How to Write a Persuasive Essay: Tips and Tricks

By Allison Bressmer

Most composition classes you’ll take will teach the art of persuasive writing. That’s a good thing.
Knowing where you stand on issues and knowing how to argue for or against something is a skill that will serve you well both inside and outside of the classroom.
Persuasion is the art of using logic to prompt audiences to change their mind or take action , and is generally seen as accomplishing that goal by appealing to emotions and feelings.
A persuasive essay is one that attempts to get a reader to agree with your perspective.

Ready for some tips on how to produce a well-written, well-rounded, well-structured persuasive essay? Just say yes. I don’t want to have to write another essay to convince you!

How Do I Write a Persuasive Essay?
What are some good topics for a persuasive essay, how do i identify an audience for my persuasive essay, how do you create an effective persuasive essay, how should i edit my persuasive essay.
Your persuasive essay needs to have the three components required of any essay: the introduction , body , and conclusion .
That is essay structure. However, there is flexibility in that structure.
There is no rule (unless the assignment has specific rules) for how many paragraphs any of those sections need.
Although the components should be proportional; the body paragraphs will comprise most of your persuasive essay.

How Do I Start a Persuasive Essay?
As with any essay introduction, this paragraph is where you grab your audience’s attention, provide context for the topic of discussion, and present your thesis statement.
TIP 1: Some writers find it easier to write their introductions last. As long as you have your working thesis, this is a perfectly acceptable approach. From that thesis, you can plan your body paragraphs and then go back and write your introduction.
TIP 2: Avoid “announcing” your thesis. Don’t include statements like this:
- “In my essay I will show why extinct animals should (not) be regenerated.”
- “The purpose of my essay is to argue that extinct animals should (not) be regenerated.”
Announcements take away from the originality, authority, and sophistication of your writing.
Instead, write a convincing thesis statement that answers the question "so what?" Why is the topic important, what do you think about it, and why do you think that? Be specific.
How Many Paragraphs Should a Persuasive Essay Have?
This body of your persuasive essay is the section in which you develop the arguments that support your thesis. Consider these questions as you plan this section of your essay:
- What arguments support your thesis?
- What is the best order for your arguments?
- What evidence do you have?
- Will you address the opposing argument to your own?
- How can you conclude convincingly?

TIP: Brainstorm and do your research before you decide which arguments you’ll focus on in your discussion. Make a list of possibilities and go with the ones that are strongest, that you can discuss with the most confidence, and that help you balance your rhetorical triangle .
What Should I Put in the Conclusion of a Persuasive Essay?
The conclusion is your “mic-drop” moment. Think about how you can leave your audience with a strong final comment.
And while a conclusion often re-emphasizes the main points of a discussion, it shouldn’t simply repeat them.
TIP 1: Be careful not to introduce a new argument in the conclusion—there’s no time to develop it now that you’ve reached the end of your discussion!
TIP 2 : As with your thesis, avoid announcing your conclusion. Don’t start your conclusion with “in conclusion” or “to conclude” or “to end my essay” type statements. Your audience should be able to see that you are bringing the discussion to a close without those overused, less sophisticated signals.

If your instructor has assigned you a topic, then you’ve already got your issue; you’ll just have to determine where you stand on the issue. Where you stand on your topic is your position on that topic.
Your position will ultimately become the thesis of your persuasive essay: the statement the rest of the essay argues for and supports, intending to convince your audience to consider your point of view.
If you have to choose your own topic, use these guidelines to help you make your selection:
- Choose an issue you truly care about
- Choose an issue that is actually debatable
Simple “tastes” (likes and dislikes) can’t really be argued. No matter how many ways someone tries to convince me that milk chocolate rules, I just won’t agree.
It’s dark chocolate or nothing as far as my tastes are concerned.
Similarly, you can’t convince a person to “like” one film more than another in an essay.
You could argue that one movie has superior qualities than another: cinematography, acting, directing, etc. but you can’t convince a person that the film really appeals to them.

Once you’ve selected your issue, determine your position just as you would for an assigned topic. That position will ultimately become your thesis.
Until you’ve finalized your work, consider your thesis a “working thesis.”
This means that your statement represents your position, but you might change its phrasing or structure for that final version.
When you’re writing an essay for a class, it can seem strange to identify an audience—isn’t the audience the instructor?
Your instructor will read and evaluate your essay, and may be part of your greater audience, but you shouldn’t just write for your teacher.
Think about who your intended audience is.
For an argument essay, think of your audience as the people who disagree with you—the people who need convincing.
That population could be quite broad, for example, if you’re arguing a political issue, or narrow, if you’re trying to convince your parents to extend your curfew.
Once you’ve got a sense of your audience, it’s time to consult with Aristotle. Aristotle’s teaching on persuasion has shaped communication since about 330 BC. Apparently, it works.

Aristotle taught that in order to convince an audience of something, the communicator needs to balance the three elements of the rhetorical triangle to achieve the best results.
Those three elements are ethos , logos , and pathos .
Ethos relates to credibility and trustworthiness. How can you, as the writer, demonstrate your credibility as a source of information to your audience?
How will you show them you are worthy of their trust?

- You show you’ve done your research: you understand the issue, both sides
- You show respect for the opposing side: if you disrespect your audience, they won’t respect you or your ideas
Logos relates to logic. How will you convince your audience that your arguments and ideas are reasonable?

You provide facts or other supporting evidence to support your claims.
That evidence may take the form of studies or expert input or reasonable examples or a combination of all of those things, depending on the specific requirements of your assignment.
Remember: if you use someone else’s ideas or words in your essay, you need to give them credit.
ProWritingAid's Plagiarism Checker checks your work against over a billion web-pages, published works, and academic papers so you can be sure of its originality.
Find out more about ProWritingAid’s Plagiarism checks.
Pathos relates to emotion. Audiences are people and people are emotional beings. We respond to emotional prompts. How will you engage your audience with your arguments on an emotional level?

- You make strategic word choices : words have denotations (dictionary meanings) and also connotations, or emotional values. Use words whose connotations will help prompt the feelings you want your audience to experience.
- You use emotionally engaging examples to support your claims or make a point, prompting your audience to be moved by your discussion.
Be mindful as you lean into elements of the triangle. Too much pathos and your audience might end up feeling manipulated, roll their eyes and move on.
An “all logos” approach will leave your essay dry and without a sense of voice; it will probably bore your audience rather than make them care.
Once you’ve got your essay planned, start writing! Don’t worry about perfection, just get your ideas out of your head and off your list and into a rough essay format.
After you’ve written your draft, evaluate your work. What works and what doesn’t? For help with evaluating and revising your work, check out this ProWritingAid post on manuscript revision .
After you’ve evaluated your draft, revise it. Repeat that process as many times as you need to make your work the best it can be.
When you’re satisfied with the content and structure of the essay, take it through the editing process .
Grammatical or sentence-level errors can distract your audience or even detract from the ethos—the authority—of your work.
You don’t have to edit alone! ProWritingAid’s Realtime Report will find errors and make suggestions for improvements.
You can even use it on emails to your professors:
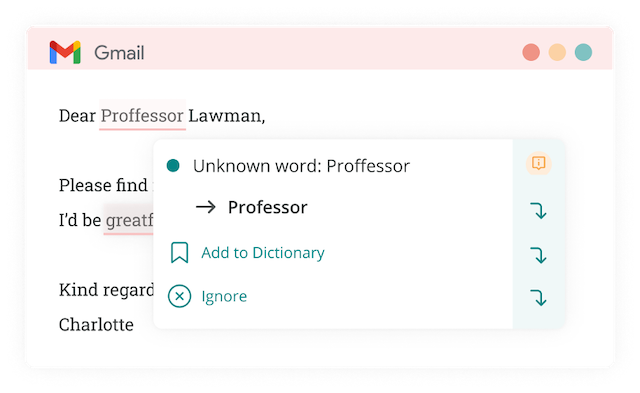
Try ProWritingAid with a free account.
How Can I Improve My Persuasion Skills?
You can develop your powers of persuasion every day just by observing what’s around you.
- How is that advertisement working to convince you to buy a product?
- How is a political candidate arguing for you to vote for them?
- How do you “argue” with friends about what to do over the weekend, or convince your boss to give you a raise?
- How are your parents working to convince you to follow a certain academic or career path?
As you observe these arguments in action, evaluate them. Why are they effective or why do they fail?
How could an argument be strengthened with more (or less) emphasis on ethos, logos, and pathos?
Every argument is an opportunity to learn! Observe them, evaluate them, and use them to perfect your own powers of persuasion.

Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Allison Bressmer
Allison Bressmer is a professor of freshman composition and critical reading at a community college and a freelance writer. If she isn’t writing or teaching, you’ll likely find her reading a book or listening to a podcast while happily sipping a semi-sweet iced tea or happy-houring with friends. She lives in New York with her family. Connect at linkedin.com/in/allisonbressmer.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via:
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Forums Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Persuasive Essay
Last Updated: September 13, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. There are 14 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 4,292,869 times.
A persuasive essay is an essay used to convince a reader about a particular idea or focus, usually one that you believe in. Your persuasive essay could be based on anything about which you have an opinion or that you can make a clear argument about. Whether you're arguing against junk food at school or petitioning for a raise from your boss, knowing how to write a persuasive essay is an important skill that everyone should have.
Sample Persuasive Essays

How to Lay the Groundwork

- Look for language that gives you a clue as to whether you are writing a purely persuasive or an argumentative essay. For example, if the prompt uses words like “personal experience” or “personal observations,” you know that these things can be used to support your argument.
- On the other hand, words like “defend” or “argue” suggest that you should be writing an argumentative essay, which may require more formal, less personal evidence.
- If you aren’t sure about what you’re supposed to write, ask your instructor.

- Whenever possible, start early. This way, even if you have emergencies like a computer meltdown, you’ve given yourself enough time to complete your essay.

- Try using stasis theory to help you examine the rhetorical situation. This is when you look at the facts, definition (meaning of the issue or the nature of it), quality (the level of seriousness of the issue), and policy (plan of action for the issue).
- To look at the facts, try asking: What happened? What are the known facts? How did this issue begin? What can people do to change the situation?
- To look at the definition, ask: What is the nature of this issue or problem? What type of problem is this? What category or class would this problem fit into best?
- To examine the quality, ask: Who is affected by this problem? How serious is it? What might happen if it is not resolved?
- To examine the policy, ask: Should someone take action? Who should do something and what should they do?

- For example, if you are arguing against unhealthy school lunches, you might take very different approaches depending on whom you want to convince. You might target the school administrators, in which case you could make a case about student productivity and healthy food. If you targeted students’ parents, you might make a case about their children’s health and the potential costs of healthcare to treat conditions caused by unhealthy food. And if you were to consider a “grassroots” movement among your fellow students, you’d probably make appeals based on personal preferences.

- It also should present the organization of your essay. Don’t list your points in one order and then discuss them in a different order.
- For example, a thesis statement could look like this: “Although pre-prepared and highly processed foods are cheap, they aren’t good for students. It is important for schools to provide fresh, healthy meals to students, even when they cost more. Healthy school lunches can make a huge difference in students’ lives, and not offering healthy lunches fails students.”
- Note that this thesis statement isn’t a three-prong thesis. You don’t have to state every sub-point you will make in your thesis (unless your prompt or assignment says to). You do need to convey exactly what you will argue.

- A mind map could be helpful. Start with your central topic and draw a box around it. Then, arrange other ideas you think of in smaller bubbles around it. Connect the bubbles to reveal patterns and identify how ideas relate. [5] X Research source
- Don’t worry about having fully fleshed-out ideas at this stage. Generating ideas is the most important step here.

- For example, if you’re arguing for healthier school lunches, you could make a point that fresh, natural food tastes better. This is a personal opinion and doesn’t need research to support it. However, if you wanted to argue that fresh food has more vitamins and nutrients than processed food, you’d need a reliable source to support that claim.
- If you have a librarian available, consult with him or her! Librarians are an excellent resource to help guide you to credible research.
How to Draft Your Essay

- An introduction. You should present a “hook” here that grabs your audience’s attention. You should also provide your thesis statement, which is a clear statement of what you will argue or attempt to convince the reader of.
- Body paragraphs. In 5-paragraph essays, you’ll have 3 body paragraphs. In other essays, you can have as many paragraphs as you need to make your argument. Regardless of their number, each body paragraph needs to focus on one main idea and provide evidence to support it. These paragraphs are also where you refute any counterpoints that you’ve discovered.
- Conclusion. Your conclusion is where you tie it all together. It can include an appeal to emotions, reiterate the most compelling evidence, or expand the relevance of your initial idea to a broader context. Because your purpose is to persuade your readers to do/think something, end with a call to action. Connect your focused topic to the broader world.

- For example, you could start an essay on the necessity of pursuing alternative energy sources like this: “Imagine a world without polar bears.” This is a vivid statement that draws on something that many readers are familiar with and enjoy (polar bears). It also encourages the reader to continue reading to learn why they should imagine this world.
- You may find that you don’t immediately have a hook. Don’t get stuck on this step! You can always press on and come back to it after you’ve drafted your essay.

- Put your hook first. Then, proceed to move from general ideas to specific ideas until you have built up to your thesis statement.
- Don't slack on your thesis statement . Your thesis statement is a short summary of what you're arguing for. It's usually one sentence, and it's near the end of your introductory paragraph. Make your thesis a combination of your most persuasive arguments, or a single powerful argument, for the best effect.

- Start with a clear topic sentence that introduces the main point of your paragraph.
- Make your evidence clear and precise. For example, don't just say: "Dolphins are very smart animals. They are widely recognized as being incredibly smart." Instead, say: "Dolphins are very smart animals. Multiple studies found that dolphins worked in tandem with humans to catch prey. Very few, if any, species have developed mutually symbiotic relationships with humans."
- "The South, which accounts for 80% of all executions in the United States, still has the country's highest murder rate. This makes a case against the death penalty working as a deterrent."
- "Additionally, states without the death penalty have fewer murders. If the death penalty were indeed a deterrent, why wouldn't we see an increase in murders in states without the death penalty?"
- Consider how your body paragraphs flow together. You want to make sure that your argument feels like it's building, one point upon another, rather than feeling scattered.

- End of the first paragraph: "If the death penalty consistently fails to deter crime, and crime is at an all-time high, what happens when someone is wrongfully convicted?"
- Beginning of the second paragraph: "Over 100 wrongfully convicted death row inmates have been acquitted of their crimes, some just minutes before their would-be death."

- Example: "Critics of a policy allowing students to bring snacks into the classroom say that it would create too much distraction, reducing students’ ability to learn. However, consider the fact that middle schoolers are growing at an incredible rate. Their bodies need energy, and their minds may become fatigued if they go for long periods without eating. Allowing snacks in the classroom will actually increase students’ ability to focus by taking away the distraction of hunger.”
- You may even find it effective to begin your paragraph with the counterargument, then follow by refuting it and offering your own argument.

- How could this argument be applied to a broader context?
- Why does this argument or opinion mean something to me?
- What further questions has my argument raised?
- What action could readers take after reading my essay?
How to Write Persuasively

- Persuasive essays, like argumentative essays, use rhetorical devices to persuade their readers. In persuasive essays, you generally have more freedom to make appeals to emotion (pathos), in addition to logic and data (logos) and credibility (ethos). [13] X Trustworthy Source Read Write Think Online collection of reading and writing resources for teachers and students. Go to source
- You should use multiple types of evidence carefully when writing a persuasive essay. Logical appeals such as presenting data, facts, and other types of “hard” evidence are often very convincing to readers.
- Persuasive essays generally have very clear thesis statements that make your opinion or chosen “side” known upfront. This helps your reader know exactly what you are arguing. [14] X Research source
- Bad: The United States was not an educated nation, since education was considered the right of the wealthy, and so in the early 1800s Horace Mann decided to try and rectify the situation.

- For example, you could tell an anecdote about a family torn apart by the current situation in Syria to incorporate pathos, make use of logic to argue for allowing Syrian refugees as your logos, and then provide reputable sources to back up your quotes for ethos.
- Example: Time and time again, the statistics don't lie -- we need to open our doors to help refugees.
- Example: "Let us not forget the words etched on our grandest national monument, the Statue of Liberty, which asks that we "Give me your tired, your poor, your huddled masses yearning to breathe free.” There is no reason why Syrians are not included in this.
- Example: "Over 100 million refugees have been displaced. President Assad has not only stolen power, he's gassed and bombed his own citizens. He has defied the Geneva Conventions, long held as a standard of decency and basic human rights, and his people have no choice but to flee."

