CBSE Expert


CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles PDF Download
Case Study Questions Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving case study-based questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles

Case Study Questions Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles
Case Study 1. A group of students is studying the properties of triangles. They came across the following scenario:
Three friends, Ankit, Bhavna, and Chetan, were discussing their recent hiking trip. During their hike, they noticed a triangular-shaped lake. They observed the following:
- The lake has three sides of different lengths.
- The sum of the lengths of any two sides of the lake is greater than the length of the third side.
- The largest angle of the lake is less than 90 degrees.
- The smallest angle of the lake is greater than 30 degrees.
Based on this information, the students were asked to analyze the properties of the triangle formed by the lake. Let’s see if you can answer the questions correctly:
MCQ Questions:
Q1. The type of triangle formed by the lake is: (a) Equilateral (b) Isosceles (c) Scalene (d) Right-angled
Answer: (c) Scalene
Q2. The sum of the measures of the three angles of the lake’s triangle is: (a) 180 degrees (b) 90 degrees (c) 360 degrees (d) It cannot be determined
Answer: (a) 180 degrees
Q3. The lake’s triangle is an example of a triangle that satisfies the: (a) Angle-side-angle (ASA) condition (b) Side-angle-side (SAS) condition (c) Side-side-side (SSS) condition (d) None of the above
Answer: (c) Side-side-side (SSS) condition
Q4. The measure of the largest angle of the lake’s triangle is: (a) 30 degrees (b) 60 degrees (c) 90 degrees (d) More than 90 degrees
Answer: (c) 90 degrees
Q5. The measure of the smallest angle of the lake’s triangle is: (a) 30 degrees (b) 60 degrees (c) 90 degrees (d) Less than 30 degrees
Answer: (d) Less than 30 degrees
Case Study 2. A group of students is studying the properties of triangles. They encountered the following scenario:
Three friends, Rahul, Sana, and Tina, participated in a kite-flying competition. They noticed that their kites formed a triangular shape in the sky. They made the following observations:
- The lengths of two sides of the kite triangle are equal.
- The measure of the largest angle of the kite triangle is 90 degrees.
- The sum of the measures of the three angles of the kite triangle is 180 degrees.
- The lengths of the three sides of the kite triangle are in the ratio 3:4:5.
Based on this information, the students were asked to analyze the properties of the triangle formed by their kites. Let’s see if you can answer the questions correctly:
Q1. The type of triangle formed by their kites is: (a) Equilateral (b) Isosceles (c) Scalene (d) Right-angled
Answer: (b) Isosceles
Q2. The length of the third side of the kite triangle is: (a) 3 units (b) 4 units (c) 5 units (d) It cannot be determined
Answer: (c) 5 units
Q3. The kite triangle is an example of a triangle that satisfies the: (a) Angle-side-angle (ASA) condition (b) Side-angle-side (SAS) condition (c) Side-side-side (SSS) condition (d) None of the above
Answer: (b) Side-angle-side (SAS) condition
Q4. The measure of the smallest angle of the kite triangle is: (a) 30 degrees (b) 45 degrees (c) 60 degrees (d) 90 degrees
Answer: (a) 30 degrees
Q5. The lengths of the two equal sides of the kite triangle are: (a) 3 units each (b) 4 units each (c) 5 units each (d) It cannot be determined
Answer: (c) 5 units each
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Case Study Questions Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about Case Study Questions Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles and Passage-Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!

(Education-Your Door To The Future)
CBSE Class 9 Maths Most Important Case Study Based Questions With Solution
Cbse class 9 mathematics case study questions.
In this post I have provided CBSE Class 9 Maths Case Study Based Questions With Solution. These questions are very important for those students who are preparing for their final class 9 maths exam.

All these questions provided in this article are with solution which will help students for solving the problems. Dear students need to practice all these questions carefully with the help of given solutions.
As you know CBSE Class 9 Maths exam will have a set of cased study based questions in the form of MCQs. CBSE Class 9 Maths Question Bank given in this article can be very helpful in understanding the new format of questions for new session.
All Of You Can Also Read
Case studies in class 9 mathematics.
The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has included case study based questions in the Class 9 Mathematics paper in current session. According to new pattern CBSE Class 9 Mathematics students will have to solve case based questions. This is a departure from the usual theoretical conceptual questions that are asked in Class 9 Maths exam in this year.
Each question provided in this post has five sub-questions, each followed by four options and one correct answer. All CBSE Class 9th Maths Students can easily download these questions in PDF form with the help of given download Links and refer for exam preparation.
There is many more free study materials are available at Maths And Physics With Pandey Sir website. For many more books and free study material all of you can visit at this website.
Given Below Are CBSE Class 9th Maths Case Based Questions With Their Respective Download Links.
- School Solutions
- Star Program
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Statistics
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Hindi
- NCERT Books Class 12
- NCERT Books Class 11
- NCERT Books Class 10
- NCERT Books Class 9
- NCERT Books Class 8
- NCERT Books Class 7
- NCERT Books Class 6
- NCERT Books Class 5
- NCERT Books Class 4
- NCERT Books Class 3
- NCERT Books Class 2
- NCERT Books Class 1
- Important Questions Class 12
- Important Questions Class 11
- Important Questions Class 10
- Important Questions Class 9
- Important Questions Class 8
- Important Questions Class 7
- important questions class 6
- CBSE Class 12 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 8 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 6 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 11 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 9 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 8 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 7 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 5 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 4 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 3 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 2 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 1 Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 5
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 4
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 3
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 2
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 1
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Science
- NEET 2021 Question Paper
- NEET 2020 Question Paper
- NEET 2019 Question Paper
- NEET 2018 Question Paper
- NEET 2017 Question Paper
- NEET 2016 Question Paper
- NEET 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Physics Questions
- NEET Chemistry Questions
- NEET Biology Questions
- NEET Sample Papers
- NEET Physics Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Biology Syllabus
- NEET Mock Test
- NEET Eligibility Criteria
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Main Sample Papers
- JEE Main Physics Syllabus
- JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Main Maths Syllabus
- JEE Main Physics Questions
- JEE Main Chemistry Questions
- JEE Main Maths Questions
- JEE main revision notes
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Advanced Physics Questions
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Questions
- JEE Advanced Maths Questions
- JEE Advanced 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Maths Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Mock Test
- ISC Class 12 Syllabus
- ISC Class 11 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 10 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 9 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 8 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 7 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 6 Syllabus
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 6
- ICSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- ICSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- ISC Important Questions for Class 12
- ISC Important Questions for Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 6
- ISC Class 12 Question Paper
- ICSE Class 10 Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Syllabus
- Maharashtra Board Sample Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Previous Year Question Paper
- AP Board Syllabus
- AP Board Sample Question Paper
- AP Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Board Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Telangana Board Syllabus
- Telangana Board Sample Question Paper
- Telangana Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Syllabus
- Karnataka Board Sample Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Examination Full Forms
- Physics Full Forms
- Chemistry Full Forms
- Biology Full Forms
- Educational Full Form
- CUET Eligibility Criteria
- CUET Exam Pattern
- CUET Cutoff
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Admit Card
- CUET Counselling
- CUET Previous Year Question Papers
- CUET Application Form
- CUET Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Centers
- CUET Exam Dates
- CUET Results
- Physics Formulas
- Chemistry Formulas
- Math Formulas
- Algebra Formulas
- Geometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Subscription
CBSE Important Questions Class 9 Maths Chapter 7
Home » CBSE » CBSE Important Questions Class 9 Maths Chapter 7

- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 6
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Extra Questions
- CBSE Sample Papers
- ISC & ICSE Syllabus
- ICSE Syllabus Class 9
- ICSE Syllabus Class 8
- ICSE Syllabus Class 7
- ICSE Syllabus Class 6
- ICSE Syllabus Class 10
- ICSE Question Paper
- ICSE Sample Question Papers
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- ICSE Revision Notes
- ICSE Important Questions
- ISC Important Questions For Class 12
- ISC Important Questions For Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 6
- Maharashtra board
- Rajasthan-Board
- Andhrapradesh Board
- AP Board syllabus
- Telangana Board
- Tamilnadu Board
- Tamilnadu Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Previous Year Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 10
- NCERT Solutions Class 11
- NCERT Solutions Class 9
- NCERT Solutions Class 8
- NCERT Solutions Class 7
- NCERT Solutions Class 6
- NCERT Solutions Class 5
- NCERT Solutions Class 4
- NCERT Solutions Class 3
- NCERT Solutions Class 2
- NCERT Solutions Class 1
- JEE Main Question Papers
- JEE Main Syllabus
- JEE Main Questions
- JEE Main Revision Notes
- JEE Advanced Question Papers
- JEE Advanced Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Questions
- JEE Advanced Sample Papers
- NEET Question Papers
- Neet 2021 Question Paper
- Neet 2020 Question Paper
- Neet 2019 Question Paper
- Neet 2018 Question Paper
- Neet 2017 Question Paper
- Neet 2016 Question Paper
- Neet 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Syllabus

