Just added to your cart


Mastering Essay Plans: Your Guide to Writing Academic Essays
"Unlock the potential of your essays with effective planning. Our guide demystifies the process, making essay writing accessible and achievable."
Navigating through the process of essay writing can often seem daunting. However, the key to writing a good essay lies in effective planning. This guide will take you through the essential steps of creating an essay plan, showing you how to outline your ideas coherently, explore different approaches to planning, and provide practical examples to help you get started. Whether you're a student tackling your first assignment or a seasoned writer looking to refine your technique, these insights will be invaluable.
Understanding the Importance of an Essay Plan Creating an essay plan is more than just a preliminary step in your writing process; it's a critical tool that guides your thinking and organises your ideas. A well-thought-out plan helps ensure that your essay is structured logically, making your arguments more persuasive and your writing more efficient.
5 Steps to Writing an Effective Essay Plan
- Analyzing the Essay Question: Begin by thoroughly understanding the question or topic. Look for keywords and consider what the question is really asking.
- Conducting Preliminary Research: Gather initial thoughts and resources on the topic. This research will form the foundation of your essay.
- Brainstorming Ideas and Arguments: Jot down all your ideas, then start sifting through them to identify the most compelling points.
- Organizing Ideas into a Cohesive Structure: Arrange your main points logically. Decide which arguments will go in the introduction, body, and conclusion.
- Detailing Each Section of the Essay: Flesh out your main points with sub-points and evidence. This step transforms your framework into a detailed guide.
Struggling to get started with your essay plan? Grammarholic's Essay Plan Writing Service offers personalized assistance to help you create structured, effective essay plans. Visit us for expert support in bringing clarity and direction to your essay writing.
Continue to the next section; Writing a Clear Essay Outline
- Share Share on Facebook
- Tweet Tweet on Twitter
- Pin it Pin on Pinterest
Leave a comment
Please note, comments must be approved before they are published
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
- Press the space key then arrow keys to make a selection.

How to plan an essay: Essay Planning
- What's in this guide
- Essay Planning
- Additional resources
How to plan an essay
Essay planning is an important step in academic essay writing.
Proper planning helps you write your essay faster, and focus more on the exact question. As you draft and write your essay, record any changes on the plan as well as in the essay itself, so they develop side by side.
One way to start planning an essay is with a ‘box plan’.
First, decide how many stages you want in your argument – how many important points do you want to make? Then, divide a box into an introduction + one paragraph for each stage + a conclusion.
Next, figure out how many words per paragraph you'll need.
Usually, the introduction and conclusion are each about 10% of the word count. This leaves about 80% of the word count for the body - for your real argument. Find how many words that is, and divide it by the number of body paragraphs you want. That tells you about how many words each paragraph can have.
Remember, each body paragraph discusses one main point, so make sure each paragraph's long enough to discuss the point properly (flexible, but usually at least 150 words).
For example, say the assignment is
Fill in the table as follows:
Next, record each paragraph's main argument, as either a heading or topic sentence (a sentence to start that paragraph, to immediately make its point clear).
Finally, use dot points to list useful information or ideas from your research notes for each paragraph. Remember to include references so you can connect each point to your reading.
The other useful document for essay planning is the marking rubric .
This indicates what the lecturer is looking for, and helps you make sure all the necessary elements are there.
Pathways and Academic Learning Support

- << Previous: What's in this guide
- Next: Additional resources >>
- Last Updated: Feb 15, 2024 1:23 PM
- URL: https://libguides.newcastle.edu.au/essay_planning

Breadcrumbs
How to write a standout graduate admissions essay, article highlights.
- Reflect before you begin your application essays.
- Outline your ideas before you put pen to paper.
- Write freely, and then return to edit your essay on the second draft.
- Take your time. Break between writing and editing for a fresh perspective.
- Gather feedback from a trusted source.
- Read your essay aloud to identify needed edits.
Everyone has a story to tell, and we know there’s more to you and your talents than what’s on your resume. But how will you stand out from the crowd when applying to Johns Hopkins Carey Business School?
The essay portion of the application is your opportunity to expand beyond your transcript and resume. Share your unique strengths, your background, your growth, or whatever else makes you a strong candidate for Johns Hopkins Carey Business School.

In this article, you will find a detailed explanation of how to write a standout admissions essay.
How to prepare
Before you begin writing, read the essay prompts carefully. Take a moment to reflect and explore why you’re pursuing a graduate business degree. Consider having a pen and notepad nearby as you participate in this reflection exercise. Think about your path thus far and pinpoint moments of growth and learning. Take note of how these moments have shaped you and how these experiences will guide you through your graduate business degree at Carey.
Map your ideas:
Now that you have an idea of how to share your story within the context of the essay prompts, it’s time to draft an outline . Map out your key points and outline the supporting examples. As you map the direction and flow of your essay through the outline, keep in mind your audience. Our admissions officers read thousands of application essays, so you want to find a creative hook to make your story stand out.
Don’t overthink it! Start writing:
As you start to write your first draft, let the words flow. At this stage, don’t fixate on grammar or finding the perfect word– just get your thoughts on paper. You will finesse and polish your essay in the second draft.
Share this Article
What to read next.

Take a break:
Once you complete your first draft, take a day or two before returning to edit it. Coming back to your writing with fresh eyes allows you to read it with a new perspective. Tackle the details of grammar, punctuation, and vocabulary during this second pass. Consider reading your essay backward to help catch typos.
Get feedback:
Once you feel your essays are in a good place, it is highly recommended that you share them for review. Share them with your advisor, a trusted colleague, friend, or even your recommender . Getting insights from a trusted source can help you make your essay stronger, as well as catch any typos or small edits.
Finalize and submit:
You are almost done. Before submitting your essays, do a final review. Run a spell check and read the essays out loud to yourself. This trick allows you to identify areas that may need clarification or tweaks. As you review your final draft, make sure that you actually answered the question posed on the application.
Remember, the essay portion of your application is your chance to stand out from the crowd. By sharing who you are as a person, your growth thus far, your passions, your goals, and your voice, you can make a lasting impression. Best of luck with your application process!
Just the facts
Discover related content.

online programs
- How to apply
- How to apply: Full-time MS
- How to apply: Full-time MBA
- 301 Academic Skills Centre
- Study skills online
Essay structure and planning
Information on how to structure and plan your essay.

