Module 4: Socialization
The importance of socialization, learning outcomes.
- Explain the importance of socialization both for individuals and society
- Distinguish nature from nurture in socialization
Socialization is the process through which people are taught to be proficient members of a society. It describes the ways that people come to understand societal norms and expectations, to accept society’s beliefs, and to be aware of societal values. Socialization is not the same as socializing (interacting with others, like family and friends); to be precise, it is a sociological process that occurs through socializing.
While Noel’s story from the beginning of the module is about a relatively advanced stage of life, socialization is crucial for early childhood. Even the most basic of human activities are learned. Learning to crawl and then walk are major milestones, but as any parent, guardian, or family member of a toddler knows, other minor accomplishments can be life-altering for the child: climbing stairs, safely getting out of bed, sitting in a regular chair, and drinking from a regular cup. Likewise, family behaviors and values must be learned, sometimes through observation and sometimes through active instruction. Thus, sociologists have also long been fascinated by circumstances in which a child receives sufficient human support to survive, but virtually no social interaction—because they highlight how much we depend on social interaction to provide the information and skills we need to be part of society or even to develop a “self.”
Socialization is critical both to individuals and to the societies in which they live. As individuals, social interaction provides us the means by which we gradually become able to see ourselves through the eyes of others, and how we learn who we are and how we fit into the larger world. In addition, to function successfully in society, we have to learn the basics of both material and nonmaterial culture, everything from how to dress ourselves to what’s suitable attire for a specific occasion; from when we sleep to what we sleep on; and from what’s considered appropriate to eat for dinner and even how to use the stove to prepare it. Most importantly, we have to learn language—whether it’s the dominant language or one common in a subculture, whether it’s verbal or through signs—in order to communicate and to think. Without socialization we have no commonly recognizable sense of self.
For society to function, the socialization of individuals is necessary. Although how this occurs and what is transmitted in terms of cultural norms and values differs, every society relies upon socialization to ensure its survival. A core value in the United States is democracy, so children in the U.S. might hear about voting or go to vote with their families before they even begin school. Once in school, they will learn about American history, civics, and citizenship. Students also learn the ways that the U.S. has not upheld democratic ideals and has disenfranchised various groups of people. Thus, in addition to voting and learning how to use material objects such as voting machines, children also learn about various social movements and leaders who resisted the existing social norms in order to facilitate change. Learning about how society has failed to live up to its ideals (and continues to struggle in certain areas) helps citizens not only to understand values and norms on a personal level, but also to see the importance of values and norms in society, as well as how these can change over time. Remember that socialization is a lifelong process, so in our example, people will continue to examine whether or not the U.S. is living up to its democratic ideals over many years.
Watch this video to learn more about what it means to be socialized, and what things contribute to socialization. The video provides an effective overview of several concepts related to socialization that will be covered in this module.

Figure 1. Socialization teaches us our society’s expectations for dining out. The manners and customs of different cultures (When can you use your hands to eat? How should you compliment the cook? Who is the “head” of the table?) are learned through socialization. (Photo courtesy of Niyam Bhushan/flickr)

Nature versus Nurture
Some experts argue that who we are is based entirely on genetics or our biological makeup. According to this belief, our temper a ments, interests, and talents are set before birth. From this perspective, who we are depends on nature . Others, including most sociologists, assert that who we are is a result of nurture —the relationships and environments that surround us.

Figure 2. Identical twins may look alike, but their differences can give us clues to the effects of socialization. (Photo courtesy of D. Flam/flickr)
One way researchers attempt to measure the impact of nature is by studying twins. Some studies have followed identical twins who were raised separately. The pairs shared the same genetic inheritance, but in some cases were socialized in different ways. Instances of this situation are rare, but studying the degree to which identical twins raised apart are the same or different can give researchers insight into the way our temperaments, preferences, and abilities are shaped by our genetic makeup versus our social environment.
For example, in 1968 twin girls born to a mentally ill mother were put up for adoption, separated from each other, and raised in different households. The adoptive parents, and certainly the adoptees themselves, did not know the girls were one of five pairs of twins who were made subjects of a scientific study (Flam 2007).
In 2003, the two women, then age thirty-five, were reunited. Elyse Schein and Paula Bernstein sat together in awe, feeling like they were looking into a mirror. Not only did they look alike but they also behaved alike, using the same hand gestures and facial expressions (Spratling 2007). Studies like these point to the genetic roots of our temperament and behavior.
Learn about the famous twins, Oskar and Jack, who were separated as infants and led strikingly different lives . You can visit the article “Separated at Birth” to read about five other sets of twins who grew up apart and discovered each other later in life.
Though genetics and hormones play an important role in human behavior, sociology’s larger concern is the effect society has on human behavior–the “nurture” side of the nature-versus-nurture debate. What race were the twins? From what social class were their parents? What about gender? Religion? All these factors affected the lives of the twins as much as their genetic makeup, and are critical to consider as we look at life through the sociological lens.
The Life of Chris Langan, the Smartest Man You’ve Never Heard Of
Bouncer. Firefighter. Factory worker. Cowboy. Chris Langan spent the majority of his adult life just getting by with jobs like these. He had no college degree, few resources, and a past filled with much disappointment. Chris Langan also had an IQ of over 195, nearly 100 points higher than the average person (Brabham 2001). So why didn’t Chris become a neurosurgeon, professor, or aeronautical engineer? According to Macolm Gladwell (2008) in his book Outliers: The Story of Success , Chris didn’t possess the set of social skills necessary to succeed on such a high level—skills that aren’t innate but learned.
Gladwell looked to a recent study conducted by sociologist Annette Lareau in which she closely shadowed 12 families from various economic backgrounds and examined their parenting techniques. Parents from lower income families followed a strategy of “accomplishment of natural growth,” which is to say they let their children develop on their own with a large amount of independence; parents from higher-income families, however, “actively fostered and accessed a child’s talents, opinions, and skills” (Gladwell 2008). These parents were more likely to engage in analytical conversation, encourage active questioning of the establishment, and foster development of negotiation skills. The parents were also able to introduce their children to a wide range of activities, from sports to music to accelerated academic programs. When one middle-class child was denied entry to a gifted and talented program, the mother petitioned the school and arranged additional testing until her daughter was admitted. Lower-income parents, however, were more likely to unquestioningly obey authorities such as school boards. Their children were not being socialized to comfortably confront the system and speak up (Gladwell 2008).
What does this have to do with Chris Langan, deemed by some the smartest man in the world (Brabham 2001)? Chris was born in severe poverty, moving across the country with an abusive and alcoholic stepfather. His genius went largely unnoticed. After accepting a full scholarship to Reed College, he lost his funding after his mother failed to fill out necessary paperwork. Unable to successfully make his case to the administration, Chris, who had received straight A’s the previous semester, was given F’s on his transcript and forced to drop out. After he enrolled in Montana State, an administrator’s refusal to rearrange his class schedule left him unable to find the means necessary to travel the 16 miles to attend classes. What Chris had in brilliance, he lacked in practical intelligence, or what psychologist Robert Sternberg defines as “knowing what to say to whom, knowing when to say it, and knowing how to say it for maximum effect” (Sternberg et al. 2000). Such knowledge was never part of his socialization.
Chris gave up on school and began working an array of blue-collar jobs, pursuing his intellectual interests on the side. Though he’s recently garnered attention for his “Cognitive Theoretic Model of the Universe,” he remains weary of and resistant to the educational system.
As Gladwell concluded, “He’d had to make his way alone, and no one—not rock stars, not professional athletes, not software billionaires, and not even geniuses—ever makes it alone” (2008).
Chris is a white male who was born in the United States, though he also faced considerable economic and domestic challenges. How would the story change if our example was a female immigrant, with dark skin? Social class and what Pierre Bourdieu calls “cultural capital” are important in directing one’s life chances, but perhaps equally important are race/ethnicity, gender, economic class, and whether one is perceived as an immigrant or a native-born citizen.
Sociologists all recognize the importance of socialization for healthy individual and societal development. But how do scholars working in the three major theoretical paradigms approach this topic?
Structural functionalists would say that socialization is essential to society, both because it trains members to operate successfully within it and because it perpetuates culture by transmitting it to new generations. Without socialization, a society’s culture would destabilize and ultimately perish as members died off.
A conflict theorist might argue that socialization reproduces inequality from generation to generation by conveying different expectations and norms to those with different social characteristics. For example, individuals are socialized differently by gender, social class, and race. As in Chris Langan’s case, this creates different (unequal) opportunities.
An interactionist studying socialization is concerned with face-to-face exchanges and symbolic communication. For example, dressing baby boys in blue and baby girls in pink is one small way we convey messages about differences in gender roles.
Think It Over
- Why are twin studies an important way to learn about the relative effects of genetics and socialization on children? What questions about human development do you believe twin studies are best for answering? For what types of questions would twin studies not be as helpful?
- Why do you think that people like Chris Langan continue to have difficulty even after they are helped through societal systems? How does this story help you understand the role of nature and the role of nurture?
- Modification, adaptation, and original content. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Why Socialization Matters. Authored by : OpenStax CNX. Located at : https://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:zeTojT9p@3/Why-Socialization-Matters . License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]
- Introduction to Socialization. Provided by : OpenStax. Located at : https://openstax.org/books/introduction-sociology-3e/pages/5-introduction . Project : Sociology 3e. License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/introduction-sociology-3e/pages/5-introduction
- Socialization: Crash Course Sociology #14. Provided by : CrashCourse. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=K-RvJQxqVQc . License : Other . License Terms : Standard YouTube License

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
The Importance of Socialization
Learning objective.
- Describe why socialization is important for being fully human.
- Explain how extreme isolation and twin studies demonstrate the role of nature versus nurture in human development.
- Identify the different questions functionalists, conflict theorists, and interactionists might ask about the role of socialization in human development.
Why Socialization Matters
Socialization is critical both to individuals and to the societies in which they live. It illustrates how completely intertwined human beings and their social worlds are. First, it is through teaching culture to new members that a society perpetuates itself. If new generations of a society don’t learn its way of life, it ceases to exist. Whatever is distinctive about a culture must be transmitted to those who join it in order for a society to survive. For U.S. culture to continue, for example, children in the United States must learn about cultural values related to democracy: they have to learn the norms of voting, as well as how to use material objects such as voting machines. Of course, some would argue that it’s just as important in U.S. culture for the younger generation to learn the etiquette of eating in a restaurant or the rituals of tailgate parties at football games. In fact, there are many ideas and objects that people in the United States teach children about in hopes of keeping the society’s way of life going through another generation.
Socialization is just as essential to us as individuals. Social interaction provides the means via which we gradually become able to see ourselves through the eyes of others, and how we learn who we are and how we fit into the world around us. In addition, to function successfully in society, we have to learn the basics of both material and nonmaterial culture, everything from how to dress ourselves to what’s suitable attire for a specific occasion; from when we sleep to what we sleep on; and from what’s considered appropriate to eat for dinner to how to use the stove to prepare it. Most importantly, we have to learn language—whether it’s the dominant language or one common in a subculture, whether it’s verbal or through signs—in order to communicate and to think. As we saw with Danielle, without socialization we literally have no self.
Nature versus Nurture

Some experts assert that who we are is a result of nurture —the relationships and caring that surround us. Others argue that who we are is based entirely in genetics. According to this belief, our temperaments, interests, and talents are set before birth. From this perspective, then, who we are depends on nature .
One way researchers attempt to measure the impact of nature is by studying twins. Some studies have followed identical twins who were raised separately. The pairs shared the same genetics but in some cases were socialized in different ways. Instances of this type of situation are rare, but studying the degree to which identical twins raised apart are the same and different can give researchers insight into the way our temperaments, preferences, and abilities are shaped by our genetic makeup versus our social environment.
For example, in 1968, twin girls born to a mentally ill mother were put up for adoption, separated from each other, and raised in different households. The adoptive parents, and certainly the babies, did not realize the girls were one of five pairs of twins who were made subjects of a scientific study (Flam 2007).
In 2003, the two women, then age thirty-five, were reunited. Elyse Schein and Paula Bernstein sat together in awe, feeling like they were looking into a mirror. Not only did they look alike but they also behaved alike, using the same hand gestures and facial expressions (Spratling 2007). Studies like these point to the genetic roots of our temperament and behavior.
Though genetics and hormones play an important role in human behavior, sociology’s larger concern is the effect society has on human behavior, the “nurture” side of the nature versus nurture debate. What race were the twins? From what social class were their parents? What about gender? Religion? All these factors affected the lives of the twins as much as their genetic makeup and are critical to consider as we look at life through the sociological lens.
Extreme Isolation
We have just noted that socialization is how culture is learned, but socialization is also important for another important reason. To illustrate this importance, let’s pretend we find a 6-year-old child who has had almost no human contact since birth. After the child was born, her mother changed her diapers and fed her a minimal diet but otherwise did not interact with her. The child was left alone all day and night for years and never went outside. We now find her at the age of 6. How will her behavior and actions differ from those of the average 6-year-old? Take a moment and write down all the differences you would find.
In no particular order, here is the list you probably wrote. First, the child would not be able to speak; at most, she could utter a few grunts and other sounds. Second, the child would be afraid of us and probably cower in a corner. Third, the child would not know how to play games and interact with us. If we gave her some food and utensils, she would eat with her hands and not know how to use the utensils. Fourth, the child would be unable to express a full range of emotions. For example, she might be able to cry but would not know how to laugh. Fifth, the child would be unfamiliar with, and probably afraid of, our culture’s material objects, including cell phones and televisions. In these and many other respects, this child would differ dramatically from the average 6-year-old youngster in the United States. She would look human, but she would not act human. In fact, in many ways she would act more like a frightened animal than like a young human being, and she would be less able than a typical dog to follow orders and obey commands.
As this example indicates, socialization makes it possible for us to fully function as human beings. Without socialization, we could not have our society and culture. And without social interaction, we could not have socialization. Our example of a socially isolated child was hypothetical, but real-life examples of such children, often called feral children, have unfortunately occurred and provide poignant proof of the importance of social interaction for socialization and of socialization for our ability to function as humans.
One of the most famous feral children was Victor of Aveyron, who was found wandering in the woods in southern France in 1797. He then escaped custody but emerged from the woods in 1800. Victor was thought to be about age 12 and to have been abandoned some years earlier by his parents; he was unable to speak and acted much more like a wild animal than a human child. Victor first lived in an institution and then in a private home. He never learned to speak, and his cognitive and social development eventually was no better than a toddler’s when he finally died at about age 40 (Lane, 1976).
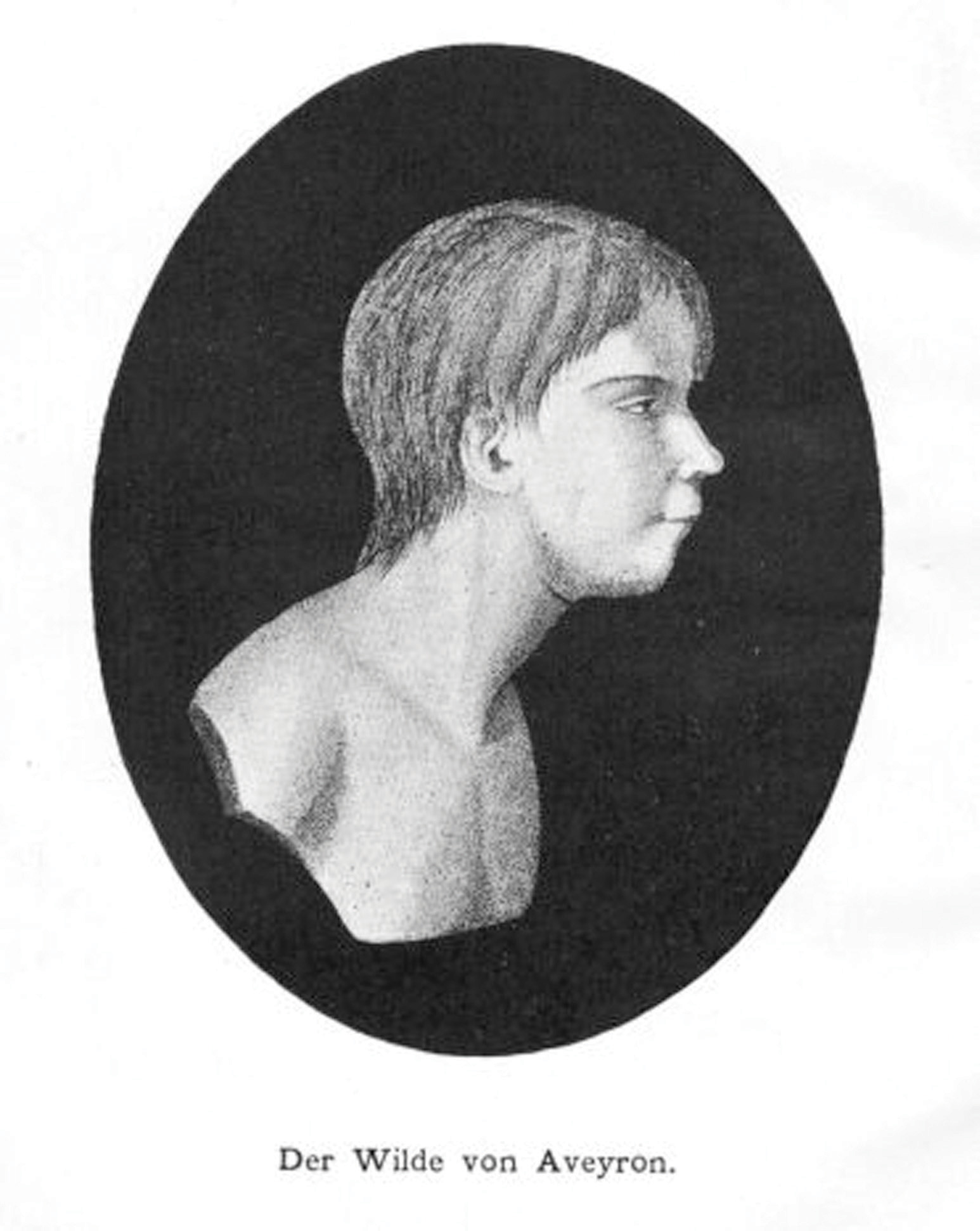

