

MLA Citation Guide (9th Edition): Book Reviews
- What Kind of Source Is This?
- Advertisements
- Books, eBooks & Pamphlets
- Book Reviews
- Class Handouts, Presentations, and Readings
- Encyclopedias & Dictionaries
- Government Documents
- Images, Artwork, Charts, Graphs & Tables
- Interviews and Emails (Personal Communications)
- Journal Articles
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Primary Sources
- Religious Texts
- Social Media
- Videos & DVDs
- In-Text Citation
- Works Quoted in Another Source
- No Author, No Date etc.
- Works Cited List & Sample Paper
- Annotated Bibliography
- Powerpoint Presentations
On This Page: Book Reviews
Book review - no title, book review - title refers to book being reviewed, book review - title doesn't refer to book being reviewed, abbreviating months.
In your works cited list, abbreviate months as follows:
January = Jan. February = Feb. March = Mar. April = Apr. May = May June = June July = July August = Aug. September = Sept. October = Oct. November = Nov. December = Dec.
Spell out months fully in the body of your paper.
Note : For your Works Cited list, all citations should be double spaced and have a hanging indent.
A "hanging indent" means that each subsequent line after the first line of your citation should be indented by 0.5 inches.
Author's Last Name, First Name. Review of Title of Book: Subtitle if Any , by Book Author's First Name Last Name. Name of Journal , vol. Volume Number, no. Issue Number, Date of Publication, pp. First Page Number-Last Page Number. Name of Database . https://doi.org/DOI Number if Given.
Note : If the book review is from a source other than an article in the library's database, view the appropriate section on the MLA guide to determine how to cite the source after the name of the book's author.
Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Review." Name of Journal , vol. Volume Number, no. Issue Number, Date of Publication, pp. First Page Number-Last Page Number. Name of Database . https://doi.org/DOI Number if Given.
Note : If the book review is from a source other than an article in the library's database, view the appropriate section on the MLA guide to determine how to cite the source.
Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Review." Review of Title of Book: Subtitle if Any, by Book Author's First Name Last Name . Name of Journal , vol. Volume Number, no. Issue Number, Date of Publication, pp. First Page Number-Last Page Number. Name of Database . https://doi.org/DOI Number if Given.
- << Previous: Books, eBooks & Pamphlets
- Next: Class Handouts, Presentations, and Readings >>
- Last Updated: Jan 5, 2024 1:52 PM
- URL: https://columbiacollege-ca.libguides.com/MLA9

MLA Citation Guide (9th Edition): Book Reviews
- Advertisements
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Books and eBooks
- Book Reviews
- Class Notes and Presentations
- Encyclopedias and Dictionaries
- Government Documents
- Images, Artwork, Charts, Graphs and Tables
- Journal Articles
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Personal Communication (Interviews, Emails)
- Primary Sources
- Religious Texts
- Social Media
- Videos and DVDs
- When Creating Digital Assignments
- When Information Is Missing
- Works Quoted in Another Source
- Paraphrasing
- Works Cited List & Sample Paper
- Annotated Bibliography
On This Page
Book review - no title.
- Title Refers to Book being Reviewed
- Title Doesn't Refer to Book being Reviewed
Note : For your Works Cited list, all citations should be double spaced and have a hanging indent.
A "hanging indent" means that each subsequent line after the first line of your citation should be indented by 0.5 inches.
Author's Last Name, First Name. Review of Title of Book: Subtitle if Any , by Book Author's First Name Last Name. Name of Journal , vol. Volume Number, no. Issue Number, Date of Publication, pp. First Page Number-Last Page Number. Name of Database . doi: DOI Number if Given.
Note : If the book review is from a source other than an article in the library's database, view the appropriate section on the MLA guide to determine how to cite the source after the name of the book's author.
Khovanova, Tanya. Review of Love and Math: The Heart of Hidden Reality , by Edward Frenkel. The College Mathematics Journal , vol. 45, no. 3, May 2014, pp. 230-231. JSTOR . doi: www.jstor.org/stable/10.4169/college.math.j.45.3.230.
(Author's Last Name Page Number)
Example: (Khovanova 230)
Learn more: See the MLA Handbook , pp. 28-29
Book Review - Title Refers to Book being Reviewed
Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Review." Name of Journal , vol. Volume Number, no. Issue Number, Date of Publication, pp. First Page Number-Last Page Number. Name of Database . doi: DOI Number if Given.
Note : If the book review is from a source other than an article in the library's database, view the appropriate section on the MLA guide to determine how to cite the source.
Grosholz, Emily R. "Book Review: Realizing Reason: A Narrative of Truth and Knowledge by Danielle Macbeth." Journal of Humanistic Mathematics , vol. 7, no. 1, Jan. 2017, pp. 263-275, Academic Search Complete . doi: 10.5642/jhummath.20170120.
Example: (Grosholz 264)
Book Review - Title Doesn't Refer to Book being Reviewed
Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Review." Review of Title of Book: Subtitle if Any by Book Author's First Name Last Name. Name of Journal , vol. Volume Number, no. Issue Number, Date of Publication, pp. First Page Number-Last Page Number. Name of Database . doi: DOI Number if Given.
Rodriques, Elias. "Lonesome for our Home." Review of Barraccon: The Story of the Last "Black Cargo", by Zora Neale Hurston. Nation , vol. 306, no. 18, 18 June 2018, pp. 35-39. MAS Ultra - School Edition .
Example: (Rodriques 35)
MLA Handbook
Abbreviating Months
In your works cited list, abbreviate months as follows:
January = Jan. February = Feb. March = Mar. April = Apr. May = May June = June July = July August = Aug. September = Sept. October = Oct. November = Nov. December = Dec.
Spell out months fully in the body of your paper.
- << Previous: Books and eBooks
- Next: Class Notes and Presentations >>
- Last Updated: Jul 4, 2023 12:01 PM
- URL: https://lcc-ca.libguides.com/mla-citation-guide-9th-ed
Using the Library
- Library Catalogue
Subject Guides
Project guides, digital resources, reading lists, quick access.
- Junior School Catalog
- Senior School Catalog
- Sora Tutorials
- Sora Web Application
- Citation Guides
Lower Canada College Libraries
514-482-9916 ext. 473
LCC is an English coeducational K-11 school leading to the MEES Secondary Leaving Diploma / LCC est une école anglophone mixte de la maternelle à la 5e secondaire menant au DES du MEES.

MLA Citation Guide (8th Edition): Book Reviews
- Advertisements
- Books, eBooks & Pamphlets
- Book Reviews
- Class Notes & Presentations
- Encyclopedias & Dictionaries
- Government Documents
- Images, Artwork, Charts, Graphs & Tables
- Indigenous Resources
- Interviews and Emails (Personal Communications)
- Journal Articles
- Live Performances
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Primary Sources
- Religious Texts
- Social Media
- Videos & DVDs
- When Creating Digital Assignments
- Works Quoted in Another Source
- No author, no date etc
- In-Text Citation
- Sample Paper
- Annotated Bibliography
On This Page: Book Reviews
Book review - no title, book review - title refers to book being reviewed, book review - title doesn't refer to book being reviewed, abbreviating months.
In your Works Cited list, abbreviate months as follows:
January = Jan. February = Feb. March = Mar. April = Apr. May = May June = June July = July August = Aug. September = Sept. October = Oct. November = Nov. December = Dec.
Spell out months fully in the body of your paper.
Note : For your Works Cited list, all citations should be double-spaced and have a hanging indent.
A "hanging indent" means that each subsequent line after the first line of your citation should be indented by 0.5 inches.
Author's Last Name, First Name. Review of Title of Book: Subtitle if Any , by Book Author's First Name Last Name. Name of Journal , vol. Volume Number, no. Issue Number, Date of Publication, pp. First Page Number-Last Page Number. Name of Database . doi: DOI Number if Given.
Note : If the book review is from a source other than an article in the library's database, view the appropriate section in the MLA guide to determine how to cite the source after the name of the book's author.
Learn more: See the MLA Handbook , pp. 28-29
Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Review." Name of Journal , vol. Volume Number, no. Issue Number, Date of Publication, pp. First Page Number-Last Page Number. Name of Database . doi: DOI Number if Given.
Note : If the book review is from a source other than an article in the library's database, view the appropriate section on the MLA guide to determine how to cite the source.
Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Review." Review of Title of Book: Subtitle if Any, by Book Author's First Name Last Name . Name of Journal , vol. Volume Number, no. Issue Number, Date of Publication, pp. First Page Number-Last Page Number. Name of Database . doi: DOI Number if Given.
