
- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.


2.7E: Exercises for Section 2.7
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 57426
1) Draw a number line, then plot the numbers \(4,3,-4,7 / 8\), and \(−8/3\) on your number line. Label each point with its value. Finally, list the numbers in order, from smallest to largest.

2) Draw a number line, then plot the numbers \(5,3,-4,5 / 7\), and \(−4/3\) on your number line. Label each point with its value. Finally, list the numbers in order, from smallest to largest.
3) Draw a number line, then plot the numbers \(-5,5,4,2 / 3\), and \(8/3\) on your number line. Label each point with its value. Finally, list the numbers in order, from smallest to largest.

4) Draw a number line, then plot the numbers \(-3,-2,4,1 / 3\), and \(5/2\) on your number line. Label each point with its value. Finally, list the numbers in order, from smallest to largest.
In Exercises 5-20, shade each of the following sets on a number line.
5) \(\{x \, | \, x \geq-7\}\)

6) \(\{x \, | \, x \geq-1\}\)
7) \(\{x \, | \, x<2\}\)

8) \(\{x \, | \, x<-6\}\)
9) \((-\infty, 2)\)

10) \((-\infty,-9)\)
11) \((6, \infty)\)

12) \((5, \infty)\)
13) \(\{x \, | \, x>7\}\)

14) \(\{x \, | \, x>-8\}\)
15) \([0, \infty)\)

16) \([7, \infty)\)
17) \(\{x \, | \, x \leq-2\}\)

18) \(\{x \, | \, x \leq 7\}\)
19) \((-\infty, 3]\)

20) \((-\infty,-1]\)
In Exercises 21-28, use set-builder notation to describe the shaded region on the given number line.

\(\{x \, | \, x \leq 9\}\)

\(\{x \, | \, x<-8\}\)

\(\{x \, | \, x>-2\}\)

\(\{x \, | \, x \geq-3\}\)

In Exercises 29-36, use interval notation to describe the shaded region on the given number line.

\((4, \infty)\)

\((-\infty,-2)\)

\((-\infty, 5]\)

\([1, \infty)\)

In Exercises 37-44, solve each of the given inequalities. Sketch the solution on a number line, then use set-builder and interval notation to describe your solution.
37) \(x+10<19\)
\((-\infty, 9)\)
38) \(x+17 \geq 7\)
39) \(4 x<8\)
\((-\infty, 2)\)
40) \(16 x \geq-2\)
41) \(-2 x \leq-2\)
42) \(-18 x>-20\)
43) \(x-18>-10\)
\((8, \infty)\)
44) \(x-8 \leq-18\)
In Exercises 45-62, solve each of the given inequalities. Sketch the solution on a number line, then use set-builder and interval notation to describe your solution.
45) \(-5 x-6 \geq 4-9 x\)
\([5 / 2, \infty)\)
46) \(2 x-7 \geq-3-4 x\)
47) \(16 x-6 \leq 18\)
\((-\infty, 3 / 2]\)
48) \(8 x-14 \leq-12\)
49) \(-14 x-6 \geq-10-4 x\)
\((-\infty, 2 / 5]\)
50) \(-13 x-4 \geq-2-5 x\)
51) \(5 x+18<38\)
\((-\infty, 4)\)
52) \(9 x+16<79\)
53) \(-16 x-5 \geq-11-6 x\)
\((-\infty, 3 / 5]\)
54) \(-11 x-7 \geq-15-5 x\)
55) \(2 x-9 \geq 5-8 x\)
\([7 / 5, \infty)\)
56) \(-3 x-6 \geq-2-9 x\)
57) \(-10 x-4 \leq 18\)
\([-11 / 5, \infty)\)
58) \(-6 x-14 \leq 1\)
59) \(-12 x+4<-56\)
\((5, \infty)\)
60) \(-18 x+6<-12\)
61) \(15 x+5<6 x+2\)
\((-\infty,-1 / 3)\)
62) \(12 x+8<3 x+5\)
In Exercises 63-76, solve each of the given inequalities. Sketch the solution on a number line, then use set-builder and interval notation describe your solution.
63) \(\dfrac{3}{2} x>\dfrac{9}{8}\)
\((3 / 4, \infty)\)
64) \(\dfrac{6}{7} x>\dfrac{3}{4}\)
65) \(x+\dfrac{3}{2}<\dfrac{9}{5}\)
\((-\infty, 3 / 10)\)
66) \(x+\dfrac{1}{4}<-\dfrac{1}{5}\)
67) \(\dfrac{4}{7}-\dfrac{1}{6} x \leq \dfrac{4}{3} x-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\([5 / 7, \infty)\)
68) \(\dfrac{5}{3}-\dfrac{3}{4} x \leq \dfrac{7}{4} x-\dfrac{3}{5}\)
69) \(x-\dfrac{3}{8} \geq-\dfrac{9}{7}\)
\([-51 / 56, \infty)\)
70) \(x-\dfrac{7}{2} \geq \dfrac{1}{5}\)
71) \(\dfrac{6}{5} x \leq-\dfrac{4}{7}\)
\([10 / 21, \infty)\)
72) \(\dfrac{4}{3} x \leq \dfrac{2}{9}\)
73) \(-\dfrac{6}{5} x-\dfrac{7}{3} \leq \dfrac{5}{9}-\dfrac{2}{9} x\)
\([-65 / 22, \infty)\)
74) \(-\dfrac{3}{7} x-\dfrac{1}{2} \leq \dfrac{3}{2}-\dfrac{2}{7} x\)
75) \(\dfrac{9}{7} x+\dfrac{9}{2}>\dfrac{1}{7} x+\dfrac{7}{2}\)
\((-7 / 8, \infty)\)
76) \(\dfrac{5}{7} x+\dfrac{9}{2}>\dfrac{1}{3} x+\dfrac{5}{2}\)
In Exercises 77-84, solve each of the given inequalities. Sketch the solution on a number line, then use set-builder and interval notation containing fractions in reduced form to describe your solution.
77) \(-3.7 x-1.98 \leq 3.2\)
\([-7 / 5, \infty)\)
78) \(-3.6 x-3.32 \leq 0.8\)
79) \(-3.4 x+3.5 \geq 0.9-2.2 x\)
\((-\infty, 13 / 6]\)
80) \(-2.6 x+3.1 \geq-2.9-1.7 x\)
81) \(-1.3 x+2.9>-2.6-3.3 x\)
\((-11 / 4, \infty)\)
82) \(2.5 x+2.1>1.4-3.8 x\)
83) \(2.2 x+1.9<-2.3\)
\((-\infty,-21 / 11)\)
84) \(1.6 x+1.2<1.6\)
Contributors and Attributions
David Arnold (Retired Professor (Mathematics) at College of the Redwoods )
- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- enVision Math
- EngageNY Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy

Texas Go Math Grade 5 Lesson 2.7 Answer Key Adjust Quotients
Refer to our Texas Go Math Grade 5 Answer Key Pdf to score good marks in the exams. Test yourself by practicing the problems from Texas Go Math Grade 5 Lesson 2.7 Answer Key Adjust Quotients.
Unlock the Problem
A new music group makes 6,127 copies of its first CD. The group sells 75 copies of the CD at each of its shows. How many shows does it take the group to sell all of the CDs?

