Data collection in research: Your complete guide
Last updated
31 January 2023
Reviewed by
Cathy Heath
In the late 16th century, Francis Bacon coined the phrase "knowledge is power," which implies that knowledge is a powerful force, like physical strength. In the 21st century, knowledge in the form of data is unquestionably powerful.
But data isn't something you just have - you need to collect it. This means utilizing a data collection process and turning the collected data into knowledge that you can leverage into a successful strategy for your business or organization.
Believe it or not, there's more to data collection than just conducting a Google search. In this complete guide, we shine a spotlight on data collection, outlining what it is, types of data collection methods, common challenges in data collection, data collection techniques, and the steps involved in data collection.

Analyze all your data in one place
Uncover hidden nuggets in all types of qualitative data when you analyze it in Dovetail
- What is data collection?
There are two specific data collection techniques: primary and secondary data collection. Primary data collection is the process of gathering data directly from sources. It's often considered the most reliable data collection method, as researchers can collect information directly from respondents.
Secondary data collection is data that has already been collected by someone else and is readily available. This data is usually less expensive and quicker to obtain than primary data.
- What are the different methods of data collection?
There are several data collection methods, which can be either manual or automated. Manual data collection involves collecting data manually, typically with pen and paper, while computerized data collection involves using software to collect data from online sources, such as social media, website data, transaction data, etc.
Here are the five most popular methods of data collection:
Surveys are a very popular method of data collection that organizations can use to gather information from many people. Researchers can conduct multi-mode surveys that reach respondents in different ways, including in person, by mail, over the phone, or online.
As a method of data collection, surveys have several advantages. For instance, they are relatively quick and easy to administer, you can be flexible in what you ask, and they can be tailored to collect data on various topics or from certain demographics.
However, surveys also have several disadvantages. For instance, they can be expensive to administer, and the results may not represent the population as a whole. Additionally, survey data can be challenging to interpret. It may also be subject to bias if the questions are not well-designed or if the sample of people surveyed is not representative of the population of interest.
Interviews are a common method of collecting data in social science research. You can conduct interviews in person, over the phone, or even via email or online chat.
Interviews are a great way to collect qualitative and quantitative data . Qualitative interviews are likely your best option if you need to collect detailed information about your subjects' experiences or opinions. If you need to collect more generalized data about your subjects' demographics or attitudes, then quantitative interviews may be a better option.
Interviews are relatively quick and very flexible, allowing you to ask follow-up questions and explore topics in more depth. The downside is that interviews can be time-consuming and expensive due to the amount of information to be analyzed. They are also prone to bias, as both the interviewer and the respondent may have certain expectations or preconceptions that may influence the data.
Direct observation
Observation is a direct way of collecting data. It can be structured (with a specific protocol to follow) or unstructured (simply observing without a particular plan).
Organizations and businesses use observation as a data collection method to gather information about their target market, customers, or competition. Businesses can learn about consumer behavior, preferences, and trends by observing people using their products or service.
There are two types of observation: participatory and non-participatory. In participatory observation, the researcher is actively involved in the observed activities. This type of observation is used in ethnographic research , where the researcher wants to understand a group's culture and social norms. Non-participatory observation is when researchers observe from a distance and do not interact with the people or environment they are studying.
There are several advantages to using observation as a data collection method. It can provide insights that may not be apparent through other methods, such as surveys or interviews. Researchers can also observe behavior in a natural setting, which can provide a more accurate picture of what people do and how and why they behave in a certain context.
There are some disadvantages to using observation as a method of data collection. It can be time-consuming, intrusive, and expensive to observe people for extended periods. Observations can also be tainted if the researcher is not careful to avoid personal biases or preconceptions.
Automated data collection
Business applications and websites are increasingly collecting data electronically to improve the user experience or for marketing purposes.
There are a few different ways that organizations can collect data automatically. One way is through cookies, which are small pieces of data stored on a user's computer. They track a user's browsing history and activity on a site, measuring levels of engagement with a business’s products or services, for example.
Another way organizations can collect data automatically is through web beacons. Web beacons are small images embedded on a web page to track a user's activity.
Finally, organizations can also collect data through mobile apps, which can track user location, device information, and app usage. This data can be used to improve the user experience and for marketing purposes.
Automated data collection is a valuable tool for businesses, helping improve the user experience or target marketing efforts. Businesses should aim to be transparent about how they collect and use this data.
Sourcing data through information service providers
Organizations need to be able to collect data from a variety of sources, including social media, weblogs, and sensors. The process to do this and then use the data for action needs to be efficient, targeted, and meaningful.
In the era of big data, organizations are increasingly turning to information service providers (ISPs) and other external data sources to help them collect data to make crucial decisions.
Information service providers help organizations collect data by offering personalized services that suit the specific needs of the organizations. These services can include data collection, analysis, management, and reporting. By partnering with an ISP, organizations can gain access to the newest technology and tools to help them to gather and manage data more effectively.
There are also several tools and techniques that organizations can use to collect data from external sources, such as web scraping, which collects data from websites, and data mining, which involves using algorithms to extract data from large data sets.
Organizations can also use APIs (application programming interface) to collect data from external sources. APIs allow organizations to access data stored in another system and share and integrate it into their own systems.
Finally, organizations can also use manual methods to collect data from external sources. This can involve contacting companies or individuals directly to request data, by using the right tools and methods to get the insights they need.
- What are common challenges in data collection?
There are many challenges that researchers face when collecting data. Here are five common examples:
Big data environments
Data collection can be a challenge in big data environments for several reasons. It can be located in different places, such as archives, libraries, or online. The sheer volume of data can also make it difficult to identify the most relevant data sets.
Second, the complexity of data sets can make it challenging to extract the desired information. Third, the distributed nature of big data environments can make it difficult to collect data promptly and efficiently.
Therefore it is important to have a well-designed data collection strategy to consider the specific needs of the organization and what data sets are the most relevant. Alongside this, consideration should be made regarding the tools and resources available to support data collection and protect it from unintended use.
Data bias is a common challenge in data collection. It occurs when data is collected from a sample that is not representative of the population of interest.
There are different types of data bias, but some common ones include selection bias, self-selection bias, and response bias. Selection bias can occur when the collected data does not represent the population being studied. For example, if a study only includes data from people who volunteer to participate, that data may not represent the general population.
Self-selection bias can also occur when people self-select into a study, such as by taking part only if they think they will benefit from it. Response bias happens when people respond in a way that is not honest or accurate, such as by only answering questions that make them look good.
These types of data bias present a challenge because they can lead to inaccurate results and conclusions about behaviors, perceptions, and trends. Data bias can be avoided by identifying potential sources or themes of bias and setting guidelines for eliminating them.
Lack of quality assurance processes
One of the biggest challenges in data collection is the lack of quality assurance processes. This can lead to several problems, including incorrect data, missing data, and inconsistencies between data sets.
Quality assurance is important because there are many data sources, and each source may have different levels of quality or corruption. There are also different ways of collecting data, and data quality may vary depending on the method used.
There are several ways to improve quality assurance in data collection. These include developing clear and consistent goals and guidelines for data collection, implementing quality control measures, using standardized procedures, and employing data validation techniques. By taking these steps, you can ensure that your data is of adequate quality to inform decision-making.
Limited access to data
Another challenge in data collection is limited access to data. This can be due to several reasons, including privacy concerns, the sensitive nature of the data, security concerns, or simply the fact that data is not readily available.
Legal and compliance regulations
Most countries have regulations governing how data can be collected, used, and stored. In some cases, data collected in one country may not be used in another. This means gaining a global perspective can be a challenge.
For example, if a company is required to comply with the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), it may not be able to collect data from individuals in the EU without their explicit consent. This can make it difficult to collect data from a target audience.
Legal and compliance regulations can be complex, and it's important to ensure that all data collected is done so in a way that complies with the relevant regulations.
- What are the key steps in the data collection process?
There are five steps involved in the data collection process. They are:
1. Decide what data you want to gather
Have a clear understanding of the questions you are asking, and then consider where the answers might lie and how you might obtain them. This saves time and resources by avoiding the collection of irrelevant data, and helps maintain the quality of your datasets.
2. Establish a deadline for data collection
Establishing a deadline for data collection helps you avoid collecting too much data, which can be costly and time-consuming to analyze. It also allows you to plan for data analysis and prompt interpretation. Finally, it helps you meet your research goals and objectives and allows you to move forward.
3. Select a data collection approach
The data collection approach you choose will depend on different factors, including the type of data you need, available resources, and the project timeline. For instance, if you need qualitative data, you might choose a focus group or interview methodology. If you need quantitative data , then a survey or observational study may be the most appropriate form of collection.
4. Gather information
When collecting data for your business, identify your business goals first. Once you know what you want to achieve, you can start collecting data to reach those goals. The most important thing is to ensure that the data you collect is reliable and valid. Otherwise, any decisions you make using the data could result in a negative outcome for your business.
5. Examine the information and apply your findings
As a researcher, it's important to examine the data you're collecting and analyzing before you apply your findings. This is because data can be misleading, leading to inaccurate conclusions. Ask yourself whether it is what you are expecting? Is it similar to other datasets you have looked at?
There are many scientific ways to examine data, but some common methods include:
looking at the distribution of data points
examining the relationships between variables
looking for outliers
By taking the time to examine your data and noticing any patterns, strange or otherwise, you can avoid making mistakes that could invalidate your research.
- How qualitative analysis software streamlines the data collection process
Knowledge derived from data does indeed carry power. However, if you don't convert the knowledge into action, it will remain a resource of unexploited energy and wasted potential.
Luckily, data collection tools enable organizations to streamline their data collection and analysis processes and leverage the derived knowledge to grow their businesses. For instance, qualitative analysis software can be highly advantageous in data collection by streamlining the process, making it more efficient and less time-consuming.
Secondly, qualitative analysis software provides a structure for data collection and analysis, ensuring that data is of high quality. It can also help to uncover patterns and relationships that would otherwise be difficult to discern. Moreover, you can use it to replace more expensive data collection methods, such as focus groups or surveys.
Overall, qualitative analysis software can be valuable for any researcher looking to collect and analyze data. By increasing efficiency, improving data quality, and providing greater insights, qualitative software can help to make the research process much more efficient and effective.
Learn more about qualitative research data analysis software
Get started today.
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 December 2023
Last updated: 16 December 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 18 May 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free

Chapter 10. Introduction to Data Collection Techniques
Introduction.
Now that we have discussed various aspects of qualitative research, we can begin to collect data. This chapter serves as a bridge between the first half and second half of this textbook (and perhaps your course) by introducing techniques of data collection. You’ve already been introduced to some of this because qualitative research is often characterized by the form of data collection; for example, an ethnographic study is one that employs primarily observational data collection for the purpose of documenting and presenting a particular culture or ethnos. Thus, some of this chapter will operate as a review of material already covered, but we will be approaching it from the data-collection side rather than the tradition-of-inquiry side we explored in chapters 2 and 4.
Revisiting Approaches
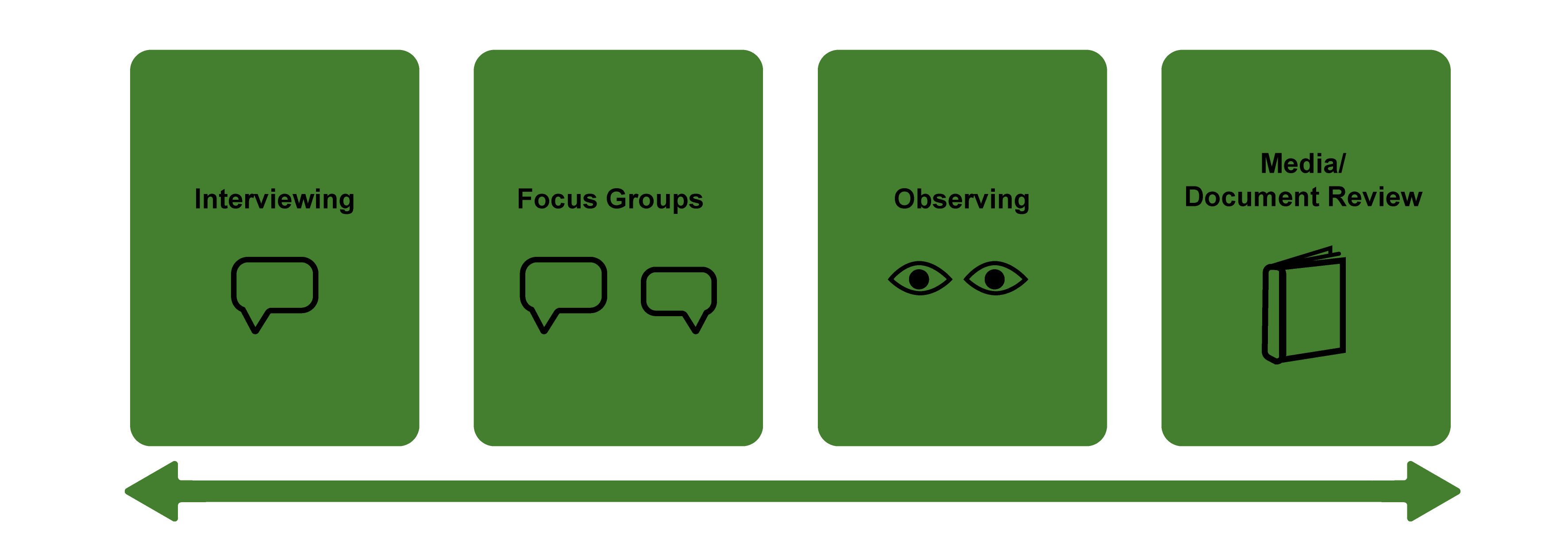
There are four primary techniques of data collection used in qualitative research: interviews, focus groups, observations, and document review. [1] There are other available techniques, such as visual analysis (e.g., photo elicitation) and biography (e.g., autoethnography) that are sometimes used independently or supplementarily to one of the main forms. Not to confuse you unduly, but these various data collection techniques are employed differently by different qualitative research traditions so that sometimes the technique and the tradition become inextricably entwined. This is largely the case with observations and ethnography. The ethnographic tradition is fundamentally based on observational techniques. At the same time, traditions other than ethnography also employ observational techniques, so it is worthwhile thinking of “tradition” and “technique” separately (see figure 10.1).
Figure 10.1. Data Collection Techniques
Each of these data collection techniques will be the subject of its own chapter in the second half of this textbook. This chapter serves as an orienting overview and as the bridge between the conceptual/design portion of qualitative research and the actual practice of conducting qualitative research.
Overview of the Four Primary Approaches
Interviews are at the heart of qualitative research. Returning to epistemological foundations, it is during the interview that the researcher truly opens herself to hearing what others have to say, encouraging her interview subjects to reflect deeply on the meanings and values they hold. Interviews are used in almost every qualitative tradition but are particularly salient in phenomenological studies, studies seeking to understand the meaning of people’s lived experiences.
Focus groups can be seen as a type of interview, one in which a group of persons (ideally between five and twelve) is asked a series of questions focused on a particular topic or subject. They are sometimes used as the primary form of data collection, especially outside academic research. For example, businesses often employ focus groups to determine if a particular product is likely to sell. Among qualitative researchers, it is often used in conjunction with any other primary data collection technique as a form of “triangulation,” or a way of increasing the reliability of the study by getting at the object of study from multiple directions. [2] Some traditions, such as feminist approaches, also see the focus group as an important “consciousness-raising” tool.
If interviews are at the heart of qualitative research, observations are its lifeblood. Researchers who are more interested in the practices and behaviors of people than what they think or who are trying to understand the parameters of an organizational culture rely on observations as their primary form of data collection. The notes they make “in the field” (either during observations or afterward) form the “data” that will be analyzed. Ethnographers, those seeking to describe a particular ethnos, or culture, believe that observations are more reliable guides to that culture than what people have to say about it. Observations are thus the primary form of data collection for ethnographers, albeit often supplemented with in-depth interviews.
Some would say that these three—interviews, focus groups, and observations—are really the foundational techniques of data collection. They are far and away the three techniques most frequently used separately, in conjunction with one another, and even sometimes in mixed methods qualitative/quantitative studies. Document review, either as a form of content analysis or separately, however, is an important addition to the qualitative researcher’s toolkit and should not be overlooked (figure 10.1). Although it is rare for a qualitative researcher to make document review their primary or sole form of data collection, including documents in the research design can help expand the reach and the reliability of a study. Document review can take many forms, from historical and archival research, in which the researcher pieces together a narrative of the past by finding and analyzing a variety of “documents” and records (including photographs and physical artifacts), to analyses of contemporary media content, as in the case of compiling and coding blog posts or other online commentaries, and content analysis that identifies and describes communicative aspects of media or documents.
In addition to these four major techniques, there are a host of emerging and incidental data collection techniques, from photo elicitation or photo voice, in which respondents are asked to comment upon a photograph or image (particularly useful as a supplement to interviews when the respondents are hesitant or unable to answer direct questions), to autoethnographies, in which the researcher uses his own position and life to increase our understanding about a phenomenon and its historical and social context.
Taken together, these techniques provide a wide range of practices and tools with which to discover the world. They are particularly suited to addressing the questions that qualitative researchers ask—questions about how things happen and why people act the way they do, given particular social contexts and shared meanings about the world (chapter 4).
Triangulation and Mixed Methods
Because the researcher plays such a large and nonneutral role in qualitative research, one that requires constant reflectivity and awareness (chapter 6), there is a constant need to reassure her audience that the results she finds are reliable. Quantitative researchers can point to any number of measures of statistical significance to reassure their audiences, but qualitative researchers do not have math to hide behind. And she will also want to reassure herself that what she is hearing in her interviews or observing in the field is a true reflection of what is going on (or as “true” as possible, given the problem that the world is as large and varied as the elephant; see chapter 3). For those reasons, it is common for researchers to employ more than one data collection technique or to include multiple and comparative populations, settings, and samples in the research design (chapter 2). A single set of interviews or initial comparison of focus groups might be conceived as a “pilot study” from which to launch the actual study. Undergraduate students working on a research project might be advised to think about their projects in this way as well. You are simply not going to have enough time or resources as an undergraduate to construct and complete a successful qualitative research project, but you may be able to tackle a pilot study. Graduate students also need to think about the amount of time and resources they have for completing a full study. Masters-level students, or students who have one year or less in which to complete a program, should probably consider their study as an initial exploratory pilot. PhD candidates might have the time and resources to devote to the type of triangulated, multifaceted research design called for by the research question.
We call the use of multiple qualitative methods of data collection and the inclusion of multiple and comparative populations and settings “triangulation.” Using different data collection methods allows us to check the consistency of our findings. For example, a study of the vaccine hesitant might include a set of interviews with vaccine-hesitant people and a focus group of the same and a content analysis of online comments about a vaccine mandate. By employing all three methods, we can be more confident of our interpretations from the interviews alone (especially if we are hearing the same thing throughout; if we are not, then this is a good sign that we need to push a little further to find out what is really going on). [3] Methodological triangulation is an important tool for increasing the reliability of our findings and the overall success of our research.
Methodological triangulation should not be confused with mixed methods techniques, which refer instead to the combining of qualitative and quantitative research methods. Mixed methods studies can increase reliability, but that is not their primary purpose. Mixed methods address multiple research questions, both the “how many” and “why” kind, or the causal and explanatory kind. Mixed methods will be discussed in more detail in chapter 15.
Let us return to the three examples of qualitative research described in chapter 1: Cory Abramson’s study of aging ( The End Game) , Jennifer Pierce’s study of lawyers and discrimination ( Racing for Innocence ), and my own study of liberal arts college students ( Amplified Advantage ). Each of these studies uses triangulation.
Abramson’s book is primarily based on three years of observations in four distinct neighborhoods. He chose the neighborhoods in such a way to maximize his ability to make comparisons: two were primarily middle class and two were primarily poor; further, within each set, one was predominantly White, while the other was either racially diverse or primarily African American. In each neighborhood, he was present in senior centers, doctors’ offices, public transportation, and other public spots where the elderly congregated. [4] The observations are the core of the book, and they are richly written and described in very moving passages. But it wasn’t enough for him to watch the seniors. He also engaged with them in casual conversation. That, too, is part of fieldwork. He sometimes even helped them make it to the doctor’s office or get around town. Going beyond these interactions, he also interviewed sixty seniors, an equal amount from each of the four neighborhoods. It was in the interviews that he could ask more detailed questions about their lives, what they thought about aging, what it meant to them to be considered old, and what their hopes and frustrations were. He could see that those living in the poor neighborhoods had a more difficult time accessing care and resources than those living in the more affluent neighborhoods, but he couldn’t know how the seniors understood these difficulties without interviewing them. Both forms of data collection supported each other and helped make the study richer and more insightful. Interviews alone would have failed to demonstrate the very real differences he observed (and that some seniors would not even have known about). This is the value of methodological triangulation.
Pierce’s book relies on two separate forms of data collection—interviews with lawyers at a firm that has experienced a history of racial discrimination and content analyses of news stories and popular films that screened during the same years of the alleged racial discrimination. I’ve used this book when teaching methods and have often found students struggle with understanding why these two forms of data collection were used. I think this is because we don’t teach students to appreciate or recognize “popular films” as a legitimate form of data. But what Pierce does is interesting and insightful in the best tradition of qualitative research. Here is a description of the content analyses from a review of her book:
In the chapter on the news media, Professor Pierce uses content analysis to argue that the media not only helped shape the meaning of affirmative action, but also helped create white males as a class of victims. The overall narrative that emerged from these media accounts was one of white male innocence and victimization. She also maintains that this narrative was used to support “neoconservative and neoliberal political agendas” (p. 21). The focus of these articles tended to be that affirmative action hurt white working-class and middle-class men particularly during the recession in the 1980s (despite statistical evidence that people of color were hurt far more than white males by the recession). In these stories fairness and innocence were seen in purely individual terms. Although there were stories that supported affirmative action and developed a broader understanding of fairness, the total number of stories slanted against affirmative action from 1990 to 1999. During that time period negative stories always outnumbered those supporting the policy, usually by a ratio of 3:1 or 3:2. Headlines, the presentation of polling data, and an emphasis in stories on racial division, Pierce argues, reinforced the story of white male victimization. Interestingly, the news media did very few stories on gender and affirmative action. The chapter on the film industry from 1989 to 1999 reinforces Pierce’s argument and adds another layer to her interpretation of affirmative action during this time period. She sampled almost 60 Hollywood films with receipts ranging from four million to 184 million dollars. In this chapter she argues that the dominant theme of these films was racial progress and the redemption of white Americans from past racism. These movies usually portrayed white, elite, and male experiences. People of color were background figures who supported the protagonist and “anointed” him as a savior (p. 45). Over the course of the film the protagonists move from “innocence to consciousness” concerning racism. The antagonists in these films most often were racist working-class white men. A Time to Kill , Mississippi Burning , Amistad , Ghosts of Mississippi , The Long Walk Home , To Kill a Mockingbird , and Dances with Wolves receive particular analysis in this chapter, and her examination of them leads Pierce to conclude that they infused a myth of racial progress into America’s cultural memory. White experiences of race are the focus and contemporary forms of racism are underplayed or omitted. Further, these films stereotype both working-class and elite white males, and underscore the neoliberal emphasis on individualism. ( Hrezo 2012 )
With that context in place, Pierce then turned to interviews with attorneys. She finds that White male attorneys often misremembered facts about the period in which the law firm was accused of racial discrimination and that they often portrayed their firms as having made substantial racial progress. This was in contrast to many of the lawyers of color and female lawyers who remembered the history differently and who saw continuing examples of racial (and gender) discrimination at the law firm. In most of the interviews, people talked about individuals, not structure (and these are attorneys, who really should know better!). By including both content analyses and interviews in her study, Pierce is better able to situate the attorney narratives and explain the larger context for the shared meanings of individual innocence and racial progress. Had this been a study only of films during this period, we would not know how actual people who lived during this period understood the decisions they made; had we had only the interviews, we would have missed the historical context and seen a lot of these interviewees as, well, not very nice people at all. Together, we have a study that is original, inventive, and insightful.
My own study of how class background affects the experiences and outcomes of students at small liberal arts colleges relies on mixed methods and triangulation. At the core of the book is an original survey of college students across the US. From analyses of this survey, I can present findings on “how many” questions and descriptive statistics comparing students of different social class backgrounds. For example, I know and can demonstrate that working-class college students are less likely to go to graduate school after college than upper-class college students are. I can even give you some estimates of the class gap. But what I can’t tell you from the survey is exactly why this is so or how it came to be so . For that, I employ interviews, focus groups, document reviews, and observations. Basically, I threw the kitchen sink at the “problem” of class reproduction and higher education (i.e., Does college reduce class inequalities or make them worse?). A review of historical documents provides a picture of the place of the small liberal arts college in the broader social and historical context. Who had access to these colleges and for what purpose have always been in contest, with some groups attempting to exclude others from opportunities for advancement. What it means to choose a small liberal arts college in the early twenty-first century is thus different for those whose parents are college professors, for those whose parents have a great deal of money, and for those who are the first in their family to attend college. I was able to get at these different understandings through interviews and focus groups and to further delineate the culture of these colleges by careful observation (and my own participation in them, as both former student and current professor). Putting together individual meanings, student dispositions, organizational culture, and historical context allowed me to present a story of how exactly colleges can both help advance first-generation, low-income, working-class college students and simultaneously amplify the preexisting advantages of their peers. Mixed methods addressed multiple research questions, while triangulation allowed for this deeper, more complex story to emerge.
In the next few chapters, we will explore each of the primary data collection techniques in much more detail. As we do so, think about how these techniques may be productively joined for more reliable and deeper studies of the social world.
Advanced Reading: Triangulation
Denzin ( 1978 ) identified four basic types of triangulation: data, investigator, theory, and methodological. Properly speaking, if we use the Denzin typology, the use of multiple methods of data collection and analysis to strengthen one’s study is really a form of methodological triangulation. It may be helpful to understand how this differs from the other types.
Data triangulation occurs when the researcher uses a variety of sources in a single study. Perhaps they are interviewing multiple samples of college students. Obviously, this overlaps with sample selection (see chapter 5). It is helpful for the researcher to understand that these multiple data sources add strength and reliability to the study. After all, it is not just “these students here” but also “those students over there” that are experiencing this phenomenon in a particular way.
Investigator triangulation occurs when different researchers or evaluators are part of the research team. Intercoding reliability is a form of investigator triangulation (or at least a way of leveraging the power of multiple researchers to raise the reliability of the study).
Theory triangulation is the use of multiple perspectives to interpret a single set of data, as in the case of competing theoretical paradigms (e.g., a human capital approach vs. a Bourdieusian multiple capital approach).
Methodological triangulation , as explained in this chapter, is the use of multiple methods to study a single phenomenon, issue, or problem.
Further Readings
Carter, Nancy, Denise Bryant-Lukosius, Alba DiCenso, Jennifer Blythe, Alan J. Neville. 2014. “The Use of Triangulation in Qualitative Research.” Oncology Nursing Forum 41(5):545–547. Discusses the four types of triangulation identified by Denzin with an example of the use of focus groups and in-depth individuals.
Mathison, Sandra. 1988. “Why Triangulate?” Educational Researcher 17(2):13–17. Presents three particular ways of assessing validity through the use of triangulated data collection: convergence, inconsistency, and contradiction.
Tracy, Sarah J. 2010. “Qualitative Quality: Eight ‘Big-Tent’ Criteria for Excellent Qualitative Research.” Qualitative Inquiry 16(10):837–851. Focuses on triangulation as a criterion for conducting valid qualitative research.
- Marshall and Rossman ( 2016 ) state this slightly differently. They list four primary methods for gathering information: (1) participating in the setting, (2) observing directly, (3) interviewing in depth, and (4) analyzing documents and material culture (141). An astute reader will note that I have collapsed participation into observation and that I have distinguished focus groups from interviews. I suspect that this distinction marks me as more of an interview-based researcher, while Marshall and Rossman prioritize ethnographic approaches. The main point of this footnote is to show you, the reader, that there is no single agreed-upon number of approaches to collecting qualitative data. ↵
- See “ Advanced Reading: Triangulation ” at end of this chapter. ↵
- We can also think about triangulating the sources, as when we include comparison groups in our sample (e.g., if we include those receiving vaccines, we might find out a bit more about where the real differences lie between them and the vaccine hesitant); triangulating the analysts (building a research team so that your interpretations can be checked against those of others on the team); and even triangulating the theoretical perspective (as when we “try on,” say, different conceptualizations of social capital in our analyses). ↵
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Data Collection: What It Is, Methods & Tools + Examples