Important Questions Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 7 – Triangles
The word “triangle” itself conveys its meaning. It is a closed figure made up of three crossing lines since the prefix “tri” implies “three”. The major objective of Chapter 7 is to study triangles and their congruence or similarity of triangles. You will learn in-depth information on triangle congruence, congruence rules, various triangle properties, and triangle inequalities in this chapter.
Quick Links
With the help of Extramarks’ Class 9 Mathematics NCERT Solutions, students can more easily and effectively prepare for all the concepts covered in the CBSE Syllabus. Revision Notes, which include a thorough explanation, key formulas, and time-saving advice, are also offered to students to assist them in getting a quick review of all the topics. By practising the NCERT Important Questions Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 7 , students can improve their test preparation.
Students’ grasp of the fundamental ideas in Mathematics is the main goal of the Important Questions Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 7 . The NCERT Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 7 Important Questions should be correctly and precisely practised by the students in order to effectively assimilate its conceptual meaning. Our subject specialists created these sample answers for Class 9 students. These answers present useful recommendations along with many beneficial tips and tactics for correctly answering the problems.
Students should practise these problems in order to achieve high grades on the class 9 Math final exam. To get better practice and a quick revision before the test, solve extra problems in addition to the Important Questions Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 7 . Triangle congruency or resemblance is a prominent topic in the questions in Chapter 7, Triangles. Students who can complete these problems will have a better understanding of the questions that will be on the test.
Important Questions Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 7 – With Solutions
The Important Questions Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 7 have been compiled by the Extramarks team from various sources. Students must be familiar with the congruence rule in order to solve questions on this subject. Therefore, read through the theory first and then have a look at the already-solved cases in the book. Start working on the exercise problems after that.
A few Chapter 7 Class 9 Mathematics Important Questions are provided here, along with their answers:
Question 1: If AD = BC and ∠ BAD = ∠ ABC, then ∠ ACB is equal to
Solution 1: (D)
Explanation: In △ABC and △ABD
AD =BC (given)
∠ BAD = ∠ ABC (Given)
AB = AB (Common side)
∴ △ABC ≅ △ABD
By CPCT theorem, ∠ACB=∠BDA ( By SAS Congruency )
Question 2: If ABCD is a quadrilateral where AD= CB, AB=CD, and ∠ D= ∠ B, then ∠CAB is equal to
Solution 2: (C)
Explanation: In △ABC and △CDA
CB = AD (Given)
AB=CD (Given)
∠B = ∠D (Given)
∴△ABC≅△CDA ( By SAS Congruency )
By CPCT theorem
Question 3: If O is a midpoint of AB and ∠ BQO = ∠ APO, then ∠ OAP is equal to
Solution 3: (C)
Explanation: In △AOP and △BOQ
AO=BO…..(O is the midpoint of AB)
∠APO=∠BQO(Given)
∠AOP=∠BOQ(Vertically opposite Angles)
∴△AOP≅△BOQ ( By AAS Congruency )
By CPCT ∠OAP=∠QBO Question 4: If AB ⊥BC and ∠ A =∠ C, then the correct statement will
Solution 4: (B) AB=BC
Explanation: In △ABC, ∠A=∠C
Opposite sides to equal angles are also equal
Question 5: If △ABC is an isosceles triangle, ∠ B = 65 0 , find ∠ A.
- none of these
Solution 5: (c)
Explanation: Since △ABC is on an isosceles triangle
∴∠A+∠B+∠C=180∘
∴∠A+130∘=180∘
∴∠A=180∘−130∘
Question 6: If AB=AC and ∠ ACD= 120 0 , find ∠A.
- none of these
Solution 6: (b)60 0
Explanation: Since AB=AC
⇒∠ABC=∠ACB=x (say)
Exterior angles = sum of interior opposite angles
120∘ =∠ABC+∠BAC
120∘=x+y−−−(1)
Again,∠ACB+∠ACD=180∘
x+120∘=180∘
Question 7: An angle is 14 0 more than its complement. Find its measure.
Solution 7: (C) 52
Explanation: Two angles whose sum equals 90 degrees are called complementary angles.
let first angle =x
it’s Complement = 90∘−x
According to the question,
x=14∘ + 90∘−x
Question 8: An angle is four times its complement. Find measure.
Solution 8: (B) 72
Explanation: Two angles, when summed up to 90 degrees, are called complementary angles.
let angle = x
Therefore, its complement = 90∘−x
Question 9: Find the measure of angles which are supplementary.
Solution 9: (D)
Explanation: Two angles which sum up to 180 degrees are called supplementary angles.
Question 10: Which of the following pair of angles will be supplementary?
- 30 0 , 120 0
- 45 0 , 135 0
- 120 0 ,30 0
- None of these.
Solution 10: (B) 45 0 , 135 0
Explanation: Because 45∘+135∘=180∘
Question 11: In an isosceles △ ABC, if AB=AC and ∠A=90 0 , Find ∠ B.
Solution 11: (A)
Explanation: Since AB = AC
⇒∠C=∠B (angles opposite equal sides are also equal )
∠A+∠B+∠C=180∘
90∘ +2∠B=180∘
⇒2∠B=180∘−90∘
Question 12: In an △ABC, if ∠B= ∠C=45 0 , Which is the longest side?
Solution 12: (A) BC
Explanation: In △ABC,
∠A+∠B+∠C=180∘
∠A+45∘+45∘=180∘
⇒∠A=180∘−90∘=90∘
This is a right-angled triangle in which the right angle is at ∠A
Therefore, the Side opposite to ∠A is the longest side (hypotenuse)
Question 13: In an △ABC, if AB=AC and ∠ B= 70 0 , Find A.
Solution 13: (A)
Explanation: In △ABC, AB=AC
∠C=∠B= 70∘
∠A+70∘+70∘=180∘
⇒∠A=180∘−140∘=40∘
Question 14: In an △ABC, if ∠A = 45 0 and ∠B =70 0 , determine the longest sides of the triangle.
Solution 14: (a) AC
Explanation: The angle opposite to the longest side is the largest
The side opposite ∠B is AC
The correct option is (a) AC
Question 15: Which of the following is not a criterion for the congruence of triangles?
Solution 15: (C) SSA
Explanation:
Two triangles are congruent when the side(S) and angles (A) of one triangle are equal to another.
And the criterion for congruence of triangles is SAS, ASA, SSS, and RHS.
So, SSA is not the criterion for the congruency of the triangle.
Question 16: If AB = QR, BC = PR and CA = PQ, then
(A) Δ PQR ≅ Δ BCA
(B) ΔCBA ≅ ΔPRQ
(C) ΔBAC ≅ Δ RPQ
(D) Δ ABC ≅ ΔPQR
Solution 16: (B) ΔCBA ≅ ΔPRQ
As per the question,
AB = QR, BC = PR and CA = PQ
Also, AB = QR, BC = PR and CA = PQ
A corresponds to Q, B corresponds to R, and C corresponds to P.
Therefore, (B) ΔCBA ≅ ΔPRQ
Question 17: In Δ ABC, AB = AC and ∠B = 50°. Then ∠C is equal to
(A)130° (B) 50° (C) 80° (D) 40°
Solution 17: (B) 50°
Δ ABC, AB = AC and ∠B = 50°.
Image Source: NCERT textbook
Since, AB = AC
Δ ABC is an isosceles triangle.
Hence, ∠B = ∠C
We know ∠B = 50°
Question 18: In Δ ABC, BC = AB and ∠B = 80°. Then ∠A is equal to
(A) 80° (B) 100° (C) 50° (D) 40°
Solution 18: (C) 50°
Given: Δ ABC, BC = AB and ∠B = 80°
Image source: NCERT textbook
Since, BC = AB
Let, ∠C = ∠A = x
∠B = 80° (given)
We know that,
Using the angle sum property,
The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is= 180o
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°
⇒ x + 80° + x = 180°
⇒ 2x = 180° – 80°
⇒ 2x = 100°
Thus, ∠C = ∠A = 50°
Question 19: In Δ PQR, ∠R = ∠P and QR = 4 cm and PR = 5 cm. Then the length of PQ is
(A) 4 cm (B)2.5 cm (C) 2 cm (D) 5 cm
Solution 19: (A) 4 cm
Explanation: Given: In ΔPQR, ∠R = ∠P and QR = 4 cm and PR = 5 cm
As given in the question, ∠R = ∠P
Therefore, Δ PQR is an isosceles triangle.
and PQ = QR
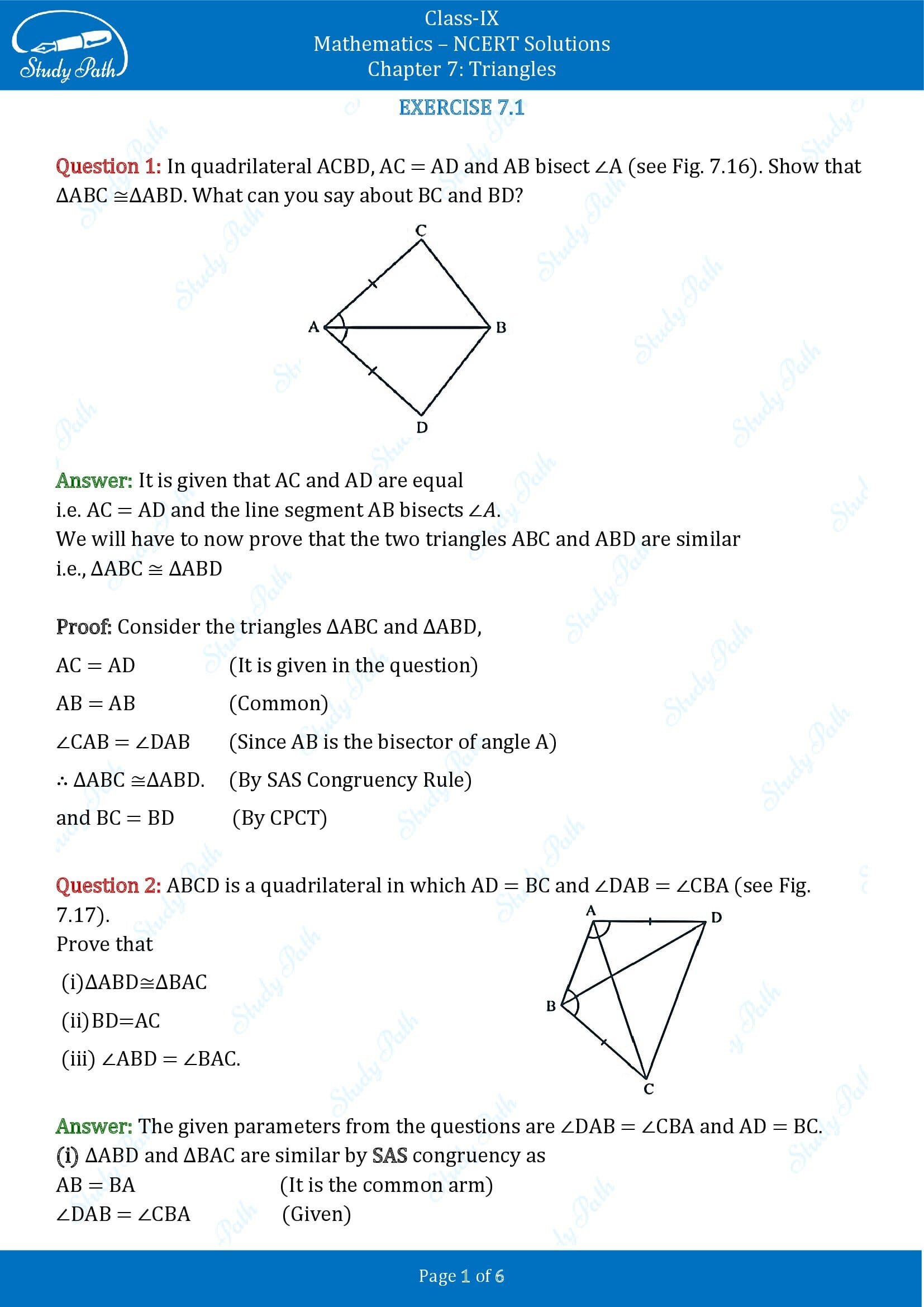
Question 20: In quadrilateral ACBD, AC = AD and AB are bisecting ∠A (see figure given below). Show that ΔABC≅ ΔABD. What can you depict about BC and BD?
Solution 20:
As given in the question, AC and AD are equal, i.e. AC = AD, and the line segment AB is bisecting ∠A.
We have to prove that the two triangles ABC and ABD are similar, i.e. ΔABC ≅ ΔABD
We consider the triangles ΔABC and ΔABD,
(i) AC = AD (It is given in the question)
(ii) AB = AB (Common side)
(iii) ∠CAB = ∠DAB (Since AB is a bisector of angle A)
So, by SAS congruency rule criterion, ΔABC ≅ ΔABD.
Again, for the 2nd part of the question, BC and BD are of equal lengths by the rule of CPCT.
Question 21: ABCD is a quadrilateral where AD = BC and ∠DAB = ∠CBA (see figure given below). Prove that
(i) ΔABD ≅ ΔBAC
(ii) BD = AC
(iii) ∠ABD = ∠BAC.
Solution 21:
Given in the question are ∠DAB = ∠CBA and AD = BC.
(i) ΔABD and ΔBAC are similar by SAS congruency rule as
AB = BA (It is the common arm)
∠DAB = ∠CBA and AD = BC (given in the question)
So, triangles ABD and BAC are quite similar, i.e. ΔABD ≅ ΔBAC. (Hence proved).
(ii) Again, we know that ΔABD ≅ ΔBAC, so,
BD = AC (by the rule of CPCT).
(iii) As ΔABD ≅ ΔBAC therefore,
Angles ∠ABD = ∠BAC (by the CPCT rule).
Question 22: AD and BC are equal perpendiculars to line segment AB (see figure given below). Show that CD is bisecting AB.
Solution 22:
Given in the question that AD and BC are the two equal perpendiculars to AB.
We are to prove that CD is the bisector of AB
Now, as per the question,
Triangles ΔAOD and ΔBOC are similar by AAS congruency rule since:
(i) ∠A = ∠B (Since perpendiculars)
(ii) AD = BC (Since given in the question)
(iii) ∠AOD = ∠BOC (Since vertically opposite angles)
∴ ΔAOD ≅ ΔBOC.
Thus, AO = OB (by CPCT rule).
Therefore, CD bisects AB (Hence proved).
Question 23: l and m are the two parallel lines that are intersected by another pair of parallel lines, such as p and q (see figure given below). Show that ΔABC ≅ ΔCDA.
Solution 23:
Given in the question that p || q and l || m
Triangles ABC and CDA are similar, i.e. ΔABC ≅ ΔCDA
We consider ΔABC and ΔCDA,
(i) ∠BCA = ∠DAC and ∠BAC = ∠DCA (Since alternate interior angles)
(ii) AC = CA (as common arm)
Thus, by ASA congruency rule criterion, ΔABC ≅ ΔCDA.
Question 24: Line l is the bisector of angle ∠A, and B is any point on l. BP and BQ are the perpendiculars from B to the arms of ∠A (see figure given below). Show that:
(i) ΔAPB ≅ ΔAQB
(ii) BP = BQ or B is equidistant from the arms of ∠A.
Solution 24:
As given in the question that the line “l” is the bisector of angle ∠A, and the line segments BP and BQ are perpendiculars drawn from l.
(i) ΔAPB and ΔAQB are similar by AAS congruency rule because:
∠P = ∠Q (Since they are two right angles)
AB = AB (Since common arm)
∠BAP = ∠BAQ (As l is the bisector of angle A)
So, ΔAPB ≅ ΔAQB.
(ii) By the CPCT rule, BP = BQ. So, it can be said that point B is equidistant from the arms of ∠A.
Question 25: In figure given below, AC = AE, AB = AD and ∠BAD = ∠EAC. Show that BC = DE.
Solution 25:
As given in the question, AB = AD, AC = AE, and ∠BAD = ∠EAC
Line segments BC and DE are similar, i.e. BC = DE
We know ∠BAD = ∠EAC
Now, by adding ∠DAC on both sides, we get,
∠BAD + ∠DAC = ∠EAC +∠DAC
Hence, ∠BAC = ∠EAD
Now, ΔABC and ΔADE are similar by the SAS congruency rule:
(i) AC = AE (given in the question)
(ii) ∠BAC = ∠EAD
(iii) AB = AD (given in the question)
Thus the triangles ABC and ADE are similar, i.e. ΔABC ≅ ΔADE.
Hence, by the CPCT rule, BC = DE.
Question 26: AB is a line segment, and P is the mid-point. D and E are the points on the same side of AB in such a way that ∠BAD = ∠ABE and ∠EPA = ∠DPB (see figure given below). Show that
(i) ΔDAP ≅ ΔEBP
(ii) AD = BE
Solution 26:
Given that P is the mid-point of line segment AB. And, ∠BAD = ∠ABE and ∠EPA = ∠DPB
(i) Also, given that ∠EPA = ∠DPB
Now, add ∠DPE on both sides,
∠EPA +∠DPE = ∠DPB+∠DPE
Hence, angles DPA and EPB are equal, i.e. ∠DPA = ∠EPB
Now, considering the triangles DAP and EBP.
∠DPA = ∠EPB
AP = BP (As P is the mid-point of AB)
∠BAD = ∠ABE (as per the question)
So, by ASA congruency rule, ΔDAP ≅ ΔEBP.
(ii) By CPCT rule, AD = BE.
Question 27: In the right triangle ABC, right-angled at C, and M is the mid-point of hypotenuse AB. Point C is joined to M and then produced to point D so that DM = CM. Point D is joined to point B (see figure given below). Show that:
(i) ΔAMC ≅ ΔBMD
(ii) ∠DBC is a right angle.
(iii) ΔDBC ≅ ΔACB
(iv) CM = ½ AB
Solution 27:
Given in the question that M is a mid-point of the line segment AB, ∠C = 90°, and DM = CM
(i) We consider the triangles ΔAMC and ΔBMD:
AM = BM (Since M is the mid-point)
CM = DM (As given in the question)
∠CMA = ∠DMB (Since vertically opposite angles)
So, by SAS congruency rule criterion, ΔAMC ≅ ΔBMD.
(ii) ∠ACM = ∠BDM (by CPCT rule)
∴ AC || BD since alternate interior angles are equal.
Now, ∠ACB +∠DBC = 180° (i.e., co-interiors angles)
⇒ 90° +∠B = 180°
∴ ∠DBC = 90°
(iii) In ΔDBC and ΔACB,
BC = CB (Since common side)
∠ACB = ∠DBC (Since they are right angles)
DB = AC (by CPCT rule)
Thus, ΔDBC ≅ ΔACB by SAS congruency rule.
(iv) DC = AB (Since ΔDBC ≅ ΔACB)
⇒ DM = CM = AM = BM (As M the is mid-point)
So, DM + CM = BM+AM
Therefore, CM + CM = AB
⇒ CM = (½) AB
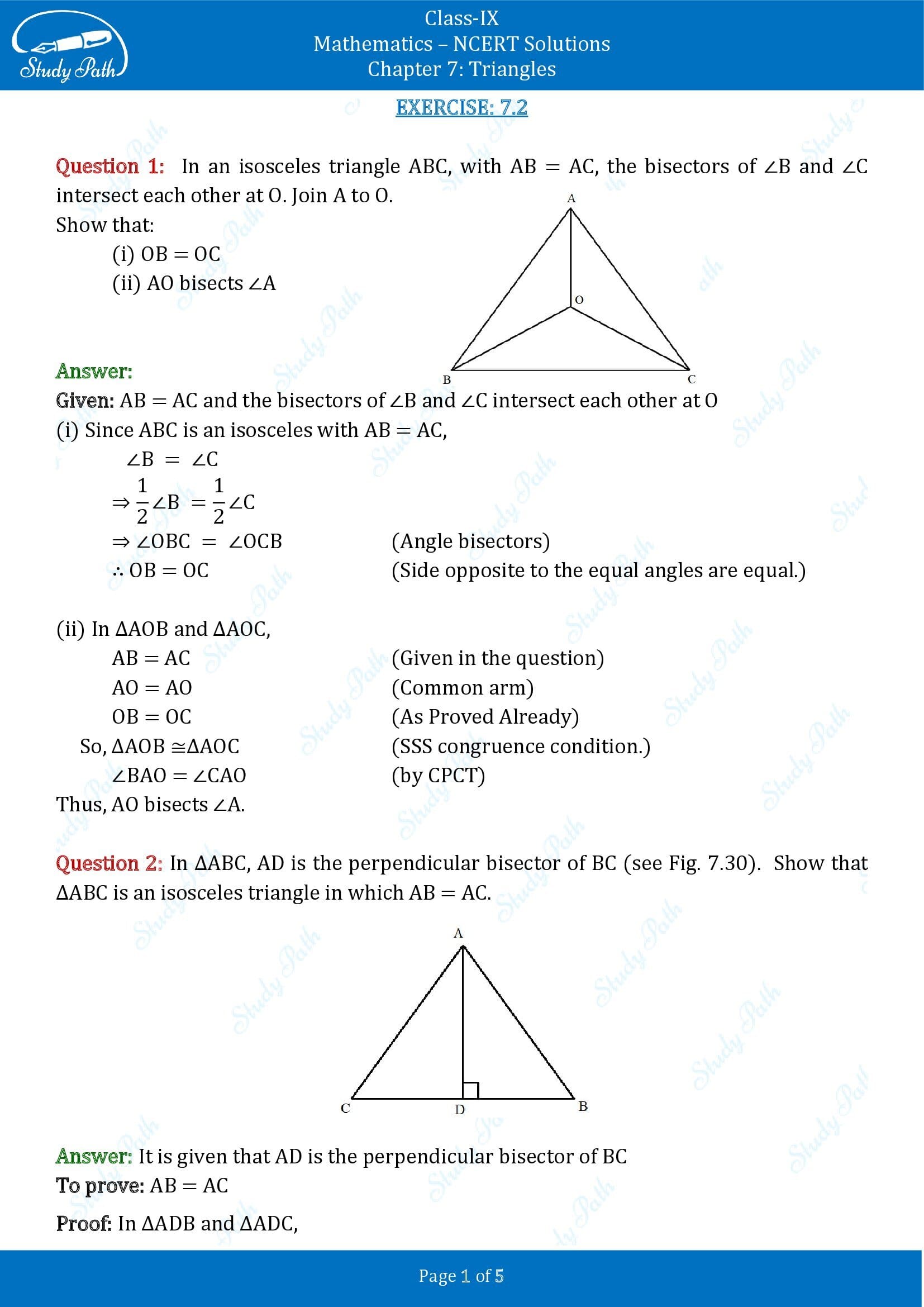
Question 28: In the isosceles triangle ABC, AB = AC, the bisectors of ∠B and ∠C intersect each other at O. Join A to O. Show that:
(i) OB = OC (ii) AO bisects ∠A
Solution 28:
AB = AC and
the bisectors of ∠B and ∠C intersect each other at O
(i) Since ABC is isosceles in which AB = AC,
½ ∠B = ½ ∠C
⇒ ∠OBC = ∠OCB (i.e., Angle bisectors)
∴ OB = OC (opposite sides to equal angles are equal.)
(ii) In ΔAOB and ΔAOC,
AB = AC (Given in the question)
AO = AO (Common arm)
OB = OC (As Proved earlier)
So, ΔAOB ≅ ΔAOC by SSS congruence rule.
BAO = CAO (by CPCT rule)
Therefore, AO bisects ∠A.
Question 29: In ΔABC, AD is the perpendicular bisector of BC (see figure given below). Show that ΔABC is an isosceles triangle where AB = AC.
Solution 29:
Given AD is the perpendicular bisector of BC
In ΔADB and ΔADC,
AD = AD (Since common arm)
∠ADB = ∠ADC
BD = CD (Because AD is the perpendicular bisector)
Thus, ΔADB ≅ ΔADC by SAS congruency rule criterion.
AB = AC (by CPCT rule)
Question 30: ABC is an isosceles triangle in which altitudes BE, and CF is drawn to equal sides AC and AB, respectively (see figure given below). Show that the two altitudes are equal.
Solution 30:
(i) BE and CF are the two altitudes.
(ii) AC = AB
Triangles ΔAEB and ΔAFC are similar to the AAS congruency rule as
∠A = ∠A (common arm)
∠AEB = ∠AFC (Since right angles)
∴ ΔAEB ≅ ΔAFC and so, BE = CF (by CPCT).
Question 31: ABC is a triangle where the altitudes BE and CF to the sides AC and AB are equal (see figure given below). Show that
(i) ΔABE ≅ ΔACF
(ii) AB = AC, i.e., ABC is an isosceles triangle.
Solution 31:
We know BE = CF
(i) In ΔABE and ΔACF,
∠A = ∠A (Since common angle)
BE = CF (Given)
Therefore, ΔABE ≅ ΔACF by AAS congruency condition.
(ii) AB = AC by CPCT rule, and thus, ABC is an isosceles triangle.
Question 32: ABC and DBC are the two isosceles triangles lying on the same base BC (see figure given below). Show that ∠ABD = ∠ACD.
Solution 32:
We have ABC and DBC are two isosceles triangles.
We are to show that ∠ABD = ∠ACD
Triangles ΔABD and ΔACD are similar to the SSS congruency rule since
AB = AC (ABC is an isosceles triangle)
BD = CD (BCD is an isosceles triangle)
As, ΔABD ≅ ΔACD.
Therefore, ∠ABD = ∠ACD by the rule of CPCT.
Question 33: ΔABC is an isosceles triangle where AB = AC. Side BA is produced to D so that AD = AB (see figure given below). Show that ∠BCD is a right angle.
Solution 33:
Given, AB = AC and AD = AB
We are to prove ∠BCD is a right angle.
We consider ΔABC,
AB = AC (given in the question)
And ∠ACB = ∠ABC (angles opposite to the equal sides are equal)
Now, we consider ΔACD,
Also, ∠ADC = ∠ACD (angles opposite to the equal sides are equal)
∠CAB + ∠ACB + ∠ABC = 180°
So, ∠CAB + 2∠ACB = 180°
⇒ ∠CAB = 180° – 2∠ACB — eq.(i)
Similarly, in ΔADC,
∠CAD = 180° – 2∠ACD — eq.(ii)
∠CAB + ∠CAD = 180° (BD is a straight line.)
Adding equations (i) and (ii), we have,
∠CAB + ∠CAD = 180° – 2∠ACB+180° – 2∠ACD
⇒ 180° = 360° – 2∠ACB-2∠ACD
⇒ 2(∠ACB+∠ACD) = 180°
⇒ ∠BCD = 90°
Question 34: ABC is a right-angled triangle where ∠A = 90° and AB = AC. Find ∠B and ∠C.
Solution 34:
∠A = 90° and AB = AC
⇒ ∠B = ∠C (angles opposite to the equal sides are equal)
∠A+∠B+∠C = 180° (We know the sum of the interior angles of the triangle)
∴ 90° + 2∠B = 180°
⇒ 2∠B = 90°
So, ∠B = ∠C = 45°
Question 35: Show all the angles of the equilateral triangle 60° each.
Solution 35:
Let ABC be the equilateral triangle as shown below:
Here, BC = AC = AB (length of all sides are same)
⇒ ∠A = ∠B =∠C (opposite sides to equal angles are equal.)
Also, we know,
∠A+∠B+∠C = 180°
⇒ 3∠A = 180°
∴ ∠A = ∠B = ∠C = 60°
Therefore, the angles of the equilateral triangle are 60° each.