- Good: "Time and time again, science has shown that arctic drilling is dangerous. It is not worth the risks environmentally or economically."
- Good: "Without pushing ourselves to energy independence, in the arctic and elsewhere, we open ourselves up to the dangerous dependency that spiked gas prices in the 80's."
- Bad: "Arctic drilling may not be perfect, but it will probably help us stop using foreign oil at some point. This, I imagine, will be a good thing."

- Good: Does anyone think that ruining someone’s semester, or, at least, the chance to go abroad, should be the result of a victimless crime? Is it fair that we actively promote drinking as a legitimate alternative through Campus Socials and a lack of consequences? How long can we use the excuse that “just because it’s safer than alcohol doesn’t mean we should make it legal,” disregarding the fact that the worst effects of the drug are not physical or chemical, but institutional?
- Good: We all want less crime, stronger families, and fewer dangerous confrontations over drugs. We need to ask ourselves, however, if we're willing to challenge the status quo to get those results.
- Bad: This policy makes us look stupid. It is not based in fact, and the people that believe it are delusional at best, and villains at worst.

- Good: While people do have accidents with guns in their homes, it is not the government’s responsibility to police people from themselves. If they're going to hurt themselves, that is their right.
- Bad: The only obvious solution is to ban guns. There is no other argument that matters.
How to Polish Your Essay

- Does the essay state its position clearly?
- Is this position supported throughout with evidence and examples?
- Are paragraphs bogged down by extraneous information? Do paragraphs focus on one main idea?
- Are any counterarguments presented fairly, without misrepresentation? Are they convincingly dismissed?
- Are the paragraphs in an order that flows logically and builds an argument step-by-step?
- Does the conclusion convey the importance of the position and urge the reader to do/think something?

- You may find it helpful to ask a trusted friend or classmate to look at your essay. If s/he has trouble understanding your argument or finds things unclear, focus your revision on those spots.

- You may find it helpful to print out your draft and mark it up with a pen or pencil. When you write on the computer, your eyes may become so used to reading what you think you’ve written that they skip over errors. Working with a physical copy forces you to pay attention in a new way.
- Make sure to also format your essay correctly. For example, many instructors stipulate the margin width and font type you should use.
Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/how-to-write-a-persuasive-essay/
- ↑ https://www.hamilton.edu/academics/centers/writing/writing-resources/persuasive-essays
- ↑ https://www.hamilton.edu/writing/writing-resources/persuasive-essays
- ↑ https://www.adelaide.edu.au/writingcentre/sites/default/files/docs/learningguide-mindmapping.pdf
- ↑ https://examples.yourdictionary.com/20-compelling-hook-examples-for-essays.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/transitions/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/common_writing_assignments/argument_papers/rebuttal_sections.html
- ↑ http://www.readwritethink.org/files/resources/lesson_images/lesson56/strategy-definition.pdf
- ↑ https://stlcc.edu/student-support/academic-success-and-tutoring/writing-center/writing-resources/pathos-logos-and-ethos.aspx
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/revising-drafts/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/proofreading_suggestions.html
About This Article

To write a persuasive essay, start with an attention-grabbing introduction that introduces your thesis statement or main argument. Then, break the body of your essay up into multiple paragraphs and focus on one main idea in each paragraph. Make sure you present evidence in each paragraph that supports the main idea so your essay is more persuasive. Finally, conclude your essay by restating the most compelling, important evidence so you can make your case one last time. To learn how to make your writing more persuasive, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Joslyn Graham
Nov 4, 2017
Did this article help you?
Jul 28, 2017
Sep 18, 2017
Jefferson Kenely
Jan 22, 2018
Chloe Myers
Jun 3, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
What is a Persuasive Essay? Full Persuasive Essay Guide

In a world where effective communication is crucial, mastering persuasive writing is essential. It transcends simply expressing opinions by enabling you to influence others and clearly articulate your message. Say goodbye to difficulties in making your point; join us as we explore how to craft persuasive essays that are both informative and genuinely compelling in our guide!
Persuasive Essay Definition
This type of essay persuades the reader to agree with your viewpoint by presenting convincing arguments, research, and ideas. You rely on logic and reason to demonstrate why your perspective is more valid than others. You must present clear arguments supported by compelling facts. Several key elements should be included in these essays:
- A clear thesis statement or main idea that guides your essay's focus.
- An opening paragraph that introduces your thesis statement and sets the stage for your argument.
- Body paragraphs that use specific research evidence to support your points.
- Smooth transitions between paragraphs that connect ideas clearly and engagingly.
- Addressing counterarguments to acknowledge and refute opposing viewpoints.
- A conclusion that reinforces your central idea without repeating it word for word.
Elements of a Persuasive Essay
Persuasive essays rely on three key elements called modes of persuasion . These were introduced by Aristotle, a famous philosopher, to help make arguments strong and convincing.
First, there's logos , which means using evidence and logical reasoning to support your points. It's crucial to clearly state your main argument and back it up with solid evidence. Remember, what counts as convincing evidence can vary depending on who you're trying to persuade.
Next up is pathos , which involves appealing to people's emotions. Sharing personal stories can be really effective here because they help readers connect emotionally with your argument. Plus, personal anecdotes can give your essay a unique voice.
Lastly, there's ethos , which is all about building trust and credibility with your audience. The way you write your essay—whether it's serious, funny, or sincere—can affect how readers see you. Using reliable sources and showing empathy can also help establish your credibility. And when you're making claims, it's important to consider what your readers already believe and try to address any doubts they might have.
Feeling overwhelmed by all this info? Just say - ' write my paper ,' and our expert writers will jump in to assist you right away!
.webp)
How to Write a Persuasive Essay in 7 Steps
Writing a persuasive essay usually follows a structured format: introduction, body, conclusion . Unlike argument essays, which involve discussing and attacking alternate views, persuasive essays aim to convince the reader of your argument's validity. They're a bit more gentle and understanding in tone. To craft a solid persuasive essay, follow the 7 steps in this section. And while you're at it, don't forget to explore our guide on how to write an argumentative essay , too. These two types of assignments are the most common in school and college.
.webp)
Step 1: Topic Selection and Research
Choosing a good topic is where you start when writing a persuasive essay. Think about things that really interest you and make you feel strongly. But it's not just about what you like; you also need to think about what matters to your readers. Do some digging to learn more about your topic. Look into different parts of it by checking out reliable sources like books, websites, and academic articles.
While you're doing your research, keep an eye out for different opinions and new ideas about your topic. This helps you get ready for arguments against your point of view. It's also important to see if there's enough evidence out there to back up what you believe. Having lots of evidence makes it easier to make a strong case.
For more help on picking a topic, check out our persuasive essay topics .
Step 2: Develop a Strong Thesis Statement
A well-developed thesis statement should be specific, concise, and debatable. Avoid saying things that are too vague or broad, as they won't give your essay a clear direction. Instead, try to come up with a thesis that clearly says what you believe and encourages people to think about it critically.
Make sure your thesis statement is backed up by the evidence you found in your research. Use facts, numbers, or opinions from experts to support what you're saying and make your argument stronger.
Also, think about how your thesis statement fits into your whole persuasive essay. It should not only outline your main argument but also give a hint about why it's important.
Step 3: Create an Outline
An academic persuasive essay outline typically follows the 'classical' structure, which is based on techniques used by ancient Roman rhetoricians. Here are the basic elements your outline should include:
Step 4: Write the Introduction
When writing a persuasive essay introduction, it should not only give background information but also frame it as a problem or issue, known as the exigence. Presenting a clearly defined problem and proposing the thesis as a solution makes for a compelling introduction, as readers naturally want to see problems solved.
Here's a breakdown of an effective persuasive essay introduction:
- Hook : Begin with a brief anecdote that highlights an emerging issue, capturing the reader's attention.
- Context : Provide background information related to the topic.
- Problem : Connect the anecdote with the emerging issue, presenting it as a problem in need of addressing.
- Debate : Mention briefly the existing debate surrounding how to respond to the problem.
- Claim : Conclude the introduction by hinting at how you intend to address the problem, presented in a conversational tone as part of an ongoing dialogue.
Step 5: Delve into Body Paragraphs
The core of a persuasive essay lies in presenting a claim supported by reasoning and evidence. This means that much of the essay's body is dedicated to providing supporting reasons backed by evidence. A common approach taught in schools and colleges is the PEAS formula:
- Point : Start by explaining your reason clearly. For example, 'Another reason why we need to recycle is because...'
- Evidence : After explaining your reason, give proof that supports it. You can mention facts or share what experts say. You might say, ' I saw in a study that.. .' or ' Scientists have found that.. .'
- Analysis : Explain how your proof supports your reason. You can say, ' This means that.. .' or ' This shows us that... '
- Summary/So what? : Finish by quickly summarizing everything you said before. Then, explain why it's important or what it means for your argument.
Step 6: Address Counterarguments
When you're dealing with counterarguments, pick the response strategy that matches your argument.
.webp)
- If you agree with some points from the counterargument, acknowledge them and explain why they're not important for your topic.
- If the counterargument uses different evidence, say why it's not trustworthy.
- If the counterargument looks at evidence in a different way, explain why their understanding is wrong.
- If the counterargument weakens your point with evidence, explain why it doesn't actually disprove your argument.
Use phrases like these to introduce counterarguments:
- Some researchers say...
- Critics argue that...
- Others might think...
- There's a different view that...
And transition like this from counterargument to response:
- While some of that makes sense, I still believe...
- Even if that's true, it doesn't change the fact that...
- Those points are interesting, but they don't affect my argument because...
- I see where you're coming from, but I can't agree because...
Step 7: Conclude with a Call to Action or a Memorable Closing Statement
A good persuasive conclusion should do two things:
- Summarize the main points of your essay. If it's a longer essay, using phrases like 'I have argued that' can help, but for shorter essays, it might not be needed since the reader will remember the main ideas.
- Address the ' So what? ' or ' Now what? ' challenge. Imagine your reader asking, 'Okay, I'm convinced by your essay, but why are these ideas important? What should I do with them? Do you expect things to change?' Depending on whether your essay aims to change how people think or act, offer brief action points or insights into the implications of your ideas.
Consider ending with an anecdote, fact, or quote that highlights the significance of your argument.
Also, take a look at our guide on how to write a synthesis essay . It's a common type of assignment you'll encounter in school and college.

Wednesday Addams
Mysterious, dark, and sarcastic
You’re the master of dark humor and love standing out with your unconventional style. Your perfect costume? A modern twist on Wednesday Addams’ gothic look. You’ll own Halloween with your unapologetically eerie vibe. 🖤🕸️
Take Your Persuasive Writing to the Next Level!
Give us your task to amaze your readers with our tried-and-true methods
Persuasive Essay Examples
Here are great examples of persuasive essays to inspire you. If you like the writing style of our authors, you can buy essay paper from them, who will ensure a high-quality document specifically tailored to your needs!
5 Tips for Writing a Persuasive Essay
Here are some additional tips to enhance your essay from our persuasive essay writing service :
- Start with a Captivating Hook : Grab your reader's attention from the beginning with an engaging hook. Instead of using common approaches like surprising facts or quotes, try incorporating a unique angle or a suspenseful story related to your topic.
- Build Your Credibility : It's crucial to establish your credibility to persuade your audience to trust your argument. In addition to presenting well-researched facts and statistics, share personal experiences or insights to demonstrate your expertise. Citing lesser-known experts or studies can also provide a fresh perspective and show a thorough exploration of the topic.
- Clearly State Your Thesis: Craft a clear and concise thesis statement that effectively addresses the nuances of your argument. Take time to consider the wording of your thesis and how it aligns with your essay's direction. Provide a brief overview of the main points you'll cover to give readers a clear roadmap.
- Use Persuasive Language : Choose words and phrases that evoke emotion and urgency, compelling the reader to take action. Experiment with rhetorical devices like parallelism or repetition to add depth to your argument. Maintain a tone that balances assertiveness with respect.
- Appeal to Emotions and Logic : While emotional appeals can be powerful, support them with solid logic and evidence. Supplement personal anecdotes with relevant data, expert opinions, or logical reasoning for a well-rounded perspective. Anticipate and address potential counterarguments to demonstrate thorough consideration of the issue.
To bring it all together, you now understand the power of persuasion - it teaches you how to express your ideas clearly and convincingly. This means you can speak up for what you believe in, making society more active and informed. These skills are super useful not just in school but also in jobs and everyday life. And, if you want to make things easier, you can always check out our essay service . We'll save you time and give you some extra help with your writing!
Want to Easily Influence Your Readers?
Buy your persuasive essay right away to start using words to change the world!
What are the 7 Tips for Persuasive Essays?
How do i make a persuasive essay.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
- Rewrote the whole article except the samples which are good and new, and FAQs section
- Added new writing steps
- Researched new information overall
1. Gladd, J. (2020, August 18). Tips for Writing Academic Persuasive Essays . Pressbooks. https://idaho.pressbooks.pub/write/chapter/structure-of-academic-persuasive-essays/
%20(1).webp)
- + 1 321 - 251 - 6977
- Book Editing Services
- Fiction Editing
- nonfiction editing
- Authors Here
- Dissertation
- Universities & Institutions
- Academics Here
- Journals and Scientific PUBLICATIONS
- Academic Editing
- Scientific Manuscript
- Subject Matter Experts
- Researchers Here
- Business Editing
- Compare Editing Services
- Executives Here
- Consultation
- Editorial Critique Services
- Publishing Here
- Instant Price Quotes
- Coupons and Discounts
- Free Editing Sample & Critique
- Your Editing Team
- CERTIFIED Story Editors
- PhD & Subject Matter Experts
- About First Editing
- October 19, 2024
Beyond Facts: Mastering Persuasive Writing in Scholarly Work
- By Denisa Cerna

Academic writing can be quite difficult in and of itself, but what if I told you there are actually different types of scholarly writing, each of which comes with its own nuanced requirements?
Descriptive, analytical, critical, persuasive…
It’s a lot.
Fortunately, there’s no need to soak up all this information in one go. How about we take it step by step instead?
Let’s focus on mastering persuasive writing first.
Sharpen your pencils, dip your quill in ink, or stretch your fingers and clean your keyboard.
It’s time to take notes.
What Is Persuasive Writing?
Persuasive writing refers to a type of writing that aims to convince the reader of the validity of a certain argument.
Most academic essays are of persuasive nature, and some sections in research papers (for example, the discussion or the conclusion) carry persuasive undertones, too. The same applies to larger bodies of work, such as a dissertation or a thesis .
In order to write persuasively, it is important to take a stand. Your main goal here is to support your main argument with valid sources and well-developed logical arguments that follow a clear line of thinking.
In other words, you’ve got to make the reader go, “Ah, that’s a good point!”
Persuasive Academic Writing in a Nutshell
Let’s break the process down, shall we?
To arrive at a strong and valid point:
- Research as many secondary sources as you can and make notes (don’t forget to include a source next to each note so that you can easily find it and reference it later on)
- Read up on all possible counterarguments (don’t ignore them – it’s important to address these)
- Look for strong evidence, patterns, and results that are produced by credible studies
To present a good persuasive argument:
- Structure your writing in a way that allows a few sub-arguments to support your main argument
- Address possible counterarguments and explain why your argument is valid despite these objections
- Organize your essay into clear paragraphs, each of which serves a specific function
- Introduction (begin with a hook, something that will immediately draw the reader in and help you set the right persuasive tone)
- Background information (contextualize the problem)
- Main argument (present your main point)
- Supporting argument 1 (support your main point)
- Supporting argument 2 (support your main point)
- Supporting argument 3 (support your main point)
- Counterarguments (address potential concerns, limitations, and objections, and explain why your argument is strong in spite of these)
- Conclusion (reinforce the main argument)
Persuasive Writing: Forget Me Nots
- Don’t stray far from your main argument – your essay should stay coherent throughout (ideally, end each paragraph by tying your point back to the main theme)
- Support all your claims with valid secondary sources and clear examples (an excellent presentation of facts is vital to mastering persuasion)
- Make sure that each statement you make is relevant, clearly explained, and rooted in critical thinking and fact
- The art of academic persuasion isn’t about fancy wording – it’s about a collection of strong logical arguments that look at the issue from multiple angles
- Always look for a way to break your arguments into well-structured parts – these can become your paragraphs or sub-sections
Persuasive Writing: An Example
Every research article that aims to prove or disprove a hypothesis is essentially persuasive – its power stems from scientific and factual results.
Let’s take a look at this paragraph in the discussion section of a systematic review about the effect of physical activity on sleep quality (the highlights are mine):
“This systematic review found that physical activity was positively associated with sleep quality among different categories of populations. This is consistent with the World Health Organization (WHO) and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommending engaging in physical activities to improve sleep quality [43,44].
The association between physical activity and sleep quality can be attributed to several mechanisms , including the release of endorphins, which can lower stress and anxiety, resulting in improved relaxation and better sleep, regulation of circadian rhythms, and a rise in body temperature followed by a subsequent decrease helping in initiating sleep [14,45]. Furthermore, exercise stimulates the release of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and norepinephrine, which are involved in mood regulation and relaxation, perhaps assisting in better sleep start and maintenance [46].”
The first sentence includes the main point: exercise can positively impact our sleep. The second sentence appeals to other credible sources, which strengthens the argument. The following sentences present sub-arguments which were explored in depth within the body of the systematic review itself.
Further down in the discussion section, the authors also discuss the study’s limitations and explain which areas require further research.
The main outcome – as the first sentence of the conclusion shows (“Regular physical activity can lead to improved sleep quality, reduced sleep latency, and better overall sleep quality”) – is that the primary argument holds true.
When you’re learning how to master the art of persuasive writing in scholarly work, you’re also perfecting many other valuable skills, including your ability to think critically, analyze and evaluate sources, and structure arguments in a clear and logical manner.
And before you go, remember: persuasive academic writing is less about emotion-laden or fancy words and more about clearly linked facts that paint a credible and therefore persuasive picture.
- Frequently Asked Questions
Share With :

Get more updates, latest tips & tricks in editing and insightful articles right in your inbox.