What is an essay?
An essay is a focused, academic discussion of a particular question, problem or issue.
Many of you have been writing essays for years, and are probably good at it. That's great, and everything you look at here will build on and develop those skills.
But it's worth asking: are there different things expected of a university essay from those for school, college, or other contexts?
The obvious answer is yes, and it takes time and effort to learn the range of writing skills needed to produce university essays effectively.
There are all sorts of reasons why essays are common forms of assessment. They allow you to explore a problem in-depth, express yourself concisely and precisely, and debate other people's published opinions on a topic.
They're also a good warm-up for traditional forms of academic publication, such as a journal article.
Academic essays usually follow an established organisational structure that helps the writer to express their ideas clearly and the reader to follow the thread of their argument.
An essay's structure is guided by its content and argument so every essay question will pose unique structural challenges.
301 Recommends: Glossary of Instruction Words
Our Essay Structure and Planning workshop will outline how to analyse your essay question, discuss approaches logically structure all your ideas, help you make your introductions and conclusions more effective, and teach how to link your ideas and ensure all essay content flows logically from the introduction. The Putting it into Practise workshop
Have a look at our Glossary of Essay Instruction Words (PDF, 100KB) , or watch this short Study Skills Hacks video on identifying the tasks in a question to help you identify what is required.
Planning stages
Essay writing is a process with many stages, from topic selection, planning and reading around, through to drafting, revising and proofreading.
Breaking the task down and creating a clear plan with milestones and intermediate deadlines will allow you to focus attention more fully on the writing process itself when you put your plan into action either as part of an assignment or an exam.
1. Understand the question
- Is the question open-ended or closed? If it is open-ended you will need to narrow it down. Explain how and why you have decided to limit it in the introduction to your essay, so the reader knows you appreciate the wider issues, but that you can also be selective.
- If it is a closed question, your answer must refer to and stay within the limits of the question (ie specific dates, texts, or countries).
- What can you infer from the title about the structure of the essay?
2. Brainstorm for ideas
- What you know about the topic – from lectures, reading etc
- What you don't know about the topic, but need to find out to answer the question
- Possible responses or answers to the question – any ideas about your conclusion.
- Consider using a mind map to organise your thoughts…
3. Make a plan
- Planning your essay makes it more likely that you have a coherent argument
- It enables you to work out a logical structure and an endpoint for your argument before you start writing
- It means you don't have to do this type of complex thinking at the same time as trying to find the right words to express your ideas
- It helps you to commit yourself to sticking to the point!
The Hourglass essay
If you're stuck on an overall structure for your essay, try this simple model for organising a typical academic essay. An hourglass essay introduces a broad area, before narrowing the focus towards the specific question that you are answering. It finishes by placing that narrow area back into a wider context.
Introduction: the funnel of the hourglass
Set the scene and lead your reader into your essay by introducing the broad area of interest and then narrowing towards your specific focus:
- Start broad with a hook to catch the reader's attention
- Provide some context for the hook. What does your project add to it?
- Focus on the narrow area of your essay: can you summarise it in a single sentence mission statement?
Body: the stem of the hourglass
The body of your essay should be as narrow and focused as possible. Body paragraphs will take one sub-topic at a time and provide a logical flow of ideas for your reader:
- Start each paragraph with a topic sentence to tell your reader what it will cover
- Fill your paragraph with a range of supporting evidence and examples
- Finish your paragraph with a final wrapping-up sentence to summarise and/or link ahead
Conclusion: the base of the hourglass
Your chance to reinforce your key messages and go out with a bang:
- Revisit your mission statement: how have you addressed it?
- Summarise the main points of your argument or findings
- Finish with a broader scope, explaining how your topic might inform future research or practice, or where gaps remain
301 Recommends: Essay Planning Template
Use this template (google doc) to plan a structure for your essay, paying particular attention to the ways in which you have broken down the topic into sub-themes for your body paragraphs.
Top tips and resources
- Start planning early, leave your plan for a couple of days, and then come back to it. This may give you a fresh perspective.
- It is often easiest to write the introduction last, but when you are planning your essay structure make sure you have your mission statement.
- A good plan will make it much easier to write a good essay. Invest the time in making a plan that works.
- Check what your tutor wants, but it is often best to focus on one element in great detail, rather than discuss several aspects superficially.
- Make sure you allow time to proofread your work before submission!
Internal resources
- Library Research and Critical Thinking - Referencing
- English Language Teaching Centre (ELTC)– Language Resources
External resources
- Royal Literary Fund– Writing Essays
- University of Reading– Planning and structuring your essay
- Cottrell, S (2008) The Study Skills Handbook. Hampshire: Palgrave Macmillan
- Bailey, S (2003) Academic Writing: A Practical Guide for Students. Routledge
- Reading University– Study Resources
- University of Manchester– Academic Phrasebank
Related information
Academic Skills Certificate
Scientific writing and lab reports
Proofreading

Be the first to hear about our new and upcoming workshops!
The 301 Academic Skills Centre newsletter is a fortnightly email for study skills, mathematics and statistics.
Be the first to find out about our:
- new and upcoming workshops,
- special events and programmes, and
- new and relevant online materials and resources.
Sheffield is a research university with a global reputation for excellence. We're a member of the Russell Group: one of the 24 leading UK universities for research and teaching.
- Start diagramming Start diagramming
Figma design
Design and prototype in one place
Collaborate with a digital whiteboard
Translate designs into code
Get the desktop, mobile, and font installer apps
See the latest features and releases
- Prototyping
- Design systems
- Wireframing
- Online whiteboard
- Team meetings
- Strategic planning
- Brainstorming
- Diagramming
- Product development
- Web development
- Design handoff
- Product managers
Organizations
Config 2024
Register to attend in person or online — June 26–27

Creator fund
Build and sell what you love
User groups
Join a local Friends of Figma group
Learn best practices at virtual events
Customer stories
Read about leading product teams
Stories about bringing new ideas to life
Get started
- Developer docs
- Best practices
- Reports & insights
- Resource library
- Help center
FigJam Build a strong foundation with our essay plan template
No shaky arguments here. Whether it’s a class assignment, personal statement, or a missive on the company blog, FigJam’s essay writing plan will help you construct a stronger essay outline from the ground up.

Essay plan template
Share ideas, hone arguments, and refine your writing with our collaborative essay plan template.

Nail down your message
Organize evidence, strengthen supporting arguments, and hammer your main point home with our essay planning sheet.
Create flow: Maintain a cohesive writing process with an essay planning template that clarifies how one section leads to the next.
Evaluate your argument from all sides: Crystallize your claim and test it out from new angles in a visual format.
Do your research: Fact check your work and sources before writing by laying out supporting evidence on an easy-to-read outline.

FigJam Make a statement together
Writing doesn’t have to be a solo act. FigJam’s Community-built widgets make it easy to draft with collaborators and source feedback from trusted peers. Fold in new ideas and fine-tune existing arguments with Badge, Storymapper, and Lil notes.
Break it down, then build it up
Perfect the nuts and bolts of your essay with a well-organized essay plan example. Next, find new ways to tell your story with templates from our Community.
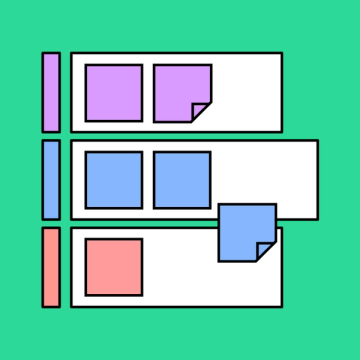
Story mapping
Design a compelling narrative step by step.

Compare and contrast the main points in your essay.
Other templates from the community
Share your message with peers, mentors, and more with interactive templates.
How to write an essay plan?
If you’re wondering how to plan an essay or how to write an effective essay plan with important points and supporting details, just tap into our free essay plan example to get started. From there, you’ll be prompted to break your essay down into the following sections:
- Introduction
- Body paragraph #1
- Body paragraph #2
- Body paragraph #3
Fill in each of these sections with relevant information and credible sources. Then, share it with your trusted collaborators and peers to make sure your argument sings.
What are the 5 aspects of planning an essay?
The 5 aspects of planning an essay correspond to the 5 main sections of your essay: the introduction, the 3 body paragraphs, and the conclusion.
- Introduction – Planning an introduction involves writing a thesis statement and a brief list that outlines the order of your supporting arguments.
- Body paragraphs (3) – As you plan your 3 body paragraphs, you’ll collect evidence—from credible sources—that backs up any supporting detail, arguments, and thesis.
- Conclusion – While you conceptualize this final section, consider how you can open up the floor for further conversation after the essay ends. Are there any related questions you wished you’d asked? What makes this a relevant topic—today? Jot down all of your ideas on a planning sheet for essays.
What is a good structure in an essay?
Many essays follow the classic 5-part structure—the introduction that states your main argument, the 3 points supporting that claim, and the conclusion that wraps everything up.
Keep in mind, however, that you don't have to follow this essay planning example exactly. Some of the best essays break the mold—so don’t be afraid to customize your essay planning sheet or collaborate on a creative structure as you outline.
Other templates you might like
Explore 1,000+ templates on the Figma community
Explore even more templates, widgets, and plugins—all built by the Figma community.