Let’s face it, no one wants to make decisions based on guesswork or gut feelings. The most important objective of data collection is to ensure that the data gathered is reliable and packed to the brim with juicy insights that can be analyzed and turned into data-driven decisions. There’s nothing better than good statistical analysis .
LEARN ABOUT: Level of Analysis
Collecting high-quality data is essential for conducting market research, analyzing user behavior, or just trying to get a handle on business operations. With the right approach and a few handy tools, gathering reliable and informative data.
So, let’s get ready to collect some data because when it comes to data collection, it’s all about the details.
Content Index
What is Data Collection?
Data collection methods, data collection examples, reasons to conduct online research and data collection, conducting customer surveys for data collection to multiply sales, steps to effectively conduct an online survey for data collection, survey design for data collection.
Data collection is the procedure of collecting, measuring, and analyzing accurate insights for research using standard validated techniques.
Put simply, data collection is the process of gathering information for a specific purpose. It can be used to answer research questions, make informed business decisions, or improve products and services.
To collect data, we must first identify what information we need and how we will collect it. We can also evaluate a hypothesis based on collected data. In most cases, data collection is the primary and most important step for research. The approach to data collection is different for different fields of study, depending on the required information.
LEARN ABOUT: Action Research
There are many ways to collect information when doing research. The data collection methods that the researcher chooses will depend on the research question posed. Some data collection methods include surveys, interviews, tests, physiological evaluations, observations, reviews of existing records, and biological samples. Let’s explore them.
LEARN ABOUT: Best Data Collection Tools
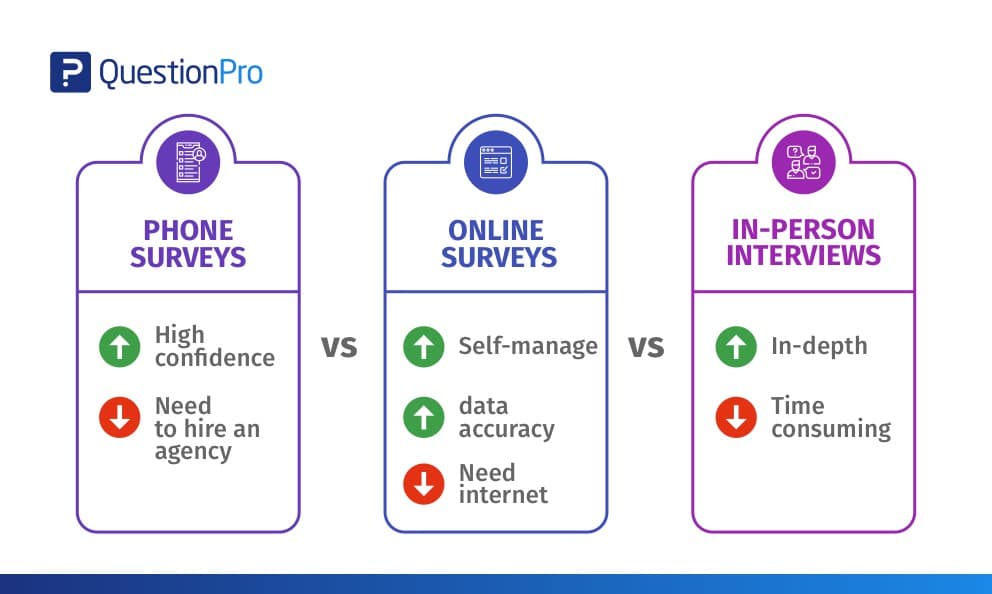
Phone vs. Online vs. In-Person Interviews
Essentially there are four choices for data collection – in-person interviews, mail, phone, and online. There are pros and cons to each of these modes.
- Pros: In-depth and a high degree of confidence in the data
- Cons: Time-consuming, expensive, and can be dismissed as anecdotal
- Pros: Can reach anyone and everyone – no barrier
- Cons: Expensive, data collection errors, lag time
- Pros: High degree of confidence in the data collected, reach almost anyone
- Cons: Expensive, cannot self-administer, need to hire an agency
- Pros: Cheap, can self-administer, very low probability of data errors
- Cons: Not all your customers might have an email address/be on the internet, customers may be wary of divulging information online.
In-person interviews always are better, but the big drawback is the trap you might fall into if you don’t do them regularly. It is expensive to regularly conduct interviews and not conducting enough interviews might give you false positives. Validating your research is almost as important as designing and conducting it.
We’ve seen many instances where after the research is conducted – if the results do not match up with the “gut-feel” of upper management, it has been dismissed off as anecdotal and a “one-time” phenomenon. To avoid such traps, we strongly recommend that data-collection be done on an “ongoing and regular” basis.
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
This will help you compare and analyze the change in perceptions according to marketing for your products/services. The other issue here is sample size. To be confident with your research, you must interview enough people to weed out the fringe elements.
A couple of years ago there was a lot of discussion about online surveys and their statistical analysis plan . The fact that not every customer had internet connectivity was one of the main concerns.
LEARN ABOUT: Statistical Analysis Methods
Although some of the discussions are still valid, the reach of the internet as a means of communication has become vital in the majority of customer interactions. According to the US Census Bureau, the number of households with computers has doubled between 1997 and 2001.
Learn more: Quantitative Market Research
In 2001 nearly 50% of households had a computer. Nearly 55% of all households with an income of more than 35,000 have internet access, which jumps to 70% for households with an annual income of 50,000. This data is from the US Census Bureau for 2001.
There are primarily three modes of data collection that can be employed to gather feedback – Mail, Phone, and Online. The method actually used for data collection is really a cost-benefit analysis. There is no slam-dunk solution but you can use the table below to understand the risks and advantages associated with each of the mediums:
Keep in mind, the reach here is defined as “All U.S. Households.” In most cases, you need to look at how many of your customers are online and determine. If all your customers have email addresses, you have a 100% reach of your customers.
Another important thing to keep in mind is the ever-increasing dominance of cellular phones over landline phones. United States FCC rules prevent automated dialing and calling cellular phone numbers and there is a noticeable trend towards people having cellular phones as the only voice communication device.
This introduces the inability to reach cellular phone customers who are dropping home phone lines in favor of going entirely wireless. Even if automated dialing is not used, another FCC rule prohibits from phoning anyone who would have to pay for the call.
Learn more: Qualitative Market Research
Multi-Mode Surveys
Surveys, where the data is collected via different modes (online, paper, phone etc.), is also another way of going. It is fairly straightforward and easy to have an online survey and have data-entry operators to enter in data (from the phone as well as paper surveys) into the system. The same system can also be used to collect data directly from the respondents.
Learn more: Survey Research
Data collection is an important aspect of research. Let’s consider an example of a mobile manufacturer, company X, which is launching a new product variant. To conduct research about features, price range, target market, competitor analysis, etc. data has to be collected from appropriate sources.
The marketing team can conduct various data collection activities such as online surveys or focus groups .
The survey should have all the right questions about features and pricing, such as “What are the top 3 features expected from an upcoming product?” or “How much are your likely to spend on this product?” or “Which competitors provide similar products?” etc.
For conducting a focus group, the marketing team should decide the participants and the mediator. The topic of discussion and objective behind conducting a focus group should be clarified beforehand to conduct a conclusive discussion.
Data collection methods are chosen depending on the available resources. For example, conducting questionnaires and surveys would require the least resources, while focus groups require moderately high resources.
Feedback is a vital part of any organization’s growth. Whether you conduct regular focus groups to elicit information from key players or, your account manager calls up all your marquee accounts to find out how things are going – essentially they are all processes to find out from your customers’ eyes – How are we doing? What can we do better?
Online surveys are just another medium to collect feedback from your customers , employees and anyone your business interacts with. With the advent of Do-It-Yourself tools for online surveys, data collection on the internet has become really easy, cheap and effective.
Learn more: Online Research
It is a well-established marketing fact that acquiring a new customer is 10 times more difficult and expensive than retaining an existing one. This is one of the fundamental driving forces behind the extensive adoption and interest in CRM and related customer retention tactics.
In a research study conducted by Rice University Professor Dr. Paul Dholakia and Dr. Vicki Morwitz, published in Harvard Business Review, the experiment inferred that the simple fact of asking customers how an organization was performing by itself to deliver results proved to be an effective customer retention strategy.
In the research study, conducted over the course of a year, one set of customers were sent out a satisfaction and opinion survey and the other set was not surveyed. In the next one year, the group that took the survey saw twice the number of people continuing and renewing their loyalty towards the organization data .
Learn more: Research Design
The research study provided a couple of interesting reasons on the basis of consumer psychology, behind this phenomenon:
- Satisfaction surveys boost the customers’ desire to be coddled and induce positive feelings. This crops from a section of the human psychology that intends to “appreciate” a product or service they already like or prefer. The survey feedback collection method is solely a medium to convey this. The survey is a vehicle to “interact” with the company and reinforces the customer’s commitment to the company.
- Surveys may increase awareness of auxiliary products and services. Surveys can be considered modes of both inbound as well as outbound communication. Surveys are generally considered to be a data collection and analysis source. Most people are unaware of the fact that consumer surveys can also serve as a medium for distributing data. It is important to note a few caveats here.
- In most countries, including the US, “selling under the guise of research” is illegal. b. However, we all know that information is distributed while collecting information. c. Other disclaimers may be included in the survey to ensure users are aware of this fact. For example: “We will collect your opinion and inform you about products and services that have come online in the last year…”
- Induced Judgments: The entire procedure of asking people for their feedback can prompt them to build an opinion on something they otherwise would not have thought about. This is a very underlying yet powerful argument that can be compared to the “Product Placement” strategy currently used for marketing products in mass media like movies and television shows. One example is the extensive and exclusive use of the “mini-Cooper” in the blockbuster movie “Italian Job.” This strategy is questionable and should be used with great caution.
Surveys should be considered as a critical tool in the customer journey dialog. The best thing about surveys is its ability to carry “bi-directional” information. The research conducted by Paul Dholakia and Vicki Morwitz shows that surveys not only get you the information that is critical for your business, but also enhances and builds upon the established relationship you have with your customers.
Recent technological advances have made it incredibly easy to conduct real-time surveys and opinion polls . Online tools make it easy to frame questions and answers and create surveys on the Web. Distributing surveys via email, website links or even integration with online CRM tools like Salesforce.com have made online surveying a quick-win solution.
So, you’ve decided to conduct an online survey. There are a few questions in your mind that you would like answered, and you are looking for a fast and inexpensive way to find out more about your customers, clients, etc.
First and foremost thing you need to decide what the smart objectives of the study are. Ensure that you can phrase these objectives as questions or measurements. If you can’t, you are better off looking at other data sources like focus groups and other qualitative methods . The data collected via online surveys is dominantly quantitative in nature.
Review the basic objectives of the study. What are you trying to discover? What actions do you want to take as a result of the survey? – Answers to these questions help in validating collected data. Online surveys are just one way of collecting and quantifying data .
Learn more: Qualitative Data & Qualitative Data Collection Methods
- Visualize all of the relevant information items you would like to have. What will the output survey research report look like? What charts and graphs will be prepared? What information do you need to be assured that action is warranted?
- Assign ranks to each topic (1 and 2) according to their priority, including the most important topics first. Revisit these items again to ensure that the objectives, topics, and information you need are appropriate. Remember, you can’t solve the research problem if you ask the wrong questions.
- How easy or difficult is it for the respondent to provide information on each topic? If it is difficult, is there an alternative medium to gain insights by asking a different question? This is probably the most important step. Online surveys have to be Precise, Clear and Concise. Due to the nature of the internet and the fluctuations involved, if your questions are too difficult to understand, the survey dropout rate will be high.
- Create a sequence for the topics that are unbiased. Make sure that the questions asked first do not bias the results of the next questions. Sometimes providing too much information, or disclosing purpose of the study can create bias. Once you have a series of decided topics, you can have a basic structure of a survey. It is always advisable to add an “Introductory” paragraph before the survey to explain the project objective and what is expected of the respondent. It is also sensible to have a “Thank You” text as well as information about where to find the results of the survey when they are published.
- Page Breaks – The attention span of respondents can be very low when it comes to a long scrolling survey. Add page breaks as wherever possible. Having said that, a single question per page can also hamper response rates as it increases the time to complete the survey as well as increases the chances for dropouts.
- Branching – Create smart and effective surveys with the implementation of branching wherever required. Eliminate the use of text such as, “If you answered No to Q1 then Answer Q4” – this leads to annoyance amongst respondents which result in increase survey dropout rates. Design online surveys using the branching logic so that appropriate questions are automatically routed based on previous responses.
- Write the questions . Initially, write a significant number of survey questions out of which you can use the one which is best suited for the survey. Divide the survey into sections so that respondents do not get confused seeing a long list of questions.
- Sequence the questions so that they are unbiased.
- Repeat all of the steps above to find any major holes. Are the questions really answered? Have someone review it for you.
- Time the length of the survey. A survey should take less than five minutes. At three to four research questions per minute, you are limited to about 15 questions. One open end text question counts for three multiple choice questions. Most online software tools will record the time taken for the respondents to answer questions.
- Include a few open-ended survey questions that support your survey object. This will be a type of feedback survey.
- Send an email to the project survey to your test group and then email the feedback survey afterward.
- This way, you can have your test group provide their opinion about the functionality as well as usability of your project survey by using the feedback survey.
- Make changes to your questionnaire based on the received feedback.
- Send the survey out to all your respondents!
Online surveys have, over the course of time, evolved into an effective alternative to expensive mail or telephone surveys. However, you must be aware of a few conditions that need to be met for online surveys. If you are trying to survey a sample representing the target population, please remember that not everyone is online.
Moreover, not everyone is receptive to an online survey also. Generally, the demographic segmentation of younger individuals is inclined toward responding to an online survey.
Learn More: Examples of Qualitarive Data in Education
Good survey design is crucial for accurate data collection. From question-wording to response options, let’s explore how to create effective surveys that yield valuable insights with our tips to survey design.
- Writing Great Questions for data collection
Writing great questions can be considered an art. Art always requires a significant amount of hard work, practice, and help from others.
The questions in a survey need to be clear, concise, and unbiased. A poorly worded question or a question with leading language can result in inaccurate or irrelevant responses, ultimately impacting the data’s validity.
Moreover, the questions should be relevant and specific to the research objectives. Questions that are irrelevant or do not capture the necessary information can lead to incomplete or inconsistent responses too.
- Avoid loaded or leading words or questions
A small change in content can produce effective results. Words such as could , should and might are all used for almost the same purpose, but may produce a 20% difference in agreement to a question. For example, “The management could.. should.. might.. have shut the factory”.
Intense words such as – prohibit or action, representing control or action, produce similar results. For example, “Do you believe Donald Trump should prohibit insurance companies from raising rates?”.
Sometimes the content is just biased. For instance, “You wouldn’t want to go to Rudolpho’s Restaurant for the organization’s annual party, would you?”
- Misplaced questions
Questions should always reference the intended context, and questions placed out of order or without its requirement should be avoided. Generally, a funnel approach should be implemented – generic questions should be included in the initial section of the questionnaire as a warm-up and specific ones should follow. Toward the end, demographic or geographic questions should be included.
- Mutually non-overlapping response categories
Multiple-choice answers should be mutually unique to provide distinct choices. Overlapping answer options frustrate the respondent and make interpretation difficult at best. Also, the questions should always be precise.
For example: “Do you like water juice?”
This question is vague. In which terms is the liking for orange juice is to be rated? – Sweetness, texture, price, nutrition etc.
- Avoid the use of confusing/unfamiliar words
Asking about industry-related terms such as caloric content, bits, bytes, MBS , as well as other terms and acronyms can confuse respondents . Ensure that the audience understands your language level, terminology, and, above all, the question you ask.
- Non-directed questions give respondents excessive leeway
In survey design for data collection, non-directed questions can give respondents excessive leeway, which can lead to vague and unreliable data. These types of questions are also known as open-ended questions, and they do not provide any structure for the respondent to follow.
For instance, a non-directed question like “ What suggestions do you have for improving our shoes?” can elicit a wide range of answers, some of which may not be relevant to the research objectives. Some respondents may give short answers, while others may provide lengthy and detailed responses, making comparing and analyzing the data challenging.
To avoid these issues, it’s essential to ask direct questions that are specific and have a clear structure. Closed-ended questions, for example, offer structured response options and can be easier to analyze as they provide a quantitative measure of respondents’ opinions.
- Never force questions
There will always be certain questions that cross certain privacy rules. Since privacy is an important issue for most people, these questions should either be eliminated from the survey or not be kept as mandatory. Survey questions about income, family income, status, religious and political beliefs, etc., should always be avoided as they are considered to be intruding, and respondents can choose not to answer them.
- Unbalanced answer options in scales
Unbalanced answer options in scales such as Likert Scale and Semantic Scale may be appropriate for some situations and biased in others. When analyzing a pattern in eating habits, a study used a quantity scale that made obese people appear in the middle of the scale with the polar ends reflecting a state where people starve and an irrational amount to consume. There are cases where we usually do not expect poor service, such as hospitals.
- Questions that cover two points
In survey design for data collection, questions that cover two points can be problematic for several reasons. These types of questions are often called “double-barreled” questions and can cause confusion for respondents, leading to inaccurate or irrelevant data.
For instance, a question like “Do you like the food and the service at the restaurant?” covers two points, the food and the service, and it assumes that the respondent has the same opinion about both. If the respondent only liked the food, their opinion of the service could affect their answer.
It’s important to ask one question at a time to avoid confusion and ensure that the respondent’s answer is focused and accurate. This also applies to questions with multiple concepts or ideas. In these cases, it’s best to break down the question into multiple questions that address each concept or idea separately.
- Dichotomous questions
Dichotomous questions are used in case you want a distinct answer, such as: Yes/No or Male/Female . For example, the question “Do you think this candidate will win the election?” can be Yes or No.
- Avoid the use of long questions
The use of long questions will definitely increase the time taken for completion, which will generally lead to an increase in the survey dropout rate. Multiple-choice questions are the longest and most complex, and open-ended questions are the shortest and easiest to answer.
Data collection is an essential part of the research process, whether you’re conducting scientific experiments, market research, or surveys. The methods and tools used for data collection will vary depending on the research type, the sample size required, and the resources available.
Several data collection methods include surveys, observations, interviews, and focus groups. We learn each method has advantages and disadvantages, and choosing the one that best suits the research goals is important.
With the rise of technology, many tools are now available to facilitate data collection, including online survey software and data visualization tools. These tools can help researchers collect, store, and analyze data more efficiently, providing greater results and accuracy.
By understanding the various methods and tools available for data collection, we can develop a solid foundation for conducting research. With these research skills , we can make informed decisions, solve problems, and contribute to advancing our understanding of the world around us.
Analyze your survey data to gauge in-depth market drivers, including competitive intelligence, purchasing behavior, and price sensitivity, with QuestionPro.
You will obtain accurate insights with various techniques, including conjoint analysis, MaxDiff analysis, sentiment analysis, TURF analysis, heatmap analysis, etc. Export quality data to external in-depth analysis tools such as SPSS and R Software, and integrate your research with external business applications. Everything you need for your data collection. Start today for free!
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