A. Is the estimate too high, too low, or correct? Answer: We know that, 75 × 9 = 675 So, 612 < 675 Hence, from the above, We can conclude that The estimate is too high
B. Adjust the number in the quotient if needed. Answer: We know that, 75 × 8 = 600 So, 612 > 600 Hence, from the above, We can conclude that The quotient can be adjusted to 8
STEP 2: Estimate the next digit in the quotient. Divide the ones. Estimate: 140 ÷ 70 = 2. Try 2 ones.
A. Is the estimate too high, too low, or correct? Answer: The remaining number in the given estimate is: 27 Now, 7 × 3 = 21 So, 21 is closer to 27 than 14 Hence, from the above, We can conclude that The estimate is too low
B. Adjust the number in the quotient if needed. Answer: We know that, 7 × 3 = 21 So, 27 > 21 Hence, from the above, We can conclude that The quotient can be adjusted to 3 So, It takes the group about 83 shows to sell all of the CDs.
Try This! When the difference is equal to or greater than the divisor, the estimate is too low.
Divide. 336 ÷ 48 Estimate. 300 ÷ 50 = 6

Adjust the estimated digit in the quotient, if needed. Then divide. Try So, 336 ÷ 48 = 6
Math Talk Mathematical Processes
Explain why using the closest estimate could be useful in solving a division problem. Answer: You can determine if an answer in the division is reasonable by learning to estimate the answers. Round the divisor to the nearest 10 or 100, depending on how many digits are in the divisor. Compare your estimate to the exact answer to determine if the exact answer is reasonable
Share and Show
Adjust the estimated digit in the quotient, if needed. Then divide.

Problem Solving
H.O.T. Algebra Write the unknown number for each ☐.
Question 4. ☐ ÷ 33 = 11 ☐ = ________ Answer: Let the missing digit be: x So, The given expression is: x ÷ 33 = 11 Now, Multiply with 33 on both sides So, x = 11 × 33 x = 363 Hence, from the above, We can conclude that The missing digit in the given expression is: 363
Question 5. 1,092 ÷ 52 = ☐ ☐ = _________ Answer: Let the missing digit be: x So, The given expression is: 1,092 ÷ 52 = x So, x = 21 Hence, from the above, We can conclude that The missing digit in the given expression is: 21
Question 6. 429 ÷ ☐ = 33 ☐ = ___________ Answer: Let the missing digit be: x So, The given expression is: 429 ÷ x = 33 Now, Divide by 33 into both sides So, x = \(\frac{429}{33}\) x = 13 Hence, from the above, We can conclude that The missing digit in the given expression is: 13
Go Math Grade 5 Lesson 2.7 Answer Key Question 7. How do you know whether an estimated quotient is too low or too high? Explain. Answer: If the multiplication of the divisor and quotient is greater than the dividend, then the estimate is too high If the multiplication of the divisor and quotient is less than the dividend, then the estimate is too low
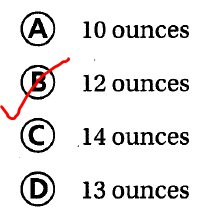
Question 8. Multi-Step A banquet hall serves 2,394 pounds of turkey during a 3-week period. If the same amount is served each day, how many pounds of turkey does the banquet hall serve each day? (A) 50,274 pounds (B) 798 pounds (C) 342 pounds (D) 114 pounds
a. What do you need to find? Answer: It is given that A banquet hall serves 2,394 pounds of turkey during a 3-week period. If the same amount is served each day Hence, The information that you need to find is the number of pounds of turkey does the banquet hall serve each day
b. What information are you given? Answer: The given information is: A banquet hall serves 2,394 pounds of turkey during a 3-week period. If the same amount is served each day
c. What other information will you use? Answer: We know that, 1 week = 7 days So, 3 weeks = 3 × 7 = 21 days Hence, from the above, We can conclude that The other information you will use is the number of days present in a 3-week period
d. Find how many days there are in 3 weeks. There are ________ days in 3 weeks. Answer: We know that, 1 week = 7 days So, 3 weeks = 3 × 7 = 21 days Hence, from the above, We can conclude that There are 21 days in 3 weeks

Question 10. The Box Sox company packs 12 pairs of socks in a box. How many boxes will the company need to pack 1,020 pairs of socks? Answer: It is given that The Box of Sox company packs 12 pairs of socks in a box So, According to the given information, The number of boxes will the company needed to pack 1,020 pairs of socks = \(\frac{1,020}{12}\) = 85 boxes Hence, from the above, We can conclude that The number of boxes will the company needed to pack 1,020 pairs of socks is: 85 boxes
Daily Assessment Task
Fill in the bubble completely to show your answer.

Texas Test Prep
Texas Go Math Grade 5 Lesson 2.7 Homework and Practice Answer Key

Write the unknown number for each ☐.