Essay and dissertation writing skills
Planning your essay
Writing your introduction
Structuring your essay
- Writing essays in science subjects
- Brief video guides to support essay planning and writing
- Writing extended essays and dissertations
- Planning your dissertation writing time
Structuring your dissertation
- Top tips for writing longer pieces of work
Advice on planning and writing essays and dissertations
University essays differ from school essays in that they are less concerned with what you know and more concerned with how you construct an argument to answer the question. This means that the starting point for writing a strong essay is to first unpick the question and to then use this to plan your essay before you start putting pen to paper (or finger to keyboard).
A really good starting point for you are these short, downloadable Tips for Successful Essay Writing and Answering the Question resources. Both resources will help you to plan your essay, as well as giving you guidance on how to distinguish between different sorts of essay questions.
You may find it helpful to watch this seven-minute video on six tips for essay writing which outlines how to interpret essay questions, as well as giving advice on planning and structuring your writing:
Different disciplines will have different expectations for essay structure and you should always refer to your Faculty or Department student handbook or course Canvas site for more specific guidance.
However, broadly speaking, all essays share the following features:
Essays need an introduction to establish and focus the parameters of the discussion that will follow. You may find it helpful to divide the introduction into areas to demonstrate your breadth and engagement with the essay question. You might define specific terms in the introduction to show your engagement with the essay question; for example, ‘This is a large topic which has been variously discussed by many scientists and commentators. The principle tension is between the views of X and Y who define the main issues as…’ Breadth might be demonstrated by showing the range of viewpoints from which the essay question could be considered; for example, ‘A variety of factors including economic, social and political, influence A and B. This essay will focus on the social and economic aspects, with particular emphasis on…..’
Watch this two-minute video to learn more about how to plan and structure an introduction:
The main body of the essay should elaborate on the issues raised in the introduction and develop an argument(s) that answers the question. It should consist of a number of self-contained paragraphs each of which makes a specific point and provides some form of evidence to support the argument being made. Remember that a clear argument requires that each paragraph explicitly relates back to the essay question or the developing argument.
- Conclusion: An essay should end with a conclusion that reiterates the argument in light of the evidence you have provided; you shouldn’t use the conclusion to introduce new information.
- References: You need to include references to the materials you’ve used to write your essay. These might be in the form of footnotes, in-text citations, or a bibliography at the end. Different systems exist for citing references and different disciplines will use various approaches to citation. Ask your tutor which method(s) you should be using for your essay and also consult your Department or Faculty webpages for specific guidance in your discipline.
Essay writing in science subjects
If you are writing an essay for a science subject you may need to consider additional areas, such as how to present data or diagrams. This five-minute video gives you some advice on how to approach your reading list, planning which information to include in your answer and how to write for your scientific audience – the video is available here:
A PDF providing further guidance on writing science essays for tutorials is available to download.
Short videos to support your essay writing skills
There are many other resources at Oxford that can help support your essay writing skills and if you are short on time, the Oxford Study Skills Centre has produced a number of short (2-minute) videos covering different aspects of essay writing, including:
- Approaching different types of essay questions
- Structuring your essay
- Writing an introduction
- Making use of evidence in your essay writing
- Writing your conclusion
Extended essays and dissertations
Longer pieces of writing like extended essays and dissertations may seem like quite a challenge from your regular essay writing. The important point is to start with a plan and to focus on what the question is asking. A PDF providing further guidance on planning Humanities and Social Science dissertations is available to download.
Planning your time effectively
Try not to leave the writing until close to your deadline, instead start as soon as you have some ideas to put down onto paper. Your early drafts may never end up in the final work, but the work of committing your ideas to paper helps to formulate not only your ideas, but the method of structuring your writing to read well and conclude firmly.
Although many students and tutors will say that the introduction is often written last, it is a good idea to begin to think about what will go into it early on. For example, the first draft of your introduction should set out your argument, the information you have, and your methods, and it should give a structure to the chapters and sections you will write. Your introduction will probably change as time goes on but it will stand as a guide to your entire extended essay or dissertation and it will help you to keep focused.
The structure of extended essays or dissertations will vary depending on the question and discipline, but may include some or all of the following:
- The background information to - and context for - your research. This often takes the form of a literature review.
- Explanation of the focus of your work.
- Explanation of the value of this work to scholarship on the topic.
- List of the aims and objectives of the work and also the issues which will not be covered because they are outside its scope.
The main body of your extended essay or dissertation will probably include your methodology, the results of research, and your argument(s) based on your findings.
The conclusion is to summarise the value your research has added to the topic, and any further lines of research you would undertake given more time or resources.
Tips on writing longer pieces of work
Approaching each chapter of a dissertation as a shorter essay can make the task of writing a dissertation seem less overwhelming. Each chapter will have an introduction, a main body where the argument is developed and substantiated with evidence, and a conclusion to tie things together. Unlike in a regular essay, chapter conclusions may also introduce the chapter that will follow, indicating how the chapters are connected to one another and how the argument will develop through your dissertation.
For further guidance, watch this two-minute video on writing longer pieces of work .
Systems & Services
Access Student Self Service
- Student Self Service
- Self Service guide
- Registration guide
- Libraries search
- OXCORT - see TMS
- GSS - see Student Self Service
- The Careers Service
- Oxford University Sport
- Online store
- Gardens, Libraries and Museums
- Researchers Skills Toolkit
- LinkedIn Learning (formerly Lynda.com)
- Access Guide
- Lecture Lists
- Exam Papers (OXAM)
- Oxford Talks
Latest student news
CAN'T FIND WHAT YOU'RE LOOKING FOR?
Try our extensive database of FAQs or submit your own question...
Ask a question
- DACA/Undocumented
- First Generation, Low Income
- International Students
- Students of Color
- Students with disabilities
- Undergraduate Students
- Master’s Students
- PhD Students
- Faculty/Staff
- Family/Supporters
- Career Fairs
- Post Jobs, Internships, Fellowships
- Build your Brand at MIT
- Recruiting Guidelines and Resources
- Connect with Us
- Career Advising
- Distinguished Fellowships
- Employer Relations
- Graduate Student Professional Development
- Prehealth Advising
- Student Leadership Opportunities
- Academia & Education
- Architecture, Planning, & Design
- Arts, Communications, & Media
- Business, Finance, & Fintech
- Computing & Computer Technology
- Data Science
- Energy, Environment, & Sustainability
- Life Sciences, Biotech, & Pharma
- Manufacturing & Transportation
- Health & Medical Professions
- Social Impact, Policy, & Law
- Getting Started & Handshake 101
- Exploring careers
- Networking & Informational Interviews
- Connecting with employers
- Resumes, cover letters, portfolios, & CVs
- Finding a Job or Internship
- Post-Graduate and Summer Outcomes
- Professional Development Competencies
- Preparing for Graduate & Professional Schools
- Preparing for Medical / Health Profession Schools
- Interviewing
- New jobs & career transitions
- Career Prep and Development Programs
- Employer Events
- Outside Events for Career and Professional Development
- Events Calendar
- Career Services Workshop Requests
- Early Career Advisory Board
- Peer Career Advisors
- Student Staff
- Mission, Vision, Values and Diversity Commitments
- News and Reports
Graduate School Application Essays
- Share This: Share Graduate School Application Essays on Facebook Share Graduate School Application Essays on LinkedIn Share Graduate School Application Essays on X
Types of Essays
Regardless of the type of school you are applying to, you will be required to submit an admissions essay as part of the application process. Graduate programs want students with clear commitment to the field. Essay prompts typically ask applicants to discuss their previous experience, future professional goals, and how the program can help them in achieving those objectives. The essay gives the applicant the chance to articulate these goals and display strong writing skills. Remember to tailor your essay to each school and the faculty committee that reviews your application. But first, take note of what kind of essay is being requested of you. Here are the two main admission essays:
Personal Statement
A personal statement is a narrative piece describing how your character and experiences have formed you into someone who will contribute positively and effectively to not only the department but the academic discipline as a whole. This is often achieved by detailing social, educational, cultural, and economic obstacles you have overcome in your journey to get to where you are today and your future objectives. A personal statement is also an opportunity to highlight what is unique about you and how you will advance diversity within the institution.
Check out Personal Statement Resources for Graduate School Applications in the Resources section of Handshake for a brainstorming activity and essay samples that can help you get started on your personal statement.
Statement of Purpose
Interchangeably called a “research statement”, a statement of purpose will prompt you to describe your research interests and professional goals, how you plan to accomplish them, and why a specific program is best suited for you to do so. Be specific about your specialized interests within your major field. Be clear about the kind of program you expect to undertake, and explain how your study plan connects with your previous training and future goals.
Use the Outlining Your Statement of Purpose guide in the Resources section of Handshake to get started on your statement outline.
How to Write a Powerful Admission Essay
Whatever required format, your essay should be thoughtful, concise, compelling, and interesting. Remember, admissions officers read hundreds of personal essays. Below are some tips for your admissions essay writing process:
Before Writing
- Read the question: Be sure you are aware of all aspects of the prompt. Failing to pay attention to details in the prompt won’t reflect well on you as a potential candidate.
- What is distinct, special, and/or impressive about me and my life story?
- Have I overcome any particular hardships or obstacles?
- When did I become interested in this field and what have I learned about it?
- What are my career goals?
- What personal traits, values, and skill sets do I have that would make me stand out from other applicants?
- Create an outline: You might have a lot that you want to say, but you will need to whittle down your many thoughts and experiences to a concrete thesis with a select number of examples to support it. Create an outline for your draft, not only to organize your points and examples, but to help tailor your essay for your readers.
- Know your audience: Consider how your narrative can best meet the expectations of admissions committee members. Will faculty be reading this? Administrators? Experts in the field? Knowing your audience ahead of time will assist you in addressing the prompt appropriately.

