What are the seven sections of a dissertation?

This is the second of three chapters about Dissertations . To complete this reader, read each chapter carefully and then unlock and complete our materials to check your understanding.
– Discuss the overall dissertation structure
– Explore the common elements of a dissertation
– Consider additional elements which may be added
Chapter 1: What is an academic dissertation?
Chapter 2: What are the seven sections of a dissertation?
Chapter 3: What is an effective dissertation topic?
When writing a dissertation , like any type of essay , it’s important that relatively inexperienced writers follow tried and trusted structures and methods so as to convey ideas, arguments and research as clearly and easily as possible. This chapter therefore offers one such prescribed structure that’s particularly used in social-science dissertations, such as for linguistics, psychology or anthropology. Although other subjects may of course use a slightly different number of sections, place these seven sections in a slightly different order, or expect a different weighting for each section, the example structure we’ve included below should cover most dissertation and thesis types that students will be required to produce.
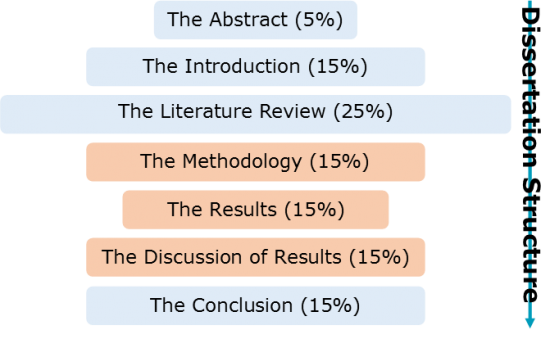
1. The Abstract (5%)
Both the shortest and first-encountered section of a dissertation , the abstract is intended to provide a very brief overview of the entire research project, highlighting to the reader the aims of the dissertation, the background and context of the investigation, the methodology that’s been used, the study’s key findings, and how this particular study has contributed to the field of knowledge.
2. The Introduction (15%)
Following the abstract , the purpose of the introduction is usually to describe the focus of the dissertation by reviewing the topic’s background and context. An introduction may also identify gaps in the research and how the writer intends to fill those gaps, as well as an outline of the scope of the investigation and the general and argumentative structure of the dissertation.
3. The Literature Review (25%)
The largest section of a dissertation is usually the literature review , which aims to provide a detailed discussion of the existing research that’s most relevant to the investigation. This section usually includes a critical review of both non-research and research literature, as well as any theoretical perspectives that require understanding to support and contextualise the study. Additionally, identification and justification of the research gap being filled in this dissertation as well as an explanation of how all of the above features have informed the dissertation are generally included.
4. The Methodology (15%)
The methodology is usually where the primary (and original) research of the dissertation begins. The purpose of this section is to highlight and justify to the reader the approach, design and processes that were followed to collect the findings, such as whether qualitative or quantitative methods were employed and whether questionnaires, interviews or recordings were used to collect the raw data. This section may include the study’s methodological approach, the research design, justification of the methods used, a discussion of the reliability and validity of those methods, and a description of the data collection and analysis procedures.
5. The Results (10%)
The fifth section (which is sometimes combined with the sixth section) of a dissertation is usually focussed on the results . The primary aim of this chapter is to present the results of the study’s primary research in a clear manner that demonstrates how these results address the dissertation’s research questions. Generally, in the results section the writer will present the relevant findings of the study, explain the implications of those findings, present evidence to support those findings, refer back to the methodology and introductory background information, and perhaps also refer forwards to the discussion of results .
6. The Discussion of Results (15%)
While the results section deals with the raw data, the discussion of results is where these findings are contextualised and their significance explained. As well as reminding the reader of the research aims and how the study’s results work to explore these aims, the writer should additionally present a discussion of how these findings have contributed to the dissertation’s hypotheses and therefore to the overall literature. Some time may also be spent interpreting the study’s findings, comparing them to other research, and evaluating their contribution to the literature.
7. The Conclusion (15%)
The final section of a dissertation is called the conclusion , the purpose of which is to remind the reader of the study’s aims, the key methodology, and the findings of the investigation. The writer may also wish to evaluate the significance of the research, commenting on how this research further develops the theory as well as highlighting any limitations that may have become apparent during the investigation. Finally, how this research can be applied practically may also be outlined to the reader, and any research gaps generated by the study explained.
Additional Sections
While these seven sections constitute the bulk of the dissertation , don’t forget to also include a table of contents , a reference list and an appendix if necessary.
Now that we’ve discussed what a dissertation is, when one might be used, and which sections such an extended essay usually contains, the final chapter on this subject is about choosing an effective dissertation topic.
To reference this reader:
Academic Marker (2022) About Dissertations . Available at: https://academicmarker.com/essay-writing/dissertations/about-dissertations/ (Accessed: Date Month Year).
- University of Reading
- University of York

Downloadables
Once you’ve completed all three chapters about dissertations , you might also wish to download our beginner, intermediate and advanced worksheets to test your progress or print for your students. These professional PDF worksheets can be easily accessed for only a few Academic Marks .
Our dissertations academic reader (including all three chapters about this topic) can be accessed here at the click of a button.
Gain unlimited access to our dissertations beginner worksheet, with activities and answer keys designed to check a basic understanding of this reader’s chapters.
To check a confident understanding of this reader’s chapters , click on the button below to download our dissertations intermediate worksheet with activities and answer keys.
Our dissertations advanced worksheet with activities and answer keys has been created to check a sophisticated understanding of this reader’s chapters .
To save yourself 5 Marks , click on the button below to gain unlimited access to all of our dissertations chapters and worksheets. The All-in-1 Pack includes every chapter in this reader, as well as our beginner, intermediate and advanced worksheets in one handy PDF.
Click on the button below to gain unlimited access to our about dissertations teacher’s PowerPoint, which should include everything you’d need to successfully introduce this topic.
Collect Academic Marks
- 100 Marks for joining
- 25 Marks for daily e-learning
- 100-200 for feedback/testimonials
- 100-500 for referring your colleages/friends
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
How to Write a Dissertation | A Guide to Structure & Content
A dissertation or thesis is a long piece of academic writing based on original research, submitted as part of an undergraduate or postgraduate degree.
The structure of a dissertation depends on your field, but it is usually divided into at least four or five chapters (including an introduction and conclusion chapter).
The most common dissertation structure in the sciences and social sciences includes:
- An introduction to your topic
- A literature review that surveys relevant sources
- An explanation of your methodology
- An overview of the results of your research
- A discussion of the results and their implications
- A conclusion that shows what your research has contributed
Dissertations in the humanities are often structured more like a long essay , building an argument by analysing primary and secondary sources . Instead of the standard structure outlined here, you might organise your chapters around different themes or case studies.
Other important elements of the dissertation include the title page , abstract , and reference list . If in doubt about how your dissertation should be structured, always check your department’s guidelines and consult with your supervisor.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Acknowledgements, table of contents, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review / theoretical framework, methodology, reference list.
The very first page of your document contains your dissertation’s title, your name, department, institution, degree program, and submission date. Sometimes it also includes your student number, your supervisor’s name, and the university’s logo. Many programs have strict requirements for formatting the dissertation title page .
The title page is often used as cover when printing and binding your dissertation .
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
The acknowledgements section is usually optional, and gives space for you to thank everyone who helped you in writing your dissertation. This might include your supervisors, participants in your research, and friends or family who supported you.
The abstract is a short summary of your dissertation, usually about 150-300 words long. You should write it at the very end, when you’ve completed the rest of the dissertation. In the abstract, make sure to:
- State the main topic and aims of your research
- Describe the methods you used
- Summarise the main results
- State your conclusions
Although the abstract is very short, it’s the first part (and sometimes the only part) of your dissertation that people will read, so it’s important that you get it right. If you’re struggling to write a strong abstract, read our guide on how to write an abstract .
In the table of contents, list all of your chapters and subheadings and their page numbers. The dissertation contents page gives the reader an overview of your structure and helps easily navigate the document.
All parts of your dissertation should be included in the table of contents, including the appendices. You can generate a table of contents automatically in Word.
If you have used a lot of tables and figures in your dissertation, you should itemise them in a numbered list . You can automatically generate this list using the Insert Caption feature in Word.
If you have used a lot of abbreviations in your dissertation, you can include them in an alphabetised list of abbreviations so that the reader can easily look up their meanings.
If you have used a lot of highly specialised terms that will not be familiar to your reader, it might be a good idea to include a glossary . List the terms alphabetically and explain each term with a brief description or definition.
In the introduction, you set up your dissertation’s topic, purpose, and relevance, and tell the reader what to expect in the rest of the dissertation. The introduction should:
- Establish your research topic , giving necessary background information to contextualise your work
- Narrow down the focus and define the scope of the research
- Discuss the state of existing research on the topic, showing your work’s relevance to a broader problem or debate
- Clearly state your objectives and research questions , and indicate how you will answer them
- Give an overview of your dissertation’s structure
Everything in the introduction should be clear, engaging, and relevant to your research. By the end, the reader should understand the what , why and how of your research. Not sure how? Read our guide on how to write a dissertation introduction .
Before you start on your research, you should have conducted a literature review to gain a thorough understanding of the academic work that already exists on your topic. This means:
- Collecting sources (e.g. books and journal articles) and selecting the most relevant ones
- Critically evaluating and analysing each source
- Drawing connections between them (e.g. themes, patterns, conflicts, gaps) to make an overall point
In the dissertation literature review chapter or section, you shouldn’t just summarise existing studies, but develop a coherent structure and argument that leads to a clear basis or justification for your own research. For example, it might aim to show how your research:
- Addresses a gap in the literature
- Takes a new theoretical or methodological approach to the topic
- Proposes a solution to an unresolved problem
- Advances a theoretical debate
- Builds on and strengthens existing knowledge with new data
The literature review often becomes the basis for a theoretical framework , in which you define and analyse the key theories, concepts and models that frame your research. In this section you can answer descriptive research questions about the relationship between concepts or variables.
The methodology chapter or section describes how you conducted your research, allowing your reader to assess its validity. You should generally include:
- The overall approach and type of research (e.g. qualitative, quantitative, experimental, ethnographic)
- Your methods of collecting data (e.g. interviews, surveys, archives)
- Details of where, when, and with whom the research took place
- Your methods of analysing data (e.g. statistical analysis, discourse analysis)
- Tools and materials you used (e.g. computer programs, lab equipment)
- A discussion of any obstacles you faced in conducting the research and how you overcame them
- An evaluation or justification of your methods
Your aim in the methodology is to accurately report what you did, as well as convincing the reader that this was the best approach to answering your research questions or objectives.
Next, you report the results of your research . You can structure this section around sub-questions, hypotheses, or topics. Only report results that are relevant to your objectives and research questions. In some disciplines, the results section is strictly separated from the discussion, while in others the two are combined.
For example, for qualitative methods like in-depth interviews, the presentation of the data will often be woven together with discussion and analysis, while in quantitative and experimental research, the results should be presented separately before you discuss their meaning. If you’re unsure, consult with your supervisor and look at sample dissertations to find out the best structure for your research.
In the results section it can often be helpful to include tables, graphs and charts. Think carefully about how best to present your data, and don’t include tables or figures that just repeat what you have written – they should provide extra information or usefully visualise the results in a way that adds value to your text.
Full versions of your data (such as interview transcripts) can be included as an appendix .
The discussion is where you explore the meaning and implications of your results in relation to your research questions. Here you should interpret the results in detail, discussing whether they met your expectations and how well they fit with the framework that you built in earlier chapters. If any of the results were unexpected, offer explanations for why this might be. It’s a good idea to consider alternative interpretations of your data and discuss any limitations that might have influenced the results.
The discussion should reference other scholarly work to show how your results fit with existing knowledge. You can also make recommendations for future research or practical action.
The dissertation conclusion should concisely answer the main research question, leaving the reader with a clear understanding of your central argument. Wrap up your dissertation with a final reflection on what you did and how you did it. The conclusion often also includes recommendations for research or practice.
In this section, it’s important to show how your findings contribute to knowledge in the field and why your research matters. What have you added to what was already known?
You must include full details of all sources that you have cited in a reference list (sometimes also called a works cited list or bibliography). It’s important to follow a consistent reference style . Each style has strict and specific requirements for how to format your sources in the reference list.
The most common styles used in UK universities are Harvard referencing and Vancouver referencing . Your department will often specify which referencing style you should use – for example, psychology students tend to use APA style , humanities students often use MHRA , and law students always use OSCOLA . M ake sure to check the requirements, and ask your supervisor if you’re unsure.
To save time creating the reference list and make sure your citations are correctly and consistently formatted, you can use our free APA Citation Generator .
Your dissertation itself should contain only essential information that directly contributes to answering your research question. Documents you have used that do not fit into the main body of your dissertation (such as interview transcripts, survey questions or tables with full figures) can be added as appendices .
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- What Is a Dissertation? | 5 Essential Questions to Get Started
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
- How to Write a Dissertation Proposal | A Step-by-Step Guide
More interesting articles
- Checklist: Writing a dissertation
- Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
- Dissertation binding and printing
- Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples
- Dissertation title page
- Example Theoretical Framework of a Dissertation or Thesis
- Figure & Table Lists | Word Instructions, Template & Examples
- How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Conclusion
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction
- How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
- List of Abbreviations | Example, Template & Best Practices
- Operationalisation | A Guide with Examples, Pros & Cons
- Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples
- Relevance of Your Dissertation Topic | Criteria & Tips
- Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
- Thesis & Dissertation Acknowledgements | Tips & Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Database Examples
- What is a Dissertation Preface? | Definition & Examples
- What is a Glossary? | Definition, Templates, & Examples
- What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
- What is a Theoretical Framework? | A Step-by-Step Guide
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
Thesis and Dissertation Guide
- « Thesis & Dissertation Resources
- The Graduate School Home
- Introduction
Copyright Page
Dedication, acknowledgements, preface (optional), table of contents.
- List of Tables, Figures, and Illustrations
List of Abbreviations
List of symbols.
- Non-Traditional Formats
- Font Type and Size
- Spacing and Indentation
- Tables, Figures, and Illustrations
- Formatting Previously Published Work
- Internet Distribution
- Open Access
- Registering Copyright
- Using Copyrighted Materials
- Use of Your Own Previously Published Materials
- Submission Steps
- Submission Checklist
- Sample Pages

I. Order and Components
Please see the sample thesis or dissertation pages throughout and at the end of this document for illustrations. The following order is required for components of your thesis or dissertation:
- Dedication, Acknowledgements, and Preface (each optional)
- Table of Contents, with page numbers
- List of Tables, List of Figures, or List of Illustrations, with titles and page numbers (if applicable)
- List of Abbreviations (if applicable)
- List of Symbols (if applicable)
- Introduction, if any
- Main body, with consistent subheadings as appropriate
- Appendices (if applicable)
- Endnotes (if applicable)
- References (see section on References for options)
Many of the components following the title and copyright pages have required headings and formatting guidelines, which are described in the following sections.
Please consult the Sample Pages to compare your document to the requirements. A Checklist is provided to assist you in ensuring your thesis or dissertation meets all formatting guidelines.
The title page of a thesis or dissertation must include the following information:

- The title of the thesis or dissertation in all capital letters and centered 2″ below the top of the page.
- Your name, centered 1″ below the title. Do not include titles, degrees, or identifiers. The name you use here does not need to exactly match the name on your university records, but we recommend considering how you will want your name to appear in professional publications in the future.
Notes on this statement:
- When indicating your degree in the second bracketed space, use the full degree name (i.e., Doctor of Philosophy, not Ph.D. or PHD; Master of Public Health, not M.P.H. or MPH; Master of Social Work, not M.S.W. or MSW).
- List your department, school, or curriculum rather than your subject area or specialty discipline in the third bracketed space. You may include your subject area or specialty discipline in parentheses (i.e., Department of Romance Languages (French); School of Pharmacy (Molecular Pharmaceutics); School of Education (School Psychology); or similar official area).
- If you wish to include both your department and school names, list the school at the end of the statement (i.e., Department of Pharmacology in the School of Medicine).
- A dissertation submitted to the faculty at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Department of Public Policy.
- A thesis submitted to the faculty at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in the School of Dentistry (Endodontics).
- A thesis submitted to the faculty at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in the Department of Nutrition in the Gillings School of Global Public Health.
- A dissertation submitted to the faculty at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the School of Education (Cultural Studies and Literacies).
- The words “Chapel Hill” must be centered 1″ below the statement.
- One single-spaced line below that, center the year in which your committee approves the completed thesis or dissertation. This need not be the year you graduate.
- Approximately 2/3 of the way across the page on the right-hand side of the page, 1″ below the year, include the phrase “Approved by:” (with colon) followed by each faculty member's name on subsequent double-spaced lines. Do not include titles such as Professor, Doctor, Dr., PhD, or any identifiers such as “chair” or “advisor” before or after any names. Line up the first letter of each name on the left under the “A” in the “Approved by:” line. If a name is too long to fit on one line, move this entire section of text slightly to the left so that formatting can be maintained.
- No signatures, signature lines, or page numbers should be included on the title page.
Include a copyright page with the following information single-spaced and centered 2″ above the bottom of the page:

© Year Author's Full Name (as it appears on the title page) ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
This page immediately follows the title page. It should be numbered with the lower case Roman numeral ii centered with a 1/2″ margin from the bottom edge.
Inclusion of this page offers you, as the author, additional protection against copyright infringement as it eliminates any question of authorship and copyright ownership. You do not need to file for copyright in order to include this statement in your thesis or dissertation. However, filing for copyright can offer other protections.
See Section IV for more information on copyrighting your thesis or dissertation.
Include an abstract page following these guidelines:

- Include the heading “ABSTRACT” in all capital letters, and center it 2″ below the top of the page.
- One double-spaced line below “ABSTRACT”, center your name, followed by a colon and the title of the thesis or dissertation. Use as many lines as necessary. Be sure that your name and the title exactly match the name and title used on the Title page.
- One single-spaced line below the title, center the phrase “(Under the direction of [advisor's name])”. Include the phrase in parentheses. Include the first and last name(s) of your advisor or formal co-advisors. Do not include the name of other committee members. Use the advisor's name only; do not include any professional titles such as PhD, Professor, or Dr. or any identifiers such as “chair” or “advisor”.
- Skip one double-spaced line and begin the abstract. The text of your abstract must be double-spaced and aligned with the document's left margin with the exception of indenting new paragraphs. Do not center or right-justify the abstract.
- Abstracts cannot exceed 150 words for a thesis or 350 words for a dissertation.
- Number the abstract page with the lower case Roman numeral iii (and iv, if more than one page) centered with a 1/2″ margin from the bottom edge.
Please write and proofread your abstract carefully. When possible, avoid including symbols or foreign words in your abstract, as they cannot be indexed or searched. Avoid mathematical formulas, diagrams, and other illustrative materials in the abstract. Offer a brief description of your thesis or dissertation and a concise summary of its conclusions. Be sure to describe the subject and focus of your work with clear details and avoid including lengthy explanations or opinions.
Your title and abstract will be used by search engines to help potential audiences locate your work, so clarity will help to draw the attention of your targeted readers.
You have an option to include a dedication, acknowledgements, or preface. If you choose to include any or all of these elements, give each its own page(s).

