chef González has trained under some of the top chefs in the world, most recently having worked under the James Beard Award-winning chef José Andrés. A native of Duluth, Georgia, chef González also has an undergraduate degree in food and beverage management. Her value to the firm is serving as “the face” and company namesake, preparing the meals, creating cuisine concepts, and running the day-to-day operations of La Vida Lola. Cameron Hamilton has worked in the hospitality industry for over twenty years and is experienced in accounting and finance. He has a master of business administration degree and an undergraduate degree in hospitality and tourism management. He has opened and managed several successful business ventures in the hospitality industry. His value to the firm is in business operations, accounting, and finance. |
Advisory Board | During the first year of operation, the company intends to keep a lean operation and does not plan to implement an advisory board. At the end of the first year of operation, the management team will conduct a thorough review and discuss the need for an advisory board. |
Supporting Professionals | Stephen Ngo, Certified Professional Accountant (CPA), of Valdosta, Georgia, will provide accounting consulting services. Joanna Johnson, an attorney and friend of chef González, will provide recommendations regarding legal services and business formation. |
Marketing Plan
Here you should outline and describe an effective overall marketing strategy for your venture, providing details regarding pricing, promotion, advertising, distribution, media usage, public relations, and a digital presence. Fully describe your sales management plan and the composition of your sales force, along with a comprehensive and detailed budget for the marketing plan. Table 11.7 shows a sample marketing plan for La Vida Lola.
| Marketing Plan Category | Content |
|---|---|
Overview | La Vida Lola will adopt a concentrated marketing strategy. The company’s promotion mix will include a mix of advertising, sales promotion, public relations, and personal selling. Given the target millennial foodie audience, the majority of the promotion mix will be centered around social media platforms. Various social media content will be created in both Spanish and English. The company will also launch a crowdfunding campaign on two crowdfunding platforms for the dual purpose of promotion/publicity and fundraising. |
Advertising and Sales Promotion | As with any crowdfunding social media marketing plan, the first place to begin is with the owners’ friends and family. Utilizing primarily Facebook/Instagram and Twitter, La Vida Lola will announce the crowdfunding initiative to their personal networks and prevail upon these friends and family to share the information. Meanwhile, La Vida Lola needs to focus on building a community of backers and cultivating the emotional draw of becoming part of the La Vida Lola family. To build a crowdfunding community via social media, La Vida Lola will routinely share its location, daily if possible, on both Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter. Inviting and encouraging people to visit and sample their food can rouse interest in the cause. As the campaign is nearing its goal, it would be beneficial to offer a free food item to backers of a specific level, say $50, on one specific day. Sharing this via social media in the day or two preceding the giveaway and on the day of can encourage more backers to commit. Weekly updates of the campaign and the project as a whole are a must. Facebook and Twitter updates of the project coupled with educational information sharing helps backers feel part of the La Vida Lola community. Finally, at every location where La Vida Lola is serving its food, signage will notify the public of their social media presence and the current crowdfunding campaign. Each meal will be accompanied by an invitation from the server for the patron to visit the crowdfunding site and consider donating. Business cards listing the social media and crowdfunding information will be available in the most visible location, likely the counter. Before moving forward with launching a crowdfunding campaign, La Vida Lola will create its website. The website is a great place to establish and share the La Vida Lola brand, vision, videos, menus, staff, and events. It is also a great source of information for potential backers who are unsure about donating to the crowdfunding campaigns. The website will include these elements: . Address the following questions: Who are you? What are the guiding principles of La Vida Lola? How did the business get started? How long has La Vida Lola been in business? Include pictures of chef González. List of current offerings with prices. Will include promotional events and locations where customers can find the truck for different events. Steps will be taken to increase social media followers prior to launching the crowdfunding campaign. Unless a large social media following is already established, a business should aggressively push social media campaigns a minimum of three months prior to the crowdfunding campaign launch. Increasing social media following prior to the campaign kickoff will also allow potential donors to learn more about La Vida Lola and foster relationship building before attempting to raise funds. |
Facebook Content and Advertising | The key piece of content will be the campaign pitch video, reshared as a native Facebook upload. A link to the crowdfunding campaigns can be included in the caption. Sharing the same high-quality video published on the campaign page will entice fans to visit Kickstarter to learn more about the project and rewards available to backers. |
Crowdfunding Campaigns | Foodstart was created just for restaurants, breweries, cafés, food trucks, and other food businesses, and allows owners to raise money in small increments. It is similar to Indiegogo in that it offers both flexible and fixed funding models and charges a percentage for successful campaigns, which it claims to be the lowest of any crowdfunding platform. It uses a reward-based system rather than equity, where backers are offered rewards or perks resulting in “low-cost capital and a network of people who now have an incentive to see you succeed.” Foodstart will host La Vida Lola’s crowdfunding campaigns for the following reasons: (1) It caters to their niche market; (2) it has less competition from other projects which means that La Vida Lola will stand out more and not get lost in the shuffle; and (3) it has/is making a name/brand for itself which means that more potential backers are aware of it. La Vida Lola will run a simultaneous crowdfunding campaign on Indiegogo, which has broader mass appeal. |
Publicity | Social media can be a valuable marketing tool to draw people to the Foodstarter and Indiegogo crowdfunding pages. It provides a means to engage followers and keep funders/backers updated on current fundraising milestones. The first order of business is to increase La Vida Lola’s social media presence on Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter. Establishing and using a common hashtag such as #FundLola across all platforms will promote familiarity and searchability, especially within Instagram and Twitter. Hashtags are slowly becoming a presence on Facebook. The hashtag will be used in all print collateral. La Vida Lola will need to identify social influencers—others on social media who can assist with recruiting followers and sharing information. Existing followers, family, friends, local food providers, and noncompetitive surrounding establishments should be called upon to assist with sharing La Vida Lola’s brand, mission, and so on. Cross-promotion will further extend La Vida Lola’s social reach and engagement. Influencers can be called upon to cross promote upcoming events and specials. The crowdfunding strategy will utilize a progressive reward-based model and establish a reward schedule such as the following: In addition to the publicity generated through social media channels and the crowdfunding campaign, La Vida Lola will reach out to area online and print publications (both English- and Spanish-language outlets) for feature articles. Articles are usually teased and/or shared via social media. Reaching out to local broadcast stations (radio and television) may provide opportunities as well. La Vida Lola will recruit a social media intern to assist with developing and implementing a social media content plan. Engaging with the audience and responding to all comments and feedback is important for the success of the campaign. Some user personas from segmentation to target in the campaign: |
Financial Plan
A financial plan seeks to forecast revenue and expenses; project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections. This section should present an accurate, realistic, and achievable financial plan for your venture (see Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting for detailed discussions about conducting these projections). Include sales forecasts and income projections, pro forma financial statements ( Building the Entrepreneurial Dream Team , a breakeven analysis, and a capital budget. Identify your possible sources of financing (discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis ). Figure 11.19 shows a template of cash-flow needs for La Vida Lola.
Entrepreneur In Action
Laughing man coffee.
Hugh Jackman ( Figure 11.20 ) may best be known for portraying a comic-book superhero who used his mutant abilities to protect the world from villains. But the Wolverine actor is also working to make the planet a better place for real, not through adamantium claws but through social entrepreneurship.
A love of java jolted Jackman into action in 2009, when he traveled to Ethiopia with a Christian humanitarian group to shoot a documentary about the impact of fair-trade certification on coffee growers there. He decided to launch a business and follow in the footsteps of the late Paul Newman, another famous actor turned philanthropist via food ventures.
Jackman launched Laughing Man Coffee two years later; he sold the line to Keurig in 2015. One Laughing Man Coffee café in New York continues to operate independently, investing its proceeds into charitable programs that support better housing, health, and educational initiatives within fair-trade farming communities. 55 Although the New York location is the only café, the coffee brand is still distributed, with Keurig donating an undisclosed portion of Laughing Man proceeds to those causes (whereas Jackman donates all his profits). The company initially donated its profits to World Vision, the Christian humanitarian group Jackman accompanied in 2009. In 2017, it created the Laughing Man Foundation to be more active with its money management and distribution.
- You be the entrepreneur. If you were Jackman, would you have sold the company to Keurig? Why or why not?
- Would you have started the Laughing Man Foundation?
- What else can Jackman do to aid fair-trade practices for coffee growers?
What Can You Do?
Textbooks for change.
Founded in 2014, Textbooks for Change uses a cross-compensation model, in which one customer segment pays for a product or service, and the profit from that revenue is used to provide the same product or service to another, underserved segment. Textbooks for Change partners with student organizations to collect used college textbooks, some of which are re-sold while others are donated to students in need at underserved universities across the globe. The organization has reused or recycled 250,000 textbooks, providing 220,000 students with access through seven campus partners in East Africa. This B-corp social enterprise tackles a problem and offers a solution that is directly relevant to college students like yourself. Have you observed a problem on your college campus or other campuses that is not being served properly? Could it result in a social enterprise?
Work It Out
Franchisee set out.
A franchisee of East Coast Wings, a chain with dozens of restaurants in the United States, has decided to part ways with the chain. The new store will feature the same basic sports-bar-and-restaurant concept and serve the same basic foods: chicken wings, burgers, sandwiches, and the like. The new restaurant can’t rely on the same distributors and suppliers. A new business plan is needed.
- What steps should the new restaurant take to create a new business plan?
- Should it attempt to serve the same customers? Why or why not?
This New York Times video, “An Unlikely Business Plan,” describes entrepreneurial resurgence in Detroit, Michigan.
- 48 Chris Guillebeau. The $100 Startup: Reinvent the Way You Make a Living, Do What You Love, and Create a New Future . New York: Crown Business/Random House, 2012.
- 49 Jonathan Chan. “What These 4 Startup Case Studies Can Teach You about Failure.” Foundr.com . July 12, 2015. https://foundr.com/4-startup-case-studies-failure/
- 50 Amy Feldman. “Inventor of the Cut Buddy Paid YouTubers to Spark Sales. He Wasn’t Ready for a Video to Go Viral.” Forbes. February 15, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestreptalks/2017/02/15/inventor-of-the-cut-buddy-paid-youtubers-to-spark-sales-he-wasnt-ready-for-a-video-to-go-viral/#3eb540ce798a
- 51 Jennifer Post. “National Business Plan Competitions for Entrepreneurs.” Business News Daily . August 30, 2018. https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/6902-business-plan-competitions-entrepreneurs.html
- 52 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition . March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf
- 53 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition. March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf; Based on 2019 RBPC Competition Rules and Format April 4–6, 2019. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2019-RBPC-Competition-Rules%20-Format.pdf
- 54 Foodstart. http://foodstart.com
- 55 “Hugh Jackman Journey to Starting a Social Enterprise Coffee Company.” Giving Compass. April 8, 2018. https://givingcompass.org/article/hugh-jackman-journey-to-starting-a-social-enterprise-coffee-company/
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Michael Laverty, Chris Littel
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Entrepreneurship
- Publication date: Jan 16, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/11-4-the-business-plan
© Jan 4, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

9 Examples: How to Write a Purpose Statement
By Status.net Editorial Team on September 30, 2023 — 15 minutes to read
- Key Elements of a Purpose Statement Part 1
- How to Write a Purpose Statement Step-by-Step Part 2
- Identifying Your Goals Part 3
- Defining Your Audience Part 4
- Outlining Your Methods Part 5
- Stating the Expected Outcomes Part 6
- Purpose Statement Example for a Research Paper Part 7
- Purpose Statement Example For Personal Goals Part 8
- Purpose Statement Example For Business Objectives Part 9
- Purpose Statement Example For an Essay Part 10
- Purpose Statement Example For a Proposal Part 11
- Purpose Statement Example For a Report Part 12
- Purpose Statement Example For a Project Part 13
- Purpose Statement Templates Part 14
A purpose statement is a vital component of any project, as it sets the tone for the entire piece of work. It tells the reader what the project is about, why it’s important, and what the writer hopes to achieve.
Part 1 Key Elements of a Purpose Statement
When writing a purpose statement, there are several key elements that you should keep in mind. These elements will help you to create a clear, concise, and effective statement that accurately reflects your goals and objectives.
1. The Problem or Opportunity
The first element of a purpose statement is the problem or opportunity that you are addressing. This should be a clear and specific description of the issue that you are trying to solve or the opportunity that you are pursuing.
2. The Target Audience
The second element is the target audience for your purpose statement. This should be a clear and specific description of the group of people who will benefit from your work.
3. The Solution
The third element is the solution that you are proposing. This should be a clear and specific description of the action that you will take to address the problem or pursue the opportunity.
4. The Benefits
The fourth element is the benefits that your solution will provide. This should be a clear and specific description of the positive outcomes that your work will achieve.
5. The Action Plan
The fifth element is the action plan that you will follow to implement your solution. This should be a clear and specific description of the steps that you will take to achieve your goals.
Part 2 How to Write a Purpose Statement Step-by-Step
Writing a purpose statement is an essential part of any research project. It helps to clarify the purpose of your study and provides direction for your research. Here are some steps to follow when writing a purpose statement:
- Start with a clear research question: The first step in writing a purpose statement is to have a clear research question. This question should be specific and focused on the topic you want to research.
- Identify the scope of your study: Once you have a clear research question, you need to identify the scope of your study. This involves determining what you will and will not include in your research.
- Define your research objectives: Your research objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. They should also be aligned with your research question and the scope of your study.
- Determine your research design: Your research design will depend on the nature of your research question and the scope of your study. You may choose to use a qualitative, quantitative, or mixed-methods approach.
- Write your purpose statement: Your purpose statement should be a clear and concise statement that summarizes the purpose of your study. It should include your research question, the scope of your study, your research objectives, and your research design.
Research question: What are the effects of social media on teenage mental health?
Scope of study: This study will focus on teenagers aged 13-18 in the United States.
Research objectives: To determine the prevalence of social media use among teenagers, to identify the types of social media used by teenagers, to explore the relationship between social media use and mental health, and to provide recommendations for parents, educators, and mental health professionals.
Research design: This study will use a mixed-methods approach, including a survey and interviews with teenagers and mental health professionals.
Purpose statement: The purpose of this study is to examine the effects of social media on teenage mental health among teenagers aged 13-18 in the United States. The study will use a mixed-methods approach, including a survey and interviews with teenagers and mental health professionals. The research objectives are to determine the prevalence of social media use among teenagers, to identify the types of social media used by teenagers, to explore the relationship between social media use and mental health, and to provide recommendations for parents, educators, and mental health professionals.
Part 3 Section 1: Identifying Your Goals
Before you start writing your purpose statement, it’s important to identify your goals. To do this, ask yourself the following questions:
- What do I want to achieve?
- What problem do I want to solve?
- What impact do I want to make?
Once you have a clear idea of your goals, you can start crafting your purpose statement. Your purpose statement should be a clear and concise statement that outlines the purpose of your work.
For example, if you’re writing a purpose statement for a business, your statement might look something like this:
“Our purpose is to provide high-quality products and services that improve the lives of our customers and contribute to the growth and success of our company.”
If you’re writing a purpose statement for a non-profit organization, your statement might look something like this:
“Our purpose is to improve the lives of underserved communities by providing access to education, healthcare, and other essential services.”
Remember, your purpose statement should be specific, measurable, and achievable. It should also be aligned with your values and goals, and it should inspire and motivate you to take action.
Part 4 Section 2: Defining Your Audience
Once you have established the purpose of your statement, it’s important to consider who your audience is. The audience for your purpose statement will depend on the context in which it will be used. For example, if you’re writing a purpose statement for a research paper, your audience will likely be your professor or academic peers. If you’re writing a purpose statement for a business proposal, your audience may be potential investors or clients.
Defining your audience is important because it will help you tailor your purpose statement to the specific needs and interests of your readers. You want to make sure that your statement is clear, concise, and relevant to your audience.
To define your audience, consider the following questions:
- Who will be reading your purpose statement?
- What is their level of knowledge or expertise on the topic?
- What are their needs and interests?
- What do they hope to gain from reading your purpose statement?
Once you have a clear understanding of your audience, you can begin to craft your purpose statement with their needs and interests in mind. This will help ensure that your statement is effective in communicating your goals and objectives to your readers.
For example, if you’re writing a purpose statement for a research paper on the effects of climate change on agriculture, your audience may be fellow researchers in the field of environmental science. In this case, you would want to make sure that your purpose statement is written in a way that is clear and concise, using technical language that is familiar to your audience.
Or, if you’re writing a purpose statement for a business proposal to potential investors, your audience may be less familiar with the technical aspects of your project. In this case, you would want to make sure that your purpose statement is written in a way that is easy to understand, using clear and concise language that highlights the benefits of your proposal.
The key to defining your audience is to put yourself in their shoes and consider what they need and want from your purpose statement.
Part 5 Section 3: Outlining Your Methods
After you have identified the purpose of your statement, it is time to outline your methods. This section should describe how you plan to achieve your goal and the steps you will take to get there. Here are a few tips to help you outline your methods effectively:
- Start with a general overview: Begin by providing a brief overview of the methods you plan to use. This will give your readers a sense of what to expect in the following paragraphs.
- Break down your methods: Break your methods down into smaller, more manageable steps. This will make it easier for you to stay organized and for your readers to follow along.
- Use bullet points: Bullet points can help you organize your ideas and make your methods easier to read. Use them to list the steps you will take to achieve your goal.
- Be specific: Make sure you are specific about the methods you plan to use. This will help your readers understand exactly what you are doing and why.
- Provide examples: Use examples to illustrate your methods. This will make it easier for your readers to understand what you are trying to accomplish.
Part 6 Section 4: Stating the Expected Outcomes
After defining the problem and the purpose of your research, it’s time to state the expected outcomes. This is where you describe what you hope to achieve by conducting your research. The expected outcomes should be specific and measurable, so you can determine if you have achieved your goals.
It’s important to be realistic when stating your expected outcomes. Don’t make exaggerated or false claims, and don’t promise something that you can’t deliver. Your expected outcomes should be based on your research question and the purpose of your study.
Here are some examples of expected outcomes:
- To identify the factors that contribute to employee turnover in the company.
- To develop a new marketing strategy that will increase sales by 20% within the next year.
- To evaluate the effectiveness of a new training program for improving customer service.
- To determine the impact of social media on consumer behavior.
When stating your expected outcomes, make sure they align with your research question and purpose statement. This will help you stay focused on your goals and ensure that your research is relevant and meaningful.
In addition to stating your expected outcomes, you should also describe how you will measure them. This could involve collecting data through surveys, interviews, or experiments, or analyzing existing data from sources such as government reports or industry publications.
Part 7 Purpose Statement Example for a Research Paper
If you are writing a research paper, your purpose statement should clearly state the objective of your study. Here is an example of a purpose statement for a research paper:
The purpose of this study is to investigate the effects of social media on the mental health of teenagers in the United States.
This purpose statement clearly states the objective of the study and provides a specific focus for the research.
Part 8 Purpose Statement Example For Personal Goals
When writing a purpose statement for your personal goals, it’s important to clearly define what you want to achieve and why. Here’s a template that can help you get started:
“I want to [goal] so that [reason]. I will achieve this by [action].”
Example: “I want to lose 10 pounds so that I can feel more confident in my body. I will achieve this by going to the gym three times a week and cutting out sugary snacks.”
Remember to be specific and realistic when setting your goals and actions, and to regularly review and adjust your purpose statement as needed.
Part 9 Purpose Statement Example For Business Objectives
If you’re writing a purpose statement for a business objective, this template can help you get started:
[Objective] [Action verb] [Target audience] [Outcome or benefit]
Here’s an example using this template:
Increase online sales by creating a more user-friendly website for millennial shoppers.
This purpose statement is clear and concise. It identifies the objective (increase online sales), the action verb (creating), the target audience (millennial shoppers), and the outcome or benefit (a more user-friendly website).
Part 10 Purpose Statement Example For an Essay
“The purpose of this essay is to examine the causes and consequences of climate change, with a focus on the role of human activities, and to propose solutions that can mitigate its impact on the environment and future generations.”
This purpose statement clearly states the subject of the essay (climate change), what aspects will be explored (causes, consequences, human activities), and the intended outcome (proposing solutions). It provides a clear roadmap for the reader and sets the direction for the essay.
Part 11 Purpose Statement Example For a Proposal
“The purpose of this proposal is to secure funding and support for the establishment of a community garden in [Location], aimed at promoting sustainable urban agriculture, fostering community engagement, and improving local access to fresh, healthy produce.”
Why this purpose statement is effective:
- The subject of the proposal is clear: the establishment of a community garden.
- The specific goals of the project are outlined: promoting sustainable urban agriculture, fostering community engagement, and improving local access to fresh produce.
- The overall objective of the proposal is evident: securing funding and support.
Part 12 Purpose Statement Example For a Report
“The purpose of this report is to analyze current market trends in the electric vehicle (EV) industry, assess consumer preferences and buying behaviors, and provide strategic recommendations to guide [Company Name] in entering this growing market segment.”
- The subject of the report is provided: market trends in the electric vehicle industry.
- The specific goals of the report are analysis of market trends, assessment of consumer preferences, and strategic recommendations.
- The overall objective of the report is clear: providing guidance for the company’s entry into the EV market.
Part 13 Purpose Statement Example For a Project
“The purpose of this project is to design and implement a new employee wellness program that promotes physical and mental wellbeing in the workplace.”
This purpose statement clearly outlines the objective of the project, which is to create a new employee wellness program. The program is designed to promote physical and mental wellbeing in the workplace, which is a key concern for many employers. By implementing this program, the company aims to improve employee health, reduce absenteeism, and increase productivity. The purpose statement is concise and specific, providing a clear direction for the project team to follow. It highlights the importance of the project and its potential benefits for the company and its employees.
Part 14 Purpose Statement Templates
When writing a purpose statement, it can be helpful to use a template to ensure that you cover all the necessary components:
Template 1: To [action] [target audience] in order to [outcome]
This template is a straightforward way to outline your purpose statement. Simply fill in the blanks with the appropriate information:
- The purpose of […] is
- To [action]: What action do you want to take?
- [Target audience]: Who is your target audience?
- In order to [outcome]: What outcome do you hope to achieve?
For example:
- The purpose of our marketing campaign is to increase brand awareness among young adults in urban areas, in order to drive sales and revenue growth.
- The purpose of our employee training program is to improve customer service skills among our frontline staff, in order to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- The purpose of our new product launch is to expand our market share in the healthcare industry, by offering a unique solution to the needs of elderly patients with chronic conditions.
Template 2: This [project/product] is designed to [action] [target audience] by [method] in order to [outcome].
This template is useful for purpose statements that involve a specific project or product. Fill in the blanks with the appropriate information:
- This [project/product]: What is your project or product?
- Is designed to [action]: What action do you want to take?
- By [method]: What method will you use to achieve your goal?
- This app is designed to provide personalized nutrition advice to athletes by analyzing their training data in order to optimize performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key elements of a purpose statement.
A purpose statement should clearly communicate the main goal or objective of your writing. It should be concise and specific, providing a clear direction for your work. The key elements of a purpose statement include the topic or subject matter, the intended audience, and the overall goal or objective of your writing.
How can a purpose statement benefit your writing?
A purpose statement can help you stay focused and on track when writing. It can also help you to avoid going off-topic or getting bogged down in unnecessary details. By clearly identifying the main goal or objective of your writing, a purpose statement can help you to stay organized and ensure that your writing is effective and impactful.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when writing a purpose statement?
One common mistake is being too vague or general in your purpose statement. Another mistake is making your purpose statement too long or complex, which can make it difficult to understand. Additionally, it’s important to avoid including unnecessary information or details that are not directly relevant to your main goal or objective.
How can you tailor your purpose statement to your audience?
When writing a purpose statement, it’s important to consider your audience and their needs. You should tailor your purpose statement to your audience by using language and terminology that they will understand. You should also consider their level of knowledge or expertise on the subject matter and adjust your purpose statement accordingly.
What are some effective templates for writing a purpose statement?
There are many effective templates for writing a purpose statement, but one common approach is to use the following structure: “The purpose of this writing is to [insert goal or objective] for [insert audience] regarding [insert topic or subject matter].”
Can you provide examples of successful purpose statements?
- “The purpose of this report is to provide an analysis of the current market trends and make recommendations for future growth strategies for our company.”
- “The purpose of this essay is to explore the impact of social media on modern communication and its implications for society.”
- “The purpose of this proposal is to secure funding for a new community center that will provide educational and recreational opportunities for local residents.”
- 20 Inspiring Examples: How to Write a Personal Mission Statement
- 5 Examples: How to Write a Letter of Employment
- 6 Example Emails: How to Ask for a Letter of Recommendation
- 2 Templates and Examples: Individual Development Plan
- 5 Effective Examples: How to Write a Two-Week Notice
- 3 Examples: Job Application Email (with Tips)
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Tips White Papers
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
The Essential Guide to Writing a Business Plan Here's the no-nonsense guide on how to write a business plan that will help you map success for your startup.
By Carolyn Sun
Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own.
President Dwight D. Eisenhower once said, "In preparing for battle I have always found that plans are useless, but planning is indispensable." If you're starting a business, you should have a business plan regardless of whether you're bootstrapping it or looking for outside funding.
The best sorts of business plans tell a clear story of what the company plans to do and how it will do it. Given the high failure rate of startups in their first year, a business plan is also an ideal opportunity to safely test out the feasibility of a business and spot flaws, set aside unrealistic projections and identify and analyze the competition.
A business plan doesn't need to be complicated, but for it to serve its purpose and set you up for success, it must be clear to whomever is reading your plan that you have a realistic handle on the why and how your business will be a success.
To get you moving in the right direction, here's a guide on how to write a business plan.
Overall tips
There's a lot of advice in the infosphere about how to write a business plan, but there's no single correct way. Your approach depends on your industry, who is reading your plan and what the plan is intended for. Are you trying to get funding? Sara Sutton Fell, founder of FlexJobs , a job site for flexible telecommuting jobs, says her business plan was an initiator for more in-depth conversation with potential investors. "A plan does help to see if investors and entrepreneurs are on the same page with general expectations for the business," she says.
A business plan serves many purposes, but there is universal consensus on the following when it comes to your business plan:
Have several versions tailored for specific audiences: "One of the mistakes that inexperienced business owners make is not understanding who they're writing the plan for," says David Ciccarelli, a small business owner who got consultation from his local Small Business Association (SBA) when he was starting his company Voices.com , which connects employers with voiceover talent.
Your plan is a living document: Tim Berry, the founder of a business planning software company Palo Alto Software , took his company from zero to $5 million in sales in its first three years. To do so requires frequent review and close tracking, says Berry, who met with his management team every month to review the plan versus what actually happened -- and then to revise. "There is no virtue to sticking to a plan if it's not useful and responsive to what actually happens," he cautions.
Be realistic about financial estimates and projections: "When you present a plan to bankers and financiers, or even to your employees, people will get way more excited about what's real rather than some huge thing that's never going to happen," says Ciccarelli. So present an achievable sales forecasts based on bottom-upwards information (i.e. how many units per month get sold in how many stores) and stop over projecting profits.
Writing your business plan is about the process and having a blueprint: Your business plan "reflects your ideas, intuitions, instincts and insights about your business and its future," according to Write Your Business Plan (Entrepreneur, 2015). The plan serves as a safe way to test these out before you commit to a course of action. And once you get your business going, the plan also serves as a reference point. "I still print the document," says Ciccarelli. "You're capturing it in time. If you're changing it all the time, you kind of don't remember where you were last year."
Back up any claims: Follow up your projections and assertions with statistics, facts or quotes from a knowledgeable source to lend your plan credibility.
Presentation counts: Reading any long, text-heavy document is hard on the eyes, so format with this in mind. Consider formatting your text pages into two-columns and break up long passages with charts or graphs. Arial, Verdana or Times New Roman are standard industry fonts.
Writing your business plan isn't busy work or a luxury; it's a vital part of the process of starting a business and arms you with information you need to know. So, let's get into what information goes into your business plan.
Related: Bu siness Plans: A Step-by-Step Guide
What goes into a business plan?
A typical business plan is 15 to 25 pages. Its length depends on a variety of factors, such as whether your business is introducing a new product or belongs to a new industry (which requires explanation to the reader), or if you're pitching to bankers, who generally expect to see a traditional written business plan and financials.
"Most equity investors prefer either an executive summary or pitch deck for first contact, but will often request a more detailed plan later in the due diligence process. Potential customers don't need all the details of your internal operation. Your management team needs access to everything," says Akira Hirai, managing director of business plan consulting service Cayenne Consulting .
Most business plans include these seven sections:
1. Executive summary : The executive summary follows the title page and explains the fundamentals of your business. It should provide a short and clear synopsis of your business plan that describes your business concept, financial features and requirements (i.e. cash flow and sales projections plus capital needed), your company's current business position (i.e. its legal form of operation, when the company was formed, principals and key personnel) and any major achievements in the company that are relevant to its success, including patents, prototypes or results from test marketing.
2. Business description : This section typically begins with a brief description of your industry and its outlook. Get into the various markets within the industry, including any new products that will benefit or hurt your business. For those seeking funding, reinforce your data with reliable sources and footnote when possible. Also provide a description of your business operation's structure (i.e. wholesale, retail or service-oriented), who you will sell to, how you will distribute your products/services, the products/services itself (what gives you the competitive edge), your business's legal structure, your principals and what they bring to the organization.
Here are some worksheets from Write Your Business Plan that will help determine your unique selling proposition and analyze your industry.
Click to Enlarge+

3. Market strategies: Here is where you define your target market and how you plan to reach them. Market analysis requires research and familiarity with the market so that the target market can be defined and the company can be positioned (i.e. are you a premium product or a price-competitive product?) in order to garner its market share. Analyze your market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends and sales/growth potential. This section also talks about distribution plans and promotion strategy and tactics that will allow you to fulfill your plans.
Here is a worksheet from Write Your Business Plan that will guide you toward identifying your target market.