In rare cases, children have grown up in extreme isolation and end up lacking several qualities that make them fully human. This is a photo of Victor of Aveyron, who emerged from the woods in southern France in 1800 after apparently being abandoned by his parents some years earlier. He could not speak, and his cognitive and social skills never advanced beyond those of a small child before he died at the age of 40.
Wikimedia Commons – public domain.
Another such child, found more than about a half-century ago, was called Anna, who “had been deprived of normal contact and had received a minimum of human care for almost the whole of her first six years of life” (Davis, 1940, p. 554). After being shuttled from one residence to another for her first 5 months, Anna ended up living with her mother in her grandfather’s house and was kept in a small, airless room on the second floor because the grandfather was so dismayed by her birth out of wedlock that he hated seeing her. Because her mother worked all day and would go out at night, Anna was alone almost all the time and lived in filth, often barely alive. Her only food in all those years was milk.
When Anna was found at the age of 6, she could not talk or walk or “do anything that showed intelligence” (Davis, 1940, p. 554). She was also extremely undernourished and emaciated. Two years later, she had learned to walk, understand simple commands, feed herself, and remember faces, but she could not talk and in these respects resembled a 1-year-old infant more than the 7-year-old child she really was. By the time she died of jaundice at about age 9, she had acquired the speech of a 2-year-old.
Shortly after Anna was discovered, another girl, called Isabelle, was found in similar circumstances at age 6. She was also born out of wedlock and lived alone with her mother in a dark room isolated from the rest of the mother’s family. Because her mother was mute, Isabelle did not learn to speak, although she did communicate with her mother via some simple gestures. When she was finally found, she acted like a wild animal around strangers, and in other respects she behaved more like a child of 6 months than one of more than 6 years. When first shown a ball, she stared at it, held it in her hand, and then rubbed an adult’s face with it. Intense training afterward helped Isabelle recover, and 2 years later she had reached a normal speaking level for a child her age (Davis, 1940).
These cases of feral children show that extreme isolation—or, to put it another way, lack of socialization—deprives children of the obvious and not-so-obvious qualities that make them human and in other respects retards their social, cognitive, and emotional development. A series of famous experiments by psychologists Harry and Margaret Harlow (1962) reinforced the latter point by showing it to be true of monkeys as well. The Harlows studied rhesus monkeys that had been removed from their mothers at birth; some were raised in complete isolation, while others were given fake mothers made of cloth and wire with which to cuddle. Neither group developed normally, although the monkeys cuddling with the fake mothers fared somewhat better than those that were totally isolated. In general, the monkeys were not able to interact later with other monkeys, and female infants abused their young when they became mothers. The longer their isolation, the more the monkeys’ development suffered. By showing the dire effects of social isolation, the Harlows’ experiment reinforced the significance of social interaction for normal development. Combined with the tragic examples of feral children, their experiments remind us of the critical importance of socialization and social interaction for human society.
Sociologists all recognize the importance of socialization for healthy individual and societal development. But how do scholars working in the three major theoretical paradigms approach this topic? Structural functionalists would say that socialization is essential to society, both because it trains members to operate successfully within it and because it perpetuates culture by transmitting it to new generations. Without socialization, a society’s culture would perish as members died off. A conflict theorist might argue that socialization reproduces inequality from generation to generation by conveying different expectations and norms to those with different social characteristics. For example, individuals are socialized differently by gender, social class, and race. An interactionist studying socialization is concerned with face-to-face exchanges and symbolic communication. For example, dressing baby boys in blue and baby girls in pink is one small way we convey messages about differences in gender roles.
Key Takeaways
- Socialization is the process through which individuals learn their culture and become fully human.
- Unfortunate examples of extreme human isolation illustrate the importance of socialization for children’s social and cognitive development.
Davis, K. (1940). Extreme social isolation of a child. American Journal of Sociology, 45, 554–565.
Harlow, H. F., & Harlow, M. K. (1962). Social deprivation in monkeys. Scientific American, 207, 137–146.
Lane, H. L. (1976). The wild boy of Aveyron . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
The process of an individual or group learning the expected norms and customs of a group or society through social interaction.
Introduction to Sociology: Understanding and Changing the Social World Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
4.1 The Importance of Socialization
Learning objective.
- Describe why socialization is important for being fully human.
We have just noted that socialization is how culture is learned, but socialization is also important for another important reason. To illustrate this importance, let’s pretend we find a 6-year-old child who has had almost no human contact since birth. After the child was born, her mother changed her diapers and fed her a minimal diet but otherwise did not interact with her. The child was left alone all day and night for years and never went outside. We now find her at the age of 6. How will her behavior and actions differ from those of the average 6-year-old? Take a moment and write down all the differences you would find.
In no particular order, here is the list you probably wrote. First, the child would not be able to speak; at most, she could utter a few grunts and other sounds. Second, the child would be afraid of us and probably cower in a corner. Third, the child would not know how to play games and interact with us. If we gave her some food and utensils, she would eat with her hands and not know how to use the utensils. Fourth, the child would be unable to express a full range of emotions. For example, she might be able to cry but would not know how to laugh. Fifth, the child would be unfamiliar with, and probably afraid of, our culture’s material objects, including cell phones and televisions. In these and many other respects, this child would differ dramatically from the average 6-year-old youngster in the United States. She would look human, but she would not act human. In fact, in many ways she would act more like a frightened animal than like a young human being, and she would be less able than a typical dog to follow orders and obey commands.
As this example indicates, socialization makes it possible for us to fully function as human beings. Without socialization, we could not have our society and culture. And without social interaction, we could not have socialization. Our example of a socially isolated child was hypothetical, but real-life examples of such children, often called feral children, have unfortunately occurred and provide poignant proof of the importance of social interaction for socialization and of socialization for our ability to function as humans.
One of the most famous feral children was Victor of Aveyron, who was found wandering in the woods in southern France in 1797. He then escaped custody but emerged from the woods in 1800. Victor was thought to be about age 12 and to have been abandoned some years earlier by his parents; he was unable to speak and acted much more like a wild animal than a human child. Victor first lived in an institution and then in a private home. He never learned to speak, and his cognitive and social development eventually was no better than a toddler’s when he finally died at about age 40 (Lane, 1976).
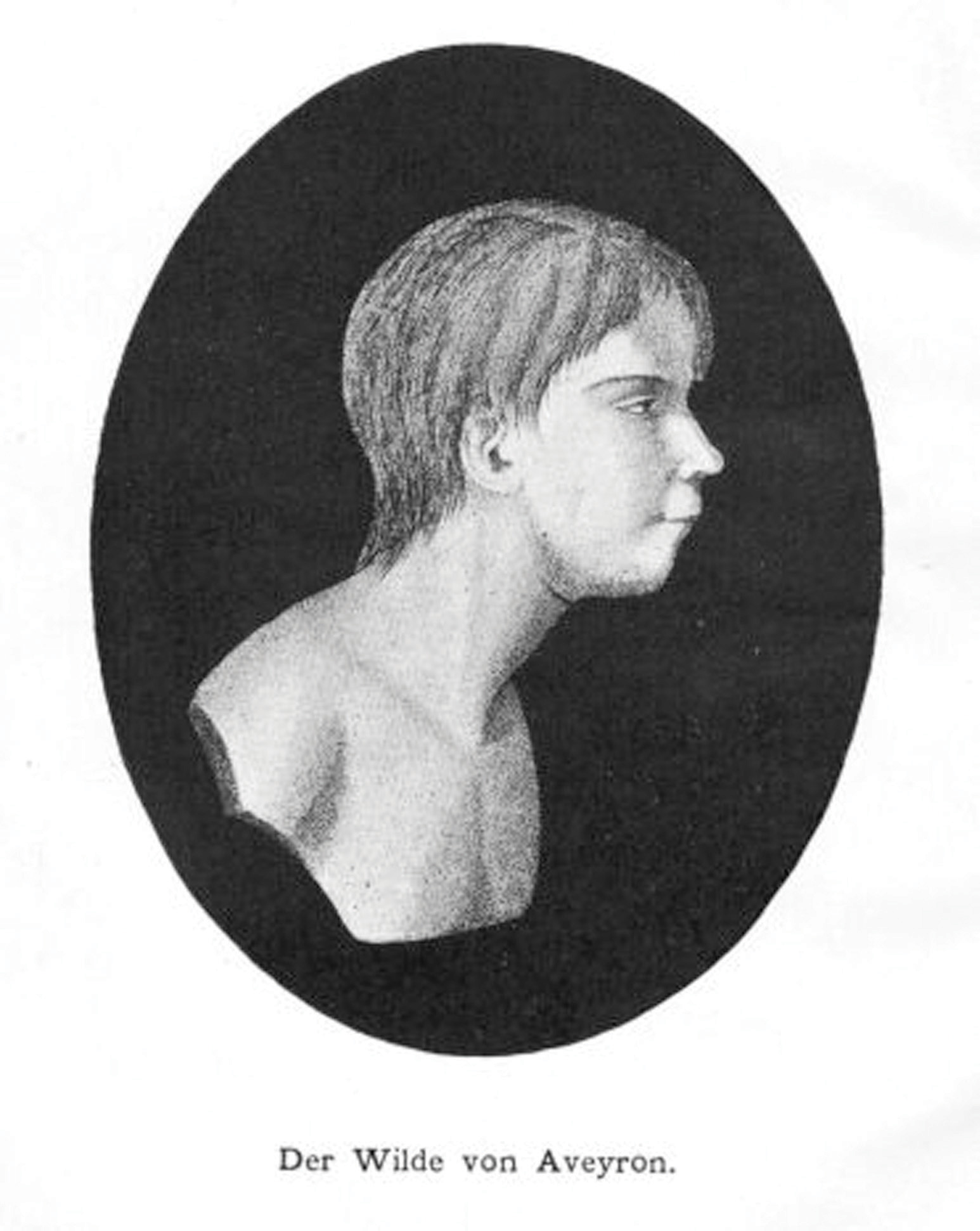

In rare cases, children have grown up in extreme isolation and end up lacking several qualities that make them fully human. This is a photo of Victor of Aveyron, who emerged from the woods in southern France in 1800 after apparently being abandoned by his parents some years earlier. He could not speak, and his cognitive and social skills never advanced beyond those of a small child before he died at the age of 40.
Wikimedia Commons – public domain.
Another such child, found more than about a half-century ago, was called Anna, who “had been deprived of normal contact and had received a minimum of human care for almost the whole of her first six years of life” (Davis, 1940, p. 554). After being shuttled from one residence to another for her first 5 months, Anna ended up living with her mother in her grandfather’s house and was kept in a small, airless room on the second floor because the grandfather was so dismayed by her birth out of wedlock that he hated seeing her. Because her mother worked all day and would go out at night, Anna was alone almost all the time and lived in filth, often barely alive. Her only food in all those years was milk.
When Anna was found at the age of 6, she could not talk or walk or “do anything that showed intelligence” (Davis, 1940, p. 554). She was also extremely undernourished and emaciated. Two years later, she had learned to walk, understand simple commands, feed herself, and remember faces, but she could not talk and in these respects resembled a 1-year-old infant more than the 7-year-old child she really was. By the time she died of jaundice at about age 9, she had acquired the speech of a 2-year-old.
Shortly after Anna was discovered, another girl, called Isabelle, was found in similar circumstances at age 6. She was also born out of wedlock and lived alone with her mother in a dark room isolated from the rest of the mother’s family. Because her mother was mute, Isabelle did not learn to speak, although she did communicate with her mother via some simple gestures. When she was finally found, she acted like a wild animal around strangers, and in other respects she behaved more like a child of 6 months than one of more than 6 years. When first shown a ball, she stared at it, held it in her hand, and then rubbed an adult’s face with it. Intense training afterward helped Isabelle recover, and 2 years later she had reached a normal speaking level for a child her age (Davis, 1940).
These cases of feral children show that extreme isolation—or, to put it another way, lack of socialization—deprives children of the obvious and not-so-obvious qualities that make them human and in other respects retards their social, cognitive, and emotional development. A series of famous experiments by psychologists Harry and Margaret Harlow (1962) reinforced the latter point by showing it to be true of monkeys as well. The Harlows studied rhesus monkeys that had been removed from their mothers at birth; some were raised in complete isolation, while others were given fake mothers made of cloth and wire with which to cuddle. Neither group developed normally, although the monkeys cuddling with the fake mothers fared somewhat better than those that were totally isolated. In general, the monkeys were not able to interact later with other monkeys, and female infants abused their young when they became mothers. The longer their isolation, the more the monkeys’ development suffered. By showing the dire effects of social isolation, the Harlows’ experiment reinforced the significance of social interaction for normal development. Combined with the tragic examples of feral children, their experiments remind us of the critical importance of socialization and social interaction for human society.
Key Takeaways
- Socialization is the process through which individuals learn their culture and become fully human.
- Unfortunate examples of extreme human isolation illustrate the importance of socialization for children’s social and cognitive development.
For Your Review
- Do you agree that effective socialization is necessary for an individual to be fully human? Could this assumption imply that children with severe developmental disabilities, who cannot undergo effective socialization, are not fully human?
- Do you know anyone with negative views in regard to race and ethnicity, sexual orientation, or religious preference? If so, how do you think this person acquired these views?
Davis, K. (1940). Extreme social isolation of a child. American Journal of Sociology, 45, 554–565.
Harlow, H. F., & Harlow, M. K. (1962). Social deprivation in monkeys. Scientific American, 207, 137–146.
Lane, H. L. (1976). The wild boy of Aveyron . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Sociology Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
19 Introduction to Socialization