Like Never Seen Before: QuestionPro CX Product Updates – Quarter 1, 2024
Apr 29, 2024

NPS Survey Platform: Types, Tips, 11 Best Platforms & Tools
Apr 26, 2024
User Journey vs User Flow: Differences and Similarities

Best 7 Gap Analysis Tools to Empower Your Business
Apr 25, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence

A Guide to Data Collection: Methods, Process, and Tools

Whether your field is development economics, international development, the nonprofit sector, or myriad other industries, effective data collection is essential. It informs decision-making and increases your organization’s impact. However, the process of data collection can be complex and challenging. If you’re in the beginning stages of creating a data collection process, this guide is for you. It outlines tested methods, efficient procedures, and effective tools to help you improve your data collection activities and outcomes. At SurveyCTO, we’ve used our years of experience and expertise to build a robust, secure, and scalable mobile data collection platform. It’s trusted by respected institutions like The World Bank, J-PAL, Oxfam, and the Gates Foundation, and it’s changed the way many organizations collect and use data. With this guide, we want to share what we know and help you get ready to take the first step in your data collection journey.
Main takeaways from this guide
- Before starting the data collection process, define your goals and identify data sources, which can be primary (first-hand research) or secondary (existing resources).
- Your data collection method should align with your goals, resources, and the nature of the data needed. Surveys, interviews, observations, focus groups, and forms are common data collection methods.
- Sampling involves selecting a representative group from a larger population. Choosing the right sampling method to gather representative and relevant data is crucial.
- Crafting effective data collection instruments like surveys and questionnaires is key. Instruments should undergo rigorous testing for reliability and accuracy.
- Data collection is an ongoing, iterative process that demands real-time monitoring and adjustments to ensure high-quality, reliable results.
- After data collection, data should be cleaned to eliminate errors and organized for efficient analysis. The data collection journey further extends into data analysis, where patterns and useful information that can inform decision-making are discovered.
- Common challenges in data collection include data quality and consistency issues, data security concerns, and limitations with offline data collection. Employing robust data validation processes, implementing strong security protocols, and using offline-enabled data collection tools can help overcome these challenges.
- Data collection, entry, and management tools and data analysis, visualization, reporting, and workflow tools can streamline the data collection process, improve data quality, and facilitate data analysis.
What is data collection?
The traditional definition of data collection might lead us to think of gathering information through surveys, observations, or interviews. However, the modern-age definition of data collection extends beyond conducting surveys and observations. It encompasses the systematic gathering and recording of any kind of information through digital or manual methods. Data collection can be as routine as a doctor logging a patient’s information into an electronic medical record system during each clinic visit, or as specific as keeping a record of mosquito nets delivered to a rural household.
Getting started with data collection

Before starting your data collection process, you must clearly understand what you aim to achieve and how you’ll get there. Below are some actionable steps to help you get started.
1. Define your goals
Defining your goals is a crucial first step. Engage relevant stakeholders and team members in an iterative and collaborative process to establish clear goals. It’s important that projects start with the identification of key questions and desired outcomes to ensure you focus your efforts on gathering the right information.
Start by understanding the purpose of your project– what problem are you trying to solve, or what change do you want to bring about? Think about your project’s potential outcomes and obstacles and try to anticipate what kind of data would be useful in these scenarios. Consider who will be using the data you collect and what data would be the most valuable to them. Think about the long-term effects of your project and how you will measure these over time. Lastly, leverage any historical data from previous projects to help you refine key questions that may have been overlooked previously.
Once questions and outcomes are established, your data collection goals may still vary based on the context of your work. To demonstrate, let’s use the example of an international organization working on a healthcare project in a remote area.
- If you’re a researcher , your goal will revolve around collecting primary data to answer specific questions. This could involve designing a survey or conducting interviews to collect first-hand data on patient improvement, disease or illness prevalence, and behavior changes (such as an increase in patients seeking healthcare).
- If you’re part of the monitoring and evaluation ( M&E) team , your goal will revolve around measuring the success of your healthcare project. This could involve collecting primary data through surveys or observations and developing a dashboard to display real-time metrics like the number of patients treated, percentage of reduction in incidences of disease,, and average patient wait times. Your focus would be using this data to implement any needed program changes and ensure your project meets its objectives.
- If you’re part of a field team , your goal will center around the efficient and accurate execution of project plans. You might be responsible for using data collection tools to capture pertinent information in different settings, such as in interviews takendirectly from the sample community or over the phone. The data you collect and manage will directly influence the operational efficiency of the project and assist in achieving the project’s overarching objectives.
2. Identify your data sources
The crucial next step in your research process is determining your data source. Essentially, there are two main data types to choose from: primary and secondary.
- Primary data is the information you collect directly from first-hand engagements. It’s gathered specifically for your research and tailored to your research question. Primary data collection methods can range from surveys and interviews to focus groups and observations. Because you design the data collection process, primary data can offer precise, context-specific information directly related to your research objectives. For example, suppose you are investigating the impact of a new education policy. In that case, primary data might be collected through surveys distributed to teachers or interviews with school administrators dealing directly with the policy’s implementation.
- Secondary data, on the other hand, is derived from resources that already exist. This can include information gathered for other research projects, administrative records, historical documents, statistical databases, and more. While not originally collected for your specific study, secondary data can offer valuable insights and background information that complement your primary data. For instance, continuing with the education policy example, secondary data might involve academic articles about similar policies, government reports on education or previous survey data about teachers’ opinions on educational reforms.
While both types of data have their strengths, this guide will predominantly focus on primary data and the methods to collect it. Primary data is often emphasized in research because it provides fresh, first-hand insights that directly address your research questions. Primary data also allows for more control over the data collection process, ensuring data is relevant, accurate, and up-to-date.
However, secondary data can offer critical context, allow for longitudinal analysis, save time and resources, and provide a comparative framework for interpreting your primary data. It can be a crucial backdrop against which your primary data can be understood and analyzed. While we focus on primary data collection methods in this guide, we encourage you not to overlook the value of incorporating secondary data into your research design where appropriate.
3. Choose your data collection method
When choosing your data collection method, there are many options at your disposal. Data collection is not limited to methods like surveys and interviews. In fact, many of the processes in our daily lives serve the goal of collecting data, from intake forms to automated endpoints, such as payment terminals and mass transit card readers. Let us dive into some common types of data collection methods:
Surveys and Questionnaires
Surveys and questionnaires are tools for gathering information about a group of individuals, typically by asking them predefined questions. They can be used to collect quantitative and qualitative data and be administered in various ways, including online, over the phone, in person (offline), or by mail.
- Advantages : They allow researchers to reach many participants quickly and cost-effectively, making them ideal for large-scale studies. The structured format of questions makes analysis easier.
- Disadvantages : They may not capture complex or nuanced information as participants are limited to predefined response choices. Also, there can be issues with response bias, where participants might provide socially desirable answers rather than honest ones.
Interviews involve a one-on-one conversation between the researcher and the participant. The interviewer asks open-ended questions to gain detailed information about the participant’s thoughts, feelings, experiences, and behaviors.
- Advantages : They allow for an in-depth understanding of the topic at hand. The researcher can adapt the questioning in real time based on the participant’s responses, allowing for more flexibility.
- Disadvantages : They can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, as they require trained interviewers and a significant amount of time for both conducting and analyzing responses. They may also introduce interviewer bias if not conducted carefully, due to how an interviewer presents questions and perceives the respondent, and how the respondent perceives the interviewer.
Observations
Observations involve directly observing and recording behavior or other phenomena as they occur in their natural settings.
- Advantages : Observations can provide valuable contextual information, as researchers can study behavior in the environment where it naturally occurs, reducing the risk of artificiality associated with laboratory settings or self-reported measures.
- Disadvantages : Observational studies may suffer from observer bias, where the observer’s expectations or biases could influence their interpretation of the data. Also, some behaviors might be altered if subjects are aware they are being observed.
Focus Groups
Focus groups are guided discussions among selected individuals to gain information about their views and experiences.
- Advantages : Focus groups allow for interaction among participants, which can generate a diverse range of opinions and ideas. They are good for exploring new topics where there is little pre-existing knowledge.
- Disadvantages : Dominant voices in the group can sway the discussion, potentially silencing less assertive participants. They also require skilled facilitators to moderate the discussion effectively.
Forms are standardized documents with blank fields for collecting data in a systematic manner. They are often used in fields like Customer Relationship Management (CRM) or Electronic Medical Records (EMR) data entry. Surveys may also be referred to as forms.
- Advantages : Forms are versatile, easy to use, and efficient for data collection. They can streamline workflows by standardizing the data entry process.
- Disadvantages : They may not provide in-depth insights as the responses are typically structured and limited. There is also potential for errors in data entry, especially when done manually.
Selecting the right data collection method should be an intentional process, taking into consideration the unique requirements of your project. The method selected should align with your goals, available resources, and the nature of the data you need to collect.
If you aim to collect quantitative data, surveys, questionnaires, and forms can be excellent tools, particularly for large-scale studies. These methods are suited to providing structured responses that can be analyzed statistically, delivering solid numerical data.
However, if you’re looking to uncover a deeper understanding of a subject, qualitative data might be more suitable. In such cases, interviews, observations, and focus groups can provide richer, more nuanced insights. These methods allow you to explore experiences, opinions, and behaviors deeply. Some surveys can also include open-ended questions that provide qualitative data.
The cost of data collection is also an important consideration. If you have budget constraints, in-depth, in-person conversations with every member of your target population may not be practical. In such cases, distributing questionnaires or forms can be a cost-saving approach.
Additional considerations include language barriers and connectivity issues. If your respondents speak different languages, consider translation services or multilingual data collection tools . If your target population resides in areas with limited connectivity and your method will be to collect data using mobile devices, ensure your tool provides offline data collection , which will allow you to carry out your data collection plan without internet connectivity.
4. Determine your sampling method
Now that you’ve established your data collection goals and how you’ll collect your data, the next step is deciding whom to collect your data from. Sampling involves carefully selecting a representative group from a larger population. Choosing the right sampling method is crucial for gathering representative and relevant data that aligns with your data collection goal.
Consider the following guidelines to choose the appropriate sampling method for your research goal and data collection method:
- Understand Your Target Population: Start by conducting thorough research of your target population. Understand who they are, their characteristics, and subgroups within the population.
- Anticipate and Minimize Biases: Anticipate and address potential biases within the target population to help minimize their impact on the data. For example, will your sampling method accurately reflect all ages, gender, cultures, etc., of your target population? Are there barriers to participation for any subgroups? Your sampling method should allow you to capture the most accurate representation of your target population.
- Maintain Cost-Effective Practices: Consider the cost implications of your chosen sampling methods. Some sampling methods will require more resources, time, and effort. Your chosen sampling method should balance the cost factors with the ability to collect your data effectively and accurately.
- Consider Your Project’s Objectives: Tailor the sampling method to meet your specific objectives and constraints, such as M&E teams requiring real-time impact data and researchers needing representative samples for statistical analysis.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can make informed choices when selecting a sampling method, maximizing the quality and relevance of your data collection efforts.
5. Identify and train collectors
Not every data collection use case requires data collectors, but training individuals responsible for data collection becomes crucial in scenarios involving field presence.
The SurveyCTO platform supports both self-response survey modes and surveys that require a human field worker to do in-person interviews. Whether you’re hiring and training data collectors, utilizing an existing team, or training existing field staff, we offer comprehensive guidance and the right tools to ensure effective data collection practices.
Here are some common training approaches for data collectors:
- In-Class Training: Comprehensive sessions covering protocols, survey instruments, and best practices empower data collectors with skills and knowledge.
- Tests and Assessments: Assessments evaluate collectors’ understanding and competence, highlighting areas where additional support is needed.
- Mock Interviews: Simulated interviews refine collectors’ techniques and communication skills.
- Pre-Recorded Training Sessions: Accessible reinforcement and self-paced learning to refresh and stay updated.
Training data collectors is vital for successful data collection techniques. Your training should focus on proper instrument usage and effective interaction with respondents, including communication skills, cultural literacy, and ethical considerations.
Remember, training is an ongoing process. Knowledge gaps and issues may arise in the field, necessitating further training.
Moving Ahead: Iterative Steps in Data Collection