4. Competitive analysis: The purpose of the competitive analysis is to determine the strengths and weaknesses of the competitors within your market, strategies that will provide you with a distinct advantage, the barriers that can be developed in order to prevent competition from entering your market, and any weaknesses that can be exploited within the product development cycle. Show why your business will be a success over others.
5. Design and development plan: You will only need this section if you have a product in development, such as an app. The purpose of this section is to provide investors with a description of the product's design, chart its development within the context of production and marketing and show a development budget that will enable the company to reach its goals.
6. Operations and management plan: This section describes how the business functions on a daily basis, its location, equipment, people, processes and surrounding environment. If you have a product that needs to be manufactured, explain the how and where; also, describe your work facility, the personnel, the legal environment (such as licensing, permits, special regulations, etc.), key suppliers and inventory. This section will also highlight the logistics of the organization such as the various responsibilities of the management team and the tasks assigned to each division within the company.
7. Financial factors: Financial data is always at the back of a business plan -- yet it's extremely important. The financial data can include your personal financial statement, startup expenses and capital, your projected cash flow statement and 12-month profit-and-loss statement. PaloAlto's Berry stresses that if you're going after investors, you'll need to show a cash flow statement and a break-even analysis -- or the breakdown to see where your business breaks even.
The best way to prepare for running a business is to have all the components of the plan ready. So if you are are showing a prospective lender your business plan on 10 PowerPoint slides and get asked about something that isn't in the presentation, you can speak knowledgeably and follow up with a more fleshed out plan -- and quickly.
Some business owners hire business plan writing services. Cayenne Consulting's Hirai says that his clients generally fall into one of two categories: those intimidated by the process and those who could write the plan themselves but would prefer to spend their time on other priorities.
If you find yourself intimidated or stuck, you can always write the parts of plan yourself that you understand and hire a consultant or researcher to help with parts that you find confusing.
Or if you're a startup watching every dollar, then tap the free services of the federal Small Business Association (SBA). Every state has a district office . Through the SBA, you can get business plan assistance through its various resource partners, which includes Women's Business Centers , Small Business Development Centers and Service Corps of Retired Executives .
Allow this business plan template for Business Plan for a Startup Business to guide you:
Different types of business plans
Generally, business plans can be divided into four categories :
Working plan: This plan is what you will use to operate your business and is not meant to be admired. This version of your plan is an internal document and will be long on detail, short on presentation. Here, you can omit descriptions that you need not explain to yourself or your team.
Mini plan: The reader may request a mini plan, or a condensed version of your business plan (1-10 pages), which includes most of the same components as in a longer traditional plan -- minus the details and explanation. This includes the business concept, financing needs, marketing plan, financial statements (especially cash flow), income project and balance sheet. This shorter plan is not meant to be a substitute for a full-length plan, but serves as an option to present to potential partners or investors.
Presentation plan: Whether you're using a pitch deck or a written business plan, the information in your presentation plan will be, more or less, the same as in your working plan but worded differently and styled for the eyes of an outsider. The reader of your presentation plan will be someone who is unfamiliar with your business, such as investor or venture capitalist, so lose any jargon or shorthand from your working plan, which only makes sense to you. Also, keep in mind that investors will want to see due diligence on your competition threats and risks as well as financial projections. In addition, looks count, so use the color printer, a nice cover and bindings and the fancy paper stock. Or else, if you're presenting your business plan as a PowerPoint presentation, you can use this business plan presentation template .
What-if plan: This is a contingency plan -- in case your worst case scenario happens, such as market share loss, heavy price competition or defection of a key member of your team. You want to think about what to do in the face of an of these, and if you're trying to get outside funds, having a contingency plan shows that you've considered what to do if things don't go according to plan. You don't necessarily need this, but if you are getting outside funding, then it can strengthen your credibility showing that you have thought about these what-if possibilities. Even if you're not going to get outside funding, shouldn't you be thinking of the what ifs?
If four plans seem like a mountain of work, don't panic. Select two to start off -- a working plan and a mini plan, which will be an abbreviated version of your working plan.
Take several months to write your business plan. Consider it a journey, not a sprint.
Related: The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Business Plan
Carolyn Sun is a freelance writer for Entrepreneur.com. Find out more on Twitter and Facebook .
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- Lock The Average American Can't Afford a House in 99% of the U.S. — Here's a State-By-State Breakdown of the Mortgage Rates That Tip the Scale
- Richard Branson Shares His Extremely Active Morning Routine : 'I've Got to Look After Myself'
- Lock This Flexible, AI-Powered Side Hustle Lets a Dad of Four Make $32 an Hour , Plus Tips: 'You Can Make a Substantial Amount of Money'
- Tennis Champion Coco Gauff Reveals the Daily Habits That Help Her Win On and Off the Court — Plus a 'No Brainer' Business Move
- Lock 3 Essential Skills I Learned By Growing My Business From the Ground Up
- 50 Cent Once Sued Taco Bell for $4 Million. Here's How the Fast-Food Giant Got on the Rapper's Bad Side .
Most Popular Red Arrow
How keeping things simple helps your company innovate and grow.
This article explores why simplicity is challenging yet essential, highlighting examples from successful companies like Ikea and Nike, and offers practical advice on how simplifying processes, communications and product development can lead to better outcomes and substantial business success.
Four Tried-and-True Ways to Better Market Your Business
With all the technology we have today, there are quite a few marketing channels business owners can leverage — but let's take a closer look at a few that work best.
I Started Over 300 Companies. Here Are 4 Things I Learned About Scaling a Business.
It takes a delicate balance of skill, hard work and instinct to grow a successful business. This serial entrepreneur loves the unique challenge; here are the key lessons she's learned along the way.
She Grew Her Side Hustle Sales From $0 to Over $6 Million in Just 6 Months — and an 'Old-School' Mindset Helped Her Do It
Cynthia Sakai, designer and founder of the luxury personal care company evolvetogether, felt compelled to help people during the pandemic.
'Why Shouldn't They Participate?': AT&T CEO Calls on Big Tech to Help Subsidize Internet Access
AT&T's CEO called out the seven biggest tech companies in the world.
5 SEO Techniques to Help Your SaaS Business Rank in 2024
Discover five game-changing SEO techniques that can help you rely less on paid ads and cut down your customer acquisition costs.
Successfully copied link
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One CURRENT ARTICLE
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
A business plan is a document that outlines a company's goals and the strategies to achieve them. It's valuable for both startups and established companies. For startups, a well-crafted business plan is crucial for attracting potential lenders and investors. Established businesses use business plans to stay on track and aligned with their growth objectives. This article will explain the key components of an effective business plan and guidance on how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document detailing a company's business activities and strategies for achieving its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to launch their venture and to attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan helps keep the executive team focused on short- and long-term objectives.
- There's no single required format for a business plan, but certain key elements are essential for most companies.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place before beginning operations. Banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before considering making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a company doesn't need additional funding, having a business plan helps it stay focused on its goals. Research from the University of Oregon shows that businesses with a plan are significantly more likely to secure funding than those without one. Moreover, companies with a business plan grow 30% faster than those that don't plan. According to a Harvard Business Review article, entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than those who don't.
A business plan should ideally be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect achieved goals or changes in direction. An established business moving in a new direction might even create an entirely new plan.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. It allows for careful consideration of ideas before significant investment, highlights potential obstacles to success, and provides a tool for seeking objective feedback from trusted outsiders. A business plan may also help ensure that a company’s executive team remains aligned on strategic action items and priorities.
While business plans vary widely, even among competitors in the same industry, they often share basic elements detailed below.
A well-crafted business plan is essential for attracting investors and guiding a company's strategic growth. It should address market needs and investor requirements and provide clear financial projections.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, gathering the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document is best. Any additional crucial elements, such as patent applications, can be referenced in the main document and included as appendices.
Common elements in many business plans include:
- Executive summary : This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services : Describe the products and services the company offers or plans to introduce. Include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique consumer benefits. Mention production and manufacturing processes, relevant patents , proprietary technology , and research and development (R&D) information.
- Market analysis : Explain the current state of the industry and the competition. Detail where the company fits in, the types of customers it plans to target, and how it plans to capture market share from competitors.
- Marketing strategy : Outline the company's plans to attract and retain customers, including anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. Describe the distribution channels that will be used to deliver products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections : Established businesses should include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. This section may also include any funding requests.
Investors want to see a clear exit strategy, expected returns, and a timeline for cashing out. It's likely a good idea to provide five-year profitability forecasts and realistic financial estimates.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can vary in format, often categorized into traditional and lean startup plans. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These are detailed and lengthy, requiring more effort to create but offering comprehensive information that can be persuasive to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These are concise, sometimes just one page, and focus on key elements. While they save time, companies should be ready to provide additional details if requested by investors or lenders.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan isn't a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections. Markets and the economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All this calls for building flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How Often Should a Business Plan Be Updated?
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on its nature. Updating your business plan is crucial due to changes in external factors (market trends, competition, and regulations) and internal developments (like employee growth and new products). While a well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary, a new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is ideal for quickly explaining a business, especially for new companies that don't have much information yet. Key sections may include a value proposition , major activities and advantages, resources (staff, intellectual property, and capital), partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.
A well-crafted business plan is crucial for any company, whether it's a startup looking for investment or an established business wanting to stay on course. It outlines goals and strategies, boosting a company's chances of securing funding and achieving growth.
As your business and the market change, update your business plan regularly. This keeps it relevant and aligned with your current goals and conditions. Think of your business plan as a living document that evolves with your company, not something carved in stone.
University of Oregon Department of Economics. " Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Business Planning Using Palo Alto's Business Plan Pro ." Eason Ding & Tim Hursey.
Bplans. " Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes ."
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
Harvard Business Review. " How to Write a Winning Business Plan ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
SCORE. " When and Why Should You Review Your Business Plan? "
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

Health & Nursing
Courses and certificates.
- Bachelor's Degrees
- View all Business Bachelor's Degrees
- Business Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Healthcare Administration – B.S.
- Human Resource Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Information Technology Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Marketing – B.S. Business Administration
- Accounting – B.S. Business Administration
- Finance – B.S.
- Supply Chain and Operations Management – B.S.
- Accelerated Information Technology Bachelor's and Master's Degree (from the School of Technology)
- Health Information Management – B.S. (from the Leavitt School of Health)
Master's Degrees
- View all Business Master's Degrees
- Master of Business Administration (MBA)
- MBA Information Technology Management
- MBA Healthcare Management
- Management and Leadership – M.S.
- Accounting – M.S.
- Marketing – M.S.
- Human Resource Management – M.S.
- Master of Healthcare Administration (from the Leavitt School of Health)
- Data Analytics – M.S. (from the School of Technology)
- Information Technology Management – M.S. (from the School of Technology)
- Education Technology and Instructional Design – M.Ed. (from the School of Education)
Certificates
- Supply Chain
- Accounting Fundamentals
- Digital Marketing and E-Commerce
- View all Business Degrees
Bachelor's Preparing For Licensure
- View all Education Bachelor's Degrees
- Elementary Education – B.A.
- Special Education and Elementary Education (Dual Licensure) – B.A.
- Special Education (Mild-to-Moderate) – B.A.
- Mathematics Education (Middle Grades) – B.S.
- Mathematics Education (Secondary)– B.S.
- Science Education (Middle Grades) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Chemistry) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Physics) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Biological Sciences) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Earth Science)– B.S.
- View all Education Degrees
Bachelor of Arts in Education Degrees
- Educational Studies – B.A.
Master of Science in Education Degrees
- View all Education Master's Degrees
- Curriculum and Instruction – M.S.
- Educational Leadership – M.S.
- Education Technology and Instructional Design – M.Ed.
Master's Preparing for Licensure
- Teaching, Elementary Education – M.A.
- Teaching, English Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Mathematics Education (Middle Grades) – M.A.
- Teaching, Mathematics Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Science Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Special Education (K-12) – M.A.
Licensure Information
- State Teaching Licensure Information
Master's Degrees for Teachers
- Mathematics Education (K-6) – M.A.
- Mathematics Education (Middle Grade) – M.A.
- Mathematics Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- English Language Learning (PreK-12) – M.A.
- Endorsement Preparation Program, English Language Learning (PreK-12)
- Science Education (Middle Grades) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Chemistry) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Physics) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Biological Sciences) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Earth Science)– M.A.
- View all Technology Bachelor's Degrees
- Cloud Computing – B.S.
- Computer Science – B.S.
- Cybersecurity and Information Assurance – B.S.
- Data Analytics – B.S.
- Information Technology – B.S.
- Network Engineering and Security – B.S.
- Software Engineering – B.S.
- Accelerated Information Technology Bachelor's and Master's Degree
- Information Technology Management – B.S. Business Administration (from the School of Business)
- View all Technology Master's Degrees
- Cybersecurity and Information Assurance – M.S.
- Data Analytics – M.S.
- Information Technology Management – M.S.
- MBA Information Technology Management (from the School of Business)
- Full Stack Engineering
- Web Application Deployment and Support
- Front End Web Development
- Back End Web Development
3rd Party Certifications
- IT Certifications Included in WGU Degrees
- View all Technology Degrees
- View all Health & Nursing Bachelor's Degrees
- Nursing (RN-to-BSN online) – B.S.
- Nursing (Prelicensure) – B.S. (Available in select states)
- Health Information Management – B.S.
- Health and Human Services – B.S.
- Psychology – B.S.
- Health Science – B.S.
- Healthcare Administration – B.S. (from the School of Business)
- View all Nursing Post-Master's Certificates
- Nursing Education—Post-Master's Certificate
- Nursing Leadership and Management—Post-Master's Certificate
- Family Nurse Practitioner—Post-Master's Certificate
- Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner —Post-Master's Certificate
- View all Health & Nursing Degrees
- View all Nursing & Health Master's Degrees
- Nursing – Education (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Leadership and Management (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Nursing Informatics (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Family Nurse Practitioner (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S. (Available in select states)
- Nursing – Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S. (Available in select states)
- Nursing – Education (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Leadership and Management (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Nursing Informatics (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Master of Healthcare Administration
- Master of Public Health
- MBA Healthcare Management (from the School of Business)
- Business Leadership (with the School of Business)
- Supply Chain (with the School of Business)
- Accounting Fundamentals (with the School of Business)
- Digital Marketing and E-Commerce (with the School of Business)
- Back End Web Development (with the School of Technology)
- Front End Web Development (with the School of Technology)
- Web Application Deployment and Support (with the School of Technology)
- Full Stack Engineering (with the School of Technology)
- Single Courses
- Course Bundles
Apply for Admission
Admission requirements.
- New Students
- WGU Returning Graduates
- WGU Readmission
- Enrollment Checklist
- Accessibility
- Accommodation Request
- School of Education Admission Requirements
- School of Business Admission Requirements
- School of Technology Admission Requirements
- Leavitt School of Health Admission Requirements
Additional Requirements
- Computer Requirements
- No Standardized Testing
- Clinical and Student Teaching Information
Transferring
- FAQs about Transferring
- Transfer to WGU
- Transferrable Certifications
- Request WGU Transcripts
- International Transfer Credit
- Tuition and Fees
- Financial Aid
- Scholarships
Other Ways to Pay for School
- Tuition—School of Business
- Tuition—School of Education
- Tuition—School of Technology
- Tuition—Leavitt School of Health
- Your Financial Obligations
- Tuition Comparison
- Applying for Financial Aid
- State Grants
- Consumer Information Guide
- Responsible Borrowing Initiative
- Higher Education Relief Fund
FAFSA Support
- Net Price Calculator
- FAFSA Simplification
- See All Scholarships
- Military Scholarships
- State Scholarships
- Scholarship FAQs
Payment Options
- Payment Plans
- Corporate Reimbursement
- Current Student Hardship Assistance
- Military Tuition Assistance
WGU Experience
- How You'll Learn
- Scheduling/Assessments
- Accreditation
- Student Support/Faculty
- Military Students
- Part-Time Options
- Virtual Military Education Resource Center
- Student Outcomes
- Return on Investment
- Students and Gradutes
- Career Growth
- Student Resources
- Communities
- Testimonials
- Career Guides
- Skills Guides
- Online Degrees
- All Degrees
- Explore Your Options
Admissions & Transfers
- Admissions Overview
Tuition & Financial Aid
Student Success
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Military and Veterans
- Commencement
- Careers at WGU
- Advancement & Giving
- Partnering with WGU
How to Develop Your Company’s Purpose Statement
- See More Tags

If you aspire to lead or start a company, you’ll play a crucial role in driving its vision, goals, and plan for success. A purpose statement establishes the foundation you need to do that effectively.
While some degree programs touch on the topic of purpose statements, you might not realize how this concept can apply to your future career .
Here’s how you can take the skills you’ve learned from your business degree and use them while writing an effective company purpose statement.
What is a Purpose Statement?
The first step to understanding a purpose statement is to distinguish it from a mission statement because each plays a different role in your business plan .
Mission Statement vs. Purpose Statement
A purpose statement is a single statement that defines the reason your company exists—beyond simply making a profit. It also illustrates how your product or service positively impacts the people you serve. Once your purpose is established, you’ll need a series of goals to drive that purpose. That’s where the mission statement comes in.
First and foremost, a mission statement is actionable. It explains the path you need to take to reach your purpose. So, while a purpose statement is focused on the future, a mission statement is rooted in the present.
Unlike a company mission, your company purpose isn’t something that can be completed or checked off a list. A purpose statement illustrates the ongoing pursuit to push your company forward.
What Does a Purpose Statement Do?
A purpose statement sets expectations, both internally (for leadership and employees) and externally (for customers and investors). It acts as your company’s blueprint for the future and helps guide all the decisions you make—from how you manufacture your products to the words you use in your marketing.
Your purpose also influences your customer. In fact, 63% of global consumers prefer to purchase products and services from companies that stand for a purpose, according to recent research.
The study found that companies that stand for something bigger than what they sell, communicate their purpose, and demonstrate commitment are more likely to attract consumers and influence purchasing decisions.
Leaders around the world are taking note of the rise of purpose-driven companies , too. Lise Kingo, CEO and executive director of the UN Global Compact, stated, “The idea of business as an agent of change and a purveyor of positive values is gaining traction and legitimacy around the world. With a growing number of companies taking steps to be more responsible in how they treat employees, communities, and the planet, we are seeing business emerge as a real player and solution-provider in the quest to put our world on a better course.”
Beyond attracting customers and increasing your bottom line, clarifying your company purpose is important for these reasons:
1. Distinguishes Your Business from Competitors
One important role of your purpose statement is to define what makes your company unique. After all, your competitors might be able to replicate your product or service, but they’d be hard pressed to duplicate your unique purpose.
People can be genuinely inspired if your company has a solid purpose. When customers and employees understand what drives your passion and ignites your purpose, they’re more likely to get on board with it.
2. Helps Meet Goals
A strong purpose statement sets a path for how your company will move forward, which will help you see and set clear goals. These goals should go beyond financial performance; they should also measure how your purpose is progressing toward the social impact you’re trying to make.
3. Informs Company Culture
A recent employee survey by Harvard Business Review found that only 28% of employees felt connected to their company’s purpose, and 34% thought they were contributing to their company’s success. According to the article, a lack of purpose among employees can create a negative company culture where employees feel unmotivated and unaligned.
So how do you avoid this?
Creating a purpose-driven culture starts with clear communication between employees and leadership—as well as listening and being open to feedback. When everyone understands and supports the company's purpose, it creates a united front where everyone from the top down is working toward the same goals.
Furthermore, multiple studies show a purpose-driven culture is a positive one. This is because employees feel more engaged and motivated when they can connect the work they do with how it contributes to the organization’s purpose .