While Writing
- Grab your reader’s attention: Start your essay with something that will grab the reader’s attention such as a personal anecdote, questions, or engaging depiction of a scene. Avoid starting things off with common phrases such as “I was born in…” or “I have always wanted to…” Consider the experiences that have shaped you or your career decision, and delve into them with a creative hook.
- Write well: Your essay is a sample of your writing abilities, so it’s important to convey your thoughts clearly and effectively. Be succinct—you don’t need to write out your full autobiography or resume in prose. Exclude anything that doesn’t support your thesis. Gentle humor is okay, but don’t overdo it. Also, don’t make things up! Be honest about your experiences.
- End strong: End your essay with a conclusion that refers back to the lead and restates your thesis. This helps unify your essay as a whole, connecting your detailed experiences back to the reason you are writing this essay in the first place—to show your qualifications for your graduate program of choice.
Final Touches
- Use resources: The MIT Communication Labs have a CommKit that collects all of the Comm Lab resources relevant to the grad application process , including recommendation letters & interviews
- Revise: Give yourself enough time to step away from your draft. Return with a fresh pair of eyes to make your edits. Be realistic with yourself, not your harshest critic. Make a few rounds of revisions if you need.
- Ask for help: Have your essay critiqued by friends, family, educators, and the MIT Writing and Communication Center or our Career Services staff.
- Proofread: Read your essay out loud or even record yourself and listen to the recording, to help you catch mistakes or poor phrasing you may have missed when reading to yourself. Also, don’t rely exclusively on your computer to check your spelling.
Guidelines for master's essay
The essay is a scholarly paper written in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the master's degree under the Plan B option. As such it should be well organized and carefully developed. Students planning to write an essay should consult with their advisor. An advisor's approval of both topic and a preliminary outline of the essay should be obtained before proceeding further.
There is no prescribed format for the text of the master's essay. A list of departmental style preferences is listed below . See the sample title sheet for essay for specific format instructions.
Submission of essays and deadlines
The title page of the essay, signed by the advisor, should be submitted to the College of Liberal Arts and Sciences Graduate Office, 2155 Old Main, no later than the deadline date established for the semester in which the student expects to graduate. The deadlines will be posted on the CLAS website prior to each semester. The title page can be delivered as hardcopy, preferred submission is as a PDF to [email protected] .
Registration for essay direction
Three hours of Master's Essay Direction (7999) are required for the degree. They may be taken in one semester or spread over two or three semesters. Students should try to organize their time so that their essay is complete by the time they have completed their third credit of essay direction.
Inquiries relating to these guidelines or to graduation requirements generally may be directed to the Liberal Arts and Sciences Graduate Office at 313-577-2516 or [email protected] .
Departmental style preferences
- Application Requirements
- Student Experience Q&A
- Business Analytics Certificate
- Finance Certificate Programs
- Tuition & Financial Aid
- International and Transfer Students
- Military Friendly
- How to Apply
- Accreditation
- Leadership Development Resources
- MBA Career Outcomes
- MSBA Career Outcomes

Grad School 101: Tips for Writing Your Admissions Essays
Like any business professional knows, planning ahead and being prepared are key factors that contribute to whether or not a graduate student’s application is strong enough to potentially earn them a space in a rigorous and respectable program.
You’re not an undergraduate student anymore, and putting off all of your application materials until the night before simply won’t cut it in graduate school—especially not when it comes to those most frightening of application materials: your admissions essays .
Thankfully, regardless of how many essays you need to complete for your application, there are several steps you can take to ensure your essay is as strong as it needs to be.

Essays can play a major role in the university’s admissions decisions, so any way to give yourself the advantage can make all the difference. By following our steps above, you can ensure your essay is in stronger shape and is better able to differentiate you from the pool of other candidates applying to the program as well.
But, if you’re still in doubt, remember to reach out to your Admissions Advisor or school coordinator with any questions or concerns!
If you’ve submitted your graduate school essay already, you might want to get ahead in the game by reviewing how to prepare for the video interview for admissions.
And if you want to learn about the William & Mary’s online business degrees from someone in the program already, hear from some of our current students as they discuss the rigor of the W&M program and the flexibility of earning an MBA, MSBA or MSM online .
Return to Online Business Blog
William & Mary has engaged Everspring , a leading provider of education and technology services, to support select aspects of program delivery.

How to write a Master's Essay

In view of writing a master’s essay, if academic writing is strange to you or you have never done it before, the prospect of choosing a topic, researching on it, and writing an academic essay can be daunting.
While some imagine that they can take their undergraduate-level writing skills and turn them into a magic wand to ace master’s level assignments, sometimes it doesn’t just cut it. A master’s level essay, for instance, requires a deeper level of independent reasoning, which is best achieved through the tips that we’ve tested, applied, and scored better grades ourselves.
Writing a master’s level assignment follows a step-by-step approach that commences from understanding the assignment to submitting the assignment. Each step is very significant, so try and take some of your time to skim through.
However, if at this point all you want is master’s essay writing help, you can trust our experienced essay writers. They are well-versed in research, writing, and polishing graduate-level assignments.
Undergraduate essay writing vs. Master’s Essay Writing
This guide can be used as an academic essay writing bible for postgraduates. We have refined everything to help you draft, craft, and revise essays at that level when completing your Master’s degree.
We intend to make you write outstanding master’s level essays that meet the expectations of your professors. Remember, when writing your essays, you should draw intellectual findings from texts written by authority researchers in your field, primary data gathered and manipulated by yourself, and logical reasoning.
Besides that, you also need to ensure that your writing demonstrates a high level of mastery, dominance, and intellectual acuity. Here are some things your essay should portray to differentiate it from undergraduate level work:
1. Show mastery
At the graduate level, it is vital that your writing demonstrated mastery of your subject. For this reason, ensure that you have contextualized the topic and arguments as you meticulously reference scholarly academic sources. In addition, refer to theoretical propositions, paradigms, norms, and themes within your chosen discipline.
2. Let the scope of your paper be known off the bat
It is also helpful that you define and delineate the scope of your graduate paper early enough. While a thesis statement ideally does this, your introduction should conclusively point out your position given the topic or subject area.
A well-defined scope shows that you’ve mastered your academic writing and possess appropriate knowledge in the field – it announces your mastery. Therefore, you must contextualize a given idea when defining your scope.
3. Display independence of thought
Although you need to ensure that your graduate essay has a flow of ideas and demonstrates proficiency, you can only achieve that through the lucid description, evaluation, arguments, and analysis. Doing so shows that you can interpret, understand, critique, and present issues from a peculiar perspective.
As you put your fingers to the keys to write that piece, ensure that you challenge any assumptions and explain the rationale for your stance.
4. Use conceptual thinking and critical reasoning.
While the temptation of critiquing academic literature might creep in, avoid the temptation. Instead, ensure that your arguments are well-interpreted, devoid of bias, and show genuine conceptual engagement from the word go.
5. Have a compelling conclusion
When making claims – persuasive or argumentative, ensure that you draw plausible conclusions. There is no reason to write an entire essay, only to realize later that it is not balanced and ideas are stiff. Instead, by weighing evidence, you can analyze the arguments, develop and defend your position. Then, once you can read your master’s level essay and convince yourself you have nailed it – your audience will be convinced too.
6. Maintain substantial originality/authenticity
As a rule of thumb, you are supposed to acknowledge your sources. Therefore, when writing a graduate and postgraduate essay, you need to display your field knowledge.
One way of doing so is through reading and reporting what is written. You can also achieve the same through evaluating and criticizing, where appropriate.
You can cite publications in your field through summarizing or direct quotations, which entails acknowledging the sources by providing in-text citations and references or bibliography at the end of your assignment.
Although citing and referencing is both arbitrary and complex, it makes you develop better arguments and avoid plagiarism. On the other hand, you do not want to present another person’s work as your own because it is not helpful, you need to develop your conclusion based on research, and it is against the academic regulations.
In as far as master’s level essay is concerned, avoid:
- Changing some sentences off a text while maintaining vocabulary and structure of the original text
- Paraphrasing ideas but mixing original content from a text
- Using phrases or quotes of a text because they are sound
- Using an argumentative organization of an author because it seems plausible
- Direct copying of content from a source
- Making small changes to a paragraph drawn from a source
- Fixing phrases from a source and piecing them to make an argument
Any of the above revokes the authenticity and originality of your essay. Some of the verbs you can use when reporting the findings or ideas from authors include: claim, speculate, hold, opine, assume, assert, comment, contend, suggest, discuss, report, note, argue, state, show, demonstrate, refute, point out, and many other essay and assignment words and phrases as we have outlined elsewhere in our blog.
At the undergrad level, you scored top grades on essays due to evidence of genuine originality. On the other hand, at a master’s level, you must routinely show originality. It is a means of showing academic perspicacity. Therefore, ensure that you present ideas as per the academic norms.
7. Display excellent research skills
Your academic paper must demonstrate that you researched well. When writing a master’s essay, ensure that you support the arguments with recent research. Maintain using recent sources unless you need primary research conducted in the past for relevance. Sometimes trends do change, and referencing old studies could lead to inaccurate conclusions.
You can extend your scope of reading beyond the list provided by your lecturers. Find scholarly sources that support or refute your arguments and incorporate them as well.
8. Maintain all the academic standards
Academic writing has its conventions : always strive to achieve them. Use the appropriate tone, language, and referencing style. If a paper requires that you use Harvard, APA, MLA, and Chicago/Turabian format, stick to the tenets of each citation.
9. Observe the 3 Cs
When writing your essay, stick to the 3 Cs: clarity, conciseness, and consistency. Ensure that your main points in the essay are clear. Ensure that you use the concise presentation of ideas instead of using long run-on sentences that make no sense. Avoid fillers and keep your writing as simple as possible. If possible, you can use headings and subheadings but maintain academic conventions.
10. Immaculate organization and presentation
Although trivial, a disorganized and poorly presented essay can cost you your grades. Therefore, ensure that you demonstrate professionalism by maintaining a good flow from introduction to conclusion.
Balance ideas in your paragraphs by maintaining each idea per paragraph. Use transition words to knit together the various paragraphs and maintain flow. You can as well use signal words to make your essay academically sound.
11. Strong editing and proofreading skills
Finally, after all, is said and done, edited and proofread, the essay scores better grades than that which is hurriedly submitted. Check for all the punctuation mechanistic, grammatical, and spelling mistakes. Although basic, such errors can cost you big time. A linguistically sound master’s essay will score the best grades; that’s a given. You can use editors and proofreaders to polish your essay if you are not confident.
Step-by-step process of writing a master’s level essay (assignment)