Once you’ve established the preliminary elements of your data collection process, you’re ready to start your data collection journey. In this section, we’ll delve into the specifics of designing and testing your instruments, collecting data, and organizing data while embracing the iterative nature of the data collection process, which requires diligent monitoring and making adjustments when needed.
6. Design and test your instruments
Designing effective data collection instruments like surveys and questionnaires is key. It’s crucial to prioritize respondent consent and privacy to ensure the integrity of your research. Thoughtful design and careful testing of survey questions are essential for optimizing research insights. Other critical considerations are:
- Clear and Unbiased Question Wording: Craft unambiguous, neutral questions free from bias to gather accurate and meaningful data. For example, instead of asking, “Shouldn’t we invest more into renewable energy that will combat the effects of climate change?” ask your question in a neutral way that allows the respondent to voice their thoughts. For example: “What are your thoughts on investing more in renewable energy?”
- Logical Ordering and Appropriate Response Format: Arrange questions logically and choose response formats (such as multiple-choice, Likert scale, or open-ended) that suit the nature of the data you aim to collect.
- Coverage of Relevant Topics: Ensure that your instrument covers all topics pertinent to your data collection goals while respecting cultural and social sensitivities. Make sure your instrument avoids assumptions, stereotypes, and languages or topics that could be considered offensive or taboo in certain contexts. The goal is to avoid marginalizing or offending respondents based on their social or cultural background.
- Collect Only Necessary Data: Design survey instruments that focus solely on gathering the data required for your research objectives, avoiding unnecessary information.
- Language(s) of the Respondent Population: Tailor your instruments to accommodate the languages your target respondents speak, offering translated versions if needed. Similarly, take into account accessibility for respondents who can’t read by offering alternative formats like images in place of text.
- Desired Length of Time for Completion: Respect respondents’ time by designing instruments that can be completed within a reasonable timeframe, balancing thoroughness with engagement. Having a general timeframe for the amount of time needed to complete a response will also help you weed out bad responses. For example, a response that was rushed and completed outside of your response timeframe could indicate a response that needs to be excluded.
- Collecting and Documenting Respondents’ Consent and Privacy: Ensure a robust consent process, transparent data usage communication, and privacy protection throughout data collection.
Perform Cognitive Interviewing
Cognitive interviewing is a method used to refine survey instruments and improve the accuracy of survey responses by evaluating how respondents understand, process, and respond to the instrument’s questions. In practice, cognitive interviewing involves an interview with the respondent, asking them to verbalize their thoughts as they interact with the instrument. By actively probing and observing their responses, you can identify and address ambiguities, ensuring accurate data collection.
Thoughtful question wording, well-organized response options, and logical sequencing enhance comprehension, minimize biases, and ensure accurate data collection. Iterative testing and refinement based on respondent feedback improve the validity, reliability, and actionability of insights obtained.
Put Your Instrument to the Test
Through rigorous testing, you can uncover flaws, ensure reliability, maximize accuracy, and validate your instrument’s performance. This can be achieved by:
- Conducting pilot testing to enhance the reliability and effectiveness of data collection. Administer the instrument, identify difficulties, gather feedback, and assess performance in real-world conditions.
- Making revisions based on pilot testing to enhance clarity, accuracy, usability, and participant satisfaction. Refine questions, instructions, and format for effective data collection.
- Continuously iterating and refining your instrument based on feedback and real-world testing. This ensures reliable, accurate, and audience-aligned methods of data collection. Additionally, this ensures your instrument adapts to changes, incorporates insights, and maintains ongoing effectiveness.
7. Collect your data
Now that you have your well-designed survey, interview questions, observation plan, or form, it’s time to implement it and gather the needed data. Data collection is not a one-and-done deal; it’s an ongoing process that demands attention to detail. Imagine spending weeks collecting data, only to discover later that a significant portion is unusable due to incomplete responses, improper collection methods, or falsified responses. To avoid such setbacks, adopt an iterative approach.
Leverage data collection tools with real-time monitoring to proactively identify outliers and issues. Take immediate action by fine-tuning your instruments, optimizing the data collection process, addressing concerns like additional training, or reevaluating personnel responsible for inaccurate data (for example, a field worker who sits in a coffee shop entering fake responses rather than doing the work of knocking on doors).
SurveyCTO’s Data Explorer was specifically designed to fulfill this requirement, empowering you to monitor incoming data, gain valuable insights, and know where changes may be needed. Embracing this iterative approach ensures ongoing improvement in data collection, resulting in more reliable and precise results.
8. Clean and organize your data
After data collection, the next step is to clean and organize the data to ensure its integrity and usability.
- Data Cleaning: This stage involves sifting through your data to identify and rectify any errors, inconsistencies, or missing values. It’s essential to maintain the accuracy of your data and ensure that it’s reliable for further analysis. Data cleaning can uncover duplicates, outliers, and gaps that could skew your results if left unchecked. With real-time data monitoring , this continuous cleaning process keeps your data precise and current throughout the data collection period. Similarly, review and corrections workflows allow you to monitor the quality of your incoming data.
- Organizing Your Data: Post-cleaning, it’s time to organize your data for efficient analysis and interpretation. Labeling your data using appropriate codes or categorizations can simplify navigation and streamline the extraction of insights. When you use a survey or form, labeling your data is often not necessary because you can design the instrument to collect in the right categories or return the right codes. An organized dataset is easier to manage, analyze, and interpret, ensuring that your collection efforts are not wasted but lead to valuable, actionable insights.
Remember, each stage of the data collection process, from design to cleaning, is iterative and interconnected. By diligently cleaning and organizing your data, you are setting the stage for robust, meaningful analysis that can inform your data-driven decisions and actions.
What happens after data collection?

The data collection journey takes us next into data analysis, where you’ll uncover patterns, empowering informed decision-making for researchers, evaluation teams, and field personnel.
Process and Analyze Your Data
Explore data through statistical and qualitative techniques to discover patterns, correlations, and insights during this pivotal stage. It’s about extracting the essence of your data and translating numbers into knowledge. Whether applying descriptive statistics, conducting regression analysis, or using thematic coding for qualitative data, this process drives decision-making and charts the path toward actionable outcomes.
Interpret and Report Your Results
Interpreting and reporting your data brings meaning and context to the numbers. Translating raw data into digestible insights for informed decision-making and effective stakeholder communication is critical.
The approach to interpretation and reporting varies depending on the perspective and role:
- Researchers often lean heavily on statistical methods to identify trends, extract meaningful conclusions, and share their findings in academic circles, contributing to their knowledge pool.
- M&E teams typically produce comprehensive reports, shedding light on the effectiveness and impact of programs. These reports guide internal and sometimes external stakeholders, supporting informed decisions and driving program improvements.
Field teams provide a first-hand perspective. Since they are often the first to see the results of the practical implementation of data, field teams are instrumental in providing immediate feedback loops on project initiatives. Field teams do the work that provides context to help research and M&E teams understand external factors like the local environment, cultural nuances, and logistical challenges that impact data results.
Safely store and handle data
Throughout the data collection process, and after it has been collected, it is vital to follow best practices for storing and handling data to ensure the integrity of your research. While the specifics of how to best store and handle data will depend on your project, here are some important guidelines to keep in mind:
- Use cloud storage to hold your data if possible, since this is safer than storing data on hard drives and keeps it more accessible,
- Periodically back up and purge old data from your system, since it’s safer to not retain data longer than necessary,
- If you use mobile devices to collect and store data, use options for private, internal apps-specific storage if and when possible,
- Restrict access to stored data to only those who need to work with that data.
Further considerations for data safety are discussed below in the section on data security .
Remember to uphold ethical standards in interpreting and reporting your data, regardless of your role. Clear communication, respectful handling of sensitive information, and adhering to confidentiality and privacy rights are all essential to fostering trust, promoting transparency, and bolstering your work’s credibility.
Common Data Collection Challenges

Data collection is vital to data-driven initiatives, but it comes with challenges. Addressing common challenges such as poor data quality, privacy concerns, inadequate sample sizes, and bias is essential to ensure the collected data is reliable, trustworthy, and secure.
In this section, we’ll explore three major challenges: data quality and consistency issues, data security concerns, and limitations with offline data collection , along with strategies to overcome them.
Data Quality and Consistency
Data quality and consistency refer to data accuracy and reliability throughout the collection and analysis process.
Challenges such as incomplete or missing data, data entry errors, measurement errors, and data coding/categorization errors can impact the integrity and usefulness of the data.
To navigate these complexities and maintain high standards, consistency, and integrity in the dataset:
- Implement robust data validation processes,
- Ensure proper training for data entry personnel,
- Employ automated data validation techniques, and
- Conduct regular data quality audits.
Data security
Data security encompasses safeguarding data through ensuring data privacy and confidentiality, securing storage and backup, and controlling data sharing and access.
Challenges include the risk of potential breaches, unauthorized access, and the need to comply with data protection regulations.
To address these setbacks and maintain privacy, trust, and confidence during the data collection process:
- Use encryption and authentication methods,
- Implement robust security protocols,
- Update security measures regularly,
- Provide employee training on data security, and
- Adopt secure cloud storage solutions.
Offline Data Collection
Offline data collection refers to the process of gathering data using modes like mobile device-based computer-assisted personal interviewing (CAPI) when t here is an inconsistent or unreliable internet connection, and the data collection tool being used for CAPI has the functionality to work offline.
Challenges associated with offline data collection include synchronization issues, difficulty transferring data, and compatibility problems between devices, and data collection tools.
To overcome these challenges and enable efficient and reliable offline data collection processes, employ the following strategies:
- Leverage offline-enabled data collection apps or tools that enable you to survey respondents even when there’s no internet connection, and upload data to a central repository at a later time.
- Your data collection plan should include times for periodic data synchronization when connectivity is available,
- Use offline, device-based storage for seamless data transfer and compatibility, and
- Provide clear instructions to field personnel on handling offline data collection scenarios.
Utilizing Technology in Data Collection

Embracing technology throughout your data collection process can help you overcome many challenges described in the previous section. Data collection tools can streamline your data collection, improve the quality and security of your data, and facilitate the analysis of your data. Let’s look at two broad categories of tools that are essential for data collection:
Data Collection, Entry, & Management Tools
These tools help with data collection, input, and organization. They can range from digital survey platforms to comprehensive database systems, allowing you to gather, enter, and manage your data effectively. They can significantly simplify the data collection process, minimize human error, and offer practical ways to organize and manage large volumes of data. Some of these tools are:
- Microsoft Office
- Google Docs
- SurveyMonkey
- Google Forms
Data Analysis, Visualization, Reporting, & Workflow Tools
These tools assist in processing and interpreting the collected data. They provide a way to visualize data in a user-friendly format, making it easier to identify trends and patterns. These tools can also generate comprehensive reports to share your findings with stakeholders and help manage your workflow efficiently. By automating complex tasks, they can help ensure accuracy and save time. Tools for these purposes include:
- Google sheets
Data collection tools like SurveyCTO often have integrations to help users seamlessly transition from data collection to data analysis, visualization, reporting, and managing workflows.
Master Your Data Collection Process With SurveyCTO
As we bring this guide to a close, you now possess a wealth of knowledge to develop your data collection process. From understanding the significance of setting clear goals to the crucial process of selecting your data collection methods and addressing common challenges, you are equipped to handle the intricate details of this dynamic process.
Remember, you’re not venturing into this complex process alone. At SurveyCTO, we offer not just a tool but an entire support system committed to your success. Beyond troubleshooting support, our success team serves as research advisors and expert partners, ready to provide guidance at every stage of your data collection journey.
With SurveyCTO , you can design flexible surveys in Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets, collect data online and offline with above-industry-standard security, monitor your data in real time, and effortlessly export it for further analysis in any tool of your choice. You also get access to our Data Explorer, which allows you to visualize incoming data at both individual survey and aggregate levels instantly.
In the iterative data collection process, our users tell us that SurveyCTO stands out with its capacity to establish review and correction workflows. It enables you to monitor incoming data and configure automated quality checks to flag error-prone submissions.
Finally, data security is of paramount importance to us. We ensure best-in-class security measures like SOC 2 compliance, end-to-end encryption, single sign-on (SSO), GDPR-compliant setups, customizable user roles, and self-hosting options to keep your data safe.
As you embark on your data collection journey, you can count on SurveyCTO’s experience and expertise to be by your side every step of the way. Our team would be excited and honored to be a part of your research project, offering you the tools and processes to gain informative insights and make effective decisions. Partner with us today and revolutionize the way you collect data.
Better data, better decision making, better world.

INTEGRATIONS
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
7 Data Collection Methods in Business Analytics

- 02 Dec 2021
Data is being generated at an ever-increasing pace. According to Statista , the total volume of data was 64.2 zettabytes in 2020; it’s predicted to reach 181 zettabytes by 2025. This abundance of data can be overwhelming if you aren’t sure where to start.
So, how do you ensure the data you use is relevant and important to the business problems you aim to solve? After all, a data-driven decision is only as strong as the data it’s based on. One way is to collect data yourself.
Here’s a breakdown of data types, why data collection is important, what to know before you begin collecting, and seven data collection methods to leverage.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Data Collection?
Data collection is the methodological process of gathering information about a specific subject. It’s crucial to ensure your data is complete during the collection phase and that it’s collected legally and ethically . If not, your analysis won’t be accurate and could have far-reaching consequences.
In general, there are three types of consumer data:
- First-party data , which is collected directly from users by your organization
- Second-party data , which is data shared by another organization about its customers (or its first-party data)
- Third-party data , which is data that’s been aggregated and rented or sold by organizations that don’t have a connection to your company or users
Although there are use cases for second- and third-party data, first-party data (data you’ve collected yourself) is more valuable because you receive information about how your audience behaves, thinks, and feels—all from a trusted source.
Data can be qualitative (meaning contextual in nature) or quantitative (meaning numeric in nature). Many data collection methods apply to either type, but some are better suited to one over the other.
In the data life cycle , data collection is the second step. After data is generated, it must be collected to be of use to your team. After that, it can be processed, stored, managed, analyzed, and visualized to aid in your organization’s decision-making.

Before collecting data, there are several factors you need to define:
- The question you aim to answer
- The data subject(s) you need to collect data from
- The collection timeframe
- The data collection method(s) best suited to your needs
The data collection method you select should be based on the question you want to answer, the type of data you need, your timeframe, and your company’s budget.
The Importance of Data Collection
Collecting data is an integral part of a business’s success; it can enable you to ensure the data’s accuracy, completeness, and relevance to your organization and the issue at hand. The information gathered allows organizations to analyze past strategies and stay informed on what needs to change.
The insights gleaned from data can make you hyperaware of your organization’s efforts and give you actionable steps to improve various strategies—from altering marketing strategies to assessing customer complaints.
Basing decisions on inaccurate data can have far-reaching negative consequences, so it’s important to be able to trust your own data collection procedures and abilities. By ensuring accurate data collection, business professionals can feel secure in their business decisions.
Explore the options in the next section to see which data collection method is the best fit for your company.
7 Data Collection Methods Used in Business Analytics
Surveys are physical or digital questionnaires that gather both qualitative and quantitative data from subjects. One situation in which you might conduct a survey is gathering attendee feedback after an event. This can provide a sense of what attendees enjoyed, what they wish was different, and areas in which you can improve or save money during your next event for a similar audience.
While physical copies of surveys can be sent out to participants, online surveys present the opportunity for distribution at scale. They can also be inexpensive; running a survey can cost nothing if you use a free tool. If you wish to target a specific group of people, partnering with a market research firm to get the survey in front of that demographic may be worth the money.
Something to watch out for when crafting and running surveys is the effect of bias, including:
- Collection bias : It can be easy to accidentally write survey questions with a biased lean. Watch out for this when creating questions to ensure your subjects answer honestly and aren’t swayed by your wording.
- Subject bias : Because your subjects know their responses will be read by you, their answers may be biased toward what seems socially acceptable. For this reason, consider pairing survey data with behavioral data from other collection methods to get the full picture.
Related: 3 Examples of Bad Survey Questions & How to Fix Them
2. Transactional Tracking
Each time your customers make a purchase, tracking that data can allow you to make decisions about targeted marketing efforts and understand your customer base better.
Often, e-commerce and point-of-sale platforms allow you to store data as soon as it’s generated, making this a seamless data collection method that can pay off in the form of customer insights.
3. Interviews and Focus Groups
Interviews and focus groups consist of talking to subjects face-to-face about a specific topic or issue. Interviews tend to be one-on-one, and focus groups are typically made up of several people. You can use both to gather qualitative and quantitative data.
Through interviews and focus groups, you can gather feedback from people in your target audience about new product features. Seeing them interact with your product in real-time and recording their reactions and responses to questions can provide valuable data about which product features to pursue.
As is the case with surveys, these collection methods allow you to ask subjects anything you want about their opinions, motivations, and feelings regarding your product or brand. It also introduces the potential for bias. Aim to craft questions that don’t lead them in one particular direction.
One downside of interviewing and conducting focus groups is they can be time-consuming and expensive. If you plan to conduct them yourself, it can be a lengthy process. To avoid this, you can hire a market research facilitator to organize and conduct interviews on your behalf.
4. Observation
Observing people interacting with your website or product can be useful for data collection because of the candor it offers. If your user experience is confusing or difficult, you can witness it in real-time.
Yet, setting up observation sessions can be difficult. You can use a third-party tool to record users’ journeys through your site or observe a user’s interaction with a beta version of your site or product.
While less accessible than other data collection methods, observations enable you to see firsthand how users interact with your product or site. You can leverage the qualitative and quantitative data gleaned from this to make improvements and double down on points of success.

5. Online Tracking
To gather behavioral data, you can implement pixels and cookies. These are both tools that track users’ online behavior across websites and provide insight into what content they’re interested in and typically engage with.
You can also track users’ behavior on your company’s website, including which parts are of the highest interest, whether users are confused when using it, and how long they spend on product pages. This can enable you to improve the website’s design and help users navigate to their destination.
Inserting a pixel is often free and relatively easy to set up. Implementing cookies may come with a fee but could be worth it for the quality of data you’ll receive. Once pixels and cookies are set, they gather data on their own and don’t need much maintenance, if any.
It’s important to note: Tracking online behavior can have legal and ethical privacy implications. Before tracking users’ online behavior, ensure you’re in compliance with local and industry data privacy standards .
Online forms are beneficial for gathering qualitative data about users, specifically demographic data or contact information. They’re relatively inexpensive and simple to set up, and you can use them to gate content or registrations, such as webinars and email newsletters.
You can then use this data to contact people who may be interested in your product, build out demographic profiles of existing customers, and in remarketing efforts, such as email workflows and content recommendations.
Related: What Is Marketing Analytics?
7. Social Media Monitoring
Monitoring your company’s social media channels for follower engagement is an accessible way to track data about your audience’s interests and motivations. Many social media platforms have analytics built in, but there are also third-party social platforms that give more detailed, organized insights pulled from multiple channels.
You can use data collected from social media to determine which issues are most important to your followers. For instance, you may notice that the number of engagements dramatically increases when your company posts about its sustainability efforts.