How Do I Write a Purpose Statement?
Creating a company purpose statement is no small task. It requires a deep understanding of why your company exists and where it hopes to go in the future. If you’re still feeling stuck, here are some steps to take as you're developing your company's purpose.
Step #1: Define what you do.
But more specifically, lay out what your company does to solve a particular problem for your customers.
Step #2: Pinpoint your passion.
Think about what inspires the work you do. For example, are you passionate about creating sustainable products? Do you strive to be the most innovative? Are you focused on serving local communities?
Step #3: List your values.
Understanding the things your company is passionate about will help you come up with specific values that align with your purpose. Those values might include things like sustainability, innovation, integrity, quality, etc.
Step #4: Create a draft.
Once you’ve defined what you do and why you do it, take pen to paper and start drafting ideas for your purpose statement.
As you’re writing, make sure your purpose statement is:
- Short (about 1-2 sentences)
- Easy to understand
- Aspirational (but not vague)
Step #5: Get feedback.
Ask others in your organization to review what you’ve written and consider their feedback as you hone your purpose statement.
Step #6: Leave room for growth.
Keep in mind that a purpose statement is a constant work in progress, and changes will happen as your business evolves.
Examples of Effective Purpose Statements
Use these company purpose statements to draw inspiration from:
- Southwest Airlines lets its personality shine through in its purpose statement: “Connect people to what's important in their lives through friendly, reliable, and low-cost air travel.”
- Kellogg’s and Coke keep it short and sweet: “Nourishing families so they can flourish and thrive.” – Kellogg’s, “Refresh the world. Make a difference.” – Coke
- If you’re looking for an example of an empowering purpose statement, here’s Dove’s: “Discovering the value of 'real' beauty and improving self-esteem worldwide.”
- Both The Red Cross and Whole Foods have purpose statements that make an emotional connection: “Our deepest purpose as an organization is helping support the health, well-being, and healing of both people—customers, Team Members, and business organizations in general—and the planet.” – Whole Foods, “To protect life and health and to ensure respect for the human being .” – The Red Cross
- Crayola and Lego lean on their ability to inspire: “Encouraging children to be creative, and enabling parents to inspire them.” – Crayola, “To inspire and develop the builders of tomorrow.” - Lego
Now that you know what a company purpose statement is, why it’s important, and how to develop your own, you’ll be ready to put this important business skill into practice in your own organization.
Ready to Start Your Journey?
HEALTH & NURSING
Recommended Articles
Take a look at other articles from WGU. Our articles feature information on a wide variety of subjects, written with the help of subject matter experts and researchers who are well-versed in their industries. This allows us to provide articles with interesting, relevant, and accurate information.
{{item.date}}
{{item.preTitleTag}}
{{item.title}}
The university, for students.
- Student Portal
- Alumni Services
Most Visited Links
- Business Programs
- Student Experience
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Student Communities
Everything you need to write a killer executive summary for your business plan
What is Executive Summary—and Why Should You Care?
Executive Summary is the first and most important section of a business plan, providing a snapshot of the overall plan with the aim to compel the reader to continue reading the full document by highlighting its most important components and strengths .
Keep reading for insider tips from a professional business writer on how exactly to write a captivating executive summary that will maximize the impact and success of your business plan.
You’ll discover:
- Why: Critical importance of an executive summary
- What: The key elements you need to include
- How: The best structure—length, layout and components
Importance: Why is Executive Summary Important in a Business Plan?
Executive summary is the most important part of a business plan because it is the first and only opportunity to grab readers’ interest as they review this section prior to deciding whether or not to read the rest of the document.
No matter how excellent your business idea, it is the executive summary alone that persuades a reader to spend more time with the plan to find out more about your venture.
Some financiers receive hundreds of business plans every month. Understandably, they do not read them all . Instead, they can tell in a couple of paragraphs if it is something they may be interested in.
The Executive Summary is so important, in fact, that some investors and lenders prefer to receive just the summary and financials before requesting the full business plan. So if you can hook your readers here, they will ask for more.
Similarly, senior decision-makers on many company or bank boards and committees will often read nothing else than an executive summary when approving a decision to back a business.
In other words, your Executive Summary is the first impression many readers will get of your business. Make sure it is a great one. Only a clear , concise , and compelling summary of your business right up front twill persuade readers to wade through the rest of the plan.
Contents: What Should an Executive Summary for a Business Plan Include?
Executive summary brings the separate parts of a business plan together to sum up what the business is, where it is going, why it will be successful – and why it is worthy of backing . Highlight the most important and impressive facts about the company , management , offering , market , strategy and financials .
When completed, your executive summary will answer these questions for your readers:
- What is your business all about ?
- What are the most compelling qualities?
- Is the business likely to succeed and why?
Executive summary is an introduction to your business, which provides a brief snapshot of your plan as a whole. To that end, concisely highlight the most important concepts and impressive features from each section of your completed plan, addressing the following areas:
| Business plan sections: | What readers look for: | What you sell | Your basic business concept makes sense |
|---|---|---|
| Your audience and ideal customer | ||
| The problem you solve for customers | ||
| Market opportunity | Opportunity in the market | A compelling market exists for your product/service |
| Future of the industry | ||
| Competitive advantage | Your business has significant competitive advantages | |
| Financial Projections | Funding requirements | Backers have an excellent chance to make money / get money back |
| Financial forecast, growth plans and expected returns | Your financial projections are realistic | |
| Strategy | Mission | Your business has been thoroughly planned—you know where you are going and how to get there |
| Goals | ||
| KPIs | ||
| Company description | Management team | The management is capable |
| Track record to date | ||
| Location |
Essentially, you should make it crystal clear to the that a compelling market opportunity exists for your product/service and demonstrate that your business is well-positioned to exploit it .
Remember to be brief and concise . Organize the information in a way that gives the best impression of your business to your target reader. Combine related topics if that improves the flow of the document.
If the readers of your executive summary conclude that the above elements exist in your business, they are likely to commit to reading the rest of your business plan.
So, let’s examine each of the key elements in more detail to make the reader excited about the potential of your business plan and interested to read further:
Mission Statement
Answer this question for your readers:
- What is your business on a mission to create and why?
Aim: Convince the reader that your basic business concept makes sense.
Give a concise overview of your business idea, purpose and goals. Summarize why you have created this company and what your business is all about in one or two sentences, but no more than a paragraph.
Products and Services
Answer these questions for your readers:
- What product(s) and/or service(s) does your business provide?
- What problems are you solving for your target customers and how?
- What makes your product/service different and compelling for the customers to buy?
Aim: Demonstrate to the reader that your product/service solves a real problem in the market and that the problem is worth solving.
Briefly describe the products and services your company provides and what problems you solve for your target customers, making the case for why your product will be successful:
Description:
List the products or services your company sells or plans to sell.
Problem & Solution:
Explain the need for the products or services:
- Problem: Summarize the problem your product/service solves and why it is worth solving. In other words, what is it that your customers need and cannot find elsewhere.
- Solution: Summarize how you will solve the problem that your customers face.
Value Proposition:
Outline why your product or service will be valuable to your customers and the advantages that will make it compelling enough for them to purchase.
Market Opportunity
- Who are your (ideal) target customers?
- Is there a real market demand for your product/service?
- What is the size of the market opportunity?
Aim: Convince the reader that large and compelling market demand opportunity exists for your product/service.
List the target market you intend to reach and explain why you chose it:
Target Market:
Provide a brief description of your ideal customers and how do they break down into recognizable types or segments.
Market Analysis:
Indicate that you have done thorough market analysis by providing a summary of your market research results, including:
- How many potential customers are there for your solution (target market)
- What proportion of the market your company can reasonably capture (market share)
- Forecast estimating what the future holds for the industry and market demand
Competitive Advantage
- Who are your competitors?
- How is the market currently divided?
- What advantages does your company have over the competition?
Aim: Convince the reader that your business has a significant competitive edge to succeed in your target market.
This section is where you describe the gap in your target market, how your solution can fill it, and the competitive advantages that will enable you to exploit this market gap.
Hence, include information about your competition and what differentiates your business:
Competitors and Market Distribution:
Who are you up against? What other options do your customers have to address their needs? Indicate the nature of your competition and how the market is currently divided.
Competitive Advantage:
What comparative advantage does your product/service have?
Show your conclusions on your company’s competitive position and why your company will be able to compete successfully. Remember to list any important distinctions, such as patents, major contracts, or letters-of-intent.
Unique Selling Proposition:
What unique selling proposition will help your business succeed?
What makes your solution better for your customers compared to the competition?
Is competition going to get tougher?
Summarize your conclusions on whether competition is going to intensify going forward.
Company Description
Company information:.
- Is the management team capable?
- What are the basic details of your business?
- What is the company’s current stage of development?
- What are some of the milestones you’ve met?
Aim: Convince the reader that your business has the right structure and capable management team in place to succeed.
Your goal is to demonstrate that you are well-positioned to exploit the market opportunity by highlighting the positive factors in your company’s management, structure and history.
Company Details:
Include a short statement that covers the basic company details, such as the company name, when your business was formed, the names of the founders and their roles, number of employees, business location(s), and legal status.
Stage of Development:
State whether your company is a startup or continuing business, when it was founded, how far along the product or service is in its creation, and if you’ve already made sales or started shipping.
Track Record:
- If you are an established business, provide a brief history of the company’s trading activity to date, including financial and market growth highlights.
- If you are just starting a business, you won’t have as much information as an established company. Instead, focus on your experience and background as well as the decisions that led you to start this particular enterprise.
Management:
Briefly describe the bios of the key members of your management team , particularly those of company founders/owners , as well as the key professional advisors .
What do they bring to the table that will position your company well to take advantage of the market opportunity and make the business a success?
Highlight management’s vision and passion , along with the relevant skills , experience , qualifications , subject-matter expertise , business acumen , industry connections and other capabilities as they relate to the venture.
Operations:
Showcase the key operational features that will give the business a competitive edge.
This could include anything from an advantageous location, through innovative manufacturing technology and processes, to preferential supplier and distribution agreements – and anything in between.
Outline the strategy to achieve the company’s goals and continuously strengthen its competitive position.
Next, indicate the keys to success that you intend to use in order to implement that strategy, such as:
- Marketing and Sales: Briefly describe the methods you will utilize to reach your target customers to market your offering and secure sales.
- Operations and Resources: Summarize the most important resources and operational features your company will deploy to implement its strategy.
Address your plans for where you would like to take your business in the future.
Spell out the objectives you have for the company, what you plan to do:
- Where do you expect the business to be in 1 year, 3 years, 5 years ?
- What are some of the key milestones you plan to meet?
- What are your long-term goals ?
- What is your potential exit strategy ?
Make an educated projection for the expected performance of your business, including:
- Sales volume and value
- Cash flow position
- Profitability
- Number of employees
- Number of locations
- Market share
- New products
Financial Forecast
Summarize the expected financial outlook and performance for your business, answering the following questions for your readers:
- How much do you expect to make in the first year of your business?
- What kind of growth do you expect to see in the following years?
- If you do not expect your business to be profitable , do you have a strategic reason for running at a loss?
- What are the key metrics that you need to watch?
- Will your backers (if any) be able to get their money back and when ?
- Are your financial projections realistic ?
In general, it is customary to indicate financial information for years one through three or five , depending on the requirements of the business plan reader. Typically, this includes Year 1 and Year 3 / 5 results; and Year 10 / long-term goals.
However, your readers can find the detail of the projected financials further on in the plan. In this section, only provide the highlights of your forecast and encourage the reader to keep reading to learn more about your company.
Funding Requirements
How will you fund your business to get it started and grow it to the next level?
- Is it already self-sufficient?
- Do you plan to invest your own money?
- Do you seek outside financing?
If the business does not require any outside financing, you can note that here or just remove this section from your plan altogether.
When you are using the business plan for financing purposes, explain how much money is needed, from whom, and how you will utilize it to grow your business, hinting at an exit opportunity:
- Existing Source of Funds: Include information about your current lenders and investors, if any.
- Funding Requirements: Indicate how much money you are seeking, from what sources, and perhaps even under what conditions.
- Use of Funds: Specify how the raised funds will be used.
- Exit Strategy: Hint at how the backers will get their money out, with the expected timing and returns.
Tips: How Do You Write an Executive Summary?
Writing an executive summary is arguably the most fun – and important – part of writing a business plan.
You have already completed all the research, thinking and writing about market demand, competition, strategy, operations and financials.
All that is left to do now is to summarize the key conclusions into a coherent narrative , answering the million-dollar question:
Why is your plan worthy of backing?
Here are 7 tried and tested tips to prepare a compelling summary of your business that will convince the readers to read through the rest of your plan:
Target Audience (Tip #1)
Ask yourself: “Who will be reading my business plan?”
Since the summary is what the reader reads first, and may be the only section read at all, you can significantly improve your chances of a positive reception if you know the answer to that question before you prepare your executive summary.
Remember, your reader is only going to spend a few minutes , or even seconds , on your executive summary. This is especially true if you are targeting busy investors or lenders for whom it is not unusual to review more than 1,000 each year.
Naturally, the readers are going to focus on the issues that interest and concern them most . If you understand their priorities, you will be better able to craft the summary to “push the right buttons”. For example:
- Bankers are likely to look for aspects of your business that minimize risk to make sure the loan is secure and they will get their money back.
- Investors are focused on aspects that maximize the potential of your company scaling significantly and rapidly, because they will receive a share of that success.
- Management may be interested in accessing new markets for the company.
Do your homework to discover the interests and concerns of your most likely business plan recipients, and then write and organize the summary in a way that most appeals to your target audience:
- Place the issues most important to the reader near the top of your summary.
- Order the sections in any way that gives the best impression of your business to your target reader.
- In the text itself, give more emphasis to those aspects that concern your reader most.
If you are not able to identify the specific person who will read your plan, just focus on the general type of a person that is most likely to receive it and their concerns.
However, it is not a good idea to tailor the executive summary for just one specific person or organization, especially if your plan is likely to end up in the hands multiple and/or unknown recipients.
To be on the safe side, target your summary to address general institutional concerns rather than individual preferences.
Insider Tips: Writing a Winning Executive Summary
Convey your enthusiasm (tip #2).
The Executive Summary enables the readers to quickly understand the highlights of your business and decide whether to commit more of their time to reading the full plan.
To that end, you need to motivate and entice the readers by your own optimism about how well-positioned your business is to exploit a compelling market opportunity, conveyed in a dynamic , positive and confident tone.
Write Executive Summary Last (Tip #3)
Your executive summary will be the last chapter of the business plan that you prepare.
Even though the executive summary always appears first in the completed document, it is usually crafted last after you have had a chance to carefully consider all key aspects of your business throughout the rest of the plan.
The executive summary is the place where you bring all your planning together and sum up the separate parts of your business proposal to provide an overall outline and highlight the strengths of your entire plan.
Therefore, you will find it much easier and faster to come back and produce this section once you have completed the rest of your business plan.
That way, you will have thought through all the elements of your business, work out the details, and be prepared to summarize them. This approach will not only increase the consistency and accuracy of the plan, but also help make it more compelling .
So, if you have not yet finalized the other sections of your plan, proceed to the next section, and return to the executive summary when you have completed the rest of your plan.
Once finished, the executive summary will become “ Chapter 1 ” of your business plan document.
Summarize Highlights (Tip #4)
A good summary contains highlights from all of the subsequent sections of the business plan.
To achieve that, select the key points from each section of your completed plan by summarizing conclusions you have reached in each area. Remember to focus only on the most important and impressive features of your business.
What sets your business apart from the competition? Early on in your summary, showcase your distinguishing qualities and make sure you describe your winning concept in a way that any reader can easily grasp .
Use logical writing to tell a story, freely changing the order of sections and combining related topics if that helps to improve the flow and make a good impression.
Make Each Word Count (Tip #5)
The executive summary provides a brief snapshot of your business, casting a spotlight on the most important facts and concepts from your entire business plan.
As a result, this section should be clear , concise and to the point. Make each word should count.
Avoid Jargon (Tip #6)
In case the summary read by people unfamiliar with your industry, avoid any technical jargon or provide sufficient explanatory notes .
Edit, Edit, … And Edit Some More (Tip #7)
By the time you reach the executive summary, you may be tired from all the planning and writing. However, remember that this really is the most important section of the business plan.
The best investment you can make is to spend sufficient time to perfect the summary, including ruthless editing . There are professional editors who can help you make it flawless.
Design: How Do You Design an Executive Summary?
Looks matter. Your business plan will be well researched, analysed and written, but it must also be well presented. While your plan will ultimately be judged on the quality of your business concept and strategy, you also want to make sure it gives the best first impression possible.
And nowhere is presentation more important than in the executive summary, because for all readers it will be the first page(s) they read – and some will read nothing else.
The key advice here is: Break it Up . Large, dense blocks of text intimidate readers.
Dividing the Summary text with paragraph headings, bullet points and white space makes the information on a page more inviting and appealing:
- Paragraphs: Break up the Summary into paragraphs that roughly mirror the sections of your business plan
- Brief: Keep each topic as brief as possible
- Subheads: Insert informative topic headings at the beginning of each paragraph to help readers’ quick comprehension
- Bullets: Use bullet points to highlight the most compelling information
- Numbers: Use numbers instead of words where appropriate
- Visuals: Include a (small) chart or graph if it helps to clarify an important point
- Spacing: Use white space to break up the text to make the page look less intimidating. Single space text, but leave an extra line of space between paragraphs.
Because you are limited to so few pages, it may seem counterintuitive to give up space for visual considerations, but these effective techniques make your Summary much more accessible to the business plan readers.
The way you prepare and present the executive summary is an indicator of your professionalism. A polished Summary sheds a favourable light on your business. A sloppy one works against you.
Length: How long is an executive summary?
The executive summary in a business plan should be no more than 2-3 pages in length, with 1 page being perfectly acceptable and often preferable. The advantage to the busy business plan reader is that they are able to skim through this short summary in a few seconds and read it in full in less than 5 minutes .
Sign up for our Newsletter
Get more articles just like this straight into your mailbox.
Related Posts
Recent Posts
How to Write a Business Plan
Last Updated: May 23, 2024, 8:30 am by TRUiC Team
Writing a business plan can be an intimidating endeavor. Whether you’ve decided to start a business , or you already have a business and need to write a business plan to apply for a loan or to pitch to investors , we cover the process in-depth.
Recommended: Our business plan generator walks you through topics like marketing and financial projections so that your business is prepared to succeed.

What Is a Business Plan?
The traditional business plan is typically a 20 to 40-page formal document that describes what your business does, what your objectives are, and how you plan to achieve them.
It lays out your plans for operating, marketing, and managing your business, along with your goals and financial projections.
There are many different types of business plans, depending on the stage of your venture and the purpose of your business plan. In the earliest stages of your business idea, you may want to start small with a three-sentence business plan , or perhaps by sketching out a lean canvas or business model canvas .
Once your business idea has been developed, you’ll be ready to begin writing your business plan .
Why Do You Need a Business Plan?
Writing a business plan requires you to think through all of the key elements of your business. This gives you insights into the challenges you’ll face and the strengths you bring.
A business plan is also often requested by lenders or investors when you are ready to seek financing.
While many companies do not need a formal business plan unless they are planning on seeking investors or applying for a business loan , writing a business plan has extensive benefits.
The process of writing your business plan allows you to take an in-depth look at your industry , market , and competitive position . It helps you set goals , determine your keys to success , and plan your strategies . It also allows you to explore your financial projections and manage cash. So, even if you do not need a formal business plan, the process of planning may still reap huge rewards.
Your Audience
You need to think carefully about who is going to read your business plan.
Although you might begin writing a business plan only to convince yourself, there are a number of stakeholders who may end up reading your business plan.
Your plan might be read by your:
- Partners or potential partners
- Board of directors
- Senior management team
- Current employees
- Employment candidates
Outside the organization , the following stakeholders may want to read your business plan before they decide to do business with you:
- Distributors
- And independent contractors
Think about your primary audience when you are writing your business plan. What are the aspects that are most important to them? This is where you will want to put the majority of your focus.
For example, lenders will be most interested in your financial projections — your cash flow statement and balance sheet.
Investors might be most interested in your business model, the uniqueness of your product or service, and your competitive advantage.
Partners, your senior management team, and current employees might be most interested in your strategic plans- your vision, your operational plan, and your organizational plan.
Find Sample Business Plans in Your Industry
One great resource you should check out before sitting down to write your business plan are sample business plans in your industry.
Not only will you have the opportunity to gain insights on your industry and your competitors, you also might be able to find troves of industry and market research that will make conducting your own analysis of the industry and market much easier.
To find example business plans in your industry, try searching the web for “ your industry business plan example.”
Writing Your Business Plan
Once you have spent some time looking at sample business plans in your industry, it is now time to start writing your business plan . An easy place to begin is by outlining the major sections you will need in your plan.
What you need to include in your business plan will depend on the type of business you are creating, your business model, and who your intended audience is.
Common business plan sections include:
- Executive Summary — a high-level overview of your business or business idea
- Venture Overview — a description of your company, vision, mission, and goals
- Product or Service Description — a detailed description of your product or service
- Industry and Market Analysis — an analysis of the industry and market you compete in
- Marketing Plan — your overall strategy and specific plans to capture market share
- Organizational Plan — the legal form of the business and the key players
- Operational Plan — how you will operate the business and your key resources
- Goals, Milestones, and Risks — short and long-term goals, milestones, and risks
- Financial Statements — Financial statements or the projected financials of your business
Not every type of venture will require every one of these sections to be included in their business plans. However, most business plans will at least include an executive summary, venture overview, a description of the products and services, and some form of financial projections.
Executive Summary
As suggested in its name, an executive summary is a summary of the key points in your business plan . This is your first chance to convey to readers the what, why, who, and how of your business or business idea.
Although there is no set structure for an executive summary, a good executive summary should summarize :
- The problem you are solving
- Your solution
- Your target market
- Any competitive advantages
- The team you’ll build
- Goals and objectives
- An overview of your financials or financial forecast
If you are writing your business plan for the purpose of acquiring funding , you will also need to discuss the amount of funding required, the purpose of the funds, as well as how your investors will get paid back.
The executive summary should be clear and concise . Ideally, this section should be one to two pages and typically follows either a synopsis or story approach, depending on the intended audience.
In the synopsis approach, you would provide a brief summary of each of the key sections of your business plan. In the story approach, your executive summary reads like a narrative, allowing you to tell the “story” of your business or idea.
With either approach to writing the executive summary, the information you want to convey remains the same. The executive summary needs to provide an overall picture of your current business or business idea.
The executive summary should include:
- A brief description of you and your venture,
- The problem your product or service is solving,
- Some information on your target market, including size, potential, & competition, and
- The solution you are offering.
The executive summary should also include:
- A statement of where you are now,
- A statement of your objectives and future plans,
- A list of what you see as keys to your success, and (if you are seeking investors)
- Any relevant financial information such as start-up costs, funding required, and how you will use investor funding.
Although the executive summary is the first section in the business plan, because it is a summary of the rest of your business plan, it is often written last.
Venture Overview
The venture overview is a top-level depiction of your company.
It contains the:
Description of the Venture
- Vision Statement
- Mission Statement
- Goals & Objectives
- Keys to Your Success
The first part of your venture overview is a description of your venture.
The description of your venture should include what you do (a brief description of your products or services), the value you provide to customers, your current operating status or a brief history of the venture, and a short description of the industry or niche in which you compete.
How to Write a Vision Statement
After describing your venture, a vision statement is a very simple, 5 to 10 word sentence or tagline that expresses the fundamental goals of your firm. Good vision statements reflect your company’s long term passion and purpose, often in a way that evokes emotion.
Take a look at the vision statements below for some inspiration:
Disney — To make people happy. Oxfam — A world without poverty. Stanford — To become the Harvard of the West. Marriott — To be the #1 hospitality company in the world. Microsoft — A computer on every desk and in every home; all running Microsoft software.
How to Write a Mission Statement
After having crafted your vision statement, you should also create a mission statement. A mission statement explains your company's goals in terms of what you do for your customers. A good mission statement should tell your reader what your company does, who you do it for, and why you do what you do.
Check out these excellent examples of compelling mission statements:
Patagonia — “Our Reason For Being: Build the best products, cause no unnecessary harm, use business to inspire and implement solutions to the environmental crisis.” Trader Joes — “Our mission is to give our customers the best food and beverage values that they can find anywhere and to provide them with the information required to make informed buying decisions. We provide these with a dedication to the highest quality of customer satisfaction delivered with a sense of warmth, friendliness, fun, individual pride, and company spirit.” Facebook — "Founded in 2004, Facebook's mission is to give people the power to build community and bring the world closer together. People use Facebook to stay connected with friends and family, to discover what's going on in the world, and to share and express what matters to them."
Goals and Objectives
In this section of the business plan, break down your most important short-term and long-term goals and objectives.
Aim for five to seven of your most important short and long term goals.
This subsection of your venture description should be kept short. You will come back to your goals at the end of your business plan.
However, your key short-term and long-term goals should be highlighted early on in your business plan as well. The rest of your business plan will act as evidence of how you plan on achieving your goals.
Keys to Success
Your keys to success are your insights into what it takes to be successful in your industry, market, or niche.
Your keys to success can include several of the most important milestones that you will need to accomplish in order to achieve your goals.
These may include providing high quality products and services, your ability to attract customers or users and gain market share, or even your ability to develop the technology to deliver your products or services.
Your keys to success may also include the major milestones that you will need to reach along the way in order to achieve your vision. You will come back to your milestones and objectives at the end of your business plan.
Product or Service Description
The product or service description section is where you will go into detail in describing your products or services.
Not only will you describe your product in more detail, you should also discuss the uniqueness of your product, and what gives you an advantage over your competitors.
These are the three main parts of the Product (or Service) Description:
Description of Products or Services
Uniqueness of product, competitive advantage.
In this subsection of your business plan, describe the products or services you will provide, why they are a fit in the market, and how you will compete with similar products and services.
Begin by clearly describing the products or services you will provide. Make sure to explain the features and characteristics of your products and services. Your product or service description does not have to be highly technical. Rather, in addition to describing the features, focus on highlighting the advantages and benefits associated with your products or services.
Also, let your reader know why your product or service is needed. How does your product or service differ from those offered by your competitors? How does it better fill your customers wants and needs?
This is where you tell your reader why your solution is unique. Is it different from everything else out there? How is it different? Why would potential users choose your product or service over your competitors? In order to stand out, you need to distinguish yourself in some way.
To describe your product or service’s uniqueness, you may want to come up with a unique value proposition (or unique selling point). A value proposition is a short description of what you do, who you do it for, and how this benefits them.
A value proposition is similar to a mission statement. However, it differs in that a mission statement is written from the perspective of the company, while a value proposition is written from the perspective of the customer.
Your value proposition should be the center of your customer messaging. It should be front and center on your website, in your marketing materials, and in your advertising.
Here a few examples of great value propositions:
Dollar Shave Club — A Great Shave for a Few Bucks a Month. No Commitment. No Fees. No B.S. Unbounce — Build, Publish, & A/B Test Landing Pages Without IT Freshbooks — Small Business Accounting Software Built for You, the Non-Accountant Skype — Skype Keeps the World Talking, for Free. Share, Message, and Call - Now with Group Video on Mobile and Tablet Too.
What makes you better than competitors?
Does your competitive advantage come from superior products and services, customer service, technical support, logistics, price? What are the factors that give you an advantage over your competitors?
Clearly defining your competitive advantage is important.
Your competitive advantage is not just some abstract concept. It is at the core of how you deliver value to your customers. Your competitive advantage lays the foundation for your business model and should be a key component of your strategic plans.
Common areas where businesses find competitive advantages include:
- Intellectual Property
- Resources/Capital
- Economies of Scale
- Knowledge/Experience
- Connections and Network
- Customer Service
- Technical Support
- Customization
- Brand Recognition/Loyalty
Industry and Market Analyses
The industry and market analysis is the “big picture” view of your industry and market.
Conducting an industry and market analysis is going to take a good deal of research. You will likely need to research your industry, your competitors, and your customers. But do not rush through this section of your business plan.
A good understanding of your industry and market is critical to your success. By understanding the forces at play within your industry, you will be better able to find additional ways to create value that will allow you to succeed in the current and anticipated competitive environment.
Conducting an industry and market analysis can be intimidating, especially if you do not know what to look for or how to find the information you need. In the next section, we will discuss what should be included in your industry analysis. Then, we will tell you where to begin looking.
Industry Analysis
The industry analysis is a big picture analysis of the industry you will compete in. What does your overall industry look like today? There are a number of insights that will help you assess the attractiveness of your idea and form a big picture view of the industry and segment you are considering competing in.
Key insights to be alert for include:
- The dominant economic features of the industry
- The industry’s driving forces
- The industry’s competitive environment
- The competitive position of major players and key competitors
- Key industry success factors
To arrive at meaningful insights from your industry analysis, try to find answers to the following questions:
- What primary products or services are provided by your industry?
- What is the size and trajectory of the industry?
- What was the annual growth rate of the industry over the past year? Three years? Five years? Ten years?
- What is the forecasted annual growth rate over the next three years? Five years? Ten years?
- What is the average profitability of firms in your industry?
- What trends are affecting your industry?
- Who are the major customer segments served by your industry?
- Who are the major players in your industry?
- Who will be your key competitors in your industry?
- What key factors determine success or failure?
Industry Research
Now that you have a better idea of what to look for, you will need to know where to begin your search. There are a number of great free resources to begin looking for industry research. However, the first step is to determine the industry you are in.
While by this point, you should have some idea of the industry you are in, it is not always so clear. You could try an internet search to see what information you can find on your industry, but you will also want to find the NAICS code. You can do a NAICS Code Lookup and find the NAICS Code for LLC that matches your industry.
Here, you use the NAICS identification tool to drill-down through a list of industries to find the appropriate NAICS code for your business.
Once you know your industry, you can begin collecting more information about the industry trends and trajectory.
www.Bizstats.com provides free industry statistics including industry averages for income statement revenues and expenses, balance sheets, and key financial ratios. This is very helpful in making financial forecasts and setting benchmarks.
The US Census Bureau also provides several tools to help you conduct industry research:
- The Economic Census provides information on employer businesses, including data sorted by industry, state, region, and more.
- Statistics of US Businesses (SUSB) provides additional data on US businesses by enterprise size and industry. Both of these tools may help in conducting your industry analysis.
Target Market Analysis
Once you have a better understanding of the industry, you can begin to narrow down to your target market. In this section of the business plan you describe who your target market is and what you know about them.
What is a target market? Your target market is the specific group of customers to whom your product is intended. And no, it is not everyone. Although many new venture founders would like to sell their product or service to everyone, you should focus your efforts on your most likely customers.
Narrowing your target market requires understanding the three types of markets for your products or services. Your venture’s market can be narrowed down into three categories, the TAM, the SAM, and the SOM.
The total available market (TAM) is the total market for your products and services. Everyone in the universe who might be your customer.
The serviceable available market (SAM) is the subset of the total market that you can actually reach. Although anyone in your universe might be your customer, you are limited in your ability to reach them all.
The share of market (SOM) is the subset of the serviceable available market that you will actually reach. These are your most likely customers. Your target market.
Target markets can be segmented in many different ways. The idea is to narrow down to your most likely customers. This is where your focus should be.
Ways you can segment the market include:
- Demographic (e.g., age, gender, family size, education, income)
- Geographic (e.g., country, state, region, city, neighborhood)
- Psychographic (e.g., benefits sought, personality, social class, lifestyle)
- Behavioral (e.g., benefits sought, usage, attitude, loyalty)
Once you understand who your target market segments are, you will be able to start determining how you can reach them. To do this, consider:
- Where does your target market get information to make purchasing decisions?
- What is it they are looking for when considering buying this product/service?
- What will your target market pay attention to?
Market Research
To determine your target market and conduct a market analysis, you will most likely have to do market research.
Market research is the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data related to your target market and target customer to support strategic decision making.
There are two types of market research : secondary market research, and primary market research.
Secondary market research is the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data that has already been collected for other purposes. Secondary market research may include the collection of data from a number of sources such as the U.S. Census Bureau, consumer agencies, and for-profit organizations.
Primary market research is the collection of new information to gain a further understanding of the problem at hand. Primary market research involves you collecting the data or hiring a market research firm to collect data for you. This is you going out and actually collecting the opinions of your potential customers.
Common methods of primary market research include customer observation, focus groups, customer surveys, and customer interviews .
Because primary market research typically takes more time to complete and may incur significant costs , secondary market research is often conducted before conducting primary market research. This allows you to gather enough insights that you can narrow your primary market research to those more likely to be your customers.
To begin conducting secondary market research, consider these sources:
Think with Google provides a number of free tools and resources to help you find and understand your target market. From tools like Find My Audience and an Insights Library to a wealth of information on customer trends and the consumer journey, Think with Google is a valuable tool in conducting your market analysis.
City Town Info provides free statistics on people and places, colleges and universities, and jobs and careers. You can search for data on more than 20,000 U.S. communities at the city and state levels.
Google Trends is another useful tool for conducting market research. Google Trends allows you to explore what people are searching on the internet. You can examine trending topics, see trends by year, or search your own topic to discover interest over time, by region, or by related queries.
Social Mention allows you to conduct a real-time social media search for topics across more than 100 social media platforms. Social Mention provides you with information on the sentiment behind topic mentions, top keywords, top hashtags, and the social media platforms where these topics are being discussed.
Needless to say, there are several other great sources for both industry and market research. The key is to get creative to find the data and information to both guide your strategy as well as justify your business opportunity.
Competitive Analysis
Once you understand your industry and market, you should also include an analysis of your major competitors.
Your competitors may include anyone offering alternatives to your solution that people are using now to solve the same problem.
You will want to understand and explain who your competitors are along with their market share , price, major competitive advantages and disadvantages, and what makes your product unique from theirs.
Start by identifying the major competitors within your industry. You should focus on your closest competitors. Those that compete with you directly.
Next, for each competitor, describe their strategies, their strengths, and their weaknesses. In doing so, try to answer the following questions:
- What are their primary products and or services?
- Who are their target customers?
- What differentiates your product or service from theirs?
- What is their pricing strategy?
- What is their marketing strategy?
- What is their main message or value proposition?
- What are their strengths and weaknesses?
- What are their competitive advantages?
You should complete a competitive analysis for your top three to five competitors. Doing so will allow you to gain a much better perspective on the competitive landscape and may provide insight into how you can distinguish yourself from your competitors and even how you can take advantage of areas where your competitors fall short.
Marketing Plan
The marketing plan depicts the overall strategy your venture pursues to capture market share.
The marketing plan describes all aspects of marketing for your venture, including the product, price, place, and promotion . This includes a big picture view of your marketing strategy, your planned marketing mix, as well as your pricing strategy, sales strategy, and advertising strategy.
The marketing plan should be well informed by your industry and market analysis. By now, you have a plethora of knowledge about who your target customer is, the problem and pain points that you are alleviating for them, and how your competitors are positioned. All of this knowledge allows you to hone your marketing plan to reach your target market with the right message in the channels they turn to for information.
Marketing Strategy
The first section of your marketing plan is your marketing strategy. Your marketing strategy refers to your overall strategy of how you will market your product. How will you get your message out to your potential customers?
Your marketing strategy should consider the four essential elements of marketing:
The 4 Ps of Marketing:
The product is everything the customer gets, whether it be a physical product, a service, or an experience.
It is what you deliver. This includes the product or service itself, along with its branding, packaging, labeling, and even benefits.
The price is what you charge. What the customer gives you. Your business plan should discuss your pricing strategy and where this fits in your marketing mix.
Are you competing on price and thus offer low pricing? Or are you focusing on value at a medium price point? Or maybe you are positioned as a luxury label or item, and compete at a high price point? Why did you choose this strategy? Does it fit with your target market and within your marketing mix?
Location refers to where your customers find you, or where you find them.
While much of today’s marketing is done online, location is still as important as ever. Once you understand the place, you will have a much better idea on how to deploy your marketing mix. Where do your ideal customers get their information? Where do they shop? What forms of social media do they use?
Promotion is how you tell customers about your products and services.
Simply put, promotion is how you raise awareness of your products, services, or brand. Promotion strategies may include public relations, content creation and curation, marketing, and advertising.
But, keep in mind, your promotional strategies should be focused on one thing: your target customer and the strategies and messaging that works for them.
Your Marketing Mix
Your marketing mix is how you allocate resources to the marketing channels that you plan to pursue. In this section of your marketing plan, you will describe the marketing messaging and channels that you plan to use, and why these are appropriate for your target market.
Inbound Marketing
Inbound marketing, or content marketing, is a form of marketing designed to draw traffic to your website by providing valuable content to your target market. This is often achieved by posting useful web content, content, videos, and blogs.
The idea behind inbound marketing is pretty simple- by providing knowledge and information on your products, services, and other information that is valuable to your customers, you generate more leads and, hopefully, more sales.
Social Media Marketing
With over 3.5 billion people around the world using social media, social media marketing is another powerful tool to reach potential customers.
Social media marketing has many advantages, including allowing you to get your message in front of your specified target audience at little to no cost.
Although there is an overabundance of social media channels to choose from. Focus on the ones that your target market uses to get their information.
For instance, if your target market is middle age or older people, you may want to focus on platforms that are more popular with these demographics such as Facebook, Twitter, and Pinterest. However, if your target market is teen agers and young adults, you are more likely to find them on platforms such as Instagram and TikTok.
The Power of Video Marketing
Do not forget to discuss the use of video marketing in your marketing mix.
In both inbound and social media marketing, video has begun to play an increasingly important role. Video marketing can be employed in inbound marketing, email marketing, and social media marketing to serve a variety of purposes. The most common uses of video marketing include explainer videos, presentation videos, testimonial videos, sales videos, and video ads.
Not only can video marketing be used in a variety of methods and contexts, it is a highly consumed type of advertising. In fact, in 2020, 96% of consumers watched an explainer video to find out more about a product or service. Video works. And marketers believe this too. 92% of marketers who utilize video marketing say that it is a key part of their marketing strategy.
Email Marketing
Depending on the type of venture your company is, email marketing may also be an important element in your marketing mix. A good email marketing strategy balances gaining new customers with keeping your existing customers engaged with your company.
Although you do not want to overdo it, and a lot of email marketing seems “spammy”, email marketing can be very effective in the right form. Welcome notes, confirmation emails, informational emails, newsletters, digital magazines, promotional emails, and seasonal and birthday campaigns are just a few of the many types of email marketing.
Referral Marketing
Another common type of marketing in a company's marketing mix is referral or recommendation marketing. Referral or recommendation marketing can take many forms. Referral marketing might include good old organic word-of-mouth marketing wherein you ask customers for referrals, or even a formal system for rewarding customers who refer new clients.
Pricing Strategy
The Marketing Plan section of the business plan should also describe your pricing strategy. How are you going to price your products and services?
There are a number of ways you can approach pricing:
Markup Pricing — Markup pricing is pricing based on your costs, plus a predetermined markup. The amount you mark up your product or service is usually expressed as a percentage, known as the gross margin. Markup pricing is most often found in high volume manufacturing industries where manufacturers must cover the cost of the products they are making.
Competitive Pricing — Competitive pricing is pricing based on your competitors prices for similar products or services. Competitive pricing is most often seen in products or services where there are numerous competitors or substitutes.
Value Pricing — Value pricing is pricing based on the value or perceived value that you deliver to your customers. In value-based pricing, you set the prices of your products and services in line with what the customer believes your product or service is worth. Value-based pricing is most often seen in higher value products and services, those that cater to self-image, or those that are niche or unique.
Penetration Pricing — Penetration pricing is setting a low initial price, and then raising it as demand increases. Penetration pricing is designed to capture market share. It is a strategy often used by a new business or in launching new products and services. The idea is to set the price low enough to draw customers from your competition.
Price skimming — Price skimming pricing is setting a high initial price and then reducing this price as the market evolves. Price skimming is most often used on new or trendy products and services. As initial demand slows and alternatives or competitors emerge, the high initial pricing must then be lowered to stay competitive in the market.
Sales Strategy
A sales strategy is how you plan on selling your products or services to your target market. This includes your sales channels (where will your product or service be available for sale) as well as how you will sell your product or service.
Your sales strategy depends on your business model and the nature of your business. If your business involves retailing, food services, or personal services where your customers come to you to make a purchase, your sales strategy may be quite simple (or even unnecessary to income). However, if your business involves personal selling, you may need a more thought-out sales strategy.
Some questions to ask to determine and document your sales strategy in your business plan:
- Will your products or services be available on your website?
- On a third-party website?
- In retail locations?
- In your own stores?
- In other retail stores?
- Directly to consumers? (Business to Consumer or B2C)
- To businesses? (Business to Business or B2B)
- Cold calling?
- Networking?
- Inside salespeople?
- Outside sales representatives?
- Sales through strategic partners?
Advertising Strategy
An advertising strategy is how you plan to use sponsored, non-personal messaging to reach and inform potential customers of your product, service, or brand.
Your advertising plan should describe the mediums you are going to advertise in , who you are targeting advertising in these mediums, your advertising message(s), and your advertising budget. A good advertising plan is also measurable, so be sure to consider how you are going to measure the effect of your advertising strategy to see if it is working.
Advertising Mediums
The most common advertising mediums typically fall into the categories of traditional advertising and digital advertising.
Traditional advertising includes print advertising such as newspapers, magazines, flyers, direct mail, and even billboards, as well as radio and tv advertising.
Digital advertising includes email advertising, search engine advertising, website advertising, social media advertising, influencer advertising, among many, many more.
The secret to finding the right advertising strategy and advertising mediums for your business is knowing where to find your most likely customers. Where is your target market, and where do they go to get their information?
Organizational Plan
The organizational (or management) plan describes:
- The legal form of the business
- Its organizational structure
- The background and roles of the leadership team
- Key personnel that are already in place or you will need to fill.
Organizational Type and Structure
The first part of your organizational plan describes your organizational type and structure . Who owns your company? And what is its legal business structure?
There are four primary types of organizational structures:
Sole Proprietorships
Partnerships.
- Limited Liability Companies (LLCs)
Corporations
Sole Proprietorships and Partnerships are informal business structures , while LLCs and Corporations are more formal business structures .
The best type of structure for your business will depend on your business’s particular characteristics and needs. A partnership structure may be the best choice for some businesses, while an LLC or a corporation might work better for others.
Sole proprietorships are an informal type of business structure. While many businesses start out as sole proprietorships because they are an informal business structure the owner is liable for 100% of the business's liabilities and risks. Thus sole proprietorships are typically not the preferred ownership structure for small businesses.
Similar to a sole proprietorship, a partnership is also an informal type of business structure. While a sole proprietorship involves only one owner, a partnership is a business structure with two or more partners where there is still no legal distinction between the owners of a partnership and their business.
An LLC is a formal business structure that distinguishes the owners from the business itself.
LLCs offer the personal liability protection of a corporation with the pass-through taxation of a sole proprietorship or partnership.
It is the simplest way of structuring your business to protect your personal assets in the event your business is sued.
LLCs can be owned by one or more people, who are known as LLC “members.” An LLC with one owner is known as a single-member LLC, and an LLC with more than one owner is a multi-member LLC.
LLCs require operating agreements . Operating agreements are legal documents that outline the ownership and member duties of your LLC. This agreement allows you to set out the financial and working relations among business owners ("members") and between members and managers.
Recommended: Learn how to form an LLC in your state using our free guides.
A corporation is a legal business entity that is owned by shareholders, run by a board of directors, and created through registration with the state.
Corporations offer limited liability and tax benefits but are required to follow more complex operating procedures than their counterpart, the limited liability company (LLC).
Ownership and Executive Team
Now it’s time to sell the single most important element in your business plan. You!
This subsection of your business plan tells readers who is in your ownership and executive team and outlines the accomplishments of your team.
You should include a short profile on each member of your ownership and executive team that will play a role in company decision making.
Who is on your ownership and executive team? What roles will each perform? What knowledge, experience, and accomplishments do you and your team bring to the table? What roles do you still need to fill, and how and when do you plan on filling them?
It is well known that many investors consider the experience and ability of the ownership and management team to be just as important as the idea itself. Do not pass over this opportunity to highlight how your knowledge, experience, and accomplishments set you up to succeed.
Also, remember that when you are writing your descriptions of your ownership team, talk about your accomplishments- as opposed to experience. Accomplishments signify that you have a track record and can get things done.
Key Personnel
This section of the business plan highlights the key personnel associated with the business . This may include members of the management team outside of the owners and executive management, the board of directors, and any outside advisors.
Here, include profiles on each key figure associated with your company, focusing on their accomplishments and the knowledge and skill they bring to the business.
Operational Plan
The operational plan describes how you will operate. The processes, strategies, and resources that you will use to operate your business on a daily basis.
This includes descriptions of production (if you produce a product) or the process you will use to carry out your service. The operational plan may also include, as necessary, descriptions of your logistics and supply chain, physical resources and needs, human resources and needs, technological resources and needs, and timetables for carrying out your plan.
Production Plan or Service Description
The production plan or service description explains how you are going to make and deliver your product(s) or provide your service(s). Although the production plans for products and services may look slightly different, both describe how your company will operate in the day-to-day.
If you are making a product , the production plan is where you will describe the process for making the product. What are your methods of production? What are the steps in your processes? How will you ensure quality? Maintain inventory? Handle Logistics?
If you are providing a service , the production plan is where you can describe the process you go through providing that service. What are your service methods? What will your sales and customer service look like? What is the customer experience like?
Most importantly, which of these might give you an advantage over your competitors? If you have any superior methods, processes, or other advantages, make sure to highlight them in your production plan or service description.
Logistics and Supply Chain
This section of the business plan describes your logistics and where you fall within the supply chain in your industry.
If you produce a product , you should discuss how you source materials, where your materials come from, and who your suppliers are. You will also need to discuss how you handle inventory, how you warehouse, and how you distribute your product(s).
If you are a service business , you may still have to discuss how you source materials used in your service, who your suppliers are, and how you handle inventory.
Physical Resources
In this section of the operational plan, you describe the physical resources that you have and the physical resources that you need to acquire. Think through everything you might need. This will become important when it is time to make financial projections.
- What facilities, machinery, equipment, and supplies do you require?
- Do you require raw materials?
- Who will be your primary suppliers?
- Secondary suppliers?
- Do you have back up suppliers and contingency plans if you cannot acquire raw materials?
Technological Resources
You should discuss the technological resources that you are developing, have, or need to create or acquire. Technological resources may include any software, applications, or websites that you have or will need to create, outsource, or purchase.
- What hardware or machinery will you require?
- What software or applications will you require?
- Can you purchase the software and applications you need?
- Are the software and applications you will need off-the-shelf or specialty?
- Will you have to create the software and applications you need?
- Do you need a website?
- Will you create and maintain your website inside the company or have it created and maintained by someone else?
Human Resources
Here, you describe the people that are a part of your team, and the human resources that you need to add to your team, hire, or outsource. Since you have already described the ownership and management team as well as key personnel, this section is more focused on production level workers and lower management.
- How much staffing will you need?
- What skills will your staff require?
- What will your staffing typically look like?
- How will you recruit, train, and retain employees?
Goals, Milestone, and Risk
The goals, milestones, and risks section of your business plan is the place to outline your goals, set key milestones, and explore and explain your preparation for the risks you will face.
Goals lay the foundation of where you intend to take your company and how you are going to get there. It is important to ascertain the short and long-term goals for your company.
Your goals should be connected to your mission and vision, your business model, and your strategic plans. They should also reflect your ambition to move the company forward and are often reflected in key performance indicators (KPIs) , such as numbers of users and customers, revenues, expenses, retention, satisfaction, and other indicators of performance.
Here are some questions to help you develop the goals for your company:
- When do you expect to break even?
- What do you expect your revenue to be in one year? Three years? Five years?
- What market share do you expect to capture in the next year? Three years? Five years?
- Where do you plan to expand from here?
- What KPIs do you need to achieve or improve?
- When do you expect to implement major objectives?
- What level of customer satisfaction do you hope to achieve?
When developing your goals, in addition to defining what your goals are, you also need to consider the how , the when , and the who . First, consider how your goals will get accomplished? What actions need to be taken to achieve your goals? What milestones do you need to accomplish along the way?
Your goals should also include your plan on when you plan on attaining each goal . Not only will your readers be curious about when you plan to achieve your goals, due dates and deadlines make for really powerful motivators.
Finally, you should also determine who is going to be responsible for working toward each goal. In a sole-proprietorship or startup it may be you, the business owner, or your founding team. However, as your organization grows, it will become more and more important to define who is responsible for pushing toward and achieving each goal.
SMART Goals
Your goals should be SMART: S pecific, M easurable, A ttainable, R ealistic, and T imely.
- Specific — Your goals should be clear and specific. They should be narrow enough that you can determine the appropriate steps to attain them. In addition to what , in planning your goals, do not forget to be specific about how , when , and who . How will your goals be attained? When do you anticipate achieving them? Who is going to be responsible?
- Measurable — Your goals should be measurable. There should be some objective metric or performance indicator by which you can tell if you have met your goals? How are you going to measure your goals? What metrics or performance indicators will you use? How will you know if you achieve your goals?
- Attainable — Your goals must also be realistic and attainable. For a goal to be attainable you must be able to achieve it. Do not be afraid to push yourself, but setting unrealistic goals will cast doubt on your entire business plan. Ask yourself, can your goals be accomplished? By you? What will it take to attain them?
- Relevant — Your goals also need to be relevant. To be relevant, they should contribute to the mission, vision, and success of your venture. Do your goals align with your company’s values? Are they within the scope of and aligned with your operational plan? Your marketing plan? Are they within the budget?
- Timely — Your goals should also be timely and time-bound. Their process and progress should be clearly defined and they should have a starting and ending date. Without a timeframe, there is no sense of urgency, or motivation to get started. Make your goals time-bound. How long do you expect it to take? When do you plan on getting started? When do you anticipate achieving each goal?
Milestones are important events in your venture’s growth that mark significant change or stage of development.
Creating a list of milestones can act as a checklist of what you need to accomplish for your venture to reach its goals. They tell the story of how you are going to get from where you are to where you are going.
Milestones might include major events and accomplishments, such as:
- Forming an LLC
- Writing a Business Plan
- Securing Seed Capital
- Develop a Prototype
- Begin Production
- First Major Sale
- Reach 10,000 Downloads
- Achieve 1,000 Paying Customers
It is alright to list a few milestones that you have already completed. Or to leave them in your business plan once you complete them. Accomplished milestones show that you are making traction.
Milestones act as a signal to potential investors and other stakeholders what to expect from your venture and when to expect it. They also signal whether the venture is progressing and growing as expected.
Implementation Timeline
The implementation timeline is where you describe where your company is in its lifespan . You should set a timeline to reach your goals and milestones. This should include a short-term timeframe as well as where you anticipate being in the long term.
This section of the business plan should not be long. A simple chart will do. You can find several free timeline templates online to plug in your milestones and the time frame you expect to achieve them.
You will also want to include a section in your business plan showing that you understand the critical risks that your business may be subject to . The risks you will face in your business include both internal and external risks. These are any areas that expose your venture to any kind of loss- assets, customers, sales, profits, and reputation, among others.
By exploring your assumptions and identifying possible risks in those assumptions, you can show that you have assessed and are prepared to handle risks and threats that may arise. There are several tools available to analyze business risks, including SWOT Analysis and contingency planning .
SWOT Analysis
You may want to conduct a SWOT analysis or even include it in your business plan. A SWOT analysis is an analysis of your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
A SWOT analysis can help you understand your industry and market, your venture, and the strategies that you should pursue.
To conduct a SWOT analysis, you will need to assess factors both inside and outside your venture.
Here is how to conduct your own:
- What does your company do well?
- What are your company’s advantages?
- What do you do better than your competitors?
- What unique or low-cost assets do you have access to?
- What does your company not do well?
- What are your company’s disadvantages?
- What do your competitors do better than you?
- What needs to be improved?
- Where can you improve?
- Where can you grow?
- How can you turn your strengths into opportunities?
- How can you turn your weaknesses into opportunities?
- Do the trends of the industry or market represent a threat?
- Is the number of competitors growing?
- Do changes in technology or regulation threaten your success?
- Do your weaknesses represent a threat?