A dedication is a message from the author prefixed to a work in tribute to a person, group, or cause. Most dedications are short statements of tribute beginning with “To…” such as “To my family”.
Acknowledgements are the author's statement of gratitude to and recognition of the people and institutions that helped the author's research and writing.
A preface is a statement of the author's reasons for undertaking the work and other personal comments that are not directly germane to the materials presented in other sections of the thesis or dissertation. These reasons tend to be of a personal nature.
Any of the pages must be prepared following these guidelines:
- Do not place a heading on the dedication page.
- The text of short dedications must be centered and begin 2″ from the top of the page.
- Headings are required for the “ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS” and “PREFACE” pages. Headings must be in all capital letters and centered 2″ below the top of the page.
- The text of the acknowledgements and preface pages must begin one double-spaced line below the heading, be double-spaced, and be aligned with the document's left margin with the exception of indenting new paragraphs.
- Subsequent pages of text return to the 1″ top margin.
- The page(s) must be numbered with consecutive lower case Roman numerals (starting with the page number after the abstract) centered with a 1/2″ margin from the bottom edge.
Include a table of contents following these guidelines:

- Include the heading “TABLE OF CONTENTS” in all capital letters, and center it 2″ below the top of the page.
- Include one double-spaced line between the heading and the first entry.
- The table of contents should not contain listings for the pages that precede it, but it must list all parts of the thesis or dissertation that follow it.
- If relevant, be sure to list all appendices and a references section in your table of contents. Include page numbers for these items but do not assign separate chapter numbers.
- Entries must align with the document's left margin or be indented to the right of the left page margin using consistent tabs.
- Major subheadings within chapters must be included in the table of contents. The subheading(s) should be indented to the right of the left page margin using consistent tabs.
- If an entry takes up more than one line, break up the entry about three-fourths of the way across the page and place the rest of the text on a second line, single-spacing the two lines.
- Include one double-spaced line between each entry.
- Page numbers listed in the table of contents must be located just inside the right page margin with leaders (lines of periods) filling out the space between the end of the entry and the page number. The last digit of each number must line up on the right margin.
- Information included in the table of contents must match the headings, major subheadings, and numbering used in the body of the thesis or dissertation.
- The Table of Contents page(s) must be numbered with consecutive lower case Roman numerals centered with a 1/2″ margin from the bottom edge.
Lists of Tables, Figures, and Illustrations
If applicable, include a list of tables, list of figures, and/or list of illustrations following these guidelines:

- Include the heading(s) in all capital letters, centered 1″ below the top of the page.
- Each entry must include a number, title, and page number.
- Assign each table, figure, or illustration in your thesis or dissertation an Arabic numeral. You may number consecutively throughout the entire work (e.g., Figure 1, Figure 2, etc.), or you may assign a two-part Arabic numeral with the first number designating the chapter in which it appears, separated by a period, followed by a second number to indicate its consecutive placement in the chapter (e.g., Table 3.2 is the second table in Chapter Three).
- Numerals and titles must align with the document's left margin or be indented to the right of the left page margin using consistent tabs.
- Page numbers must be located just inside the right page margin with leaders (lines of periods) filling out the space between the end of the entry and the page number. The last digit of each number must line up on the right margin.
- Numbers, titles, and page numbers must each match the corresponding numbers, titles, and page numbers appearing in the thesis or dissertation.
- All Lists of Tables, Figures, and Illustrations page(s) must be numbered with consecutive lower case Roman numerals centered with a 1/2″ margin from the bottom edge.
If you use abbreviations extensively in your thesis or dissertation, you must include a list of abbreviations and their corresponding definitions following these guidelines:

- Include the heading “LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS” in all capital letters, and center it 1″ below the top of the page.
- Arrange your abbreviations alphabetically.
- Abbreviations must align with the document's left margin or be indented to the right of the left page margin using consistent tabs.
- If an entry takes up more than one line, single-space between the two lines.
- The List of Abbreviations page(s) must be numbered with consecutive lower case Roman numerals centered with a 1/2″ margin from the bottom edge.
If you use symbols in your thesis or dissertation, you may combine them with your abbreviations, titling the section “LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS AND SYMBOLS”, or you may set up a separate list of symbols and their definitions by following the formatting instructions above for abbreviations. The heading you choose must be in all capital letters and centered 1″ below the top of the page.
Previous: Introduction
Next: Format
- How it works

How to Structure a Dissertation – A Step by Step Guide
Published by Owen Ingram at August 11th, 2021 , Revised On September 20, 2023
A dissertation – sometimes called a thesis – is a long piece of information backed up by extensive research. This one, huge piece of research is what matters the most when students – undergraduates and postgraduates – are in their final year of study.
On the other hand, some institutions, especially in the case of undergraduate students, may or may not require students to write a dissertation. Courses are offered instead. This generally depends on the requirements of that particular institution.
If you are unsure about how to structure your dissertation or thesis, this article will offer you some guidelines to work out what the most important segments of a dissertation paper are and how you should organise them. Why is structure so important in research, anyway?
One way to answer that, as Abbie Hoffman aptly put it, is because: “Structure is more important than content in the transmission of information.”
Also Read: How to write a dissertation – step by step guide .
How to Structure a Dissertation or Thesis
It should be noted that the exact structure of your dissertation will depend on several factors, such as:
- Your research approach (qualitative/quantitative)
- The nature of your research design (exploratory/descriptive etc.)
- The requirements set for forth by your academic institution.
- The discipline or field your study belongs to. For instance, if you are a humanities student, you will need to develop your dissertation on the same pattern as any long essay .
This will include developing an overall argument to support the thesis statement and organizing chapters around theories or questions. The dissertation will be structured such that it starts with an introduction , develops on the main idea in its main body paragraphs and is then summarised in conclusion .
However, if you are basing your dissertation on primary or empirical research, you will be required to include each of the below components. In most cases of dissertation writing, each of these elements will have to be written as a separate chapter.
But depending on the word count you are provided with and academic subject, you may choose to combine some of these elements.
For example, sciences and engineering students often present results and discussions together in one chapter rather than two different chapters.
If you have any doubts about structuring your dissertation or thesis, it would be a good idea to consult with your academic supervisor and check your department’s requirements.
Parts of a Dissertation or Thesis
Your dissertation will start with a t itle page that will contain details of the author/researcher, research topic, degree program (the paper is to be submitted for), and research supervisor. In other words, a title page is the opening page containing all the names and title related to your research.
The name of your university, logo, student ID and submission date can also be presented on the title page. Many academic programs have stringent rules for formatting the dissertation title page.
Acknowledgements
The acknowledgments section allows you to thank those who helped you with your dissertation project. You might want to mention the names of your academic supervisor, family members, friends, God, and participants of your study whose contribution and support enabled you to complete your work.
However, the acknowledgments section is usually optional.
Tip: Many students wrongly assume that they need to thank everyone…even those who had little to no contributions towards the dissertation. This is not the case. You only need to thank those who were directly involved in the research process, such as your participants/volunteers, supervisor(s) etc.
Perhaps the smallest yet important part of a thesis, an abstract contains 5 parts:
- A brief introduction of your research topic.
- The significance of your research.
- A line or two about the methodology that was used.
- The results and what they mean (briefly); their interpretation(s).
- And lastly, a conclusive comment regarding the results’ interpretation(s) as conclusion .
Stuck on a difficult dissertation? We can help!
Our Essay Writing Service Features:
- Expert UK Writers
- Plagiarism-free
- Timely Delivery
- Thorough Research
- Rigorous Quality Control

“ Our expert dissertation writers can help you with all stages of the dissertation writing process including topic research and selection, dissertation plan, dissertation proposal , methodology , statistical analysis , primary and secondary research, findings and analysis and complete dissertation writing. “
Tip: Make sure to highlight key points to help readers figure out the scope and findings of your research study without having to read the entire dissertation. The abstract is your first chance to impress your readers. So, make sure to get it right. Here are detailed guidelines on how to write abstract for dissertation .
Table of Contents
Table of contents is the section of a dissertation that guides each section of the dissertation paper’s contents. Depending on the level of detail in a table of contents, the most useful headings are listed to provide the reader the page number on which said information may be found at.
Table of contents can be inserted automatically as well as manually using the Microsoft Word Table of Contents feature.
List of Figures and Tables
If your dissertation paper uses several illustrations, tables and figures, you might want to present them in a numbered list in a separate section . Again, this list of tables and figures can be auto-created and auto inserted using the Microsoft Word built-in feature.
List of Abbreviations
Dissertations that include several abbreviations can also have an independent and separate alphabetised list of abbreviations so readers can easily figure out their meanings.
If you think you have used terms and phrases in your dissertation that readers might not be familiar with, you can create a glossary that lists important phrases and terms with their meanings explained.
Looking for dissertation help?
Researchprospect to the rescue then.
We have expert writers on our team who are skilled at helping students with quantitative dissertations across a variety of STEM disciplines. Guaranteeing 100% satisfaction!

Introduction
Introduction chapter briefly introduces the purpose and relevance of your research topic.
Here, you will be expected to list the aim and key objectives of your research so your readers can easily understand what the following chapters of the dissertation will cover. A good dissertation introduction section incorporates the following information:
- It provides background information to give context to your research.
- It clearly specifies the research problem you wish to address with your research. When creating research questions , it is important to make sure your research’s focus and scope are neither too broad nor too narrow.
- it demonstrates how your research is relevant and how it would contribute to the existing knowledge.
- It provides an overview of the structure of your dissertation. The last section of an introduction contains an outline of the following chapters. It could start off with something like: “In the following chapter, past literature has been reviewed and critiqued. The proceeding section lays down major research findings…”
- Theoretical framework – under a separate sub-heading – is also provided within the introductory chapter. Theoretical framework deals with the basic, underlying theory or theories that the research revolves around.
All the information presented under this section should be relevant, clear, and engaging. The readers should be able to figure out the what, why, when, and how of your study once they have read the introduction. Here are comprehensive guidelines on how to structure the introduction to the dissertation .
“Overwhelmed by tight deadlines and tons of assignments to write? There is no need to panic! Our expert academics can help you with every aspect of your dissertation – from topic creation and research problem identification to choosing the methodological approach and data analysis.”
Literature Review
The literature review chapter presents previous research performed on the topic and improves your understanding of the existing literature on your chosen topic. This is usually organised to complement your primary research work completed at a later stage.
Make sure that your chosen academic sources are authentic and up-to-date. The literature review chapter must be comprehensive and address the aims and objectives as defined in the introduction chapter. Here is what your literature research chapter should aim to achieve:
- Data collection from authentic and relevant academic sources such as books, journal articles and research papers.
- Analytical assessment of the information collected from those sources; this would involve a critiquing the reviewed researches that is, what their strengths/weaknesses are, why the research method they employed is better than others, importance of their findings, etc.
- Identifying key research gaps, conflicts, patterns, and theories to get your point across to the reader effectively.
While your literature review should summarise previous literature, it is equally important to make sure that you develop a comprehensible argument or structure to justify your research topic. It would help if you considered keeping the following questions in mind when writing the literature review:
- How does your research work fill a certain gap in exiting literature?
- Did you adopt/adapt a new research approach to investigate the topic?
- Does your research solve an unresolved problem?
- Is your research dealing with some groundbreaking topic or theory that others might have overlooked?
- Is your research taking forward an existing theoretical discussion?
- Does your research strengthen and build on current knowledge within your area of study? This is otherwise known as ‘adding to the existing body of knowledge’ in academic circles.
Tip: You might want to establish relationships between variables/concepts to provide descriptive answers to some or all of your research questions. For instance, in case of quantitative research, you might hypothesise that variable A is positively co-related to variable B that is, one increases and so does the other one.
Research Methodology
The methods and techniques ( secondary and/or primar y) employed to collect research data are discussed in detail in the Methodology chapter. The most commonly used primary data collection methods are:
- questionnaires
- focus groups
- observations
Essentially, the methodology chapter allows the researcher to explain how he/she achieved the findings, why they are reliable and how they helped him/her test the research hypotheses or address the research problem.
You might want to consider the following when writing methodology for the dissertation:
- Type of research and approach your work is based on. Some of the most widely used types of research include experimental, quantitative and qualitative methodologies.
- Data collection techniques that were employed such as questionnaires, surveys, focus groups, observations etc.
- Details of how, when, where, and what of the research that was conducted.
- Data analysis strategies employed (for instance, regression analysis).
- Software and tools used for data analysis (Excel, STATA, SPSS, lab equipment, etc.).
- Research limitations to highlight any hurdles you had to overcome when carrying our research. Limitations might or might not be mentioned within research methodology. Some institutions’ guidelines dictate they be mentioned under a separate section alongside recommendations.
- Justification of your selection of research approach and research methodology.
Here is a comprehensive article on how to structure a dissertation methodology .
Research Findings
In this section, you present your research findings. The dissertation findings chapter is built around the research questions, as outlined in the introduction chapter. Report findings that are directly relevant to your research questions.
Any information that is not directly relevant to research questions or hypotheses but could be useful for the readers can be placed under the Appendices .
As indicated above, you can either develop a standalone chapter to present your findings or combine them with the discussion chapter. This choice depends on the type of research involved and the academic subject, as well as what your institution’s academic guidelines dictate.
For example, it is common to have both findings and discussion grouped under the same section, particularly if the dissertation is based on qualitative research data.
On the other hand, dissertations that use quantitative or experimental data should present findings and analysis/discussion in two separate chapters. Here are some sample dissertations to help you figure out the best structure for your own project.
Sample Dissertation
Tip: Try to present as many charts, graphs, illustrations and tables in the findings chapter to improve your data presentation. Provide their qualitative interpretations alongside, too. Refrain from explaining the information that is already evident from figures and tables.
The findings are followed by the Discussion chapter , which is considered the heart of any dissertation paper. The discussion section is an opportunity for you to tie the knots together to address the research questions and present arguments, models and key themes.
This chapter can make or break your research.
The discussion chapter does not require any new data or information because it is more about the interpretation(s) of the data you have already collected and presented. Here are some questions for you to think over when writing the discussion chapter:
- Did your work answer all the research questions or tested the hypothesis?
- Did you come up with some unexpected results for which you have to provide an additional explanation or justification?
- Are there any limitations that could have influenced your research findings?
Here is an article on how to structure a dissertation discussion .
Conclusions corresponding to each research objective are provided in the Conclusion section . This is usually done by revisiting the research questions to finally close the dissertation. Some institutions may specifically ask for recommendations to evaluate your critical thinking.
By the end, the readers should have a clear apprehension of your fundamental case with a focus on what methods of research were employed and what you achieved from this research.
Quick Question: Does the conclusion chapter reflect on the contributions your research work will make to existing knowledge?
Answer: Yes, the conclusion chapter of the research paper typically includes a reflection on the research’s contributions to existing knowledge. In the “conclusion chapter”, you have to summarise the key findings and discuss how they add value to the existing literature on the current topic.
Reference list
All academic sources that you collected information from should be cited in-text and also presented in a reference list (or a bibliography in case you include references that you read for the research but didn’t end up citing in the text), so the readers can easily locate the source of information when/if needed.
At most UK universities, Harvard referencing is the recommended style of referencing. It has strict and specific requirements on how to format a reference resource. Other common styles of referencing include MLA, APA, Footnotes, etc.
Each chapter of the dissertation should have relevant information. Any information that is not directly relevant to your research topic but your readers might be interested in (interview transcripts etc.) should be moved under the Appendices section .
Things like questionnaires, survey items or readings that were used in the study’s experiment are mostly included under appendices.
An Outline of Dissertation/Thesis Structure
How can We Help you with your Dissertation?
If you are still unsure about how to structure a dissertation or thesis, or simply lack the motivation to kick start your dissertation project, you might be interested in our dissertation services .
If you are still unsure about how to structure a dissertation or thesis, or lack the motivation to kick start your dissertation project, you might be interested in our dissertation services.
Whether you need help with individual chapters, proposals or the full dissertation paper, we have PhD-qualified writers who will write your paper to the highest academic standard. ResearchProspect is UK-based, and a UK-registered business, which means the UK consumer law protects all our clients.
All You Need to Know About Us Learn More About Our Dissertation Services
FAQs About Structure a Dissertation
What does the title page of a dissertation contain.
The title page will contain details of the author/researcher, research topic , degree program (the paper is to be submitted for) and research supervisor’s name(s). The name of your university, logo, student number and submission date can also be presented on the title page.
What is the purpose of adding acknowledgement?
The acknowledgements section allows you to thank those who helped you with your dissertation project. You might want to mention the names of your academic supervisor, family members, friends, God and participants of your study whose contribution and support enabled you to complete your work.
Can I omit the glossary from the dissertation?
Yes, but only if you think that your paper does not contain any terms or phrases that the reader might not understand. If you think you have used them in the paper, you must create a glossary that lists important phrases and terms with their meanings explained.
What is the purpose of appendices in a dissertation?
Any information that is not directly relevant to research questions or hypotheses but could be useful for the readers can be placed under the Appendices, such as questionnaire that was used in the study.
Which referencing style should I use in my dissertation?
You can use any of the referencing styles such as APA, MLA, and Harvard, according to the recommendation of your university; however, almost all UK institutions prefer Harvard referencing style .
What is the difference between references and bibliography?
References contain all the works that you read up and used and therefore, cited within the text of your thesis. However, in case you read on some works and resources that you didn’t end up citing in-text, they will be referenced in what is called a bibliography.
Additional readings might also be present alongside each bibliography entry for readers.
You May Also Like
A list of glossary in a dissertation contains all the terms that were used in your dissertation but the meanings of which may not be obvious to the readers.
Have you failed dissertation, assignment, exam or coursework? Don’t panic because you are not alone. Get help from our professional UK qualified writers!
Do dissertations scare you? Struggling with writing a flawless dissertation? Well, congratulations, you have landed in the perfect place. In this blog, we will take you through the detailed process of writing a dissertation. Sounds fun? We thought so!
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
- Jump to menu
- Student Home
- Accept your offer
- How to enrol
- Student ID card
- Set up your IT
- Orientation Week
- Fees & payment
- Academic calendar
- Special consideration
- Transcripts
- The Nucleus: Student Hub
- Referencing
- Essay writing
- Learning abroad & exchange
- Professional development & UNSW Advantage
- Employability
- Financial assistance
- International students
- Equitable learning
- Postgraduate research
- Health Service
- Events & activities
- Emergencies
- Volunteering
- Clubs and societies
- Accommodation
- Health services
- Sport and gym
- Arc student organisation
- Security on campus
- Maps of campus
- Careers portal
- Change password
Thesis Structure
This page outlines the stages of an honours thesis and provides links to other pages that will give you more information and some examples from past theses.

