- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research

What is Field Research: Definition, Methods, Examples and Advantages
What is Field Research?
Field research is defined as a qualitative method of data collection that aims to observe, interact and understand people while they are in a natural environment. For example, nature conservationists observe behavior of animals in their natural surroundings and the way they react to certain scenarios. In the same way, social scientists conducting field research may conduct interviews or observe people from a distance to understand how they behave in a social environment and how they react to situations around them.
Learn more about: Market Research
Field research encompasses a diverse range of social research methods including direct observation, limited participation, analysis of documents and other information, informal interviews, surveys etc. Although field research is generally characterized as qualitative research, it often involves multiple aspects of quantitative research in it.
Field research typically begins in a specific setting although the end objective of the study is to observe and analyze the specific behavior of a subject in that setting. The cause and effect of a certain behavior, though, is tough to analyze due to presence of multiple variables in a natural environment. Most of the data collection is based not entirely on cause and effect but mostly on correlation. While field research looks for correlation, the small sample size makes it difficult to establish a causal relationship between two or more variables.
LEARN ABOUT: Best Data Collection Tools
Methods of Field Research
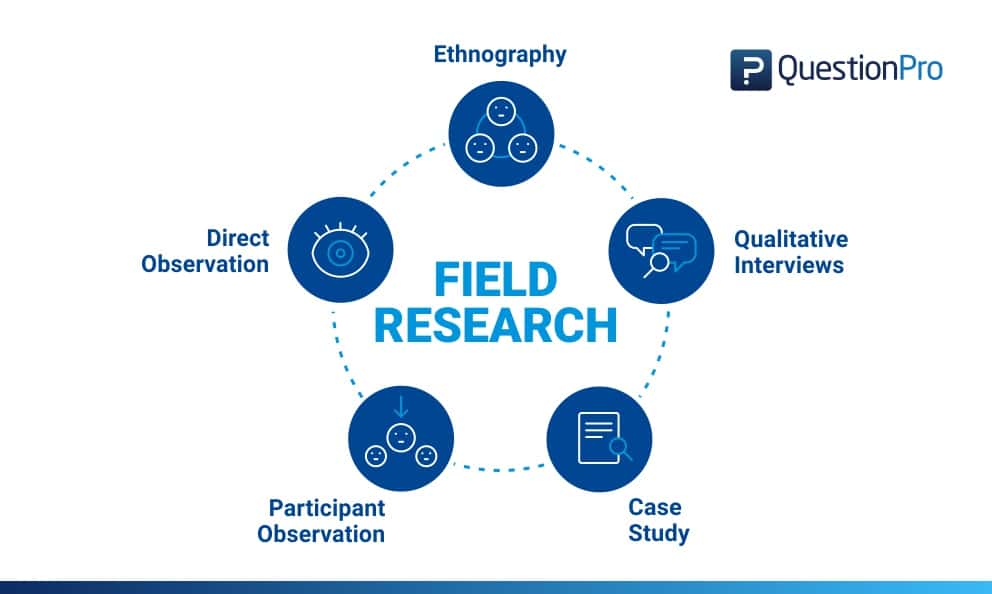
Field research is typically conducted in 5 distinctive methods. They are:
- Direct Observation
In this method, the data is collected via an observational method or subjects in a natural environment. In this method, the behavior or outcome of situation is not interfered in any way by the researcher. The advantage of direct observation is that it offers contextual data on people management , situations, interactions and the surroundings. This method of field research is widely used in a public setting or environment but not in a private environment as it raises an ethical dilemma.
- Participant Observation
In this method of field research, the researcher is deeply involved in the research process, not just purely as an observer, but also as a participant. This method too is conducted in a natural environment but the only difference is the researcher gets involved in the discussions and can mould the direction of the discussions. In this method, researchers live in a comfortable environment with the participants of the research design , to make them comfortable and open up to in-depth discussions.
- Ethnography
Ethnography is an expanded observation of social research and social perspective and the cultural values of an entire social setting. In ethnography, entire communities are observed objectively. For example, if a researcher would like to understand how an Amazon tribe lives their life and operates, he/she may chose to observe them or live amongst them and silently observe their day-to-day behavior.
LEARN ABOUT: Behavioral Targeting
- Qualitative Interviews
Qualitative interviews are close-ended questions that are asked directly to the research subjects. The qualitative interviews could be either informal and conversational, semi-structured, standardized and open-ended or a mix of all the above three. This provides a wealth of data to the researcher that they can sort through. This also helps collect relational data. This method of field research can use a mix of one-on-one interviews, focus groups and text analysis .
LEARN ABOUT: Qualitative Interview
A case study research is an in-depth analysis of a person, situation or event. This method may look difficult to operate, however, it is one of the simplest ways of conducting research as it involves a deep dive and thorough understanding the data collection methods and inferring the data.
Steps in Conducting Field Research
Due to the nature of field research, the magnitude of timelines and costs involved, field research can be very tough to plan, implement and measure. Some basic steps in the management of field research are:
- Build the Right Team: To be able to conduct field research, having the right team is important. The role of the researcher and any ancillary team members is very important and defining the tasks they have to carry out with defined relevant milestones is important. It is important that the upper management too is vested in the field research for its success.
- Recruiting People for the Study: The success of the field research depends on the people that the study is being conducted on. Using sampling methods , it is important to derive the people that will be a part of the study.
- Data Collection Methodology: As spoken in length about above, data collection methods for field research are varied. They could be a mix of surveys, interviews, case studies and observation. All these methods have to be chalked out and the milestones for each method too have to be chalked out at the outset. For example, in the case of a survey, the survey design is important that it is created and tested even before the research begins.
- Site Visit: A site visit is important to the success of the field research and it is always conducted outside of traditional locations and in the actual natural environment of the respondent/s. Hence, planning a site visit alongwith the methods of data collection is important.
- Data Analysis: Analysis of the data that is collected is important to validate the premise of the field research and decide the outcome of the field research.
- Communicating Results: Once the data is analyzed, it is important to communicate the results to the stakeholders of the research so that it could be actioned upon.
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
Field Research Notes
Keeping an ethnographic record is very important in conducting field research. Field notes make up one of the most important aspects of the ethnographic record. The process of field notes begins as the researcher is involved in the observational research process that is to be written down later.
Types of Field Research Notes
The four different kinds of field notes are:
- Job Notes: This method of taking notes is while the researcher is in the study. This could be in close proximity and in open sight with the subject in study. The notes here are short, concise and in condensed form that can be built on by the researcher later. Most researchers do not prefer this method though due to the fear of feeling that the respondent may not take them seriously.
- Field Notes Proper: These notes are to be expanded on immediately after the completion of events. The notes have to be detailed and the words have to be as close to possible as the subject being studied.
- Methodological Notes: These notes contain methods on the research methods used by the researcher, any new proposed research methods and the way to monitor their progress. Methodological notes can be kept with field notes or filed separately but they find their way to the end report of a study.
- Journals and Diaries: This method of field notes is an insight into the life of the researcher. This tracks all aspects of the researchers life and helps eliminate the Halo effect or any research bias that may have cropped up during the field research.
LEARN ABOUT: Causal Research
Reasons to Conduct Field Research
Field research has been commonly used in the 20th century in the social sciences. But in general, it takes a lot of time to conduct and complete, is expensive and in a lot of cases invasive. So why then is this commonly used and is preferred by researchers to validate data? We look at 4 major reasons:
- Overcoming lack of data: Field research resolves the major issue of gaps in data. Very often, there is limited to no data about a topic in study, especially in a specific environment analysis . The research problem might be known or suspected but there is no way to validate this without primary research and data. Conducting field research helps not only plug-in gaps in data but collect supporting material and hence is a preferred research method of researchers.
- Understanding context of the study: In many cases, the data collected is adequate but field research is still conducted. This helps gain insight into the existing data. For example, if the data states that horses from a stable farm generally win races because the horses are pedigreed and the stable owner hires the best jockeys. But conducting field research can throw light into other factors that influence the success like quality of fodder and care provided and conducive weather conditions.
- Increasing the quality of data: Since this research method uses more than one tool to collect data, the data is of higher quality. Inferences can be made from the data collected and can be statistically analyzed via the triangulation of data.
- Collecting ancillary data: Field research puts the researchers in a position of localized thinking which opens them new lines of thinking. This can help collect data that the study didn’t account to collect.
LEARN ABOUT: Behavioral Research
Examples of Field Research
Some examples of field research are:
- Decipher social metrics in a slum Purely by using observational methods and in-depth interviews, researchers can be part of a community to understand the social metrics and social hierarchy of a slum. This study can also understand the financial independence and day-to-day operational nuances of a slum. The analysis of this data can provide an insight into how different a slum is from structured societies.
- U nderstand the impact of sports on a child’s development This method of field research takes multiple years to conduct and the sample size can be very large. The data analysis of this research provides insights into how the kids of different geographical locations and backgrounds respond to sports and the impact of sports on their all round development.
- Study animal migration patterns Field research is used extensively to study flora and fauna. A major use case is scientists monitoring and studying animal migration patterns with the change of seasons. Field research helps collect data across years and that helps draw conclusions about how to safely expedite the safe passage of animals.
LEARN ABOUT: Social Communication Questionnaire
Advantages of Field Research
The advantages of field research are:
- It is conducted in a real-world and natural environment where there is no tampering of variables and the environment is not doctored.
- Due to the study being conducted in a comfortable environment, data can be collected even about ancillary topics.
- The researcher gains a deep understanding into the research subjects due to the proximity to them and hence the research is extensive, thorough and accurate.
Disadvantages of Field Research
The disadvantages of field research are:
- The studies are expensive and time-consuming and can take years to complete.
- It is very difficult for the researcher to distance themselves from a bias in the research study.
- The notes have to be exactly what the researcher says but the nomenclature is very tough to follow.
- It is an interpretive method and this is subjective and entirely dependent on the ability of the researcher.
- In this method, it is impossible to control external variables and this constantly alters the nature of the research.
LEARN ABOUT: 12 Best Tools for Researchers
MORE LIKE THIS

Zero Correlation: Definition, Examples + How to Determine It
Jul 1, 2024

When You Have Something Important to Say, You want to Shout it From the Rooftops
Jun 28, 2024

The Item I Failed to Leave Behind — Tuesday CX Thoughts
Jun 25, 2024

Feedback Loop: What It Is, Types & How It Works?
Jun 21, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
United States Institute of Peace
Home ▶ Publications
Getting to the Source: The Importance of Field Research
An academic and intellectual decline is inevitable without a post-pandemic revival of fieldwork.
By: Alastair Reed, Ph.D. ; Boglarka Bozsogi
Publication Type: Analysis
Travel restrictions and social distancing practices put in place in response to the COVID-19 pandemic have largely ground field research to a halt. Fieldwork plays an essential but often underappreciated role in both understanding violent extremism and developing policy responses to it. It is vital, therefore, that funders and policymakers support the return of such important work in a post-pandemic world.

Fieldwork brings important local perspectives to the fore, helping to contextualize conflicts within their wider ecosystems and societal and cultural realities. This forces researchers to challenge their preconceptions and theoretical assumptions as they come face to face with the realities on the ground. And, perhaps most importantly, fieldwork brings to life the human dimension — the human suffering and resilience of the communities affected by violence and the motivations and drivers of the violent actors.
Without understanding the view from the ground, we will continue to struggle to understand violent extremism and develop effective policy responses.
The Human Side
As many field researchers will admit, there is something about the smell and feel of a place that being on the ground provides and that reading reports and analyzing data cannot capture. On the ground, a researcher has the opportunity to diversify their primary sources and data. They can also better appreciate and absorb the context of the conflict. Without understanding the human side, the unique cultural and societal setting and the physical geography and climate, which together forge the contours within which the violence evolves, we can only have a partial understanding of the conflict ecosystem.
“The value of engagement with human beings cannot be underestimated,” Haroro Ingram, a senior research fellow at the Program on Extremism at George Washington University and member of the RESOLVE Research Advisory Council, told a recent RESOLVE Forum session.
Absorbing the context can help the researcher understand and interpret the collected data, but also to reinterpret what they learned from desk-based studies. The subjective experience of sharing is humbling; it offers an intellectual appreciation not only of the complexity on the ground but also of the breadth and depth of the literature and its gaps.
Researchers are only human and bring along preconceived perceptions, biases and assumptions — implicit or explicit — internalized from academic literature and media reports. Seeing the realities on the ground forces them to confront these preconceived assumptions and challenge, reinterpret or discard them. Theoretical explanations and conceptual analysis can only be tested when applied against the world they purport to explain. Field research gives us a chance to improve and develop our understanding, and a chance to glimpse the unknown unknowns, the missing factors that we cannot see or conceive from our academic ivory towers.
It is easy to overlook the human side — the victims of violence and conflict-affected communities that bear the brunt of the human tragedy of extremism — when researching a conflict from a distance. Observing and talking to the most affected communities reminds us of the horrors of war and the depths of depravity humanity can sink to. However, it also brings to light the human side of violent actors on all sides, an insight into the motivations and drivers that led them down the path to violence. Conflicts are ultimately about people; attempts to understand conflicts need to start with understanding the people that drive them. To do that, field researchers need to adopt a methodical approach, informed by the literature, and ensure their research and findings are triangulated, ethical and trustworthy.
“Mindanao, in the last 50 years, has experienced cycles of failed peace processes that international actors tried to support with a top-down understanding, often from a distance, in the absence of genuine bottom-up, grassroot perspectives,” said Ingram, who focuses his field research on the Middle East and Southeast Asia. “Since the most important actors in the grassroots population do not have electricity, let alone internet, the only effective outreach is getting to the source to build trust, engage with communities respectfully and learn of cultural subtleties through conversations. Collaborative effort, trust and the contribution to research can create actionable, nuanced and effective recommendations for policy and practice,” he added.
Contextual Understanding
Field research strengthens academic rigor, theories and methodologies, complements desk research and brings a different vantage point to understanding conflict. One constant risk in academic research is the tendency to be reductionist, and to focus on an isolated issue and miss the dynamic connections between it and its wider context. It can be appealing to zoom in on a particular violent extremist group and examine a singular aspect, such as ideology and group dynamics, rather than to see it as part of a complex ecosystem and dynamic processes. Conflict contexts often comprise multiple, interlinked armed actors, all influenced by and influencing each other. These contexts are further complicated by cross-cutting dynamics of ethnic, customary, kinship or religious dimensions.
Field research contextualizes the conflict and the issues that matter, helps understand drivers and motivations behind conflict actors and breaks free of embedded preconceptions. It can bring to life the unseen complexities: policemen fighting rebelling siblings, women fleeing insurgent cousins, parents losing children to armed groups, government officials persecuting family members as non-state actors. “People often said: ‘My brother joined that armed group, my cousin is in the police force,’” said Ingram, recalling conversations with locals in conflict areas that may seem, on the surface, to be absurd but that actually reflect a sober, clinical rational choice decision-making. Conflict ecosystems are invariably messy, counterintuitive and seemingly incomprehensible, yet remain the reality we seek to understand.
Sukanya Podder, defense studies senior lecturer at King’s College London and member of the RESOLVE Research Advisory Council, who also participated in the RESOLVE Forum session, conducted research in Mindanao, the Philippines, and Liberia where she focused on children and young people recruited into armed groups. Observing youth relationships with families and commanders in their communities, she was able to break free of preconceptions from media imagery and simplistic assumptions that children join community-based armed groups because they are drugged. Her fieldwork unearthed much more diverse motivations and choices: many children chose to join or decided to refrain of their own will.
Ethics and Safety
With any type of research, ethics and safety must be paramount. Fieldwork poses distinct challenges for each venue, context and participant. “Do no harm” should be the central principle of fieldwork planning to ensure the safety and integrity of researchers, respondents and their communities. Research fatigue is a growing issue that has negative implications on the quality of data. If respondents are wary about the benefits of research and are hesitant to participate, the authenticity of results is harder to determine. Researchers must be careful not to instrumentalize fieldwork and budget enough time and resources for in-depth quality research to produce authentic, reliable and valid data; this data should be periodically updated.
Getting approval from institutional review boards for fieldwork can often be challenging, and rightly so, but this rigor helps researchers address potential challenges and ensure the integrity of their research. While standards procedures, bureaucratic processes, reviews, clearances and preparations may seem taxing, they are indispensable for rich contributions of the highest integrity.
Strengthening Research and Policy
The effectiveness and ultimate success — however we choose to measure it — of policy approaches to countering violent extremism depend on a thorough understanding of the phenomenon they try to address. Sound research should be the rock on which good policy is built. Podder’s research in West Africa has informed disarmament, demobilization and reintegration programs with a nuanced understanding of the implications of different types of armed groups. Returnees from community-based armed groups or community defense groups found reintegration less problematic, as reconciliation could be locally administered through local, tribal judicial processes. Such findings from field research can avoid wasting money on programs that cannot yield the desired outcome.
Our understanding of violent extremism has benefitted from an interdisciplinary research field where each discipline and method, qualitative and quantitative, brings a new lens to gathering and analyzing data. Collectively, this cross-pollination of research methods has allowed us to see further than one approach alone ever could. Within a complementary and overlapping web of methods, fieldwork has an important but sometimes overlooked role to play. Without a post-pandemic revival of fieldwork, an academic and intellectual decline is inevitable.
Boglarka Bozsogi is executive coordination and network manager at the RESOLVE Network housed at USIP.
Related Publications

Israel and Hezbollah Change the Rules, Test Redlines — Will it lead to War?
Wednesday, June 26, 2024
By: Mona Yacoubian
Tensions between Israel and the Lebanese Shia militia Hezbollah are at their highest point since their 2006 war. They have exchanged tit-for-tat attacks since October, displacing tens of thousands from northern Israel and southern Lebanon. But in recent weeks, both sides have escalated the violence and rhetoric. USIP’s Mona Yacoubian looks at what’s driving this escalation, what each side is trying to tell the other and the diplomatic efforts underway to lower the temperature.
Type: Question and Answer
Conflict Analysis & Prevention

First Ladies of Peace: Women’s Role in Reducing Conflict in Africa
Tuesday, June 25, 2024
By: Fatoumatta Bah Barrow; Joyce Banda
Women have long been key partners and leaders in peace across Africa, and the African First Ladies Peace Mission (AFLPM) was created to help further women’s representation in promoting peace and security throughout the continent. Fatoumatta Bah Barrow, the first lady of The Gambia and the president of AFLPM, and former Malawi President Joyce Banda discuss how USIP and AFLPM are working together to reduce and prevent violent conflict.
Conflict Analysis & Prevention ; Gender

Gaza at the G7: The Daunting Divide between Rhetoric and Reality
Thursday, June 20, 2024
By: Lucy Kurtzer-Ellenbogen ; Robert Barron
The ongoing war in Gaza was only one of several items on the agenda for last week’s summit of leading Western economies, known as the Group of 7 (G7). But, given the global attention on Gaza and coming on the heels of the Biden administration’s most recent push to achieve a cease-fire — including sponsorship of a U.N. Security Council resolution toward that end — questions around the prospects for a negotiated pause in fighting and hostage agreement dominated the discussions.
Type: Analysis

Five Factors Shaping the Future of Egypt-Israel Relations
Thursday, June 13, 2024
By: Ambassador Hesham Youssef
The Gaza war has strained Egyptian-Israeli relations to an unprecedented level and raised questions about the future of their 1979 peace treaty that has been a cornerstone of Arab-Israeli peace. U.S. officials met recently in Cairo with their Israeli and Egyptian counterparts against a backdrop of mutually diminishing confidence between the two parties, particularly following Israel’s ground offensive in Rafah. This comes on the heels of a shooting incident between Israeli and Egyptian forces that left at least one Egyptian soldier dead, and Egypt joining South Africa’s case against Israel at the International Court of Justice (ICJ). Along with Qatar, Egypt is a key broker in the current Israel-Hamas cease-fire efforts and engages in extensive security cooperation with the U.S. and Israel.
Related Projects

