- Our Mission

What Is Education For?
Read an excerpt from a new book by Sir Ken Robinson and Kate Robinson, which calls for redesigning education for the future.

What is education for? As it happens, people differ sharply on this question. It is what is known as an “essentially contested concept.” Like “democracy” and “justice,” “education” means different things to different people. Various factors can contribute to a person’s understanding of the purpose of education, including their background and circumstances. It is also inflected by how they view related issues such as ethnicity, gender, and social class. Still, not having an agreed-upon definition of education doesn’t mean we can’t discuss it or do anything about it.
We just need to be clear on terms. There are a few terms that are often confused or used interchangeably—“learning,” “education,” “training,” and “school”—but there are important differences between them. Learning is the process of acquiring new skills and understanding. Education is an organized system of learning. Training is a type of education that is focused on learning specific skills. A school is a community of learners: a group that comes together to learn with and from each other. It is vital that we differentiate these terms: children love to learn, they do it naturally; many have a hard time with education, and some have big problems with school.

There are many assumptions of compulsory education. One is that young people need to know, understand, and be able to do certain things that they most likely would not if they were left to their own devices. What these things are and how best to ensure students learn them are complicated and often controversial issues. Another assumption is that compulsory education is a preparation for what will come afterward, like getting a good job or going on to higher education.
So, what does it mean to be educated now? Well, I believe that education should expand our consciousness, capabilities, sensitivities, and cultural understanding. It should enlarge our worldview. As we all live in two worlds—the world within you that exists only because you do, and the world around you—the core purpose of education is to enable students to understand both worlds. In today’s climate, there is also a new and urgent challenge: to provide forms of education that engage young people with the global-economic issues of environmental well-being.
This core purpose of education can be broken down into four basic purposes.
Education should enable young people to engage with the world within them as well as the world around them. In Western cultures, there is a firm distinction between the two worlds, between thinking and feeling, objectivity and subjectivity. This distinction is misguided. There is a deep correlation between our experience of the world around us and how we feel. As we explored in the previous chapters, all individuals have unique strengths and weaknesses, outlooks and personalities. Students do not come in standard physical shapes, nor do their abilities and personalities. They all have their own aptitudes and dispositions and different ways of understanding things. Education is therefore deeply personal. It is about cultivating the minds and hearts of living people. Engaging them as individuals is at the heart of raising achievement.
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights emphasizes that “All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights,” and that “Education shall be directed to the full development of the human personality and to the strengthening of respect for human rights and fundamental freedoms.” Many of the deepest problems in current systems of education result from losing sight of this basic principle.
Schools should enable students to understand their own cultures and to respect the diversity of others. There are various definitions of culture, but in this context the most appropriate is “the values and forms of behavior that characterize different social groups.” To put it more bluntly, it is “the way we do things around here.” Education is one of the ways that communities pass on their values from one generation to the next. For some, education is a way of preserving a culture against outside influences. For others, it is a way of promoting cultural tolerance. As the world becomes more crowded and connected, it is becoming more complex culturally. Living respectfully with diversity is not just an ethical choice, it is a practical imperative.
There should be three cultural priorities for schools: to help students understand their own cultures, to understand other cultures, and to promote a sense of cultural tolerance and coexistence. The lives of all communities can be hugely enriched by celebrating their own cultures and the practices and traditions of other cultures.
Education should enable students to become economically responsible and independent. This is one of the reasons governments take such a keen interest in education: they know that an educated workforce is essential to creating economic prosperity. Leaders of the Industrial Revolution knew that education was critical to creating the types of workforce they required, too. But the world of work has changed so profoundly since then, and continues to do so at an ever-quickening pace. We know that many of the jobs of previous decades are disappearing and being rapidly replaced by contemporary counterparts. It is almost impossible to predict the direction of advancing technologies, and where they will take us.
How can schools prepare students to navigate this ever-changing economic landscape? They must connect students with their unique talents and interests, dissolve the division between academic and vocational programs, and foster practical partnerships between schools and the world of work, so that young people can experience working environments as part of their education, not simply when it is time for them to enter the labor market.
Education should enable young people to become active and compassionate citizens. We live in densely woven social systems. The benefits we derive from them depend on our working together to sustain them. The empowerment of individuals has to be balanced by practicing the values and responsibilities of collective life, and of democracy in particular. Our freedoms in democratic societies are not automatic. They come from centuries of struggle against tyranny and autocracy and those who foment sectarianism, hatred, and fear. Those struggles are far from over. As John Dewey observed, “Democracy has to be born anew every generation, and education is its midwife.”
For a democratic society to function, it depends upon the majority of its people to be active within the democratic process. In many democracies, this is increasingly not the case. Schools should engage students in becoming active, and proactive, democratic participants. An academic civics course will scratch the surface, but to nurture a deeply rooted respect for democracy, it is essential to give young people real-life democratic experiences long before they come of age to vote.
Eight Core Competencies
The conventional curriculum is based on a collection of separate subjects. These are prioritized according to beliefs around the limited understanding of intelligence we discussed in the previous chapter, as well as what is deemed to be important later in life. The idea of “subjects” suggests that each subject, whether mathematics, science, art, or language, stands completely separate from all the other subjects. This is problematic. Mathematics, for example, is not defined only by propositional knowledge; it is a combination of types of knowledge, including concepts, processes, and methods as well as propositional knowledge. This is also true of science, art, and languages, and of all other subjects. It is therefore much more useful to focus on the concept of disciplines rather than subjects.
Disciplines are fluid; they constantly merge and collaborate. In focusing on disciplines rather than subjects we can also explore the concept of interdisciplinary learning. This is a much more holistic approach that mirrors real life more closely—it is rare that activities outside of school are as clearly segregated as conventional curriculums suggest. A journalist writing an article, for example, must be able to call upon skills of conversation, deductive reasoning, literacy, and social sciences. A surgeon must understand the academic concept of the patient’s condition, as well as the practical application of the appropriate procedure. At least, we would certainly hope this is the case should we find ourselves being wheeled into surgery.
The concept of disciplines brings us to a better starting point when planning the curriculum, which is to ask what students should know and be able to do as a result of their education. The four purposes above suggest eight core competencies that, if properly integrated into education, will equip students who leave school to engage in the economic, cultural, social, and personal challenges they will inevitably face in their lives. These competencies are curiosity, creativity, criticism, communication, collaboration, compassion, composure, and citizenship. Rather than be triggered by age, they should be interwoven from the beginning of a student’s educational journey and nurtured throughout.
From Imagine If: Creating a Future for Us All by Sir Ken Robinson, Ph.D and Kate Robinson, published by Penguin Books, an imprint of Penguin Publishing Group, a division of Penguin Random House, LLC. Copyright © 2022 by the Estate of Sir Kenneth Robinson and Kate Robinson.

Getting Into College , Tips for Online Students , Tips for Students , Why Go to College
Top 10 Reasons Why Is Education Important
Updated: February 1, 2024
Published: April 15, 2020

Most of us have grown up being taught the importance of education. But why is education important? Through your frustrating school years, you may have thought that it was a waste of time, or was just something that you needed to do in order to get a job. Truth be told, however, education goes so much beyond just getting a job and making your parents happy. In fact, it’s one of the most powerful tools out there.
What Is Education?
Education means studying in order to obtain a deeper knowledge and understanding of a variety of subjects to be applied to daily life. Education is not limited to just knowledge from books, but can also be obtained through practical experiences outside of the classroom.
Top 10 Reasons: Why Is Education Important?
There are many different understandings and definitions of what education is, but one thing can be universally agreed upon, which is the importance of education — and here’s why.
1. Provides Stability
Education provides stability in life, and it’s something that no one can ever take away from you. By being well-educated and holding a college degree , you increase your chances for better career opportunities and open up new doors for yourself.
2. Provides Financial Security
On top of stability, education also provides financial security, especially in today’s society. A good education tends to lead to a higher paying job, as well as provide you with the skills needed to get there. Educated and well-informed individuals also know how to use money-saving tactics. They are more likely to use coupon websites like EMUCoupon while shopping online to save their hard-earned money.
3. Needed For Equality
In order for the entire world to really become equal, it needs to start with education. If everyone was provided with the same opportunities to education , then there would be less gaps between social classes. Everyone would be able to have an equal chance at higher paying jobs — not just those that are already well-off.
4. Allows For Self-Dependency
The importance of education is evident when it comes to being self-dependent. If we are we educated, then it’s something that belongs to us, and only us, allowing us to rely on no one else other than ourselves. It can allow you to not only be financially independent, but also to make your own choices.
5. Make Your Dreams Come True
If you can dream it, you can achieve it. An education is the most powerful weapon you can possibly have, and with it, you can make all of your dreams come true. There are of course certain exceptions, depending on what you’re aiming for, but generally an education will take you as far as you’re willing to go.
6. A Safer World
Education is something that’s not only needed on a personal level, but also on a global level, as it’s something that keeps our world safe and makes it a more peaceful place. Education tends to teach people the difference between right and wrong, and can help people stay out of risky situations.
7. Confidence
Being self-confident is a major part of being successful in life. And what better way to gain that confidence than with an education? Your level of education is often considered a way to prove your knowledge, and it can give you the confidence to express your opinions and speak your mind.
8. A Part Of Society
In today’s society, having an education is considered a vital part of being accepted by those around you. Having an education is believed to make you a useful part of society, and can make you feel like a contributing member as well.
9. Economic Growth On A National Level
An educated society is crucial for economic growth. We need people to continue to learn and research in order to constantly stay innovative. Countries with higher literacy rates also tend to be in better economic situations. With a more educated population, more employment opportunities are opened.
10. Can Protect You
Education can protect you more than you know, not only on a financial level, but it can help prevent you from being taken advantage of by knowing how to read and write, such as knowing not to sign any bogus documents.
Photo by Pixabay from Pexels
Education is important for children.
Children are the future of our world, making education crucial for them. Their knowledge is what’s going to keep our world alive and flourishing.
At Childhood
During the childhood development stages, the importance of education is stronger than ever. It’s a time for children to learn social and mental skills that will be crucial for their growth and success in the future. Education at childhood also offers a chance for self-discovery and to learn about their unique interests.
The importance of education in our lives goes far beyond what we can read in a textbook. Education also provides childhood with knowledge such as how to produce artwork and make music. Education allows us to analyze what’s in front of us, and even learn from our mistakes.
Goal Building
By learning from a young age, children are given the chance to start building goals for themselves. Education means having the logic to set your mind to something and achieve it.
Importance Of Education In Society
For a modern society, education is of utmost importance. There are so many influences coming from all directions, and education can help us decipher what we should take as true, and what we should take with a grain of salt. Education can mold people into functional members of society with the right kinds of values.
Productivity
Education is needed for a productive society. Our population only continues to increase, and in turn, so do our needs. We need a strong and efficient workforce of educated people to provide us with the services we need for everyday life.
Why Is Education Important For a Nation?
The importance of education is seen in every aspect of life, and is especially crucial for the growth of a nation.
The Impact Education Has On The World
With education, people can become better citizens, knowing right from wrong, allowing for a better society where laws are followed. An educated nation knows about the importance of voting, doing so with the knowledge not blindly, but also having an understanding of what their party truly stands for. Education can also help people get jobs, which is what a nation thrives on.
Inspiring Quotes On What Education Truly Is
Why is education important, and what is it exactly? While every person has a different understanding of its true meaning, here are some of the most inspiring quotes by some legendary people.
- “Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.” — Nelson Mandela
- “Education is the passport to the future, for tomorrow belongs to those who prepare for it today.” — Malcolm X
- “An investment in knowledge pays the best interest.” — Benjamin Franklin
- “Education is not preparation for life; education is life itself.” — John Dewey
What Are Some Other Reasons Why Education Is Important?
There are endless reasons why education is so important, especially since it also has endless connotations and meanings.
Mind And Body
Our mind and bodies are connected more than we know. With a powerful, well-educated mind, so too are our bodies.
We can not only know how to best take care of ourselves, but we can feel confident and good about ourselves, which will likely have a positive effect on our physical well-being . Education has even been proven to add years to our life . To be exact, each additional year of education was found to add as much as 1.7 years to our lives at the age of 35.
Personal Growth
The importance of education even extends itself to our personal growth. By constantly educating ourselves, asking questions and wanting to know more, we can move forward and achieve things we never imagined before.
Get To Know Yourself
Education can allow us to get to know ourselves better than ever. We can learn things about ourselves, whether it be through books, courses, or even consulting with a professional.
Photo by Burst from Pexels
Worldwide value.
Education is the best way to ensure a positive world value and view. Without a proper education, how else do we know what’s considered appropriate and how to behave?
While world peace may unfortunately seem like a far-fetched concept, with education we can get closer to this goal than we know. Education can teach us about our place in this world, and about our responsibility to humanity.
Teaches Values
Values are taught through education! Education exists far beyond the classroom or an exam. It’s taught at home, through what our parents and peers show us, and although not necessarily written down somewhere, such a teaching method is still a large aspect of what education entails.
Sharpens Your Thinking
Education is needed to think sharply and clearly!
Makes You Informed
Education makes you informed about the world around you, what’s going on and what kind of people are around you. Education can help you be more self-aware about your strengths and weaknesses, showing you were to shift your focus.
Logical Reasoning
When in an argument, if you aren’t well educated and don’t have your facts straight, then you aren’t likely to win. If you get upset about something, then being educated can also help you logically work through the situation and make sense of it, understanding all aspects.
Stay Focused
Education can help you stay focused and on track in the right direction by knowing what the right path is for you.
Allows For Innovation And Creativity
When it comes to being creative, in any way, shape, or form, the mind can only really reach its full potential if it’s been fed with the knowledge it needs to think outside the box.
Develop Life Skills
Education is the foundation of basic life skills and street smarts. While education might sound like a fancy technical term, it’s really everything we learn in life about how to best conduct ourselves from day to day.
Education can be the most freeing and empowering thing in the entire world!
Live Life To The Fullest
Truly living life to the fullest means being well-educated and holding a vast amount of knowledge about the world around us. It also means we continue to learn every day in all kinds of forms, whether it be from the people around us, newspapers, experiences, research, or traditional classes.
Breaks Barriers
Education breaks barriers between people, and allows people from across the globe to be empowered.
University of the People, a tuition-free , online university, is one powerful example of how education is being revolutionized – they offer students of all socio-economic backgrounds an equal chance at education.
Once upon a time, such a thing wouldn’t have been possible, but today such places like UoPeople have proven that these barriers truly can be broken through to receive higher education.
You Become Your Highest You
Education can allow you to become the best, fullest version of yourself, learning about what interests you, what you’re good at, becoming self-aware and conscious about the world around you. It can help you establish your place in this world, and feel complete.
Education In The Modern World
Education today is more important than ever before, and has reached new heights with new understandings of what it truly entails. Ask yourself “Why is education important?” and it will surely not be the same as anyone else’s answer.
While in modern society, holding a college degree is considered to be highly beneficial for a successful career and to be socially accepted, it is not the only means of education. Education is all around us in everything that we do, so use it wisely!
Related Articles
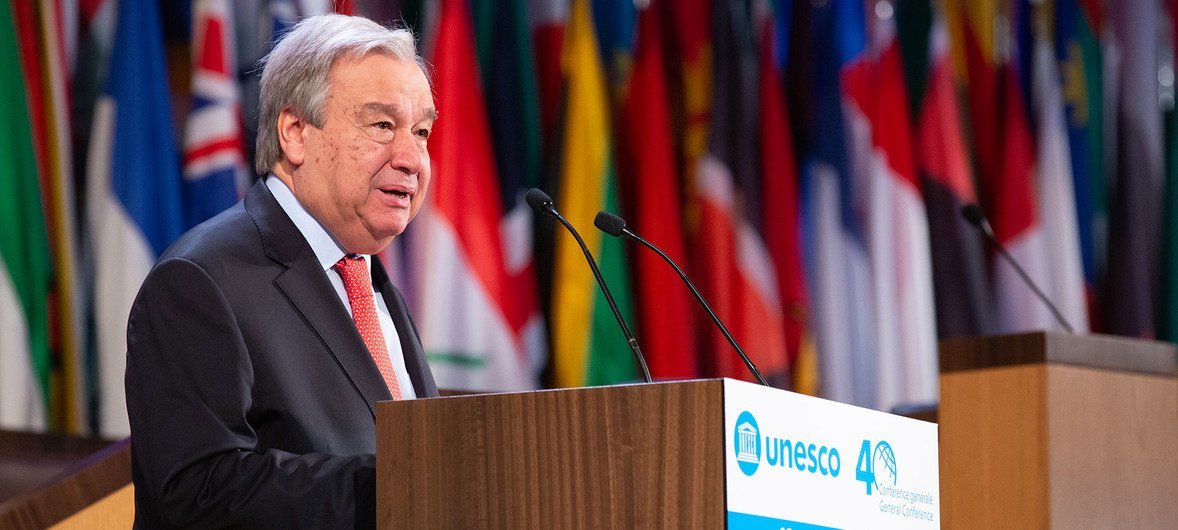
Quality education an ‘essential pillar’ of a better future, says UN chief