Building Your Data Capabilities
Understanding the variety of data collection methods available can help you decide which is best for your timeline, budget, and the question you’re aiming to answer. When stored together and combined, multiple data types collected through different methods can give an informed picture of your subjects and help you make better business decisions.
Do you want to become a data-driven professional? Explore our eight-week Business Analytics course and our three-course Credential of Readiness (CORe) program to deepen your analytical skills and apply them to real-world business problems. Not sure which course is right for you? Download our free flowchart .
This post was updated on October 17, 2022. It was originally published on December 2, 2021.

About the Author
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips

What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
Published on 25 February 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 10 October 2022.
Your research methodology discusses and explains the data collection and analysis methods you used in your research. A key part of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, the methodology chapter explains what you did and how you did it, allowing readers to evaluate the reliability and validity of your research.
It should include:
- The type of research you conducted
- How you collected and analysed your data
- Any tools or materials you used in the research
- Why you chose these methods
- Your methodology section should generally be written in the past tense .
- Academic style guides in your field may provide detailed guidelines on what to include for different types of studies.
- Your citation style might provide guidelines for your methodology section (e.g., an APA Style methods section ).
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
How to write a research methodology, why is a methods section important, step 1: explain your methodological approach, step 2: describe your data collection methods, step 3: describe your analysis method, step 4: evaluate and justify the methodological choices you made, tips for writing a strong methodology chapter, frequently asked questions about methodology.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Your methods section is your opportunity to share how you conducted your research and why you chose the methods you chose. It’s also the place to show that your research was rigorously conducted and can be replicated .
It gives your research legitimacy and situates it within your field, and also gives your readers a place to refer to if they have any questions or critiques in other sections.
You can start by introducing your overall approach to your research. You have two options here.
Option 1: Start with your “what”
What research problem or question did you investigate?
- Aim to describe the characteristics of something?
- Explore an under-researched topic?
- Establish a causal relationship?
And what type of data did you need to achieve this aim?
- Quantitative data , qualitative data , or a mix of both?
- Primary data collected yourself, or secondary data collected by someone else?
- Experimental data gathered by controlling and manipulating variables, or descriptive data gathered via observations?
Option 2: Start with your “why”
Depending on your discipline, you can also start with a discussion of the rationale and assumptions underpinning your methodology. In other words, why did you choose these methods for your study?
- Why is this the best way to answer your research question?
- Is this a standard methodology in your field, or does it require justification?
- Were there any ethical considerations involved in your choices?
- What are the criteria for validity and reliability in this type of research ?
Once you have introduced your reader to your methodological approach, you should share full details about your data collection methods .
Quantitative methods
In order to be considered generalisable, you should describe quantitative research methods in enough detail for another researcher to replicate your study.
Here, explain how you operationalised your concepts and measured your variables. Discuss your sampling method or inclusion/exclusion criteria, as well as any tools, procedures, and materials you used to gather your data.
Surveys Describe where, when, and how the survey was conducted.
- How did you design the questionnaire?
- What form did your questions take (e.g., multiple choice, Likert scale )?
- Were your surveys conducted in-person or virtually?
- What sampling method did you use to select participants?
- What was your sample size and response rate?
Experiments Share full details of the tools, techniques, and procedures you used to conduct your experiment.
- How did you design the experiment ?
- How did you recruit participants?
- How did you manipulate and measure the variables ?
- What tools did you use?
Existing data Explain how you gathered and selected the material (such as datasets or archival data) that you used in your analysis.
- Where did you source the material?
- How was the data originally produced?
- What criteria did you use to select material (e.g., date range)?
The survey consisted of 5 multiple-choice questions and 10 questions measured on a 7-point Likert scale.
The goal was to collect survey responses from 350 customers visiting the fitness apparel company’s brick-and-mortar location in Boston on 4–8 July 2022, between 11:00 and 15:00.
Here, a customer was defined as a person who had purchased a product from the company on the day they took the survey. Participants were given 5 minutes to fill in the survey anonymously. In total, 408 customers responded, but not all surveys were fully completed. Due to this, 371 survey results were included in the analysis.
Qualitative methods
In qualitative research , methods are often more flexible and subjective. For this reason, it’s crucial to robustly explain the methodology choices you made.
Be sure to discuss the criteria you used to select your data, the context in which your research was conducted, and the role you played in collecting your data (e.g., were you an active participant, or a passive observer?)
Interviews or focus groups Describe where, when, and how the interviews were conducted.
- How did you find and select participants?
- How many participants took part?
- What form did the interviews take ( structured , semi-structured , or unstructured )?
- How long were the interviews?
- How were they recorded?
Participant observation Describe where, when, and how you conducted the observation or ethnography .
- What group or community did you observe? How long did you spend there?
- How did you gain access to this group? What role did you play in the community?
- How long did you spend conducting the research? Where was it located?
- How did you record your data (e.g., audiovisual recordings, note-taking)?
Existing data Explain how you selected case study materials for your analysis.
- What type of materials did you analyse?
- How did you select them?
In order to gain better insight into possibilities for future improvement of the fitness shop’s product range, semi-structured interviews were conducted with 8 returning customers.
Here, a returning customer was defined as someone who usually bought products at least twice a week from the store.
Surveys were used to select participants. Interviews were conducted in a small office next to the cash register and lasted approximately 20 minutes each. Answers were recorded by note-taking, and seven interviews were also filmed with consent. One interviewee preferred not to be filmed.
Mixed methods
Mixed methods research combines quantitative and qualitative approaches. If a standalone quantitative or qualitative study is insufficient to answer your research question, mixed methods may be a good fit for you.
Mixed methods are less common than standalone analyses, largely because they require a great deal of effort to pull off successfully. If you choose to pursue mixed methods, it’s especially important to robustly justify your methods here.
Next, you should indicate how you processed and analysed your data. Avoid going into too much detail: you should not start introducing or discussing any of your results at this stage.
In quantitative research , your analysis will be based on numbers. In your methods section, you can include:
- How you prepared the data before analysing it (e.g., checking for missing data , removing outliers , transforming variables)
- Which software you used (e.g., SPSS, Stata or R)
- Which statistical tests you used (e.g., two-tailed t test , simple linear regression )
In qualitative research, your analysis will be based on language, images, and observations (often involving some form of textual analysis ).
Specific methods might include:
- Content analysis : Categorising and discussing the meaning of words, phrases and sentences
- Thematic analysis : Coding and closely examining the data to identify broad themes and patterns
- Discourse analysis : Studying communication and meaning in relation to their social context
Mixed methods combine the above two research methods, integrating both qualitative and quantitative approaches into one coherent analytical process.
Above all, your methodology section should clearly make the case for why you chose the methods you did. This is especially true if you did not take the most standard approach to your topic. In this case, discuss why other methods were not suitable for your objectives, and show how this approach contributes new knowledge or understanding.
In any case, it should be overwhelmingly clear to your reader that you set yourself up for success in terms of your methodology’s design. Show how your methods should lead to results that are valid and reliable, while leaving the analysis of the meaning, importance, and relevance of your results for your discussion section .
- Quantitative: Lab-based experiments cannot always accurately simulate real-life situations and behaviours, but they are effective for testing causal relationships between variables .
- Qualitative: Unstructured interviews usually produce results that cannot be generalised beyond the sample group , but they provide a more in-depth understanding of participants’ perceptions, motivations, and emotions.
- Mixed methods: Despite issues systematically comparing differing types of data, a solely quantitative study would not sufficiently incorporate the lived experience of each participant, while a solely qualitative study would be insufficiently generalisable.
Remember that your aim is not just to describe your methods, but to show how and why you applied them. Again, it’s critical to demonstrate that your research was rigorously conducted and can be replicated.
1. Focus on your objectives and research questions
The methodology section should clearly show why your methods suit your objectives and convince the reader that you chose the best possible approach to answering your problem statement and research questions .
2. Cite relevant sources
Your methodology can be strengthened by referencing existing research in your field. This can help you to:
- Show that you followed established practice for your type of research
- Discuss how you decided on your approach by evaluating existing research
- Present a novel methodological approach to address a gap in the literature
3. Write for your audience
Consider how much information you need to give, and avoid getting too lengthy. If you are using methods that are standard for your discipline, you probably don’t need to give a lot of background or justification.
Regardless, your methodology should be a clear, well-structured text that makes an argument for your approach, not just a list of technical details and procedures.
Methodology refers to the overarching strategy and rationale of your research. Developing your methodology involves studying the research methods used in your field and the theories or principles that underpin them, in order to choose the approach that best matches your objectives.
Methods are the specific tools and procedures you use to collect and analyse data (e.g. interviews, experiments , surveys , statistical tests ).
In a dissertation or scientific paper, the methodology chapter or methods section comes after the introduction and before the results , discussion and conclusion .
Depending on the length and type of document, you might also include a literature review or theoretical framework before the methodology.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population. Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research.
For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
Statistical sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population. There are various sampling methods you can use to ensure that your sample is representative of the population as a whole.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved 29 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/methodology/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Grad Med Educ
- v.8(2); 2016 May
Design: Selection of Data Collection Methods
Associated data.
Editor's Note: The online version of this article contains resources for further reading and a table of strengths and limitations of qualitative data collection methods.
The Challenge
Imagine that residents in your program have been less than complimentary about interprofessional rounds (IPRs). The program director asks you to determine what residents are learning about in collaboration with other health professionals during IPRs. If you construct a survey asking Likert-type questions such as “How much are you learning?” you likely will not gather the information you need to answer this question. You understand that qualitative data deal with words rather than numbers and could provide the needed answers. How do you collect “good” words? Should you use open-ended questions in a survey format? Should you conduct interviews, focus groups, or conduct direct observation? What should you consider when making these decisions?
Introduction
Qualitative research is often employed when there is a problem and no clear solutions exist, as in the case above that elicits the following questions: Why are residents complaining about rounds? How could we make rounds better? In this context, collecting “good” information or words (qualitative data) is intended to produce information that helps you to answer your research questions, capture the phenomenon of interest, and account for context and the rich texture of the human experience. You may also aim to challenge previous thinking and invite further inquiry.
Coherence or alignment between all aspects of the research project is essential. In this Rip Out we focus on data collection, but in qualitative research, the entire project must be considered. 1 , 2 Careful design of the data collection phase requires the following: deciding who will do what, where, when, and how at the different stages of the research process; acknowledging the role of the researcher as an instrument of data collection; and carefully considering the context studied and the participants and informants involved in the research.
Types of Data Collection Methods
Data collection methods are important, because how the information collected is used and what explanations it can generate are determined by the methodology and analytical approach applied by the researcher. 1 , 2 Five key data collection methods are presented here, with their strengths and limitations described in the online supplemental material.
- 1 Questions added to surveys to obtain qualitative data typically are open-ended with a free-text format. Surveys are ideal for documenting perceptions, attitudes, beliefs, or knowledge within a clear, predetermined sample of individuals. “Good” open-ended questions should be specific enough to yield coherent responses across respondents, yet broad enough to invite a spectrum of answers. Examples for this scenario include: What is the function of IPRs? What is the educational value of IPRs, according to residents? Qualitative survey data can be analyzed using a range of techniques.
- 2 Interviews are used to gather information from individuals 1-on-1, using a series of predetermined questions or a set of interest areas. Interviews are often recorded and transcribed. They can be structured or unstructured; they can either follow a tightly written script that mimics a survey or be inspired by a loose set of questions that invite interviewees to express themselves more freely. Interviewers need to actively listen and question, probe, and prompt further to collect richer data. Interviews are ideal when used to document participants' accounts, perceptions of, or stories about attitudes toward and responses to certain situations or phenomena. Interview data are often used to generate themes , theories , and models . Many research questions that can be answered with surveys can also be answered through interviews, but interviews will generally yield richer, more in-depth data than surveys. Interviews do, however, require more time and resources to conduct and analyze. Importantly, because interviewers are the instruments of data collection, interviewers should be trained to collect comparable data. The number of interviews required depends on the research question and the overarching methodology used. Examples of these questions include: How do residents experience IPRs? What do residents' stories about IPRs tell us about interprofessional care hierarchies?
- 3 Focus groups are used to gather information in a group setting, either through predetermined interview questions that the moderator asks of participants in turn or through a script to stimulate group conversations. Ideally, they are used when the sum of a group of people's experiences may offer more than a single individual's experiences in understanding social phenomena. Focus groups also allow researchers to capture participants' reactions to the comments and perspectives shared by other participants, and are thus a way to capture similarities and differences in viewpoints. The number of focus groups required will vary based on the questions asked and the number of different stakeholders involved, such as residents, nurses, social workers, pharmacists, and patients. The optimal number of participants per focus group, to generate rich discussion while enabling all members to speak, is 8 to 10 people. 3 Examples of questions include: How would residents, nurses, and pharmacists redesign or improve IPRs to maximize engagement, participation, and use of time? How do suggestions compare across professional groups?
- 4 Observations are used to gather information in situ using the senses: vision, hearing, touch, and smell. Observations allow us to investigate and document what people do —their everyday behavior—and to try to understand why they do it, rather than focus on their own perceptions or recollections. Observations are ideal when used to document, explore, and understand, as they occur, activities, actions, relationships, culture, or taken-for-granted ways of doing things. As with the previous methods, the number of observations required will depend on the research question and overarching research approach used. Examples of research questions include: How do residents use their time during IPRs? How do they relate to other health care providers? What kind of language and body language are used to describe patients and their families during IPRs?
- 5 Textual or content analysis is ideal when used to investigate changes in official, institutional, or organizational views on a specific topic or area to document the context of certain practices or to investigate the experiences and perspectives of a group of individuals who have, for example, engaged in written reflection. Textual analysis can be used as the main method in a research project or to contextualize findings from another method. The choice and number of documents has to be guided by the research question, but can include newspaper or research articles, governmental reports, organization policies and protocols, letters, records, films, photographs, art, meeting notes, or checklists. The development of a coding grid or scheme for analysis will be guided by the research question and will be iteratively applied to selected documents. Examples of research questions include: How do our local policies and protocols for IPRs reflect or contrast with the broader discourses of interprofessional collaboration? What are the perceived successful features of IPRs in the literature? What are the key features of residents' reflections on their interprofessional experiences during IPRs?
How You Can Start TODAY
- • Review medical education journals to find qualitative research in your area of interest and focus on the methods used as well as the findings.
- • When you have chosen a method, read several different sources on it.
- • From your readings, identify potential colleagues with expertise in your choice of qualitative method as well as others in your discipline who would like to learn more and organize potential working groups to discuss challenges that arise in your work.
What You Can Do LONG TERM
- • Either locally or nationally, build a community of like-minded scholars to expand your qualitative expertise.
- • Use a range of methods to develop a broad program of qualitative research.
Supplementary Material
How To Write The Methodology Chapter
The what, why & how explained simply (with examples).
By: Jenna Crossley (PhD) | Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | September 2021 (Updated April 2023)
So, you’ve pinned down your research topic and undertaken a review of the literature – now it’s time to write up the methodology section of your dissertation, thesis or research paper . But what exactly is the methodology chapter all about – and how do you go about writing one? In this post, we’ll unpack the topic, step by step .
Overview: The Methodology Chapter
- The purpose of the methodology chapter
- Why you need to craft this chapter (really) well
- How to write and structure the chapter
- Methodology chapter example
- Essential takeaways
What (exactly) is the methodology chapter?
The methodology chapter is where you outline the philosophical underpinnings of your research and outline the specific methodological choices you’ve made. The point of the methodology chapter is to tell the reader exactly how you designed your study and, just as importantly, why you did it this way.
Importantly, this chapter should comprehensively describe and justify all the methodological choices you made in your study. For example, the approach you took to your research (i.e., qualitative, quantitative or mixed), who you collected data from (i.e., your sampling strategy), how you collected your data and, of course, how you analysed it. If that sounds a little intimidating, don’t worry – we’ll explain all these methodological choices in this post .

Why is the methodology chapter important?
The methodology chapter plays two important roles in your dissertation or thesis:
Firstly, it demonstrates your understanding of research theory, which is what earns you marks. A flawed research design or methodology would mean flawed results. So, this chapter is vital as it allows you to show the marker that you know what you’re doing and that your results are credible .
Secondly, the methodology chapter is what helps to make your study replicable. In other words, it allows other researchers to undertake your study using the same methodological approach, and compare their findings to yours. This is very important within academic research, as each study builds on previous studies.
The methodology chapter is also important in that it allows you to identify and discuss any methodological issues or problems you encountered (i.e., research limitations ), and to explain how you mitigated the impacts of these. Every research project has its limitations , so it’s important to acknowledge these openly and highlight your study’s value despite its limitations . Doing so demonstrates your understanding of research design, which will earn you marks. We’ll discuss limitations in a bit more detail later in this post, so stay tuned!
Need a helping hand?
How to write up the methodology chapter
First off, it’s worth noting that the exact structure and contents of the methodology chapter will vary depending on the field of research (e.g., humanities, chemistry or engineering) as well as the university . So, be sure to always check the guidelines provided by your institution for clarity and, if possible, review past dissertations from your university. Here we’re going to discuss a generic structure for a methodology chapter typically found in the sciences.
Before you start writing, it’s always a good idea to draw up a rough outline to guide your writing. Don’t just start writing without knowing what you’ll discuss where. If you do, you’ll likely end up with a disjointed, ill-flowing narrative . You’ll then waste a lot of time rewriting in an attempt to try to stitch all the pieces together. Do yourself a favour and start with the end in mind .
Section 1 – Introduction
As with all chapters in your dissertation or thesis, the methodology chapter should have a brief introduction. In this section, you should remind your readers what the focus of your study is, especially the research aims . As we’ve discussed many times on the blog, your methodology needs to align with your research aims, objectives and research questions. Therefore, it’s useful to frontload this component to remind the reader (and yourself!) what you’re trying to achieve.
In this section, you can also briefly mention how you’ll structure the chapter. This will help orient the reader and provide a bit of a roadmap so that they know what to expect. You don’t need a lot of detail here – just a brief outline will do.
Section 2 – The Methodology
The next section of your chapter is where you’ll present the actual methodology. In this section, you need to detail and justify the key methodological choices you’ve made in a logical, intuitive fashion. Importantly, this is the heart of your methodology chapter, so you need to get specific – don’t hold back on the details here. This is not one of those “less is more” situations.
Let’s take a look at the most common components you’ll likely need to cover.
Methodological Choice #1 – Research Philosophy
Research philosophy refers to the underlying beliefs (i.e., the worldview) regarding how data about a phenomenon should be gathered , analysed and used . The research philosophy will serve as the core of your study and underpin all of the other research design choices, so it’s critically important that you understand which philosophy you’ll adopt and why you made that choice. If you’re not clear on this, take the time to get clarity before you make any further methodological choices.
While several research philosophies exist, two commonly adopted ones are positivism and interpretivism . These two sit roughly on opposite sides of the research philosophy spectrum.
Positivism states that the researcher can observe reality objectively and that there is only one reality, which exists independently of the observer. As a consequence, it is quite commonly the underlying research philosophy in quantitative studies and is oftentimes the assumed philosophy in the physical sciences.
Contrasted with this, interpretivism , which is often the underlying research philosophy in qualitative studies, assumes that the researcher performs a role in observing the world around them and that reality is unique to each observer . In other words, reality is observed subjectively .
These are just two philosophies (there are many more), but they demonstrate significantly different approaches to research and have a significant impact on all the methodological choices. Therefore, it’s vital that you clearly outline and justify your research philosophy at the beginning of your methodology chapter, as it sets the scene for everything that follows.