RESOLVE Network; Researching Solutions to Violent Extremism
The RESOLVE Network is a global consortium of researchers and research organizations in agreement that factors contributing to community vulnerability and resilience to violent extremism are contextual.
Violent Extremism
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- About International Studies Review
- About the International Studies Association
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Article Contents
Introduction, what is fieldwork, purpose of fieldwork, physical safety, mental wellbeing and affect, ethical considerations, remote fieldwork, concluding thoughts, acknowledgments, funder information.
- < Previous
Field Research: A Graduate Student's Guide
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Ezgi Irgil, Anne-Kathrin Kreft, Myunghee Lee, Charmaine N Willis, Kelebogile Zvobgo, Field Research: A Graduate Student's Guide, International Studies Review , Volume 23, Issue 4, December 2021, Pages 1495–1517, https://doi.org/10.1093/isr/viab023
- Permissions Icon Permissions
What is field research? Is it just for qualitative scholars? Must it be done in a foreign country? How much time in the field is “enough”? A lack of disciplinary consensus on what constitutes “field research” or “fieldwork” has left graduate students in political science underinformed and thus underequipped to leverage site-intensive research to address issues of interest and urgency across the subfields. Uneven training in Ph.D. programs has also left early-career researchers underprepared for the logistics of fieldwork, from developing networks and effective sampling strategies to building respondents’ trust, and related issues of funding, physical safety, mental health, research ethics, and crisis response. Based on the experience of five junior scholars, this paper offers answers to questions that graduate students puzzle over, often without the benefit of others’ “lessons learned.” This practical guide engages theory and praxis, in support of an epistemologically and methodologically pluralistic discipline.
¿Qué es la investigación de campo? ¿Es solo para académicos cualitativos? ¿Debe realizarse en un país extranjero? ¿Cuánto tiempo en el terreno es “suficiente”? La falta de consenso disciplinario con respecto a qué constituye la “investigación de campo” o el “trabajo de campo” ha causado que los estudiantes de posgrado en ciencias políticas estén poco informados y, por lo tanto, capacitados de manera insuficiente para aprovechar la investigación exhaustiva en el sitio con el objetivo de abordar los asuntos urgentes y de interés en los subcampos. La capacitación desigual en los programas de doctorado también ha provocado que los investigadores en las primeras etapas de su carrera estén poco preparados para la logística del trabajo de campo, desde desarrollar redes y estrategias de muestreo efectivas hasta generar la confianza de las personas que facilitan la información, y las cuestiones relacionadas con la financiación, la seguridad física, la salud mental, la ética de la investigación y la respuesta a las situaciones de crisis. Con base en la experiencia de cinco académicos novatos, este artículo ofrece respuestas a las preguntas que desconciertan a los estudiantes de posgrado, a menudo, sin el beneficio de las “lecciones aprendidas” de otras personas. Esta guía práctica incluye teoría y praxis, en apoyo de una disciplina pluralista desde el punto de vista epistemológico y metodológico.
En quoi consiste la recherche de terain ? Est-elle uniquement réservée aux chercheurs qualitatifs ? Doit-elle être effectuée dans un pays étranger ? Combien de temps faut-il passer sur le terrain pour que ce soit « suffisant » ? Le manque de consensus disciplinaire sur ce qui constitue une « recherche de terrain » ou un « travail de terrain » a laissé les étudiants diplômés en sciences politiques sous-informés et donc sous-équipés pour tirer parti des recherches de terrain intensives afin d'aborder les questions d'intérêt et d'urgence dans les sous-domaines. L'inégalité de formation des programmes de doctorat a mené à une préparation insuffisante des chercheurs en début de carrière à la logistique du travail de terrain, qu'il s'agisse du développement de réseaux et de stratégies d’échantillonnage efficaces, de l'acquisition de la confiance des personnes interrogées ou des questions de financement, de sécurité physique, de santé mentale, d’éthique de recherche et de réponse aux crises qui y sont associées. Cet article s'appuie sur l'expérience de cinq jeunes chercheurs pour proposer des réponses aux questions que les étudiants diplômés se posent, souvent sans bénéficier des « enseignements tirés » par les autres. Ce guide pratique engage théorie et pratique en soutien à une discipline épistémologiquement et méthodologiquement pluraliste.
Days before embarking on her first field research trip, a Ph.D. student worries about whether she will be able to collect the qualitative data that she needs for her dissertation. Despite sending dozens of emails, she has received only a handful of responses to her interview requests. She wonders if she will be able to gain more traction in-country. Meanwhile, in the midst of drafting her thesis proposal, an M.A. student speculates about the feasibility of his project, given a modest budget. Thousands of miles away from home, a postdoc is concerned about their safety, as protests erupt outside their window and state security forces descend into the streets.
These anecdotes provide a small glimpse into the concerns of early-career researchers undertaking significant projects with a field research component. Many of these fieldwork-related concerns arise from an unfortunate shortage in curricular offerings for qualitative and mixed-method research in political science graduate programs ( Emmons and Moravcsik 2020 ), 1 as well as the scarcity of instructional materials for qualitative and mixed-method research, relative to those available for quantitative research ( Elman, Kapiszewski, and Kirilova 2015 ; Kapiszewski, MacLean, and Read 2015 ; Mosley 2013 ). A recent survey among the leading United States Political Science programs in Comparative Politics and International Relations found that among graduate students who have carried out international fieldwork, 62 percent had not received any formal fieldwork training and only 20 percent felt very or mostly prepared for their fieldwork ( Schwartz and Cronin-Furman 2020 , 7–8). This shortfall in training and instruction means that many young researchers are underprepared for the logistics of fieldwork, from developing networks and effective sampling strategies to building respondents’ trust. In addition, there is a notable lack of preparation around issues of funding, physical safety, mental health, research ethics, and crisis response. This is troubling, as field research is highly valued and, in some parts of the field, it is all but expected, for instance in comparative politics.
Beyond subfield-specific expectations, research that leverages multiple types of data and methods, including fieldwork, is one of the ways that scholars throughout the discipline can more fully answer questions of interest and urgency. Indeed, multimethod work, a critical means by which scholars can parse and evaluate causal pathways, is on the rise ( Weller and Barnes 2016 ). The growing appearance of multimethod research in leading journals and university presses makes adequate training and preparation all the more significant ( Seawright 2016 ; Nexon 2019 ).
We are five political scientists interested in providing graduate students and other early-career researchers helpful resources for field research that we lacked when we first began our work. Each of us has recently completed or will soon complete a Ph.D. at a United States or Swedish university, though we come from many different national backgrounds. We have conducted field research in our home countries and abroad. From Colombia and Guatemala to the United States, from Europe to Turkey, and throughout East and Southeast Asia, we have spanned the globe to investigate civil society activism and transitional justice in post-violence societies, conflict-related sexual violence, social movements, authoritarianism and contentious politics, and the everyday politics and interactions between refugees and host-country citizens.
While some of us have studied in departments that offer strong training in field research methods, most of us have had to self-teach, learning through trial and error. Some of us have also been fortunate to participate in short courses and workshops hosted by universities such as the Consortium for Qualitative Research Methods and interdisciplinary institutions such as the Peace Research Institute Oslo. Recognizing that these opportunities are not available to or feasible for all, and hoping to ease the concerns of our more junior colleagues, we decided to compile our experiences and recommendations for first-time field researchers.
Our experiences in the field differ in several key respects, from the time we spent in the field to the locations we visited, and how we conducted our research. The diversity of our experiences, we hope, will help us reach and assist the broadest possible swath of graduate students interested in field research. Some of us have spent as little as ten days in a given country or as much as several months, in some instances visiting a given field site location just once and in other instances returning several times. At times, we have been able to plan weeks and months in advance. Other times, we have quickly arranged focus groups and impromptu interviews. Other times still, we have completed interviews virtually, when research participants were in remote locations or when we ourselves were unable to travel, of note during the coronavirus pandemic. We have worked in countries where we are fluent or have professional proficiency in the language, and in countries where we have relied on interpreters. We have worked in settings with precarious security as well as in locations that feel as comfortable as home. Our guide is not intended to be prescriptive or exhaustive. What we offer is a set of experience-based suggestions to be implemented as deemed relevant and appropriate by the researcher and their advisor(s).
In terms of the types of research and data sources and collection, we have conducted archival research, interviews, focus groups, and ethnographies with diplomats, bureaucrats, military personnel, ex-combatants, civil society advocates, survivors of political violence, refugees, and ordinary citizens. We have grappled with ethical dilemmas, chief among them how to get useful data for our research projects in ways that exceed the minimal standards of human subjects’ research evaluation panels. Relatedly, we have contemplated how to use our platforms to give back to the individuals and communities who have so generously lent us their time and knowledge, and shared with us their personal and sometimes harrowing stories.
Our target audience is first and foremost graduate students and early-career researchers who are interested in possibly conducting fieldwork but who either (1) do not know the full potential or value of fieldwork, (2) know the potential and value of fieldwork but think that it is excessively cost-prohibitive or otherwise infeasible, or (3) who have the interest, the will, and the means but not necessarily the know-how. We also hope that this resource will be of value to graduate programs, as they endeavor to better support students interested in or already conducting field research. Further, we target instructional faculty and graduate advisors (and other institutional gatekeepers like journal and book reviewers), to show that fieldwork does not have to be year-long, to give just one example. Instead, the length of time spent in the field is a function of the aims and scope of a given project. We also seek to formalize and normalize the idea of remote field research, whether conducted because of security concerns in conflict zones, for instance, or because of health and safety concerns, like the Covid-19 pandemic. Accordingly, researchers in the field for shorter stints or who conduct fieldwork remotely should not be penalized.
We note that several excellent resources on fieldwork such as the bibliography compiled by Advancing Conflict Research (2020) catalogue an impressive list of articles addressing questions such as ethics, safety, mental health, reflexivity, and methods. Further resources can be found about the positionality of the researcher in the field while engaging vulnerable communities, such as in the research field of migration ( Jacobsen and Landau 2003 ; Carling, Bivand Erdal, and Ezzati 2014 ; Nowicka and Cieslik 2014 ; Zapata-Barrero and Yalaz 2019 ). However, little has been written beyond conflict-affected contexts, fragile settings, and vulnerable communities. Moreover, as we consulted different texts and resources, we found no comprehensive guide to fieldwork explicitly written with graduate students in mind. It is this gap that we aim to fill.
In this paper, we address five general categories of questions that graduate students puzzle over, often without the benefit of others’ “lessons learned.” First, What is field research? Is it just for qualitative scholars? Must it be conducted in a foreign country? How much time in the field is “enough”? Second, What is the purpose of fieldwork? When does it make sense to travel to a field site to collect data? How can fieldwork data be used? Third, What are the nuts and bolts? How does one get ready and how can one optimize limited time and financial resources? Fourth, How does one conduct fieldwork safely? What should a researcher do to keep themselves, research assistants, and research subjects safe? What measures should they take to protect their mental health? Fifth, How does one conduct ethical, beneficent field research?
Finally, the Covid-19 pandemic has impressed upon the discipline the volatility of research projects centered around in-person fieldwork. Lockdowns and closed borders left researchers sequestered at home and unable to travel, forced others to cut short any trips already begun, and unexpectedly confined others still to their fieldwork sites. Other factors that may necessitate a (spontaneous) readjustment of planned field research include natural disasters, a deteriorating security situation in the field site, researcher illness, and unexpected changes in personal circumstances. We, therefore, conclude with a section on the promise and potential pitfalls of remote (or virtual) fieldwork. Throughout this guide, we engage theory and praxis to support an epistemologically and methodologically pluralistic discipline.
The concept of “fieldwork” is not well defined in political science. While several symposia discuss the “nuts and bolts” of conducting research in the field within the pages of political science journals, few ever define it ( Ortbals and Rincker 2009 ; Hsueh, Jensenius, and Newsome 2014 ). Defining the concept of fieldwork is important because assumptions about what it is and what it is not underpin any suggestions for conducting it. A lack of disciplinary consensus about what constitutes “fieldwork,” we believe, explains the lack of a unified definition. Below, we discuss three areas of current disagreement about what “fieldwork” is, including the purpose of fieldwork, where it occurs, and how long it should be. We follow this by offering our definition of fieldwork.
First, we find that many in the discipline view fieldwork as squarely in the domain of qualitative research, whether interpretivist or positivist. However, field research can also serve quantitative projects—for example, by providing crucial context, supporting triangulation, or illustrating causal mechanisms. For instance, Kreft (2019) elaborated her theory of women's civil society mobilization in response to conflict-related sexual violence based on interviews she carried out in Colombia. She then examined cross-national patterns through statistical analysis. Conversely, Willis's research on the United States military in East Asia began with quantitative data collection and analysis of protest events before turning to fieldwork to understand why protests occurred in some instances but not others. Researchers can also find quantifiable data in the field that is otherwise unavailable to them at home ( Read 2006 ; Chambers-Ju 2014 ; Jensenius 2014 ). Accordingly, fieldwork is not in the domain of any particular epistemology or methodology as its purpose is to acquire data for further information.
Second, comparative politics and international relations scholars often opine that fieldwork requires leaving the country in which one's institution is based. Instead, we propose that what matters most is the nature of the research project, not the locale. For instance, some of us in the international relations subfield have interviewed representatives of intergovernmental organizations (IGOs) and international nongovernmental organizations (INGOs), whose headquarters are generally located in Global North countries. For someone pursuing a Ph.D. in the United States and writing on transnational advocacy networks, interviews with INGO representatives in New York certainly count as fieldwork ( Zvobgo 2020 ). Similarly, a graduate student who returns to her home country to interview refugees and native citizens is conducting a field study as much as a researcher for whom the context is wholly foreign. Such interviews can provide necessary insights and information that would not have been gained otherwise—one of the key reasons researchers conduct fieldwork in the first place. In other instances, conducting any in-person research is simply not possible, due to financial constraints, safety concerns, or other reasons. For example, the Covid-19 pandemic has forced many researchers to shift their face-to-face research plans to remote data collection, either over the phone or virtually ( Howlett 2021 , 2). For some research projects, gathering data through remote methods may yield the same if not similar information than in-person research ( Howlett 2021 , 3–4). As Howlett (2021 , 11) notes, digital platforms may offer researchers the ability to “embed ourselves in other contexts from a distance” and glimpse into our subjects’ lives in ways similar to in-person research. By adopting a broader definition of fieldwork, researchers can be more flexible in getting access to data sources and interacting with research subjects.
Third, there is a tendency, especially among comparativists, to only count fieldwork that spans the better part of a year; even “surgical strike” field research entails one to three months, according to some scholars ( Ortbals and Rincker 2009 ; Weiss, Hicken, and Kuhonta 2017 ). The emphasis on spending as much time as possible in the field is likely due to ethnographic research traditions, reflected in classics such as James Scott's Weapons of the Weak , which entail year-long stints of research. However, we suggest that the appropriate amount of time in the field should be assessed on a project-by-project basis. Some studies require the researcher to be in the field for long periods; others do not. For example, Willis's research on the discourse around the United States’ military presence in overseas host communities has required months in the field. By contrast, Kreft only needed ten days in New York to carry out interviews with diplomats and United Nations staff, in a context with which she already had some familiarity from a prior internship. Likewise, Zvobgo spent a couple of weeks in her field research sites, conducting interviews with directors and managers of prominent human rights nongovernmental organizations. This population is not so large as to require a whole month or even a few months. This has also been the case for Irgil, as she had spent one month in the field site conducting interviews with ordinary citizens. The goal of the project was to acquire information on citizens’ perceptions of refugees. As we discuss in the next section, when deciding how long to spend in the field, scholars must consider the information their project requires and consider the practicalities of fieldwork, notably cost.
Thus, we highlight three essential points in fieldwork and offer a definition accordingly: fieldwork involves acquiring information, using any set of appropriate data collection techniques, for qualitative, quantitative, or experimental analysis through embedded research whose location and duration is dependent on the project. We argue that adopting such a definition of “fieldwork” is necessary to include the multitude of forms fieldwork can take, including remote methods, whose value and challenges the Covid-19 pandemic has impressed upon the discipline.
When does a researcher need to conduct fieldwork? Fieldwork can be effective for (1) data collection, (2) theory building, and (3) theory testing. First, when a researcher is interested in a research topic, yet they could not find an available and/or reliable data source for the topic, fieldwork could provide the researcher with plenty of options. Some research agendas can require researchers to visit archives to review historical documents. For example, Greitens (2016) visited national archives in the Philippines, South Korea, Taiwan, and the United States to find historical documents about the development of coercive institutions in past authoritarian governments for her book, Dictators and Their Secret Police . Also, newly declassified archival documents can open new possibilities for researchers to examine restricted topics. To illustrate, thanks to the newly released archival records of the Chinese Communist Party's communications, and exchange of visits with the European communist world, Sarotte (2012) was able to study the Party's decision to crack down on Tiananmen protesters, which had previously been deemed as an unstudiable topic due to the limited data.
Other research agendas can require researchers to conduct (semistructured) in-depth interviews to understand human behavior or a situation more closely, for example, by revealing the meanings of concepts for people and showing how people perceive the world. For example, O'Brien and Li (2005) conducted in-depth interviews with activists, elites, and villagers to understand how these actors interact with each other and what are the outcomes of the interaction in contentious movements in rural China. Through research, they revealed that protests have deeply influenced all these actors’ minds, a fact not directly observable without in-depth interviews.
Finally, data collection through fieldwork should not be confined to qualitative data ( Jensenius 2014 ). While some quantitative datasets can be easily compiled or accessed through use of the internet or contact with data-collection agencies, other datasets can only be built or obtained through relationships with “gatekeepers” such as government officials, and thus require researchers to visit the field ( Jensenius 2014 ). Researchers can even collect their own quantitative datasets by launching surveys or quantifying data contained in archives. In a nutshell, fieldwork will allow researchers to use different techniques to collect and access original/primary data sources, whether these are qualitative, quantitative, or experimental in nature, and regardless of the intended method of analysis. 2
But fieldwork is not just for data collection as such. Researchers can accomplish two other fundamental elements of the research process: theory building and theory testing. When a researcher finds a case where existing theories about a phenomenon do not provide plausible explanations, they can build a theory through fieldwork ( Geddes 2003 ). Lee's experience provides a good example. When studying the rise of a protest movement in South Korea for her dissertation, Lee applied commonly discussed social movement theories, grievances, political opportunity, resource mobilization, and repression, to explain the movement's eruption and found that these theories do not offer a convincing explanation for the protest movement. She then moved on to fieldwork and conducted interviews with the movement participants to understand their motivations. Finally, through those interviews, she offered an alternative theory that the protest participants’ collective identity shaped during the authoritarian past played a unifying factor and eventually led them to participate in the movement. Her example shows that theorization can take place through careful review and rigorous inference during fieldwork.
Moreover, researchers can test their theory through fieldwork. Quantitative observational data has limitations in revealing causal mechanisms ( Esarey 2017 ). Therefore, many political scientists turn their attention to conducting field experiments or lab-in-the-field experiments to reveal causality ( Druckman et al. 2006 ; Beath, Christia, and Enikolopov 2013 ; Finseraas and Kotsadam 2017 ), or to leveraging in-depth insights or historical records gained through qualitative or archival research in process-tracing ( Collier 2011 ; Ricks and Liu 2018 ). Surveys and survey experiments may also be useful tools to substantiate a theoretical story or test a theory ( Marston 2020 ). Of course, for most Ph.D. students, especially those not affiliated with more extensive research projects, some of these options will be financially prohibitive.
A central concern for graduate students, especially those working with a small budget and limited time, is optimizing time in the field and integrating remote work. We offer three pieces of advice: have a plan, build in flexibility, and be strategic, focusing on collecting data that are unavailable at home. We also discuss working with local translators or research assistants. Before we turn to these more practical issues arising during fieldwork, we address a no less important issue: funding.
The challenge of securing funds is often overlooked in discussions of what constitutes field research. Months- or year-long in-person research can be cost-prohibitive, something academic gatekeepers must consider when evaluating “what counts” and “what is enough.” Unlike their predecessors, many graduate students today have a significant amount of debt and little savings. 3 Additionally, if researchers are not able to procure funding, they have to pay out of pocket and possibly take on more debt. Not only is in-person fieldwork costly, but researchers may also have to forego working while they are in the field, making long stretches in the field infeasible for some.
For researchers whose fieldwork involves travelling to another location, procuring funding via grants, fellowships, or other sources is a necessity, regardless of how long one plans to be in the field. A good mantra for applying for research funding is “apply early and often” ( Kelsky 2015 , 110). Funding applications take a considerable amount of time to prepare, from writing research statements to requesting letters of recommendation. Even adapting one's materials for different applications takes time. Not only is the application process itself time-consuming, but the time between applying for and receiving funds, if successful, can be quite long, from several months to a year. For example, after defending her prospectus in May 2019, Willis began applying to funding sources for her dissertation, all of which had deadlines between June and September. She received notifications between November and January; however, funds from her successful applications were not available until March and April, almost a year later. 4 Accordingly, we recommend applying for funding as early as possible; this not only increases one's chances of hitting the ground running in the field, but the application process can also help clarify the goals and parameters of one's research.
Graduate students should also apply often for funding opportunities. There are different types of funding for fieldwork: some are larger, more competitive grants such as the National Science Foundation Political Science Doctoral Dissertation Improvement Grant in the United States, others, including sources through one's own institution, are smaller. Some countries, like Sweden, boast a plethora of smaller funding agencies that disburse grants of 20,000–30,0000 Swedish Kronor (approx. 2,500–3,500 U.S. dollars) to Ph.D. students in the social sciences. Listings of potential funding sources are often found on various websites including those belonging to universities, professional organizations (such as the American Political Science Association or the European Consortium for Political Research), and governmental institutions dealing with foreign affairs. Once you have identified fellowships and grants for which you and your project are a good match, we highly recommend soliciting information and advice from colleagues who have successfully applied for them. This can include asking them to share their applications with you, and if possible, to have them, another colleague or set of colleagues read through your project description and research plan (especially for bigger awards) to ensure that you have made the best possible case for why you should be selected. While both large and small pots of funding are worth applying for, many researchers end up funding their fieldwork through several small grants or fellowships. One small award may not be sufficient to fund the entirety of one's fieldwork, but several may. For example, Willis's fieldwork in Japan and South Korea was supported through fellowships within each country. Similarly, Irgil was able to conduct her fieldwork abroad through two different and relatively smaller grants by applying to them each year.
Of course, situations vary in different countries with respect to what kinds of grants from what kinds of funders are available. An essential part of preparing for fieldwork is researching the funding landscape well in advance, even as early as the start of the Ph.D. We encourage first-time field researchers to be aware that universities and departments may themselves not be aware of the full range of possible funds available, so it is always a good idea to do your own research and watch research-related social media channels. The amount of funding needed thereby depends on the nature of one's project and how long one intends to be in the field. As we elaborate in the next section, scholars should think carefully about their project goals, the data required to meet those goals, and the requisite time to attain them. For some projects, even a couple of weeks in the field is sufficient to get the needed information.
Preparing to Enter “the field”
It is important to prepare for the field as much as possible. What kind of preparations do researchers need? For someone conducting interviews with NGO representatives, this might involve identifying the largest possible pool of potential respondents, securing their contact information, sending them study invitation letters, finding a mutually agreeable time to meet, and pulling together short biographies for each interviewee in order to use your time together most effectively. If you plan to travel to conduct interviews, you should reach out to potential respondents roughly four to six weeks prior to your arrival. For individuals who do not respond, you can follow up one to two weeks before you arrive and, if needed, once more when you are there. This is still no guarantee for success, of course. For Kreft, contacting potential interviewees in Colombia initially proved more challenging than anticipated, as many of the people she targeted did not respond to her emails. It turned out that many Colombians have a preference for communicating via phone or, in particular, WhatsApp. Some of those who responded to her emails sent in advance of her field trip asked her to simply be in touch once she was in the country, to set up appointments on short notice. This made planning and arranging her interview schedule more complicated. Therefore, a general piece of advice is to research your target population's preferred communication channels and mediums in the field site if email requests yield no or few responses.
In general, we note for the reader that contacting potential research participants should come after one has designed an interview questionnaire (plus an informed consent protocol) and sought and received, where applicable, approval from institutional review boards (IRBs) or other ethical review procedures in place (both at one's home institution/in the country of the home institution as well as in the country where one plans to conduct research if travelling abroad). The most obvious advantage of having the interview questionnaire in place and having secured all necessary institutional approvals before you start contacting potential interviewees is that you have a clearer idea of the universe of individuals you would like to interview, and for what purpose. Therefore, it is better to start sooner rather than later and be mindful of “high seasons,” when institutional and ethical review boards are receiving, processing, and making decisions on numerous proposals. It may take a few months for them to issue approvals.
On the subject of ethics and review panels, we encourage you to consider talking openly and honestly with your supervisors and/or funders about the situations where a written consent form may not be suitable and might need to be replaced with “verbal consent.” For instance, doing fieldwork in politically unstable contexts, highly scrutinized environments, or vulnerable communities, like refugees, might create obstacles for the interviewees as well as the researcher. The literature discusses the dilemma in offering the interviewees anonymity and requesting signed written consent in addition to the emphasis on total confidentiality ( Jacobsen and Landau 2003 ; Mackenzie, McDowell, and Pittaway 2007 ; Saunders, Kitzinger, and Kitzinger 2015 ). Therefore, in those situations, the researcher might need to take the initiative on how to act while doing the interviews as rigorously as possible. In her fieldwork, Irgil faced this situation as the political context of Turkey did not guarantee that there would not be any adverse consequences for interviewees on both sides of her story: citizens of Turkey and Syrian refugees. Consequently, she took hand-written notes and asked interviewees for their verbal consent in a safe interview atmosphere. This is something respondents greatly appreciated ( Irgil 2020 ).
Ethical considerations, of course, also affect the research design itself, with ramifications for fieldwork. When Kreft began developing her Ph.D. proposal to study women's political and civil society mobilization in response to conflict-related sexual violence, she initially aimed to recruit interviewees from the universe of victims of this violence, to examine variation among those who did and those who did not mobilize politically. As a result of deeper engagement with the literature on researching conflict-related sexual violence, conversations with senior colleagues who had interviewed victims, and critical self-reflection of her status as a researcher (with no background in psychology or social work), she decided to change focus and shift toward representatives of civil society organizations and victims’ associations. This constituted a major reconfiguration of her research design, from one geared toward identifying the factors that drive mobilization of victims toward using insights from interviews to understand better how those mobilize perceive and “make sense” of conflict-related sexual violence. Needless to say, this required alterations to research strategies and interview guides, including reassessing her planned fieldwork. Kreft's primary consideration was not to cause harm to her research participants, particularly in the form of re-traumatization. She opted to speak only with those women who on account of their work are used to speaking about conflict-related sexual violence. In no instance did she inquire about interviewees’ personal experiences with sexual violence, although several brought this up on their own during the interviews.
Finally, if you are conducting research in another country where you have less-than-professional fluency in the language, pre-fieldwork planning should include hiring a translator or research assistant, for example, through an online hiring platform like Upwork, or a local university. Your national embassy or consulate is another option; many diplomatic offices have lists of individuals who they have previously contracted. More generally, establishing contact with a local university can be beneficial, either in the form of a visiting researcher arrangement, which grants access to research groups and facilities like libraries or informally contacting individual researchers. The latter may have valuable insights into the local context, contacts to potential research participants, and they may even be able to recommend translators or research assistants. Kreft, for example, hired local research assistants recommended by researchers at a Bogotá-based university and remunerated them equivalent to the salary they would have received as graduate research assistants at the university, while also covering necessary travel expenses. Irgil, on the other hand, established contacts with native citizens and Syrian gatekeepers, who are shop owners in the area where she conducted her research because she had the opportunity to visit the fieldwork site multiple times.
Depending on the research agenda, researchers may visit national archives, local government offices, etc. Before visiting, researchers should contact these facilities and make sure the materials that they need are accessible. For example, Lee visited the Ronald Reagan Presidential Library Archives to find the United States’ strategic evaluations on South Korea's dictator in the 1980s. Before her visit, she contacted librarians in the archives, telling them her visit plans and her research purpose. Librarians made suggestions on which categories she should start to review based on her research goal, and thus she was able to make a list of categories of the materials she needed, saving her a lot of her time.
Accessibility of and access to certain facilities/libraries can differ depending on locations/countries and types of facilities. Facilities in authoritarian countries might not be easily accessible to foreign researchers. Within democratic countries, some facilities are more restrictive than others. Situations like the pandemic or national holidays can also restrict accessibility. Therefore, researchers are well advised to do preliminary research on whether a certain facility opens during the time they visit and is accessible to researchers regardless of their citizenship status. Moreover, researchers must contact the staff of facilities to know whether identity verification is needed and if so, what kind of documents (photo I.D. or passport) should be exhibited.
Adapting to the Reality of the Field
Researchers need to be flexible because you may meet people you did not make appointments with, come across opportunities you did not expect, or stumble upon new ideas about collecting data in the field. These happenings will enrich your field experience and will ultimately be beneficial for your research. Similarly, researchers should not be discouraged by interviews that do not go according to plan; they present an opportunity to pursue relevant people who can provide an alternative path to your work. Note that planning ahead does not preclude fortuitous encounters or epiphanies. Rather, it provides a structure for them to happen.
If your fieldwork entails travelling abroad, you will also be able to recruit more interviewees once you arrive at your research site. In fact, you may have greater success in-country; not everyone is willing to respond to a cold email from an unknown researcher in a foreign country. In Irgil's fieldwork, she contacted store owners that are known in the area and who know the community. This eased her process of introduction into the community and recruiting interviewees. For Zvobgo, she had fewer than a dozen interviews scheduled when she travelled to Guatemala to study civil society activism and transitional justice since the internal armed conflict. But she was able to recruit additional participants in-country. Interviewees with whom she built a rapport connected her to other NGOs, government offices, and the United Nations country office, sometimes even making the call and scheduling interviews for her. Through snowball sampling, she was able to triple the number of participants. Likewise, snowball sampling was central to Kreft's recruitment of interview partners. Several of her interviewees connected her to highly relevant individuals she would never have been able to identify and contact based on web searches alone.
While in the field, you may nonetheless encounter obstacles that necessitate adjustments to your original plans. Once Kreft had arrived in Colombia, for example, it transpired quickly that carrying out in-person interviews in more remote/rural areas was near impossible given her means, as these were not easily accessible by bus/coach, further complicated by a complex security situation. Instead, she adjusted her research design and shifted her focus to the big cities, where most of the major civil society organizations are based. She complemented the in-person interviews carried out there with a smaller number of phone interviews with civil society activists in rural areas, and she was also able to meet a few activists operating in rural or otherwise inaccessible areas as they were visiting the major cities. The resulting focus on urban settings changed the kinds of generalizations she was able to make based on her fieldwork data and produced a somewhat different study than initially anticipated.
This also has been the case for Irgil, despite her prior arrangements with the Syrian gatekeepers, which required adjustments as in the case of Kreft. Irgil acquired research clearance one year before, during the interviews with native citizens, conducting the interviews with Syrian refugees. She also had her questionnaire ready based on the previously collected data and the media search she had conducted for over a year before travelling to the field site. As she was able to visit the field site multiple times, two months before conducting interviews with Syrian refugees, she developed a schedule with the Syrian gatekeepers and informants. Yet, once she was in the field, influenced by Turkey's recent political events and the policy of increasing control over Syrian refugees, half of the previously agreed informants changed their minds or did not want to participate in interviews. As Irgil was following the policies and the news related to Syrian refugees in Turkey closely, this did not come as that big of a surprise but challenged the previously developed strategy to recruit interviewees. Thus, she changed the strategy of finding interviewees in the field site, such as asking people, almost one by one, whether they would like to participate in the interview. Eventually, she could not find willing Syrian women refugees as she had planned, which resulted in a male-dominant sample. As researchers encounter such situations, it is essential to remind oneself that not everything can go according to plan, that “different” does not equate to “worse,” but that it is important to consider what changes to fieldwork data collection and sampling imply for the study's overall findings and the contribution it makes to the literature.
We should note that conducting interviews is very taxing—especially when opportunities multiply, as in Zvobgo's case. Depending on the project, each interview can take an hour, if not two or more. Hence, you should make a reasonable schedule: we recommend no more than two interviews per day. You do not want to have to cut off an interview because you need to rush to another one, whether the interviews are in-person or remote. And you do not want to be too exhausted to have a robust engagement with your respondent who is generously lending you their time. Limiting the number of interviews per day is also important to ensure that you can write comprehensive and meaningful fieldnotes, which becomes even more essential where it is not possible to audio-record your interviews. Also, be sure to remember to eat, stay hydrated, and try to get enough sleep.
Finally, whether to provide gifts or payments to the subject also requires adapting to the reality of the field. You must think about payments beforehand when you apply for IRB approval (or whatever other ethical review processes may be in place) since these applications usually contain questions about payments. Obviously, the first step is to carefully evaluate whether the gifts and payments provided can harm the subject or are likely to unduly affect the responses they will give in response to your questions. If that is not the case, you have to make payment decisions based on your budget, field situation, and difficulties in recruitment. Usually, payment of respondents is more common in survey research, whereas it is less common in interviews and focus groups.
Nevertheless, payment practices vary depending on the field and the target group. In some cases, it may become a custom to provide small gifts or payments when interviewing a certain group. In other cases, interviewees might be offended if they are provided with money. Therefore, knowing past practices and field situations is important. For example, Lee provided small coffee gift cards to one group while she did not to the other based on previous practices of other researchers. That is, for a particular group, it has become a custom for interviewers to pay interviewees. Sometimes, you may want to reimburse your subject's interview costs such as travel expenses and provide beverages and snacks during the conduct of research, as Kreft did when conducting focus groups in Colombia. To express your gratitude to your respondents, you can prepare small gifts such as your university memorabilia (e.g., notebooks and pens). Since past practices about payments can affect your interactions and interviews with a target group, you want to seek advice from your colleagues and other researchers who had experiences interacting with the target group. If you cannot find researchers who have this knowledge, you can search for published works on the target population to find if the authors share their interview experiences. You may also consider contacting the authors for advice before your interviews.
Researching Strategically
Distinguishing between things that can only be done in person at a particular site and things that can be accomplished later at home is vital. Prioritize the former over the latter. Lee's fieldwork experience serves as a good example. She studied a conservative protest movement called the Taegeukgi Rally in South Korea. She planned to conduct interviews with the rally participants to examine their motivations for participating. But she only had one month in South Korea. So, she focused on things that could only be done in the field: she went to the rally sites, she observed how protests proceeded, which tactics and chants were used, and she met participants and had some casual conversations with them. Then, she used the contacts she made while attending the rallies to create a social network to solicit interviews from ordinary protesters, her target population. She was able to recruit twenty-five interviewees through good rapport with the people she met. The actual interviews proceeded via phone after she returned to the United States. In a nutshell, we advise you not to be obsessed with finishing interviews in the field. Sometimes, it is more beneficial to use your time in the field to build relationships and networks.
Working With Assistants and Translators
A final consideration on logistics is working with research assistants or translators; it affects how you can carry out interviews, focus groups, etc. To what extent constant back-and-forth translation is necessary or advisable depends on the researcher's skills in the interview language and considerations about time and efficiency. For example, Kreft soon realized that she was generally able to follow along quite well during her interviews in Colombia. In order to avoid precious time being lost to translation, she had her research assistant follow the interview guide Kreft had developed, and interjected follow-up questions in Spanish or English (then to be translated) as they arose.
Irgil's and Zvobgo's interviews went a little differently. Irgil's Syrian refugee interviewees in Turkey were native Arabic speakers, and Zvobgo's interviewees in Guatemala were native Spanish speakers. Both Irgil and Zvobgo worked with research assistants. In Irgil's case, her assistant was a Syrian man, who was outside of the area. Meanwhile, Zvobgo's assistant was an undergraduate from her home institution with a Spanish language background. Irgil and Zvobgo began preparing their assistants a couple of months before entering the field, over Skype for Irgil and in-person for Zvobgo. They offered their assistants readings and other resources to provide them with the necessary background to work well. Both Irgil and Zvobgo's research assistants joined them in the interviews and actually did most of the speaking, introducing the principal investigator, explaining the research, and then asking the questions. In Zvobgo's case, interviewee responses were relayed via a professional interpreter whom she had also hired. After every interview, Irgil and Zvobgo and their respective assistants discussed the answers of the interviewees, potential improvements in phrasing, and elaborated on their hand-written interview notes. As a backup, Zvobgo, with the consent of her respondents, had accompanying audio recordings.
Researchers may carry out fieldwork in a country that is considerably less safe than what they are used to, a setting affected by conflict violence or high crime rates, for instance. Feelings of insecurity can be compounded by linguistic barriers, cultural particularities, and being far away from friends and family. Insecurity is also often gendered, differentially affecting women and raising the specter of unwanted sexual advances, street harassment, or even sexual assault ( Gifford and Hall-Clifford 2008 ; Mügge 2013 ). In a recent survey of Political Science graduate students in the United States, about half of those who had done fieldwork internationally reported having encountered safety issues in the field, (54 percent female, 47 percent male), and only 21 percent agreed that their Ph.D. programs had prepared them to carry out their fieldwork safely ( Schwartz and Cronin-Furman 2020 , 8–9).
Preventative measures scholars may adopt in an unsafe context may involve, at their most fundamental, adjustments to everyday routines and habits, restricting one's movements temporally and spatially. Reliance on gatekeepers may also necessitate adopting new strategies, such as a less vehement and cold rejection of unwanted sexual advances than one ordinarily would exhibit, as Mügge (2013) illustratively discusses. At the same time, a competitive academic job market, imperatives to collect novel and useful data, and harmful discourses surrounding dangerous fieldwork also, problematically, shape incentives for junior researchers to relax their own standards of what constitutes acceptable risk ( Gallien 2021 ).
Others have carefully collected a range of safety precautions that field researchers in fragile or conflict-affected settings may take before and during fieldwork ( Hilhorst et al. 2016 ). Therefore, we are more concise in our discussion of recommendations, focusing on the specific situations of graduate students. Apart from ensuring that supervisors and university administrators have the researcher's contact information in the field (and possibly also that of a local contact person), researchers can register with their country's embassy or foreign office and any crisis monitoring and prevention systems it has in place. That way, they will be informed of any possible unfolding emergencies and the authorities have a record of them being in the country.
It may also be advisable to set up more individualized safety protocols with one or two trusted individuals, such as friends, supervisors, or colleagues at home or in the fieldwork setting itself. The latter option makes sense in particular if one has an official affiliation with a local institution for the duration of the fieldwork, which is often advisable. Still, we would also recommend establishing relationships with local researchers in the absence of a formal affiliation. To keep others informed of her whereabouts, Kreft, for instance, made arrangements with her supervisors to be in touch via email at regular intervals to report on progress and wellbeing. This kept her supervisors in the loop, while an interruption in communication would have alerted them early if something were wrong. In addition, she announced planned trips to other parts of the country and granted her supervisors and a colleague at her home institution emergency reading access to her digital calendar. To most of her interviews, she was moreover accompanied by her local research assistant/translator. If the nature of the research, ethical considerations, and the safety situation allow, it might also be possible to bring a local friend along to interviews as an “assistant,” purely for safety reasons. This option needs to be carefully considered already in the planning stage and should, particularly in settings of fragility or if carrying out research on politically exposed individuals, be noted in any ethical and institutional review processes where these are required. Adequate compensation for such an assistant should be ensured. It may also be advisable to put in place an emergency plan, that is, choose emergency contacts back home and “in the field,” know whom to contact if something happens, and know how to get to the nearest hospital or clinic.
We would be remiss if we did not mention that, when in an unfamiliar context, one's safety radar may be misguided, so it is essential to listen to people who know the context. For example, locals can give advice on which means of transport are safe and which are not, a question that is of the utmost importance when traveling to appointments. For example, Kreft was warned that in Colombia regular taxis are often unsafe, especially if waved down in the streets, and that to get to her interviews safely, she should rely on a ride-share service. In one instance, a Colombian friend suggested that when there was no alternative to a regular taxi, Kreft should book through the app and share the order details, including the taxi registration number or license plate, with a friend. Likewise, sharing one's cell phone location with a trusted friend while traveling or when one feels unsafe may be a viable option. Finally, it is prudent to heed the safety recommendations and travel advisories provided by state authorities and embassies to determine when and where it is safe to travel. Especially if researchers have a responsibility not only for themselves but also for research assistants and research participants, safety must be a top priority.
This does not mean that a researcher should be careless in a context they know either. Of course, conducting fieldwork in a context that is known to the researcher offers many advantages. However, one should be prepared to encounter unwanted events too. For instance, Irgil has conducted fieldwork in her country of origin in a city she knows very well. Therefore, access to the site, moving around the site, and blending in has not been a problem; she also has the advantage of speaking the native language. Yet, she took notes of the streets she walked in, as she often returned from the field site after dark and thought she might get confused after a tiring day. She also established a closer relationship with two or three store owners in different parts of the field site if she needed something urgent, like running out of battery. Above all, one should always be aware of one's surroundings and use common sense. If something feels unsafe, chances are it is.
Fieldwork may negatively affect the researcher's mental health and mental wellbeing regardless of where one's “field” is, whether related to concerns about crime and insecurity, linguistic barriers, social isolation, or the practicalities of identifying, contacting and interviewing research participants. Coping with these different sources of stress can be both mentally and physically exhausting. Then there are the things you may hear, see and learn during the research itself, such as gruesome accounts of violence and suffering conveyed in interviews or archival documents one peruses. Kreft and Zvobgo have spoken with women victims of conflict-related sexual violence, who sometimes displayed strong emotions of pain and anger during the interviews. Likewise, Irgil and Willis have spoken with members of other vulnerable populations such as refugees and former sex workers ( Willis 2020 ).
Prior accounts ( Wood 2006 ; Loyle and Simoni 2017 ; Skjelsbæk 2018 ; Hummel and El Kurd 2020 ; Williamson et al. 2020 ; Schulz and Kreft 2021 ) show that it is natural for sensitive research and fieldwork challenges to affect or even (vicariously) traumatize the researcher. By removing researchers from their regular routines and support networks, fieldwork may also exacerbate existing mental health conditions ( Hummel and El Kurd 2020 ). Nonetheless, mental wellbeing is rarely incorporated into fieldwork courses and guidelines, where these exist at all. But even if you know to anticipate some sort of reaction, you rarely know what that reaction will be until you experience it. When researching sensitive or difficult topics, for example, reactions can include sadness, frustration, anger, fear, helplessness, and flashbacks to personal experiences of violence ( Williamson et al. 2020 ). For example, Kreft responded with episodic feelings of depression and both mental and physical exhaustion. But curiously, these reactions emerged most strongly after she had returned from fieldwork and in particular as she spent extended periods analyzing her interview data, reliving some of the more emotional scenes during the interviews and being confronted with accounts of (sexual) violence against women in a concentrated fashion. This is a crucial reminder that fieldwork does not end when one returns home; the after-effects may linger. Likewise, Zvobgo was physically and mentally drained upon her return from the field. Both Kreft and Zvobgo were unable to concentrate for long periods of time and experienced lower-than-normal levels of productivity for weeks afterward, patterns that formal and informal conversations with other scholars confirm to be common ( Schulz and Kreft 2021 ). Furthermore, the boundaries between “field” and “home” are blurred when conducting remote fieldwork ( Howlett 2021 , 11).
Nor are these adverse reactions limited to cases where the researcher has carried out the interviews themselves. Accounts of violence, pain, and suffering transported in reports, secondary literature, or other sources can evoke similar emotional stress, as Kreft experienced when engaging in a concentrated fashion with additional accounts of conflict-related sexual violence in Colombia and with the feminist literature on sexual and gender-based violence in the comfort of her Swedish office. This could also be applicable to Irgil's fieldwork as she interviewed refugees whose traumas have come out during the interviews or recall specific events triggered by the questions. Likewise, Lee has reviewed primary and secondary materials on North Korean defectors in the national archives and these materials contain violent, intense, emotional narratives.
Fortunately, there are several strategies to cope with and manage such adverse consequences. In a candid and insightful piece, other researchers have discussed the usefulness of distractions, sharing with colleagues, counseling, exercise, and, probably less advisable in the long term, comfort eating and drinking ( Williamson et al. 2020 ; see also Loyle and Simoni 2017 ; Hummel and El Kurd 2020 ). Our experiences largely tally with their observations. In this section, we explore some of these in more detail.
First, in the face of adverse consequences on your mental wellbeing, whether in the field or after your return, it is essential to be patient and generous with yourself. Negative effects on the researcher's mental wellbeing can hit in unexpected ways and at unexpected times. Even if you think that certain reactions are disproportionate or unwarranted at that specific moment, they may simply have been building up over a long time. They are legitimate. Second, the importance of taking breaks and finding distractions, whether that is exercise, socializing with friends, reading a good book, or watching a new series, cannot be overstated. It is easy to fall into a mode of thinking that you constantly have to be productive while you are “in the field,” to maximize your time. But as with all other areas in life, balance is key and rest is necessary. Taking your mind off your research and the research questions you puzzle over is also a good way to more fully soak up and appreciate the context in which you find yourself, in the case of in-person fieldwork, and about which you ultimately write.
Third, we cannot stress enough the importance of investing in social relations. Before going on fieldwork, researchers may want to consult others who have done it before them. Try to find (junior) scholars who have done fieldwork on similar kinds of topics or in the same country or countries you are planning to visit. Utilizing colleagues’ contacts and forging connections using social media are valuable strategies to expand your networks (in fact, this very paper is the result of a social media conversation and several of the authors have never met in person). Having been in the same situation before, most field researchers are, in our experience, generous with their time and advice. Before embarking on her first trip to Colombia, Kreft contacted other researchers in her immediate and extended network and received useful advice on questions such as how to move around Bogotá, whom to speak to, and how to find a research assistant. After completing her fieldwork, she has passed on her experiences to others who contacted her before their first fieldwork trip. Informal networks are, in the absence of more formalized fieldwork preparation, your best friend.
In the field, seeking the company of locals and of other researchers who are also doing fieldwork alleviates anxiety and makes fieldwork more enjoyable. Exchanging experiences, advice and potential interviewee contacts with peers can be extremely beneficial and make the many challenges inherent in fieldwork (on difficult topics) seem more manageable. While researchers conducting remote fieldwork may be physically isolated from other researchers, even connecting with others doing remote fieldwork may be comforting. And even when there are no precise solutions to be found, it is heartening or even cathartic to meet others who are in the same boat and with whom you can talk through your experiences. When Kreft shared some of her fieldwork-related struggles with another researcher she had just met in Bogotá and realized that they were encountering very similar challenges, it was like a weight was lifted off her shoulders. Similarly, peer support can help with readjustment after the fieldwork trip, even if it serves only to reassure you that a post-fieldwork dip in productivity and mental wellbeing is entirely natural. Bear in mind that certain challenges are part of the fieldwork experience and that they do not result from inadequacy on the part of the researcher.
Finally, we would like to stress a point made by Inger Skjelsbæk (2018 , 509) and which has not received sufficient attention: as a discipline, we need to take the question of researcher mental wellbeing more seriously—not only in graduate education, fieldwork preparation, and at conferences, but also in reflecting on how it affects the research process itself: “When strong emotions arise, through reading about, coding, or talking to people who have been impacted by [conflict-related sexual violence] (as victims or perpetrators), it may create a feeling of being unprofessional, nonscientific, and too subjective.”
We contend that this is a challenge not only for research on sensitive issues but also for fieldwork more generally. To what extent is it possible, and desirable, to uphold the image of the objective researcher during fieldwork, when we are at our foundation human beings? And going even further, how do the (anticipated) effects of our research on our wellbeing, and the safety precautions we take ( Gifford and Hall-Clifford 2008 ), affect the kinds of questions we ask, the kinds of places we visit and with whom we speak? How do they affect the methods we use and how we interpret our findings? An honest discussion of affective responses to our research in methods sections seems utopian, as emotionality in the research process continues to be silenced and relegated to the personal, often in gendered ways, which in turn is considered unconnected to the objective and scientific research process ( Jamar and Chappuis 2016 ). But as Gifford and Hall-Clifford (2008 , 26) aptly put it: “Graduate education should acknowledge the reality that fieldwork is scholarly but also intimately personal,” and we contend that the two shape each other. Therefore, we encourage political science as a discipline to reflect on researcher wellbeing and affective responses to fieldwork more carefully, and we see the need for methods courses that embrace a more holistic notion of the subjectivity of the researcher.
Interacting with people in the field is one of the most challenging yet rewarding parts of the work that we do, especially in comparison to impersonal, often tedious wrangling and analysis of quantitative data. Field researchers often make personal connections with their interviewees. Consequently, maintaining boundaries can be a bit tricky. Here, we recommend being honest with everyone with whom you interact without overstating the abilities of a researcher. This appears as a challenge in the field, particularly when you empathize with people and when they share profound parts of their lives with you for your research in addition to being “human subjects” ( Fujii 2012 ). For instance, when Irgil interviewed native citizens about the changes in their neighborhood following the arrival of Syrian refugees, many interviewees questioned what she would offer them in return for their participation. Irgil responded that her primary contribution would be her published work. She also noted, however, that academic papers can take a year, sometimes longer, to go through the peer-reviewed process and, once published, many studies have a limited audience. The Syrian refugees posed similar questions. Irgil responded not only with honesty but also, given this population's vulnerable status, she provided them contact information for NGOs with which they could connect if they needed help or answers to specific questions.
For her part, Zvobgo was very upfront with her interviewees about her role as a researcher: she recognized that she is not someone who is on the frontlines of the fight for human rights and transitional justice like they are. All she could/can do is use her platform to amplify their stories, bringing attention to their vital work through her future peer-reviewed publications. She also committed to sending them copies of the work, as electronic journal articles are often inaccessible due to paywalls and university press books are very expensive, especially for nonprofits. Interviewees were very receptive; some were even moved by the degree of self-awareness and the commitment to do right by them. In some cases, this prompted them to share even more, because they knew that the researcher was really there to listen and learn. This is something that junior scholars, and all scholars really, should always remember. We enter the field to be taught. Likewise, Kreft circulated among her interviewees Spanish-language versions of an academic article and a policy brief based on the fieldwork she had carried out in Colombia.
As researchers from the Global North, we recognize a possible power differential between us and our research subjects, and certainly an imbalance in power between the countries where we have been trained and some of the countries where we have done and continue to do field research, particularly in politically dynamic contexts ( Knott 2019 ). This is why we are so concerned with being open and transparent with everyone with whom we come into contact in the field and why we are committed to giving back to those who so generously lend us their time and knowledge. Knott (2019 , 148) summarizes this as “Reflexive openness is a form of transparency that is methodologically and ethically superior to providing access to data in its raw form, at least for qualitative data.”
We also recognize that academics, including in the social sciences and especially those hailing from countries in the Global North, have a long and troubled history of exploiting their power over others for the sake of their research—including failing to be upfront about their research goals, misrepresenting the on-the-ground realities of their field research sites (including remote fieldwork), and publishing essentializing, paternalistic, and damaging views and analyses of the people there. No one should build their career on the backs of others, least of all in a field concerned with the possession and exercise of power. Thus, it is highly crucial to acknowledge the power hierarchies between the researcher and the interviewees, and to reflect on them both in the field and beyond the field upon return.
A major challenge to conducting fieldwork is when researchers’ carefully planned designs do not go as planned due to unforeseen events outside of our control, such as pandemics, natural disasters, deteriorating security situations in the field, or even the researcher falling ill. As the Covid-19 pandemic has made painfully clear, researchers may face situations where in-person research is simply not possible. In some cases, researchers may be barred entry to their fieldwork site; in others, the ethical implications of entering the field greatly outweigh the importance of fieldwork. Such barriers to conducting in-person research require us to reconsider conventional notions of what constitutes fieldwork. Researchers may need to shift their data collection methods, for example, conducting interviews remotely instead of in person. Even while researchers are in the field, they may still need to carry out part of their interviews or surveys virtually or by phone. For example, Kreft (2020) carried out a small number of interviews remotely while she was based in Bogotá, because some of the women's civil society activists with whom she intended to speak were based in parts of the country that were difficult and/or dangerous to access.
Remote field research, which we define as the collection of data over the internet or over the phone where in-person fieldwork is not possible due to security, health or other risks, comes with its own sets of challenges. For one, there may be certain populations that researchers cannot reach remotely due to a lack of internet connectivity or technology such as cellphones and computers. In such instances, there will be a sampling bias toward individuals and groups that do have these resources, a point worth noting when scholars interpret their research findings. In the case of virtual research, the risk of online surveillance, hacking, or wiretapping may also produce reluctance on the part of interviewees to discuss sensitive issues that may compromise their safety. Researchers need to carefully consider how the use of digital technology may increase the risk to research participants and what changes to the research design and any interview guides this necessitates. In general, it is imperative that researchers reflect on how they can ethically use digital technology in their fieldwork ( Van Baalen 2018 ). Remote interviews may also be challenging to arrange for researchers who have not made connections in person with people in their community of interest.
Some of the serendipitous happenings we discussed earlier may also be less likely and snowball sampling more difficult. For example, in phone or virtual interviews, it is harder to build good rapport and trust with interviewees as compared to face-to-face interviews. Accordingly, researchers should be more careful in communicating with interviewees and creating a comfortable interview environment. Especially when dealing with sensitive topics, researchers may have to make several phone calls and sometimes have to open themselves to establishing trust with interviewees. Also, researchers must be careful in protecting interviewees in phone or virtual interviews when they deal with sensitive topics of countries interviewees reside in.
The inability to physically visit one's community of interest may also encourage scholars to critically reflect on how much time in the field is essential to completing their research and to consider creative, alternative means for accessing information to complete their projects. While data collection techniques such as face-to-face interviews and archival work in the field may be ideal in normal times, there exist other data sources that can provide comparably useful information. For example, in her research on the role of framing in the United States base politics, Willis found that social media accounts and websites yielded information useful to her project. Many archives across the world have also been digitized. Researchers may also consider crowdsourcing data from the field among their networks, as fellow academics tend to collect much more data in the field than they ever use in their published works. They may also elect to hire someone, perhaps a graduate student, in a city or a country where they cannot travel and have the individual access, scan, and send archival materials. This final suggestion may prove generally useful to researchers with limited time and financial resources.
Remote qualitative data collection techniques, while they will likely never be “the gold-standard,” also pose several advantages. These techniques may help researchers avoid some of the issues mentioned previously. Remote interviews, for example, are less time-consuming in terms of travel to the interview site ( Archibald et al. 2019 ). The implication is that researchers may have less fatigue from conducting interviews and/or may be able to conduct more interviews. For example, while Willis had little energy to do anything else after an in-person interview (or two) in a given day, she had much more energy after completing remote interviews. Second, remote fieldwork also helps researchers avoid potentially dangerous situations in the field mentioned previously. Lastly, remote fieldwork generally presents fewer financial barriers than in-person research ( Archibald et al. 2019 ). In that sense, considering remote qualitative data collection, a type of “fieldwork” may make fieldwork more accessible to a greater number of scholars.
Many of the substantive, methodological and practical challenges that arise during fieldwork can be anticipated. Proper preparation can help you hit the ground running once you enter your fieldwork destination, whether in-person or virtually. Nonetheless, there is no such thing as being perfectly prepared for the field. Some things will simply be beyond your control, and especially as a newcomer to field research, and you should be prepared for things to not go as planned. New questions will arise, interview participants may cancel appointments, and you might not get the answers you expected. Be ready to make adjustments to research plans, interview guides, or questionnaires. And, be mindful of your affective reactions to the overall fieldwork situation and be gentle with yourself.
We recommend approaching fieldwork as a learning experience as much as, or perhaps even more than, a data collection effort. This also applies to your research topic. While it is prudent always to exercise a healthy amount of skepticism about what people tell you and why, the participants in your research will likely have unique perspectives and knowledge that will challenge yours. Be an attentive listener and remember that they are experts of their own experiences.
We encourage more institutions to offer courses that cover field research preparation and planning, practical advice on safety and wellbeing, and discussion of ethics. Specifically, we align with Schwartz and Cronin-Furman's (2020 , 3) contention “that treating fieldwork preparation as the methodology will improve individual scholars’ experiences and research.” In this article, we outline a set of issue areas in which we think formal preparation is necessary, but we note that our discussion is by no means exhaustive. Formal fieldwork preparation should also extend beyond what we have covered in this article, such as issues of data security and preparing for nonqualitative fieldwork methods. We also note that field research is one area that has yet to be comprehensively addressed in conversations on diversity and equity in the political science discipline and the broader academic profession. In a recent article, Brielle Harbin (2021) begins to fill this gap by sharing her experiences conducting in-person election surveys as a Black woman in a conservative and predominantly white region of the United States and the challenges that she encountered. Beyond race and gender, citizenship, immigration status, one's Ph.D. institution and distance to the field also affect who is able to do what type of field research, where, and for how long. Future research should explore these and related questions in greater detail because limits on who is able to conduct field research constrict the sociological imagination of our field.
While Emmons and Moravcsik (2020) focus on leading Political Science Ph.D. programs in the United States, these trends likely obtain, both in lower ranked institutions in the broader United States as well as in graduate education throughout North America and Europe.
As all the authors have carried out qualitative fieldwork, this is the primary focus of this guide. This does not, however, mean that we exclude quantitative or experimental data collection from our definition of fieldwork.
There is great variation in graduate students’ financial situations, even in the Global North. For example, while higher education is tax-funded in most countries in Europe and Ph.D. students in countries such as Sweden, Norway, Denmark, the Netherlands, and Switzerland receive a comparatively generous full-time salary, healthcare and contributions to pension schemes, Ph.D. programs in other contexts like the United States and the United Kingdom have (high) enrollment fees and rely on scholarships, stipends, or departmental duties like teaching to (partially) offset these, while again others, such as Germany, are commonly financed by part-time (50 percent) employment at the university with tasks substantively unrelated to the dissertation. These different preconditions leave many Ph.D. students struggling financially and even incurring debt, while others are in a more comfortable financial position. Likewise, Ph.D. programs around the globe differ in structure, such as required coursework, duration and supervision relationships. Naturally, all of these factors have a bearing on the extent to which fieldwork is feasible. We acknowledge unequal preconditions across institutions and contexts, and trust that those Ph.D. students interested in pursuing fieldwork are best able to assess the structural and institutional context in which they operate and what this implies for how, when, and how long to carry out fieldwork.
In our experience, this is not only the general cycle for graduate students in North America, but also in Europe and likely elsewhere.
For helpful advice and feedback on earlier drafts, we wish to thank the editors and reviewers at International Studies Review , and Cassandra Emmons. We are also grateful to our interlocuters in Argentina, Canada, Colombia, Germany, Guatemala, Japan, Kenya, Norway, the Philippines, Sierra Leone, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Turkey, the United Kingdom, and the United States, without whom this reflection on fieldwork would not have been possible. All authors contributed equally to this manuscript.
This material is based upon work supported by the Forskraftstiftelsen Theodor Adelswärds Minne, Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation(KAW 2013.0178), National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship Program(DGE-1418060), Southeast Asia Research Group (Pre-Dissertation Fellowship), University at Albany (Initiatives for Women and the Benevolent Association), University of Missouri (John D. Bies International Travel Award Program and Kinder Institute on Constitutional Democracy), University of Southern California (Provost Fellowship in the Social Sciences), Vetenskapsrådet(Diarienummer 2019-06298), Wilhelm och Martina Lundgrens Vetenskapsfond(2016-1102; 2018-2272), and William & Mary (Global Research Institute Pre-doctoral Fellowship).
Advancing Conflict Research . 2020 . The ARC Bibliography . Accessed September 6, 2020, https://advancingconflictresearch.com/resources-1 .
Google Scholar
Google Preview
Archibald Mandy M. , Ambagtsheer Rachel C. , Casey Mavourneen G. , Lawless Michael . 2019 . “ Using Zoom Videoconferencing for Qualitative Data Collection: Perceptions and Experiences of Researchers and Participants .” International Journal of Qualitative Methods 18 : 1 – 18 .
Beath Andrew , Christia Fotini , Enikolopov Ruben . 2013 . “ Empowering Women Through Development Aid: Evidence from a Field Experiment in Afghanistan .” American Political Science Review 107 ( 3 ): 540 – 57 .
Carling Jorgen , Erdal Marta Bivand , Ezzati Rojan . 2014 . “ Beyond the Insider–Outsider Divide in Migration Research .” Migration Studies 2 ( 1 ): 36 – 54 .
Chambers-Ju Christopher . 2014 . “ Data Collection, Opportunity Costs, and Problem Solving: Lessons from Field Research on Teachers’ Unions in Latin America .” P.S.: Political Science & Politics 47 ( 2 ): 405 – 9 .
Collier David . 2011 . “ Understanding Process Tracing .” P.S.: Political Science and Politics 44 ( 4 ): 823 – 30 .
Druckman James N. , Green Donald P. , Kuklinski James H. , Lupia Arthur . 2006 . “ The Growth and Development of Experimental Research in Political Science .” American Political Science Review 100 ( 4 ): 627 – 35 .
Elman Colin , Kapiszewski Diana , Kirilova Dessislava . 2015 . “ Learning Through Research: Using Data to Train Undergraduates in Qualitative Methods .” P.S.: Political Science & Politics 48 ( 1 ): 39 – 43 .
Emmons Cassandra V. , Moravcsik Andrew M. . 2020 . “ Graduate Qualitative Methods Training in Political Science: A Disciplinary Crisis .” P.S.: Political Science & Politics 53 ( 2 ): 258 – 64 .
Esarey Justin. 2017 . “ Causal Inference with Observational Data .” In Analytics, Policy, and Governance , edited by Bachner Jennifer , Hill Kathryn Wagner , Ginsberg Benjamin , 40 – 66 . New Haven : Yale University Press .
Finseraas Henning , Kotsadam Andreas . 2017 . “ Does Personal Contact with Ethnic Minorities Affect anti-immigrant Sentiments? Evidence from a Field Experiment .” European Journal of Political Research 56 : 703 – 22 .
Fujii Lee Ann . 2012 . “ Research Ethics 101: Dilemmas and Responsibilities .” P.S.: Political Science & Politics 45 ( 4 ): 717 – 23 .
Gallien Max . 2021 . “ Solitary Decision-Making and Fieldwork Safety .” In The Companion to Peace and Conflict Fieldwork , edited by Ginty Roger Mac , Brett Roddy , Vogel Birte , 163 – 74 . Cham, Switzerland : Palgrave Macmillan .
Geddes Barbara . 2003 . Paradigms and Sand Castles: Theory Building and Research Design in Comparative Politics . Ann Arbor : University of Michigan Press .
Gifford Lindsay , Hall-Clifford Rachel . 2008 . “ From Catcalls to Kidnapping: Towards an Open Dialogue on the Fieldwork Experiences of Graduate Women .” Anthropology News 49 ( 6 ): 26 – 7 .
Greitens Sheena C. 2016 . Dictators and Their Secret Police: Coercive Institutions and State Violence . Cambridge : Cambridge University Press .
Harbin Brielle M. 2021 . “ Who's Able to Do Political Science Work? My Experience with Exit Polling and What It Reveals about Issues of Race and Equity .” PS: Political Science & Politics 54 ( 1 ): 144 – 6 .
Hilhorst Dorothea , Hogson Lucy , Jansen Bram , Mena Rodrigo Fluhmann . 2016 . Security Guidelines for Field Research in Complex, Remote and Hazardous Places . Accessed August 25, 2020, http://hdl.handle.net/1765/93256 .
Howlett Marnie. 2021 . “ Looking At the ‘Field’ Through a Zoom Lens: Methodological Reflections on Conducting Online Research During a Global Pandemic .” Qualitative Research . Online first .
Hsueh Roselyn , Jensenius Francesca Refsum , Newsome Akasemi . 2014 . “ Fieldwork in Political Science: Encountering Challenges and Crafting Solutions: Introduction .” PS: Political Science & Politics 47 ( 2 ): 391 – 3 .
Hummel Calla , El Kurd Dana . 2020 . “ Mental Health and Fieldwork .” P.S.: Political Science & Politics 54 ( 1 ): 121 – 5 .
Irgil Ezgi. 2020 . “ Broadening the Positionality in Migration Studies: Assigned Insider Category .” Migration Studies . Online first .
Jacobsen Karen , Landau Lauren B. . 2003 . “ The Dual Imperative in Refugee Research: Some Methodological and Ethical Considerations in Social Science Research on Forced Migration .” Disasters 27 ( 3 ): 185 – 206 .
Jamar Astrid , Chappuis Fairlie . 2016 . “ Conventions of Silence: Emotions and Knowledge Production in War-Affected Research Environments .” Parcours Anthropologiques 11 : 95 – 117 .
Jensenius Francesca R. 2014 . “ The Fieldwork of Quantitative Data Collection .” P.S.: Political Science & Politics 47 ( 2 ): 402 – 4 .
Kapiszewski Diana , MacLean Lauren M. , Read Benjamin L. . 2015 . Field Research in Political Science: Practices and Principles . Cambridge : Cambridge University Press .
Kelsky Karen . 2015 . The Professor Is In: The Essential Guide to Turning Your Ph.D. Into a Job . New York : Three Rivers Press .
Knott Eleanor . 2019 . “ Beyond the Field: Ethics After Fieldwork in Politically Dynamic Contexts .” Perspectives on Politics 17 ( 1 ): 140 – 53 .
Kreft Anne-Kathrin . 2019 . “ Responding to Sexual Violence: Women's Mobilization in War .” Journal of Peace Research 56 ( 2 ): 220 – 33 .
Kreft Anne-Kathrin . 2020 . “ Civil Society Perspectives on Sexual Violence in Conflict: Patriarchy and War Strategy in Colombia .” International Affairs 96 ( 2 ): 457 – 78 .
Loyle Cyanne E. , Simoni Alicia . 2017 . “ Researching Under Fire: Political Science and Researcher Trauma .” P.S.: Political Science & Politics 50 ( 1 ): 141 – 5 .
Mackenzie Catriona , McDowell Christopher , Pittaway Eileen . 2007 . “ Beyond ‘do No Harm’: The Challenge of Constructing Ethical Relationships in Refugee Research .” Journal of Refugee Studies 20 ( 2 ): 299 – 319 .
Marston Jerome F. 2020 . “ Resisting Displacement: Leveraging Interpersonal Ties to Remain Despite Criminal Violence in Medellín, Colombia .” Comparative Political Studies 53 ( 13 ): 1995 – 2028 .
Mosley Layna , ed. 2013 . Interview Research in Political Science . Ithaca : Cornell University Press .
Mügge Liza M. 2013 . “ Sexually Harassed by Gatekeepers: Reflections on Fieldwork in Surinam and Turkey .” International Journal of Social Research Methodology 16 ( 6 ): 541 – 6 .
Nexon Daniel. 2019 . International Studies Quarterly (ISQ) 2019 Annual Editorial Report . Accessed August 25, 2020, https://www.isanet.org/Portals/0/Documents/ISQ/2019_ISQ%20Report.pdf?ver = 2019-11-06-103524-300 .
Nowicka Magdalena , Cieslik Anna . 2014 . “ Beyond Methodological Nationalism in Insider Research with Migrants .” Migration Studies 2 ( 1 ): 1 – 15 .
O'Brien Kevin J. , Li Lianjiang . 2005 . “ Popular Contention and Its Impact in Rural China .” Comparative Political Studies 38 ( 3 ): 235 – 59 .
Ortbals Candice D. , Rincker Meg E. . 2009 . “ Fieldwork, Identities, and Intersectionality: Negotiating Gender, Race, Class, Religion, Nationality, and Age in the Research Field Abroad: Editors’ Introduction .” P.S.: Political Science & Politics 42 ( 2 ): 287 – 90 .
Read Benjamin. 2006 . “ Site-intensive Methods: Fenno and Scott in Search of Coalition .” Qualitative & Multi-method Research 4 ( 2 ): 10 – 3 .
Ricks Jacob I. , Liu Amy H. . 2018 . “ Process-Tracing Research Designs: A Practical Guide .” P.S.: Political Science & Politics 51 ( 4 ): 842 – 6 .
Sarotte Mary E. 2012 . “ China's Fear of Contagion: Tiananmen Square and the Power of the European Example .” International Security 37 ( 2 ): 156 – 82 .
Saunders Benjamin , Kitzinger Jenny , Kitzinger Celia . 2015 . “ Anonymizing Interview Data: Challenges and Compromise in Practice .” Qualitative Research 15 ( 5 ): 616 – 32 .
Schulz Philipp , Kreft Anne-Kathrin . 2021 . “ Researching Conflict-Related Sexual Violence: A Conversation Between Early Career Researchers .” International Feminist Journal of Politics . Advance online access .
Schwartz Stephanie , Cronin-Furman Kate . 2020 . “ Ill-Prepared: International Fieldwork Methods Training in Political Science .” Working Paper .
Seawright Jason . 2016 . “ Better Multimethod Design: The Promise of Integrative Multimethod Research .” Security Studies 25 ( 1 ): 42 – 9 .
Skjelsbæk Inger . 2018 . “ Silence Breakers in War and Peace: Research on Gender and Violence with an Ethics of Engagement .” Social Politics: International Studies in Gender , State & Society 25 ( 4 ): 496 – 520 .
Van Baalen Sebastian . 2018 . “ ‘Google Wants to Know Your Location’: The Ethical Challenges of Fieldwork in the Digital Age .” Research Ethics 14 ( 4 ): 1 – 17 .
Weiss Meredith L. , Hicken Allen , Kuhonta Eric Martinez . 2017 . “ Political Science Field Research & Ethics: Introduction .” The American Political Science Association—Comparative Democratization Newsletter 15 ( 3 ): 3 – 5 .
Weller Nicholas , Barnes Jeb . 2016 . “ Pathway Analysis and the Search for Causal Mechanisms .” Sociological Methods & Research 45 ( 3 ): 424 – 57 .
Williamson Emma , Gregory Alison , Abrahams Hilary , Aghtaie Nadia , Walker Sarah-Jane , Hester Marianne . 2020 . “ Secondary Trauma: Emotional Safety in Sensitive Research .” Journal of Academic Ethics 18 ( 1 ): 55 – 70 .
Willis Charmaine . 2020 . “ Revealing Hidden Injustices: The Filipino Struggle Against U.S. Military Presence .” Minds of the Movement (blog). October 27, 2020, https://www.nonviolent-conflict.org/blog_post/revealing-hidden-injustices-the-filipino-struggle-against-u-s-military-presence/ .
Wood Elizabeth Jean . 2006 . “ The Ethical Challenges of Field Research in Conflict Zones .” Qualitative Sociology 29 ( 3 ): 373 – 86 .
Zapata-Barrero Ricard , Yalaz Evren . 2019 . “ Qualitative Migration Research Ethics: Mapping the Core Challenges .” GRITIM-UPF Working Paper Series No. 42 .
Zvobgo Kelebogile . 2020 . “ Demanding Truth: The Global Transitional Justice Network and the Creation of Truth Commissions .” International Studies Quarterly 64 ( 3 ): 609 – 25 .
| Month: | Total Views: |
|---|---|
| June 2021 | 456 |
| July 2021 | 77 |
| August 2021 | 58 |
| September 2021 | 67 |
| October 2021 | 49 |
| November 2021 | 36 |
| December 2021 | 67 |
| January 2022 | 69 |
| February 2022 | 61 |
| March 2022 | 50 |
| April 2022 | 50 |
| May 2022 | 23 |
| June 2022 | 90 |
| July 2022 | 87 |
| August 2022 | 103 |
| September 2022 | 109 |
| October 2022 | 144 |
| November 2022 | 146 |
| December 2022 | 74 |
| January 2023 | 162 |
| February 2023 | 177 |
| March 2023 | 273 |
| April 2023 | 194 |
| May 2023 | 225 |
| June 2023 | 246 |
| July 2023 | 262 |
| August 2023 | 279 |
| September 2023 | 307 |
| October 2023 | 333 |
| November 2023 | 441 |
| December 2023 | 357 |
| January 2024 | 431 |
| February 2024 | 386 |
| March 2024 | 481 |
| April 2024 | 356 |
| May 2024 | 356 |
| June 2024 | 287 |
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1468-2486
- Print ISSN 1521-9488
- Copyright © 2024 International Studies Association
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
What is Field Research? Definition, Types, Methods, Examples
Appinio Research · 05.04.2024 · 30min read