Facebook Twitter Print Email
Education is an “essential pillar” to achieving the UN’s 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, UN chief António Guterres told an audience on Tuesday at the Paris headquarters of UNESCO, the UN Educational, Scientific and Culture Organization, ahead of the agency’s General Conference .
We must ensure universal access to basic education for every child, everywhere. Tijjani Muhammad-Bande, President, UN General Assembly
Mr. Guterres, who noted that one-fifth of young people are out of work, lack education or adequate training, praised UNESCO ’s fundamental role in coordinating and monitoring global efforts, such as the agency’s initiative on the future of education.
The theme was taken up by Tijjani Muhammad-Bande, President of the UN General Assembly, in his opening remarks to a ministerial meeting on education at the Conference.
Mr. Muhammad-Bande referred to estimates showing that some 265 million children are out of school. The number is projected to fall to 220 million over the next decade, but he declared that the illiteracy figures forecast for 2030 remain a scandal: “We must remove all barriers to education. We must ensure, at a minimum, universal access to basic education for every child, everywhere.”
He also highlighted the importance of educating children effectively, and equipping them with the necessary analytical and critical thinking abilities, in “an ever-changing and more complex world”.
Recalling his former experience as an educator in his home country of Nigeria, Mr. Muhammad-Bande called for more efforts to ensure that teachers are adequately qualified, because “no educational system can rise above the quality of its teachers”.
We must treat young people not as subjects to be protected, but as powerful agents for change.I was very pleased to meet a few of these changemakers at @UNESCO this morning. pic.twitter.com/DjgZP0jNh9 António Guterres, UN Secretary-General antonioguterres
Other important measures cited by the General Assembly President include strong curricula that fully integrate Information and Communications Technology (ICT); ensuring that girls complete at least 12 years of education (which, according to the World Bank, would add some $30 trillion to the global economy); and the effective monitoring and evaluation of learning.
Mr. Muhammad-Bande called on nations to meet their commitments to education spending, and for donor countries to increase international aid directed towards education.
‘Powerful agents of change’
As well as the difficulties in accessing quality education, Mr. Guterres also outlined several other challenges faced by young people: the fact that millions of girls become mothers while they are still children; that one quarter are affected by violence or conflict; and that online bullying and harassment are adding to high levels of stress, which see some 67,000 adolescents die from suicide or self-harm every year.
World leaders, and others who wield power, he continued, must treat young people not as subjects to be protected, but as powerful agents for change, and the role of the powerful is not to solve the enormous challenges faced by young people, but rather to give them the tools to tackle their problems.
Mr Guterres underscored the importance of bringing young people to the table as key partners, and praised UNESCO’s efforts to include their voices, which include holding a major event at the General Conference, and the Youth Forum .
- quality education

Online Students
For All Online Programs
International Students
On Campus, need or have Visa
Campus Students
For All Campus Programs
Why is Education Important and What Impact Has It Had on Your Life?

At Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU), we believe in the power of education to transform lives – and we witness the transformative journeys our students embark on while they earn their degrees and beyond. The stories are personal but each learner begins with a simple premise: Education is important.
We asked SNHU leaders and staff to share their thoughts on education and how it has impacted their lives.
Dr. Paul LeBlanc, President, Southern New Hampshire University

We know that people with college degrees vote more, divorce less, smoke less and the list goes on . Take the two together - personal development and social mobility - and education is an incredible force for good. In many ways, it is critical to the American narrative of self-improvement, merit and mobility.
It (education) has changed everything. It put me on a trajectory to an incredibly rewarding career. It has allowed a life for my daughters that their grandparents could scarcely imagine. It has allowed me to connect with the distant past through literature and history and art and to imagine a better future through philosophy, political science, and sociology.
Really, it feels like the question might be "Is there any aspect of your life education hasn't touched?" and then the answer could be simple. It would be "no."
Amelia Manning, Chief Operating Officer

Four years later, after minoring in gender studies and reading Toni Morrison’s “The Bluest Eye,” I had what some would call a light-bulb moment. The actual message I had been given, but wasn’t at the time ready to hear, was about power and privilege. It was not a personal attack, as I’d initially interpreted it to be, but instead about expanding my awareness and understanding of how power works and the conscious and unconscious ways it influences each of us. It wasn’t until I read “The Bluest Eye,” and saw the world through the eyes of a child who believed she’d be happy if only she had blue eyes, that I fully understood.
Education, and learning, at its best pushes the boundaries of what we believe to be true. It opens doors and windows on our world that sheds light on our own beliefs and, in turn, on our understanding of the world and how it works and how we can make it a better place. Education is, and should be, transformative, not only for an individual, but for society.
As I stated earlier, I believe that education is transformative. It can change the trajectory of your life just as it can help to shine the light for you on opportunities that you would never have considered or believed were possible. I have seen impact not only for me, but for the thousands of students I’ve had the honor of working with here at SNHU.
Dr. Gregory Fowler, former President, Global Campus

Humans are constantly forced to make choices (some don’t recognize that even choosing not to choose is a choice), all of which have repercussions. Education positions us to make the most informed choices and therefore live with the consequences, even when things don’t turn out as we expect, because even then, the learned person understands that they are being educated.
Education has led me on a journey around the world—to Europe, Australia, Central America, as well as almost every state in the U.S. I continue to be awed by the various permutations of our existence. They are so different and yet at their core, they all operate with the same basic principles that reinforce that no matter how different we are, we all continue to be so very human, driven not only by basic human needs but by our passions, our fears and our hopes.
Autumn Earnshaw Fillion, Military Academic Advising Team Lead

Education gives us a wider range of experience, makes us think about things and see things in a way we might not have before. Education can build confidence and trust within us. Beyond the "book" knowledge an education provides, it displays commitment and determination.
I know it is cliché to say, but education has opened doors for me professionally and personally. I love my job and the career that my master's degree led me to. I have met awesome people along the way that have shaped my life. Education has become my profession so all I have and am has been influenced by my education.
Amy Stevens, Vice President, Academic Resources & Technology, Executive Director of CBE Programs

I can’t think of anything in my life that hasn’t been touched by education. I am on my fourth career, three of which didn’t exist when I graduated college. I can recreate myself because I have a strong foundation in critical thinking skills, I can write and do some basic math, I can learn what I don’t know and gain wisdom from my mistakes.
Education continues to have an impact on my life, and hopefully I can continue to add value to the education SNHU students earn through my work in and out of the classroom.
Dr. Jeffrey Czarnec, Associate Dean, Criminal Justice and Social Sciences

Education has allowed for ME to have a positive impact on scores of others. An education is to be shared, it must contribute to the well-being of others and must provoke change where none had previously occurred.
Cheryl Frederick, Senior Associate Dean, STEM

I grew up in a small town and was raised by a single mother. I watched my mother's job opportunities improve after she finished her college degree. This instilled how important education is and I made a decision at a young age that I would go to college. I always loved STEM-related classes and the latest innovations in technology. Education has allowed me to participate in the forefront of the application of innovative information technology and to connect with very interesting individuals. I have had the privilege of working for some amazing companies, on interesting projects, and been able to see different areas of the country due to work travel.
Kristi Durette, Associate Vice President | Institutional Advancement

I believe at my core I have a curiosity that encourages me to always be a learner; that every interaction is an opportunity to educate and be educated. And in those exchanges, the opportunity to build a more informed and engaged community. Teachers who created opportunities for students like me to engage in learning, decision-making about community values and shared responsibility for building the community come in the form of leaders, peers, students, neighbors and strangers we encounter as life unfolds. I feel like I learn something about myself and my world every day and that is the greatest gift.
Matthew Belanger, Associate Vice President of Academic Strategy and Operations

My education has had a profound impact on my life. It has provided me with the opportunity to positively impact the lives of others in various, countless ways. Without my education I would not be where I am today, in a position to help other students (many of whom are the first in their family like I was) be successful in their own pursuit of a degree.
The process of earning my education also had a significant impact. I was able to work with students of all ages to understand how students learn best and what that learning (and education) really means to them. My own education has taught me about diversity, strength, hard work, motivation and fulfillment.
Now as a father, what I have learned about education will be passed down to my children and my children’s children. They will grow up knowing how important their education is and how much I’ll be there to support them.
Tim Lehmann, Vice President of Student Financial Services

It has had an incredible impact on my life. It continues to impact my attitudes and altitude. I continue to believe that there is an "education effect" that correlates to better social and economic outcomes based on how much education a person has. I know in my life this is true.
Dr. Gwen Britton, Associate Vice President, STEM Professions

Knowledge also contributes to understanding of how different cultures and geographies live out their lives – differences in perspective, beliefs, experiences and how they influence the world as a whole; again, more knowledge, more connections between what we know and how we know it.
I feel like I have lived a pretty charmed life. I’ve lived in many different places across the United States, from east to west and in the middle too. I also lived in Europe and Guam. I was exposed to different cultures and educational perspectives from the first day of my education. Learning from different people in different places made me want to try to teach others as well. The biggest impact it has had on my life is my desire to pay it forward and help others discover their own potential through learning.
Tiffany Fifer, Director of Online Engagement

My father has a high school GED and this limited his career choices in life. While he is one of the hardest workers I know, furthering his education would have opened so many more doors for him. It was very important to him that his children have the chance to go to college.
Through Alternative Break trips , I have seen college students be transformed by relief work in an impacted community. These students put their own luxuries aside, learned about new cultures and rolled up their sleeves to make the world a little better. Many have gone on to work in service organizations and share their talents with the world. Education makes this type of growth possible.
Education has taken me around the world. I have learned new languages, lived with students from different countries, helped students study abroad and traveled with students through Italy and the Dominican Republic.
Education has also taught me how to solve problems. The position I now hold in online student engagement didn’t exist when I was in college and there aren’t many colleagues in the field doing this work yet. My education has given me the confidence to take risks, analyze opportunities and determine how we can lead in this area.
Finally, education has given me the opportunity to pay it forward. So many wonderful mentors had such an impact on me growing up and I feel it is my duty (and complete pleasure) to support our students through their own journey of co-curricular involvement and education.
Pamme Boutselis ‘15, ‘17G is a staff writer and senior content director in higher education. Follow her on Twitter @pammeb or connect on LinkedIn .
Explore more content like this article

Academic Spotlight: Executive Director of Academic Effectiveness Dr. Meleena Eaton

Why It Pays to Advance from an Associate to Bachelor’s Degree

The Leadership and Legacy of Gertrude Shapiro
About southern new hampshire university.

SNHU is a nonprofit, accredited university with a mission to make high-quality education more accessible and affordable for everyone.
Founded in 1932, and online since 1995, we’ve helped countless students reach their goals with flexible, career-focused programs . Our 300-acre campus in Manchester, NH is home to over 3,000 students, and we serve over 135,000 students online. Visit our about SNHU page to learn more about our mission, accreditations, leadership team, national recognitions and awards.
Why a good education benefits us all — even if you’re long past being a student

To hear exactly how it works, listen to this talk . His fresh perspective moves the topic of improving schools away from the altruistic “wouldn’t it be nice if…” level. In fact, it forces us to ask not “How can I get a good education for my kids?” but “How can I get a good education for everyone else’s kids?” It’s a shift in thinking — one that reframes the discussion about education reform.
The TEDx program, with its global reach, is privileged to have a unique perspective on education. Below, watch five TEDx Talks (and one bonus TED Talk) that explore some of the social, economic and political implications of guaranteeing good schools.
The impact desegregation had on schools: Rucker Johnson at TEDxMiamiUniversity As schools were desegregated in the 1950s and 1960s, opponents feared that embracing students from low-performing, all-black schools would lower standards and unfairly disrupt white students’ performances. It’s been 60 years — were they right? No. As Rucker Johnson shows with his extensive research, desegregation had virtually no effect on white students, but propelled minority students to unprecedented levels of success.
No more easy answers: Adrián Paenza at TEDxJoven@RiodelaPlata All too often, school lessons set concrete problems with clean answers. Which, suggests Adrián Paenza, can limit students’ creative problem-solving abilities. But perhaps more importantly, it can engender arrogance — setting classist expectations for the answers everyone ought to know. With humor and a few touching stories, he looks at some of the effects that unequal educational opportunities have on society. ( In Spanish with English subtitles .)
Don’t mistake a dialect for a disorder: Sade Wilson at TEDxEMU African American Vernacular English is a common dialect in the US. It’s not bad English, yet kids who grow up speaking it at home are too often misdiagnosed with speech and learning disabilities by teachers who either don’t recognize the dialect or give tests in their own dialect of English. At TEDxEMU , speech pathologist Sade Wilson sheds light on the issue and makes six recommendations to improve how teachers work with students who speak a dialect.
Where’s the R&D for better schools? Jim Shelton at TEDxMidAtlantic If education is an essential social good, shouldn’t we make a bigger effort to figure out what’s worth investing in and what’s not? Governments invest in education, and governments invest in research, but according to Jim Shelton, many countries don’t invest much in education research. In this talk from TEDxMidAtlantic, he calls for expanding public investment into the research and development of new education practices and platforms.
[ted id=1672]
A girl who demanded school: Kakenya Ntaiya at TEDxMidAtlantic Kakenya Ntaiya made an unusual deal with her father in order to go to high school – something unheard-of for girls in her Maasai village. After continuing on to college in the US., Ntaiya returned to her village and set up a school for girls. In this talk, she shows how the school is changing the local culture by creating an alternative path for girls uninterested in marriage in their early teens.
[ted id=1002]
Teaching design for change: Emily Pilloton at TEDGlobal 2010 And now for a TED Talk with a similar theme: Bertie County was known for being the poorest region of North Carolina. In this talk, Emily Pilloton suggests that teaching design in school may be key to lifting the entire area. By giving students the tools to dream up and fabricate real projects for the community good, Bertie County got bus shelters and a farmer’s market – while students got paying summer jobs.
- Subscribe to TED Blog by email
Comments (12)
Pingback: Benefits of Being Educated | thefourthr.ca
Pingback: Secondary Research: Education | Shayna Lauer
Pingback: In praise of ignorance | TokNok Multi Social Blogging Solutions
Pingback: Judging from reactions to my TED talk, here are some common misunderstandings about pre-K research | investinginkids
Pingback: My preschool and economic development presentation is TED’s “talk of the day” | investinginkids
- Current Students
- Faculty / Staff
- Paying for College
- Alumni Services
- Partnerships
- Program Finder
- Affordable, Flexible, Accessible
- Distance Education
- All Online Courses & Degrees
- Baccalaureate Online
- Graduate Online
- Start Dates
- Admissions, Costs & Aid
- Faculty and Contacts
- Academic and Career Support
- Student Testimonials
- Distance Education Advantage
- About Hybrid Learning
- Hybrid Learning Degrees
- Student Life
- Academic Support
- Academic Calendar
- Faculty & Contacts
- Technical Institute for Environmental Professions
- Term Calendar
- Sustainable Ventures
- Careers & Outcomes
- About Unity
- Office of the President
- Announcing Our Evolution
- Sustainable Achievements & Initiatives
- Reinventing College
- Extended Reality (XR)
- Commencement
- Give to Unity Environmental University
- Institutional Communications
- Unity Environmental University News

Home / News / Why Is Education Important? The Power Of An Educated Society

Why Is Education Important? The Power Of An Educated Society
Looking for an answer to the question of why is education important? We address this query with a focus on how education can transform society through the way we interact with our environment.
Whether you are a student, a parent, or someone who values educational attainment, you may be wondering how education can provide quality life to a society beyond the obvious answer of acquiring knowledge and economic growth. Continue reading as we discuss the importance of education not just for individuals but for society as a whole.