In the summer of 2005, police detective Mark Holste followed an investigator from the Department of Children and Families to a home in Plant City, Florida. They were there to look into a statement from the neighbor concerning a shabby house on Old Sydney Road. A small girl was reported peering from one of its broken windows. This seemed odd because no one in the neighborhood had seen a young child in or around the home, which had been inhabited for the past three years by a woman, her boyfriend, and two adult sons.
Who was the mystery girl in the window?
Entering the house, Detective Holste and his team were shocked. It was the worst mess they’d ever seen, infested with cockroaches, smeared with feces and urine from both people and pets, and filled with dilapidated furniture and ragged window coverings.
Detective Holste headed down a hallway and entered a small room. That’s where he found the little girl, with big, vacant eyes, staring into the darkness. A newspaper report later described the detective’s first encounter with the child: “She lay on a torn, moldy mattress on the floor. She was curled on her side . . . her ribs and collarbone jutted out . . . her black hair was matted, crawling with lice. Insect bites, rashes and sores pocked her skin . . . She was naked—except for a swollen diaper. … Her name, her mother said, was Danielle. She was almost seven years old” (DeGregory 2008).
Detective Holste immediately carried Danielle out of the home. She was taken to a hospital for medical treatment and evaluation. Through extensive testing, doctors determined that, although she was severely malnourished, Danielle was able to see, hear, and vocalize normally. Still, she wouldn’t look anyone in the eyes, didn’t know how to chew or swallow solid food, didn’t cry, didn’t respond to stimuli that would typically cause pain, and didn’t know how to communicate either with words or simple gestures such as nodding “yes” or “no.” Likewise, although tests showed she had no chronic diseases or genetic abnormalities, the only way she could stand was with someone holding onto her hands, and she “walked sideways on her toes, like a crab” (DeGregory 2008).
What had happened to Danielle? Put simply: beyond the basic requirements for survival, she had been neglected. Based on their investigation, social workers concluded that she had been left almost entirely alone in rooms like the one where she was found. Without regular interaction—the holding, hugging, talking, the explanations and demonstrations given to most young children—she had not learned to walk or to speak, to eat or to interact, to play or even to understand the world around her. From a sociological point of view, Danielle had not been socialized.
Socialization is the process through which people are taught to be proficient members of a society. It describes the ways that people come to understand societal norms and expectations, to accept society’s beliefs, and to be aware of societal values. Socialization is not the same as socializing (interacting with others, like family, friends, and coworkers); to be precise, it is a sociological process that occurs through socializing. As Danielle’s story illustrates, even the most basic of human activities are learned. You may be surprised to know that even physical tasks like sitting, standing, and walking had not automatically developed for Danielle as she grew. And without socialization, Danielle hadn’t learned about the material culture of her society (the tangible objects a culture uses): for example, she couldn’t hold a spoon, bounce a ball, or use a chair for sitting. She also hadn’t learned its nonmaterial culture, such as its beliefs, values, and norms. She had no understanding of the concept of “family,” didn’t know cultural expectations for using a bathroom for elimination, and had no sense of modesty. Most importantly, she hadn’t learned to use the symbols that make up language—through which we learn about who we are, how we fit with other people, and the natural and social worlds in which we live.
Sociologists have long been fascinated by circumstances like Danielle’s—in which a child receives sufficient human support to survive, but virtually no social interaction—because they highlight how much we depend on social interaction to provide the information and skills that we need to be part of society or even to develop a “self.”
The necessity for early social contact was demonstrated by the research of Harry and Margaret Harlow. From 1957 to 1963, the Harlows conducted a series of experiments studying how rhesus monkeys, which behave a lot like people, are affected by isolation as babies. They studied monkeys raised under two types of “substitute” mothering circumstances: a mesh and wire sculpture, or a soft terrycloth “mother.” The monkeys systematically preferred the company of a soft, terrycloth substitute mother (closely resembling a rhesus monkey) that was unable to feed them, to a mesh and wire mother that provided sustenance via a feeding tube. This demonstrated that while food was important, social comfort was of greater value (Harlow and Harlow 1962; Harlow 1971). Later experiments testing more severe isolation revealed that such deprivation of social contact led to significant developmental and social challenges later in life.

In the following sections, we will examine the importance of the complex process of socialization and how it takes place through interaction with many individuals, groups, and social institutions. We will explore how socialization is not only critical to children as they develop but how it is also a lifelong process through which we become prepared for new social environments and expectations in every stage of our lives. But first, we will turn to scholarship about self-development, the process of coming to recognize a sense of self, a “self” that is then able to be socialized.
DeGregory, Lane. 2008. “The Girl in the Window.” St. Petersburg Times , July 31. Retrieved January 31, 2012 ( http://www.tampabay.com/features/humaninterest/article750838.ece ).
Introduction to Sociology 2e Copyright © 2012 by OSCRiceUniversity (Download for free at https://openstax.org/details/books/introduction-sociology-2e) is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Communities
- Toggle navigation
- [ Course Profile ]
- Announcements
- About Sociology
- Sociology Topics
- Sociology Resources
- Textbook info
- H.W. Due 2/11
- H.W due 2/13
- Week 1 Online: 3/19 – 3/22: H.W 3 Due 3/24
- Week 2 Online: 3/23 – 3/29: H.W 4 Due 3/31: Society and Social Interaction
- Week 3 Online: H.W 5: Socialization and Personal Development – Due 4/7
- Week 4 Online: 4/6 – 4/12: H.W. 6 -Social Movements / Civic Engagement Survey Due 4/14
- Week 5 Online: 4/13 – 4/19 : H.W. 7 Socialization Across the Life Course Due 4/21
- Week 6 Online: 4/21 – 4/26: H.W. 8. Education Due 4/28
- Week 7 Online: H.W 9 Social Stratification: Upward Mobility Due 5/12
- Week 8 Online: 5/4 – 5/10: H.W 10 – Global Inequality / Survey on Social Inequality Due 5 / 17
- Reflections 1: Sociological Perspective
- Reflections 2: Culture and Society Due 3/24
- Reflections 3: Gender, Sex and Sexual Orientation Due 3/31
Reflections 4: Socialization and Social Interaction Due 4/7
- Reflections 5: Race and Ethnicity Due 4/28
- Reflection 6: Social Inequality Due 5/12
- Zoom / BB Collaborate course sessions: TUESDAYS AT 530PM – 830PM
- FINAL EXAM FOR SOC 100
- Events attended for SOC 100
Reflection 4: Socialization and Social Interaction
Read Next →
Write a 1-2 (no more than 3) pages essay on Socialization and Social interaction: Verbal and Non-Verbal Communication. How does culture or society influence the ways in which individuals and groups socialize and interact with one another?
Social interaction is the process by which we act and react to people around us causing people’s behavior to change. In any human social activity, verbal and nonverbal communication is being done. People are going to interact differently depending on what’s at stake for them. But this can be controlled due to social structure since rules are put into place for proper behavior which affects all social interaction and can produce different personal outcomes. Social structure is an organized pattern of behavior that governs people’s relationships. Social structure shapes people’s actions, their lives are typically orderly and predictable rather than chaotic and random. Since people are not aware of the impact of the social structure until they violate culture rules in formal or informal settings.
Everyone in society has a role. A role is the behavior expected of a person who has a particular status. For example, a college student status but the role of a college student requires many formal behaviors such as going to class, reading, thinking, completing weekly assignments, writing papers, and taking exams. Informal behaviors can be joining a student club, befriending classmates, attending football games, and even drinking alcohol at parties on the weekend. Having a role can lead to role conflict and role strain. They can produce tension, hostility, aggression, and stress-related problems that can lead to insomnia, ulcers, eating disorders, weight loss or gain, and drug and alcohol abuse. In order to manage these conflicts or prevent them, you should compromise or negotiate between certain activities. Also, prioritize the activities that will benefit you the most. Finally, decide whether not to take on more roles than you have.
Nonverbal communications come in many forms. Nonverbal communications refer to messages sent without using words. Some of the most common nonverbal messages are silence, visual cues, touch, and personal space. Silence expresses a variety of emotions: agreements, fear, thoughtfulness, confusion, disagreement, embarrassment, regret, respect, sadness, and many more. In various contexts and depending on particular points in a conversation, silence means different things to different people. Sometimes silence saves us from embarrassing ourselves. Visual cues are another form of non-verbal communication that includes gestures, facial expressions, and eye contact. Most people believe certain gestures like folding your arms across your chest indicates a closed defensive attitude; leaning forward often shows interest; smiling and nodding shows agreement. But these gestures should be interpreted in context because of habit or hearing problems for instance an employee may always lean forward when listening regardless of whether he or she is interested. But the same gestures may have different meanings in different countries. For instance, tapping, one’s elbowed several times with the palm of one’s hand indicates that someone is sneaky in Holland, stupid in Germany and Austria, or mean or stingy in South America.
Verbal communication is a type of oral communication where messages are transmitted through spoken words. The sender gives words to she’s/his feelings, thoughts, ideas, and opinions and expresses them in the form of speeches, discussions, presentations, and conversations. There’s immediate feedback since there is a simultaneous transmission. Verbal communication is applicable in both formal and informal situations.
Leslie Huiracocha
- Announcements (1)
- Events attended for SOC 100 (2)
- FINAL EXAM FOR SOC 100 (1)
- H.W 3 Due 3/24 (4)
- H.W due 2/13 (3)
- H.W. Due 2/11 (2)
- Reflection 6: Social Inequality Due 5/12 (1)
- Reflections 1: Sociological Perspective (2)
- Reflections 2: Culture and Society Due 3/24 (3)
- Reflections 3: Gender, Sex and Sexual Orientation – Due 3/31 (2)
- Reflections 4: Socialization and Social Interaction Due 4/7 (2)
- Reflections 5: Race and Ethnicity (1)
- Reflections 5: Race and Ethnicity Due 4/28 (1)
- Sociology Resources (2)
- Sociology Topics (1)
- Uncategorized (1)
- Week 2 Online: 3/23 – 3/29: H.W 4 Due 3/31: Society and Social Interaction (5)
- Week 3 Online: 3/30 – 4/5: H.W 5 Due 4/7: Socialization and Personal Development (2)
- Week 3 Online: H.W 5: Socialization and Personal Development – Due 4/7 (3)
- Week 4 Online: 4/6 – 4/12: H.W. 5 -Social Movements / Civic Engagement Survey Due 4/14 (1)
- Week 5 Online: 4/13 – 4/19 : H.W. 7 Socialization Across the Life Course Due 4/21 (3)
- Week 6 Online: 4/21 – 4/26: H.W. 8. Education Due 4/28 (3)
- Week 7 Online: H.W 8 Social Stratification: Upward Mobility Due 5/12 (1)
- Week 7 Online: H.W 9 Social Stratification: Upward Mobility Due 5/12 (2)
- Week 8 Online: 5/4 – 5/10: H.W 10 – Global Inequality / Survey on Social Inequality Due 5 / 17 (1)
- Zoom / BB Collaborate course sessions: TUESDAYS AT 530PM – 830PM (1)
- May 2020 (9)
- April 2020 (10)
- March 2020 (23)
- February 2020 (7)
- January 2020 (2)
Welcome to the BMCC OpenLab!
BMCC’s OpenLab is an online platform where the College’s students, faculty and staff can come together to learn, work, play and share ideas.
Powered by:
Psychology Discussion
Essay on socialization.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Essay on Socialization!
Socialization is the process through which the individual learns to become an accepted member of the society. At birth the neonate is neither social nor unsocial. Because of this helplessness at birth he has to depend on other social beings for his care and welfare. As he grows in a social environment and in a social context, he develops various types of behaviour which are called social and gradually grows to become a social animal.
The interaction of the baby with his environment and particularly mother helps him in the above process. Thus the learning to adopt to the social norms, values and standards is called socialization.
The human organism is a byproduct of the society and social force. The manner in which the human child learns to become an accepted member of the society is called the socialization process. Anyone who does not accept or follow the dos and donots, rules and regulations, values and norms of the society is not called a socialised individual.
The socialization of the child takes place through action and reaction between the child and other individual members of the society. The child begins interaction with his mother first, then with his father and subsequently with other members of the family.
The process of socialization is quite complex. It involves the multiplicity of processes as it involves the multiplicity of social norms. It involves the various roles which the individual has to play in order to fulfil the expectations of the society. Not only the parental influence, and the influence of other adults but also the neighbourhood is of tremendous value in the socialization of the child.
Through the process of socialization the various values, codes, norms and mores of the society become a part of his personality, part of his personal values. When he accepts these willingly rather than as a matter of compulsion he is said to be socialized. The child’s behaviour is modified and remodified to conform to the expectations held by the members of the groups of which he is a member.
During the first three four years and before attending school the child is trained to meet the expectations of family members.
They teach him to follow the socially accepted behavioural patterns which are considered as good and reject unacceptable behavioural patterns which are considered as bad. But when he is admitted to a preschool or a nursery school or a primary school, he is also influenced by teachers and friends.
The child learns to adjust with a wider world of school teachers, class mates and play mates and a host of other persons. He learns the social norms, how to behave with the teachers and show respect to them, how to deal with the class mates. In this way as he grows and grows and reaches adulthood he comes across varied agents of socialization who mould his personality in the manner the society wants.
Not only the parental influence and the influence of the other adults also the neighbourhood is of tremendous value in the socialization of the child. Besides the effects of books, radio, TV and motion pictures are of tremendous value for the moral and social development of the child.
The child is socialized on the basis of his past and present experiences. Thus family, neighbourhood peers, playmates and classmates etc. mould the personality of the child according to the pattern of the society. Fundamentally socialization is possible through affiliation.
The early helplessness of the baby makes him dependent upon others. So he has to affiliate himself with others for his living. Love, comfort, respect, power, achievement and other secondary needs cannot be satisfied in isolation. Hence the child acquires many needs through social and affiliation learning which leads to socialization.
Major Features of the Process of Socialization :
The process of socialization is a continuous one. It continues from birth till death. Results of various experimental studies, observations of children in day-to-day life, interviews with parents, studies in different cultures taken together point out the major aspects of the process of socialization.
The dependency of the new born infant, the need for affiliation, the role of the reference group, the need for education and therefore admission to school, the effect of reward and punishment imposed by the parents, school and the society, delay in fulfilment of needs, desires and wishes, identification with the loved ones all have their respective roles in the socialization of the human infant.
The infant’s dependence upon the mother for food, care and nursing provides the essential condition for socialization of personality. But the help of reinforcement certain responses of the child are rewarded and certain other responses are not rewarded. Sometimes, the child is punished for not following the dos of the society. In this manner the dependent and helpless child is taught to be a member of the society.
The child also learns many values and traditions through imitation and incidental learning since parents do not always teach like a teacher. When a child sees that his mother is lying at the feet of God or Goddess he also does the same. When a child sees his mother showing her respect to a senior person by bowing her head she also learns to do the same.
Sears (1957) is of opinion that through dependence the process of identification develops. The desire to identify occurs when the child is given food and love and such reinforcements are periodically withdrawn so that the child will be rewarded by reproducing the mother’s behaviours.
The child also depends upon his parents and close family members for various informations about his surrounding and about the world at large. He also needs their help to clarify certain matters and to fulfil his curiosity. For this he has to obey them and follow what they say.
The need for affiliation also develops out of dependency. The desire to remain with others and be happy when one is in a group is an outcome of the helplessness of the child during early period. The desire to remain with others throughout one’s life has a direct link with the process of socialization.
Schachter (1959) found that isolation produces fear and affiliation reduces fear. Thus he concluded that persons with higher fear would affiliate more than those with low fears as through affiliation man tries to reduce his emotion of fear.
When a child grows up his socialization process is subject to the influence of outside agents of the society like the play group, teachers and peers. Now he becomes a member of several groups and clubs. Those groups which strongly influence the child are called the reference groups. The individual evaluates himself through the reference groups which serves as the standard for him.
New Comb (1943) while finding out the changes in the attitude of students that accompanied socialisation in a college observed the important role of reference group on socialisation. Sherif and Sherif (1964) also observe that like the family group, the reference groups influence the conduct of the individual.
The reference group serves as a norm, standard or model for the individual. The growing children and adolescents become a member of many groups and are influenced by the action, model ideal and values of such groups. A reference group serves as a standard for evaluation.
Out of the socialisation process the ‘self’ develops. The individual then learns to perceive himself and his self concept affects his social behaviour. A person perceives himself from three aspects i.e. from the cognitive, effective and behavioural components. His self concept becomes ultimately a source of motivation to him. The self concept develops out of the interaction of the individual with others.
When others say some one beautiful, sincere and intelligent, he develops a positive self concept and when people start saying negative things about one’s action and behaviour, he develops a negative self concept. A person who becomes regularly unsuccessful in examination perceives himself as academically poor. Thus the self concept develops through the process of social interaction and socialization.
When others say that he is an excellent boy he perceives himself as such and tries to repeat these characteristics in future which have brought him praise and reward. Those actions which bring him blame are given up and unlearned. A person who continuously become unsuccessful in an interview also develops negative self-image and inferiority complex.
The development of self therefore depends on continuous learning unlearning and releasing. Through the process of adjustment and readjustment the individual’s self is socialised.
Some have tried to compare the process of socialization with the procedures by which many human beings using raw materials construct automobiles. Many human beings interacting with the raw organism, the human infant, turn him to a socialized personality.
Nevertheless personality is not a mechanical by product of the society. Socialization is never a passive process and no personality is a mechanical by product of the society. A number of automobiles of similar type are produced using raw materials.
But no two human personalities are equal. Every personality is unique by itself. Every in the same family two brothers may have totally different personalities. One brother may have a very high social status while the other may be a delinquent and disgrace to the society.
Since no two personalities in the world are identically equal it would be erroneous to compare living human infants with the raw materials of automobiles which are dead materials.
When an infant undergoes the process of socialization he reacts in diverse ways. Sometimes he resists rules, regulations, traditions and customs of the society. At home, during training of feeding habits, there may be conflict between the child and the mother.
The child may resist to take certain types of good, to wear dresses of certain designs, he may like to go naked in summer, he may not like to follow certain traditions and customs which do not give him pleasure.
Sometimes a child may find it difficult to adjust with the demands and the needs of the society. He may find it difficult to control his emotions. If he is scolded by parents he is adviced to remain silent. He is not allowed to react. When he feels hungry he is not allowed to eat. He is allowed to eat only at a scheduled time and place.
Thus, the more rules and regulations he has to obey, the more disciplines, he has to follow, the more resistances are found. Since he has to meet a great deal of difficulty to conform to the expectations and norms of the groups he often resists conformity to social norms during infancy when it is mostly ‘id’.
But gradually when the ego develops, training of socialisation becomes stronger than the resistances and when he accepts the social values and norms as a matter of principle as his own values rather through compulsion, the conflict in the process of socialization is reduced and the person is said to be socialized.
The individual and society mutually respond to the process of socialization. The society tries to mould the individual through its rules, regulations, traditions and customs and the individual while trying to belong to the group, sometimes tries to modify the social standard as far as practicable.
A sense of belongingness helps one to feel secured and satisfied. Thus the process of socialisation helps one to develop a normal personality. One who is properly socialized, when he becomes a parent he undertakes the responsibility of socializing his own children and at this time, his attitude towards the prevalent social norms undergoes tremendous change.
With the change in the socio-cultural values and spirit of time, there is always a continuous change in the rules, regulations, standards, customs and traditions of the society. As a result, there is change in the socialisation of the human personality.
The socialization process is therefore never rigid but dynamic. It varies and changes from time to time and generation to generation. The parents, teachers and individuals have to adjust with the changing social customs and values and socialize their children accordingly.
They have to develop proper social attitudes and behaviours appropriate to his particular society. Otherwise there will be conflict due to generation gap. The child must behave in such a way which is approved by the group or society. Since the aim of socialization is to induce the individual to conform willingly to the ways of the society and the groups to which he belongs, parents and teachers should see that his personality is built up accordingly.
Otherwise in future there may be tremendous adjustment problems. Since socialization is a dynamic process a person who rigidly conforms to the rules and regulations of the society is not an ideal product of socialization.
A properly socialized person should be flexible and dynamic in approach to conform to the changing social standards of the society and culture. A person who is unable to adjust with this is therefore said to be unsocial or a social.
As previously indicated, the socialization practices change constantly. Social class has also an important role to play in this regard. Middle class mothers in comparison to working class mothers are more permissive towards the child’s expressed needs and wishes, are more equalitarian in their handling of the child and are less likely to use physical punishment.
Early learning experiences have a lasting impact on personality and socialization. In various studies of socialization process child psychologists have tried to investigate the effects of infant disciplines, child care programmes and post childhood discontinuities on adult personality. They have found that during the early years the parental influences on child is maximum and have powerful impact on socialization.
But during the later stage to reshape the unsatisfactory and socially inappropriate behaviours found in many adolescents, application of desocialization and resocialization processes are found essential.
Desocialization attempts to remove the previous attitudes and habits which are not conducive to proper socialization. Many had habits, antisocial and irresponsible, socially unacceptable behaviours can be reduced by this technique.
Resocialization on the other hand is a process by which the group induces a person to adopt one set of behaviour standards as a substitute for another. Sometimes after desocialization resocialization may be a necessary consequence. While removing the old values new values are to be substituted in their place.
Related Articles:
- Dependence Process of a Child | Essay | Child | Social Psychology
- Notes on Socialization: Introduction, Culture, Structure, Status and Conflict | Psychology
- Consequences of Socialization Process | Essay | Social Psychology
- Importance of Occupational Socialization