- << Previous: Books, eBooks & Pamphlets
- Next: Class Notes & Presentations >>
- Last Updated: Jan 17, 2023 10:37 AM
- URL: https://libguides.capilanou.ca/mla

Cite Your Sources in MLA 9th: Book Reviews
- Books and eBooks
- Encyclopedia and Dictionary Entries
- Government Documents
- Images, Artwork, Charts, Graphs and Tables
- Journal Articles
- Newspaper and Magazine Articles
- Social Media
- Videos and Other Multimedia
- Advertisements
- Book Reviews
- ChatGPT and Generative AI
- Emails, Interviews, and Personal Communications
- Religious Texts
- Formatting Your Paper
- How to Identify Source Types
- Other Styles
How to Cite Book Reviews
Book review without a title.
Review Author(s). Review of Title of Book: Subtitle if Any , by Book Author's First Name Last Name. Name of Journal , vol. Volume Number, no. Issue Number, Publication Date, pp. Page Numbers. Name of Database , https://doi.org/DOI [if any].
Khovanova, Tanya. Review of Love and Math: The Heart of Hidden Reality , by Edward Frenkel. The College Mathematics Journal , vol. 45, no. 3, May 2014, pp. 230-231. JSTOR , https://doi.org/10.4169/college.math.j.45.3.230.
Book Review With a Title
Review Author(s). "Title of Review with Book Title Italicized." Name of Journal , vol. Volume Number, no. Issue Number, Publication Date, pp. Page Numbers. Name of Database , https://doi.org/DOI [if any].
Grosholz, Emily R. "Book Review: Realizing Reason: A Narrative of Truth and Knowledge by Danielle Macbeth." Journal of Humanistic Mathematics , vol. 7, no. 1, Jan. 2017, pp. 263-275. Academic Search Complete , https://doi.org/10.5642/jhummath.20170120.
How to Format Author Names
- Works Cited List
- In-Text Citation
Last Name, First Name or Last Name, First Name Middle Name or Initial (if provided in source)
Name Examples:
Anzaldúa, Gloria Kendi, Ibram X. Wallace, David Foster
Citation Example:
Anzaldúa, Gloria. Borderlands / La Frontera: The New Mestiza . 4th ed., Aunt Lute Books, 2012.
Two Authors
Last Name, First Name, and First Name Last Name
Wykes, Maggie, and Barrie Gunter. The Media and Body Image: If Looks Could Kill. Sage, 2005.
Three or More Authors
First Author's Last Name, First Name, et al.
Chan, Sabrina S., et al. Learning Our Names: Asian American Christians on Identity, Relationships, and Vocation. InterVarsity Press, 2022.
Group or Corporate Author
If the group author is different from publisher.
If the group author and the publisher are different entities, list the Group Name as the author.
Calgary Educational Partnership Foundation. Employability Skills: Creating My Future . Nelson, 1996.
If the Group Author and Publisher Are the Same
If the group author and the publisher are the same, skip the author and list the title first. Then, list the group author only as the publisher.
Fair Housing—Fair Lending . Aspen Law & Business, 1985.
If a source has no author, skip the author and start with the title. Do not use "Anonymous" as the author name.
"How to Teach Yourself Guitar." eHow, Demand Media, www.ehow.com/how_5298173_teach-yourself-guitar.html. Accessed 24 June 2016.
(Last Name Page Number)
(Anzaldúa 30)
(First Author's Last Name and Second Author's Last Name Page Number)
(Wykes and Gunter 53)
(First Author's Last Name et al. Page Number)
(Chan et al. 97)
(Group Name Page Number)
(Calgary Educational Partnership Foundation 230)
If your full citation for a group author starts with the title rather than the group's name, follow the "No Author" in-text citation rules instead.
( Title of Longer Work or "Title of Shorter Work" Page Number)
( Fair Housing 15)
("How to Teach")
Frequently Asked Questions
How do i format dates.
Dates in your Works Cited list should be formatted like this: Day Month Year. Month names should be abbreviated using the list below. Example: 17 Oct. 2021.
For publication dates, include as much information as the source provides. This may be a full date, only the month and year, a season (such as Spring 2019), or just a publication year.
Month Abbreviations
In your Works Cited list, abbreviate months as follows:
January = Jan. February = Feb. March = Mar. April = Apr. May = May June = June July = July August = Aug. September = Sept. October = Oct. November = Nov. December = Dec.
Spell out months fully in the body of your paper.
What is a DOI?
Digital Object Identifiers, or DOIs, are unique numbers or hyperlinks assigned to some online resources, such as journal articles, to make them easier to find.
If a DOI is provided for a source, include it at the end of your citation after any page numbers. In your Works Cited list, you should always format a DOI as a URL beginning with "https://doi.org/" followed immediately by the DOI number.
Example: For DOI "10.5642/jhummath.20170120," the URL version would be: https://doi.org/10.5642/jhummath.20170120
If no DOI is provided but a permalink or stable link is present, you can use that instead.
What if some information is missing?
If a source is missing information that you need for your Works Cited citation, you can skip that element and move on to the next element in the citation.
Examples: Some sources don't have an author; in this case, we skip the author and start our citation with the title. Most academic journals are published in volumes and issues, but some only have volumes; in this case, we list the volume number and skip the issue number.
What if I don't know which source type I'm citing?
If you're not sure what type of source you're working with, don't worry! This is a very common challenge. Check out our page on Identifying Source Types .
What if I need to cite multiple sources by the same author?
Works Cited List: To cite two or more works by the same author, give the name in the first entry only. For subsequent works by the same author, replace the author's name with three hyphens followed by a period (---.), which signifies that the name is the same as the preceding entry. Alphabetize works with the same author by title.
In-Text Citations: To distinguish multiple works by the same author, add a comma followed by a shortened version of the title (usually the first 2-4 words) between the author name and the page number. Example: (Anzaldúa, Borderlands / La Frontera 38). Alternately, you can mention the author and title in the sentence, and then only include the page number.
For page numbers, should I use p. or pp.?
If you are citing a single page, use "p." If you are citing multiple pages, use "pp."
Example: If an article runs from page 10 to page 15, your citation should say "pp. 10-15" because it covers multiple pages. If it's a short article that only appears on page 11, your citation should say "p. 11".
More Information on MLA 9th
- Pierce Library's MLA 9th Quick Citation Guide Downloadable PDF with sample citations (including in-text) for different types of sources and a sample Works Cited page.
- MLA Style Center Tips for working in MLA Style, answers to common questions, and more.
- Purdue OWL MLA 9 Formatting & Style Guide Very thorough overview of MLA 9th with examples for how to construct both in-text and Works Cited entries.

- << Previous: Advertisements
- Next: ChatGPT and Generative AI >>
- Last Updated: Feb 29, 2024 5:12 PM
- URL: https://library.piercecollege.edu/mla9

Citation Help for MLA, 8th Edition: Book Review
- Book Review
- Email and Tweets
- Encyclopedia
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Master's Thesis or Project
- Music Albums & Songs
- Newspaper Article
- Formatting Your Paper
- Parenthetical Documentation
- Ethically Use Sources
Month Abbreviations
According to p. 95 of the MLA Handbook 8th ed. Spell out months in the body of your paper and abbreviate as follows in your works cited list: January = Jan. February = Feb. March = Mar. April = Apr. May = May June = June July = July August = Aug. September = Sept. October = Oct. November = Nov. December = Dec.
Multiple Authors?
Example: McGill, Ivan, John Kurt Glenn, and Alice Brockbank. The Action Learning Handbook: Powerful Techniques for Education . Rutledge Falmer, 2014.
Explanation: List the first author last name first followed by the first and middle names followed by a comma. All other authors are listed first name followed by the last name. Insert the word "and" and a comma before the last author. Note: If there are more than three authors, just list the first one followed by et al., which is Latin for and others . There is a period after al but not et. Example: Nelson, Karl, et al. Fish Is for Everyone . Penguin Press, 2016.
Bell, Madison Smartt. "Are You My Mother?" Review of Let the Northern Lights Erase Your Name , by Vendela Vida. The New York Times Book Review, 31 Dec. 2016, p. 10.