Harness the power of education to build a more sustainable modern society with a degree from Unity Environmental University .
How Education Is Power: The Importance Of Education In Society
Why is education so important? Nelson Mandela famously said, “Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.” An educated society is better equipped to tackle the challenges that face modern America, including:
- Climate change
- Social justice
- Economic inequality
Education is not just about learning to read and do math operations. Of course, gaining knowledge and practical skills is part of it, but education is also about values and critical thinking. It’s about finding our place in society in a meaningful way.
Environmental Stewardship
A study from 2022 found that people who belong to an environmental stewardship organization, such as the Leave No Trace Center for Outdoor Ethics, are likely to have a higher education level than those who do not. This suggests that quality education can foster a sense of responsibility towards the environment.
With the effects of climate change becoming increasingly alarming, this particular importance of education is vital to the health, safety, and longevity of our society. Higher learning institutions can further encourage environmental stewardship by adopting a framework of sustainability science .

The Economic Benefits Of Education
Higher education can lead to better job opportunities and higher income. On average, a person with a bachelor’s degree will make $765,000 more in their lifetime than someone with no degree. Even with the rising costs of tuition, investment in higher education pays off in the long run. In 2020, the return on investment (ROI) for a college degree was estimated to be 13.5% to 35.9% .
Green jobs like environmental science technicians and solar panel installers have high demand projections for the next decade. Therefore, degrees that will prepare you for one of these careers will likely yield a high ROI. And, many of these jobs only require an associate’s degree or certificate , which means lower overall education costs.
Unity helps students maximize their ROI with real-world experience in the field as an integral part of every degree program.
10 Reasons Why School Is Important
Education is not just an individual pursuit but also a societal one. In compiling these reasons, we focused on the question, “How does education benefit society?” Overall, higher education has the power to transform:
- Individuals’ sense of self
- Interpersonal relationships
- Social communities
- Professional communities
Cognitive Development
Neuroscience research has proven that the brain is a muscle that can retain its neuroplasticity throughout life. However, like other muscles, it must receive continual exercise to remain strong. Higher education allows people of any age to improve their higher-level cognitive abilities like problem-solving and decision-making. This can make many parts of life feel more manageable and help society run smoothly.
Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence is key to workplace success. Studies show that people with emotional intelligence exhibit more:
- Self-awareness
- Willingness to try new things
- Innovative thinking
- Active listening
- Collaboration skills
- Problem-solving abilities
By attending higher education institutions that value these soft skills, students can improve their emotional intelligence as part of their career development in college.
Technological Literacy
Many careers in today’s job market use advanced technology. To prepare for these jobs, young people likely won’t have access to these technologies to practice on their own. That’s part of why so many STEM career paths require degrees. It’s essential to gain technical knowledge and skills through a certified program to safely use certain technologies. And, educated scientists are more likely to make new technological discoveries .
Cultural Awareness
Education exposes individuals to different cultures and perspectives. Being around people who are different has the powerful ability to foster acceptance. Acceptance benefits society as a whole. It increases innovation and empathy.
College also gives students an opportunity to practice feeling comfortable in situations where there are people of different races, genders, sexualities, and abilities. Students can gain an understanding of how to act respectfully among different types of people, which is an important skill for the workplace. This will only become more vital as our world continues to become more globalized.
Ethical and Moral Development
Another reason why school is important is that it promotes ethical and moral development. Many schools require students to take an ethics course in their general education curriculum. However, schools can also encourage character development throughout their programs by using effective pedagogical strategies including:
- Class debates and discussions
- Historical case studies
- Group projects
Unity’s distance learning programs include an ethical decision-making class in our core curriculum.

Ready To Learn More About Unity Environmental University?
Communication Skills
Effective written and verbal communication skills are key for personal and professional success. Higher education programs usually include at least one communication course in their general education requirements. Often the focus in these classes is on writing skills, but students can also use college as an opportunity to hone their presentation and public speaking skills. Courses such as Multimedia Communication for Environmental Professionals provide many opportunities for this.
Civic Engagement
According to a Gallup survey , people with higher education degrees are:
- More likely to participate in civic activities such as voting and volunteering
- Less likely to commit crimes
- More likely to get involved in their local communities
All these individual acts add up to make a big difference in society. An educated electorate is less likely to be swayed by unethical politicians and, instead, make choices that benefit themselves and their community. Because they are more involved, they are also more likely to hold elected officials accountable.
Financial Stability
The right degree can significantly expand your career opportunities and improve your long-term earning potential. Not all degrees provide the same level of financial stability, so it’s important to research expected salary offers after graduation and job demand outlook predictions for your desired field. Consider the return on investment for a degree from an affordable private school such as Unity Environmental University .
Environmental Awareness
We have already discussed why education is important for environmental stewardship. Education can also lead to better environmental practices in the business world. By building empathy through character education and ethics courses, institutions can train future business leaders to emphasize human rights and sustainability over profits. All types and sizes of businesses can incorporate sustainable practices, but awareness of the issues and solutions is the first step.
Lifelong Learning
The reasons why education is important discussed so far focus on institutional education. However, education can happen anywhere. Attending a university that values all kinds of learning will set students up with the foundation to become lifelong learners. Research demonstrates that lifelong learners tend to be healthier and more fulfilled throughout their lives. When societies emphasize the importance of education, they can boost their overall prosperity.

The Role Of Unity Environmental University In Society
Environmentally conscious education is extremely valuable and should be accessible to all. Unity Environmental University offers tuition prices that are comparable to public universities, and financial aid is available to those who qualify. Courses last five weeks so that students can focus on only one class at a time. This ensures all learners are set up for academic success.
Unity believes in supporting students holistically to maximize the power of education. This includes mental health services, experiential learning opportunities , and job placement assistance . Students in our hybrid programs can take classes at several field stations throughout Maine and enjoy the beautiful nature surrounding the campus for outdoor recreation.
Sustainable Initiatives
Some highlights from Unity Environmental University’s many sustainable initiatives:
- All programs include at least one sustainability learning outcome
- All research courses are focused on sustainability research
- Reduced building energy use by 25% across campus
- 100% of food waste is recycled into energy
- Campus features a net-zero LEED Platinum-certified classroom/office building
While many schools value sustainability, Unity stands out because everything we do is about sustainability. We also recognize our responsibility to model how a sustainable business can operate in a manner that’s fiscally viable and socially responsible.
Make An Impact At Unity Environmental University
While the phrase ‘education is power’ may sound cliche, it is also resoundingly true. Higher education has the power to transform individuals and societies. Unity Environmental University understands its power to make a positive impact on the world. That’s why we were the first university to divest from fossil fuels.
This year, we celebrated our largest incoming class ever , showing that students want an education system that aligns with their values. In addition to our commitment to sustainability, we offer flexibility to students with start dates all year round for our online degree programs .

Start Your Journey

Looking for Answers
Get More Info
© Unity Environmental University 2024. “America’s Environmental University.™”
Privacy Overview

The World Bank Group is the largest financier of education in the developing world, working in 90 countries and committed to helping them reach SDG4: access to inclusive and equitable quality education and lifelong learning opportunities for all by 2030.
Education is a human right, a powerful driver of development, and one of the strongest instruments for reducing poverty and improving health, gender equality, peace, and stability. It delivers large, consistent returns in terms of income, and is the most important factor to ensure equity and inclusion.
For individuals, education promotes employment, earnings, health, and poverty reduction. Globally, there is a 9% increase in hourly earnings for every extra year of schooling . For societies, it drives long-term economic growth, spurs innovation, strengthens institutions, and fosters social cohesion. Education is further a powerful catalyst to climate action through widespread behavior change and skilling for green transitions.
Developing countries have made tremendous progress in getting children into the classroom and more children worldwide are now in school. But learning is not guaranteed, as the 2018 World Development Report (WDR) stressed.
Making smart and effective investments in people’s education is critical for developing the human capital that will end extreme poverty. At the core of this strategy is the need to tackle the learning crisis, put an end to Learning Poverty , and help youth acquire the advanced cognitive, socioemotional, technical and digital skills they need to succeed in today’s world.
In low- and middle-income countries, the share of children living in Learning Poverty (that is, the proportion of 10-year-old children that are unable to read and understand a short age-appropriate text) increased from 57% before the pandemic to an estimated 70% in 2022.
However, learning is in crisis. More than 70 million more people were pushed into poverty during the COVID pandemic, a billion children lost a year of school , and three years later the learning losses suffered have not been recouped . If a child cannot read with comprehension by age 10, they are unlikely to become fluent readers. They will fail to thrive later in school and will be unable to power their careers and economies once they leave school.
The effects of the pandemic are expected to be long-lasting. Analysis has already revealed deep losses, with international reading scores declining from 2016 to 2021 by more than a year of schooling. These losses may translate to a 0.68 percentage point in global GDP growth. The staggering effects of school closures reach beyond learning. This generation of children could lose a combined total of US$21 trillion in lifetime earnings in present value or the equivalent of 17% of today’s global GDP – a sharp rise from the 2021 estimate of a US$17 trillion loss.
Action is urgently needed now – business as usual will not suffice to heal the scars of the pandemic and will not accelerate progress enough to meet the ambitions of SDG 4. We are urging governments to implement ambitious and aggressive Learning Acceleration Programs to get children back to school, recover lost learning, and advance progress by building better, more equitable and resilient education systems.
Last Updated: Mar 25, 2024
The World Bank’s global education strategy is centered on ensuring learning happens – for everyone, everywhere. Our vision is to ensure that everyone can achieve her or his full potential with access to a quality education and lifelong learning. To reach this, we are helping countries build foundational skills like literacy, numeracy, and socioemotional skills – the building blocks for all other learning. From early childhood to tertiary education and beyond – we help children and youth acquire the skills they need to thrive in school, the labor market and throughout their lives.
Investing in the world’s most precious resource – people – is paramount to ending poverty on a livable planet. Our experience across more than 100 countries bears out this robust connection between human capital, quality of life, and economic growth: when countries strategically invest in people and the systems designed to protect and build human capital at scale, they unlock the wealth of nations and the potential of everyone.
Building on this, the World Bank supports resilient, equitable, and inclusive education systems that ensure learning happens for everyone. We do this by generating and disseminating evidence, ensuring alignment with policymaking processes, and bridging the gap between research and practice.
The World Bank is the largest source of external financing for education in developing countries, with a portfolio of about $26 billion in 94 countries including IBRD, IDA and Recipient-Executed Trust Funds. IDA operations comprise 62% of the education portfolio.
The investment in FCV settings has increased dramatically and now accounts for 26% of our portfolio.
World Bank projects reach at least 425 million students -one-third of students in low- and middle-income countries.
The World Bank’s Approach to Education
Five interrelated pillars of a well-functioning education system underpin the World Bank’s education policy approach:
- Learners are prepared and motivated to learn;
- Teachers are prepared, skilled, and motivated to facilitate learning and skills acquisition;
- Learning resources (including education technology) are available, relevant, and used to improve teaching and learning;
- Schools are safe and inclusive; and
- Education Systems are well-managed, with good implementation capacity and adequate financing.
The Bank is already helping governments design and implement cost-effective programs and tools to build these pillars.
Our Principles:
- We pursue systemic reform supported by political commitment to learning for all children.
- We focus on equity and inclusion through a progressive path toward achieving universal access to quality education, including children and young adults in fragile or conflict affected areas , those in marginalized and rural communities, girls and women , displaced populations, students with disabilities , and other vulnerable groups.
- We focus on results and use evidence to keep improving policy by using metrics to guide improvements.
- We want to ensure financial commitment commensurate with what is needed to provide basic services to all.
- We invest wisely in technology so that education systems embrace and learn to harness technology to support their learning objectives.
Laying the groundwork for the future
Country challenges vary, but there is a menu of options to build forward better, more resilient, and equitable education systems.
Countries are facing an education crisis that requires a two-pronged approach: first, supporting actions to recover lost time through remedial and accelerated learning; and, second, building on these investments for a more equitable, resilient, and effective system.
Recovering from the learning crisis must be a political priority, backed with adequate financing and the resolve to implement needed reforms. Domestic financing for education over the last two years has not kept pace with the need to recover and accelerate learning. Across low- and lower-middle-income countries, the average share of education in government budgets fell during the pandemic , and in 2022 it remained below 2019 levels.
The best chance for a better future is to invest in education and make sure each dollar is put toward improving learning. In a time of fiscal pressure, protecting spending that yields long-run gains – like spending on education – will maximize impact. We still need more and better funding for education. Closing the learning gap will require increasing the level, efficiency, and equity of education spending—spending smarter is an imperative.
- Education technology can be a powerful tool to implement these actions by supporting teachers, children, principals, and parents; expanding accessible digital learning platforms, including radio/ TV / Online learning resources; and using data to identify and help at-risk children, personalize learning, and improve service delivery.
Looking ahead
We must seize this opportunity to reimagine education in bold ways. Together, we can build forward better more equitable, effective, and resilient education systems for the world’s children and youth.
Accelerating Improvements
Supporting countries in establishing time-bound learning targets and a focused education investment plan, outlining actions and investments geared to achieve these goals.
Launched in 2020, the Accelerator Program works with a set of countries to channel investments in education and to learn from each other. The program coordinates efforts across partners to ensure that the countries in the program show improvements in foundational skills at scale over the next three to five years. These investment plans build on the collective work of multiple partners, and leverage the latest evidence on what works, and how best to plan for implementation. Countries such as Brazil (the state of Ceará) and Kenya have achieved dramatic reductions in learning poverty over the past decade at scale, providing useful lessons, even as they seek to build on their successes and address remaining and new challenges.
Universalizing Foundational Literacy
Readying children for the future by supporting acquisition of foundational skills – which are the gateway to other skills and subjects.
The Literacy Policy Package (LPP) consists of interventions focused specifically on promoting acquisition of reading proficiency in primary school. These include assuring political and technical commitment to making all children literate; ensuring effective literacy instruction by supporting teachers; providing quality, age-appropriate books; teaching children first in the language they speak and understand best; and fostering children’s oral language abilities and love of books and reading.
Advancing skills through TVET and Tertiary
Ensuring that individuals have access to quality education and training opportunities and supporting links to employment.
Tertiary education and skills systems are a driver of major development agendas, including human capital, climate change, youth and women’s empowerment, and jobs and economic transformation. A comprehensive skill set to succeed in the 21st century labor market consists of foundational and higher order skills, socio-emotional skills, specialized skills, and digital skills. Yet most countries continue to struggle in delivering on the promise of skills development.
The World Bank is supporting countries through efforts that address key challenges including improving access and completion, adaptability, quality, relevance, and efficiency of skills development programs. Our approach is via multiple channels including projects, global goods, as well as the Tertiary Education and Skills Program . Our recent reports including Building Better Formal TVET Systems and STEERing Tertiary Education provide a way forward for how to improve these critical systems.
Addressing Climate Change
Mainstreaming climate education and investing in green skills, research and innovation, and green infrastructure to spur climate action and foster better preparedness and resilience to climate shocks.
Our approach recognizes that education is critical for achieving effective, sustained climate action. At the same time, climate change is adversely impacting education outcomes. Investments in education can play a huge role in building climate resilience and advancing climate mitigation and adaptation. Climate change education gives young people greater awareness of climate risks and more access to tools and solutions for addressing these risks and managing related shocks. Technical and vocational education and training can also accelerate a green economic transformation by fostering green skills and innovation. Greening education infrastructure can help mitigate the impact of heat, pollution, and extreme weather on learning, while helping address climate change.
Examples of this work are projects in Nigeria (life skills training for adolescent girls), Vietnam (fostering relevant scientific research) , and Bangladesh (constructing and retrofitting schools to serve as cyclone shelters).
Strengthening Measurement Systems
Enabling countries to gather and evaluate information on learning and its drivers more efficiently and effectively.
The World Bank supports initiatives to help countries effectively build and strengthen their measurement systems to facilitate evidence-based decision-making. Examples of this work include:
(1) The Global Education Policy Dashboard (GEPD) : This tool offers a strong basis for identifying priorities for investment and policy reforms that are suited to each country context by focusing on the three dimensions of practices, policies, and politics.
- Highlights gaps between what the evidence suggests is effective in promoting learning and what is happening in practice in each system; and
- Allows governments to track progress as they act to close the gaps.
The GEPD has been implemented in 13 education systems already – Peru, Rwanda, Jordan, Ethiopia, Madagascar, Mozambique, Islamabad, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Sierra Leone, Niger, Gabon, Jordan and Chad – with more expected by the end of 2024.
(2) Learning Assessment Platform (LeAP) : LeAP is a one-stop shop for knowledge, capacity-building tools, support for policy dialogue, and technical staff expertise to support student achievement measurement and national assessments for better learning.
Supporting Successful Teachers
Helping systems develop the right selection, incentives, and support to the professional development of teachers.
Currently, the World Bank Education Global Practice has over 160 active projects supporting over 18 million teachers worldwide, about a third of the teacher population in low- and middle-income countries. In 12 countries alone, these projects cover 16 million teachers, including all primary school teachers in Ethiopia and Turkey, and over 80% in Bangladesh, Pakistan, and Vietnam.
A World Bank-developed classroom observation tool, Teach, was designed to capture the quality of teaching in low- and middle-income countries. It is now 3.6 million students.
While Teach helps identify patterns in teacher performance, Coach leverages these insights to support teachers to improve their teaching practice through hands-on in-service teacher professional development (TPD).
Our recent report on Making Teacher Policy Work proposes a practical framework to uncover the black box of effective teacher policy and discusses the factors that enable their scalability and sustainability.
Supporting Education Finance Systems
Strengthening country financing systems to mobilize resources for education and make better use of their investments in education.
Our approach is to bring together multi-sectoral expertise to engage with ministries of education and finance and other stakeholders to develop and implement effective and efficient public financial management systems; build capacity to monitor and evaluate education spending, identify financing bottlenecks, and develop interventions to strengthen financing systems; build the evidence base on global spending patterns and the magnitude and causes of spending inefficiencies; and develop diagnostic tools as public goods to support country efforts.
Working in Fragile, Conflict, and Violent (FCV) Contexts
The massive and growing global challenge of having so many children living in conflict and violent situations requires a response at the same scale and scope. Our education engagement in the Fragility, Conflict and Violence (FCV) context, which stands at US$5.35 billion, has grown rapidly in recent years, reflecting the ever-increasing importance of the FCV agenda in education. Indeed, these projects now account for more than 25% of the World Bank education portfolio.
Education is crucial to minimizing the effects of fragility and displacement on the welfare of youth and children in the short-term and preventing the emergence of violent conflict in the long-term.
Support to Countries Throughout the Education Cycle
Our support to countries covers the entire learning cycle, to help shape resilient, equitable, and inclusive education systems that ensure learning happens for everyone.
The ongoing Supporting Egypt Education Reform project , 2018-2025, supports transformational reforms of the Egyptian education system, by improving teaching and learning conditions in public schools. The World Bank has invested $500 million in the project focused on increasing access to quality kindergarten, enhancing the capacity of teachers and education leaders, developing a reliable student assessment system, and introducing the use of modern technology for teaching and learning. Specifically, the share of Egyptian 10-year-old students, who could read and comprehend at the global minimum proficiency level, increased to 45 percent in 2021.
In Nigeria , the $75 million Edo Basic Education Sector and Skills Transformation (EdoBESST) project, running from 2020-2024, is focused on improving teaching and learning in basic education. Under the project, which covers 97 percent of schools in the state, there is a strong focus on incorporating digital technologies for teachers. They were equipped with handheld tablets with structured lesson plans for their classes. Their coaches use classroom observation tools to provide individualized feedback. Teacher absence has reduced drastically because of the initiative. Over 16,000 teachers were trained through the project, and the introduction of technology has also benefited students.
Through the $235 million School Sector Development Program in Nepal (2017-2022), the number of children staying in school until Grade 12 nearly tripled, and the number of out-of-school children fell by almost seven percent. During the pandemic, innovative approaches were needed to continue education. Mobile phone penetration is high in the country. More than four in five households in Nepal have mobile phones. The project supported an educational service that made it possible for children with phones to connect to local radio that broadcast learning programs.
From 2017-2023, the $50 million Strengthening of State Universities in Chile project has made strides to improve quality and equity at state universities. The project helped reduce dropout: the third-year dropout rate fell by almost 10 percent from 2018-2022, keeping more students in school.
The World Bank’s first Program-for-Results financing in education was through a $202 million project in Tanzania , that ran from 2013-2021. The project linked funding to results and aimed to improve education quality. It helped build capacity, and enhanced effectiveness and efficiency in the education sector. Through the project, learning outcomes significantly improved alongside an unprecedented expansion of access to education for children in Tanzania. From 2013-2019, an additional 1.8 million students enrolled in primary schools. In 2019, the average reading speed for Grade 2 students rose to 22.3 words per minute, up from 17.3 in 2017. The project laid the foundation for the ongoing $500 million BOOST project , which supports over 12 million children to enroll early, develop strong foundational skills, and complete a quality education.
The $40 million Cambodia Secondary Education Improvement project , which ran from 2017-2022, focused on strengthening school-based management, upgrading teacher qualifications, and building classrooms in Cambodia, to improve learning outcomes, and reduce student dropout at the secondary school level. The project has directly benefited almost 70,000 students in 100 target schools, and approximately 2,000 teachers and 600 school administrators received training.
The World Bank is co-financing the $152.80 million Yemen Restoring Education and Learning Emergency project , running from 2020-2024, which is implemented through UNICEF, WFP, and Save the Children. It is helping to maintain access to basic education for many students, improve learning conditions in schools, and is working to strengthen overall education sector capacity. In the time of crisis, the project is supporting teacher payments and teacher training, school meals, school infrastructure development, and the distribution of learning materials and school supplies. To date, almost 600,000 students have benefited from these interventions.
The $87 million Providing an Education of Quality in Haiti project supported approximately 380 schools in the Southern region of Haiti from 2016-2023. Despite a highly challenging context of political instability and recurrent natural disasters, the project successfully supported access to education for students. The project provided textbooks, fresh meals, and teacher training support to 70,000 students, 3,000 teachers, and 300 school directors. It gave tuition waivers to 35,000 students in 118 non-public schools. The project also repaired 19 national schools damaged by the 2021 earthquake, which gave 5,500 students safe access to their schools again.
In 2013, just 5% of the poorest households in Uzbekistan had children enrolled in preschools. Thanks to the Improving Pre-Primary and General Secondary Education Project , by July 2019, around 100,000 children will have benefitted from the half-day program in 2,420 rural kindergartens, comprising around 49% of all preschool educational institutions, or over 90% of rural kindergartens in the country.
In addition to working closely with governments in our client countries, the World Bank also works at the global, regional, and local levels with a range of technical partners, including foundations, non-profit organizations, bilaterals, and other multilateral organizations. Some examples of our most recent global partnerships include:
UNICEF, UNESCO, FCDO, USAID, Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation: Coalition for Foundational Learning
The World Bank is working closely with UNICEF, UNESCO, FCDO, USAID, and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation as the Coalition for Foundational Learning to advocate and provide technical support to ensure foundational learning. The World Bank works with these partners to promote and endorse the Commitment to Action on Foundational Learning , a global network of countries committed to halving the global share of children unable to read and understand a simple text by age 10 by 2030.
Australian Aid, Bernard van Leer Foundation, Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Canada, Echida Giving, FCDO, German Cooperation, William & Flora Hewlett Foundation, Conrad Hilton Foundation, LEGO Foundation, Porticus, USAID: Early Learning Partnership
The Early Learning Partnership (ELP) is a multi-donor trust fund, housed at the World Bank. ELP leverages World Bank strengths—a global presence, access to policymakers and strong technical analysis—to improve early learning opportunities and outcomes for young children around the world.
We help World Bank teams and countries get the information they need to make the case to invest in Early Childhood Development (ECD), design effective policies and deliver impactful programs. At the country level, ELP grants provide teams with resources for early seed investments that can generate large financial commitments through World Bank finance and government resources. At the global level, ELP research and special initiatives work to fill knowledge gaps, build capacity and generate public goods.
UNESCO, UNICEF: Learning Data Compact
UNESCO, UNICEF, and the World Bank have joined forces to close the learning data gaps that still exist and that preclude many countries from monitoring the quality of their education systems and assessing if their students are learning. The three organizations have agreed to a Learning Data Compact , a commitment to ensure that all countries, especially low-income countries, have at least one quality measure of learning by 2025, supporting coordinated efforts to strengthen national assessment systems.
UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS): Learning Poverty Indicator
Aimed at measuring and urging attention to foundational literacy as a prerequisite to achieve SDG4, this partnership was launched in 2019 to help countries strengthen their learning assessment systems, better monitor what students are learning in internationally comparable ways and improve the breadth and quality of global data on education.
FCDO, Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation: EdTech Hub
Supported by the UK government’s Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO), in partnership with the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the EdTech Hub is aimed at improving the quality of ed-tech investments. The Hub launched a rapid response Helpdesk service to provide just-in-time advisory support to 70 low- and middle-income countries planning education technology and remote learning initiatives.
MasterCard Foundation
Our Tertiary Education and Skills global program, launched with support from the Mastercard Foundation, aims to prepare youth and adults for the future of work and society by improving access to relevant, quality, equitable reskilling and post-secondary education opportunities. It is designed to reframe, reform, and rebuild tertiary education and skills systems for the digital and green transformation.