Methodological Choice #2 – Research Type
The next thing you would typically discuss in your methodology section is the research type. The starting point for this is to indicate whether the research you conducted is inductive or deductive .
Inductive research takes a bottom-up approach , where the researcher begins with specific observations or data and then draws general conclusions or theories from those observations. Therefore these studies tend to be exploratory in terms of approach.
Conversely , d eductive research takes a top-down approach , where the researcher starts with a theory or hypothesis and then tests it using specific observations or data. Therefore these studies tend to be confirmatory in approach.
Related to this, you’ll need to indicate whether your study adopts a qualitative, quantitative or mixed approach. As we’ve mentioned, there’s a strong link between this choice and your research philosophy, so make sure that your choices are tightly aligned . When you write this section up, remember to clearly justify your choices, as they form the foundation of your study.
Methodological Choice #3 – Research Strategy
Next, you’ll need to discuss your research strategy (also referred to as a research design ). This methodological choice refers to the broader strategy in terms of how you’ll conduct your research, based on the aims of your study.
Several research strategies exist, including experimental , case studies , ethnography , grounded theory, action research , and phenomenology . Let’s take a look at two of these, experimental and ethnographic, to see how they contrast.
Experimental research makes use of the scientific method , where one group is the control group (in which no variables are manipulated ) and another is the experimental group (in which a specific variable is manipulated). This type of research is undertaken under strict conditions in a controlled, artificial environment (e.g., a laboratory). By having firm control over the environment, experimental research typically allows the researcher to establish causation between variables. Therefore, it can be a good choice if you have research aims that involve identifying causal relationships.
Ethnographic research , on the other hand, involves observing and capturing the experiences and perceptions of participants in their natural environment (for example, at home or in the office). In other words, in an uncontrolled environment. Naturally, this means that this research strategy would be far less suitable if your research aims involve identifying causation, but it would be very valuable if you’re looking to explore and examine a group culture, for example.
As you can see, the right research strategy will depend largely on your research aims and research questions – in other words, what you’re trying to figure out. Therefore, as with every other methodological choice, it’s essential to justify why you chose the research strategy you did.
Methodological Choice #4 – Time Horizon
The next thing you’ll need to detail in your methodology chapter is the time horizon. There are two options here: cross-sectional and longitudinal . In other words, whether the data for your study were all collected at one point in time (cross-sectional) or at multiple points in time (longitudinal).
The choice you make here depends again on your research aims, objectives and research questions. If, for example, you aim to assess how a specific group of people’s perspectives regarding a topic change over time , you’d likely adopt a longitudinal time horizon.
Another important factor to consider is simply whether you have the time necessary to adopt a longitudinal approach (which could involve collecting data over multiple months or even years). Oftentimes, the time pressures of your degree program will force your hand into adopting a cross-sectional time horizon, so keep this in mind.
Methodological Choice #5 – Sampling Strategy
Next, you’ll need to discuss your sampling strategy . There are two main categories of sampling, probability and non-probability sampling.
Probability sampling involves a random (and therefore representative) selection of participants from a population, whereas non-probability sampling entails selecting participants in a non-random (and therefore non-representative) manner. For example, selecting participants based on ease of access (this is called a convenience sample).
The right sampling approach depends largely on what you’re trying to achieve in your study. Specifically, whether you trying to develop findings that are generalisable to a population or not. Practicalities and resource constraints also play a large role here, as it can oftentimes be challenging to gain access to a truly random sample. In the video below, we explore some of the most common sampling strategies.
Methodological Choice #6 – Data Collection Method
Next up, you’ll need to explain how you’ll go about collecting the necessary data for your study. Your data collection method (or methods) will depend on the type of data that you plan to collect – in other words, qualitative or quantitative data.
Typically, quantitative research relies on surveys , data generated by lab equipment, analytics software or existing datasets. Qualitative research, on the other hand, often makes use of collection methods such as interviews , focus groups , participant observations, and ethnography.
So, as you can see, there is a tight link between this section and the design choices you outlined in earlier sections. Strong alignment between these sections, as well as your research aims and questions is therefore very important.
Methodological Choice #7 – Data Analysis Methods/Techniques
The final major methodological choice that you need to address is that of analysis techniques . In other words, how you’ll go about analysing your date once you’ve collected it. Here it’s important to be very specific about your analysis methods and/or techniques – don’t leave any room for interpretation. Also, as with all choices in this chapter, you need to justify each choice you make.
What exactly you discuss here will depend largely on the type of study you’re conducting (i.e., qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods). For qualitative studies, common analysis methods include content analysis , thematic analysis and discourse analysis . In the video below, we explain each of these in plain language.
For quantitative studies, you’ll almost always make use of descriptive statistics , and in many cases, you’ll also use inferential statistical techniques (e.g., correlation and regression analysis). In the video below, we unpack some of the core concepts involved in descriptive and inferential statistics.
In this section of your methodology chapter, it’s also important to discuss how you prepared your data for analysis, and what software you used (if any). For example, quantitative data will often require some initial preparation such as removing duplicates or incomplete responses . Similarly, qualitative data will often require transcription and perhaps even translation. As always, remember to state both what you did and why you did it.
Section 3 – The Methodological Limitations
With the key methodological choices outlined and justified, the next step is to discuss the limitations of your design. No research methodology is perfect – there will always be trade-offs between the “ideal” methodology and what’s practical and viable, given your constraints. Therefore, this section of your methodology chapter is where you’ll discuss the trade-offs you had to make, and why these were justified given the context.
Methodological limitations can vary greatly from study to study, ranging from common issues such as time and budget constraints to issues of sample or selection bias . For example, you may find that you didn’t manage to draw in enough respondents to achieve the desired sample size (and therefore, statistically significant results), or your sample may be skewed heavily towards a certain demographic, thereby negatively impacting representativeness .
In this section, it’s important to be critical of the shortcomings of your study. There’s no use trying to hide them (your marker will be aware of them regardless). By being critical, you’ll demonstrate to your marker that you have a strong understanding of research theory, so don’t be shy here. At the same time, don’t beat your study to death . State the limitations, why these were justified, how you mitigated their impacts to the best degree possible, and how your study still provides value despite these limitations .
Section 4 – Concluding Summary
Finally, it’s time to wrap up the methodology chapter with a brief concluding summary. In this section, you’ll want to concisely summarise what you’ve presented in the chapter. Here, it can be a good idea to use a figure to summarise the key decisions, especially if your university recommends using a specific model (for example, Saunders’ Research Onion ).
Importantly, this section needs to be brief – a paragraph or two maximum (it’s a summary, after all). Also, make sure that when you write up your concluding summary, you include only what you’ve already discussed in your chapter; don’t add any new information.

Methodology Chapter Example
In the video below, we walk you through an example of a high-quality research methodology chapter from a dissertation. We also unpack our free methodology chapter template so that you can see how best to structure your chapter.
Wrapping Up
And there you have it – the methodology chapter in a nutshell. As we’ve mentioned, the exact contents and structure of this chapter can vary between universities , so be sure to check in with your institution before you start writing. If possible, try to find dissertations or theses from former students of your specific degree program – this will give you a strong indication of the expectations and norms when it comes to the methodology chapter (and all the other chapters!).
Also, remember the golden rule of the methodology chapter – justify every choice ! Make sure that you clearly explain the “why” for every “what”, and reference credible methodology textbooks or academic sources to back up your justifications.
If you need a helping hand with your research methodology (or any other component of your research), be sure to check out our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through every step of the research journey. Until next time, good luck!

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

51 Comments
highly appreciated.
This was very helpful!
This was helpful
Thanks ,it is a very useful idea.
Thanks ,it is very useful idea.
Thank you so much, this information is very useful.
Thank you very much. I must say the information presented was succinct, coherent and invaluable. It is well put together and easy to comprehend. I have a great guide to create the research methodology for my dissertation.
Highly clear and useful.
I understand a bit on the explanation above. I want to have some coach but I’m still student and don’t have any budget to hire one. A lot of question I want to ask.
Thank you so much. This concluded my day plan. Thank you so much.
Thanks it was helpful
Great information. It would be great though if you could show us practical examples.
Thanks so much for this information. God bless and be with you
Thank you so so much. Indeed it was helpful
This is EXCELLENT!
I was totally confused by other explanations. Thank you so much!.
justdoing my research now , thanks for the guidance.
Thank uuuu! These contents are really valued for me!
This is powerful …I really like it
Highly useful and clear, thank you so much.
Highly appreciated. Good guide
That was helpful. Thanks
This is very useful.Thank you
Very helpful information. Thank you
This is exactly what I was looking for. The explanation is so detailed and easy to comprehend. Well done and thank you.
Great job. You just summarised everything in the easiest and most comprehensible way possible. Thanks a lot.
Thank you very much for the ideas you have given this will really help me a lot. Thank you and God Bless.
Such great effort …….very grateful thank you
Please accept my sincere gratitude. I have to say that the information that was delivered was congruent, concise, and quite helpful. It is clear and straightforward, making it simple to understand. I am in possession of an excellent manual that will assist me in developing the research methods for my dissertation.
Thank you for your great explanation. It really helped me construct my methodology paper.
thank you for simplifieng the methodoly, It was realy helpful
Very helpful!
Thank you for your great explanation.
The explanation I have been looking for. So clear Thank you
Thank you very much .this was more enlightening.
helped me create the in depth and thorough methodology for my dissertation
Thank you for the great explaination.please construct one methodology for me
I appreciate you for the explanation of methodology. Please construct one methodology on the topic: The effects influencing students dropout among schools for my thesis
This helped me complete my methods section of my dissertation with ease. I have managed to write a thorough and concise methodology!
its so good in deed
wow …what an easy to follow presentation. very invaluable content shared. utmost important.
Peace be upon you, I am Dr. Ahmed Khedr, a former part-time professor at Al-Azhar University in Cairo, Egypt. I am currently teaching research methods, and I have been dealing with your esteemed site for several years, and I found that despite my long experience with research methods sites, it is one of the smoothest sites for evaluating the material for students, For this reason, I relied on it a lot in teaching and translated most of what was written into Arabic and published it on my own page on Facebook. Thank you all… Everything I posted on my page is provided with the names of the writers of Grad coach, the title of the article, and the site. My best regards.
A remarkably simple and useful guide, thank you kindly.
I real appriciate your short and remarkable chapter summary
Bravo! Very helpful guide.
Only true experts could provide such helpful, fantastic, and inspiring knowledge about Methodology. Thank you very much! God be with you and us all!
highly appreciate your effort.
This is a very well thought out post. Very informative and a great read.
THANKS SO MUCH FOR SHARING YOUR NICE IDEA
I love you Emma, you are simply amazing with clear explanations with complete information. GradCoach really helped me to do my assignment here in Auckland. Mostly, Emma make it so simple and enjoyable
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

How to Write a Data Collection Plan (Templates and Examples Included)
In a world where data drives decisions, how do you make sure you're gathering the right information? With a clear data collection plan in place, you ensure that the collected data leads to actionable insights.
Effective data collection is key to smart decision-making, grounding strategies in solid evidence rather than guesses. A well-designed data collection plan guarantees that you're collecting not just any data, but the right data, crucial for spotting trends, refining processes, and deeply understanding customer needs in any sector.
By the end of this article, you'll understand the importance of planning your data collection and how to do it effectively.
What is a data collection plan?
A data collection plan is a roadmap for identifying what data you need, the ways in which you'll collect it, and how you'll analyze it. The core purpose is to ensure that your data collection is targeted, efficient, and reliable, providing meaningful insights for your project or study.
Data collection plans should be developed at the start of a project or study, before any data is collected. Typically, this responsibility falls to project leaders, researchers, data analysts, or a designated team member with expertise in data management.
What does a typical data collection plan document cover
From setting clear objectives to establishing robust communication channels, each section of the plan is a stepping stone towards having a thorough data collection strategy:
- Objectives: Start with a specific goal for your data collection. Clearly state why this data is crucial and how it will impact your project or decision-making. This step ensures that every part of your plan aligns with your end goal.
- Data typology: Decide whether you need quantitative (numerical) or qualitative (descriptive) data. Clarify the importance of each data type in the context of your objectives. This clarity helps in selecting the right tools and methods for data collection.
- Collection methodology: Select appropriate methods like surveys, interviews, or analysis of existing data. Prioritize data quality; for surveys, this means clear, unbiased questions; for interviews, standardized interviewing techniques; etc.
- Data management protocols: Plan for the storage, organization, and protection of your data. Address ethical considerations, especially for sensitive information. Include a system for updating and correcting data to maintain its accuracy over time.
- Project timeline : Outline a realistic timeline with start and end dates, including key milestones. Incorporate flexibility for unforeseen delays or challenges.
- Needed resources: Identify the team, tools, and budget required. Clearly define roles and responsibilities to ensure a smooth data collection process.
- Data analysis strategy: Determine how you'll analyze the collected data. Include methods for dealing with unexpected findings, like ambiguous, conflicting, corrupted, or incomplete data.
- Feedback mechanisms: Establish a mechanism for ongoing assessment and adjustment of your data collection methods. This allows you to adapt and refine your approach as needed.
- Communication framework: Decide how and when you'll communicate your findings. Depending on the project, you might need to keep stakeholders updated throughout the process, not just at the end, to maintain engagement and transparency.
Try to meticulously address each of these elements to set the stage for successful data gathering.
Ways to collect data
Collecting data is akin to gathering and sorting the pieces for a puzzle. Each piece, or data point, is critical to form a complete and accurate picture of the subject under study.
To ensure that this picture is as clear and precise as possible, researchers and analysts employ a variety of data collection methods outlined in the image below.
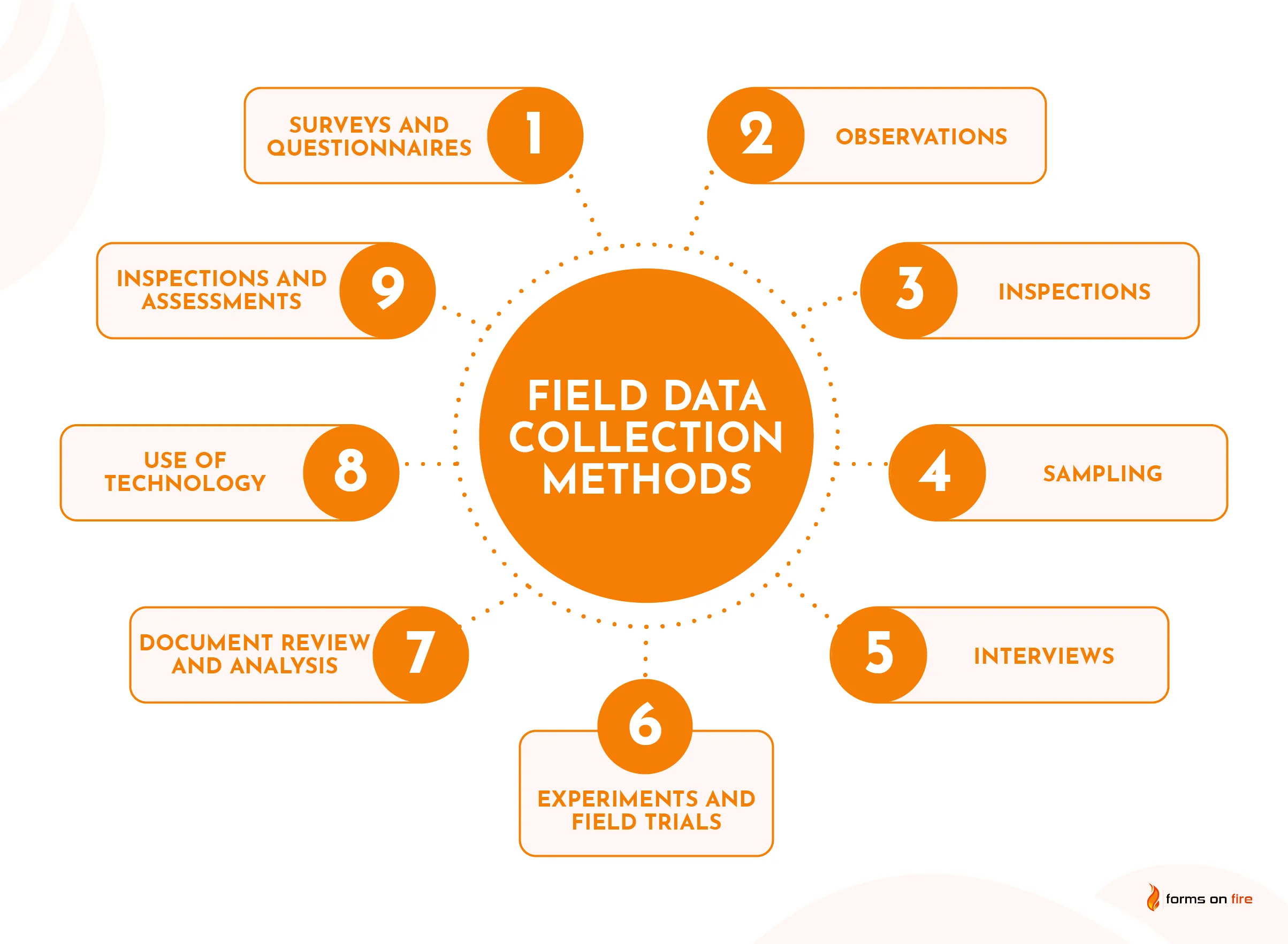
- Surveys and questionnaires: These involve asking structured questions to a large group of people. Consider the timing of your survey distribution — sending out surveys at a time when your target audience is likely to be available and attentive can significantly improve the response quality.
- Interviews: One-on-one conversations that allow for deep dives into subjects' thoughts and experiences. Record interviews (with permission) and note non-verbal cues. These can provide context often lost in written notes, like the respondent's tone or hesitation.
- Focus groups: Small groups of people discuss specific topics, providing qualitative data on opinions and behaviors. Use a skilled moderator who can encourage quieter members to speak up and keep dominant personalities from overtaking the conversation.
- Observations: Watching and recording behavior or events as they naturally occur. If possible, conduct observations at different times or in varied settings. This helps in understanding if the observed behavior is consistent or situation-dependent.
- Inspections and assessments: Examining objects, processes, or places in detail, often using a structured approach supported by pre-made checklists.
- Document review and analysis: Systematically reviewing and interpreting existing documents to extract data. Cross-reference information from different documents for a more comprehensive understanding. This triangulation can validate findings and reveal deeper insights.
Each of these methods offers a unique way to gather data and comes with its own set of pros and cons. Take your time to decide which data collection methods are the best fit for your use case.
Steps for writing an effective data collection plan
With the theory out of the way, let’s see how to write a proper data collection plan, step by step.
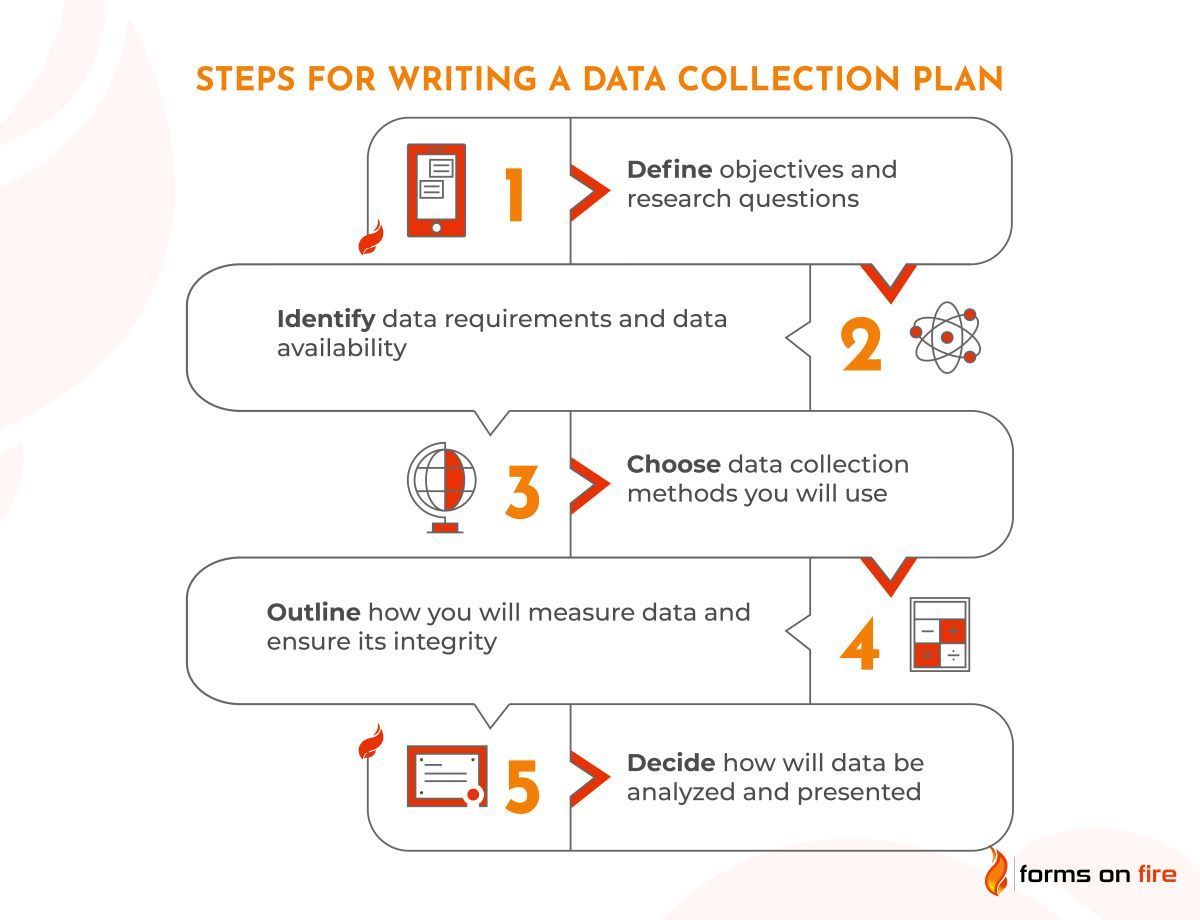
1. Define objectives and research questions
Write down a statement of purpose that explains what you intend to discover, decide, or achieve. This statement will act as the compass for your data collection journey.
Your research questions must be clear, focused, and aligned with your stated objectives. For every objective, draft at least one research question that, when answered, will bring you closer to your goal.
When finalizing your list of research questions, don't overlook the "so what?" factor. For each one, ask yourself what the implications are if the question is answered or the objective is met. How will it change your understanding, decision-making, or actions? This ensures that your plan has practical value and isn't just an academic exercise.
2. Identify data requirements and availability
Identifying your data requirements is a two-part process: you need to understand the type of data you need and assess the data that is already available to you.
Here's how to understand the type of data you need:
- Consider the nature of your research questions: What data will provide the answers? Is it demographic information, behavioral metrics, financial statistics, etc.?
- Determine the data quantity: How much data is enough to make your results reliable? This can depend on the statistical methods you plan to use and the scale of your project.
- Think about the data quality: What level of accuracy is required? Does the data need to be current, historical, or predictive?
Create a data inventory list. For each research question, list the types of data that could potentially answer it. Next to each type, note down the attributes of the data you need (timeframe, demographic details, granularity, etc.).
To assess the data that is already available to you, follow these:
- Look internally first: Does your organization already have some of the data you need? This could be sales records, customer feedback, or past survey results.
- Consider external sources: Is there public data available that fits your needs, such as government databases, research papers, or industry reports?
- Evaluate accessibility: Can you easily access this data, or are there barriers (e.g., paywalls, privacy laws, data sharing agreements) that you need to consider?
For each piece of required data, try to record its source, format, any costs associated with obtaining it, and any potential challenges in accessing it. If data is not available, note down what proxies could be used or whether secondary data collection is necessary.
Completing this step will form the backbone of your data collection strategy, guiding you on where to focus your resources.
3. Choose how you will collect data
Based on your data requirements, select the most suitable collection methods. Will you use surveys, interviews, observations, experiments, or a combination of multiple methods?
Match data collection methods to the type of data you need. For quantitative data, you might use surveys or sensor data. For qualitative data, consider interviews or focus groups. Think about the context of your research — does it call for controlled experiments, or would field studies yield better results?
Once you've selected a method, it's time to think about who will shoulder the task. The 'who' could range from your own team members to external professionals, depending on the expertise required.
Incorporate quality control measures right from the start. This should include when and where data will be collected, the tools or technologies used, and the step-by-step process for gathering the data.
Finally, address ethical considerations, especially if you’re dealing with human subjects or sensitive data. Obtain necessary permissions and ensure you’re compliant with relevant laws and regulations.
4. Outline how you will measure data and ensure its integrity
Clearly specify what you are measuring and how it will be quantified. Are you looking at frequencies, averages, percentages, or growth rates? Ensure that the chosen metrics align directly with your research questions and objectives.
Develop and document standardized procedures for data measurement: define operational terms, detail measurement techniques, and specify the equipment or software used.
For each variable, write down a clear operational definition, which is a detailed description of the procedures used to measure it . For example, if you're measuring customer satisfaction, define what constitutes satisfaction and the scale you're using (e.g., 1-5 likert scale ).
To ensure data integrity, team members tasked with collecting and analyzing data really need to know what they’re doing. If you’re using instruments or software, ensure they are calibrated and tested before data collection begins. Consider running a pilot study or trial to test your measurement processes and make adjustments where necessary. This helps you catch potential issues before you roll out large-scale data collection.
Create a data log that records when and by whom data was collected, entered, and verified. Make sure to regularly check a sample of data entries against the original data to ensure accuracy. If you’re using mobile forms or other digital tools to collect data, most of this can be automated.
Lastly, decide in advance how you will deal with missing data or outliers. Will you use imputation methods , or will you exclude it? Make sure your approach is consistent and documented.
5. Decide how will data be analyzed and presented
Outlines each step of your analysis process: the methods you'll use, the required tools, and the sequence of analysis.
Choose analysis methods that align with your data types and objectives. For analyzing quantitative data , statistical methods like regression analysis, ANOVA, or cluster analysis might be appropriate. For analyzing qualitative data , try content analysis, thematic analysis, or discourse analysis.