Have you ever wondered how researchers gather data about real-life situations, behaviors, and interactions? Field research holds the answer. Field research is like stepping into the world around us to study things as they naturally happen. It's about going beyond the confines of a lab or a controlled environment to observe, interact with, and collect data from people, communities, or natural settings. Whether it's understanding how people make decisions, studying the behavior of animals in their habitats, or exploring cultural practices in different societies, field research offers a window into the complexities of our world. It's a hands-on approach that allows you to immerse yourself in the context you're studying, gaining firsthand insights and uncovering patterns that might not be apparent in artificial settings. From interviewing participants to conducting observations and surveys, field researchers employ a variety of techniques to capture the richness and diversity of human experiences and natural phenomena. In this guide, we'll explore the ins and outs of field research, from its importance and applications to practical tips for planning, conducting, and analyzing field studies.
What is Field Research?
Field research is a qualitative data collection method that involves studying phenomena in their natural settings. Unlike laboratory experiments or simulations, field research takes place in real-world environments, allowing you to observe, interact with, and gather data from participants or phenomena as they naturally occur. This approach enables researchers to gain firsthand insights into complex social, behavioral, or environmental dynamics, providing rich and contextually embedded data for analysis and interpretation.
Importance of Field Research
Field research plays a crucial role in various disciplines and industries, serving as a cornerstone for generating new knowledge, understanding real-world phenomena, and informing decision-making and practice.
Here is why field research is important:
- Contextual Understanding: Field research allows researchers to study phenomena in their natural contexts, providing a nuanced understanding of the social, cultural, and environmental factors that shape behavior, attitudes, and experiences. By immersing themselves in the field, you can capture the intricacies and complexities of real-life situations that may not be apparent in controlled laboratory settings.
- Insights into Human Behavior: Field research provides valuable insights into human behavior, interactions, and relationships in diverse contexts. By observing and interacting with participants in their natural environments, researchers can uncover patterns, motivations, and social dynamics that influence individual and group behaviors. This understanding is essential for addressing societal challenges, designing interventions, and improving policy and practice.
- Generating Grounded Theory: Field research often serves as the foundation for grounded theory development, where theoretical frameworks and hypotheses emerge from empirical observations and data analysis. By systematically collecting and analyzing data from the field, you can generate new theories, concepts, or models that are grounded in real-world phenomena and have practical relevance and applicability.
- Validating and Supplementing Existing Knowledge: Field research provides an opportunity to validate or supplement existing knowledge derived from laboratory studies, surveys, or secondary data sources. By corroborating findings across different methods and contexts, you can enhance the credibility and robustness of their conclusions and contribute to the accumulation of knowledge in their respective fields.
- Informing Policy and Practice: Field research findings have direct implications for policy development, program planning, and practice in various sectors such as healthcare, education, social services, and environmental management . By generating evidence-based insights and recommendations, field research can inform decision-making processes, guide resource allocation, and improve the effectiveness and relevance of interventions and policies.
Field research offers a unique opportunity to explore, understand, and address real-world phenomena in their natural contexts. By embracing the complexities and nuances of the field, researchers can generate valuable insights, advance theoretical understanding, and make meaningful contributions to scholarship, practice, and society at large.
How to Prepare for Field Research?
Laying the groundwork for your research journey is crucial before diving into the field. This involves a series of preparatory steps aimed at ensuring clarity, focus, and feasibility in your approach.
1. Define Research Objectives
Your research objectives serve as the guiding light throughout your field research endeavor. They delineate the purpose of your study and provide a clear direction for your investigative efforts. When defining your objectives, consider the overarching goals you aim to achieve and the specific outcomes you hope to attain through your research. Whether it's understanding a particular phenomenon, exploring a societal issue, or testing a theoretical proposition, articulate your objectives with precision and clarity.
2. Choose a Research Topic
Selecting the right research topic is paramount to the success of your field research project. Your topic should be aligned with your interests, expertise, and the broader context of your field of study. Consider the relevance, novelty, and significance of potential topics, and choose one that resonates with your intellectual curiosity and research goals. Additionally, ensure that your chosen topic is feasible within the constraints of time, resources, and access to data or participants.
3. Develop Research Questions
Research questions serve as the compass that guides your inquiry and shapes the trajectory of your research journey. These questions should be framed in a way that allows for systematic investigation and exploration of the phenomenon under study. When developing your research questions, strive for clarity, specificity, and relevance to your chosen topic. Consider the scope of inquiry, the level of detail required, and the potential implications of your questions for theory, practice, or policy.
4. Formulate Hypotheses
Hypotheses provide a framework for hypothesis-driven research, allowing you to make predictions about the relationships or patterns you expect to observe in your data. If your research is hypothesis-driven, formulate clear and testable hypotheses that articulate the expected outcomes or associations based on existing theory or empirical evidence. Ensure your hypotheses are falsifiable, meaning they can be rigorously tested and potentially disproven through empirical investigation.
5. Review Existing Literature
Before venturing into the field, take the time to immerse yourself in the existing literature relevant to your research topic. A comprehensive literature review not only provides valuable insights into the current state of knowledge but also helps you identify gaps, contradictions, or areas needing further exploration. Synthesize and critically evaluate the findings, theories, and methodologies presented in the literature, and use this knowledge to inform your own research design , questions, and hypotheses.
6. Secure Necessary Permissions and Resources
Obtaining the requisite permissions and resources is essential for the smooth execution of your field research project. Depending on the nature of your study, you may need to seek ethical approval from institutional review boards or obtain permits for conducting research in specific locations or with certain populations.
Additionally, ensure you have access to the necessary resources, such as funding, equipment, transportation, and logistical support, to carry out your research effectively. Be proactive in addressing potential challenges or barriers that may arise during the planning phase, and seek guidance or assistance as needed to navigate the regulatory and logistical requirements of your research endeavor.
How to Plan Field Research?
As you transition from the preparatory phase to the implementation stage, meticulous planning becomes essential to ensure the success and efficiency of your field research endeavors. Let's delve into the key components of planning field research, from selecting appropriate methodologies to anticipating and mitigating potential challenges.
1. Select Suitable Research Methods
Choosing the proper research methods is pivotal to the success of your field research project. Your research objectives, questions, and the nature of the phenomenon under investigation should guide the selection process. Consider the strengths and limitations of various research methodologies, such as qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods approaches, and choose the one that best aligns with your research goals. Factors to consider include:
- The level of depth and detail required.
- The type of data you aim to collect.
- The accessibility of research participants or sites.
Be prepared to adapt and refine your chosen methods as you gain insights and experience in the field.
2. Design Research Instruments
Once you've identified your research methods, the next step is to design the instruments or tools you'll use to collect data. Whether it's interview guides, survey questionnaires , observation protocols, or experimental materials , your research instruments should be meticulously crafted to elicit relevant and reliable information from your participants.
Pay attention to the clarity, comprehensiveness, and validity of your instruments, ensuring that they align with your research objectives and are appropriate for your target population or context. Pilot testing your instruments with a small sample of participants can help identify and address any ambiguities or issues before full-scale implementation.
3. Determine Sampling Techniques
Sampling is a critical aspect of field research, influencing the representativeness and generalizability of your findings. There are various sampling techniques available, each suited to different research designs and objectives. Consider factors such as the size and diversity of your target population, the accessibility of potential participants, and the level of precision required for your study.
Standard sampling techniques include probability sampling methods like simple random sampling, stratified sampling , or cluster sampling , as well as non-probability sampling methods like convenience sampling, purposive sampling, or snowball sampling. Choose the sampling technique that best balances practical considerations with the need for valid and reliable data.
4. Create a Research Schedule
Developing a well-structured research schedule is essential for keeping your field research project on track and ensuring you meet your deadlines and milestones. Start by breaking down your research activities into manageable tasks and allocating timeframes for each stage of the process, from pre-fieldwork preparation to data analysis and reporting.
- Be realistic in your estimations and build in buffer time for unexpected delays or challenges that may arise during fieldwork.
- Consider factors such as seasonal variations, logistical constraints, and the availability of participants when scheduling your research activities.
- Regularly review and update your schedule as needed to accommodate changes or revisions to your plans.
5. Identify Potential Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
Field research is inherently unpredictable, and you're likely to encounter various challenges and obstacles along the way. Anticipating these challenges proactively and developing mitigation strategies can help minimize their impact on your research outcomes. Common challenges in field research include logistical issues, recruitment difficulties, ethical dilemmas, and interpersonal conflicts.
Take the time to identify potential risks and vulnerabilities inherent in your research design and context, and develop contingency plans or alternative courses of action to address them. Collaborate with peers, mentors, or experienced researchers to brainstorm solutions and draw on their insights and expertise. By being prepared and adaptable, you can navigate the complexities of field research with confidence and resilience.
How to Conduct Field Research?
Now that you've laid the groundwork and meticulously planned your field research project, it's time to roll up your sleeves and immerse yourself in the field.
Data Collection Techniques
Data collection is the heart of field research, enabling you to gather firsthand insights and observations from the field. You can employ several techniques to collect data, depending on your research objectives, context, and the nature of your study.
- Observational Methods: Direct observation involves systematically observing and documenting behaviors, interactions, or phenomena in natural settings without interfering or influencing the subjects. This method is particularly useful for studying social interactions, environmental dynamics, or animal behavior.
- Interviewing: Interviews allow researchers to engage in structured, semi-structured, or unstructured conversations with participants to gather in-depth insights, perspectives, or experiences related to the research topic. Depending on logistical constraints and participant preferences, interviews can be conducted face-to-face, over the phone, or via digital platforms.
- Surveys and Questionnaires : Surveys involve administering standardized questionnaires or surveys to a sample of respondents to collect quantitative data on their attitudes, beliefs, behaviors, or demographics. Surveys can be distributed in person, via mail, email, or online platforms, depending on the target population and accessibility.
- Focus Groups : Focus groups bring together a small group of participants to engage in facilitated discussions or brainstorming sessions around specific topics or issues. This method allows you to explore group dynamics, consensus, or dissent among participants and generate rich qualitative data through interaction and dialogue.
Choose the data collection techniques that best align with your research objectives, methodology, and participants' preferences. Be mindful of ethical considerations, informed consent procedures, and the need to maintain confidentiality and privacy during data collection.
As you navigate the intricacies of data collection in your field research journey, imagine streamlining the process and gaining valuable insights in a fraction of the time. With Appinio 's intuitive platform, you can accelerate your research endeavors, transforming hours of data collection into minutes of actionable insights. Empower yourself to make informed decisions swiftly and seamlessly, all while embracing the dynamic nature of field research. Ready to experience the efficiency of Appinio firsthand? Book a demo now and unlock the power of real-time data collection and research!
Book a Demo
Fieldwork Logistics
Effective management of fieldwork logistics is essential for the smooth execution of your research project and the well-being of both researchers and participants. This entails careful planning, coordination, and organization of various logistical aspects, including participant recruitment, site selection, equipment management, and safety protocols.
- Recruiting Participants: Identify and recruit eligible participants using appropriate sampling techniques and recruitment strategies. Clearly communicate the purpose and expectations of the study, obtain informed consent, and address any concerns or questions raised by participants.
- Establishing Field Sites: Select and secure suitable field sites or locations where data collection will take place. Consider factors such as accessibility, safety, privacy, and the relevance of the site to your research objectives. Obtain any necessary permits or permissions required for conducting research in specific locations.
- Managing Equipment and Supplies: Ensure that you have all the necessary equipment, materials, and resources required for data collection, recording, and storage. This may include audio or video recording devices, notebooks, pens, measuring instruments, or digital devices for data entry.
- Ensuring Research Ethics and Safety: Adhere to ethical principles and guidelines governing research with human subjects, animals, or sensitive environments. Prioritize participant welfare and safety by implementing appropriate risk management measures, emergency procedures, and protocols for handling sensitive or confidential information.
Regularly assess and reassess the logistical needs and challenges encountered during fieldwork, and be prepared to adapt and improvise as needed to overcome obstacles and ensure the successful completion of your research objectives.
Data Recording and Management
Accurate and systematic data recording is crucial for maintaining the integrity and reliability of your research findings. Establish clear protocols and procedures for recording, organizing, and managing your data throughout the fieldwork process.
- Data Recording: Document observations, interviews, survey responses, or other forms of data systematically and consistently. Use standardized formats, codes, or identifiers to ensure uniformity and ease of analysis. Consider using digital tools or software for data collection and recording to streamline the process and minimize errors.
- Data Storage and Backup: Store your data securely and responsibly to prevent loss, theft, or unauthorized access. Back up your data regularly using reliable storage devices or cloud-based platforms to safeguard against data loss or corruption. Implement encryption, password protection, or other security measures to protect sensitive or confidential information.
- Data Validation and Quality Control: Conduct periodic checks and validations to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and validity of your data. Double-check entries, reconcile discrepancies, and address any outliers or inconsistencies identified during the data collection process. Maintain detailed documentation of any revisions or corrections made to the dataset.
By implementing robust data recording and management practices, you can enhance the reliability, transparency, and reproducibility of your research outcomes and facilitate the analysis and interpretation of your findings.
Field Research Examples
Field research plays a pivotal role in helping businesses understand their customers, market dynamics, and competitive landscape. Here are some examples of how field research can be applied in real-world scenarios.
Customer Observation and Ethnography
Imagine a retail company seeking to improve its store layout and enhance customers' shopping experience. By conducting field research through customer observation and ethnographic studies , researchers can immerse themselves in the retail environment, observing how customers navigate the store, interact with products , and make purchasing decisions.
Through careful observation and note-taking, you can uncover valuable insights into customer preferences, behaviors, and pain points, informing strategic decisions around product placement, signage, and store design.
In-Depth Interviews and Focus Groups
A tech startup developing a new mobile app wants to gather feedback from potential users to refine its features and user interface. Through in-depth interviews and focus groups conducted in the field, researchers can engage directly with target users, exploring their needs, preferences , and usage patterns.
Asking probing questions and facilitating group discussions can elicit rich qualitative insights into user experiences, pain points, and desired functionalities. This firsthand feedback can guide the iterative development process, ensuring that the app meets the needs and expectations of its intended audience.
Market Research and Competitive Analysis
A multinational corporation launching a new product in a foreign market conducts field research to assess market demand and understand local competitors. Researchers may conduct surveys, interviews, and market observations to gather data on consumer preferences, buying behavior, and competitor offerings.
By analyzing this data, the company can identify market opportunities, refine its marketing strategy, and tailor its product offerings to meet the specific needs and preferences of the target market . Field research also provides valuable insights into competitive positioning, allowing the company to differentiate itself and capitalize on its unique strengths.
User Testing and Usability Studies
A software development company wants to ensure that its website is user-friendly and intuitive for visitors. Through field research methods such as user testing and usability studies , researchers can observe real users interacting with the website in a naturalistic setting.
By monitoring users' actions, navigation patterns, and feedback, you can identify usability issues, areas of confusion, and opportunities for improvement. This iterative process of testing and refinement helps optimize the website's design and functionality, ultimately enhancing the user experience and driving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Employee Feedback and Organizational Culture
A large corporation embarks on a field research initiative to better understand employee satisfaction, engagement, and organizational culture. Through surveys, focus groups, and participatory observation, researchers gather feedback from employees across different departments and hierarchical levels.
By exploring topics such as work-life balance, communication channels, and leadership effectiveness, you can identify areas of strength and areas for improvement within the organization. This insights-driven approach enables the company to implement targeted interventions, policies, and initiatives to foster a positive and inclusive work environment, ultimately enhancing employee morale, productivity, and retention.
In each of these examples, field research serves as a valuable tool for generating actionable insights, informing strategic decision-making, and driving business success. By embracing a hands-on, experiential approach to research, businesses can gain a competitive edge in today's dynamic and rapidly evolving marketplace.
How to Analyze Field Research Data?
Once you've collected data in the field, the next critical step is to analyze it to derive meaningful insights and draw conclusions.
1. Clean and Organize Data
Before delving into the analysis, it's essential to clean and organize your data to ensure its quality and integrity. Data cleaning involves identifying and rectifying errors, inconsistencies, or missing values in your dataset. Data cleaning tasks include:
- Removing Outliers: Identify and remove any extreme or erroneous data points that may skew your analysis or distort your findings.
- Handling Missing Data: Address missing values by imputing them using appropriate techniques such as mean imputation, regression imputation, or multiple imputation.
- Standardizing Variables: Ensure consistency in measurement units, scales, or formats across variables to facilitate comparison and analysis.
- Checking for Data Entry Errors: Review data entries for typos, duplicates, or other inaccuracies that may arise during data collection or recording.
Once the data cleaning process is complete, organize your dataset in a structured and systematic manner to facilitate analysis. Create variables, labels, or categories as needed, and document any transformations or manipulations applied to the data for transparency and reproducibility.
2. Apply Analytical Techniques
With a clean and organized dataset in hand, you can now apply analytical techniques to uncover patterns, relationships, or trends within the data. The choice of analytical techniques will depend on your research questions, objectives, and the nature of your data.
Analytical methods used in field research include:
- Descriptive Statistics : Calculate measures of central tendency, variability, and distribution to summarize and describe your data.
- Inferential Statistics : Use statistical tests such as t-tests, chi-square tests, regression analysis , or analysis of variance (ANOVA) to test hypotheses, compare groups, or examine relationships between variables.
- Qualitative Analysis: Employ qualitative data analysis techniques such as thematic analysis , content analysis, or grounded theory to explore themes, patterns, or meanings embedded within textual or narrative data.
- Mixed Methods Analysis: Integrate quantitative and qualitative data to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the research phenomenon through triangulation or data transformation techniques.
Select analytical techniques appropriate for your research design, data type, and research questions. Ensure your analyses are conducted rigorously and transparently, adhering to established standards and guidelines in your field.
3. Interpret Findings
Once the analysis is complete, it's time to interpret the findings and draw meaningful conclusions from your data. Interpretation involves making sense of the results in the context of your research objectives, theoretical framework, and empirical evidence.
- Contextualizing Results: Situate your findings within the broader context of existing literature, theoretical perspectives, or real-world phenomena to provide meaningful insights and interpretations.
- Identifying Patterns and Trends: Highlight recurring patterns, trends, or relationships observed in the data and discuss their implications for theory, practice, or policy.
- Exploring Alternative Explanations: Consider alternative explanations or interpretations of the findings and discuss their potential implications for the validity and reliability of your conclusions.
- Addressing Unexpected Findings: Acknowledge and address any unexpected or counterintuitive findings that may challenge existing assumptions or theories and offer plausible explanations or avenues for further exploration.
Communicate your interpretations clearly and concisely, using evidence from your data to support your claims and conclusions. Be transparent about the limitations and uncertainties inherent in your findings, and discuss their implications for future research or practice.
4. Address Limitations and Bias
No research study is without limitations or biases, and it's essential to acknowledge and address these shortcomings transparently. To address limitations and bias in your field research:
- Methodological Limitations: Discuss any limitations or constraints inherent in your research design, sampling methods, or data collection techniques that may have influenced the validity or generalizability of your findings.
- Selection Bias : Be mindful of selection bias, where certain groups or individuals are overrepresented or underrepresented in your sample, and consider its potential impact on the reliability and validity of your results.
- Social Desirability Bias: Recognize the influence of social desirability bias, where participants may provide responses that are perceived as socially acceptable rather than truthful, and consider strategies to mitigate its effects.
- Researcher Bias: Reflect on your own biases, assumptions, or preconceptions that may have influenced the research process or interpretation of findings, and strive for objectivity and reflexivity in your analysis and reporting.
By acknowledging and addressing limitations and biases transparently, you demonstrate intellectual honesty and integrity, and contribute to the credibility and robustness of your research outcomes.
How to Report Field Research Results?
Communicating your research findings effectively is essential for sharing your insights with the academic community, policymakers, practitioners, and other stakeholders. Here are some strategies for reporting and presenting your results:
- Structuring the Research Report: Organize your research report in a clear and logical manner, following the conventions of academic writing. Include sections such as introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusions. Each section should flow cohesively, guiding the reader through the research process from inception to conclusion.
- Writing Techniques and Guidelines: Use clear, concise, and jargon-free language to convey your findings to a diverse audience. Structure your sentences and paragraphs logically, and use headings, subheadings, and bullet points to enhance readability. Pay attention to grammar, spelling, and punctuation, and adhere to the formatting style prescribed by your discipline or publication venue.
- Creating Visual Representations: Enhance your research report or presentation with visual representations such as tables, charts, graphs, heatmaps , or diagrams. Choose visual formats that effectively illustrate key findings or trends in your data. Ensure that your visuals are clear, accurate, and appropriately labeled, and provide a brief caption or explanation to contextualize the information presented.
- Preparing Presentations: Design engaging and informative presentations highlighting your research's main findings and implications. Use slides, visuals, and storytelling techniques to capture your audience's attention and convey your message effectively. Structure your presentation logically, with a clear introduction, main body, and conclusion, and allow time for questions and discussion.
- Sharing Findings with Stakeholders: Share your research findings with relevant stakeholders, including academic peers, policymakers, practitioners, or community members. Tailor your communication approach to the needs and preferences of your audience, and choose appropriate dissemination channels such as conferences, seminars, publications, or social media platforms. Invite feedback or collaboration whenever possible, and be open to engaging in dialogue and knowledge exchange with your audience.
Effective reporting and presentation of research results not only showcase the significance and impact of your work but also contribute to knowledge dissemination, collaboration, and informed decision-making in your field. Strive for clarity, coherence, and engagement in your communication efforts, and consider your audience's diverse needs and interests when crafting your messages.
Conclusion for Field Research
Field research is a powerful tool for gaining a deeper understanding of the world around us. By venturing into real-life settings, you can uncover valuable insights into human behavior, societal dynamics, and natural phenomena. Whether studying the behavior of animals in their natural habitats or exploring the intricacies of human interactions, field research offers a unique perspective that complements other research methods. By embracing the complexities and nuances of the field, researchers can generate knowledge that is grounded in real-world experiences and has practical implications for addressing pressing societal challenges. Furthermore, field research isn't just about collecting data—it's about making a difference. The i nsights gained from field studies can inform policy decisions, shape interventions, and drive positive change in communities and organizations . By sharing their findings with stakeholders, you can contribute to evidence-based decision-making and foster collaboration between academia, government, and civil society.
How to Conduct Research in Minutes?
Introducing Appinio , your gateway to lightning-fast market research within the realm of field research. As a real-time market research platform, Appinio revolutionizes how companies access consumer insights, empowering them to make swift, data-driven decisions. With Appinio, conducting your own market research becomes a breeze, eliminating the challenges typically associated with field research.
Here's why Appinio stands out:
- From questions to insights in minutes: Say goodbye to lengthy research processes. With Appinio, you can gather crucial consumer insights in mere minutes, allowing you to keep pace with the dynamic business landscape.
- Intuitive platform for everyone: No need for a PhD in research. Appinio's user-friendly interface makes it accessible to anyone, empowering you to delve into market research without the hassle of complex technicalities.
- Rapid response time: With an average field time of less than 23 minutes for 1,000 respondents, Appinio ensures swift data collection without compromising quality or accuracy.
Get free access to the platform!
Join the loop 💌
Be the first to hear about new updates, product news, and data insights. We'll send it all straight to your inbox.
Get the latest market research news straight to your inbox! 💌
Wait, there's more