Problem-Solving

Lesson Check

Share this:
Leave a comment cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Answer Key 2.7
- [latex]x=ky[/latex]
- [latex]x=kyz[/latex]
- [latex]x=\dfrac{k}{y}[/latex]
- [latex]x=ky^2[/latex]
- [latex]x=kzy[/latex]
- [latex]x=\dfrac{k}{y^3}[/latex]
- [latex]x=ky^2\sqrt{z}[/latex]
- [latex]x=\dfrac{k}{y^6}[/latex]
- [latex]x=\dfrac{ky^3}{\sqrt{z}}[/latex]
- [latex]x=\dfrac{k}{y^2\sqrt{z}}[/latex]
- [latex]x=\dfrac{kzy}{p^3}[/latex]
- [latex]x=\dfrac{k}{y^3z^2}[/latex]
- [latex]\phantom{a}[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{rrl} A&=&kB \\ \\ (15)&=&k(5) \\ \\ \dfrac{15}{5}&=&\dfrac{k(5)}{5} \\ \\ k&=&3 \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\phantom{a}[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{rrl} P&=&kQR \\ \\ (12)&=&k(8)(3) \\ \\ \dfrac{12}{24}&=&\dfrac{k(8)(3)}{24} \\ \\ k&=&\dfrac{1}{2} \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\phantom{a}[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{rrl} A&=&\dfrac{k}{B} \\ \\ (7)&=&\dfrac{k}{(4)} \\ \\ (4)7&=&\dfrac{k}{\cancel{4}}\cancel{(4)} \\ \\ k&=&28 \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\phantom{a}[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{rrl} A&=&kB^2 \\ \\ (6)&=&k(3)^2 \\ \\ \dfrac{6}{9}&=&\dfrac{k(3)^2}{9} \\ \\ k&=&\dfrac{6}{9}\text{ or }\dfrac{2}{3} \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\phantom{a}[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{rrl} C&=&kAB \\ \\ (24)&=&k(3)(2) \\ \\ \dfrac{24}{6}&=&\dfrac{k(3)(2)}{6} \\ \\ k&=&4 \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\phantom{a}[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{rrl} y&=&\dfrac{k}{x^3} \\ \\ (54)&=&\dfrac{k}{(3)^3} \\ \\ 54&=&\dfrac{k}{27} \\ \\ 27\cdot 54&=&\dfrac{k}{\cancel{27}}\cdot \cancel{27} \\ \\ k&=&1458 \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\phantom{a}[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{rrl} x&=&kY \\ \\ (12)&=&k(8) \\ \\ \dfrac{12}{8}&=&\dfrac{k(8)}{8} \\ \\ k&=&\dfrac{12}{8}\text{ or }\dfrac{3}{2} \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\phantom{a}[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{rrl} A&=&kB^2\sqrt{C} \\ \\ (25)&=&k(5)^2\sqrt{(9)} \\ \\ 25&=&k(75) \\ \\ k&=&\dfrac{25}{75} \\ \\ k&=&\dfrac{1}{3} \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\phantom{a}[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{rrl} y&=&\dfrac{kmn^2}{d} \\ \\ (10)&=&\dfrac{k(4)(5)^2}{(6)} \\ \\ k&=&\dfrac{\cancel{10}\cancel{5}\cdot \cancel{6}3}{\cancel{(4)}(5)^{\cancel{2}}} \\ \\ k&=&\dfrac{3}{5} \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\phantom{a}[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{rrl} P&=&\dfrac{kT}{V} \\ \\ (10)&=&\dfrac{k(250)}{(400)} \\ \\ k&=&\dfrac{10(400)}{250} \\ \\ k&=&16 \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]I=kV[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{ll} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{1st Data} \\ I&=&5 \text{ A} \\ V&=&15\text{ V} \\ k&=&\text{find} \\ \\ I&=&kV \\ 5\text{ A}&=&k(\text{15 V}) \\ \\ k&=&\dfrac{\text{5 A}}{\text{15 V}} \\ \\ k&=&\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ A/V} \end{array} & \hspace{0.5in} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{2nd Data} \\ I&=&\text{find} \\ k&=&\dfrac{1}{3} \\ \\ V&=&\text{25 V} \\ \\ I&=&kV \\ I&=&\left(\dfrac{1}{3}\right)(25) \\ \\ I&=&8\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ A} \end{array} \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]I=\dfrac{k}{R}[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{ll} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{1st Data} \\ I&=&\text{12 A} \\ k&=&\text{find} \\ R&=&240\Omega \\ \\ I&=&\dfrac{k}{R} \\ \\ \text{12 A}&=&\dfrac{k}{240\Omega} \\ \\ k&=&(\text{12 A})(240\Omega) \\ k&=&2880\text{ A}\Omega \end{array} & \hspace{0.5in} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{2nd Data} \\ I&=&\text{find} \\ k&=&2880 \\ R&=&540\Omega \\ \\ I&=&\dfrac{k}{R} \\ \\ I&=&\dfrac{2880\text{ A}\Omega}{540\Omega} \\ \\ I&=&5.