If you have a complex project and plan to use specific software to analyze data, decide which one that is going to be. Options could range from statistical software like SPSS or R for quantitative analysis to software like NVivo for qualitative data analysis.
Think about how you will present your data. This could be in the form of reports, infographics, dashboards, or presentations. Choose the format with your audience in mind — what format will be most clear and persuasive to them?
Try sketching out a draft of your final report or presentation early in the planning process. This helps you visualize the end product and ensure that your data collection and analysis will support this outcome.
Data collection plan examples and templates
Below are four different examples and templates you can use to build your own data collection plans.
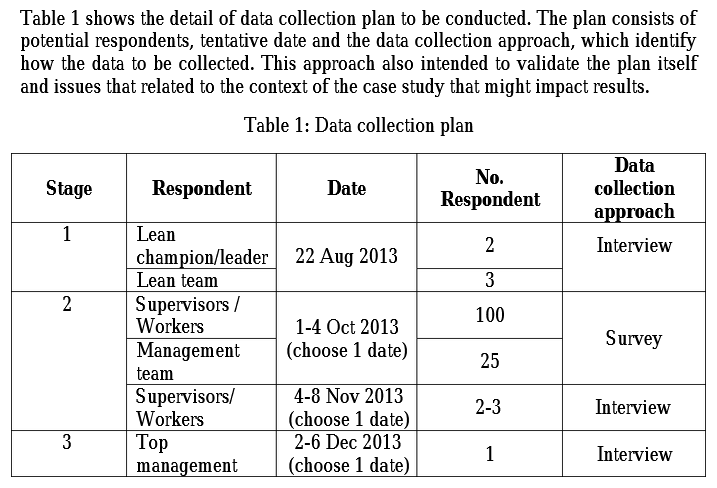
Streamline data collection process with Forms On Fire
Forms on Fire offers a flexible, accessible, and efficient platform for automating and simplifying data collection and management:
- Customizable forms and mobile accessibility: Design forms specific to your needs and capture data on the go, even offline, with mobile device support.
- Automated workflows and integration capabilities: Automate processes like notifications and data analysis upon form submission, while seamlessly integrating with over 1,500 systems.
- Real-time data access and reporting: Access and analyze data instantly for timely decision-making, trend spotting, and addressing issues quickly.
- Cloud-based data storage: Securely store all data in the cloud, ensuring safety and availability from any location at any time.
- User-friendly interface: Enjoy an intuitive platform that requires no coding skills, making it easy for anyone in your organization to create and use forms.
Ready to transform your data collection process? Start a free trial below or schedule a product demo and see how our solution can answer your data management needs!
+1 (425) 214-1920
10900 NE 4th Street, Suite 2300
Bellevue, WA 98004

© 2023 Forms On Fire, All Rights Reserved
Policy Center | Terms of Service | Privacy
- Privacy Policy

Home » Dissertation Methodology – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Dissertation Methodology – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
- Table of Contents

Dissertation Methodology
In any research, the methodology chapter is one of the key components of your dissertation. It provides a detailed description of the methods you used to conduct your research and helps readers understand how you obtained your data and how you plan to analyze it. This section is crucial for replicating the study and validating its results.
Here are the basic elements that are typically included in a dissertation methodology:
- Introduction : This section should explain the importance and goals of your research .
- Research Design : Outline your research approach and why it’s appropriate for your study. You might be conducting an experimental research, a qualitative research, a quantitative research, or a mixed-methods research.
- Data Collection : This section should detail the methods you used to collect your data. Did you use surveys, interviews, observations, etc.? Why did you choose these methods? You should also include who your participants were, how you recruited them, and any ethical considerations.
- Data Analysis : Explain how you intend to analyze the data you collected. This could include statistical analysis, thematic analysis, content analysis, etc., depending on the nature of your study.
- Reliability and Validity : Discuss how you’ve ensured the reliability and validity of your study. For instance, you could discuss measures taken to reduce bias, how you ensured that your measures accurately capture what they were intended to, or how you will handle any limitations in your study.
- Ethical Considerations : This is where you state how you have considered ethical issues related to your research, how you have protected the participants’ rights, and how you have complied with the relevant ethical guidelines.
- Limitations : Acknowledge any limitations of your methodology, including any biases and constraints that might have affected your study.
- Summary : Recap the key points of your methodology chapter, highlighting the overall approach and rationalization of your research.
Types of Dissertation Methodology
The type of methodology you choose for your dissertation will depend on the nature of your research question and the field you’re working in. Here are some of the most common types of methodologies used in dissertations:
Experimental Research
This involves creating an experiment that will test your hypothesis. You’ll need to design an experiment, manipulate variables, collect data, and analyze that data to draw conclusions. This is commonly used in fields like psychology, biology, and physics.
Survey Research
This type of research involves gathering data from a large number of participants using tools like questionnaires or surveys. It can be used to collect a large amount of data and is often used in fields like sociology, marketing, and public health.
Qualitative Research
This type of research is used to explore complex phenomena that can’t be easily quantified. Methods include interviews, focus groups, and observations. This methodology is common in fields like anthropology, sociology, and education.
Quantitative Research
Quantitative research uses numerical data to answer research questions. This can include statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques. It’s common in fields like economics, psychology, and health sciences.
Case Study Research
This type of research involves in-depth investigation of a particular case, such as an individual, group, or event. This methodology is often used in psychology, social sciences, and business.
Mixed Methods Research
This combines qualitative and quantitative research methods in a single study. It’s used to answer more complex research questions and is becoming more popular in fields like social sciences, health sciences, and education.
Action Research
This type of research involves taking action and then reflecting upon the results. This cycle of action-reflection-action continues throughout the study. It’s often used in fields like education and organizational development.
Longitudinal Research
This type of research involves studying the same group of individuals over an extended period of time. This could involve surveys, observations, or experiments. It’s common in fields like psychology, sociology, and medicine.
Ethnographic Research
This type of research involves the in-depth study of people and cultures. Researchers immerse themselves in the culture they’re studying to collect data. This is often used in fields like anthropology and social sciences.
Structure of Dissertation Methodology
The structure of a dissertation methodology can vary depending on your field of study, the nature of your research, and the guidelines of your institution. However, a standard structure typically includes the following elements:
- Introduction : Briefly introduce your overall approach to the research. Explain what you plan to explore and why it’s important.
- Research Design/Approach : Describe your overall research design. This can be qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods. Explain the rationale behind your chosen design and why it is suitable for your research questions or hypotheses.
- Data Collection Methods : Detail the methods you used to collect your data. You should include what type of data you collected, how you collected it, and why you chose this method. If relevant, you can also include information about your sample population, such as how many people participated, how they were chosen, and any relevant demographic information.
- Data Analysis Methods : Explain how you plan to analyze your collected data. This will depend on the nature of your data. For example, if you collected quantitative data, you might discuss statistical analysis techniques. If you collected qualitative data, you might discuss coding strategies, thematic analysis, or narrative analysis.
- Reliability and Validity : Discuss how you’ve ensured the reliability and validity of your research. This might include steps you took to reduce bias or increase the accuracy of your measurements.
- Ethical Considerations : If relevant, discuss any ethical issues associated with your research. This might include how you obtained informed consent from participants, how you ensured participants’ privacy and confidentiality, or any potential conflicts of interest.
- Limitations : Acknowledge any limitations in your research methodology. This could include potential sources of bias, difficulties with data collection, or limitations in your analysis methods.
- Summary/Conclusion : Briefly summarize the key points of your methodology, emphasizing how it helps answer your research questions or hypotheses.
How to Write Dissertation Methodology
Writing a dissertation methodology requires you to be clear and precise about the way you’ve carried out your research. It’s an opportunity to convince your readers of the appropriateness and reliability of your approach to your research question. Here is a basic guideline on how to write your methodology section:
1. Introduction
Start your methodology section by restating your research question(s) or objective(s). This ensures your methodology directly ties into the aim of your research.
2. Approach
Identify your overall approach: qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods. Explain why you have chosen this approach.
- Qualitative methods are typically used for exploratory research and involve collecting non-numerical data. This might involve interviews, observations, or analysis of texts.
- Quantitative methods are used for research that relies on numerical data. This might involve surveys, experiments, or statistical analysis.
- Mixed methods use a combination of both qualitative and quantitative research methods.
3. Research Design
Describe the overall design of your research. This could involve explaining the type of study (e.g., case study, ethnography, experimental research, etc.), how you’ve defined and measured your variables, and any control measures you’ve implemented.
4. Data Collection
Explain in detail how you collected your data.
- If you’ve used qualitative methods, you might detail how you selected participants for interviews or focus groups, how you conducted observations, or how you analyzed existing texts.
- If you’ve used quantitative methods, you might detail how you designed your survey or experiment, how you collected responses, and how you ensured your data is reliable and valid.
5. Data Analysis
Describe how you analyzed your data.
- If you’re doing qualitative research, this might involve thematic analysis, discourse analysis, or grounded theory.
- If you’re doing quantitative research, you might be conducting statistical tests, regression analysis, or factor analysis.
Discuss any ethical issues related to your research. This might involve explaining how you obtained informed consent, how you’re protecting participants’ privacy, or how you’re managing any potential harms to participants.
7. Reliability and Validity
Discuss the steps you’ve taken to ensure the reliability and validity of your data.
- Reliability refers to the consistency of your measurements, and you might discuss how you’ve piloted your instruments or used standardized measures.
- Validity refers to the accuracy of your measurements, and you might discuss how you’ve ensured your measures reflect the concepts they’re supposed to measure.
8. Limitations
Every study has its limitations. Discuss the potential weaknesses of your chosen methods and explain any obstacles you faced in your research.
9. Conclusion
Summarize the key points of your methodology, emphasizing how it helps to address your research question or objective.
Example of Dissertation Methodology
An Example of Dissertation Methodology is as follows:
Chapter 3: Methodology
- Introduction
This chapter details the methodology adopted in this research. The study aimed to explore the relationship between stress and productivity in the workplace. A mixed-methods research design was used to collect and analyze data.
Research Design
This study adopted a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative surveys with qualitative interviews to provide a comprehensive understanding of the research problem. The rationale for this approach is that while quantitative data can provide a broad overview of the relationships between variables, qualitative data can provide deeper insights into the nuances of these relationships.
Data Collection Methods
Quantitative Data Collection : An online self-report questionnaire was used to collect data from participants. The questionnaire consisted of two standardized scales: the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS) to measure stress levels and the Individual Work Productivity Questionnaire (IWPQ) to measure productivity. The sample consisted of 200 office workers randomly selected from various companies in the city.
Qualitative Data Collection : Semi-structured interviews were conducted with 20 participants chosen from the initial sample. The interview guide included questions about participants’ experiences with stress and how they perceived its impact on their productivity.
Data Analysis Methods
Quantitative Data Analysis : Descriptive and inferential statistics were used to analyze the survey data. Pearson’s correlation was used to examine the relationship between stress and productivity.
Qualitative Data Analysis : Interviews were transcribed and subjected to thematic analysis using NVivo software. This process allowed for identifying and analyzing patterns and themes regarding the impact of stress on productivity.
Reliability and Validity
To ensure reliability and validity, standardized measures with good psychometric properties were used. In qualitative data analysis, triangulation was employed by having two researchers independently analyze the data and then compare findings.
Ethical Considerations
All participants provided informed consent prior to their involvement in the study. They were informed about the purpose of the study, their rights as participants, and the confidentiality of their responses.
Limitations
The main limitation of this study is its reliance on self-report measures, which can be subject to biases such as social desirability bias. Moreover, the sample was drawn from a single city, which may limit the generalizability of the findings.
Where to Write Dissertation Methodology
In a dissertation or thesis, the Methodology section usually follows the Literature Review. This placement allows the Methodology to build upon the theoretical framework and existing research outlined in the Literature Review, and precedes the Results or Findings section. Here’s a basic outline of how most dissertations are structured:
- Acknowledgements
- Literature Review (or it may be interspersed throughout the dissertation)
- Methodology
- Results/Findings
- References/Bibliography
In the Methodology chapter, you will discuss the research design, data collection methods, data analysis methods, and any ethical considerations pertaining to your study. This allows your readers to understand how your research was conducted and how you arrived at your results.
Advantages of Dissertation Methodology
The dissertation methodology section plays an important role in a dissertation for several reasons. Here are some of the advantages of having a well-crafted methodology section in your dissertation:
- Clarifies Your Research Approach : The methodology section explains how you plan to tackle your research question, providing a clear plan for data collection and analysis.
- Enables Replication : A detailed methodology allows other researchers to replicate your study. Replication is an important aspect of scientific research because it provides validation of the study’s results.
- Demonstrates Rigor : A well-written methodology shows that you’ve thought critically about your research methods and have chosen the most appropriate ones for your research question. This adds credibility to your study.
- Enhances Transparency : Detailing your methods allows readers to understand the steps you took in your research. This increases the transparency of your study and allows readers to evaluate potential biases or limitations.
- Helps in Addressing Research Limitations : In your methodology section, you can acknowledge and explain the limitations of your research. This is important as it shows you understand that no research method is perfect and there are always potential weaknesses.
- Facilitates Peer Review : A detailed methodology helps peer reviewers assess the soundness of your research design. This is an important part of the publication process if you aim to publish your dissertation in a peer-reviewed journal.
- Establishes the Validity and Reliability : Your methodology section should also include a discussion of the steps you took to ensure the validity and reliability of your measurements, which is crucial for establishing the overall quality of your research.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and...