Explanation
- << Previous: Book
- Next: eBook >>
- Last Updated: Feb 19, 2024 2:51 PM
- URL: https://libguides.css.edu/MLA8
- MyExperience
MLA Citation Style, 9th Edition: Book Review
- In-Text References
- Works Cited
- One Author or Editor
- Multiple Authors or Editors
- Author and Editor
- Author and Translator
- Organization as Author
- Anonymous Work
- Chapter from an Edited Work
- Introduction, Preface, Foreword, or Afterword
- Multivolume Work
- Edition Other than the First
- Dictionary or Encyclopedia
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Book Review
- Basic Webpage
- Video Recording
- Sound Recording
- YouTube Video
- Interview or Personal Communication
- Lecture or Presentation
- Thesis or Dissertation
- Indirect Source
- Government Document
- AI Generated Content
Book Review - Examples
In-Text:
(Powers 10)
Works Cited:
NOTE: If a review is untitled, include a title which incorporates the work that is being reviewed:
Help & Guide Contents
Home General Guidelines In-Text Reference Works Cited Books One Author or Editor Multiple Authors or Editors Author and Editor Author and Translator Organization as Author Anonymous Work Chapter from an Edited Work Introduction, Preface, Foreword, or Afterword Multivolume Work Edition Other than the First Dictionary or Encyclopedia E-Book Articles Journal Article Magazine Article Newspaper Article Book Review Websites Basic Webpage Blog Post Tweet Audiovisual Media Video Recording Sound Recording YouTube Video Other Sources Interview or Personal Communication Lecture or Presentation Thesis or Dissertation Scripture Indirect Source Government Document Plagiarism
- << Previous: Newspaper Article
- Next: Websites >>
- Last Updated: Mar 26, 2024 3:57 PM
- URL: https://library.ulethbridge.ca/mlastyle9

MLA Citation Guide: Book Reviews
- Advertisements
- Books, eBooks & Pamphlets
- Book Reviews
- Class Notes & Presentations
- Encyclopedias & Dictionaries
- Government Documents
- Images, Artwork, Charts, Graphs & Tables
- Interviews and Emails (Personal Communications)
- Journal Articles
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Primary Sources
- Religious Texts
- Social Media
- Videos & DVDs
- When Creating Digital Assignments
- When Information Is Missing
- Works Quoted in Another Source
- In-Text Citation
- Works Cited List
- Annotated Bibliography
- How Did We Do?
Abbreviating Months
In your works cited list, abbreviate months as follows:
January = Jan. February = Feb. March = Mar. April = Apr. May = May June = June July = July August = Aug. September = Sept. October = Oct. November = Nov. December = Dec.
Spell out months fully in the body of your paper.
Note : For your Works Cited list, all citations should be double spaced and have a hanging indent.
A "hanging indent" means that each subsequent line after the first line of your citation should be indented by 0.5 inches.
Book Review - No Title
Author's Last Name, First Name. Review of Title of Book: Subtitle if Any , by Book Author's First Name Last Name. Name of Journal , vol. Volume Number, no. Issue Number, Date of Publication, pp. First Page Number-Last Page Number. Name of Database . doi: DOI Number if Given.
Note : If the book review is from a source other than an article in the library's database, view the appropriate section on the MLA guide to determine how to cite the source after the name of the book's author.
Learn more: See the MLA Handbook , pp. 28-29
Book Review - Title Refers to Book being Reviewed
Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Review." Name of Journal , vol. Volume Number, no. Issue Number, Date of Publication, pp. First Page Number-Last Page Number. Name of Database . doi: DOI Number if Given.
Note : If the book review is from a source other than an article in the library's database, view the appropriate section on the MLA guide to determine how to cite the source.
Book Review - Title Doesn't Refer to Book being Reviewed
Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Review." Review of Title of Book: Subtitle if Any, by Book Author's First Name Last Name . Name of Journal , vol. Volume Number, no. Issue Number, Date of Publication, pp. First Page Number-Last Page Number. Name of Database . doi: DOI Number if Given.
- << Previous: Books, eBooks & Pamphlets
- Next: Class Notes & Presentations >>
- Last Updated: Mar 5, 2024 9:42 AM
- URL: https://libguides.brenau.edu/MLAnew
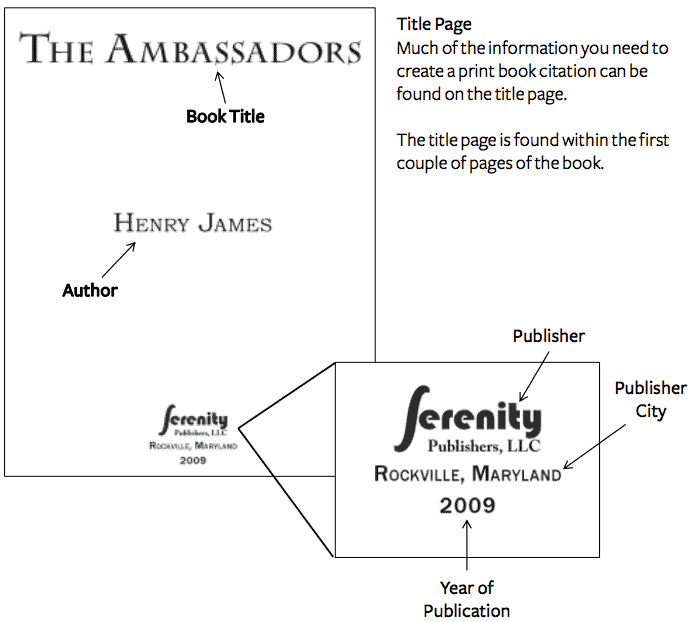
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format / MLA Book Citation
How to Cite a Book in MLA
Books are written works or compositions that have been published. They are no longer restricted to paper and have evolved into the online realm.
Below are examples of how to cite different types of books in MLA 9. If you need a different citation style, there is also a guide on citing a book in APA .
In MLA, a basic book citation includes the following information:
- Author’s name
- Title of book
- Publisher of the book
- Year published
Additional information is needed when citing:
- Name of website or database
- Name of e-book device
- Name of the translator or editor
- Name of book editor or author
- Name of chapter author
- Page numbers or ranges used
- Volume number of the book
- City the book was published in
Citing a book in MLA (print)
View Screenshot | Cite your book
Citing a book found on a Website or database in MLA
Many books are now found online. Popular sites or databases that hold e-books include Google Books, Project Gutenberg, and EBSCO.
Cite your book
*Keep “https:” at the beginning of the URL only when citing a DOI.
Digital sources with no page numbers means that no page numbers should be included in the in-text citation.
Citing an E-book in MLA (found via an e-reader)
E-Readers are electronic devices that display e-books. Kindles and Nooks are some of the more popular e-readers available today. Individuals can purchase or borrow e-books and read them on their e-readers.
Cite your ebook
Since the page numbers of an e-book can vary across e-reader, text preferences, and other factors, you should not include a page number. This is because a consistent page number does not exist. You can include section numbers (sec., secs.) or chapter numbers (ch., chs.) instead, if they exist and you feel it would be helpful.

Citing a translated or edited book in MLA
Citing a chapter of a book in mla.
*In the above citation example, The Body of the Queen: Gender and Rule in the Courtly World, 1500-2000 is an edited book that features a chapter by Louis Montrose. The title of the chapter that he wrote is found in quotation marks (“Elizabeth Through the Looking Glass: Picturing the Queen’s Two Bodies”).
Citing a book with multiple authors in MLA
*et al. is Latin for “and others.”
Published October 20, 2011. Updated May 9, 2021.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- Works Cited
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
In the works cited: If the organization is the author and publisher, don’t include an author and start the citation with the book’s title. If the author and publisher are different, use the organization name as the author.
When the chapter’s author is different from the book’s editor or author. Chapters are usually cited when you use anthologies, multi-volume sets, or a foreword/afterword written by someone other than the book’s main author.
Place the author’s last name and the quote chapter number in parenthesis after the borrowed quote or information. Example: “Feeling that Peter was on his way back, the Neverland had again woke into life” (Barrie ch. 5).
MLA is the style most often used in literature, language, history, art and theater subjects.
If any important information is missing (e.g., author’s name, title, publishing date, URL, etc.), first see if you can find it in the source yourself. If you cannot, leave the information blank and continue creating your citation.
Yes! Whether you’d like to learn how to construct citations on your own, our Autocite tool isn’t able to gather the metadata you need, or anything in between, manual citations are always an option. Click here for directions on using creating manual citations.
To cite a book with multiple authors in MLA style, you need to have basic information including the authors, publication year, book title, and publisher. The templates for in-text citation and works-cited-list entry of a book written by multiple authors and some examples are given below:
In-text citation template and example:
Citation in prose:
For sources with two authors, use both full author names in prose (e.g., Harold Napoleon and Richard Harris). For sources with three or more authors, use the first name and surname of the first author followed by “and others” or “and colleagues” (e.g., Harold Napoleon and others). In subsequent citations, use only the surname of the first author followed by “and others” or “and colleagues” (e.g., Napoleon and others).
First mention: Harold Napoleon and colleagues…. or Harold Napoleon and others ….