Contingency Plans
After assessing your risks and your SWOT analysis, you should address any major threats or risks that your venture faces with contingency plans.
Contingency plans are plans to help mitigate these risks by establishing a plan of action should an adverse event happen.
Contingency plans show that you understand the threats and risks to your venture, and you have a plan in place to lessen the damage should these risks emerge. There are various ways to prepare for adverse events. One is through planning- identifying alternatives and determining the best course of action. Another is business insurance.
Business Insurance
Business insurance protects against risk from several sources. The type of business insurance you will need varies greatly depending on the nature of your business.
While there are standard types of coverage like general liability insurance , professional liability insurance , workers’ compensation , insurance for commercial property and commercial auto insurance , there are also insurance policies that cover specific business activities and specialized equipment.
You can bundle most of these into what is called a Business Owner’s Policy (BOP) by a trusted insurance provider to get you started doing business.
Financial Statements
Your financial statements should include detailed projections of your income statement , cash flow statement, and balance sheet for the first year. You should also provide quarterly projections for the first three (or preferably five) years as well.
You also will likely need to include some sort of financial statement in your business plan. If you are a new venture, you will supply pro forma financial statements. Pro forma financial statements are simply financial projections.
Financial statements can help you to evaluate the cash needs of your venture, determine whether your venture is feasible and desirable, compare your expected returns with the alternatives, identify milestones and benchmarks, and demonstrate the value of your venture to investors.
Financial Assumptions
Before you begin completing your financial statements, you should first sit down and list the assumptions you will rely on to project your financial statements .
These should include projections concerning your:
- Initial revenue level per month
- Your growth and factors affecting growth
- Your inventory and inventory turnover
- And your operating expenses.
One of the biggest mistakes new ventures make is in making unrealistic assumptions .
Remember, revenue assumptions are key assumptions in determining whether your business will be viable. However, many entrepreneurs are overly optimistic about their revenue assumptions and tend to underestimate their expenses.
In order to make more accurate financial assumptions, back up your assumptions with data whenever possible. To find data to back up your assumptions, look for things like industry averages, market trends, and comparisons with similar ventures. You should already have a substantial amount of this data from your industry and market research.
Pro Forma Income Statements
The income statement , also known as the profit and loss statement , is a statement that shows the projections of your venture’s income and expenses over a fiscal year. On the income statement, you will detail your revenue and sources of revenue based on the assumptions you have made. You will also detail your anticipated expenses and use these to estimate your net income.
The typical income statement includes:
- Revenue — the total amount of sales, or revenue, projected to be brought in by your business.
- Cost of Goods Sold — the total direct cost of producing your product or delivering your service.
- Gross Margin — the difference between revenue and cost of goods sold.
- Operating Expenses — this section of your income statement details all of the expenses associated with operating your business. Common operating expenses might include rent, utilities, office
- expenses, salary expenses, and marketing and advertising expenses, among others.
- Total Operating Expenses — the total of your operating expenses, excluding interest, depreciation, and taxes.
- Operating Income — the difference between your gross margin and operating expenses.
- Interest, Depreciation, and Taxes — this section of your income statement lists your non-operating expenses- expenses such as interest, depreciation, amortization, and taxes.
- Net Profit — the total of how much you actually made. This is calculated by subtracting interest, depreciation, and taxes from your operating income.
Pro Forma Cash Flow Statements
The cash flow statement is a financial statement that shows when and where cash (and cash equivalents) flow in and out of your venture. This tells you how much cash you will have on hand at any single point in time.
- Cash from Operating — Cash flowing into and out of your venture from operating, beginning with “cash on hand.” Cash flowing into your venture from operating includes cash from sales, payments from credit sales, investment income, and any other types of cash income related to operations. Cash flowing out of your venture from operations, your expenses, includes costs of raw goods, materials, inventory, salary expenses, office expenses, marketing and advertising expenses, rent, interest, taxes, insurance, or any other expenses that are paid by the venture.
- Capital Cash Flow — Cash flow, in or out of the venture, for capital assets such as the purchase or sale of fixed assets.
- Cash from Financing — Cash flow from financing includes cash flowing in or out of your venture relating to venture financing activities. Inflows of cash from financing include the investments by founders or owners, any loans taken out during the period, or the issuance of any equity. The outflow of cash from financing may include the payment of the principal of any loans, along with the repurchase of any outstanding equity.
Pro Forma Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is a financial statement that balances a venture's finances at a specific point in time. It describes how much the company is worth. The balance sheet uses the accounting equation: assets = liabilities + equity . In fact, these are the main components of the balance sheet:
- Assets — Resources that hold economic value. A business's assets include current assets and fixed assets. Current assets are resources that can be accessed in the short term. These include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and other currently available resources. Fixed assets are resources that are intended for long-term use but hold economic value. These include land and buildings, machinery and equipment, furniture and fixtures, vehicles, and other fixed resources.
- Liabilities — What the business owes. Like assets, a business’s liabilities are also current liabilities and long-term liabilities. Current liabilities are liabilities that are due within 12 months. Current liabilities include accounts payable, loans, and taxes. Long-term liabilities are liabilities that are due after one year. These include long-term loans, notes, and other long-term debts.
- Equity — What the owners or shareholders own. Equity is also composed of two parts: Capital and Retained Earnings. Retained earnings is the amount of profit that has been retained by the company over the life of the venture. Capital earnings , then, is what’s left. It is what has been invested. For new ventures, this may be the founder’s or early investors’ initial investments. For larger corporations, this would be the value of their shares of stock.
Break-Even Analysis
The break-even analysis shows you how much you have to sell before you break even. The break-even analysis uses fixed and variable costs in order to determine the sales volume you have to attain to reach a break-even point. This is the point where your sales volume covers both your fixed costs and your variable costs.
The break-even point is most often expressed as a number of units. You can calculate the break-even point by dividing fixed cost by the average profit per unit (average price per unit minus the variable cost).
Break-Even Point = Fixed Costs/ Profit Per Unit (Avg. Price - Avg. Variable Costs)
You can also calculate the break-even point in terms of $ of sales. To calculate the break-even point in $ of sales, you can divide total fixed costs for the period by the contribution margin ratio (net sales minus total variable cost / net sales).
Break-Even Point ($ of Sales) = Fixed Costs / Contribution Margin Ratio Contribution Margin Ratio = (Net Sales - Total Variable Cost) / Net Sales
Startup/Funds Required
If you are writing your business plan for the purpose of seeking funding, you should conclude your business plan by describing the investment opportunity.
With your financial projections in place, you will now be able to determine the amount of startup capital or investment you require.
This is because the funding you need is highly dependent on your profit and loss, cash flow, and break-even point. With well-researched assumptions and the evidence to back them up, you are ready to make the case that your business is worth the investment and will be able to pay it back or reward investors in the future.
In this section of the business plan, you will need to explain the amount of funding you are requesting as well as describe what those funds will be used for. The startup funding request will need to cover all expenses (maybe even your own personal expenses) at least until you reach your break-even point.
Business Plan Appendices (Optional)
If you have additional evidence to support your business idea, your business model, or your ability to achieve your goals and meet your financial objectives, you may want to consider including it as an appendix to your business plan.
Additional / Optional Evidence
Owners’ Resumes — One thing you may want to consider including in your business plan is the resume for each owner. Investors often invest as much in the startup team as they do in the idea itself. Illustrations of Product — Another helpful appendix is pictures or illustrations of your product. These are especially helpful for new products or those which are difficult to depict with words. Storyboard of Customer Experience — If your business is a service business, you could also consider including a storyboard depicting your customer’s experience. Customer Survey Results — You can also include any market research that you have conducted in an appendix. Showing that you have solicited feedback from real customers or potential customers provides further credence to your venture and venture idea.
Develop Your Business Idea
Before writing your business plan, it is important to take some time to develop your business idea .
If you are starting a new company, there are likely many details of the venture that have not been fully worked through. If you already have an existing venture, the following tools can also be useful in evaluating your business model:
- A three-sentence business plan
The Lean Canvas
The business model canvas, three-sentence business plan.
An easy place to start is with a three-sentence business plan . The three-sentence business plan is easy to construct, and consists of three parts:
- your product or service
- your market and marketing
- your revenue model.
Your Product or Service
The first sentence of your business plan clearly yet simply states your business's primary product or service. This includes the what and the where.
Example: “CoffeeMe is an upscale bakery and coffee shop specializing in imported coffees and international delicacies that will be located in downtown Atlanta.”
Your Market(ing)
The second sentence of your three-sentence business plan describes who your target market is and how you will promote to them.
Example: “CoffeeMe’s target market is urban professionals living and working in downtown Atlanta, marketed and promoted through traditional advertising, company partnerships, and social media.”
Your Revenue Model
The third sentence of your three-sentence business plan explains your revenue model. How will you make money?
Example: “CoffeeMe’s revenue model includes one-time retail sales as well as a unique subscription model featuring all-you-can-drink coffee for subscribers.”
Put it all together, and you have your three-sentence business plan:
Example: “CoffeeMe is an upscale bakery and coffee shop specializing in imported coffees and international delicacies that will be located in downtown Atlanta. CoffeeMe’s target market is urban professionals living and working in downtown Atlanta, marketed and promoted through traditional advertising, company partnerships, and social media. Our revenue model includes one-time retail sales as well as a unique subscription model featuring all-you-can-drink coffee for subscribers.”
Another useful tool for developing your business idea is the Lean Canvas . The Lean Canvas takes a problem-solution approach to helping you plan your business, focusing on the problems you are solving for your customers.
The Lean Canvas helps you describe and visualize your problem, solution, customers, value proposition, key performance indicators, and competitive advantage.
The steps to complete the Lean Canvas are:
- Define your target customers or users
- List the problems you are solving for them and how they are currently solving those problems today
- Describe your solution
- Explain your unique value proposition
- Describe your revenue streams
- Depict how you will reach customers
- Define the key metrics that will tell if you are doing well
- Detail your cost structure
- Explain your unfair advantage
The Lean Canvas, created by Ash Maurya, and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License: https://leanstack.com/lean-canvas
The Business Model Canvas helps you describe and visualize the key aspects of your venture including your customers, value proposition, infrastructure, and revenue and cost models.
If you have already completed a Lean Canvas, you will already have several of the central parts of the Business Model Canvas complete.
The steps to complete the Business Model Canvas are:
- Explain your value proposition
- Describe how you interact with customers
- List the key activities that you will need to do to deliver on your value proposition
- List the key assets that you will need to deliver on your value proposition
- Describe the key partnerships that you will need to put in place to deliver on your value proposition
Related Articles
Best llc services.
How to Build a Website

Small Business Credit Cards
- Scroll to top
- / Sign Up
- HOW WE HELP CLIENTS
- schedule your conversation
Business Plan Roadmap: Building Your Path to Business Success
Published: 31 December, 2023
Social Share:

Table of Contents
In today’s fast-paced entrepreneurial landscape, a meticulously crafted business plan functions as the guiding star for your venture’s journey toward success. Whether you’re an experienced entrepreneur or a budding startup creator, possessing a comprehensive business plan is indispensable, serving as the key to securing funding, making well-informed decisions, and effectively navigating the ever-evolving business environment.
Within the confines of this article, we will embark on a comprehensive exploration of the art of crafting an engaging and impactful business plan . We shall dissect critical components, including in-depth market research, meticulous financial projections, savvy marketing strategies, and effective operational blueprints. Additionally, we will unveil a plethora of tips and best practices designed to elevate your business plan above the competition, rendering it a value proposition for those seeking to invest in or collaborate with your enterprise.
What is a Business Plan
A business plan definition is a written document that outlines the goals, strategies, and detailed operational and financial plans of a business. It serves as a roadmap for the business, providing a clear direction for its growth and development. A typical business plan includes information about the company’s mission and vision, its products or services, market analysis, competition, target audience, marketing and sales strategies, organizational structure, financial projections, and funding requirements. Business plans are commonly used to secure funding from investors or lenders, guide the company’s operations, and communicate its vision and strategy to stakeholders.

