Home — Essay Samples — Education — School Uniform — The Benefits of School Uniforms

The Benefits of School Uniforms
- Categories: Art History School Uniform
About this sample

Words: 585 |
Published: Mar 16, 2024
Words: 585 | Page: 1 | 3 min read
Table of contents
Promoting equality, improving academic performance, enhancing school safety, instilling a sense of pride and belonging.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof Ernest (PhD)
Verified writer
- Expert in: Arts & Culture Education

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 653 words
1 pages / 616 words
3 pages / 1514 words
5 pages / 2188 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on School Uniform
Franklin, Aretha. 'Think.' Atlantic Records, 1968.
One of the ongoing debates in the education system is whether students should be required to wear school uniforms. While some argue that uniforms promote equality and discipline, I believe that enforcing a dress code on students [...]
For years, schools have implemented dress codes with the intention of maintaining a sense of decorum and discipline among students. However, many argue that dress codes restrict students' freedom of expression and can perpetuate [...]
School uniforms have been a topic of debate in educational institutions for decades. While proponents argue that uniforms promote equality and discipline among students, opponents argue that they stifle individuality and impede [...]
Introduction to the debate on whether students should wear uniforms Mention of the reasons for and against school uniforms Discussion of the role of uniforms in enhancing school security Potential risks of [...]
Education is crucial for everyone as it provides people with the necessary knowledge and skills they need to thrive in the world. For students to obtain the education required for future investments, it is vital [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Follow us on Facebook
- Follow us on Twitter
- Criminal Justice
- Environment
- Politics & Government
- Race & Gender
Expert Commentary
School uniforms: Do they really improve student achievement, behavior?
This updated collection of research looks at how mandatory school uniforms impact student achievement, attendance and behavior as well as the presence of gangs in public schools.

Republish this article

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License .
by Denise-Marie Ordway, The Journalist's Resource April 20, 2018
This <a target="_blank" href="https://journalistsresource.org/education/school-uniforms-research-achievement/">article</a> first appeared on <a target="_blank" href="https://journalistsresource.org">The Journalist's Resource</a> and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.<img src="https://journalistsresource.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/cropped-jr-favicon-150x150.png" style="width:1em;height:1em;margin-left:10px;">
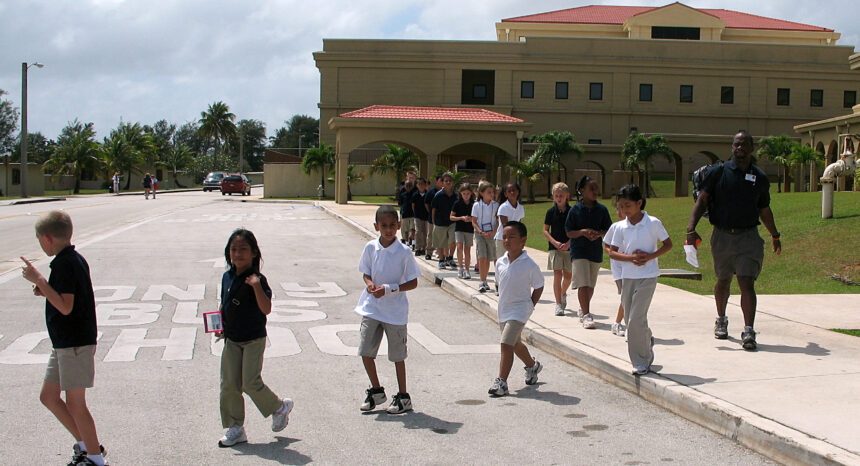
Decades ago, uniforms were mostly worn by students who went to private or parochial schools. But as local school boards have focused more on improving standardized test scores and campus safety, a growing number have begun requiring school uniforms — typically, a polo shirt of a particular color paired with navy or khaki pants, skirts or shorts. Nearly 22 percent of public schools in the United States required uniforms in 2015-16 — up from almost 12 percent in 1999-2000, according to the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES).
Proponents argue that students will pay more attention to their classwork if they aren’t preoccupied with fashion, and that they’ll be better behaved. Meanwhile, school administrators say uniforms help eliminate gang-related styles and logos. They also make it easier to spot a stranger on campus.
Despite their reported benefits, mandatory uniforms are controversial because a lot of parents and students don’t like the idea of forcing children to dress alike, which they say suppresses freedom of expression. Some families complain about the financial burden of purchasing uniforms in addition to their kids’ other clothing. Years ago, parents also complained that it was difficult to find uniforms, but that ceased to be an issue after large chain stores like Target and Wal-Mart began selling them.
As public schools debate the merits of uniforms — some school boards have been bouncing the idea around for years — it’s important for journalists to know what the research says on this topic. School officials do not always consult academic research before they put a plan on the table.
To help journalists ground their reporting and fact-check claims, Journalist’s Resource has rounded up several academic studies worth reviewing. Reporters may also want to examine reports on uniform use from the NCES, which collects and reports data related to school uniforms, dress codes and book bags in public schools.