26.06.2024 | 35min read
Brand Development: Definition, Process, Strategies, Examples

18.06.2024 | 7min read
Future Flavors: How Burger King nailed Concept Testing with Appinio's Predictive Insights

18.06.2024 | 32min read
What is a Pulse Survey? Definition, Types, Questions
A guide to field studies
Last updated
18 April 2023
Reviewed by
Cathy Heath
Short on time? Get an AI generated summary of this article instead
Field studies allow researchers to observe and collect data in real-world settings. Unlike laboratory-based or traditional research methods, field studies enable researchers to investigate complex phenomena within their environment, providing a deeper understanding of the research context.
Researchers can use field studies to investigate a wide range of subjects, from the behavior of animals to the practices of businesses or the experiences of individuals in a particular setting.
Make research less tedious
Dovetail streamlines research to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- What is a field study?
A field study is a research method that involves conducting observations and collecting data in a natural setting. This method includes observing, interviewing, and interacting with participants in their environment, such as a workplace, community, or natural habitat.
Field studies can take many forms, from ethnographic studies involving extended periods of observation and using an anthropological lens to shorter-term studies focusing on specific behaviors or events. Regardless of its form, a successful field study requires careful planning, preparation, and execution to ensure the data collected is valid and reliable.
- How to plan a field study
Planning a field study is a critical first step in ensuring successful research. Here are some steps to follow when preparing your field study:
1. Define your research question
When developing a good research question , you should make it clear, concise, and specific. It should also be open-ended, allowing for various possible answers rather than a simple yes or no response. Your research question should also be relevant to the broader field of study and contribute new knowledge to the existing literature.
Once you have a defined research question, identify the key variables you need to study and the data you need to collect. It might involve developing a hypothesis or research framework outlining the relationships between different variables and how you’ll measure them in your study.
2. Identify your research site
A research site is a location where you’ll conduct your study and collect data. Here are the types of research sites to consider when planning a field study:
Natural habitats: For environmental or ecological research, you may need to conduct your study in a natural habitat, such as a forest, wetland, or coral reef.
Communities : If your research relates to social or cultural factors, you may need to study a particular community, such as a neighborhood, village, or city.
Organizations : For questions relating to organizational behavior or management, your location will be in a business environment, like a nonprofit or government agency.
Events : If your research question relates to a particular event, you may need to conduct your study at that event, such as, at a protest, festival, or natural disaster.
Ensure your research site represents the population you're studying. For example, if you're exploring cultural beliefs, ensure the community represents the larger population and you have access to a diverse group of participants.
3. Determine your data collection methods
Choosing a suitable method will depend on the research question, the type of data needed, and the characteristics of the participants. Here are some commonly used data collection methods in field studies:
Interviews : You can collect data on people's experiences, perspectives, and attitudes. In some instances, you can use phone or online interviews.
Observations : This method involves watching and recording behaviors and interactions in a specific setting.
Surveys : By using a survey , you can easily standardize and tailor the questions to provide answers for your research. Respondents can complete the survey in person, by mail, or online.
Document analysis : Organizational reports, letters, diaries, public records, policies, or social media posts can be analyzed to gain context.
When selecting data collection methods, consider factors such as the availability of participants, the ethical considerations involved, and the resources needed to carry out each method. For example, conducting interviews may require more time and resources than administering a survey.
4. Obtain necessary permissions
Depending on the research location and the nature of the study, you may require permission from local authorities, organizations, or individuals before conducting your research.
This process is vital when working with human or animal subjects and conducting research in sensitive or protected environments.
Here are some steps you can take to obtain the necessary permissions:
Identify the relevant authorities , including local governments, regulatory bodies, research institutions, or private organizations, to obtain permission for your research.
Reach out to the relevant authorities to explain the nature of your study. Be ready to hand out detailed information about your research.
If you're conducting research with human participants, you must have their consent . You'll also need to ensure the participants have the right to withdraw from the study at any time.
Obtain necessary permits from regulatory bodies or local authorities. For example, if you're conducting research in a protected area, you may need a research permit from the relevant government agency.
The process of obtaining permissions can be time-consuming, and failure to obtain the necessary permits can lead to legal and ethical issues.
- Examples of field research
Researchers can apply field research to a wide range of disciplines and phenomena. Here are some examples of field research in different fields:
Anthropology : Anthropologists use field research methods to study different communities' social and cultural practices. For instance, an anthropologist might conduct participant observation in a remote community to understand their customs, beliefs, and practices.
Ecology : Ecologists use field research methods to learn the behavior of organisms and their interactions with the environment. For example, an ecologist might conduct field research on the behavior of birds in their natural habitat to understand their feeding habits, nesting patterns, and migration.
Sociology : Sociologists may use field research methods to study social behavior and interactions. For instance, a sociologist might conduct participant observation in a workplace to understand organizational culture and communication dynamics.
Geography : Geographers use field research methods to study different regions’ physical and human contexts. For example, a geographer might conduct field research on the impact of climate change on a particular ecosystem, such as a forest or wetland.
Psychology : Psychologists use field research methods to study human behavior in natural settings. For instance, a psychologist might conduct field research on the effects of stress on students in a school setting.
Education : Researchers studying education may use field research methods to study teaching and learning in real-world settings. For example, you could use field research to test the effectiveness of a new teaching method in a classroom setting.
By using field research methods, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the complexities of the natural world, human behavior, and social interaction theory and how they affect each other.
- Advantages of field research
Field research has several advantages over other research methods, including:
Authenticity : Field research conducted in natural settings allows researchers to observe and study real-life phenomena as it happens. This authenticity enhances the validity and accuracy of the data collected.
Flexibility : Field research methods are flexible and adaptable to different research contexts. Researchers can adjust their strategies to meet the specific needs of their research questions and participants and uncover new insights as the research unfolds.
Rich data : Field research provides rich and detailed data, often including contextual information that’s difficult to capture through other research methods. This depth of knowledge allows for a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the research topic.
Novel insights : Field research can lead to discoveries that may not be possible with other research methods. Observing and studying phenomena in natural settings can provide unique perspectives and new understandings of complex issues.
Field research methods can enhance the quality and validity of research findings and lead to new insights and discoveries that may not be possible with other research methods.
- Disadvantages of field research
While field research has several advantages, there are also some disadvantages that researchers need to consider, including:
Time-consuming : Researchers need to spend time in the field, possibly weeks or months, which can be challenging, especially if the research site is remote or requires travel.
Cost : Conducting field research can be costly, especially if the research site is remote or requires specialized equipment or materials.
Reliance on participants : It may be challenging to recruit participants, and various factors, such as personal circumstances, attitudes, and beliefs, may influence their participation.
Ethical considerations : Field research may raise ethical concerns, mainly if the research involves vulnerable populations or sensitive topics.
Causality: Researchers may have little control over the environmental or contextual variables they are studying. This can make it difficult to establish causality and then generalize their results with previous research.
Researchers must carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages of field research and select the most appropriate research method based on their research question, participants, and context.
What is another name for field study?
Field study is also known as field research or fieldwork. These terms are often used interchangeably and refer to research methods that involve observing and collecting data in natural settings.
What is the difference between a field study and a case study?
Why is field study important.
Field study is critical because it allows researchers to study real-world phenomena in natural settings. This study can also lead to novel insights that may not be possible with other research methods.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 6 February 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 7 March 2023
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
- What is Field Research: Meaning, Examples, Pros & Cons

Introduction
Field research is a method of research that deals with understanding and interpreting the social interactions of groups of people and communities by observing and dealing with people in their natural settings.
The field research methods involve direct observation, participant observation, and qualitative interviews.
Let’s take a deeper look at field research, what it entails, some examples as well as the pros and cons of field research.
What is Field Research
Field research can be defined as a qualitative method of data collection focused on observing, relating, and understanding people while they are in their natural environment. It is somewhat similar to documentaries on Nat Geo wild where the animals are observed in their natural habitat.
Similarly, social scientists, who are sometimes called men watchers carry out interviews and observe people from a distance to see how they act in a social environment and react to situations around them.
Field research usually begins in a specific setting and the end game is to study, observe and analyze the subject within that setting. It looks at the cause and effect as well as the correlation between the participants and their natural setting. Due to the presence of multiple variables, it is sometimes difficult to properly analyze the results of field research.
Field research adopts a wide range of social research methods, such as limited participation, direct observation, document analysis, surveys, and informal interviews. Although field research is generally considered qualitative research , it often involves multiple elements of quantitative research.
Methods of Field Research
There are 5 different methods of conducting Field Research and they are as follows;
1. Direct Observation
In this method of research, the researcher watches and records the activities of groups of people or individuals as they go about their daily activities. Direct observation can be structured or unstructured.
Structured here means that the observation takes place using a guide or process developed before that time.
Unstructured, on the other hand, means that the researcher conducted the observation, watching people and events, and taking notes as events progressed, without the aid of any predetermined technique.
Some other features of direct observation include the following;
- The observer does not attempt to actively engage the people being observed in conversations or interviews, rather he or she blends into the crowd and carries out their observation.
- Data collected include field notes, videos, photographs, rating scales, etc.
- Direct observation most times occurs in the open, usually public settings, that requires no permission to gain entry. Conducting direct observation in a private setting would raise ethical concerns.
- The outcome of direct observation is not in any way influenced by the researcher.
2. Participant Observation
This research method has an understanding with a group of individuals, to take part in their daily routines and their scheduled events. In this case, the researcher dwells among the group or community being observed for as long as is necessary to build trust and evoke acceptance.
Data from the participant’s observation take the following varying forms;
- Field notes are the primary source of data. These notes are taken during the researcher’s observations and from the events they experienced and later developed the notes into formal field notes.
- A diary is used to record special intimate events that occur within the setting.
- The process of participant observation is intent on developing relationships with the members which breed conversations that are sometimes formal or informal. Formal here refers to deliberate depth interviews, while informal could stem from everyday conversations that give insight into the study.
Data from these events can be part of the field notes or separate interview transcripts.
The method of participant observation aims to make the people involved comfortable enough to share what they know freely without any inhibition.
3. Ethnography
Ethnography is a form of field research that carries out observation through social research, social perspective, and the cultural values of a social setting. In this scenario, the observation is carried out objectively, hence the researcher may choose to live within a social environment of a cultural group and silently observe and record their daily routines and behavior.
4. Qualitative Interviews
Qualitative interviews are a type of field research method that gets information by asking direct questions from individuals to gather data on a particular subject. Qualitative interviews are usually conducted via 3 methods namely;
- Informal Interviews
- Semi Structured Interviews
- Standardized Open ended Interviews
Let’s take a look at each of them briefly along with their advantages and disadvantages.
This kind of interview is often conversational and occurs during participant and direct observations.
The interview is triggered, most times spontaneously by conversing with a member of the group on the areas of interest and as the conversation progresses, the researcher fluidly introduces the specific question.
- Semi-Structured Interviews
In this scenario, the researcher already has a list of prepared questions, that are open-ended and can evoke as much information as possible. The researcher can venture into other topics as the interview progresses, using a call-and-response style.
This method of field research can adopt a mix of one-on-one interviews or focus groups.
- Standardized, Open-Ended Interviews
These are scripted interviews with the questions prepped and written before the interview following a predetermined order. It is similar to a survey and the questions are open-ended to gather detailed information from the respondents and sometimes it involves multiple interviewers.
5. Case Study
A case study research is a detailed analysis of a person, situation, or event. This method may seem a bit complex, however, it is one of the easiest ways of conducting research. difficult to operate, however, it is one of the simplest ways of researching as it involves only a detailed study of an individual or a group of people or events. Every aspect of the subject life and history is analyzed to identify patterns and causes of behavior.
Steps to Conduct Field Research
Due to the nature of field research, the tight timelines, and the associated costs involved, planning and implementing can be a bit overwhelming. We have put together steps to adopt that would make the whole process hitch free for you.
Set Up The Right Team : To begin your field research, the first step is to have the right team. The role of the researcher and the team members has to be well defined from the start, with the relevant milestones agreed upon to measure progress.
Recruiting People for the Study : The success of field research largely depends on the people being studied. Evaluate the individuals selected for the research to be sure that they tick all the boxes required for successful research in the area of study that is being researched.
Data Collection Methodology : The methodology of data collection adopted must be suited to the area or kind of research being conducted. It could be one of the methods or a combination of two or more methods.
Visit The Site: A prior visit to the site is essential to the success of the field research. This should be done to also help determine the best methodology that would be suitable for the location.
Data Analysis: Analyzing the data gathered is important to validate the hypothesis of the field research.
Communicating Results : Once the data is analyzed, communicate the results to the stakeholders involved in the research so that the relevant action required based on the results can be decided and carried out promptly.
Reasons to Conduct Field Research
Field research has been widely used in the 20th century in the social sciences. However, it can be time-consuming and costly to implement. Despite this fact, there exist a lot of reasons to conduct field research.
Here are 4 major reasons to conduct field research:
Solves the problem of lack of data : Field research fixes the issue of gaps in data, especially in cases where there is very little or no data about a topic. In cases like this, the only way to validate any hypothesis is through primary research and data. Conducting field research solves the problem of data lapses and provides material evidence to support any findings.
Understanding the context of the study : In many cases, the data collected is appropriate, however for a deep understanding of the data gathered there is a need for field research to help understand other factors in the study. For instance, if data show that students from rich homes generally do well academically.
Conducting field research can bring to the fore other factors like, discipline, well-equipped teachers, motivation from their forebears to excel in whatever they do, etc. but field research is still conducted.
Increasing data quality: Since this research, method employs the use of multiple tools to collect data and varying methodologies, the quality of data is higher.
Collecting ancillary data : Field research puts the researchers in a position of being at the center of the data collection process, in terms of location, one on one relationship with the participants, etc. This exposes them to new lines of thought that would have hitherto been overlooked and they can now collect data, that was not planned for at the beginning of the study.
Examples of Field Research
1. Interprete social metrics in a slum By employing the use of observation methods and formal interviews, researchers can now understand the social indicators and social hierarchy that exist in a slum.
Financial independence and the way the slum is run daily are part of the study and data collected from these areas can give insight into the way a slum operates differently from structured societies.
2. Understand the impact of sports on a child’s development This method of field research takes years to conduct and the sample size can be quite huge. Data collected and analyzed from this study provides insight into how children from different physical locations and backgrounds are influenced by sports and the impact of sporting activities on a child’s development.
3. The study of animal migration patterns Field research is used immensely to study flora and fauna. A major use case is scientists observing and studying animal migration patterns alongside the change of seasons and its influence on animal migration patterns.
Field research takes time and uses months and sometimes years to help gather data that show how to safely expedite the passage of animals.
Advantages of Field Research
Field research and the various methodology employed have their pros and cons.
Let’s take a look at some of them.
- Provide context to the data being analyzed in terms of settings, interactions, or individuals.
- The source of data does not require or involve verbal interactions, and there is no intrusion of anyone’s personal, space because everything is done quietly, from a distance.
- The researcher develops a deep and detailed understanding of a setting and the members within the setting.
- It is carried out in a real-world and natural environment which eliminates tampering with variables.
- The study is conducted in a comfortable environment, hence data can be gathered even about an ancillary topic, that would have been undiscovered in other circumstances.
- The researcher’s deep understanding of the research subjects due to their proximity to them makes the research thorough and precise.
- It helps the researcher to be flexible and respond to individual differences while capturing emerging information. Allows the researcher to be responsive to individual differences and to capture emerging information.
Disadvantages of Field Research
- The researcher might not be able to capture all that is being said and there is the risk of losing information.
- The quality of the information derived is dependent, on the researcher’s skills.
- Significant interactions and events may occur when an observer is not present.
- Some topics cannot easily be interpreted by mere observation.g., attitudes, emotions, affection).
- The reliability of observations can be complex due to the presence of multiple observers with different interpretations.
- It requires a lot of time (and resources)and can take years to complete.
- The researcher may lose objectivity as they spend more time among the members of the group.
- It is a subjective and interpretive method that is solely dependent on the researcher’s ability.
Field research helps researchers to gain firsthand experience and knowledge about the events, processes, and people, being studied. No other method provides this kind of close-up view of the everyday life of people and events. It is a very detailed method of research and is excellent for understanding the role of social context in shaping the lives, perspectives, and experiences of people. Alongside this, it may uncover aspects of a person that might never have been discovered.

Connect to Formplus, Get Started Now - It's Free!
- Data Collection
- field research
- qualitative research
- Angela Kayode-Sanni

You may also like:
Projective Techniques In Surveys: Definition, Types & Pros & Cons
Introduction When you’re conducting a survey, you need to find out what people think about things. But how do you get an accurate and...

The McNamara Fallacy: How Researchers Can Detect and to Avoid it.
Introduction The McNamara Fallacy is a common problem in research. It happens when researchers take a single piece of data as evidence...
Research Summary: What Is It & How To Write One
Introduction A research summary is a requirement during academic research and sometimes you might need to prepare a research summary...
Unit of Analysis: Definition, Types & Examples
Introduction A unit of analysis is the smallest level of analysis for a research project. It’s important to choose the right unit of...
Formplus - For Seamless Data Collection
Collect data the right way with a versatile data collection tool. try formplus and transform your work productivity today..

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 12: Field Research: A Qualitative Research Technique
12.1 Field Research: What it is?
Field research is a qualitative method of data collection aimed at understanding, observing, and interacting with people in their natural settings. In the context of research, observation is more than just looking. It involves looking in a planned and strategic way with a purpose (Palys & Atchison, 2014, p. 189). As such, when social scientists talk about being in “the field,” they are talking about being out in the real world and involved in the everyday lives of the people they are studying. Sometimes researchers use the terms ethnography or participant observation to refer to this method of data collection; the former is most commonly used in anthropology, while the latter is used commonly in sociology. For our purposes, we will use two main terms: field research and participant observation . You might think of field research as an umbrella term that includes the myriad activities that field researchers engage in when they collect data: they participate; they observe; they usually interview some of the people they observe; and they typically analyze documents or artifacts created by the people they observe.
Researchers conducting participant observation vary in the extent to which they participate or observe. Palys and Atchison (2014, p. 198) refer to this as the “participant-observer continuum,” ranging from complete participant to complete observer. This continuum is demonstrated in Figure 12.1. However, these researchers, as to do other researchers, question whether a researcher can be at the “complete observer” end of the continuum. Rather, they contend, it is increasingly acknowledged that, even as an observer, the researcher is participating in what is being studied and therefore cannot really be a complete observer.

Indeed, it is important to acknowledge that there are pros and cons associated with both aspects of the participant/observer’s role. For example, depending upon how fully researchers observer their subjects (as opposed to participating), they may miss important aspects of group interaction and may not have the opportunity to fully grasp what life is like for the people they observe. At the same time, sitting back and observing may grant researchers opportunities to see interactions that they would miss, were they more involved.
Ethnography is not to be confused with ethnomethodology. Ethnomethodology will be defined and described in Chapter 13
Participation has the benefit of allowing researchers a real taste of life in the group that they study. Some argue that participation is the only way to understand what it is that is being investigated. On the other hand, fully immersed participants may find themselves in situations that they would rather not face but from which cannot excuse themselves because they have adopted the role of a fully immersed participant. Further, participants who do not reveal themselves as researchers must face the ethical quandary of possibly deceiving their subjects. In reality, much field research lies somewhere near the middle of the observer/participant continuum. Field researchers typically participate to at least some extent in their field sites, but there are also times when they may strictly observe.
Research Methods for the Social Sciences: An Introduction Copyright © 2020 by Valerie Sheppard is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Field Research
- Reference work entry
- First Online: 01 January 2021
- pp 3108–3112
- Cite this reference work entry

- Emily Lescak 3
52 Accesses
Gathering information by observing individuals in their natural setting.
Introduction
Field research (“fieldwork”) refers to information gathered by observing individuals in their natural setting. Field research can be both qualitative and quantitative in nature. Qualitative research emphasizes the importance of observing variables and their interactions. Quantitative research attempts to objectively gather data to make associations, comparisons, and predictions among variables. Field studies that sought to associate behavior with inter-individual interactions and/or the environment formed the foundation for the field of behavioral ecology (Martin and Bateson 2007 ).
Field research involves observations of free-living wild animals in their natural habitats while minimizing perturbations or disturbances to their environment or behavior. Field excursions may require some or all of the following (Lagler 1956 ): funding for travel, salary, supplies, and...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Bart, J., Fligner, M., & Notz, W. (1998). Sampling and statistical methods for behavioral ecologists . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Cochran, W. (1977). Sampling techniques . Hoboken: Wiley.
Google Scholar
Crook, J. H. (1964). The evolution of social organisation and visual communication in the weaver birds ( Ploceinae ). Behaviour, 10 , 1–178.
Darwin, C. (1859). On the origin of species by means of natural selection, or the preservation of favoured races in the struggle for life . London: John Murray.
Dewsbury, D. A. (2003). The 1973 Nobel Prize for physiology or medicine: Recognition for behavioral science? American Psychology, 58 (9), 747–752.
Article Google Scholar
Goodall, J. (1990). Through a window: My thirty years with the chimpanzees of Gombe . New York: Soko Publications Limited.
Lack, D. (1947). Darwin’s finches . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Lagler, K. (1956). Freshwater fishery biology . Dubuque: Wm. C. Brown Company Publishers.
Lahti, D., & Lahti, A. (2002). How precise is egg discrimination in weaverbirds? Animal Behaviour, 63 , 1135–1142.
Lehner, P. (1996). Handbook of ethological methods . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Martin, P., & Bateson, P. (2007). Measuring behavior: An introductory guide . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Nice, M. M. (1937). Studies in the life history of the song sparrow. I. A population study of the song sparrow. Transactions of the Linnean Society of New York, 4 , 1–247.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Alaska Anchorage, Anchorage, AK, USA
Emily Lescak
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Emily Lescak .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Psychology, Oakland University, Rochester, MI, USA
Todd K Shackelford
Viviana A Weekes-Shackelford
Section Editor information
University of Idaho, Moscow, ID, USA
Russell Jackson
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Lescak, E. (2021). Field Research. In: Shackelford, T.K., Weekes-Shackelford, V.A. (eds) Encyclopedia of Evolutionary Psychological Science. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-19650-3_2742
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-19650-3_2742
Published : 22 April 2021
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-19649-7
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-19650-3
eBook Packages : Behavioral Science and Psychology Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Field research is a qualitative method of data collection aimed at understanding, observing, and interacting with people in their natural settings. In the context of research, observation is more than just looking. It involves looking in a planned and strategic way with a purpose (Palys & Atchison, 2014, p. 189). As such, when social scientists talk about being in “the field,” they are talking about being out in the real world and involved in the everyday lives of the people they are studying. Sometimes researchers use the terms ethnography or participant observation to refer to this method of data collection; the former is most commonly used in anthropology, while the latter is used commonly in sociology. For our purposes, we will use two main terms: field research and participant observation . You might think of field research as an umbrella term that includes the myriad activities that field researchers engage in when they collect data: they participate; they observe; they usually interview some of the people they observe; and they typically analyze documents or artifacts created by the people they observe.
Researchers conducting participant observation vary in the extent to which they participate or observe. Palys and Atchison (2014, p. 198) refer to this as the “participant-observer continuum,” ranging from complete participant to complete observer. This continuum is demonstrated in Figure 12.1. However, these researchers, as to do other researchers, question whether a researcher can be at the “complete observer” end of the continuum. Rather, they contend, it is increasingly acknowledged that, even as an observer, the researcher is participating in what is being studied and therefore cannot really be a complete observer.