A conventional business plan typically divides into two primary segments:
- The Explanatory Segment: This portion encompasses written content that serves the business purpose of providing a detailed description of the business idea and/or the company. It covers elements such as the executive summary, company overview, market analysis, product or service particulars, marketing and sales strategies, organizational structure, operational blueprints, and funding needs.
- The Financial Segment: Within this section, you’ll discover financial data and projections, encompassing income statements, balance sheets, cash flow forecasts, and detailed information regarding financing prerequisites and potential sources. This segment offers a quantitative view of the business’s financial situation and future expectations.
Components of a Business Plan: What is Included in a Business Plan
Crafting a thorough and compelling business plan is a fundamental step for entrepreneurs and business leaders seeking to chart a successful course for their ventures. A well-structured business plan not only serves as a roadmap for your business’s growth but also communicates your vision, strategy, and potential to investors, partners, and stakeholders. The key components of a business plan make up a robust business plan, offering valuable insights and practical tips to help you create a document that inspires confidence and aligns your team with a shared vision. Each key element plays a critical role in constructing a business plan that not only secures financial support but also guides your organization toward sustainable success. Let’s delve deeper into these components, adding depth and clarity to your business plan ‘s narrative.
- Executive Summary: This should succinctly encapsulate the essence of your business plan . It should briefly touch on the market opportunity, your unique value proposition, revenue projections, funding requirements, and the overarching goals of the business.
- Company Description: Elaborate on your company’s history, including significant milestones and achievements. Clearly define your mission, vision, and values, providing insight into what drives the company’s culture and decisions.
- Market Analysis: Delve into the market’s nuances by discussing not only its size but also its growth rate, trends, and dynamics. Highlight specific target market segments, customer personas, and pain points that your business aims to address. Include a SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis to showcase your understanding of the competitive landscape.
- Products or Services: Offer a detailed explanation of your offerings, emphasizing their key features and benefits. Describe how these offerings fulfill specific customer needs or solve problems, and explain any proprietary technology or intellectual property.
- Marketing and Sales Strategy: Provide a comprehensive overview of your marketing and sales plans. Discuss your pricing strategy in depth, outlining how it aligns with market dynamics. Explain your distribution channels and marketing tactics, including digital and traditional methods.
- Organizational Structure: Present bios of key team members, underscoring their relevant experience, expertise, and roles within the organization. Include an organizational chart to illustrate reporting relationships and the structure’s scalability.
- Operational Plan: Go into detail about your daily operations, covering everything from production processes and supply chain management to facility requirements and technology utilization. Discuss quality control measures and scalability strategies.
- Financial Projections: Provide a thorough breakdown of financial forecasts, including monthly or quarterly projections for at least three to five years. Explain the assumptions behind these numbers, including factors such as market growth rates and pricing strategies. Highlight critical financial metrics like burn rate, customer acquisition costs, and return on investment.
- Funding Requirements: Specify the exact amount of capital you’re seeking, the purpose of the funds, and how the investment will be utilized to achieve specific milestones. Outline potential sources of funding, such as equity investment, loans, or grants. Clarify the expected terms and conditions.
- Appendix: In the appendix, include supplementary materials that reinforce your business plan’s credibility and depth. This can encompass market research reports, letters of intent, prototypes, patents, legal contracts, and any other relevant documentation that adds value to your case.
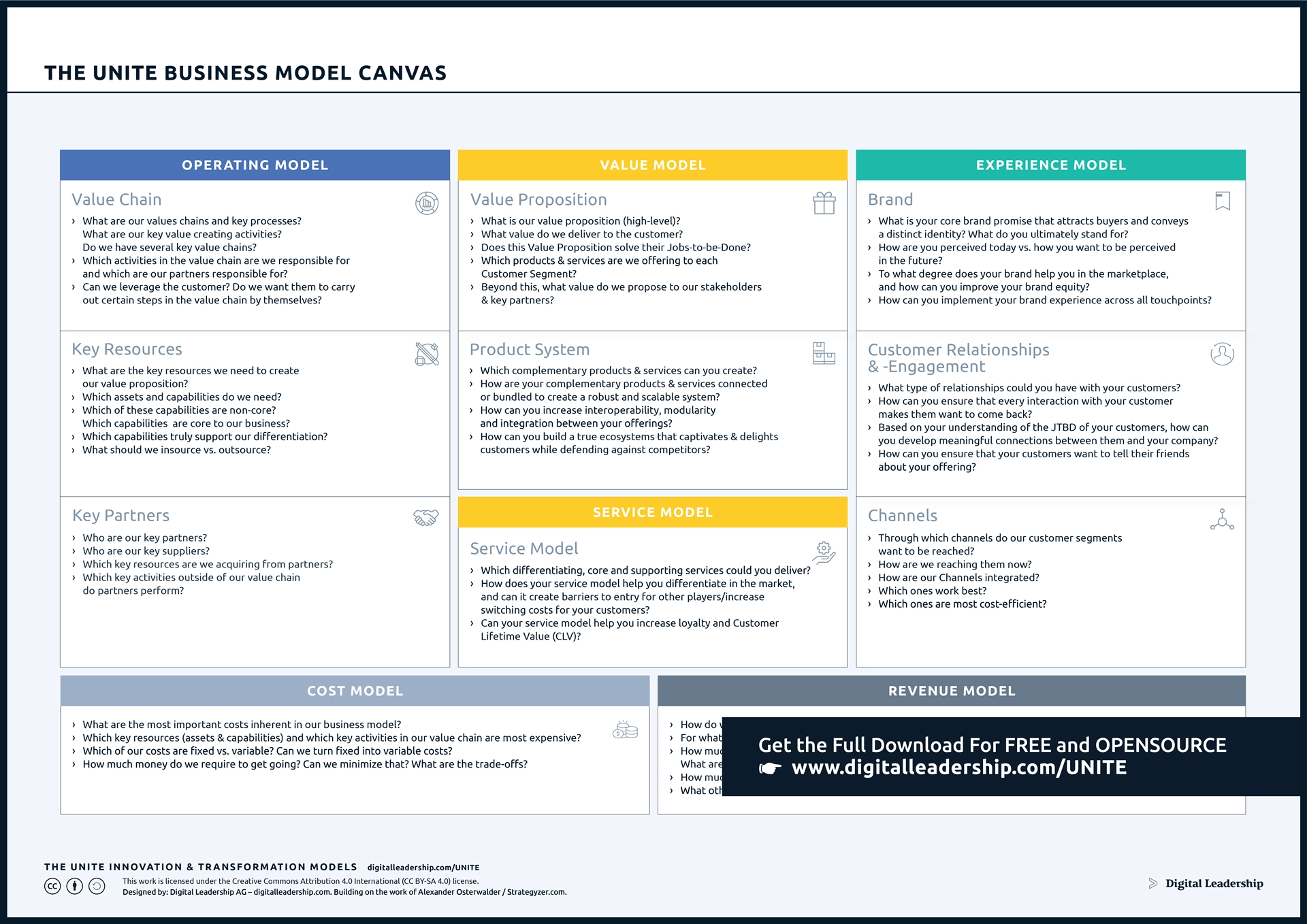
Your download is now available!
You can now access the complete Business Model Canvas Package, including a full presentation, related models and instructions for use.
The UNITE Business Model Canvas
Creating a business plan essential steps.
Creating a business plan is a crucial step in launching or growing a business. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you create an effective business plan :
1- Draft an Executive Summary:
- Write a concise overview of your business, including the mission, vision, and goals.
- Summarize the business concept, target market, and unique value proposition.
- Keep it brief but compelling to grab the reader’s attention.
2- Compose a Business Description:
- Provide detailed information about your business, industry, and the problem or need your product/service addresses.
- Explain your mission, vision, and core values.
- Describe the legal structure of your business (e.g., sole proprietorship, LLC, corporation).
3- Conduct a Market Analysis:
- Conduct thorough market research to understand your industry, target market, and competitors.
- Define your target audience and demonstrate a clear understanding of market trends.
- Conduct a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats).
4- Outline Organization and Management:
- Outline the organizational structure of your business.
- Introduce key team members and their roles, highlighting their relevant experience.
- Provide an overview of your advisory board or external support.
5- Detail the Product or Service Line:
- Describe your products or services in detail.
- Highlight the features, benefits, and unique selling points.
- Explain how your offerings meet the needs of your target market.
6- Develop a Marketing and Sales Strategy:
- Develop a comprehensive marketing strategy to reach your target audience.
- Outline your sales process, distribution channels , and pricing strategy.
- Include a sales forecast and customer acquisition plan.
7- Specify Funding Request (if applicable):
- Specify the amount of funding you are seeking (if any) and how you plan to use it.
- Justify the funding request with clear financial projections and a solid business case.
8- Prepare Financial Projections:
- Prepare detailed financial statements, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
- Provide assumptions and methodologies used for financial forecasts.
- Demonstrate your business’s profitability and financial viability.
9- Include an Appendix:
- Include supplementary materials such as resumes, permits, contracts, market research, or any other relevant documents.
- Keep this section optional but use it to provide additional context.
10- Review and Revise:
- Review your business plan thoroughly for clarity, consistency, and completeness.
- Seek feedback from mentors, advisors, or potential investors.
- Revise the plan based on feedback and ensure it aligns with your business goals.
Remember, a business plan is a dynamic document that should be revisited and updated regularly to reflect changes in your business environment. It serves as a roadmap for your business and a valuable tool for communicating your vision to others.
Types of Business Plans
Startup business plan:.
A comprehensive document crafted by entrepreneurs to outline the vision, mission, target market, competition analysis, financial projections, and strategies for launching and operating a new business.
Feasibility Business Plan:
A plan designed to assess the viability of a business idea or project by analyzing market demand, potential challenges, financial feasibility, and overall sustainability before committing resources.
One-Page Business Plan:
A condensed version of a traditional business plan, focusing on key elements such as the business concept, target market, value proposition, marketing strategy, and financial projections—all presented on a single page.
What-If Business Plan:
A flexible and dynamic plan that explores various scenarios and outcomes based on changing factors or assumptions. It helps businesses anticipate challenges and adjust strategies accordingly.
Growth Business Plan:
Tailored for businesses aiming to expand, this plan outlines strategies for scaling operations, entering new markets, launching products or services, and includes financial projections to support growth initiatives.
Operations Business Plan:
Geared towards day-to-day activities, this plan details operational procedures, resource allocation, supply chain management, and other aspects essential for the smooth functioning of the business.
Strategic Business Plan:
A long-term plan outlining the organization’s mission, vision, core values, and strategic initiatives. It guides decision-making, sets priorities, and aligns the company toward achieving overarching objectives.
The purpose of a business plan
A business plan is not a static document with a limited shelf life; rather, it evolves alongside the company it represents. It serves as a dynamic tool that adapts to changing market conditions, emerging opportunities, and evolving strategic priorities. Here’s a closer look at its continuous relevance:
- Guiding the Business ( Business Concept/Business Idea and Strategy ) : A business plan serves as an internal guide that helps entrepreneurs and management teams set clear objectives, develop business strategies, and make informed decisions. It provides a framework for prioritizing tasks, allocating resources, and monitoring progress toward achieving business goals.
- Securing Financing: One of the primary reasons for creating a business plan is to secure financing from lenders, investors, or banks. A well-prepared plan presents a compelling case for why the business is a viable and profitable investment. It includes financial projections, market research, and a clear explanation of how the funds will be used to achieve growth.
- Attracting Investors: For startups and early-stage companies, attracting equity investors is often crucial for rapid growth. A comprehensive business plan not only showcases the business opportunity but also outlines how investors can potentially realize significant returns on their investment. It highlights the company’s unique value proposition and competitive advantage.
- Setting Goals and Objectives: Business plan s articulate both short-term and long-term objectives for the company. Specific, measurable, and time-bound goals are essential for motivating employees, aligning efforts, and tracking progress. Objectives can encompass revenue targets, market share goals, expansion plans, and more.
- Managing Operations: Business plans include detailed operational plans, covering aspects such as production processes, supply chain management, inventory control, quality assurance, and logistics. These operational details ensure that the business runs smoothly and efficiently.
- Market Analysis: Comprehensive market research within the business plan helps the company understand its target market, customer demographics, and competitive landscape. This knowledge enables the business to adapt to changing market conditions and identify opportunities for growth, product development, or market expansion.
- Communicating the Vision: A well-crafted business plan communicates the company’s mission, vision, and values to both internal and external stakeholders. This clarity fosters a shared sense of purpose among employees and resonates with customers and partners.
- Risk Management: Business plans identify potential risks and challenges that the company may encounter. By acknowledging these risks upfront, the plan can outline strategies for risk mitigation or contingency plans. This proactive approach helps the business better navigate unforeseen challenges.
- Measuring Progress: A business plan serves as a benchmark for assessing the company’s performance and growth. By comparing actual results to the plan’s projections, the business can identify areas where it is excelling and areas that require adjustment. Regularly measuring progress is crucial for making data-driven decisions.
- Exit Strategy: In some cases, especially for entrepreneurs and investors, a business plan includes an exit strategy. This strategy outlines how the business owners plan to realize their investment, whether through selling the company, going public, or transitioning leadership to others.
- Competitive Adaptation: In the face of a constantly changing competitive landscape, a well-maintained business plan allows a company to regularly assess its competitive position. It aids in identifying emerging competitors, market shifts, and areas where the business can gain a competitive edge.
- Performance Measurement: By providing a baseline for projected financials and key performance indicators (KPIs), a business plan becomes a tool for measuring actual performance against expectations. This ongoing evaluation enables the organization to identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement.
- Resource Allocation: As a company grows, it often requires additional resources such as capital, personnel, or technology. The business plan assists in rationalizing and justifying resource allocation decisions to support expansion or address operational challenges.
- Innovation and Adaptation: In today’s rapidly changing business environment, adaptation and innovation are essential. A business plan encourages a culture of adaptability by fostering discussions on new opportunities and strategies for staying ahead of industry trends.
- External Engagement: Externally, the business plan remains a valuable tool for engaging with investors, partners, lenders, and other stakeholders. It provides a transparent and comprehensive view of the company’s past performance and future potential.
Important External Tasks of a Business Plan
A business plan holds significance beyond its internal utility, as it acts as the company’s calling card in external contexts. Primarily, it serves as a persuasive tool for potential investors, bolstering the chances of securing essential financing, whether during startup or later stages for marketing initiatives or product development. Additionally, a well-crafted business plan proves valuable in negotiation discussions with potential key partners and regulatory bodies, enhancing the stability of current and future business relationships with customers and suppliers alike.
Here are some significant external tasks associated with a business plan:
- Securing Financial Support: One of the primary external objectives of a business plan is to attract external financing from investors or lenders. A well-prepared plan should clearly communicate the company’s financial requirements and how those funds will be utilized to achieve its objectives.
- Presenting to Investors: If you are seeking investment from angel investors, venture capitalists, or private equity firms, you must effectively present your business plan . This entails pitching your business to potential investors, highlighting key aspects of your plan, and addressing their inquiries and concerns.
- Applying for Financing or Grants: If you intend to secure loans or grants to fund your business, your business plan will be a crucial component of your application. It should demonstrate your capacity to repay loans or meet grant criteria, as well as how the funds will drive growth.
- Negotiating Partnerships and Collaborations: When pursuing partnerships, joint ventures, or alliances with other businesses, a business plan can outline the strategic advantages and potential outcomes of the collaboration. This is vital for persuading potential partners of the value of working together.
- Ensuring Regulatory Compliance: Depending on your industry and location, you may need to submit your business plan to regulatory agencies for approval or compliance. This is particularly common in sectors like healthcare, finance, and energy.
- Obtaining Licenses and Permits: If your business requires specific licenses or permits to operate, your business plan may be requested during the application process to demonstrate your readiness and compliance with regulations.
- Facilitating Mergers and Acquisitions: In mergers or acquisitions, both the acquiring and target companies may need to provide business plans to potential investors or lenders involved in the transaction. This aids in evaluating the financial viability and strategic fit of the merger or acquisition.
- Attracting Strategic Partners: In addition to traditional investors, you may seek to attract strategic partners who can offer resources, expertise, or distribution channels. You r business plan should compellingly illustrate why potential partners should collaborate with your company.
- Preparing for an IPO (Initial Public Offering): If your long-term strategy includes taking your company public, a comprehensive business plan is essential to attract public market investors. It must provide a detailed view of your company’s financial health, growth potential, and market position.
- Undergoing Due Diligence: When external parties consider investing in or partnering with your company, they often conduct due diligence. Your business plan should be precise and comprehensive to withstand scrutiny during this process.
When is a Business Plan Needed
When starting a new business, it makes sense to write a business plan . A strong business concept helps you find investors and convince big business figures, investors, or banks of your business idea.
In addition, a business plan forces a start-up to confront the strengths but also weaknesses of its business idea. However, an already existing company can equally benefit from a business plan. Many companies often lack a clearly recognizable strategy or guidelines against which success can be measured.
A business plan also leads to more transparency in entrepreneurial decisions and is necessary for an already existing company when raising outside capital and investors. An increasing number of investors and capital providers demand the submission of such a plan, thus making a strong business concept so important.
- Startup Phase : A business plan is essential when starting a new venture as it helps define your business concept, target market, and competitive strategy. It outlines your initial funding requirements, revenue projections, and expected milestones, providing a roadmap for the early stages of your business.
- Securing Financing : Whether you’re seeking a bank loan, angel investment, venture capital, or crowdfunding, a detailed business plan is a prerequisite. It should include financial forecasts, an analysis of your industry and competitors, and a clear description of how the funds will be used to grow the business.
- Strategic Planning : Regularly updating your business plan is crucial for strategic planning . It allows you to assess your company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis) and adjust your strategies accordingly. It provides a long-term vision and helps align the organization’s efforts toward common goals.
- New Product or Service Launch : Before launching a new offering, a business plan helps you research the market, understand underserved customer needs, and determine the product’s unique selling points. It outlines your marketing and sales strategy, pricing structure, and expected return on investment.
- Mergers and Acquisitions : In mergers and acquisitions (M&A) transactions, a business plan is used to evaluate the financial viability and strategic fit of the deal. It provides insights into the target company’s operations, revenue streams , and potential synergies with the acquiring company.
- Partnerships and Alliances : When exploring collaborations with other businesses, a business plan outlines the mutual benefits and objectives of the partnership. It clarifies roles and responsibilities, risk-sharing arrangements, and how the partnership aligns with each party’s strategic goals.
- Regulatory Compliance : Certain industries, like healthcare, finance, and energy, require businesses to submit comprehensive business plans to regulatory authorities. These plans demonstrate compliance with industry-specific regulations and provide transparency in operations.
- Licensing and Permits : When applying for licenses or permits, particularly in regulated industries such as food service, healthcare, or construction, a business plan may be necessary to prove that your operations meet safety, health, and environmental standards.
- IPO (Initial Public Offering) : Making a company public is a complex process. A thorough business plan is crucial to attract public investors. It should provide historical financial performance, future growth prospects, and a clear value proposition for potential shareholders.
- Crisis Management : In times of financial distress or operational challenges, businesses may develop a crisis management or turnaround plan. This specialized business plan outlines the steps needed to stabilize the company’s finances, restructure operations, and restore profitability.
Example of Business Plan Structure
Generally, there are no fixed guidelines as to how a business plan should be structured. Business concepts heavily depend on the recipient of the business plan and the orientation and structure of the company. The following bullet points are therefore only to be understood as basic building blocks that must be adapted to the individual situation.
1. Business Concept/Business Idea and Strategy:
- Illustrate your business concept, including the idea and methods for successful implementation.
- Include a timeline for implementing the concept.
- Optionally, provide information about your company and headquarters.
2. Company Description:
- Provide detailed information about your company, including its name, location, legal structure, and history.
- Explain your business’s purpose and the problems it aims to solve.
- Describe your target market and your business’s role within it.
3. Target Market:
- Market volume and potential.
- Growth potential.
- Barriers to entry and market restrictions.
- Supplier positioning.
- Relevant laws and regulations.
- Competitor analysis (strengths, weaknesses, product range).
- Identifying potential customers.
4- Operational Plan:
- Describe your business’s day-to-day operations, including location, facilities, equipment, and technology.
- Explain your supply chain, production processes, and quality control.
- Address any regulatory or compliance requirements.
5. Products and Services:
- Describe your products or services, highlighting how they differentiate from competitors.
- Unique Selling Proposition.
- Customer Benefits.
- Competitive Advantages.
- Innovation or optimization of existing products.
- Patent or property rights.
6. Marketing and Sales Planning:
- Outline your marketing strategy and timetable.
- Specify market entry plans.
- Set company goals related to market leadership, market share, revenue, and brand awareness.
- Discuss sales policy, pricing policy, and communication policy & advertising.
- Address sales methods, future developments, and pricing strategy justification.
7. Management, Employees, and Organization:
- Highlight management skills, qualifications, and key team members.
- Emphasize industry knowledge, social skills, previous successes, and professional experience.
- Mention personnel development strategies.
- Describe the organizational structure , focusing on procurement, development, production, sales, and administration.
8. Opportunities and Risks:
- In the ‘Opportunities’ section, showcase the potential of your business idea and the conditions for exploiting that potential.
- Address risks comprehensively, demonstrating a detailed and critical approach.
- Include potential risk scenarios and proposed solutions.
9. Financial Planning:
- Present concrete financial figures derived from previous analyses and plans.
- Profit Planning: Include a profit and loss statement (P&L).
- Balance Sheet: Provide an overview of assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Liquidity Plan: Compare expenditures with available funds.
10. Appendix:
- Include necessary documents like commercial register excerpts, business registrations, shareholder agreements, and legal forms.
- Attach CVs and references of key team members.
- Include relevant financial spreadsheets, patents, permits, licenses, brochures, leaflets, and organizational charts or graphs.
Reasons for Business Plan Failures
- Lack of Market Research: Failing to thoroughly understand the target market and its needs can lead to products or services that don’t resonate with customers.
- Inflexibility: A rigid plan that doesn’t adapt to changing market conditions or feedback from customers can become obsolete quickly.
- Overly Optimistic Projections: Unrealistic financial projections can mislead investors and hinder the business’s ability to meet expectations.
- Poor Execution: Even the best plan will fail without proper execution. A lack of skilled team members, resources, or a clear execution strategy can doom a business.
- Ignoring Competition: Ignoring or underestimating competitors can lead to a business being unprepared for market competition.
- Insufficient Funding: Underestimating the capital required to launch and sustain the business can lead to financial troubles.
- Inadequate Marketing: Without effective marketing, even great products or services may go unnoticed by potential customers.
- Ignoring Customer Feedback: Not listening to customer feedback and adjusting the business accordingly can result in products or services that don’t meet market needs.
Connecting The Dots: Importance of Business Model Canvas in Business Plan
Integrating the Business Model Canvas (BMC) into a traditional business plan is a pivotal process in crafting a comprehensive and highly effective business strategy . The Business Model Canvas , with its visual and succinct approach, offers a distinctive viewpoint on your business model. It functions as a complementary tool to the in-depth components of a traditional plan, strengthening your strategic capabilities. You can download it now.
The synergy between these two strategic instruments not only facilitates communication but also empowers you to analyze and adjust your business strategy with precision, ultimately fostering a pathway to success. In the following discussion, we delve into the significance of bridging the gap between these two potent tools within the domain of business planning. Here’s why the Business Model Canvas is essential within the context of a business plan:
- Visual Representation: The Business Model Canvas provides a visual framework that allows you to quickly grasp and convey the fundamental elements of your business model. This visual clarity is especially valuable when presenting your business concept to potential investors, partners, or team members.
- Concise Overview: While a traditional business plan can be lengthy and detailed, the BMC offers a concise summary of key components, including customer segments, value propositions, channels, revenue streams, and cost structures . It distills complex business concepts into a simplified format, making it easier to communicate and understand.
- Iterative Planning: The BMC encourages an iterative approach to business strategic planning . It enables you to experiment with different business model hypotheses and make adjustments as you gather feedback and insights. This agility is vital, especially for startups and businesses in rapidly evolving markets.
- Focus on Value: The Business Model Canvas places a strong emphasis on understanding customer needs and value creation . It prompts you to identify your unique value propositions and how they address customer pain points, aligning your strategy with customer-centric principles.
- Holistic View: By using the BMC, you’re prompted to consider all aspects of your business model, from customer acquisition to revenue generation and cost management. This holistic perspective helps identify potential gaps, dependencies, and opportunities that might be overlooked in a traditional plan.
- Alignment and Coordination: The BMC fosters alignment among team members and stakeholders. It’s a collaborative tool that encourages discussions about the business model, ensuring that everyone shares a common understanding and vision. This alignment is critical for execution.
- Integration with Traditional Plan: While the BMC is an excellent starting point, it can be seamlessly integrated into a traditional business plan. The insights and clarity gained from the BMC can inform and enrich the sections of the plan related to products/services, target market, marketing strategy, and financial projections.
- Efficiency: The BMC saves time and resources, particularly in the early stages of planning when you’re exploring different business model scenarios. It allows you to focus on the most critical aspects of your strategy before diving into the details.
- Adaptability: In a rapidly changing business environment, having a flexible and adaptable business model is essential. The BMC’s modular structure makes it easier to pivot or adapt your strategy in response to market shifts, competitive pressures, or emerging opportunities.
In summary, a business plan is a multifaceted and indispensable tool for businesses at every stage of their journey. It serves as a compass, guiding strategic decisions, securing essential financing, and attracting potential investors. Its ongoing relevance is a testament to its adaptability, enabling businesses to measure performance, allocate resources, and manage risks effectively. Beyond its practical utility, a business plan is a communication tool, conveying a company’s vision and objectives to both internal teams and external stakeholders. It is a dynamic and ever-evolving document that empowers businesses to navigate uncertainties, foster innovation, and drive sustainable growth, making it an indispensable companion in the pursuit of business success.
Frequently Asked Questions
1- how does a business plan relate to business strategy.
A business plan is closely intertwined with a company’s business strategy. The plan lays out the specific actions and tactics required to achieve the strategic goals of the business. It provides a roadmap for implementing the chosen strategy, outlining how resources will be allocated, what markets will be targeted, and how the business will position itself in the competitive landscape.
2- Is a business plan necessary if I already have a solid business strategy?
Yes, a business plan is still essential, even if you have a well-defined strategy. It serves as the detailed execution plan for your strategy, providing clarity on how you will achieve your strategic objectives. It also helps you anticipate challenges, manage risks, and secure financing or investments by demonstrating the viability of your strategy.
3- Can I use the Business Model Canvas in place of a business plan for a startup?
While the Business Model Canvas is an excellent tool for conceptualizing and validating your business model, it is often not a substitute for a comprehensive business plan , especially when seeking financing or investments. Startups may begin with Canvas to clarify their model but should eventually develop a full business plan to provide in-depth financial projections, market analysis, and operational details.
4- How often should I update my business plan to align with my evolving strategy?
It’s advisable to review and update your business plan regularly, typically at least once a year. However, major changes in your business environment, such as shifts in market conditions or strategic pivots, may require more frequent updates. Keeping your plan current ensures it remains a relevant and effective tool for guiding your business.
Related Posts
Business level strategy: examples & types for business strategy success.
In strategic management, businesses use a variety of approaches to craft a1
50 Innovation Examples: Exciting Innovative Ideas in Business
In the Business environment, strategic innovation has taken centre stage as a1
Innovation Strategy: Developing Innovative Strategies in Business
Innovation has become an imperative for organizations worldwide, yet the multitude of1
Minimum Viable Product (MVP) Examples and Definition
The MVP or Minimum Viable Product approach is an idea that was1
Recent Posts

Examples and Types of Effective Functional Level Strategy for Business Support
A key objective of any business strategy is to improve operational efficiencies...

The Three Levels of Strategy: Corporate Strategy, Business Strategy, and Functional Strategy
Understanding the intricate levels of strategy is crucial for any organization aiming...

Register For Your FREE Innovation WorkShop Seat Now!
Learn how to overcome the 90% failure rate in innovation from a master innovator and best-selling author.