\bar{3}\text{ A or }5\dfrac{1}{3} \end{array} \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]d_{\text{s}}=km[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{ll} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{1st Data} \\ d_{\text{s}}&=&18\text{ cm} \\ k&=&\text{find} \\ m&=&3\text{ kg} \\ \\ 18\text{ cm}&=&k(3\text{ kg}) \\ \\ k&=&\dfrac{\text{18 cm}}{\text{3 kg}} \\ \\ k&=&\text{6 cm/kg} \end{array} & \hspace{0.5in} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{2nd Data} \\ d_{\text{s}}&=&\text{find} \\ k&=&\text{6 cm/kg} \\ m&=&\text{5 kg} \\ \\ d_{\text{s}}&=&(\text{6 cm/kg})(\text{5 kg}) \\ d_{\text{s}}&=&\text{30 cm} \end{array} \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]V=\dfrac{k}{P}[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{ll} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{1st Data} \\ P&=&32\text{ kg/cm}^2 \\ V&=&200\text{ cm}^3 \\ k&=&\text{find} \\ \\ 200\text{ cm}^3&=&\dfrac{k}{32\text{ kg/cm}^2} \\ \\ k&=&(200\text{ cm}^3)(32\text{ kg/cm}^2) \\ k&=&6400\text{ kg cm} \end{array} & \hspace{0.5in} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{2nd Data} \\ P&=&40 \\ V&=&\text{find} \\ k&=&6400 \\ \\ V&=&\dfrac{6400}{40} \\ \\ V&=&160\text{ cm}^3 \end{array} \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]c=kP[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{ll} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{1st Data} \\ c&=&60,000 \\ k&=&\text{find} \\ P&=&250 \\ \\ 60,000&=&k(250) \\ \\ k&=&\dfrac{60,000}{250} \\ \\ k&=&240 \end{array} & \hspace{0.5in} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} && \textbf{2nd Data} \\ c&=&\text{find} \\ k&=&240 \\ P&=&1,000,000 \\ \\ c&=&(240)(1,000,000) \\ c&=&240,000,000\text{ or 240 million} \end{array} \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]t=\dfrac{k}{b}[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{ll} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{1st Data} \\ t&=&5\text{ h} \\ k&=&\text{find} \\ b&=&7 \\ \\ 5\text{ h}&=&\dfrac{k}{7} \\ \\ k&=&\text{(5 h)}(7) \\ k&=&35 \end{array} & \hspace{0.5in} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{2nd Data} \\ t&=&\text{find} \\ k&=&35 \\ b&=&10 \\ \\ t&=&\dfrac{35}{10} \\ \\ t&=&3.5\text{ h} \end{array} \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\lambda=\dfrac{k}{f}[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{ll} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{1st Data} \\ \lambda&=&250\text{ m} \\ k&=&\text{find} \\ f&=&1200\text{ kHz} \\ \\ 250&=&\dfrac{k}{1200} \\ \\ k&=&(250)(1200) \\ k&=&300,000 \end{array} & \hspace{0.5in} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{2nd Data} \\ \lambda&=&\text{find} \\ k&=&300,000 \\ f&=&60\text{ kHz} \\ \\ \lambda&=&\dfrac{300,000}{60} \\ \\ \lambda&=&5000\text{ m} \end{array} \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]w=km[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{ll} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} && \textbf{1st Data} \\ w&=&64\text{ kg} \\ k&=&\text{find} \\ m&=&96\text{ kg} \\ \\ 64&=&k(96) \\ \\ k&=&\dfrac{64}{96} \\ \\ k&=&\dfrac{2}{3} \end{array} & \hspace{0.5in} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{2nd Data} \\ w&=&\text{find} \\ k&=&\dfrac{2}{3} \\ m&=&60\text{ kg} \\ \\ w&=&\left(\dfrac{2}{3}\right)(60\text{ kg}) \\ \\ w&=&40\text{ kg} \end{array} \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]t=\dfrac{d}{v}[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{ll} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{1st Data} \\ t&=&\text{5 h} \\ d&=&\text{find} \\ v&=&\text{80 km/h} \\ \\ \text{5 h}&=&\dfrac{d}{\text{80 km/h}} \\ \\ d&=&5(80) \\ d&=&\text{400 km} \end{array} & \hspace{0.5in} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{2nd Data} \\ t&=&\text{4.2 h} \\ d&=&\text{400 km} \\ v&=&\text{find} \\ \\ 4.2&=&\dfrac{400}{v} \\ \\ v&=&\dfrac{400}{4.2} \\ \\ v&=&95.24\text{ km/h} \end{array} \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]V=khr^2[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{ll} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{1st Data} \\ V&=&33.5\text{ cm}^3 \\ k&=&\text{find} \\ h&=&\text{8 cm} \\ r&=&\text{2 cm} \\ \\ 33.5&=&k(8)(2)^2 \\ \\ k&=&\dfrac{33.5}{(8)(2)^2} \\ \\ k&=&1.046875 \end{array} & \hspace{0.5in} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{2nd Data} \\ V&=&\text{find} \\ k&=&1.046875 \\ h&=&\text{6 cm} \\ r&=&\text{4 cm} \\ \\ V&=&khr^2 \\ V&=&(1.046875)(6)(4)^2 \\ V&=&100.5\text{ cm}^3 \end{array} \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]F_{\text{e}}=\dfrac{kv^2}{r}[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{ll} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{1st Data} \\ F_{\text{e}}&=&100\text{ N} \\ k&=&\text{find} \\ v&=&10\text{ m/s} \\ r&=&\text{0.5 m} \\ \\ 100\text{ N}&=&\dfrac{k(10 \text{ m/s})^2}{\text{0.5 m}} \\ \\ k&=&\dfrac{(0.5)(100)}{(10)^2} \\ \\ k&=&0.5 \end{array} & \hspace{0.5in} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{2nd Data} \\ F_{\text{e}}&=&\text{find} \\ k&=&0.5 \\ v&=&25\text{ m/s} \\ r&=&1.0\text{ m} \\ \\ F_{\text{e}}&=&\dfrac{0.5(25)^2}{1.0} \\ \\ F_{\text{e}}&=&312.5\text{ N} \end{array} \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]L_{\text{max}}=\dfrac{kd^4}{h^2}[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{ll} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{1st Data} \\ L_{\text{max}}&=&64\text{ tonnes} \\ k&=&\text{find} \\ d&=&2.0\text{ m} \\ h&=&8.0\text{ m} \\ \\ 64&=&\dfrac{k(2)^4}{(8)^2} \\ \\ k&=&\dfrac{64(8)^2}{(2)^4} \\ \\ k&=&256 \end{array} & \hspace{0.5in} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{2nd Data} \\ L_{\text{max}}&=&\text{find} \\ k&=&256 \\ d&=&3.0\text{ m} \\ h&=&12.0\text{ m} \\ \\ L_{\text{max}}&=&\dfrac{(256)(3.0)^4}{(12.0)^2} \\ \\ L_{\text{max}}&=&144\text{ tonnes} \end{array} \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]V=\dfrac{kT}{P}[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{ll} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{1st Data} \\ V&=&225\text{ cc} \\ k&=&\text{find} \\ T&=&300\text{ K} \\ P&=&100\text{ N/cm}^2 \\ \\ V&=&\dfrac{kT}{P} \\ \\ 225&=&\dfrac{k(300)}{100} \\ \\ k&=&\dfrac{225(100)}{300} \\ \\ k&=&75 \end{array} & \hspace{0.5in} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{2nd Data} \\ V&=&\text{find} \\ k&=&75 \\ T&=&270 \\ P&=&150 \\ \\ V&=&\dfrac{75(270)}{150} \\ \\ V&=&135\text{ cc} \end{array} \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]R=\dfrac{kl}{d^2}[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{ll} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{1st Data} \\ R&=&20\Omega \\ k&=&\text{find} \\ l&=&5.0\text{ m} \\ d&=&0.25\text{ cm} \\ \\ R&=&\dfrac{kl}{d^2} \\ \\ 20\Omega&=&\dfrac{k(5.0\text{ m})}{\text{(0.25 cm)}^2} \\ \\ k&=&\dfrac{(20 \Omega)\text{(0.25 cm)}^2}{\text{5.0 m}} \\ \\ k&=&0.25 \end{array} & \hspace{0.5in} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{2nd Data} \\ R&=&\text{find} \\ k&=&0.25 \\ l&=&10.0\text{ m} \\ d&=&0.50\text{ cm} \\ \\ R&=&\dfrac{(0.25)\text{(10.0 m)}}{\text{(0.50 cm)}^2} \\ \\ R&=&10\Omega \end{array} \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]V=khd^2[/latex] [latex]\begin{array}[t]{ll} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{1st Data} \\ V&=&377\text{ m}^3 \\ k&=&\text{find} \\ h&=&30\text{ m} \\ d&=&2.0\text{ m} \\ \\ 377\text{ m}^3&=&k(30)(2.0)^2 \\ \\ k&=&\dfrac{377}{(30)(2.0)^2} \\ \\ k&=&3.1416 \end{array} & \hspace{0.5in} \begin{array}[t]{rrl} &&\textbf{2nd Data} \\ V&=&225\text{ m}^3 \\ k&=&3.1416 \\ h&=&\text{find} \\ d&=&1.75\text{ m} \\ \\ 225&=&\pi h(1.75)^2 \\ \\ h&=&\dfrac{225}{\pi (1.75)^2} \\ \\ h&=&23.4\text{ m} \end{array} \end{array}[/latex]
Intermediate Algebra Copyright © 2020 by Terrance Berg is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Share This Book
- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy
Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 7 Lesson 15 Answer Key
Engage ny eureka math 2nd grade module 7 lesson 15 answer key, eureka math grade 2 module 7 lesson 15 sprint answer key.
A. Adding and Subtracting by 2
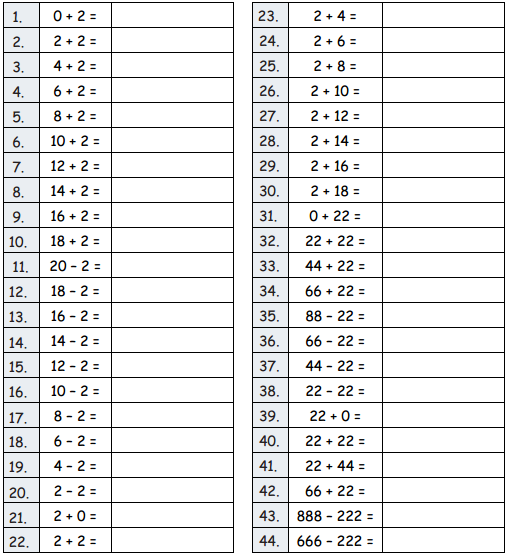
Question 1. 0 + 2 = Answer: 0 + 2 = 2 Explanation: Adding any two numbers gives us Sum. Adding any number to 0 gives the sum the number itself.
Question 2. 2 + 2 = Answer: 2 + 2 = 4
Question 3. 4 + 2 = Answer: 4 + 2 = 6
Question 4. 6 + 2 = Answer: 6 + 2 = 8
Question 5. 8 + 2 = Answer: 8 + 2 = 10 Explanation: Adding 8 and 2 gives the sum 10. Here 1 is carried to the tens place and 0 is represented in the ones place.
Question 6. 10 + 2 = Answer: 10 + 2 = 12
Question 7. 12 + 2 = Answer: 12 + 2 = 14
Question 8. 14 + 2 = Answer: 14 + 2 = 16
Question 9. 16 + 2 = Answer: 16 +2 = 18
Question 10. 18 + 2 = Answer: 18 + 2 = 20
Question 11. 20 – 2 = Answer: 20 – 2 = 18
Question 12. 18 – 2 = Answer: 18 – 2 = 16
Question 13. 16 – 2 = Answer: 16 – 2 = 14
Question 14. 14 – 2 = Answer: 14 – 2 = 12
Question 15. 12 – 2 = Answer: 12 – 2 = 10
Question 16. 10 – 2 = Answer: 10 – 2 = 8 Explanation: Subtracting 10 and 2 gives the difference 8. Here 1 in tens place and 0 in ones place and subtracting 2 from ones place. Since 0 is less than 2 we borrow 1 from tens place 1 becomes 0 and 0 in the ones place becomes 10 and we subtract 2 from ones 10 we get the difference 8.
Question 17. 8 – 2 = Answer: 8 – 2 = 6
Question 18. 6 – 2 = Answer: 6 – 2 = 4
Question 19. 4 – 2 = Answer:
4 – 2 = 2
Question 20. 2 – 2 = Answer: 2 – 2 = 0
Question 21. 2 + 0 = Answer: 2 + 0 = 2
Question 22. 2 + 2 = Answer: 2 + 2 = 4
Question 23. 2 + 4 = Answer: 2 + 4 = 6
Question 24. 2 + 6 = Answer: 2 + 6 = 8
Question 25. 2 + 8 = Answer: 2 + 8 = 10
Question 26. 2 + 10 = Answer: 2 + 10 = 12
Question 27. 2 + 12 = Answer: 2 + 12 = 14
Question 28. 2 + 14 = Answer: 2 + 14 = 16
Question 29. 2 + 16 = Answer: 2 + 1 6 = 18
Question 30. 2 + 18 = Answer: 2 + 1 8 = 20