Subsequent occurrences: Napoleon and colleagues…. or Napoleon and others ….
Parenthetical:
In parenthetical citations, use only the author’s surname (e.g., Napoleon). For sources with two authors, use two surnames (e.g., Napoleon and Harris). For sources with three or more author names, use the first author’s surname followed by “et al.”
….(Napoleon et al.)
Works-cited-list entry template and example:
The title of the book is given in italics and title case.
Surname, F. M., et al. Title of the Book . Publisher, Publication Date.
Napoleon, Harold, et al. Yuuyaraq the Way of the Human Being: With Commentary . University of Alaska, 1996.
Use only the first author’s name in surname–first name order in the entry and follow it with “et al.”
A book is a printed copy, whereas an e-book is an online version and is available via different electronic media (e.g., epub and Kindle).
To cite a print book in MLA format, you need to know the names of the authors, the title of the book, publisher name, publication date, and page range (optional). You need the same information to cite an e-book, however, you will not include page numbers unless they are the same as those in the print version of the book. MLA mostly treats citations for print books and e-books the same, except for noting that the e-book version is being cited within the entry.
The templates and examples for in-text citations and works cited list entries for a book and an e-book are provided below:
In-text citation template and example for a book:
Author Surname
(Author Surname Page)
(Damasio 7)
Works cited list entry template and example:
Surname, First Name. Title of the Book . Publisher, Publication Date, Page range.
Damasio, Antonio. Emotion, Reason and the Feeling Brain . Penguin, 1994.
In-text citation template and example for an e-book:
(Author Surname)
Author’s Surname, First Name. Title of the Book . E-book ed., Publisher, Publication Date.
Davis, Barbara. The Keeper of Happy Endings . E-book ed., Lake Union Publishing, 2021.
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Organizing Research for Arts and Humanities Papers and Theses
- General Guide Information
- Developing a Topic
- What are Primary and Secondary Sources
- What are Scholarly and Non-Scholarly Sources
- Writing an Abstract
- Writing Academic Book Reviews
- Writing A Literature Review
- Using Images and other Media
Purpose of a Book Review
Note: This information is geared toward researchers in the arts and humanities. For a detailed guide on writing book reviews in the social sciences, please check the USC Libraries guide to Writing and Organizing Research in the Social Sciences , authored by Dr. Robert Labaree.
When writing an academic book review, start with a bibliographic citation of the book you are reviewing [e.g., author, title, publication information, length]. Adhere to a particular citation style, such as Chicago, MLA, or APA. Put your name at the very end of the book review text.
The basic purpose of a book review is to convey and evaluate the following:
a. what the book is about;
b. the expertise of the author(s);
c. how well the book covers its topic(s) and whether it breaks new ground;
d. the author’s viewpoint, methodology, or perspective;
e. the appropriateness of the evidence to the topical scope of the book;
f. the intended audience;
g. the arrangement of the book (chapters, illustrations) and the quality of the scholarly apparatus, such as notes and bibliographies.
Point "c. how well the book covers its topics and whether it breaks new ground" requires your engagement with the book, and can be approached in a variety of ways. The question of whether the book breaks new ground does not necessarily refer to some radical or overarching notion of originality in the author’s argument. A lot of contemporary scholarship in the arts or humanities is not about completely reorienting the discipline, nor is it usually about arguing a thesis that has never been argued before. If an author does that, that's wonderful, and you, as a book reviewer, must look at the validity of the methods that contextualize the author's new argument.
It is more likely that the author of a scholarly book will look at the existing evidence with a finer eye for detail, and use that detail to amplify and add to existing scholarship. The author may present new evidence or a new "reading" of the existing evidence, in order to refine scholarship and to contribute to current debate. Or the author may approach existing scholarship, events, and prevailing ideas from a more nuanced perspective, thus re-framing the debate within the discipline.
The task of the book reviewer is to “tease out” the book’s themes, explain them in the review, and apply a well-argued judgment on the appropriateness of the book’s argument(s) to the existing scholarship in the field.
For example, you are reviewing a book on the history of the development of public libraries in nineteenth century America. The book includes a chapter on the role of patronage by affluent women in endowing public libraries in the mid-to-late-1800s. In this chapter, the author argues that the role of women was overlooked in previous scholarship because most of them were widows who made their financial bequests to libraries in the names of their husbands. The author argues that the history of public library patronage, and moreover, of cultural patronage, should be re-read and possibly re-framed given the evidence presented in this chapter. As a book reviewer you will be expected to evaluate this argument and the underlying scholarship.
There are two common types of academic book reviews: short summary reviews, which are descriptive, and essay-length critical reviews. Both types are described further down.
[Parenthetically, writing an academic/scholarly book review may present an opportunity to get published.]
Short summary book reviews
For a short, descriptive review, include at least the following elements:
a. the bibliographic citation for the book;
b. the purpose of the book;
c. a summary of main theme(s) or key points;
d. if there is space, a brief description of the book’s relationship to other books on the same topic or to pertinent scholarship in the field.
e. note the author's affiliation and authority, as well as the physical content of the book, such as visual materials (photographs, illustrations, graphs) and the presence of scholarly apparatus (table of contents, index, bibliography, footnotes, endnotes, credit for visual materials);
f. your name and affiliation.
Critical or essay-length book reviews
For a critical, essay-length book review consider including the following elements, depending on their relevance to your assignment:
b. an opening statement that ought to peak the reader’s interest in the book under review
c. a section that points to the author’s main intentions;
d. a section that discusses the author’s ideas and the book’s thesis within a scholarly perspective. This should be a critical assessment of the book within the larger scholarly discourse;
e. if you found errors in the book, point the major ones and explain their significance. Explain whether they detract from the thesis and the arguments made in the book;
f. state the book's place within a strand of scholarship and summarize its importance to the discipline;
g. include information about the author's affiliation and authority, as well as the physical content of the book, such as visual materials (photographs, illustrations, graphs) and the presence of scholarly apparatus (table of contents, index, bibliography, footnotes, endnotes, credit for visual materials);
h. indicate the intended readership of the book and whether the author succeeds in engaging the audience on the appropriate level;
i. your name and affiliation.
Good examples of essay-length reviews may be found in the scholarly journals included in the JSTOR collection, in the New York Review of Books , and similar types of publications, and in cultural publications like the New Yorker magazine.
Remember to keep track of your sources, regardless of the stage of your research. The USC Libraries have an excellent guide to citation styles and to citation management software .
- << Previous: Writing an Abstract
- Next: Writing A Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Jan 19, 2023 3:12 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/ah_writing
How do I cite a review of a product?
To cite a review of a product, such as a toaster, follow the examples for citing reviews provided in appendix 2 of the MLA Handbook . How you cite the review will depend on whether it is signed (i.e., whether it lists the author’s name or was published anonymously) and on whether it has a unique title. The following shows an example works-cited-list entry for a signed review with a unique title:
Sullivan, Michael, and Sabrina Imbler. “The Best Toaster.” The New York Times , 19 July 2022, www.nytimes.com/wirecutter/reviews/best-toaster/.
Below is an example of a review that has a unique title but was published anonymously:
“Five Best Toasters of 2022, Tested by Food Network Kitchen.” Food Network , 15 June 2022, www.foodnetwork.com/how-to/packages/shopping/product-reviews/best-toasters.
If the review does not have a unique title, use a description in the Title of Source element ( MLA Handbook 5.23), as in the following example:
Review of Café Couture Smart Toaster Oven with Air Fry. Consumer Reports , 2022, www.consumerreports.org/products/toasters-toaster-ovens-28972/toaster-oven-28731/cafe-couture-smart-toaster-oven-with-air-fry-407059/.
MLA Handbook . 9th ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2021. MLA Handbook Plus , 2021, mlahandbookplus.org/.
MLA Citation Examples
- Volume and Issue Numbers
- Page Numbers
- Citing a Source within a Source
- DOIs and URLs
- In-Text Citations
- Academic Journals
- Encyclopedia Articles
- Book, Film, and Product Reviews
Review without a specific title
Review with a title.
- Online Classroom Materials
- Conference Papers
- Technical and Research Reports
- Dissertations and Theses
- Interviews and E-mail Messages
- AI: ChatGPT, etc.
- Review of Title of Work , by Author.
- Title of Journal ,
- Volume number, issue number,
- Publication Date,
- Page number(s).
- Title of Database ,
- DOI or URL.
Reviewer. Review of Title of Work , by Author. Title of Journal , vol. #, no. #, date, pp. #-#. Title of Database , DOI or URL.