Stages of a thesis (in order)
Write this last. It is an overview of your whole thesis, and is between 200-300 words.
See writing abstracts for honours theses for what to include in your abstract or see some example abstracts .
Introduction
Usually longer than an abstract, and provides the following:
- background to the topic;
- brief review of current knowledge (Can include literature review in some schools);
- indicates gap in knowledge, states aim of your research and how it fits into the gap;
- can include hypotheses; can include an outline of the following chapters.
See thesis introductions exercises for more information.
- Literature review
Often part of the Introduction, but can be a separate section. It is an evaluation of previous research on your topic, where you show that there is a gap in the knowledge that your research will attempt to fill. The key word here is evaluation.
See literature reviews for more information and examples to get you started on your literature review.
Often the easiest part of the thesis to write. Outlines which method you chose and why (your methodology); what, when, where, how and why you did what you did to get your results.
Here are some sample methods .
Outlines what you found out in relation to your research questions or hypotheses, presented in figures and in written text.
Results contain the facts of your research. Often you will include a brief comment on the significance of key results, with the expectation that more generalised comments about results will be made in the Discussion section. Sometimes Results and Discussion are combined: check with your supervisor and with highly rated past theses in your School.
Here are some suggestions for writing up results .
The Discussion section:
- comments on your results;
- explains what your results mean;
- interprets your results in a wider context; indicates which results were expected or unexpected;
- provides explanations for unexpected results.
The Discussion should also relate your specific results to previous research or theory. You should point out what the limitations were of your study, and note any questions that remain unanswered. The Discussion CAN also include Conclusions/Future Research. Check with your supervisor.
See our theses in discussion page for more information or try these exercises .
- Conclusions
Very important! This is where you emphasise that your research aims/objectives have been achieved.
You also emphasise the most significant results, note the limitations and make suggestions for further research.
Conclusions can include Future Directions. Check with your supervisor.
For more information see conclusions in honours theses or sample conclusions .
Engineering & science
- Report writing
- Technical writing
- Writing lab reports
- Introductions
- Writing up results
- Discussions
- Writing tools
- Case study report in (engineering)
- ^ More support
Scholarly Resources 4 Students | scite.ai 21 May 2024
Discover your Library: Main Library 21 May 2024

- Manuscript Preparation
Know How to Structure Your PhD Thesis
- 4 minute read
- 34.8K views
Table of Contents
In your academic career, few projects are more important than your PhD thesis. Unfortunately, many university professors and advisors assume that their students know how to structure a PhD. Books have literally been written on the subject, but there’s no need to read a book in order to know about PhD thesis paper format and structure. With that said, however, it’s important to understand that your PhD thesis format requirement may not be the same as another student’s. The bottom line is that how to structure a PhD thesis often depends on your university and department guidelines.
But, let’s take a look at a general PhD thesis format. We’ll look at the main sections, and how to connect them to each other. We’ll also examine different hints and tips for each of the sections. As you read through this toolkit, compare it to published PhD theses in your area of study to see how a real-life example looks.
Main Sections of a PhD Thesis
In almost every PhD thesis or dissertation, there are standard sections. Of course, some of these may differ, depending on your university or department requirements, as well as your topic of study, but this will give you a good idea of the basic components of a PhD thesis format.
- Abstract : The abstract is a brief summary that quickly outlines your research, touches on each of the main sections of your thesis, and clearly outlines your contribution to the field by way of your PhD thesis. Even though the abstract is very short, similar to what you’ve seen in published research articles, its impact shouldn’t be underestimated. The abstract is there to answer the most important question to the reviewer. “Why is this important?”
- Introduction : In this section, you help the reviewer understand your entire dissertation, including what your paper is about, why it’s important to the field, a brief description of your methodology, and how your research and the thesis are laid out. Think of your introduction as an expansion of your abstract.
- Literature Review : Within the literature review, you are making a case for your new research by telling the story of the work that’s already been done. You’ll cover a bit about the history of the topic at hand, and how your study fits into the present and future.
- Theory Framework : Here, you explain assumptions related to your study. Here you’re explaining to the review what theoretical concepts you might have used in your research, how it relates to existing knowledge and ideas.
- Methods : This section of a PhD thesis is typically the most detailed and descriptive, depending of course on your research design. Here you’ll discuss the specific techniques you used to get the information you were looking for, in addition to how those methods are relevant and appropriate, as well as how you specifically used each method described.
- Results : Here you present your empirical findings. This section is sometimes also called the “empiracles” chapter. This section is usually pretty straightforward and technical, and full of details. Don’t shortcut this chapter.
- Discussion : This can be a tricky chapter, because it’s where you want to show the reviewer that you know what you’re talking about. You need to speak as a PhD versus a student. The discussion chapter is similar to the empirical/results chapter, but you’re building on those results to push the new information that you learned, prior to making your conclusion.
- Conclusion : Here, you take a step back and reflect on what your original goals and intentions for the research were. You’ll outline them in context of your new findings and expertise.
Tips for your PhD Thesis Format
As you put together your PhD thesis, it’s easy to get a little overwhelmed. Here are some tips that might keep you on track.
- Don’t try to write your PhD as a first-draft. Every great masterwork has typically been edited, and edited, and…edited.
- Work with your thesis supervisor to plan the structure and format of your PhD thesis. Be prepared to rewrite each section, as you work out rough drafts. Don’t get discouraged by this process. It’s typical.
- Make your writing interesting. Academic writing has a reputation of being very dry.
- You don’t have to necessarily work on the chapters and sections outlined above in chronological order. Work on each section as things come up, and while your work on that section is relevant to what you’re doing.
- Don’t rush things. Write a first draft, and leave it for a few days, so you can come back to it with a more critical take. Look at it objectively and carefully grammatical errors, clarity, logic and flow.
- Know what style your references need to be in, and utilize tools out there to organize them in the required format.
- It’s easier to accidentally plagiarize than you think. Make sure you’re referencing appropriately, and check your document for inadvertent plagiarism throughout your writing process.
PhD Thesis Editing Plus
Want some support during your PhD writing process? Our PhD Thesis Editing Plus service includes extensive and detailed editing of your thesis to improve the flow and quality of your writing. Unlimited editing support for guaranteed results. Learn more here , and get started today!

- Publication Process
Journal Acceptance Rates: Everything You Need to Know

- Publication Recognition
How to Make a PowerPoint Presentation of Your Research Paper
You may also like.

Make Hook, Line, and Sinker: The Art of Crafting Engaging Introductions

Can Describing Study Limitations Improve the Quality of Your Paper?

A Guide to Crafting Shorter, Impactful Sentences in Academic Writing

6 Steps to Write an Excellent Discussion in Your Manuscript

How to Write Clear and Crisp Civil Engineering Papers? Here are 5 Key Tips to Consider

The Clear Path to An Impactful Paper: ②

The Essentials of Writing to Communicate Research in Medicine

Changing Lines: Sentence Patterns in Academic Writing
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
Thesis Structure: Writing Guide For Your Success

If you are about to start writing your thesis, then it is extremely important to know as much as possible about the thesis structure. Learning the main thesis chapters should enable you to quickly structure your academic paper. Keep in mind that not structuring the paper correctly usually leads to severe penalties. We know some of you are probably having questions about numbering dissertation chapters. Basically, you just need to give all the major sections consecutive numbers. Use Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, and so on). Check out the most frequently asked questions and them move on to the 7 parts of the thesis or dissertation structure.
Thesis Structure Frequently Asked Questions
- What is a basic good structure for a thesis? A: The best structure is the one listed below. It contains the 7 important parts any thesis should have.
- What does “the structure of this dissertation is in manuscript style” mean? A: It means that the thesis includes one or more manuscripts that have been written in a way that facilitates publication. The thesis can, in this case, be a collection of papers that have been written or co-authored by the student.
- Which chapters of dissertation are mandatory? A: All the 7 chapters below are necessary, if you want to get a top score on your paper.
- Where can I get a thesis structure template? A: You can quickly get a thesis structure example from one of our seasoned academic writers. Don’t base your thesis on mediocre samples you find online.
- What is the preferred thesis sentence structure? A: There is no set sentence structure that you have to follow. Just make sure your writing is organized in a logical manner and that all complex terms are explained the first time you use them.
Thesis Abstract
The first part of the thesis structure is the abstract. It is basically an overview of the entire paper. There is no set dissertation abstract structure. It is just a summary of your thesis and it should be just 200 to 300 words long.
Thesis Introduction
The introduction is one of the most important dissertation chapters. It should contain all of the following information:
A bit of background about the topic. Some information about the current knowledge. The aim of your research (the gap in knowledge that prompted you to write the thesis).
Remember that the introduction must present the thesis statement. It is very important to learn more about the thesis statement structure. A great thesis statement will pique the interest of the evaluation committee.

Thesis Literature Review
Many students who are looking to learn how to structure a thesis don’t know about the Literature Review section. Why? Because many people prefer to include it into the introduction. However, by separating the literature review from the intro, you can focus more on why your research is important. You can evaluate the most important research on your topic and clearly show the gap in knowledge.
Thesis Methods
In most cases, the Methods section is the easiest part of the structure of a thesis. All you have to do is present the method or methods you chose for the research. Don’t forget to also explain why you chose that specific research method. Your audience needs to understand that the chosen method is the best for the task.
Thesis Results
This is one of the most important chapters of a dissertation. In the Results chapter, you need to present your findings. Remember that written text is not enough. You need figures, stats, graphs, and other forms of data. This section contains all the facts of your research and should be written in an objective, neutral manner. It would be unusual for your to discuss your findings in this section.
Thesis Discussion
The Discussion chapter is very important in the dissertation chapters structure. It is the reason why you didn’t discuss your findings in the Results section. This is the section you can use to talk about your findings and provide your own opinions about the results. Here is what you can do in the discussion section:
Explain to the audience what your results mean for the scientific community. Comment on each of the results and discuss how your findings support your thesis. Explain any unexpected results so the evaluation committee can see that you know what you’re doing. Interpret the results and tie them with other research on the subject. How does your research help the academic community?
Thesis Conclusion
While not the most important chapter, the conclusion is one of the important chapters in a dissertation. It is the part where you can show your readers that you have achieved your research objectives. You can talk a bit about what you’ve learned in the process and even make some suggestions regarding the need for future research. In most cases, students also reiterate the thesis statement at the beginning of the conclusion, followed by a short summary of the paper’s most important chapters.
Still Not Sure How to Structure Thesis?
In case you are still struggling to find the best history dissertation structure, you should get some help as fast as possible. Remember that writing a thesis takes weeks, if not months. Don’t spend too much time trying to find the best structure. Instead, get in touch with a reliable academic company and get some quick assistance. For examples, one of our writers can create a thesis outline for you. You can just follow the outline and everything will be just fine.
Of course, you can also get some help with the thesis formatting. Citations and references can be difficult to master. Each academic writing style (MLA, Chicago, APA, etc.) has its own requirements. The way you format your academic paper is very important. Bolding and italicizing can emphasize certain ideas. A professional editor can help you make the thesis stand out from the rest. After all, a pleasantly-formatted dissertation that impresses the evaluation committee with its structure and quality of content has a very high chance of getting a top score.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates
How To Write A Dissertation Introduction
A Simple Explainer With Examples + Free Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By Dr Eunice Rautenbach (D. Tech) | March 2020
If you’re reading this, you’re probably at the daunting early phases of writing up the introduction chapter of your dissertation or thesis. It can be intimidating, I know.
In this post, we’ll look at the 7 essential ingredients of a strong dissertation or thesis introduction chapter, as well as the essential things you need to keep in mind as you craft each section. We’ll also share some useful tips to help you optimize your approach.
Overview: Writing An Introduction Chapter
- The purpose and function of the intro chapter
- Craft an enticing and engaging opening section
- Provide a background and context to the study
- Clearly define the research problem
- State your research aims, objectives and questions
- Explain the significance of your study
- Identify the limitations of your research
- Outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis
A quick sidenote:
You’ll notice that I’ve used the words dissertation and thesis interchangeably. While these terms reflect different levels of research – for example, Masters vs PhD-level research – the introduction chapter generally contains the same 7 essential ingredients regardless of level. So, in this post, dissertation introduction equals thesis introduction.

Start with why.
To craft a high-quality dissertation or thesis introduction chapter, you need to understand exactly what this chapter needs to achieve. In other words, what’s its purpose ? As the name suggests, the introduction chapter needs to introduce the reader to your research so that they understand what you’re trying to figure out, or what problem you’re trying to solve. More specifically, you need to answer four important questions in your introduction chapter.
These questions are:
- What will you be researching? (in other words, your research topic)
- Why is that worthwhile? (in other words, your justification)
- What will the scope of your research be? (in other words, what will you cover and what won’t you cover)
- What will the limitations of your research be? (in other words, what will the potential shortcomings of your research be?)
Simply put, your dissertation’s introduction chapter needs to provide an overview of your planned research , as well as a clear rationale for it. In other words, this chapter has to explain the “what” and the “why” of your research – what’s it all about and why’s that important.
Simple enough, right?
Well, the trick is finding the appropriate depth of information. As the researcher, you’ll be extremely close to your topic and this makes it easy to get caught up in the minor details. While these intricate details might be interesting, you need to write your introduction chapter on more of a “need-to-know” type basis, or it will end up way too lengthy and dense. You need to balance painting a clear picture with keeping things concise. Don’t worry though – you’ll be able to explore all the intricate details in later chapters.

Now that you understand what you need to achieve from your introduction chapter, we can get into the details. While the exact requirements for this chapter can vary from university to university, there are seven core components that most universities will require. We call these the seven essential ingredients .
The 7 Essential Ingredients
- The opening section – where you’ll introduce the reader to your research in high-level terms
- The background to the study – where you’ll explain the context of your project
- The research problem – where you’ll explain the “gap” that exists in the current research
- The research aims , objectives and questions – where you’ll clearly state what your research will aim to achieve
- The significance (or justification) – where you’ll explain why your research is worth doing and the value it will provide to the world
- The limitations – where you’ll acknowledge the potential limitations of your project and approach
- The structure – where you’ll briefly outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis to help orient the reader
By incorporating these seven essential ingredients into your introduction chapter, you’ll comprehensively cover both the “ what ” and the “ why ” I mentioned earlier – in other words, you’ll achieve the purpose of the chapter.
Side note – you can also use these 7 ingredients in this order as the structure for your chapter to ensure a smooth, logical flow. This isn’t essential, but, generally speaking, it helps create an engaging narrative that’s easy for your reader to understand. If you’d like, you can also download our free introduction chapter template here.
Alright – let’s look at each of the ingredients now.