——————————–
“School Discipline, School Uniforms and Academic Performance” Baumann, Chris; Krskova, Hana. International Journal of Educational Management , 2016. DOI: 10.1108/IJEM-09-2015-0118.
Summary: This study examines test scores and student behavior in the United States, Canada and 37 other countries to determine whether uniforms affect student discipline. The researchers found that the highest-performing students are the most disciplined. In addition, “for countries where students wear school uniforms, our study found that students listen significantly better, there are lower noise levels, and lower teaching waiting times with classes starting on time.”
“Dressed for Success? The Effect of School Uniforms on Student Achievement and Behavior” Gentile, Elizabetta; Imberman, Scott A. Journal of Urban Economics , 2012, Vol. 71. doi: 10.1016/j.jue.2011.10.002.
Abstract: “Uniform use in public schools is rising, but we know little about how they affect students. Using a unique dataset from a large urban school district in the southwest United States, we assess how uniforms affect behavior, achievement and other outcomes. Each school in the district determines adoption independently, providing variation over schools and time. By including student and school fixed-effects we find evidence that uniform adoption improves attendance in secondary grades, while in elementary schools they generate large increases in teacher retention.”
“Uniforms in the Middle School: Student Opinions, Discipline Data, and School Police Data” Sanchez, Jafeth E.; Yoxsimer, Andrew; Hill, George C. Journal of School Violence , 2012. DOI: 10.1080/15388220.2012.706873.
Summary: Researchers asked students at an urban middle school in Nevada what they thought of having to wear uniforms. Their public school had adopted a uniform policy after staff members became frustrated with the earlier dress code policy, which resulted in girls wearing revealing clothing and boys wearing shirts with inappropriate messages and images. The study’s main takeaway: The vast majority of students said they dislike uniforms, although some agreed there were benefits. “For example, in reference to gender, more than expected females than males indicated students treated them better with uniforms. Also, fewer females than males got detention for not wearing a uniform or for wearing a uniform inappropriately.”
“Are School Uniforms a Good Fit? Results from the ECLS-K and the NELS” Yeung, Ryan. Educational Policy , 2009, Vol. 23. doi: 10.1177/0895904808330170.
Abstract: “One of the most common proposals put forth for reform of the American system of education is to require school uniforms. Proponents argue that uniforms can make schools safer and also improve school attendance and increase student achievement. Opponents contend that uniforms have not been proven to work and may be an infringement on the freedom of speech of young people. Within an econometric framework, this study examines the effect of school uniforms on student achievement. It tackles methodological challenges through the use of a value-added functional form and the use of multiple data sets. The results do not suggest any significant association between school uniform policies and achievement. Although the results do not definitely support or reject either side of the uniform argument, they do strongly intimate that uniforms are not the solution to all of American education’s ills.”
“Effects of Student Uniforms on Attendance, Behavior Problems, Substance Use, and Academic Achievement” Brunsma, David L.; Rockquemore, Kerry A. The Journal of Educational Research , 1998, Vol. 92. doi: 10.1080/00220679809597575.
Abstract: “Mandatory uniform policies have been the focus of recent discourse on public school reform. Proponents of such reform measures emphasize the benefits of student uniforms on specific behavioral and academic outcomes. Tenth-grade data from The National Educational Longitudinal Study of 1988 was used to test empirically the claims made by uniform advocates. The findings indicate that student uniforms have no direct effect on substance use, behavioral problems, or attendance. Contrary to current discourse, the authors found a negative effect of uniforms on student academic achievement. Uniform policies may indirectly affect school environment and student outcomes by providing a visible and public symbol of commitment to school improvement and reform.”
“School Uniforms, Academic Achievement, and Uses of Research” Bodine, Ann. The Journal of Educational Research , 2003, Vol. 97. doi: 10.1080/00220670309597509.
Abstract: “School uniforms are being advocated for a range of social, educational, economic, and familial reasons. In 1998, The Journal of Educational Research (The JER) published an article by D. Brunsma and K. Rockquemore that claims that uniforms correlate negatively with academic achievement, but data presented in this article actually show positive correlation between uniforms and achievement for the total sample, and for all but 1 school sector. Examination of structure of argument reveals that the erroneous claim results from misleading use of sector analysis. Simultaneous with The JER article, and on the basis of the same National Education Longitudinal Study: 1988 database, an Educational Testing Service article reported that no correlation exists between uniforms and achievement. The two articles are contrasted in this study. The effect of new communication technology in amplifying political uses of academic research is discussed.”
“Public School Uniforms: Effect on Perceptions of Gang Presence, School Climate, and Student Self-Perceptions” Wade, Kathleen Kiley; Stafford, Mary E. Education and Urban Society , 2003, Vol. 35. doi: 10.1177/0013124503255002.