Figure 12.1 (Palys & Atchison, 2014)
Indeed, it is important to acknowledge that there are pros and cons associated with both aspects of the participant/observer’s role. For example, depending upon how fully researchers observer their subjects (as opposed to participating), they may miss important aspects of group interaction and may not have the opportunity to fully grasp what life is like for the people they observe. At the same time, sitting back and observing may grant researchers opportunities to see interactions that they would miss, were they more involved.
Ethnography is not to be confused with ethnomethodology. Ethnomethodology will be defined and described in Chapter13
Participation has the benefit of allowing researchers a real taste of life in the group that they study. Some argue that participation is the only way to understand what it is that is being investigated. On the other hand, fully immersed participants may find themselves in situations that they would rather not face but from which cannot excuse themselves because they have adopted the role of a fully immersed participant. Further, participants who do not reveal themselves as researchers must face the ethical quandary of possibly deceiving their subjects. In reality, much field research lies somewhere near the middle of the observer/participant continuum. Field researchers typically participate to at least some extent in their field sites, but there are also times when they may strictly observe.
Research Methods, Data Collection and Ethics Copyright © 2020 by Valerie Sheppard is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Last updated 27/06/24: Online ordering is currently unavailable due to technical issues. We apologise for any delays responding to customers while we resolve this. For further updates please visit our website: https://www.cambridge.org/news-and-insights/technical-incident
We use cookies to distinguish you from other users and to provide you with a better experience on our websites. Close this message to accept cookies or find out how to manage your cookie settings .
Login Alert

- > Handbook of Research Methods in Social and Personality Psychology
- > Field Research Methods

Book contents
- Handbook of Research Methods in Social and Personality Psychology
- Copyright page
- Contributors
- Introduction to the Second Edition
- Introduction to the First Edition
- Chapter one Scratch an Itch with a Brick
- Part one Design and Inference Considerations
- Chapter two Research Design and Issues of Validity
- Chapter three Research Design
- Chapter four Causal Inference and Generalization in Field Settings
- Chapter five Field Research Methods
- Part two Procedural Possibilities
- Part three Data Analytic Strategies
- Author Index
- Subject Index
Chapter five - Field Research Methods
from Part one - Design and Inference Considerations
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 June 2014
Access options
Save book to kindle.
To save this book to your Kindle, first ensure [email protected] is added to your Approved Personal Document E-mail List under your Personal Document Settings on the Manage Your Content and Devices page of your Amazon account. Then enter the ‘name’ part of your Kindle email address below. Find out more about saving to your Kindle .
Note you can select to save to either the @free.kindle.com or @kindle.com variations. ‘@free.kindle.com’ emails are free but can only be saved to your device when it is connected to wi-fi. ‘@kindle.com’ emails can be delivered even when you are not connected to wi-fi, but note that service fees apply.
Find out more about the Kindle Personal Document Service .
- Field Research Methods
- By Elizabeth Levy Paluck , Robert B. Cialdini
- Edited by Harry T. Reis , University of Rochester, New York , Charles M. Judd , University of Colorado Boulder
- Book: Handbook of Research Methods in Social and Personality Psychology
- Online publication: 05 June 2014
- Chapter DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511996481.008
Save book to Dropbox
To save content items to your account, please confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you use this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your account. Find out more about saving content to Dropbox .
Save book to Google Drive
To save content items to your account, please confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you use this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your account. Find out more about saving content to Google Drive .

Conducting Field Research
Some of the most valuable information in the world isn't located in a library or online. Field research is a way of unearthing that information. If you enjoy meeting and talking with people and don't mind what reporters call "legwork," you will relish the fun and satisfaction of obtaining ideas and information first hand.
Field research can be an extraordinarily exciting and rewarding experience leading to important discoveries and breakthrough ideas. Its goal is the same as research done in the library or on the Internet: to gather information that contributes to your understanding of an issue or question and to organize those findings in a cohesive and persuasive document that proposes a new insight, answer or solution.
Far from being at odds with one another-philosophically or practically-these three research techniques actually complement each other. Library and Internet research provides critical background information that prepares the researcher for making observations, and conducting interviews and surveys in the field.
The results will verify or refute, inform and help shape the answer to your research question.
Observing in the Field
First-hand observations will often be a key component in your research project. Your task is to take it all in, recording what you observe while being as unobtrusive as possible. You will want to take notes for future reference: interesting facts, telling details and sensory impressions (sights, sounds and smells), all help when it comes time to reconstruct your observations on paper.
Before you begin, it's important to do a little "legwork". Library and Internet research will help you build a list of possible sites from which to conduct your observation. Depending on the type of site you wish to observe, you may or may not need permission. It's important to find out.
A few phone calls or email inquiries will identify the contact person from whom you can get that information and the procedures you will be expected to follow. You may need to schedule an appointment, for instance.
A private business or a school will likely require identification when you arrive, so be prepared. You might ask your instructor for a statement on college or department letterhead declaring that you are a bona fide student and some specifics about your project and what you intend to do with the results.
In addition to note-taking, you may want to take some photographs or video-tape while observing. Permission for this will also likely be required, as well as waivers or releases signed by the human subjects involved.
Finally, before leaving the observation site, it's a good idea to schedule or request permission for a follow-up visit. When evaluating your initial observations it is highly likely that you will find gaps in your information that can only be filled by further observation. It is also quite possible that your evaluation will produce new ideas or expose areas of interest, previously unthought-of, that you may like to pursue. If not, you can always cancel the follow-up.
Interviewing Experts
Sometimes, the best information comes "straight from the horse's mouth". An interview is a conversation with a purpose; that being, to gather information from a person with first-hand knowledge-a primary source. Whenever possible, arrange a meeting with an expert in the field of your inquiry. Or, if you are investigating a particular group of people, interview a typical member, someone who represents the whole group and can speak for all of them.
You'll be surprised just how many people, from all walks of life, are willing to be interviewed-some even flattered by your attention. Choose them carefully. Regardless of who they are, prepare to interview them thoroughly. Chapter 4 "Writing from Conversation," in the Bedford Guide to Writing, offers some good advice:
- Make an appointment and schedule enough time-at least an hour.
- Be prompt and be prepared. Bring a list of carefully thought-out questions.
- Make sure your subject is willing to be quoted in writing.
- Really listen. This is the art of the interview. Let the person open up.
- Be flexible and allow the interview to go in unexpected directions.
- If a question goes unanswered, go on to the next question. You may be able to come back to it later.
- At the end of the interview, be sure to confirm any direct quotations you may use in your document.
- Make additional notes immediately after the interview, while the conversation is still fresh in your mind.
Be sure to take notes during the interview. These will come in handy later, when you reconstruct the interview on paper. Even when audio-recording, you should do this: In addition to recording important points and accurate quotations, notes allow you to record details that do not lend themselves to audio-recording. Your subject's mood, appearance and behavior, for instance, as well as your sensory impressions of the interview setting will come in handy when you begin constructing your document.
If an expert isn't readily available-perhaps the nearest one is too far away-you may be able to arrange a telephone interview. Make an appointment for a time convenient for both you and your subject. A busy person may not be able to give you even ten minutes on the spur of a moment, but all the time in the world if arranged for in advance. A further word of advice, don't try to wing-it; have written questions in hand before you dial. Take notes and follow all the other rules just as if you were doing the interview in person.
Note: Federal regulations forbid recording an interview over the phone without notifying the person being interviewed. When recording over the phone, you must also use a recorder connector with a warning device that emits a beeping signal at fifteen second intervals.
Corresponding with Experts
Is there a person whose knowledge or opinions you'd like to include in your research gathering but who lives too far away for a personal interview? A letter or e-mail message may do the trick. Be sure to make it short and polite. If you're sending a letter, it's a real good idea to enclose a stamped, self-addressed envelope along with your questions. And, if you're using e-mail, place your questions directly into the text of your email message so that the recipient can respond using the reply button.
Large corporations and organizations, branches of the military and the federal government as well as elected officials are all accustomed to being solicited in this manner. In fact, many of them employ public relations officers whose duties include responding to such solicitation. They will often supply you with free brochures, press releases and other source materials geared toward your inquiry.
Conducting Surveys
Surveys and questionnaires are as much a part of contemporary life as iPods and cell phones. In fact, many people enjoy having their knowledge tapped or their opinion solicited. Filling out a questionnaire can even have a game-like appeal: self-quiz features appear in popular magazines and tabloid newspapers all the time. "How Ambitious Are You?" will headline a thirty-question quiz that you can score yourself. Used judiciously, and with the following points in mind, you may find it useful to conduct a small survey yourself, as part of a research project.
Survey Basics
As a rule, professional pollsters, opinion testers, and survey takers solicit thousands of individuals when exploring the answers to a question. They are chosen to represent either a certain segment of society or a broad range of the populace diversified in geography, income, ethnic background, and education.
The purpose of a survey may be to inform a manufacturer when test-marketing a new product or identifying a new market. Politicians use them to plan their campaigns and judge the mood of their constituents. Regardless, they are widely used because they deliver large stores of useful information quickly and efficiently.
Few student research-writers conduct such extensive surveys as the time, money and effort required is prohibitive. For smaller, less prohibitive surveys then, it is best to report the results of your survey in non-statistical terms.
It's one thing to say that "many of the students" who filled out a questionnaire on reading habits hadn't read a newspaper in the past month; it's another to claim such is true of "seventy-two percent" of the student population when you were only able to give questionnaires to the twenty-two percent who were in the dining hall the day you were there and half of those threw them in the trash on the way out.
A far more useful and reliable way to use a questionnaire is to think of it as a group interview. Use it when you want to collect the same information from a large number of people or when you're more interested in what a group thinks as a whole than what a particular individual thinks. Treat the information you collect as representative and use your findings to build an overall knowledge of the subject or to cull them for interesting or persuasive details and quotations.
Define Your Purpose
If you think you want to use a survey to gather information, you need have a clearly defined purpose. You need to ask yourself:
- What am I trying to discover with this questionnaire?
You will want to build questions that are well thought out and which fulfill your purpose. If, for instance, you want to know how effective a day-care center is in the eyes of working mothers who entrust their children to it's care, you might ask questions like:
- Do your children report that they are happy there?
- Have you ever had reason to complain?
- If so, about what?
Keep it Simple
Any questionnaire you design has to be one that people are willing to answer. The main point is to make participation easy and inviting. If it's too complex or time-consuming, the recipient may throw it away.
Ask questions that call for a check mark in a list of alternative answers, a simple yes or no, or one word (at the most, just a few). As you write each question, check carefully for how well it fits your stated purpose. Check for ambiguity and whether they will elicit the kind of responses for which you are looking. It's a good idea to ask for just one piece of information per question.
Ask Open-Ended Questions
In addition to simple yes/no and multiple-choice questions, you might find it worth while to ask a few "open-ended questions". These call for short written responses. Although they are typically difficult to tally and are likely to draw a smaller number of responses, those you do get might supply a memorable quote or suggest some new ideas when you assess and analyze the results.

Avoid Slanted Questions
Be careful to build unbiased questions that will solicit factual responses. Don't ask:
- How religious are you?
You want to be able to report actual numbers or draw logical inferences about the respondents. Better questions might be:
- What is your religious affiliation?
- How often do you attend religious services?
Make it Easy for People to Respond
Whenever possible, distribute questionnaire at the end of a meeting or discussion. If that's not possible, assemble a group and have them fill out your questionnaire on the spot-at an evening coffee for parents with children in day-care, for instance. Facing them, you can explain the purpose of your research and invite questions, the answers to which will instill confidence and build interest.
If you must mail your questionnaire, include a concise letter explaining your purpose and what use you will make of the replies along with a self-addressed, stamped envelope. You might also indicate how much time will be required: no more than ten minutes, for instance, or some estimate identifying the task as reasonable and easy.
Professional pollsters often offer a small inducement, a morsel of bait to increase the rate of response: a small check or a coupon good for a free jar of pickles. You might promise a copy of your finished document, a brief report of the results, or a listing of each respondent's name in an acknowledgment.
Even with such inducements, professionals find a response rate of fifty percent or higher difficult, if not impossible, to achieve. That is why they often conduct surveys by telephone, with the caller filling in the questionnaire for the respondent. You might also use this technique, but better results will come if you distribute your questionnaire in person.
Tally the Results
When all the responses that you can reasonably expect to collect have been received, sit down and tally up the results. It's easy to count the short answers: the yes's and no's and the one word answers-like Republican or Democrat-but the longer ones are more difficult.
- What is your goal in life?
The answers to open-ended questions need to be summed up or paraphrased and then sorted into rough categories.
- To grow rich
- To serve humanity
- To save my soul
Similar responses can be lumped together and counted, accurately measuring the extent of, or pattern to, the available responses.
Media Genres: Television, Radio, Film, etc.
Intriguing possibilities for field research lie in the media. For a research paper about television and radio, movies, theater or music, you may find the materials close at hand. In the case of television, it's as close as the remote.
Our only advice is to review plenty: watch (or listen) to a large amount before drawing conclusions. Use a VCR, DVD, or other audio-video recording device to keep track of your research and to preserve a record for future reference.
Transcripts, broadcast tapes or telecasts may be available on request, or for a small fee, from network or cable stations. Call, write or email your inquiries.
Lectures, Conferences, Online Forums, and Other Public Discussions
Field research often involves attending a lecture, conference or other public discussion. College organizations frequently bring interesting speakers to campus: the science club might sponsor a nationally known marine biologist, for instance, or the film club might bring in the producer of a successful television program.
Likewise, bound by mutual affiliation, professionals and members of special-interest groups are brought together at regularly scheduled regional and national conferences across this country every day. Regardless of cost, you may want to attend one that addresses your particular research interests.
Health-care providers, legal experts, engineers, scientists and teachers attend them frequently in the course of their professional duties and to further they're careers. You can do the same. They can be a fertile source of fresh ideas and are often open to the public: sometimes admission is free or student discounts are available.
Regardless of cost, attending a professional conference affords an opportunity for taking notes at lectures given by experts and the chance to meet and talk with speakers and fellow attendees as well as to learn and practice the language of a discipline. In addition, you may be able to obtain a copy of the proceedings-usually a set of all the lectures delivered, sometimes with accompanying commentary.
Be on the lookout as well for online discussions such as Chat Room sessions sponsored by Yahoo or CNN Online-that are relevant to your research topic. You can participate in the discussion as an observer, or participate by posting questions. Remember to use your Chat Room program to record the session for later review. You can learn how to record a transcript by consulting the program's online help.
Palmquist, Mike, & Peter Connor. (2007). Conducting Field Research. Writing@CSU . Colorado State University. https://writing.colostate.edu/guides/guide.cfm?guideid=23
- Marketing Research
Field Research - Definition and its important sources
Field Research deals with creation and collection of actual and authentic information by field of operation in any organization.
The process involves determining what precise data is necessary and from where this information needs to be obtained. After determining this information the data is actually gathered. Thus this research technique is treated as the primary research approach because the determined data is specific to the purpose of gathering that data.
Field research is generally performed in person, telephonic or by electronic media like teleconferencing, web-meetings and emails .
Many of the big organizations involve outside vendors or companies to perform this task which they usually refer as outsourcing, but small organizations or new companies do this themselves by involving their internal resources.
The outsourcing depends on the type and amount of information to be gathered in the research. If the required data is less and limited to some small and specific modules then big organization also prefer to do this task in-house.
Field research is expensive and involves more and experienced resources as compared to desk research which is not as accurate as field research.
Being expensive it is required to perform the research in efficient manner and obtain or determine only specific information and answer only particular questions as irrelevant data is a waste and will be of no use for further research processes.
The following are the importance sources for field research:

There are many other less prominent sources like interviews, trade shows, and promotional programs etc. and much of the relevant information could be gathered from these sources as well. All the information gathered from the above sources is then manipulated and segmented.
As in field research most of the information is relevant as it is actually gathered for a particular purpose, so regular round of work around on the data is not required.
After validating the information it is then fetched into the CRM system and is converted into intelligent data which can be accessed on real time.
Related Articles
- Market Research and CRM
- Market Research Process
- Desk Research
- Data Analysis and Compilation
- Report Preparation
View All Articles
Authorship/Referencing - About the Author(s)
The article is Written and Reviewed by Management Study Guide Content Team . MSG Content Team comprises experienced Faculty Member, Professionals and Subject Matter Experts. We are a ISO 2001:2015 Certified Education Provider . To Know more, click on About Us . The use of this material is free for learning and education purpose. Please reference authorship of content used, including link(s) to ManagementStudyGuide.com and the content page url.
- Marketing Research - Introduction
- Limitations of Marketing Research
- Marketing Research: Step by Step Execution
- Data Collection in Marketing Research
- Qualitative and Quantitative Research - Concept
- Types of Marketing Research and their Application
- Focus Groups
- Depth Interview
- Projective Techniques
- Survey Method
- Techniques of Survey Method
- Observation Method
- Secondary Data
- Sources of Data
- What is Big Data ?
- Big Data and the Power to Predict
- Attitude Measurement Scales
- Questionnaire Design
- Statistical Tools and their Usage - Factor Analysis
- Conjoint Analysis - Meaning, Usage and its Limitations
- What is Mystery Shopping ?
- Regression Analysis
- Concept Testing
- Brand Health Survey
- Importance of Market Research to Organizations in an Age of Unpredictability
- It’s Not Just the Data that is collected that Counts, but, the Quality of the Data as well
- What is the Efficient Market Hypothesis and How it Works and Doesn’t Work in Practice
Principles of Sociological Inquiry
Chapter 10: field research: a qualitative technique, chapter 10 field research: a qualitative technique, why field research.
If we wanted to know who conducts more of the housework in households, how could we find the answer? One way might be to interview people and simply ask them. That is exactly what Arlie Hochschild did in her study of the second shift , her term for the work that goes on in the home after the day’s work for pay is completed. Hochschild (1989) Hochschild, A. (1989). The second shift: Working parents and the revolution at home (1st ed.). New York, NY: Viking. interviewed 50 heterosexual, married couples with children to learn about how they did, or did not, share the work of the second shift. Many of these couples reported to her that they shared the load of the second shift equally, sometimes dividing the house into areas that were “her responsibility” and those that were “his.” But Hochschild wasn’t satisfied with just people’s personal accounts of second-shift work. She chose to observe 12 of these couples in their homes as well, to see for herself just how the second shift was shared.
What Hochschild discovered was that even those couples who claimed to share the second shift did not have as equitable a division of duties as they’d professed. For example, one couple who told Hochschild during their interview that they shared the household work equally had explained that the wife was responsible for the upstairs portion of the house and the husband took responsibility for the downstairs portion. Upon conducting observations in this couple’s home, however, Hochschild discovered that the upstairs portion of the house contained all the bedrooms and bathrooms, the kitchen, the dining room, and the living room, while the downstairs included a storage space and the garage. This division of labor meant that the woman actually carried the weight of responsibility for the second shift. Without a field research component to her study, Hochschild might never have uncovered these and other truths about couples’ behaviors and sharing (or not sharing) of household duties.
10.1 Field Research: What Is It and When to Use It?
Learning objectives.
- Define field research.
- Define participant observation and describe the continuum of participant observation.
- Discuss at least two examples of field research.
There’s a New Yorker cartoon that pretty accurately portrays life for a field researcher (Cotham, 2003). Cotham, F. (2003, September 1). Two barbarians and a professor of barbarian studies. The New Yorker . Retrieved from http://www.cartoonbank.com/2003/two-barbarians-and-a-professor-of-barbarian-studies/invt/126562 It depicts “Two Barbarians and a Professor of Barbarian Studies.” As field researchers, just as in the cartoon, we immerse ourselves in the settings that we study. While the extent to which we immerse ourselves varies (note in the cartoon the professor is riding a horse but has chosen to retain his professorial jacket and pipe), what all field researchers have in common is their participation in “the field.”
Field research A qualitative method of data collection that involves observing, interacting with, and interviewing people in their natural settings. is a qualitative method of data collection aimed at understanding, observing, and interacting with people in their natural settings. Thus when social scientists talk about being in “the field,” they’re talking about being out in the real world and involved in the everyday lives of the people they are studying. Sometimes researchers use the terms ethnography or participant observation to refer to this method of data collection; the former is most commonly used in anthropology, while the latter is used commonly in sociology. In this text, we’ll use two main terms: field research and participant observation . You might think of field research as an umbrella term that includes the myriad activities that field researchers engage in when they collect data: they participate, they observe, they usually interview some of the people they observe, and they typically analyze documents or artifacts created by the people they observe.
Figure 10.2