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

4.7D: Stages of Socialization Throughout the Life Span
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 8009
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
The socialization process can be separated into two main stages: primary socialization and secondary socialization.
Learning Objectives
- Give examples of how the socialization process progresses throughout a person’s life
- The life process of socialization is generally divided into two parts: primary and secondary socialization.
- Primary socialization takes place early in life, as a child and adolescent. This is when an individual develops their core identity.
- Secondary socialization takes place throughout an individual’s life, both as a child and as one encounters new groups. This involves more specific changes in response to the acquisition of new group memberships and roles and differently structured social situations.
- Some of the more significant contributors to the socialization process are: parents, guardians, friends, schools, siblings or other family members, social clubs (like religions or sports teams), life partners (romantic or platonic), and co-workers.
- secondary socialization : The socialization that takes place throughout one’s life, both as a child and as one encounters new groups that require additional socialization.
- primary socialization : The socialization that takes place early in life, as a child and adolescent.
Socialization is a life process, but is generally divided into two parts: primary and secondary socialization.

Primary socialization takes place early in life, as a child and adolescent. Secondary socialization refers to the socialization that takes place throughout one’s life, both as a child and as one encounters new groups that require additional socialization. While there are scholars who argue that only one or the other of these occurs, most social scientists tend to combine the two, arguing that the basic or core identity of the individual develops during primary socialization, with more specific changes occurring later—secondary socialization—in response to the acquisition of new group memberships and roles and differently structured social situations. The need for later-life socialization may stem from the increasing complexity of society with its corresponding increase in varied roles and responsibilities.

Mortimer and Simmons outline three specific ways these two parts of socialization differ:
- Content: Socialization in childhood is thought to be concerned with the regulation of biological drives. In adolescence, socialization is concerned with the development of overarching values and the self-image. In adulthood, socialization involves more overt and specific norms and behaviors, such as those related to the work role as well as more superficial personality features.
- Context: In earlier periods, the socializee (the person being socialized) more clearly assumes the status of learner within the context of the initial setting (which may be a family of orientation, an orphanage, a period of homelessness, or any other initial social groups at the beginning of a child’s life), the school (or other educational context), or the peer group. Also, relationships in the earlier period are more likely to be affectively charged, i.e., highly emotional. In adulthood, though the socializee takes the role of student at times, much socialization occurs after the socializee has assumed full incumbency of the adult role. There is also a greater likelihood of more formal relationships due to situational contexts (e.g., work environment), which moderates down the affective component.
- Response: The child and adolescent may be more easily malleable than the adult. Also, much adult socialization is self-initiated and voluntary; adults can leave or terminate the process at any time if they have the proper resources (symbolic, financial, and social) to do so.
Socialization is, of course, a social process. As such, it involves interactions between people. Socialization, as noted in the distinction between primary and secondary, can take place in multiple contexts and as a result of contact with numerous groups. Some of the more significant contributors to the socialization process are: parents, guardians, friends, schools, siblings or other family members, social clubs (like religions or sports teams), life partners (romantic or platonic), and co-workers. Each of these groups include a culture that must be learned and to some degree appropriated by the socializee in order to gain admittance to the group.
Understanding Socialization in Sociology
Overview and Discussion of a Key Sociological Concept
- Key Concepts
- Major Sociologists
- News & Issues
- Research, Samples, and Statistics
- Recommended Reading
- Archaeology
- Ph.D., Sociology, University of California, Santa Barbara
- M.A., Sociology, University of California, Santa Barbara
- B.A., Sociology, Pomona College
Socialization is a process that introduces people to social norms and customs. This process helps individuals function well in society, and, in turn, helps society run smoothly. Family members, teachers, religious leaders, and peers all play roles in a person's socialization.
This process typically occurs in two stages: Primary socialization takes place from birth through adolescence, and secondary socialization continues throughout one's life. Adult socialization may occur whenever people find themselves in new circumstances, especially those in which they interact with individuals whose norms or customs differ from theirs.
The Purpose of Socialization
During socialization, a person learns to become a member of a group, community, or society. This process not only accustoms people to social groups but also results in such groups sustaining themselves. For example, a new sorority member gets an insider's look at the customs and traditions of a Greek organization. As the years pass, the member can apply the information she's learned about the sorority when newcomers join, allowing the group to carry on its traditions.
On a macro level, socialization ensures that we have a process through which the norms and customs of society are transmitted. Socialization teaches people what is expected of them in a particular group or situation; it is a form of social control .
Socialization has numerous goals for youth and adults alike. It teaches children to control their biological impulses, such as using a toilet instead of wetting their pants or bed. The socialization process also helps individuals develop a conscience aligned with social norms and prepares them to perform various roles.
The Socialization Process in Three Parts
Socialization involves both social structure and interpersonal relations. It contains three key parts: context, content and process, and results. Context, perhaps, defines socialization the most, as it refers to culture, language, social structures and one’s rank within them. It also includes history and the roles people and institutions played in the past. One's life context will significantly affect the socialization process. For example, a family's economic class may have a huge impact on how parents socialize their children.
Research has found that parents emphasize the values and behaviors most likely to help children succeed given their station in life. Parents who expect their children to work blue-collar jobs are more likely to emphasize conformity and respect for authority, while those who expect their children to pursue artistic, managerial, or entrepreneurial professions are more likely to emphasize creativity and independence.
Gender stereotypes also exert a strong influence on socialization processes. Cultural expectations for gender roles and gendered behavior are imparted to children through color-coded clothes and types of play. Girls usually receive toys that emphasize physical appearance and domesticity such as dolls or dollhouses, while boys receive playthings that involve thinking skills or call to mind traditionally male professions such as Legos, toy soldiers, or race cars. Additionally, research has shown that girls with brothers are socialized to understand that household labor is expected of them but not of their male siblings. Driving the message home is that girls tend not to receive pay for doing chores, while their brothers do .
Race also plays a factor in socialization. Since White people don't disproportionately experience police violence, they can encourage their children to know their rights and defend them when the authorities try to violate them. In contrast, parents of color must have what's known as "the talk" with their children, instructing them to remain calm, compliant, and safe in the presence of law enforcement.
While context sets the stage for socialization, the content and process constitute the work of this undertaking. How parents assign chores or tell their kids to interact with police are examples of content and process, which are also defined by the duration of socialization, those involved, the methods used, and the type of experience .
School is an important source of socialization for students of all ages. In class, young people receive guidelines related to behavior, authority, schedules, tasks, and deadlines. Teaching this content requires social interaction between educators and students. Typically, rules and expectations are both written and spoken, and student conduct is either rewarded or penalized. As this occurs, students learn behavioral norms suitable for school.
In the classroom, students also learn what sociologists describe as "hidden curricula." In her book "Dude, You're a Fag," sociologist C.J. Pasco revealed the hidden curriculum of gender and sexuality in U.S. high schools. Through in-depth research at a large California school, Pascoe revealed how faculty members and events like pep rallies and dances reinforce rigid gender roles and heterosexism. In particular, the school sent the message that aggressive and hypersexual behaviors are generally acceptable in White boys but threatening in Black ones. Though not an "official" part of the schooling experience, this hidden curriculum tells students what society expects of them based on their gender, race, or class background.
Results are the outcome of socialization and refer to the way a person thinks and behaves after undergoing this process. For example, with small children, socialization tends to focus on control of biological and emotional impulses, such as drinking from a cup rather than from a bottle or asking permission before picking something up. As children mature, the results of socialization include knowing how to wait their turn, obey rules, or organize their days around a school or work schedule. We can see the results of socialization in just about everything, from men shaving their faces to women shaving their legs and armpits.
Stages and Forms of Socialization
Sociologists recognize two stages of socialization: primary and secondary. Primary socialization occurs from birth through adolescence. Caregivers, teachers, coaches, religious figures, and peers guide this process.
Secondary socialization occurs throughout our lives as we encounter groups and situations that were not part of our primary socialization experience. This might include a college experience, where many people interact with members of different populations and learn new norms, values, and behaviors. Secondary socialization also takes place in the workplace or while traveling somewhere new. As we learn about unfamiliar places and adapt to them, we experience secondary socialization.
Meanwhile , group socialization occurs throughout all stages of life. For example, peer groups influence how one speaks and dresses. During childhood and adolescence, this tends to break down along gender lines. It is common to see groups of children of either gender wearing the same hair and clothing styles.
Organizational socialization occurs within an institution or organization to familiarize a person with its norms, values, and practices. This process often unfolds in nonprofits and companies. New employees in a workplace have to learn how to collaborate, meet management's goals, and take breaks in a manner suitable for the company. At a nonprofit, individuals may learn how to speak about social causes in a way that reflects the organization's mission.
Many people also experience anticipatory socialization at some point. This form of socialization is largely self-directed and refers to the steps one takes to prepare for a new role, position, or occupation. This may involve seeking guidance from people who've previously served in the role, observing others currently in these roles, or training for the new position during an apprenticeship. In short, anticipatory socialization transitions people into new roles so they know what to expect when they officially step into them.
Finally, forced socialization takes place in institutions such as prisons, mental hospitals, military units, and some boarding schools. In these settings, coercion is used to re-socialize people into individuals who behave in a manner fitting of the norms, values, and customs of the institution. In prisons and psychiatric hospitals, this process may be framed as rehabilitation. In the military, however, forced socialization aims to create an entirely new identity for the individual.
Criticism of Socialization
While socialization is a necessary part of society, it also has drawbacks. Since dominant cultural norms, values, assumptions, and beliefs guide the process, it is not a neutral endeavor. This means that socialization may reproduce the prejudices that lead to forms of social injustice and inequality.
Representations of racial minorities in film, television, and advertising tend to be rooted in harmful stereotypes. These portrayals socialize viewers to perceive racial minorities in certain ways and expect particular behaviors and attitudes from them. Race and racism influence socialization processes in other ways too. Research has shown that racial prejudices affect treatment and discipline of students . Tainted by racism, the behavior of teachers socializes all students to have low expectations for youth of color. This kind of socialization results in an over-representation of minority students in remedial classes and an under-representation of them in gifted class. It may also result in these students being punished more harshly for the same kinds of offenses that White students commit, such as talking back to teachers or coming to class unprepared.
While socialization is necessary, it's important to recognize the values, norms, and behaviors this process reproduces. As society's ideas about race, class, and gender evolve, so will the forms of socialization that involve these identity markers.
- Understanding Resocialization in Sociology
- What Is Gender Socialization? Definition and Examples
- How Gender Differs From Sex
- What Is a Reference Group?
- What Is Social Oppression?
- What Is Cultural Hegemony?
- Definition of Social Control
- What Is Political Socialization? Definition and Examples
- The Sociology of Gender
- Units of Analysis as Related to Sociology
- What is a Norm? Why Does it Matter?
- What Is Social Learning Theory?
- Sociology of Deviance and Crime
- Using Ethnomethodology to Understand Social Order
- The Importance Customs in Society
- Goffman's Front Stage and Back Stage Behavior

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 5. Socialization
5.2. Why Socialization Matters
Socialization is critical both to individuals and to the societies in which they live. It illustrates how completely intertwined human beings and their social worlds are. First, it is through teaching culture to new members that a society perpetuates itself. If new generations of a society do not learn its way of life, it ceases to exist. Whatever is distinctive about a culture must be transmitted to those who join it, in order for a society to survive. For Canadian culture to continue, for example, children in Canada must learn about cultural values related to democracy: They have to learn the norms of voting, as well as how to use material objects such as a ballot. Of course, some would argue that it is just as important in Canadian culture for the younger generation to learn the etiquette of eating in a restaurant or the rituals of tailgate parties after baseball games. In fact, there are many ideas and objects that Canadians teach children in hopes of keeping the society’s way of life going through another generation.