Question 36: ΔABC and ΔDBC are the two isosceles triangles lying on the same base BC and the vertices A and D lying on the same side of BC (see figure given below). If AD is extended so that it intersects BC at P, show that
(i) ΔABD ≅ ΔACD
(ii) ΔABP ≅ ΔACP
(iii) AP bisects ∠A and ∠D.
(iv) AP is the perpendicular bisector of the side BC.
Solution 36:
As per the question, ΔABC and ΔDBC are the two isosceles triangles.
(i) ΔABD and ΔACD are similar as per the SSS congruency because:
AD = AD (common arm)
AB = AC (As ΔABC is an isosceles triangle)
BD = CD (Since ΔDBC is an isosceles triangle)
∴ ΔABD ≅ ΔACD.
(ii) ΔABP and ΔACP are similar because:
AP = AP (Since common side)
∠PAB = ∠PAC (by CPCT rule since ΔABD ≅ ΔACD)
AB = AC (As ΔABC is an isosceles triangle )
Thus, ΔABP ≅ ΔACP by SAS congruency rule condition.
(iii) ∠PAB = ∠PAC by CPCT rule as ΔABD ≅ ΔACD.
AP bisects ∠A. — eq. (i)
Also, ΔBPD and ΔCPD are similar in the SSS congruency rule as
PD = PD (Since common side)
BD = CD (Since ΔDBC is an isosceles triangle.)
BP = CP (by CPCT rule as ΔABP ≅ ΔACP)
Thus, ΔBPD ≅ ΔCPD.
Thus, ∠BDP = ∠CDP by CPCT. — eq. (ii)
Now by comparing equations (i) and (ii), we can say that AP bisects ∠A and ∠D.
(iv) ∠BPD = ∠CPD (by CPCT rule as ΔBPD ΔCPD)
and BP = CP — eq.(i)
∠BPD +∠CPD = 180° (Since BC is a straight line.)
⇒ 2∠BPD = 180°
⇒ ∠BPD = 90° —eq.(ii)
Now, from equations (i) and (ii), it can be concluded that
AP is the perpendicular bisector of BC.
Question 37: AD is an altitude of an isosceles triangle ABC where AB = AC. Show that
(i) AD bisects BC
(ii) AD bisects ∠A.
Solution 37:
Given AD is an altitude and AB = AC.
(i) In ΔABD and ΔACD,
∠ADB = ∠ADC = 90°
Therefore, ΔABD ≅ ΔACD by RHS congruence condition.
Now, by the CPCT rule,
Thus, AD bisects BC
(ii) Again, by CPCT, ∠BAD = ∠CAD
Hence, AD bisects ∠A.
Question 38: Two sides AB and BC and the median AM of triangle ABC are respectively equal to the sides PQ and QR and the median PN of ΔPQR (see figure given below). Show that:
(i) ΔABM ≅ ΔPQN
(ii) ΔABC ≅ ΔPQR
Solution 38:
Some given parameters are:
BC = QR and
(i) ½ BC = BM and ½ QR = QN (As AM and PN are the medians)
Also, BC = QR
So, ½ BC = ½ QR
In ΔABM and ΔPQN,
AM = PN and AB = PQ (As per the question)
BM = QN (proved earlier)
∴ ΔABM ≅ ΔPQN by SSS rule congruency.
(ii) In ΔABC and ΔPQR,
AB = PQ and BC = QR (As per the question)
∠ABC = ∠PQR (by CPCT)
Therefore, ΔABC ≅ ΔPQR by SAS congruency.
Question 39: BE and CF are the two equal altitudes of triangle ABC. Using the RHS congruence condition, prove that triangle ABC is isosceles.
Solution 39:
We know that BE and CF are two equal altitudes.
Now, in ΔBEC and ΔCFB,
∠BEC = ∠CFB = 90° (Since same altitudes)
BE = CF (Since common side)
Thus, ΔBEC ≅ ΔCFB by RHS congruence rule criterion.
And, ∠C = ∠B (by CPCT rule)
Therefore, AB = AC as opposite sides to the equal angles is always equal.
Question 40: ABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC. Draw AP ⊥ BC to show that ∠B = ∠C.
Solution 40:
Given in the question that AB = AC
Now, ΔABP and ΔACP are similar by RHS congruency rule as
∠APB = ∠APC = 90° (AP is altitude)
AP = AP (Common side)
So, ΔABP ≅ ΔACP.
∴ ∠B = ∠C (by CPCT)
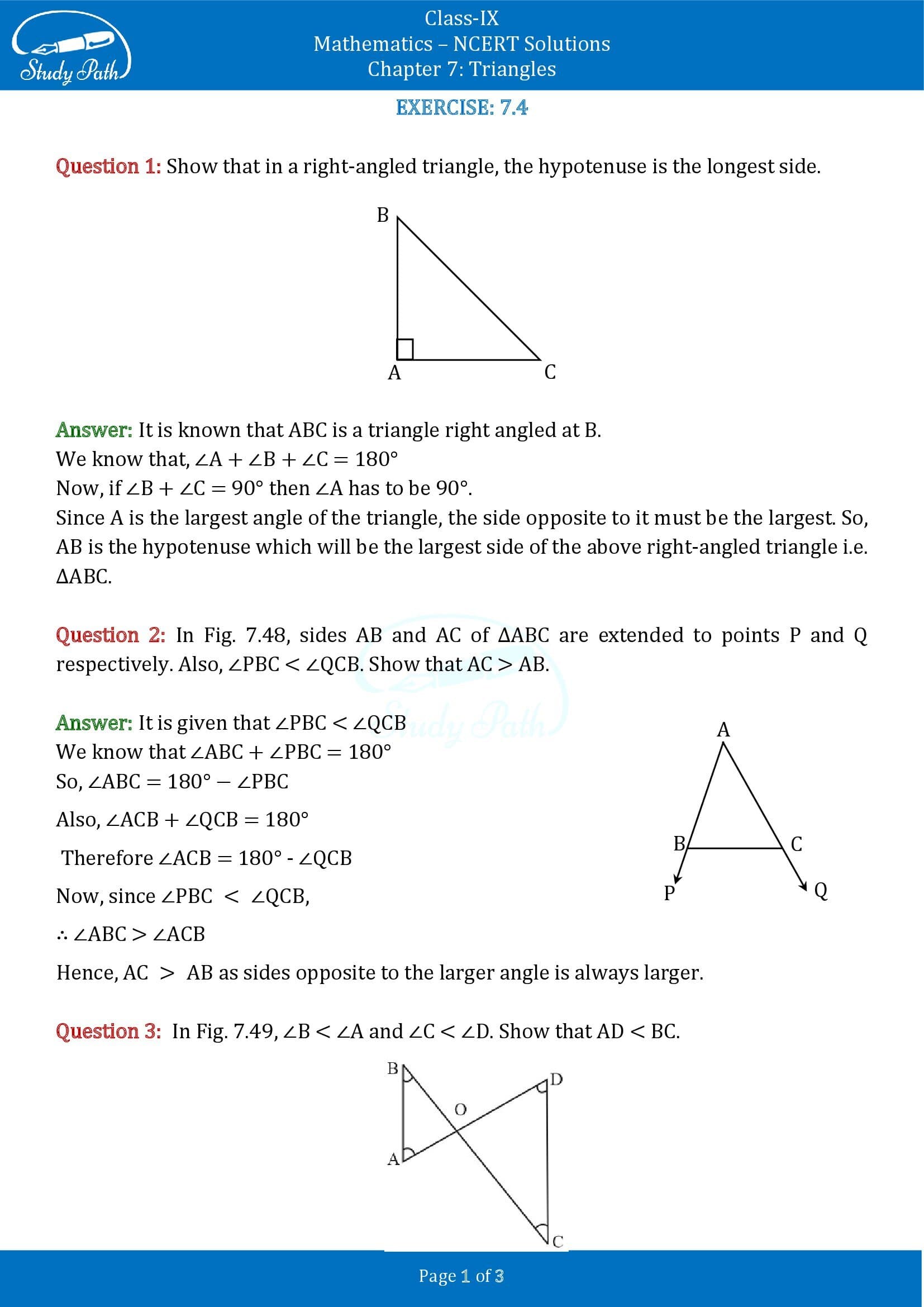
Question 41: Show that in any right-angled triangle, the hypotenuse is the longest side.
Solution 41:
We suppose ABC is a triangle with the right angled at B.
Thus we know,
∠A +∠B+∠C = 180°
Now, when ∠B+∠C = 90°, then ∠A has to be 90°.
Again, if A is the largest angle of the triangle, the side opposite to it has to be the largest.
So, AB is the hypotenuse and is the largest side of the right-angled triangle, i.e. ΔABC.
Question 42: In figure given below, both the sides AB and AC of ΔABC are extended to the points P and Q, respectively. Also, ∠PBC < ∠QCB. Show that AC> AB.
Solution 42:
Given in the question, ∠PBC < ∠QCB
We know ∠ABC + ∠PBC = 180°
Thus, ∠ABC = 180°-∠PBC
∠ACB +∠QCB = 180°
So, ∠ACB = 180° -∠QCB
Now, since ∠PBC < ∠QCB,
∴ ∠ABC > ∠ACB
Therefore, AC > AB as opposite sides to the larger angle are larger.
Question 43: In figure given below, ∠B < ∠A and ∠C < ∠D. Show that AD < BC.
Solution 43:
Given in the question that angles B and angle C are smaller than angles A and D respectively, i.e. ∠B < ∠A and ∠C < ∠D.
Since the opposite side to the smaller angle is always smaller
AO < BO — eq.(i)
And OD < OC —eq.(ii)
By adding equations (i) and (ii), we get
AO+OD < BO + OC
Therefore, AD < BC
Question 44: △ABC is an isosceles triangle with AB=AC and ∠B = 45 0 . Find ∠A.
Solution 44: In △ABC, AB=AC
⇒∠A=180∘−90∘=90∘
Question 45: AB and CD are the smallest and longest sides of a quadrilateral ABCD, respectively.
Show that ∠A > ∠C and ∠B > ∠D.
Solution 45:
In ΔABD, we see,
AB < AD < BD
So, ∠ADB < ∠ABD — equation(i) (as the angle opposite to the longer side is always larger)
Now, in ΔBCD,
BC < DC < BD
Therefore, it can be said that
∠BDC < ∠CBD — equation(ii)
Now, by adding equations (i) and (ii), we get,
∠ADB + ∠BDC < ∠ABD + ∠CBD
∠ADC < ∠ABC
In a similar manner in triangle ABC,
∠ACB < ∠BAC — equation(iii) (Since the angle opposite to the larger side is always larger)
Again, In ΔADC,
∠DCA < ∠DAC — equation(iv)
By adding equations (iii) and (iv), we have,
∠ACB + ∠DCA < ∠BAC+∠DAC
⇒ ∠BCD < ∠BAD
Therefore, ∠A > ∠C
Question 46: In figure given below, PR > PQ and PS bisect ∠QPR. Prove that ∠PSR> ∠PSQ.
Solution 46:
Given in the question PR> PQ and PS bisects ∠QPR
We have to prove that angle PSR is smaller than PSQ, i.e. ∠PSR> ∠PSQ
∠PQR> ∠PRQ — equation(i) (Since PR > PQ as angle opposite to the larger side is larger)
∠QPS = ∠RPS — equation (ii) (Since PS bisects ∠QPR)
∠PSR = ∠PQR + ∠QPS — equation (iii) (Since the exterior angle of a triangle equals the sum of opposite interior angles)
∠PSQ = ∠PRQ + ∠RPS —equation (iv) (As the exterior angle of a triangle equals the sum of the opposite interior angles)
By adding equation(i) and (ii)
∠PQR +∠QPS > ∠PRQ +∠RPS
Therefore, from (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv), we get
∠PSR > ∠PSQ
Question 47: Show that of all the line segments drawn from a given point, not on it, the perpendicular line segment is the shortest.
Solution 47:
First, we suppose “l” be a line segment, and “B” is a point lying on it. A line AB which is perpendicular to l, is drawn. Also, let C be any other point on l.
In ΔABC, ∠B = 90°
∴ ∠A +∠C = 90°
Thus, ∠C must be an acute angle implying ∠C < ∠B
So, AB < AC (As we know that the side opposite to the larger angle is always larger)
Question 48: In the triangles ABC and PQR, ∠A = ∠Q and ∠B = ∠R. Which side of Δ PQR must be equal to the side AB of Δ ABC so that the two given triangles are congruent? Give a reason for your answer.
Solution 48:
In triangles ABC and PQR, we have
∠A = ∠Q [Given]
∠B = ∠R [Given]
For the triangle to be congruent, AB must be equal to QR.
Thus, triangle ABC and PQR may be congruent by the ASA congruence rule.
Question 49: In the triangles ABC and PQR, ∠A = ∠Q and ∠B = ∠R. Which side of Δ PQR must be equal to side BC of Δ ABC so that the two triangles are congruent? Give a reason for your answer.
Solution 49:
In the triangles ABC and PQR, we have
∠A = ∠Q and ∠B = ∠R [Given]
For the triangles to be congruent, we should have
Thus, triangle ABC and PQR are congruent by following the AAS congruence rule.
Question 50: “If the two sides and an angle of one of the triangles are equal to the two sides and an angle of another triangle, then the two triangles should be congruent.” Is this statement true? If so, why?
Solution 50:
No, the statement, “If the two sides and an angle of one of the triangles are equal to the two sides and an angle of another triangle, then the two triangles should be congruent.”, is false.
Justification:
Because by the congruency rule,
The two sides and the included angle of one triangle are equal to the two sides, and the included angle of the other triangle, i.e., the SAS rule.
Question 51: “If the two angles and a side of one of the triangles are equal to the two angles and a side of another triangle, then the two triangles must be congruent.” Is this statement true? Why?
Solution 51:
The statement, “If the two angles and a side of one of the triangles are equal to the two angles and a side of another triangle, then the two triangles must be congruent.” is true.
The statement is true since the triangles would be congruent either by the ASA rule or the AAS rule. This is so because the two angles and one side are enough to construct two congruent triangles.
Question 52: Is it possible to construct any triangle with lengths of sides 4 cm, 3 cm and 7 cm? Give a reason for your answer.
Solution 52:
No, it is not possible to construct any triangle with lengths of sides 4 cm, 3 cm and 7 cm.
The sum of any two sides of a triangle is always greater than the third side.
But here, the sum of two sides whose lengths are 4 cm and 3 cm = 4 cm + 3 cm = 7 cm,
which is equal to the length of the third side, i.e., 7 cm.
Therefore, it is not possible to construct a triangle with lengths of sides 4 cm, 3 cm and 7 cm.
Question 53: It is given that Δ ABC ≅ Δ RPQ. Is it true to state that BC = QR? Why?
Solution 53:
It is False that BC = QR. This is because BC = PQ as ΔABC ≅ ΔRPQ.
Question 54: ABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC and BD and CE are the two medians. Show that BD = CE.
Solution 54:
ΔABC is an isosceles triangle where AB = AC, BD and CE are its two medians
From ΔABD and ΔACE,
2 AE = 2 AD (since D and E are the midpoints)
So, AE = AD
∠A = ∠A (common between the triangles)
Thus, ΔABD ≅ ΔACE (using the SAS rule)
⇒ BD = CE (by CPCT rule)
Hence proved.
Question 55: In the figure given below, D and E are points on side BC of Δ ABC in such a way that BD = CE and AD = AE.
Show that Δ ABD ≅ Δ ACE.
Solution 55:
BD = CE and AD = AE.
As opposite angles to equal sides are equal,
Therefore we have,
∠ADE = ∠AED … eq.(1)
Now, ∠ADE + ∠ADB = 180° (since linear pair)
∠ADB = 180° – ∠ADE … eq. (2)
Also, ∠AED + ∠AEC = 180° (since linear pair)
∠AEC = 180° – ∠AED
As, ∠ADE = ∠AED
∠AEC = 180° – ∠ADE … eq.(3)
From equation (2) and (3)
∠ADB = ∠AEC … eq.(4)
Again, In ΔADB and ΔAEC,
AD = AE (given)
BD = EC (given)
∠ADB = ∠AEC (from eq. (4)
Thus, ΔABD ≅ΔACE (by SAS rule)
Question 56: CDE is the equilateral triangle formed on the side CD of square ABCD in figure given below. Show that
Δ ADE ≅ Δ BCE.
Solution 56:
CDE is an equilateral triangle which is formed on a side CD of a square ABCD.
In ΔADE and ΔBCE,
DE = CE (sides of an equilateral triangle)
∠ADC = ∠BCD = 90°
Also, ∠EDC = ∠ECD = 60°
Thus, ∠ADE = ∠ADC + ∠CDE = 90° + 60° = 150°
And ∠BCE = ∠BCD + ∠ECD = 90° + 60° = 150°
⇒ ∠ADE = ∠BCE
AD = BC (sides of the square)
Therefore, ΔADE ≅ΔBCE (by SAS rule)
Question 57: In figure given below, BA ⊥ AC, DE ⊥ DF such that BA = DE and BF = EC. Show that Δ ABC ≅ Δ DEF.
Solution 57:
BA ⊥ AC, DE ⊥ DF in such a way that BA = DE and BF = EC.
In ΔABC and ΔDEF
BA = DE (given)
BF = EC (given)
∠A = ∠D (both 90°)
BC = BF + FC
EF = EC + FC = BF + FC (∵ EC = BF)
Hence, ΔABC ≅ ΔDEF (by RHS)
Question 58: Q is any point on the side SR of a Δ PSR so that PQ = PR. Prove that PS> PQ.
Solution 58:
Given: In ΔPSR, Q is any point on the side SR so that PQ = PR.
PR = PQ (given)
⇒ ∠PRQ = ∠PQR (angles opposite to equal sides are equal)
But ∠PQR> ∠PSR (i.e., the exterior angle of a triangle is greater than each of the opposite interior angles)
⇒ ∠PRQ > ∠PSR
⇒ PS> PR (sides opposite to the greater angle is greater)
⇒ PS > PQ (since PR = PQ)
Question 59: Find the angles of an equilateral triangle.
Solution 59:
We know in an equilateral triangle,
all sides are equal.
Thus, all angles are equal as well
Let x be the angles of an equilateral triangle
Now, following the angle sum property,
We know the sum of the interior angles=180o.
Hence, all angles of an equilateral triangle are 60°
Question 60: The image of an object which is placed at point A before a plane mirror LM such that it is seen at point B by an observer standing at D, as shown in figure given below. Prove that the image is as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror.
[Note: CN is normal to mirror. Also, angle of incidence = angle of reflection].
Solution 60:
We suppose that AB intersects LM at O. We have to prove that AO = BO.
Now, ∠i = ∠r …(1)
[∵Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection]
∠B = ∠i [Corresponding angles] …(2)
And ∠A = ∠r [Alternate interior angles] …(3)
From (1), (2) and (3), we get
⇒ ∠BCO = ∠ACO
In ΔBOC and ΔAOC, we have
∠1 = ∠2 [Each = 90o]
OC = OC [i.e., Common side]
And ∠BCO = ∠ACO [Proved earlier]
ΔBOC ≅ ΔAOC [ASA congruency rule]
Therefore, AO = BO [CPCT]
Question 61: ABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC, and D is the point on BC in such a way that AD ⊥ BC (in figure given below). To prove that ∠BAD = ∠CAD, a student started as follows:
In Δ ABD and Δ ACD,
AB = AC (Given)
∠B = ∠C (since AB = AC)
And ∠ADB = ∠ADC
Thus Δ ABD Δ Δ ACD (AAS)
So, ∠BAD = ∠CAD (CPCT rule)
What is the defect/problem in the above arguments?
[Hint: Recall how ∠B = ∠C is proved when AB = AC].
Solution 61:
In Δ ABD and Δ ADC, we have
AD = AD [Since common side]
By the RHS criterion of congruence rule,
Δ ABD ≅ Δ ACD
∠BAD = ∠CAD [CPCT rule]
Hence Proved.
Question 62: P is the point on the bisector of ∠ABC. If the line passing through P, parallel to BA, meets BC at Q, we are to prove that BPQ is an isosceles triangle.
Solution 62:
To prove: BPQ is an isosceles triangle.
As BP is the bisector of ∠ABC,
∠1 = ∠2 … eq. (1)
Here, PQ is parallel to BA, and BP cuts them
∠1 = ∠3 [Since alternate angles] … eq.(2)
Now from equations (1) and (2),
Therefore, BPQ is an isosceles triangle.
Question 63: ABCD is a quadrilateral with AB = BC and AD = CD. Show that BD is bisecting both the angles ABC and ADC.
Solution 63:
In ΔABC and ΔCBD,
BD = BD [As common side]
ΔABC ≅ ΔCBD [By SSS congruence rule]
⇒ ∠1 = ∠2 [CPCT rule]
And ∠3 = ∠4
Therefore, BD bisects both ∠ABC and ∠ADC.
Question 64: ABC is a right triangle with AB = AC. The bisector of ∠A meets BC at D. Prove that BC = 2 AD.
Solution 64:
Given: A right-angled triangle with AB = AC bisector of ∠A meets BC at D.
To prove: BC = 2AD
In the right Δ ABC,
Since hypotenuse is the longest side,
BC is hypotenuse
In Δ CAD and Δ BAD,
Since AD is the bisector of ∠A,
AD = AD [Common side]
By SAS criterion of congruence,
Δ CAD ≅ Δ BAD
CD = BD [CPCT]
Since the mid-point of the hypotenuse of the right triangle is equidistant from the three vertices of the triangle.
AB = BD = CD …eq.(1)
Here, BC = BD + CD
⇒ BC = AD + AD [Using eq(1)]
Hence, proved.
Question 65: O is the point in the interior of the square ABCD in such that OAB is an equilateral triangle. Show that Δ OCD is an isosceles triangle.
Solution 65:
Given in the question, A square ABCD and OA = OB = AB.
To prove: Δ OCD is an isosceles triangle.
In square ABCD,
As ∠1 and ∠2 is equal to 90o
∠1 = ∠2 …eq.(1)
Now, in Δ OAB, we have
As ∠3 and ∠4 is equal to 60o
∠3 = ∠4 …(2)
Subtracting equations (2) from (1),
∠1−∠3 = ∠2 −∠4
In Δ DAO and Δ CBO,
AD = BC [Given]
∠5 = ∠6 [Proved earlier]
OA = OB [Given]
By the SAS criterion of congruence rule,
Δ DAO ≅ Δ CBO
⇒ Δ OCD is an isosceles triangle.
Question 66: ABC and DBC are the two triangles on the same base BC such that A and D lie on opposite sides of BC, AB = AC and DB = DC. Show that AD is the perpendicular bisector of BC.
Solution 66:
Given: Δ ABC and Δ DBC lie on the same base BC. Also, AB = AC and BD = DC.
To prove: AD is the perpendicular bisector of BC, i.e., OB = OC
Proof: In Δ BAD and Δ CAD, we have
AB = AC [Given]
BD = CD [Given]
So, by the SSS criterion of congruence, we have
Δ BAD ≅ Δ CAD
∠1 = ∠2 [CPCT]
Now, in Δ BAO and Δ CAO, we have
∠1 = ∠2 [Proved above]
AO = AO [Common side]
So, by the SAS criterion of congruence, we have
Δ BAO ≅ Δ CAO
BO = CO [CPCT]
And, ∠3 = ∠4 [CPCT]
But, ∠3+∠4 =180o [Linear pair axiom]
⇒ ∠3+∠3 =180
⇒ ∠3 =180/2
Since BO = CO and ∠3 = 90o,
AD is a perpendicular bisector of BC.
Question 67: ABC is an isosceles triangle with AC = BC. AD and BE are two altitudes to sides BC and AC, respectively. Prove that AE = BD.
Solution 67:
In Δ ADC and Δ BEC,
AC = BC [Given] …eq(1)
As ∠ADC and ∠BEC = 90o
∠ADC = ∠BEC
∠ACD = ∠BCE [Since common angle]
Δ ADC ≅ Δ BEC [By ASA congruence rule]
CE = CD … (2) [CPCT rule]
Subtracting equation (2) from (1),
AC – CE = BC – CD
Question 68: Prove that sum of any two sides of a triangle is greater than twice the median with respect to the third side.