Abstract: “This study attempts to clarify the relationships between public school uniforms and some of their intended results: student self-worth and student and staff perceptions of gang presence and school climate. The instruments used in the study included a questionnaire on gang presence and identity, the National Association of School Principals Comprehensive Assessment of School Environments, and the Harter Self-Perception Profile for Children. Participants consisted of 415 urban public middle school students and 83 teachers. Findings indicate that, although perceptions did not vary for students across uniform policy, teachers from schools with uniform policies perceived lower levels of gang presence. Although the effect size was small, students from schools without uniforms reported higher self-perception scores than students from schools with uniform policies. Student and teacher perceptions of school climate did not vary across uniform policy.”
“The Effect of Uniforms on Nonuniform Apparel Expenditures” Norum, Pamela S.; Weagley, Robert O.; Norton, Marjorie J. Family & Consumer Sciences , 1998. doi: 10.1177/1077727X980263001.
Abstract: “The uniform industry has grown steadily the past 20 years with increased attention from employers trying to create a professional image among workers as well as school administrators considering uniforms to curtail school violence. Although an important part of human dress for centuries, uniforms have received little attention from researchers of the clothing market. This study examines the impact of uniform purchases on household expenditures for selected nonuniform apparel subcategories based on an economic model of conditional demand. Expenditure equations are estimated using the 1990-1991 Consumer Expenditure Survey. The results suggest that, on average, consumers do not substitute uniforms for other apparel purchases. Rather, uniforms and nonuniform apparel appear to be complements in consumers’ purchases, resulting in greater household expenditures on nonuniform apparel. These results are a first step in understanding the economic effect that uniform purchases, mandated by employers, schools, or others, have on household clothing expenditures.”
Looking for more research on student achievement? Check out our write-ups on how teacher salaries , school vouchers and school shootings impact learning.
About The Author
Denise-Marie Ordway
Question and Answer forum for K12 Students

School Uniforms Essay | Short and Long Essays, Importance and Benefits of School Uniforms
School Uniforms Essay: School uniforms should be utilized in educational systems. Uniforms are both as useful for schools just as for the pupils. Wearing outfits will help construct a feeling of solidarity inside the school. Rather than everybody as a different group, everybody will be in a similar group. Wearing regalia will help free pupils of the pressure of what to wear in the first part of the day. Wearing school outfits will help improve understudy distinction and improve their confidence. To start with, wearing coordinating outfits can cause pupils to feel equivalent. Helpless pupils would at this point don’t feel rejected on the grounds that they are not wearing name-brand garments like the more extravagant children.
You can read more Essay Writing about articles, events, people, sports, technology many more.
What is a School Uniform?
In straightforward words, we comprehend that the Uniform or material which is recommended by the school for pupils to wear in school is called school uniform. Generally in all schools uniform is mandatory.The Uniform gives balance and comparability between the pupils, everything being equal. These days, all schools keep the principles of wearing a normalized uniform for all pupils.
How to Write a School Uniform Essay?
To write an essay students should know the proper format. Also, they should be well aware of the topic on which they have to write the essay. Writing an essay on school uniforms requires the knowledge of the merits and demerits of wearing a school uniform. Students should list down the advantages of uniforms in schools.
Remember these points while writing the essay on school uniform:
- Give introduction on school uniform in the first paragraph
- Explain the advantages and disadvantages of wearing a school uniform
- Explain how wearing a uniform brings changes in students
- Conclude the essay in the last paragraph
Short Essay on School Uniform 150 Words in English
School uniforms are the solitary most apparent fundamental components of any school. We can distinguish the understudy by assessing their regalia.
It is said that, in the sixteenth century, Christ’s Hospital School originally utilized the school uniform. There has been a discussion everywhere in the world on whether the subject of school uniforms is positive or negative. Common liberties activists say that school uniforms are removing their opportunity of wearing anything. In guard, the School Committee says they give a school uniform to instruct them in order and solidarity.
School uniforms can build the pay of a custom-fitted local area. And furthermore, a business organization can bring in cash by creating school regalia. School uniforms are a conventional clothing standard including a shirt and full gasp for young men and pullovers and creased skirts for young ladies. School dress can lessen fabric harassment.
Yet in addition, these days youngsters are more cognizant about their design sense and sexual direction, so they don’t prefer to wear a similar unisex clothing standard. However, after every one of those contentions and dubious speculations, we can say, school regalia are as a matter of fact pride for an understudy.

Long Essay on School Uniform 650 Words
Schools are instructive establishments where kids go not exclusively to learn course readings however to develop as a general person. Schools likewise have the assignment of showing youngsters the desire for garments and mention to them what is proper for what event. School outfits are a basic type of garments for pupils during their visit at school during school hours, and outside during true school exercises. A school uniform is normal in a large portion of the schools. They have direct requests to wear the school uniform as a matter of course.
The necessity of School Uniform
Initially, school is where we all progress at an extremely youthful age. In a single word, life starts at school. It’s schooling, as well as school, gives us the stage to sustain our confidence, feelings in the beginning phase of life. The significance of making companions, functioning as a group we get familiar with every one of these in school. What’s more, wearing a similar dress unquestionably brings a feeling of solidarity among pupils. In each school, there are pupils from various foundations yet with the school uniform everybody becomes one-the lone character rules at that point is every one of them is the delegate of a similar school. This is an incredible inclination of harmony. This likewise assists kids with defeating the inadequacy (or predominance) complex which here and their kids have due to the climate they have been raised in. School outfits streak out a large portion of the drops of social contentions.