Socialization is just as essential to individuals. Social interaction provides the means by which people gradually become able to see themselves through the eyes of others, learning who they are and how they fit into the world around them. In addition, to function successfully in society, people must learn the basics of their culture, everything from how to dress themselves to what is suitable attire for a specific occasion; from when to sleep to what to sleep on; and from what is considered appropriate to eat for dinner to how to use the stove to prepare it. Most importantly, people have to learn language — whether it is the dominant language or a minority language, whether it is verbal or through signs — in order to communicate and to think. As discussed earlier with the case of Danielle, without socialization, an individual would literally have no self. An individual would be unable to function socially.
Nature versus Nurture
Some experts assert that who people are is the result of nurture — the relationships and caring that surround them. Others argue that who people are is based on genetics. According to this belief, a person’s temperaments, interests, and talents are set before birth. From this perspective, then, who people are depends on nature .

One way researchers attempt to prove the impact of nature is by studying twins. Some studies followed identical twins (i.e., monozygotic twins) who were raised separately. The pairs shared the same genetics, but in some cases were socialized in different ways. Instances of this type of situation are rare, but studying the degree to which identical twins raised apart are the same or different can give researchers insight into how temperaments, preferences, and abilities are shaped by our genetic makeup versus our social environment.
For example, in 1968, twin girls born to a mentally ill mother were put up for adoption. However, they were also separated from each other and raised in different households. The parents, and certainly the babies, did not realize they were one of five pairs of twins who were made subjects of a scientific study (Flam, 2007). In 2003, the two women, by then age 35 years, were reunited. Elyse Schein and Paula Bernstein sat together in awe, feeling like they were looking into a mirror. Not only did they look alike, but they behaved alike, using the same hand gestures and facial expressions (Spratling, 2007).
Studies like this point to the genetic roots of temperament and behaviour. The Minnesota Study of Twins Raised Apart (MISTRA) included 81 identical (or monozygotic) twin pairs and 56 fraternal (or dizygotic) twin pairs who were raised apart (Segal, 2017). One study based on this data set compared twins using 11 personality scales. It showed that the median correlations of the test results were 0.49 for identical twins raised apart versus 0.51 for identical twins raised together, whereas the correlations for fraternal twins raised apart and together were 0.21 and 0.23 respectively. This seems to show the strong impact of shared genes, as the identical twins raised apart were much more similar than fraternal twins raised together. Another study based on the data set compared IQ tests of identical twins raised apart and discovered that the measures correlated on average 0.73, suggesting that 73% of the difference in general intelligence measured by the tests was genetically influenced.
On the other hand, parents of identical twins start noticing behavioural differences from a very young age.
It is not as hard to tell my sons apart now, but we often recognize them more based on personality differences than looks. One is adventurous, daring — the first to nosedive off a sofa, the first to fall down stairs. He also crawled, stood, cruised, and walked first. He hollers and cries when we leave the room. Our other boy is an observer. He can be laser-focused, able to spend 30 minutes trying to click together a buckle as his brother marches around with his chest puffed, in need of constant movement and entertainment (Hayasaki, 2018).
Studies of identical twins also have difficulty accounting for divergences in the development of inherited diseases. In the case of schizophrenia, epidemiological studies show that there is a strong biological component to the disease. The closer one’s familial connection to someone with the condition, the more likely one will develop it. However, even if an identical twin develops schizophrenia the other twin is less than 50 per cent likely to develop it themselves (Carey, 2012). Why is it not 100 per cent likely? What occurs to produce the divergence between genetically identical twins?
One explanation combines sociology and genetics. This is the field of epigenetics , the study of social or environmental impacts on the expression of genes (Segal et al., 2017). Cellular variations in gene expression between identical twins can lead to large differences in health, personality, and even physical appearance. For example, the impact of astronaut Scott Kelly’s stay on the International Space Station meant that 7 per cent of his genes changed their expression, even months after his return to earth, although his genes themselves remained the same as his identical twin Mark (also an astronaut). With epigenetics, gene activity reacts in response to environmental stimuli at a cellular level. In other words, environment and lifestyle influence how genes are expressed.
Though genetics and hormones play an important role in individual human characteristics, biological explanations of social behaviour have serious deficiencies from a sociological point of view, especially when they are used to try to explain complex aspects of human social life like homosexuality, male aggressiveness, female spatial skills, and the like. As noted in Chapter 3. Culture , the logic of biological explanation usually involves three components: the identification of a supposedly universal quality or trait of human behaviour, an attribution of a genetic source of the behavioural trait, and an evolutionary fitness argument why this behaviour makes it more likely that the genes that code for it will be passed successfully to descendents. The conclusion of this reasoning is that this behaviour or quality is hard-wired or difficult to change (Lewontin, 1991).
However, an argument, for example that males are naturally aggressive because of their hormonal structure or other biological mechanisms, does not take into account the huge variations in the meaning or practice of aggression between cultures, nor the huge variations in what counts as aggressive in different situations — let alone the fact that many men are not aggressive by any definition, and that men and women both have “male” hormones like testosterone. More interesting for the sociologist in this example is that men who are not aggressive often get called “sissies.” This indicates that male aggression has to do more with a normative structure within male culture than with a genetic or hormonal structure that explains aggressive behaviour.
Sociology’s larger concern is the effect that society has on human behaviour, the nurture side of the nature versus nurture debate. To what degree are processes of identification and “self-fulfilling prophecy” at work in the lives of the twins Elyse Schein and Paula Bernstein? Despite growing up apart, do they share common racial, class, or religious characteristics? Aside from the environmental or epigenetic factors that lead to the divergence of twins with regard to schizophrenia, what happens to the social standing and social relationships of a person when the condition develops? What happens to people who are living with schizophrenia in different societies? How does the social role of a person living with schizophrenia integrate them into a society (or not)? Whatever the role of genes or biology in people’s lives, genes are never expressed in a vacuum. Environmental influence always matters.
Making Connections: Case Study
The life of chris langan, the smartest man you’ve never heard of.

Bouncer. Firefighter. Factory worker. Cowboy. Chris Langan (b. 1952) has spent the majority of his adult life just getting by with jobs like these. He has no college degree, few resources, and a past filled with much disappointment. Chris Langan also has an IQ of over 195, nearly 100 points higher than the average person (Brabham, 2001). So why didn’t Chris become a neurosurgeon, professor, or aeronautical engineer? According to Macolm Gladwell in his book Outliers: The Story of Success (2008), Chris didn’t possess the set of social skills necessary to succeed on such a high level — skills that aren’t innate, but learned.
Gladwell (2008) looked to a recent study conducted by sociologist Annette Lareau in which she closely shadowed 12 families from various economic backgrounds and examined their parenting techniques. Parents from lower-income families followed a strategy of “accomplishment of natural growth,” which is to say they let their children develop on their own with a large amount of independence; parents from higher-income families, however, “actively fostered and accessed a child’s talents, opinions, and skills” (Gladwell, 2008). These parents were more likely to engage in analytical conversation, encourage active questioning of the establishment, and foster development of negotiation skills. The parents were also able to introduce their children to a wider range of activities, from sports to music to accelerated academic programs. When one middle class child was denied entry to a gifted and talented program, the mother petitioned the school and arranged additional testing until her daughter was admitted. Lower-income parents, however, were more likely to unquestioningly obey authorities such as school boards. Their children were not being socialized to comfortably confront the system and speak up.
What does this have to do with Chris Langan, deemed by some as the smartest man in the world (Brabham, 2001)? Chris was born in severe poverty, and he was moved across the country with an abusive and alcoholic stepfather. Chris’s genius went greatly unnoticed. After accepting a full scholarship to Reed College, his funding was revoked after his mother failed to fill out necessary paperwork. Unable to successfully make his case to the administration, Chris, who had received straight A’s the previous semester, was given F’s on his transcript and forced to drop out. After enrolling in Montana State University, an administrator’s refusal to rearrange his class schedule left him unable to find the means necessary to travel the 16 miles to attend classes. What Chris has in brilliance, he lacks in practical intelligence, or what psychologist Robert Sternberg defines as “knowing what to say to whom, knowing when to say it, and knowing how to say it for maximum effect” (Sternberg et al., 2000). Such knowledge was never part of his socialization.
Chris gave up on school and began working an array of blue-collar jobs, pursuing his intellectual interests on the side. Though he’s recently garnered attention from work on his “Cognitive Theoretic Model of the Universe,” he remains weary and resistant of the educational system.
As Gladwell (2008) concluded, “He’d had to make his way alone, and no one — not rock stars, not professional athletes, not software billionaires, and not even geniuses —ever makes it alone.”
Individual and Society
How do sociologists explain both the conformity of behaviour in society and the existence of individual uniqueness? The concept of socialization raises a classic problem of sociological analysis: the problem of individual agency . As described in Chapter 1. An Introduction to Sociology , individual agency is the capacity of individuals to act and make decisions independently. However socialization is about conformity: learning how to conform to social expectations and norms. How is it possible for there to be individual differences, individual choice, or individuality at all if human development is about assuming socially-defined roles? How can an individual have agency, the ability to choose and act independently of external constraints?
Erving Goffman described this paradox in Asylums: Essays on the social situation of mental patients and other inmates (1961) . As discussed at the end of this chapter, in a total institution , like an asylum, a prison, or an Indian residential school, individuals are typically stripped of anything that identifies them as individuals and then resocialized to conform to rigid expectations of appearance and behaviour. There is very little space provided for unique individuality. Yet, as Goffman (1961) puts it, there is a dynamic that pits the status, the need to belong, and stable “sense of being a person” against a more intimate, individual “sense of selfhood”:
it is . . . against something that the self can emerge . . . . Without something to belong to, we have no stable self, and yet total commitment and attachment to any social unit implies a kind of selflessness. Our sense of being a person can come from being drawn into a wider social unit; our sense of selfhood can arise through the little ways in which we resist the pull. Our status is backed by the solid buildings of the world, while our sense of personal identity often resides in the cracks (Goffman, 1961).
Since Western society places such value on individuality, in being oneself or in resisting peer pressure and other pressures to conform, the question of where society ends and where the individual begins often is foremost in the minds of students of sociology. Numerous debates in the discipline focus on this question.
However, from the point of view emphasized in this chapter, it is a false question. As noted previously, for Mead the individual “agent” is already a “social structure.” No separation exists between the individual and society; the individual is thoroughly social from the inside out and vice versa.

Mead addressed the question of agency at the level of the relationship between the “I” and the “me” as two “phases” that flip back and forth in the life of the self. The “me” is the part of the self in which one recognizes and assumes the expectations or “organized sets of attitudes” of others: one’s social roles, one’s designations, one’s personalities (as they appear to others), and so on. On the basis of the “me” people know what is expected of them in a social situation and what the consequences of following or breaking a norm will be. The “I” represents the part of the self which acts or responds to the organized attitudes of others. It is the unpredictable part of the self. It has the capacity to step outside of social role and expectations. As part of the self, it embodies the principles of novelty, spontaneity, freedom, initiative (and the possibility of change) in social action. Even the individual can never be sure in advance how they will act in a situation, nor be certain of the outcome of their actions. “Exactly how we will act never gets into experience until after the action takes place” (Mead, 1934). Both phases are thoroughly social — the individual only ever experiences themself “indirectly” from the standpoint of others — but without the two phases “there could be no conscious responsibility, and there would be nothing novel in experience” (Mead, 1934).
In a similar manner, sociologists argue that individuals vary because the social environments to which they adapt vary. The socialization process occurs in different social environments — i.e., environments made up of the responses of others — each of which impose distinctive and unique requirements. In one family, children are permitted unlimited access to TV and video games; in another, there are no TV or video games, for example. Even within the same family, children’s upbringing varies. When they are growing up, children adapt and develop different strategies of play and recreation. Their parents and others respond to the child’s choices, either by reinforcing them or encouraging different choices. They are older, younger, or middle siblings with different responsibilities and roles within the family. Along a whole range of social environmental differences and responses, support and resistance, children gradually develop stable and consistent orientations to the world, each to some degree unique because each is formed from a vantage point unique to the place in society the child occupies. Individual variation and individual agency are possible because society itself varies in each social situation. Indeed, the configuration of society itself differs according to each individual’s contribution to each social situation.

Structural Functionalism, Critical Sociology, and Symbolic Interactionism
Sociologists all recognize the importance of socialization for healthy individual and societal development. But how do scholars working in the theoretical paradigms of structural functionalism, critical sociology, and symbolic interactionism approach this topic?
Structural functionalists would say that socialization is an essential function in society, both because it trains members to operate successfully within it and because it perpetuates culture by transmitting it to new generations. Individuals learn and assume different social roles as they age because different responsibilities and tasks are expected of them. These roles come with relatively fixed norms and social expectations attached, which allow for predictable interactions between people. Nevertheless, how the individual lives and balances their roles is subject to variation. There can also be role conflict when the expectations or functions of different roles conflict. During the COVID-19 pandemic for example, working remotely from home often involved a careful negotiation between meeting an employer’s expectations while also being available as a parent for children unable to go to school.
A critical sociologist might argue that socialization reproduces inequality from generation to generation by conveying different expectations and norms to those with different social characteristics. For example, individuals are socialized with different expectations about their place in society according to their gender, social class, and race. As in the life of Chris Langan, this creates different and unequal opportunities and, therefore, socialization is a process that can perpetuate and naturalize power relationships in society.
A symbolic interactionist studying socialization is concerned with face-to-face exchanges and symbolic communication. For example, dressing baby boys in blue and baby girls in pink is one small way that messages are conveyed about differences in gender roles. The idea that “the self is a social structure” encapsulates the symbolic interactionist position. Even that which seems most “one’s own” — one’s private thoughts, self-feelings, bodily experiences, agency — is a product of social messages that continually mirror the self back to the self. For the symbolic interactionist, though, how these messages are formulated and how they are interpreted are always situational, always renewed, and defined by the specific interactions in which the communication occurs. The identity of the self is not fixed, it is an ongoing process.
Media Attributions
- Figure 5.12 FullCircle by Niyam Bhushan, via Flickr, is used under a CC BY 2.0 licence.
- Figure 5.13 John Everett Millais (1829-1896) – The Twins, Kate and Grace Hoare – PD.36-2005 – Fitzwilliam Museum , by John Everetty Millais/ Fizwilliam Museum, ID 125024 , via Wikimedia Commons, is in the public domain .
- Figure 5.14 Christopher Langan Young , from Darien Long, via Wikimedia Commons, is used under a CC BY 2.0 licence.
- Figure 5.15 [ figures, holzfigur, pinocchio, males, arts crafts, wood carving …] from PxHere is used under a CC0 Universal Public Domain Dedication licence.
Introduction to Sociology – 3rd Canadian Edition Copyright © 2023 by William Little is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Agents of Socialization: Definition & Examples
Charlotte Nickerson
Research Assistant at Harvard University
Undergraduate at Harvard University
Charlotte Nickerson is a student at Harvard University obsessed with the intersection of mental health, productivity, and design.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Agents of socialization are the people, groups, and social institutions that affect one’s self-concept, attitudes, and behaviors. For example, parents, teachers, priests, television personalities, rock stars, etc.
Agents of socialization teach people what society expects of them. They tell them what is right and wrong, and they give them the skills they need to function as members of their culture.