In a nutshell, while writing a graduate-level essay essentially follows the steps you took during your undergraduate, you need to go the extra mile to convince your professor to give you top grades. The process begins by reading the instructions, internalizing them, researching and drafting, and finally editing and submitting. Below is a detailed step-by-step process to write your Master’s, MBA, or Ph.D. essay and get a good grade.
Step 1 – Understand the instructions.
It would help if you commenced writing the essay by understanding the instructions for the assignment. To do so, read the prompt, rubric, and any accompanying material from your instructor. The assignment description files have everything you will need. If something is not clear, you are always encouraged to ask your instructor early enough before the deadline. In most cases, the class announcements will have clarifications for various assignments. While reading the instructions, identify the verbs, key terms, and referencing instructions.
Step 2 – Create an outline or plan.
With the description decoded, you must take your time to get immersed into your paper. Of course, by now, you have settled for a topic or made a selection of the question that your essay or paper is going to handle.
Therefore, you need to decide what your main argument, the paper's focus, will be about. With this information, you then create a preliminary thesis statement. You need to ask yourself:
- What are my main ideas in this paper?
- How do these ideas support my main argument or the thesis statement?
Doing this helps contextualize research, determine the scope of your paper, and know what to put where in your essay.
Along with the thesis, plan on the type of hook you will integrate into the introduction to enthuse your audience to want to read your essay.
It would help if you then created an outline for your essay, noting down the main points that fall in your essay's introduction, body, and conclusion. Note that, as you become skilled in academic writing, you might often get the temptation of ignoring the planning aspect and going straight to looking for resources for your paper. When such happens, overcome it and do the step.
Step 3 – Come up with a thesis statement.
When creating the preliminary essay or research paper plan, you already have a preliminary thesis statement. Therefore, you only need to polish it to define the scope and direction of your paper strongly.
Remember, a strong thesis statement gives your readers and yourself clear scope of what you are discussing in the paper. For instance, if you are writing about why a certain municipality should eliminate feral cats from the arboretum, you need to identify the ethical method to be used and justifiable reasons for the method.
To write a great thesis statement, think about how you would describe the paper to a layperson or total stranger in one or two sentences. If you have a hard time doing so, you probably need to revisit and refine the thesis.
Step 4 – Research your topic.
As you advance through writing your essay, you need to determine the type of essay that you’ll be writing. For example, is it expository , argumentative , persuasive, analytical, narrative , compare and contrast , or descriptive?
Understanding the type of paper you are writing further helps you know the resources to use when supporting or refuting your stance/arguments. Some papers require gathering and analyzing primary data; make sure you have factored in that one too.
You can then look for books, journal articles, policy briefs, statistical data, newspapers, blogs, legislation, white papers, conference proceedings, periodicals, government documents, and organizational publications. Understand what is scholarly and non-scholarly when searching for sources to use. Also, understand whether a source is primary, secondary, or tertiary and determine its suitability for your paper.
You can begin your search in Google, then proceed to Google Scholar, institutional database, and specialized databases, in that order. This enables you to understand your research, add to your outline to refine it further, and develop better arguments.
Step 5 – Refine your outline.
Now that you’ve gathered the correct data and organized the references using either Word Document or online referencing tools like Citation Machine, BibMe, Citefast, or citethisforme, you need to finalize your outline.
You will be adding flesh to it using the new information from your thinking and research. As you fill in the outline, ensure consistency and sound logic, and flow in your plan from sentence to paragraph level.
Remember, academic paragraphing demands that you discuss only one idea per paragraph. You should also have topic sentences, conclusion sentences, and supporting facts. You also have to use transitions.
Step 6 – Revisit the research.
You then need to double-check your research resources to determine if they still support the thesis. For example, if you rephrased and changed the thesis statement, you need to do further research. As you do this, ensure that your paper is flowing well. Do not mix ideas in the name of filling the pages; this might affect your grades.
Step 7 – Write the first draft.
With the refined outline, you can start writing the first draft of your essay. But, first, ensure that you have all the information needed to organize the flow of your paper.
As you write the paper at this point, do not perfect it so much for later. A draft is supposed to be what its name is, a piece that will be refined later.
Most of your time will be spent drafting the paper. Be wary of writers’ block because it is at this point that it creeps into you uninvited.
Step 8 – Be wary of writer’s block (plan well).
Now, everybody suffers writers’ block when they are working on a paper. How each person handles theirs is what differs. However, when you realize that writer’s block has affected you:
- Take a break from writing. You can do other things like walking, riding a bike, taking a nap, or swimming to relieve the thought and pressure of a paper.
- Manage your time well so that you do not stress over a last-minute essay.
- Check whether you have sufficient information or too much information and come up with a strategy.
- Seek help from a trustworthy writing website – one where you and the writer work hand-in-hand.
- Listen to music
- Brainstorm on how to improve your writing
- Spend time with people who bring the best out of you
- Brew some coffee
- Ask help from your writing center; they can help you get relevant material
The goal is to stay focused. Any way you can achieve these counts at the end of the day.
Step 9 – Revise the draft.
With the preliminary draft in place, you need to revise and edit it to make it a final draft. Here, you should check:
- Flow of ideas
- Logic and arguments
This means that you will be mostly rewriting, rewording, paraphrasing, and adding as well as deleting sections. As you revise, ask yourself:
- Is the essay answering the questions in the prompt?
- Do I meet the higher band in the essay rubric?
- Does the paper require a major revision such as deleting, moving, reworking, or paraphrasing a section?
- Does the content support the thesis statement?
- Is there a logical flow in the paper?
- Is the paper grammatically sound?
- Are the paragraphs logical?
- Does each paragraph maintain only one idea?
- Is the work well-cited?
- Are all the direct quotes balanced and cited?
Step 10 – Edit your Draft
You need to edit the paper for a top grade. Otherwise, all the effort will be in vain. Here are some things to do when editing your master’s essay:
- Highlight the thesis statement. It is either the last sentence or the last two sentences.
- Check whether the topic sentences of each paragraph support, expand, or explain the thesis statement.
- Review the assignment instructions and determine whether your written piece meets the requirements.
- Sparingly use direct quotations. For example, for a 1000-words essay, you can use one or two direct quotes. However, use parenthetical citations as they show your level of analysis and critical thinking.
- Ensure that the in-text citations are consistent with your chosen formatting style.
- Ensure that the cover page follows the chosen format.
- Make use of spell-checker and grammar checkers to refine the arguments and maintain flow.
- Reword all the sentences that begin with there is; there are, this is, it is, they are… etc. Reword these sentences to make them begin with a stronger subject. For example, “There are five critical factors to consider” can be better stated as “Five important factors require consideration.” The second sentence is stronger because it has a specific subject and verb. Some sentences cannot be reworded, so leave those as they are.
- Edit random paragraphs in the paper to focus on what is actually on the page versus what you think is there.
- Read each paragraph aloud. You will be surprised how many minor errors you can catch with this method of self-editing. For example, errors like mistyping “form” instead of “from” or “hen” instead of “then” are easier to find when you read out loud.
When editing the paper, focus on the thesis, purpose, audience, organization and flow, ideas (examples, citations, and evidence), sentence structuring, punctuation, word choice, spelling, and grammar.
Step 11 – Prepare the Final Draft
Now that everything is in its rightful place, you need to do the last ritual before submitting the paper.
- Create a relevant cover page for your essay
- Compare the final essay against your outline or essay plan
- Check if the changes you made still make the paper relevant to the instructions
- Fix all the minor errors
- Read the paper loud
- Allow someone to revise, edit, and proofread your paper. Gradecrest has the best editing and proofreading services .
- Ensure that the paper reflects your understanding and knowledge of the subject matter
Step 12 – Submit the Right Assignment
Countercheck your assignment to ensure that the instructions are followed. Also, check that every detail is covered as per the rubric. For example, your personal information should be on the first page, as per your recommended cover page and format.
If everything is okay, click on the submit button. Most institutions have integrated plagiarism checkers to check every submission. If you wrote your essay from scratch or had help from an expert, you need not worry about plagiarism. Otherwise, avoid pre-written essays as they are full of plagiarism.
There you go, sit back, relax, and wait for that good grade.
Parting Shot
Writing a master’s essay is not a walk in the park. At first, it might seem like a distant idea, but soon as you master the steps above, you can even write an 8-page essay in a day. It is possible; our expert essay writers do this when you pay them to write your essays.
Now, we hope that these insights will enable you to perfect your essay writing skills. You can as well check our general essay writing guide for details we probably missed in this guide.
Otherwise, if you have any questions or need help, do not hesitate to reach out to us.