#1 – The Opening Section
The very first essential ingredient for your dissertation introduction is, well, an introduction or opening section. Just like every other chapter, your introduction chapter needs to start by providing a brief overview of what you’ll be covering in the chapter.
This section needs to engage the reader with clear, concise language that can be easily understood and digested. If the reader (your marker!) has to struggle through it, they’ll lose interest, which will make it harder for you to earn marks. Just because you’re writing an academic paper doesn’t mean you can ignore the basic principles of engaging writing used by marketers, bloggers, and journalists. At the end of the day, you’re all trying to sell an idea – yours is just a research idea.
So, what goes into this opening section?
Well, while there’s no set formula, it’s a good idea to include the following four foundational sentences in your opening section:
1 – A sentence or two introducing the overall field of your research.
For example:
“Organisational skills development involves identifying current or potential skills gaps within a business and developing programs to resolve these gaps. Management research, including X, Y and Z, has clearly established that organisational skills development is an essential contributor to business growth.”
2 – A sentence introducing your specific research problem.
“However, there are conflicting views and an overall lack of research regarding how best to manage skills development initiatives in highly dynamic environments where subject knowledge is rapidly and continuously evolving – for example, in the website development industry.”
3 – A sentence stating your research aims and objectives.
“This research aims to identify and evaluate skills development approaches and strategies for highly dynamic industries in which subject knowledge is continuously evolving.”.
4 – A sentence outlining the layout of the chapter.
“This chapter will provide an introduction to the study by first discussing the background and context, followed by the research problem, the research aims, objectives and questions, the significance and finally, the limitations.”
As I mentioned, this opening section of your introduction chapter shouldn’t be lengthy . Typically, these four sentences should fit neatly into one or two paragraphs, max. What you’re aiming for here is a clear, concise introduction to your research – not a detailed account.
PS – If some of this terminology sounds unfamiliar, don’t stress – I’ll explain each of the concepts later in this post.
#2 – Background to the study
Now that you’ve provided a high-level overview of your dissertation or thesis, it’s time to go a little deeper and lay a foundation for your research topic. This foundation is what the second ingredient is all about – the background to your study.
So, what is the background section all about?
Well, this section of your introduction chapter should provide a broad overview of the topic area that you’ll be researching, as well as the current contextual factors . This could include, for example, a brief history of the topic, recent developments in the area, key pieces of research in the area and so on. In other words, in this section, you need to provide the relevant background information to give the reader a decent foundational understanding of your research area.
Let’s look at an example to make this a little more concrete.
If we stick with the skills development topic I mentioned earlier, the background to the study section would start by providing an overview of the skills development area and outline the key existing research. Then, it would go on to discuss how the modern-day context has created a new challenge for traditional skills development strategies and approaches. Specifically, that in many industries, technical knowledge is constantly and rapidly evolving, and traditional education providers struggle to keep up with the pace of new technologies.
Importantly, you need to write this section with the assumption that the reader is not an expert in your topic area. So, if there are industry-specific jargon and complex terminology, you should briefly explain that here , so that the reader can understand the rest of your document.
Don’t make assumptions about the reader’s knowledge – in most cases, your markers will not be able to ask you questions if they don’t understand something. So, always err on the safe side and explain anything that’s not common knowledge.

#3 – The research problem
Now that you’ve given your reader an overview of your research area, it’s time to get specific about the research problem that you’ll address in your dissertation or thesis. While the background section would have alluded to a potential research problem (or even multiple research problems), the purpose of this section is to narrow the focus and highlight the specific research problem you’ll focus on.
But, what exactly is a research problem, you ask?
Well, a research problem can be any issue or question for which there isn’t already a well-established and agreed-upon answer in the existing research. In other words, a research problem exists when there’s a need to answer a question (or set of questions), but there’s a gap in the existing literature , or the existing research is conflicting and/or inconsistent.
So, to present your research problem, you need to make it clear what exactly is missing in the current literature and why this is a problem . It’s usually a good idea to structure this discussion into three sections – specifically:
- What’s already well-established in the literature (in other words, the current state of research)
- What’s missing in the literature (in other words, the literature gap)
- Why this is a problem (in other words, why it’s important to fill this gap)
Let’s look at an example of this structure using the skills development topic.
Organisational skills development is critically important for employee satisfaction and company performance (reference). Numerous studies have investigated strategies and approaches to manage skills development programs within organisations (reference).
(this paragraph explains what’s already well-established in the literature)
However, these studies have traditionally focused on relatively slow-paced industries where key skills and knowledge do not change particularly often. This body of theory presents a problem for industries that face a rapidly changing skills landscape – for example, the website development industry – where new platforms, languages and best practices emerge on an extremely frequent basis.
(this paragraph explains what’s missing from the literature)
As a result, the existing research is inadequate for industries in which essential knowledge and skills are constantly and rapidly evolving, as it assumes a slow pace of knowledge development. Industries in such environments, therefore, find themselves ill-equipped in terms of skills development strategies and approaches.
(this paragraph explains why the research gap is problematic)
As you can see in this example, in a few lines, we’ve explained (1) the current state of research, (2) the literature gap and (3) why that gap is problematic. By doing this, the research problem is made crystal clear, which lays the foundation for the next ingredient.
#4 – The research aims, objectives and questions
Now that you’ve clearly identified your research problem, it’s time to identify your research aims and objectives , as well as your research questions . In other words, it’s time to explain what you’re going to do about the research problem.
So, what do you need to do here?
Well, the starting point is to clearly state your research aim (or aims) . The research aim is the main goal or the overarching purpose of your dissertation or thesis. In other words, it’s a high-level statement of what you’re aiming to achieve.
Let’s look at an example, sticking with the skills development topic:
“Given the lack of research regarding organisational skills development in fast-moving industries, this study will aim to identify and evaluate the skills development approaches utilised by web development companies in the UK”.
As you can see in this example, the research aim is clearly outlined, as well as the specific context in which the research will be undertaken (in other words, web development companies in the UK).
Next up is the research objective (or objectives) . While the research aims cover the high-level “what”, the research objectives are a bit more practically oriented, looking at specific things you’ll be doing to achieve those research aims.
Let’s take a look at an example of some research objectives (ROs) to fit the research aim.
- RO1 – To identify common skills development strategies and approaches utilised by web development companies in the UK.
- RO2 – To evaluate the effectiveness of these strategies and approaches.
- RO3 – To compare and contrast these strategies and approaches in terms of their strengths and weaknesses.
As you can see from this example, these objectives describe the actions you’ll take and the specific things you’ll investigate in order to achieve your research aims. They break down the research aims into more specific, actionable objectives.
The final step is to state your research questions . Your research questions bring the aims and objectives another level “down to earth”. These are the specific questions that your dissertation or theses will seek to answer. They’re not fluffy, ambiguous or conceptual – they’re very specific and you’ll need to directly answer them in your conclusions chapter .
The research questions typically relate directly to the research objectives and sometimes can look a bit obvious, but they are still extremely important. Let’s take a look at an example of the research questions (RQs) that would flow from the research objectives I mentioned earlier.
- RQ1 – What skills development strategies and approaches are currently being used by web development companies in the UK?
- RQ2 – How effective are each of these strategies and approaches?
- RQ3 – What are the strengths and weaknesses of each of these strategies and approaches?
As you can see, the research questions mimic the research objectives , but they are presented in question format. These questions will act as the driving force throughout your dissertation or thesis – from the literature review to the methodology and onward – so they’re really important.
A final note about this section – it’s really important to be clear about the scope of your study (more technically, the delimitations ). In other words, what you WILL cover and what you WON’T cover. If your research aims, objectives and questions are too broad, you’ll risk losing focus or investigating a problem that is too big to solve within a single dissertation.
Simply put, you need to establish clear boundaries in your research. You can do this, for example, by limiting it to a specific industry, country or time period. That way, you’ll ringfence your research, which will allow you to investigate your topic deeply and thoroughly – which is what earns marks!
Need a helping hand?
#5 – Significance
Now that you’ve made it clear what you’ll be researching, it’s time to make a strong argument regarding your study’s importance and significance . In other words, now that you’ve covered the what, it’s time to cover the why – enter essential ingredient number 5 – significance.
Of course, by this stage, you’ve already briefly alluded to the importance of your study in your background and research problem sections, but you haven’t explicitly stated how your research findings will benefit the world . So, now’s your chance to clearly state how your study will benefit either industry , academia , or – ideally – both . In other words, you need to explain how your research will make a difference and what implications it will have .
Let’s take a look at an example.
“This study will contribute to the body of knowledge on skills development by incorporating skills development strategies and approaches for industries in which knowledge and skills are rapidly and constantly changing. This will help address the current shortage of research in this area and provide real-world value to organisations operating in such dynamic environments.”
As you can see in this example, the paragraph clearly explains how the research will help fill a gap in the literature and also provide practical real-world value to organisations.
This section doesn’t need to be particularly lengthy, but it does need to be convincing . You need to “sell” the value of your research here so that the reader understands why it’s worth committing an entire dissertation or thesis to it. This section needs to be the salesman of your research. So, spend some time thinking about the ways in which your research will make a unique contribution to the world and how the knowledge you create could benefit both academia and industry – and then “sell it” in this section.

#6 – The limitations
Now that you’ve “sold” your research to the reader and hopefully got them excited about what’s coming up in the rest of your dissertation, it’s time to briefly discuss the potential limitations of your research.
But you’re probably thinking, hold up – what limitations? My research is well thought out and carefully designed – why would there be limitations?
Well, no piece of research is perfect . This is especially true for a dissertation or thesis – which typically has a very low or zero budget, tight time constraints and limited researcher experience. Generally, your dissertation will be the first or second formal research project you’ve ever undertaken, so it’s unlikely to win any research awards…
Simply put, your research will invariably have limitations. Don’t stress yourself out though – this is completely acceptable (and expected). Even “professional” research has limitations – as I said, no piece of research is perfect. The key is to recognise the limitations upfront and be completely transparent about them, so that future researchers are aware of them and can improve the study’s design to minimise the limitations and strengthen the findings.
Generally, you’ll want to consider at least the following four common limitations. These are:
- Your scope – for example, perhaps your focus is very narrow and doesn’t consider how certain variables interact with each other.
- Your research methodology – for example, a qualitative methodology could be criticised for being overly subjective, or a quantitative methodology could be criticised for oversimplifying the situation (learn more about methodologies here ).
- Your resources – for example, a lack of time, money, equipment and your own research experience.
- The generalisability of your findings – for example, the findings from the study of a specific industry or country can’t necessarily be generalised to other industries or countries.
Don’t be shy here. There’s no use trying to hide the limitations or weaknesses of your research. In fact, the more critical you can be of your study, the better. The markers want to see that you are aware of the limitations as this demonstrates your understanding of research design – so be brutal.
#7 – The structural outline
Now that you’ve clearly communicated what your research is going to be about, why it’s important and what the limitations of your research will be, the final ingredient is the structural outline.The purpose of this section is simply to provide your reader with a roadmap of what to expect in terms of the structure of your dissertation or thesis.
In this section, you’ll need to provide a brief summary of each chapter’s purpose and contents (including the introduction chapter). A sentence or two explaining what you’ll do in each chapter is generally enough to orient the reader. You don’t want to get too detailed here – it’s purely an outline, not a summary of your research.
Let’s look at an example:
In Chapter One, the context of the study has been introduced. The research objectives and questions have been identified, and the value of such research argued. The limitations of the study have also been discussed.
In Chapter Two, the existing literature will be reviewed and a foundation of theory will be laid out to identify key skills development approaches and strategies within the context of fast-moving industries, especially technology-intensive industries.
In Chapter Three, the methodological choices will be explored. Specifically, the adoption of a qualitative, inductive research approach will be justified, and the broader research design will be discussed, including the limitations thereof.
So, as you can see from the example, this section is simply an outline of the chapter structure, allocating a short paragraph to each chapter. Done correctly, the outline will help your reader understand what to expect and reassure them that you’ll address the multiple facets of the study.
By the way – if you’re unsure of how to structure your dissertation or thesis, be sure to check out our video post which explains dissertation structure .
Keep calm and carry on.
Hopefully you feel a bit more prepared for this challenge of crafting your dissertation or thesis introduction chapter now. Take a deep breath and remember that Rome wasn’t built in a day – conquer one ingredient at a time and you’ll be firmly on the path to success.
Let’s quickly recap – the 7 ingredients are:
- The opening section – where you give a brief, high-level overview of what your research will be about.
- The study background – where you introduce the reader to key theory, concepts and terminology, as well as the context of your study.
- The research problem – where you explain what the problem with the current research is. In other words, the research gap.
- The research aims , objectives and questions – where you clearly state what your dissertation will investigate.
- The significance – where you explain what value your research will provide to the world.
- The limitations – where you explain what the potential shortcomings and limitations of your research may be.
- The structural outline – where you provide a high-level overview of the structure of your document
If you bake these ingredients into your dissertation introduction chapter, you’ll be well on your way to building an engaging introduction chapter that lays a rock-solid foundation for the rest of your document.
Remember, while we’ve covered the essential ingredients here, there may be some additional components that your university requires, so be sure to double-check your project brief!

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

42 Comments
Thanks very much for such an insight. I feel confident enough in undertaking my thesis on the survey;The future of facial recognition and learning non verbal interaction
Glad to hear that. Good luck with your thesis!
Thanks very much for such an insight. I feel confident now undertaking my thesis; The future of facial recognition and learning non verbal interaction.
Thanks so much for this article. I found myself struggling and wasting a lot of time in my thesis writing but after reading this article and watching some of your youtube videos, I now have a clear understanding of what is required for a thesis.
Thank you Derek, i find your each post so useful. Keep it up.
Thank you so much Derek ,for shedding the light and making it easier for me to handle the daunting task of academic writing .
Thanks do much Dereck for the comprehensive guide. It will assist me queit a lot in my thesis.
thanks a lot for helping
i LOVE the gifs, such a fun way to engage readers. thanks for the advice, much appreciated
Thanks a lot Derek! It will be really useful to the beginner in research!
You’re welcome
This is a well written, easily comprehensible, simple introduction to the basics of a Research Dissertation../the need to keep the reader in mind while writing the dissertation is an important point that is covered../ I appreciate the efforts of the author../
The instruction given are perfect and clear. I was supposed to take the course , unfortunately in Nepal the service is not avaialble.However, I am much more hopeful that you will provide require documents whatever you have produced so far.
Thank you very much
Thanks so much ❤️😘 I feel am ready to start writing my research methodology
This is genuinely the most effective advice I have ever been given regarding academia. Thank you so much!
This is one of the best write up I have seen in my road to PhD thesis. regards, this write up update my knowledge of research
I was looking for some good blogs related to Education hopefully your article will help. Thanks for sharing.
This is an awesome masterpiece. It is one of the most comprehensive guides to writing a Dissertation/Thesis I have seen and read.
You just saved me from going astray in writing a Dissertation for my undergraduate studies. I could not be more grateful for such a relevant guide like this. Thank you so much.
Thank you so much Derek, this has been extremely helpful!!
I do have one question though, in the limitations part do you refer to the scope as the focus of the research on a specific industry/country/chronological period? I assume that in order to talk about whether or not the research could be generalized, the above would need to be already presented and described in the introduction.
Thank you again!
Phew! You have genuinely rescued me. I was stuck how to go about my thesis. Now l have started. Thank you.
This is the very best guide in anything that has to do with thesis or dissertation writing. The numerous blends of examples and detailed insights make it worth a read and in fact, a treasure that is worthy to be bookmarked.
Thanks a lot for this masterpiece!
Powerful insight. I can now take a step
Thank you very much for these valuable introductions to thesis chapters. I saw all your videos about writing the introduction, discussion, and conclusion chapter. Then, I am wondering if we need to explain our research limitations in all three chapters, introduction, discussion, and conclusion? Isn’t it a bit redundant? If not, could you please explain how can we write in different ways? Thank you.
Excellent!!! Thank you…
Thanks for this informative content. I have a question. The research gap is mentioned in both the introduction and literature section. I would like to know how can I demonstrate the research gap in both sections without repeating the contents?
I’m incredibly grateful for this invaluable content. I’ve been dreading compiling my postgrad thesis but breaking each chapter down into sections has made it so much easier for me to engage with the material without feeling overwhelmed. After relying on your guidance, I’m really happy with how I’ve laid out my introduction.
Thank you for the informative content you provided
Hi Derrick and Team, thank you so much for the comprehensive guide on how to write a dissertation or a thesis introduction section. For some of us first-timers, it is a daunting task. However, the instruction with relevant examples makes it clear and easy to follow through. Much appreciated.
It was so helpful. God Bless you. Thanks very much
I thank you Grad coach for your priceless help. I have two questions I have learned from your video the limitations of the research presented in chapter one. but in another video also presented in chapter five. which chapter limitation should be included? If possible, I need your answer since I am doing my thesis. how can I explain If I am asked what is my motivation for this research?
Thank you guys for the great work you are doing. Honestly, you have made the research to be interesting and simplified. Even a novice will easily grasp the ideas you put forward, Thank you once again.
Excellent piece!
I feel like just settling for a good topic is usually the hardest part.
Thank you so much. My confidence has been completely destroyed during my first year of PhD and you have helped me pull myself together again
Happy to help 🙂
I am so glad I ran into your resources and did not waste time doing the wrong this. Research is now making so much sense now.
Gratitude to Derrick and the team I was looking for a solid article that would aid me in drafting the thesis’ introduction. I felt quite happy when I came across the piece you wrote because it was so well-written and insightful. I wish you success in the future.
thank you so much. God Bless you
Thank you so much Grad Coach for these helpful insights. Now I can get started, with a great deal of confidence.
It’s ‘alluded to’ not ‘eluded to’.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Dissertation Structure – Definition, Parts and Other Guidelines
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Definition: Dissertation Structure
- 3 Parts of a Dissertation Structure
- 4 Other Dissertation Structure Guidelines
- 5 In a Nutshell
Definition: Dissertation Structure
A dissertation structure is the arrangement of research contents. It contains numerous parts which are also divided into paragraphs. It is essential to the flow of ideas in a research paper and to helping the reader navigate the ideas.
Different academic disciplines require a certain dissertation structure, so it is important to verify with your department of studies what type of structure is needed.
How do I start my dissertation?
Pick a dissertation topic of interest and determine the issue to be explored. Previous research is sufficient in preparation since gaps identified in the previous dissertations are targeted. Talk to supervisors or fellow students to help you get a rough idea of the whole dissertation structure. Narrow down the topic to a specific issue to be tackled; this increases the chances that the topic is accepted by the board. Read broadly on the topic and take notes. By doing so, the next steps are easy to follow and keep the dissertation structure intact.
How to reduce plagiarism in my dissertation?
Ensure all works written by other authors are appropriately paraphrased and cited. Be sure that you’re using the correct referencing and citation method before you begin writing. Plagiarism is an academic offence which in some universities can lead to immediate failure, or even expulsion.
What is the acceptable dissertation structure?
All dissertation structures are similar, but they differ in relation to the discipline. It is recommended that you consult with your supervisor and your department to find out what the acceptable dissertation structure is. Sections such as the dissertation introduction and conclusion are standard in most pieces of academic writing. However, health and social sciences are examples of disciplines with completely different dissertation structures.
What is the dissertation word count?
The word count is dependent on the institution. Most institutions have a word count limit of 6000 give or take 10%. Some parts of the dissertation structure, such as the bibliography or the table of contents do not factor into the word count of a dissertation. But check with your institution to play it safe.
What are the main components of a dissertation structure?
The main dissertation structure features that need to be included are a title, an introduction, headings, a conclusion and a bibliography. These key components must be in any dissertation presented for a bachelor’s thesis, master’s thesis or doctoral program. Depending on the institution, different formatting and referencing styles such as APA or MLA may be required.
Parts of a Dissertation Structure
A dissertation starts with a title page. It contains the research title and the name of the institution where the research is being submitted. Different disciplines require different arrangements of the title page components. Be sure to inquire with your faculty.