Conn, David R. Review of The World as We Knew It: Dispatches from a Changing Climate , by Amy Brady and Tajja Isen. Library Journal , vol. 147, no. 4, Apr. 2022, p. 104. EBSCOhost , ezproxy.umgc.edu/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ehh&AN=155859448&site=eds-live&scope=site.
- "Title of Review."
Reviewer. "Title of Review." Review of Title of Work , by Author. Title of Journal , vol. #, no. #, date, pp. ##-##. Title of Database , DOI or URL.
Grimes, William. "Beyond Mandalay, the Road to Isolation and Xenophobia." Review of The River of Lost Footsteps: Histories of Burma , by Thant Myint-U. New York Times , 13 Dec. 2006, pp. E8+. ProQuest , ezproxy.umgc.edu/login?url=https://www.proquest.com/docview/433471566?accountid=14580.
- << Previous: Encyclopedia Articles
- Next: Websites >>
- Last Updated: Dec 11, 2023 10:40 AM
- URL: https://libguides.umgc.edu/mla-examples
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Citing sources
- How to Cite a Book | APA, MLA, & Chicago Examples
How to Cite a Book | APA, MLA, & Chicago Examples
Published on February 26, 2021 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on January 17, 2024.
To cite a book, you need a brief in-text citation and a corresponding reference listing the author’s name, the title, the year of publication, and the publisher. The order and format of information depends on the citation style you’re using. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago style .
Use the interactive example generator to explore the format of book citations in MLA and APA.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Citing a book in mla style, citing a book in apa style, citing a book in chicago style, where to find source information in a book, frequently asked questions about citations.
An MLA book citation includes the author’s name , the book title (in italics, capitalized headline-style), the edition (if specified), the publisher, and the year of publication. If it’s an e-book , write “e-book” (or a more specific description, e.g. “Kindle ed.”) before the publisher name.
The corresponding in-text citation lists the author’s last name and the page number of the passage cited.
You can also use our free MLA Citation Generator to create your book citations.
Generate accurate MLA citations with Scribbr
Citing a book chapter in mla.
To cite a book chapter , first give the author and title (in quotation marks) of the chapter cited, then information about the book as a whole and the page range of the specific chapter.
The in-text citation lists the author of the chapter and the page number of the relevant passage.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
An APA Style book citation lists the author’s last name and initials, the year of publication, the title and any subtitle (in italics, capitalizing only the first word), the edition (if specified), and the publisher. Add a DOI or URL to the end of the entry if available (e.g. for e-books or books accessed online ).
In an in-text citation, state the author’s last name and the publication year, and a page number if you need to show the location of a specific quote or paraphrase .
You can also use our free APA Citation Generator to automatically generate your book citations. Search for a title, DOI, or ISBN to retrieve the details.
Generate accurate APA citations with Scribbr
Citing a book chapter in apa.
To cite a book chapter , list information about the chapter first, followed by information about the book, including the book’s editor(s) and the chapter’s page range within the book.
The author of the chapter, not the editor of the book, is listed in the in-text citation.
Chicago notes and bibliography style uses footnotes to cite sources instead of parenthetical citations. These notes refer to a bibliography at the end giving full source details.
A Chicago bibliography entry for a book includes the author’s name, the book title and subtitle, the edition (if stated), the location and name of the publisher, and the year of publication. For an e-book , add the e-book format (e.g. “Kindle”) at the end.
Chicago also has an alternative style, Chicago author-date . You can see examples of book citations in this style here .
Citing a book chapter in Chicago
To cite a book chapter , start with the author and the title of the chapter (in quotation marks), then give the title (in italics) and editor of the book, the page range of the chapter, the location and name of the publisher, and the year of publication.
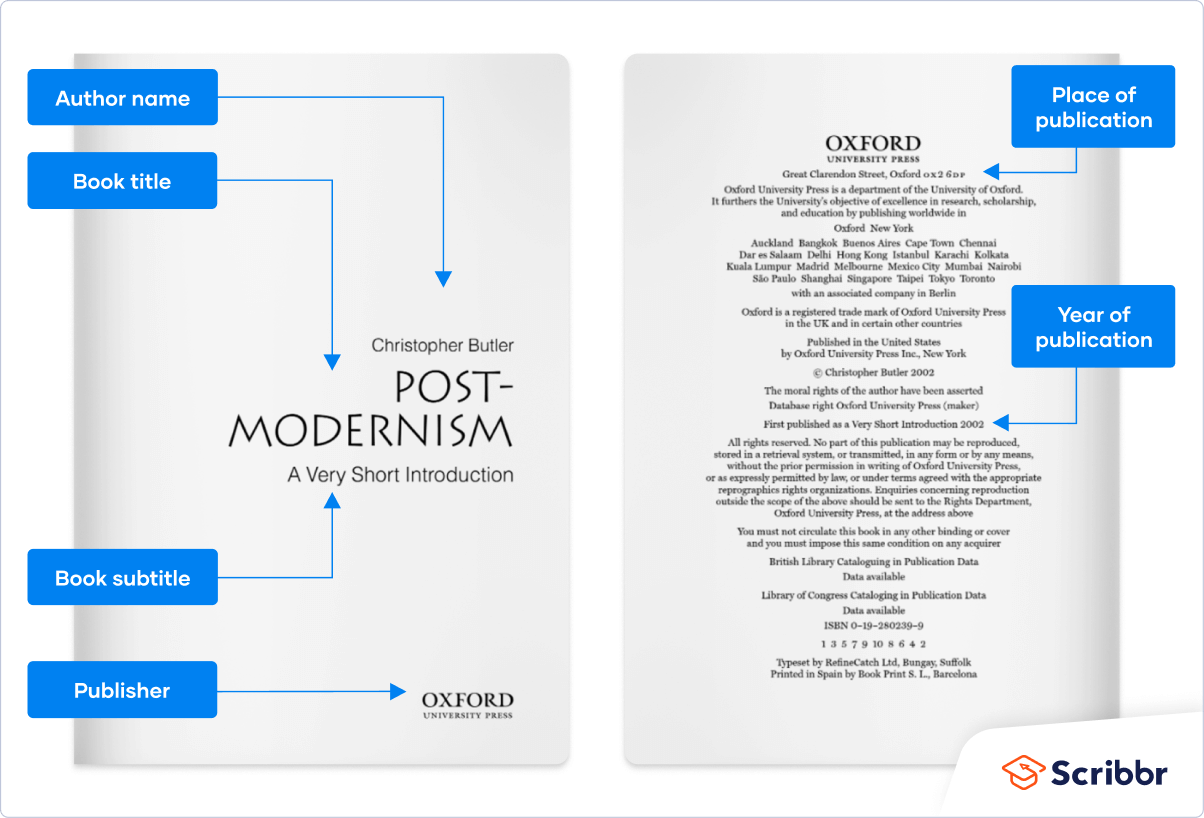
All the information you need for a book citation can usually be found on the book’s title page and copyright page. The main things you’re looking for are:
- the title (and subtitle if present)
- name(s) of the author(s)
- year of publication
- place of publication
You should also check if the book specifies an edition (e.g. 2nd edition, revised edition) and if any other contributors are named (e.g. editor, translator).
The image below shows where to find the relevant information on the title and copyright pages of a typical book.
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

The main elements included in all book citations across APA , MLA , and Chicago style are the author, the title, the year of publication, and the name of the publisher. A page number is also included in in-text citations to highlight the specific passage cited.
In Chicago style and in the 6th edition of APA Style , the location of the publisher is also included, e.g. London: Penguin.
When a book’s chapters are written by different authors, you should cite the specific chapter you are referring to.
When all the chapters are written by the same author (or group of authors), you should usually cite the entire book, but some styles include exceptions to this.
- In APA Style , single-author books should always be cited as a whole, even if you only quote or paraphrase from one chapter.
- In MLA Style , if a single-author book is a collection of stand-alone works (e.g. short stories ), you should cite the individual work.
- In Chicago Style , you may choose to cite a single chapter of a single-author book if you feel it is more appropriate than citing the whole book.
Check if your university or course guidelines specify which citation style to use. If the choice is left up to you, consider which style is most commonly used in your field.
- APA Style is the most popular citation style, widely used in the social and behavioral sciences.
- MLA style is the second most popular, used mainly in the humanities.
- Chicago notes and bibliography style is also popular in the humanities, especially history.
- Chicago author-date style tends to be used in the sciences.
Other more specialized styles exist for certain fields, such as Bluebook and OSCOLA for law.
The most important thing is to choose one style and use it consistently throughout your text.
The abbreviation “ et al. ” (Latin for “and others”) is used to shorten citations of sources with multiple authors.