As school makes our crucial nuts and bolts of the future it is critical to cause one to feel as a piece of the school. A youngster with a specific school uniform constantly feels that he has a place with the school. It makes the youngster more cognizant about his distinction which thus helps to build fearlessness. A kid would be more thoughtful to his kindred cohort who has a similar uniform as his. As referenced before there would be consistently a blended group in each school. Some of them are rich, some have a place with the upper working class and some lower than that-this distinction remains all over, aside from those 8 hours in school due to the school uniform. The supposed status cognizance doesn’t exist with this.
Benefits of School Uniform
Another admirable sentiment comes up while examining the benefits of school uniform is younger students go through two most significant progress times of life in school-they burn through 12 long a long time in school-from adolescence to teen, from adolescent to youth-the school observer the progressions ( both physical and mental) happen inside one. During these changes, somebody barely thinks often about the world. That time there is a propensity among us all to disrupt the norm which should be managed cautiously and strategically.
Now wearing school regalia assumes a quiet yet urgent part in our lives. It ingrains a profound established feeling of control in the psyche mind. Subsequently, typically even the riskiest formally dressed understudy wonders whether or not to do any underhandedness outside the school as the moment suspected plays to him that he will let down his school with his activity. School uniform assists an understudy with focusing on his necessities-where school and scholastics start things out.
Even after some elegantly composed diagrams of papers on school uniforms, the contention on whether a school uniform abuses the pupils’ privilege of articulation will stay a ceaseless conversation. Be that as it may, truly, wearing of regalia should all rely upon the conditions and the picture a given school is attempting to depict. In any case, the significance of school uniforms appears to win the day today even as I compose this end and surprisingly after so many school uniform articles have been composed. On the last note, we should attempt to discover perpetual methods of tackling the developing issues looked at by pupils. We ought not to depend on school regalia to swipe the issues away from view, this does the pupils nothing but bad.
Importance of School Uniform
The uniform is a necessary piece of our life. The dress is a character of somebody. Through the dress, we become acquainted with which school the understudy is. The educator has a crucial part in picking a dress. He chooses the school uniform by taking a gander at all the classes. Uniform symbols, alongside schooling, order, and decorum help in altering the state and course of society.
Wearing legitimate clothing expands our trust in the public arena since it positively affects our work and thinking. These days, our local area has gotten a matter of rivalry for our kids. It appears to be that their dress is influencing them every day.
The wearing of our kids has additionally become an essential factor somewhat for the criminal occurrences occurring in the public eye. In an understudy’s life, the educator and parent are the types of God. School dress is viewed as a recipe for equity.
Advantages of School Uniform
- School uniforms are a need in many schools to achieve consistency in pupils.
- School uniform binds together all pupils, paying little heed to their social, strict, and monetary foundation.
- It imparts a feeling of having a place in the pupils.
- It assists with restraining pupils and keeps everything under control since they are not occupied by their special garments.
- pupils don’t have to object about what to wear each day in the event that they have school regalia.
- It is hard for low-pay families to purchase school regalia each spending year, and it might make a strain in their financial plan.
- School outfits force consistency and consequently make pupils a mass of anonymous kids and with no singularity.
- It is hard for pupils to check their friend’s monetary condition in the event that they are wearing school dresses.
- pupils can be not kidding about their examinations and figure out how to endeavor to be deserving of the custom.
- School dress can make pupils unoriginal.
FAQ’s on Schools Uniforms Essay
Question 1. What students should wear uniforms in school?
Answer: Uniforms are both as useful for schools just as for the pupils. Wearing uniforms will help fabricate a feeling of loneliness inside the school. To start with, wearing coordinating uniforms can cause pupils to feel equivalent. Helpless pupils would presently don’t feel barred in light of the fact that they are not wearing name-brand garments like the more extravagant children.
Question 2. How to write an essay on a school uniform?
Answer: Start with an introduction, discuss the debate going on school uniforms by students, write the cons and pros of school uniforms. Explains the advantages and changes that wearing a school uniform can bring in students. End the essay with a conclusion.
Question 3. What is good about school uniforms?
Answer: School uniforms have been demonstrated to raise test scores, support confidence, diminish savagery and wrongdoing, and make a feeling of freshly discovered pride in pupils. They assist youngsters with zeroing in on learning and homework, not on the thing every other person is wearing or whether they fit in. Outfits are not the answer for the entirety of the issues that adolescents, instructors, and schools face today, however, examination and insights propose that they might be a positive development.
Question 4. Should students wear school uniforms?
Answer: Yes, all students should wear school uniforms since it represents discipline and equality among students in school.

Should Students Wear School Uniforms Essay (Tips and Sample)

School uniforms are a hotly contested debate, which makes it a controversial topic preferred for school essays. Even though writing a school uniform essay should be easy, students' confessions after being assigned both long and short essays on school uniform show mixed results. Most students who have been given an essay on school uniforms have highlighted it as exciting and tricky.