Question 31. 0 + 22 = Answer: 0 + 22 = 22
Question 32. 22 + 22 = Answer: 22 + 22 = 44
Question 33. 44 + 22 = Answer: 44 + 22 = 66
Question 34. 66 + 22 = Answer: 66 + 22 = 88
Question 35. 88 – 22 = Answer: 88 – 22 = 66
Question 36. 66 – 22 = Answer: 66 – 22 = 44
Question 37. 44 – 22 = Answer: 44 – 22 = 22
Question 38. 22 – 22 = Answer: 22 -22 = 0 Explanation: Subtracting any number by itself gives the difference zero.0
Question 39. 22 + 0 = Answer: 22 + 0 = 22 Explanation: Adding Zero to any number gives the sum the number itself.
Question 40. 22 + 22 = Answer: 22 + 22 = 44
Question 41. 22 + 44 = Answer: 22 + 44 = 66
Question 42. 66 + 22 = Answer: 66 + 22 = 88
Question 43. 888 – 222 = Answer: 888 – 222 = 666 Explanation: Here a 3 digit number is subtracted from a 3 digit number. First ones places are subtracted then tens place and then hundreds place. 8 – 6 = 2, 8 – 6 = 2 , 8 – 6 = 2. 222 is the difference.
Question 44. 666 – 222 = Answer: 666 – 222 = 444
B. Adding and Subtracting by 2
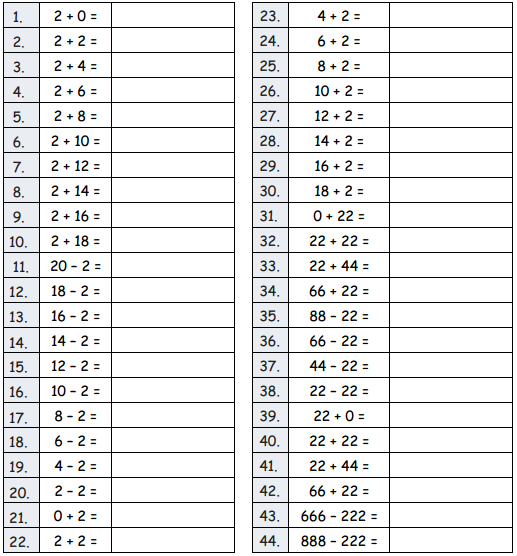
Question 1. 2 + 0 = Answer: 2 + 0 = 2
Question 3. 2 + 4 = Answer: 2 + 4 = 6
Question 4. 2 + 6 = Answer: 2 + 6 = 8
Question 5. 2 + 8 = Answer: 2 + 8 = 10
Question 6. 2 + 10 = Answer: 2 + 10 = 12
Question 7. 2 + 12 = Answer: 2 + 12= 14
Question 8. 2 + 14 = Answer: 2 + 14 = 16
Question 9. 2 + 16 = Answer: 2 + 16 = 18
Question 10. 2 + 18 = Answer: 2 + 18 = 20
Question 16. 10 – 2 = Answer: 10 – 2 = 8
Question 19. 4 – 2 = Answer: 4 – 2 = 2
Question 21. 0 + 2 = Answer: 0 + 2 = 2
Question 23. 4 + 2 = Answer: 4 + 2 = 6
Question 24. 6 + 2 = Answer: 6 + 2 = 8
Question 25. 8 + 2 = Answer: 8 + 2 = 10
Question 26. 10 + 2 = Answer: 10 + 2 = 12
Question 27. 12 + 2 = Answer: 12 + 2 = 14
Question 28. 14 + 2 = Answer: 14 + 2 = 16
Question 29. 16 + 2 = Answer: 16 + 2 = 18
Question 30. 18 + 2 = Answer: 18 + 2 = 20
Question 32. 22 + 22 = Answer: 22 +22 = 44
Question 33. 22 + 44 = Answer: 22 +44 = 66
Question 38. 22 – 22 = Answer: 22 -22 = 0
Question 39. 22 + 0 = Answer: 22 + 0 = 22
Question 40. 22 + 22 = Answer: 22 +22 = 44
Question 43. 666 – 222 = Answer: 666 – 222 = 444
Question 44. 888 – 222 = Answer: 888 – 222 = 666.
Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 7 Lesson 15 Problem Set Answer Key
Use your ruler to measure the length of the objects below in inches. Using your ruler, draw a line that is the same length as each object.
Question 1. a. A pencil is _____ inches. Answer: A pencil is _7_ inches.
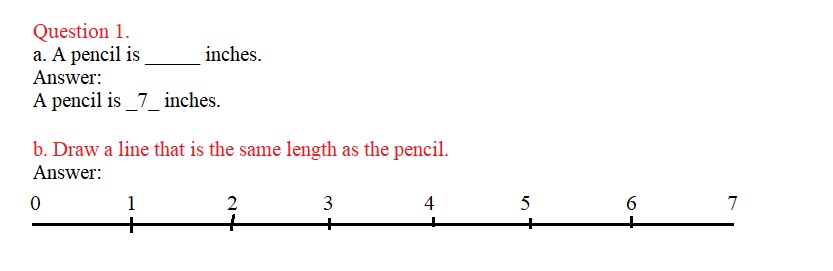
Question 2. a. An eraser is ______ inches. Answer: An eraser is _3__ inches.
Question 3. a. A crayon is ______ inches. Answer: A crayon is __4____ inches.
Question 4. a. A marker is _____ inches. Answer: A marker is _6____ inches.
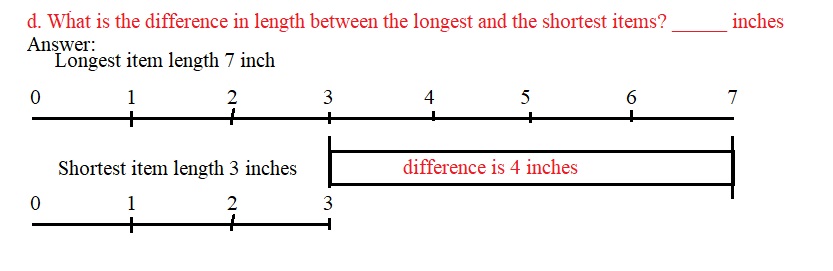
Question 5. a. What is the longest item that you measured? Answer: The longest item that i measured is Pencil which is 7 inches.
b. How long is the longest item? ______ inches Answer: The longest item is 7 inch long.
c. How long is the shortest item? _______ inches Answer: The shortest item is 3 inch long and it is an eraser.
Question 6. Measure and label the length of each side of the triangle using your ruler.
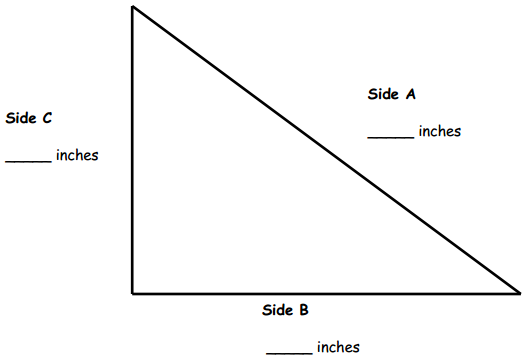
a. Which side is the shortest? 1. Side A 2. Side B 3. Side C Answer: Side A = 5 inches Side B = 4 inches Side C = 3 inches The shortest side is Side C with 3 inches.
b. What is the length of Side A? ______ inches Answer: The length of Side A = 5 inches.
c. What is the length of Sides C and B together? _____ inches Answer: The length of Side C and B together is 3 + 4 = 7 inches.
d. What is the difference between the shortest and longest sides? _____ inches Answer: The difference between the shortest and the longest side is 5 – 3 = 2 inches.
Question 7. Solve.
a. ______ inches = 1 foot Answer: 1 foot equal to 12 inches. _ 12 __ inches = 1 foot
b. 5 inches + ______ inches = 1 foot Answer: 1 foot = 12 inches 12 inches – 5 inches = 7 inches 5 inches + _ 7 __inches = 1 foot
c. ______ inches + 4 inches = 1 foot Answer: 1 foot = 12 inches 12 inches – 4 inches = 8 inches _ 8 __ inches + 4 inches = 1 foot
Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 7 Lesson 15 Exit Ticket Answer Key
Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 7 Lesson 15 Homework Answer Key
Measure the length of each household object with your ruler, and then use your ruler to draw a line equal to the length of each object in the space provided.
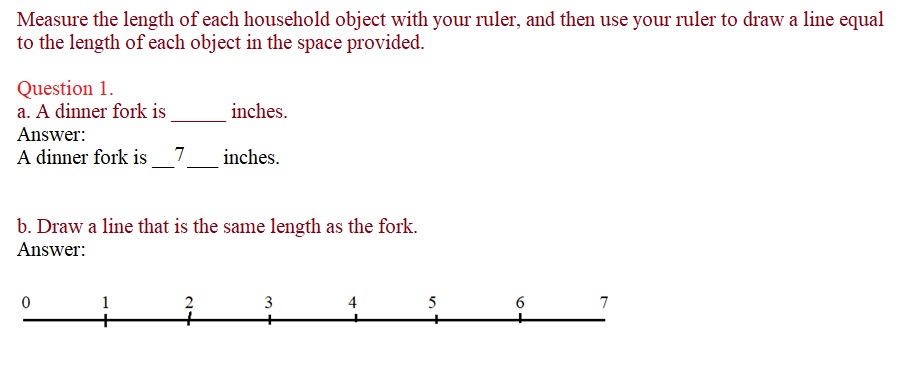
Question 1. a. A dinner fork is _____ inches. Answer: A dinner fork is __ 7 ___ inches.
Question 2. a. A tablespoon is ______ inches. Answer: A tablespoon is __8____ inches.