“Et al.” is used in APA in-text citations of sources with 3+ authors, e.g. (Smith et al., 2019). It is not used in APA reference entries .
Use “et al.” for 3+ authors in MLA in-text citations and Works Cited entries.
Use “et al.” for 4+ authors in a Chicago in-text citation , and for 10+ authors in a Chicago bibliography entry.
When you want to cite a specific passage in a source without page numbers (e.g. an e-book or website ), all the main citation styles recommend using an alternate locator in your in-text citation . You might use a heading or chapter number, e.g. (Smith, 2016, ch. 1)
In APA Style , you can count the paragraph numbers in a text to identify a location by paragraph number. MLA and Chicago recommend that you only use paragraph numbers if they’re explicitly marked in the text.
For audiovisual sources (e.g. videos ), all styles recommend using a timestamp to show a specific point in the video when relevant.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2024, January 17). How to Cite a Book | APA, MLA, & Chicago Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 25, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/citing-sources/cite-a-book/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to cite an image | photographs, figures, diagrams, how to cite a journal article | apa, mla, & chicago examples, how to cite a lecture | apa, mla & chicago examples, scribbr apa citation checker.
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!
- Plagiarism and grammar
- Citation guides
Cite a Review in MLA
Don't let plagiarism errors spoil your paper, consider your source's credibility. ask these questions:, contributor/author.
- Has the author written several articles on the topic, and do they have the credentials to be an expert in their field?
- Can you contact them? Do they have social media profiles?
- Have other credible individuals referenced this source or author?
- Book: What have reviews said about it?
- What do you know about the publisher/sponsor? Are they well-respected?
- Do they take responsibility for the content? Are they selective about what they publish?
- Take a look at their other content. Do these other articles generally appear credible?
- Does the author or the organization have a bias? Does bias make sense in relation to your argument?
- Is the purpose of the content to inform, entertain, or to spread an agenda? Is there commercial intent?
- Are there ads?
- When was the source published or updated? Is there a date shown?
- Does the publication date make sense in relation to the information presented to your argument?
- Does the source even have a date?
- Was it reproduced? If so, from where?
- If it was reproduced, was it done so with permission? Copyright/disclaimer included?
- Citation Machine® Plus
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style
- Harvard Referencing
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO
- Research Guides
- CUNY Graduate Center's Mina Rees Library
Cite Your Sources
- Citation Styles
- Citing Sources
- Chicago & Turabian Style
- Additional Style Guides & Resources
- Citing Social Media & Other Digital Sources This link opens in a new window
- Mendeley & EndNote
- Citation Managers Compared
- Citation Generators
- Avoiding Plagiarism
Choosing a Style
The Graduate Center does not recommend a single citation style, so follow the style recommended by the professor for your course. If you are writing for a publication, look for the preferred citation style in the author guidelines. In both cases, ask if you are not certain. And no matter which style you are following, be sure to apply it consistently throughout your document.
- Style Guide Overview - Purdue OWL This guide from the Purdue Online Writing Lab provides a summary of common styles, especially APA and MLA but also AP, Chicago, IEEE, AMA, ACM, and ASME, and offers tips on how and when to use them.
Antiquity in Gotham: The Ancient Architecture of New York City - References
This humanities title from Fordham University Press has a References section at the end of the book.

Macaulay-Lewis, Elizabeth. Antiquity in Gotham: The Ancient Architecture of New York City. New York: Fordham University Press, 2021. Available online and in print. See the OneSearch record for details.
- << Previous: Citing Sources
- Next: APA Style >>
- Last Updated: Mar 26, 2024 10:32 AM
- URL: https://libguides.gc.cuny.edu/citation
- Buy Custom Assignment
- Custom College Papers
- Buy Dissertation
- Buy Research Papers
- Buy Custom Term Papers
- Cheap Custom Term Papers
- Custom Courseworks
- Custom Thesis Papers
- Custom Expository Essays
- Custom Plagiarism Check
- Cheap Custom Essay
- Custom Argumentative Essays
- Custom Case Study
- Custom Annotated Bibliography
- Custom Book Report
- How It Works
- AI Essay Writer
- Essay Samples
- Essay Topics
- Research Topics
- Uncategorized
- Writing Tips
How to Cite a Survey in MLA Style
November 17, 2023
Understanding MLA Format in an Essay
MLA (Modern Language Association) format is a commonly used citation style in academic writing. When citing a survey in MLA, it is important to follow the specific guidelines to ensure accuracy and credibility. Begin by including the author’s name and the survey title in quotation marks. Next, provide the publication or sponsoring organization, followed by the date of publication. When citing an online survey, include the URL or DOI (Digital Object Identifier). It is also crucial to indicate the type of resource, such as a web page, book, or journal article. MLA format also requires in-text citations, usually in parentheses, with the author’s last name and page number. It is essential to adhere to MLA format guidelines to maintain consistency and provide proper credit to the original survey source.
Components of a Survey Citation in MLA
When citing a survey in MLA format, it is important to include specific components to provide accurate and complete information. Here are the essential elements that should be included in your citation:
- Author’s Name: Begin with the author’s last name, followed by their first name or initials. If the author is not available, use the survey title as the first element.
- Survey Title: Enclose the survey title in quotation marks. If the survey has a specific name or is part of a larger work, include the title of the overall work in italics or underlined.
- Publication or Sponsoring Organization: Include the name of the organization or publication responsible for the survey. If it is an online survey, provide the name of the website or platform where the survey was accessed.
- Date of Publication: Include the date when the survey was published or conducted. If the date is not available, use “n.d.” to indicate no date.
- URL or DOI: If the survey is accessed online, include the URL (web address) for the web page where the survey can be found. Alternatively, use the DOI (Digital Object Identifier) if provided.
- Type of Resource: Indicate the type of resource that the survey belongs to, such as a web page, book, journal article, or conference proceeding.
By including these components in your MLA citation, you provide the necessary information for readers to locate and verify the survey you have used in your essay.
Citing a Survey Conducted by the Author(s)
When citing a survey conducted by the author(s) in MLA format, you should include specific details to properly acknowledge their work. Here are the key components to include in your citation:
- Author(s) of the Survey: Begin with the last name of the author(s), followed by their first name or initials. If there are multiple authors, separate their names using commas.
- Survey Title: Enclose the title of the survey in quotation marks. If the survey is part of a larger work, italicize or underline the title of the overall work.
- Title of the Overall Work: If applicable, include the title of the larger work in which the survey is published. Italicize or underline the title.
- Publication Information: Include the publisher’s name, followed by the year of publication. If the survey is unpublished, use “unpublished” instead of the publisher’s name.
- Medium of Publication: Indicate the medium of the survey, such as print or digital. For example, if the survey was distributed through an online platform, specify that it is a “Web” survey.
- In-text Citation: Use parenthetical citations within the essay to reference the survey. Include the author’s last name and the page number (if available).
By accurately citing a survey conducted by the author(s) in MLA format, you give credit to the original source and enable readers to locate the survey for further research.
Citing a Survey Conducted by Someone Else
When citing a survey conducted by someone else in MLA format, you should include specific details to give proper credit to the source. Here are the key components to include in your citation:
- Publication Information: Provide information about where the survey was published, such as the name of the book, journal, or website. Include the publisher’s name, if available, and the year of publication (or date the survey was conducted).
- Medium of Publication: Indicate the medium of the survey, such as print or digital. If accessed online, include the URL or DOI.
By accurately citing a survey conducted by someone else in MLA format, you give credit to the original source and enable readers to locate the survey for further research.
Survey Citation Examples for Various Sources
Citing a survey in MLA format requires adapting the citation depending on the source type. Here are some examples of how to cite surveys from different sources:
- Survey from a Book: Last Name, First Name. “Survey Title.” Book Title, Publisher, Year, Page(s).
- Survey from a Journal Article: Last Name, First Name. “Survey Title.” Journal Title, vol. #, no. #, Year, Page(s).
- Survey from a Website: Last Name, First Name. “Survey Title.” Website Title, Publisher or Sponsor, Date, URL.
- Survey from a Conference Proceedings: Last Name, First Name. “Survey Title.” Conference Title, edited by Editor’s Name(s), Publisher, Year, Page(s).
- Survey from an Online Database: Last Name, First Name. “Survey Title.” Database Name, Publisher, Year, URL or DOI.
Remember to format the citations with appropriate punctuation and italics/underlining for titles. In-text citations should also be used to correspond to the full citations.
By following these examples, you can create accurate and consistent MLA citations for surveys from various sources.