Author Services
- Nonfiction Editing
- Copy Editing
- Content Editing
- Line Editing Services
- Proofreading Services
- Additional Editing Services
- Editing Consultation
- Business Copy Editing Services
Academic & Scientific Researchers
- Academic English Editing
- Scientific Research Editing
- Technical Copy Editing
- Universities & Institutions
- Thesis Editing
- Dissertation Editing
- How to Cite White Papers
Editing Help
- Editing Service Price Quote
- Client Login
- Satisfaction Guarantee
- Terms of Service
- Return Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
Writer Resources
- Samples of Editing Levels
- PODCAST – Publishing Power!
- BLOG for Writers
- Writing Tools
- Coupons & Special Offers
About FirstEditing
- CERTIFIED Structural Editors
- Published Authors
- Customer Reviews
- Professional Editors
- Affiliate Program
- Partner with First Editing
- Refer a Friend
- Editing Jobs
- Guest Blogging

Publications

COUPON QUIZ Does it feel scary to finish your manuscript?
Get 19% Off Now Expires November 05
Add Your Heading Text Here
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

How to Write Perfect Persuasive Essays in 5 Simple Steps
WHAT IS A PERSUASIVE ESSAY?

A persuasive text presents a point of view around a topic or theme that is backed by evidence to support it.
The purpose of a persuasive text can be varied. Maybe you intend to influence someone’s opinion on a specific topic, or you might aim to sell a product or service through an advertisement.
The challenge in writing a good persuasive text is to use a mix of emotive language and, in some cases, images that are supported by hard evidence or other people’s opinions.
In a persuasive essay or argument essay, the student strives to convince the reader of the merits of their opinion or stance on a particular issue. The student must utilise several persuasive techniques to form a coherent and logical argument to convince the reader of a point of view or to take a specific action.

PERSUADING PEOPLE REQUIRES A CONSISTENT APPROACH…
Persuasive texts are simple in structure. You must clearly state your opinion around a specific topic and then repeatedly reinforce your opinions with external facts or evidence. A robust concluding summary should leave little doubt in the reader’s mind. ( Please view our planning tool below for a detailed explanation. )
TYPES OF PERSUASIVE TEXT
We cover the broad topic of writing a general persuasive essay in this guide, there are several sub-genres of persuasive texts students will encounter as they progress through school. We have complete guides on these text types, so be sure to click the links and read these in detail if required.
- Argumentative Essays – These are your structured “Dogs are better pets than Cats” opinion-type essays where your role is to upsell the positive elements of your opinions to your audience whilst also highlighting the negative aspects of any opposing views using a range of persuasive language and techniques.
- Advertising – Uses persuasive techniques to sell a good or service to potential customers with a call to action.
- Debating Speeches – A debate is a structured discussion between two teams on a specific topic that a moderator judges and scores. Your role is to state your case, sell your opinions to the audience, and counteract your opposition’s opinions.
- Opinion Articles, Newspaper Editorials. – Editorials often use more subtle persuasive techniques that blur the lines of factual news reporting and opinions that tell a story with bias. Sometimes they may even have a call to action at the end.
- Reviews – Reviews exist to inform others about almost any service or product, such as a film, restaurant, or product. Depending on your experiences, you may have firm opinions or not even care that much about recommending it to others. Either way, you will employ various persuasive techniques to communicate your recommendations to your audience.
- Please note a DISCUSSION essay is not a traditional persuasive text, as even though you are comparing and contrasting elements, the role of the author is to present an unbiased account of both sides so that the reader can make a decision that works best for them. Discussions are often confused as a form of persuasive writing.
A COMPLETE TEACHING UNIT ON PERSUASIVE WRITING SKILLS
Teach your students to produce writing that PERSUADES and INFLUENCES thinking with this HUGE writing guide bundle covering: ⭐ Persuasive Texts / Essays ⭐ Expository Essays⭐ Argumentative Essays⭐ Discussions.
A complete 140 PAGE unit of work on persuasive texts for teachers and students. No preparation is required.
THE STRUCTURE OF A PERSUASIVE ESSAY

1. Introduction
In the introduction, the student will naturally introduce the topic. Controversial issues make for great topics in this writing genre. It’s a cliche in polite society to discourage discussions involving politics, sex, or religion because they can often be very divisive. While these subjects may not be the best topics of conversation for the dinner table at Thanksgiving, they can be perfect when deciding on a topic for persuasive writing. Obviously, the student’s age and abilities should be considered, as well as cultural taboos, when selecting a topic for the essay. But the point holds, the more controversial, the better.
Let’s take a look at some of the critical elements of the introduction when writing a persuasive essay:
Title: Tell your audience what they are reading.
This will often be posed as a question; for example, if the essay is on the merits of a vegetarian lifestyle, it may be called something like: To Eat Meat or Not?
Hook : Provide your audience with a reason to continue reading.
As with any genre of writing, capturing the reader’s interest from the outset is crucial. There are several methods of doing this, known as hooks. Students may open their essays with anecdotes, jokes, quotations, or relevant statistics related to the topic under discussion.
Background: Provide some context to your audience.
In this introductory section, students will provide the reader with some background on the topic. This will place the issue in context and briefly weigh some opinions on the subject.
Thesis statement: Let the audience know your stance.
After surveying the topic in the first part of the introduction, it is now time for the student writer to express their opinion and briefly preview the points they will make later in the essay.
2. Body Paragraphs
The number of paragraphs forming this essay section will depend on the number of points the writer chooses to make to support their opinion. Usually three main points will be sufficient for beginning writers to coordinate. More advanced students can increase the number of paragraphs based on the complexity of their arguments, but the overall structure will largely remain intact.
Be sure to check out our complete guide to writing perfect paragraphs here .
The TEEL acronym is valuable for students to remember how to structure their paragraphs. Read below for a deeper understanding.
Topic Sentence:
The topic sentence states the central point of the paragraph. This will be one of the reasons supporting the thesis statement made in the introduction.
These sentences will build on the topic sentence by illustrating the point further, often by making it more specific.
These sentences’ purpose is to support the paragraph’s central point by providing supporting evidence and examples. This evidence may be statistics, quotations, or anecdotal evidence.
The final part of the paragraph links back to the initial statement of the topic sentence while also forming a bridge to the next point to be made. This part of the paragraph provides some personal analysis and interpretation of how the student arrived at their conclusions and connects the essay as a cohesive whole.
3. Conclusion
The conclusion weaves together the main points of the persuasive essay. It does not usually introduce new arguments or evidence but instead reviews the arguments made already and restates them by summing them up uniquely. It is important at this stage to tie everything back to the initial thesis statement. This is the writer’s last opportunity to drive home their point, to achieve the essay’s goal, to begin with – persuade the reader of their point of view.

Ending an essay well can be challenging, but it is essential to end strongly, especially for persuasive essays. As with the hooks of the essay’s opening, there are many tried and tested methods of leaving the reader with a strong impression. Encourage students to experiment with different endings, for example, concluding the essay with a quotation that amplifies the thesis statement.
Another method is to have the student rework their ending in simple monosyllabic words, as simple language often has the effect of being more decisive in impact. The effect they are striving for in the final sentence is the closing of the circle.
Several persuasive writing techniques can be used in the conclusion and throughout the essay to amp up the persuasive power of the writing. Let’s take a look at a few.
ETHOS, PATHOS & LOGOS TUTORIAL VIDEO (2:20)

TIPS FOR WRITING A GREAT PERSUASIVE ESSAY

PERSUASIVE TECHNIQUES
In this article, we have outlined a basic structure that will be helpful to students in approaching the organization of their persuasive writing. It will also be helpful for the students to be introduced to a few literary techniques that will help your students to present their ideas convincingly. Here are a few of the more common ones:
Repetition: There is a reason why advertisements and commercials are so repetitive – repetition works! Students can use this knowledge to their advantage in their persuasive writing. It is challenging to get the reader to fully agree with the writer’s opinion if they don’t fully understand it. Saying the same thing in various ways ensures the reader gets many bites at the ‘understanding’ cherry.
Repetition Example: “The use of plastic bags is not only bad for the environment, but it is also bad for our economy. Plastic bags are not biodegradable, meaning they will not decompose and will continue to take up space in landfills. Plastic bags are also not recyclable, meaning they will not be reused and will instead end up in landfills. Plastic bags are not only bad for the environment, but they are also bad for our economy as they are costly to dispose of and take up valuable space in landfills.”
In this example, the phrase “not only bad for the environment but also bad for our economy” is repeated multiple times to reinforce the idea that plastic bags are not just a problem for the environment but also the economy. The repetition of the phrase emphasizes the point and makes it more persuasive.
It is also important to note that repetition could be used differently, such as repeating a word or phrase to create rhythm or emphasis.
Storytelling: Humans tend to understand things better through stories. Think of how we teach kids important values through time-tested fables like Peter and the Wolf . Whether through personal anecdotes or references to third-person experiences, stories help climb down the ladder of abstraction and reach the reader on a human level.
Storytelling Example: “Imagine you are walking down the street, and you come across a stray dog clearly in need of food and water. The dog looks up at you with big, sad eyes, and you cannot help but feel a twinge of compassion. Now, imagine that same scenario, but instead of a stray dog, it’s a homeless person sitting on the sidewalk. The person is clearly in need of food and shelter, and their eyes also look up at her with a sense of hopelessness.
The point of this story is to show that just as we feel compelled to help a stray animal in need, we should also feel compelled to help a homeless person. We should not turn a blind eye to the suffering of our fellow human beings, and we should take action to address homelessness in our community. It is important to remember that everyone deserves a roof over their head and a warm meal to eat. The story is designed to elicit an emotional response in the reader and make the argument more relatable and impactful.
By using storytelling, this passage creates an image in the reader’s mind and creates an emotional connection that can be more persuasive than just stating facts and figures.

Dissent: We live in a cynical age, so leaving out the opposing opinion will smack of avoidance to the reader. Encourage your students to turn to that opposing viewpoint and deal with those arguments in their essays .
Dissent Example: “Many people argue that students should not have to wear uniforms in school. They argue that uniforms stifle creativity and individuality and that students should be able to express themselves through their clothing choices. While these are valid concerns, I strongly disagree.
In fact, uniforms can actually promote individuality by levelling the playing field and removing the pressure to dress in a certain way. Furthermore, uniforms can promote a sense of community and belonging within a school. They can also provide a sense of discipline and structure, which can help to create a more focused and productive learning environment. Additionally, uniforms can save families money and eliminate the stress of deciding what to wear daily .
While some may argue that uniforms stifle creativity and individuality, the benefits of uniforms far outweigh the potential drawbacks. It is important to consider the impact of uniforms on the school as a whole, rather than focusing solely on individual expression.”
In this example, the writer presents the opposing viewpoint (uniforms stifle creativity and individuality) and then provides counterarguments to refute it. By doing so, the writer can strengthen their own argument and present a more convincing case for why uniforms should be worn in school.
A Call to Action: A staple of advertising, a call to action can also be used in persuasive writing. When employed, it usually forms part of the conclusion section of the essay and asks the reader to do something, such as recycle, donate to charity, sign a petition etc.
A quick look around reveals to us the power of persuasion, whether in product advertisements, newspaper editorials, or political electioneering; persuasion is an ever-present element in our daily lives. Logic and reason are essential in persuasion, but they are not the only techniques. The dark arts of persuasion can prey on emotion, greed, and bias. Learning to write persuasively can help our students recognize well-made arguments and help to inoculate them against the more sinister manifestations of persuasion.
Call to Action Example: “Climate change is a pressing issue that affects us all, and it’s important that we take action now to reduce our carbon footprint and protect the planet for future generations. As a society, we have the power to make a difference and it starts with small changes that we can make in our own lives.
I urge you to take the following steps to reduce your carbon footprint:
- Reduce your use of single-use plastics
- Use public transportation, carpool, bike or walk instead of driving alone.
- Support clean energy sources such as solar and wind power
- Plant trees and support conservation efforts
It’s easy to feel like one person can’t make a difference, but the truth is that every little bit helps. Together, we can create a more sustainable future for ourselves and for the planet.
So, let’s take action today and make a difference for a better future, it starts with minor changes, but it all adds up and can make a significant impact. We need to take responsibility for our actions and do our part to protect the planet.”
In this example, the writer gives a clear and specific call to action and encourages the reader to take action to reduce their carbon footprint and protect the planet. By doing this, the writer empowers the reader to take action and enables them to change.
Now, go persuade your students of the importance of perfecting the art of persuasive writing!
A COMPLETE UNIT ON TEACHING FACT AND OPINION

This huge 120-page resource combines four different fact and opinion activities that you can undertake as a WHOLE GROUP or as INDEPENDENT READING GROUP TASKS in either DIGITAL or PRINTABLE TASKS.
20 POPULAR PERSUASIVE ESSAY TOPICS FOR STUDENTS
Writing an effective persuasive essay demonstrates a range of skills that will be of great use in nearly all aspects of life after school.