Well, to write an essay that will score you an excellent grade, you need to understand your perspective, viewpoint, or stand before writing. As yourself, whether you will support school uniforms or you will be against them in your essay.
In most cases, the essay can be argumentative where you argue either for or against, then proceed to state your stand on whether or not you support school uniforms in learning institutions. You can also write an informative essay or a persuasive school uniform essay.
This article covers some aspects to consider when writing such an essay, some suitable topics, and general advice on how to write an outstanding school uniforms essay.
How to begin a School Uniforms Essay
You aim to demystify the school uniforms debate. Therefore, you need to strategize on how to begin the essay. Like other essays, starting with an essay hook would make it interesting to the readers. After the hook, head straight to writing some background information on school uniforms. You can then incorporate a thesis statement that presents your central stance on the paper.
Here is a sample school uniform hook:
A recent study by North Dakota State University revealed that an average American household spends close to 3.8% of their income on clothing, translating to approximately $2000 annually per household.
The hook above is essential when you argue from a cost perspective where you say that school uniforms save families from expenditures on buying different clothes for kids, which equalizes the rich and poor households.
In your background, you can try reference instances when school uniforms have stirred public debates. Inform your reader about these debates and highlight the key issues you will handle in your essay.
At the end of the introduction paragraph, state your thesis statement.
What goes to the body of a school uniform essay?
With the introduction done, you now need to develop the body paragraphs. As a general rule, always maintain a single idea per paragraph. If you are doing your essay in a five-paragraph essay format, ensure that the body of your essay takes 80% of the total word count while the introduction and the conclusion each take 10%.
Here are some key ideas you can incorporate in the body of your essay:
- Explain the essence of having school uniforms on students, teachers, and learning institutions. Issues such as security and safety, uniformity, and promoting togetherness or unity as benefits. It is easy to spot a student in uniform. School uniforms also enforce some self-respect and self-worth among students. As well, uniforms foster a sense of belonging among students.
- Explore the issue from a cost-saving perspective for the parents. Unlike having different clothes daily, having a few pieces of school uniforms reduces the expenditure per household.
- Connect school uniforms to issues such as creativity, comfort, and affordability. Lack of funds, for instance, can hinder some families from sending their children to school as they have no school uniforms.
- You can also present the pros and cons of school uniforms
- Connect the school uniforms to identity formation
- School uniforms equalize students, which boosts their self-confidence
- School uniform makes students not be imaginative
- In the end, present recommendations that can solve the school uniform quagmire in schools
Like any other essay, ensure that your essay about school uniforms is engaging. Take a multi-stakeholder approach if you are recommending a policy.
If you have real-life examples of how school uniforms are beneficial, present them to support your body paragraphs. As you strive to present your viewpoints, ensure that each paragraph transitions to the next paragraph.
If possible, benchmark your arguments on schools that have successfully implemented school uniforms.
How to end an essay on school uniform
Like the introduction, the conclusion of your essay matters a lot. It can be the only place a marker checks to know what your stance was when writing your school uniforms essay.
Let your readers know whether school uniforms are good or not. Do not just stop there explore the why and why not for each of your points.
If there are recommendations, especially if you were writing an essay based on a school uniforms case study, present them in the conclusion.
DO not introduce new ideas that are not in your essay. However, crystalize and relate to your thesis and make sure your readers enjoy your essay to the last dot.
Sample School Uniforms Essay Topics
School uniform essays differ in perspective or stance, which hugely depends on the choice of topic. We can advise you to choose a school essay topic that has practical points and one that you can support with evidence from scholarly literature.
- Is school uniform a good thing?
- The importance of school uniforms
- Should students wear uniforms?
- Pros and Cons of school uniforms
- The negative impacts of school uniforms
- Rhetorical analysis of school uniforms
- Positive effects of school uniforms
- Are school uniforms a dress for success?
- Why schools should have uniforms
- History of school dress code
- School uniforms in private and public schools
- Should all schools have the same uniform?
- Are school uniforms necessary?
- School uniforms and diversity
- School uniforms and student discipline
- Comparison of school uniforms in U.S. and Japan
School Uniforms Essay Check List
With your essay written, ensure that it ticks most if not all these lists of facts that make a school uniform score great grades.
- Does the essay have a great hook?
- Is the background of your introduction relatable to the selected topic?
- Does the introduction have supporting facts from scholarly sources?
- Does your introduction have a clear thesis statement?
- Is the main idea clearly illustrated in the body?
- Does each body paragraph have an idea of its own?
- Does the essay have transition words for effective flow?
- Does the body discuss important concepts?
- Is the body paragraph having an opening sentence, facts, and closing sentence?
- Has all borrowed information been cited?
- Does the essay have strong evidence?
- Is the essay grammatically correct?
- Is the conclusion a summary of the argument?
- Has the thesis been restated?
- Is the conclusion flowing with the body of the essay?
- Has the essay used formal language?
- Are the sentences free from unnecessary words?