- Primary agents of socialization include people with whom we have a close intimate relationship, such as parents, and usually occur when people are very young.
- The family is usually considered the primary agent of socialization , and schools, peer groups, and the mass media are considered secondary socialization agencies.
- Secondary agents of socialization are groups or institutions that influence an individual’s socialization process after or alongside primary agents like family.
- They include secondary relationships (not close, personal, or intimate) and function to “Liberate the individual from a dependence upon the primary attachments and relationships formed within the family group” (Parsons, 1951).
- Unlike primary agents of socialization (such as family and peers), secondary agents are typically less influential in shaping an individual’s fundamental beliefs and values.
What is Socialization?
Socialization is the process of learning the norms and customs of a society. Through socialization, people learn how to behave in a way that is acceptable to their culture.
Socialization also helps to ensure that members of a society know and understand the rules that they are expected to follow so that they can function effectively in society or within a particular group (Ochs, 1999).
The process of socialization can happen throughout one’s life, but it is most intense during childhood and adolescence when people are learning about their roles and how to interact with others.
Adult socialization may occur when people find themselves in new circumstances, especially in a culture with norms and customs that differ from theirs.
Several agents of socialization play a role in shaping a person’s identity, including family, media, religion, schools, and peer groups (Ochs, 1999).
The Purpose of Socialization
The purpose of socialization is to teach people the norms and customs of their culture so that they can function within it.
Norms are the rules that dictate how people are expected to behave in a given situation. Customs, meanwhile, are the traditional practices of a culture, such as its values, beliefs, and rituals (Ochs, 1999).
Socialization also helps to instill a sense of social control within members of a society so that they conform to its rules and regulations.
Social control is the process by which a society tries to ensure that its members behave acceptably. It can be done through punishments, rewards, or simply by teaching people what is expected of them. In some cases, social control is necessary to maintain order and prevent chaos.
In other cases, it may be used to protect the interests of those in power or to promote a certain ideology (Ochs, 1999).
Example Agents of Socialization
We normally refer to the people responsible for our socialization as agents of socialization and, by extension, we can also talk about agencies of socialization (such as our family, the education system, the media, and so forth).
Family members can include parents, siblings, grandparents, aunts, uncles, and cousins. The family is the first and most important agent of socialization for children.
It is through families that people learn about culture and how to behave in a way that is acceptable to society. Families also teach people about language and communication, how to relate to others, and how the world works.
For example, families teach their children the difference between strangers and friends and what is real and imagined (Kinsbury & Scanzoni, 2009).
Race, social class, religion, and other societal factors influence the experiences of families and, as a result, the socialization of children.
Families from some cultures may socialize for obedience and conformity, while those from others may do so for creativity and individualism. Families from different social classes may have different lifestyles and provide their children with different opportunities for learning.
Gender norms, perceptions of race, and class-related behaviors also influence family socialization. For example, countries that provide paternity leave and accept stay-at-home fathers in the social landscape are more likely to socialize male children to be more willing to care for children when they are adults (Kinsbury & Scanzoni, 2009).
Schools are an important secondary agent of socialization. Most students spend most of the day at school, immersing themselves in both academic subjects and behaviors like teamwork, following a schedule, and using textbooks (Durkheim, 1898).
These school rituals reinforce what society expects from children. As Bowles and Gintis (1976) discuss, schools in much of the US and Western Europe instill a sense of competition into the way grades are awarded, and the way teachers evaluate students.
By participating in a race or math contest, children learn that in order to succeed, they must be better than others. This is an important value in capitalist societies , where people are expected to strive for personal gain.
In contrast, schools may also place more emphasis on working together and cooperating with others, as this is seen as a way to achieve the collective good.
Alternatively, in countries like Japan, children are expected to conform to group norms and not question teachers.
The type of school a child attends also shapes their socialization. For example, children who attend private schools are more likely to have parents who are wealthy and well-educated.
As a result, these children learn different values and beliefs than those who attend public school. Nonetheless, schools everywhere teach children the essential features of their societies and how to cope with bureaucracy, rules, expectations, waiting their turn, and sitting still for hours during the day (Bowles & Gintis, 1976).
3. Community / Neighborhood
Communities or neighborhoods consist of a group of people living in the same geographic area under common laws or groups of people sharing fellowship, a friendly association, and common interests.
The community is a socializing agent because it is where children learn the role expectations for adults as well as themselves. The community provides a sense of identity to individuals and helps to define what is right or wrong.
Children can acquire this socialization by modeling adults, having rules enforced on them, or experiencing consequences for their behavior (Putnam, 2000).
It also teaches children how to interact with people who are different from them in terms of race, ethnicity, social class, and religion. For example, children learn that it is polite to speak quietly in the library, but they can be loud when they are playing with friends at the park.
The community also offers opportunities for children to explore their interests and talents. For example, some communities have youth clubs, sports teams, and scouting groups. These activities allow children to try new things, make friends, and develop a sense of responsibility (Putnam, 2000).
People learn from their peers (the people of their own age and similar social status) how to dress, talk, and behave. People also learn about what is important to one’s peer group and what is not.
During adolescence, peers become even more important as agents of socialization. This is because adolescents are exploring their identities and trying to figure out who they are and where they fit in the world.
Peers provide support and guidance during this time and help people learn about the norms and values of their culture — as well as what to wear, eat, watch, and where to spend time.
On the downside, adolescent peer influences have been seen as responsible for underage drinking, drug use, delinquency, and hate crimes (Agnew, 2015).
During peoples’ 20s and 30s, peer groups tend to diminish in importance. This is because people are more likely to be working and have less free time. In addition, people are more likely to be married or in a committed relationship.
As a result, they are less likely to spend time with friends and more likely to socialize within their families.
However, parents with young children may broaden their peer groups further and accept more influence as they reach out to their surrounding communities to care for their children (Vandall, 2000).
5. Mass Media
The media works by providing information to a wide audience via television, newspapers, radio, and the Internet. This broad dissemination of information greatly influences social norms (Roberts, Foehr, and Rideout 2005).
The media teaches people about material objects, current events, and fashion but also enforces nonmaterial culture: beliefs, values, and norms. It also teaches people how to think about and react to political events, such as elections.
In addition, it provides information about what is happening in other parts of the world, how people in other cultures live, and how people from a particular society should perceive the way that others live.
6. Religion
Religions can be both formal and informal institutions and are an important avenue of socialization for many people.
Synagogues, temples, churches, mosques, and similar religious communities teach participants how to interact with their religion’s material culture — for example, the mezuzah, a prayer rug, or a communion wafer.
The ceremonies upheld by religion can often relate to family structure — like marriage and birth rituals, and religious institutions can reinforce gender norms through socialization. This reinforces the family unit’s power dynamics and fosters a shared set of values transmitted through the rest of society (Pearson-Merkowitz & Gimpel, 2009).
Historically, religious institutions have played a significant role in social change. For example, the civil rights movement in the United States was led by religious leaders such as Reverend Martin Luther King Jr. Similarly, the women’s suffrage movement was also partly motivated by religious beliefs.
Today, religion continues to shape people”s socialization experiences. For instance, some religions encourage members to protest wars and volunteer to help the poor. In all of these cases, religious institutions socialize people to behave in a way that favors once-vulnerable groups (Pearson-Merkowitz & Gimpel, 2009).
7. Government
The government is another agent of socialization. It enacts laws that uphold social norms and values, and it also provides institutions and services that support citizens.
Government is notable in that it can fund a number of institutions that encourage socialization. For example, the government funds public schools, which play a key role in children”s socialization.
The government also funds other programs that provide opportunities for social interaction, such as after-school programs, parks, and recreation centers (Oberfield, 2014).
The military is another example of how the government can influence people”s socialization experiences.
For instance, the military teaches people how to work together in a hierarchy, follow orders, and use violence to achieve objectives. People who serve in the military often come from different backgrounds and have different values.
As a result, the military can be an agent for socializing people to collaborate with those from disparate races and classes against a common opponent (Oberfield, 2014).
The government can also create roles through legislation. For example, governments usually define an “adult” as being at least eighteen years old, the age at which a person becomes legally responsible for themselves.
Meanwhile, 65 brings the onset of “old age” as seniors become eligible for benefits. These roles motivate people to be socialized into a different category, learning to conform to both the government”s and broader society”s expectations of age (Oberfield, 2014).
Other Agents of Socialization (Ethnicity and class)
Ethnic socialization is the process by which people learn about their ethnic group’s culture and history. It is a type of socialization that occurs within ethnic groups.
Ethnic socialization helps prepare children for the challenges and opportunities they will face as members of an ethnic group. It also helps them develop a positive sense of self and a strong sense of identity.
It can also lead to the acquisition of patterns of speech, beliefs, perceptions, and attitudes of an ethnic group by an individual who comes to see themselves come to see themselves and others as members of that group.
Both parents and peers are primary ethnic socialization agents, but agents as large as the media and the wider community also play a role (Conger & Dogan, 2007).
Class socialization is the process by which people learn about their social class and how to behave in a way that is appropriate for their class. It is a type of socialization that occurs within social classes.
Like ethnic socialization, class socialization helps prepare children for the challenges and opportunities they will face as members of a social class.
Children who undergo class socialization learn to discern other members of their social class as well as develop attitudes of trust and mistrust toward those from other social groups (Conger & Dogan, 2007).
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between socialization and enculturation.
Enculturation is a process by which people learn the customs and traditions of their culture. Socialization, on the other hand, is the process by which people learn the norms and values of their society.
While socialization is the process of learning socially acceptable behavior in every culture, enculturation is the process of socialization in a particular culture. That is to say, enculturation is a product of socialization (Cromdal, 2006).
What is the difference between culture and socialization?
Culture is the unique set of beliefs, values, customs, and knowledge of a group of people. Socialization is the process by which people learn the norms and values of their culture. Culture is passed down from generation to generation through socialization (Cromdal, 2006).
One way to think about the difference between culture and socialization is that culture is what people believe, and socialization is how those beliefs are transmitted.
For example, American culture is often classified as highly individualistic. Individualism is the idea that each person is responsible for themselves. This belief is passed down through socialization experiences, such as parents teaching their children to be independent.
What are the most important agents of socialization?
Agents of socialization are the individuals, groups, or institutions that influence our self-concepts, attitudes, behaviors, and orientations toward life. They play a crucial role in shaping us into socially adept individuals.
The most important agents of socialization typically include:
Family: The family is usually the first and most impactful agent of socialization. From infancy, family members impart values, norms, and biases, influencing a child’s personality, emotional development, and behavior.
Schools: After the family, schools play a significant role in socialization. They expose children to new cultural values, expectations, and peer groups, and help them develop a sense of independence.
Agnew, R. (2015). General strain theory and delinquency. The handbook of juvenile delinquency and juvenile justice, 2 , 239-256
Bowles, S., & Gintis, H. (2011). Schooling in capitalist America: Educational reform and the contradictions of economic life . Haymarket Books.
Cromdal, J. (2006). Socialization .
Conger, R. D., & Dogan, S. J. (2007). Social Class and Socialization in Families .
Kingsbury, N., & Scanzoni, J. (2009). Structural-functionalism. In Sourcebook of family theories and methods (pp. 195-221). Springer.
Parsons, T. E., & Shils, E. A. (1951). Toward a general theory of action .
Pearson-Merkowitz, S., & Gimpel, J. G. (2009). Religion and political socialization. The Oxford handbook of religion and American politics , 164-190.
Oberfield, Z. W. (2014). Becoming bureaucrats: Socialization at the front lines of government service . University of Pennsylvania Press.
Ochs, E. (1999). Socialization. Journal of Linguistic Anthropology, 9 (1/2), 230-233.
Putnam, R. D. (2000). Bowling alone: The collapse and revival of American community . Simon and schuster.
Rideout, V., Roberts, D. F., & Foehr, U. G. (2005). Generation M: Media in the Lives of 8-18-Year-olds . Executive Summary.
Vandell, D. L. (2000). Parents, peer groups, and other socializing influences. Developmental psychology, 36 (6), 699.
Related Articles