In essence, if you can influence a person to change their ideas or thoughts on a given topic through how you structure your words and thoughts, you possess a very powerful skill.
Be careful not to rant wildly. Use facts and other people’s ideas who think similarly to you in your essay to strengthen your concepts.
Your biggest challenge in getting started may be choosing a suitable persuasive essay topic. These 20 topics for a persuasive essay should make this process a little easier.
- WHY ARE WE FASCINATED WITH CELEBRITIES AND WEALTHY PEOPLE ON TELEVISION AND SOCIAL MEDIA?
- IS IT RIGHT FOR SCHOOLS TO RAISE MONEY BY SELLING CANDY AND UNHEALTHY FOODS TO STUDENTS?
- SHOULD GIRLS BE ALLOWED TO PLAY ON BOYS SPORTING TEAMS?
- IS TEACHING HANDWRITING A WASTE OF TIME IN THIS DAY AND AGE?
- SHOULD THERE BE FAR GREATER RESTRICTIONS AROUND WHAT CAN BE POSTED ON THE INTERNET?
- SHOULD PROFESSIONAL ATHLETES HAVE TO TAKE DRUG TESTS?
- ARE TEENAGE PREGNANCY SHOWS A NEGATIVE OR POSITIVE INFLUENCE ON VIEWERS?
- SHOULD GAMBLING BE PROMOTED IN ANY WAY IN SPORTS EVEN THOUGH IT BRINGS IN LARGE AMOUNTS OF REVENUE?
- SHOULD SPORTING TEAMS THAT LOSE BE REWARDED BY RECEIVING INCENTIVES SUCH AS HIGH DRAFT PICKS AND / OR FINANCIAL BENEFITS?
- SHOULD SHARKS THAT ATTACK PEOPLE BE DESTROYED? SHOULD WE GET INVOLVED IN FOREIGN CONFLICTS AND ISSUES THAT DON’T DIRECTLY AFFECT OUR COUNTRY?
- SHOULD WE GET INVOLVED IN FOREIGN CONFLICTS AND ISSUES THAT DON’T DIRECTLY AFFECT OUR COUNTRY?
- COULD VIDEO GAMES BE CONSIDERED AS A PROFESSIONAL SPORT?
- IF YOU WERE THE LEADER OF YOUR COUNTRY AND HAD A LARGE SURPLUS TO SPEND, WHAT WOULD YOU DO WITH IT?
- WHEN SHOULD A PERSON BE CONSIDERED AND TREATED AS AN ADULT?
- SHOULD SMOKING BECOME AN ILLEGAL ACTIVITY?
- SHOULD THE VOTING AGE BE LOWERED?
- DOES PROTECTIVE PADDING IN SPORTS MAKE IT MORE DANGEROUS?
- SHOULD CELL PHONES BE ALLOWED IN THE CLASSROOM?
- IS TEACHING A FOREIGN LANGUAGE A WASTE OF TIME?
- SHOULD WE TEACH ETIQUETTE IN SCHOOLS?
PERSUASIVE PROMPTS FOR RELUCTANT WRITERS
If your students need a little more direction and guidance, here are some journal prompts that include aspects to consider.
- Convince us that students would be better off having a three-day weekend . There are many angles you could take with this, such as letting children maximize their childhood or trying to convince your audience that a four-day school week might actually be more productive.
- Which is the best season? And why? You will really need to draw on the benefits of your preferred season and sell them to your audience. Where possible, highlight the negatives of the competing seasons. Use lots of figurative language and sensory and emotional connections for this topic.
- Aliens do / or don’t exist? We can see millions of stars surrounding us just by gazing into the night sky, suggesting alien life should exist, right? Many would argue that if there were aliens we would have seen tangible evidence of them by now. The only fact is that we just don’t know the answer to this question. It is your task to try and convince your audience through some research and logic what your point of view is and why.
- Should school uniforms be mandatory? Do your research on this popular and divisive topic and make your position clear on where you stand and why. Use plenty of real-world examples to support your thoughts and points of view.
- Should Smartphones be banned in schools? Whilst this would be a complete nightmare for most students’ social lives, maybe it might make schools more productive places for students to focus and learn. Pick a position, have at least three solid arguments to support your point of view, and sell them to your audience.
VISUAL JOURNAL PROMPTS FOR PERSUASIVE WRITING
Try these engaging, persuasive prompts with your students to ignite the writing process . Scroll through them.

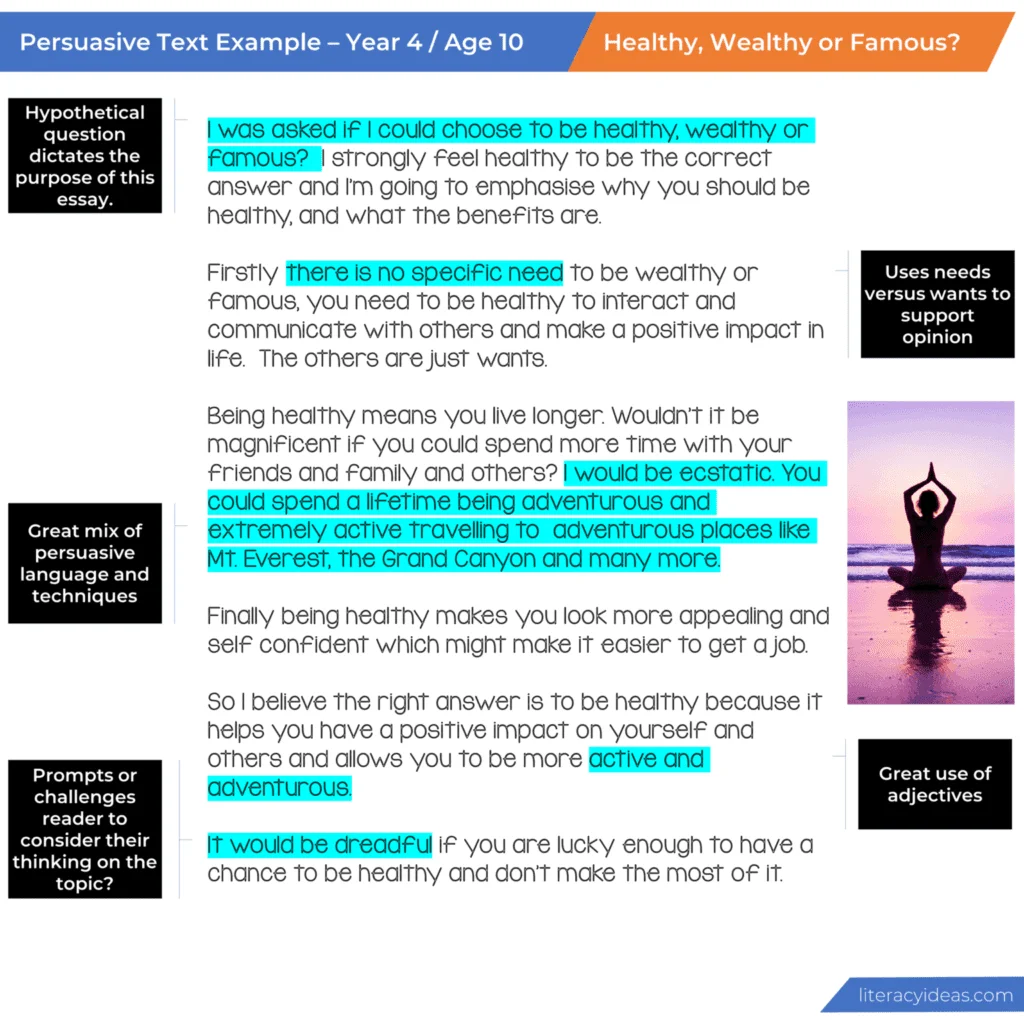
Persuasive Essay Examples (Student Writing Samples)
Below are a collection of persuasive essay samples. Click on the image to enlarge and explore them in greater detail. Please take a moment to read the persuasive texts in detail and the teacher and student guides highlight some of the critical elements of writing a persuasion.
Please understand these student writing samples are not intended to be perfect examples for each age or grade level but a piece of writing for students and teachers to explore together to critically analyze to improve student writing skills and deepen their understanding of persuasive text writing.
We recommend reading the example either a year above or below, as well as the grade you are currently working with, to gain a broader appreciation of this text type.
VIDEO TUTORIALS FOR PERSUASIVE WRITING

OTHER GREAT ARTICLES RELATED TO PERSUASIVE ESSAY WRITING

Teaching Resources
Use our resources and tools to improve your student’s writing skills through proven teaching strategies.
WHERE CAN I FIND A COMPLETE UNIT OF WORK ON HOW TO WRITE PERSUASIVE ESSAYS?

We pride ourselves on being the web’s best resource for teaching students and teachers how to write a persuasive text. We value the fact you have taken the time to read our comprehensive guides to understand the fundamentals of writing skills.
We also understand some of you just don’t have the luxury of time or the resources to create engaging resources exactly when you need them.
If you are time-poor and looking for an in-depth solution that encompasses all of the concepts outlined in this article, I strongly recommend looking at the “ Writing to Persuade and Influence Unit. ”
Working in partnership with Innovative Teaching Ideas , we confidently recommend this resource as an all-in-one solution to teach how to write persuasively.
This unit will find over 140 pages of engaging and innovative teaching ideas.
PERSUASIVE ESSAY WRITING CHECKLIST AND RUBRIC BUNDLE

⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (92 Reviews)

The Ultimate Guide to Opinion Writing for Students and Teachers

Top 5 Persuasive Writing Techniques for Students

5 Top Persuasive Writing Lesson Plans for Students and Teachers

23 Persuasive writing Topics for High School students

How to Write an Advertisement: A Complete Guide for Students and Teachers

How to Start an Essay with Strong Hooks and Leads
How to Write a Persuasive Essay
by Guest Blogger | 0 comments
So you've been assigned a persuasive paper and you're staring at a blinking cursor. What do you do first? How do you pick a good topic? Today we're going to learn how to write a persuasive essay, so you can get that assignment done.

As we continue our back-to-school series on writing essays, today we look at the persuasive essay.
Today's article is written by guest writer Cora Weems who is a senior at the University of South Carolina. She typically writes narrative poetry, slightly depressing short stories, and effective academic essays. Her hobbies include trying to get through a tall stack of unread books and handcrafts like card-making. Welcome, Cora!
What is a Persuasive Essay?
A persuasive essay is a piece of writing that aims to convince the reader to adopt a specific viewpoint or take action. To support it, you'll use logical arguments, compelling evidence, emotional appeals, and personalization.
In school, teachers often assign controversial issues, but you can develop your own topic too.
Learning to write a persuasive essay though is terrific practice for all kinds of writing. From public debate to sales letters and marketing, persuasive writing skills can carry you far beyond your school experience.
Let's go through the full process!
How to Write a Persuasive Essay: 6 Steps to Help You Start
Here are six steps to help you get your essay started.
Step 1: Pick a Suitable Topic
Maybe your teacher's already given you a prompt, or a specific topic to follow. Or maybe they've sent you on your way with just the rubric and an example paper to help you with formatting.
When it comes to persuasive writing, you need a position that you develop into a central idea. You'll have to support that position with all your evidence and reasoning.
Ideally, it should be a topic you're already familiar with and interested in. That will give you a better starting position and help keep you motivated to keep researching and writing!
When you are given a topic, you'll still want to develop a debatable position.
Here are three examples of broad persuasive essay topics:
- The Impact of Social Media on Society
- Climate Change and Environmental Responsibility
- The Role of Education in Reducing Income Inequality
It should not be a topic that has a specific single right answer or solution, but rather, a number of positions and solutions that you can take.
Your topic should be one of the very first things you address in your essay, in the topic sentence of your introductory paragraph, so your reader can immediately know what you're writing about.
To choose a suitable topic, ask yourself if the topic has multiple positions to take, and if you can reasonably research and take one position. That leads us to step 2:
Step 2: Research Both Sides, But Only Pick One
Even though you're only trying to advocate for one side of your argument, you should know the perspectives of both sides. Not only will this give you a better understanding of your topic, but it will help you prepare a counter argument that will make your essay more convincing.
If you've chosen a controversial topic, then there should be at least two opposing viewpoints that you can read about for supporting evidence.
Perhaps when you picked your topic, you already had a preferred stance, but researching the other side will give you fresh insight into what you actually believe, rather than relying on what you already knew.
Strong arguments typically address the opposing side's perspective and acknowledge them, for the purpose of refuting that argument and making your own appear stronger.
Or maybe you think both sides of your argument have valid points, so you think you'll about both and let the reader decide. Don't do that!
Not only is it more work for you, but the reader will be confused about your point.
You can acknowledge the strongest parts of the opposing view while you counter with your own perspective.
Step 3: Craft a Thesis Statement
Writing a thesis statement is a skill that goes beyond just persuasive writing. It's particularly important in this case because it gives both you and the reader a clear vision on how the rest of your paper is going to go.
You should explicitly state what you position is and what the rest of your paper is going to be about. It's usually a sentence or two long, so don't worry about being thorough or too specific. You'll Expand on it in your body paragraphs.
Typically, your thesis statement is located at the end of your introductory paragraph which allows for a natural transition from introducing your topic to the more specific reasons for your position on that topic.
You can use this statement to outline the rest of your paper, from what each paragraph is going to addressing the type of evidence you'll be using.
For example, if you choose the topic about the impact of social media on society, you want a thesis statement that covers the position and scope of your paper. Here's an example:
Social media like Facebook negatively impacts society through the ease of sharing misinformation, and both individuals and social media platforms need to do more to curb the spread of misinformation.
Notice how the position this writer takes is that Facebook negatively impacts society because of how it's used to share misinformation.
Now how would they support that thesis?
Step 4: Use the Right Evidence
Once you take a position, it's the time to show the reader why your viewpoint in particular is the one they should follow.
For academic writing, the most effective evidence is peer-reviewed articles published in academic journals. Peer-reviewed articles are seen as the most credible because they've been viewed and cleared by a number of different people, which means multiple people agreed that this article is reliable.
If you chose the wrong evidence, your entire argument is at risk of falling apart. You should not be choosing evidence that is false or unreliable, because your evidence is the foundation that your position stands upon.
Even if you don't want to go searching through databases for jargon-filled journal articles, all the evidence you choose should be from credible sources. It could be an expert opinion or some form of anecdotal evidence that could help personalize the issue for your reader.
You may have heard the terms “ethos,” “pathos,” and “logos” in class. When crafting something persuasive, you should appeal to authority, emotion, and logic.
Using evidence from an expert is an appeal to ethos or authority, credibility.
If you cite statistics from a reputable source, that might be an appeal to logic.
A related anecdote that makes the reader angry or sympathetic may be an emotional appeal.
The best persuasive essays use all three.
A persuasive argument is typically supported by a number of different sources that appeal to all parts of the reader, from their logical side to their more heartfelt one. All of those different perspectives will come together to make your argument stronger and more effective.
For example, in our example above on the impact of social media, the thesis statement reads: “Social media like Facebook negatively impacts society through the ease of sharing misinformation, and both individuals and social media platforms need to do more to curb the spread of misinformation.”
To support, this paper would need to show data about misinformation on Facebook, demonstrate the ways that misinformation negatively impacts society, and then offer the best solutions in the form of individual and company interventions.
Step 5: Use Natural Transitions
As you add evidence to your argument, use transitions that help the reader see the connections you're making.
If you've ever felt your eyes begin to glaze over when you see a wall of text or a bunch of graphs and statistics in one place, the writer lost you in making the needed connections and transitions. You don't want to do that to your reader.
Introduce a point, then use evidence to support that point, and then expand on that evidence. Whether it's by paraphrasing it so the reader can more easily digest it, or by showing the reader exactly how it connects back to what you're trying to persuade them.
This not only applies to evidence, but also moving between paragraphs. There should be a topic sentence near the beginning of every paragraph to tell the reader what that paragraph is about, and you should use the last sentence of the previous paragraph to lead into it.
Doing this helps improve the flow of your essay and keeps the reader's attention. If they never have to stop and wonder how you got to a certain point, then you can keep all their attention purely on your argument.
Step 6: Make It Applicable
As you bring your essay to a close, most persuasive papers end with some call to action. It might be that you are asking the reader to understand an issue differently. Maybe you want to them to change their minds or donate money or take other action.
Make sure your conclusion answers the question, “So what?” Give your reader something to occupy their mind even after they're done reading. You want to tell them why reading your argument was important, and give them a reason to keep thinking about your argument even after you're done.
Doing so will leave a lasting impression of your paper on your reader, which will make your essay more persuasive and effective.
Persuade us!
So there you have it. Some ways to help move that blinking cursor.
It's okay to start with a draft that's just you cramming all your ideas onto a document. Don't worry about formal language yet. Reorganizing and rewriting that rough draft is part of what makes a good paper.
Plus, writing it all out will let you see what you actually thought the most important parts were, and revision allows you to highlight those strong points and focus on what you think the reader should know.
Here's a question to help you keep going even after you've finished the messy first draft: What makes this essay important to you?
Beyond the grade it will get in class, beyond how it will affect your GPA or academic standing, what about this essay is important? What about this will affect more people than just you?
Throughout your life, you'll constantly find times where you have to use persuasion. Maybe it won't be in essay format or presented in a Power Point, but finding ways to be persuasive is something that will help you in the rest of your life.
So let's think of this essay as practice, and learn how to be as persuasive as we can.
What are your best tips for persuasive writing? Share in the comments .
Set your timer for fifteen minutes . Choose a persuasive topic that you can take a clear position on. Make a list of the reasons for your current view point. Then, do some research and read possible evidence both in support and in opposition to your view. Choose the strongest two to three pieces.
If you still have time, craft a thesis statement that distills your argument, and begin writing the essay. While it will take you longer than fifteen minutes to write the essay, sometimes just getting started in fifteen minutes is enough to make a difference!
When finished, post your thesis and current direction in the Pro Practice Workshop , and leave feedback for a few other writers.
Guest Blogger
This article is by a guest blogger. Would you like to write for The Write Practice? Check out our guest post guidelines .