Introduction
The introduction explains more on the abstract. As earlier stated, the abstract is short and concise hence an introduction broadens its contents. A reader can identify how, what and why of the specific research after reading the introduction.
Literature review
To write a literature review one needs to read previous work and research on the topic. Journals, books and research articles are used in collection of information which is later analysed, then connections are made from the different information collected. Gaps are identified, hence finding ways to build more on what is present.
Methodology
It explains how the research will be conducted. The type of research to be used is presented, the method used to collect data, the research area is stated, data analysis is described, any tool used, limitations and the justification of the choices made when collecting data. The methodology needs to be convincing to meet the research goals.
The findings give the results of the methodology. In some departments, findings and discussions may be explained together, while in others they are different entities. Charts, histograms and tables are useful in showing the findings.
It is the research summary. An abstract gives the overall goal of the research in a page or less. Anyone reading an abstract should have a rough idea of the whole research since it contains a stand-alone thesis. Some institutions have a word limit of the abstract that need to be adhered to the latter. Despite its location in the dissertation structure, an abstract is often written last after the whole research is done. Although some people prefer to write it first since it provides a framework for writing the dissertation. An abstract is short but concise.
Acknowledgements
In an acknowledgement individuals who helped through the research are mentioned. Individuals mentioned include supervisors, parents, spouses, children and friends among others.
Table of content
The dissertation structure is well-written and it includes sub-sections. In Microsoft Word, the table of contents is clicked and automatically takes one to a specific section.
List of figures and tables
In case your research has figures and tables, number them and insert caption such that when one clicks on it the figure or table opens.
List of abbreviations
Abbreviations used in the dissertation are written with what they represent. They are arranged in an alphabetical order.
The findings are explained in detail forming different relationships from the literature review. Recommendations are presented to help improve the issue being discussed.
It brings all the dissertation together to explain the findings and research questions. Contribution to the current literature is highlighted in the conclusion section.
Reference list
A reference list includes all the sources used in the research. Most dissertation is written in either APA or MLA citation.
It is the last part of a dissertation structure, and it includes questionnaires, surveys, or transcripts.
Other Dissertation Structure Guidelines
- The most common font is Times New Roman, font size 12, double spaced.
- The margins for bottom, top and right are 1 inch while the left margin is 1.5 inches.
- Figures and tables need to fit on the page; if they do not, you can change that particular page to landscape format.
- The table of contents must be updated using Microsoft Word headings.
In a Nutshell
- Always consult with your supervisor and instructor regarding the dissertation structure since this can vary from one faculty to the next. Ensure you follow the required dissertation structure.
- Proofread and edit the document for grammar. A dissertation structure with very few grammatical errors increases the chances of success.
- Be clear and direct when writing a dissertation. This will ensure that it is approved by the examination board. When an institution does not have dissertation structure guidelines, ensure the dissertation structure components listed above are included.
- Ensure the dissertation structure specifications are followed to the letter. Specifications include font and paper size, among others.
- Abbreviations are a part of the dissertation structure; a list of all abbreviated words used in the dissertation should be included.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint

Library Guides
Dissertations 4: methodology: methods.
- Introduction & Philosophy
- Methodology
Primary & Secondary Sources, Primary & Secondary Data
When describing your research methods, you can start by stating what kind of secondary and, if applicable, primary sources you used in your research. Explain why you chose such sources, how well they served your research, and identify possible issues encountered using these sources.
Definitions
There is some confusion on the use of the terms primary and secondary sources, and primary and secondary data. The confusion is also due to disciplinary differences (Lombard 2010). Whilst you are advised to consult the research methods literature in your field, we can generalise as follows:
Secondary sources
Secondary sources normally include the literature (books and articles) with the experts' findings, analysis and discussions on a certain topic (Cottrell, 2014, p123). Secondary sources often interpret primary sources.
Primary sources
Primary sources are "first-hand" information such as raw data, statistics, interviews, surveys, law statutes and law cases. Even literary texts, pictures and films can be primary sources if they are the object of research (rather than, for example, documentaries reporting on something else, in which case they would be secondary sources). The distinction between primary and secondary sources sometimes lies on the use you make of them (Cottrell, 2014, p123).
Primary data
Primary data are data (primary sources) you directly obtained through your empirical work (Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill 2015, p316).
Secondary data
Secondary data are data (primary sources) that were originally collected by someone else (Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill 2015, p316).
Comparison between primary and secondary data
Use
Virtually all research will use secondary sources, at least as background information.
Often, especially at the postgraduate level, it will also use primary sources - secondary and/or primary data. The engagement with primary sources is generally appreciated, as less reliant on others' interpretations, and closer to 'facts'.
The use of primary data, as opposed to secondary data, demonstrates the researcher's effort to do empirical work and find evidence to answer her specific research question and fulfill her specific research objectives. Thus, primary data contribute to the originality of the research.
Ultimately, you should state in this section of the methodology:
What sources and data you are using and why (how are they going to help you answer the research question and/or test the hypothesis.
If using primary data, why you employed certain strategies to collect them.
What the advantages and disadvantages of your strategies to collect the data (also refer to the research in you field and research methods literature).
Quantitative, Qualitative & Mixed Methods
The methodology chapter should reference your use of quantitative research, qualitative research and/or mixed methods. The following is a description of each along with their advantages and disadvantages.
Quantitative research
Quantitative research uses numerical data (quantities) deriving, for example, from experiments, closed questions in surveys, questionnaires, structured interviews or published data sets (Cottrell, 2014, p93). It normally processes and analyses this data using quantitative analysis techniques like tables, graphs and statistics to explore, present and examine relationships and trends within the data (Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, 2015, p496).
Qualitative research
Qualitative research is generally undertaken to study human behaviour and psyche. It uses methods like in-depth case studies, open-ended survey questions, unstructured interviews, focus groups, or unstructured observations (Cottrell, 2014, p93). The nature of the data is subjective, and also the analysis of the researcher involves a degree of subjective interpretation. Subjectivity can be controlled for in the research design, or has to be acknowledged as a feature of the research. Subject-specific books on (qualitative) research methods offer guidance on such research designs.
Mixed methods
Mixed-method approaches combine both qualitative and quantitative methods, and therefore combine the strengths of both types of research. Mixed methods have gained popularity in recent years.
When undertaking mixed-methods research you can collect the qualitative and quantitative data either concurrently or sequentially. If sequentially, you can for example, start with a few semi-structured interviews, providing qualitative insights, and then design a questionnaire to obtain quantitative evidence that your qualitative findings can also apply to a wider population (Specht, 2019, p138).
Ultimately, your methodology chapter should state:
Whether you used quantitative research, qualitative research or mixed methods.
Why you chose such methods (and refer to research method sources).
Why you rejected other methods.
How well the method served your research.
The problems or limitations you encountered.
Doug Specht, Senior Lecturer at the Westminster School of Media and Communication, explains mixed methods research in the following video:
LinkedIn Learning Video on Academic Research Foundations: Quantitative
The video covers the characteristics of quantitative research, and explains how to approach different parts of the research process, such as creating a solid research question and developing a literature review. He goes over the elements of a study, explains how to collect and analyze data, and shows how to present your data in written and numeric form.

Link to quantitative research video
Some Types of Methods
There are several methods you can use to get primary data. To reiterate, the choice of the methods should depend on your research question/hypothesis.
Whatever methods you will use, you will need to consider:
why did you choose one technique over another? What were the advantages and disadvantages of the technique you chose?
what was the size of your sample? Who made up your sample? How did you select your sample population? Why did you choose that particular sampling strategy?)
ethical considerations (see also tab...)
safety considerations
validity
feasibility
recording
procedure of the research (see box procedural method...).
Check Stella Cottrell's book Dissertations and Project Reports: A Step by Step Guide for some succinct yet comprehensive information on most methods (the following account draws mostly on her work). Check a research methods book in your discipline for more specific guidance.
Experiments
Experiments are useful to investigate cause and effect, when the variables can be tightly controlled. They can test a theory or hypothesis in controlled conditions. Experiments do not prove or disprove an hypothesis, instead they support or not support an hypothesis. When using the empirical and inductive method it is not possible to achieve conclusive results. The results may only be valid until falsified by other experiments and observations.
For more information on Scientific Method, click here .
Observations
Observational methods are useful for in-depth analyses of behaviours in people, animals, organisations, events or phenomena. They can test a theory or products in real life or simulated settings. They generally a qualitative research method.
Questionnaires and surveys
Questionnaires and surveys are useful to gain opinions, attitudes, preferences, understandings on certain matters. They can provide quantitative data that can be collated systematically; qualitative data, if they include opportunities for open-ended responses; or both qualitative and quantitative elements.
Interviews
Interviews are useful to gain rich, qualitative information about individuals' experiences, attitudes or perspectives. With interviews you can follow up immediately on responses for clarification or further details. There are three main types of interviews: structured (following a strict pattern of questions, which expect short answers), semi-structured (following a list of questions, with the opportunity to follow up the answers with improvised questions), and unstructured (following a short list of broad questions, where the respondent can lead more the conversation) (Specht, 2019, p142).
This short video on qualitative interviews discusses best practices and covers qualitative interview design, preparation and data collection methods.
Focus groups
In this case, a group of people (normally, 4-12) is gathered for an interview where the interviewer asks questions to such group of participants. Group interactions and discussions can be highly productive, but the researcher has to beware of the group effect, whereby certain participants and views dominate the interview (Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill 2015, p419). The researcher can try to minimise this by encouraging involvement of all participants and promoting a multiplicity of views.
This video focuses on strategies for conducting research using focus groups.
Check out the guidance on online focus groups by Aliaksandr Herasimenka, which is attached at the bottom of this text box.
Case study
Case studies are often a convenient way to narrow the focus of your research by studying how a theory or literature fares with regard to a specific person, group, organisation, event or other type of entity or phenomenon you identify. Case studies can be researched using other methods, including those described in this section. Case studies give in-depth insights on the particular reality that has been examined, but may not be representative of what happens in general, they may not be generalisable, and may not be relevant to other contexts. These limitations have to be acknowledged by the researcher.
Content analysis
Content analysis consists in the study of words or images within a text. In its broad definition, texts include books, articles, essays, historical documents, speeches, conversations, advertising, interviews, social media posts, films, theatre, paintings or other visuals. Content analysis can be quantitative (e.g. word frequency) or qualitative (e.g. analysing intention and implications of the communication). It can detect propaganda, identify intentions of writers, and can see differences in types of communication (Specht, 2019, p146). Check this page on collecting, cleaning and visualising Twitter data.
Extra links and resources:
Research Methods
A clear and comprehensive overview of research methods by Emerald Publishing. It includes: crowdsourcing as a research tool; mixed methods research; case study; discourse analysis; ground theory; repertory grid; ethnographic method and participant observation; interviews; focus group; action research; analysis of qualitative data; survey design; questionnaires; statistics; experiments; empirical research; literature review; secondary data and archival materials; data collection.
Doing your dissertation during the COVID-19 pandemic
Resources providing guidance on doing dissertation research during the pandemic: Online research methods; Secondary data sources; Webinars, conferences and podcasts;
- Virtual Focus Groups Guidance on managing virtual focus groups
5 Minute Methods Videos
The following are a series of useful videos that introduce research methods in five minutes. These resources have been produced by lecturers and students with the University of Westminster's School of Media and Communication.

Case Study Research
Research Ethics
Quantitative Content Analysis
Sequential Analysis
Qualitative Content Analysis
Thematic Analysis
Social Media Research
Mixed Method Research
Procedural Method
In this part, provide an accurate, detailed account of the methods and procedures that were used in the study or the experiment (if applicable!).
Include specifics about participants, sample, materials, design and methods.
If the research involves human subjects, then include a detailed description of who and how many participated along with how the participants were selected.
Describe all materials used for the study, including equipment, written materials and testing instruments.
Identify the study's design and any variables or controls employed.
Write out the steps in the order that they were completed.
Indicate what participants were asked to do, how measurements were taken and any calculations made to raw data collected.
Specify statistical techniques applied to the data to reach your conclusions.
Provide evidence that you incorporated rigor into your research. This is the quality of being thorough and accurate and considers the logic behind your research design.
Highlight any drawbacks that may have limited your ability to conduct your research thoroughly.
You have to provide details to allow others to replicate the experiment and/or verify the data, to test the validity of the research.
Bibliography
Cottrell, S. (2014). Dissertations and project reports: a step by step guide. Hampshire, England: Palgrave Macmillan.
Lombard, E. (2010). Primary and secondary sources. The Journal of Academic Librarianship , 36(3), 250-253
Saunders, M.N.K., Lewis, P. and Thornhill, A. (2015). Research Methods for Business Students. New York: Pearson Education.
Specht, D. (2019). The Media And Communications Study Skills Student Guide . London: University of Westminster Press.
- << Previous: Introduction & Philosophy
- Next: Ethics >>
- Last Updated: Sep 14, 2022 12:58 PM
- URL: https://libguides.westminster.ac.uk/methodology-for-dissertations
CONNECT WITH US
While Sandel argues that pursuing perfection through genetic engineering would decrease our sense of humility, he claims that the sense of solidarity we would lose is also important.
This thesis summarizes several points in Sandel’s argument, but it does not make a claim about how we should understand his argument. A reader who read Sandel’s argument would not also need to read an essay based on this descriptive thesis.
Broad thesis (arguable, but difficult to support with evidence)
Michael Sandel’s arguments about genetic engineering do not take into consideration all the relevant issues.
This is an arguable claim because it would be possible to argue against it by saying that Michael Sandel’s arguments do take all of the relevant issues into consideration. But the claim is too broad. Because the thesis does not specify which “issues” it is focused on—or why it matters if they are considered—readers won’t know what the rest of the essay will argue, and the writer won’t know what to focus on. If there is a particular issue that Sandel does not address, then a more specific version of the thesis would include that issue—hand an explanation of why it is important.
Arguable thesis with analytical claim
While Sandel argues persuasively that our instinct to “remake” (54) ourselves into something ever more perfect is a problem, his belief that we can always draw a line between what is medically necessary and what makes us simply “better than well” (51) is less convincing.
This is an arguable analytical claim. To argue for this claim, the essay writer will need to show how evidence from the article itself points to this interpretation. It’s also a reasonable scope for a thesis because it can be supported with evidence available in the text and is neither too broad nor too narrow.
Arguable thesis with normative claim
Given Sandel’s argument against genetic enhancement, we should not allow parents to decide on using Human Growth Hormone for their children.
This thesis tells us what we should do about a particular issue discussed in Sandel’s article, but it does not tell us how we should understand Sandel’s argument.
Questions to ask about your thesis
- Is the thesis truly arguable? Does it speak to a genuine dilemma in the source, or would most readers automatically agree with it?
- Is the thesis too obvious? Again, would most or all readers agree with it without needing to see your argument?
- Is the thesis complex enough to require a whole essay's worth of argument?
- Is the thesis supportable with evidence from the text rather than with generalizations or outside research?
- Would anyone want to read a paper in which this thesis was developed? That is, can you explain what this paper is adding to our understanding of a problem, question, or topic?
- picture_as_pdf Thesis
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write an excellent thesis conclusion [with examples]