Bridging the AI divide: Breaking down barriers to ensure women’s leadership and participation in the Fifth Industrial Revolution

Common challenges and tailored solutions: How policymakers are strengthening early learning systems across the world

Compulsory education boosts learning outcomes and climate action
Areas of focus.
Digital Technologies
Early Childhood Development
Education Data & Measurement
Education Finance
Education in Fragile, Conflict & Violence Contexts
Girls’ Education
Higher Education
Inclusive Education
Initiatives
- Show More +
- Tertiary Education and Skills Program
- Service Delivery Indicators
- Evoke: Transforming education to empower youth
- Global Education Policy Dashboard
- Global Education Evidence Advisory Panel
- Show Less -
Collapse and Recovery: How the COVID-19 Pandemic Eroded Human Capital and What to Do About It
BROCHURES & FACT SHEETS
Flyer: Education Factsheet - May 2024
Publication: Realizing Education's Promise: A World Bank Retrospective – August 2023
Education and Climate Change flyer - November 2022
Learning Losses Brochure - October 2022
World Bank Group Education Fact Sheet - September 2022
STAY CONNECTED

Human Development Topics
Around the bank group.
Find out what the Bank Group's branches are doing in education

Global Education Newsletter - March 2024
What's happening in the World Bank Education Global Practice? Read to learn more.

Human Capital Project
The Human Capital Project is a global effort to accelerate more and better investments in people for greater equity and economic growth.

Impact Evaluations
Research that measures the impact of education policies to improve education in low and middle income countries.

Education Videos
Watch our latest videos featuring our projects across the world
Additional Resources
This site uses cookies to optimize functionality and give you the best possible experience. If you continue to navigate this website beyond this page, cookies will be placed on your browser. To learn more about cookies, click here .
A good education is important to achieving the American Dream
- Download Chapter 5: Education
- Explore the full report
Subscribe to the Center for Economic Security and Opportunity Newsletter
Aei-brookings working group on poverty and opportunity awgopao aei-brookings working group on poverty and opportunity.
December 3, 2015

For much of the 20 th century, a cornerstone of the American Dream has been the belief that, with hard work, all adults should be able to lift themselves and their families out of poverty.
But over the last several decades, it has become clear that achieving the American Dream now takes both hard work and good education—good enough to command a job that pays a non-poverty wage.
The education level of adult heads of households has been increasingly associated with their income as the income gap between the well-educated and the less-educated has grown steadily over the last four decades.
In Chapter 5 of a new report from the AEI-Brookings Working Group on Poverty and Opportunity , the Working Group recommends policies that:
- Increase public investment in two underfunded stages of education: preschool and postsecondary;
- Educate the whole child to promote social-emotional as well as academic skills;
- Modernize the organization and accountability of the educational system; and
- Close resource gaps to reduce education gaps.
Related Content
AEI-Brookings Working Group on Poverty and Opportunity
Richard V. Reeves
May 29, 2014
Ron Haskins, Isabel V. Sawhill
May 7, 2013
Early Childhood Education Higher Education K-12 Education
Economic Studies
Center for Economic Security and Opportunity
Katharine Meyer
May 7, 2024
Jamie Klinenberg, Jon Valant, Nicolas Zerbino
Thinley Choden
May 3, 2024

- High contrast
- Press Centre
Search UNICEF
Every child has the right to learn..

- Available in:
Overview | What we do | Reports | Data | News
A child’s right to education entails the right to learn. Yet, for too many children across the globe, schooling does not lead to learning.
Over 600 million children worldwide are unable to attain minimum proficiency levels in reading and mathematics, even though two thirds of them are in school. For out-of-school children, foundational skills in literacy and numeracy are further from grasp.
Children are deprived of education for various reasons. Poverty remains one of the most obstinate barriers. Children living through economic fragility, political instability, conflict or natural disaster are more likely to be cut off from schooling – as are those with disabilities, or from ethnic minorities. In some countries, education opportunities for girls remain severely limited.
Even in schools, a lack of trained teachers, inadequate education materials and poor infrastructure make learning difficult for many students. Others come to class too hungry, ill or exhausted from work or household tasks to benefit from their lessons.
Compounding these inequities is a digital divide of growing concern: Most of the world’s school-aged children do not have internet connection in their homes, restricting their opportunities to further their learning and skills development.
Without quality education, children face considerable barriers to employment later in life. They are more likely to suffer adverse health outcomes and less likely to participate in decisions that affect them – threatening their ability to shape a better future for themselves and their societies.
Education is a basic human right. In 147 countries around the world, UNICEF works to provide quality learning opportunities that prepare children and adolescents with the knowledge and skills they need to thrive. We focus on:
Equitable access : Access to quality education and skills development must be equitable and inclusive for all children and adolescents, regardless of who they are or where they live. We make targeted efforts to reach children who are excluded from education and learning on the basis of gender, disability, poverty, ethnicity and language.
Quality learning : Outcomes must be at the centre of our work to close the gap between what students are learning and what they need to thrive in their communities and future jobs. Quality learning requires a safe, friendly environment, qualified and motivated teachers, and instruction in languages students can understand. It also requires that education outcomes be monitored and feed back into instruction.
Education in emergencies : Children living through conflict, natural disaster and displacement are in urgent need of educational support. Crises not only halt children’s learning but also roll back their gains. In many emergencies, UNICEF is the largest provider of educational support throughout humanitarian response, working with UNHCR, WFP and other partners.

Our programmes

Our strategy

Get involved
Help us tackle the learning crisis.

Skills for a green transition
Solutions for youth on the move

ICTD annual report 2022
Information and Communication Technology Division
Tracking progress on foundational learning
Findings from the RAPID 2023 analysis

Global annual results report 2022: Goal Area 2
Every child, including adolescents, learns and acquires skills for the future
Data and insights

Our research

Our insights

Children call for access to quality climate education
On Earth Day, UNICEF urges governments to empower every child with learning opportunities to be a champion for the planet

An entire generation of children in Sudan faces a catastrophe as the war enters its second year

Teachers wanted
Empowering teachers at the forefront of the learning crisis
Children and teachers killed in air strikes on schools in eastern Myanmar
Why education is the key to development