Solution 68:
We have Δ ABC with AD as its median.
AB + AC > 2AD
AB + BC > 2AD
BC + AC > 2AD
Construction:
We extend AD to E such that DE = AD
In Δ ADB and Δ EDC,
AD = ED [By construction]
∠1 = ∠2 [Vertically opposite angles are equal]
DB = DC [Given]
Δ ADB ≅ Δ EDC
AB = EC [CPCT]
And ∠3 = ∠4 [CPCT]
Now, in Δ AEC,
Since the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle must be greater than the third side,
AC + CE > AE
⇒ AC + CE > AD + DE
⇒ AC +CE > AD+ AD [\AD = DE]
⇒ AC + CE > 2AD
⇒ AC + AB > 2AD [∵AB = CE]
AB + BC > 2AD and BC + AC >2AD.
Question 69: ABCD is a quadrilateral where AD = BC and ∠DAB = ∠CBA. Prove that
Solution 69:
∠DAB = ∠CBA and AD = BC.
(i) ΔABD and ΔBAC are similar by following SAS rule congruency as
AB = BA (the common arm)
∠DAB = ∠CBA and AD = BC (given)
Thus, triangles ABD and BAC are similar
i.e. ΔABD ≅ ΔBAC. (Hence proved).
(ii) Since it is already proven,
ΔABD ≅ ΔBAC
BD = AC (by CPCT)
(iii) As ΔABD ≅ ΔBAC
So, the angles are equal,
∠ABD = ∠BAC (by CPCT).
Question 70: AD and BC are equal and perpendicular to the line segment AB. Show that CD bisects AB.
Solution 70:
Given AD and BC are two equal perpendiculars to AB.
To prove: CD is the bisector of AB
The triangles ΔAOD and ΔBOC are similar by AAS rule congruency
(i) ∠A = ∠B (perpendicular angles)
(ii) AD = BC (given in the question)
(iii) ∠AOD = ∠BOC (i.e., vertically opposite angles)
Thus, AO = OB ( by CPCT).
Hence, CD bisects AB (Hence proved).
Question 71: Line l is the bisector of the angle ∠A, and B is any point on the line l. BP and BQ are the perpendiculars from B to the arms of ∠A. Show that:
Solution 71:
It is given in the question that line “l” is the bisector of angle ∠A, and the line segments BP and BQ are perpendiculars drawn from line l.
(i) ΔAPB and ΔAQB are similar by following the AAS congruency rule because;
∠P = ∠Q (right angles)
AB = AB (common arm)
∠BAP = ∠BAQ (l is the bisector of angle A)
Thus, ΔAPB ≅ ΔAQB.
(ii) By CPCT rule, BP = BQ. Thus, we can say that point B is equidistant from the arms of ∠A.
Question 72: AB is the line segment, and P is the mid-point. D and E are the points on the same side of AB, so ∠BAD = ∠ABE and ∠EPA = ∠DPB. Show that
Solution 72:
Given that P is the mid-point of line segment AB.
And, ∠BAD = ∠ABE and ∠EPA = ∠DPB
(i) Given, ∠EPA = ∠DPB
Now, adding ∠DPE on both sides,
∠EPA + ∠DPE = ∠DPB + ∠DPE
Thus it can be said that angles DPA and EPB are equal, i.e. ∠DPA = ∠EPB
AP = BP (As P is the mid-point of line segment AB)
∠BAD = ∠ABE (given)
Thus, by the ASA congruency criterion,
ΔDAP ≅ ΔEBP.
(ii) By CPCT rule,
Question 73: In the right triangle, ABC, which is right-angled at C and M, is the mid-point of hypotenuse AB. C is joined to M and is produced to a point D so that DM = CM. Point D is joined to point B. Show that:
(iv) CM = 1/2 AB
Solution 73:
We know M is the mid-point of the line segment AB, ∠C = 90°, and DM = CM
CM = DM (Given)
∠CMA = ∠DMB (Vertically opposite angles)
So, by SAS congruency criterion, ΔAMC ≅ ΔBMD.
(ii) ∠ACM = ∠BDM (by CPCT)
∴ AC ∥ BD as alternate interior angles is equal.
Now, ∠ACB + ∠DBC = 180° (Since they are co-interiors angles)
⇒ 90° + ∠B = 180°
∠ACB = ∠DBC (Both are right angles)
⇒ DM = CM = AM = BM (Since M is the mid-point)
Thus, DM + CM = BM + AM
Question 74: ABC is an isosceles triangle with altitudes BE and CF, which are drawn to equal sides, AC and AB, respectively. Show that the altitudes are equal.
Solution 74:
(i) BE and CF are the altitudes.
Triangles ΔAEB and ΔAFC are similar by the AAS congruency rule since;
∠A = ∠A (Since common arm)
∠AEB = ∠AFC (As both are right angles)
Therefore, ΔAEB ≅ ΔAFC
and BE = CF (by CPCT rule).
Question 75: ΔABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC. Side BA is produced to D such that AD = AB. Show that ∠BCD is a right angle.
Solution 75:
To prove: ∠BCD is a right angle.
Consider ΔABC,
Also, ∠ACB = ∠ABC (Angles opposite to equal sides)
Now, consider ΔACD,
Also, ∠ADC = ∠ACD (Angles opposite to equal sides)
Therefore, ∠CAB + 2∠ACB = 180°
In a similar manner in ΔADC,
∠CAB + ∠CAD = 180° (BD is the straight line.)
∠CAB + ∠CAD = 180° – 2∠ACB + 180° – 2∠ACD
⇒ 180° = 360° – 2∠ACB – 2∠ACD
⇒ 2(∠ACB + ∠ACD) = 180°
Question 76: ΔABC and ΔDBC are the two isosceles triangles on the same base BC, with vertices A and D on the same side of BC. If AD is extended so that it intersects BC at P, show that
(iv) AP is perpendicular bisector of BC.
Solution 76:
We have ΔABC and ΔDBC are the two isosceles triangles.
(i) ΔABD and ΔACD are similar by SSS congruency rule because:
AD = AD (i.e., common arm)
AB = AC (ΔABC is isosceles)
BD = CD (ΔDBC is isosceles)
AP = AP (common side)
∠PAB = ∠PAC ( by CPCT rule since ΔABD ≅ ΔACD)
AB = AC (As ΔABC is isosceles)
Thus, ΔABP ≅ ΔACP by SAS congruency rule.
AP bisects ∠A. ………… eq. (1)
Again, ΔBPD and ΔCPD are similar by SSS congruency rule as
Thus, ∠BDP = ∠CDP by CPCT. ……………. eq.(2)
Now we compare equations (1) and (2), and it can be interpreted that AP is bisecting ∠A and ∠D.
(iv) ∠BPD = ∠CPD (by CPCT rule as ΔBPD ≅ ΔCPD)
and BP = CP — eq.(1)
∠BPD + ∠CPD = 180° (Since BC is a straight line.)
⇒ ∠BPD = 90° —eq.(2)
Now, from equations (1) and (2), it can be said that
Question 77: Two sides AB and BC and median AM of one triangle ABC are equal to sides PQ and QR, respectively, and the median PN of ΔPQR. Show that:
Solution 77:
Given in the question;
(i) 1/2 BC = BM and 1/2QR = QN (AM and PN are medians)
And BC = QR
Thus, 1/2 BC = 1/2QR
AM = PN and AB = PQ (Given)
∴ ΔABM ≅ ΔPQN by SSS congruency rule.
AB = PQ and BC = QR (Given)
∠ABC = ∠PQR (by CPCT rule)
So, ΔABC ≅ ΔPQR by SAS congruency rule.
Question 78: In the Figure, PR > PQ and PS bisect ∠QPR. Prove that ∠PSR> ∠PSQ.
Solution 78:
Given in the question, PR> PQ and PS bisects ∠QPR
To prove: ∠PSR> ∠PSQ
∠QPS = ∠RPS — eq.(1) (PS bisects ∠QPR)
∠PQR > ∠PRQ — eq.(2) (Since PR > PQ as angle opposite to the larger side is always larger)
∠PSR = ∠PQR + ∠QPS — eq.(3) (Since the exterior angle of a triangle equals the sum of opposite interior angles)
∠PSQ = ∠PRQ + ∠RPS — eq.(4) (As the exterior angle of a triangle equals the sum of opposite interior angles)
By adding equations (1) and (2), we get
∠PQR + ∠QPS > ∠PRQ + ∠RPS
Now, from (1), (2), (3) and (4), we have
Question 79: AD and BC are equal perpendiculars to line segment AB. Show that CD bisects AB.
Solution 79:
In △BOC and △AOD
OBC = OAD = [Given]
BOC = AOD [Since Vertically Opposite angles]
BC = AD [Given]
BOC = AOD [By ASA congruency rule]
OB = OA and OC = OD [By C.P.C.T. rule]
Question 80: In quadrilateral ABCD. AC = AD and AB are bisecting ∠A. Show that △ABC ≅ △ABD. What can you depict about BC and BD?
Solution 80: Given: In quadrilateral ABCD
AC = AD and AB bisect ∠A.
To prove △ABC ≅△ABD.
Proof: In △ABC and △ABD,
AC = AD [Given]
∠BAC = ∠BAD [ AB bisects ∠A]
AB = AB [Common side]
△ABC≅ △ABD [By SAS congruency rule]
Hence, BC = BD [By C.P.C.T. rule]
Question 81: ABCD is a quadrilateral where AD = BC and ∠ DAB = ∠CBA. Prove that:
(i) △ABD ≅△BAC
Solution 81: In ABC and ABD,
DAB = CBA [Given]
ABC≅ABD[By SAS congruency rule]
Thus AC = BD [By C.P.C.T.]
(ii) BD = AC
Solution: Since △ABC ≅△ABD
AC = BD [By C.P.C.T.]
(iii) ∠ ABD = ∠ BAC
Solution: Since △ABC≅ △ABD
∠ABD = ∠BAC [By C.P.C.T.]
Question 82: l and m are two parallel lines which are intersected by another pair of parallel lines, p and q. Show that △ABC ≅ △CDA.
Solution 82: AC is a transversal.
Given ∠DAC = ∠ACB [Alternate angles]
Now p∥q [Given]
AC is a transversal. [Given]
Thus ∠BAC = ∠ACD [Since Alternate angles]
Now In △ABC and △ADC,
∠ACB = ∠DAC [Proved above]
∠BAC = ∠ACD [Proved above]
AC = AC [Common]
△ABC≅ △CDA [By ASA congruency]
Question 83: Line l is the bisector of the angle A. B is any point on BP. BP and BQ are perpendicular from B to the arms of A. Show that:
(i). △APB ≅ △AQB
Solution 83:
Given: Line l bisects ∠A
∠BAP = ∠BAQ
In △ABP and △ABQ
∠BAP = ∠BAQ[Given]
∠BPA = ∠BQA = [Given]
AB = AB [Common]
△APB≅ △AQB [By ASA congruency]
(ii). BP = BQ or P is equidistant from the arms of ∠A
Solution: As △APB≅△AQB
BP = BQ [By C.P.C.T.]
B is equidistant from the arms of ∠A.
Question 84: In the given triangle, AC = AB, AB = AD and ∠ BAD = ∠ EAC. Show that BC = DE
Solution 84:
Given ∠BAD = ∠EAC
Adding ∠DAC on both sides,
we get,∠BAD + ∠DAC = ∠EAC + ∠DAC
BAC = EAD………………(i)
Now in △ABC and △ADE
AB = AD
and AC = AE [Given]
∠BAC = ∠DAE [From eq. (i)]
△ABC≅ △ADE [By SAS rule congruency]
BC = DE [By C.P.C.T. rule]
Question 85: AB is a line segment, and P is the mid-point. D and E are the points on the same side of AB, so BAD = ABE and EPA = DPB. Show that: (i) DAF FBPE D (ii) AD = BE
Solution 85:
Given that ∠EPA = ∠DPB
Adding ∠EPD on both sides, we get,
∠EPA + ∠EPD = ∠DPB + ∠EPD
∠APD = ∠BPE ………….eq.(i)
Here, in △APD and △BPE,
∠PAD = ∠PBE [∠BAD = ∠ABE (given)]
∠PAD = ∠PBE
AP = PB [P is the mid-point of AB]
∠APD = ∠BPE [From eq. (i)]
∠DPA = ∠EBP [By ASA congruency]
AD = BE [ By C.P.C.T. rule]
Question 86: In an isosceles triangle ABC, where AB = AC, the bisectors of B and C are intersecting each other at O. Join A to O. Show that:
(i) OB = OC
Solution 86:
ABC is an isosceles triangle where AB = AC
⇒ C = B [Angles opposite to equal sides]
△ OCA + △OCB = △OBA + △OBC
OB bisects ∠B, and OC bisects ∠C
∠OBA = ∠OBC and ∠OCA = ∠OCB
∠OCB + ∠OCB = ∠OBC + ∠OBC
2∠OCB = 2∠OBC
∠OCB = ∠OBC
Now in △OBC,
∠OCB = ∠OBC [Proved above]
OB = OC [Sides opposite to equal sides]
(ii) AO bisects A
Solution: In △AOB and △AOC,
AB = AC [Given]
∠OBA = ∠OCA[Given]
And ∠B = ∠C
1 2 ∠B = 1 2 ∠C
∠OBA = ∠OCA
OB = OC [Proved above]
△AOB ≅△AOC [By SAS congruency]
Question 87: In ABC, AD is a perpendicular bisector of BC. Show that ABC is an isosceles triangle where AB = AC.
Solution 87:
In △AOB and △AOC,
BD = CD [AD bisects BC]
∠ADB = ∠ADC [[ Since AD = BC]
AD = AD [Common]
∴△ABD ≅ △ACD [By SAS congruency]
therefore, AB = AC [By C.P.C.T.]
Thus, ABC is an isosceles triangle.
Question 88: ABC is an isosceles triangle whose altitudes BE and CF are drawn to sides AC and AB, respectively. Show that these altitudes are equal.
Solution 88: In △ABE and △ACF,
∠A = ∠A [Common]
∠AEB = ∠AFC[ Since AD⊥BC] [Given]
△ABE ≅ △ACF [By ASA congruency]
BE = CF [By C.P.C.T.]
Therefore, the altitudes are equal.
Question 89: ABC is a triangle whose altitudes BE and CF to sides AC and AB are equal. Show that:
(i). In △ABE and △ACF,
Solution 89: In △ABE and △ACF,
∠AEB = ∠AFC = 90 0 [Given]
BE = CF [Given]
(ii) AB = AC or △ABC is an isosceles triangle.
Solution: Since, △ABE ≅ △ACF
Thus, △ABC is an isosceles triangle.
Question 90: ABC and DBC are the two isosceles triangles on the same base BC. Show that
∠ABD = ∠ACD.
Solution 90: In the isosceles triangle ABC, AB = AC [Given]
∠ACB = ∠ABC ……….(i) [i.e. Angles opposite to equal sides]
Also, in the isosceles triangle BCD.
∠BCD = ∠CBD ………..(ii)[i.e., Angles opposite to equal sides]
Adding eq. (i) and (ii), we get
∠ACB + ∠BCD = ∠ABC + ∠CBD
∠ACD = ∠ABD or
∠ABD = ∠ACD
Question 91: ABC is a right-angled triangle where ∠A = 90 0 and AB = AC. Find ∠B and ∠C.
Solution 91: △ABC is a right triangle where,
∠A = 90 0 And AB = AC
AB = AC ⇒∠C = ∠B …………eq(i)
We know,in △ABC, ∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180 0 [Angle sum property]
90 0 + B + B = 180 0 [ ∠A = 90 0 (given) and ∠B = ∠C (from eq. (i)]
2 ∠B = 90 0
∠B = 90 0
Also ∠C = 45 0 [ ∠B = ∠C]
Question 92: AD is the altitude of an isosceles triangle ABC w AB = AC. Show that:
(i) AD bisects BC.
Solution 92: In △ABD and △ACD,
△ADB = △ADC = 90 0
△ADB = △ADC = 90 0 [AD⊥BC]
△ABD ≅ △ACD [RHS rule of congruency]
BD = DC [By C.P.C.T.]
AD bisects BC
(ii) AD bisects A.
Since, ∠BAD = ∠CAD [By C.P.C.T.]
and AD bisects ∠A.
Question 93: Show that in a right-angled triangle, the hypotenuse is the longest side.
Solution 93: We suppose that ABC be a right-angled triangle, ∠ B =900.
To prove: Hypotenuse AC is the longest side.
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = ∠A + 90 0 + ∠C = [∠ B = 90 0 ]
∠A + ∠C = 180 0 – 90 0
And ∠B = 90 0
∠B > ∠C and ∠B > ∠A
Since the greater angle has a side longer as opposed to it.
AC > AB and AC > AB
Therefore, ∠B being the greatest angle, has the longest opposite side AC, i.e. hypotenuse.
Question 94: In ABC, the sides AB and AC are extended to points P and Q, respectively. Also PBC < QCB. Show that AC> AB.
Solution 94: Given: In △ABC, ∠PBC < ∠QCB
To prove: AC > AB
Proof: In △ABC, ∠4 > ∠2 [Given]
Now ∠1 + ∠2 = ∠3 + ∠4 = 180 0 [Linear pair]
∠1 > ∠3 [ ∵∠4 > ∠ 2]
AC> AB [Side opposite to the greater angle is longer]
Question 95: In the given triangle, B < A and C < D. Show that AD < BC.
Solution 95: In △AOB
∠B < ∠A [Given]
OA < OB………..(i)[Side opposite to the greater angle is longer]
In △COD, ∠C < ∠ D [Given]
OD < OC ……….(ii) [opposite side to greater angle is longer]
OA + OD < OB + OC
AD < BC
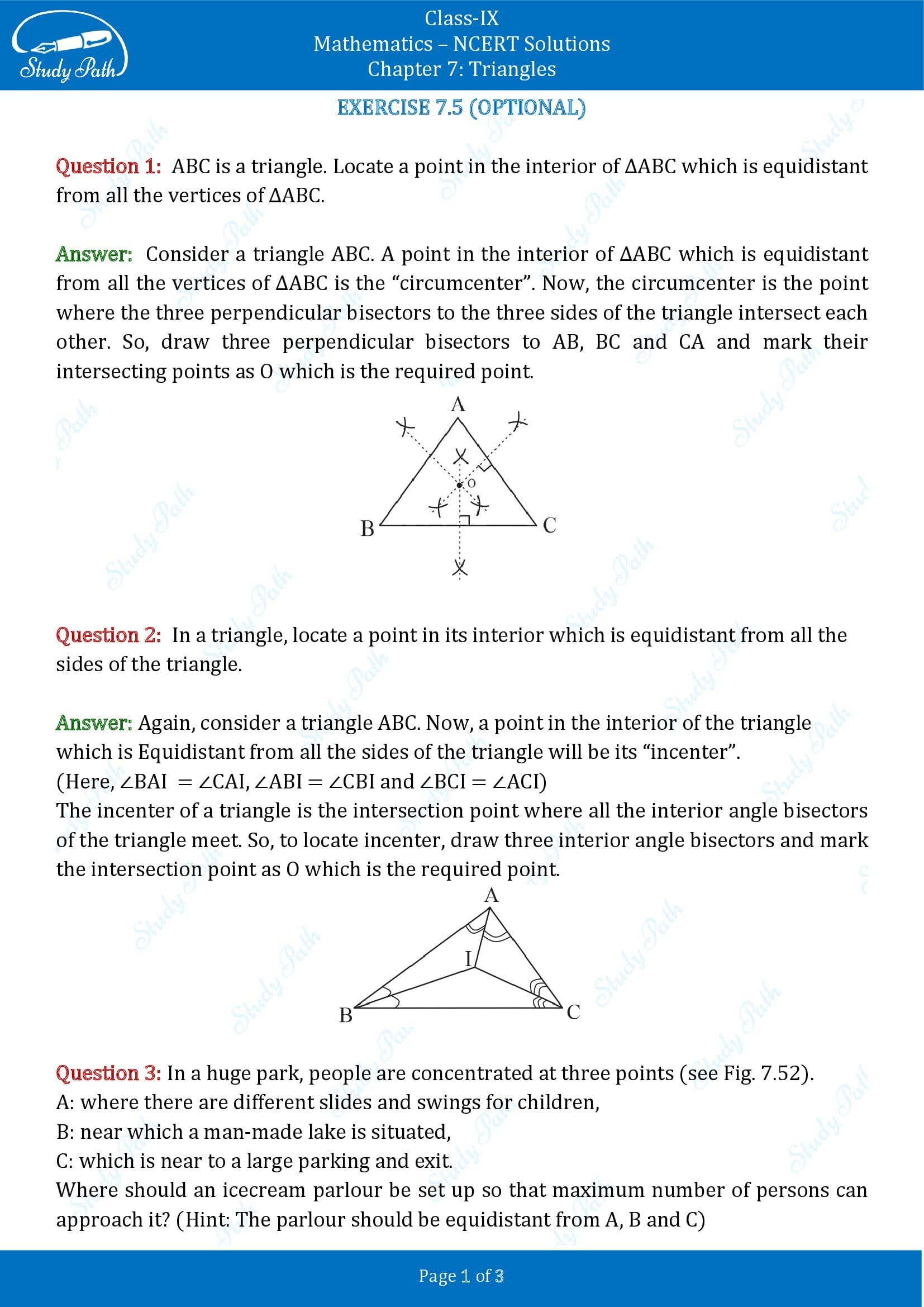
Question 96: In a triangle, locate any point in its interior that is equidistant from all sides of a triangle.
Solution 96: Let △ABC be a triangle.
We draw the bisectors of ∠B and ∠C.
We suppose that these angle bisectors intersect each other at a point I.
Draw IK⊥BC
Also, draw IJ⊥AB and IL⊥AC.
In △BIK and △BIJ,
∠ IKB = ∠IJB = 90 0 [By construction]
∠ IBK = ∠IBJ
BI is the bisector of ∠B (By construction)]
BI = BI [Common side]
△BIK ≅ △BIJ [ASA criteria of congruency rule]
IK = IJ [By C.P.C.T.rule]……….eq.(i)
In a similar way, △CIK ≅ △CIL
∴IK = IL [By C.P.C.T.]……….eq.(ii)
From eq (i) and (ii),
IK = IJ = IL
Thus, I is a point of intersection of the angle bisectors of any two angles of △ABC which are equidistant from its sides.
Question 97: In quadrilateral ACBD, AB=AD and AC are bisecting at A. show ABC ≅ ACD?
Solution 97: In △ABC and △ACD,
AD = AB (Given)
∠BAC = ∠CAD ……(AC bisects A)
And AC = AC……………… (Common side)
△ABC ≅ △ACD………….. (By SAS axiom)
Question 98: If DA and CB are equal perpendiculars to line segment AB. Show that CD is bisecting AB.
Solution 98: In
△AOD and △BOC,
AD = BC ……………. (Given)
∠A = ∠B and
∠AOD = ∠BOC(vertically opp. Angles)
∴∠AOD = ∠BOC(AAS rule)
∴OA = OB(CPCT)
Hence, CD bisects AB.
Question 99: l and m are two parallel lines that are intersected by another pair of parallel lines, p and q. show that △ABC ≅ △CDA.
Solution 99:
L∥M and AC cuts them (given)
∴∠ACB=∠CAD(alternate angles)
P ∥ Q and AC cuts them (Given)
∴∠CAB=∠ACD(Alternate angles)
AC = CA(common)
∴ΔABC≅ΔCDA(ASA rule)
Benefits of Solving Important Questions Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 7
Triangles are a crucial topic since the underlying ideas discussed there are applied at higher educational levels. Students are advised to complete the additional textbook questions that the CBSE Board has approved for this purpose after finishing the questions from the NCERT Textbook. Our Mathematics specialists make sure to give all the questions, which are based on the NCERT textbook and the CBSE curriculum. The only method to ace the examinations is to correctly answer these Mathematics Class 9 Chapter 7 Important Questions . Thus, the exams can be taken without any fear by the students.
Below are a few benefits for students to practise from our set of Important Questions Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 7:
- It is a one-stop solution, meaning students will get questions from many different sources. Consequently, they will save time during preparation by gathering the questions and answers in advance.
- A team of expert Mathematics teachers reviews and verifies the questions and answers before providing them to the students. So we have lakhs of students who have trusted Extramarks teaching resources.
- After studying the updated CBSE curriculum, experienced Mathematics teachers have created these solutions. So they adhere to the latest NCERT guidelines.
- Since every question and answer is created with the exam in mind, students can confidently approach exams and overcome exam anxiety.
Be in touch with us at Extramarks to get the important exam questions for CBSE Class 9 Mathematics, all chapters, with solutions. Use the additional questions offered here by clicking on the links below to fasten your preparation.
- CBSE revision notes
- CBSE syllabus
- CBSE sample papers
- CBSE past years’ question papers
- CBSE extra questions and solutions
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Q.1 Prove that the perimeter of a triangle is greater than the sum of its altitudes.