- Is the grammar and spelling in the essay correct?
- Are the references correct?
- Are the references recent?
- Are the sources used credible?
- Does the essay have a title and reference page?
Sample Argumentative Essay on Should Students Wear School Uniforms
Disclaimer – DO NOT COPY this sample essay. It is meant to help you see how you can present your essay ideas given your perspective/viewpoint. Submitting any part of this essay as your own might land you in trouble. We will not be in any way be a party to such consequences. If you need a model essay based on your selected topic for research purposes, please place an order or contact our support team for assistance with outlines, potential references, and some ideas on writing an excellent essay on school uniforms.
Numerous debates have been carried out on whether students should wear uniforms or not. Parents, teachers, students, and school administrations have all given their views on school uniforms with different arguments and opinions on all sides. Supporters of school uniforms argue that school uniforms are essential as they give students an identity and foster discipline, while others argue that uniforms are annoying, uncomfortable, and lack creativity. Regardless of the position one takes on students wearing uniforms, it is clear that uniforms are an essential part of students, and students wearing uniforms is more advantageous to both the students and schools. Thus, all students should wear uniforms as the uniforms instill a sense of discipline and identity, erase differences between the students, and are less costly (thesis statement)
School uniforms eliminate the differences between students in regard to their social and economic backgrounds ( School uniforms promote equality ) . Schools have students from different social and economic backgrounds. The school environment has students from both poor and rich families. Hence, uniforms are important as they are modest and identical clothing that propagate a sense of equality among the students (Freeburg and Workman, 6). Accordingly, all students should wear school uniforms to avoid a situation where some students feel inadequate for being able to afford expensive clothing like their more affluent counterparts. A learning environment and education, in general, are supposed to bridge the social-economic differences that exist in society.
Parents can save much money that would otherwise go to buying a wide variety of school clothes for their children ( school uniforms save parents money spent on clothing ). School uniforms provide a cheaper and more consistent alternative to regular clothing. If students are allowed to wear regular clothing to school, parents and guardians have to buy clothes that are in line with the latest fashion trends and the individual tastes of their children, both of which can be expensive. In this case, students should wear school uniforms that are affordable and identical to save parents money that can be used for more important things (Baumann and Krskova 1003). Affordability is essential for parents considering the enormous expenses associated with bringing up children in the modern era. Therefore, all students should wear uniforms as uniforms protect the financial interest of the parents and guardians.
Wearing school uniforms saves teachers, students, and administrators valuable time ( Bringing in the time-saving perspective of school uniforms ). Without uniforms, teachers and schools, administrators spend significant amounts of time regulating the dress code. For instance, time wasted deciding which clothes are appropriate, what skirt-size is too short, among other issues that arise in regulating regular clothes to make appropriate for the school environment (Ruggerone 573). Such challenges would not exist if all students wore uniforms. Consequently, students also waste valuable time because of the distractions that might be caused by clothes that their peers are wearing. Therefore, to eliminate time wastage and distractions in school, students should wear uniforms.
According to individuals and parties who oppose school uniforms, the uniforms limit the personal expression of students and can forcibly define gender roles for the children as girls have to wear skirts and boys’ trousers ( school uniforms stifle independence and creativity) - COUNTERARGUMENT . People express themselves through their clothes, which means that forcing students to wear uniforms affects their personal expressions (Masuch and Hefferon 227). Additionally, uniforms are gender-specific, which means that they can negatively impact the personalities of students as they are forced to wear uniforms that they do not feel reflect what they want to be or do with their lives. Thus, as the proponents against school uniforms argue, uniforms should be eliminated as they infringe on the independence of young students.
To sum up, there are numerous arguments that either support or oppose the wearing of uniforms by students. Supporters of school uniforms claim that uniforms give students a sense of identity and discipline, enhance social and economic equality, and save costs. On the other side, proponents against school uniforms claim that school uniforms limit the personal expression of students and force them into specified gender roles. Judging from the advantages and disadvantages of uniforms, it is clear that all students should wear uniforms as they distinguish students from civilians and enhance equality in the school environment.
Baumann, Chris, and Hana Krskova. "School discipline, school uniforms, and academic performance." International Journal of Educational Management 30.6 (2016): 1003-1029.
Freeburg, Beth W., and Jane E. Workman. "Dress Codes and Uniforms." Encyclopedia of Adolescence (2016): 1-13.
Masuch, Christoph-Simon, and Kate Hefferon. "Understanding the links between positive psychology and fashion: A grounded theory analysis." International Journal of Fashion Studies 1.2 (2014): 227-246.
Ruggerone, Lucia. "The feeling of being dressed: Affect studies and the clothed body." Fashion Theory 21.5 (2017): 573-593.

Gradecrest is a professional writing service that provides original model papers. We offer personalized services along with research materials for assistance purposes only. All the materials from our website should be used with proper references. See our Terms of Use Page for proper details.

77 School Uniforms Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best school uniforms topic ideas & essay examples, 📌 most interesting school uniforms topics to write about, 👍 good research topics about school uniforms, ❓ the school uniform question essay.