Field research typically involves a combination of participant observation, interviewing, and document or artifact analysis. This chapter focuses primarily on participant observation.
Because we cover interviews and document/artifact analysis in Chapter 9 “Interviews: Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches” and Chapter 11 “Unobtrusive Research: Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches” , here we’ll focus only on the participation and observation aspects of field research. These aspects of field research are usually referenced together and are known as participant observation The parts of field research that involve spending time with and watching one’s research participants; interviewing and document/artifact analysis are the other two components of field research. . Like field research, participant observation also has multiple meanings. Researchers conducting participant observation vary in the extent to which they participate or observe (Junker, 1960). Junker, B. H. (1960). Field work: An introduction to the social sciences . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press. You might say that there’s a continuum of participant observation, where complete observation lies at end of the continuum and complete participation lies at the other end.
In other chapters, we discuss two works that could fall on either end of the participant observation continuum. Barrie Thorne’s (1993) Thorne, B. (1993). Gender play: Girls and boys in school . New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press. observations of children in classrooms, school cafeterias, hallways, and playgrounds rest near the complete observation end of the continuum. Rather than actually pretending to be an elementary school student and interacting with her research participants as they would each other, Thorne observed (which, as discussed in Chapter 4 “Beginning a Research Project” , was probably a wise move since it would have been difficult to convince the students that she was one of them). Laud Humphreys’s (1970) Humphreys, L. (1970). Tearoom trade: Impersonal sex in public places . London, UK: Duckworth. research on the tearoom trade, described in Chapter 3 “Research Ethics” , could be said to rest on the other end of the continuum. Rather than only observe, Humphreys played the key tearoom role of watch queen, a role that nonresearcher participants in the trade also played. Humphreys also did not tell many of the people he observed that he was a researcher; thus from the perspectives of many of his “subjects,” he was only a participant. The participant observation continuum is represented in Figure 10.3 .
There are pros and cons associated with both aspects of the participant observer’s role. Complete observers may miss important aspects of group interaction and don’t have the opportunity to fully grasp what life is like for the people they observe. At the same time, sitting back and observing may grant them opportunities to see interactions that they would miss were they more involved. Complete participation has the benefit of allowing researchers a real taste of life in the group that they study. Some argue that participation is the only way to understand what it is that we investigate. On the other hand, complete participants may find themselves in situations that they’d rather not face but cannot excuse themselves from because they’ve adopted the role of complete participant. Also, complete participants who do not reveal themselves as researchers must face the ethical quandary of possibly deceiving their “subjects.” In reality, most field research projects lie somewhere near the middle of the observer-participant continuum. Field researchers typically participate to at least some extent in their field sites, but there are also times when they may just observe. Where would you feel most comfortable as a field researcher—as an observer, a participant, or a bit of both?
As you might have imagined based on the examples of Thorne’s and Humphreys’s work, field research is well equipped to answer “how” kinds of questions. Whereas survey researchers often aim to answer “why” questions, field researchers ask how the processes they study occur, how the people they spend time with in the field interact, and how events unfold. Table 10.1 “Field Research Examples” presents just a few examples of the kinds of questions field researchers have asked in past projects along with a brief summary of where and what role those researchers took in the field. The examples presented in Table 10.1 “Field Research Examples” by no means represent an exhaustive list of the variations of questions field researchers have asked or of the range of field research projects that have been conducted over the years, but they do provide a snapshot of the kinds of work sociological field researchers engage in.
Table 10.1 Field Research Examples
| Question | Researcher role | Author (year) |
|---|---|---|
| How is the social structure of a local “slum” organized? | Over 3 years of participation and observations among an Italian community in Boston’s North End | Whyte (1942)William Foote Whyte is considered by many to be the pioneer of the use of participant observation methods in sociological studies. Whyte, W. F. (1942). . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press. |
| How do the urban poor live? | Twenty months of participation and observations among an African American community in Washington, DC | Liebow (1967)Liebow, E. (1967). . Boston, MA: Little, Brown. |
| Why and how do workers consent to their own exploitation? | Ten months of participation as a machine operator in a Chicago factory along with observations of workers in the factory | Burawoy (1979)Burawoy, M. (1979). . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press. |
| How is erotic labor organized in two different countries, and what are sex workers’ experiences in each? | Brief participation in sex transactions in the Netherlands and California along with observations of and interviews with sex workers in both locations | Chapkis (1997)Chapkis, W. (1997). . New York, NY: Routledge. |
| How does childrearing differ across social classes? | Approximately one month each participating and observing in the homes and lives of 12 different families | Lareau (2003)Lareau, A. (2003). . Berkeley: University of California Press. |
| How is masculinity constructed by and among high school students, and what does this mean for our understandings of gender and sexuality? | Eighteen months of observations and interviews in a racially diverse working-class high school | Pascoe (2007)Pascoe, C. J. (2007). . Berkeley: University of California Press. |
| How do sports play a role in shaping gender, class, family, and community? | Participation as a youth soccer volunteer along with observations and interviews | Messner (2009)Messner, M. (2009). . Berkeley: University of California Press. |
Field research is a method that was originally crafted by anthropologists for the purpose of cultural understanding and interpretation (Wolcott, 2008). Wolcott, H. F. (2008). Ethnography: A way of seeing (2nd ed.). Lanham, MD: Altamira Press. Dissatisfied with studying groups of people based solely on secondhand accounts and inspection of artifacts, several anthropologists decided to try living in or near the communities they studied to learn from and about them. Two anthropologists in particular, Franz Boas (1888) Boas, F. (1888). The central Eskimo . Washington, DC: Bureau of American Ethnology. and Bronislaw Malinowski (1922), Malinowski, B. (1922). Argonauts of the western Pacific: An account of native enterprise and adventure in the archipelagoes of Melanesian New Guinea . London, UK: G. Routledge & Sons; New York, NY: E. P. Dutton. are credited with developing this method around the turn of the 20th century. Boas lived with native populations in Canada and in the American Northwest. Malinowski lived in Papua New Guinea with people who were native to the area. Sociologists picked up on the idea and on the benefits of field research (which we’ll examine in Section 10.2 “Pros and Cons of Field Research” ). Soon a number of sociologists had embraced this new method and adapted field research for their own studies of groups. Many of the early field researchers in sociology were former social workers who got interested in sociological research because of experiences in their roles as social reformers. The University of Chicago in particular played a key role in the development of American field research through, among other projects, its involvement in Hull House, Jane Addams Hull House Association. Retrieved from http://www.hullhouse.org a social settlement founded for European immigrants in Chicago (Deegan, 1986). Deegan, M. J. (1986). Jane Addams and the men of the Chicago School, 1892–1918 . New Brunswick, NJ: Transaction Books.
Key Takeaways
- Field research typically involves a combination of participant observation, interviewing, and document or artifact analysis.
- Different participant observation projects rest in different places on the continuum of complete observer to complete participant; most lie near the middle of the continuum.
- Field research has its origins in anthropology.
- As a preview to some of the pros, cons, joys, and frustrations of doing field research, watch the following clip, which shows “news” personality Stephen Colbert interviewing sociologist Sudhir Venkatesh Venkatesh’s work was introduced in Chapter 2 “Linking Methods With Theory” , the chapter on linking methods with theory. about his field research in some of Chicago’s poorest neighborhoods: http://www.colbertnation.com/the-colbert-report-videos/156631/march-13-2008/sudhir-venkatesh . The clip highlights some of the advantages field research has over survey interviewing; it also highlights some of the disadvantages of field research. Based on what you see in the clip, what are some of the main advantages of field research as compared to survey interviewing? What are some of the main disadvantages?
- If you would like to learn more about William Foote Whyte’s groundbreaking field research, a 40-minute interview with Whyte and several of his research participants, conducted nearly 40 years after the publication of Street Corner Society , can be found at the following link: http://www.northendwaterfront.com/home/2010/6/18/street-corner-society-video-of-william-foote-whyte-north-end.html . What role did Whyte play in the field: complete observer, complete participant, or something in between? Use evidence from the interview to support your answer. What pros and cons of field research come up in the interview?
- Where do you think is the best place to reside on the observer-participant continuum? Why? What are the pros and cons of each of the various places on the continuum?
10.2 Pros and Cons of Field Research
- Identify and explain the strengths of field research.
- Identify and explain the weaknesses of field research.
Field research has many benefits, as well as a set of drawbacks. We’ll explore both here.
Strengths of Field Research
Field research allows researchers to gain firsthand experience and knowledge about the people, events, and processes that they study. No other method offers quite the same kind of closeup lens on everyday life. This close-up on everyday life means that field researchers can obtain very detailed data about people and processes, perhaps more detailed than they can obtain using any other method.
Field research is an excellent method for understanding the role of social context in shaping people’s lives and experiences. It enables a greater understanding of the intricacies and complexities of daily life. Field research may also uncover elements of people’s experiences or of group interactions of which we were not previously aware. This in particular is a unique strength of field research. With other methods, such as interviews and surveys, we certainly can’t expect a respondent to answer a question to which they do not know the answer or to provide us with information of which they are not aware. And because field research typically occurs over an extended period of time, social facts that may not even be immediately revealed to a researcher but that become discovered over time can be uncovered during the course of a field research project.
In sum, the major benefits of field research are the following:
- It yields very detailed data.
- It emphasizes the role and relevance of social context.
- It can uncover social facts that may not be immediately obvious or of which research participants may be unaware.
Weaknesses of Field Research
Earlier I described the fact that field researchers are able to collect very detailed data as a benefit of this method. This benefit, however, does come at a cost. Because a field researcher’s focus is so detailed, it is by necessity also somewhat narrow. Field researchers simply are not able to gather data from as many individuals as, say, a survey researcher can reach. Indeed, field researchers generally sacrifice breadth in exchange for depth. Related to this point is the fact that field research is extremely time intensive.
Field research can also be emotionally taxing. In Chapter 9 “Interviews: Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches” , I assert that interview research requires, to a certain extent, the development of a relationship between a researcher and her participants. But if interviews and field research both require relationship development, you might say that interviews are more like casual dating while field research is more like a full-blown, committed marriage.
The relationships you develop as a field researcher are sustained over a much longer period than the hour or two it might take you to conduct an interview. Not only do the relationships last longer, but they are also more intimate. A number of field researchers have documented the complexities of relationships with research participants (Arditti, Joest, Lambert-Shute, & Walker, 2010; Keinman & Copp, 1993; MacLeod, 1995). MacLeod, J. (1995). On the making of ain’t no makin’ it. In J. MacLeod (Ed.), Ain’t no makin’ it: Aspirations and attainment in a low-income neighborhood (pp. 270–302). Boulder, CO: Westview Press; Arditti, J. A., Joest, K. A., Lambert-Shute, J., & Walker, L. (2010). The role of emotions in fieldwork: A self-study of family research in a corrections setting. The Qualitative Report, 15, 1387–1414; Keinman, S., & Copp, M. A. (1993). Emotions and fieldwork . Newbury Park, CA: Sage. On the plus side, these relationships can be very rewarding (and yield the rich, detailed data noted as a strength in the preceding discussion). But, as in any relationship, field researchers experience not just the highs but also the lows of daily life and interactions. And participating in day-to-day life with one’s research subjects can result in some tricky ethical quandaries (see Chapter 3 “Research Ethics” for a discussion of some of these quandaries). It can also be a challenge if your aim is to observe as “objectively” as possible.
Finally, documentation can be challenging for field researchers. Where survey researchers have the questionnaires participants complete and interviewers have recordings, field researchers generally have only themselves to rely on for documenting what they observe. This challenge becomes immediately apparent upon entering the field. It may not be possible to take field notes as you observe, nor will you necessarily know which details to document or which will become the most important details to have noted. And when you take notes after some observation, you may not recall everything exactly as you saw it when you were there.
In sum, the weaknesses of field research include the following:
- It may lack breadth; gathering very detailed information means being unable to gather data from a very large number of people or groups.
- It may be emotionally taxing.
- Documenting observations may be more challenging than with other methods.
- Strengths of field research include the fact that it yields very detailed data, it is designed to pay heed to social context, and it can uncover social facts that are not immediately obvious.
- Weaknesses of field research include that researchers may have to sacrifice breadth for depth, the possibility that the research will be emotionally taxing, and the fact that documenting observations can be challenging.
- In your opinion, what is the most important strength of field research? What do you view as its greatest weakness? Explain your position.
- Find an article reporting results from field research. You can do this by using the Sociological Abstracts database, which was introduced in Chapter 4 “Beginning a Research Project” . How do the authors describe the strengths and weaknesses of their study? Are any of the strengths or weaknesses described in this section mentioned in the article? Are there additional strengths or weaknesses not mentioned in this section?
10.3 Getting In
- Identify the two major considerations with respect to “getting in” field research sites.
- Describe the factors one should consider when choosing a field research site.
- Explain how one’s social location is relevant for choosing a field research site.
- Describe the factors one should consider when deciding what role to play in a field research site.
- Explain the difference between overt and covert roles in field research.
When embarking on a field research project, there are two major things to consider: where to observe and what role you’ll take in your field site. Your decision about each of these will be shaped by a number of factors, some of which you’ll have control over and others which you won’t. Your decision about where to observe and what role to play will also have consequences for the data you are able to gather and how you analyze and share those data with others. We’ll examine each of these contingencies in the following subsections.
Choosing a Site
Where you observe might be determined by your research question, but because field research often works inductively, you may not have a totally focused question before you begin your observations. In some cases, field researchers home in on a research question once they embark on data collection. Other times, they begin with a research question but remain open to the possibility that their focus may shift as they gather data. In either case, when you choose a site, there are a number of factors to consider. What do you hope to accomplish with your field research? What is your topical/substantive interest? Where are you likely to observe behavior that has something to do with that topic? How likely is it that you’ll actually have access to the locations that are of interest to you? How much time do you have to conduct your participant observations? Will your participant observations be limited to a single location, or will you observe in multiple locations?
Perhaps the best place to start as you work to identify a site or sites for your field research is to think about your limitations . One limitation that could shape where you conduct participant observation is time. Field researchers typically immerse themselves in their research sites for many months, sometimes even years. In my field research on activism in the breast cancer and antirape movements, I conducted over 300 hours of participant observation over a period of 3 years and conducted interviews with more than 60 activists (Blackstone, 2003). Blackstone, A. (2003). Racing for the cure and taking back the night: Constructing gender, politics, and public participation in women’s activist/volunteer work (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Department of Sociology, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN. And as shown in Table 10.1 “Field Research Examples” , other field researchers have spent as much or even more time in the field. Do you have several years available to conduct research, or are you seeking a smaller-scale field research experience? How much time do you have to participate and observe per day? Per week? Identifying how available you’ll be in terms of time will help you determine where and what sort of research sites to choose.
Also think about where you live and whether travel is an option for you. Some field researchers actually move to live with or near their population of interest. Is this something you might consider? Is it even an option? How you answer these questions will shape how you identify your research site. Professor Erik Larson’s (2010) Larson, E. (2010). Time and the constitution of markets: Internal dynamics and external relations of stock exchanges in Fiji, Ghana, and Iceland. Economy and Society, 39, 460–487. research on variations in economic institutions in a global environment, for example, has taken him across the globe, from Fiji to Ghana to Iceland. Sociologist Sara Dorow’s (2006) Dorow, S. (2006). Transnational adoption: A cultural economy of race, gender, and kinship . New York, NY: New York University Press. research on transnational adoption took her from the United States to China. And the work of Wendy Chapkis (1997), Chapkis, W. (1997). Live sex acts: Women performing erotic labor . New York, NY: Routledge. described in Table 10.1 “Field Research Examples” , required her to conduct research not only in her original home state of California but also in the Netherlands. These are just a few of many examples of sociological researchers who have traveled the globe for the purpose of collecting data. Where might your field research questions take you?
In choosing a site, also consider how your social location might limit what or where you can study. The ascribed aspects of our locations are those that are involuntary, such as our age or race or mobility. How might my ascribed status as a middle-aged woman, for example, shape my ability to conduct complete participation in a study of children’s birthday parties? The achieved aspects of our locations, on the other hand, are those that we have some choice about. In field research, we may also have some choice about whether or the extent to which we reveal the achieved aspects of our identities. There are numerous examples of field researchers whose achieved statuses granted them access to field sites into which they might not have otherwise been allowed. Jennifer Pierce (1995), Pierce, J. L. (1995). Gender trials: Emotional lives in contemporary law firms . Berkeley: University of California Press. for example, utilized her achieved status as a paralegal to gain entry into two law offices for her ethnographic study of the gendered division of labor in corporate law firms. In Lauraine Leblanc’s (1999) Leblanc, L. (1999). Pretty in punk: Girls’ gender resistance in a boys’ subculture . New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press. case, the achieved status of her appearance, including tattoos and a “punk” hairstyle and color, helped her gain the acceptance of research participants in her study of punk girls.
The preceding discussion should not be taken to mean that sociologists cannot, should not, or do not study those from whom we differ. In fact there have been plenty of successful field studies conducted by researchers who may have looked out of place in the sites they chose to investigate. Teresa Gowan, a self-described “small, white English woman” (2010, p. 16), Gowan, T. (2010). Hobos, hustlers, and backsliders: Homeless in San Francisco . Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press. conducted field research with homeless men in some of San Francisco’s most notoriously rough neighborhoods. The aim here is not to reify the socially constructed categories upon which our society places so much emphasis in organizing itself. Rather, the point is to be aware of which ascribed and achieved aspects of your identity may shape your decisions about field sites.
Finally, in choosing a research site consider whether your research will be a collaborative project or whether you are on your own (Douglas, 1976). Douglas, J. D. (1976). Investigative social research: Individual and team field research . Beverly Hills, CA: Sage. Collaborating with others has many benefits; you can cover more ground and therefore collect more data than you can on your own. And having collaborators in any research project, but especially field research, means having others with whom to share your trials and tribulations in the field. However, collaborative research comes with its own set of challenges such as possible personality conflicts among researchers, competing commitments in terms of time and contributions to the project, and differences in methodological or theoretical perspectives (Shaffir, Marshall, & Haas, 1979). Shaffir, W., Marshall, V., & Haas, J. (1979). Competing commitments: Unanticipated problems of field research. Qualitative Sociology, 2, 56–71. If you are considering collaborative field research, you are in good company; many fascinating examples precede you. David Snow and Leon Anderson (1993) Snow, D. A., & Anderson, L. (1993). Down on their luck: A study of homeless street people . Berkeley: University of California Press. conducted a collaborative study of homelessness in Austin, Texas. And researchers at the University of Minnesota recently conducted a large-scale, cross-country field study of how forms of difference such as race and religion shape American life and experience ( http://www.soc.umn.edu/research/amp.html ). When considering something that is of interest to you, consider also whether you have possible collaborators. How might having collaborators shape the decisions you make about where to conduct participant observation?
I began this discussion by asking you to think about limitations that might shape your field site decisions. But it makes sense to also think about the opportunities —social, geographic, and otherwise—that your location affords. Perhaps you are already a member of an organization where you’d like to conduct research. Maybe you know someone who knows someone else who might be able to help you access a site. Perhaps you have a friend you could stay with, enabling you to conduct participant observations away from home. Choosing a site for participation is shaped by all these factors—your research question and area of interest, a few limitations, some opportunities, and sometimes a bit of being in the right place at the right time.
Choosing a Role
As with choosing a research site, some limitations and opportunities beyond your control might shape the role you take once you begin your participant observation. You’ll also need to make some deliberate decisions about how you enter the field and “who” you’ll be once you’re in.
In terms of entering the field, one of the earliest decisions you’ll need to make is whether to be overt or covert. As an overt Researcher enters the field by revealing status as a researcher; participants know they are being studied. researcher, you enter the field with research participants having some awareness about the fact that they are the subjects of social scientific research. Covert Researcher enters the field by pretending to be a participant only; participants do not know they are being studied. researchers, on the other hand, enter the field as though they are full participants, opting not to reveal that they are also researchers or that the group they’ve joined is being studied. As you might imagine, there are pros and cons to both approaches. A critical point to keep in mind is that whatever decision you make about how you enter the field will affect many of your subsequent experiences in the field.
As an overt researcher, you may experience some trouble establishing rapport at first. Having an insider at the site who can vouch for you will certainly help, but the knowledge that subjects are being “watched” will inevitably (and understandably) make some people uncomfortable and possibly cause them to behave differently than they would were they not aware of being research subjects. Because field research is typically a sustained activity that occurs over several months or years, it is likely that participants will become more comfortable with your presence over time. Overt researchers also avoid a variety of moral and ethical dilemmas that they might otherwise face. A Far Side cartoon demonstrates this point perfectly. It depicts a “researcher” dressed up like a gorilla, hanging out with a few other gorillas. In the cartoon, one of the real gorillas is holding out a few beetle grubs to the researcher, and the caption reads, “So you’re a real gorilla, are you? Well I guess you wouldn’t mind munchin’ down a few beetle grubs, would you? In fact, we wanna see you chug ’em!” ( http://www.e-noah.net/asa/asashoponlineservice/ProductDetails.aspx?productID=ASAOE710N04 ).
As a covert researcher, “getting in” your site might be easier, but then you might face other issues. For how long would you plan to conceal your identity? How might participants respond once they discover you’ve been studying them? And how will you respond if asked to engage in activities you find unsettling or unsafe? Field researcher Richard Mitchell (1991) Mitchell, R. G., Jr. (1991). Secrecy and disclosure in fieldwork. In W. B. Shaffir and R. A. Stebbins (Eds.), Experiencing fieldwork: An inside view of qualitative research (pp. 97–108). Newbury Park, CA: Sage. was forced to consider these very questions during his covert research among right-wing survivalists when he was asked to participate in the swapping of violently racist and homophobic stories, an experience over which he later expressed profound grief and deep regret. Beyond your own personal level of comfort with deceiving participants and willingness to take risks, it is possible that the decision about whether to enter the field covertly will be made for you. If you are conducting research while associated with any federally funded agency (and even many private entities), your institutional review board (IRB) probably will have something to say about any planned deception of research subjects. Some IRBs approve deception, but others look warily upon a field researcher engaging in covert participation. The extent to which your research site is a public location, where people may not have an expectation of privacy, might also play a role in helping you decide whether covert research is a reasonable approach.
I mentioned that having an insider at your site who can vouch for you is helpful. Such insiders, with whom a researcher may have some prior connection or a closer relationship than with other site participants, are called key informants Field site insider with whom the field researcher has a closer relationship and who can provide insider knowledge about a group being observed. . A key informant can provide a framework for your observations, help “translate” what you observe, and give you important insight into a group’s culture. If possible, having more than one key informant at a site is ideal, as one informant’s perspective may vary from another’s.
Once you’ve made a decision about how to enter your field site, you’ll need to think about the role you’ll adopt while there. Aside from being overt or covert, how close will you be to participants? In the words of Fred Davis (1973), Davis, F. (1973). The Martian and the convert: Ontological polarities in social research. Urban Life, 2, 333–343. who coined these terms in reference to researchers’ roles, will you be a Martian , a Convert , or a bit of both? Davis describes the Martian role as one in which a field researcher stands back a bit, not fully immersed in the lives of his subjects, in order to better problematize, categorize, and see with the eyes of a newcomer what’s being observed. From the Martian perspective, a researcher should remain disentangled from too much engagement with participants. The Convert, on the other hand, intentionally dives right into life as a participant. From this perspective, it is through total immersion that understanding is gained. Which approach do you feel best suits you?
In the preceding section we examined how ascribed and achieved statuses might shape how or which sites you choose for your field research. They also shape the role you adopt in your field site. The fact that I am a professor, for example, is an achieved status, and I can choose the extent to which I share this aspect of my identity with field study participants. In some cases perhaps sharing that I am a professor would enhance my ability to establish rapport; in other field sites it might stifle conversation and rapport-building. As you’ve seen from the examples provided throughout this chapter, different field researchers have taken different approaches when it comes to using their social locations to help establish rapport and dealing with ascribed statuses that differ from those of their “subjects.”
Whatever role you choose, many of the points made in Chapter 9 “Interviews: Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches” about power and relationships with participants apply to field research as well. In fact, the researcher-researched relationship is even more complex in field studies, where interactions with participants last far longer than the hour or two it might take to interview someone. Moreover, the potential for exploitation on the part of the researcher is even greater in field studies as relationships are usually closer and lines between “research” and personal or off-the-record interaction may get blurred. These precautions should be seriously considered before deciding to embark upon a field research project.
- When beginning a field research project, one must take care in planning where to conduct observations and what role to adopt in one’s field site.
- The time you have available to spend in the field will be a major factor in choosing your research site.
- There are pros and cons to both the overt and the covert researcher roles.
- Ascribed and achieved statuses both shape the choices that field researchers make about their sites and about their roles within those sites.
- Try to name at least three different locations where you might like to conduct field research. What barriers would you face were you to attempt to enter those sites as a researcher? In what ways might your entrée into the sites be facilitated by your social location?
- What is your opinion about researchers taking on a covert as compared with an overt role in field research? Which role would you like to take in a field research project? Why?
10.4 Field Notes
- Define descriptive field notes.
- Cite the variety of ways that field researchers might take notes while in the field.
- Describe what should be noted when taking field notes.
Field notes are your opportunity to write poorly and get away with it. I say that in jest, but there is some truth to it. This is one type of writing where you should not be going for literary value, to make your writing interesting, and even to make it readable for anyone other than yourself. Instead, the aim is to record your observations as straightforwardly and, while in the field, as quickly as possible in a way that makes sense to you . Field notes In field research, the official record that affirms what you observed. are the first—and a necessary—step toward developing quality analysis. They are also the record that affirms what you observed. In other words, field notes are not to be taken lightly or overlooked as unimportant.
Some say that there are two different kinds of field notes: descriptive and analytic. Though the lines between what counts as “description” and what counts as “analysis” can get pretty fuzzy, the distinction is nevertheless useful when thinking about how to write and how to interpret field notes. In this section, we’ll focus on descriptive field notes. Descriptive field notes Notes that describe a field researcher’s observations as straightforwardly as possible. are notes that simply describe a field researcher’s observations as straightforwardly as possible. These notes typically do not contain explanations of or comments about those observations. Instead, the observations are presented on their own, as clearly as possible. In the following section, we’ll examine the uses and writing of analytic field notes more closely.
Writing in the Field
Field researchers use a variety of strategies to take notes while in the field. Some research is conducted in settings where sitting with a notebook, iPad, or computer is no problem (e.g., if conducting observations in a classroom or at a meeting), but this is probably the exception rather than the norm. More often, field researchers must find creative ways to note their observations while engaged in the field. I’ve heard about field researchers jotting notes on their hands and arms, keeping very small notebooks in their pockets and occasionally jotting notes there, carrying small recorders to make quick observations, and even writing notes on toilet paper during visits to the restroom. With the advent of smartphones, taking notes in the field has become less arduous than it once was, as it is common to see someone texting or surfing the web from their phone in almost any setting.
Your strategy for recording your observations while in the field will be determined mostly by the site you choose and the role you play in that site. Will you be in a setting where having a notebook or smartphone in your hands will look out of place? If no, by all means, take notes! But don’t let your note taking distract you from what’s happening around you. Writing notes while in the field requires a fine balance between jotting down your observations and actually engaging in the setting. If you are strictly an observer, these will be easy to balance. But if you are also a participant, don’t let your note taking keep you from participating. If you do happen to be in a location where taking notes “in the moment” would be too obvious, rude, or distracting, you may still be able to occasionally jot down a few things very quickly. You may also need to develop a way of jotting down observations that doesn’t require complete sentences or perhaps even words. I know several field researchers who developed their own version of shorthand to take notes, using some combination of abbreviations and symbols, without taking too much time away from their participation in the field.
As with other proficiencies one develops, writing field notes is a skill that can be improved with practice. Recall the discussion in Chapter 1 “Introduction” about the dangers of informal observation. Conducting field research and taking field notes are decidedly not informal activities. In field research, observation is deliberate, not haphazard. That said, for a first-time field researcher, taking field notes can feel like a pretty haphazard activity. Understanding when to write, what to write, where to write, and how to write are all skills that field researchers develop with experience. I demonstrate this point to students early in our discussion of field methods by sending them out of the classroom in groups of two or three each and having them take notes about what they observe over a 15-minute period of time. No problem, they say. How hard can it be? Pretty tough, as it turns out. Students typically return from their 15 minutes of observation frustrated, confused, and annoyed with me for putting them through the experience.
So why torture my students in this way? It isn’t just to be a jerk, I promise. When students return to the classroom, I ask them to compare notes with their group members and discuss what strategies they used in making and recording observations. Typically, students have some overlap in the kinds of things noted, but inevitably one person will have paid more attention to conversations overheard, another to actions and unspoken physical expressions such how people walked or dressed, and yet another to nonhuman surroundings such as the landscape, sounds, and scents. Students conducting this exercise also often use different note-taking strategies, some drawing more pictures, others writing in complete sentences, others using abbreviations. I ask them to talk about what they’ve learned from the experience and the following two “lessons” are among the most frequently cited: (a) taking field notes is hard, and (b) it would have been nice to have some more direction before the exercise so they knew what to zero in on.
I’m always glad to hear that students recognize the difficulty of the task, and it’s true that I give them very few instructions prior to the field note exercise. This is intentional. In part I hope to make the point that while field research projects often occur inductively, this doesn’t mean that field researchers enter the field with absolutely no idea about what they plan to observe. Having a research question or topic in mind helps a researcher focus her or his observations. At the same time, it is important that field researchers not allow their original question or topic blind them to occurrences in the field that may not seem particularly important at the time. As I share with my students, you never know whether or how some observation might be important down the line. We’ll take a closer look at this point in Section 10.5 “Analysis of Field Research Data” .
No matter how difficult it can be to write notes while in the field, it is worth the effort. Field researchers rely on the notes they take in the field to develop more complete notes later and, eventually, to develop analysis. Have you heard the popular philosophical question about trees falling? It goes something like this: If a tree falls in the woods but nobody hears it, did it actually make a sound? I don’t have a good answer for you from a philosophical perspective, but I can say that when it comes to field research, if you observe something but neglect to note it, it might as well not have happened. This is because you, like any other human being, cannot possibly be expected to remember everything that you see happen over the hours, days, months, or years that you spend collecting data in the field. For this reason, writing notes in the field (to the extent possible) is important, as is “filling in” those notes as soon as you are in a location where you can focus on more formal note taking. We examine this more formal aspect of note taking next.
Writing out of the Field
Immediately upon leaving any observation in the field, you should take the time to complete the brief notes you took while in the field. Even if you feel that the notes you’ve taken in the field are complete, you’ll be surprised by how much more you’ll recall once you sit down without distractions and read through what you’ve jotted down. You’ll also have the opportunity to add your own reflections, or observations about your observations, when you write up more complete notes.
When you type up notes upon returning from an observation, you should “fill in the blanks” and write as much as possible about what you’ve just observed. Even if it seems mundane, I think it’s fair to say that one’s field notes can never contain too much detail. Writing as much as possible, in as much detail as possible, should also help you avoid generalizing in your field notes. Be specific about what you observe; rather than saying that “everyone” said or did something, make note of exactly who said or did X (or note that you’re not sure exactly who did so but that it seemed as if most everyone did). Rather than saying that someone you observed was “angry,” describe what gave you that impression. For example, was that person yelling, red in the face, or shaking her fist?
Don’t forget to describe exactly where you were and detail your surroundings (in addition to describing the interactions and conversations you observed and participated in). Early in a field research project you may focus slightly more on describing the “lay of the land” than you do later on. This might mean writing up very detailed descriptions of the locations you observe and the people with whom you interact. You might also draw a map or, if appropriate in your setting, take pictures of your field sites. If your observations will be conducted in the same place and with the same people, these descriptive details you write up early on will become less noticeable to you over time. It will be helpful to have some documentation of your first impressions and of the sort of details that later become so much a part of the everyday scene that you stop noticing them. The following excerpt from my own field notes comes from my first meeting with two of the key informants in my field research in the breast cancer movement.
1/14/99, 11:00am Met Jane and Polly at the XX office today. I was scheduled to be there at 10:30 but traffic was so bad due to last night’s snow storm that I did not get there until 11:00am. Jane and Polly did not seem bothered by my tardiness (Polly, “We don’t keep a time clock around here.”). I walked into the building and took the elevator up to the second floor. I was a little unsure about where to go from there so I just walked into the first open door and said, “I’m looking for the XX office.” A woman showed me into a large office (long and slightly irregular shape with windows on one wall, a desk and table and many chairs. Also two computers set up on a counter that runs along the wall across from the windows.) Two women were looking at a computer screen that was on the counter. When I walked in I introduced myself and Jane and Polly introduced themselves to me. Both women shook my hand, though Jane was the first to do so and did so with slightly more self-assurance than Polly. Polly told me to hang my coat on one of the “coat racks” and gestured to the many chairs that were around the office. I placed my coat and purse in what I hoped would be the most out of the way location; a corner behind the table. (Blackstone, 2003) Blackstone, A. (2003). Racing for the cure and taking back the night: Constructing gender, politics, and public participation in women’s activist/volunteer work (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Department of Sociology, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN.
The description in my field notes continues for several more paragraphs, but I won’t torture you with those details. As you can see, this field notes excerpt is definitely not going to win the Pulitzer Prize for its riveting story or prose. Thankfully, that isn’t its purpose. Instead, the goal was to describe a location where I knew I’d be spending a fair amount of time and to describe my first impressions of the two women I knew would be likely candidates for key informants. One thing you’ll notice is that I used quotation marks every time I directly quoted a person. Including as many direct quotes as you can is a good idea, as such quotes provide support for the analytic points you’ll make when you later describe patterns in your data. This is another reason that taking notes in the field (to the extent possible) is a good idea. Direct quotes may be difficult to remember hours or even minutes after hearing them. For this reason you may wish to write verbatim quotes while in the field and then take the time to describe the circumstances under which something was said later on when you write up your full notes after leaving the scene.
Another thing you might find were you to read through the many pages of field notes I took during my participant observation is that I use all capital letters and brackets in some places. This is the strategy I developed for expressing my own personal feelings and impressions in my field notes. While the distinction between what one actually observed and what one thinks about what he or she observed is not always easy to make, most field researchers do attempt to distinguish between these two categories of information.
The bracketed portions of your field notes may never be used, but in some cases they will become the very early stages in your analysis of data. My notes from three years of participant observation include bracketed notes of both types. Sometimes, I used bracketed notes to express emotion or purge difficult thoughts or feelings. This was especially helpful when I felt upset about or annoyed by something that had occurred in the field. Because field research requires developing personal relationships with “subjects,” and because interpersonal relationships all experience various highs and lows, it is important to express your feelings about those relationships in your notes. Writing these more personal reflections may become important for analysis later or they may simply be cathartic at the moment. They might also reveal biases you have about the participants that you should confront and be honest about.
Every field researcher’s approach to writing up field notes will vary according to whatever strategy works best for that individual. Where I used brackets to document personal feelings and reflections on bits of data, other field researchers may use the “comments” function in a word processing program or use a different font type, size, or color to distinguish observations from reflections. Others might create two columns for their full field notes—one containing notes only about what was observed directly and the other containing reactions and impressions. There isn’t a wrong way to write field notes. What’s important is that you adopt a strategy that enables you to write accurately, to write as much detail as possible, and to distinguish observations from reflections.
- When taking descriptive field notes, researchers should try to make note of their observations as straightforwardly as possible.
- Field researchers might use any number of tools or strategies to facilitate taking notes in the field such as writing on one’s own hands, dictating observations into a handheld recorder, or taking notes in the form of text messages on one’s phone.
- In field research, observation is deliberate, not haphazard.
- Note taking does not end when a researcher exits an observation; handwritten notes are typed up immediately upon leaving the field so that researchers can “fill in the blanks” in their brief notes taken while in the field.
- Try out the note-taking exercise that my students complete in class. Find another person or two with whom you can conduct observations and take notes for about 15 minutes (perhaps someplace in your campus library, student union, or dorm). Sit near your peers who are also taking notes but do not talk with them during this portion of the exercise. Be sure to use all of your senses as you take notes: your eyes, your ears, your nose, your mouth, and your sense of touch. When your 15 minutes are up, compare notes with your peers. Where are there similarities? Where are their differences? Why do those similarities and differences exist? What strategy did you each employ to take notes? How might you approach field note taking differently were you asked to do it again?
10.5 Analysis of Field Research Data
- Define analytic field notes and explain how they differ from descriptive field notes.
- Explain why making note of mundane details is a good idea.
- Describe the process by which field researchers analyze their data.
- Define grounded theory.
Field notes are data. But moving from having pages of data to presenting findings from a field study in a way that will make sense to others requires that those data be analyzed. Analysis of field research data is the focus in this final section of the chapter.
From Description to Analysis
Writing and analyzing field notes involves moving from description to analysis. In Section 10.4 “Field Notes” , we considered field notes that are mostly descriptive in nature. Here we’ll consider analytic field notes. Analytic field notes Notes that include the researcher’s impressions about her or his observations. are notes that include the researcher’s impressions about his observations. Analyzing field note data is a process that occurs over time, beginning at the moment a field researcher enters the field and continuing as interactions are happening in the field, as the researcher writes up descriptive notes, and as the researcher considers what those interactions and descriptive notes mean.
Often field notes will develop from a more descriptive state to an analytic state when the field researcher exits a given observation period, messy jotted notes or recordings in hand (or in some cases, literally on hand), and sits at a computer to type up those notes into a more readable format. We’ve already noted that carefully paying attention while in the field is important; so too is what goes on immediately upon exiting the field. Field researchers typically spend several hours typing up field notes after each observation has occurred. This is often where the analysis of field research data begins. Having time outside of the field to reflect upon your thoughts about what you’ve seen and the meaning of those observations is crucial to developing analysis in field research studies.
Once the analytic field notes have been written or typed up, the field researcher can begin to look for patterns across the notes by coding the data. This will involve the iterative process of open and focused coding that is outlined in Chapter 9 “Interviews: Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches” . As mentioned several times in Section 10.4 “Field Notes” , it is important to note as much as you possibly can while in the field and as much as you can recall after leaving the field because you never know what might become important. Things that seem decidedly unimportant at the time may later reveal themselves to have some relevance.
In my field research experience, I was often surprised by the bits of data that turned out to hold some analytic relevance later on. For example, my field notes included a number of direct quotes and descriptions of informal interactions with participants that I didn’t expect would be important but that I nevertheless jotted down. Several of these quotes eventually made their way into my analysis. For example, Polly, who ran the volunteer office for a breast cancer organization, once remarked to me, “We [in the volunteer office] don’t use disposable cups here. It is always best to have coffee in a real mug. It’s much nicer that way” (Blackstone, 2004, p. 187). Blackstone, A. (2004). Sociability, work, and gender. Equal Opportunities International, 23, 29–44.
It didn’t occur to me at the time that this was just one of many tasks that Polly and other women volunteers do that remains largely invisible to the beneficiaries of their work. Because it is “much nicer” for volunteers to drink out of a real mug instead of a disposable cup, Polly actually spends a large amount of time washing mugs every day, and throughout the day, so that a clean, real mug is always available to the many volunteers who show up for brief volunteer shifts at the office each day. Had I not made a note of the coffee cup interaction with Polly, which at the time seemed rather mundane, I may have missed an important analytic point about the invisibility of some components of women’s volunteer labor that I was later able to make in presentations and publications of the work.
Sometimes the analytic process of field researchers and others who conduct inductive analysis is referred to as grounded theory A systematic process in which a researcher generates new theory by inductively analyzing her or his qualitative empirical observations. (Charmaz, 2006; Glaser & Strauss, 1967). Glaser, B. G., & Strauss, A. L. (1967). The discovery of grounded theory: Strategies for qualitative research . Chicago, IL: Aldine; Charmaz, K. (2006). Constructing grounded theory: A practical guide through qualitative analysis . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. Grounded theory occurs, as you might imagine, from the “ground up.” It requires that one begin with an open-ended and open-minded desire to understand a social situation or setting and involves a systematic process whereby the researcher lets the data guide her rather than guiding the data by preset hypotheses. The goal when employing a grounded theory approach is, perhaps not surprisingly, to generate theory. Its name not only implies that discoveries are made from the ground up but also that theoretical developments are grounded in a researcher’s empirical observations and a group’s tangible experiences.
As exciting as it might sound to generate theory from the ground up, the experience can also be quite intimidating and anxiety-producing as the open nature of the process can sometimes feel a little out of control. Without hypotheses to guide their analysis, researchers engaged in grounded theory work may experience some feelings of frustration or angst. The good news is that the process of developing a coherent theory that is grounded in empirical observations can be quite rewarding—not only to researchers but also to their peers who can contribute to the further development of new theories through additional research and to research participants who may appreciate getting a bird’s-eye view of their everyday experiences.
- In analytic field notes, a researcher makes note of impressions about her or his observations.
- Details that may seem unimportant in the moment may turn out to be important during later analysis; it is therefore crucial that field researchers make note of these observations when conducting field research.
- In analyzing their data, many field researchers conduct grounded theory.
- Grounded theory involves generating theory from the ground up.
- Interested in learning more about grounded theory? Read all about it at the Grounded Theory Institute’s website: http://www.groundedtheory.com/ . What do you think about grounded theory? Is this way of conducting research something that is of interest to you? Why or why not?
- Principles of Sociological Inquiry: Qualitative and Quantitative Methods. Provided by : Saylor Academy. Located at : https://saylordotorg.github.io/text_principles-of-sociological-inquiry-qualitative-and-quantitative-methods/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike

Privacy Policy
Find Study Materials for
- Explanations
- Business Studies
- Combined Science
- Computer Science
- Engineering
- English literature
- Environmental Science
- Human Geography
- Macroeconomics
- Microeconomics
- Social Studies
- Browse all subjects
- Textbook Solutions
- Read our Magazine
Create Study Materials
- Flashcards Create and find the best flashcards.
- Notes Create notes faster than ever before.
- Study Sets Everything you need for your studies in one place.
- Study Plans Stop procrastinating with our smart planner features.
- Field Research
Despite the risk of coming across as rather biased, sociologists believe that their discipline is one of the most important in the academic world. They explain that while it's important to understand the laws of physics and human bodies at the cellular level, our man-made systems, everyday interactions and normalized behaviors are just as important.

Create learning materials about Field Research with our free learning app!
- Instand access to millions of learning materials
- Flashcards, notes, mock-exams and more
- Everything you need to ace your exams
- American Identity
- Beliefs in Society
- Crime and Deviance
- Cultural Identity
- Education With Methods in Context
- Families and Households
- Famous Sociologists
- Global Development
- Research Methods in Sociology
- Social Institutions
- Social Relationships
- Social Stratification
- Sociological Approach
- Sociology of Education
- Sociology of Family
- Stratification and Differentiation
- Theories and Methods
- American Sociological Association
Case Studies
Ethnography.
- Experiments
- Founders of Sociology
- Functionalism
- Interpretivism
- Longitudinal Studies
- Observation
- Official Statistics
- Postmodernism
- Questionnaire
- Research Considerations
- Research Design
- Social Action Theory
- Social Policy
- Sociological Imagination
- Sociological Research Methods
- Sociological Theories
- Sociology as a Science
- Sources of Data
- Types of Data
- Value Neutrality
- Values in Research
- What is the Study of Sociology?
- Work Poverty And Welfare
For this reason, sociologists often step out into the 'real world' to ask and answer difficult questions about the human condition. This is known as field research .
- In this explanation, we will explore the method of field research (sometimes referred to as 'fieldwork').
- We'll start by unpacking a field research definition, and then we'll explore the importance of field research in the social sciences.
- Next, we'll look at the various types of field research, as well as their relative uses in sociology.
- To cement our understanding of this method, we'll then take a look at some famous field research examples.
- Finally, we'll look at the various advantages and disadvantages of field research.
Definition of Field Research
Field research goes by a few different names depending on the specific aims and methods used in the research process. For instance, fieldwork , ethnography and observation are all often used interchangeably with the term 'field research'.

What is Field Research?
Field research is a qualitative method in which researchers observe how people live their real lives in their natural environment s .
Fieldwork tends to take a qualitative form because researchers are usually interested in collecting rich and detailed primary data. They tend to observe and analyze existing social situations to develop theories and concept s , which can potentially be generalized to broader populations.
Building theories from data is known as inductive research . This is the opposite of deductive research , which involves testing existing theories with research methods and data.
The field researcher also has to be willing to explore, participate in and experience new environments. Examples of fieldwork topics include:
- the work environment in a corporate office,
- the learning methods used in a middle school classroom,
- the work dynamics in a popular restaurant's kitchen, or
- the daily life of a homeless person.
Conducting Field Research
As we will come to learn, there are various kinds of field research that have their own uses, advantages and limitations. However, there are certain steps that are universal to field (and other types of) research, including:
Identifying a social problem or 'puzzle' that is misunderstood or unexplored.
Examining whether it would be possible to gain access to the site of that problem, whether this is a large corporate office or a remote tribe.
Deciding which method(s) would be suitable for your research aims.
If you were to study a corporate office culture, you might gain more insight by hiding the fact that you are a researcher to gain the trust of the research participants. On the other hand, when studying a remote tribe, overt, participant research would be more ethical, and unstructured interviews could provide more insight.
Another factor which influences the choice of methods is the ability to note down findings. If participants are aware of your presence as a researcher, you can take note of your observation out in the open.
However, if you are 'undercover', you may need to step away every once in a while to take notes in private, or retain your observations throughout the day, so you can make note of them at home in the evening.
Analyzing the data after it has been collected, and drawing conclusions from the findings.
Communicating your research findings and evaluating your methods for any strengths or limitations that came up throughout the process.
The Importance of Field Research
Field research is an important method because it involves observing people's behaviors in their natural environments . For example, when research subjects participate in laboratory research, the awareness of being in a laboratory (and knowing that they are being evaluated) may cause those subjects to behave in unnatural ways. Field research helps make up for this lack of validity by taking away the artificial environment and its unintended effects.
Regardless, it is still difficult to narrow down the causes and impacts of particular aspects in a natural environment - because it is totally uncontrolled! For this reason, fieldwork is important not for establishing cause and effect , but for making correlations .
When studying relationships between multiple variables, causation implies that some variables are the result of others. A correlational relationship simply suggests that the variables are connected in some way.
Types of Field Research
As mentioned earlier, there are various types of field research - each suited to unique aims, practicalities and research orientations.