Measure two other household objects.
Question 3. a. ______ is ______ inches. Answer: A Tea Glass is 3 inches.

Question 4. a. _________ is ______ inches. Answer: The Curry Spoon is 10 inches.
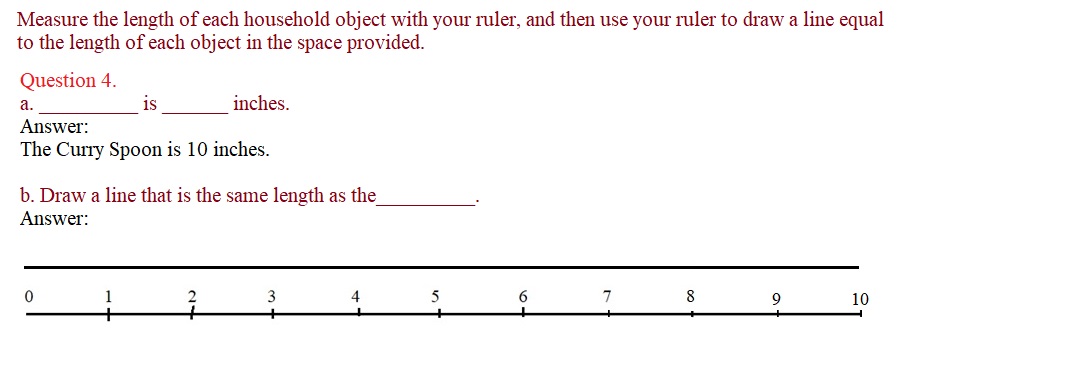
Question 5. a. What was the longest object you measured? Answer: The longest object i measured is Curry Spoon.
b. What was the shortest object you measured? Answer: The shortest object i measured is the Tea Glass.
c. The difference between the longest object and the shortest object is _______ inches. Answer: The difference between the shortest and longest object is 10 inches – 3 inches = 7 inches.
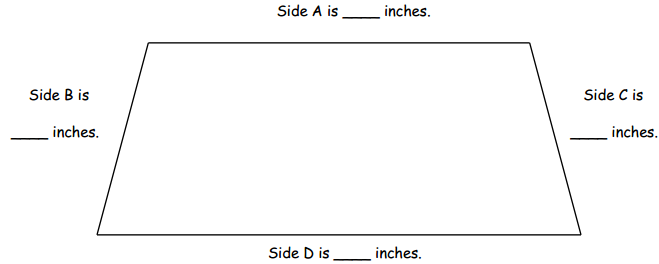
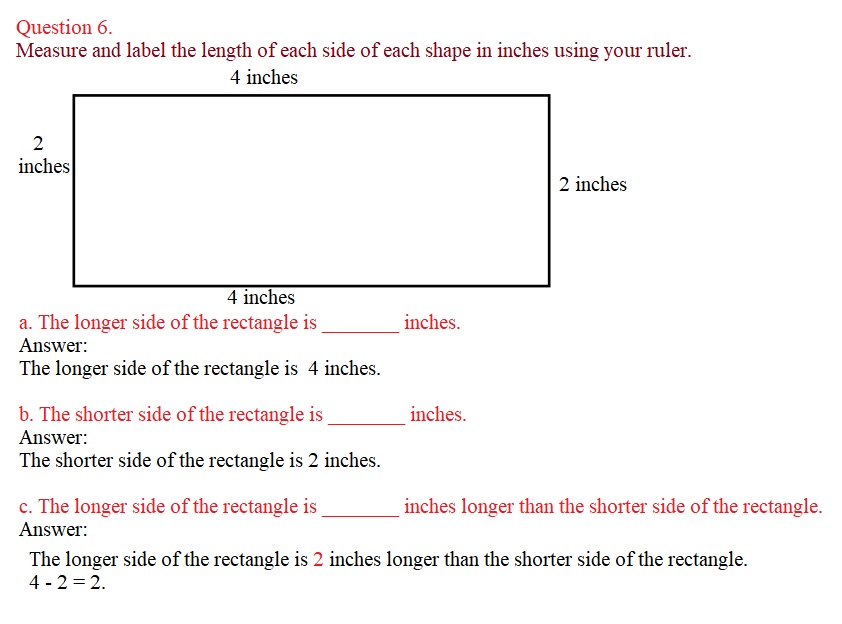
Question 6. Measure and label the length of each side of each shape in inches using your ruler.