GivenatriangleABCinwhichAD BC,BE ACandCF AB. To Prove : AD + BE + CF < AB + BC + AC AB > AD and AC > AD AD BC AB + AC > Ad + AD AB + AC > 2 AD . .. 1 BC > BE and BA > BE BE AC BC + BA > BE + BE BC + BA > 2 BE . .. 2 and , AC > CF and BC > CF CF AB AC + BC > 2 CF . .. 3 Adding 1 , 2 and 3 ,weget AB + AC + AB + BC + AC + BC > 2 AD + 2 BE + 2 CF 2 AB + BC + AC > 2 AD + 2 BE + 2 CF AB + BC + AC > AD + BE + CF
Q.2 ABCD is a parallelogram and BEFC is a square. Show that triangles ABE and DCF are congruent.
Marks: 2 Ans
In the parallelogram ABCD, BA = CD. In the square BEFC, EB = FC. Since EB is parallel to FC and BA is parallel to CD then, EBA = FCD Now, in ABE and DCF, we have EBA = FCD BA = CD EB = FC Therefore, ABE … DCF (By SAS congruence criterion)

Marks: 4 Ans
Marks: 3 Ans
In DAC, AD = AC (Given) So, ADC = ACD (Angles opposite to equal sides) Now, ADC is an exterior angle for ABD. So, ADC > ABD or, ACD > ABD or, ACB > ABC So, AB > AC (Side opposite to larger angle in ABC) or, AB > AD (AD = AC)
Q.5 In Figure, B < A and C < D. Show that AD < BC.
Given:-Infigure B< Aand C < D Toprove:- AD < BC . Proof:-In AOB , B < A so , AO < BO . .. 1 Oppositesideofsmallerangleissmaller in COD , C < D So , OD < OC . .. 2 Oppositesideofsmallerangleissmaller Addingrelation 1 and 2 ,we​get AO+OD<BO+OC AD<BC.Henceproved.
Please register to view this section
Faqs (frequently asked questions), 1. is ncert important questions class 9 mathematics chapter 7 the best source of reference for the students.
One of the best sources of reference for students in Class 9 is the Important Questions Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 7 . It will not help students to perform well to muddle over concepts a few days before the board exams. In order to pass the exam without worry, conceptual knowledge is therefore crucial. Daily effort should go into solving the important questions in a good time. Students will be better able to sort and identify the kinds of questions that will come up in the board exams as a result and work on them for a higher academic grade.
2. Where can I find the Class 9 Mathematics Important questions?
Class 9 is a significant milestone in a student’s life since their academic performance will help them realise their career aspirations. To get high grades on the tests, students can download the Important Questions Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 7 or consult them online as they work through the textbook questions.
CBSE Related Links