Ethnography is the systematic study of human cultures, communities and livelihoods.
The main aim of ethnography is to understand how research subjects understand their livelihoods on their own, as well as in relation to the broader community. While ethnographic research is a field of study , it can use of participant observation, which is a research method . It often takes place over an extended period of time - perhaps even up to a few years.
Some examples of different types of ethnography include:
Institutional ethnography , which looks at how various institutions impact our day-to-day lives and activities.
Business ethnographic research targets consumer behavior by examining markets, target markets and demands.
Educational ethnographic research helps researchers observe and analyze teaching and learning methods.
Medical ethnographic research tells researchers about the needs of those seeking healthcare.
To learn more about ethnography, take a look at the dedicated explanation on the Vaia web-app!
Participant Observation
In participant observation , the researcher integrates themselves into a group to study their way of life, their culture, and how they structure their community.
This research method is useful for field researchers who want to understand the workings of a particular environment as an insider in that community. The researcher will take part in the group's daily activities and routines to understand (and perhaps even take up) their perspective.
This also means that the researcher should try to avoid influencing any group behavior or opinions. For this reason, the researcher might go undercover and carry out a covert participant observation .
In covert research , the participants aren't aware that there's a researcher present among them.
In overt research , the research participants are aware of the researcher's presence and their task.
A field researcher may also choose to carry out a non-participant observational study . In non-participant observation , the researcher doesn't join the group being studied, but simply observes that group in their natural environment.
To learn more about observation, take a look at the dedicated explanation on the Vaia web-app!
In-depth explorations of a particular person, group, community, organization, situation or event are called case studies .
Case studies are conducted with a narrow focus in mind, so they can't be used to make wide, generalizable claims about particular situations.
A sociologist might use this method to study a particular case in-depth. Examples of cases they might explore are:
- gang members,
- a cancer patient,
- adoptive parents,
- victims of abuse, or
- a special needs carer.
Case studies can be considered fieldwork because they involve a close, often lengthy investigation of a situation. The researcher might immerse themselves in the case study's day-to-day lives. They might also use relevant personal documents, like diaries or letters, to help their analysis.
To learn more about case studies, take a look at the dedicated explanation on the Vaia web-app!
Field Research Examples
Let's take a look at some examples of field research in sociology.
Ethnographic Study Example: The Making of Middletown
Robert and Helen Lynd (1924) conducted an ethnographic study in Muncie, Indiana. They aimed to examine the day-to-day lives of the average American. The ethnography involved the use of observation, interviews, surveys and secondary data analysis.
Two types of classes were identified in Muncie - business class groups and the working class groups . These class groups had very different lifestyles, levels of wealth, and life goals.
Participant Observational Study Example: On the Run
A very famous participant observation was conducted by Alice Goffman (2014) over the span of six years. Goffman observed the lives of a poor, Black, community subjected to high levels of surveillance, in West Philadelphia. Goffman had a community member introduce her as his sister to gain access for a covert, participant observation.
Case Study Example
Another famous example of field research - this time, a case study - was conducted by Stephen Ball (1981). Over a span of three years, Ball closely observed two groups of students at the Beachside Comprehensive school. He aimed to find out why working-class students underperformed, particularly in the context of this specific school.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Field Research
As is the case with all sociological methods, field research has several advantages and disadvantages. Let's take a look at these now.
Benefits of Field Research
The main appeal of fieldwork is that the research subjects can be observed in their own environments carrying out their regular, daily routines. This increases the validity of results.
From this, researchers can obtain detailed and accurate information in real time.
Field research may involve combining various methods (such as observation and interviews). This is known as methodological pluralism or triangulation . It also helps generate high levels of validity and holism .
Through fieldwork, researchers try to get access to important information and experiences by gaining the trust of their research subjects. This can help researchers understand what people do, as well as why and how they do it.
Limitations of Field Research
Fieldwork, especially as case studies and participant observational studies, tend to examine a particular situation. This means the results don't tend to be generalizable to wider populations or groups.
Notably, field research is subjected to many ethical considerations. A researcher who immerses themselves into the lives of a community, particularly if they are doing so covertly, raises questions about informed consent , privacy and confidentiality .
Some researchers suggest that all observation is theory-dependent . This means that, to understand the behavior and environment they are observing, the researcher already needs to have a certain level of knowledge about it. Not having this knowledge may lead to misinterpretations and inaccurate findings .
If conducting fieldwork on a dangerous or deviant situation, there is a risk that the researcher will get involved in such behavior in order to avoid being exposed as a researcher.
On the other hand, if the presence of the researcher is known, the validity of the study is compromised because of the Hawthorne effect . This is when research subjects change their behavior because they know they are being observed.
Field Research - Key takeaways
- Field research can be defined as a qualitative method in which researchers observes how people live their real lives in their natural environment s .
- Fieldwork tends to take a qualitative form because researchers are usually interested in collecting rich and detailed primary data.
- Types of field research include ethnography, participant observation and case studies.
- Field research is beneficial because it provides high levels of validity due to the natural conditions in which it is conducted.
- On the other hand, field research is subjected to limitations such as a lack of generalizability, ethical breaches and the Hawthorne effect.
Flashcards in Field Research 20
What are some terms that people might use to refer to 'field research'?
Fieldwork , ethnography and observation are all often used interchangeably with the term 'field research'.
What is the definition of 'field research'?
Field research can be defined as a qualitative method in which researchers observes how people live their real lives in their natural environments .
Field research tends to take...
An inductive approach.
What is the difference between inductive and deductive research?
Building theories from data is known as inductive research , whereas testing existing theories with research methods and data is known as deductive research.
What is an example of a field research topic?
Any of the following:
What is a limitation of laboratory studies that field research makes up for?
When research subjects participate in laboratory research, the fact of being in a laboratory and aware that they are being evaluated may cause those subjects to behave in unnatural ways. Field research helps make up for this lack of validity by taking away the artificial environment and its unintended effects.

Learn with 20 Field Research flashcards in the free Vaia app
We have 14,000 flashcards about Dynamic Landscapes.
Already have an account? Log in
Frequently Asked Questions about Field Research
What is field research in sociology?
Field research can be defined as a qualitative method in which researchers observe how people live their real lives in their natural environments.
What is an example of field research?
A famous example of field research was conducted by Alice Goffman (2014), who observed the lives of a poor, Black community subjected to high levels of surveillance in West Philadelphia. She used covert participant observation as her main research method.
What are the three types of field research?
The three types of field research are ethnography, participant observation and case study.
What can you get from field research?
The main appeal of fieldwork is that it tends to generate high levels of validity within rich, detailed and accurate information in real time.
Why is field research important?
Field research is an important method because it involves observing people's behaviors in their natural environments. This makes for high levels of validity by removing the barrier of artificial environments and set ups.
Test your knowledge with multiple choice flashcards
Field research can help researchers establish cause and effect. True or false?
Which set of statements is correct?

Join the Vaia App and learn efficiently with millions of flashcards and more!
Keep learning, you are doing great.
Discover learning materials with the free Vaia app

Vaia is a globally recognized educational technology company, offering a holistic learning platform designed for students of all ages and educational levels. Our platform provides learning support for a wide range of subjects, including STEM, Social Sciences, and Languages and also helps students to successfully master various tests and exams worldwide, such as GCSE, A Level, SAT, ACT, Abitur, and more. We offer an extensive library of learning materials, including interactive flashcards, comprehensive textbook solutions, and detailed explanations. The cutting-edge technology and tools we provide help students create their own learning materials. StudySmarter’s content is not only expert-verified but also regularly updated to ensure accuracy and relevance.

Vaia Editorial Team
Team Sociology Teachers
- 11 minutes reading time
- Checked by Vaia Editorial Team
Study anywhere. Anytime.Across all devices.
Create a free account to save this explanation..
Save explanations to your personalised space and access them anytime, anywhere!
By signing up, you agree to the Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy of Vaia.
Sign up to highlight and take notes. It’s 100% free.
Join over 22 million students in learning with our Vaia App
The first learning app that truly has everything you need to ace your exams in one place
- Flashcards & Quizzes
- AI Study Assistant
- Study Planner
- Smart Note-Taking

Privacy Overview
Get unlimited access with a free vaia account..
- Instant access to millions of learning materials.
- Flashcards, notes, mock-exams, AI tools and more.
- Everything you need to ace your exams.

Covering a story? Visit our page for journalists or call (773) 702-8360.

Inside the Lab
Top stories.
- Thirty-one UChicago faculty members receive named, distinguished service professorships in 2024
- UChicago researchers invent new fabric that reduces heat
- Feeling stuck? Here’s how to achieve a breakthrough, with Adam Alter (Ep. 139)
Field experiments, explained
Editor’s note: This is part of a series called “The Day Tomorrow Began,” which explores the history of breakthroughs at UChicago. Learn more here.
A field experiment is a research method that uses some controlled elements of traditional lab experiments, but takes place in natural, real-world settings. This type of experiment can help scientists explore questions like: Why do people vote the way they do? Why do schools fail? Why are certain people hired less often or paid less money?
University of Chicago economists were early pioneers in the modern use of field experiments and conducted innovative research that impacts our everyday lives—from policymaking to marketing to farming and agriculture.
Jump to a section:
What is a field experiment, why do a field experiment, what are examples of field experiments, when did field experiments become popular in modern economics, what are criticisms of field experiments.
Field experiments bridge the highly controlled lab environment and the messy real world. Social scientists have taken inspiration from traditional medical or physical science lab experiments. In a typical drug trial, for instance, participants are randomly assigned into two groups. The control group gets the placebo—a pill that has no effect. The treatment group will receive the new pill. The scientist can then compare the outcomes for each group.
A field experiment works similarly, just in the setting of real life.
It can be difficult to understand why a person chooses to buy one product over another or how effective a policy is when dozens of variables affect the choices we make each day. “That type of thinking, for centuries, caused economists to believe you can't do field experimentation in economics because the market is really messy,” said Prof. John List, a UChicago economist who has used field experiments to study everything from how people use Uber and Lyft to how to close the achievement gap in Chicago-area schools . “There are a lot of things that are simultaneously moving.”
The key to cleaning up the mess is randomization —or assigning participants randomly to either the control group or the treatment group. “The beauty of randomization is that each group has the same amount of bad stuff, or noise or dirt,” List said. “That gets differenced out if you have large enough samples.”
Though lab experiments are still common in the social sciences, field experiments are now often used by psychologists, sociologists and political scientists. They’ve also become an essential tool in the economist’s toolbox.
Some issues are too big and too complex to study in a lab or on paper—that’s where field experiments come in.
In a laboratory setting, a researcher wants to control as many variables as possible. These experiments are excellent for testing new medications or measuring brain functions, but they aren’t always great for answering complex questions about attitudes or behavior.
Labs are highly artificial with relatively small sample sizes—it’s difficult to know if results will still apply in the real world. Also, people are aware they are being observed in a lab, which can alter their behavior. This phenomenon, sometimes called the Hawthorne effect, can affect results.
Traditional economics often uses theories or existing data to analyze problems. But, when a researcher wants to study if a policy will be effective or not, field experiments are a useful way to look at how results may play out in real life.
In 2019, UChicago economist Michael Kremer (then at Harvard) was awarded the Nobel Prize alongside Abhijit Banerjee and Esther Duflo of MIT for their groundbreaking work using field experiments to help reduce poverty . In the 1990s and 2000s, Kremer conducted several randomized controlled trials in Kenyan schools testing potential interventions to improve student performance.
In the 1990s, Kremer worked alongside an NGO to figure out if buying students new textbooks made a difference in academic performance. Half the schools got new textbooks; the other half didn’t. The results were unexpected—textbooks had no impact.
“Things we think are common sense, sometimes they turn out to be right, sometimes they turn out to be wrong,” said Kremer on an episode of the Big Brains podcast. “And things that we thought would have minimal impact or no impact turn out to have a big impact.”
In the early 2000s, Kremer returned to Kenya to study a school-based deworming program. He and a colleague found that providing deworming pills to all students reduced absenteeism by more than 25%. After the study, the program was scaled nationwide by the Kenyan government. From there it was picked up by multiple Indian states—and then by the Indian national government.
“Experiments are a way to get at causal impact, but they’re also much more than that,” Kremer said in his Nobel Prize lecture . “They give the researcher a richer sense of context, promote broader collaboration and address specific practical problems.”
Among many other things, field experiments can be used to:
Study bias and discrimination
A 2004 study published by UChicago economists Marianne Bertrand and Sendhil Mullainathan (then at MIT) examined racial discrimination in the labor market. They sent over 5,000 resumes to real job ads in Chicago and Boston. The resumes were exactly the same in all ways but one—the name at the top. Half the resumes bore white-sounding names like Emily Walsh or Greg Baker. The other half sported African American names like Lakisha Washington or Jamal Jones. The study found that applications with white-sounding names were 50% more likely to receive a callback.
Examine voting behavior
Political scientist Harold Gosnell , PhD 1922, pioneered the use of field experiments to examine voting behavior while at UChicago in the 1920s and ‘30s. In his study “Getting out the vote,” Gosnell sorted 6,000 Chicagoans across 12 districts into groups. One group received voter registration info for the 1924 presidential election and the control group did not. Voter registration jumped substantially among those who received the informational notices. Not only did the study prove that get-out-the-vote mailings could have a substantial effect on voter turnout, but also that field experiments were an effective tool in political science.
Test ways to reduce crime and shape public policy
Researchers at UChicago’s Crime Lab use field experiments to gather data on crime as well as policies and programs meant to reduce it. For example, Crime Lab director and economist Jens Ludwig co-authored a 2015 study on the effectiveness of the school mentoring program Becoming a Man . Developed by the non-profit Youth Guidance, Becoming a Man focuses on guiding male students between 7th and 12th grade to help boost school engagement and reduce arrests. In two field experiments, the Crime Lab found that while students participated in the program, total arrests were reduced by 28–35%, violent-crime arrests went down by 45–50% and graduation rates increased by 12–19%.
The earliest field experiments took place—literally—in fields. Starting in the 1800s, European farmers began experimenting with fertilizers to see how they affected crop yields. In the 1920s, two statisticians, Jerzy Neyman and Ronald Fisher, were tasked with assisting with these agricultural experiments. They are credited with identifying randomization as a key element of the method—making sure each plot had the same chance of being treated as the next.
The earliest large-scale field experiments in the U.S. took place in the late 1960s to help evaluate various government programs. Typically, these experiments were used to test minor changes to things like electricity pricing or unemployment programs.
Though field experiments were used in some capacity throughout the 20th century, this method didn’t truly gain popularity in economics until the 2000s. Kremer and List were early pioneers and first began experimenting with the method in the 1990s.
In 2004, List co-authored a seminal paper defining field experiments and arguing for the importance of the method. In 2008, he and UChicago economist Steven Levitt published another study tracing the history of field experiments and their impact on economics.
In the past few decades, the use of field experiments has exploded. Today, economists often work alongside NGOs or nonprofit organizations to study the efficacy of programs or policies. They also partner with companies to test products and understand how people use services.
There are several ethical discussions happening among scholars as field experiments grow in popularity. Chief among them is the issue of informed consent. All studies that involve human test subjects must be approved by an institutional review board (IRB) to ensure that people are protected.
However, participants in field experiments often don’t know they are in an experiment. While an experiment may be given the stamp of approval in the research community, some argue that taking away peoples’ ability to opt out is inherently unethical. Others advocate for stricter review processes as field experiments continue to evolve.
According to List, another major issue in field experiments is the issue of scale . Many experiments only test small groups—say, dozens to hundreds of people. This may mean the results are not applicable to broader situations. For example, if a scientist runs an experiment at one school and finds their method works there, does that mean it will also work for an entire city? Or an entire country?
List believes that in addition to testing option A and option B, researchers need a third option that accounts for the limitations that come with a larger scale. “Option C is what I call critical scale features. I want you to bring in all of the warts, all of the constraints, whether they're regulatory constraints, or constraints by law,” List said. “Option C is like your reality test, or what I call policy-based evidence.”
This problem isn’t unique to field experiments, but List believes tackling the issue of scale is the next major frontier for a new generation of economists.
Hero photo copyright Shutterstock.com
More Explainers

Improv, Explained

Cosmic rays, explained
Get more with UChicago News delivered to your inbox.
Recommended Stories

An economist illuminates our giving habits—during the pandemic and…

Collaborating with Kenyan government on development innovations is…
Related Topics
Latest news, big brains podcast: feeling stuck here’s how to achieve a breakthrough.

Can you find good health information on TikTok? UChicago study advises caution

Dispatches from Abroad
Aboard a drilling rig in the Mediterranean, scientists seek to understand Earth’s past climates

A UChicago student finds connection and career path in Berlin

Go 'Inside the Lab' at UChicago
Explore labs through videos and Q and As with UChicago faculty, staff and students

Upgraded synchrotron starts up at Argonne National Laboratory

Materials science
UChicago scientists pioneer technique to visualize anti-ferroelectric materials
Around uchicago.

Pride Month
How UChicago’s Center for the Study of Gender and Sexuality ‘is here for everyone’
Quantrell and PhD Teaching Awards
UChicago announces 2024 winners of Quantrell and PhD Teaching Awards
Campus News
Project to improve accessibility, sustainability of Main Quadrangles
National Academy of Sciences
Five UChicago faculty elected to National Academy of Sciences in 2024

UChicago graduate student selected as 2024 Paul and Daisy Soros Fellow

Kavli Prize
UChicago President Paul Alivisatos shares 2024 Kavli Prize in Nanoscience
Biological Sciences Division
“You have to be open minded, planning to reinvent yourself every five to seven years.”

First student awarded scholarship in honor of historian, civil rights activist Timuel D. Black
Marketing91
Field Research – Reasons And Methods
June 12, 2023 | By Hitesh Bhasin | Filed Under: Marketing
Field research can be defined as a qualitative method of data collection that aims at observing, understanding, and interacting with people. This observation of people is done in the natural environment of the people.
For example, nature enthusiasts observe animal behavior in their wild surroundings to find the way they react in specific scenarios. Similarly, social scientists conduct field research and observe people and conduct interviews to understand their behavior in their social environment and how they respond to different situations.
There are different methods of social research methods that are used by field research like direct observation, document analysis, limited participation, surveys, and interviews, etc. Field research is categorized as qualitative research , and it involves many aspects of quantitative research.
Field research starts in a specific setting and even though the end objective is to analyze and observe the behavior of the subject in their natural environment. Although it is difficult to understand the cause and effect of the particular behavior of the subject, it is due to multiple variables. Most of the data which is collected is not based entirely on cause and effect correlation. Typically the small sample size makes it difficult to establish cause and effect relation.
Table of Contents
Reasons for conducting field research
Field research can be used in many cases in social sciences, but it takes a lot of time to complete and is very expensive as well as invasive. But it is also commonly used and is preferred by many researchers to validate the data. Here are a few significant reasons why this is so:
- Overcoming data lacking: A significant gap in data is resolved by field research. Usually, there are fewer data about a study topic, and this is especially true in specific environments. The problem may or may not be known, but there is no way to prove it without the data collection and analysis and primary research . Field research not only helps to plug in the gaps in data but also collects supporting material. This is why it is a preferred method of researchers.
- Understanding: Data collection is insufficient in many cases, but the field research is conducted nevertheless. This gains insight into the present and existing data. For example, if the data says that a pizza place sells a pepperoni pizza, the most and the owner says the reason for it is they use fresh pepperoni. But research will help to gain new insights and other factors which are leading people to buy pizza. It may be the price of the product .
- Improving the data quality: Because the research method uses more than a single tool for data collection, the data is of very high quality. Inferences may be made from the data collected, and it can be analyzed structurally.
- Supplementary data: Field research habituates the researchers to adopt localized thinking which opens a new line of thinking. This can assist in collecting the data which the study did not want to collect.
How to conduct Field research?

Owing to the nature of field research, the costs and the timeline required, it can be challenging for field research to plan and be implemented. However, the following are a few of the necessary steps in field research:
- Building the right team : It is essential to have the right team to conduct field research. The role of the researcher and every other team member is crucial. It is equally important to define the tasks which they have to carry out with properly defined milestones. Also, senior management is vested in the process of field research and for its success.
- Recruiting the people: The ultimate success of field research depends entirely on the people on which the study is being conducted. With the use of sampling methods, it is crucial to derive the people who will be a part of your study. The better the sampling method is implemented, the better the people will be who will participate in the study.
- Data collection method: Methods of data collection are various. There could be interviews, surveys, observations, case studies, and a mix of them. Everything has to be written out properly, and the milestones for every method should be pre-defined at the beginning. For example, the survey design is crucial in the case of a survey that is created and tested before the research.
- Site Visit: It is essential to have a site visit for the success of field research. Usually, the site visit is conducted outside of regular locations and in the natural environment of the respondent. Therefore planning a site visit is crucial with data collection.
- Data Analysis : Data analysis is crucial to validate the assumptions of the research and decide the conclusion of the field research.
- Communicating the results: After the data analysis is complete, it is crucial to communicate the results obtained to the stakeholders of that research. This is done so that the stakeholders can take necessary action on the results.
4 Methods of field research

Following are the methods of the field research:
1. Direct observation
In the case of direct observation, the data is collected with the help of close inspection of natural behavior or setting. Rather than engaging the members actively in conversations, the direct observer tries to be detached and does not cause any obstruction in the setting. Direct observation may not be an alternative to different types of field research like participant observation.
It may be a preliminary approach for understanding an environment or form of behavior or individuals or groups before interacting with the members or developing the protocols of the interview. Using direct observation is not recommended in a private environment.
Advantages of direct observation method
- It offers a first hand and unfiltered data on individuals and their settings, interactions, etc.
- The data can be reliable and trustworthy since it is collected first hand.
Disadvantages of Direct observation method
- There could be many unusual behaviors that would not be typical. Reporting such behavior is not only challenging but including them in the report could affect the results and conclusions.
- Gathering the data by direct observation is a difficult and challenging task. Sometimes it could also cost a lot since the observers would be required to travel to the natural setting.
- Chances of researcher induced research bias are high.
Types of Data collected during direct observation
- The primary form of direct observation in the field notes. Field notes consist of detailed behavior, setting, or conversations that are recorded by the researcher.
- Structured protocols may be used as an alternative approach. Structured protocols contain a rating scale or checklist.
- Video clips and photographs are also a form of data collected.
This method of direct observation is useful when open, or public settings are used. As mentioned above, ethical concerns may arise through the use of direct observation methods in private settings.
2. Participant Observation

The participant method is a method of field research in which the researcher develops a detailed understanding of the composition of a specific society or setting by participating in the everyday rituals with its members. It was initially conceived in the early 20th century by anthropologists who were researching for native communities in different developing countries.
Now the method has become popular and is used by researchers to study a lot of issues. This is the primary research method which is used by ethnographers. Ethnographers are the ones who work in sociology and anthropology.
They focus on recording the specific details of social life, which occurs in a particular society or setting. The ethnographer who lives amongst the members of the community for many months or years tries to build long-lasting, trusting relations so that he can become a part of their social setting. Slowly, the ethnographer gains the trust of the members, and they start behaving naturally in the ethnographer’s presence.
- The ethnographer, with the help of participant observation, develops a thick understanding of the setting and its members in a society.
- This provides him with a privilege to observe the people in a natural setting with them. This generates useful data for the research.
Disadvantages
- The researcher is expected to spend a lot of time and money to develop this understanding of people.
- The objectivity of the ethnographer may reduce by spending a lot of time with the members.
Types of data collected from the participant observation method
- The primary data obtained from this research are field notes. The ethnographer notes down all the observations as well as his experiences and then develops it into detailed formal notes.
- Ethnographers usually keep a diary which is a more close and informal record of all the things happening in their surroundings.
- The art of participant observation with the emphasis on developing relations with the members may lead to informal and conversational interviews rather than in-depth interviews. The data collected from these interviews become a part of field notes. The data may also consist of different interview transcripts.
Ethnography and ethical issues
One of the primary issues which confront ethnographers is deciding how and when to inform the members about them being a part of a research study. The ethnographer can identify himself as an observer at the beginning of the participant observation.
A general description of the objectives of the research should suffice. As time goes and relation develops with participants, then he can disclose the controversial aspects of the study, if any. Informed consent should be gotten from any member who agrees for a formal interview.
3. Qualitative Interviews
These are the types of field research that gathers data by directly asking questions to the participants. There are three types of qualitative interviews:
- Informal conversational interview
- Semi-structured
- Standardized open-ended interviews
- Informal conversational interview: These are the ones that typically occur during observation of participant or after direct observation The researcher starts by conversing with a single member about the setting. As the conversation proceeds, the researcher formulates particular questions, randomly, and starts asking them. This is done informally. When the researcher needs maximum flexibility to pursue the ideas and topics as and when they emerge in the conversation.
- These interviews allow the researcher to be very responsive to the individual differences and also to capture the emerging information.
Disadvantage:
- It may generate very less systematic data which is difficult to classify.
- Semi- Structured Interviews : This method involves recruiting the members formally from a setting to conduct an interview. Before the interview, a list of predetermined questions which is also known as an interview guide are prepared so that every participant will respond to similar questions. These questions are open-ended so that a lot of data can be collected from the participant. The researcher can pursue other topics as they emerge during the interview.
- Semi-structured interviews help to capture systematic data across the participants.
- Semi-structured interviews do not offer a lot of flexibility to respond to the new topics which unfold during the interview.
- Standardized open-ended interviews: These interviews are very much like surveys because the questions are scripted carefully and written before the interview. This helps to reduce the variability in the wordings of the questions. The researcher usually asks a series of questions in the same order to every participant. This method is suitable for qualitative studies which involve multiple participants.
Advantage: Compatibility is enabled across participants.
Disadvantage: This does not offer a lot of flexibility to respond to the new topics which come up during the interview.
Both semi-structured and standard interviews are recorded and should start by obtaining informed consent from the participant before the interview begins. The researcher also can write a separate note to describe the reaction of members to the interview or to the events which happened pre or post-interview.
4. Case Study

An in-depth analysis of a person or event is called a case study. This method is challenging to operate, but it is one of the easiest ways of researching since it involves a deep dive and with the understanding of data collection methods thoroughly and then concluding the data.
Advantages of field research
Following are the advantages of field research:
- The field research is usually carried out in a real-world environment where there is hardly any tampering of the variables, and the environment is not manipulated.
- Because the study is being conducted in a comfortable environment, the data collection can be done about supplementary topics which can be used elsewhere.
- The researcher gets a deep understanding of the research topics since he has proximity to them. This leads the research to be extensive and accurate.
Disadvantages of Field research
Following are the disadvantages of Field research:
- The field research studies are costly as well as time-consuming. They can take years to complete at times.
- Research bias is a common problem arising in almost every field of research.
- The method of field research is interpretive and is dependent on the ability of researchers to collect, analyze, as well as interpret data.
- External variables and interferences are challenging to control with this method, and it affects the outcome of the research at times..
Here is a video by Marketing91 on Field Research.
Examples of Field research
Understanding the impact of sports on child development
This kind of research can take several years to conduct since the sample size is enormous. The analysis of the collected data will provide insight into how sports affects the overall development of the kids. These kids may be present in different geographies or single geography, and several sports may be studied, or an only sport or a combination of both can be used.
Liked this post? Check out the complete series on Market research
Related posts:
- What is Field Testing and How to do It? Advantages & Disadvantages
- 11 Reasons Why Importance of Research Advice for Business
- What is Behavioral research? Importance, Methods & Examples
- Descriptive Research – Characteristics, Methods, Examples, Advantages
- Research Methodology – Overview, Types and Methods
- What is Research Design? Type of Research Designs
- How to Write Research Proposal? Research Proposal Format
- 7 Key Differences between Research Method and Research Methodology
- Qualitative Research: Meaning, and Features of Qualitative Research
- Research Ethics – Importance and Principles of Ethics in Research
About Hitesh Bhasin
Hitesh Bhasin is the CEO of Marketing91 and has over a decade of experience in the marketing field. He is an accomplished author of thousands of insightful articles, including in-depth analyses of brands and companies. Holding an MBA in Marketing, Hitesh manages several offline ventures, where he applies all the concepts of Marketing that he writes about.
All Knowledge Banks (Hub Pages)
- Marketing Hub
- Management Hub
- Marketing Strategy
- Advertising Hub
- Branding Hub
- Market Research
- Small Business Marketing
- Sales and Selling
- Marketing Careers
- Internet Marketing
- Business Model of Brands
- Marketing Mix of Brands
- Brand Competitors
- Strategy of Brands
- SWOT of Brands
- Customer Management
- Top 10 Lists
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- About Marketing91
- Marketing91 Team
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Terms of Use
- Editorial Policy
WE WRITE ON
- Digital Marketing
- Human Resources
- Operations Management
- Marketing News
- Marketing mix's
- Competitors
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Arab J Urol
- v.12(1); 2014 Mar
Why should I do research? Is it a waste of time?
Athanasios dellis.
a 2nd Department of Surgery, Aretaieion Hospital, University of Athens, Greece
Andreas Skolarikos
b 2nd Department of Urology, Sismanogleion Hospital, University of Athens, Greece
Athanasios G. Papatsoris
- • In medicine, research is the search for scientific knowledge, which is crucial for the development of novel medications and techniques.
- • Conducting research provides a deeper understanding of several scientific topics of the specialty of each doctor.
- • Research through RCTs represents the principal methodological approach.
- • There are two main research processes; qualitative and quantitative studies.
- • It is important to develop Research Units in hospitals and medical centres.
- • Ethics and the high quality of research are ensured by committees (i.e., Internal Board Review, Ethics Research Committee).
- • Research sessions could be implemented in the job plans of doctors.
- • Research is not a waste of time, but a scientific investment.
To answer the questions ‘Why should I do research? Is it a waste of time?’ and present relevant issues.
Medline was used to identify relevant articles published from 2000 to 2013, using the following keywords ‘medicine’, ‘research’, ‘purpose’, ‘study’, ‘trial’, ‘urology’.
Research is the most important activity to achieve scientific progress. Although it is an easy process on a theoretical basis, practically it is a laborious process, and full commitment and dedication are of paramount importance. Currently, given that the financial crisis has a key influence in daily practice, the need to stress the real purpose of research is crucial.
Research is necessary and not a waste of time. Efforts to improving medical knowledge should be continuous.
What is research?
Research is a general term that covers all processes aiming to find responses to worthwhile scientific questions by means of a systematic and scientific approach. In fact, research is the search for scientific knowledge, a systematically formal process to increase the fund of knowledge and use it properly for the development of novel applications.
There are several types of research, such as basic science laboratory research, translational research, and clinical and population-based research. Medical research through randomised clinical trials (RCTs) represents the principal methodological approach for the structured assessment of medical outcomes. RCTs provide prospective and investigator-controlled studies, representing the highest level of evidence (LoE) and grade of recommendation, and define the ultimate practice guideline [1] . However, many constraints, such as ethical, economic and/or social issues, render the conduct of RCTs difficult and their application problematic. For instance, in one of the largest RCTs in urology, on preventing prostate cancer with finasteride, the LoE was 1 [2] . In this RCT, after 7 years of finasteride chemoprevention, the rate of cancer decreased from 24.4% to 18.4%. Based on this study, it could be postulated that finasteride chemoprevention should be offered to men in the general population in an attempt to reduce the risk of prostate cancer. However, the findings of this RCT could not be implemented universally due to financial issues [3] .
There are two main research processes, i.e., qualitative and quantitative studies. Although very different in structure and methods, these studies represent two arms of the same research body. Qualitative studies are based mainly on human experience, using notions and theoretical information without quantifying variables, while quantitative studies record information obtained from participants in a numerical form, to enable a statistical analysis of the data. Therefore, quantitative studies can be used to establish the existence of associative or causal relationships between variables.
From a practical perspective, adding a Research Unit to a Medical Department would ultimately enhance clinical practice and education. As such, almost all hospitals in Western countries have research and development (R&D) departments, where the R&D can be linked with clinical innovation. Basic areas in this field include business planning, sales policies and activities, model design, and strategic propositions and campaign development. However, if researchers are not motivated, the research could be counterproductive, and the whole process could ultimately be a waste of time and effort [4] .
The ethics and the high quality of research are ensured by committees, such as the Internal Review Board, and Ethics Research Committees, especially in academic hospitals. They consist of highly educated and dedicated scientists of good faith as well as objectivity, to be the trustees of ethical and properly designed and performed studies.
Do we need research?
Research is the fuel for future progress and it has significantly shaped perspectives in medicine. In urology there are numerous examples showing that current practice has rapidly changed as a result of several key research findings. For example, from the research of Huggins and Hodges (who won the Nobel Prize in 1966), hormone therapy has become the standard treatment for patients with advanced/metastatic prostate cancer. The use of ESWL to treat stones in the urinary tract is another example of research that has improved practice in urology. The current trend in urology to use robotic assistance in surgery is a relatively recent example of how constant research worldwide improves everyday clinical practice [5] . Furthermore, in a more sophisticated field, research is used to identify factors influencing decision-making, clarify the preferred alternatives, and encourage the selection of a preferred screening option in diseases such as prostate cancer [6,7] .
Conducting research provides a deeper understanding of several scientific topics within the specialty of each doctor. Furthermore, it helps doctors of a particular specialty to understand better the scientific work of other colleagues. Despite the different areas of interest between the different specialties, there are common research methods.
In a University, PhD and MSc students concentrate their efforts at higher research levels. Apart from having to produce a challenging and stimulating thesis, young researchers try to develop their analytical, conceptual and critical thinking skills to the highest academic level. Also, postgraduate students thus prepare themselves for a future job in the global market.
During the research process several approaches can be tested and compared for their safety and efficacy, while the results of this procedure can be recorded and statistically analysed to extract the relevant results. Similarly, any aspects of false results and side-effects, e.g., for new medications, can be detected and properly evaluated to devise every possible improvement. Hence, research components under the auspices of dedicated supervisors, assisted by devoted personnel, are of utmost importance. Also, funding is a catalyst for the optimum progress of the research programme, and it must be independent from any other financial source with a possible conflict. Unfortunately, in cases of economic crisis in a hospital, the first department that is trimmed is research.
Is research time a waste of time?
Even if the right personnel are appointed and the funding is secured, it would be a great mistake to believe that the results are guaranteed. Full commitment and dedication are of utmost importance for successful research. Also, these questions are raised in relation to the scientific papers that are accepted for publication in medical journals. About US$ 160 billion is spent every year on biomedical research [8] . Recently, in the Lancet [9] it was estimated that 85% of research is wasteful or inefficient, with deficiencies presented in the following questions: (1) is the research question relevant for clinicians or patients?; (2) are the design and methods appropriate?; (3) is the full report accessible?; (4) is it unbiased and clinically meaningful? Such questions about the importance, purpose and impact of research should surely be answered during the research. The view of the general public is that the purpose of medical research is to advance knowledge for the good of society, to invent new substances to fight disease, to create diagnostic and therapeutic algorithms, to improve public health, to prevent diseases, to improve the quality of life and to prolong overall survival.
Pharmaceutical companies that sponsor research are financially orientated. This fact leads to a sole result, i.e., profit, as a return on their investment. In this framework it would be impossible for academic institutions to operate on any other basis but finance. Economic indicators, even better benefits and the commercial potential of research are important for their survival. Nevertheless, the purpose of research is more than that. It is time to reframe the way research is done and rewarded, leaving profits in second place. We need to remind ourselves about the real purpose of scientific research. Moreover, we need to decide what research is needed and what impact it is likely to have. Researchers and those who benefit from research (i.e., patients, practising doctors) have a crucial role in the research process. Academic institutions should assess and reward researchers on a long-term basis, and help them to concentrate on meaningful research. Researchers must defend their selection of topics as being those appropriate to benefit public health.
Each medical specialty has a different working plan, and surgical specialties such as urology are characterised by a lack of time for research. It is suggested that specific sessions for research could be implemented in the job plan of urologists, and for other doctors. This is more important for the ‘academic doctor’, but even non-academic doctors could undertake research, if only of the current updated medical literature.
Last but not least is the issue of teaching research to junior doctors. This is very important, as the sooner each doctor is involved in the research process the better for his or her career. Even for junior doctors who are not interested in an academic career, understanding the research process helps them to develop their scientific skills. Young doctors should be motivated to understand and undertake research. However, it is important to guide them through the basic principles of research and to mentor them during their first scientific projects. Furthermore, specific academic training opportunities should be offered within developing programmes, such as the academic specialist registrar’s career pathways in the UK [10] .
In conclusion, research is necessary and not a waste of time. All relevant components of the research engine should co-operate to achieve scientific progress that will help patients and the general population.
Take-home messages
- • Ethics and the high quality of research are ensured by committees (i.e. Internal Board Review, Ethical Research Committee).
Conflict of interest
Source of funding.
Peer review under responsibility of Arab Association of Urology.