Dissertation – Format, Example and Template

Dissertation vs Thesis – Key Differences

Ethical Considerations – Types, Examples and...
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 6. The Methodology
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The methods section describes actions taken to investigate a research problem and the rationale for the application of specific procedures or techniques used to identify, select, process, and analyze information applied to understanding the problem, thereby, allowing the reader to critically evaluate a study’s overall validity and reliability. The methodology section of a research paper answers two main questions: How was the data collected or generated? And, how was it analyzed? The writing should be direct and precise and always written in the past tense.
Kallet, Richard H. "How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper." Respiratory Care 49 (October 2004): 1229-1232.
Importance of a Good Methodology Section
You must explain how you obtained and analyzed your results for the following reasons:
- Readers need to know how the data was obtained because the method you chose affects the results and, by extension, how you interpreted their significance in the discussion section of your paper.
- Methodology is crucial for any branch of scholarship because an unreliable method produces unreliable results and, as a consequence, undermines the value of your analysis of the findings.
- In most cases, there are a variety of different methods you can choose to investigate a research problem. The methodology section of your paper should clearly articulate the reasons why you have chosen a particular procedure or technique.
- The reader wants to know that the data was collected or generated in a way that is consistent with accepted practice in the field of study. For example, if you are using a multiple choice questionnaire, readers need to know that it offered your respondents a reasonable range of answers to choose from.
- The method must be appropriate to fulfilling the overall aims of the study. For example, you need to ensure that you have a large enough sample size to be able to generalize and make recommendations based upon the findings.
- The methodology should discuss the problems that were anticipated and the steps you took to prevent them from occurring. For any problems that do arise, you must describe the ways in which they were minimized or why these problems do not impact in any meaningful way your interpretation of the findings.
- In the social and behavioral sciences, it is important to always provide sufficient information to allow other researchers to adopt or replicate your methodology. This information is particularly important when a new method has been developed or an innovative use of an existing method is utilized.
Bem, Daryl J. Writing the Empirical Journal Article. Psychology Writing Center. University of Washington; Denscombe, Martyn. The Good Research Guide: For Small-Scale Social Research Projects . 5th edition. Buckingham, UK: Open University Press, 2014; Lunenburg, Frederick C. Writing a Successful Thesis or Dissertation: Tips and Strategies for Students in the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press, 2008.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Groups of Research Methods
There are two main groups of research methods in the social sciences:
- The e mpirical-analytical group approaches the study of social sciences in a similar manner that researchers study the natural sciences . This type of research focuses on objective knowledge, research questions that can be answered yes or no, and operational definitions of variables to be measured. The empirical-analytical group employs deductive reasoning that uses existing theory as a foundation for formulating hypotheses that need to be tested. This approach is focused on explanation.
- The i nterpretative group of methods is focused on understanding phenomenon in a comprehensive, holistic way . Interpretive methods focus on analytically disclosing the meaning-making practices of human subjects [the why, how, or by what means people do what they do], while showing how those practices arrange so that it can be used to generate observable outcomes. Interpretive methods allow you to recognize your connection to the phenomena under investigation. However, the interpretative group requires careful examination of variables because it focuses more on subjective knowledge.
II. Content
The introduction to your methodology section should begin by restating the research problem and underlying assumptions underpinning your study. This is followed by situating the methods you used to gather, analyze, and process information within the overall “tradition” of your field of study and within the particular research design you have chosen to study the problem. If the method you choose lies outside of the tradition of your field [i.e., your review of the literature demonstrates that the method is not commonly used], provide a justification for how your choice of methods specifically addresses the research problem in ways that have not been utilized in prior studies.
The remainder of your methodology section should describe the following:
- Decisions made in selecting the data you have analyzed or, in the case of qualitative research, the subjects and research setting you have examined,
- Tools and methods used to identify and collect information, and how you identified relevant variables,
- The ways in which you processed the data and the procedures you used to analyze that data, and
- The specific research tools or strategies that you utilized to study the underlying hypothesis and research questions.
In addition, an effectively written methodology section should:
- Introduce the overall methodological approach for investigating your research problem . Is your study qualitative or quantitative or a combination of both (mixed method)? Are you going to take a special approach, such as action research, or a more neutral stance?
- Indicate how the approach fits the overall research design . Your methods for gathering data should have a clear connection to your research problem. In other words, make sure that your methods will actually address the problem. One of the most common deficiencies found in research papers is that the proposed methodology is not suitable to achieving the stated objective of your paper.
- Describe the specific methods of data collection you are going to use , such as, surveys, interviews, questionnaires, observation, archival research. If you are analyzing existing data, such as a data set or archival documents, describe how it was originally created or gathered and by whom. Also be sure to explain how older data is still relevant to investigating the current research problem.
- Explain how you intend to analyze your results . Will you use statistical analysis? Will you use specific theoretical perspectives to help you analyze a text or explain observed behaviors? Describe how you plan to obtain an accurate assessment of relationships, patterns, trends, distributions, and possible contradictions found in the data.
- Provide background and a rationale for methodologies that are unfamiliar for your readers . Very often in the social sciences, research problems and the methods for investigating them require more explanation/rationale than widely accepted rules governing the natural and physical sciences. Be clear and concise in your explanation.
- Provide a justification for subject selection and sampling procedure . For instance, if you propose to conduct interviews, how do you intend to select the sample population? If you are analyzing texts, which texts have you chosen, and why? If you are using statistics, why is this set of data being used? If other data sources exist, explain why the data you chose is most appropriate to addressing the research problem.
- Provide a justification for case study selection . A common method of analyzing research problems in the social sciences is to analyze specific cases. These can be a person, place, event, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis that are either examined as a singular topic of in-depth investigation or multiple topics of investigation studied for the purpose of comparing or contrasting findings. In either method, you should explain why a case or cases were chosen and how they specifically relate to the research problem.
- Describe potential limitations . Are there any practical limitations that could affect your data collection? How will you attempt to control for potential confounding variables and errors? If your methodology may lead to problems you can anticipate, state this openly and show why pursuing this methodology outweighs the risk of these problems cropping up.
NOTE : Once you have written all of the elements of the methods section, subsequent revisions should focus on how to present those elements as clearly and as logically as possibly. The description of how you prepared to study the research problem, how you gathered the data, and the protocol for analyzing the data should be organized chronologically. For clarity, when a large amount of detail must be presented, information should be presented in sub-sections according to topic. If necessary, consider using appendices for raw data.
ANOTHER NOTE : If you are conducting a qualitative analysis of a research problem , the methodology section generally requires a more elaborate description of the methods used as well as an explanation of the processes applied to gathering and analyzing of data than is generally required for studies using quantitative methods. Because you are the primary instrument for generating the data [e.g., through interviews or observations], the process for collecting that data has a significantly greater impact on producing the findings. Therefore, qualitative research requires a more detailed description of the methods used.
YET ANOTHER NOTE : If your study involves interviews, observations, or other qualitative techniques involving human subjects , you may be required to obtain approval from the university's Office for the Protection of Research Subjects before beginning your research. This is not a common procedure for most undergraduate level student research assignments. However, i f your professor states you need approval, you must include a statement in your methods section that you received official endorsement and adequate informed consent from the office and that there was a clear assessment and minimization of risks to participants and to the university. This statement informs the reader that your study was conducted in an ethical and responsible manner. In some cases, the approval notice is included as an appendix to your paper.
III. Problems to Avoid
Irrelevant Detail The methodology section of your paper should be thorough but concise. Do not provide any background information that does not directly help the reader understand why a particular method was chosen, how the data was gathered or obtained, and how the data was analyzed in relation to the research problem [note: analyzed, not interpreted! Save how you interpreted the findings for the discussion section]. With this in mind, the page length of your methods section will generally be less than any other section of your paper except the conclusion.
Unnecessary Explanation of Basic Procedures Remember that you are not writing a how-to guide about a particular method. You should make the assumption that readers possess a basic understanding of how to investigate the research problem on their own and, therefore, you do not have to go into great detail about specific methodological procedures. The focus should be on how you applied a method , not on the mechanics of doing a method. An exception to this rule is if you select an unconventional methodological approach; if this is the case, be sure to explain why this approach was chosen and how it enhances the overall process of discovery.
Problem Blindness It is almost a given that you will encounter problems when collecting or generating your data, or, gaps will exist in existing data or archival materials. Do not ignore these problems or pretend they did not occur. Often, documenting how you overcame obstacles can form an interesting part of the methodology. It demonstrates to the reader that you can provide a cogent rationale for the decisions you made to minimize the impact of any problems that arose.
Literature Review Just as the literature review section of your paper provides an overview of sources you have examined while researching a particular topic, the methodology section should cite any sources that informed your choice and application of a particular method [i.e., the choice of a survey should include any citations to the works you used to help construct the survey].
It’s More than Sources of Information! A description of a research study's method should not be confused with a description of the sources of information. Such a list of sources is useful in and of itself, especially if it is accompanied by an explanation about the selection and use of the sources. The description of the project's methodology complements a list of sources in that it sets forth the organization and interpretation of information emanating from those sources.
Azevedo, L.F. et al. "How to Write a Scientific Paper: Writing the Methods Section." Revista Portuguesa de Pneumologia 17 (2011): 232-238; Blair Lorrie. “Choosing a Methodology.” In Writing a Graduate Thesis or Dissertation , Teaching Writing Series. (Rotterdam: Sense Publishers 2016), pp. 49-72; Butin, Dan W. The Education Dissertation A Guide for Practitioner Scholars . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin, 2010; Carter, Susan. Structuring Your Research Thesis . New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2012; Kallet, Richard H. “How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper.” Respiratory Care 49 (October 2004):1229-1232; Lunenburg, Frederick C. Writing a Successful Thesis or Dissertation: Tips and Strategies for Students in the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press, 2008. Methods Section. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Rudestam, Kjell Erik and Rae R. Newton. “The Method Chapter: Describing Your Research Plan.” In Surviving Your Dissertation: A Comprehensive Guide to Content and Process . (Thousand Oaks, Sage Publications, 2015), pp. 87-115; What is Interpretive Research. Institute of Public and International Affairs, University of Utah; Writing the Experimental Report: Methods, Results, and Discussion. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Methods and Materials. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College.
Writing Tip
Statistical Designs and Tests? Do Not Fear Them!
Don't avoid using a quantitative approach to analyzing your research problem just because you fear the idea of applying statistical designs and tests. A qualitative approach, such as conducting interviews or content analysis of archival texts, can yield exciting new insights about a research problem, but it should not be undertaken simply because you have a disdain for running a simple regression. A well designed quantitative research study can often be accomplished in very clear and direct ways, whereas, a similar study of a qualitative nature usually requires considerable time to analyze large volumes of data and a tremendous burden to create new paths for analysis where previously no path associated with your research problem had existed.
To locate data and statistics, GO HERE .
Another Writing Tip
Knowing the Relationship Between Theories and Methods
There can be multiple meaning associated with the term "theories" and the term "methods" in social sciences research. A helpful way to delineate between them is to understand "theories" as representing different ways of characterizing the social world when you research it and "methods" as representing different ways of generating and analyzing data about that social world. Framed in this way, all empirical social sciences research involves theories and methods, whether they are stated explicitly or not. However, while theories and methods are often related, it is important that, as a researcher, you deliberately separate them in order to avoid your theories playing a disproportionate role in shaping what outcomes your chosen methods produce.
Introspectively engage in an ongoing dialectic between the application of theories and methods to help enable you to use the outcomes from your methods to interrogate and develop new theories, or ways of framing conceptually the research problem. This is how scholarship grows and branches out into new intellectual territory.
Reynolds, R. Larry. Ways of Knowing. Alternative Microeconomics . Part 1, Chapter 3. Boise State University; The Theory-Method Relationship. S-Cool Revision. United Kingdom.
Yet Another Writing Tip
Methods and the Methodology
Do not confuse the terms "methods" and "methodology." As Schneider notes, a method refers to the technical steps taken to do research . Descriptions of methods usually include defining and stating why you have chosen specific techniques to investigate a research problem, followed by an outline of the procedures you used to systematically select, gather, and process the data [remember to always save the interpretation of data for the discussion section of your paper].
The methodology refers to a discussion of the underlying reasoning why particular methods were used . This discussion includes describing the theoretical concepts that inform the choice of methods to be applied, placing the choice of methods within the more general nature of academic work, and reviewing its relevance to examining the research problem. The methodology section also includes a thorough review of the methods other scholars have used to study the topic.
Bryman, Alan. "Of Methods and Methodology." Qualitative Research in Organizations and Management: An International Journal 3 (2008): 159-168; Schneider, Florian. “What's in a Methodology: The Difference between Method, Methodology, and Theory…and How to Get the Balance Right?” PoliticsEastAsia.com. Chinese Department, University of Leiden, Netherlands.
- << Previous: Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Next: Qualitative Methods >>
- Last Updated: Apr 29, 2024 1:49 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

Data Collection Methods
Data collection is a process of collecting information from all the relevant sources to find answers to the research problem, test the hypothesis (if you are following deductive approach ) and evaluate the outcomes. Data collection methods can be divided into two categories: secondary methods of data collection and primary methods of data collection.
Secondary Data Collection Methods
Secondary data is a type of data that has already been published in books, newspapers, magazines, journals, online portals etc. There is an abundance of data available in these sources about your research area in business studies, almost regardless of the nature of the research area. Therefore, application of appropriate set of criteria to select secondary data to be used in the study plays an important role in terms of increasing the levels of research validity and reliability.
These criteria include, but not limited to date of publication, credential of the author, reliability of the source, quality of discussions, depth of analyses, the extent of contribution of the text to the development of the research area etc. Secondary data collection is discussed in greater depth in Literature Review chapter.
Secondary data collection methods offer a range of advantages such as saving time, effort and expenses. However they have a major disadvantage. Specifically, secondary research does not make contribution to the expansion of the literature by producing fresh (new) data.
Primary Data Collection Methods
Primary data is the type of data that has not been around before. Primary data is unique findings of your research. Primary data collection and analysis typically requires more time and effort to conduct compared to the secondary data research. Primary data collection methods can be divided into two groups: quantitative and qualitative.
Quantitative data collection methods are based on mathematical calculations in various formats. Methods of quantitative data collection and analysis include questionnaires with closed-ended questions, methods of correlation and regression, mean, mode and median and others.
Quantitative methods are cheaper to apply and they can be applied within shorter duration of time compared to qualitative methods. Moreover, due to a high level of standardisation of quantitative methods, it is easy to make comparisons of findings.
Qualitative research methods , on the contrary, do not involve numbers or mathematical calculations. Qualitative research is closely associated with words, sounds, feeling, emotions, colours and other elements that are non-quantifiable.
Qualitative studies aim to ensure greater level of depth of understanding and qualitative data collection methods include interviews, questionnaires with open-ended questions, focus groups, observation, game or role-playing, case studies etc.
Your choice between quantitative or qualitative methods of data collection depends on the area of your research and the nature of research aims and objectives.
My e-book, The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Dissertation in Business Studies: a step by step assistance offers practical assistance to complete a dissertation with minimum or no stress. The e-book covers all stages of writing a dissertation starting from the selection to the research area to submitting the completed version of the work within the deadline.
John Dudovskiy


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Data Collection | Definition, Methods & Examples. Published on June 5, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari.Revised on June 21, 2023. Data collection is a systematic process of gathering observations or measurements. Whether you are performing research for business, governmental or academic purposes, data collection allows you to gain first-hand knowledge and original insights into your research problem.
Qualitative Research Methodology. This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of non-numerical data such as words, images, and observations. This type of research is often used to explore complex phenomena, to gain an in-depth understanding of a particular topic, and to generate hypotheses.
Tips for writing your data collection procedures. Quantitative Methodology. Your data collection plan is a crucial key to developing a sound study. The plan indicates how you will access and gather information from your participants. A clear data collection plan at the proposal stage can alleviate stress and ensure that future researchers can ...
For instance, if you need qualitative data, you might choose a focus group or interview methodology. If you need quantitative data, then a survey or observational study may be the most appropriate form of collection. 4. Gather information. When collecting data for your business, identify your business goals first.
Figure 10.1. Data Collection Techniques. Each of these data collection techniques will be the subject of its own chapter in the second half of this textbook. This chapter serves as an orienting overview and as the bridge between the conceptual/design portion of qualitative research and the actual practice of conducting qualitative research.
The approach to data collection is different for different fields of study, depending on the required information. LEARN ABOUT: Action Research. Data Collection Methods. There are many ways to collect information when doing research. The data collection methods that the researcher chooses will depend on the research question posed. Some data ...
Surveys, interviews, observations, focus groups, and forms are common data collection methods. Sampling involves selecting a representative group from a larger population. Choosing the right sampling method to gather representative and relevant data is crucial. Crafting effective data collection instruments like surveys and questionnaires is ...
PDF | Learn how to choose the best data collection methods and tools for your research project, with examples and tips from ResearchGate experts. | Download and read the full-text PDF.
7 Data Collection Methods Used in Business Analytics. 1. Surveys. Surveys are physical or digital questionnaires that gather both qualitative and quantitative data from subjects. One situation in which you might conduct a survey is gathering attendee feedback after an event.
Step 2: Choose your data collection method. Based on the data you want to collect, decide which method is best suited for your research. Experimental research is primarily a quantitative method. Interviews, focus groups, and ethnographies are qualitative methods. Surveys, observations, archival research, and secondary data collection can be ...
Revised on 10 October 2022. Your research methodology discusses and explains the data collection and analysis methods you used in your research. A key part of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, the methodology chapter explains what you did and how you did it, allowing readers to evaluate the reliability and validity of your research.
Now you need to plan your data collection procedures, especially if you're doing quantitative research! This video will walk you through some key steps for g...
Data collection is the process of gathering and collecting information from various sources to analyze and make informed decisions based on the data collected. This can involve various methods, such as surveys, interviews, experiments, and observation. In order for data collection to be effective, it is important to have a clear understanding ...
Types of Data Collection Methods. Data collection methods are important, because how the information collected is used and what explanations it can generate are determined by the methodology and analytical approach applied by the researcher. 1, 2 Five key data collection methods are presented here, with their strengths and limitations described ...
You don't need a lot of detail here - just a brief outline will do. Section 2 - The Methodology. The next section of your chapter is where you'll present the actual methodology. In this section, you need to detail and justify the key methodological choices you've made in a logical, intuitive fashion.
Each of these methods offers a unique way to gather data and comes with its own set of pros and cons. Take your time to decide which data collection methods are the best fit for your use case. Steps for writing an effective data collection plan. With the theory out of the way, let's see how to write a proper data collection plan, step by step.
Here is a basic guideline on how to write your methodology section: 1. Introduction. ... Data Collection Methods. Quantitative Data Collection: An online self-report questionnaire was used to collect data from participants. The questionnaire consisted of two standardized scales: the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS) to measure stress levels and the ...
Bem, Daryl J. Writing the Empirical Journal Article. Psychology Writing Center. University of Washington; Denscombe, Martyn. The Good Research Guide: For Small-Scale Social Research Projects. 5th edition.Buckingham, UK: Open University Press, 2014; Lunenburg, Frederick C. Writing a Successful Thesis or Dissertation: Tips and Strategies for Students in the Social and Behavioral Sciences.
Data Collection Methods. Data collection is a process of collecting information from all the relevant sources to find answers to the research problem, test the hypothesis (if you are following deductive approach) and evaluate the outcomes. Data collection methods can be divided into two categories: secondary methods of data collection and ...