Common Errors to Avoid in Survey Citations
When citing a survey in MLA format, it’s important to be aware of common errors to ensure accurate and properly formatted citations. Here are some common errors to avoid:
- Missing or Incomplete Author Information: Make sure to include the author’s full name (last name, first name) or the organization responsible for the survey.
- Incorrect Formatting of Survey Titles: Use quotation marks for survey titles and italicize or underline the titles of larger works.
- Omitting Publication Information: Include the name of the publisher or sponsoring organization, as well as the publication date or the date the survey was conducted.
- Neglecting to Indicate Medium of Publication: Specify whether the survey was accessed in print or digitally (e.g., Web survey).
- Improper Use of In-text Citations: Ensure that in-text citations include the author’s last name and, if available, the page number where the information was found.
- Inaccurate or Missing URLs or DOIs: If the survey is accessed online, include the URL or DOI to provide a direct link to the survey.
Double-checking your citations for these errors will help ensure that you provide complete and correct information for your survey citations in MLA format.
Sociology Research Topics Ideas
Importance of Computer in Nursing Practice Essay
History Research Paper Topics For Students
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy. We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related emails.
Latest Articles
Why is AI bad for education? Or why do people continue thinking that way? As the digital era continues to...
In today’s digital age, AI tools stand at the forefront of transforming how students approach academic writing. These sophisticated technologies...
Embarking on writing a legal research paper can be a daunting yet intellectually rewarding endeavor. This comprehensive guide aims to...
I want to feel as happy, as your customers do, so I'd better order now
We use cookies on our website to give you the most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits. By clicking “Accept All”, you consent to the use of ALL the cookies. However, you may visit "Cookie Settings" to provide a controlled consent.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA Works Cited: Other Common Sources

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (8 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Several sources have multiple means for citation, especially those that appear in varied formats: films, DVDs, television shows, music, published and unpublished interviews, interviews over e-mail, published and unpublished conference proceedings. The following section discusses these sorts of citations as well as others not covered in the print, periodical, and electronic sources sections.
Use the following format for all sources:
Author. Title. Title of container (self contained if book), Other contributors (translators or editors), Version (edition), Number (vol. and/or no.), Publisher, Publication Date, Location (pages, paragraphs URL or DOI). 2 nd container’s title, Other contributors, Version, Number, Publisher, Publication date, Location, Date of Access (if applicable).
An Interview
Interviews typically fall into two categories: print or broadcast published and unpublished (personal) interviews, although interviews may also appear in other, similar formats such as in e-mail format or as a Web document.
Personal Interviews
Personal interviews refer to those interviews that you conduct yourself. List the interview by the name of the interviewee. Include the descriptor Personal interview and the date of the interview.
Smith, Jane. Personal interview. 19 May 2014.
Published Interviews (Print or Broadcast)
List the interview by the full name of the interviewee. If the name of the interview is part of a larger work like a book, a television program, or a film series, place the title of the interview in quotation marks and place the title of the larger work in italics. If the interview appears as an independent title, italicize it. For books, include the author or editor name after the book title.
Note: If the interview from which you quote does not feature a title, add the descriptor, Interview by (unformatted) after the interviewee’s name and before the interviewer’s name.
Gaitskill, Mary. Interview with Charles Bock. Mississippi Review , vol. 27, no. 3, 1999, pp. 129-50.
Amis, Kingsley. “Mimic and Moralist.” Interviews with Britain’s Angry Young Men , By Dale Salwak, Borgo P, 1984.
Online-only Published Interviews
List the interview by the name of the interviewee. If the interview has a title, place it in quotation marks. Cite the remainder of the entry as you would other exclusive web content. Place the name of the website in italics, give the publisher name (or sponsor), the publication date, and the URL.
Note: If the interview from which you quote does not feature a title, add the descriptor Interview by (unformatted) after the interviewee’s name and before the interviewer’s name.
Zinkievich, Craig. Interview by Gareth Von Kallenbach. Skewed & Reviewed , 27 Apr. 2009, www.arcgames.com/en/games/star-trek-online/news/detail/1056940-skewed-%2526-reviewed-interviews-craig. Accessed 15 May 2009.
Speeches, Lectures, or Other Oral Presentations (including Conference Presentations)
Start with speaker’s name. Then, give the title of the speech (if any) in quotation marks. Follow with the title of the particular conference or meeting and then the name of the organization. Name the venue and its city (if the name of the city is not listed in the venue’s name). Use the descriptor that appropriately expresses the type of presentation (e.g., Address, Lecture, Reading, Keynote Speech, Guest Lecture, Conference Presentation).
Stein, Bob. “Reading and Writing in the Digital Era.” Discovering Digital Dimensions, Computers and Writing Conference, 23 May 2003, Union Club Hotel, West Lafayette, IN. Keynote Address.
Panel Discussions and Question-and-Answer Sessions
The MLA Handbook makes a distinction between the formal, rehearsed portion of a presentation and the informal discussion that often occurs after. To format an entry for a panel discussion or question-and-answer session, treat the panel members or speakers as authors by listing them first. If these people are formally listed as panelists, indicate this by following their names with a comma and the title "panelist(s)." Follow with the title of the discussion, or, if there is no title, a simple description. In the latter case, don't capitalize the description. Follow this with the title of the conference or event. End with the date and the location.
Bavis, Jim and Stein, Tammi, panelists. Panel discussion. Dawn or Doom Conference, 4 Nov. 2018, Stewart Hall, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN.
Treat recorded discussions as instances of the appropriate medium (e.g., if you want to cite a recording of a panel discussion hosted on YouTube, cite it the same way you would cite an ordinary online video ).
Published Conference Proceedings
Cite published conference proceedings like a book. If the date and location of the conference are not part of the published title, add this information after the published proceedings title.
Last Name, First Name, editor. Conference Title , Conference Date and Location, Publisher, Date of Publication.
To cite a presentation from published conference proceedings, begin with the presenter’s name. Place the name of the presentation in quotation marks. Follow with publication information for the conference proceedings.
Last Name, First Name. “Conference Paper Title.” Conference Title that Includes Conference Date and Location , edited by Conference Editor(s), Publisher, Date of Publication.
A Painting, Sculpture, or Photograph
Provide the artist's name, the title of the artwork in italics, and the date of composition. Finally, provide the name of the institution that houses the artwork followed by the location of the institution (if the location is not listed in the name of the institution, e.g. The Art Institute of Chicago).
Goya, Francisco. The Family of Charles IV . 1800, Museo del Prado, Madrid.
If the medium and/or materials (e.g., oil on canvas) are important to the reference, you can include this information at the end of the entry. However, it is not required.
For photographic reproductions of artwork (e.g. images of artwork in a book), treat the book or website as a container. Remember that for a second container, the title is listed first, before the contributors. Cite the bibliographic information as above followed by the information for the source in which the photograph appears, including page or reference numbers (plate, figure, etc.).
Goya, Francisco. The Family of Charles IV . 1800, Museo del Prado, Madrid. Gardener's Art Through the Ages , 10 th ed., by Richard G. Tansey and Fred S. Kleiner, Harcourt Brace, p. 939.
If you viewed the artwork on the museum's website, treat the name of the website as the container and include the website's publisher and the URL at the end of the citation. Omit publisher information if it is the same as the name of the website. Note the period after the date below, rather than the comma: this is because the date refers to the painting's original creation, rather than to its publication on the website. Thus, MLA format considers it an "optional element."
Goya, Francisco. The Family of Charles IV . 1800 . Museo del Prado, museodelprado.es/en/the-collection/art-work/the-family-of-carlos-iv/f47898fc-aa1c-48f6-a779-71759e417e74.
A Song or Album
Music can be cited multiple ways. Mainly, this depends on the container that you accessed the music from. Generally, citations begin with the artist name. They might also be listed by composers or performers. Otherwise, list composer and performer information after the album title. Put individual song titles in quotation marks. Album names are italicized. Provide the name of the recording manufacturer followed by the publication date.
If information such as record label or name of album is unavailable from your source, do not list that information.
Morris, Rae. “Skin.” Cold, Atlantic Records, 2014. Spotify , open.spotify.com/track/0OPES3Tw5r86O6fudK8gxi.
Online Album
Beyoncé. “Pray You Catch Me.” Lemonade, Parkwood Entertainment, 2016, www.beyonce.com/album/lemonade-visual-album/.
Nirvana. "Smells Like Teen Spirit." Nevermind , Geffen, 1991.
Films or Movies
List films by their title. Include the name of the director, the film studio or distributor, and the release year. If relevant, list performer names after the director's name.
Speed Racer . Directed by Lana Wachowski and Lilly Wachowski, performances by Emile Hirsch, Nicholas Elia, Susan Sarandon, Ariel Winter, and John Goodman, Warner Brothers, 2008.