Scientific breakthroughs: 2024 emerging trends to watch

December 28, 2023
Across disciplines and industries, scientific discoveries happen every day, so how can you stay ahead of emerging trends in a thriving landscape? At CAS, we have a unique view of recent scientific breakthroughs, the historical discoveries they were built upon, and the expertise to navigate the opportunities ahead. In 2023, we identified the top scientific breakthroughs , and 2024 has even more to offer. New trends to watch include the accelerated expansion of green chemistry, the clinical validation of CRISPR, the rise of biomaterials, and the renewed progress in treating the undruggable, from cancer to neurodegenerative diseases. To hear what the experts from Lawrence Liverpool National Lab and Oak Ridge National Lab are saying on this topic, join us for a free webinar on January 25 from 10:00 to 11:30 a.m. EDT for a panel discussion on the trends to watch in 2024.
The ascension of AI in R&D

While the future of AI has always been forward-looking, the AI revolution in chemistry and drug discovery has yet to be fully realized. While there have been some high-profile set-backs , several breakthroughs should be watched closely as the field continues to evolve. Generative AI is making an impact in drug discovery , machine learning is being used more in environmental research , and large language models like ChatGPT are being tested in healthcare applications and clinical settings.
Many scientists are keeping an eye on AlphaFold, DeepMind’s protein structure prediction software that revolutionized how proteins are understood. DeepMind and Isomorphic Labs have recently announced how their latest model shows improved accuracy, can generate predictions for almost all molecules in the Protein Data Bank, and expand coverage to ligands, nucleic acids, and posttranslational modifications . Therapeutic antibody discovery driven by AI is also gaining popularity , and platforms such as the RubrYc Therapeutics antibody discovery engine will help advance research in this area.
Though many look at AI development with excitement, concerns over accurate and accessible training data , fairness and bias , lack of regulatory oversight , impact on academia, scholarly research and publishing , hallucinations in large language models , and even concerns over infodemic threats to public health are being discussed. However, continuous improvement is inevitable with AI, so expect to see many new developments and innovations throughout 2024.
‘Greener’ green chemistry

Green chemistry is a rapidly evolving field that is constantly seeking innovative ways to minimize the environmental impact of chemical processes. Here are several emerging trends that are seeing significant breakthroughs:
- Improving green chemistry predictions/outcomes : One of the biggest challenges in green chemistry is predicting the environmental impact of new chemicals and processes. Researchers are developing new computational tools and models that can help predict these impacts with greater accuracy. This will allow chemists to design safer and more environmentally friendly chemicals.
- Reducing plastics: More than 350 million tons of plastic waste is generated every year. Across the landscape of manufacturers, suppliers, and retailers, reducing the use of single-use plastics and microplastics is critical. New value-driven approaches by innovators like MiTerro that reuse industrial by-products and biomass waste for eco-friendly and cheaper plastic replacements will soon be industry expectations. Lowering costs and plastic footprints will be important throughout the entire supply chain.
- Alternative battery chemistry: In the battery and energy storage space, finding alternatives to scarce " endangered elements" like lithium and cobalt will be critical. While essential components of many batteries, they are becoming scarce and expensive. New investments in lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries that do not use nickel and cobalt have expanded , with 45% of the EV market share being projected for LFP in 2029. Continued research is projected for more development in alternative materials like sodium, iron, and magnesium, which are more abundant, less expensive, and more sustainable.
- More sustainable catalysts : Catalysts speed up a chemical reaction or decrease the energy required without getting consumed. Noble metals are excellent catalysts; however, they are expensive and their mining causes environmental damage. Even non-noble metal catalysts can also be toxic due to contamination and challenges with their disposal. Sustainable catalysts are made of earth-abundant elements that are also non-toxic in nature. In recent years, there has been a growing focus on developing sustainable catalysts that are more environmentally friendly and less reliant on precious metals. New developments with catalysts, their roles, and environmental impact will drive meaningful progress in reducing carbon footprints.
- Recycling lithium-ion batteries: Lithium-ion recycling has seen increased investments with more than 800 patents already published in 2023. The use of solid electrolytes or liquid nonflammable electrolytes may improve the safety and durability of LIBs and reduce their material use. Finally, a method to manufacture electrodes without solvent s could reduce the use of deprecated solvents such as N-methylpyrrolidinone, which require recycling and careful handling to prevent emissions.
Rise of biomaterials

New materials for biomedical applications could revolutionize many healthcare segments in 2024. One example is bioelectronic materials, which form interfaces between electronic devices and the human body, such as the brain-computer interface system being developed by Neuralink. This system, which uses a network of biocompatible electrodes implanted directly in the brain, was given FDA approval to begin human trials in 2023.
- Bioelectronic materials: are often hybrids or composites, incorporating nanoscale materials, highly engineered conductive polymers, and bioresorbable substances. Recently developed devices can be implanted, used temporarily, and then safely reabsorbed by the body without the need for removal. This has been demonstrated by a fully bioresorbable, combined sensor-wireless power receiver made from zinc and the biodegradable polymer, poly(lactic acid).
- Natural biomaterials: that are biocompatible and naturally derived (such as chitosan, cellulose nanomaterials, and silk) are used to make advanced multifunctional biomaterials in 2023. For example, they designed an injectable hydrogel brain implant for treating Parkinson’s disease, which is based on reversible crosslinks formed between chitosan, tannic acid, and gold nanoparticles.
- Bioinks : are used for 3D printing of organs and transplant development which could revolutionize patient care. Currently, these models are used for studying organ architecture like 3D-printed heart models for cardiac disorders and 3D-printed lung models to test the efficacy of drugs. Specialized bioinks enhance the quality, efficacy, and versatility of 3D-printed organs, structures, and outcomes. Finally, new approaches like volumetric additive manufacturing (VAM) of pristine silk- based bioinks are unlocking new frontiers of innovation for 3D printing.
To the moon and beyond

The global Artemis program is a NASA-led international space exploration program that aims to land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon by 2025 as part of the long-term goal of establishing a sustainable human presence on the Moon. Additionally, the NASA mission called Europa Clipper, scheduled for a 2024 launch, will orbit around Jupiter and fly by Europa , one of Jupiter’s moons, to study the presence of water and its habitability. China’s mission, Chang’e 6 , plans to bring samples from the moon back to Earth for further studies. The Martian Moons Exploration (MMX) mission by Japan’s JAXA plans to bring back samples from Phobos, one of the Mars moons. Boeing is also expected to do a test flight of its reusable space capsule Starliner , which can take people to low-earth orbit.
The R&D impact of Artemis extends to more fields than just aerospace engineering, though:
- Robotics: Robots will play a critical role in the Artemis program, performing many tasks, such as collecting samples, building infrastructure, and conducting scientific research. This will drive the development of new robotic technologies, including autonomous systems and dexterous manipulators.
- Space medicine: The Artemis program will require the development of new technologies to protect astronauts from the hazards of space travel, such as radiation exposure and microgravity. This will include scientific discoveries in medical diagnostics, therapeutics, and countermeasures.
- Earth science: The Artemis program will provide a unique opportunity to study the Moon and its environment. This will lead to new insights into the Earth's history, geology, and climate.
- Materials science: The extreme space environment will require new materials that are lightweight, durable, and radiation resistant. This will have applications in many industries, including aerospace, construction, and energy.
- Information technology: The Artemis program will generate a massive amount of data, which will need to be processed, analyzed, and shared in real time. This will drive the development of new IT technologies, such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and machine learning.
The CRISPR pay-off

After years of research, setbacks, and minimal progress, the first formal evidence of CRISPR as a therapeutic platform technology in the clinic was realized. Intellia Therapeutics received FDA clearance to initiate a pivotal phase 3 trial of a new drug for the treatment of hATTR, and using the same Cas9 mRNA, got a new medicine treating a different disease, angioedema. This was achieved by only changing 20 nucleotides of the guide RNA, suggesting that CRISPR can be used as a therapeutic platform technology in the clinic.
The second great moment for CRISPR drug development technology came when Vertex and CRISPR Therapeutics announced the authorization of the first CRISPR/Cas9 gene-edited therapy, CASGEVY™, by the United Kingdom MHRA, for the treatment of sickle cell disease and transfusion-dependent beta-thalassemia. This was the first approval of a CRISPR-based therapy for human use and is a landmark moment in realizing the potential of CRISPR to improve human health.
In addition to its remarkable genome editing capability, the CRISPR-Cas system has proven to be effective in many applications, including early cancer diagnosis . CRISPR-based genome and transcriptome engineering and CRISPR-Cas12a and CRISPR-Cas13a appear to have the necessary characteristics to be robust detection tools for cancer therapy and diagnostics. CRISPR-Cas-based biosensing system gives rise to a new era for precise diagnoses of early-stage cancers.
MIT engineers have also designed a new nanoparticle DNA-encoded nanosensor for urinary biomarkers that could enable early cancer diagnoses with a simple urine test. The sensors, which can detect cancerous proteins, could also distinguish the type of tumor or how it responds to treatment.
Ending cancer

The immuno-oncology field has seen tremendous growth in the last few years. Approved products such as cytokines, vaccines, tumor-directed monoclonal antibodies, and immune checkpoint blockers continue to grow in market size. Novel therapies like TAC01-HER2 are currently undergoing clinical trials. This unique therapy uses autologous T cells, which have been genetically engineered to incorporate T cell Antigen Coupler (TAC) receptors that recognize human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) presence on tumor cells to remove them. This could be a promising therapy for metastatic, HER2-positive solid tumors.
Another promising strategy aims to use the CAR-T cells against solid tumors in conjunction with a vaccine that boosts immune response. Immune boosting helps the body create more host T cells that can target other tumor antigens that CAR-T cells cannot kill.
Another notable trend is the development of improved and effective personalized therapies. For instance, a recently developed personalized RNA neoantigen vaccine, based on uridine mRNA–lipoplex nanoparticles, was found effective against pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Major challenges in immuno-oncology are therapy resistance, lack of predictable biomarkers, and tumor heterogenicity. As a result, devising novel treatment strategies could be a future research focus.
Decarbonizing energy

Multiple well-funded efforts are underway to decarbonize energy production by replacing fossil fuel-based energy sources with sources that generate no (or much less) CO2 in 2024.
One of these efforts is to incorporate large-scale energy storage devices into the existing power grid. These are an important part of enabling the use of renewable sources since they provide additional supply and demand for electricity to complement renewable sources. Several types of grid-scale storage that vary in the amount of energy they can store and how quickly they can discharge it into the grid are under development. Some are physical (flywheels, pumped hydro, and compressed air) and some are chemical (traditional batteries, flow batteries , supercapacitors, and hydrogen ), but all are the subject of active chemistry and materials development research. The U.S. government is encouraging development in this area through tax credits as part of the Inflation Reduction Act and a $7 billion program to establish regional hydrogen hubs.
Meanwhile, nuclear power will continue to be an active R&D area in 2024. In nuclear fission, multiple companies are developing small modular reactors (SMRs) for use in electricity production and chemical manufacturing, including hydrogen. The development of nuclear fusion reactors involves fundamental research in physics and materials science. One major challenge is finding a material that can be used for the wall of the reactor facing the fusion plasma; so far, candidate materials have included high-entropy alloys and even molten metals .
Neurodegenerative diseases

Neurodegenerative diseases are a major public health concern, being a leading cause of death and disability worldwide. While there is currently no cure for any neurodegenerative disease, new scientific discoveries and understandings of these pathways may be the key to helping patient outcomes.
- Alzheimer’s disease: Two immunotherapeutics have received FDA approval to reduce both cognitive and functional decline in individuals living with early Alzheimer's disease. Aducannumab (Aduhelm®) received accelerated approval in 2021 and is the first new treatment approved for Alzheimer’s since 2003 and the first therapy targeting the disease pathophysiology, reducing beta-amyloid plaques in the brains of early Alzheimer’s disease patients. Lecanemab (Leqembi®) received traditional approval in 2023 and is the first drug targeting Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology to show clinical benefits, reducing the rate of disease progression and slowing cognitive and functional decline in adults with early stages of the disease.
- Parkinson’s disease: New treatment modalities outside of pharmaceuticals and deep brain stimulation are being researched and approved by the FDA for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease symptoms. The non-invasive medical device, Exablate Neuro (approved by the FDA in 2021), uses focused ultrasound on one side of the brain to provide relief from severe symptoms such as tremors, limb rigidity, and dyskinesia. 2023 brought major news for Parkinson’s disease research with the validation of the biomarker alpha-synuclein. Researchers have developed a tool called the α-synuclein seeding amplification assay which detects the biomarker in the spinal fluid of people diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease and individuals who have not shown clinical symptoms.
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS): Two pharmaceuticals have seen FDA approval in the past two years to slow disease progression in individuals with ALS. Relyvrio ® was approved in 2022 and acts by preventing or slowing more neuron cell death in patients with ALS. Tofersen (Qalsody®), an antisense oligonucleotide, was approved in 2023 under the accelerated approval pathway. Tofersen targets RNA produced from mutated superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) genes to eliminate toxic SOD1 protein production. Recently published genetic research on how mutations contribute to ALS is ongoing with researchers recently discovering how NEK1 gene mutations lead to ALS. This discovery suggests a possible rational therapeutic approach to stabilizing microtubules in ALS patients.
Gain new perspectives for faster progress directly to your inbox.
Drive industry-leading advancements and accelerate breakthroughs by unlocking your data’s full potential. Contact our CAS Custom Services SM experts to find the digital solution to your information challenges.
- Personal Finance
- Today's Paper
- Budget 2024
- T20 World Cup
- Partner Content
- Entertainment
- Social Viral
- Pro Kabaddi League
World UFO Day 2024: History, importance, celebration ideas, and more
Every year on july 2, people all over the planet observe world ufo day. this day is about learning more about unidentified flying objects (ufos) and the possibility of life beyond earth.
)
World UFO Day
Listen to This Article
What is a ufo, more from this section.
)
Wickremesinghe defends Sri Lanka's debt restructuring deal amid criticism
)
S'pore to recognise Palestine in principle at appropriate time: Foreign min
)
Shell to pause construction work at Dutch biofuels project as market sags
)
Hungary's PM visits Ukraine for talks with Zelenskyy, first since war began
)
Won't quit, would rather face vote of confidence: Nepal PM Prachanda
What is the history behind world ufo day, what is the importance of this ufo day, how to celebrate world ufo day this year, what is the future of ufo research .
)
Aliens might be living among us disguised as humans, claims Harvard Study
)
Parliament LIVE: PM Modi to reply to Motion of Thanks on President's address at 4:00 pm
)
Stock Market Highlights, July 02: Sensex, Nifty end marginally in red; Infy, L&T shine
)
LIVE news: Delhi High Court directs CBI to file detailed reply on CM Kejriwal's arrest
)
US treasury yields boost dollar, leave Japan's yen dazed at 38-year low
Don't miss the most important news and views of the day. Get them on our Telegram channel
First Published: Jul 02 2024 | 4:04 PM IST
Explore News
- Suzlon Energy Share Price Adani Enterprises Share Price Adani Power Share Price IRFC Share Price Tata Motors Share Price Tata Steel Share Price Yes Bank Share Price Infosys Share Price SBI Share Price Tata Power Share Price
- Latest News Company News Market News India News Politics News Cricket News Personal Finance Technology News World News Industry News Education News Opinion Shows Economy News Lifestyle News Health News
- Today's Paper About Us T&C Privacy Policy Cookie Policy Disclaimer Investor Communication GST registration number List Compliance Contact Us Advertise with Us Sitemap Subscribe Careers BS Apps
- ICC T20 World Cup 2024 Budget 2024 Lok Sabha Election 2024 Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP)

Belot Research Investigates Employment Match Quality
The quality of an employment match is an important aspect of understanding labor market dynamics, according to Professor Michèle Belot , but measuring match quality presents many challenges.
In “ Measuring the quality of a match ,” forthcoming in “ Labour Economics ,” Belot examines the advantages and drawbacks of various measures of match quality and presents novel evidence from a survey sample of U.S. employees where several measures were collected simultaneously.
“This is a theme that touches on the type of work and research going on at the ILR School,” Belot said. “When you think about the labor market, we are interested in understanding what determines the quality of a match. But what does that actually mean? What is this concept of a good quality match?”
Belot, the Frances Perkins Professor of Industrial and Labor Relations and Economics, notes that there are many different ways to determine the quality of a match – asking the employee about job satisfaction, looking at performance evaluations, noting longevity and wages – but the effectiveness of those ways is problematic.
To examine the success of these measures, Belot surveyed 500 U.S. employees to collect various measures, such as their wage, tenure length, job satisfaction, performance evaluation and perception of the fit of their skills with their jobs.
Belot found that some of these measures correlate well, such as wages, performance evaluations and measures of self-reported skill fit, while others do not. For example, job satisfaction and tenure length do not correlate well.
Also, when considering changes over the course of tenure, she found striking differences in trends. Wages, performance evaluations and skill fit all trend upwards, while job satisfaction trends downwards.
“The punch line is that these measures actually correlate, but not as well as one might expect,” Belot said. “So, for example, one thing that I found really puzzling and that really made me want to write this paper is that many of these measures increase over time, while others don’t. So, the wage, the skill fit and performance evaluations go up, but job satisfaction goes down.
“It's actually a known phenomenon. There is literature that studies job satisfaction over tenure. It’s actually a phenomenon that's true in many other relationships.”
Belot’s research found that even if she focused exclusively on those who experienced decreased job satisfaction, all the other variables still trended upward. This means that even if job satisfaction is down, those employees still enjoy increased wages, better skill fit and positive performance evaluations.
“So that's a puzzle we want to bring forward,” Belot says. “We must be a little bit careful when we think about what we want to measure as we evaluate how match quality is changing over time. You get quite a different story.”
Cornell Department of Economics graduate students Xiaoying Liu and Vaios Triantafyllou co-authored the paper.
Weekly Inbox Updates
5 Important Takeaways From The 2024–2025 U.S. News And World Report Best Global University Rankings
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Harvard University
This morning, U.S. News and World Report released their much-anticipated 2024-2025 Best Global University Rankings. These annual rankings are a cornerstone in the field, influencing decisions that range from student applications to institutional funding and providing a glimpse into the current state of affairs in the world of higher education. This list can provide helpful insights into the relative merits of the schools students may be considering adding to their college lists. In order to use this list effectively, however, it is important to understand the nuances of the ranking system and the factors considered therein.
Here is a breakdown of the rankings’ methodology, as well as key takeaways from this year’s list:
Methodology
The U.S. News and World Report Best Global University Rankings are based on a comprehensive methodology that evaluates colleges and universities across thirteen key metrics. These include:
- Global research reputation (12.5%)
- Regional research reputation (12.5%)
- Publications (10%)
- Books (2.5%)
- Conferences (2.5%)
- Normalized citation impact (10%)
- Total citations (7.5%)
- Number of publications that are among the 10% most cited (12.5%)
- Percentage of total publications that are among the 10% most cited (10%)
- International collaboration – relative to country (5%)
- International collaboration (5%)
- Number of highly cited papers that are among the top 1% most cited in their respective field 5%
- Percentage of total publications that are among the top 1% most highly cited papers 5%
In addition to the overall global rankings and country-specific rankings, U.S. News and World Report published a subject-specific ranking list , evaluating schools’ global positions in over 50 individual disciplines.
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024.
These rankings offer quantitative data students can consider when building their college lists, providing a fairly comprehensive picture of universities’ academic prowess and institutional reach. That being said, students using the rankings to build their college lists should note that many of these factors do not capture the qualitative aspects of students’ experiences.
Key Takeaways from the 2024–25 Rankings
1. The number of universities considered rose by more than 10%.
This year, 2,250 universities across over 100 countries were considered—up more than ten percent from the 2,000 schools considered in the previous ranking.
2. Harvard University lands on top.
As in the last cycle, Harvard University claimed the #1 spot in the global rankings list. This prestigious accolade reflects Harvard's unparalleled academic excellence, groundbreaking research, and global influence. Known for its distinguished faculty, cutting-edge facilities, and a tradition of innovation, Harvard continues to set the standard in higher education, making it the leading choice for students and scholars worldwide.
3. The U.S. dominates the rankings for another year.
Nearly half of the top 50 schools in the ranking are located in the U.S., totaling 24 of the top 50 on the rankings list. Additionally, four out of the top five are U.S. schools: Harvard University, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Stanford University, and University of California, Berkeley. This remarkable achievement underscores the global prestige of U.S. universities, known for their world-class research, innovative academic programs, and extensive resources.
4. UT Austin and Brown University dropped in the rankings.
Both Brown University and The University of Texas at Austin surprisingly dropped in the rankings, falling out of the top 50. Given both schools’ excellence, this shift demonstrates the fierce competition for top spots in the rankings this year.
5. U.S. News and World Report adds new subjects to the rankings.
This year, four new disciplines were added to the subject-specific rankings, including: ecology; green and sustainable science and technology; environmental engineering; and marine and freshwater biology. These additions not only demonstrate the ranking system’s commitment to reflecting the most relevant information in higher education today, but also provide a glimpse into recent trends and changes in the disciplinary offerings at the most prestigious universities in the world.
The 2024–2025 U.S. News and World Report Rankings offer students valuable information regarding the trends in the global higher education landscape. While students should take their personal preferences and the intangible elements of a school’s culture that draw them to a specific school into account, these rankings can be a helpful first step for students as they set their collegiate goals and assemble their college lists.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Facility for Rare Isotope Beams
At michigan state university, msu to expand chip-testing facility at frib to meet critical national need.
Today, the Michigan State University (MSU) Board of Trustees (BOT) authorized construction of a high-bay addition to the west end of FRIB. The addition will triple the testing capacity of the current chip-testing facility by providing two additional user vaults. The K500 Chip Testing Facility at FRIB will help meet the current national shortfall of testing capacity for advanced microelectronics, including those used for commercial spaceflight, wireless technology, and autonomous vehicles.
The 2018 National Academies report, “ Testing at the Speed of Light ,” outlined a critical national shortfall of testing capacity of space-bound electronic components. Supporting the national need for testing capacity, FRIB currently operates the FRIB Single Events Effects (FSEE) facility , which uses heavy-ion beams to measure the response of electronic components to such ions. This simulates in a few minutes the effect of cosmic rays on electronics over decades of operation.
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles that bombard Earth from all directions in space. These include heavy ions that are known to cause serious issues with the performance and longevity of electronic systems on spacecraft and satellites, as well as electronics on land-based systems such as autonomous vehicles and medical devices.
The federal government awarded $14 million to MSU to establish the K500 Chip Testing Facility, which supports the refurbishment of the world’s first superconducting cyclotron—the K500 built at MSU in the 1980s —into a heavy-ion chip testing facility.
The addition will also provide student opportunities through the MSU Space Electronics Center started by FRIB and the MSU College of Engineering. The MSU Space Electronics Center—transitioning to the MSU Space Electronics Initiative—together with the K500 Chip Testing Facility at FRIB will position MSU as a national leader in chip design and testing, and it will provide additional capacity to educate students in chip design and testing. The K500 facility at FRIB will be a magnet for attracting high-tech companies to Michigan, increasing the state’s impact to the nation’s semiconductor and aerospace infrastructure.
MSU Research Foundation Professor John Papapolymerou will transition from his role as chair of the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering to the inaugural director role for the MSU Space Electronics Initiative effective 1 July. The change in title from “center” to ‘initiative” addresses the breadth of the aligned efforts toward expanding MSU’s impact in this essential field.
Papapolymerou emphasized that the MSU Space Electronics Initiative promotes collaboration between industry, government, and MSU's faculty, students, and researchers, creating an unparalleled framework that the K500 Chip Testing Facility at FRIB broadens and bolsters.
"The K500 Chip Testing Facility at FRIB marks a pivotal expansion of our thriving exceptional ecosystem, dedicated to advancing radiation-hardened components and cutting-edge space electronics, and more crucially, to nurturing the next generation of talent essential for sustaining this technology's future and solidifying our nation’s leadership in the field,” said Papapolymerou. "Space electronics applications are poised to inspire a new wave of engineers and scientists, crucial to filling the anticipated 50,000 positions in semiconductor-related fields over the next five years. MSU is positioned at the forefront of molding this critical talent pipeline."
“This is an exciting next step in expanding MSU’s impact in this critical area in service to the nation—both in providing testing capacity and cultivating a skilled workforce,” said MSU College of Engineering Dean Leo Kempel. “By partnering to foster talent and innovation, MSU, FRIB, and the College of Engineering are forging a path that ensures America's leadership in this vital field for generations to come, with Spartan engineers leading the way."
The K500 Chip Testing Facility is an addition to FRIB’s west side, between FRIB and the Chemistry, Biomedical and Physical Sciences, and Biochemistry buildings. Construction is expected to last about 14 months. As part of the construction process, MSU will take the opportunity to better integrate the addition into the MSU campus scenery using vertical greenery, and will incorporate public art into the project.
“Expanding from our current FSEE facility not only enhances our capabilities, but also underscores our commitment to supporting scientific users in their efforts toward advancing our nation's technological resilience,” said FRIB Radiation Effects Facility Manager Steve Lidia. “We are eager to serve more users and support this national need, leveraging the unique capabilities of FRIB in a most essential and impactful way.”
“We are grateful for the continued trust placed in us to operate FRIB and leverage our skilled workforce to deliver significant and synergistic activities like chip testing that serve national needs,” said FRIB Laboratory Director Thomas Glasmacher. “This is truly a testament to the enduring importance of long-term vision and consistent action toward leveraging skills and assets afforded by public investment in FRIB to address new opportunities for the betterment of society.”
Michigan State University has been advancing the common good with uncommon will for more than 165 years. One of the world's leading research universities, MSU pushes the boundaries of discovery to make a better, safer, healthier world for all while providing life-changing opportunities to a diverse and inclusive academic community through more than 400 programs of study in 17 degree-granting colleges.
Michigan State University operates the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams as a user facility for the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science (DOE-SC) with funding from by a cooperative agreement between DOE-SC and MSU, supporting the mission of the DOE-SC Office of Nuclear Physics.
The U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of today’s most pressing challenges. For more information, visit energy.gov/science .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Field research is defined as a qualitative method of data collection that aims to observe, interact and understand people while they are in a natural environment. This article talks about the reasons to conduct field research and their methods and steps. This article also talks about examples of field research and the advantages and disadvantages of this research method.
Travel restrictions and social distancing practices put in place in response to the COVID-19 pandemic have largely ground field research to a halt. Fieldwork plays an essential but often underappreciated role in both understanding violent extremism and developing policy responses to it. It is vital, therefore, that funders and policymakers support the return of such important work in a post ...
Field research, field studies, or fieldwork is the collection of raw data outside a laboratory, library, or workplace setting. The approaches and methods used in field research vary across disciplines.For example, biologists who conduct field research may simply observe animals interacting with their environments, whereas social scientists conducting field research may interview or observe ...
In a nutshell, fieldwork will allow researchers to use different techniques to collect and access original/primary data sources, whether these are qualitative, quantitative, or experimental in nature, and regardless of the intended method of analysis. 2. But fieldwork is not just for data collection as such.
Here is why field research is important: Contextual Understanding: Field research allows researchers to study phenomena in their natural contexts, providing a nuanced understanding of the social, cultural, and environmental factors that shape behavior, attitudes, and experiences. By immersing themselves in the field, you can capture the ...
Planning a field study is a critical first step in ensuring successful research. Here are some steps to follow when preparing your field study: 1. Define your research question. When developing a good research question, you should make it clear, concise, and specific.
Field research is a qualitative method of data collection aimed at understanding, observing, and interacting with people in their natural settings. In the context of research, observation is more than just looking. It involves looking in a planned and strategic way with a purpose (Palys & Atchison, 2014, p. 189).
Introduction. Field research is a method of research that deals with understanding and interpreting the social interactions of groups of people and communities by observing and dealing with people in their natural settings. The field research methods involve direct observation, participant observation, and qualitative interviews.
Field research is a qualitative method of data collection aimed at understanding, observing, and interacting with people in their natural settings. In the context of research, observation is more than just looking. It involves looking in a planned and strategic way with a purpose (Palys & Atchison, 2014, p. 189).
From anthropology to zoology, immersion within communities, cultural settings, and study systems is integral to research and learning (1, 2). Fieldwork, the direct observation and collection of data in natural settings, enables researchers to collect relevant data, connect theory to complex social and ecological systems, and apply research findings to the real world (1). However, in addition ...
Field research ("fieldwork") refers to information gathered by observing individuals in their natural setting. Field research can be both qualitative and quantitative in nature. Qualitative research emphasizes the importance of observing variables and their interactions. Quantitative research attempts to objectively gather data to make ...
96. Field research is a qualitative method of data collection aimed at understanding, observing, and interacting with people in their natural settings.In the context of research, observation is more than just looking.It involves looking in a planned and strategic way with a purpose (Palys & Atchison, 2014, p. 189).As such, when social scientists talk about being in "the field," they are ...
It explains what one means by field research as opposed to laboratory research, and discusses advantages that come from finding and testing ideas in the field. Observational methods can be put to many important uses in field settings. The chapter examines the experimental research in the field that is explicitly designed for the purpose of ...
Field research refers to the process and methods of gathering qualitative data about the interactions of people or groups in their natural environments. Social scientists use field research methods to collect information and develop new theories about sociology, human nature and interpersonal interactions. Field research aims to establish and ...
Figure 3.3.2.1 3.3.2. 1: Field research typically involves a combination of participant observation, interviewing, and document or artifact analysis. This chapter focuses primarily on participant observation. Because we cover interviews and document/artifact analysis in Chapter 3.1 "Interviews: Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches" and ...
Field research is a way of unearthing that information. If you enjoy meeting and talking with people and don't mind what reporters call "legwork," you will relish the fun and satisfaction of obtaining ideas and information first hand. Field research can be an extraordinarily exciting and rewarding experience leading to important discoveries and ...
Customers are the most important and efficient sources for field research process and can provide following useful information: Useful information regarding competitors and new strategies they are going to implement. Present market trend. Actual and innovative market requirement. Market distribution channels. Production and consumption channels ...
Key Takeaways. Field research typically involves a combination of participant observation, interviewing, and document or artifact analysis. Different participant observation projects rest in different places on the continuum of complete observer to complete participant; most lie near the middle of the continuum.
The Importance of Field Research. Field research is an important method because it involves observing people's behaviors in their natural environments. For example, when research subjects participate in laboratory research, the awareness of being in a laboratory (and knowing that they are being evaluated) may cause those subjects to behave in ...
Why Is Research Important? The significance of research cannot be understated. It is an integral part of school and many professions, including law, writing, and finance. The main purpose of research is to inform action, gather evidence for theories, and contribute to developing knowledge in a field of study.
Field experiments, explained. Editor's note: This is part of a series called "The Day Tomorrow Began," which explores the history of breakthroughs at UChicago. Learn more here. A field experiment is a research method that uses some controlled elements of traditional lab experiments, but takes place in natural, real-world settings.
Field research not only helps to plug in the gaps in data but also collects supporting material. This is why it is a preferred method of researchers. Understanding: Data collection is insufficient in many cases, but the field research is conducted nevertheless. This gains insight into the present and existing data.
Research is the most important activity to achieve scientific progress. Although it is an easy process on a theoretical basis, practically it is a laborious process, and full commitment and dedication are of paramount importance. ... Furthermore, in a more sophisticated field, research is used to identify factors influencing decision-making ...
Green chemistry is a rapidly evolving field that is constantly seeking innovative ways to minimize the environmental impact of chemical processes. Here are several emerging trends that are seeing significant breakthroughs: Improving green chemistry predictions/outcomes: One of the biggest challenges in green chemistry is predicting the environmental impact of new chemicals and processes.
The list includes ways artificial intelligence is accelerating scientific research with a focus on applications in health, communication, infrastructure and sustainability. AI-powered scientific discovery, carbon-capturing microbes, and elastocalorics are among the 10 listed technologies.
World UFO Day is important because it raises awareness of the possibility that the universe may contain intelligent life somewhere else too. It likewise urges individuals to contemplate the chance of UFOs and to conduct research into the subject. ... As we celebrate World UFO Day 2024, the field of alien research is evolving: Government ...
The quality of an employment match is an important aspect of understanding labor market dynamics, according to Professor Michèle Belot, but measuring match quality presents many challenges.. In "Measuring the quality of a match," forthcoming in "Labour Economics," Belot examines the advantages and drawbacks of various measures of match quality and presents novel evidence from a survey ...
This morning, U.S. News and World Report released their much-anticipated 2024-2025 Best Global University Rankings. These annual rankings are a cornerstone in the field, influencing decisions that ...
Today, the Michigan State University (MSU) Board of Trustees (BOT) authorized construction of a high-bay addition to the west end of FRIB. The addition will triple the testing capacity of the current chip-testing facility by providing two additional user vaults. The K500 Chip Testing Facility at FRIB will help meet the current national shortfall of testing capacity for advanced ...