Restate the thesis
Review or reiterate key points of your work, explain why your work is relevant, a take-away for the reader, more resources on writing thesis conclusions, frequently asked questions about writing an excellent thesis conclusion, related articles.
At this point in your writing, you have most likely finished your introduction and the body of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper . While this is a reason to celebrate, you should not underestimate the importance of your conclusion. The conclusion is the last thing that your reader will see, so it should be memorable.
A good conclusion will review the key points of the thesis and explain to the reader why the information is relevant, applicable, or related to the world as a whole. Make sure to dedicate enough of your writing time to the conclusion and do not put it off until the very last minute.
This article provides an effective technique for writing a conclusion adapted from Erika Eby’s The College Student's Guide to Writing a Good Research Paper: 101 Easy Tips & Tricks to Make Your Work Stand Out .
While the thesis introduction starts out with broad statements about the topic, and then narrows it down to the thesis statement , a thesis conclusion does the same in the opposite order.
- Restate the thesis.
- Review or reiterate key points of your work.
- Explain why your work is relevant.
- Include a core take-away message for the reader.
Tip: Don’t just copy and paste your thesis into your conclusion. Restate it in different words.
The best way to start a conclusion is simply by restating the thesis statement. That does not mean just copying and pasting it from the introduction, but putting it into different words.
You will need to change the structure and wording of it to avoid sounding repetitive. Also, be firm in your conclusion just as you were in the introduction. Try to avoid sounding apologetic by using phrases like "This paper has tried to show..."
The conclusion should address all the same parts as the thesis while making it clear that the reader has reached the end. You are telling the reader that your research is finished and what your findings are.
I have argued throughout this work that the point of critical mass for biopolitical immunity occurred during the Romantic period because of that era's unique combination of post-revolutionary politics and innovations in smallpox prevention. In particular, I demonstrated that the French Revolution and the discovery of vaccination in the 1790s triggered a reconsideration of the relationship between bodies and the state.
Tip: Try to reiterate points from your introduction in your thesis conclusion.
The next step is to review the main points of the thesis as a whole. Look back at the body of of your project and make a note of the key ideas. You can reword these ideas the same way you reworded your thesis statement and then incorporate that into the conclusion.
You can also repeat striking quotations or statistics, but do not use more than two. As the conclusion represents your own closing thoughts on the topic , it should mainly consist of your own words.
In addition, conclusions can contain recommendations to the reader or relevant questions that further the thesis. You should ask yourself:
- What you would ideally like to see your readers do in reaction to your paper?
- Do you want them to take a certain action or investigate further?
- Is there a bigger issue that your paper wants to draw attention to?
Also, try to reference your introduction in your conclusion. You have already taken a first step by restating your thesis. Now, check whether there are other key words, phrases or ideas that are mentioned in your introduction that fit into your conclusion. Connecting the introduction to the conclusion in this way will help readers feel satisfied.
I explored how Mary Wollstonecraft, in both her fiction and political writings, envisions an ideal medico-political state, and how other writers like William Wordsworth and Mary Shelley increasingly imagined the body politic literally, as an incorporated political collective made up of bodies whose immunity to political and medical ills was essential to a healthy state.
Tip: Make sure to explain why your thesis is relevant to your field of research.
Although you can encourage readers to question their opinions and reflect on your topic, do not leave loose ends. You should provide a sense of resolution and make sure your conclusion wraps up your argument. Make sure you explain why your thesis is relevant to your field of research and how your research intervenes within, or substantially revises, existing scholarly debates.
This project challenged conventional ideas about the relationship among Romanticism, medicine, and politics by reading the unfolding of Romantic literature and biopolitical immunity as mutual, co-productive processes. In doing so, this thesis revises the ways in which biopolitics has been theorized by insisting on the inherent connections between Romantic literature and the forms of biopower that characterize early modernity.
Tip: If you began your thesis with an anecdote or historical example, you may want to return to that in your conclusion.
End your conclusion with something memorable, such as:
- a call to action
- a recommendation
- a gesture towards future research
- a brief explanation of how the problem or idea you covered remains relevant
Ultimately, you want readers to feel more informed, or ready to act, as they read your conclusion.
Yet, the Romantic period is only the beginning of modern thought on immunity and biopolitics. Victorian writers, doctors, and politicians upheld the Romantic idea that a "healthy state" was a literal condition that could be achieved by combining politics and medicine, but augmented that idea through legislation and widespread public health measures. While many nineteenth-century efforts to improve citizens' health were successful, the fight against disease ultimately changed course in the twentieth century as global immunological threats such as SARS occupied public consciousness. Indeed, as subsequent public health events make apparent, biopolitical immunity persists as a viable concept for thinking about the relationship between medicine and politics in modernity.
Need more advice? Read our 5 additional tips on how to write a good thesis conclusion.
The conclusion is the last thing that your reader will see, so it should be memorable. To write a great thesis conclusion you should:
The basic content of a conclusion is to review the main points from the paper. This part represents your own closing thoughts on the topic. It should mainly consist of the outcome of the research in your own words.
The length of the conclusion will depend on the length of the whole thesis. Usually, a conclusion should be around 5-7% of the overall word count.
End your conclusion with something memorable, such as a question, warning, or call to action. Depending on the topic, you can also end with a recommendation.
In Open Access: Theses and Dissertations you can find thousands of completed works. Take a look at any of the theses or dissertations for real-life examples of conclusions that were already approved.

The Michael Schwartz Library
- Michael Schwartz Library
- Ask A Librarian
Q. How do I number pages differently in the various sections of my thesis or dissertation?
- 18 General (hours, borrowing, employment, etc)
- 10 Remote Access to Library Resources & Services
- 12 Research
- 16 Technical Support
Answered By: Jeff Beuck Last Updated: Apr 03, 2020 Views: 1400017
See Also: How do I add page numbers in Microsoft Word?
To use different page numbering schemes in different sections of your Word document, there are two tricks: 1) you must include a "Section Break - Next page" between each section of your document where the numbering will change, and 2) you must "unlink" each section's footer from the one before it.
To start, temporarily turn on the viewing of hidden formatting symbols by clicking the "Show/Hide" symbol on the "Home" tab in the "Paragraph" box -- this will enable you to see the Section Breaks between sections of your document.
One of the required page numbering changes for your thesis or dissertation is that you need to use Roman numerals (e.g., "i, ii, iii") for your introductory sections (Abstract, Table of Contents), and then switch to Arabic numerals (e.g., "1, 2, 3") and begin the page numbering at "1" at the start of Chapter I of your main text.
If you do not already have a "Section Break" between these two sections of your document, you will need to add one. Place your cursor at the very end of the text in the first section (after your Table of Contents and any Lists of Tables and Figures), being careful NOT to place it in the footer where the page number is (if the text above becomes grayed out, you are in the footer – try clicking higher).
Add a "Section Break – Next Page" by selecting the "Page Layout" tab on the menu, clicking the arrow next to "Breaks", and selecting "Next Page" under Section Breaks.
After doing this, you should see a "Section Break (Next Page)" code inserted into your document. This tells Word that the next page begins a new section which may have a different header or footer.

Go down to the next page below the section break (in this example, the first page of Chapter I), and click on the page number in the Footer. If your cursor is in the Footer, you should see "Footer -Section [#]-" to the left, and "Same as Previous" on the right.

You should also see a new tab appear on the menu, labeled "Header & Footer Tools: Design". Select this. (Be careful not to confuse this with another tab labeled "Design" between the "Insert" and "Page Layout" tabs.) In the "Navigation" section of this tab, you will see a highlighted button labeled "Link to Previous" which tells Word to link the footer in this section to the previous section and to continue its page numbering scheme. Click the "Link to Previous" button to UNSELECT it.
After clicking this, the "Link to Previous" button should no longer be highlighted. The "Same as Previous" box to the right of your footer should also disappear.
Confirm your cursor is still next to the page number in the Footer, then go back to the Header & Footer Tools – Design tab on the menu, and in the "Header & Footer" section, select Page Number > Format Page Numbers.
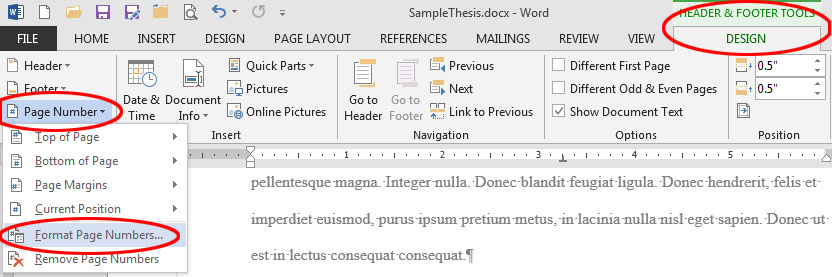
The "Page Number Format" window will appear. Select the appropriate "Number format" for this section ("1, 2, 3," or "i, ii, iii", etc.), and tell Word whether to continue the page numbering from the previous section or to start at "1" or another number. In this example, we want Section 2 (which begins at Chapter I and contains the main text of our thesis or dissertation) to use Arabic numerals and to start numbering this section from page 1. Click "OK" to finish.
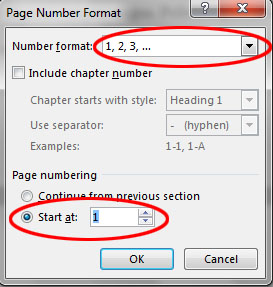
You will notice that the page numbering for the current section has now been corrected, and if you unlinked it properly from the previous sections, the numbering in those sections should remain as it was before.

Next, you will need to change the page number format to lower-case Roman numerals (i.e., "i, ii, iii, ...") for the section with your Abstract and Table of Contents. Click your cursor on the footer of your Abstract or Table of Contents page.
Open the "Format Page Numbers" window by going to the Header & Footer Tools – Design tab on the menu, and in the "Header & Footer" section, select Page Number > Format Page Numbers.
Next to "Number format", select the "i, ii, iii, ..." option for lower-case Roman numerals, then click "OK".

The page numbering for the section with your Abstract and Table of Contents should change to lower-case Roman numerals. As long as you correctly unlinked the following section from this one, the page numbering in the following section, the main body of your text, should remain Arabic numerals starting with 1.
You will also need to remove page numbers completely from the title page and other preliminary pages of your thesis or dissertation. To do this, you will use the same method as above, but delete the page numbers from the first section of your document.
Place your cursor at the very end of the last page which will not be numbered (probably your approval page, dedication, or acknowledgment), being careful NOT to place it in the footer where the page number is (if the text above becomes grayed out, you are in the footer – try clicking higher).

After doing this, you should see a "Section Break (Next Page)" code inserted into your document on the page before your Abstract.
Go down to the next page below the section break (in this example, the Abstract), and click on the page number in the Footer. If your cursor is in the Footer, you should see "Footer -Section [#]-" to the left, and "Same as Previous" on the right. Be sure you are not in Section 1 of your document.

On the main menu, select the "Header & Footer Tools: Design" tab, then in the "Navigation" section of this tab, click the "Link to Previous" button if it is highlighted to UNSELECT it and unlink this section from the section above. This will allow you to modify the page number in the first section without affecting this or subsequent sections.
Return to your Title Page (or any page in Section 1 which will not be numbered) and click on the page number in the footer. Click-and-drag your cursor over the page number to select it.

Click the "Delete" key on your keyboard to delete the page number from this section. As long as you removed the "Link to Previous" connection from the next section, you should the page number disappear from the first section, but remain in the following sections.

If your paper includes additional sections (for example, if your Approval Page was added as a separate section from your Title page), you may have to experiment with linking and unlinking sections from each other -- unlink a section if its page numbering will be different from the one before it, but link together any sections where the page numbering will continue from the one before it. It is generally a good idea to start with the last section of your document and work your way backwards.
When you are finished, don't forget that you can hide the formatting symbols to make it easier to view your text by turning off the "Show/Hide" symbol on the "Home" tab in the "Paragraph" box.