Fill this form to view question paper
Otp verification.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles are provided here. Our NCERT Maths solutions contain all the questions of the NCERT textbook that are solved and explained beautifully. Here you will get complete NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 all exercises Exercise in one place. These solutions are prepared by the subject experts and as per the latest NCERT syllabus and guidelines. CBSE Class 9 Students who wish to score good marks in the maths exam must practice these questions regularly.
Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles NCERT Solutions
Below we have provided the solutions of each exercise of the chapter. Go through the links to access the solutions of exercises you want. You should also check out our NCERT Class 9 Solutions for other subjects to score good marks in the exams.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Exercise 7.1
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Exercise 7.2
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Exercise 7.3

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Exercise 7.4
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Exercise 7.5
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 – Topic Discussion
Below we have listed the topics that have been discussed in this chapter.
- Congruence of triangles.
- Criteria for congruence of triangles (SAS congruence rule, ASA congruence rule, SSS congruence rule, RHS congruence rule).
- Properties of triangles.
- Inequalities of triangle.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
myCBSEguide
- Mathematics
- CBSE Class 9 Mathematics...
CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
If you’re looking for a comprehensive and reliable study resource and case study questions for class 9 CBSE, myCBSEguide is the perfect door to enter. With over 10,000 study notes, solved sample papers and practice questions, it’s got everything you need to ace your exams. Plus, it’s updated regularly to keep you aligned with the latest CBSE syllabus . So why wait? Start your journey to success with myCBSEguide today!
Significance of Mathematics in Class 9
Mathematics is an important subject for students of all ages. It helps students to develop problem-solving and critical-thinking skills, and to think logically and creatively. In addition, mathematics is essential for understanding and using many other subjects, such as science, engineering, and finance.
CBSE Class 9 is an important year for students, as it is the foundation year for the Class 10 board exams. In Class 9, students learn many important concepts in mathematics that will help them to succeed in their board exams and in their future studies. Therefore, it is essential for students to understand and master the concepts taught in Class 9 Mathematics .
Case studies in Class 9 Mathematics
A case study in mathematics is a detailed analysis of a particular mathematical problem or situation. Case studies are often used to examine the relationship between theory and practice, and to explore the connections between different areas of mathematics. Often, a case study will focus on a single problem or situation and will use a variety of methods to examine it. These methods may include algebraic, geometric, and/or statistical analysis.
Example of Case study questions in Class 9 Mathematics
The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has included case study questions in the Class 9 Mathematics paper. This means that Class 9 Mathematics students will have to solve questions based on real-life scenarios. This is a departure from the usual theoretical questions that are asked in Class 9 Mathematics exams.
The following are some examples of case study questions from Class 9 Mathematics:
Class 9 Mathematics Case study question 1
There is a square park ABCD in the middle of Saket colony in Delhi. Four children Deepak, Ashok, Arjun and Deepa went to play with their balls. The colour of the ball of Ashok, Deepak, Arjun and Deepa are red, blue, yellow and green respectively. All four children roll their ball from centre point O in the direction of XOY, X’OY, X’OY’ and XOY’ . Their balls stopped as shown in the above image.
Answer the following questions:
Answer Key:
Class 9 Mathematics Case study question 2
- Now he told Raju to draw another line CD as in the figure
- The teacher told Ajay to mark ∠ AOD as 2z
- Suraj was told to mark ∠ AOC as 4y
- Clive Made and angle ∠ COE = 60°
- Peter marked ∠ BOE and ∠ BOD as y and x respectively
Now answer the following questions:
- 2y + z = 90°
- 2y + z = 180°
- 4y + 2z = 120°
- (a) 2y + z = 90°
Class 9 Mathematics Case study question 3
- (a) 31.6 m²
- (c) 513.3 m³
- (b) 422.4 m²
Class 9 Mathematics Case study question 4
How to Answer Class 9 Mathematics Case study questions
To crack case study questions, Class 9 Mathematics students need to apply their mathematical knowledge to real-life situations. They should first read the question carefully and identify the key information. They should then identify the relevant mathematical concepts that can be applied to solve the question. Once they have done this, they can start solving the Class 9 Mathematics case study question.
Students need to be careful while solving the Class 9 Mathematics case study questions. They should not make any assumptions and should always check their answers. If they are stuck on a question, they should take a break and come back to it later. With some practice, the Class 9 Mathematics students will be able to crack case study questions with ease.
Class 9 Mathematics Curriculum at Glance
At the secondary level, the curriculum focuses on improving students’ ability to use Mathematics to solve real-world problems and to study the subject as a separate discipline. Students are expected to learn how to solve issues using algebraic approaches and how to apply their understanding of simple trigonometry to height and distance problems. Experimenting with numbers and geometric forms, making hypotheses, and validating them with more observations are all part of Math learning at this level.
The suggested curriculum covers number systems, algebra, geometry, trigonometry, mensuration, statistics, graphing, and coordinate geometry, among other topics. Math should be taught through activities that include the use of concrete materials, models, patterns, charts, photographs, posters, and other visual aids.
CBSE Class 9 Mathematics (Code No. 041)
Class 9 Mathematics question paper design
The CBSE Class 9 mathematics question paper design is intended to measure students’ grasp of the subject’s fundamental ideas. The paper will put their problem-solving and analytical skills to the test. Class 9 mathematics students are advised to go through the question paper pattern thoroughly before they start preparing for their examinations. This will help them understand the paper better and enable them to score maximum marks. Refer to the given Class 9 Mathematics question paper design.
QUESTION PAPER DESIGN (CLASS 9 MATHEMATICS)
Mycbseguide: blessing in disguise.
Class 9 is an important milestone in a student’s life. It is the last year of high school and the last chance to score well in the CBSE board exams. myCBSEguide is the perfect platform for students to get started on their preparations for Class 9 Mathematics. myCBSEguide provides comprehensive study material for all subjects, including practice questions, sample papers, case study questions and mock tests. It also offers tips and tricks on how to score well in exams. myCBSEguide is the perfect door to enter for class 9 CBSE preparations.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
14 thoughts on “CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Case Study Questions”
This method is not easy for me
aarti and rashika are two classmates. due to exams approaching in some days both decided to study together. during revision hour both find difficulties and they solved each other’s problems. aarti explains simplification of 2+ ?2 by rationalising the denominator and rashika explains 4+ ?2 simplification of (v10-?5)(v10+ ?5) by using the identity (a – b)(a+b). based on above information, answer the following questions: 1) what is the rationalising factor of the denominator of 2+ ?2 a) 2-?2 b) 2?2 c) 2+ ?2 by rationalising the denominator of aarti got the answer d) a) 4+3?2 b) 3+?2 c) 3-?2 4+ ?2 2+ ?2 d) 2-?3 the identity applied to solve (?10-?5) (v10+ ?5) is a) (a+b)(a – b) = (a – b)² c) (a – b)(a+b) = a² – b² d) (a-b)(a+b)=2(a² + b²) ii) b) (a+b)(a – b) = (a + b
MATHS PAAGAL HAI
All questions was easy but search ? hard questions. These questions was not comparable with cbse. It was totally wastage of time.
Where is search ? bar
maths is love
Can I have more questions without downloading the app.
I love math
Hello l am Devanshu chahal and l am an entorpinior. I am started my card bord business and remanded all the existing things this all possible by math now my business is 120 crore and my business profit is 25 crore in a month. l find the worker team because my business is going well Thanks
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths - Pdf PDF Download
Cbse case study questions for class 9 maths.
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths are a type of assessment where students are given a real-world scenario or situation and they need to apply mathematical concepts to solve the problem. These types of questions help students to develop their problem-solving skills and apply their knowledge of mathematics to real-life situations.
Chapter Wise Case Based Questions for Class 9 Maths
The CBSE Class 9 Case Based Questions can be accessed from Chapetrwise Links provided below:
Chapter-wise case-based questions for Class 9 Maths are a set of questions based on specific chapters or topics covered in the maths textbook. These questions are designed to help students apply their understanding of mathematical concepts to real-world situations and events.
Chapter 1: Number System
- Case Based Questions: Number System
Chapter 2: Polynomial
- Case Based Questions: Polynomial
Chapter 3: Coordinate Geometry
- Case Based Questions: Coordinate Geometry
Chapter 4: Linear Equations
- Case Based Questions: Linear Equations - 1
- Case Based Questions: Linear Equations -2
Chapter 5: Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry
- Case Based Questions: Lines and Angles
Chapter 7: Triangles
- Case Based Questions: Triangles
Chapter 8: Quadrilaterals
- Case Based Questions: Quadrilaterals - 1
- Case Based Questions: Quadrilaterals - 2
Chapter 9: Areas of Parallelograms
- Case Based Questions: Circles
Chapter 11: Constructions
- Case Based Questions: Constructions

Chapter 12: Heron’s Formula
- Case Based Questions: Heron’s Formula
Chapter 13: Surface Areas and Volumes
- Case Based Questions: Surface Areas and Volumes
Chapter 14: Statistics
- Case Based Questions: Statistics
Chapter 15: Probability
- Case Based Questions: Probability
Weightage of Case Based Questions in Class 9 Maths
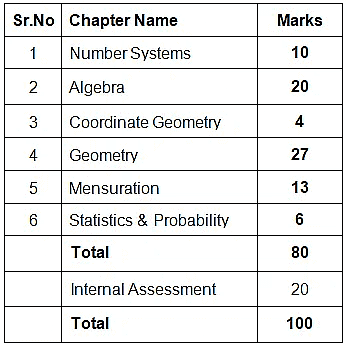
Why are Case Study Questions important in Maths Class 9?
- Enhance critical thinking: Case study questions require students to analyze a real-life scenario and think critically to identify the problem and come up with possible solutions. This enhances their critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Apply theoretical concepts: Case study questions allow students to apply theoretical concepts that they have learned in the classroom to real-life situations. This helps them to understand the practical application of the concepts and reinforces their learning.
- Develop decision-making skills: Case study questions challenge students to make decisions based on the information provided in the scenario. This helps them to develop their decision-making skills and learn how to make informed decisions.
- Improve communication skills: Case study questions often require students to present their findings and recommendations in written or oral form. This helps them to improve their communication skills and learn how to present their ideas effectively.
- Enhance teamwork skills: Case study questions can also be done in groups, which helps students to develop teamwork skills and learn how to work collaboratively to solve problems.
In summary, case study questions are important in Class 9 because they enhance critical thinking, apply theoretical concepts, develop decision-making skills, improve communication skills, and enhance teamwork skills. They provide a practical and engaging way for students to learn and apply their knowledge and skills to real-life situations.
Class 9 Maths Curriculum at Glance
The Class 9 Maths curriculum in India covers a wide range of topics and concepts. Here is a brief overview of the Maths curriculum at a glance:
- Number Systems: Students learn about the real number system, irrational numbers, rational numbers, decimal representation of rational numbers, and their properties.
- Algebra: The Algebra section includes topics such as polynomials, linear equations in two variables, quadratic equations, and their solutions.
- Coordinate Geometry: Students learn about the coordinate plane, distance formula, section formula, and slope of a line.
- Geometry: This section includes topics such as Euclid’s geometry, lines and angles, triangles, and circles.
- Trigonometry: Students learn about trigonometric ratios, trigonometric identities, and their applications.
- Mensuration: This section includes topics such as area, volume, surface area, and their applications.
- Statistics and Probability: Students learn about measures of central tendency, graphical representation of data, and probability.
The Class 9 Maths curriculum is designed to provide a strong foundation in mathematics and prepare students for higher education in the field. The curriculum is structured to develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills, and to promote the application of mathematical concepts in real-life situations. The curriculum is also designed to help students prepare for competitive exams and develop a strong mathematical base for future academic and professional pursuits.
Students can also access Case Based Questions of all subjects of CBSE Class 9
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 Science
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 Social Science
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 English
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 Hindi
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 Sanskrit
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Case Based Questions for Class 9 Maths
What is case-based questions.
Case-Based Questions (CBQs) are open-ended problem solving tasks that require students to draw upon their knowledge of Maths concepts and processes to solve a novel problem. CBQs are often used as formative or summative assessments, as they can provide insights into how students reason through and apply mathematical principles in real-world problems.
What are case-based questions in Maths?
Case-based questions in Maths are problem-solving tasks that require students to apply their mathematical knowledge and skills to real-world situations or scenarios.
What are some common types of case-based questions in class 9 Maths?
Common types of case-based questions in class 9 Maths include word problems, real-world scenarios, and mathematical modeling tasks.
Top Courses for Class 9
Faqs on cbse case study questions for class 9 maths - pdf, past year papers, semester notes, important questions, video lectures, practice quizzes, sample paper, shortcuts and tricks, cbse case study questions for class 9 maths - pdf, viva questions, previous year questions with solutions, study material, extra questions, mock tests for examination, objective type questions.

CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths - Pdf Free PDF Download
Importance of cbse case study questions for class 9 maths - pdf, cbse case study questions for class 9 maths - pdf notes, cbse case study questions for class 9 maths - pdf class 9, study cbse case study questions for class 9 maths - pdf on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country.

Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 9th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Are you preparing for your Class 9 Maths board exams and looking for an effective study resource? Well, you’re in luck! In this article, we will provide you with a collection of Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths specifically designed to help you excel in your exams. These questions are carefully curated to cover various mathematical concepts and problem-solving techniques. So, let’s dive in and explore these valuable resources that will enhance your preparation and boost your confidence.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

CBSE Class 9 Maths Board Exam will have a set of questions based on case studies in the form of MCQs. The CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Question Bank on Case Studies, provided in this article, can be very helpful to understand the new format of questions. Share this link with your friends.
If you want to want to prepare all the tough, tricky & difficult questions for your upcoming exams, this is where you should hang out. CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 will provide you with detailed, latest, comprehensive & confidence-inspiring solutions to the maximum number of Case Study Questions covering all the topics from your NCERT Text Books !
Table of Contents
CBSE Class 9th – MATHS: Chapterwise Case Study Question & Solution
Case study questions are a form of examination where students are presented with real-life scenarios that require the application of mathematical concepts to arrive at a solution. These questions are designed to assess students’ problem-solving abilities, critical thinking skills, and understanding of mathematical concepts in practical contexts.
Chapterwise Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths
Case study questions play a crucial role in the field of mathematics education. They provide students with an opportunity to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, thereby enhancing their comprehension of mathematical concepts. By engaging with case study questions, students develop the ability to analyze complex problems, make connections between different mathematical concepts, and formulate effective problem-solving strategies.
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 1 Number System
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 2 Polynomials
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 4 Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 5 Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 6 Lines and Angles
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 7 Triangles
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 8 Quadilaterals
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 9 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 10 Circles
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 11 Constructions
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 12 Heron’s Formula
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 13 Surface Area and Volumes
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 14 Statistics
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 Probability
The above Case studies for Class 9 Mathematics will help you to boost your scores as Case Study questions have been coming in your examinations. These CBSE Class 9 Maths Case Studies have been developed by experienced teachers of schools.studyrate.in for benefit of Class 10 students.
- Class 9 Science Case Study Questions
- Class 9 Social Science Case Study Questions
How to Approach Case Study Questions
When tackling case study questions, it is essential to adopt a systematic approach. Here are some steps to help you approach and solve these types of questions effectively:
- Read the case study carefully: Understand the given scenario and identify the key information.
- Identify the mathematical concepts involved: Determine the relevant mathematical concepts and formulas applicable to the problem.
- Formulate a plan: Devise a plan or strategy to solve the problem based on the given information and mathematical concepts.
- Solve the problem step by step: Apply the chosen approach and perform calculations or manipulations to arrive at the solution.
- Verify and interpret the results: Ensure the solution aligns with the initial problem and interpret the findings in the context of the case study.
Tips for Solving Case Study Questions
Here are some valuable tips to help you effectively solve case study questions:
- Read the question thoroughly and underline or highlight important information.
- Break down the problem into smaller, manageable parts.
- Visualize the problem using diagrams or charts if applicable.
- Use appropriate mathematical formulas and concepts to solve the problem.
- Show all the steps of your calculations to ensure clarity.
- Check your final answer and review the solution for accuracy and relevance to the case study.
Benefits of Practicing Case Study Questions
Practicing case study questions offers several benefits that can significantly contribute to your mathematical proficiency:
- Enhances critical thinking skills
- Improves problem-solving abilities
- Deepens understanding of mathematical concepts
- Develops analytical reasoning
- Prepares you for real-life applications of mathematics
- Boosts confidence in approaching complex mathematical problems
Case study questions offer a unique opportunity to apply mathematical knowledge in practical scenarios. By practicing these questions, you can enhance your problem-solving abilities, develop a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts, and boost your confidence for the Class 9 Maths board exams. Remember to approach each question systematically, apply the relevant concepts, and review your solutions for accuracy. Access the PDF resource provided to access a wealth of case study questions and further elevate your preparation.
Q1: Can case study questions help me score better in my Class 9 Maths exams?
Yes, practicing case study questions can significantly improve your problem-solving skills and boost your performance in exams. These questions offer a practical approach to understanding mathematical concepts and their real-life applications.
Q2: Are the case study questions in the PDF resource relevant to the Class 9 Maths syllabus?
Absolutely! The PDF resource contains case study questions that align with the Class 9 Maths syllabus. They cover various topics and concepts included in the curriculum, ensuring comprehensive preparation.
Q3: Are the solutions provided for the case study questions in the PDF resource?
Yes, the PDF resource includes solutions for each case study question. You can refer to these solutions to validate your answers and gain a better understanding of the problem-solving process.
You Might Also Like
Class 9 science case study questions chapter 12 sound, class 9 science case study questions chapter 10 gravitation, class 9 science case study questions chapter 4 structure of atom, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles
Ncert solutions for class 9 maths chapter 7 triangles| pdf download.

Page No: 118

- Exercise 7.1 Chapter 7 Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 7.2 Chapter 7 Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 7.3 Chapter 7 Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 7.4 Chapter 7 Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 7.5 Chapter 7 Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapters:
How many exercises in chapter 7 triangles, each of the equal angles of an isosceles triangle is 38°, what is the measure of the third angle, find the measure of each of acute angle in a right angle isosceles triangle., if two angles are (30 ∠ a)º and (125 + 2a)º and they are supplement of each other. find the value of ‘a’., contact form.
CBSE MCQ for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles Free PDF

Guys, we are working very hard to provide you with TOPIC-WISE MCQs (as listed below). Till then, attached below is the Master PDF having all the topics. Hope you understand. Enjoy your preparation! All the Best!
CBSE MCQ for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles PDF
The CBSE MCQ for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles are provided above, in detailed and free to download PDF format. The solutions are latest , comprehensive , confidence inspiring , with easy to understand explanation . To download NCERT Class 9 Solutions PDF for Free, just click ‘ Download pdf ’.
Other MCQ Questions for Maths Class 9th CBSE
- CBSE MCQ for Class 9 Maths Chapter 5 Euclid’s Geometry
- CBSE MCQ for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles
- CBSE MCQ for Class 9 Maths Chapter 8 Quadrilaterals
- CBSE MCQ for Class 9 Maths Chapter 9 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles
How should I study for my upcoming exams?
First, learn to sit for at least 2 hours at a stretch
Solve every question of NCERT by hand, without looking at the solution.
Solve NCERT Exemplar (if available)
Sit through chapter wise FULLY INVIGILATED TESTS
Practice MCQ Questions (Very Important)
Practice Assertion Reason & Case Study Based Questions
Sit through FULLY INVIGILATED TESTS involving MCQs. Assertion reason & Case Study Based Questions
After Completing everything mentioned above, Sit for atleast 6 full syllabus TESTS.
Contact Form
Privacy Policy
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7: Triangles - Exercise 7.5
- NCERT Solutions

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 (Ex 7.5)
Free PDF download of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Exercise 7.5 and all chapter exercises at one place prepared by expert teacher as per NCERT (CBSE) books guidelines. Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles Exercise 7.5 Questions with Solutions to help you to revise complete Syllabus and Score More marks. Register and get all exercise solutions in your emails.
You can also download Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.

Access NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 7 - Triangles
Exercise 7.5
1. ABC is a triangle. Locate a point in the interior of ΔABC which is equidistant from all the vertices of ΔABC.
Ans: The circumcentre of a triangle is always equidistant from all of its vertices.
The circumcentre is the point where the perpendicular bisectors of all the triangle's sides meet.
By sketching the perpendicular bisectors of the triangle's sides AB, BC, and CA, we may determine the circumcentre in$\Delta ABC$. The intersection of these bisectors is marked by the letter O. As a result, O is the point that is equidistant from all of $\Delta ABC$'s vertices.
2. In a triangle locate a point in its interior which is equidistant from all the sides of the triangle.
Ans: The incentre of a triangle is the point that is equidistant from all the triangle's sides. The intersection point of the angle bisectors of a triangle's interior angles is the centre of the triangle.
By drawing the angle bisectors of the interior angles of this triangle in $\Delta ABC$, we may get the incentive of this triangle. It is the point at which these angle bisectors cross each other. As a result, it is the point that is equidistant from all of $\Delta ABC$'s sides.
3. In a huge park people are concentrated at three points
A. where there are different slides and swings for children,
B. near which a man-made lake is situated,
C. which is near to a large parking and exit.
Where should an ice-cream parlour be set up so that the maximum number of persons can approach it?
(Hint: The parlor should be equidistant from A, B and C)
Ans: If the ice cream parlour is equidistant from A, B, and C, the maximum number of people can approach it. A, B, and C now form a triangle. The circumcentre is the only point in a triangle that is equidistant from its vertices. As a result, the ice cream parlour should be located near ΔABC's circumcenter O.
The maximum number of people can approach it in this case.
By drawing perpendicular bisectors of the sides of this triangle, we can find the circumcentre O.
4. Complete the hexagonal and star shaped Rangolies by filling them with as many equilateral triangles of side 1 cm as you can. Count the number of triangles in each case. Which has more triangles?
Ans: We can see that the hexagonal shaped rangoli has a total of 6 equilateral triangles of side 5 cm in it.
The star-shaped rangoli also has 6 equilateral triangles of side 5cm and a hexagon in the middle.
Therefore, star-shaped rangoli will be filled with more equilateral triangles of side 1 cm in it.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles
Opting for the NCERT solutions for Ex 7.5 Class 9 Maths is considered as the best option for the CBSE students when it comes to exam preparation. This chapter consists of many exercises. Out of which we have provided the Exercise 7.5 Class 9 Maths NCERT solutions on this page in PDF format. You can download this solution as per your convenience or you can study it directly from our website/ app online.
Vedantu in-house subject matter experts have solved the problems/ questions from the exercise with the utmost care and by following all the guidelines by CBSE. Class 9 students who are thorough with all the concepts from the Subject Triangles textbook and quite well-versed with all the problems from the exercises given in it, then any student can easily score the highest possible marks in the final exam. With the help of this Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Exercise 7.5 solutions, students can easily understand the pattern of questions that can be asked in the exam from this chapter and also learn the marks weightage of the chapter. So that they can prepare themselves accordingly for the final exam.
Besides these NCERT solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Exercise 7.5, there are plenty of exercises in this chapter which contain innumerable questions as well. All these questions are solved/answered by our in-house subject experts as mentioned earlier. Hence all of these are bound to be of superior quality and anyone can refer to these during the time of exam preparation. In order to score the best possible marks in the class, it is really important to understand all the concepts of the textbooks and solve the problems from the exercises given next to it.
Do not delay any more. Download the NCERT solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Exercise 7.5 from Vedantu website now for better exam preparation. If you have the Vedantu app in your phone, you can download the same through the app as well. The best part of these solutions is these can be accessed both online and offline as well.

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7: Triangles - Exercise 7.5
1. What are the properties of an isosceles triangle, according to Chapter 7 of Class 9 Maths?
In an isosceles triangle, the two sides of a triangle are equal, and the angles opposite to the equal sides are also equal. To get more answers related to the exercises in this chapter, visit Vedantu and get all the explained answers for Chapter 7 of Class 9 Maths in one place. Practicing these will give students a good idea of how the questions should be solved from an exam point of view.
2. Can students solve Exercise 7.5 of Chapter 7 of Class 9 Maths in two days?
Yes, students can solve the entire Chapter 7 of Class 9 Maths exercises within two days. All they need is a good hold over the basics of the chapter. The best place to get the basics stronger is Vedantu. Students can get step-to-step answers for every question in all the exercises of the Chapter 7 of Class 9 Maths book. These answers have been brought to you by experts who give their best to make solutions as simple as possible.
3. Why should we do the optional Exercise 7.5 of Chapter 7 of Class 9 Maths?
You should solve the optional Exercise 7.5 of Chapter 7 of Class 9 Maths because it helps strengthen your basics in triangles' properties, especially in the equalities and inequalities in a triangle. This exercise is not so important from an exam viewpoint. However, it can add to your knowledge base and help you get a much clearer understanding of what you have been studying.
4. What is an SAS congruent triangle, according to Chapter 7 of Class 9 Maths?
If the two sides and one included angle of a triangle are equal to the two sides, and one included angle of the other triangle. Then we can say that the two triangles meet the criteria for SAS (side-angle-side) congruency. You will get full NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 on Vedantu. The explanations to sums have been provided by experts who know how students can score well in their examinations.
5. Is Chapter 7 of Class 9 Maths very tough?
Maths is a subject that seems tough to students, but with rigorous practice, students can easily get command over Chapter 7 of Class 9 Maths. So, considering Maths a difficult subject is a matter of mindset. If you practice Chapter 7 of Class 9 Maths daily, you will not lag and will understand everything that is being taught. If you get stuck anywhere, you can easily check out the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 7 of Class 9 Maths available at free of cost on the Vedantu website and on the Vedantu app for any clarifications.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9
Cbse study materials for class 9, cbse study materials.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 7 Maths
- Last modified on: 7 months ago
- Reading Time: 7 Minutes

Table of Contents
Here in this article, we are providing case study questions for class 7 maths.
Maths Class 7 Chapter List
Latest chapter list (2023-24).
There is total 13 chapters.
Chapter 1 Integers Case Study Questions Chapter 2 Fractions and Decimals Case Study Questions Chapter 3 Data Handling Case Study Questions Chapter 4 Simple Equations Case Study Questions Chapter 5 Lines and Angles Case Study Questions Chapter 6 The Triangles and its Properties Case Study Questions Chapter 7 Comparing Quantities Case Study Questions Chapter 8 Rational Numbers Case Study Questions Chapter 9 Perimeter and Area Case Study Questions Chapter 10 Algebraic Expressions Case Study Questions Chapter 11 Exponents and Powers Case Study Questions Chapter 12 Symmetry Case Study Questions Chapter 13 Visualising Solid Shapes Case Study Questions
Old Chapter List
Chapter 1 Integers Chapter 2 Fractions and Decimals Chapter 3 Data Handling Chapter 4 Simple Equations Chapter 5 Lines and Angles Chapter 6 The Triangles and its Properties Chapter 7 Congruence of Triangles Chapter 8 Comparing Quantities Chapter 9 Rational Numbers Chapter 10 Practical Geometry Chapter 11 Perimeter and Area Chapter 12 Algebraic Expressions Chapter 13 Exponents and Powers Chapter 14 Symmetry Chapter 15 Visualising Solid Shapes
Deleted Chapter:
- Chapter 7 Congruence of Triangles
- Chapter 10 Practical Geometry
Tips for Answering Case Study Questions for Class 7 Maths in Exam