.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Børge Brende

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Infrastructure is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, infrastructure.
Education is a human right. And, like other human rights, it cannot be taken for granted. Across the world, 59 million children and 65 million adolescents are out of school . More than 120 million children do not complete primary education.
Behind these figures there are children and youth being denied not only a right, but opportunities: a fair chance to get a decent job, to escape poverty, to support their families, and to develop their communities. This year, decision-makers will set the priorities for global development for the next 15 years. They should make sure to place education high on the list.
The deadline for the Millennium Development Goals is fast approaching. We have a responsibility to make sure we fulfill the promise we made at the beginning of the millennium: to ensure that boys and girls everywhere complete a full course of primary schooling.
The challenge is daunting. Many of those who remain out of school are the hardest to reach, as they live in countries that are held back by conflict, disaster, and epidemics. And the last push is unlikely to be accompanied by the double-digit economic growth in some developing economies that makes it easier to expand opportunities.
Nevertheless, we can succeed. Over the last 15 years, governments and their partners have shown that political will and concerted efforts can deliver tremendous results – including halving the number of children and adolescents who are out of school. Moreover, most countries are closing in on gender parity at the primary level. Now is the time to redouble our efforts to finish what we started.
But we must not stop with primary education. In today’s knowledge-driven economies, access to quality education and the chances for development are two sides of the same coin. That is why we must also set targets for secondary education, while improving quality and learning outcomes at all levels. That is what the Sustainable Development Goal on education, which world leaders will adopt this year, aims to do.
Addressing the fact that an estimated 250 million children worldwide are not learning the basic skills they need to enter the labor market is more than a moral obligation. It amounts to an investment in sustainable growth and prosperity. For both countries and individuals, there is a direct and indisputable link between access to quality education and economic and social development.
Likewise, ensuring that girls are not kept at home when they reach puberty, but are allowed to complete education on the same footing as their male counterparts, is not just altruism; it is sound economics. Communities and countries that succeed in achieving gender parity in education will reap substantial benefits relating to health, equality, and job creation.
All countries, regardless of their national wealth, stand to gain from more and better education. According to a recent OECD report , providing every child with access to education and the skills needed to participate fully in society would boost GDP by an average 28% per year in lower-income countries and 16% per year in high-income countries for the next 80 years.
Today’s students need “twenty-first-century skills,” like critical thinking, problem solving, creativity, and digital literacy. Learners of all ages need to become familiar with new technologies and cope with rapidly changing workplaces.
According to the International Labour Organization, an additional 280 million jobs will be needed by 2019. It is vital for policymakers to ensure that the right frameworks and incentives are established so that those jobs can be created and filled. Robust education systems – underpinned by qualified, professionally trained, motivated, and well-supported teachers – will be the cornerstone of this effort.
Governments should work with parent and teacher associations, as well as the private sector and civil-society organizations, to find the best and most constructive ways to improve the quality of education. Innovation has to be harnessed, and new partnerships must be forged.
Of course, this will cost money. According to UNESCO, in order to meet our basic education targets by 2030, we must close an external annual financing gap of about $22 billion. But we have the resources necessary to deliver. What is lacking is the political will to make the needed investments.
This is the challenge that inspired Norway to invite world leaders to Oslo for a Summit on Education for Development , where we can develop strategies for mobilizing political support for increasing financing for education. For the first time in history, we are in the unique position to provide education opportunities for all, if only we pull together. We cannot miss this critical opportunity.
To be sure, the responsibility for providing citizens with a quality education rests, first and foremost, with national governments. Aid cannot replace domestic-resource mobilization. But donor countries also have an important role to play, especially in supporting least-developed countries. We must reverse the recent downward trend in development assistance for education, and leverage our assistance to attract investments from various other sources. For our part, we are in the process of doubling Norway’s financial contribution to education for development in the period 2013-2017.
Together, we need to intensify efforts to bring the poorest and hardest to reach children into the education system. Education is a right for everyone. It is a right for girls, just as it is for boys. It is a right for disabled children, just as it is for everyone else. It is a right for the 37 million out-of-school children and youth in countries affected by crises and conflicts. Education is a right regardless of where you are born and where you grow up. It is time to ensure that the right is upheld.
This article is published in collaboration with Project Syndicate . Publication does not imply endorsement of views by the World Economic Forum.
To keep up with the Agenda subscribe to our weekly newsletter .
Author: Erna Solberg is Prime Minister of Norway. Børge Brende is Norway’s Minister of Foreign Affairs.
Image: Students attend a class at the Oxford International College in Changzhou. REUTERS/Aly Song.
Share this:
- Share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Economic Growth .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

UK leaves recession with fastest growth in 3 years, and other economics stories to read
Kate Whiting
May 10, 2024

How a pair of reading glasses could increase your income
Emma Charlton
May 8, 2024

Why shifting from prediction to foresight can help us plan for future disruption
Roger Spitz
May 3, 2024

5 ways businesses can help to alleviate poverty
Sreevas Sahasranamam and Vivek Soundararajan

The state of world prosperity: 4 key data points you need to understand
Wolfgang Fengler and Homi Kharas

Money matters: Your guide to financial literacy
Meagan Andrews and Haleh Nazeri

- October 26, 2022
- Academic Advice
15 Benefits of Education That Can Impact Your Future
UOTP Marketing

While everyone might have a different definition of education, its importance remains undisputed. By receiving a systematic education, people gain knowledge and develop skills and character traits crucial for a certain standard of life.
While primary and secondary education is compulsory in most countries worldwide, that is not the case with tertiary schooling. Pursuing a college or university degree is a person’s choice based on needs, career preferences, and abilities. Whether a university education is a requirement for your preferred career or not, a college degree can significantly impact your future. If you are considering the various options, you may want to explore different type of degrees offered by educational institutions to align your choice with your needs, career preferences, and abilities.
15 Benefits of Education
Most people agree on the importance of education, but only a fraction of that is truly aware of the impact of education on our lives. Receiving an education has a significant impact not only on our quality of life but on our physical and psychological well-being. Below you will find 15 different benefits of education that can impact your life in the future.
1. Creating More Employment Opportunities
“Finding a job” is probably one of the most common reasons people choose to pursue a college degree, as we are all well aware of the difficulties of landing a good job. In most cases, tens of candidates are applying for the same position, and a college degree can help set you apart from others. In addition, a college education will create more employment opportunities as you will be qualified for more than low-paying and entry-level jobs.
2. Leading to Career Advancement
If you have already joined the workforce and love your job, you might think you don’t need to pursue a college or university education. We are here to tell you that a college degree can have other benefits than just landing you a job. By receiving higher education, you gain the knowledge and skills that will give you a competitive edge and allow you to advance your career in a chosen field.
3. Securing a Better Income

As previously mentioned, a college education can be grounds for career advancement. Advancement in your field comes in the form of a new job title and greater responsibilities—consequently, a higher salary and added benefits. You will also qualify for higher-paying entry-level jobs by getting a higher education degree. As a result, a higher wage can grant you financial stability and improve your quality of life.
4. Developing Critical-Thinking Skills
Higher education equips you with the knowledge and essential skills necessary to join the workforce. One of the most vital skills you will develop when pursuing a college degree is the ability to think critically. Critical thinking skills are an advantage and sometimes even a requirement to succeed in your career. By developing critical-thinking skills, you can improve your work’s quality, solve problems, and prevent possible issues that might arise.
5. Improving Self-Discipline

The amount of work that one has to put in to get a college degree is sometimes precisely what improves one’s self-discipline. When pursuing higher education, you have assignments that you must deliver on time and tests you must study for—all of which require self-discipline. Improved self-discipline will, in turn, help you in your future career by making you a reliable and hardworking team member.
6. Developing Cognitive And Communication Skills
Learning how to communicate with others is a highly valuable skill in the job market and one that will significantly contribute to your career success. Pursuing a university or college degree is a great way to further develop your cognitive and communication skills. During your studies, you will constantly be in contact and collaborate with colleagues and professors, giving you insight into a typical work environment.
7. Promoting Equality And Empowerment
One of the most important benefits of education is probably the promotion of equality and empowerment within society. Higher education can make people more open-minded in accepting others’ ideas and opinions regardless of race, gender, age, etc. In addition, education empowers people through expert knowledge and valuable skills and gives them the mental capacity to make decisions and create a life of their own independently.
8. Providing a Prosperous And Healthy Life

The list of highest-paying careers contains mostly professions that require a higher education degree. This is why one must pursue a college education to land a well-paying job. A high-paying job career has many benefits, including a comfortable life for you and your family, the respect and admiration of your family and friends, etc. Being financially secure will also contribute to your and your family’s overall happiness and quality of life.
Interested in pursuing a degree?
Fill out the form and get all admission information you need regarding your chosen program.
This will only take a moment.
Message Received!
Thank you for reaching out to us. we will review your message and get right back to you within 24 hours. if there is an urgent matter and you need to speak to someone immediately you can call at the following phone number:.
By clicking the Send me more information button above, I represent that I am 18+ years of age, that I have read and agreed to the Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy , and agree to receive email marketing and phone calls from UOTP. I understand that my consent is not required to apply for online degree enrollment. To speak with a representative without providing consent, please call +1 (202) 274-2300
- We value your privacy.
9. Instilling a Sense of Accomplishment
There are still advantages to a college or university degree, even if we were to take out the “landing a job” benefit. Another great benefit of pursuing a degree is the sense of accomplishment you gain when you obtain your degree. Feeling like you accomplished something important will, in turn, make you more confident in pursuing other things you want in life and getting them.
10. Spreading Awareness
Nowadays, technological advancement has made it possible for people to easily connect and communicate with virtually anyone anywhere in the world. This, of course, includes students in colleges and universities. Getting a college education will, directly and indirectly, expose students to different cultures around the world, thus increasing cultural awareness.
11. Enhancing Productivity
Getting a college degree is a lot of hard work, requiring self-discipline and good time-management skills . Pursuing and obtaining a college degree will improve these skills and qualities in a person. Such essential attributes and skills will make you a valuable employee and asset for the companies you work for as they help enhance your overall productivity.
12. Offering the Opportunity to Socialize And Network

Another way a college education will prepare you for your future career is through socializing and networking. When pursuing a college degree, you are surrounded by other students who will soon enter the same job market as you. Socializing or creating a network with them early on will be a great advantage when pursuing a career or seeking career advancement.
13. Pursuing a Passion
Pursuing a college or university degree in a field you are passionate about is a great way to land a fulfilling career. A college education will allow you to turn your passion into a stable job and income you need to live comfortably. In addition, the specialized knowledge you gain during your studies will help you plunge deeper into the things you love.
14. Opening Your Horizons
Pursuing higher education is a great way to open your horizons regarding knowledge, understanding, or experience. Whether it is the specialized knowledge and understanding you gain, the different things you experience, or the relationships you form, a college education will expose you to things you can’t find elsewhere.
15. Contributing to the Community
Lastly, all the benefits of education mentioned above will make you a better member of society. By receiving higher education and landing a fulfilling and high-paying job, you can then turn your energy into giving back to the community and helping others. Educated people are aware of the role an individual must play in society for it to function well, so they do their part accordingly.
The Bottom Line
There are many ways higher education can impact your future as an individual and a community member. By pursuing a college education, one can become a financially stable, knowledgeable, skilled, and happy individual that will contribute to a better society.
Share it with your friends!
Explore more.

Accounting vs. Finance Degree: Which Major to Choose?

12 Important Bookkeeping Skills You Need for a Successful Career
Recent resources.

What Can You Do With a Hospitality Management Degree? Best Hospitality Careers

What Can You Do with an International Studies Degree [2024]

9 Benefits of Learning a Second Language

Associate’s vs. Bachelor’s: Which One To Choose?
INTERESTED IN LEARNING MORE?
Chat with an Admissions Officer Now!

- Associates Degree
- Bachelors Degrees
- Masters Degrees
- Doctoral Degrees
- Faculty & Staff
- Accreditation
- Student Experience
QUICK LINKS
- Admission Requirements
- Military Students
- Financial Aid
Request More Information

10 Benefits Showing Why Education Is Important to Our Society

Do you think attending school and doing projects for your college is a waste of time? If you do, you might want to reconsider that claim as education is a key part of a society’s growth and progress. When people are educated, they can significantly contribute to their families and society in various aspects and fields, thus creating a stable and stimulating community. Why is education important to society? Let’s take into account some reasons.
1. Creating More Employment Opportunities
Finding a job is not easy, especially in times of economic turmoil. You often need to compete with hundreds of other candidates for a vacant position. In addition, the lower the education level, the greater the number of people applying for the same low-paying entry-level post. However, with the right qualifications and educational background, you will increase your chances of landing a fulfilling job. Would you like to find a way to stand out from a pool of applicants? Learn, educate yourself, graduate and get as many qualifications, skills, knowledge, and experience as possible.
2. Securing a Higher Income
People with higher education and varied experience are more likely to get high-paying , expert jobs. Study hard, dedicate your time and effort to acquire knowledge and reach a high level of competence if you would like to lead a comfortable lifestyle. Your credentials are what will motivate a potential employer to choose you instead of another candidate. Studying hard throughout your school and studies shows you are not afraid of hard work and are able to fulfill your goals. Employers see this as a huge advantage as they all prefer a responsible and knowledgeable workforce. Once you graduate, you can start searching for jobs that will give you the opportunity to practice what you have learned and, at the same time, secure sufficient pay for your needs.
3. Developing Problem-solving Skills
One of the benefits of education is that the educational system teaches us how to obtain and develop critical and logical thinking and make independent decisions. When children become adults, they are faced with a lot of challenging issues – pay off your student loans, get a job, buy a car and a house, provide for your family, etc. However, if one has spent years educating themselves, they should be able to make sound decisions on these various quandaries. Not only are people able to form their own opinions, but they are also good at finding solid and reliable arguments and evidence to back up and confirm their decisions.
4. Improving the Economy

People with good academic and educational backgrounds tend to get well-paid jobs. The higher their education and accomplishments, the better employment options they get. People who grew up poor but educated themselves have high chances to transform their lives, thus contributing to a decrease in society’s poverty rates. Education helps countries grow economically since it is about getting knowledge and being able to apply it wisely to our lives and, at the same time, improving other people’s lives.
5. Providing a Prosperous and Happy Life
Education has always secured respect from society. In order to ensure a comfortable lifestyle, people should educate themselves and obtain a well-paid job to be successful and satisfied. It helps gain a better reputation and increases the chances of climbing the career ladder more easily and faster. In turn, it provides financial resources for stable lives – people can afford to buy their own house or apartment and thus secure their children’s happiness and success. Furthermore, being able to own your own home provides stability and increases self-confidence. It leads to creating a positive environment for families and communities. “Children of homeowners are 116% more likely to graduate from college than children of renters of the same age, race, and income. They are also 25% more likely to graduate from high school and have higher math and reading scores, with fewer behavioral problems,” according to research at the University of Tennessee.
6. Giving Back to the Community
How does education benefit society? Educated people understand how valuable it is to live in a stable and secure community. They are more prone to taking part in projects that help improve not only their neighborhood but society, as well. In addition, when people are able to afford their own home, they are more likely to take part not only in improving their homes but in solving local problems , as well. After all, it is quite important to get involved and give a hand to the less fortunate ones in order to build a better place for all of us to live in.
7. Creating Modern Society
Education is of key essence for modern society. One needs to learn about culture, history and other important aspects so that they would be able to contribute to modern society. Education molds people into leaders not only with knowledge about (college) subjects, but it also shows them how to lead with emotions and true values. Educated people can easily differentiate between right and wrong, thus education helps reduce the crime rate. Bad events are happening around the world – only competent leaders can help guide us down a good and right path.
8. Bridging the Borders
Digital education helps connect with people and organizations around the world. Borders are no longer there. Being able to communicate and share opinions with people from other countries and cultures, widens horizons and helps us understand and appreciate each other.
9. Creating equal opportunities

The importance of education in society has always been great as it is irrespective of caste, race, gender, religion. Educated people are treated as equals on the basis of their knowledge and competence. In addition to this, educated people are open-minded and are able to listen and accept other people’s views regardless of the fact of how different they are. Education offers a possibility to live independently and thus be free. It is our shelter against financial storms and wrong decisions.
10. Introducing Empowerment
Education is the key to turn a weakness into a strength. It offers different tools and ways to understand problems that lay ahead of us and helps resolve them. More importantly, education provides us with considerable mental agility to make the right decisions and spring into action when needed. Many types of research show that educated women can more easily stand up against gender bias and marital violence as they have improved their decision-making capabilities.
Whether it is about respect, a higher position in society and a professional environment, financial security, family stability, education provides all of these and much more. Home stability provided by owning your own home helps children who grew up in their own houses or apartments become more successful. They are more likely to graduate high school (25%) and finish college (116%). “Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world,” as Nelson Mandela said. It helps people become better citizens, get a better-paid job, shows the difference between good and bad. Education shows us the importance of hard work and, at the same time, helps us grow and develop. Thus, we are able to shape a better society to live in by knowing and respecting rights, laws, and regulations. Learning languages through educational processes helps interact with different people in order to exchange ideas, knowledge, good practices. It teaches us to live in harmony.
Are you ready to give back? Help the families from your community that need it the most. Get involved , today.
About Habitat for Humanity of Broward
Seeking to put God’s love into action, Habitat for Humanity of Broward brings people together to build homes, communities and hope. Habitat Broward offers a “hand up” not a “hand out” to families who are unable to qualify for conventional home financing but are willing to work hard to improve their family’s lives and achieve the economic empowerment of homeownership. For more information about Habitat for Humanity of Broward please call (954) 396-3030 or visit habitatbroward.org or check us out on Facebook at www.facebook.com/HabitatBroward .
- 888 NW 62nd Street, 2nd Floor Fort Lauderdale, FL 33309
- Phone: (954) 396-3030
- Fax: (954) 570-0054
- Email: [email protected]
- Hours Monday – Friday, 9:00 AM – 5:00 PM


The right to education
Education is a basic human right that works to raise men and women out of poverty, level inequalities and ensure sustainable development. But worldwide 244 million children and youth are still out of school for social, economic and cultural reasons. Education is one of the most powerful tools in lifting excluded children and adults out of poverty and is a stepping stone to other fundamental human rights. It is the most sustainable investment. The right to quality education is already firmly rooted in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and international legal instruments, the majority of which are the result of the work of UNESCO and the United Nations.
- What you need to know about the right to education
- Q&A with the UN Special Rapporteur on the right to education
Understanding the right to education
Enforcing the right to education.
Developing norms and standards
in reviewing and developing education legal and policy frameworks
Responding to challenges
The start of a global conversation

Say no to discrimination in education! - #RightToEducation campaign
Monitoring tools.