Footer Sections and page numbering can be very complex, especially if your document has multiple sections. If you need additional assistance getting your page numbering correct, contact Jeff Beuck at 216-523-7486 to set up an appointment.
- Share on Facebook
Was this helpful? Yes 0 No 0
Comments (378)
- Very helpful by Tashy on Nov 16, 2017
- Thank you so much!!! by Wraith on Feb 26, 2018
- Excellent and easy to follow instructions. Exactly what I needed. by Mira on Mar 12, 2018
- Thanks Sir So much. You are very kind to people. by Nur Alam on Apr 04, 2018
- Thank you so much! This was extremely helpful and a total time saver! by Brittany on Apr 10, 2018
- Thank you, it really is helpful by Sadia on Apr 29, 2018
- Wow impressive it was very helpful to me. Am glad with the informative words and direction. Shalom. by Josphine Gwehona on May 17, 2018
- EXTREMELY Helpful - Thank you so much. I learnt something too by TIM on May 25, 2018
- Interesting by Dawit Yosef on Jul 02, 2018
- Thank you, your article is very helpful http://glodoksafety.com by Andre Kurniawan on Aug 14, 2018
- it worked well for me..thank you sir.. by Kalya on Aug 18, 2018
- Useful for me. Thanks very much. by Kwesi on Aug 19, 2018
- This was of great help, thanks by Euny on Sep 12, 2018
- Very helpful, concise and comprehensive. Keeps it up Jeff! by Nawas on Sep 15, 2018
- Wow very informative and helpful. Thanks! by Uchy Masika on Sep 19, 2018
- You are so good, thank you by olanrewaju balogun on Oct 25, 2018
- super very helpful. I finally understood it. by Michael on Nov 22, 2018
- This has been very helpful. Thank you. by J on Nov 30, 2018
- Thank you so much for this, it is so helpful! by thankfulalmostmaster on Dec 04, 2018
- This post was a life saver. It was crunch time and I underestimated the pagination of my APA action research. "Hidden formatting symbol", "Section Break"? I NEVER would have thought to do those things. Thanks to you I submitted at 11:51 pm, lol, in the nick of time, lol. by KMo on Dec 13, 2018
- This really was the most useful ''how to'' on the topic - I really battled with the other sites. by Francois on Dec 28, 2018
- Very detail with clearly explained, simple and helpful by Dave T on Jan 06, 2019
- Very helpful.... by Reginescorner on Jan 08, 2019
- Thank you so much by Augustine on Jan 10, 2019
- EXCELLENT!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! by Natasha on Jan 11, 2019
- Great tip. Thanks for adding. I had the same question for my thesis. by Manuel Duarte on Feb 08, 2019
- This was so helpful and clearly presented; I would have never figured it our otherwise - thank you!!! by Janice on Feb 26, 2019
- Great help 👍🏽👍🏽👍🏽 by Nge on Mar 01, 2019
- Spot on! Thanks! by Jonathan E on Mar 15, 2019
- awesome procedure. by Derick Musi on Mar 31, 2019
- Thank you! Saved me. by KK on Apr 01, 2019
- very helpful, thank you by silas on Apr 04, 2019
- Thank you for this elaborate explanation. Very helpful. by Prucy on Apr 18, 2019
- Brilliant! Got me a first ! by Bob on Apr 25, 2019
- noice by ye_boi on Apr 25, 2019
- very very helpful, thank you. by Lucy Jackson on Apr 28, 2019
- This was really helpful and straightforward. by Deeya on Apr 30, 2019
- Jeff Beuck is the Hero we deserve by anonymous on May 05, 2019
- Thank you from the University of Kansas! by Owen on May 14, 2019
- THANK YOU! your info help me a lot (",). by AURORA on May 15, 2019
- Exceptionally helpful - thank you! by Karin W on May 28, 2019
- Thanks! I watched a couple of youtube videos before seeing this and had been struggling with pages refusing to take any number at all. It's all useful, but the most satisfying statement here was "begin at the bottom". by Tracie Hall on Jun 04, 2019
- Life is saved! by Uki on Jun 05, 2019
- Useful by Naveed on Jun 08, 2019
- Very helpful indeed by Mwanakasale Muche on Jul 09, 2019
- So helpful! Thank you very much for the detailed tutorial. by Jes on Jul 17, 2019
- Very helpful by Shauri Mbugua on Jul 21, 2019
- Thank you very much. This is the best material I have ever read on this subject. The writer wrote in detail. by Abraham on Jul 26, 2019
- Thanks so much, very useful by Henlee on Jul 29, 2019
- Thank you Very helpful by Zayn on Aug 02, 2019
- Very very useful, i didnt have any idea to number different sections. by Rashid Mwatebela on Aug 07, 2019
- It resolve my querry.... really very helpful Great work👍 by Shikha on Aug 11, 2019
- very helpful and thank u😍 by madhushi on Aug 17, 2019
- Thanks,just got it. by Emmanuel on Aug 21, 2019
- Very helpful by Monseur on Aug 26, 2019
- I am so grateful for this important information. i have used it successfully insert preliminary pages in my report. I am so grateful. by Caroline N. Ateenyi on Aug 28, 2019
- Incredibly helpful. I looked at several different sites for an answer to this, and none of them mentioned the section break (I thought page break did this for me). Thank you for explicitly detailing every step. by Jeremy on Sep 07, 2019
- This was amazingly helpful and straight to the point. Other people have made fifteen minute long videos to explain what this post does in a quick five minute read. Thank you kindly for putting this online! by Kate F. on Sep 07, 2019
- Very helpful indeed by JOJO on Nov 04, 2019
- Very very helpful by Mbogora Malima on Nov 07, 2019
- A detailed step by step explanation. Thank you. by Kavitha Gopalakrishnan on Nov 11, 2019
- Very helpful find it hard to change page number by section but after i've seen this info its way more easier by now by Omni.shade on Nov 26, 2019
- it was very useful. by Esther on Dec 06, 2019
- Thank you ...really clear instructions saved me a lot of time. by Rich on Dec 14, 2019
- Thank you very much. Very helpful! by Dusan on Dec 16, 2019
- Super helpful, thanks. by PhD Student on Jan 24, 2020
- Very helpful, sorted out such a frustrating problem I couldn't work out. by Labeeb on Feb 10, 2020
- Thank you so much. This material was much more helpful than YouTube videos. Very detailed. God bless the writer. Totally time saving. by Judith on Mar 09, 2020
- Very helpful article indeed. This has solved a very important for my articles. Many thanks! by Jamil Ahmed on Mar 21, 2020
- This is very helpful. Thank you so much!! by Glen Parry on Mar 27, 2020
- Was very helpful. Thank you. by Hunja Amos on Apr 16, 2020
- Excellent description, it worked for me. Thank you !!! by Akshay on Apr 20, 2020
- Your information saved me some embarrassment. It works like a " where there is no doctor" strategy. I gratefully appreciate you. by DAMIAN BAKYENGA on Apr 26, 2020
- Very helpful, thank you! by Tugce on Apr 30, 2020
- Thank you SO MUCH for this easy-to-follow tutorial. You made my day! by Don, Graduate Student, CSUN on May 02, 2020
- This is very helpful and thank you a million. by Tafirenyika Gwenzi on May 12, 2020
- Thank You!! This was Helpful!!! by Kehinde Miracle Alabi on May 18, 2020
- So clear and helpful🧡 by Wel on May 25, 2020
- Very helpful indeed! by Havelinus Shemuketa on Jun 06, 2020
- These instructions were excellent - very clear and detailed - user friendly. I had viewed some videos here on Google and they were not as clear as these instructions. Thank you!! by Sharon W. on Jun 06, 2020
- Wow, unbelievable by Tito Titus on Jun 07, 2020
- very helpful. thank you very much by verah Tena on Jun 12, 2020
- This really helped me by Berto on Jun 12, 2020
- THANK YOU!! Very clear and helpful directions!! Thank you! by PhD Student on Jun 15, 2020
- Very Helpful. Thank you so much by Amanuel Zinare on Jun 17, 2020
- Does anyone know how to do this with page numbers in the main body of the document rather than the header/footer? by John on Jun 19, 2020
- Many thanks by Melosum on Jun 21, 2020
- Extremely helpful!!! by Esther on Jun 23, 2020
- Thank you so much for this. Very helpful for my dissertation. by Amelia on Jun 25, 2020
- Thank you so much by hadi on Jun 28, 2020
- Thanks a lot for evrything this saved me by Sasikafsal on Jul 03, 2020
- This was really helpful. Exactly what I needed. Thank you. 👍 by PAP on Jul 03, 2020
- This was very helpful. Thank you so much for providing such a detailed description. by Zainab on Jul 07, 2020
- Very useful. Thank you. by Issah on Jul 16, 2020
- Thank you so much....i have really been battling with numbering pages....your guide made it very smooth.. by Eben on Jul 16, 2020
- Great work. This is the best guide for inserting page numbers on thesis. Great relief for me. Thanks a lot. by abdul quddus on Jul 19, 2020
- Thanks alot by Yasser on Jul 24, 2020
- Easier to follow and so helpful. Thank you by Hawa on Jul 29, 2020
- Very clear and concise. It works exactly as explained. Many thanks indeed. by Adhiambo on Aug 06, 2020
- Very helpful! by Erin on Aug 07, 2020
- Wow, that was lovely. Thanks so much for the help by Emmanuel Macnelly on Aug 10, 2020
- Great resource and simple to understand by Valentine on Aug 20, 2020
- Thank you so much. very helpful by Ay on Aug 20, 2020
- What a wonderful piece, very easy to follow tutorial. Thanks alot. It is something I had failed to learn but now, I am good to go🙂 by Shalom. on Aug 21, 2020
- Wow!! This was super helpful.. I owe you a lot!! Wow!! Super easy to follow!! I never knew this before today.. Many many many thanks.. You're a life saver!! by Bileme Miller on Aug 25, 2020
- Thanks so much for dis, its really helpful 😍 Ave gone through a lot of troubles only to find dis here by Abby on Aug 28, 2020
- Thank you very much, this is so helpful by MoyinOlúwa on Aug 31, 2020
- wow, thanks so much. you can also tell us how to remove the empty pages that show up after the page break. Thanks by DCT on Aug 31, 2020
- Thanks for the remarkable advice and the step by step made it easy for me. by Lynette Wyatt on Sep 01, 2020
- Thank you so much! by Dene on Sep 04, 2020
- This was very very helpful by Ratakane Baptista Maime on Sep 07, 2020
- Wonderful step-by-step detailed explanation!! Wonderful and very helpful indeed!! by Rajsekhar Choudhury on Sep 07, 2020
- This my guy just saved me. Thank you by Andy on Sep 09, 2020
- This is so helpful... Many thanks! by Dieudonne on Sep 10, 2020
- Extremely helpful, many thanks! by Enesi on Sep 22, 2020
- Very easy to follow. Excellent work, thank you very much. by Vimbie on Sep 23, 2020
- This is absolutely educational, thank you so much by Ahadyson on Sep 25, 2020
- thank you so much.it has been very helpful by joan on Oct 02, 2020
- Bery helpful thanks by Kanjau on Oct 05, 2020
- Excellent Explanation by Jayanarasimha on Oct 07, 2020
- Very useful and clear explanation. It was very helpful. Thanks a lot by NJoshi on Oct 08, 2020
- thanks by blabla on Oct 09, 2020
- very helpful, thank you by Celestina Chinenye on Oct 09, 2020
- Thanks for the help, I'm very grateful. by Josephine on Oct 15, 2020
- Thank you so much! You are good in teaching! by Fanta on Oct 15, 2020
- Thankyou. Very nice. by Abd.k on Oct 17, 2020
- This was actually the MOST useful explanation I found on google. Thank you so much, you really deserve an award. by B on Oct 19, 2020
- Aww..it was really helpful. Thank you so much! by Nishinki on Oct 27, 2020
- You are blessed in simplifying things. Great! keep at it by Dtk on Nov 01, 2020
- Thank you so much for your help. I have been thinking of how to do this. by Dr Shamsuddeen Yusuf on Nov 04, 2020
- This is amazing. It worked perfectly. Thanks alot. by Majale_Jr on Nov 04, 2020
- Thanks a lot, really helped a lot. by AbdulWaahid on Nov 09, 2020
- Very very helpful...Thank you so much!!!! by Lucy.K on Nov 13, 2020
- Absolute legend, I spent hours onto microsoft helpdesk at the end of my dissertation to get this fixed. Completely forgot how to do it again for my next dissertation and this page had me sorted in 5 minutes. You are an total lifesaver, thank you!!! by James on Nov 14, 2020
- This was very helpful. Thank you very much. by Tony on Nov 16, 2020
- Wow.... This was really helpful......... Thanks a lot by Boo on Nov 16, 2020
- AMAZIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIING!! Very helpful, many thanks. by Wambui on Nov 18, 2020
- Oh my gosh - it worked! by SJCD on Nov 18, 2020
- It is best info thank you I have aquestion how to insert page number without the first three document page by nigus on Nov 18, 2020
- this was very helpful. thank you so much by Zakaa Zuamo Zechariah on Nov 19, 2020
- Exactly what I wanted. Thank you. by Sokiri Richard on Nov 22, 2020
- Thanks so much! This was extremely helpful! by Yembu on Nov 24, 2020
- This is the best explanation for inserting page numbers. Thanks for a lot for this. by Furqan on Nov 30, 2020
- Thank you very much. this has really helped me. by Mary Chioma on Dec 06, 2020
- Very helpful! Thank you so much! by Dhea on Dec 08, 2020
- Thank you, this was really helpful and easy to understand! by Christina on Dec 08, 2020
- This is on point and super helpful, and exactly what I needed. Thank you. by NB on Dec 23, 2020
- Thank you that was helpful by KellyMuchenje on Dec 30, 2020
- Very helpful. Thx by Aidah on Jan 02, 2021
- This information is fantastic and helpful✔ by https://delightedgloryservices.com.ng on Jan 05, 2021
- MANY MANY THANKS. THIS IS 100% ACCURATE AND VERY USEFUL. THANK YOU SO SO MUCH by God's grace on Jan 07, 2021
- This is very helpful...thanks a ton by Kenpaul on Jan 08, 2021
- been searching for a way to do this, and yours explanation was the one that really help me, thank you! by bel on Jan 11, 2021
- Many thanks. This is a very good guide! by Joe on Jan 11, 2021
- Very helpfull, thanks a lot. by cyrus on Jan 12, 2021
- Very helpful. At a glance I got scared when I saw its length, but this was resolved by including illustrations. They were quite useful. Thanks so much. by Emmanuel 12/01/2021 on Jan 12, 2021
- thank you, super helpful!! by aiyana on Jan 17, 2021
- Thank you very much! This helped a lot by Ibrahim on Jan 17, 2021
- Am greatful by Muhammad on Jan 18, 2021
- Thank you so much for this simple and clear explanation. by Jihene on Jan 19, 2021
- This was really helpful. It was by far the most useful bit of information I've found online. Thank you by Corey on Jan 23, 2021
- Very helpful. Thank you. by TRams on Jan 25, 2021
- I felt the need to write this message and thank you for your perfect explanation! I was struggling with numbering every section differently until I found this article of yours! thank you and God bless you! by Andrea on Jan 31, 2021
- thank you so much it was boring for me before i get this guidance keep it up for other difficulty also by betelhem on Jan 31, 2021
- Wonderful.Easy to follow.Thank you. by Esperanza Lizz on Feb 03, 2021
- This is so well explained. Thank you by Janet on Feb 07, 2021
- Thank you! ^_^ by Pranjal on Feb 07, 2021
- Thank you, than you, thank you!! I finally did it! Why did MS make this so convoluted? by GM on Feb 09, 2021
- Thanks for this explicit presentation of knowledge . It was apt and accurate. I deeply appreciate your time by Nsikak CICERO on Feb 15, 2021
- Thanks a lot for the guidance. It helped me a lot. by Sudeepa on Feb 17, 2021
- Extremely helpful, thank you so much! by Rasha on Feb 21, 2021
- This is really helpful by Abiodun on Feb 25, 2021
- At 1:00am, these instructions were a relief. Thank you! by Brandy on Feb 28, 2021
- Excellent service, am thankful by James Gachau on Mar 01, 2021
- Thanks, much better than microsoft help! by Bioprocess engineer on Mar 05, 2021
- Thanks a million! This was very helpful! by Esther on Mar 08, 2021
- Very systematic, informative and to the point steps. Thank you by Doris on Mar 09, 2021
- Very helpful thank you by Edgar on Mar 22, 2021
- The Guide is very beneficial. Thank you so much by Gideon Biwott on Mar 22, 2021
- Thanks. Very helpful indeed by Felix Wanjala on Mar 23, 2021
- Excellent ! This article helped me paginate my dissertation as expected. Thank you very much by Latha on Mar 24, 2021
- really helpful, totally a good guide by jann on Mar 25, 2021
- Excellent explanation, thank you! by Dionne on Mar 25, 2021
- Thanks a lot sir, this is cool, it helped me a lot by Sir Richard on Mar 30, 2021
- very helpful and easy to understand, thank you sir! by FASYA on Apr 02, 2021
- Just want to thank the person, who explained this so well! This is how it must be done, highly appreciated, thanks again! by Ilja on Apr 06, 2021
- Very helpful. Thank you! by Tobi on Apr 07, 2021
- You're a godsend, dont know why this isnt easier to do on word but I'm very happy that you uploaded this guide. My thesis is saved! by Josh Herrera on Apr 07, 2021
- Thank you so much ,it is very helpful by Suji on Apr 10, 2021
- Thank you very much. Was very stuck and I got it now by Yola on Apr 13, 2021
- Very useful information indeed. Thank you so much! by Anthony on Apr 15, 2021
- Thank you very much. Quite helpful, had been looking through YouTube videos, and something was still not showing on my word document, but your steps solved the problem. :) by Taflex on Apr 15, 2021
- Very useful. Thank you so much. by BangTanS on Apr 17, 2021
- wow, have been struggling with this for now, finally got help on my own pace, this is very helpful, thank you so much by ken on Apr 26, 2021
- This is really helpful. Thank you so much. by Swapnika on Apr 27, 2021
- Thank you so so much the data is so so helping by Mugizi Gilverse and Mugizi Ronnet on May 01, 2021
- well explained thank you! by RASH on May 05, 2021
- Thank you so much! by Just J on May 08, 2021
- Excellent by Balendran Nanthini on May 09, 2021
- On point. Well explained and easy to follow.Am impressed.🤗🤗🤗 by Proc on May 09, 2021
- This was very simple and easily understandable.I was amazed and respect your profession. by Aregawi on May 10, 2021
- Very simple and easy to follow! Thank you. by Yash on May 10, 2021
- Thank you so much! This was so easy to follow! by J Lee on May 13, 2021
- This is very helpful because of the detailed explanation. Thank you so much by Thank you so much on May 20, 2021
- Thank you so much. It has helped me by Naume on May 21, 2021
- Very helpful and very well done, congratulations and thank you for your help. by Cesare on May 29, 2021
- Thank you, that was vey helpful. by Rose P on Jun 02, 2021
- Very Very Helpful Cudos by Dipesh Bista on Jun 09, 2021
- Amazing by Sagar on Jun 09, 2021
- Bro.. om’gosh dude, this is amazing... I would legit pay someone 500$ to figure this out for me, but your website was free...yo how can I show my support, no cap, this is amazing.. by Bk on Jun 10, 2021
- Thank you so much for this! Very helpful and easy to follow - appreciate it! by MMason on Jun 15, 2021
- Thank you very much for these helpful tips and easily understandable. by Mathias Mahenge on Jun 26, 2021
- Woooow brilliante xplanation, you really helped by Fafie on Jun 27, 2021
- Whooohoo thank you so much for clear cut explanation saved almost a 6 hours by Ashok on Jul 01, 2021
- It has always been helpful to use this! by Alim on Jul 01, 2021
- This was completely Helpful by Kingsley on Jul 02, 2021
- Thank you!! super concise instructions!! :)) big thanks by d on Jul 04, 2021
- Wow! It was very helpful, God bless you for the wonderful explanations and easy guidance of yours by Lembao on Jul 05, 2021
- Perfect explanation by June on Jul 07, 2021
- Very helpful. Thanks by Smartoskylalasky on Jul 11, 2021
- Excellent and easy to follow instructions. Exactly what I needed. by Ahmad Hussain on Jul 13, 2021
- Wow!! Brilliant guide. This is really helpful by Racheal on Jul 19, 2021
- helpful thank you by Justin on Jul 20, 2021
- Thank you so much Mr Beuck for your excellent explanation / illustration, it’s so clear and helpful. It’s also heart-warming to see the many comments of gratitude (and relief!) above; you’ve helped so many people! Thank you! :) by Sinead on Jul 31, 2021
- very helpful.thank you by julia muteyo on Aug 08, 2021
- It was very helpful thank you by Ivy on Aug 23, 2021
- Thank you very much! Very detailed and helpful with screenshots. by Sasha on Aug 23, 2021
- Awesome👍👍 Your instructions are clear and precise, showing unparallel clarity! Thank you so much! by Manouri on Aug 25, 2021
- Very useful and easy to follow the steps! by Mo on Aug 25, 2021
- Thanks a million. This was highly helpful. by Mashazi Mahoto on Aug 30, 2021
- This is a MUST SAVE page!! I come back here every time I need to format my document. You are a life saver! Thank you! by Zoe on Sep 10, 2021
- Thanks by Caleb Onyango on Sep 12, 2021
- Thank you, this is very helpful and simple to follow. by Abdislam Rhebi on Sep 18, 2021
- Thank you so much so helpful by Beauty on Sep 18, 2021
- Thanks a lot! Helped a lot. Quick, easy and to the point explanation. :-) by Pragya on Sep 20, 2021
- Thank very much. Easy to understand by Nana Kwame on Sep 23, 2021
- The best guidance ever!!!!! by Godfridah on Sep 30, 2021
- Practical step-by-step guidance. This is easy to follow and simply can't forget by NICHOLAS GWENGI on Oct 04, 2021
- This was so explicit and clear. Thank you so much! by Manisha on Oct 08, 2021
- You have absolutely made my work easy by RICHK on Oct 10, 2021
- So helpful. Thank you. by Jade on Oct 11, 2021
- Thank you so much for the clear instructions! It was really helpful. by Nirmal HETTIARACHCHI on Oct 13, 2021
- Very easy and straightforward Thank you by Luke on Oct 13, 2021
- Very helpful thank you so much by Sabelo on Oct 16, 2021
- whao! thanks greatly.... it was straight and easy to grasp by geoeffy on Oct 21, 2021
- Used this for my undergrad thesis, still used it for my postgrad paper. So helpful, thank you. by Wambui on Oct 23, 2021
- Thank you very much. That was awesome. Really helpful by Phd Candidate on Nov 10, 2021
- Am grateful you are my mentor thank you so much may God Bless you for me by Calvince Juma on Nov 19, 2021
- Excellent, thank you so much! by Cristiana on Nov 21, 2021
- very helpful. thank you so much by Faith Ashley on Nov 26, 2021
- That was perfect. I have been writing reports for school for a couple years and this is by far the best explanation and demonstrations I have come across! Thank you!!! by Benjamin on Nov 27, 2021
- Simple and straight forward quick steps, totally helpful by Esther on Nov 29, 2021
- FANTASTIC, thorough, clear, and detailed instructions!! I am so grateful for this super helpful guidance during the horrendous last stages of dissertation defense! I hope the human that wrote this knows how much they are appreciated by stressed graduate students! by Brielle on Dec 03, 2021
- Very much helpful. Many thanks!! by Abebe on Dec 06, 2021
- Thank you so much. This was so helpful. by Faves on Dec 08, 2021
- thank you. it is very helpful. by Abdul Rehman on Dec 09, 2021
- Thank you so much. This was very helpful and easy to follow! by Chinedu Anyaji on Dec 21, 2021
- Very insightful. I've appreciated it. by Makuei Ghai Makuei on Dec 23, 2021
- The guide is perfect. I was almost resorting to go and ask at some business centre and low and behold I found this!! Thank you very much by Casserdy Magaya on Dec 31, 2021
- I liked the way it is "explained" in detail. I was able to understand. Thank you very much! by Vida Nunez on Jan 03, 2022
- Like everyone else in the comments, I would just like to say thank you for this saving grace of a post. So helpful and the visuals really made it so easy to use. by hanseoulo on Jan 03, 2022
- Very excellent,; precise and concise by Aliyu idris KANKARA on Jan 04, 2022
- Very helpful, thank you! by gshoffma on Jan 06, 2022
- The help topics on Microsoft website are useless. After struggling there I fortunately found this page. Thank you very much. by Firas on Jan 17, 2022
- Its so easy to use and very helpful. i doing it will easy after reading the comment..keep it up... by Mukoya Edward Rumeta on Jan 27, 2022
- Thank you very much Sir ,much appreciated this has been very very useful to me by Gimses on Feb 09, 2022
- Very wonderful how-to and appreciate the screenshots throughout. Helpful, succinct, excellent work by the librarians at CSU Ohio. I think I'll consider sending my son to this university as I can see they really care about solving problems and adding value to society. by Hugh Janus on Feb 09, 2022
- Correct and direct explanation. Thanks so much by Alexander Talam on Feb 15, 2022
- Amazing!! Thank you so much! by Angie on Feb 17, 2022
- Are you kidding. This was AWESOME!! I was doing all the right things for 4 days; but here, we completed this in literally less than 20 minutes. So cool, keep this website going, Thanks Ben!! by Pam on Feb 17, 2022
- Great Minds!!! Thank you very very helpful by Esther on Mar 10, 2022
- This is great help, exactly what I was looking for. Thanks a lot. Really appreciated. by Umar on Mar 12, 2022
- Thank you!! Wonderfully helpful!! by Andi on Mar 15, 2022
- Internet is undefeated because of people like you. Thanks a lot! by Arun on Mar 20, 2022
- Easy to follow, explained in a lucid manner. Was very helpful. by Ivin Tomy on Mar 23, 2022
- This was SOOOO darn helpful! Whew! by Kels on Mar 24, 2022
- Thank you! by Paul on Mar 27, 2022
- I hate numbering word pages but this is THE BEST and MOST HELPFUL guide ever!! by Melissa on Mar 27, 2022
- Thank you for the guide, super easy to follow and very helpful. by Minky Masombuka on Apr 10, 2022
- Very helpful, thanks indeed by Joel Oraku on Apr 13, 2022
- very very helpful and interesting . thank you very much by zubieda on Apr 23, 2022
- thanks ,very helpful. by Modester on Apr 26, 2022
- Thanks,this was helpful by Metuge on Apr 26, 2022
- Very helpful!! by Gladness on May 07, 2022
- OMG THE MOST HELPFUL POST. Thank you SO MUCH!! I have never seen a better tutorial.🤩🤩🤩 by Katerina on May 10, 2022
- Excellent really clear and so helpful.. Thanks by Queen Bee on May 13, 2022
- Thank you.. this was very helpful by F Abujalala on May 13, 2022
- Very helpful! Thanks! by MS on May 15, 2022
- Very explicit. Good by Divine on May 17, 2022
- You are the best. You just saved us from days of a headache around this pagination. Well explained with images. I salute you and your team. Thumbs up. by Ola on May 26, 2022
- Very helpful. Thanks a lot! by Beatrice on May 30, 2022
- Thank you soo much! Very useful. Clear and easy guidance by Chaminie on Jun 08, 2022
- Very helpful indeed. Easy to follow and understand by Wilson Maiyo on Jun 11, 2022
- You're the man Jeff by LeBron on Jun 23, 2022
- I love the simplification of this, very easy to understand. by Azenda Cephas Dajo on Jun 27, 2022
- I highly appreciate your sincere help by Bildad on Jun 29, 2022
- Exactly what i wanted and to the point without wasting much of the readers time. I salute you sir. by Steve on Jun 29, 2022
- This was incredibly helpful! I was so confused until I came across this, thank you so much!! by McKenna O'Shea on Jul 06, 2022
- Fantastic and detailed procedure this is. Keep it up! by Xquort on Jul 07, 2022
- Perfect explanation. Thanks very much for this. by Sylvain Mbuta on Jul 11, 2022
- This was helpful and easy to follow,thank you by Bree Hildah on Jul 12, 2022
- Can we also change the total number of pages? I tried using this and it does restart the page number but the total number of pages do not change. by Mayur on Jul 13, 2022
- You have been super helpful, thank you. by Chichi on Jul 13, 2022
- Thank you! It is really helpful by Andinet on Jul 17, 2022
- Very useful. Thanks by OLAOSEBIKAN on Jul 21, 2022
- Extremely useful, easy to follow. by KANDASWAMY CHENNIMALAI on Jul 22, 2022
- Thank you. Very helpful by Ife on Jul 24, 2022
- much appreciation. the step by step procedure was very helpful. by IAN ARABU on Aug 30, 2022
- thank you.easy to follow by chamunoorwa matanhike on Aug 30, 2022
- Thanks a lot it was very helpful by Amabel on Sep 05, 2022
- I am extremely grateful by Kwabena Agyare on Sep 07, 2022
- Thank you so much. it is conducive. by fatima tayyab on Sep 15, 2022
- Thank you so much, this is the most helpful explanation, i have received on this subject. Excellent job. by Law on Sep 15, 2022
- OMG amazing, thank you thank you!!! by Mariana on Sep 19, 2022
- It was really helpful. Thank you very much indeed. by Adeteju Adeniran on Oct 03, 2022
- This was very helpful. Thanks. by Stephen on Oct 10, 2022
- A very detailed response to the problem. Thank you so much for giving a procedure that is easy to follow by Gummadivalli Shiva Kumar on Oct 12, 2022
- it was very helpful and its very easy to follow because you have used very easy words to explain. Thank u sooo much (JazakAllah u Khaiira) by Osama Shabir on Oct 14, 2022
- very helpful!! Thank you. by Monsurat Raimi on Oct 20, 2022
- If I were to meet I'll give you a kiss, this really helped alot by Ahmad Nalado on Nov 06, 2022
- Thank you very much. Pretty easy steps to follow. by Nandila on Nov 06, 2022
- Thanks, it's very helpful by Adebayo R.O on Nov 12, 2022
- very helpful, thanks by Simiyu Omuriti on Nov 15, 2022
- Was very helpful, thank you very much by Eddy_Yang on Nov 19, 2022
- This was very very helpful. It was indeed very easy to follow. thank you so much for uploading this by Taiwo on Nov 22, 2022
- Easy steps to follow toward the target. A lot of thanks to you. Now nimeelewa ahsante kwa maelezo mazuri😇👏🤝🏼 by Fadhili on Nov 30, 2022
- I followed the instructions exactly as they are laid down, and voila, I got the page numbering right! by Cherry on Nov 30, 2022
- People like you make it possible to do everything in word and avoid latex. Cant thank you enough by Pranav on Dec 01, 2022
- Such a life safer!! by Flashy on Dec 07, 2022
- Thankyou. Jah Bless ! by Kalidou on Dec 16, 2022
- Very useful document ! by Cyprien on Dec 17, 2022
- One word, THANKS 😊 by Masher on Dec 18, 2022
- Thank you very much. Pretty easy steps to follow. google games by Smith on Dec 24, 2022
- Thank you so much for your help by Mshelia on Jan 05, 2023
- This is the most elaborate and clear help in page formatting I have ever received. Thank you. by Yunia on Jan 07, 2023
- Thanks, got to understand section break for different page number by Rashil Maharjan on Jan 08, 2023
- Very useful. Thank you! by Sara on Jan 10, 2023
- It is very interesting and helpful by Mohammed A on Jan 14, 2023
- Thank you very much.... Problem solved by Ian Yohane on Jan 18, 2023
- Very helpful. Thank you for the effort by Success on Jan 24, 2023
- thank you by kiya fikadu on Jan 26, 2023
- wao your illutrations makes the work so easy to follow. by ziizozi on Jan 30, 2023
- Very clearly expressed and helpful. Thank you! by Roland on Feb 09, 2023
- This was of great help to me today, thank you soo much. by Sevu Mueni on Mar 05, 2023
- I give it a 5 star, perfectly explained and elaborated!! thank you.... by cornelius Kiprotich on Mar 07, 2023
- This was well illustrated and clearly elaborated. Thank you, you have really saved my time. by RBI on Mar 17, 2023
- This was such a helpful and concise mind refresher thank you very. I am even more grateful that I could send my gratitude. So much better than listening to a whole 5 min YouTube video. Though also helpful. by Nomonde Foli on Mar 19, 2023
- Thank you so much. I struggled with this numbering on my previous degree, now I know. I am already applying the knowledge gained on my current thesis. Many thanks indeed! by Edmore on Mar 30, 2023
- it is very supportive and interesting ! by Andualem on Apr 01, 2023
- thank you by onyango on Apr 03, 2023
- Wow, this is exactly what I needed to number the pages of my dissertation. Amazingly clear instructions, thank you so much! by Jac on Apr 12, 2023
- Thank You Very Much😊 by Hardik on Apr 19, 2023
- Wow, I followed step by step and made it👍👍 Thanks for this information by Sseguya on Apr 21, 2023
- To the person who created this how-to guide, THANK YOU. This was perfect in every way. Thank you so much for making this available to us all. by supermegstar on Apr 23, 2023
- This is great for section numbering, for which I've added to the bottom of the page. Now, is it possible to add an overall document page number to the top of the page? Essentially, have two different page numbering systems in the same document. by Abbi on Apr 26, 2023
- Super helpful and saved so much time troubleshooting! I went through every step exactly and was able to finally get it! by Haley Cari on May 12, 2023
- Amazingly well explained...You have saved me a great amount of time dealing with page numbers writting my thesis... Thank you! by MS on May 14, 2023
- it is indeed helpful to me. I was about to pay for it to be done for me. I was reluctant to give out my work to an external person to avoid data misplacement. Thank you a million. by Adeduntan on May 20, 2023
- Thanks a lot. Best concise guide! by Stan on May 27, 2023
- Finally, with these instructions, I did it. Thanks by Bernice-kay on May 28, 2023
- Very helpful info! I'm grateful by Praise on May 31, 2023
- Thanks so much. I spent my time watching a YouTube but it did not work. Just two clicks and it's done. Thanks again by VANEN on Jun 06, 2023
- Amazing!! Thanks Jeff Beuck, this is very helpful. by Sine on Jun 07, 2023
- thank you so much by Lillian on Jun 11, 2023
- Starting a new format of paging after the preface was daunting. I tried for a long time to have it done until after got How to do pages differently in the previous section on Ask library. by Loding Joseph on Jun 12, 2023
- Thank you so much for this! It was easy to follow and exactly what I needed 😍 by Kate on Jun 13, 2023
- This is very good article. I followed the steps and succeeded 100% Thank you very much by Nakudo on Jun 18, 2023
- Just awesome writing. Its essential for all researches. by Khanom Popy on Jun 19, 2023
- Thank you very much! This was of such tremendous help while formatting my dissertation. by ts on Jun 26, 2023
- Thank you so much, you saved my life with this write-up... by Nosa on Jun 28, 2023
- very helpful thankyou so much by Mrs G on Jun 29, 2023
- Thank you so much for your online lessen. It is very easy to understand the way you presented. I used it at the time when I badly needed it. Nice and supportive material. by Eyob Getachew on Jul 02, 2023
- its working thank you very much. by aizak on Jul 04, 2023
- You, my man, are a lifesaver. Thank you so much for this. I needed this like yesterday and all other tutorials are just not working for me for some reason. Thank you and I hope you have a nice day or night wherever you are in the world. by Cw on Jul 11, 2023
- Thank you 😊, was a relief indeed. Perfect and comprehensive instructions. by Nana Akomea on Jul 29, 2023
- This was really helpful. Thank you so much by Divine Yancho on Aug 02, 2023
- This saves me from materials I've searched for decates. I really appreciate. by Mohammed Amin on Aug 12, 2023
- Thank you so much for the valuable tutorial! by Basil on Aug 16, 2023
Related Topics