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Best Resources for Writers Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.
You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.
Want to Get Published?
Enter your email to get our free interactive checklist to writing and publishing a book.
How to Write a Persuasive Essay (This Convinced My Professor!)
.png)
Table of contents

Meredith Sell
You can make your essay more persuasive by getting straight to the point.
In fact, that's exactly what we did here, and that's just the first tip of this guide. Throughout this guide, we share the steps needed to prove an argument and create a persuasive essay.
This AI tool helps you improve your essay > This AI tool helps you improve your essay >

Key takeaways: - Proven process to make any argument persuasive - 5-step process to structure arguments - How to use AI to formulate and optimize your essay
Why is being persuasive so difficult?
"Write an essay that persuades the reader of your opinion on a topic of your choice."
You might be staring at an assignment description just like this 👆from your professor. Your computer is open to a blank document, the cursor blinking impatiently. Do I even have opinions?
The persuasive essay can be one of the most intimidating academic papers to write: not only do you need to identify a narrow topic and research it, but you also have to come up with a position on that topic that you can back up with research while simultaneously addressing different viewpoints.
That’s a big ask. And let’s be real: most opinion pieces in major news publications don’t fulfill these requirements.
The upside? By researching and writing your own opinion, you can learn how to better formulate not only an argument but the actual positions you decide to hold.
Here, we break down exactly how to write a persuasive essay. We’ll start by taking a step that’s key for every piece of writing—defining the terms.
What Is a Persuasive Essay?
A persuasive essay is exactly what it sounds like: an essay that persuades . Over the course of several paragraphs or pages, you’ll use researched facts and logic to convince the reader of your opinion on a particular topic and discredit opposing opinions.
While you’ll spend some time explaining the topic or issue in question, most of your essay will flesh out your viewpoint and the evidence that supports it.
The 5 Must-Have Steps of a Persuasive Essay
If you’re intimidated by the idea of writing an argument, use this list to break your process into manageable chunks. Tackle researching and writing one element at a time, and then revise your essay so that it flows smoothly and coherently with every component in the optimal place.
1. A topic or issue to argue
This is probably the hardest step. You need to identify a topic or issue that is narrow enough to cover in the length of your piece—and is also arguable from more than one position. Your topic must call for an opinion , and not be a simple fact .
It might be helpful to walk through this process:
- Identify a random topic
- Ask a question about the topic that involves a value claim or analysis to answer
- Answer the question
That answer is your opinion.
Let’s consider some examples, from silly to serious:
Topic: Dolphins and mermaids
Question: In a mythical match, who would win: a dolphin or a mermaid?
Answer/Opinion: The mermaid would win in a match against a dolphin.
Topic: Autumn
Question: Which has a better fall: New England or Colorado?
Answer/Opinion: Fall is better in New England than Colorado.
Topic: Electric transportation options
Question: Would it be better for an urban dweller to buy an electric bike or an electric car?
Answer/Opinion: An electric bike is a better investment than an electric car.
Your turn: Walk through the three-step process described above to identify your topic and your tentative opinion. You may want to start by brainstorming a list of topics you find interesting and then going use the three-step process to find the opinion that would make the best essay topic.
2. An unequivocal thesis statement
If you walked through our three-step process above, you already have some semblance of a thesis—but don’t get attached too soon!
A solid essay thesis is best developed through the research process. You shouldn’t land on an opinion before you know the facts. So press pause. Take a step back. And dive into your research.
You’ll want to learn:
- The basic facts of your topic. How long does fall last in New England vs. Colorado? What trees do they have? What colors do those trees turn?
- The facts specifically relevant to your question. Is there any science on how the varying colors of fall influence human brains and moods?
- What experts or other noteworthy and valid sources say about the question you’re considering. Has a well-known arborist waxed eloquent on the beauty of New England falls?
As you learn the different viewpoints people have on your topic, pay attention to the strengths and weaknesses of existing arguments. Is anyone arguing the perspective you’re leaning toward? Do you find their arguments convincing? What do you find unsatisfying about the various arguments?
Allow the research process to change your mind and/or refine your thinking on the topic. Your opinion may change entirely or become more specific based on what you learn.
Once you’ve done enough research to feel confident in your understanding of the topic and your opinion on it, craft your thesis.
Your thesis statement should be clear and concise. It should directly state your viewpoint on the topic, as well as the basic case for your thesis.
Thesis 1: In a mythical match, the mermaid would overcome the dolphin due to one distinct advantage: her ability to breathe underwater.
Thesis 2: The full spectrum of color displayed on New England hillsides is just one reason why fall in the northeast is better than in Colorado.
Thesis 3: In addition to not adding to vehicle traffic, electric bikes are a better investment than electric cars because they’re cheaper and require less energy to accomplish the same function of getting the rider from point A to point B.
Your turn: Dive into the research process with a radar up for the arguments your sources are making about your topic. What are the most convincing cases? Should you stick with your initial opinion or change it up? Write your fleshed-out thesis statement.

3. Evidence to back up your thesis
This is a typical place for everyone from undergrads to politicians to get stuck, but the good news is, if you developed your thesis from research, you already have a good bit of evidence to make your case.
Go back through your research notes and compile a list of every …
… or other piece of information that supports your thesis.
This info can come from research studies you found in scholarly journals, government publications, news sources, encyclopedias, or other credible sources (as long as they fit your professor’s standards).
As you put this list together, watch for any gaps or weak points. Are you missing information on how electric cars versus electric bicycles charge or how long their batteries last? Did you verify that dolphins are, in fact, mammals and can’t breathe underwater like totally-real-and-not-at-all-fake 😉mermaids can? Track down that information.
Next, organize your list. Group the entries so that similar or closely related information is together, and as you do that, start thinking through how to articulate the individual arguments to support your case.
Depending on the length of your essay, each argument may get only a paragraph or two of space. As you think through those specific arguments, consider what order to put them in. You’ll probably want to start with the simplest argument and work up to more complicated ones so that the arguments can build on each other.
Your turn: Organize your evidence and write a rough draft of your arguments. Play around with the order to find the most compelling way to argue your case.
4. Rebuttals to disprove opposing theses
You can’t just present the evidence to support your case and totally ignore other viewpoints. To persuade your readers, you’ll need to address any opposing ideas they may hold about your topic.
You probably found some holes in the opposing views during your research process. Now’s your chance to expose those holes.
Take some time (and space) to: describe the opposing views and show why those views don’t hold up. You can accomplish this using both logic and facts.
Is a perspective based on a faulty assumption or misconception of the truth? Shoot it down by providing the facts that disprove the opinion.
Is another opinion drawn from bad or unsound reasoning? Show how that argument falls apart.
Some cases may truly be only a matter of opinion, but you still need to articulate why you don’t find the opposing perspective convincing.
Yes, a dolphin might be stronger than a mermaid, but as a mammal, the dolphin must continually return to the surface for air. A mermaid can breathe both underwater and above water, which gives her a distinct advantage in this mythical battle.
While the Rocky Mountain views are stunning, their limited colors—yellow from aspen trees and green from various evergreens—leaves the autumn-lover less than thrilled. The rich reds and oranges and yellows of the New England fall are more satisfying and awe-inspiring.
But what about longer trips that go beyond the city center into the suburbs and beyond? An electric bike wouldn’t be great for those excursions. Wouldn’t an electric car be the better choice then?
Certainly, an electric car would be better in these cases than a gas-powered car, but if most of a person’s trips are in their hyper-local area, the electric bicycle is a more environmentally friendly option for those day-to-day outings. That person could then participate in a carshare or use public transit, a ride-sharing app, or even a gas-powered car for longer trips—and still use less energy overall than if they drove an electric car for hyper-local and longer area trips.
Your turn: Organize your rebuttal research and write a draft of each one.
5. A convincing conclusion
You have your arguments and rebuttals. You’ve proven your thesis is rock-solid. Now all you have to do is sum up your overall case and give your final word on the subject.
Don’t repeat everything you’ve already said. Instead, your conclusion should logically draw from the arguments you’ve made to show how they coherently prove your thesis. You’re pulling everything together and zooming back out with a better understanding of the what and why of your thesis.
A dolphin may never encounter a mermaid in the wild, but if it were to happen, we know how we’d place our bets. Long hair and fish tail, for the win.
For those of us who relish 50-degree days, sharp air, and the vibrant colors of fall, New England offers a season that’s cozier, longer-lasting, and more aesthetically pleasing than “colorful” Colorado. A leaf-peeper’s paradise.
When most of your trips from day to day are within five miles, the more energy-efficient—and yes, cost-efficient—choice is undoubtedly the electric bike. So strap on your helmet, fire up your pedals, and two-wheel away to your next destination with full confidence that you made the right decision for your wallet and the environment.
3 Quick Tips for Writing a Strong Argument
Once you have a draft to work with, use these tips to refine your argument and make sure you’re not losing readers for avoidable reasons.
1. Choose your words thoughtfully.
If you want to win people over to your side, don’t write in a way that shuts your opponents down. Avoid making abrasive or offensive statements. Instead, use a measured, reasonable tone. Appeal to shared values, and let your facts and logic do the hard work of changing people’s minds.
Choose words with AI

You can use AI to turn your general point into a readable argument. Then, you can paraphrase each sentence and choose between competing arguments generated by the AI, until your argument is well-articulated and concise.
2. Prioritize accuracy (and avoid fallacies).
Make sure the facts you use are actually factual. You don’t want to build your argument on false or disproven information. Use the most recent, respected research. Make sure you don’t misconstrue study findings. And when you’re building your case, avoid logical fallacies that undercut your argument.
A few common fallacies to watch out for:
- Strawman: Misrepresenting or oversimplifying an opposing argument to make it easier to refute.
- Appeal to ignorance: Arguing that a certain claim must be true because it hasn’t been proven false.
- Bandwagon: Assumes that if a group of people, experts, etc., agree with a claim, it must be true.
- Hasty generalization: Using a few examples, rather than substantial evidence, to make a sweeping claim.
- Appeal to authority: Overly relying on opinions of people who have authority of some kind.
The strongest arguments rely on trustworthy information and sound logic.
Research and add citations with AI

We recently wrote a three part piece on researching using AI, so be sure to check it out . Going through an organized process of researching and noting your sources correctly will make sure your written text is more accurate.
3. Persuasive essay structure

If you’re building a house, you start with the foundation and go from there. It’s the same with an argument. You want to build from the ground up: provide necessary background information, then your thesis. Then, start with the simplest part of your argument and build up in terms of complexity and the aspect of your thesis that the argument is tackling.
A consistent, internal logic will make it easier for the reader to follow your argument. Plus, you’ll avoid confusing your reader and you won’t be unnecessarily redundant.
The essay structure usually includes the following parts:
- Intro - Hook, Background information, Thesis statement
- Topic sentence #1 , with supporting facts or stats
- Concluding sentence
- Topic sentence #2 , with supporting facts or stats
- Concluding sentence Topic sentence #3 , with supporting facts or stats
- Conclusion - Thesis and main points restated, call to action, thought provoking ending
Are You Ready to Write?
Persuasive essays are a great way to hone your research, writing, and critical thinking skills. Approach this assignment well, and you’ll learn how to form opinions based on information (not just ideas) and make arguments that—if they don’t change minds—at least win readers’ respect.
Share This Article:
%20(1).webp)
8 Tips for E-commerce Copywriting Success (with Examples!)
.webp)
The Brand Strategy Deck You Need to Drive Social Media Results + 5 Examples

Grammarly Alternatives: Which Writing Assistant is the Best Choice for You?
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
MAKE WAVES WITH THIS FREE WEEKLONG VOCABULARY UNIT!

10 Steps to Teach Persuasive Writing

Kids are natural-born persuaders. They do it all the time. The trick as a teacher is to take their set of skills and help them use their power for good. And by good, I mean to channel these skills into writing effective persuasive pieces.
So, what exactly do we need to do to teach persuasive writing? I won’t lie to you…it’s not an easy task, but I’ll try to break it down here and simplify the steps to hopefully make this something that you can use in your classroom.
1. Teach Paragraph Writing FIRST
Before I even begin to think about teaching students to create an opinion piece, I make sure that my class has learned the basics of writing a good paragraph. We spend a lot of time with each component, and after they’ve mastered one paragraph, we move on to the five-paragraph essay.
Since I teach 4th/5th, this is one of the standards we need to reach. Once I know that students can write a reasonably good essay, then they can learn an opinion essay a little more easily.

2. Use Mentor Texts to Introduce Opinion Writing
I am a big fan of mentor texts. I just love how picture books easily capture the attention of my “big” kids, while quickly teaching them so many lessons.
When I teach opinion writing, I like to gather several of these persuasive mentor texts and share them with my class. We talk about how the character used persuasive techniques well, or how he/she didn’t.

3. Start With the Big Picture
Before we start to officially write, we talk about what an opinion essay is and isn’t. I like to give students three choices with similar topics and ask them which one is the opinion essay. For example, they might choose between these titles: The Magical Elephant, Elephants and Their Families, and How to Save the Elephants. Next, I have a handout that shows the structure of an opinion essay. Since we’ve written five-paragraph essays before, they have a good handle on the basic essay structure. Then I guide them step by step through each component. We absolutely do not write a single opinion essay until we’ve had the opportunity to have lots of mini-lessons, see many examples, and practice all parts of the essay in a very low-stakes environment.
4. The Introduction Paragraph is First
A. introduce hooks.
Now we spend some time focusing on how to start the essay. We start by using a hook (also called a lead).
I like to describe a writing “hook” using a fishing analogy. The fisherman puts a nice pink, juicy worm on the hook, hoping to attract the attention of the fish. If the fish bites, the fisherman’s happy. If the fish doesn’t bite, that means that it wasn’t interested in the hook, and there won’t be any fish caught.
Our goal as a writer is to get the reader interested by “hooking” them into reading our essay, from the very first sentence.
We go over six different types of hooks and practice these. I also love using opinion writing posters as I introduce each new opinion essay concept. They’re a great reference for students on the wall or printed in miniature for writing notebooks.
B. Review Topic Sentences
For an opinion essay, the topic sentence is the opinion sentence. It is the author’s viewpoint. We do a lesson reviewing the five types of topic sentences we use for paragraph and essay writing, and I show students how to tweak these into opinion statements.
C. Time to Add the Three Reasons
The last part of the introduction lists the three reasons for our opinion. I teach students that these can be listed as a single sentence with commas between them, or we can write three separate sentences, one for each reason.
For the first lesson on reasons, I give students a topic (cell phones or vending machines at school or which season is the best, etc.) and then ask students to write three bullet points on their whiteboards. Next to each one, they write a word to describe a reason they like/dislike this idea.
For example, if the topic was school uniforms, the child might write lack of individuality, gets boring, uncomfortable… I can quickly glance at their lists while we discuss a few of them, and then we’re ready to practice with the next topic.
Without writing a whole essay, this is teaching students to think about organization and how reasons help support their opinions. I think this kind of practice is great!
When we transition this activity to a full essay, these reasons would turn into the topic sentences for each body paragraph of a five-paragraph opinion essay!
Btw.. if you don’t have whiteboards for your class, this is something you’ll really want to consider. They’re great for writing practice and so many things. I actually purchased shower boards at Home Depot for about $15 to make into whiteboards. They cut them into 12 x 12-inch squares for me for free!
5. Review, Review, Review
After we spend some time on each main section of the opinion essay (the introduction, the body paragraphs, and the conclusion), I like to give my students activities to really reinforce what they’ve learned. Besides review worksheets, we do games (like Stump the Expert), sorts, and color coding.

I really like to have students color code already-made paragraphs so they can see examples of quality writing, and they can master the structure of the paragraph . Once we’ve reviewed the introduction, it’s time to move on to the body paragraphs.
6. The Three Body Paragraphs are Next
There are three parts of each body paragraph, and I teach each part separately, one by one. The parts include a topic sentence that starts with a transition, three to five details to describe and explain the author’s reason for his/her viewpoint, and a conclusion sentence.
These three paragraphs are the meat of the essay. This is where students explain why they support or don’t support something.
We spend time doing activities like looking at three sentences and identifying which one is the topic sentence, which one is a detail, and which one is a conclusion sentence.
We look at pre-made topic sentences and related conclusion sentences and rate them as part of a great class discussion and then in pairs or independently. Then, we review with more color coding, games, and sorts.