For any information, please contact: [email protected]

Monitoring SDG 4: access to education
Resources from UNESCO’s Global Education Monitoring Report.
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Education, training and skills
- School curriculum
- Secondary curriculum, key stage 3 and key stage 4 (GCSEs)
- GCSE changes and reforms
Nick Gibb: what is a good education in the 21st century?
Schools Minister Nick Gibb explains the importance of a core academic curriculum and the value of excellent teachers.

Can I start by saying thank you for inviting me to come and speak to you today. It is a great pleasure to be back at my old college.
One thing that I miss enormously from my undergraduate days is the time to think, and the time to read. Ministerial duties permitting, I still try to carve out spare hours to enjoy a good book. Ever since becoming Schools Minister, I have been particularly entertained by passages in novels which address English schools.
Zadie Smith’s wonderful account of life in modern London, ‘NW’, features the protagonist Natalie Blake - an upwardly mobile Londoner who goes from her inner-city school to university, and then on to a successful career as a lawyer. Whilst seeking out a primary school for her son, she visits a medieval parish church which has been engulfed in the urban sprawl of north-west London.
A dedicated autodictat, we are treated to Natalie Blake’s stream of consciousness as she picks up and reads a leaflet in the church: “…present church dates from around 1315 … Cromwellian bullet holes in the door…”.
Natalie’s reading continues: “… the famous shrine of Our Lady of Willesden, ‘The Black Madonna’, destroyed in the Reformation and burnt, along with the ladies of Walsingham, Ipswich and Worcester - by the Lord Privy Seal. Also a Cromwell. Different Cromwell. Doesn’t say. This is where decent history GCSE -level teaching would have come in helpful…”.
On reading that passage, I wondered whether Natalie’s life is irretrievably held back by her inability to distinguish between Oliver and Thomas Cromwell? Perhaps not. But the situation described in this passage of the novel is indicative of a broader phenomenon: that the recipient of a core academic curriculum leaves school with an intellectual hinterland, which allows them to make sense of the world around them.
Since coming into government in 2010, our reforms to the A levels , GCSEs , and the national curriculum have focused on bringing a new level of academic rigour to English state schooling. And central to this mission has been elevating knowledge to become a central component of a good school education.
Had Natalie studied for the new reformed history GCSE , due to be taught from September 2016, she would have stood a better chance of knowing about both Oliver and Thomas Cromwell, thus having the knowledge to understand the historical significance of her parish church.
‘Knowledge’, I hear people gasp. ‘Surely education is about so much more than that. It is about creativity, problem solving, thinking critically, and inventing?’.
Yes, I agree whole-heartedly that a good education is about all those things. But each of them is dependent upon, and impossible without, a fundamental basis of knowledge about the subject in question. Put simply, a commitment to social justice requires us to place knowledge at the heart of our education system. And this is not a statement of opinion – it is a fact established by decades of research by cognitive scientists, as I shall soon explain.
It is an unfortunate fact, however, that many modern conceptions of education either ignore the importance of knowledge, or actively deride it. During the 1960s, it became fashionable amongst educationists to dismiss the accumulation of knowledge as a joyless anachronism: rote learning of unconnected facts, inflicted upon bored and unwilling pupils. School curricula were increasingly rewritten to focus not upon subject content, but upon skills and dispositions.
History became less about mastering the understanding of a period, and more about analysing primary sources. Foreign languages teaching moved away from learning grammatical structures and a wide vocabulary, and towards communication. And in maths, it was believed that memorisation of times tables and basic arithmetic at an early age could be bypassed by learning through real-life mathematical problems.
This philosophy endured and strengthened over the next half century, and had a marked effect on the quality of education that generations of children have received in Britain. For me, the crowning glory of this dumbing down was the 2007 rewrite of the national curriculum, which systematically expunged any mention of subject content, replacing it with references to ‘processes’, ‘concepts’, and with an overlay of ‘personal, learning and thinking skills’ such as ‘independent learning’ and ‘learning to learn’.
As Schools Minister, I have visited around 400 schools, watched thousands of classes, and seen countless examples of this philosophy in action. It always saddens me to see thrilling content of education, be it timeless literature, scientific wonders, or great historical events, being relegated to a backseat, so that these comparatively joyless ‘skills’ and ‘processes’ can come to the fore.
Now, I am sure that many here may be thinking back to their own recent education, and contending that you studied a core, subject-based academic curriculum at school. If that is the case, you should feel fortunate that you were part of a minority.
On entering government in 2010, we were concerned that nationwide only 31% of pupils were taking a GCSE in history. Only 26% of pupils were taking a GCSE in geography. Worse still, only 43% of pupils were studying a GCSE in a foreign language, down from 76% in 2000.
We saw that the majority of English pupils were not studying a combination of academic subjects which - up to the age of 16 - would be seen as entirely standard at most independent schools, and indeed in many foreign countries.
And even for those who did enter GCSEs in academic subjects, the examination content had been so watered down that it no longer represented a mastery of any given subject. A history GCSE could consist entirely of 20th-century topics; a religious studies GCSE could consist of just 1 religion, or very little religion at all; and around 90% of pupils entering the English literature GCSE delivered by 1 exam board answered questions on a single text: ‘Of Mice and Men’. Now, John Steinbeck is a great author - ‘East of Eden’ is my all-time favourite novel - but even I doubt this short novella was deserving of such overwhelming attention.
In addition, grade inflation had been allowed to diminish the value of our qualifications. From 2005 to 2010, the proportion of pupils achieving 5 good GCSEs increased year on year. But as Professor Robert Coe of this university showed, English pupils’ performance in international assessments and annual benchmarked aptitude tests showed no improvement at all.
This was the state of English education that we inherited on coming into government in 2010. Since then, our reforms have focused on raising the ambition of what pupils are expected to study at school, and putting subject content - which I believe to be the real joy of education - at the core of school life.
We have removed over 3,000 low-value qualifications from performance tables and introduced rigorous new standards for the technical and professional qualifications that remain.
We introduced the English Baccalaureate ( EBacc ) measure in 2010, which shows the proportion of pupils in a school being entered for a combination of GCSEs in English, mathematics, 2 sciences, history or geography, and a foreign language. Schools have risen to this challenge: the proportion of pupils entering this EBacc combination of subjects nationwide has risen from 23% in 2012 to 39% in 2015.
And due to a long process of examination reform which is only just coming to fruition, the examinations that children are taking are becoming more academically ambitious, not less. Since September, pupils have been studying the reformed English literature GCSE for the first time, including the study of both a 19th-century novel and a modern text. Instead of a strict diet of Steinbeck, pupils can read George Orwell and Jane Austen, Kazuo Ishiguro and Charlotte Bronte - and they will be reading the whole novel, not just extracts.
From September, the new history GCSE will be studied, which will supplement 20th-century global history with British depth studies, from the reign of King Edward I to the English Civil War and Restoration.
Our curriculum reforms also look to the future, as the school curriculum must adapt to incorporate the breakthroughs of the technological age. That is why we have introduced a new national curriculum for computing, which focuses on programming languages, computational thinking, and Boolean logic - making this country, I believe, the first in the G20 to do so. The old IT curriculum simply taught children to use programmes such as Microsoft Word: now, pupils are learning to code and create programmes for themselves.
This culture of increasing academic ambition is having a beneficial knock on effect for A level studies, where since 2010 there has been a 27% increase in pupil entries for further maths, a 15% increase in pupil entries for physics, and a 15% increase in pupil entries for chemistry.
Non- STEM (science, technology, engineering and mathematics) subjects are seeing similar increases at A level . Economics, up 29%. Religious studies, up 19%. Spanish and geography, both up 16%. Whilst for years, comments about ‘the youth of today’ have implied decline and disappointment, today’s youngsters will be better educated and better informed about the world than the generations preceding them.
In England, it has always been possible to secure a good education, through top comprehensive schools, grammar schools or independent schools. But it is socially disadvantaged pupils who have historically missed out, and found their life chances limited by the quality of education they received. Research by the Sutton Trust in 2014 showed that pupils eligible for free school meals who scored in the top 10% nationally at the end of primary school were significantly less likely to be entered for the EBacc than their wealthier peers who achieved the same level aged 11. Disadvantaged pupils - the very children most in need of an academic, knowledge-based curriculum - were the least likely to be given the opportunity to benefit from it.
It is the driving ambition for this government that a core academic curriculum should not be the preserve of a social elite, but instead the entitlement of every single child. Though there are some inequalities which schools cannot address, the unequal distribution of intellectual and cultural capital is one that they can.
But there remain many working within education who would challenge my assumption that a core academic curriculum is a valuable inheritance for all pupils. Such figures think it superfluous to know, for example, Oliver Cromwell from Thomas. I am sure many here will have seen the Royal Society of Arts talk by the educationist Sir Ken Robinson, now pushing 14 million views on YouTube. In his talk, he accuses the traditional, academic curriculum of being a relic of the 19th century, a ‘factory model’ of schooling, which squanders pupil creativity.
As his enormous popularity shows, Sir Ken Robinson’s views are superficially appealing. But I believe them to be profoundly wrong.
An educationist who has shaped my thinking on this more than any other is Daniel Willingham, professor of cognitive science at the University of Virginia. With reference to robust scientific evidence, he explains how the ‘thinking skills’ most prized by schools and employers - problem solving, creativity, inventiveness - are dependent upon considerable background knowledge.
You may suppose that ‘thinking scientifically’ is a discrete skill, that when learnt can be applied to any new context, but this is not the case.
To give one of the many examples that Professor Willingham cites, in one experiment, eighth-grade pupils in America were given 2 tasks. In 1, they had to manipulate a computer simulation to keep imaginary creatures alive. In another, the pupils had to evaluate how the surface area of swimming pools was related to the cooling rate of its water.
Students were consistently better at thinking scientifically on the first problem, rather than the second - something that the researchers attributed to pupils’ greater familiarity with the relevant variables. In general, American eighth-graders are better informed about health and survival, compared to volume, surface area and cooling rates.
And it is a well-known principle that great inventions are made, not through a moment of pure inspiration, but through analogical thinking. The ‘eureka moment’ of any great invention occurs when existing knowledge is brought to bear in new contexts: the novel application of what is already known.
Alexander Graham Bell’s first diagrams for the telephone made explicit reference to the biological structure of the human ear. George de Mestral invented Velcro through looking at the tiny hooks of the cockle-burs which stuck to his dog’s fur when he was hunting in the Alps.
This insight, that complex thinking depends upon background knowledge, can be applied to any subject of study.
It underlies our recent announcement that all pupils will be tested on their multiplication tables at the end of year 6, an announcement which was strongly opposed by the General Secretary of the National Union of Teachers. She expressed the classic anti-knowledge view, suggesting that number recall is not necessary for understanding mathematical concepts, and arguing that children today can always look up their times tables on their mobile phones.
Such a position is called into question by 5 decades of research by cognitive psychologists, which shows that pupils and adults who are able to solve complex mathematical problems, also have strong recall of their times tables and basic arithmetic. This should not come as a surprise - it is far easier to simplify the ratio 21:63 when you instantly recognise that both numbers are divisible by seven.
In 2013, a controlled trial was carried out where 195 first grade pupils in America who were struggling with mathematics were given 16 weeks of specific tutoring where they practiced their number knowledge. The pupils were then tested on areas such as word problems, simple arithmetic and 2-digit calculations. Compared to the control group who received no such tutoring, these pupils had a statistically signification improvement in all 4 areas tested.
Number knowledge tutoring does improve maths ability and the repeated practice of simple arithmetic helps pupils to solve more complex mathematical problems. Yet some educationists still insist that such practices are old-fashioned and unpleasant for pupils, and impoverish the education that our pupils receive. Little better exemplifies the unwitting cruelty of good intentions.
The anti-knowledge - and, I would argue, anti-evidence - position in education debates has, in recent years, been bolstered by the advent of the internet. One well known educationist shot to fame a few years ago with a popular TED talk, extolling the ability of pupils to learn independently from the internet. He asked in his talk: ‘if there’s stuff on Google, why would you need to stuff it into your head?’, and added ‘I decided that groups of children can navigate the internet to achieve educational objectives on their own.’
However, according to research from academics such as Professor Hattie, web-based education has so far been a great disappointment in raising education standards. This is backed up by international evidence from the OECD which shows that increased internet use in schools does not lead to higher academic outcomes. The 5 countries where pupils spend the least time using the internet in school - Poland, Japan, Hong Kong, Shanghai and South Korea - are all amongst the world’s highest achieving jurisdictions in international tests.
Now, I am a great supporter of the intelligent use of computers in schools, but it is mistaken to believe you can outsource your memory to Google and still expect to think well. Say, for example, you are reading an article about nuclear energy, and come across an unfamiliar term: radiation. So you Google it. But the first paragraph on the Wikipedia article mentions another unfamiliar term: particles. So you look it up, but the definition for ‘particles’ uses another unfamiliar term: ‘subatomic’. The definition of which in turn contains the unfamiliar terms ‘electrons’, ‘photons’ and ‘neutrons’, and so on and so forth in an infinite series of google searches which take the reader further and further away from the original term ‘radiation’.
It is no more possible to think fluently on a given topic with the help of the internet, than it is to talk fluently in a foreign language with the help of a bilingual dictionary.
As cognitive psychologists such as Daniel Willingham explain, the interaction between long-term and working memory is foundational to how we learn. Our working memory can only cope with between 5 and 7 new pieces of information at once. All other information must already reside within long-term memory for new information to be assimilated, or else cognitive overload is the result. This is precisely why it is so difficult for a novice to learn new information by browsing articles on the internet.
Many of us here will have a rough understanding of the structure of atoms, and the science behind radiation. We have known about it for so long, that we tend to take for granted. That, and so many other bits of factual knowledge that we draw upon in our daily life, reside in our long term memory because once, in the dim and distant past, a teacher took the time to teach it to us.
From talking to officials and teachers who have visited schools in the Far East, it is clear that countries such as China and Singapore have a pronounced pro-education culture. But I worry that in the West, we can have a tendency to disparage the importance of school. People like to quote great intellects, such as Mark Twain, who stated ‘I’ve never let my school interfere with my education’, or Albert Einstein who purportedly, but probably didn’t, say ‘education is what remains after one has forgotten what one has learned at school’. I could not disagree more strongly: a good education is transformative, and I am sure everyone in this room can think of at least one teacher who changed the direction that their life has taken.
When I defend the merits of an academic curriculum, I am often assailed with the same argument: ‘I learnt all about algebra at school’, or ‘I learnt all about atoms and radiation, and have now forgotten the lot. What use has it been?’ To that argument, I would have 2 answers.
Firstly, when knowledge recedes from instant retrieval in our memory, it still remains logged in our long-term memory.
This is shown by a cognitive principle is known as savings in relearning. Say, for example, that 15 years ago you gain an A grade in GCSE Spanish, but have forgotten it all in the intervening years. Ten years later, you find yourself working in Spain. You will have to learn Spanish again from scratch, but will it be easier second time round? Your intuition may say yes, and it would be correct.
This phenomenon has been confirmed by researchers in Japan. Japanese missionaries, who had spent time doing working in Korea up to 45 years previously, were tested on Korean words. They were then made to learn those that they did not get correct. At the same time, they were made to learn pseudo-words to act as a control. The former missionaries relearnt the Korean words much more quickly, even though the initial test suggested they had been forgotten. This shows that a residue of knowledge remains in the mind even when it can no longer be recalled.
But even if you never relearn content learnt at school, I would maintain that such content was not learnt in vain. Perhaps you are now firmly attached to your English literature degree, and resent all of those hours spent learning about enzymes, ecosystems and eukaryotic cells for your biology GCSE .
But at the age of 14, would you really have been in a position to decide where to specialise? Being exposed to a broad and encompassing academic curriculum at a young age is a great privilege, as it enables you to make an informed decision about which paths you wish to pursue later in life.
On this point, I often consider the novel ‘Of Human Bondage’ by Somerset Maugham. In a story based on Maugham’s own difficult youth, which was full of failures and false starts, the protagonist studies German in Heidelberg, he studies to be a painter in Paris, he works as an accountant and a dressmaker, before finally realising his calling to be a doctor.
In his first anatomy lecture at medical school, the lecturer tells the young students: “You will have to learn many tedious things, which you will forget the moment you have passed your final examination, but in anatomy it is better to have learned and lost than never to have learned at all.”
I think that Maugham was onto something. What is true in anatomy, is true in wider life. The lecturer was, of course, paraphrasing Tennyson’s famous couplet in his poem ‘In Memoriam’, that it is better to have loved and lost than never to have loved at all.
As such phrases demonstrate, great poetry has a remarkable ability to etch itself into the conversation of society. Thomas Gray’s poem ‘Elegy Written in a Country Churchyard’ is, I believe, one of the most moving poems in the English language. Its verses leant the title to both Thomas Hardy’s novel ‘Far From the Madding Crowd’, and Stanley Kubrick’s film ‘Paths of Glory’.
Much like Natalie’s visit to a medieval church in ‘NW’, Thomas Gray’s poem was inspired by an evening looking at a graveyard, which sets his mind wandering. In particular, he regrets the potential that must be squandered when people are brought up in poverty and in ignorance - this was 1751, a long time before universal state education. As he puts it: ‘Knowledge to their eyes her ample page | Rich with the spoils of time did ne’er unroll’. Gray suggests that within the country graveyard, there may be ‘some mute inglorious Milton’, whose lack of a good education forever left his potential untapped: ‘Full many a flow’r is born to blush unseen’.
It is this thought that animates me most as Schools Minister: the generations of school children whose potential was squandered by schools which never taught them the rudiments of literacy and mathematics, which never challenged them to read timeless works of literature, which fobbed them off with so-called vocational courses when they were more than capable of benefiting from a core academic curriculum or high-quality technical and vocational qualifications.
Our education system should be an engine of social mobility, extending opportunity to every young person, ensuring that they reach their potential.
We have already made significant progress in building an education system which delivers on that vision. But we have further to go, and you could help realise that objective. I think the final message I would like to give today, particularly to the undergraduates in this room, is of the joys of being a teacher.
I have always hated that lazy saying, ‘if you can’t do, teach’. My mother was a primary school teacher, and I am a profound believer that teachers have the power to change children’s lives.
The thought that always strikes me when I see an inspiring teacher, communicating the subject that they love with warmth and passion, is what a remarkable and difficult craft effective teaching can be.
Great teachers are masters of their subject, who tell stories, impart wisdom and inspire curiosity. They motivate, cajole and guide pupils to surpass their own expectations of themselves. And evidence suggests that teaching is finally gaining the status it deserves in this country.
In 2010, 61% of trainee teachers had an undergraduate degree at level 2:1 or above. This year, that figure is 74%. Crucially, in 2012 the proportion of trainee teachers with a 2:1 or above surpassed the national average of that year’s graduating cohort for the first time. The annual initial teacher training census shows us that the proportion of new teachers holding a first-class degree is at an all-time high.
To ensure that the calibre of teachers keeps on improving, we have expanded schemes such as Teach First, which this year has sent over 1,500 teachers to work in primary and secondary schools serving low-income communities in every region of England. Teach First is now the single largest graduate recruiter in the UK , a remarkable achievement.
Since 2010, we have put teachers in the driving seat of our reforms to improve state education in England. We have given schools, and teachers, unprecedented freedom to teach as they see fit, without an overbearing education bureaucracy driving their actions.
To this end, we have removed 21,000 pages of unnecessary school guidance, reducing the volume by 75%. In addition, teachers who believe that they are able to create something better within the state education system than the status quo, are now empowered to do so through the free schools programme, which is providing outlets for idealism across the country.
We are working to create a teaching profession which recognises talent and ambition, as well as time-served. We have funded targeted programmes to develop excellent teachers for challenging schools, such as High Potential Senior Leaders, currently delivered by Future Leaders. For bright and ambitious young graduates, a career in teaching now offers rapid advancement opportunities to rival any other profession.
I genuinely believe that there has never been a better time to become a teacher. So if you love your subject, and want to share that love with eager young minds, then there can be few better careers for you than teaching. And if you do not, then at least be thankful of the enormous privilege it is to be the recipient of a good education.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey .

Why is Education Important? The Significance of Education in the Philippines
- February 5, 2024
Education is the cornerstone of society, shaping people and communities. Over time, ideas and skills were passed through various forms of teaching. However, education has evolved, from oral traditions to the creation of modern schools. So why is education important? In this blog, we’ll explore its impact on our society, along with the challenges it faces today .
What is Education?
Education isn’t just about the lessons learned in school — it’s also a dynamic process that covers learning from diverse experiences. From a young age, we are always learning ideas from the world around us, whether it’s through family, peers, media, or other sources.
This informal education, along the formal schooling, shapes our minds, values, and skills. It teaches us to think, be creative, and solve problems, crucial for personal growth and success.
Why Education is Important
Education has a huge impact for a number of reasons. Here are the factors that prove vital for us and our society.
1. Empowering People
Education is like a magic key that unlocks our full potential. Whether we’re a kid or an adult, it gives us the knowledge and skills we need to do well in life. Learning basics like reading and math or diving into complex subjects sets us up for a lifetime of growth.
2. Bridging Economic Gaps
Good education is everyone’s right. It levels the playing field, making it easier for people from diverse backgrounds to succeed. When all have equal access to school, it narrows the gap between the rich and the poor, fostering fairness in society.
3. Driving Innovation and Growth
Investing in this pays off big time because it helps people work well and grow their careers. When people are educated, it boosts a country’s edge in the world market. This leads to more growth, fortune, and success.
4. Fostering Critical Thinking
It isn’t just about learning stuff; it’s also about training our brains to think smart. Teaching us to question, analyze, and figure things out helps us solve tricky problems in our fast-changing world. With today’s constant change, thinking well is crucial.
5. Creating Informed Citizens
Smart citizens make a strong democracy. Education helps people understand the world, know their rights, and make good choices. Teaching people about how society works and their role in it, it makes a country stronger and keeps it going.

Challenges Faced by the Education in the Philippines
Despite its value, the Philippine education system grapples with many hardships. Research showed that around 18.6% of Filipino children were not attending school in 2022 . Here are some problems faced by the system and latent answers to address them.
One of the pressing problems in the country is ensuring fair access to education for all. Though we’re striving to increase school attendance, many children in rural areas still face challenges. Not having enough money and traveling long distances to school make fewer kids attend and more kids drop out.
Access and quality of teaching are vital. In the country, gaps in education quality between urban and rural areas persist. Many schools lack skilled teachers, enough resources, and up-to-date courses, leading to subpar learning outcomes. Improving teaching requires investing in training, upgrading schools, and ensuring that lessons benefit everyone in the country.
Language Barriers
The country has many languages, but Filipino and English are the main languages used in teaching. But many students, particularly those from local communities, face language barriers that hinder their learning. When students don’t learn in their language, it’s harder for them to understand and do well in school. To overcome language problems, we need to have rules that help students who speak different languages.
Technological Divide
In this digital age, access to technology is vital in schools. However, many schools in the Philippines lack facilities and the Internet, limiting students’ access to online resources and learning tools. To narrow the technology gap, we must spend money on gadgets, train teachers to use them, and ensure there are plenty of learning materials for all.
Socioeconomic Challenges
These factors play a major role in shaping educational opportunities in the country. Kids from low-income families often face financial barriers to education, such as the cost of school supplies, transportation, and fees. Some cultures believe boys should go to school more than girls. This makes it tougher for girls to attend school than boys. To handle money and social issues in education, we need to do certain things. These include giving grants, offering meals at school, and helping families that need extra support.
Educational Reforms
Lastly, dealing with changes and rules in education is hard and brings its own problems. Too much paperwork, problems with politics, and people looking out for their own interests can stop good plans from happening. Making sure that the people in charge of teaching do their job well is really crucial. It means making sure money and rules are used right and that students’ needs come first.

Education as a Tool for Development
Despite these problems, education remains a major driving force in our country’s success. Investing into this will pay off in the long run, for it will help people come up with new ideas, making society better. If the country works on improving teaching and dealing with its major issues, it can get even better and help future generations succeed, too.
Thus, it is vital for making people’s lives better and making modern society progress. By learning its impact, we can make a better future for the country and beyond.
Our Advocacy for Education
Why is education important? There is a myriad of reasons which Childhope Philippines firmly believes will help street children have better lives. We promote non-formal education for street children as it teaches them skills outside the regular school. We also want them to receive basic quality education , the same way other kids have access to it. We try to make sure street children can go to school like everyone else. We talk about the issues, ask for fair rules, and advocate programs to help them.
Contact us today to learn more!
Subscribe to our Mailing List
©1989-2024 All Rights Reserved.
Here’s How Ivy League Schools Evaluate Student GPAs
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
One of the main gates on the Brown University campus, decorated with the University crest. (Photo by ... [+] Rick Friedman/Corbis via Getty Images)
A stellar GPA is one of the building blocks of a successful Ivy League application, and as the school year winds down, many students are anxiously seeking to give theirs a final boost. While most students and families understand the importance of a 4.0, few are aware of how top colleges evaluate student GPAs or what they look for when reviewing student transcripts. Though your GPA may seem to be a simple metric, nothing could be further from the case—colleges consider more than just the number, accounting for complexities such as diverse grading systems across schools, trends in grade inflation, and level of course rigor.
Here are three important facts to keep in mind about your GPA as you choose your courses:
1. Your GPA doesn’t directly compare to that of students at other schools.
One common misconception among college applicants is that they can compare their GPAs with those of students attending different schools. However, the GPA is not a universal metric but rather a reflection of an individual's academic performance within their specific educational environment. As a result, comparing GPAs from different schools is like comparing apples and oranges. For instance, some schools offer a plethora of AP, IB, and honors courses, while others may have limited options or offer none at all. Additionally, the weight assigned to AP versus honors versus regular classes varies from school to school. So, your GPA may not hold the same weight as those of your peers at different schools, even if you all have 4.0s.
Admissions officers understand that schools vary in their rigor, curriculum, and grading policies. Therefore, they evaluate your GPA in the context of your high school, considering the courses offered and the academic challenges presented. Instead of fixating on how your GPA compares to your friends’ from other schools, focus on challenging yourself and taking advantage of all the opportunities available to you at your school.
2. GPAs across the country are inflated—and colleges know it.
The last few years have seen surges in high school student GPAs nationwide. While GPA inflation has been on the rise over the last decade, average ACT composite scores are steadily declining. “For the 1.4 million ACT test-takers in the high school class of 2023, the average composite score on the exam was 19.5 out of 36, the lowest score since 1991,” according to The New York Times . The parallel differences, coupled with academic differences across schools, suggest that GPA must be considered in tandem with multiple other factors. Simply put, an A no longer means what it used to on a transcript.
It s Possible The Russian Army Is Tricking The Ukrainian Army With A Fake Offensive
Writer explains johnny depp and amber heard joke in ‘the fall guy’, northern lights could be visible again tonight here s updated advice on how to watch.
Ivy League and other top colleges are well aware of this trend and evaluate student GPAs alongside other metrics such as standardized test scores and AP exam scores in order to better understand a student’s academic skill sets. While some Ivy League and other top schools remain test-optional , they still place emphasis on course rigor and the context offered by your high school profile in order to understand the grades on your transcript.
3. Colleges will recalculate your GPA.
Given the abundance of variables in GPA calculations, colleges often recalculate the metric to create a standardized baseline for comparison between students across different schools. The recalibration may involve adjusting for variations in grading scales or the weighting of honors, International Baccalaureate (IB) or Advanced Placement (AP) courses. The University of California system, for example, calculates students’ UC GPAs by converting grades to grade points (an A is equivalent to 4 points, a B to three points, etc.) for classes taken between summer after 9th and summer after 11th grade, and adding one point for each honors class, and dividing by total classes taken to yield final GPA.*
Other colleges also take additional factors that impact academic performance into consideration, and envelop GPA into a broader, holistic consideration. For instance, the Harvard University lawsuit over affirmative action revealed that Harvard rates students on a scale of 1–6 (with one being the most desirable) in academic, extracurricular, athletic and personal categories. A student’s GPA and test scores are folded together into an academic score which “summarizes the applicant’s academic achievement and potential based on grades, testing results, letters of recommendation, academic prizes, and any submitted academic work.”
This process aims to provide a fair and equitable evaluation of students from different educational backgrounds. Keep in mind that Harvard considers not only your grades, test scores, and academic rigor in this score, but also “evidence of substantial scholarship” and “academic creativity,” which can make the difference between a 1 and a 2 in the scoring system. These systems underscore the importance of taking advantage of every opportunity, showcasing your unique personality and creativity, and seeking to maximize opportunities to improve your performance within the academic landscape of your institution.
By understanding the complex way by which colleges evaluate students’ GPAs, you are better equipped to present a comprehensive and competitive picture of your academic achievements on your transcript and stand out in the competitive Ivy League admissions landscape.
*Variations exist for in-state versus out-of-state students and by high school. Be sure to calculate your GPA following the UC issued guidelines.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
How to Become a Financial Advisor
Becoming a financial advisor can lead to a lucrative career, but the real reward is helping clients achieve their dreams.

Getty Images
As a financial planner, you might work in a bank or brokerage firm or settle into a niche in a smaller firm or as an independent consultant.
"Financial advisor" is more than just a title. It means you've committed to guiding people through their financial journey. You can help others with their money and future goals, guiding them to make smart choices about saving, investing and planning for what's ahead. Depending on factors like experience, location and the type of firm, financial advisor salaries can range from $61,960 to $165,590.
Advisor's Corner