- School Uniform and Maintenance of Discipline Some prefer to implement the use of school uniform citing various benefits such as improvement of discipline in schools while others see the whole issue of school uniform as a cover up of failed social […]
- School Uniforms: Conflicting Opinions It might be wise to teach a child from the early age what clothes it is suitable to put on when they go to school.
- Fashion in Society: School Uniforms and Self-Expression The use of school uniforms can actually enhance a child’s personal character development as “such requirements of standardized dress also include a symbolic rhetoric of legitimate authority, a reservoir of institutional and organizational values of […]
- Mandatory School Uniforms: Pros and Cons Finally, opponents of school uniforms claim that the ‘sense of community’ that is believed to be an advantage is, in fact, imposed on students and borders on some form of extreme uniformity.
- LA School Uniforms as Mandatory Attire for All Students On the one hand, school uniforms have to be mandatory in all LA schools in order to make students concentrate on their educative processes, and on the other hand, students may feel a kind of […]
- School Uniforms: Conflicting Viewpoints Over the course of the previous assignment, I have stated that I do not support the enforcement of school uniforms for the following reasons.
- School Uniform Dress Code Should Be Enforced
- Market Structure of School Uniform in Medway
- Public Schools Should Adopt A School Uniform Policy
- The Chief Benefits of School Uniform
- The Effects of a School Uniform Policy on Conflict Reduction and Academic Performance
- How School Uniform Can Reduce Social Inequality
- Is the Enforcement of School Uniform Indoctrination
- Advantages Of The Mandatory School Uniform
- The Complexity of the Issue of a Standard School Uniform in American Schools
- Scholastic Performance, Resolving Conflict, and the Impact of a School Uniform Policy
- The Pros and Cons of Wearing School Uniform
- Effects of Implementation of a School Uniform Policy
- Why School Uniform Should Not Be Abolished
- School Uniform: Good Tradition or Outdated Habit
- School Uniform Policy And Student Achievement
- Why The School Uniform Policy Is Such A Bad Idea
- Positive Outcomes of School Uniform Use
- School Uniform Is Not A Public School Tradition
- School Uniform Is Beneficial And Essential For The Success
- The Mandatory System of Wearing School Uniform
- Penetrating the High School Uniform Business in the US
- Does Wearing School Uniform Have An Influence On Student
- Should School Require Students to Wear a School Uniform?
- The Controversial Issue on the Mandatory Wearing of School Uniform
- Students Should Wear School Uniform
- The Advantages and Disadvantages of Wearing a School Uniform
- The School Uniform Movement And What It Tells Us About
- School Dress Issues and Public School Uniform Codes
- Why Do Students Need A School Uniform
- Implementation of School Uniform
- School Uniform Policy Increase Student Self Esteem And Improve Learning
- Importance Of Uniform In The Middle School Uniform
- Why School Uniform Is Not Always The Best
- The Implementation of School Uniform Policies
- School Uniform Policies Around The World
- Pros on School Uniform in Public Schools
- Speech About Why Student Should Wear School Uniform
- The Pros Of Having A School Uniform Policy
- Vote for School Uniform: Vote for a Bright Future
- Introducing and Analyzing the School Uniform Concept
- What Are Reasons Why Schools Need to Implement the Idea of School Uniforms?
- Should School Uniforms Improve Our Education System?
- Why Do School Uniforms Cause Controversy?
- Are School Uniforms Beneficial or Not?
- Why Should School Uniforms Be Enforced?
- Should School Uniforms Improve Academic and Social Behavior?
- Why Should School Uniforms Not Be Forced on Students?
- How Are School Uniforms Stereotyped Throughout Children’s School Years?
- Why Should Middle School Pupils Wear School Uniforms?
- Should School Uniforms Hinder Psychological Development?
- Why Should the High School Student Wear Uniforms?
- Are School Uniforms Cure Violence and Gang Prone Violence?
- Should School Uniforms Help Rein Student Violence?
- How Do School Uniforms Impact Public High Schools?
- Should Public School Uniforms Be Banned?
- Are School Uniforms Effective for Students?
- Should Children Wear Uniforms to School?
- Are School Uniforms Necessary for Students?
- Should College Uniforms Always Be Banned?
- Are Teenagers Hidden Behind Their School Uniforms?
- Should Mandatory School Uniforms Be Implemented in Public Schools?
- Why Are School Uniforms Used as a Method of Assimilation?
- Should School Uniforms Make Schools Safer for Students?
- What Are Advantages and Disadvantages of School Uniforms?
- Why Is It Important to Wear Uniforms in the School?
- Do Uniforms Make Schools Better?
- How Do Uniforms Affect Students?
- Who Created School Uniforms?
- How Do Uniforms Make Students Feel?
- Do Students Work Better Without Uniforms?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, October 26). 77 School Uniforms Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/school-uniforms-essay-examples/
"77 School Uniforms Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 26 Oct. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/school-uniforms-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2023) '77 School Uniforms Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 26 October.