7. Focus on the Conclusion Paragraph
Conclusions can be a little intimidating for some students. Maybe it’s because they’re tired from the heavy lifting of the other four paragraphs, but with practice, you can help take away some of their apprehension and replace it with confidence!
The conclusion paragraph is a shorter paragraph (in 3rd – 5th grade) than a body paragraph. It has three distinct parts, an opinion sentence that starts with a transition, the three reasons, and a final thought or call to action.
A. The Opinion Sentence Starting with a Transition
The opinion sentence is really a topic sentence. It reinforces the same idea presented in the introduction paragraph but uses synonyms and usually a different type of topic sentence than the introduction to add variety.
We go over specific transitions that can be used for conclusions. While students may not always use a transition for their conclusion later on, I think it gives students structure and helps them break the ice of crafting a strong conclusion paragraph.
B. The Three Reasons (again!)
Just like the introduction paragraph, the conclusion paragraph lists the three reasons, usually in a single sentence with commas. Like always, you’ll want students to reword the sentence using synonyms to add variety.
C. The Conclusion, The Ending, The VERY LAST SENTENCE!
This last sentence is another place students may feel apprehensive to write at first. We go over the difference between a final thought and a call to action and practice by seeing lots of exemplars and then creating our own.
By the time we’re finished, most students understand how to gracefully and effectively add the conclusion sentence to finish the opinion essay.
Just like we usually do, once we finish a section, we review that section carefully using handouts, sorts, color coding, games, and reviews.
8. Share an Opinion Essay Example
It’s one thing to talk about an opinion essay’s components and to even practice them. It’s another thing to see a really good example of an essay and to get to go through it and discuss what makes it work and why.
I have several great examples I’ve saved over the years (and I have two that I wrote and included in my opinion essay unit). We take time to color code the essay and then create a reverse outline for it. They save this essay as an example.
9. Make an Outline and an Essay as a Whole Class (Eeek!)
Okay, here’s where your perseverance has to kick in.
Trying to complete an essay as a whole class will drive even the most saintly of teachers to want to pull their hair out at times, but this hard part is crucial. There, I said it. It is that important that this is a step you shouldn’t miss.
Here’s how I do it. I break it down into two to four days. On the first day, we created an outline together. I have students write this outline in their Writer’s Notebooks as a model to refer to when they need to make their own outline later.
We always do school uniforms, because I find it to be a great topic and one that my students feel strongly about.

I tell them for the sake of continuity, we need to take a stand as a class for the essay, whether they really agree with that stand or not. We take a class vote and then stick with it, whether it’s for or against the uniform idea.
On the second day, when we have the outline in place, I make a deal with the kids…I tell them if they stick with me, stay on task, and participate…I’ll do the writing (this time), and they can just tell me what to write.
If they don’t stay focused, then they’ll have to write it themselves. This works like magic. I’ve never had a class that lost out on this “deal.”
So, using yesterday’s outline, we go step by step and write each paragraph together. Students feed me sentences (I write these on the SmartBoard), which I try to use or gently guide them a bit where needed.
Usually, we do about 2 paragraphs in one day. The attention spans of 8 – 11-year-olds can be a killer, so I find that breaking it into several days helps.
10. Before Students Write – Go over Expectations Using a Rubric
I really like to use rubrics for lots of assignments. It breaks down the activity into its components, and it also serves as a road map for students to know what is expected of them. I think the more we can explain to students exactly what we’re looking for, the more they can meet and sometimes exceed (hallelujah) our expectations.
There’s never a reason to hide what we want from students, in my opinion. So, we go over the rubric together, and it’s a kind of review for all the lessons leading up to this. You can three-hole punch it so they can store it in their binders, or you can print it in a smaller size to fit their Writer’s Notebooks if you wish.
BONUS #11. Practice Writing Opinion Essays…Over and Over and…
Once your students have practiced each part of the opinion essay and are very familiar with its structure, it’s their turn to write independently. I choose several different topics for them over the next few weeks, and we do about an essay a week in class. The students get better as time goes by, and usually, I let them choose a topic for the last essay or two. It’s interesting to see what they come up with.
Whew…such a huge unit and so many skills to fit in, but in my mind, it is an awesome unit. I love teaching it because of the great number of discussions it provides and because I see it as an important set of tools for them to have in their writing toolboxes.

If you’d like some resources for opinion writing , I love this unit I created. It’s a bundle with over 100 printable pages and includes a digital format too. It will take you through the entire process with teaching pages, and detailed teaching notes, student practice pages, activities, and posters for 3rd – 5th grade.
Sarah is a 4th Grade Teacher and uses this unit and process in her classroom. This is what she had to say.

CLICK HERE TO FIND THE OPINION WRITING BUNDLE ON TPT!

- Read more about: Writing & Grammar
You might also like...

How to Help Reluctant Writers: Strategies to Overcome Cognitive Overload
Writing is one of the most challenging subjects for students. It requires them to juggle multiple tasks at once. From understanding the prompt to organizing

Step-By-Step Success: Teaching Fictional Narrative with Explicit Writing Instruction
Fictional Narrative, Storytelling, and the Impact on Childhood I used to think the most important writing unit I taught was the expository and research unit.

Unlocking Student Writing Success: The Power of Explicit Writing Instruction
As upper elementary teachers, our goal is to create strong writers. However, the lack of Explicit Writing Instruction has caused students in the US to
Hi, I’m Jenn, CEO and owner of The Teacher Next Door!
I know that you strive to be an effective upper elementary teacher while maintaining a healthy work-life balance.
In order to do that, you need resources that are impactful, yet simple .
The problem is that most resources and curriculums out there are far from simple. The pages upon pages of daily lesson plans are just plain overwhelming .
At TTND, we believe teachers should be living their lives outside of the classroom, and not spend hours lesson planning and searching for resources.
We understand that now, more than ever, teachers need space to be themselves which is why we create and support teachers with timesaving tips and standards-aligned resources.
Want access to TTND's Free Resource Library? Sign up for our newsletter and we'll email you the exclusive password!
Trending posts.

SEARCH BY TOPIC
- Classroom Ideas
- Holidays and Seasonal
- Mentor Texts
- Reading Block
- Uncategorized
- Writing & Grammar
POPULAR RESOURCES

JOIN MY NEWSLETTER
Gain access to a library of FREE resources for upper elementary grades!

Facebook Group
Teachers Pay Teachers
Free Resource Library
💌 Contact Us
Disclosures
Privacy Policy
Refund Policy
Purchase Orders
Your Downloads
Reward Points
© The Teacher Next Door, LLC. All rights reserved.
* Please note: If your school has strong email filters, you may wish to use your personal email to ensure access.
Essay Papers Writing Online
10 effective techniques to master persuasive essay writing and convince any audience.

As a skilled communicator, your ability to persuade others is crucial in many areas of life. Whether you’re presenting an argument, advocating for a cause, or simply trying to convince someone of your point of view, your persuasive essay can be a powerful tool. However, crafting an essay that truly convinces your reader requires more than just strong opinions and eloquent language. It requires a strategic approach that combines logical reasoning, emotional appeal, and effective writing techniques.
1. Craft a Compelling Introduction: Your introduction is the first impression you make on your reader, so it’s essential to capture their attention right from the start. Consider using a captivating anecdote, a thought-provoking question, or a shocking statistic to engage your audience and set the tone for your essay. By immediately grabbing their interest, you increase the chances that they’ll continue reading and be open to your persuasive arguments.
2. Clearly Define Your Position: Before launching into the main body of your essay, make sure to clearly state your position on the topic. This will help your reader understand your stance and follow your line of reasoning throughout the essay. Use concise and assertive language to communicate your position, and consider reinforcing it with strong evidence or expert opinions that support your viewpoint.
3. Appeal to Emotions: While rational arguments are important, emotions often play a significant role in persuasive writing. Connect with your reader on an emotional level by using vivid descriptions, personal anecdotes, or powerful metaphors. By eliciting an emotional response, you can create a deeper connection with your audience and make your arguments more compelling.
Choose a compelling topic that ignites your passion

When crafting a persuasive essay, it is crucial to select a topic that not only captivates and engages your readers but also resonates strongly with you. By choosing a compelling topic that ignites your passion, you will be able to infuse enthusiasm and conviction into your writing, making it more convincing and persuasive.
While it may be tempting to select a popular or trending topic, it is essential to choose something that you deeply care about and have a genuine interest in. Your passion for the subject matter will shine through in your writing, capturing the attention and interest of your readers.
- Explore your hobbies and personal interests.
- Reflect on societal issues that deeply affect you.
- Consider topics that challenge conventional thinking.
- Analyze current events and their impact on your community or society as a whole.
- Look for subjects that inspire debate and differing opinions.
- Examine topics that align with your values and beliefs.
By choosing a topic that you are not only knowledgeable about but also passionate about, you will have a stronger emotional connection to your writing. This emotional connection will allow you to effectively convey your argument, influence your readers’ perspectives, and ultimately convince them to see things from your point of view.
Remember, the key to writing a persuasive essay lies in your ability to convey your ideas convincingly. By selecting a compelling topic that ignites your passion, you will have a solid foundation for crafting a persuasive essay that will resonate with readers and leave a lasting impact. So, take the time to explore your interests and choose a topic that truly captivates you.
Conduct thorough research to gather supporting evidence
Gathering strong evidence is a vital step in writing a persuasive essay. Convincing your readers requires you to present compelling facts, statistics, expert opinions, and examples that support your arguments. To achieve this, it is crucial to conduct thorough research to collect relevant and reliable information.
Begin by determining the main points you want to convey in your essay. These points should align with your thesis statement and support your overall argument. Once you have a clear idea of what you are trying to communicate, start gathering supporting evidence.
Research various credible sources such as academic journals, books, reputable websites, and expert interviews. Look for information that directly relates to your topic and can be used to reinforce your arguments. Be sure to verify the credibility and reliability of your sources to ensure the accuracy of the information.
Take notes as you conduct your research, highlighting key points, supporting evidence, and any quotes or statistics that you may want to include in your essay. It is essential to organize your findings in a way that makes sense and flows logically in your essay.
When using statistics or data, make sure to cite the sources properly to give credit to the original authors and establish your credibility as a writer. This will also allow your readers to verify the information themselves if they wish to do so.
By conducting thorough research and gathering strong supporting evidence, you will be able to present a persuasive and well-supported argument in your essay. This will not only convince your readers but also showcase your knowledge, understanding, and dedication to the topic at hand.
Develop a clear and concise thesis statement
One of the most important aspects of writing a persuasive essay is developing a thesis statement that is clear, concise, and compelling. A thesis statement serves as the main argument or central idea of your essay. It sets the tone for the entire piece and helps to guide your reader through your argument.
When developing your thesis statement, it’s essential to choose a strong and persuasive statement that clearly states your position on the topic. Avoid vague or ambiguous language that can confuse your reader and weaken your argument. Instead, use strong and specific language that clearly conveys your main point.
Your thesis statement should be concise, meaning it should be expressed in a clear and straightforward manner. Avoid unnecessary words or phrases that can dilute your message and make it less powerful. Instead, focus on getting your point across in as few words as possible while still maintaining clarity and impact.
Additionally, your thesis statement should be compelling and persuasive. It should motivate your reader to continue reading and consider your argument. Use persuasive language and strong evidence to support your thesis statement and convince your reader of its validity.
In summary, developing a clear and concise thesis statement is crucial for writing a persuasive essay. Choose a strong statement that clearly conveys your position, use concise language to express your point, and make your statement compelling and persuasive. By doing so, you will create a strong foundation for your entire essay and increase your chances of convincing your reader.
Use persuasive language and rhetorical devices

When it comes to crafting a compelling persuasive essay, one must master the art of persuasive language and employ various rhetorical devices. The way you choose your words and structure your sentences can make all the difference in captivating and convincing your readers.
One effective technique is to use strong and powerful language that evokes emotion and creates a sense of urgency. The use of vivid and descriptive words can paint a picture in the minds of your readers, making your arguments more relatable and engaging.
Additionally, employing rhetorical devices such as metaphors, similes, and analogies can effectively convey your message and help your readers understand complex ideas. By drawing comparisons and creating associations, you can make abstract concepts more tangible and easier to grasp.
Another valuable device is repetition. By repeating key phrases or ideas throughout your essay, you can emphasize your points and reinforce your arguments. This technique can help make your arguments more memorable and leave a lasting impact on your readers.
Furthermore, using rhetorical questions can encourage your readers to think critically about your topic and consider your perspective. By posing thought-provoking questions, you can guide your readers towards your desired conclusions and make them actively engage with your essay.
Lastly, employing the use of anecdotes and personal stories can make your essay more relatable and establish a connection with your readers. By sharing real-life examples or experiences, you can offer concrete evidence to support your arguments and establish credibility.
In conclusion, mastering persuasive language and employing rhetorical devices can greatly enhance the effectiveness of your persuasive essay. By choosing your words carefully, using powerful language, and incorporating various rhetorical techniques, you can captivate your readers and present your arguments in a compelling and convincing manner.
Address counterarguments and refute them with strong evidence
When writing a persuasive essay, it is crucial to anticipate and address potential counterarguments to strengthen your argument. By acknowledging opposing viewpoints and then refuting them with strong evidence, you can demonstrate the credibility and validity of your own position.
One effective way to address counterarguments is to acknowledge them upfront and present them in an objective and unbiased manner. By doing so, you show that you have considered different perspectives and are willing to engage in a fair and balanced discussion. This approach also helps you connect with readers who may initially hold opposing views, as it shows respect for their opinions and demonstrates your willingness to engage in thoughtful debate.
To effectively refute counterarguments, it is important to use strong evidence that supports your own position. This can include data, statistics, expert opinions, research findings, and real-life examples. By providing convincing evidence, you can demonstrate the superiority of your argument and weaken the credibility of counterarguments. Be sure to cite credible sources and use persuasive language to present your evidence in a convincing way.
In addition to providing strong evidence, it is also important to anticipate and address potential weaknesses in your own argument. By acknowledging and addressing these weaknesses, you can show that you have thoroughly considered your stance and are able to respond to potential criticisms. This helps to build trust and credibility with your readers, as they can see that you are aware of the limitations of your argument and have taken steps to address them.
In conclusion, addressing counterarguments and refuting them with strong evidence is a crucial component of persuasive writing. By acknowledging opposing viewpoints and providing solid evidence to support your own position, you can strengthen your argument and convince readers to adopt your point of view. Remember to always approach counterarguments objectively, use persuasive language, and address any potential weaknesses in your own argument. By doing so, you can create a compelling and persuasive essay that will resonate with your readers.
Edit and proofread your essay for grammar and clarity
Once you’ve completed your persuasive essay, the work isn’t quite finished. It’s essential to go back and review your writing with a critical eye, focusing on grammar and clarity. This final step is crucial in ensuring that your arguments are effectively communicated and that your reader can easily understand and follow your points.
First and foremost, pay attention to grammar. Look for any errors in your sentence structure, verb tense, subject-verb agreement, and punctuation. Make sure that your sentences are clear and concise, without any unnecessary or confusing phrases. Correct any spelling mistakes or typos that may have slipped through the cracks.
Next, consider the overall clarity of your essay. Read through each paragraph and ensure that your ideas flow logically and cohesively. Are your arguments supported by evidence and examples? Are your transitions smooth and seamless? If necessary, revise or rearrange your paragraphs to strengthen the overall structure of your essay.
It’s also important to check for any ambiguous or vague language. Make sure that your words and phrases have precise meanings and can be easily understood by your reader. Consider whether there are any areas where you could provide more clarification or add further details to strengthen your points.
When editing and proofreading, it can be helpful to read your essay out loud. This can help you identify any awkward or convoluted sentences, as well as any areas where you may have used repetitive or redundant language. Reading aloud also allows you to hear the natural rhythm and flow of your writing, giving you a better sense of how your words will be perceived by the reader.
Finally, consider seeking feedback from others. Share your essay with a trusted friend, family member, or teacher and ask for their input. They may be able to offer valuable suggestions or catch any errors that you may have missed. Sometimes, a fresh set of eyes can provide a new perspective and help you improve your essay even further.
By taking the time to edit and proofread your essay for grammar and clarity, you can ensure that your persuasive arguments are presented in the most effective and compelling way possible. This attention to detail will not only demonstrate your strong writing skills, but it will also increase the chances of convincing your reader to see things from your perspective.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, unlock success with a comprehensive business research paper example guide, unlock your writing potential with writers college – transform your passion into profession, “unlocking the secrets of academic success – navigating the world of research papers in college”, master the art of sociological expression – elevate your writing skills in sociology.
Home / Guides / Writing Guides / Paper Types / How to Write a Persuasive Essay
How to Write a Persuasive Essay
The entire point of a persuasive essay is to persuade or convince the reader to agree with your perspective on the topic. In this type of essay, you’re not limited to facts. It’s completely acceptable to include your opinions and back them up with facts, where necessary.
Guide Overview
- Be assertive
- Use words that evoke emotion
- Make it personal
- Topic selection hints
Tricks for Writing a Persuasive Essay
In this type of writing, you’ll find it is particularly helpful to focus on the emotional side of things. Make your reader feel what you feel and bring them into your way of thinking. There are a few ways to do that.
Be Assertive
A persuasive essay doesn’t have to be gentle in how it presents your opinion. You really want people to agree with you, so focus on making that happen, even if it means pushing the envelope a little. You’ll tend to get higher grades for this, because the essay is more likely to convince the reader to agree. Consider using an Persuasive Essay Template to understand the key elements of the essay.
Use Words that Evoke Emotion
It’s easier to get people to see things your way when they feel an emotional connection. As you describe your topic, make sure to incorporate words that cause people to feel an emotion. For example, instead of saying, “children are taken from their parents” you might say, “children are torn from the loving arms of their parents, kicking and screaming.” Dramatic? Yes, but it gets the point across and helps your reader experience the
Make it Personal
By using first person, you make the reader feel like they know you. Talking about the reader in second person can help them feel included and begin to imagine themselves in your shoes. Telling someone “many people are affected by this” and telling them “you are affected by this every day” will have very different results.
While each of these tips can help improve your essay, there’s no rule that you have to actually persuade for your own point of view. If you feel the essay would be more interesting if you take the opposite stance, why not write it that way? This will require more research and thinking, but you could end up with a very unique essay that will catch the teacher’s eye.
Topic Selection Hints
A persuasive essay requires a topic that has multiple points of view. In most cases, topics like the moon being made of rock would be difficult to argue, since this is a solid fact. This means you’ll need to choose something that has more than one reasonable opinion related to it.
A good topic for a persuasive essay would be something that you could persuade for or against.
Some examples include:
- Should children be required to use booster seats until age 12?
- Should schools allow the sale of sugary desserts and candy?
- Should marijuana use be legal?
- Should high school students be confined to school grounds during school hours?
- Should GMO food be labeled by law?
- Should police be required to undergo sensitivity training?
- Should the United States withdraw troops from overseas?
Some topics are more controversial than others, but any of these could be argued from either point of view . . . some even allow for multiple points of view.
As you write your persuasive essay, remember that your goal is to get the reader to nod their head and agree with you. Each section of the essay should bring you closer to this goal. If you write the essay with this in mind, you’ll end up with a paper that will receive high grades.
Finally, if you’re ever facing writer’s block for your college paper, consider WriteWell’s template gallery to help you get started.
EasyBib Writing Resources
Writing a paper.
- Academic Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- College Admissions Essay
- Expository Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Research Paper
- Thesis Statement
- Writing a Conclusion
- Writing an Introduction
- Writing an Outline
- Writing a Summary
EasyBib Plus Features
- Citation Generator
- Essay Checker
- Expert Check Proofreader
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tools
Plagiarism Checker
- Spell Checker
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Grammar and Plagiarism Checkers
Grammar Basics
Plagiarism Basics
Writing Basics
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics
Persuasive Essay Outline – Examples, Templates & Structure