1. Comprehensive Reading for Context: Prioritize a thorough understanding of the provided case study. Absorb the contextual details and data meticulously to establish a strong foundation for your solution.
2. Relevance Identification: Pinpoint pertinent mathematical concepts applicable to the case study. By doing so, you can streamline your thinking process and apply appropriate methods with precision.
3. Deconstruction of the Problem: Break down the complex problem into manageable components or steps. This approach enhances clarity and facilitates organized problem-solving.
4. Highlighting Key Data: Emphasize critical information and data supplied within the case study. This practice aids quick referencing during the problem-solving process.
5. Application of Formulas: Leverage pertinent mathematical formulas, theorems, and principles to solve the case study. Accuracy in formula selection and unit usage is paramount.
6. Transparent Workflow Display: Document your solution with transparency, showcasing intermediate calculations and steps taken. This not only helps track progress but also offers insight into your analytical process.
7. Variable Labeling and Definition: For introduced variables or unknowns, offer clear labels and definitions. This eliminates ambiguity and reinforces a structured solution approach.
8. Step Explanation: Accompany each step with an explanatory note. This reinforces your grasp of concepts and demonstrates effective application.
9. Realistic Application: When the case study pertains to real-world scenarios, infuse practical reasoning and logic into your solution. This ensures alignment with real-life implications.
10. Thorough Answer Review: Post-solving, meticulously review your answer for accuracy and coherence. Assess its compatibility with the case study’s context.
11. Solution Recap: Before submission, revisit your solution to guarantee comprehensive coverage of the problem and a well-organized response.
12. Previous Case Study Practice: Boost your confidence by practicing with past case study questions from exams or textbooks. This familiarity enhances your readiness for the question format.
13. Efficient Time Management: Strategically allocate time for each case study question based on its complexity and the overall exam duration.
14. Maintain Composure and Confidence: Approach questions with poise and self-assurance. Your preparation equips you to conquer the challenges presented.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Class 9
- NCERT 9 Maths
- Chapter 7: Geometry Of Triangles
- Exercise 7.1
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles Exercise 7.1
Exercise 7.1 of Chapter 7 of NCERT Class 9 Maths deals with the “Congruence of Triangles”. You must be wondering why this topic has been included in the syllabus, although we rarely see its applications. Well, in real life, two triangles are rarely congruent. However, studying this topic becomes crucial because it is used in the construction of large buildings or other architectural designs. Mathematicians have found the Triangle to be a very stable shape, and congruence is needed to create even surfaces. Also, you must have noticed congruent triangles in geometric art, carpeting designs, stepping stone designs, architectural designs, etc. Thus, this chapter plays a major role in daily life, and students have to focus on it using NCERT Solutions .
The NCERT Class 9 Maths Exercise is full of proof. Therefore, it’s important that you first know theorems related to it and then go for the exercise questions. Here, we have provided step-by-step NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles Exercise 7.1. Students can refer to it whenever they find difficulty in solving the questions. The NCERT Class 9 Maths solutions are created by the subject experts and are solved in a simple way. These solutions will also help learn to answer complex questions so that students can score high marks in the annual exams. You can download the NCERT Solution PDF from the link below.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 – Triangles Exercise 7.1
carouselExampleControls112

Previous Next
Access other Exercise Solutions of Chapter 7 – Triangles
You should practise all the questions of Exercise 7.1. To get the detailed solutions of all the exercises of NCERT Class 9 Chapter 7, visit the links provided below:
Exercise 7.2 Solution 8 Questions (6 Short Answer Questions, 2 Long Answer Question)
Exercise 7.3 Solution 5 Questions (3 Short Answer Questions, 2 Long Answer Question)
Exercise 7.4 Solution 6 Questions (5 Short Answer Questions, 1 Long Answer Question)
Exercise 7.5 (Optional) Solution 4 Questions
Access Answers to NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 – Triangles Exercise 7.1
1. In quadrilateral ACBD, AC = AD and AB bisect ∠A (see Fig. 7.16). Show that ΔABC≅ ΔABD. What can you say about BC and BD?

It is given that AC and AD are equal i.e. AC = AD and the line segment AB bisects ∠A.
We will have to now prove that the two triangles ABC and ABD are similar i.e. ΔABC ≅ ΔABD
Consider the triangles ΔABC and ΔABD,
(i) AC = AD (It is given in the question)
(ii) AB = AB (Common)
(iii) ∠CAB = ∠DAB (Since AB is the bisector of angle A)
So, by SAS congruency criterion , ΔABC ≅ ΔABD.
For the 2 nd part of the question, BC and BD are of equal lengths by the rule of C.P.C.T.
2. ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AD = BC and ∠DAB = ∠CBA (see Fig. 7.17). Prove that
(i) ΔABD ≅ ΔBAC
(ii) BD = AC
(iii) ∠ ABD = ∠ BAC.

The given parameters from the questions are ∠ DAB = ∠ CBA and AD = BC.
(i) ΔABD and ΔBAC are similar by SAS congruency as
AB = BA (It is the common arm)
∠ DAB = ∠ CBA and AD = BC (These are given in the question)
So, triangles ABD and BAC are similar i.e. ΔABD ≅ ΔBAC. (Hence proved).
(ii) It is now known that ΔABD ≅ ΔBAC so,
BD = AC (by the rule of CPCT).
(iii) Since ΔABD ≅ ΔBAC so,
Angles ∠ ABD = ∠ BAC (by the rule of CPCT).
3. AD and BC are equal perpendiculars to a line segment AB (see Fig. 7.18). Show that CD bisects AB.

It is given that AD and BC are two equal perpendiculars to AB.
We will have to prove that CD is the bisector of AB
Triangles ΔAOD and ΔBOC are similar by AAS congruency since:
(i) ∠A = ∠B (They are perpendiculars)
(ii) AD = BC (As given in the question)
(iii) ∠AOD = ∠BOC (They are vertically opposite angles)
∴ ΔAOD ≅ ΔBOC.
So, AO = OB (by the rule of CPCT).
Thus, CD bisects AB (Hence proved).
4. l and m are two parallel lines intersected by another pair of parallel lines p and q (see Fig. 7.19). Show that ΔABC ≅ ΔCDA.

It is given that p || q and l || m
Triangles ABC and CDA are similar i.e. ΔABC ≅ ΔCDA
Consider the ΔABC and ΔCDA,
(i) ∠BCA = ∠DAC and ∠BAC = ∠DCA Since they are alternate interior angles
(ii) AC = CA as it is the common arm
So, by ASA congruency criterion, ΔABC ≅ ΔCDA.
5. Line l is the bisector of an angle ∠A and B is any point on l . BP and BQ are perpendiculars from B to the arms of ∠A (see Fig. 7.20). Show that:
(i) ΔAPB ≅ ΔAQB
(ii) BP = BQ or B is equidistant from the arms of ∠A.

It is given that the line “ l ” is the bisector of angle ∠A and the line segments BP and BQ are perpendiculars drawn from l .
(i) ΔAPB and ΔAQB are similar by AAS congruency because:
∠P = ∠Q (They are the two right angles)
AB = AB (It is the common arm)
∠BAP = ∠BAQ (As line l is the bisector of angle A)
So, ΔAPB ≅ ΔAQB.
(ii) By the rule of CPCT, BP = BQ. So, it can be said the point B is equidistant from the arms of ∠A.
6. In Fig. 7.21, AC = AE, AB = AD and ∠BAD = ∠EAC. Show that BC = DE.

It is given in the question that AB = AD, AC = AE, and ∠BAD = ∠EAC
The line segment BC and DE are similar i.e. BC = DE
We know that ∠BAD = ∠EAC
Now, by adding ∠DAC on both sides we get,
∠BAD + ∠DAC = ∠EAC +∠DAC
This implies, ∠BAC = ∠EAD
Now, ΔABC and ΔADE are similar by SAS congruency since:
(i) AC = AE (As given in the question)
(ii) ∠BAC = ∠EAD
(iii) AB = AD (It is also given in the question)
∴ Triangles ABC and ADE are similar i.e. ΔABC ≅ ΔADE.
So, by the rule of CPCT, it can be said that BC = DE.
7. AB is a line segment and P is its mid-point. D and E are points on the same side of AB such that ∠BAD = ∠ABE and ∠EPA = ∠DPB (see Fig. 7.22). Show that
(i) ΔDAP ≅ ΔEBP
(ii) AD = BE

In the question, it is given that P is the mid-point of line segment AB. Also, ∠BAD = ∠ABE and ∠EPA = ∠DPB
(i) It is given that ∠EPA = ∠DPB
Now, add ∠DPE on both sides,
∠EPA +∠DPE = ∠DPB+∠DPE
This implies that angles DPA and EPB are equal i.e. ∠DPA = ∠EPB
Now, consider the triangles DAP and EBP.
∠DPA = ∠EPB
AP = BP (Since P is the mid-point of the line segment AB)
∠BAD = ∠ABE (As given in the question)
So, by ASA congruency , ΔDAP ≅ ΔEBP.
(ii) By the rule of CPCT, AD = BE.
8. In right triangle ABC, right angled at C, M is the mid-point of hypotenuse AB. C is joined to M and produced to a point D such that DM = CM. Point D is joined to point B (see Fig. 7.23). Show that:
(i) ΔAMC ≅ ΔBMD
(ii) ∠DBC is a right angle.
(iii) ΔDBC ≅ ΔACB
(iv) CM = ½ AB

It is given that M is the mid-point of the line segment AB, ∠C = 90°, and DM = CM
(i) Consider the triangles ΔAMC and ΔBMD:
AM = BM (Since M is the mid-point)
CM = DM (Given in the question)
∠CMA = ∠DMB (They are vertically opposite angles)
So, by SAS congruency criterion , ΔAMC ≅ ΔBMD.
(ii) ∠ACM = ∠BDM (by CPCT)
∴ AC || BD as alternate interior angles are equal.
Now, ∠ACB +∠DBC = 180° (Since they are co-interiors angles)
⇒ 90° +∠B = 180°
∴ ∠DBC = 90°
(iii) In ΔDBC and ΔACB,
BC = CB (Common side)
∠ACB = ∠DBC (They are right angles)
DB = AC (by CPCT)
So, ΔDBC ≅ ΔACB by SAS congruency .
(iv) DC = AB (Since ΔDBC ≅ ΔACB)
⇒ DM = CM = AM = BM (Since M the is mid-point)
So, DM + CM = BM+AM
Hence, CM + CM = AB
⇒ CM = (½) AB
The students of Class 9 will learn the concepts of Congruence of Triangles, the Criteria for Congruence and the theorem related to it in Exercise 7.1. In the exercise, the questions are related to the proof. So, while solving these questions, it’s very important that students should mention the congruence rule. Also, they should not miss any steps while solving it. To know how to write answers in a better way to score good marks, download the NCERT solution PDF.
We hope this information on “ NCERT Solution Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles Exercise 7.1” is useful for students.
Click on NCERT Solutions to get the solved answers from the NCERT book for all the classes. Stay tuned for further updates on CBSE and other competitive exams. To access interactive Maths and Science Videos, download the BYJU’S App and subscribe to our YouTube Channel.
Thank you for your help this really helped me.
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Counselling

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Answer: (a) 30 degrees. Q5. The lengths of the two equal sides of the kite triangle are: (a) 3 units each. (b) 4 units each. (c) 5 units each. (d) It cannot be determined. Answer: (c) 5 units each. Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Case Study Questions Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles with ...
Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles Here we are providing case study questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles. Students are suggested to solve the questions by themselves first and then check the answers. This will help students to check their grasp on this particular chapter Triangles. Case Study Questions: … Continue reading Case Study Questions for Class 9 ...
Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 Chapter 7 -Triangles are provided here by our experts, along with their solutions. These questions are extracted from the NCERT book as per CBSE syllabus.Students who are preparing for standard 9 Maths final exam (2022 - 2023) should practise these questions to score excellent marks.. Solve extra questions along with important questions for class 9 Maths ...
According to new pattern CBSE Class 9 Mathematics students will have to solve case based questions. This is a departure from the usual theoretical conceptual questions that are asked in Class 9 Maths exam in this year. Each question provided in this post has five sub-questions, each followed by four options and one correct answer.
Important Questions Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 7 - Triangles. The word "triangle" itself conveys its meaning. It is a closed figure made up of three crossing lines since the prefix "tri" implies "three". The major objective of Chapter 7 is to study triangles and their congruence or similarity of triangles. You will learn in-depth ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles provides the answers and questions related to the chapter as included in the CBSE Syllabus for 2023-24. The word triangle itself describes its meaning. "Tri" means "three",; so a closed figure formed by three intersecting lines is known as a Triangle. Students must have already ...
According to Chapter 7 of Class 9 Maths, we need at least one of the following information to construct a triangle: Length of all three sides. Length of two sides and included angle. The measurement of any two angles and the included side. The length of the hypotenuse and one side in case of a right triangle.
Here you will get complete NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 all exercises Exercise in one place. These solutions are prepared by the subject experts and as per the latest NCERT syllabus and guidelines. CBSE Class 9 Students who wish to score good marks in the maths exam must practice these questions regularly.
The questions require students to find the values of the sides and angles of similar triangles. Access NCERT Answers for Class-9 Maths Chapter 7 - Triangles. Exercise-7.1. 1. In quadrilateral ACBD, AC = AD and AB bisects \ [\angle A\] (See the given figure). Show that \ [\Delta ABC {\text { }} \cong \Delta ABD\].
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles Ex 7.3. Ex 7.3 Class 9 Maths Question 1. ∆ABC and ∆DBC are two isosceles triangles on the same base BC and vertices A and D are on the same side of BC (see figure). If AD is extended to intersect BC at P, show that. (iv) AP is the perpendicular bisector of BC.
Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles Case Study Questions | Important for Exams #casestudybasedquestions #mathsbyshweta #coordinategeometry
Class 9 Mathematics Case study question 2. Read the Source/Text given below and answer any four questions: Maths teacher draws a straight line AB shown on the blackboard as per the following figure. Now he told Raju to draw another line CD as in the figure. The teacher told Ajay to mark ∠ AOD as 2z.
Introduction of CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths - Pdf in English is available as part of our Class 9 preparation & CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths - Pdf in Hindi for Class 9 courses. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 Probability. The above Case studies for Class 9 Mathematics will help you to boost your scores as Case Study questions have been coming in your examinations. These CBSE Class 9 Maths Case Studies have been developed by experienced teachers of schools.studyrate.in for benefit of Class 10 students.
Find the measure of each of acute angle in a right angle isosceles triangle. Let the measure of each of the equal acute angle of the Δ be x. ∴ We have: x + x + 90° = 180°. ⇒ x + x = 180° - 90° = 90°. ⇒ x= (90°/2)= 45°. If two angles are (30 ∠ a)º and (125 + 2a)º and they are supplement of each other.
Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles MCQs are provided here with answers, online. All the MCQs are prepared as per the latest exam pattern. Students can practice these objective questions to score good marks in the final exam. All the problems here are based on the CBSE syllabus (2022-2023) and the NCERT curriculum.
The CBSE MCQ for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles are provided above, in detailed and free to download PDF format. The solutions are latest, comprehensive, confidence inspiring, with easy to understand explanation. To download NCERT Class 9 Solutions PDF for Free, just click ' Download pdf '.
Maths NCERT solutions class 9 chapter 7 exercise 7.3 solutions help students to select a higher-grade stream according to their interest. NCERT solutions offered by Vedantu are well-prepared according to the guidelines of the CBSE board. By practicing NCERT exercise 7.3 solutions, students can find it hassle-free to solve questions asked from ...
2 months ago February 2, 2024 Physics Gurukul Leave a Comment on Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 9 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles. ... January 7, 2023 July 29, 2023 Physics Gurukul 4 Comments on Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 4 Linear Equations in Two Variables.
Free PDF download of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Exercise 7.5 and all chapter exercises at one place prepared by expert teacher as per NCERT (CBSE) books guidelines. Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles Exercise 7.5 Questions with Solutions to help you to revise complete Syllabus and Score More marks. Register and get all exercise solutions in your emails.
Tips for Answering Case Study Questions for Class 7 Maths in Exam. 1. Comprehensive Reading for Context: Prioritize a thorough understanding of the provided case study. Absorb the contextual details and data meticulously to establish a strong foundation for your solution. 2.
Here, we have provided step-by-step NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles Exercise 7.1. Students can refer to it whenever they find difficulty in solving the questions. The NCERT Class 9 Maths solutions are created by the subject experts and are solved in a simple way. These solutions will also help learn to answer complex ...