Gradecrest is a professional writing service that provides original model papers. We offer personalized services along with research materials for assistance purposes only. All the materials from our website should be used with proper references. See our Terms of Use Page for proper details.

Login or sign up to be automatically entered into our next $10,000 scholarship giveaway
Get Started
- College Search
- College Search Map
- Graduate Programs
- Featured Colleges
- Scholarship Search
- Lists & Rankings
- User Resources
Articles & Advice
- All Categories
- Ask the Experts
- Campus Visits
- Catholic Colleges and Universities
- Christian Colleges and Universities
- College Admission
- College Athletics
- College Diversity
- Counselors and Consultants
- Education and Teaching
- Financial Aid
- Graduate School
- Health and Medicine
- International Students
- Internships and Careers
- Majors and Academics
- Performing and Visual Arts
- Public Colleges and Universities
- Science and Engineering
- Student Life
- Transfer Students
- Why CollegeXpress
- $10,000 Scholarship
- CollegeXpress Store
- Corporate Website
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- CA and EU Privacy Policy
Articles & Advice > Graduate School > Articles

3 Great Grad School Application Essay Examples
The grad school personal statement is an important part of your application. Here are a few good graduate admission essay examples to inspire you.
by CollegeXpress
Last Updated: Jan 3, 2024
Originally Posted: Jun 15, 2017
Graduate school application essays, personal statements, and letters of intent can be a major hurdle to overcome in the application process. Getting just the right words on paper to convey why you want to go to grad school and the impact you intend to have using your degree is a lot to ask. To help you get some inspiration and tell your story the right way, check out these three essay examples. Every essay here comes from a successful grad school application, and after reading the essay we break down just what makes it good. And you’re going to love their stories.
Daniel Masciello, Juris Doctor
University of Connecticut Class of 2015
T ry. To get. Some. Slee—it’s no use.
It’s 3:00 am, 90 minutes before our day at work in the landfills of rural Thailand is set to begin, and the 60-watt bulb is still shining bright overhead. It is radiant.
Directly on my left is one grown man’s bare armpit; to my right is more of the same. I keep my nose pointed at the ceiling. I can’t lift my arms because I am too big, a Caucasian beetle trying to fit into this Thai ant colony.
I’ve been lying still for the better part of six hours now, unable to determine exactly why my host family insists on leaving the brightest light in the house on all night (to this day, still a mystery). It is not for a child’s sake; I, at 22 years old, am the youngest in the home. I’m also the only American. Five grown men, lined up snugly on a queen-sized mattress, are soundly sleeping while I contemplate excuses for not working in the landfill that day.
Twelve hours later, over sticky rice and “fresh” vegetables (from the landfill), I try to call out some of my bunkmates for being afraid of the dark. Nobody laughs at my jokes, but they don’t stop smiling either. Perhaps they don’t understand my infantile Thai. From what I can understand of them, they enjoy talking about how grumpy I’ve been all day. No sleep for some 60-odd hours and putting in two grueling days in the landfill, filtering through mountains of trash from the nearby city of Khon Kaen, looking for yogurt containers and car batteries in the hot Thai sun—these things can change a man’s general disposition.
But I did wake up and go to work with my host family. No, I was not prepared physically or mentally, nor was I in the best of moods that day. But the smiling way of the Thai people is infectious, and it wasn’t long before I was smiling too that night, stomach full and ready for more...
That was back in the fall of 2008. The study abroad program I was participating in revolved around studying specific issues (damning rivers, mining minerals, razing slums, etc.), staying with a village that was negatively affected by an issue, and then working to help solve the problem. It was not uncommon to have sessions lasting eight or nine hours just to prepare for a town meeting the next day. Free time after exchanges and interviews would be spent working in the fields with the villagers or perhaps working on our program’s publications. It was not your typical study abroad experience. I have yet to learn of another like it.
It was also challenging at times. Thailand changed my view on a lot of things for the better, including what it means to truly work hard. As a waiter back home, it was a routine practice to work 40 hours a week in addition to going to class and studying. Still, sometimes I wonder if I used jobs outside of class as a crutch. I always had the excuse: I have to work to support myself. But so do a lot of people. And for some of those people, like many of the villagers in Thailand, working extra hours is not temporary. It's a way of life.
At the time I'm not sure I truly appreciated the privilege I had of going to college, as my undergraduate GPA might indicate. Part of that disappointing number is that I feel as if I was afraid of putting 100% of my effort into school. If I was to put all my effort in and still get mediocre grades, I would have considered myself a failure. Apparently I couldn’t or refused to handle that. How cowardly, not to mention foolish!
But while I was in Thailand, I developed a confidence in myself that I simply hadn’t been able to locate before. On multiple occasions I tasted the failure that comes with studying complex issues in a foreign land. Each time it tasted horrible. But I worked on these failures.
For example, I nagged my homestay families to help me with my Thai and forced myself to request constructive criticism in a group setting. Through these trials I discovered the sweetest feeling of them all: perseverance. That meal next to the landfill, described above, was one of the most deliciously memorable meals of my life for that same reason. I was exhausted and maybe a little bit grumpy, but I learned to work through it—and smile too.
I am well aware that law school will probably force me to even further revise my definition of hard work and present challenges and setbacks the likes of which I may not have yet experienced. But I would like to face these challenges, and most importantly overcome them, at your school. I hope my letters of recommendation and LSAT score give the indication that I am capable of doing so. This essay, lastly, is a chance for me to convince you that I can and will. I look forward to hearing from you.
Why this essay is great
Try to stop reading this personal statement, we dare you. The introduction grabs you and doesn’t let go. But besides spinning a great yarn that also says a lot about Daniel’s values, this application essay has an important function: it thoughtfully and maturely addresses any concerns the graduate admission committee might have regarding Daniel’s undergraduate academic performance. Showing rather than telling, he depicts a person who is prepared to do the work to overcome obstacles and learn from mistakes. And since he was admitted to the grad program, clearly it worked.
Related: How to Know If Law School Is Right for You
Bridget Sullivan, Master of Arts in Higher Education Administration
Boston College Class of 2017
I did not know higher education existed as a field until I came to college. Despite this, it has surprisingly been the field that has had the largest impact on my college experience. It has given me direction going forward.
College has been my most important experience so far, in that it has allowed me to better understand how I interact with my environment and how others experience the world around them. Without the Student Affairs professionals I have interacted with over the past four years, I would not be where I am today. I hope that in my future as a Student Affairs professional I can give students the great experience I have been privileged to receive. I will take the lessons I have learned and those that I will learn in the future to improve the college experience for many future generations going forward.
I have enjoyed being a Resident Advisor, a Parent Orientation Leader, and an Assistant Resident Director while attending the University of Massachusetts Lowell for the past four years. All of these jobs fall under the Office of Residence Life. These opportunities have been cornerstones of my college education. They have taught me the long-term and transferrable skills of organization, conflict management, and supervision.
I have most enjoyed being an Assistant Resident Director, as I get to work with the Resident Advisors and Resident Director in a more administrative capacity. The ARD works closely with the RD to get the work done and hold RAs accountable. I think my favorite part of being an ARD this year has been working with the RAs to make sure they have the best experience they can, while at the same time making sure they complete their work well and on time. I enjoy helping RAs and other students reach their full potential, and I feel that it is a learning process for me too. The ARD position has shown me how much I value helping others on the path I have set for myself through my experiences with the RAs I supervise.
Because of the ARD role I have been afforded, I have had the opportunity to see how this potential career may play out. I feel confident about my ability to transition to the professional side of the field because the ARD position has already forced me to take on many of these steps. I tested the waters of the potential career in my RA role last year; this year as an ARD has shown me that I know I can succeed.
I am passionate about student affairs and higher education because it is an opportunity to work with college students and help them grow and develop. I truly believe that there isn’t a more rewarding career than one that allows you to help others. This field allows me to assist others every day at a time in their lives when many students need it most. It was my developmental path, and I want to give that support to others.
So far my academics and daily practice have not been linked nor intentional. I am excited to be able to make this so by starting a graduate program in higher education. Understanding my former responsibilities in terms of theory and learning how to turn new theories into practice is a process I cannot wait to begin.
I know the Lynch School of Education can assist me in achieving this goal through their program in Higher Education Administration. The opportunity to study in the Boston area will give me a multitude of professional development opportunities that would be hard to find anywhere else. If I am admitted, I will work hard to maximize my time at the Lynch School and become a young professional who can innovate and improve upon current practices in the field.
This personal statement takes you on a journey, as Bridget discovers her calling as an undergrad, gets all the hands-on experience in it she can, and figures out the perfect way to make it her career: grad school. And not just any grad school—Boston College in particular! There’s no doubt in your mind that she’s going to take advantage of everything BC’s master’s program has to offer, and she has the real-world experience to back her claims up.
Related: Great Alternative Jobs for Education Majors Who Don't Want to Teach
Haviland Johannesson-Forgit, Master of Arts in Arts Administration
Vermont State University , formerly Castleton University Class of 2018
While contemplating how I should approach my personal and professional goals and how earning an advanced degree will support them, I came upon my application essay for Goddard College that I wrote close to three years ago:
“Oftentimes, children who lack positive, authoritative figures and emotional support end up making unwise choices that stay with them and induce prejudice and judgment from other people who may be ignorant to what caused these children to make the choices in the first place. This cultural stigmatism that exists in our society often leads to these children being segmented into a disenfranchised group as adults. The misunderstanding and neglect that occurs in communities towards socially disenfranchised children goes against everything that I was raised to take in regard when attempting to understand a person.
I envision my studies reaching children and young adults in many different communities. It is my goal to immerse myself in rural, inner-city, and lower-income communities and meet these children before or in the midst of their time when the decisions they make can influence where their life may lead. I believe that the teachings of dance as a holistic lifestyle will provide outlets of knowledge and self-expression for these children and young adults that will lead them in positive directions.”
In this essay we were expected to write about our intentions and ambitions for our studies; to address the passions that acted as the drive for our work during our attendance at the college as well as after graduation. In returning to this essay, I was pleased to discover that my ambition and dedication to using the performing arts as a source of structure and reliability for youth in this country has not changed. When applying to Goddard College for my undergraduate degree I knew that I would want to continue on to pursue my graduate degree afterwards to enhance myself as a qualified candidate working in my field. Earning my advanced degree will enable me to go forth in the world as a confident and learned individual prepared to create the positive opportunities I envisioned years ago.
While earning my advanced degree, I intend to learn the details and structure that is needed to successfully run arts organizations. The closeness that Castleton University has with the Association for Arts Administration in developing its program for the MA in Arts Administration encourages me; it assures me that the quality and rigor of the program at Castleton is the right fit for my personal and professional aspirations. The efficacy of the program combined with the professional portfolio of projects demonstrating a mastery of skills in a range of areas in the arts and the six-credit culminating internship is exactly what I am looking for in an advanced degree program.
My background in the performing arts is broad. Not only have I have spent many years performing in productions of theater and dance, but I have also devoted my time and learning to other aspects of performance arts, whether it be technical, political, or social. My time attending Goddard College has proven to be extremely educational in training me in areas of social justice and cultural realizations of privilege, class, and human rights. With an accomplished and culturally diverse faculty and staff, the College requires its students to incorporate this training into their degrees, which makes for globally conscious citizens.
What I stand to bring to Castleton University’s campus is a vibrant love for the performing arts accompanied by acute social awareness training. My dedication to improving myself as an individual in my career is resolute; earning my advanced degree is vital to my continuing as a professional in a field so important to the foundation of our culture. I look forward to the opportunity of earning my Master of Arts in Arts Administration at Castleton University.
Haviland draws a remarkable line from her undergraduate studies and goals to the present day . She’s been on a clear path for a long time, and grad school has always been part of the plan and the logical next step for her career. Her unwavering commitment to arts education and dance as a means for furthering social justice will serve her well professionally—and it probably impressed the graduate admission folks too. Haviland also references specific features of Castleton University’s graduate program, showing she’s genuinely interested in the school and its unique strengths.
Related: Careers for People Who Want to Use Their Creativity
We hope these essay examples helped you get a better idea of where to take your grad school personal statements. The most important part of writing your essay is ensuring every word you put on the page is authentically you and true to your goals. You can write a great essay and get into a good grad school; just give yourself the time and flexibility by starting early and focusing on your story. Good luck!
Need help getting the ball rolling on your graduate essays? Check out these Good Strategies for Writing Grad School Personal Essays from the experts at GradSchools.com.
Like what you’re reading?
Join the CollegeXpress community! Create a free account and we’ll notify you about new articles, scholarship deadlines, and more.
Tags: admission essays essay examples grad school grad school admission grad school applications personal statement examples personal statements
Join our community of over 5 million students!
CollegeXpress has everything you need to simplify your college search, get connected to schools, and find your perfect fit.