Amanda Green was born in a small town in the west of Scotland, where everyone knows everyone. I joined the Toastmasters 15 years ago, and I served in nearly every office in the club since then. I love helping others gain confidence and skills they can apply in every day life.
Writing a good persuasive essay can help convince others of a point that means a lot to you. It can be anything from an environmental crisis to something as simple as the importance of ebooks to the modern reader. But how do you write a persuasive essay? Where do you even start? Right here! I’ll explain everything you need to know and even show you an example of a persuasive essay.
What Is a Persuasive Essay?

Persuasive essays are meant to convince someone or a group of people to agree with you on a certain topic or point of view. As the writer, you’ll use definitive evidence, simple reasoning, and even examples to support your argument and persuade them to understand the point of the essay.
Why Write a Persuasive Essay?
Believe it or not, you’ll have to form convincing arguments throughout real life. This could be in the form of college essays or academic essays, speeches for debate club that requires a valid argument, or even presenting an idea for change to your town council.
Argumentative vs. Persuasive Essay
An argumentative essay presents an argument on a specific topic and tries to persuade people to accept that argument as valid. It uses evidence, logic, and sometimes counterarguments to support the main point.
A persuasive essay is similar but presents an argument and focuses more on appealing to the reader’s emotions and values to convince them of your point of view. Think of it as convincing vs. persuading. And, yes, persuasive essays can also use evidence, but they often rely more on personal anecdotes and moral appeals to plead their case.
Let me give you an example. I’m a content writer, but I’m also a published author. If I were going to write an argumentative essay, I’d probably choose a topic like “Do you think authors should self-edit their work?”
But if I were doing a persuasive essay with a similar angle, the topic would look more like “The benefits of self-editing for authors.” Make sense?
Can We Write Your Speech?
Get your audience blown away with help from a professional speechwriter. Free proofreading and copy-editing included.
Basically, the main difference between argumentative and persuasive essays is all in the emphasis placed on logic and emotion.
How Many Paragraphs in a Persuasive Essay?
A decent persuasive essay should be around five or six paragraphs with double line spacing, depending on the topic, and can range from 500-2000 words in length. This includes your introduction and conclusion.
Introduction of a Persuasive Essay Example
Our world is facing a crisis, and that crisis is plastic pollution! Every day, a disgusting amount of plastic waste is just dumped into our oceans, killing and harming innocent marine life and ultimately affecting the entire food chain, including us.
Even though there is a clear and present danger that plastic presents, there are still a lot of people and corporations that continue to use single-use plastics with zero regards for their impact on our environment. It’s time for people to really look around and take some responsibility.
We can make a change by learning and using environmentally friendly alternatives in our everyday lives. So, in this essay, I’ll argue that using reusable bags, water bottles, and containers is not only necessary for the health of our precious planet but also a simple and effective way to make a real difference.
A Persuasive Essay Structure
As persuasive essay writers, you can write it however you like, but to follow a traditional persuasive essay structure, use this basic layout to get an effective paper:
- An Introduction: You need a good hook to grab the reader’s attention, a thesis statement presenting the main argument, and a roadmap of the essay, so they know what to expect.
- The Body Paragraphs: 2-3 paragraphs should suffice to provide strong evidence, examples, and any reasoning to support the thesis statement. Each paragraph should focus on a single main idea.
- The Counterargument: This section acknowledges and refutes the opposing viewpoint, strengthening your argument but still without being as forward as an argumentative essay.
- A Conclusion or Closing Statement: Here is where you would summarize the main points of the essay and a restatement of the thesis, including a call to action for the reader and/or a final thought.
In the end, a persuasive essay usually consists of 5-6 paragraphs and needs to be clear, concise, and logically structured to really persuade the reader on the point.
Tips for Persuasive Writing

- Choose a strong, clear thesis statement that presents your argument well.
- Know your audience and tailor your language and arguments to them. You’ll need a different approach if you’re speaking to a group of teenagers versus a team of adults.
- Use credible and reliable sources to support your argument so no one can second guess your point.
- Expect that people will have counterarguments and prepare a few talking points to address them.
- Use strong pieces of evidence and back them up with facts, statistics, examples, and personal anecdotes. Putting a personal touch on it helps ground the essay and lets people know you’re serious about the topic.
- Use an emotional appeal to engage the reader and make a personal connection to your argument. Basically, tug at their heartstrings and play into their guilt.
- Use clear and concise wordage. Try and avoid confusing technical jargon that might confuse people, and maintain a consistent tone throughout the essay.
- Make sure you’re confident and use an assertive tone but avoid being overly aggressive or confrontational. That will just spark a fight.
- Finish up with a powerful call to action or a final thought that leaves a lasting impact on the reader or listener.
- Use the same font throughout your essay, even for headings and titles. Go with easy-to-read fonts like Calibri, Times New Roman, or Garamond.
- Proofread and edit your essay for clarity, grammar, and style. I cannot stress this one enough. If you’re not confident, use programs like Grammarly to help spot typos and inconsistencies.
Persuasive Essay Topic Ideas
If you’re stuck on some ideas of what to form your essay around, here’s a list of some popular topics to inspire you.
- Importance of recycling and reducing waste in today’s climate.
- The need for stricter gun control laws all over the world.
- A paper on abortion rights in today’s age.
- Benefits of alternative energy sources over fossil fuels and how we can be using them.
- How social media has negative impacts on mental health in kids.
- Key benefits of a vegetarian or vegan diet and how it can help the planet.
- The value of a college education.
- Rise of plastic pollution on the environment and sea life and how it is affecting us.
- Why physical exercise and leading an active lifestyle are important.
- The dangers of texting while driving.
- How our public schools need better funding.
- Benefits of a diverse and inclusive workplace both online and in-person.
Any of these could be used as logical arguments. Still, to make a persuasive argument from either of them, just follow the basic persuasive essay outline examples I’ve given you.
Example of a Persuasive Essay
Introduction.
In today’s age of ever-changing technology, the way we consume and experience books have changed dramatically in just a short time. While physical books were once the only option, ebooks have grown increasingly popular in recent years. In my essay, I’ll argue that, while we all still love paperbacks and hardcovers, ebooks offer so many benefits over physical books, making them the number one choice for most readers today.
Body Paragraph 1: Convenience
Ebooks are convenient; there’s just no denying it. They’re easily accessible through devices like smartphones, tablets, and e-readers, and they allow readers to carry hundreds of books with them at all times. This makes them perfect for traveling or heading to work, or even going to the gym. Readers can now have an entire library with them without the added weight of physical books. Plus, ebooks are easily bought online with just the click of a button, further adding to their convenience.
Body Paragraph 2: Customization
Ebooks offer a level of customization that physical books just can’t match. For one, the font size can be adjusted for easier reading, which is great for those who have eyesight problems. The background color can also be changed from light to dark to reduce eye strain. Personally, as someone who suffers from Meniere’s disease, this is a great feature. All of these options make ebooks a great choice for people with visual impairments, neurological disorders, or reading difficulties.
Body Paragraph 3: Affordability
Ebooks are often far cheaper than physical books, especially when purchased in bulk. You can get an entire series for a fraction of the cost of one paperback. This makes them a more accessible option for budget-conscious readers and people who simply don’t have the disposable funds for books. Also, tons of ebooks are available for free, which is a great option for readers that are looking for ways to save money but keep up with their reading habits.
Body Paragraph 4: Environmentally Friendly
626,000 tons of paper is used to produce all the books we see published every year. That’s a scary number when you consider the rate of deforestation and the state of our world in terms of global warming. We simply can’t afford to move ahead at a rate like that. Ebooks help tackle the issue because they require zero trees to produce.
In conclusion, ebooks offer endless benefits over physical books, including convenience, customization, and affordability. While physical books will always hold a special place in our hearts, you have to admit that the benefits of ebooks just can’t be ignored. For modern, busy, on-the-go readers, ebooks are the preferred choice. It’s time to embrace the digital age and make the switch to ebooks.
Now Write Your Persuasive Essay!
I hope this guide has helped you figure out persuasive essay writing and how to put together powerful arguments. Just stick to the facts and ease the reader into your point with gentle arguments that continue to prove your point. Don’t be afraid to get personal if it can help the essay and convince the reader.
Writing a Thesis Statement – Template & Examples
Intrigue Your Classmates: 9 Unique Ways to Commence Your Class Presentation
Leave a Comment
I accept the Privacy Policy
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class
How to Write a Persuasive Essay: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples
Have you ever tried to get somebody round to your way of thinking? Then you should know how daunting the task is. Still, if your persuasion is successful, the result is emotionally rewarding.
A persuasive essay is a type of writing that uses facts and logic to argument and substantiate such or another point of view. The purpose is to assure the reader that the author’s position is viable. In this article by Custom-writing experts, you can find a guide on persuasive writing, compelling examples, and outline structure. Continue reading and learn how to write a persuasive essay!
⚖️ Argumentative vs. Persuasive Essay
- 🐾 Step-by-Step Writing Guide
🔗 References
An argumentative essay intends to attack the opposing point of view, discussing its drawbacks and inconsistencies. A persuasive essay describes only the writer’s opinion, explaining why it is a believable one. In other words, you are not an opponent; you are an advocate.
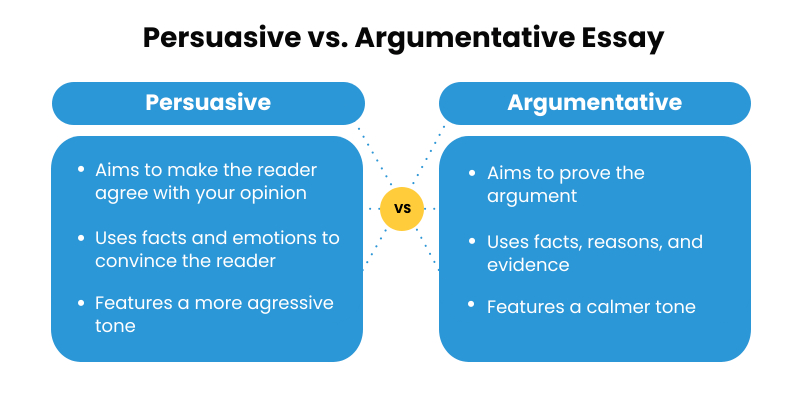
A persuasive essay primarily resorts to emotions and personal ideas on a deeper level of meaning, while an argumentative one invokes logic reasoning. Despite the superficial similarity of these two genres, argumentative speech presupposes intense research of the subject, while persuasive speech requires a good knowledge of the audience.
🐾 How to Write a Persuasive Essay Step by Step
These nine steps are the closest thing you will find to a shortcut for writing to persuade. With practice, you may get through these steps quickly—or even figure out new techniques in persuasive writing.
📑 Persuasive Essay Outline
Below you’ll find an example of a persuasive essay outline . Remember: papers in this genre are more flexible than argumentative essays are. You don’t need to build a perfectly logical structure here. Your goal is to persuade your reader.
Note that the next section contains a sample written in accordance with this outline.
Persuasive Essay Introduction
- Hook: start with an intriguing sentence.
- Background: describe the context of the discussed issue and familiarize the reader with the argument.
- Definitions: if your essay dwells upon a theoretical subject matter, be sure to explain the complicated terms.
- Thesis statement: state the purpose of your piece of writing clearly and concisely. This is the most substantial sentence of the entire essay, so take your time formulating it.
Persuasive Essay Body
Use the following template for each paragraph.
- Topic sentence: linking each new idea to the thesis, it introduces a paragraph. Use only one separate argument for each section, stating it in the topic sentence.
- Evidence: substantiate the previous sentence with reliable information. If it is your personal opinion, give the reasons why you think so.
- Analysis: build the argument, explaining how the evidence supports your thesis.
Persuasive Essay Conclusion
- Summary: briefly list the main points of the essay in a couple of sentences.
- Significance: connect your essay to a broader idea.
- Future: how can your argument be developed?
⭐ Persuasive Essay Examples
In this section, there are three great persuasive essay examples. The first one is written in accordance with the outline above, will the components indicated. Two others are downloadable.
Example #1: Being a Millionaire is a Bad Thing
Introduction, paragraph #1, paragraph #2, paragraph #3, example #2: teachers or doctors.
The importance of doctors in the period of the COVID-19 pandemic is difficult to overstate. The well-being of the nation depends on how well doctors can fulfill their duties before society. The US society acknowledges the importance of doctors and healthcare, as it is ready to pay large sums of money to cure the diseases. However, during the lockdown, students and parents all around the world began to understand the importance of teachers.
Before lockdown, everyone took the presence of teachers for granted, as they were always available free of charge. In this country, it has always been the case that while doctors received praises and monetary benefits, teachers remained humble, even though they play the most important role for humanity: passing the knowledge through generations. How fair is that? The present paper claims that even in the period of the pandemic, teachers contribute more to modern society than doctors do.
Example #3: Is Online or Homeschool More Effective?
The learning process can be divided into traditional education in an educational institution and distance learning. The latter form has recently become widely popular due to the development of technology. Besides, the COVID-19 pandemic is driving the increased interest in distance learning. However, there is controversy about whether this form of training is sufficient enough. This essay aims to examine online and homeschooling in a historical and contemporary context and to confirm the thesis that such activity is at least equivalent to a standard type of education.
Persuasive Essay Topics
- Why do managers hate the performance evaluation?
- Why human cloning should be prohibited.
- Social media have negative physical and psychological effect on teenagers.
- Using cell phones while driving should be completely forbidden.
- Why is business ethics important?
- Media should change its negative representation of ageing and older people.
- What is going on with the world?
- Good communication skills are critical for successful business.
- Why capitalism is the best economic system.
- Sleep is extremely important for human health and wellbeing.
- Face-to-face education is more effective than online education.
- Why video games can be beneficial for teenagers.
- Bullies should be expelled from school as they encroach on the school safety.
- Why accountancy is a great occupation and more people should consider it as a future career.
- The reasons art and music therapy should be included in basic health insurance.
- Impact of climate change on the indoor environment.
- Parents should vaccinate their children to prevent the spread of deadly diseases.
- Why celebrities should pay more attention to the values they promote.
- What is wrong with realism?
- Why water recycling should be every government’s priority.
- Media spreads fear and panic among people.
- Why e-business is very important for modern organizations.
- People should own guns for self-protection.
- The neccessity of container deposit legislation.
- We must save crocodiles to protect ecological balance.
- Why we should pay more attention to renewable energy projects.
- Anthropology is a critically relevant science.
- Why it’s important to create a new global financial order.
- Why biodiversity is crucial for the environment?
- Why process safety management is crucial for every organization.
- Speed limits must not be increased.
- What’s wrong with grades at school ?
- Why tattoos should be considered as a form of fine art.
- Using all-natural bath and body products is the best choice for human health and safety.
- What is cancel culture?
- Why the Internet has become a problem of modern society.
- Illegal immigrants should be provided with basic social services.
- Smoking in public places must be banned for people’s safety and comfort.
- Why it is essential to control our nutrition.
- How to stimulate economic growth?
- Why exercise is beneficial for people.
- Studying history is decisive for the modern world.
- We must decrease fuel consumption to stop global warming.
- Why fighting social inequality is necessary.
- Why should businesses welcome remote work?
- Social media harms communication within families.
- College athletes should be paid for their achievements.
- Electronic books should replace print books.
- People should stop cutting down rainforest.
- Why every company should have a web page.
- Tips To Write An Effective Persuasive Essay: The College Puzzle, Stanford University
- 31 Powerful Persuasive Writing Techniques: Writtent
- Persuasive Essay Outline: Houston Community College System
- Essays that Worked: Hamilton College
- Argumentative Essays // Purdue Writing Lab
- Persuasion – Writing for Success (University of Minnesota)
- Persuasive Writing (Manitoba Education)
- Share to Facebook
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email
![how to write a school persuasive essay Common Essay Mistakes—Writing Errors to Avoid [Updated]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/avoid-mistakes-ccw-284x153.jpg)
One of the most critical skills that students gain during their college years is assignment writing. Composing impressive essays and research papers can be quite challenging, especially for ESL students. Nonetheless, before learning the art of academic writing, you may make numerous common essay mistakes. Such involuntary errors appear in:...