Latour’s Actor Network Theory

Cultural Lag: 10 Examples & Easy Definition

Value Free in Sociology

Cultural Capital Theory Of Pierre Bourdieu

Pierre Bourdieu & Habitus (Sociology): Definition & Examples

Two-Step Flow Theory Of Media Communication
Introduction to Socialization
Chapter outline.
In the summer of 2005, police detective Mark Holste followed an investigator from the Department of Children and Families to a home in Plant City, Florida. They were there to look into a statement from the neighbor concerning a shabby house on Old Sydney Road. A small girl was reported peering from one of its broken windows. This seemed odd because no one in the neighborhood had seen a young child in or around the home, which had been inhabited for the past three years by a woman, her boyfriend, and two adult sons.
Who was the mystery girl in the window?
Entering the house, Detective Holste and his team were shocked. It was the worst mess they’d ever seen, infested with cockroaches, smeared with feces and urine from both people and pets, and filled with dilapidated furniture and ragged window coverings.
Detective Holste headed down a hallway and entered a small room. That’s where he found the little girl, with big, vacant eyes, staring into the darkness. A newspaper report later described the detective’s first encounter with the child: “She lay on a torn, moldy mattress on the floor. She was curled on her side . . . her ribs and collarbone jutted out . . . her black hair was matted, crawling with lice. Insect bites, rashes and sores pocked her skin . . . She was naked—except for a swollen diaper. … Her name, her mother said, was Danielle. She was almost seven years old” (DeGregory 2008).
Detective Holste immediately carried Danielle out of the home. She was taken to a hospital for medical treatment and evaluation. Through extensive testing, doctors determined that, although she was severely malnourished, Danielle was able to see, hear, and vocalize normally. Still, she wouldn’t look anyone in the eyes, didn’t know how to chew or swallow solid food, didn’t cry, didn’t respond to stimuli that would typically cause pain, and didn’t know how to communicate either with words or simple gestures such as nodding “yes” or “no.” Likewise, although tests showed she had no chronic diseases or genetic abnormalities, the only way she could stand was with someone holding onto her hands, and she “walked sideways on her toes, like a crab” (DeGregory 2008).
What had happened to Danielle? Put simply: beyond the basic requirements for survival, she had been neglected. Based on their investigation, social workers concluded that she had been left almost entirely alone in rooms like the one where she was found. Without regular interaction—the holding, hugging, talking, the explanations and demonstrations given to most young children—she had not learned to walk or to speak, to eat or to interact, to play or even to understand the world around her. From a sociological point of view, Danielle had not been socialized.
Socialization is the process through which people are taught to be proficient members of a society. It describes the ways that people come to understand societal norms and expectations, to accept society’s beliefs, and to be aware of societal values. Socialization is not the same as socializing (interacting with others, like family, friends, and coworkers); to be precise, it is a sociological process that occurs through socializing. As Danielle’s story illustrates, even the most basic of human activities are learned. You may be surprised to know that even physical tasks like sitting, standing, and walking had not automatically developed for Danielle as she grew. And without socialization, Danielle hadn’t learned about the material culture of her society (the tangible objects a culture uses): for example, she couldn’t hold a spoon, bounce a ball, or use a chair for sitting. She also hadn’t learned its nonmaterial culture, such as its beliefs, values, and norms. She had no understanding of the concept of “family,” didn’t know cultural expectations for using a bathroom for elimination, and had no sense of modesty. Most importantly, she hadn’t learned to use the symbols that make up language—through which we learn about who we are, how we fit with other people, and the natural and social worlds in which we live.
Sociologists have long been fascinated by circumstances like Danielle’s—in which a child receives sufficient human support to survive, but virtually no social interaction—because they highlight how much we depend on social interaction to provide the information and skills that we need to be part of society or even to develop a “self.”
The necessity for early social contact was demonstrated by the research of Harry and Margaret Harlow. From 1957 to 1963, the Harlows conducted a series of experiments studying how rhesus monkeys, which behave a lot like people, are affected by isolation as babies. They studied monkeys raised under two types of “substitute” mothering circumstances: a mesh and wire sculpture, or a soft terrycloth “mother.” The monkeys systematically preferred the company of a soft, terrycloth substitute mother (closely resembling a rhesus monkey) that was unable to feed them, to a mesh and wire mother that provided sustenance via a feeding tube. This demonstrated that while food was important, social comfort was of greater value (Harlow and Harlow 1962; Harlow 1971). Later experiments testing more severe isolation revealed that such deprivation of social contact led to significant developmental and social challenges later in life.
In the following sections, we will examine the importance of the complex process of socialization and how it takes place through interaction with many individuals, groups, and social institutions. We will explore how socialization is not only critical to children as they develop but how it is also a lifelong process through which we become prepared for new social environments and expectations in every stage of our lives. But first, we will turn to scholarship about self-development, the process of coming to recognize a sense of self, a “self” that is then able to be socialized.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/introduction-sociology-2e/pages/1-introduction-to-sociology
- Authors: Heather Griffiths, Nathan Keirns
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Introduction to Sociology 2e
- Publication date: Apr 24, 2015
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/introduction-sociology-2e/pages/1-introduction-to-sociology
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/introduction-sociology-2e/pages/5-introduction-to-socialization
© Feb 9, 2022 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
112 Socialization Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best socialization topic ideas & essay examples, 👍 good essay topics on socialization, ⭐ simple & easy socialization essay titles, ❓ questions related to socialization.
- The Role of Family in the Process of Socialization Although each parent in a family has a role in the upbringing of a child, in many cases, the mother initiates the socialization process in a child.
- Family as an Agent of Socialization Essay The family regardless of its nature and size is the fundamental factor in socialization. The family is a storehouse of warmth and compassion and stands in resistance to the aggressive world of trade.
- Ann Oakley’s Gender Socialization Theory Essay She received her bachelor degree in 1965.she continued her studies at Bedford College, University of London, Anne has gained a PhD in 1969.main spheres of her investigations included sociology of medicine and health of women.
- “The Cycle of Socialization” by Harro The article entitled “The cycle of socialization” by Harro discusses the nature of people’s prejudices, looks at how they are developed and what factors influence the formation of people’s assumptions and stances.
- The Impact of Socialization on My Life Therefore this paper is going to discuss on the issues of the impact that my socialization in conformity and obedience to authority and how has affected my life.
- Cooking at Home vs. Eating Out: Lunch as a Ritual for Emotional Pleasure, Creativity, and Socialization Many secondary factors influence the decision to eat at home or out, but it is cooking on my own that unlocks creativity and likewise allows me to gather friends and socialize in my kitchen.
- Socialization as a Lifelong Process Some social researchers say socialization speaks to the procedure of learning all through life and is a focal impact on the conduct, convictions, and activities of grownups and kids.
- Challenges of the Socialization Process In conclusion, the described problem of the dependency of socialization on the external environment presents a threat to youngsters’ future. Their interactions online for all occasions cannot substitute real-life communication and, consequently, do not contribute […]
- Western and Eastern Conceptions of Self and Socialization Buddhism is one of the oldest religions in the world which is based on old traditions and cultural norms of the Eastern hemisphere.
- Socialization for the Transmission of Culture Cultural transmission is one of the basic constituents of recreating cultures and passing values from one person or group to others.
- Socialization Process and Conflict Resolution This study aims to understand the process of socialization as well as find out how I deal with conflicts arising from the various agents of socialization The process of socialization starts in the family as […]
- Impact of Mass Media on Socialization The mass media and the social media have been major agents of socialization. On the social media, Facebook, Tweeter, and YouTube are the main agents of socialization.
- Socialization Process and Its Main Factors All in all, I can note that my social position is favorable and enables me to become a successful member of the American society.
- Impact of Media in Socialization The media is one of the agents that have nearly permanent effect on people social lifestyles because of its manipulative style of shaping the society. The media consumes the behavioural pattern of many and mostly […]
- The Role of Family in Political Socialization When children grow up they try to find out the political parties their parents prefer and investigate the issues that make them to be members of these parties.
- Socialization in a Multicultural Framework In particular, it is necessary to explain the roles played by school and families in the upbringing of a child, especially if we are speaking about appreciation of other traditions, values, worldviews, and so forth. […]
- Education Impact on Socialization To pursue the American Dream, young Americans should complete all the stages of socialization effectively, and the process of receiving the education is the important stage.
- Student-Athletes and Socialization Many student-athletes focus on their athletic performance and often try to succeed in their athletic career at the expense of their academic performance.
- Children’s Socialization From the observation carried out in a number of families it was observed that in the family where parents are very close to their children and offered guidance or assistance to the children, discipline them […]
- Socialization, Adaptation, and Isolation Scientists propose to establish the boundaries of the influence of these factors depending on the intensity of their impact, the age of a person, their satisfaction with their own life, or according to the principles […]
- Socialization as a Human Nature Development Factor However, regarding the fact that people are social creatures, human nature is formed in the process of socialization under the impact of multiple essential factors.
- Socialization Factors for Personal Development The religion and culture that I embrace at the present moment are a result of the interaction that I had with my family.
- Socializing Agents in Shaping One’s Life From my parents’ experience, I have come to appreciate the importance of unity and cooperation in the family. The way my parents related to other family members and friends taught me how I should behave.
- Socialization and Consideration of Others However, it is of vital importance to make sure that one’s actions and words are ethical in order not to spread immorality and negativity.
- Socialization of Adolescents in Modern Psychology The growth and development of adolescents is a major concern for many parents; the use of sports and physical activities is becoming common in finding a solution to teenagers’ socialization challenges.
- The Cycle of Socialization Following the cycle of socialization introduced by Harro, aspects of my life will be examined to identify the influences which brought me to this point and continue to guide me further.
- Child Socialization: Bronfenbrenner’s Ecological Systems Theory I played with my neighbors in both China and the US. I adhere to the norms in my macrosystem because they are sensible and make me a better citizen.
- Gender Socialization Therefore, in order to reconstruct the role of race, class and gender in society, it is important to examine them in the context of power relations.
- Culture, Socialization, and Society The third perspective is conflict theory, in which society constantly competes for resources and social position. In this perspective, each individual understands the world based on their social status.
- Socialization in Cultural Anthropology If I were to return to the gym, I would be directly involved in the communication processes. After taking my notes and observing people exercising for approximately an hour, I turned my attention to the […]
- Socialization: The Importance for Children In this case, it is essential to realize that one’s environment and genes play a significant role in determining the outcome of people’s lives.
- Workplace Socialization and Newcomer Turnover It is important to address the issue of newcomer turnover as it can lead to a poor image in the labour market.
- Socialization: Obeying the Established Rules This duality raises the question of whether the rules that exist at any given time are too restrictive for people to follow blindingly in real life.
- Importance of Socialization for Personality Socialization is the assimilation of social experience and the training of an individual in social roles and behavior, without which they cannot become a full-fledged member of society.
- Sports as a Socialization Tool in Minority Groups In essence, parents are integral when it comes to the increase in the number of children from minority groups who engage in sports.
- The Socialization Processes Case The case study entails the relationships between managers and employees in the workplace and strategies that can be used to keep the employees engaged and motivated.
- Gender Identity Applied in Human Socialization Gender identity concept is applied in the socialization and culture of humans. Throughout a person’s lifespan, gender socialization transpires in fluctuating contexts such as in school, among parents, or in the media.
- Socialization and the Life Course: Human Behavior and Sociology This is a rather hyperbolized statement; however, it may be seen as a reference to how people are integrated into society and how it may form them as individuals.
- The Islamic State of Iraq and Syria and Its Socialization Practices ISIS, or the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria, is a terrorist group that appeared as a branch of Al-Qaeda in 2014 and conquered large parts of Iraq and Syria.
- Internet Impact on Children’s Intelligence and Socialization Ninety percent of children today already have an online history once they reach the age of two, and most use the internet regularly by the age of seven or eight.
- Social Inequality, Socialization, and Values Living in terms of limited access to resources also influences career choice and the level of income. As a result, the problem remains unresolved, and communities suffer from the unfair distribution of benefits.
- Gender Socialization and Its Impact An example of a norm in a society is that women are expected to be polite and dress accordingly while men are expected to be solid and aggressive.
- Socialization Issue in an Incarcerated Girl With the help of language is a process of making sense of the world around us and knowing yourself. Through the study of language, each newborn person gets access to the collective experience and joins […]
- Assisting New Nurses With Socialization Into the Profession In nursing, socialization necessitates being familiar with the roles and responsibilities, and values to uphold while in the field of practice.
- The Games Children Play as Agents of Socialization In my play, I was in charge of the ‘kitchen’ and ‘toy children.’ I snapped when my sister came to my cafeteria because I thought it would be my fault if anything goes wrong.
- The Role of Media in Socialization As per the theory of sanctions, they evoke the desire in people to enforce compliance with these principles. The failure to do so is viewed as a threat, and male violence can be partially explained […]
- Residents of Saudi Arabia: Question of Socialization The purpose of this research study is to: Explore Saudi citizens desire to communicate with international visitors To measure the level of ethnocentrism which may affect their ability to communicate well with people from other […]
- Registered Nurse Socialization Observation In case they need to talk to specific individuals in the health center, it will be a pleasure to get him or her in time in order to enhance the diffusion of their anger.
- Socialization Skills and Children Who Have a Physical Impairment The most appropriate place for Cherry is the corner seat at the table near the door as it provides easy access to the workplace, but the girl is among the children.
- Juvenile Delinquency and the Importance of Socialization At the time of the incident, according to the authors of the article, twenty students out of a total of thirty had arrived for the lecture.
- Racial and Ethnic Socialization Racial/ethnic socialization and parental involvement in education as predictors of cognitive ability and achievement in African American children. Racial/ethnic socialization and parental involvement in education as predictors of cognitive ability and achievement in African American […]
- My View of Political Socialization Political socialization is the process of peoples’ acquiring political values in the course of time and living in a particular community.
- Theory of Socialization Analysis For instance, according to the supporters of the conflict theory, mass media, act only as a means of control, and they only advance the interests of ruling classes.
- Socialization and Development of Life Skills This work might be useful to the extent that it provides clear guidelines for the assessment of the relations in the family.
- Age and the Agents of Socialization The process of socialization is a slow and strong one, with most of the knowledge and prejudices being a result of this process.
- Various Psychologists’ Relation to Socialization The SUPERGO instills morality to the child in accordance to the values of the society and persistently strives for faultlessness. The disadvantage of Erickson theory in relation to socialization is that there is Intra-family relationship […]
- Socialization and Identity Analysis Social self therefore we can say is the one that makes or helps the individual to identify themselves and act accordingly.
- The Socialization of the Caregivers Therefore, it would be relevant to speak on the issue of the influence of the caregivers’ socialization on the improvement of the socialization skills and their impact on patients’ health.
- Socialization Over the Internet: Personality Deception or Personality Embellishment? Anonymous socialization was not possible and the people who lacked the self confidence to present themselves to others for all sorts of judgment in the name of friendship and social relationships. The advent of the […]
- Elderly Woman’s Behavior and Socialization Change The log also presents the analysis of the social characteristics, attitudes of other people to the observed individual, and the general conclusions about the developmental stage and its relevance to the theories of aging.
- Symbolic Interactionism and Socialization These basic functions initiate from our biological life cycle, and fulfil the necessity to be fully utilised to that extent where they are useful to the members of any society who teach the young how […]
- Digital Socialization in Modern Society With the rise of the Internet and citizen journalism, everyone is capable of having a voice and swaying the opinions of millions with solid facts, innovative ideas, and moving imagery.
- Parenting, Child Development, and Socialization Relationships in the family, as it is known, are formed largely due to the participation of parents and their desire to lay the foundations of morality and social values in the process of raising children.
- Socialization Theories and Whistleblowers Merton’s theory involves the notion of anomie and its meaning of confusion created by the conflict of social norms. Wrong’s views, the behavior of whistleblowers can be explained by their unwillingness to conform to the […]
- Socialization and Cultural Background of People Hardships of Tan’s mother and Lia’s parents can be regarded as an illustration of the importance of speaking the same language which is not limited to speaking ‘perfect’ English but it also means to be […]
- Socialization, Social Barriers and Opportunities In other words, the concept of socialization encompasses ways in which a person learns the way of life adopted by the members of his society by getting inculcated in the culture.
- Ex-Military Socialization and Mental Treatment Furthermore, behavioral avoidance is common by the refusal of participation in particular activities as it may be a reminder of the trauma and Brown’s injuries.
- Evidence-Based Practice for Recovery and Socialization As for the healthcare sector, its development remains the main priority as it maintains the state of the nations health and tries to improve the quality of peoples life.
- Poor Socialization in the United States Finally, the lack of communication between the educator and the parent often hampers the progress of socializing in the early age.
- Socialization in Early Childhood Center Habits, surroundings, and the regime of the day have a significant impact on the adaptation of children in the society, and the role of teachers and parents is essential.
- Child’s Misbehavior and Socialization Issues Developing the theory, the author defines the approximate age which corresponds to the description of the stages. Apart from that, it may be necessary to search the signs of traumatic experience in a person’s behavior.
- Socialization: Working with Groups In order to increase it, this person can list a range of topics/questions to guide the conversation. It can also be advantageous to state the eventual mutual goal of this discussion.
- Child Development and Socialization Recognition and cognitive processing of information is learned through participation in various activities, and the more social interaction there is, the better a child will adjust to the environment.
- Early Childhood Socialization It is during the secondary socialization that the child will learn to think independently. However, to the child, he is not doing something wrong.
- Religious Socialization in America This essay will try to explain factors that are influential in shaping the future of religion in America. These activities by the media will help in the distribution of religion because it is no doubt […]
- Socialization and Career Development For instance, effective socialization structures have enabled employees of institutions that operate in the tourism sector in the US to understand the needs of customers and what is expected of them.
- Culture and Socialization of Lightspan Biogas Company Given the high rate of globalization, the company will have to adopt the use of technology, especially the use of the internet in order to reach the entire globe.
- Socialization and Social Interactions: The Case of Chinese Support Group The main aim of this group is to help Chinese students and scholars solve problems afflicting them, create social bonds among members and with other groups in the wider society and enhance the Chinese culture […]
- Media and Technologies as Agents of Socialization In the modern world, cloud computing has reshaped the usage of the web, as well as the storage of data in most companies.
- Socialization in Malls in the 21st Century The way people socialized in the 19th and 20th century is different with the way people socialize in the 21st century.
- Socialization Skills Role in the Child Development When he was done, I observed the three shapes that he had made; two of them looked like two people but I could not identify the last one so I decided to ask him what […]
- How Does Socialization Affect Human Growth and Culture?
- Which Students Are More Likely to Experience Financial Socialization Opportunities?
- What Happens if a Person Is Not Socialized?
- How Does Socialization Affect Human Behavior?
- How Has the Internet Changed Us – Socialization in the Digital Universe?
- How Does Autism Affect Regular Brain Functions as Well as Socialization Skills?
- How Socialization Shapes Society?
- What Is the Most Critical Socialization?
- How Does Socialization Affect the Behavior of an Individual?
- What Are the Most Important Agents of Socialization?
- What Causes Poor Social Skills?
- What Impact Does the Denial of Socialization and Enculturation Have if the Development of the Individual?
- How Culture and Socialization Link Individuals and Society?
- What Are the Types of Socialization?
- What Is Socialization in Culture?
- How Does Gender Role Socialization Effect Girls More?
- How Social Class Shapes Adolescent Financial Socialization?
- How Does Socialization Help Develop Personality?
- Does Socialization Matter?
- How Socialization and Its Roles Affect the Lives of Brothers?
- How Does the Self Develop Through Socialization?
- What Are Socialization and Its Importance?
- What Are the Characteristics of Socialization?
- What Affects Our Socialization?
- How Does Socialization Affect Our Lives?
- What Are the Benefits of Socialization?
- How Does Socialization Change Over the Life Cycle?
- How Does Media Affect the Socialization of Children?
- How Does Socialization Help Individuals in Their Self Development?
- How Does Socialization Affect the Self Concept?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 29). 112 Socialization Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/socialization-essay-topics/
"112 Socialization Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 29 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/socialization-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '112 Socialization Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 29 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "112 Socialization Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/socialization-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "112 Socialization Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/socialization-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "112 Socialization Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/socialization-essay-topics/.
- Relationship Research Ideas
- Sociological Imagination Topics
- Autism Essay Topics
- Cultural Identity Research Topics
- Homeschooling Ideas
- Personal Identity Paper Topics
- Social Class Research Ideas
- Academic Dishonesty Research Ideas
Arab States
Asia and the pacific, europe & central asia, latin america & the caribbean.
You’re using an outdated browser. Old browsers are unstable, unsafe and do not support the features of of this website. Please upgrade to continue.
Your browser does not support JavaScript. This site relies on JavaScript to structure its navigation and load images across all pages. Please enable JavaScript to continue.
What is climate change mitigation and why is it urgent?
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Facebook
- Share on twitter
- Share via email