File(s) under embargo
until file(s) become available
Policing America: Patrolling the Streets and Controlling the Public, 1832-1916
Date created, date modified, defense date, research director(s), committee members.
- Doctor of Philosophy
Degree Level
- Doctoral Dissertation
Library Record
Oclc number, program name, usage metrics.


COMMENTS
Time to recap…. And there you have it - the traditional dissertation structure and layout, from A-Z. To recap, the core structure for a dissertation or thesis is (typically) as follows: Title page. Acknowledgments page. Abstract (or executive summary) Table of contents, list of figures and tables.
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
1. The Abstract (5%) Both the shortest and first-encountered section of a dissertation, the abstract is intended to provide a very brief overview of the entire research project, highlighting to the reader the aims of the dissertation, the background and context of the investigation, the methodology that's been used, the study's key findings ...
The structure of a dissertation depends on your field, but it is usually divided into at least four or five chapters (including an introduction and conclusion chapter). The most common dissertation structure in the sciences and social sciences includes: An introduction to your topic. A literature review that surveys relevant sources.
Example 1: Passive construction. The passive voice is a common choice for outlines and overviews because the context makes it clear who is carrying out the action (e.g., you are conducting the research ). However, overuse of the passive voice can make your text vague and imprecise. Example: Passive construction.
The title page of a thesis or dissertation must include the following information: The title of the thesis or dissertation in all capital letters and centered 2″ below the top of the page. Your name, centered 1″ below the title. Do not include titles, degrees, or identifiers. The name you use here does not need to exactly match the name on ...
To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough. Note.
Perhaps the smallest yet important part of a thesis, an abstract contains 5 parts: A brief introduction of your research topic. The significance of your research. A line or two about the methodology that was used. The results and what they mean (briefly); their interpretation(s).
A typical thesis structure. 1. Abstract. The abstract is the overview of your thesis and generally very short. This section should highlight the main contents of your thesis "at a glance" so that someone who is curious about your work can get the gist quickly. Take a look at our guide on how to write an abstract for more info.
See thesis introductions exercises for more information. Literature review. Often part of the Introduction, but can be a separate section. It is an evaluation of previous research on your topic, where you show that there is a gap in the knowledge that your research will attempt to fill. The key word here is evaluation.
6 PART I. TAKING CHARGE OF YOURSELF AND YOUR WORK DISSERTATION CHAPTERS Order and format of dissertation chapters may vary by institution and department. 1. Introduction 2. Literature review 3. Methodology 4. Findings 5. Analysis and synthesis 6. Conclusions and recommendations Chapter 1: Introduction This chapter makes a case for the signifi-
Dissertation OverviewThe traditional dissertation is organized into 5 chapters and includes the following elements and pages:Title page (aka cover page) Signature ...
We'll also examine different hints and tips for each of the sections. As you read through this toolkit, compare it to published PhD theses in your area of study to see how a real-life example looks. Main Sections of a PhD Thesis. In almost every PhD thesis or dissertation, there are standard sections.
Thesis Abstract. The first part of the thesis structure is the abstract. It is basically an overview of the entire paper. There is no set dissertation abstract structure. It is just a summary of your thesis and it should be just 200 to 300 words long. Thesis Introduction. The introduction is one of the most important dissertation chapters.
Craft an enticing and engaging opening section. Provide a background and context to the study. Clearly define the research problem. State your research aims, objectives and questions. Explain the significance of your study. Identify the limitations of your research. Outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis.
Revised on April 16, 2024. A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
Writing a Dissertation For Dummies. Most dissertations follow the same basic structure and are made up of five parts: an abstract, introduction, methods and discussion, conclusions and references. Although the exact detail of each part can vary (such as the numbers of words allowed in the abstract), the inclusion of each part is standard and fixed.
A dissertation structure is the arrangement of research contents. It contains numerous parts which are also divided into paragraphs. It is essential to the flow of ideas in a research paper and to helping the reader navigate the ideas. Different academic disciplines require a certain dissertation structure, so it is important to verify with ...
The video covers the characteristics of quantitative research, and explains how to approach different parts of the research process, such as creating a solid research question and developing a literature review. ... Resources providing guidance on doing dissertation research during the pandemic: Online research methods; Secondary data sources ...
Thesis. Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore ...
A good conclusion will review the key points of the thesis and explain to the reader why the information is relevant, applicable, or related to the world as a whole. Make sure to dedicate enough of your writing time to the conclusion and do not put it off until the very last minute. Organize your papers in one place. Try Paperpile.
When starting your thesis or dissertation process, one of the first requirements is a research proposal or a prospectus. It describes what or who you want to examine, delving into why, when, where, and how you will do so, stemming from your research question and a relevant topic. The proposal or prospectus stage is crucial for the development ...
One of the required page numbering changes for your thesis or dissertation is that you need to use Roman numerals (e.g., "i, ii, iii") for your introductory sections (Abstract, Table of Contents), and then switch to Arabic numerals (e.g., "1, 2, 3") and begin the page numbering at "1" at the start of Chapter I of your main text.
Our contemporary way of tea drinking is deeply influenced by the late-Ming way. However, when examining the development of tea production and consumption within this period, we can find so many changes. This study examines tea consumption in China's domestic market from the 1550s to the 1700s. During this period, some commodities rose to the top in the market, such as Longjing tea and Yixing ...
In this dissertation, I compare the founding and early evolution of police forces in three American cities—Philadelphia, Chicago, and San Francisco---from 1832 to 1915. Most modern police histories focus on a single city, but using sources from these three cities allows me to tell a broader story. American urban policing developed quickly, with many cities establishing their own police ...