Advisor's Corner is a collection of columns written by certified financial planners, financial advisors and experts for everyday investors like you.
As a financial planner myself, I can tell you that beyond the numbers, the real reward is seeing your clients achieve their dreams. If you're thinking about becoming a financial planner or are already set on it as a career choice, I'll walk you through how to make it happen:
- What is a financial advisor?
- What does a financial advisor do?
- Financial advisor qualifications.
- Important skills for financial advisors.
- How long does becoming a financial advisor take?
- Is being a financial advisor right for you?
What Is a Financial Advisor?
A financial advisor is a trained professional who helps people with their finances. They offer guidance and expertise on the intricacies of managing money, from retirement and estate planning to real estate and investment opportunities.
As a financial planner, you might work in a bank or brokerage firm or settle into a niche in a smaller firm or as an independent consultant. You could also choose to specialize in a specific financial area or work with people who fall within a certain net worth or age bracket.
What Does a Financial Advisor Do?
The role of a financial advisor is as varied as the clients they serve. As Adam Breazeale, a senior financial planner at Schwab Wealth Advisory, puts it, "We look at where our clients are relative to where they want to be, then provide the tools and solutions necessary to create a road map for success."
As a financial advisor, you'll help with financial planning by creating long-term strategies to build wealth and manage risk. We analyze our clients' current financial situation and seek to understand their goals and objectives. "If you understand the psychology of money, and how emotions and childhood experiences impact financial decisions, this will let you better serve and understand your future clients," says Jude Wilson, founder of Centrus Financial Strategies.
Then you develop a tailored plan to help them achieve those goals. You might offer advice on investment options, manage their investment portfolios , recommend insurance needs, map out a tax strategy, or provide any other type of financial planning or advice.
Financial Advisor Qualifications
I can attest that there's no "one right path" to becoming a financial advisor. For instance, my professional journey began at a Japanese investment bank. However, I wasn't able to connect on a deeper level with clients to truly help with their personal financial well-being. I took my career in a new direction and became a certified financial planner, or CFP.
Financial advisor careers are open to almost anyone, which is one of my favorite aspects of the profession. The financial industry is strictly regulated, but the requirements you'll need to meet can depend on the type of service you want to provide.
Many financial planners come from backgrounds in finance, economics or business. I suggest taking courses in investments, taxes, estate planning and risk management to help you get a solid grasp on financial principles, investment strategies and economic trends.
While you don't need a bachelor's degree to become a financial advisor, a career in finance is difficult to start without one. Keep in mind that educational guidelines can depend on your career aspirations, too. For instance, I wanted to become a CFP, which requires CFP Board-approved coursework and a bachelor's degree.
Professional Licenses
Professional licenses are required for some financial advisors. If you want to sell investment products or operate in multiple states, a common occurrence at broker-dealers and banks, you'll need to pass exams administered by the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, or FINRA. The Securities Industry Essentials (SIE) Exam is a common requirement for many in the financial services industry. You may need to pass additional exams as well, depending on your situation:
- Series 6: The Investment Company and Variable Contracts Products Representative Qualification Examination (IR), required to sell mutual funds, variable annuities or other limited investment products.
- Series 7: The General Securities Representative Qualification Examination (GS), required to sell common and preferred stocks and other fixed-income investments as a stockbroker.
- Series 3 or 31: The National Commodities Futures Exam or the Futures Managed Funds Exam, required to sell commodity or managed futures contracts.
- Series 63: The Uniform Securities Agent State Law Exam, required to satisfy state law registration requirements.
- Series 65: The Uniform Investment Adviser Law Exam, required to provide fee-based investment advisory services.
- Series 66: The Uniform Combined State Law Exam, which merges the Series 63 and 65 exams.
If you establish a practice as an individual, you may also need to register your firm as a registered investment advisor, or RIA, with the Securities and Exchange Commission and register yourself as its representative.
Certifications
These professional certifications can enhance your credibility and are encouraged by financial advisory firms, but they're not mandatory for becoming a financial advisor. Many certifications and designations are available, and deciphering them can feel like navigating a complex maze of acronyms.
The CFP certification is a well-known badge of expertise in the industry. Earning it demands several years in financial planning, a formal degree, clearing the CFP exam and adhering to high ethical standards. You must also act as a fiduciary , which means prioritizing your clients' needs over your own.
In addition to the CFP, other notable financial planner certifications include:
- Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA): A globally recognized certification for investment professionals, especially in the areas of investment management and research.
- Chartered Financial Consultant (ChFC): A certification focused on advanced areas of financial planning, such as retirement, real estate, insurance and income tax planning.
- Certified Investment Management Analyst (CIMA): Focuses on asset management and investment consulting.
- Certified Private Wealth Advisor (CPWA): Designed for professionals who work with high-net-worth clients on wealth management.
- Certified Fund Specialist (CFS): Specializes in mutual funds and the mutual fund industry.
- Personal Financial Specialist (PFS): Offered to certified public accountants, or CPAs, who want to specialize in personal financial planning.
Professional Experience
Starting with internships or entry-level roles is more than just a resume builder; it offers valuable experience in the financial industry. You learn more than the mechanics as you navigate client interactions, strategy crafting and problem solving. The hands-on learning prepares you for future hurdles and deepens your understanding of the industry.
Mentorship, too, is invaluable in this journey. A seasoned mentor not only shares wisdom and strategies but also offers insights based on personal experiences that textbooks can't capture.
Wilson's experience underscores the importance of this. Being among the less than 2% of Black financial planners in the U.S., he faced unique challenges and perspectives. "I recommend to anyone, especially those in the minority, to find a mentor or to intern with a professional," says Wilson.
You may eventually arrive at the crossroads that many financial advisors face: joining an established firm or forging your own path. Both have merits. While existing firms offer stability, going solo can be rewarding for the entrepreneurial at heart.
Important Skills for Financial Advisors
Technical knowledge is undoubtedly essential, yet it's our ability to build trust, understand our clients' needs and effectively communicate that can make all the difference for success. One crucial aspect of being a financial planner is the ability to break down complex financial jargon and explain it to clients in a way they understand.
In my experience, financial advisors should ideally have:
- An ability to build and maintain strong client relationships.
- A keen ear to actively listen to a client's financial worries and goals.
- The acumen to analyze investment opportunities and gauge market trends .
- Creativity to find solutions that fit individual client needs.
- Time management skills to balance client consultations, planning and market research.
- A solid moral compass to uphold the highest standards of integrity and trust.
Financial planning does not use a one-size-fits-all approach, and every client will have different challenges and goals. A versatile skill set can empower you to address these needs effectively.
How Long Does Becoming a Financial Advisor Take?
Your path to becoming a financial advisor depends on where you start your journey. It can vary from a few months to a few years. One of the quickest routes is to get your series licenses with FINRA, which require no prior job experience.
Hazel Secco, a certified financial planner and president and founder of Align Financial Solutions, reflects on her initial journey. "I began with four different licenses: Series 6, 63, 65 and an insurance license. This process took approximately three months before I officially commenced my role as a financial advisor," says Secco.
She didn't stop there. "I decided to pursue the CFP designation right from the beginning of my career. It took me three years to accumulate all the necessary experience and complete the required courses," says Secco.
You must also factor in the time it takes to complete an internship or gather experience.
Michelle Bender, a certified financial planner at Potomac Financial Consultants, says she'd "struggle to bring in" for an interview an applicant who lacked experience and had not taken the appropriate courses.
Is Being a Financial Advisor Right for You?
Becoming a financial advisor can be a fulfilling and rewarding career choice, but it's important to consider whether it's the right fit for you . Think about your strengths and interests and evaluate the educational and regulatory requirements. But above all, consider where your heart lies.
Being a financial advisor requires technical knowledge, but it's more than crunching numbers. It's about nurturing a passion for finance, combined with a genuine desire to help others achieve their financial goals.
10 Best Financial Certifications
Julie Pinkerton Sept. 19, 2023

U.S. News wants to hear from you!
Send us your topic ideas for the next Advisor's Corner.
U.S. News makes no representations or warranties in connection with the information provided herein, nor to the accuracy or applicability thereof. U.S. News does not give, offer, or render tax, credit, or legal advice. Before making financial or investment decisions, U.S. News recommends that you contact an investment advisor, or tax or legal professional.
Tags: financial advisors , financial literacy , financial goals , investing , money , retirement , financial regulation , careers , second careers , Advisor's Corner
The Most Important Ages for Retirement Planning

Comparative assessments and other editorial opinions are those of U.S. News and have not been previously reviewed, approved or endorsed by any other entities, such as banks, credit card issuers or travel companies. The content on this page is accurate as of the posting date; however, some of our partner offers may have expired.
You May Also Like
Biggest tech companies in the world.
Wayne Duggan May 10, 2024

7 Best Car Stocks to Invest in Now
Jeff Reeves May 10, 2024

5 Best Mutual Funds to Buy
Coryanne Hicks May 10, 2024

Fidelity Mutual Funds to Buy and Hold
Tony Dong May 10, 2024

Should You Buy Solana? 3 Pros, 3 Cons
Wayne Duggan May 9, 2024

7 Best Marijuana ETFs
Matt Whittaker May 9, 2024

10 Best-Performing ETFs of 2024
Jeff Reeves May 9, 2024

5 Best Gold Stocks to Buy Now
Glenn Fydenkevez May 9, 2024

9 Best Cheap Stocks to Buy Under $5
Ian Bezek May 9, 2024

Dividend Stocks to Buy and Hold
Wayne Duggan May 8, 2024

6 of the Best AI ETFs to Buy Now
Tony Dong May 8, 2024

Will the Stock Market Crash in 2024?
Brian O'Connell May 8, 2024

10 Best Artificial Intelligence Stocks
Wayne Duggan May 7, 2024

7 Best ETFs to Buy Now
Jeff Reeves May 7, 2024

9 of the Best Bond ETFs to Buy Now
Tony Dong May 7, 2024

7 Best Large-Cap ETFs to Buy in 2024
Marc Guberti May 7, 2024

7 Best Vanguard Funds to Buy and Hold
Tony Dong May 6, 2024

7 Best Monthly Dividend Stocks to Buy
Glenn Fydenkevez May 6, 2024

Best Marijuana Stocks for 2024
Matt Whittaker May 3, 2024

6 Funds to Add to Your HSA
Tony Dong May 3, 2024

- Ag and Extension
- Minnesota News
- National News
- International News
- News of Record
- Public Notices
- Local Sports
- Sports Columns
- Minnesota Sports
- National Sports
- Community Voices
- Letters to the Editor
- Engagements, Weddings, Anniversaries
- Classifieds
- Garage Sales
- Submit News
- Pick Up A Copy
- Statement of Values
- Terms of Service
- Browse Notices
- Place Notice

- Today's Paper
Subscribe Today
Laura fennell named friend of education at mps.

Laura Fennell was recently named this year’s Friend of Education by the Marshall Education Association. Fennell works in the Student Services office at Marshall Middle School.
MARSHALL — Over the past couple of years, Laura Fennell has become a familiar person for many students at Marshall Middle School. She can usually be found in the MMS Student Services office, and Fennell said it’s an important place to be to help support the students.
“It’s good to have a friendly face,” she said.
This spring, members of the Marshall Education Association recognized Fennell with the Friend of Education award. The annual recognition is given to a person from the Marshall area, community or schools who goes above and beyond in giving their time, resources or talents.
The MEA received a record number of nominations for Friend of Education this year, with a total of nine nominees, said MEA president Stef Scarset.
Fennell said the recognition came as a surprise for her.
“I was definitely shocked, especially as it’s just my second year being here,” she said.
Fennell and her family have lived in Marshall since 2008. Fennell managed Shopko Optical in Marshall, before coming to MMS. With three children in school, the work hours and schedule of the Student Services position were a great fit for her, she said.
Working in Student Services means helping out with a variety of issues affecting students, Fennell said.
“It’s an array of things,” she said, from class schedules to attendance. She’s also there for students who are just having a hard day.
“If kids need breaks, they can come in and sit down,” she said. “We have ones who will pop in and just say hi.”
In nominations, MEA members said Fennell stood out for both her work ethic and for being a supportive person for MMS students and staff.
“She consistently exceeds expectations, taking on multiple personalities with a cheerful and encouraging attitude,” MEA members said.
Fennell said there have been a lot of positive things about her job at MMS, from the staff to the students, and the variety of the work.
“I feel like every day is different,” she said. “It keeps you on your toes.”
She’s also enjoyed getting to know the students at MMS over the past two years. “I’m going to miss all the eighth graders that will be moving on,” Fennell said.
Being able to be a positive presence in the office is something that Fennell said is important to her.
“You never know what someone is going through, whether it’s a teacher or a student,” she said. “Having that friendly face there is what’s important, so people feel like they can come to you.”
Today's breaking news and more in your inbox
- Daily Newsletter
- Breaking News

Hwy. 68 construction delayed to May 20
MARSHALL — The start of a planned construction project on Minnesota Highway 68 has been pushed back a week, the ...

Downtown parking lot construction makes progress
Anderson to file for re-election on lyon co. board.
MARSHALL — There will be a total of three Lyon County commissioners running for re-election this year. ...

Growth of craft beer, wine industries chugging along

Interest ‘picking up’ for fishing opener
Starting at $4.38/week..

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
We just need to be clear on terms. There are a few terms that are often confused or used interchangeably—"learning," "education," "training," and "school"—but there are important differences between them. Learning is the process of acquiring new skills and understanding. Education is an organized system of learning.
6. A Safer World. Education is something that's not only needed on a personal level, but also on a global level, as it's something that keeps our world safe and makes it a more peaceful place. Education tends to teach people the difference between right and wrong, and can help people stay out of risky situations. 7.
The link between education to health and well-being is clear. Education develops the skills, values and attitudes that enable learners to lead healthy and fulfilled lives, make informed decisions, and engage in positive relationships with everyone around them. Poor health can have a detrimental effect on school attendance and academic performance.
Transforming education requires a significant increase in investment in quality education, a strong foundation in comprehensive early childhood development and education, and must be underpinned by strong political commitment, sound planning, and a robust evidence base. Learning and skills for life, work and sustainable development.
ity education for all and promote lifelong learning. Why does education matter? Education enables upward socioeconomic mobility and is a key to escaping poverty. Education helps reduce
Other important measures cited by the General Assembly President include strong curricula that fully integrate Information and Communications Technology (ICT); ensuring that girls complete at least 12 years of education (which, according to the World Bank, would add some $30 trillion to the global economy); and the effective monitoring and evaluation of learning.
Many are responding to this shift with innovations that aim to address the persistent challenges faced by girls and women in education. By highlighting these key practices through the Prize, we can contribute to inspiring more action for girls and women. We speak about the importance of gender-transformative change both in and beyond education.
Education helps a person hone their communication skills by learning how to read, write, speak and listen. Education develops critical thinking. This is vital in teaching a person how to use logic when making decisions and interacting with people (e.g., boosting creativity, enhancing time management).
Having a degree opens doors. The process of learning and becoming educated creates a person who is well-rounded, can think critically, be prepared to make hard decisions, read, write, do arithmetic, learn societal norms, express your emotions and more. These create quality and are critically important to society.
Why a good education benefits us all — even if you're long past being a student. Timothy Bartik says that investing in early childhood education is not just good for the children involved — but for communities as a whole. In today's talk, he offers a detailed look at how preschool education boosts local economies in colossal ways ...
Nelson Mandela famously said, "Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.". An educated society is better equipped to tackle the challenges that face modern America, including: Climate change. Social justice. Economic inequality.
Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world. — Nelson Mandela, 1918-2013, South African President, philanthropist. The object of education is to teach us to love ...
Education is a human right, a powerful driver of development, and one of the strongest instruments for reducing poverty and improving health, gender equality, peace, and stability. It delivers large, consistent returns in terms of income, and is the most important factor to ensure equity and inclusion. For individuals, education promotes ...
The importance of education in life. We'll start off by exploring some of the reasons why education is important for individual lives. This will include the ways that education is good for the physical, psychological and social wellbeing of human individuals. Creates stability during childhood.
Taking proper care of one's body and discovering the drivers of one's general well-being are essential skills to succeed at life. Schools might help students find a good balance between effort, exercise and relaxation, and to define their personal priorities in life. This is not a debate for politicians and civil servants alone.
A good education is important to achieving the American Dream. For much of the 20 th century, a cornerstone of the American Dream has been the belief that, with hard work, all adults should be ...
Education in emergencies: Children living through conflict, natural disaster and displacement are in urgent need of educational support. Crises not only halt children's learning but also roll back their gains. In many emergencies, UNICEF is the largest provider of educational support throughout humanitarian response, working with UNHCR, WFP ...
Education is a right for everyone. It is a right for girls, just as it is for boys. It is a right for disabled children, just as it is for everyone else. It is a right for the 37 million out-of-school children and youth in countries affected by crises and conflicts. Education is a right regardless of where you are born and where you grow up.
Quality education reduces poverty. If all children in low-income countries left school able to read, global poverty would fall by 12 %. 1 If all adults completed secondary education, 420 million people could be lifted out of poverty, reducing the total number of poor people by more than half worldwide. 2 An extra year of school can increase men's income by at least 10 %, women's income by at ...
7. Promoting Equality And Empowerment. One of the most important benefits of education is probably the promotion of equality and empowerment within society. Higher education can make people more open-minded in accepting others' ideas and opinions regardless of race, gender, age, etc. In addition, education empowers people through expert ...
Education liberates the intellect, unlocks the imagination and is fundamental for self-respect. It is the key to prosperity and opens a world of opportunities, making it possible for each of us to contribute to a progressive, healthy society. Learning benefits every human being and should be available to all. Resources.
The right to education is a human right and indispensable for the exercise of other human rights. Quality education aims to ensure the development of a fully-rounded human being. It is one of the most powerful tools in lifting socially excluded children and adults out of poverty and into society. UNESCO data shows that if all adults completed ...
"Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world," as Nelson Mandela said. It helps people become better citizens, get a better-paid job, shows the difference between good and bad. Education shows us the importance of hard work and, at the same time, helps us grow and develop.
The right to education. Every human being has the right to quality education and lifelong learning opportunities. Education is a basic human right that works to raise men and women out of poverty, level inequalities and ensure sustainable development. But worldwide 244 million children and youth are still out of school for social, economic and ...
Educators' values and beliefs. A distinction between teacher training and teacher education is that teacher training is the acquisition of competencies pre-determined by others - knowing what a teacher does, and how to do it - whereas teacher education is about understanding why teacher do what they do: the rationale. As Craft (Citation 1984) observed, this distinction resonates with the ...
In his talk, he accuses the traditional, academic curriculum of being a relic of the 19th century, a 'factory model' of schooling, which squanders pupil creativity. As his enormous popularity ...
1. Empowering People. Education is like a magic key that unlocks our full potential. Whether we're a kid or an adult, it gives us the knowledge and skills we need to do well in life. Learning basics like reading and math or diving into complex subjects sets us up for a lifetime of growth. 2.
Here are three important facts to keep in mind about your GPA as you choose your courses: 1. Your GPA doesn't directly compare to that of students at other schools. One common misconception ...
Wilson's experience underscores the importance of this. Being among the less than 2% of Black financial planners in the U.S., he faced unique challenges and perspectives. "I recommend to anyone ...
Staff Writer. [email protected]. Laura Fennell was recently named this year's Friend of Education by the Marshall Education Association. Fennell works in the Student Services office ...