Kyla McClain
High School Class of 2024
I found CollegeXpress when you partnered with Bold.org for a scholarship. I found your website, put my information in, and got connected. I only wanted to stay in North Carolina [for college] and not move far from home, but you all opened a door up for me. I started researching colleges you suggested for me. On your social media platforms, you also give really good test-taking tips that I used and suggested others to do the same. It helped me a lot on my exams, so thank you.

Tinuola Dada
$2,000 Community Service Scholarship Winner, 2015
I am very excited to be this year's recipient of the Multicultural Student Community Service Scholarship. This scholarship will bring me ever closer to my academic and professional goals. CollegeXpress has been an exceptional resource to me, and I recommend it to all rising seniors as they begin to navigate the college application process.
Joseph Johnsly
High School Class of 2021
It's an honor for me to be writing to share a little about my experience with CollegeXpress. I've been using CollegeXpress for about a year now, and the reason why I chose it is because it provides astonishing scholarships for every student around the globe. Besides that, this organization dispenses all the information necessary to help students get to college. CollegeXpress has helped me have an easier experience with applying to colleges and choosing the best fit for myself.

Brooke Maggio
CollegeXpress has helped me tremendously in my college search in narrowing down the schools I’m interested in. Using the college search tool, I was able to narrow down my choices to schools that matched what I was looking for. I also used CollegeXpress for their scholarship search, which helped me find scholarships that I meet the requirements of.

Laura Wallace
High School Class of 2019
My favorite part of CollegeXpress is that it features student writers so I get an inside perspective from students slightly older and farther along than me. I realize that other college websites also utilize student writers; however, I relate the most to the college writers that I read articles from on CollegeXpress.
- Our Best Advice for Aspiring Graduate Students
- The Top Things to Know About Prerequisites for Graduate School
- When Is the Best Time to Apply to Law School?
- The Ultimate Guide to Graduate School Applications
- What You Need to Know About 5 Common Graduate Admission Exams
Colleges You May Be Interested In
Freed-Hardeman University
Henderson, TN
Moody Theological Seminary
Chicago, IL
Waynesburg University
Waynesburg, PA
Dallas Baptist University
Wentworth Institute of Technology
Personalize your experience on CollegeXpress.
With this information, we'll display content relevant to your interests. By subscribing, you agree to receive CollegeXpress emails and to make your information available to colleges, scholarship programs, and other companies that have relevant/related offers.
Already have an account?
Log in to be directly connected to
Not a CollegeXpress user?
Don't want to register.
Provide your information below to connect with
- Penn Engineering Online Degrees
- Penn Engineering Online Dual Dual Degree
- Online Graduate Certificates
- Take a Course
- On-Demand Learning
- MSE-AI Online
- MSE-AI Academics
- Request Info
Next-Level Opportunities With AI
Help shape the future of a revolutionary technology. Our online Master of Science in Engineering (MSE) in Artificial Intelligence (AI) degree program gives you the technical foundation you need to lead the development and implementation of AI systems — along with the broad perspective to deploy new tools in an ethical and responsible way.
Taught by some of the world’s leading experts in artificial intelligence, the program combines Ivy League excellence with the convenience of an entirely online curriculum. No matter where in the world you live, you’ll learn at your own pace and on your schedule.
The MSE-AI program explores the mathematical, computational and algorithmic foundation for AI and develops strong competencies in machine learning, statistical modeling and optimization. Students will be equipped with the latest knowledge on the data center infrastructures that are powering the AI revolution, namely distributed systems, networking and GPU programming. At the same time, gain understanding of the ethical implications of AI and prepare to mitigate its risks.
“AI is one of the most important areas in technology today. It’s generating an incredible amount of enthusiasm and a massive amount of investment. With this program, our goal is to educate a new generation of engineers who have the skills to analyze trends as they emerge — not only from the technological perspective, but also from the societal and ethical perspective. ”