a. The longer side of the rectangle is _______ inches. Answer: The longer side of the rectangle is __4_____ inches.
b. The shorter side of the rectangle is _______ inches. Answer: The shorter side of the rectangle is __ 2 _____ inches.
d. The shortest side of the trapezoid is _______ inches. Answer: The shortest side of the trapezoid is __ 1 _____ inches.
e. The longest side of the trapezoid is _______ inches. Answer: The longest side of the trapezoid is __ 3_ ____ inches.
f. The longest side of the trapezoid is _______ inches longer than the shortest side. Answer: The longest side of the trapezoid is __ 3 – 1 = 2 _____ inches longer than the shortest side.
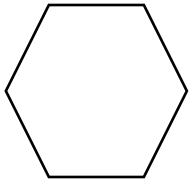
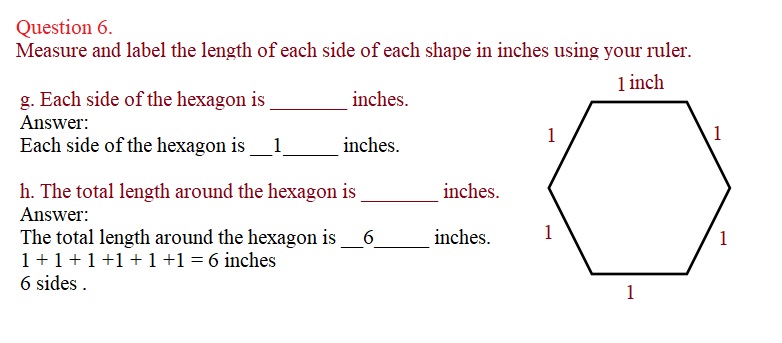
g. Each side of the hexagon is _______ inches. Answer: Each side of the hexagon is __1_____ inches.
h. The total length around the hexagon is _______ inches. Answer: The total length around the hexagon is __ 6 _____ inches. 1 + 1 + 1 +1 + 1 +1 = 6 inches 6 sides .
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The pages I used can be found here:https://www.engageny.org/file/15866/download/math-g2-m7-full-module.pdf?token=5q9qWQ_8
1. Given 2. Vertical angles are congruent. 3. Transitive Property of Congruence. 4. Vertical angles are congruent. 5. Transitive Property of Congruence 16.
Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 7 Lesson 22 Problem Set Answer Key. Question 1. Each unit length on both number lines is 10 centimeters. (Note: Number lines are not drawn to scale.) a. Show 30 centimeters more than 65 centimeters on the number line. b. Show 20 centimeters more than 75 centimeters on the number line.
Go Math! Practice Book (TE), G5. Name Interpret the Remainder Interpret the remainder to solve. Lesson 2.7 COMMON CORE STANDARD CC.5.NF.3 Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division to multiply and divide fractions. Marcia has 412 bouquets of flowers for centerpieces. She uses 8 flowers for each centerpiece.
7. Estimate: _ 961 × __2 8. Estimate: _ 837 × __9 1,458 1,200 240 + __18 11. WRITE Math Explain how you can find 4 × 754 using two different methods. COMMON CORE STANDARD— 4.NBT.B.5 Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. Practice and Homework Lesson 2.7
From Open Up Resources, https://openupresources.org/ Grade 7 Unit 2 Lesson 7
Go Math! Practice Book (TE), G5. Name Multiply Fractions and Whole Numbers use the model to find the product. 12 Find the product. Lesson 7.2 COMMON CORE STANDARD CC.5.NF.4a Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division to multiply and divide fractions. , or 21 5. 14 , or , or 21ž 35 12 , or Problem Solving REAL WORLD 9.
Homework Students reflect on the components of a strong argument as they evaluate and revise their own writing. HOMEWORK 5 Family Homework Experience (optional) Explaining the human microbiome to a member of their household supports student learning through shared experiences with family. HOMEWORK Microbiome Lesson Guides Lesson 2.7
2.7E: Exercises for Section 2.7 is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. Back to top 2.7: Solve Linear Inequalities
The adjusted estimated digit in the quotient is: 3. Go Math 5th Grade Lesson 2.7 Answer Key Adjust Quotients Question 2. Answer: The given division expression is: 416 ÷ 16. Now, 16 × 2 = 32. So, 41 > 32. Hence, from the above,
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to McDougal Littell Algebra 2 Practice Workbook - 9780618736966, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence. ... Lesson 7.6. Section 7.7: Lesson 7.7. Exercise 1. Exercise 2. Exercise 3. Exercise 4. Exercise 5. Exercise 6. Exercise 7. ... you'll learn how to solve your ...
6.3 Scientific Notation (Homework Assignment) 6.4 Basic Operations Using Polynomials. 6.5 Multiplication of Polynomials. 6.6 Special Products. ... Answer Key 7.10. Midterm 2: Prep Answer Key. Midterm 2: Version A Answer Key. Midterm 2: Version B Answer Key. Midterm 2: Version C Answer Key.
Answer Key Eureka Math® Grade 2 Module 4 TEKS EDITION Special thanks go to the Gordon A. Cain Center and to the Department of Mathematics at Louisiana State University for their support in the development of
You can find the homework pages here:https://www.engageny.org/resource/grade-2-mathematics-module-7They are shared under this license:http://creativecommons....
Eureka Math Grade 7 Module 2 Lesson 11 Example Answer Key. Example 1. Part A: Complete quadrants I and IV of the table below to show how sets of matching integer cards will affect a player's score in the Integer Game. For example, three 2's would increase a player's score by 0+2+2+2=6 points. a.
You can get the homework pages here:https://www.engageny.org/file/15866/download/math-g2-m7-full-module.pdf?token=5q9qWQ_8They are shared under this license:...
Answer: The fractional form is 10 25 = 2×5 5×5 ; and, since 5 5 = 1, then 2×5 5×5 = 25. The denominator lacks a factor of 2 to be a power of ten. To arrive at the decimal form, I multiply the fractional form by 22 to arrive at 25 × 22 = 410, and 410 = 0.4. f. Write the number 8 40 as a decimal. Describe your process.
We develop general methods for solving linear equations using properties of equality and inverse operations. Thorough review is given to review of equation solving from Common Core 8th Grade Math. Solutions to equations and inequalities are defined in terms of making statements true. This theme is emphasized throughout the unit.
Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 7 Lesson 21 Problem Set Answer Key. Find the value of the point on each part of the meter strip marked by a letter. For each number line, one unit is the distance from one hash mark to the next. Question 1. Each unit has a length of _____ centimeters. Question 2. Each unit has a length of _____ centimeters. Question 3.
Here is a link to all the pages for module 7: https://www.engageny.org/file/15866/download/math-g2-m7-full-module.pdf?token=5q9qWQ_8
Substance Boiling Point (C) Nitrogen dioxide (NO) 21 Sulfur dioxide (S0, -10 Carbon tetrafluoride (CF) -128 Unit 2 Cher HANDOUT 27.8 Use the following graph to answer questions 4-6. Boiling Point Trends for Hydrides 150 100 HO Group 14 Group 15 Group 16 Group 17 50 HF 0 Н.Те Boiling point (C) NH Hyse Hos HC SbH HI SH HE -100 PH) SIM -150 CHE ...
Answer: Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 7 Lesson 14 Exit Ticket Answer Key. Measure the lines below with an inch tile. Question 1. Line A is about _____ inches. Answer: Question 2. Line B is about _____ inches. Answer: Question 3. Line C is about _____ inches. Answer: Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 7 Lesson 14 Homework Answer Key. Question 1.
Answer: Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 7 Lesson 15 Homework Answer Key. Measure the length of each household object with your ruler, and then use your ruler to draw a line equal to the length of each object in the space provided. Question 1. a. A dinner fork is _____ inches. Answer: A dinner fork is __7___ inches. b.