Expert tactics to boost your innovation odds.
Insights on capturing customer needs for innovation.
Tools that turn your ideas into triumphs.
First name *
Last name *
Professional E-mail *
I want to be kept up-to-date and accept the privacy statement *
By signing up, you agree to receive news and accept the privacy statement (mandatory)
Verify your e-mail address now by entering the 6-digit code we’ve just sent to your inbox
Don't receive Code? Resend code
Last one step
Help us better understand our innovation Show members
Country * Please Select Afghanistan Albania Algeria Andorra Angola Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin (Dahomey) Bolivia Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil Brunei Brunswick and Lüneburg Bulgaria Burkina Faso (Upper Volta) Burundi Cabo Verde Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cayman Islands Central African Republic Central American Federation Chad Chile China Colombia Comoros Congo Free State Costa Rica Cote d’Ivoire (Ivory Coast) Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czechia Democratic Republic of the Congo Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Eswatini Ethiopia Fiji Finland France Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Grand Duchy of Tuscany Greece Grenada Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Holy See Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iran Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Korea Kosovo Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Laos Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Libya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Mauritania Mauritius Mexico Micronesia Moldova Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Morocco Mozambique Namibia Nassau Nauru Nepal Netherlands New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria North Macedonia Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papal States Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Piedmont-Sardinia Poland Portugal Qatar Republic of Congo Republic of Korea (South Korea) Republic of the Congo Romania Russia Rwanda Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Samoa San Marino Sao Tome and Principe Saudi Arabia Schaumburg-Lippe Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands Somalia South Africa South Sudan Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Sweden Switzerland Syria Tajikistan Tanzania Thailand Timor-Leste Togo Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Venezuela Vietnam Württemberg Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe Industry * Please Select Automotive, mobilty & transport Financial Services Chemical & agriculture Construction & Real Estate Consulting Education Energy Banking, insurance & FS FMCG Food Gov / Public Industry Health & lifestyle Logistics, Aero & Shipping Media & Entertainment Natural resources & mining Pharma & Biotech Retail & trade Tech & E-Commerce Telco Tourism design Information technology & services Management consulting Retail Pharmaceuticals International trade & development Professional training & coaching luxury goods & jewelry Automotive Insurance Mechanical or industrial engineering Company Size * XS - 1-10 S - 10-100 M - 100-1000 L - 1000-5000 XL - > 5000
Seniority * Please Select Junior Consultant Senior Consultant Manager Senior Manager Director VP SVP Partner CXO Board Member
Areas of interest * Innovation Digital Transformation Culture & Organization IT Strategy & Bus. Alignment Customer Experience
Discover the largest library of innovation & transformation tools on the entire Internet!
LOG IN VIA E-MAIL
| | |
Forgot password?
New to Digital Leadership? Create your account
Thanks, We’ve Received Your Updated Details

Learn how to overcome the 90% failure rate in innovation from a master innovator & bestselling author!
Your e-mail address: * Your first name: *

One Last Step..
Help us better understand the UNITE community
Free guide to improve your innovation success rate*
Our 35-page comprehensive innovation guide covers the key areas why innovation fails. While it cannot cover all the solutions (that would take books to fill), it provides you with a convenient starting point for your analysis and provides further resources and links to the corresponding UNITE models, ultimately allowing you to work towards a doubling and tripling your chances of success.

Get access to the UNITE Models now!
Discover the largest library of innovation & transformation tools on the internet!
Choose Your Password *
Confirm Your Password *
Already have an account? Log in
Country * Please Select Afghanistan Albania Algeria Andorra Angola Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin (Dahomey) Bolivia Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil Brunei Brunswick and Lüneburg Bhutan Bulgaria Burkina Faso (Upper Volta) Burundi Cabo Verde Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cayman Islands Central African Republic Central American Federation Chad Chile China Colombia Comoros Congo Free State Costa Rica Cote d’Ivoire (Ivory Coast) Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czechia Democratic Republic of the Congo Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Eswatini Ethiopia Fiji Finland France Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Grand Duchy of Tuscany Greece Grenada Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Holy See Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iran Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Korea Kosovo Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Laos Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Libya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Mauritania Mauritius Mexico Micronesia Moldova Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Morocco Mozambique Myanmar Namibia Nassau Nauru Nepal Netherlands New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria North Macedonia Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papal States Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Piedmont-Sardinia Poland Portugal Qatar Republic of Congo Republic of Korea (South Korea) Republic of the Congo Romania Russia Rwanda Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Samoa San Marino Sao Tome and Principe Saudi Arabia Schaumburg-Lippe Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands Somalia South Africa South Sudan Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Sweden Switzerland State of Palestine Syria Tajikistan Tanzania Thailand Timor-Leste Togo Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United States United Arab Emirates United Kingdom Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Venezuela Vietnam Württemberg Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe Industry * Please Select Automotive, mobilty & transport Financial Services Chemical & agriculture Construction & Real Estate Consulting Education Energy Banking, insurance & FS FMCG Food Gov / Public Industry Health & lifestyle Logistics, Aero & Shipping Media & Entertainment Natural resources & mining Pharma & Biotech Retail & trade Tech & E-Commerce Telco Tourism design Information technology & services Management consulting Retail Pharmaceuticals International trade & development Professional training & coaching luxury goods & jewelry Automotive Insurance Mechanical or industrial engineering Company Size * XS - 1-10 S - 10-100 M - 100-1000 L - 1000-5000 XL - > 5000
Editable UNITE models (PowerPoint) included
Most of our models and canvases are designed to be applied!
To help you personalize them to your exact business requirements, you can download fully editable versions of the UNITE models available (PowerPoint format)!
They are straightforward to work with, and you can directly incorporate them into your presentations as you need…thus saving countless hours of replication!
PS: did you know that you are also getting hi-res print-ready versions for your workshops?
Monthly live webinars
Each month we host our exclusive, invitation-only webinar series where one of our industry-leading experts updates our members on the latest news, progress and concepts around business strategy, innovation and digital transformation, as well as other related topics.
You will receive the book in PDF and EPUB formats, ideal for your computer, Kindle, Tablet or other eReading device.
Bi-weekly live group Q&A sessions
These sessions are your opportunity to bring any questions or challenges you’re facing and receive expert guidance on the spot.
Come and be a part of engaging discussions where your unique concerns are heard and addressed.
1x personal coaching session / month
If you are occasionally looking for a sparring partner or you need limited support, then this option will be ideal for you. Coaching sessions are 1-2 hours where we can discuss any challenge or opportunity you are currently facing.
If you need a few more hours outside of this provision, then these could be billed transparently.
Unlimited video call support! – it’s like always making the right decision!
We believe support shouldn’t be limited. Because we typically find that the occasional hour just doesn’t cut it – particularly if you and your team are in the midst of a large and complex project.
Your time with Stefan is therefore unlimited (fair usage applies) – in his function as coach and sparring partner. That does mean that you will still have to do the work – we cannot take that off you, unless you hire us as consultants. But you will get valuable strategic insight and direction to make sure you are always focusing your efforts where they will lead to the best results.
One personal coaching session / month + unlimited support via e-mail & WhatsApp
We believe support shouldn’t be limited. If you generally know what you are doing but want a sparring partner to frequently raise questions to, this is the perfect choice!
In addition to your monthly 1-1 live coaching sessions with Stefan, you will also get unlimited support from him via email and WhatsApp messaging (fair usage applies). This not only allows you to get valuable strategic direction in your calls, but also gives you instant access to expert help as you work through your plans each month.
The fact that support is text-based means that we can speed up our responses to you while keeping the overall cost of support down.
Welcome gift of our book “How to Create Innovation” (digital + physical editions)*
As a welcome gift, you will receive the both the digital and physical version of our book “How to Create Innovation”, which covers numerous relevant resources and provides additional deep dives into our UNITE models and concepts.
The print version will be shipped out to you on sign-up. The digital version will be emailed to you, and comes in PDF and EPUB formats, ideal for your computer, Kindle, Tablet or other eReading device.
1x major workshop or 2x smaller workshops / month
1x major or 2x smaller workshops based on the UNITE models.
- Topics covered: almost any challenge under the header of #strategy, #innovation or #transformation, leveraging the UNITE models.
- Hands-On Learning: solve your challenges while learning the practical application of the UNITE models and walk away with concrete plans and tools to take your next steps.
- Industry thought leadership: facilitated by Stefan, the founder of Digital Leadership and the main author of the UNITE models, ensuring top-tier guidance and knowledge sharing.
- Collaborative approach: engage in interactive sessions that foster collaboration, idea exchange, and real-time problem-solving among peers and industry leaders.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular workshops ensure ongoing development in your organization staying ahead of industry trends and customer needs.
Access all of our UNITE models, (incl. editable & print versions)
All of our Professional plans offer full access to the following:
- 6x UNITE model package downloads are included per month, if you need something in addition to these however, please let us know!
- Hi-res, print-ready versions you can use in your workshops
- Fully editable PowerPoint versions where applicable – personalize to your needs.
- Exclusive access to our vault of never-before-published strategic materials. We have much more to share – a lot of our concepts have never been published!
Exclusive access to our private UNITE community (upcoming)
We are currently in the process of launching our brand new community., we are designing our community to specifically help you:.
- Get answers to questions (“How do I …”)
- Share leading practices & knowledge
- Jointly develop new models
- Network amongst a highly qualified group of peers
Please, select the reason
Cancelling your plan will deactivate your plan after the current billing period ends. You will not be charged further, but also won’t be able to access [exclusive features/services].
- Cost-related issues
- Unsatisfied with the service
- Features I need are missing
- Switching to a different service
- Other (Please specify)
Book Your Initial Blueprint Session Now
Simply fill out the below form and book in a time for our initial session that works for you. This initial session is free, no strings attached, and is where we can discuss your Blueprint needs more in-depth before moving forward.

Stefan F. Dieffenbacher
Founder of digital leadership.
Adam D. Wisniewski
Partner for it strategy & business alignment.

Get in touch with Digital Leadership
Speak to our team today to find the best solution for your business to grow and scale.
We are here to support you across the entire lifecycle in all topics related to #digital, #innovation, #transformation and #marketing!

Stefan F. Dieffenbacher Founder of Digital Leadership
Contact Us!
Contact form, contact details, book a call.
Title, first name & last name * Email address * Phone number Please let us know how we can best support you! *
By clicking “Send”, I agree to Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.
Let’s have a conversation!
“Please be invited to reach out! We are happy to help and look forward to a first meeting!”
+41 (0) 44 562 42 24
Schedule Your Call With Our Team
Find a time on our calender that best suits you !

Founder and CEO of Digital Leadership
SCHEDULE YOUR INITIAL CALL
A Quick Survey!
What is the main challenge you're currently facing in your business?
You Want To Drive Change?
Let’s find the best solution for your business to grow and scale sustainably!
Let’s kick start it!
We will uncover your current business situation and goals and provide you with a bespoke solution that helps you drastically grow your business working with us.

Stefan F. Dieffenbacher, M.B.A.
Feedback about our consulting that we are proud of
Read the reviews and make sure that this is not a waste of time, but a super effective tool.
You want to drive change?
Schedule your free business assessment call with our founder.
On this call, we will uncover your current business situation and goals and talk about how to drive change and solve your need.
Choose the meeting type that applies to your needs and schedule a time to meet with someone from our team. We look forward to speaking with you soon!

Schedule Your Free Business Assessment

Schedule Your Free Business Assessment Call With Adam D. Wisniewski
Welcome to our scheduling page.

Let’s Design your Customer Experience Blueprint !
In a uniquely designed 60 or 90 minute session* , we will …
- > identify where to start with near-certainty
- > define what approach it takes to create success in your organization
Based on the Blueprinting session, you will receive a tailored blueprint that aligns with your objectives, vision and goals, ensuring that your initiative is a success from start to finish.

In this session, you will be working together with Patrick Zimmermann, Associate Partner for Customer Experience

Let’s Design your Culture & Org-Change Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Dr. Andreas Rein, Partner at Digital Leadership for Culture & Org Change
Let’s Design your Innovation Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Sascha Martini, Partner at Digital Leadership for Innovation and Digital Transformation
Let’s Design your Transformation Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Stefan F. Dieffenbacher, Founder of Digital Leadership Stefan is a global thought leader in the innovation space
Let’s Design your IT Strategy & Business Alignment Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Adam D. Wisniewski, Partner for IT Strategy & Business Alignment

Patrick Zimmermann

Sascha Martini

Dr. Andreas Rein
Write a personalized review! Log in
Create Review


- Meet Dean Anil Menon, Ph.D.
- Compare Programs
- Executive MBA
- Early-Advantage MBA
- Executive Doctorate
- Accelerated Management Program
- Graduate Certificates
- Advanced Entrepreneurship
- Center for Leadership Development
- Management & Executive Education
- Philanthropy & Nonprofit Leadership
Crafting a Compelling Statement of Purpose: Tips for Effective Writing

Are you applying to your top business schools, but continuing to stare at a blinking cursor instead of writing your statement of purpose? Crafting a personal statement that conveys your experiences, professional goals, career goals, and what sets you apart can feel daunting. It is difficult to retract our focus and take an objective look at our goals, accomplishments, and qualities — much less write them out in one place.
A statement of purpose example tells the admissions committee who you are, what you want to do, how their program will help you do that, your professional goals, and why you are a good candidate. Your statement of purpose is your opportunity to showcase the skills, experiences, and qualities you have that show the admissions committee that you are a perfect fit for their program. Admissions officers need to see how you align with their program, so crafting a strong statement of purpose is crucial to securing your admission or the funding you need.
When drafting your statement of purpose, ask your mentors to identify and explain qualities in you that stand out. Think of all relevant experiences — even internships — that make you a more qualified candidate for the program you are applying for. Your statement of purpose should communicate your career plans and convince faculty members that they should accept you into their program.
Understanding Your Purpose
Self-reflection is a significant part of crafting your statement of purpose. Self-reflection allows you to objectively look at your life and career experiences to define your goals and aspirations and identify your unique selling points. The process of self-reflection helps you gain clarity about what you want to achieve and the steps you need to take to get there.
This self-awareness will show through in your writing and help you become more confident in yourself and your career choices. Reflect on any accomplishments from high school, extracurricular activities, and coursework. Reference your academic background and how it relates to your field of study or the specific school you are applying to.
Highlight the aspects that enable you to identify your strengths and opportunities for progress, which will assist you in writing a statement that emphasizes your best qualities and defines you from other applicants. Also highlight specific research interests and academic interests, as this shows that you are willing to put forth the effort to pursue them if accepted to the program. Ensure that you include any other area of interest that demonstrates your willingness to grow or highlights your strengths.
Structuring Your Statement of Purpose
Your statement of purpose needs to be cohesive. Having a clear structure to your writing will guide the admissions committee through your statement and allow them to pinpoint the factors they are looking for. Keep in mind that the structure of your statement of purpose could vary depending on if you are applying to a Ph.D. program or a master’s program. Ensure that your essay is organized within a clear format, such as the following:
- First Paragraph: Introduce yourself, your professional experience, and your career goals.
- Second Paragraph: Explain your interests, research experience, and any relevant experience to your interests and why getting admitted to this program is important in helping you dive into these interests and achieve your goals.
- Third and Fourth Paragraphs: Expound upon what makes you the perfect candidate for their program. Give an overview of your work experience within your industry and how it relates to the program you are applying for. Connect personal experiences to qualities they are looking for. This is a chance to demonstrate your personality, work ethic, and willingness to commit to their program.
- Closing Paragraph: List your long-term professional goals and how this program will help you get there. The admissions committee wants to see that you are serious about using what you learn within their program. This is a chance for you to demonstrate their program as a critical part of your vision.
A well-structured statement of purpose is easy to read and provides a roadmap for the faculty to follow. A clear format also helps you organize your thoughts and present your information logically and concisely. Follow this resource for statement of purpose examples.
Enhancing Your Writing
Possessing strong writing skills will help you knock out the first draft of your SOP. Then, it’s time to proofread and enhance it. The clearer and more effective your writing is, the more you will stand out, considering good writing skills are essential in graduate programs.
Your statement of purpose is more of your first impression and gives the faculty a chance to see who you are beyond your GRE test scores, GPA, and resume. You want to make the best first impression possible.
Most programs have a maximum word count of 1,000 words for the statement of purpose. Clearer thoughts with a shorter word count are better than a longer statement of purpose that is unclear and unorganized. Your thoughts should be concise and lie between two single-spaced pages in a formal 12-point font.
Make It Engaging
Drolling over your GRE test scores and highlights from your letters of recommendation is going to make the admissions officers yawn when reading your statement. These are important factors in their consideration of you, so make it more engaging by demonstrating your knowledge and weaving in personal experiences with brief descriptions.
Use Formal Language
Think of your statement as a classroom presentation. You need to present yourself professionally, with a confident and hopeful tone. Avoid familiar and informal vocabulary — remember, you are speaking to higher-education experts. Your statement should sound academic and positive.
Avoid Clichés
Clichés are lazy and unoriginal. They tell your ideas instead of showing them — you want to convey a full understanding of information and ideas, not a superficial overview. Opt for using your perspective instead of comparisons and generalized opinions.
Avoid Overuse of Adverbs
Overuse of adverbs shows a need for more effort in your writing. There are better ways to convey your thoughts or describe events, and you should opt for solid verbs rather than adverbs. Ensure that you keep your descriptions short and clear so that you do not exceed the recommended word limit.
Revise Ambiguous Pronoun References
Pronouns should refer to their antecedent. If the antecedent is unclear, your entire sentence is unclear. This demonstrates poor writing skills and confuses the admissions officer who is reading your statement. Always ensure that your sentences are clear and concise.
Personalizing Your Statement of Purpose
Personalizing your statement of purpose is what sets it apart from other applicants and makes it truly compelling. It’s not just a step in your graduate school application — personalization is what makes your statement unique and reflects your individuality. This is an opportunity for you to increase your chance of graduate admissions by adding personal stories, your purpose for grad school, and highlighting your interests.
Your graduate school statement should answer these questions : What industry are you interested in studying during grad school? What makes you a great candidate for the program you’re applying to? What matters to you? What sets you apart from other candidates?
Proofreading and Editing
Proofread and edit your statement of purpose to ensure that the statement is free of errors and accurately reflects your message. Having a well-edited statement of purpose not only improves the readability of your writing but also shows that you take your application seriously and are committed to presenting your best self.
Make a List of Common Errors
Grammar and punctuation errors can be easy to miss. To make sure you correct any errors within your statement, make a list of common errors. If you often make the same error or have a hard time remembering grammar or punctuation rules, add those to your list so you can double-check them when proofreading.
For example, scan your writing to ensure that all of your commas and apostrophes are in the right place, eliminate run-on sentences or wordiness, and make sure your verbs are in the correct tense.
Double Checking Everything
Read and reread your statement until you are confident it fully reflects you as the best possible candidate for the program you are applying for. Double-check that your ideas are presented clearly. Revise any typos or grammar and punctuation errors. Make sure that your writing is formal and academic and that the format makes sense. Also, compare your statement of purpose to other examples so you get a better idea of flow and format.
Watch Your Tone and Flow
Your tone should be formal, positive, and confident. Identify and revise any phrases or sentences that sound confusing or out of place. If you aren’t sure, read it aloud to see how it flows. You can also get a trusted colleague or mentor to proofread it for you. Pinpoint any disruptions in your flow and formatting. Make sure that what you are saying makes sense, and keep one idea within one paragraph. Clear and concise writing is key!
Final Thoughts
Whether you are pursuing a master’s degree or applying for a Ph.D. program, we know that you have what you need to write a compelling statement of purpose that will get you into grad school! Graduate school is not the right path for everyone, so give yourself credit for applying to a graduate program.
Pursuing a graduate degree requires a hefty application process. Remember that your statement of purpose isn’t just a check in the box — it’s your first impression on the admissions committee of the degree program. Each particular program will have its requirements and set of values.
Make sure that you align with a specific program before applying for graduate study, and highlight the areas that resonate within your statement of purpose. Format and compose your statement of purpose in a way that engages the reader and compels them to accept you as a graduate student. Be sure to include personalization and relevant experiences. Before submitting your statement of purpose, revise and enhance your statement so that it is formal and confident.
If you are on the fence about which graduate program you want to apply for, we can help you make that decision. Here’s to making a compelling first impression in the next step of your career!
Related Articles
Exploring the differences: data science vs data analytics.
Data Science and Data Analytics are two related but distinctly different fields that are concerned with processing and analyzing large volumes of data. But what are the key differences?
Maximizing Your Potential: The Endless Possibilities with an MBA Degree
An MBA degree opens doors to many interesting career paths. See the business world through an MBA career lens and make the most of your opportunities.
MBA Starting Salary Statistics for 2023
Regardless of your reason or industry, obtaining your MBA is an excellent way to increase your earning potential. Learn more about the starting salary statistics for 2023.

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

SOP (Statement of Purpose): Format, Samples, and Tips

- Updated on
- Feb 17, 2024

To aesthetically present a movie on the screen, great actors are the requisites. Similar is the case when one is carving their own career path. From choosing the right course to getting into your dream university, you need to take each step carefully. As a crucial part of the eligibility criteria, the universities often demand LOR s, SOPs or entrance test scores to assess the candidates and their suitability for the chosen course. A Statement of Purpose (SOP) is one such element that beholds great value in the admission process of those aspiring to study abroad. Creating an alluring SOP is essential to help the assessment committee understand your willingness for the program you have applied for. This blog aims to provide a comprehensive step-by-step guide on drafting a statement of purpose that can help you sail smoothly through the assessment process and get entry into your dream academic institution.
This Blog Includes:
What is a statement of purpose (sop), why is sop important, sop format, 2. formulate, 3. revise and modify, what do colleges look for in an sop, how to write a perfect statement of purpose (sop / admissions essay), introduction, academic background and professional experience, career goals, why this course, why this university, how long should an sop be, what to include in an sop, what not to include in an sop, 10 tips to write a successful statement of purpose, sop sample for business analytics, sample statement of purpose for mba , sample statement of purpose for masters, sop formats for usa, canada, uk, and australia, top 5 mistakes to avoid while writing an sop, how can you reduce your chances of rejection from your chosen university, can sops help with scholarships, sop vs letter of motivation, sop vs personal statement.
A Statement of Purpose can be referred to as an informative document, containing personal statements, and is essentially required as part of the admission procedure of study abroad programs. Also referred to as an application essay, it comprises the basic details of a candidate along with their professional and personal interests, academic highlights as well as future aspirations. An SOP plays an integral role in the application process of a study abroad program as it provides the admission board with the key information about the candidate and why they want to study a particular course at their institution. It not only describes who you are as an individual but also gives an idea about your writing skills and proficiency in the English language.
A well-written SOP is an extremely significant element during your admission process. While the academic record and other exam scorecards, academic transcripts and backlog certificates are essentially objective in nature, an SOP is the only truly subjective aspect of your application. It is the only document in your application that allows you to prove that you have something unique which makes you stand out from the crowd. As such, it is the document of your application docket that can hugely determine your admission.
Also Read: Statement of Purpose vs Personal Statement
As such, there is no particular or proper format for writing a statement of purpose or an SOP. Students have to write an SOP just like an elaborative and descriptive English essay dividing the whole context into different paragraphs. Each paragraph must be having distinctive features describing different scenarios, features or characteristics about yourself. You can take the help of the below-provided structure and get started with writing an SOP for the university you want to study in.
| Self-introduction Your background, in brief, Your long term goals/vision Purpose to opt for this university and course (briefly)Remember: the first impression is the last impression | |
| Past academic background Professional experience (if any) | |
| Academic achievements Strengths Opportunities Academic recognition Projects undertook Professional achievements Industrial exposure | |
| Discuss in detail, Why do you want to study this course or program. Discuss your goals and your future expectations from this course or program. | |
| Where do you see yourself in 5 years after you will be graduate from this university/college? Discuss your future objectives and your career plans and goals. | |
| Why this university/college? Mention about different departments, different university activities, recognition, awards, faculty members, environment, infrastructure, the methodology adopted etc. | |
| Ending/ closure of the SOP on a thankful note. |
How to Write a Statement of Purpose?
As a pivotal document for any study abroad application, an SOP needs to be precisely well-written. To help you understand the different elements of this document, we have curated a step-by-step procedure that you can follow to curate an impressive statement of purpose.
The first step of the process of drafting a statement of purpose is to think about the varied aspects of your candidature that you should mention in it. The mandatory inclusions of an SOP are academic achievements (especially at the undergraduate level), prior work exposure or volunteering experiences. Start with framing an outline for the document and ask yourself the following questions:
- Which field of study excites me the most?
- Why do I want to pursue this degree?
- What are my expectations from this degree?
- What outgrowth can this degree offer me?
- Where can this degree take me, personally and professionally?
- Through my pre-requisites, what values can I add to this program?
Once you have made key pointers for most of the questions mentioned above, you can begin jotting them down in a thorough and comprehensive manner.
Now that you know what you want to mention in your SOP, it’s time to curate a rough outline for the document. Here is a list of some essential tips you need to keep in mind while formulating your statement of purpose:
- Since the admission committee strives to understand your candidature through the SOP, you need to be honest in describing your career aspirations and objectives. Focus centrally on maintaining the authenticity of your mentioned details. Duly elaborate on your advantageous perception of the chosen course.
- Creatively cite your personal and professional interests. Mention what you are passionate about and what excites you. Then, sensibly connect it with your chosen program and how it will assist you in grooming your skills. For instance, you can state that you are aspiring to gain experiential learning or training in your desired industry through the course.
- What brought you here should be a sure-shot mention in your SOP. You can begin with stating those features of your chosen course that convinced you to opt for it. Then, write down the objectives you want to fulfil by studying the program. It can be personal growth or professional upliftment or even both. Try to be unique and precise when listing your reasons.
Once you have jotted down your SOP as per the above-mentioned necessary tips, the final and concluding step is to revise and make changes accordingly. Go through the list that you created in the beginning and ensure that you have added all of them.
- The word limit for a statement of purpose is between 500-1000.
- Do not miss out the predefined sizes for spacing, margins and font size.
- Try getting a second opinion but getting your SOP read from a friend or an experienced professional.
Many foreign and even national universities ask for a Statement of Purpose (SOP) from candidates wanting to enrol in suitable courses that the university has to offer. They ask for the SOP from candidates in order to check and look at the following things:
- The writing capabilities of the writer or the candidate
- The X factor that makes their writing stand out from the crowd
- Choice of thoughts and ideas that has been explained in the SOP
- The unique personality of the candidate
- Candidate’s talent, previous experiences, interests and potential
- How and what can the candidate contribute to the department of the college/university
- Candidate’s motivation or inspiration to study a selected course must be evident and justified
- The reason behind to choose a particular university/college and a particular course of study
- Academic and extracurricular achievements and recognitions (if any)
- Originality and clarity of the SOP as a whole.
To know more, read our blog on – How to Write an SOP?
Check out the video on the same below!
How to Write a Powerful and Convincing SOP?
Whether applying for undergraduate, graduate, or post-graduate programmes, the strategy of writing a powerful statement of purpose should be sound focused throughout. Starting from your academic and professional background to your career aspirations, you need to carefully connect all the dots between reaching your goals through your choice of school and course. The essay should always go in a flow covering your past experience, present involvements, and future plans. An important point to remember while writing your SOP would be to divide it into paragraphs that cover all the pointers. Here is a look at how you may write the SOP presenting your profile strongly:
This paragraph is often confused with self-introduction. It should not introduce you but should discuss what you are about to discuss in your SOP. There are multiple approaches you may adopt to go about this paragraph:
- Discuss your long-term goal and connect it with your idea of pursuing the course you are applying to
- Present your understanding of the chosen field and write how you want to contribute to that field
- Explain your background in 2-3 lines and connect it with your future goals
- Write about an anecdote that helped you realise your professional interest in the chosen field
This comprises of your academic background: what you have done so far, what you are currently pursuing, your academic strengths and projects, and the industrial exposure you have attained.
This is the most important paragraph, where you should discuss your short and long-term goals. Your immediate goal would be where you would want to work right after completing this course. You should be able to name some companies within India along with the designation you see yourself working at. This should explain the kind of job profile you would be working on.
Then comes your long-term goal, wherein you should mention where you see yourself from 10-12 or 15 years down the line. This may include your desire of working at the CEO/CFO/CTO level or maybe establish a firm that you own. It may also include your dream of expanding your existing family business overseas. You may also be interested in further studies like a PhD which can be included here.
More in this section may include your desire of becoming a professor or researcher. In any case, it is suggested that you discuss your business aim, principles, and core values or how you would influence the young aspirants of this industry. You should be able to portray ‘how you wish to make a difference in the industry keeping in mind the current industrial scenarios and emerging trends.
In this paragraph, you should discuss why you want to join a course and what modules would you tap during this course. It should also cover the skills you would acquire in this duration along with the exposure that would help in developing the skills desired to realise your goals.
This is a specific paragraph wherein you can convince a university as in how they are suitable for your profile and you are an ideal candidate for their university. You should discuss the course curriculum, research work, faculty names, as well as the university-specific activities that would help you in enhancing your profile.
Also Read: How to Write a Best Statement of Purpose?
Ideally, if considering an internationally renowned university, then the statement of purpose should be at least 1-2 pages long. In terms of word count, then the same should be around 1000 words. Having said that, the word limit and the length may also sometimes depend on the university that the candidate is targeting and also on the level of degree. Like for example, a candidate who is writing an SOP for an undergraduate program may not exceed 800 to 1000 words whereas a candidate who is writing an SOP for a PhD or M.Phil degree course has to write it in around 1200 words and sometimes even more. Some universities even have a fixed length and word count which is uniform for all the programs and courses.
| Bachelors and Masters | 800-1000 | 1-2 pages |
| Doctoral (Ph.D)/ Research | 1000-1200 | 2-3 pages |
There are many elements to an SOP. Universities could ask question-based essays or simply a general statement of purpose. Until and unless categorically asked, an SOP must include your goals and the career path you have taken up so far as well as your academic progress. Other elements that are further important to the SOP are also the personal motivations that lead you to choose the university/course you have applied to as well as how you intend to use that experience to achieve that goal.
Following are a few things that you must do in order to make your SOP application strong:
- Your Statement of Purpose should have a unique and engaging beginning as well as an end. It must be original, a reflection of you.
- Explain your academic background, present and future aspirations. Through this, you must justify your choice of a particular course for masters or doctorate courses.
- Upon reading your SOP, the admission officer should be able to understand how you can contribute to the university in terms of research and further scope in your chosen area.
- Always write your SOP in an active voice and ensure you provide information in a manner that is a reflection of your passion and optimism. If you have any statements or references, try quoting them with relevant examples rather than being direct.
Often universities come across a lengthy statement of purpose and yet they reject it. Even when you cannot find one grammatical error, the seemingly excellent SOP would be rejected. And the primary reason is – too much unnecessary information. For instance, just because you might want to talk about your family, does not mean you go on and on to talk about only your family. While your SOP should be a brag sheet, it should be a brag sheet with a substance. You need to pick and choose what to include. Pick a theme and mention the accomplishments that make the most sense to your candidacy.
- Weave your career path into a story, not statements.
- Do not write what you think should be written. Personalise the SOP and make it your own.
- Do not stress over it. Although it is an important part of your application, the SOP should be a direct reflection of you.
- Find the deeper meaning behind the events of your life and pen them down.
- Give a strong reason as to why you chose the particular school and course.
- Be specific in the timeline of events.
- Use a formal but conversational tone.
- Accept your mistakes and explain how you are willing to act on improving. Use action items.
- Give yourself enough time to write the SOP and edit it constantly.
- Proofread, edit, re-edit and then edit it again! There is always room for improvement, remember that.
Also Read: SOP for Scholarship
Statement of Purpose Samples
Here are some good examples of well structured SOPs that you can refer to while writing your own.
“ A successful career in Business Management requires adequate knowledge to utilise the strengths and weaknesses of an individual. In my undergraduate degree, I majored in economics and psychology because I believe that understanding these two fields is important for leading a successful business. I want to increase my experiences and knowledge further by pursuing an Executive MBA, which will equip me with advanced skills that are necessary to achieve my career goals.
As I have carried out various leadership positions, I have learned how to efficiently work in teams and pursue the specified goals. In my previous company, ABC, I successfully implemented the strength-cum-weakness finder software which helped us assign projects to the groups based on the mapped data. As employees got allotted tasks as per their efficiency, it resulted in a 30% net gain for the company over the following year. I believe that a successful business leader understands the importance of strategically utilizing a company’s resources to ensure the maximum potential and development of the company. Further, the pivotal thing I learned about myself by taking up leadership roles is that teamwork is a crucial element of successfully achieving an organisation’s objectives. An Executive MBA will help me furnish my leadership skills imparting me with the knowledge of hierarchical structures and how to work with other leaders of different domains in an effective manner.
Studying for an Executive MBA, I plan to take charge of multiple team projects throughout the duration of the degree so that I can polish my teamwork skills. I aspire to work under industry leaders and attain global exposure. Pursuing this degree from your institution, I aim to gain professional as well as personal skills that can help me soar through my career journey. ”
I had a keen interest in Biology since childhood. I was eager to learn about the living organisms around my surroundings and how they function. I took this interest forward and decided to pursue my higher education in biology. When I was first introduced to the field of biotechnology, I was mesmerized by what technology can do to improve the life of any living organism. This inspired me to look at various research programmes in biotechnology and how we are moving towards a phase where technology can alter even the basic fragments of any living organism and change the course of life an organism goes through. I observed the various research patterns that have been taking place in the agricultural industry with the advent of GMO (Genetically Modified Organisms) giving birth to the Green Revolution. This was only one potential achievement in the extensive list of achievements that biotechnology was progressing towards. I worked with a reputed biotech firm which gave me an insight into how fast-paced the research in biotechnology is. The firm gave me the necessary exposure leading me to decide that I want to pursue MS in Biotechnology. My ambition to work in this field lies essentially in bringing changes in the lifestyle of people in a way that I can research and extensively study the required positive steps towards climate change. My goal is to achieve a sustainable lifestyle for every individual. The exposure that your esteemed institution will give me in the field of research will help me achieve this goal by working at a reputed platform
- Sample SOP for Australian Student Visa
- SOP for MIM
- SOP Samples for MS
- SOP for Business Analytics
- Sample SOP for MS in CS
- SOP for PG Diploma in Canada
- SOP for MBA: Essentials to Mention & Samples
- SOP for Australia
Here is the basic format for USA, Canada, UK and Australia:

If you are planning to study abroad and want to write a good and outstanding statement of purpose for the university that you are targeting, then here are some of the common mistakes that you can avoid from the very beginning while writing an SOP:
- Writing the SOP at the last moment without any plan of action or a roadmap
- Writing a weak and vague introduction and conclusion
- Using informal language, slangs, short forms in your SOP
- Exceeding the word limit and not reaching the correct word limit at all
- Making your SOP excessively flashy and flattery

If you are eligible for any college-specific scholarships, then during the application process you will be required to write a separate essay/SOP. Either you will be given an essay prompt/question along with a word limit or they would simply ask for an SOP stating the reasons why you think you deserve this scholarship and/or what makes you unique from the rest of the candidates? Thus, a generic SOP is different from a scholarship SOP.
Must Read: LOR: Types, Format, Sample and Tip s
A Letter of Motivation is a letter directly addressed to the admission committee/department faculty explaining your objectives, motivation and goals related to the course. The SOP is not addressed to any specific person or department, it is drafted in an essay format, whereas, the motivational letter is always addressed to a professor or department under whose guidance you will be studying.
Also Read: How to Write a Motivation Letter?
Very much similar to an SOP, Personal Statements are an on-page essay where you write about your motivation, inspiration, goals, and achievements. Personal Statements usually have a more intimate tone than SOP as it talks about the highlighted incidents of your life. Another crucial difference between an SOP and a Personal Statement is that an SOP is addressed to no one in particular, while a Personal Statement is addressed to a professor or department under who you choose to study.
Relevant Reads:
Only your LORs need to be attested by your college or company. An SOP need not be attested/self-attested until and unless specified by the university. If you take a LOR from your college professor/school teacher or a Principal/Dean, then that LOR needs to be signed by the recommender along with the college/school stamp and letterhead. Similarly, for professional LORs, they need to be signed by their respective recommenders on the company’s letterhead and company stamp.
Once you have finalised your SOP draft, give it a double-check for grammatical and formatting mistakes. Your next step should be to analyse and critique your essay. Look at your SOP through the eyes of the Adcom and see what you find lacking. For more effective inputs, you can show your drafts to your friends and family and see how they react to them. Accordingly, you can make some changes but do not overdo it or deviate from the format. Lastly, check for spacing errors and save the final SOP which you will be using for the application process.
You should avoid mentioning any low marks or shortcomings about yourself in any of the application documents, including SOP. There are very few universities that ask you about your gap year. For them, you can mention the reason for the gap between your studies. Generally, no university asks about low grades during your study period as your selection depends on various criteria like exam scores, student profile, financials, and so on. Thus, it is advised against mentioning any flaws or low marks.
Hence, we hope that now you are geared up with all the quintessential tips to start carving out your SOP. If you still have doubts or need further professional guidance, you can always reach out to our Leverage Edu experts and we’ll assist you throughout the admission process, be it selecting a suitable course and university or drafting impressive SOPs and LORs. Call us immediately at 1800 57 2000 for a free 30-minute counselling session.
Team Leverage Edu
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
I was really impressed and happy with the informations I was able to get reading through your well documented page.
I am really impressed reading through your sample and guides in writing an SOP.I was able to put mine together and I have submitted awaiting feedback from the Admissions office. Thanks so much.

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
- Testimonials
- Plans & Pricing
- Free GRE Practice Test

Study Like a Superhero!
- Track your strengths and weaknesses
- Study only what you really need. Anytime. Anywhere
- Learn from expert tutors who are just a phone call away
Join over 172,586 students who are studying the smart way!
11 Tips for Writing a Powerful Statement of Purpose [Sample SOP Included]

By Jitta Raghavender Rao • GradSchool Admissions
The Statement of Purpose is probably one of the most misunderstood aspects of graduate applications. Most students pass it off like it is just another essay about themselves, and naturally, write monotonous stuff that doesn’t stand out. That is why, the university admissions committee puts a hefty weight on statement of purposes and their structure – they want to see whether you take the interest in letting them know how much you want to study at their university.
Most Statements Of Purpose Start Off Like This:
“I am applying to the Master of Science program in Something Engineering at the University of Example because I believe my technical skills will blossom at your program as it is a place where I will be challenged and where I can develop my scientific and technical knowledge.”
Or Like This:
“I am honored to apply for the Master of Science program at the University of Example because for as long as I can remember, I have had a love affair with science. Since I was a kid in school, I have known I wanted to be a scientist/engineer.”
Now, almost 99% of the statements are structured similarly, and often times, students copy-paste, and edit statement of purposes from their seniors or friends, making it sound even more generic or irrelevant to their applications. If you want to stand out from the crowd; if you want the admissions committee to remember your essay at the end of the day, even after going through hundreds of applications; if you want to gain that extra advantage by being somewhat special and unique, you will have to draft a great statement of purpose. Great, but original .

How Can Your Statement Of Purpose Stand Out From The Crowd?
How do you write a great statement of purpose that sounds original, but at the same time gives the admissions committee what they are looking for? Simple. Basically, every university expects a student to answer to some basic questions that the admissions committee has. They may not ask you openly, but these are generally what they expect you to answer:
- What you want to study at graduate school?
- Why you want to study only this degree?
- Why do you want to study at this particular college? What do you like in us?
- Why did you choose to study in this particular country? What do you like about it?
- How much and what kind of experience you have in your field?
- Is your experience related to you choice of degree?
- If you are already experienced, what additional skills are you planning to gain from the degree?
- What you plan to do with your degree after graduation?
- Would you choose to end up with a job or take up research?
- What are your expectations from both the graduate program, and the university?
- Would you like to study or do research under any particular professor? If yes, why only them?
- How can you contribute to our university and our program? What specific skills do you bring to the table?
- Apart from work and education, what are your hobbies, interests, and habits? What are you like, as a person?
- What do you understand about our student community and culture? Why do you think you will fit in?
- What is that one unique aspect/characteristic about you that we should know? Why does it matter to us or to the fellow students of your class?
Now, these are the questions you will have to consider before starting off with your statement of purpose. Write down answers separately to each of the questions asked above, and try to build a story that the admissions committee would love to read. Remember, unlike an MBA program, you won’t be having any personal interviews for a graduate program, so the only way to impress the admissions officers is by telling your story through the statement of purpose . You will have to convey your story in the best possible way, such that the committee finds you interesting enough. And if you are interesting enough to them, you will end up with not only admission, but also a decent scholarship as well .
Strategies to Write a Powerful Statement of Purpose
It is important that you follow a specific strategy when it comes to drafting your statement of purpose. Though most students write whatever comes to their mind, or whatever they see on the internet, you are not most people. You would want your statement of purpose to sound brilliant, and original . And for that, you’ll need some strategies.
1. Write Stories. Not Statements
If given a choice, would you prefer reading a novel or a newspaper?
A novel, without a doubt. Do you know why?
Because while a newspaper gives you mere news and some eye-catching headlines, a novel tells you a story; a beautifully written piece of literature that you will be emotionally connected to . It brings those humanly feelings out of you, and involves you in its storyline. You imagine yourself in place of the narrator/character, and understand why he/she has done that, or taken such decisions. We remember stories much easier than statements.
Because stories connect to us, statements don’t.
For example, most people say this:
“I used to work in a multinational software company in the development team, and I had to do the same job every day: code stuff. There was nothing new for me to learn at work, and there was nothing very exciting about going to the office. One day I decided that I had to get out of there, so I applied to college to study higher courses and get a better job.”
Doesn’t that sound like most stories? Albeit, a very normal story? Instead, how about saying this:
“Late in the night one Monday, I had found myself in the middle of a deserted office, and fifteen thousand lines of code. Full of caffeine in my bloodstream, and an empty life beyond office, I realized that the computers started coding my brain, and controlling my life. No longer wanting to let the machines feed on me, I decided that college would be my salvation.”
Both the stories come to about four lines. But which narrative do you think will keep the admissions committee reading? Which story do you think will be remembered by them even after reading 5000 applications?
Think again. Do you want your statement of purpose to read like a novel or a newspaper? If the former is your answer, then you need to put in a lot of effort to tell your story. Think about ‘why’ you want to study what you want to study. Is there a strong reason behind it? Is the reason emotional, economical, or any other? Think hard, and you will find a connection. The reason might not seem obvious in plain sight, but when you think hard enough, you will understand that there is strong reason why you want to study a particular course/degree.
Now, when you have found this strong reason, tell it as a story. Write a short, but great narrative about what made you make this choice. About why you have chosen to study this course at this university. Impress the committee with your creative storyline, and you will reap the benefits big time.
2. Quantify Your Stories
Even though we asked you to write a story, you will have to remember that your story should not read like a thesis . It should rather serve as the best source of information about you. And when it comes to information, numbers play a key role. Your story should be not only qualitative, but also quantitative. And that means, your story must contain measurable quantities instead of just stories, so the reader can understand the depth of it.
For example, if you have worked for a local NGO teaching math to primary kids, you could say:
“During my engineering days, I helped a local NGO by joining as a math tutor, where I taught basic math concepts to school children.”
Now even though this sounds really good, it doesn’t give the reader the entire picture and they certainly do not know how much of an impact you made on those children.
So, you could change that bit to something like this:
“During my second year of engineering, I joined ‘Teach Math’, a local NGO, where I was a part of the Math tutoring team. For a period of 10 months , I taught basic math like algebra, geometry and arithmetic to more than thirty 5th and 6th grade students. And every single student I taught to, secured an A in math that year. I’ve never been prouder in my life.”
Do you see the difference? These numbers suddenly give a whole new perspective to the readers, and their respect for you is suddenly multiplied. That’s the power of numbers; they add authenticity, and authority to your stories . If you can quantify your stories properly, and show the results instead of just actions, the committee will not forget your name. You can use the same strategy for the rest of your story, no matter what it is about.
Whether it is a research project you did, or a college fest you organized, or a college sports team you led, whatever it is, add numbers to your stories, and make them sound more realistic, and more beautiful.
3. Be Specific
You have to make sure that whatever you say in your statement of purpose, you need to be very specific with it. Don’t just say something because you think it will impress the admissions committee. Whatever you say, you have to really dig into details . Be introspective. Don’t just say “I chose this degree because I love this field.” Explain clearly why you love this field, what made you decide that you want to work in this field for the rest of your life, what skills you are trying to amass, why it completes you as a person, etc.
Don’t beat around the bush like you normally would, when you talk to your friends. Don’t use ideal sentences like ‘I want to change the world’ or ‘I want to find my inner self’ or any of those cheesy lines. Just be straightforward and always to the point, but not so much as to come off as arrogant. Find your reasons and then find a nice, memorable way to say it .
Grad school admissions officers require the statement of purpose not just because they want to find about you and your dreams. More importantly, they want you to think for yourself , as to why you are taking such a life-changing step; why you think this is the best thing that can happen to you; and why you think you truly need it to succeed in life.
The ‘why’ is always profoundly important , and also an extremely difficult question to answer, which is why, if you can find answers to all the whys, then you are almost in.
4. Customize Your Essay
One of the biggest mistakes students make is to prepare a basic template for their statement of purpose, and if they are applying to more than one university, they simply change the relevant names and details. But the rest of the statement is an exact copy.
This is never a good idea, because though they might seem quite similar to each other, every university is vastly different from the others. Each of them has a diverse set of characteristics that define them, and their cultures, methodologies, visions, values, mottos, strengths, weaknesses , etc., vary greatly. These things are much more important than the departments, or university rankings, or number of Ph.D.’s or other materialistic qualities.
So, if you are applying to multiple universities, you need to factor in all these qualities of every university, and customize your statement accordingly. Mere changes in names and details won’t suffice. You need to tailor your essay such that the admissions officers think you will fit in well into their community. Remember, every student community is like a family , and if you give hints that you cannot fit into a family or their culture, you may not be welcomed easily.
Speaking of cultures, different countries obviously have different cultures, but even a large country like the US has different cultures in different parts of the country. So, before you begin writing, try and research the general culture within the region in which your target university is, and learn something about it. It may also help in aiding your decision process; if a culture doesn’t attract you much, then there’s no point in wasting an application .
5. Use a Formal But Conversational Tone
Nearly all statements or essays come under two categories: The super formal, and the super friendly . The first category is when you write a statement of purpose that is so formal, it looks like you are writing to your lieutenant in the military. The second one, of course, looks like a casual email to a friend. Now, when asked which one seems like a better choice, most students say the formal way is the way to go, and super friendliness is a big no. And still, a minor set of applicants think they can outsmart the admissions committee by sounding friendly, welcoming, and funny.
But, on further reflection, you would understand that neither of the approaches is ideal . And you are right, neither of them is right. Like we talked about it already, your statement of purpose should read like a novel: slightly formal language, but still a tinge of fun and uniqueness. That is what you need. A conversational tone is the best and the safest way to go. Write like you are talking to someone, but avoid using casual language.
Imagine you are talking to your dean, or the director of your college . What would your language be like? That’s how your statement of purpose should sound. Now, occasional humor is okay, but you shouldn’t try to sound too funny or too smart. No intentional jokes or funny lines should find their way into your statement. After all, it’s a statement of purpose, and the purpose is to pursue a graduate degree , not to impress people with your sense of humor. So, if what you write brings a smile on the readers face, then it’s perfectly alright. But it shouldn’t make them throw away your application because you didn’t seem serious enough to them.
6. Decide How You Want To Portray Yourself. And Learn How to Portray Indirectly.
You must see that the statement of purpose serves as a medium to convey your attitude, your personality and your character. Alright, those are some heavy words, and it can actually be difficult to them on paper. So, what you can do is, learn what your statement of purpose should portray you as , in terms of a few criteria, which tell the admissions committee that you are:
- Very passionate about the field of study you have chosen.
- An Intelligent student who can withstand the academic workload of a graduate program.
- Well-prepared academically and personally, and eager to study new courses.
- Able to take on the challenges of studying at an international graduate school.
- Able to build and maintain a good rapport with professors and fellow grad students.
- Able to finish the graduate degree within time, and graduate with a good percentage.
- A potential remarkable representative of that grad school in your future career.
- A successful alumni of the grad school who in the future can help in recruiting graduates.
- A responsible alumni who in the future will help raise funds for the grad school, to spend on research, infrastructure, facilities, student scholarships, etc.
These are basically the parameters that grad school admissions officers look at, when they decide who is joining their class.
Now, you might be wondering that the statement of purpose can only be as long as 1000 words, and that there’s quite a lot to cover in that little space. This is where your writing skills should come in. You simply can’t just go ahead and write “I am very passionate about the field of study I have chosen.” That is the last think you would want to write. What you should instead write is a sentence that indirectly means the same. You will have to choose your words wisely so as to indirectly communicate your “passion. You can use brief examples to show why you are so passionate about it.
For example, you can say something like:
“My grandfather was a car mechanic. I remember when I was nine, he took me to his garage for the first time and showed me how he could repair my damaged bicycle so I could ride it again. When he passed away a few years later, he left me the entire garage. It was a turning point in my life. Some of my best days were spent inside the garage, where after coming back from school, I tried fixing various appliances in the house. That was what led me to choose to be a Mechanical Engineer.”
The above paragraph speaks volumes about you as a person and your passion for Mechanical Engineering without you actually saying it. Any admissions officer in the world wouldn’t reject an applicant with such a deep reason , and such a wonderful story behind him/her. Now, remember, you don’t have to lie. Try and remember stories from your life that have shaped your decisions. And connect them beautifully to your goals and dreams.
Now similarly, your “intelligence” can be conveyed by how you write . The quality of the statement of purpose, the organization, expression, etc. of your statement tells how intelligent you are. Demonstrating knowledge of the field, and using related jargon shows that you are “well-prepared”. Showing what you have done already describes your ability “to take on the challenges of grad school”. Your grades and your previous performance prove your ability “to finish the graduate program in time”. Being a “future remarkable alumni” can be implied by your being a commendable representative of your previous institutions, like your high school, or undergraduate school. Similarly, you will have to try and represent all the qualities mentioned above in an indirect, but powerful way.
7. Don’t Create Stories. Be Yourself
Because we asked you to write stories, there would naturally be an inclination to “create” stories out of thin air. Do not do this at all. Write great stories only if you have great stories . Some people might come from normal backgrounds, who had normal lives, and probably didn’t achieve anything spectacular. It’s completely okay. If you don’t have anything great to write, don’t write it . Be normal, and write normal stories.
It is better to be normal than to pretend to be someone you are not. The admissions officers are expert psychologists, and they can spot a true applicant from a false applicant with just one reading. So, you will badly hurt your chances of getting into your dream school if you try to be someone else. Just be yourself, and write only about the things that have happened to you, and the things that you are passionate about.
For instance, saying “I love research” just because you think they will like it, isn’t going to help you a lot. Whatever you say just for the sake of it, won’t appeal much to the committee, as they would look for relevant evidences in your stories and in your past . So, don’t even think about fooling the committee with a false storyline. Try and be yourself throughout the essay.
8. Address Your Problems
The Statement of Purpose is a great opportunity for you to address some of your problems. If you have had any problematic academic background, or a gap year in your career, or if you had any work-related problems, you can address them on the statement of purpose in order to reassure the admissions committee. You must try and be as honest as possible , and talk about your problems in a matured manner.
Instead of trying to defend yourself, you can point out the actual reasons that led to the problems, but more importantly, you should highlight ‘how’ you overcame the situation, and ‘what’ you have learnt from the experience. For example, let’s say that you got all C’s or all D’s in one semester. This normally isn’t the kind of academic profile a good grad school would want from you, unless there is a strong reason behind it. So, take some time and dedicate a few lines to explain whatever happened .
If you had a health problem during your semester exams, or if you faced any emotional setback during that time, if you experience any personal loss, or if you had to take up additional family responsibilities other than studying, you can mention that in your statement. But, more importantly, you should not forget to demonstrate how your grades have been steadily improving since then, and that you now have a decent grade-point average in the discipline.
If you can spin this story well enough for the committee to empathize with you, then your story will enhance the admissions committee’s image of you as a matured student , with the abilities to “take on additional challenges” and “to finish on time”, even when things are against you.
9. Do Your Homework
This is one very important point you should exercise while you are writing a statement of purpose. You should be thorough with the details of all the universities you are applying to, and list down all the things you like about each university, before you write the essays.
Most students simply write generic sentences like “I am impressed by the importance your university gives to research” or “I would like to study here because you have 100 Ph.D.’s and 20 Nobel prize winners.” etc. No, that is not how you do it. The admissions committee knows how great their college is; you don’t have to remind them again and again . But, you should let them know what exactly you like about them, that you so badly want to be there. The specifics are really important .
For example, you could say something like this. (Excuse the random jargon, it is only to give you an idea.)
“I would fully utilize the resources that the Wallenberg Hall provides, as I am particularly interested in the field of molecular chemistry. The special 24/7 laboratories provided for student research on molecular processing is exactly the kind of opportunity I am looking for, as I could totally see myself working in the labs day and night.”
And something like:
“I especially want to study under Dr. Mark Adams, Ph.D., as I have been an avid follower and admirer of his work in the field of quantum chemistry, which is not only the field I would choose for my research study, but also is a topic that I am zealous about, personally. I would be more than honoured if I can earn a spot in his research group.”
Do you see how professional it sounds? Such things show how well prepared you are, and how eager you are to study at that university. Now, to write something like this, you obviously need to do lots of research both online and offline, and be very thorough about the college, its facilities, courses, and professors. Yes, it is very difficult, but you better believe it is completely worth all the hard work.
10. Proofread, Edit, and Re-edit. Ask Friends and Family To Grade Your Essay
Another mistake students make is, they try and keep their essays to themselves. Maybe they are shy, or maybe they think their friends and family aren’t necessarily experts on the subject. So they think there’s no point in asking friends and family to critique on their essays. Wrong. Your statement of purpose speaks about you as a student, as an individual. Yes, there is technical slang involved, and yes your family members may not be experts on that. But, they sure are experts on ‘you’ . Which is exactly why you should approach them.
They can not only give you additional points to add, but they can give you valuable stories about your childhood or schooling days, which you probably won’t remember. Plus, it’s very easy to say something about others, but at the same time, it’s painfully difficult to describe yourself to someone. Which is why someone very close to you, like friends and family, can describe you accurately. You will get new perspectives on your stories , which sometimes are better than your own versions, and including them in your statement of purpose will do you a lot of good. Also, remember to proofread your statement time and again, and keep on re-editing content until you, your family and friends think you have the best statement in the world.
Remember that your statement of purpose is a literary picture of ‘you’ as a person , and it is representing on your behalf. So, make it a top priority to avoid typos, misplaced commas and semicolons, overused quotes, being too wordy, using too many complex words and sentences, and being too straightforward. Be careful. Be a perfectionist when it comes to writing . It shows how much you care about going to a particular college. And, once you are done with everything, do not forget to ask your friends and family to grade your statement of purpose, and ask them to criticize it accurately, so you can avoid submitting a less than perfect copy of your statement.
11. Take Advice From Professors.
If you know a professor at your undergrad institution, don’t hesitate to approach him/her for advice regarding your statement of purpose. They are of course very experienced prospects, and they might have seen thousands of statement of purposes and students in their careers. So, it wouldn’t hurt to ask for their opinion. Plus, since unlike your family, they are technically sound, they can also provide you valuable insights on how to project your technical expertise and project works in the statement.
After all, a professor knows what another professor looks for in a prospective student , so it would only help if you approach your college professors. And, if they are really close to you, you can also ask them for a really good letter of recommendation . So whichever way you look at it, there are only benefits for you.
Checklist for a Powerful Statement of Purpose
Here’s a basic checklist designed to help you draft a flawless Statement of Purpose. Make sure you write in an organized manner, and cover your points in a proper order. We have given this checklist so that you can write your statement of purpose without confusing yourself and the readers. Following a meticulous order like this will make your statement of purpose a lot better to read and understand about you and your story. Feel free to add anything else to the list if you think it will boost your chances, but remember to not write too much because you would then be exceeding the word limit.
Organization:
- Introducing yourself in a unique manner.
- Demonstrating your passion for the field.
- Story about your background or experience in the field you’ve chosen.
- Description of your academic background in the field you’ve chosen.
- Specific classes or special courses you have taken, that are related to your field of interest.
- Some of the professors you have studied under, especially if they are well-known in that field.
- Co-curricular and Extracurricular activities in the field of you interest.
- Publications or other professional accomplishments in the field (perhaps conference presentations or public readings)
- Any community service or leadership experience while in college.
- Explanations about problems in background (if needed)
- Explanation of why you have chosen the specific grad school and other related questions as discussed in the beginning of this article.
- Mention what you like about the university you are applying for, and why: facilities, infrastructure, etc.
- Mention names of one or two professors in that school and what you know of and appreciate about their work, and why you want to study or work under their guidance.
- Specific features of the grad program and the university, which attract you personally. And why.
- Get advice from several of your professors, family, and close friends. Ask for stories about yourself.
- Proofread and edit; ask friends and family to proofread for you as well.
So, those are some strategies and tips for you to write a powerful statement of purpose, impress the committee, and thereby ace the admissions process. Make sure you do every one of these things, and you won’t be far away from the college of your dreams. Do you have any strategies that worked well for you? Do let us know in the comments section.
We almost forgot! We are giving away a sample Statement of Purpose for download, so you can get an actual glimpse of how the aforementioned tips and strategies have been incorporated in a real Statement Of Purpose. But remember, this should serve only as an inspiration to your own Statement of Purpose, but not a source to copy from. Close to 10000 students check this space regularly, and if every single one of them uses the same phrases in their own statement of purposes, very soon, everyone will be held for plagiarism. So, try and copy only the framework and the organization, but not the actual content. Happy Writing!
Download your free sample SOP now:

Download Sample Statement Of Purpose
Also get Free GRE tips directly in your inbox!
Other posts you'll love:

DID YOU ENJOY READING THIS POST?
If so, subscribe to updates and receive exclusive weekly GRE resources and tips. Also get a FREE COPY of our eBook, GRE Prep the Smart Way! (Valued at $30)
No spam, unsubscribe any time!
127 Comments to “11 Tips for Writing a Powerful Statement of Purpose [Sample SOP Included]”
I am confused about a question that why you want to pursue MS in CS ? I don’t have any research paper for technical work. But i have solid final year system project. and i want to go for higher education.
Need Help….
It’s a question many students face when applying for a Computer Science program. In your case, if your final year project is related to Computer Science, try and emphasise how doing that project made you realize your interest for Computers. If you have any relevant work experience (software) then it will be easy for you to convince them about your choice of study. If you are applying for a top program, this is really important.
Try and build stories around your interest for computers, and use all the techniques given above. If you are still unsure, then maybe you should take a break, work for a year or two in a relevant field, and apply again. But, if you really want to go ‘now’, you should emphasise your project really well. Be positive! Good luck! 🙂
Hi Sachin, Thanks for useful insight on difficult doubt. I have tried hard for my SOP. i need someone could just refer it so i could get more correction and may help me build a good SOP.
If possible give me your mail-id. so i could mail to you !!!
I sincerely appreciate the time and the effort you put to carefully explaining these steps, I am really grateful.
Thank you for all you do.
I have mailed my SOP on mentioned Email-Id. Could you please let me know any improvements in my SOP asap…..
Just sent you a mail with steps you should take to improve your SOP. Let me know if you need help! 🙂
Just had a look around your suggestion. I would surely work around it. But I am confused which content to be removed because I have had much extracurricular activities and projects too!
Still I will concise it and will make improvements soon.
Thanks a lot!
Hi Jitta/ Sachin,
I have revised my SOP. Made necessary changes as suggested by you, Jitta. Thanks for your help! 🙂
I sincerely appreciate the team that up this wonderful work together which I we take my time to follow accordingly but and I get a direct SOP format on my mail or something to prove read for me when done with it
Sachin yar , why you guys do not send the pdf man . I get a message that I will be delivered on the mail but I never receive it
Geat advice. Thank you so much!
Where is the sample sop? Can you please give me the download link?
The download link is available right at the end of the blog post. Hope you have found it already.
The essay is not available from the download link. I received one sample sop as a .vcf file which is not opening.
Paul, I just checked and the download link is working. Mind trying again?
Ok im trying again . but i told you that i got the mail after i clicked on the link. the mail has a .vcf file attached, which is not opening.
Could you check your email? We have sent you the direct download link. Happy Studying! 🙂
got it 🙂 Thanks so much 🙂
Awesome! Would love to hear how it helped you 🙂
Hey Sachin,
Thanks for the article! I really appreciate it!
I have already confirmed my email but can’t download the sample SOP.If you can send me the direct link as you did with “shaoni paul”, this will be nice .
Please re-enter your mail id and you will taken to the download page. Let me know if it doesn’t work 🙂
I hope you find the sample SOP helpful!
Just sending a .vcf file and downloading the same. Tried it twice.
Hey Keerthi,
I am sorry to hear that you had to go through this process twice. I just checked and it looks like your email isn’t confirmed yet. Please re-enter your email and make sure you confirm your subscription. You should receive an email with a link to the SOP after a few minutes. Let me know if you don’t receive this mail 🙂
Hello, what is an ideal length for SOP? Please reply quickly as I need to finalize my SOP within this week. This article helped me a lot. Thanks in Advance.
Shrawan, there is no definitive ideal length for a statement of purpose. It entirely depends on the course you are applying to. For instance, if you are applying for an engineering school and send a 5 page SOP, the admissions committee may conclude that you are unable to express yourself concisely. And if you are applying for a literature school and send a 1 page SOP, that would again be a disaster too.
The general norm is a two to three pages statement of purpose. If you are going beyond that, it just means you are writing things that are totally unnecessary and would only act as a hindrance to your admission.
It was great to me~ It’s so helpful~
This article was really helpful and readable. It was very surprising that your article actually answered what I was asking inwardly! I think you just have an insight into a person’s mind! Thank you very much 🙂
Thanks for the kind words, Sarah, I’m happy to hear that the article helped you answer your questions.
Let me know if there is anything I can do 🙂
Hi Thanks for your useful post. I made my SOP based on your tips and I emailed it now. Could you please kindly review my SOP and give notes about it? I’m in a hurry, because I’m going to apply tomorrow, or the day after tomorrow for universities where their deadlines are 5 Jan. So I appreciate if you do me the favor urgently 🙂
Hey Ali, Please check your inbox and let me know if there is anything else I can do 🙂
The blog is excellently written and I am confident that it will certainly help me with my personal statement. Thanks.
Thank you very much for the article. It was very useful! Last year, I applied to a couple of grad schools and got rejected, which I believe was in part due to my weak SOP. This year, I’ve tried to improve it and would be grateful if you could please review it for me, and let me know of its flaws. Thanks. Keep the good work going.
Thanks for the write-up. I really need the sample SOP. Thank you.
I really needed some advise and you really provided with excellent explanation and SOP. And want to tell you thank you very much for all this. Now I know what was the biggest mistake in my prior SOP and why University did not admit me. Thank you very much again!!! ^_^
Excellent information with unique content and it is very useful to know about the information based on blogs.
Hi, Thanks for such a wonderful article being made. It helped me in stating the exact way of writing and proposing in the way the reader expects….. Thanks a lot…. 🙂
Thank u immensely for that great inside on SOP,I HV a better idea now on what to write.
There’s definitely a lot to know about this issue. I like all the points you made.
Thank you very much For such a creative blog,its much helpful. I really found answers of my all questions in this pretty written blog and it really awakened my mind to show that creativity which i had once before 3 years. Thanks once more dude.
it’s really helpful, thank you!
These tips are damn cool and intuitive hope so this will push me to touch zenith
This is the best blog i have seen so far that fully explains how to write a SOP. Most blogs show you a lot of wordy stuff which forces you to copy since you don’t understand the structure instead of writing something original for yourself. With this information, it really bring out the saying; “Teach a man how to fish rather than giving him fish…” Thanks for all the help.
Thank you for the tips and strategies am hopeful to write a good SOP and I have just started preparing my SOP and will continue to seek for your guide indue course.
This article is quite amazing and full of insight. I am going to take to the above instructions with due attention to details.
Thank you so much! Very helpful.
This blog is excellently written, wished I found you earlier.
High sachin, Thank you for your wonderful explanations on how to write a powerful SOP, To be sincere with you I really understand everything that you just explained and how you articulated it, I believed that it’s really going to help me a lots but the issues that I am having right now is that I don’t know if it’s actually possible for a computer science undergraduate that is currently in final year now at University to apply for any scholarship to pursue his MS in CS because I don’t have any research work though I’m still doing my project work
Thank You So Much For Helping The World.
Happy to help, Adikalie! Glad to know you found it useful. 🙂
Thank you so much for this guide.
Hello plz when can I get a reply yet?
Hi, Thank you for this wonderful information on writing SOP. It covers everything I was looking for
Very informative…Thanks.
Hy. Thank you, it is very helpful. now, I work on my own SOP for student exchange and this article solved my problem.
Simply wonderful!
Thank you for sharing this great source of information! I will prepare my statement accordingly!
Hi, I find this article really impressive and useful.I hope this will help me a lot writing my SOP.
GOOD JOB HERE.
Thanks for the detailed tips
Thanks for the detailed tips. Am so grateful for this.
This article is so informative! Thanks a lot for such useful tips! Some students underestimate the role of the statement of purpose and as a result, they get rejections. So, without an appealing, error-free, interesting and sweet SOP it is almost impossible to get a place at grad school or any other institution. Some students prefer writing this piece of paper on their own while others consider hiring professional SOP writers to help them out and make their lives a bit easier. Anyway, as the author said, a statement of purpose is a chance to impress the assessing committee and distinguish yourself from the crowd. Let’s do this 🙂
Fantastic SOP guide! I’m gonna apply to top universities this year so it’s going to be useful.
Hi! the instructions are amazing and gave me great insights on how to write my ideal SOP! Thank you so much!
Hello The post was wonderful and so much helpful
Thank you very much
What a nice guidance… Thank you… I like the way you explain
Sop writing is not a piece of cake but you have jotted down all the points in beautiful way. Keep It UP
Your article is very helpful!
Thank you, Ray
Hi, thank you for your helpful guidance.
Hi! Thank you so much for these useful tips. They really helped me with getting started.
Hi! Thanks for the tips they really helped.
This was extremely helpful!
Excellent post! very useful information. you are the best
Hi, Sachin!
Thank you very much for great advices and tips!
Hi.. the post is amazing….
Helpful tips!
Thanks so much! This is really helpful.
It was very helpful. Thank you so much!
As much as I am still left tensed and pumped to work towards my SOP, this helped me calm down and have a sit-down with my own brain and work my way around it more steadily! Thank you so much!!!
Hi,thank you for this, I’ve been thinking of how to compose my sop, but with this guide I believe I will be able to come up with something that’ll impress the grad school committee and gain my place in the university.
Thanks for the detailed information.
Helpful information
The guide is excellent. All students aspiring to write SOP must get it. THANKS SIR
I found this article very useful and I appreciate the effort you put into it to keep us abreast. Cheers.
Hello ! Just found out about your brilliant article.
Have a good day !
That was great, complete and truly helpful.
Thanks for this write up.
Thank you for the useful article. An ever-increasing number of students will utilize this to compose their personal statement. The admissions committee will utilize this to enable them to see exactly your identity and to judge your reasonableness for their school, so it should be composed consummately. This will be the most critical piece of your application necessities and should be composed superbly. The application process for whichever school you’re applying for will expect you to supply a personal statement as a major aspect of your application. Thank you.
Thank you for this wonderful steps in achieving a better SOP.
Thank you very much for this important information. Actually I have realized that most of the mistakes I have been making are here mentioned. This time I will not repeat the mistakes. Thank you very much.
Hi, Thanks, the tips are beautiful and really helpful
Hi, thank you for the amazing article. I will apply these tips and tricks as soon as possible.
Thanks for this brilliant article;
I have always wondered how should my SOP look like ? I always wanted to have my own unique version as I am applying now. Though I had a rough idea, after going through this blog,I must say that I am more clear about what the contents should be and how the SOP should sound. Thanks a lot for sharing the tips.
You are the best for sure! i am satisfied and i hope that i am going to make a very good SOP
wow This is great
Very useful post.
We all appreciate your kind helpfulness,continue your good work.thanks
This Piece was well put together. Thanks
This is a valuable article so I hope to get a free sample SOP as you have mentioned above. Thank you in advance
WOW just what I was searching for. Came here by searching for Help Writing Essay Homework
Thank you very much for this post. It is extremely helpful.
Thanks & regards, Debanjana Dey
Nowadays it’s very rare to come across an article like this. And it’s even rarer that I read a full article without getting bored. I read this one beginning to end. Brilliant!
Glad you enjoyed it, Flyod! Feel free to message us if you have any questions! 🙂
It’s has been very helpful
It’s has been very helpful, educative and interesting
This has lighten my burden about SOP to a great extent. Thanks for these tips.
Thanks for these wonderful tips.
Really helpful post. This post has the all the information which I need. Thank you so much.
Hi! Thank you very much for such priceless tips.
Again, thanks a lot
Excellent article..its a good site to explore ..Thanks for the blog post.Really thank you! Much obliged..
Very good post. I think these tips are helpful and needed. Writers often struggle with purpose statements, yet they are so important. What I like about your post is that you delve into various ideas and explain them well. Thank you for helping writers!!
I am writing my SOP with the help of your brilliant tips. Thank you
Thank you so much for what you’ve given us!
Such a great help!
Wow, the concept of writing the statement of purpose for graduate programme admission vividly explained and well understood
Great job ! I’m thoroughly impressed with your tips here. Thanks!
This article is excellent and helpful.
Thanks for this great post. It exposed a lot of flaws in my SOP and made me to believe that what caused the rejection of my grad application is the SOP. The admission committee states in the comment section that I met the minimum requirements but my application is not competitive.
Sure, I will do a hard think and find answers to all the why questions.
Thank you for such nice tips. SOP are now becoming a requirement of every reputable college and university. I am also very worried as I want to apply for my masters in a reputable US university but I fear that my SOP writing skills are not very good. I hope these tips help and I get into a reputable university.
Hey! I found the article to be AMAZING and so helpful! Thank you!
It was great reading the writing skills of SOP, more in a story manner rather a statement. I will try to work on these lines. Thank you.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

Download The Free GRE Guide (Valued at $30)
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Applying to graduate school
How to Write a Statement of Purpose | Example
Published on February 13, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on June 1, 2023.
When you apply for graduate programs or scholarships, the admissions committee is looking for more than just a list of grades. The statement of purpose (also known as a statement of intent or motivation letter) is your chance to stand out from the crowd and showcase your motivation, skills and potential. It should:
- Outline your academic or professional interests and goals
- Discuss relevant skills, experience and achievements
- Demonstrate why you’d be a good fit for the program
Table of contents
Successful statement of purpose example, requirements and prompts, personal introduction, experience and achievements, goals and motivations, fit with the program, tips for an effective statement of purpose, other interesting articles.
The torment of the Founding Fathers is responsible for my interest in Classics. My desire to learn Latin stemmed from reading American Revolutionary-era history during junior high and high school, and particularly from the countless Latin quotations I found in John Adams’ writings. Always eager for a challenge, I was intrigued by the American founders’ accounts of the torture of learning such a difficult language. In my first semester at university, I started learning Latin and thoroughly loved it. As I learned more and more about classical civilization through the language, I realized that I was passionately interested in many aspects of the field of Classics. I have since taken courses on mythology, art and archaeology, and religion, on ancient history, and on the classical tradition. I have also learned Greek, of course, starting with an intensive two-semester course at the university’s summer school. My experience studying abroad in Florence and traveling through Italy and Greece intensified my zeal for the field and, in particular, fueled my ambition to specialize in classical archaeology.
My personal philosophy of life is that everything is connected, and this conviction drives my desire to study Classics. The most rewarding moments for me are discovering and investigating connections – both broad ones, between fields and disciplines, and more specific ones, like the relationship between a piece of literature and an object of material culture. My liberal arts education has equipped me with a broad base of knowledge in the sciences, social sciences, humanities, and arts, and in the honors program I pursued independent projects exploring academic and personal connections, including a paper on ancient Mayan astronomy, a self-observation study on the effects of nutrition and hydration on exercise performance, and a paper on the influence of political context on the changing artistic representations of John Adams. By seeking out connections between seemingly unrelated areas of academia, I have acquired a well-rounded outlook which helps me approach new ideas with both a range of prior experiences and a mind always open to different interpretations.
In accordance with my personal philosophy, I have also continued to explore connections within Classics and between Classics and other fields. In 2007, I published an article in my university’s undergraduate humanities journal; inspired by my studies in Florence, I compared representations of the birth of Venus in ancient and Renaissance literature and art. My major academic achievement to date, however, has been my senior honor thesis on John Adams’ connection to the Classics. Funded by a Hilldale Research Fellowship, I conducted research in the Adams Papers at the Massachusetts Historical Society and in John Adams’ personal library at the Boston Public Library on the influence of the classical tradition on Adams’ worldview and how he consciously modeled himself on classical ideals. It was particularly fulfilling to connect historical and classical research in writing about the figure most responsible for instigating my study of the Classics.
As well as my research skills, I have demonstrated proficiency in the classical languages, winning prizes for both Latin and Greek translation from the Classics Department, as well as receiving an enthusiastic nomination from the department for the Pearson Fellowship from the American Philological Association. I am also the president of the undergraduate Classics Society, which allows me to share my enthusiasm for Classics with other students and the larger community.
One of the most appealing aspects of studying Classics is the vast range of topics encompassed by the field. Because my interests are broad and I value an interdisciplinary approach, I would like to pursue graduate study ultimately leading to a PhD in Classical Archaeology. Archaeology in itself is, of course, a multi-faceted field, requiring knowledge of history, language, anthropology, and various scientific and technological methods. I have already started building my skills in this area: I participated in a microartifact analysis from the excavation of a Maya site in Belize as part of an honors project, and this summer I will take part in two archaeological projects in Turkey after working as a research assistant on related material in the spring semester. This PhD program includes many other opportunities I am eager to explore, such as palaeography and papyrology courses, and especially the variety of fieldwork and museum experiences available. I believe that my strong background in the classical languages and wide range of courses on classical civilization and archaeological methods have prepared me well for this program, and I am convinced that, guided by my philosophy of interconnectedness, I will flourish in this program.
The first step is to read the application instructions. These should include the length of the document (usually 1-2 pages), any formatting requirements, and often a question or prompt that indicates what you should focus on.
In some cases, you might also be asked to submit a personal statement . Similar advice applies to both of these documents—both should give a sense of who you are, what you’ve done and what you want to do. But a statement of purpose is often more formal, tightly focused on your academic background and your suitability for the program.
If you are working on multiple applications, don’t try to write a one-size-fits-all text—tailor your statement of purpose to each program. Make sure to respond to the prompt and include all the information you’re asked for. A typical statement of purpose prompt looks like this:
Your focus will be slightly different depending on whether you’re applying for research-based academic programs (such as a PhD ) or professional qualifications (such as an MBA). But all statements of purpose should contain the following elements.
This is your chance to introduce yourself to the admissions committee and let them hear your voice. The statement of purpose shouldn’t tell your life story, but it should give a glimpse into who you are.
Academic and personal background
Give an overview of your academic background, and show what drives your interest in this field or profession. You might want to include some personal background too—your family history, social circumstances, personal relationships and life experiences have all shaped your trajectory and perspective. What unique insights will you bring with you?
Characteristics and personality
Think about aspects of your character that make you well-suited for graduate school. Don’t just list generic adjectives—give examples that demonstrate your strengths and show why they’re relevant.
- Are you organized enough to handle a high-pressure workload?
- Do you have the creativity needed to develop original ideas, or a systematic mindset perfect for problem-solving?
- Do you have strong leadership skills, or are you great at working collaboratively?
Avoid including irrelevant autobiographical detail in the statement of purpose. Everything you include should be aimed at showing why you’d be a strong candidate for the program.
Your experience shows that you have the necessary skills to succeed in graduate school. Don’t just summarize everything you’ve done—pick out some highlights to build a clear picture of your strengths and priorities, illustrating how you’ve learned and developed along the way.
Academic experience
If you’re applying for a research-focused program, such as a PhD, show your knowledge of the field and outline your research experience. This might include:
- A brief summary of your thesis or final project
- Courses that you found particularly valuable
- Projects you contributed to
- Publications
- Presentations
- Extracurriculars that gave you relevant skills or experience
Professional experience
If you’re applying for a professional program, such as an MBA, outline your experience so far and show how it relates to your career plans. This might include:
- Past or current job roles
- Projects you led or participated in
- Internships
- Voluntary work
- Training courses
In all cases, give specific examples with details of what you worked on, what you achieved, and what you got out of the experience.
As well as showing that you’re prepared for the program, explain what you expect to get out of it. What are your motivations for applying? How do you plan to make the most of its opportunities, and how will it help you achieve your goals?
Academic motivations
For academic programs, indicate your research interests, showing how they follow from and build upon what you have studied so far. This might include:
- A subfield that you want to strengthen your expertise in
- A specific problem or question that you’d like to address
- An initial idea for a research project
- A theoretical or methodological approach that you want to develop
This isn’t the place for an in-depth research plan, but it’s a chance to show your enthusiasm and knowledge of your field.
Professional motivations
For professional programs, outline your career aspirations and show how your experience informs your goals. This might include:
- The next step you want to take in your career. What position are you aiming for and how will the program help you achieve it?
- Your motivations for a career change. Can you make a link between your previous experience and your new direction?
- Your long-term goals. Where do you want to be in five or ten years, and how do you see yourself getting there?
The admissions committee wants to know that you’re genuinely motivated to complete the program, and the clearer your plans, the more convincing your commitment.
It’s important to show not only why you want to study this subject, but also why you want to do it in this particular institution and department.
- Do your research, and mention particular classes, specialisms or faculty that attracted you.
- Show why you’re a good fit. Do your priorities align with the values and culture of the institution? What will you contribute to the department?
- Discuss the specific skills, knowledge and experience you expect to get from the program.
The statement of purpose isn’t only about selling yourself—it’s about illustrating an ideal match between you and the program.
Once you’ve made sure to cover all the key elements, you can work on strengthening and polishing the text. Follow these tips to make your application the best it can be.
Stay focused
It can be tempting to try to cram in everything you’ve done, but a good statement of purpose requires careful selection to craft a focused narrative. One way to do this is by building your text around a central theme—for example, a character trait, an intellectual interest, or a career goal.
This strategy helps structure your text and puts your priorities centre stage. Link each paragraph back to the central idea, making it clear how everything fits together.
Think about your structure
The structure of a statement of purpose is somewhat flexible, as long as you include all the relevant information in an order that makes sense.
For example, you might start with a chronological story of where your interests began, or you might open with your goals and then select a series of examples that show your capacity to achieve them. If you’re desperate to study in this specific program, you could lead with a summary of why it’s your ideal choice, and then elaborate on each aspect to show why you’re a perfect fit.
The important thing is that the text showcases your strengths and motivations in a compelling, coherent way. As in any other piece of academic writing, make sure each paragraph communicates one main idea, and that each sentence flows smoothly and logically from the last. Use transition words and topic sentences to move between paragraphs.
Add meaning to your resume
The bare facts of your achievements—grades, prizes, work experience—are already included in your graduate school resume and transcripts. Use the statement of purpose not to repeat yourself, but to add personal meaning and texture to these facts.
If you got top marks for your thesis, describe the research process and demonstrate your enthusiasm for the topic. If you completed an internship or participated in a project, explain what new skills you learned and which aspects you found most valuable. If you already have lots of experience in the field, show how each step developed your skills and shaped your current plans.
Revise, edit, proofread
Your statement of purpose isn’t only about the content—it’s also a chance to show that you can express yourself fluently, confidently and coherently in writing. Spend plenty of time revising, editing and proofreading your text before you submit.
Make sure you stay within the recommended length, and check if there are any specific formatting requirements. If not, use a standard 12pt font, 1-inch margins and 1.5 line spacing.
When you have a final draft, our professional statement of purpose proofreading service can offer an extra pair of eyes to make sure every sentence is perfect.
Proofread my statement of purpose
Checklist: Statement of purpose
My statement of purpose clearly responds to the prompt.
I have introduced my academic, professional and/or personal background.
I have described any relevant experience and shown my development over time.
I have highlighted key achievements that demonstrate my talents.
There is a clear connection between my previous experience and my future plans.
I have explained how the program will help me achieve my goals.
I have mentioned specific aspects of the program, department and institution that appeal to me.
Every paragraph focuses on one central idea.
The paragraphs are organized in a logical order and tell a clear, coherent story.
You're on the way to a successful application. To maximize your chances of getting accepted, a Scribbr editor can help you improve your language, style, and structure.
If you want to know more about college essays , academic writing , and AI tools , make sure to check out some of our other language articles with explanations, examples, and quizzes.
College essays
- College essay examples
- College essay format
- College essay style
- College essay length
- Diversity essays
- Scholarship essays
Academic writing
- Writing process
- Avoiding repetition
- Literature review
- Conceptual framework
- Dissertation outline
- Thesis acknowledgements
- Burned or burnt
- Canceled or cancelled
- Dreamt or dreamed
- Gray or grey
- Theater vs theatre
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, June 01). How to Write a Statement of Purpose | Example. Scribbr. Retrieved June 24, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/graduate-school/statement-of-purpose/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a graduate school resume | template & example, how (and who) to ask for a letter of recommendation, master's vs phd | a complete guide to the differences, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The business plan should be written by the owners of the venture, since it forces a firsthand examination of the business operations and allows them to focus on areas that need improvement. Refer to the business venture throughout the document. Generally speaking, a business plan should not be written in the first person.
The first element of a purpose statement is the problem or opportunity that you are addressing. This should be a clear and specific description of the issue that you are trying to solve or the opportunity that you are pursuing. 2. The Target Audience. The second element is the target audience for your purpose statement.
Mini plan: The reader may request a mini plan, or a condensed version of your business plan (1-10 pages), which includes most of the same components as in a longer traditional plan -- minus the ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
1. Investors Are Short On Time. If your chief goal is using your business plan to secure funding, then it means you intend on getting it in front of an investor. And if there's one thing investors are, it's busy. So keep this in mind throughout writing a business plan.
Those values might include things like sustainability, innovation, integrity, quality, etc. Step #4: Create a draft. Once you've defined what you do and why you do it, take pen to paper and start drafting ideas for your purpose statement. As you're writing, make sure your purpose statement is: Step #5: Get feedback.
Executive summary is an introduction to your business, which provides a brief snapshot of your plan as a whole. To that end, concisely highlight the most important concepts and impressive features from each section of your completed plan, addressing the following areas: Business plan sections: What readers look for: Products and services.
The executive summary should be clear and concise. Ideally, this section should be one to two pages and typically follows either a synopsis or story approach, depending on the intended audience. In the synopsis approach, you would provide a brief summary of each of the key sections of your business plan.
•Some applications call for one statement, while others require two or more different statements. Word limits can vary wildly. Always read the instructions carefully! When in doubt, call the department or program for clarification. •In general, a statement of purpose is about 1-2 single-spaced pages (standard font, 12pt, 1"margins).
A business purpose statement is an official declaration of business objectives in usually a sentence or two. It describes why a business operates and the products or services they offer. A business purpose statement is all-encompassing and includes details about how the business services customer needs. It focuses more on the business's actions ...
Which of the following statement is incorrect about business plans? A) A business plan is typically 25 to 35 pages long. B) The business plan should be written while the feasibility analysis is being completed. C) A large percentage of entrepreneurs do not write business plans for their new ventures. D) For most new ventures, the business plan is a dual-purpose document used both inside and ...
Effective business plans contain several key components that cover various aspects of a company's goals. The most important parts of a business plan include: 1. Executive summary. The executive summary is the first and one of the most critical parts of a business plan. This summary provides an overview of the business plan as a whole and ...
A conventional business plan typically divides into two primary segments: The Explanatory Segment: This portion encompasses written content that serves the business purpose of providing a detailed description of the business idea and/or the company. It covers elements such as the executive summary, company overview, market analysis, product or service particulars, marketing and sales ...
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like 64) A well-prepared business plan helps determine the risks facing the venture., 65) The business plan has two essential functions; it helps the entrepreneur determine if the business will succeed and it helps recruit management talent to run the new company., 66) The primary purpose of building a business plan is to raise ...
Most programs have a maximum word count of 1,000 words for the statement of purpose. Clearer thoughts with a shorter word count are better than a longer statement of purpose that is unclear and unorganized. Your thoughts should be concise and lie between two single-spaced pages in a formal 12-point font. Make It Engaging
T or F: The first part of the business plan you should compile would include the introductory materials, such as the statement of purpose and executive summary. F. T or F: Lenders want to know where your business will be located because the location of a business is often a critical factor to its success. T.
Ideally, if considering an internationally renowned university, then the statement of purpose should be at least 1-2 pages long. In terms of word count, then the same should be around 1000 words. Having said that, the word limit and the length may also sometimes depend on the university that the candidate is targeting and also on the level of ...
9. Do Your Homework. This is one very important point you should exercise while you are writing a statement of purpose. You should be thorough with the details of all the universities you are applying to, and list down all the things you like about each university, before you write the essays.
The statement of purpose (also known as a statement of intent or motivation letter) is your chance to stand out from the crowd and showcase your motivation, skills and potential. It should: Outline your academic or professional interests and goals. Discuss relevant skills, experience and achievements. Demonstrate why you'd be a good fit for ...
false. A small business, as defined by the SBA, serves a limited geographic area and employs no more than 100 people. false. There are 10 essential parts of a business plan. partnership. a __________________ is owned and run by two or more people. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like market analysis, A vision ...
B) For most new ventures, the business plan is a dual-purpose document used both inside and outside the firm. C) A business plan is typically 25 to 35 pages long. D) A large percentage of entrepreneurs do not write business plans for their new ventures. E) The business plan should be written while the feasibility analysis is being completed.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like benefit of making a business plan, cover sheet should identify, statement of purpose should state and more.
A (n) ________ may be defined as a description of a proposed company that explains how it expects to achieve its marketing, financial, and operational goals. business plan. During the third (and final) proofreading stage of your formal report, you should check for ________. formatting and consistency.