- Climate change mitigation involves actions to reduce or prevent greenhouse gas emissions from human activities.
- Mitigation efforts include transitioning to renewable energy sources, enhancing energy efficiency, adopting regenerative agricultural practices and protecting and restoring forests and critical ecosystems.
- Effective mitigation requires a whole-of-society approach and structural transformations to reduce emissions and limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels.
- International cooperation, for example through the Paris Agreement, is crucial in guiding and achieving global and national mitigation goals.
- Mitigation efforts face challenges such as the world's deep-rooted dependency on fossil fuels, the increased demand for new mineral resources and the difficulties in revamping our food systems.
- These challenges also offer opportunities to improve resilience and contribute to sustainable development.
What is climate change mitigation?
Climate change mitigation refers to any action taken by governments, businesses or people to reduce or prevent greenhouse gases, or to enhance carbon sinks that remove them from the atmosphere. These gases trap heat from the sun in our planet’s atmosphere, keeping it warm.
Since the industrial era began, human activities have led to the release of dangerous levels of greenhouse gases, causing global warming and climate change. However, despite unequivocal research about the impact of our activities on the planet’s climate and growing awareness of the severe danger climate change poses to our societies, greenhouse gas emissions keep rising. If we can slow down the rise in greenhouse gases, we can slow down the pace of climate change and avoid its worst consequences.
Reducing greenhouse gases can be achieved by:
- Shifting away from fossil fuels : Fossil fuels are the biggest source of greenhouse gases, so transitioning to modern renewable energy sources like solar, wind and geothermal power, and advancing sustainable modes of transportation, is crucial.
- Improving energy efficiency : Using less energy overall – in buildings, industries, public and private spaces, energy generation and transmission, and transportation – helps reduce emissions. This can be achieved by using thermal comfort standards, better insulation and energy efficient appliances, and by improving building design, energy transmission systems and vehicles.
- Changing agricultural practices : Certain farming methods release high amounts of methane and nitrous oxide, which are potent greenhouse gases. Regenerative agricultural practices – including enhancing soil health, reducing livestock-related emissions, direct seeding techniques and using cover crops – support mitigation, improve resilience and decrease the cost burden on farmers.
- The sustainable management and conservation of forests : Forests act as carbon sinks , absorbing carbon dioxide and reducing the overall concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Measures to reduce deforestation and forest degradation are key for climate mitigation and generate multiple additional benefits such as biodiversity conservation and improved water cycles.
- Restoring and conserving critical ecosystems : In addition to forests, ecosystems such as wetlands, peatlands, and grasslands, as well as coastal biomes such as mangrove forests, also contribute significantly to carbon sequestration, while supporting biodiversity and enhancing climate resilience.
- Creating a supportive environment : Investments, policies and regulations that encourage emission reductions, such as incentives, carbon pricing and limits on emissions from key sectors are crucial to driving climate change mitigation.

Photo: Stephane Bellerose/UNDP Mauritius

Photo: La Incre and Lizeth Jurado/PROAmazonia
What is the 1.5°C goal and why do we need to stick to it?
In 2015, 196 Parties to the UN Climate Convention in Paris adopted the Paris Agreement , a landmark international treaty, aimed at curbing global warming and addressing the effects of climate change. Its core ambition is to cap the rise in global average temperatures to well below 2°C above levels observed prior to the industrial era, while pursuing efforts to limit the increase to 1.5°C.
The 1.5°C goal is extremely important, especially for vulnerable communities already experiencing severe climate change impacts. Limiting warming below 1.5°C will translate into less extreme weather events and sea level rise, less stress on food production and water access, less biodiversity and ecosystem loss, and a lower chance of irreversible climate consequences.
To limit global warming to the critical threshold of 1.5°C, it is imperative for the world to undertake significant mitigation action. This requires a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 45 percent before 2030 and achieving net-zero emissions by mid-century.
What are the policy instruments that countries can use to drive mitigation?
Everyone has a role to play in climate change mitigation, from individuals adopting sustainable habits and advocating for change to governments implementing regulations, providing incentives and facilitating investments. The private sector, particularly those businesses and companies responsible for causing high emissions, should take a leading role in innovating, funding and driving climate change mitigation solutions.
International collaboration and technology transfer is also crucial given the global nature and size of the challenge. As the main platform for international cooperation on climate action, the Paris Agreement has set forth a series of responsibilities and policy tools for its signatories. One of the primary instruments for achieving the goals of the treaty is Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) . These are the national climate pledges that each Party is required to develop and update every five years. NDCs articulate how each country will contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhance climate resilience. While NDCs include short- to medium-term targets, long-term low emission development strategies (LT-LEDS) are policy tools under the Paris Agreement through which countries must show how they plan to achieve carbon neutrality by mid-century. These strategies define a long-term vision that gives coherence and direction to shorter-term national climate targets.

Photo: Mucyo Serge/UNDP Rwanda

Photo: William Seal/UNDP Sudan
At the same time, the call for climate change mitigation has evolved into a call for reparative action, where high-income countries are urged to rectify past and ongoing contributions to the climate crisis. This approach reflects the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) which advocates for climate justice, recognizing the unequal historical responsibility for the climate crisis, emphasizing that wealthier countries, having profited from high-emission activities, bear a greater obligation to lead in mitigating these impacts. This includes not only reducing their own emissions, but also supporting vulnerable countries in their transition to low-emission development pathways.
Another critical aspect is ensuring a just transition for workers and communities that depend on the fossil fuel industry and its many connected industries. This process must prioritize social equity and create alternative employment opportunities as part of the shift towards renewable energy and more sustainable practices.
For emerging economies, innovation and advancements in technology have now demonstrated that robust economic growth can be achieved with clean, sustainable energy sources. By integrating renewable energy technologies such as solar, wind and geothermal power into their growth strategies, these economies can reduce their emissions, enhance energy security and create new economic opportunities and jobs. This shift not only contributes to global mitigation efforts but also sets a precedent for sustainable development.
What are some of the challenges slowing down climate change mitigation efforts?
Mitigating climate change is fraught with complexities, including the global economy's deep-rooted dependency on fossil fuels and the accompanying challenge of eliminating fossil fuel subsidies. This reliance – and the vested interests that have a stake in maintaining it – presents a significant barrier to transitioning to sustainable energy sources.
The shift towards decarbonization and renewable energy is driving increased demand for critical minerals such as copper, lithium, nickel, cobalt, and rare earth metals. Since new mining projects can take up to 15 years to yield output, mineral supply chains could become a bottleneck for decarbonization efforts. In addition, these minerals are predominantly found in a few, mostly low-income countries, which could heighten supply chain vulnerabilities and geopolitical tensions.
Furthermore, due to the significant demand for these minerals and the urgency of the energy transition, the scaled-up investment in the sector has the potential to exacerbate environmental degradation, economic and governance risks, and social inequalities, affecting the rights of Indigenous Peoples, local communities, and workers. Addressing these concerns necessitates implementing social and environmental safeguards, embracing circular economy principles, and establishing and enforcing responsible policies and regulations .
Agriculture is currently the largest driver of deforestation worldwide. A transformation in our food systems to reverse the impact that agriculture has on forests and biodiversity is undoubtedly a complex challenge. But it is also an important opportunity. The latest IPCC report highlights that adaptation and mitigation options related to land, water and food offer the greatest potential in responding to the climate crisis. Shifting to regenerative agricultural practices will not only ensure a healthy, fair and stable food supply for the world’s population, but also help to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Photo: UNDP India

Photo: Nino Zedginidze/UNDP Georgia
What are some examples of climate change mitigation?
In Mauritius , UNDP, with funding from the Green Climate Fund, has supported the government to install battery energy storage capacity that has enabled 50 MW of intermittent renewable energy to be connected to the grid, helping to avoid 81,000 tonnes of carbon dioxide annually.
In Indonesia , UNDP has been working with the government for over a decade to support sustainable palm oil production. In 2019, the country adopted a National Action Plan on Sustainable Palm Oil, which was collaboratively developed by government, industry and civil society representatives. The plan increased the adoption of practices to minimize the adverse social and environmental effects of palm oil production and to protect forests. Since 2015, 37 million tonnes of direct greenhouse gas emissions have been avoided and 824,000 hectares of land with high conservation value have been protected.
In Moldova and Paraguay , UNDP has helped set up Green City Labs that are helping build more sustainable cities. This is achieved by implementing urban land use and mobility planning, prioritizing energy efficiency in residential buildings, introducing low-carbon public transport, implementing resource-efficient waste management, and switching to renewable energy sources.
UNDP has supported the governments of Brazil, Costa Rica, Ecuador and Indonesia to implement results-based payments through the REDD+ (Reducing emissions from deforestation and forest degradation in developing countries) framework. These include payments for environmental services and community forest management programmes that channel international climate finance resources to local actors on the ground, specifically forest communities and Indigenous Peoples.
UNDP is also supporting small island developing states like the Comoros to invest in renewable energy and sustainable infrastructure. Through the Africa Minigrids Program , solar minigrids will be installed in two priority communities, Grand Comore and Moheli, providing energy access through distributed renewable energy solutions to those hardest to reach.
And in South Africa , a UNDP initative to boost energy efficiency awareness among the general population and improve labelling standards has taken over commercial shopping malls.

What is UNDP’s role in supporting climate change mitigation?
UNDP aims to assist countries with their climate change mitigation efforts, guiding them towards sustainable, low-carbon and climate-resilient development. This support is in line with achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly those related to affordable and clean energy (SDG7), sustainable cities and communities (SDG11), and climate action (SDG13). Specifically, UNDP’s offer of support includes developing and improving legislation and policy, standards and regulations, capacity building, knowledge dissemination, and financial mobilization for countries to pilot and scale-up mitigation solutions such as renewable energy projects, energy efficiency initiatives and sustainable land-use practices.
With financial support from the Global Environment Facility and the Green Climate Fund, UNDP has an active portfolio of 94 climate change mitigation projects in 69 countries. These initiatives are not only aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions, but also at contributing to sustainable and resilient development pathways.
Explore More Stories
Pacific shores, solar solutions: harnessing renewable energy in the pacific islands.

Photo: Yuichi Ishida/UNDP Timor-Leste
West Africa has great potential for solar energy. It’s time to release it.

Photo: UNDP Niger
Electric vehicles are driving a greener future in Viet Nam

Ho Tuan Anh delivers goods with his new e-motorbike. Photo by: Phan Huong Giang/UNDP Viet Nam
Why the Western Balkans are choosing decarbonization

Photo: UNDP Bosnia and Herzegovina
Six lessons on how to achieve future-smart energy efficient buildings

Solar photovoltaic systems on roofs in Lebanon. Photo: Fouad Choufany / UNDP Lebanon
Six ways to achieve sustainable energy for all

Photo: UNDP Zimbabwe

COMMENTS
Conformity to socialization is the way a person tends to have the same behaviors of a group of people he or she is attached to. Conformity and obedience to authority in socialization is responsible in shaping or bringing up a morally upright person. The impacts of this can have diverse influences on a individuals in the ways of his/her living.
Socialization is the process whereby the young of society learn the values, ideas and practices and roles of that society. The socialization process is a semi-conscious one, in that the primary agency of socialization, the family, would not necessarily see itself in this role, while some secondary socialization agencies such as education are ...
Socialization is the process through which people are taught to be proficient members of a society. It describes the ways that people come to understand societal norms and expectations, to accept society's beliefs, and to be aware of societal values. Socialization is not the same as socializing (interacting with others, like family and ...
Because socialization is so important, scholars in various fields have tried to understand how and why it occurs, with different scholars looking at different aspects of the process. Their efforts mostly focus on infancy, childhood, and adolescence, which are the critical years for socialization, but some have also looked at how socialization ...
Describe why socialization is important for being fully human. Explain how extreme isolation and twin studies demonstrate the role of nature versus nurture in human development. Identify the different questions functionalists, conflict theorists, and interactionists might ask about the role of socialization in human development.
Learning Objective. Describe why socialization is important for being fully human. We have just noted that socialization is how culture is learned, but socialization is also important for another important reason. To illustrate this importance, let's pretend we find a 6-year-old child who has had almost no human contact since birth.
Key Terms. socialization: The process of learning one's culture and how to live within it.; Jeffrey J. Arnett: In his 1995 paper, "Broad and Narrow Socialization: The Family in the Context of a Cultural Theory," sociologist Jeffrey J. Arnett outlined his interpretation of the three primary goals of socialization.; norm: A rule that is enforced by members of a community.
As this example indicates, socialization makes it possible for us to fully function as human beings. Without socialization, we could not have our society and culture. And without social interaction, we could not have socialization. Our example of a socially isolated child was hypothetical, but real-life examples of such children, often called ...
Socialization is the process through which people are taught to be proficient members of a society. It describes the ways that people come to understand societal norms and expectations, to accept society's beliefs, and to be aware of societal values. Socialization is not the same as socializing (interacting with others, like family, friends ...
Write a 1-2 (no more than 3) pages essay on Socialization and Social interaction: Verbal and Non-Verbal Communication. ... writing papers, and taking exams. Informal behaviors can be joining a student club, befriending classmates, attending football games, and even drinking alcohol at parties on the weekend. Having a role can lead to role ...
Socialization is the process through which the individual learns to become an accepted member of the society. At birth the neonate is neither social nor unsocial. Because of this helplessness at birth he has to depend on other social beings for his care and welfare. As he grows in a social environment and in a social context, he develops ...
Key Terms. secondary socialization: The socialization that takes place throughout one's life, both as a child and as one encounters new groups that require additional socialization.; primary socialization: The socialization that takes place early in life, as a child and adolescent.; Socialization is a life process, but is generally divided into two parts: primary and secondary socialization.
Socialization is a process that introduces people to social norms and customs. This process helps individuals function well in society, and, in turn, helps society run smoothly. Family members, teachers, religious leaders, and peers all play roles in a person's socialization. This process typically occurs in two stages: Primary socialization ...
Society portal. v. t. e. In sociology, socialization (Modern English; or socialisation - see spelling differences) is the process of internalizing the norms and ideologies of society. Socialization encompasses both learning and teaching and is thus "the means by which social and cultural continuity are attained".
The concept of socialization raises a classic problem of sociological analysis: the problem of individual agency. As described in Chapter 1. An Introduction to Sociology, individual agency is the capacity of individuals to act and make decisions independently. However socialization is about conformity: learning how to conform to social ...
Purpose. Examples. Agents of socialization are the people, groups, and social institutions that affect one's self-concept, attitudes, and behaviors. For example, parents, teachers, priests, television personalities, rock stars, etc. Agents of socialization teach people what society expects of them. They tell them what is right and wrong, and ...
Socialization is not the same as socializing (interacting with others, like family, friends, and coworkers); to be precise, it is a sociological process that occurs through socializing. As Danielle's story illustrates, even the most basic of human activities are learned.
Essay on Socialization. Socialization Socialization is the process by which culture is learned; also called enculturation. During socialization individuals internalize a culture's social controls, along with values and norms about right and wrong. Socialization is a complex process that involves many individuals, groups, and social institutions.
Ann Oakley's Gender Socialization Theory Essay. She received her bachelor degree in 1965.she continued her studies at Bedford College, University of London, Anne has gained a PhD in 1969.main spheres of her investigations included sociology of medicine and health of women. "The Cycle of Socialization" by Harro.
Answer: Socialization affects us in so many ways far beyond the visible. Our individual socialization patterns shape our mentalities. The things we individual experiences in society directly affect our minds, which explains how our minds register and react to incidents and situations we encounter differently.Socialization is the lifelong process of inheriting and disseminating norms, customs ...
Climate change mitigation refers to any action taken by governments, businesses or people to reduce or prevent greenhouse gases, or to enhance carbon sinks that remove them from the atmosphere. These gases trap heat from the sun in our planet's atmosphere, keeping it warm. Since the industrial era began, human activities have led to the ...