You’re probably thinking: I’m no Mahatma Gandhi or Steve Jobs—what could I possibly write in my memoir? I don’t even know how to start an autobiography, let alone write the whole thing. But don’t worry: essay writing can be easy, and this autobiography example for students is here to show...
![how to write a school persuasive essay Why I Want to Be a Teacher Essay: Writing Guide [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/senior-male-professor-writing-blackboard-with-chalk3-284x153.jpg)
Some people know which profession to choose from childhood, while others decide much later in life. However, and whenever you come to it, you may have to elaborate on it in your personal statement or cover letter. This is widely known as “Why I Want to Be a Teacher” essay.
![how to write a school persuasive essay Friendship Essay: Writing Guide & Topics on Friendship [New]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/smiley-female-friends-fist-bumping-284x153.jpg)
Assigned with an essay about friendship? Congrats! It’s one of the best tasks you could get. Digging through your memories and finding strong arguments for this paper can be an enjoyable experience. I bet you will cope with this task effortlessly as we can help you with the assignment. Just...

When you are assigned an autobiography to write, tens or even hundreds of questions start buzzing in your head. How do you write autobiography essay parts? What to include? How do you make your autobiography writing flow? Don’t worry about all this! Use the following three simple principles and 60...

“Where is your thesis statement?” asks your teacher in a dramatic tone. “Where is my what?” you want to reply, but instead, you quickly point your finger at a random sentence in your paper, saying, “Here it is…” To avoid this sad situation (which is usually followed by a bad...

A life experience essay combines the elements of narration, description, and self-reflection. Such a paper has to focus on a single event that had a significant impact on a person’s worldview and values. Writing an essay about life experience prompts students to do the following: You may struggle with such...

Who has made a significant impact in your life and why? Essay on the topic might be challenging to write. One is usually asked to write such a text as a college admission essay. A topic for this paper can be of your choice or pre-established by the institution. Either...

Are you about to start writing a financial assistance essay? Most probably, you are applying for a scholarship that will provide additional funding for your education or that will help you meet some special research objectives.
![how to write a school persuasive essay Growing Up Essay: Guide & Examples [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/gardening-concept-with-mother-daughter-284x153.jpg)
What does it mean to grow up? Essays on this topic might be entertaining yet challenging to write. Growing up is usually associated with something new and exciting. It’s a period of everything new and unknown. Now, you’ve been assigned to write a growing up essay. You’re not a kid...
![how to write a school persuasive essay Murder Essay: Examples, Topics, and Killer Tips [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/man-holding-gun-as-evidence-284x153.jpeg)
Probably, a murder essay is not a fascinating assignment to complete. Talking about people’s deaths or crazy murderers can be depressing. However, all assignments are different, and you are supposed to work on every task hard. So, how are you going to deal with a murder essay? You can make...

Are you a nursing student? Then, you will definitely have an assignment to compose a nursing reflective essay. This task might be quite tough and challenging. But don’t stress out! Our professionals are willing to assist you.
Thank you for posting this!! I am trying to get notice to bring up a new language in our school because it doesn’t allow many languages so this really helped 🙂
Beautiful content
Useful article for blogging. I believe, for business, these blog tips will help me a lot.

Glad to know our tips are helpful for you! Hope you visit our blog again!
- Exam Prep >
- Prepare for Business School >
- Business School & Careers >
- Explore Programs >
- Connect with Schools >
- How to Apply >
- Help Center >
- About the Exam
- Register for the Exam
- Plan for Exam Day
- Prep for the Exam
- About the Executive Assessment
- Register for the Executive Assessment
- Plan for Assessment Day
- Prepare for the Assessment
- NMAT by GMAC
- Business Writing Assessment
- Shop GMAT™ Official Prep
- About GMAT™ Official Prep
- Prep Strategies
- Personalized Prep Plan
- GMAT Mini Quiz
- Executive Assessment Exam Prep
- NMAT by GMAC Exam Prep
- Business Writing Assessment Prep
Prepare For Business School
- Business Fundamentals
- Skills Insight
Business School & Careers
- Why Business School
- Student Experience
- Business Internships
- B-School Go
- Quiz: Are You Leadership Material?
- MBA Return on Investment (ROI) Calculator
- Estimate Your Salary
- Success Stories
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Women in Business
Explore Programs
- Top Business School Programs
- Quiz: Which Post Graduate Program is Right for You?
- Quiz: Find the Best Program for Your Personality
- Business School Rankings
- Business Master's Programs
- MBA Programs
- Study Destinations
- Find Programs Near Me
- Find MBA Programs
- Find Master's Programs
- Find Executive Programs
- Find Online Programs
Connect with Schools
- About GradSelect
- Create a GradSelect Profile
- Prep Yourself for B-School
- Quiz: Can You Network Like An MBA?
- Events Calendar
- School Events
- GMAC Tours Events
- In-Person Events
- Online Events
How to Apply
- Apply to Programs
- The Value of Assessments
- Admissions Essays
- Letters of Recommendation
- Admissions Interviews
- Scholarships and Financing
- Quiz: What's Your Ideal Learning Style?
Help Center
Gmac™ business writing assessment.

The “Write” Tool for B-School
With the Business Writing Assessment, admissions teams at participating schools will gain valuable insights into how you synthesize and convey complex ideas .
Within a 30-minute timeframe , you will be tasked with analyzing a brief argument. Rather than sharing your personal perspective, the objective is to critique the argument's reasoning and evidence objectively and cohesively.
A well-structured, persuasive response will demonstrate to schools that you have the logical reasoning and communications skills necessary to succeed in the classroom and beyond.

Assessment Format
The Business Writing Assessment is a 30-minute, online writing assessment that asks you to analyze the reasoning behind a given argument, and then write a critique of that argument. You will need to evaluate the line of reasoning and the use of evidence presented in the argument.
The arguments include a range of topics relevant to both business and general interest. Specific knowledge of the topic is not required. Learn more about essay questions here .
Each assessment is evaluated using a standardized rubric, scoring in one-point increments on a scale of 0 to 6. Within 3-5 days of completing the Business Writing Assessment, you will receive your score. You can send your results for free to participating schools. Learn more about scoring here .
Benefits of the Business Writing Assessment
Flexible Scheduling
Minimal Preparation
Fast Results
Free Score Sending
One Global Price

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
TIP 1: Some writers find it easier to write their introductions last. As long as you have your working thesis, this is a perfectly acceptable approach. From that thesis, you can plan your body paragraphs and then go back and write your introduction. TIP 2: Avoid "announcing" your thesis. Don't include statements like this:
Choose a position you're passionate about. The first step in writing a persuasive essay is choosing a topic and picking a side. If the topic is something you believe in, it will make the entire experience of researching, writing, and arguing your perspective more personal. Choosing a topic that appeals to you on an emotional or sentimental ...
It should be specific, debatable, and reflect the stance you'll defend throughout the essay. For example, "The government should defund itself and de-regulate to grow the economy and reduce red tape" is a strong persuasive essay thesis statement. 4. Create a Well-Structured Outline.
Pick a topic that appeals to you. Because a persuasive essay often relies heavily on emotional appeals, you should choose to write on something about which you have a real opinion. Pick a subject about which you feel strongly and can argue convincingly. [3] 6. Look for a topic that has a lot of depth or complexity.
1 Choose wording carefully. Word choice—the words and phrases you decide to use—is crucial in persuasive writing as a way to build a personal relationship with the reader. You want to always pick the best possible words and phrases in each instance to convince the reader that your opinion is right. Persuasive writing often uses strong ...
How to Write a Persuasive Essay in 7 Steps. Writing a persuasive essay usually follows a structured format: introduction, body, conclusion. Unlike argument essays, which involve discussing and attacking alternate views, persuasive essays aim to convince the reader of your argument's validity. They're a bit more gentle and understanding in tone.
Most academic essays are of persuasive nature, and some sections in research papers (for example, the discussion or the conclusion) carry persuasive undertones, too. The same applies to larger bodies of work, such as a dissertation or a thesis. In order to write persuasively, it is important to take a stand.
Harvard College Writing Center 2 Tips for Reading an Assignment Prompt When you receive a paper assignment, your first step should be to read the assignment prompt carefully to make sure you understand what you are being asked to do. Sometimes your assignment will be open-ended ("write a paper about anything in the course that interests you").
Thesis statement: Let the audience know your stance. After surveying the topic in the first part of the introduction, it is now time for the student writer to express their opinion and briefly preview the points they will make later in the essay. 2. Body Paragraphs.
Step 1: Pick a Suitable Topic. Maybe your teacher's already given you a prompt, or a specific topic to follow. Or maybe they've sent you on your way with just the rubric and an example paper to help you with formatting. When it comes to persuasive writing, you need a position that you develop into a central idea.
Contact Sales Learn More. The last time you wrote a persuasive essay may have been in high school or college, but the skill of writing a strong persuasive argument is always a useful one to have. Persuasive writing begins with a writer forming their own opinion on a topic, which they then attempt to convince their reader of this opinion by ...
A better idea would be to choose one impact on American life the wars had (such as changes in female employment) and focus on that. Doing so will make researching and writing your persuasive essay much more feasible. List of 113 Good Persuasive Essay Topics. Below are over 100 persuasive essay ideas, organized into ten categories.
What are the steps to write a persuasive essay? Start by picking a good topic that can easily be argued. Write the title and the hook sentence to grab the reader's attention. Jot down the main ...
The 5 Must-Have Steps of a Persuasive Essay. If you're intimidated by the idea of writing an argument, use this list to break your process into manageable chunks. Tackle researching and writing one element at a time, and then revise your essay so that it flows smoothly and coherently with every component in the optimal place. 1.
1. Teach Paragraph Writing FIRST. Before I even begin to think about teaching students to create an opinion piece, I make sure that my class has learned the basics of writing a good paragraph. We spend a lot of time with each component, and after they've mastered one paragraph, we move on to the five-paragraph essay.
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
1. Craft a Compelling Introduction: Your introduction is the first impression you make on your reader, so it's essential to capture their attention right from the start. Consider using a captivating anecdote, a thought-provoking question, or a shocking statistic to engage your audience and set the tone for your essay.
Here are the steps you need to take: Step 1: Create a Compelling Introduction. You want to hook your readers with a great opening for your persuasive essay, so they'll want to keep reading. Here are 3 tips for writing an attention-grabbing introduction for your next essay. Use a strong hook statement.
As you write your persuasive essay, remember that your goal is to get the reader to nod their head and agree with you. Each section of the essay should bring you closer to this goal. If you write the essay with this in mind, you'll end up with a paper that will receive high grades. Finally, if you're ever facing writer's block for your ...
Writing an essay for scholarship applications involves clearly illustrating your unique qualities, ambition, and the distinct perspective you will bring to the college. More than just ranting about your achievements, it requires you to tell a compelling story about yourself which accentuates your personality, drives, and ambitions. Here are some ideas: 1.
As persuasive essay writers, you can write it however you like, but to follow a traditional persuasive essay structure, use this basic layout to get an effective paper: An Introduction: You need a good hook to grab the reader's attention, a thesis statement presenting the main argument, and a roadmap of the essay, so they know what to expect.
Writing a compelling thesis statement for a persuasive essay is crucial, as it sets the tone and direction for the rest of your essay. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you craft an effective thesis statement: 1. Understand the Essay Prompt: Before crafting your thesis, ensure you thoroughly understand the essay prompt or question. This ...
Learn More. Note that the next section contains a sample written in accordance with this outline. Persuasive Essay Introduction. Hook: start with an intriguing sentence. Background: describe the context of the discussed issue and familiarize the reader with the argument. Definitions: if your essay dwells upon a theoretical subject matter, be sure to explain the complicated terms.
The efficacy of a persuasive essay largely hinges on how compelling and clear its strong thesis statement is. Without it, readers might be left unsure about the writer's intent or the purpose of the essay. Is a claim a thesis statement for a persuasive essay? Yes, in persuasive writing, the thesis statement is often referred to as a claim.
The effort it will take to make ChatGPT write an essay paragraph by paragraph is not worth getting caught cheating. But there are ethical ways it can help you along the way.
Essays are written due to various reasons and purposes. Some of the authors want to inform, some want to expose while some want to persuade. However, in descriptive essay writing, the essayist composes for the sake of displaying a picture out of his/her describing words.It may sound easy and simple but don't be deceived, there are still more to learn.
With the Business Writing Assessment, admissions teams at participating schools will gain valuable insights into how you synthesize and convey complex ideas.. Within a 30-minute timeframe, you will be tasked with analyzing a brief argument.Rather than sharing your personal perspective, the objective is to critique the argument's reasoning and evidence objectively and cohesively.