To emphasize specific performers or directors, begin the citation with the name of the desired performer or director, followed by the appropriate title for that person.
Lucas, George, director. Star Wars Episode IV: A New Hope . Twentieth Century Fox, 1977.
Television Shows
Recorded Television Episodes
Cite recorded television episodes like films (see above). Begin with the episode name in quotation marks. Follow with the series name in italics. When the title of the collection of recordings is different than the original series (e.g., the show Friends is in DVD release under the title Friends: The Complete Sixth Season), list the title that would help researchers to locate the recording. Give the distributor name followed by the date of distribution.
"The One Where Chandler Can't Cry." Friends: The Complete Sixth Season , written by Andrew Reich and Ted Cohen, directed by Kevin Bright, Warner Brothers, 2004.
Broadcast TV or Radio Program
Begin with the title of the episode in quotation marks. Provide the name of the series or program in italics. Also include the network name, call letters of the station followed by the date of broadcast and city.
"The Blessing Way." The X-Files . Fox, WXIA, Atlanta, 19 Jul. 1998.
Netflix, Hulu, Google Play
Generally, when citing a specific episode, follow the format below.
“94 Meetings.” Parks and Recreation, season 2, episode 21, NBC, 29 Apr. 2010. Netflix, www.netflix.com/watch/70152031.
An Entire TV Series
When citing the entire series of a TV show, use the following format.
Daniels, Greg and Michael Schur, creators. Parks and Recreation . Deedle-Dee Productions and Universal Media Studios, 2015.
A Specific Performance or Aspect of a TV Show
If you want to emphasize a particular aspect of the show, include that particular information. For instance, if you are writing about a specific character during a certain episode, include the performer’s name as well as the creator’s.
“94 Meetings.” Parks and Recreation, created by Greg Daniels and Michael Schur, performance by Amy Poehler, season 2, episode 21, Deedle-Dee Productions and Universal Media Studios, 2010.
If you wish to emphasize a particular character throughout the show’s run time, follow this format.
Poehler, Amy, performer. Parks and Recreation. Deedle-Dee Productions and Universal Media Studios, 2009-2015.
Begin with the title of the episode in quotation marks. Provide the name of the series in italics. Then follow with MLA format per usual.
“Best of Not My Job Musicians.” Wait Wait…Don’t Tell Me! from NPR, 4 June 2016, www.npr.org/podcasts/344098539/wait-wait-don-t-tell-me.
Spoken-Word Albums such as Comedy Albums
Treat spoken-word albums the same as musical albums.
Hedberg, Mitch. Strategic Grill Locations . Comedy Central, 2003.
Digital Files (PDFs, MP3s, JPEGs)
Determine the type of work to cite (e.g., article, image, sound recording) and cite appropriately. End the entry with the name of the digital format (e.g., PDF, JPEG file, Microsoft Word file, MP3). If the work does not follow traditional parameters for citation, give the author’s name, the name of the work, the date of creation, and the location.
Beethoven, Ludwig van. Moonlight Sonata . Crownstar, 2006.
Smith, George. “Pax Americana: Strife in a Time of Peace.” 2005. Microsoft Word file.
Council of Writing Program Administrators, National Council of Teachers of English, and National Writing Project. Framework for Success in Postsecondary Writing . CWPA, NCTE, and NWP, 2011, wpacouncil.org/files/framework-for-success-postsecondary-writing.pdf.
Bentley, Phyllis. “Yorkshire and the Novelist.” The Kenyon Review , vol. 30, no. 4, 1968, pp. 509-22. JSTOR , www.jstor.org.iii/stable/4334841.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Note: If the book review is from a source other than an article in the library's database, view the appropriate section on the MLA guide to determine how to cite the source after the name of the book's author.
Note: If the book review is from a source other than an article in the library's database, view the appropriate section on the MLA guide to determine how to cite the source. Works Cited List Example Grosholz, Emily R. "Book Review: Realizing Reason: A Narrative of Truth and Knowledge by Danielle Macbeth."
Works may include an essay in an edited collection or anthology, or a chapter of a book. The basic form is for this sort of citation is as follows: Last name, First name. "Title of Essay." Title of Collection, edited by Editor's Name (s), Publisher, Year, Page range of entry. Some examples: Harris, Muriel.
Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Review." Name of Journal, vol. Volume Number, no. Issue Number, Date of Publication, pp.First Page Number-Last Page Number. Name of Database. doi: DOI Number if Given.. Note: If the book review is from a source other than an article in the library's database, view the appropriate section on the MLA guide to determine how to cite the source.
The examples on this page are for book reviews published in academic journals and found through library databases. If the book review is from a different type of source, such as a newspaper or a website , view the appropriate section on the MLA guide to determine how to cite the source.
Proceed title with the words Review of and follow rules of capitalization stated above. Italicize title. Separate from author with a comma. Author of book: by Vendela Vida. Precede name with the word 'by,' then first name and last. End with a period. Title & subtitle of the periodical the review appears in: The New York Times Book Review ...
If the book cover or title page specifies an edition, add the edition number or name, followed by the abbreviation "ed.", after the title. Note that versions of the Bible are treated slightly differently. MLA format. Author last name, First name. Book Title. Edition ed., Publisher, Year.
Book Review - Examples. In-Text: (Powers 10) Works Cited: Powers, Thomas. "The Road to West Egg." Review of Careless People: Murder, Mayhem and the Invention of The Great Gatsby, by Sarah Churchwell, London Review of Books, 4 July 2013, pp. 9-11. NOTE: If a review is untitled, include a title which incorporates the work that is being reviewed:
Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Review." Name of Journal, vol. Volume Number, no. Issue Number, Date of Publication, pp.First Page Number-Last Page Number. Name of Database. doi: DOI Number if Given.. Note: If the book review is from a source other than an article in the library's database, view the appropriate section on the MLA guide to determine how to cite the source.
Cite your book. *Keep "https:" at the beginning of the URL only when citing a DOI. Digital sources with no page numbers means that no page numbers should be included in the in-text citation. In-text Citation. Structure. (Last Names) OR Last Names. Example. (Austen and Grahame-Smith) OR Austen and Grahame-Smith.
How to Cite a Book. To create a basic works-cited-list entry for a book, list the author, the title, the publisher, and the publication date. You may need to include other elements depending on the type of book you are citing (e.g., an edited book, a translation) and how it is published (e.g., in print, as an e-book, online).
A Review. To cite a review, include the title of the review (if available), then the phrase, "Review of" and provide the title of the work (in italics for books, plays, and films; in quotation marks for articles, poems, and short stories). Finally, provide performance and/or publication information.
Adhere to a particular citation style, such as Chicago, MLA, or APA. Put your name at the very end of the book review text. The basic purpose of a book review is to convey and evaluate the following: a. what the book is about; b. the expertise of the author(s); c. how well the book covers its topic(s) and whether it breaks new ground; d.
To cite a review of a product, such as a toaster, follow the examples for citing reviews provided in appendix 2 of the MLA Handbook. How you cite the review will depend on whether it is signed (i.e., whether it lists the author's name or was published anonymously) and on whether it has a unique title.
Elements: Reviewer. Review of Title of Work, by Author.; Title of Journal,; Volume number, issue number, Publication Date, Page number(s). Title of Database,; DOI or ...
To cite a book chapter, first give the author and title (in quotation marks) of the chapter cited, then information about the book as a whole and the page range of the specific chapter. The in-text citation lists the author of the chapter and the page number of the relevant passage. Author last name, First name.
In-text citations: Author-page style. MLA format follows the author-page method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the page number (s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your Works Cited page. The author's name may appear either in the ...
MLA Citation Generator >. Cite a Review. Citation Machine® helps students and professionals properly credit the information that they use. Cite sources in APA, MLA, Chicago, Turabian, and Harvard for free.
Note: The MLA considers the term "e-book" to refer to publications formatted specifically for reading with an e-book reader device (e.g., a Kindle) or a corresponding web application. These e-books will not have URLs or DOIs. If you are citing book content from an ordinary webpage with a URL, use the "A Page on a Web Site" format above.
The Graduate Center does not recommend a single citation style, so follow the style recommended by the professor for your course. If you are writing for a publication, look for the preferred citation style in the author guidelines. In both cases, ask if you are not certain.
Citing a survey in MLA format requires adapting the citation depending on the source type. Here are some examples of how to cite surveys from different sources: Survey from a Book: Last Name, First Name. "Survey Title." Book Title, Publisher, Year, Page(s). Survey from a Journal Article: Last Name, First Name. "Survey Title."
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (8 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.