Chris Callison-Burch
- Professor, Computer and Information Science Department
- Program Director, MSE-AI Online
“We’ve specifically designed our curriculum to provide both cutting-edge technical skills and an understanding of the impact this technology will have on people’s lives. Students will not only learn about the algorithms and models underpinning AI applications, they will also be equipped with the latest knowledge on the data center infrastructures that are powering the AI revolution, namely distributed systems, networking and GPU programming”

Boon Thau Loo
- RCA Professor, Computer and Information Science Department
- Associate Dean for Graduate Programs
- Director, Distributed Systems Laboratory
MSE-AI Online Academic Journey
Mse-ai online course catalog.
Explore our extensive course catalog, providing a comprehensive overview of available courses, including detailed descriptions and prerequisites.
MSE-AI Online Sample Degree Plan
Students benefit from the support of a dedicated Student Success Advising Team, available to assist them in crafting tailored degree pathways and navigating various options for degree completion.

Expanding Your Academic Journey
Mse-ai online + online graduate certificate.
Gain expertise in crucial computer science areas and expand your career horizons with our certificates in Data Science and Software Systems.
Eligibility – Graduates of MSE-AI Online.
Academic Plan – If you graduated in the last five (5) years, you may transfer in two courses for your Certificate. Certificates consist of four courses from the certificate plan.

MSE-AI Online + Take a Course
Discover newly launched elective courses that delve into the latest advancements in technology. Embrace a shift in your learning focus to explore emerging areas, expanding your horizons to unveil a myriad of career possibilities.
Eligibility – Graduates of MSE-AI Online
Academic Plan – Join Penn Engineering Online for a single semester to boost your knowledge and discover new areas.
Try Before You Apply
Not sure if MSE-AI Online is for you? Try an open-enrollment specialization to find out if this interests you.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Essentials with Python Specialization

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Revised on July 23, 2023. An essay outline is a way of planning the structure of your essay before you start writing. It involves writing quick summary sentences or phrases for every point you will cover in each paragraph, giving you a picture of how your argument will unfold. You'll sometimes be asked to submit an essay outline as a separate ...
Plan on making a few rounds of revisions. Most importantly, ask for help! Have your essay critiqued by friends, family, educators, and our staff (make an appointment via CareerConnect). • Proofread: Proofread your statement carefully and try reading your essay out loud to help catch any mistakes or poor phrasing.
Introduction: The introductory paragraph of your essay should outline the topic, provide background information necessary to understand your argument, outline the evidence you will present and include your thesis statement. Your thesis should be a concise summary of the main point of your essay. 2. First body paragraph: Each body paragraph ...
A well-thought-out plan helps ensure that your essay is structured logically, making your arguments more persuasive and your writing more efficient. 5 Steps to Writing an Effective Essay Plan. Analyzing the Essay Question: Begin by thoroughly understanding the question or topic. Look for keywords and consider what the question is really asking.
Essay plans. An essay plan is a way to identify, select, and order the points you want to make in your essay. It helps you to work out your argument and your structure before writing, which should make the writing process more efficient and focussed. Sometimes essay plans are set as formative assignments so tutors can provide feedback before ...
Essay planning is an important step in academic essay writing. Proper planning helps you write your essay faster, and focus more on the exact question. As you draft and write your essay, record any changes on the plan as well as in the essay itself, so they develop side by side. One way to start planning an essay is with a 'box plan'.
Academic Essay Writing for Postgraduates is designed to help you plan, draft and revise the assignments you will be doing for your Master's degree at Edinburgh. the English grammar and vocabulary used to signal these key elements. There are seven Units, each dealing with an important element of academic assignment work at postgraduate level.
Grab the Reader's Attention. A strong grad school personal statement starts with writing a concise introduction that gains the reader's attention. The writer can make the essay more memorable by using a brief anecdote, quotation, compelling statistic, or rhetorical question.
Compelling conclusions. When considering how to write a master's essay, you need to ensure that your arguments and conclusions are plausible; try throughout to make them properly convincing. Weigh evidence, analyse arguments and develop your own position. If on reading you have successfully convinced yourself, you will more likely convince the ...
Article Highlights. Reflect before you begin your application essays. Outline your ideas before you put pen to paper. Write freely, and then return to edit your essay on the second draft. Take your time. Break between writing and editing for a fresh perspective. Gather feedback from a trusted source. Read your essay aloud to identify needed ...
Essay plan template. Skills@cumbria LMA 09/21. Essay plan template. Identify the main topics of your essay and organise them in the most logical sequence for your answer. You may find it useful to cut this up and rearrange your ideas once you have filled out the template. You might need to use a couple of pages for your full essay.
Essay outlines can be used for any college essay, research papers, a contrast essay, speech writing, or an expository essay. There are a range of essay outline templates to use, and they vary depending on the style of essay you are writing. These include: Argumentative essay outline. Narrative essay outline. Contrast essay outline.
301 Recommends: Glossary of Instruction Words. Our Essay Structure and Planning workshop will outline how to analyse your essay question, discuss approaches logically structure all your ideas, help you make your introductions and conclusions more effective, and teach how to link your ideas and ensure all essay content flows logically from the ...
Organize evidence, strengthen supporting arguments, and hammer your main point home with our essay planning sheet. Create flow: Maintain a cohesive writing process with an essay planning template that clarifies how one section leads to the next. Evaluate your argument from all sides: Crystallize your claim and test it out from new angles in a ...
A PDF providing further guidance on writing science essays for tutorials is available to download.. Short videos to support your essay writing skills. There are many other resources at Oxford that can help support your essay writing skills and if you are short on time, the Oxford Study Skills Centre has produced a number of short (2-minute) videos covering different aspects of essay writing ...
Essay prompts typically ask applicants to discuss their previous experience, future professional goals, and how the program can help them in achieving those objectives. The essay gives the applicant the chance to articulate these goals and display strong writing skills. Remember to tailor your essay to each school and the faculty committee that ...
The essay is a scholarly paper written in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the master's degree under the Plan B option. As such it should be well organized and carefully developed. ... See the sample title sheet for essay for specific format instructions. Submission of essays and deadlines. The title page of the essay, signed by the ...
Essays can play a major role in the university's admissions decisions, so any way to give yourself the advantage can make all the difference. By following our steps above, you can ensure your essay is in stronger shape and is better able to differentiate you from the pool of other candidates applying to the program as well. But, if you're ...
Here is an example of an essay topic and a possible plan. (Note that the thesis statement and topic sentences have been written as complete sentences, rather than just as dot points. Writing them out fully helps you formulate the idea or argument clearly). Essay question / topic. For most individuals, sporting activities are not associated with ...
Essay planning step 2: Brainstorming or freewriting. Once you know how many ideas you need, the next step is writing down what you know (and what you still have to find out). There are many ways that this can be achieved. You can either create a mind map, or just write out all your ideas on a piece of paper.
When writing your essay, stick to the 3 Cs: clarity, conciseness, and consistency. Ensure that your main points in the essay are clear. Ensure that you use the concise presentation of ideas instead of using long run-on sentences that make no sense. Avoid fillers and keep your writing as simple as possible.
T ry. To get. Some. Slee—it's no use. It's 3:00 am, 90 minutes before our day at work in the landfills of rural Thailand is set to begin, and the 60-watt bulb is still shining bright overhead. It is radiant. Directly on my left is one grown man's bare armpit; to my right is more of the same.
MSE-AI Online + Online Graduate Certificate. Gain expertise in crucial computer science areas and expand your career horizons with our certificates in Data Science and Software Systems. Eligibility - Graduates of MSE-AI Online. Academic Plan - If you graduated in the last five (5) years, you may transfer in two courses for your Certificate.