IvyPanda . 2023. "77 School Uniforms Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." October 26, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/school-uniforms-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "77 School Uniforms Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." October 26, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/school-uniforms-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "77 School Uniforms Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." October 26, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/school-uniforms-essay-examples/.
- College Education Essay Ideas
- Teamwork Research Ideas
- Pedagogy Topics
- Classroom Management Essay Topics
- Academic Achievements Research Topics
- Personal Identity Paper Topics
- Equality Topics
- Freedom Of Expression Questions
Essays About School Uniforms: Top 5 Examples And Prompts
Uniforms are a hotly-debated topic in schools worldwide; if you are writing essays about school uniforms, get inspired by reading our essay examples and writing prompts.
School uniforms have been an education emblem for centuries; they are commonplace in primary and secondary school. They are a set of clothing that students attending a particular institution must wear during school hours and are said to encourage discipline, unity, and belonging, among other things.
However, they are a significant point of contention. As time has passed, more and more schools have discontinued their requirements for uniforms, which has sparked a heated debate over their necessity.
If you want to write essays about school uniforms, look at the examples and writing prompts below to start.
1. I believe students should not have to wear uniforms. by Evan
2. taking a new look at uniforms and their impact on schools by james sterngold, 3. uniforms: the pros and cons by grace chen, 4. what’s the point of school uniform by rudolph carroll, 5. not wearing the trousers: why do some schools still have sexist uniform rules by hadley freeman, 1. should school uniforms be a requirement , 2. how do school uniforms effect behaviour, 3. what’s the history and purpose of school uniforms, 4. are school uniform requirements a form of indoctrination , 5. what are the advantages of school uniforms.
“When wearing uniforms, it is a struggle to be an individual. Teachers are always saying how important it is to just be ourselves and not worry about what others might think. Having a uniform takes that away from us, and this may lead students to try to find other ways to be different. They might begin to act out so they stick out from the crowd.”
In his essay, Evan explains his opposition to school uniform requirements, including the loss of individuality and confidence. He believes that they add too much stress to an already stressful environment and that this unnecessary burden can be alleviated with a dress code. It regulates students’ clothing while still allowing them to choose and will teach them responsibility in choosing what to wear.
”There is no direct link between uniforms and performance,’ Mr. Flanary said, ‘’but we know there is a link between the school environment and performance. Uniforms might be one way of affecting the environment, but just one.”
Sterngold writes about the introduction of uniforms at a Long Beach school. It leads to higher grades and fewer absences, and disciplinary issues. He also discusses other schools in which uniform policies appear to work in making students “better.” Finally, he notes that the school environment affects a student’s performance.
“Deciding whether uniforms are right for your child depends upon individual circumstances. If your child has a high need for self-expression and personal comfort in her clothing, then uniforms may create unhealthy resentment and result in negative behaviors from your child.”
In her essay, Chen lists the advantages and disadvantages of uniforms in public schools. They establish a safer learning environment and may reduce gang-related violence, but they restrict comfort and self-expression. Ultimately, she leaves it up to parents to decide whether uniforms are essential, depending on their children’s personalities.
“Imagine having to wear school uniforms everyday. The same dress code every week., the same color pants and shirts every week. Uniforms especially those that have color and style requirements for every part of the outfit are not easy for many parents to afford. Students should be able to have a choice to wear whatever they want.”
Carroll advocates for the banning of school uniforms. He writes that they suppress freedom of expression and force students to wear something they may not find comfortable; they should be able to express themselves and wear whatever they want.
“Doubtless, some people out there will say – some waggishly, others less so – that if girls should be allowed to wear trousers at school then boys should be able to wear dresses. My personal feeling on that is, sure, boys can wear dresses if they want but women’s clothing, from skirts to stilettos, was designed to restrict women’s movement, whereas men’s clothing is all about freedom. ”
Freeman writes about school uniform policies she feels are discriminatory. For example, some schools do not allow girls to wear trousers and impose a standard on their female students. She believes that young children should be able to behave freely, including in their dressing habits. Freeman believes that the world’s standard of femininity has become more open, and the idea that girls must wear skirts is outdated.
Top 5 Prompts on Essays About School Uniforms

Plain and simple, you can write about your position on uniforms; decide whether or not you believe students should be required to wear school uniforms. Your essay should include a clear statement of your position, a rebuttal of the opposing viewpoint, and plenty of details to support your argument- use statistics, anecdotes, and other online sources, as well as your opinions.
Write about the effects of uniforms on students’ positive or negative behavior within school learning environments. For example, does it make them more disciplined, reserved, confident, outgoing, or cheerful? You must include research in your essay to show a clear connection. Looking for more? Check out these essays about classroom .
For your essay, read about the history of school uniforms and write about their usage. Also include their original purpose/s and how it has changed over time. Then, if you wish, you can add whether these purposes or standards have held up in the present day or not.
For an engaging essay, write about school uniforms and indoctrination. Though it may seem like an exaggeration, some say that school uniform requirements are being used to indoctrinate students from a young age. Where do you stand?
From a more objective standpoint, try writing about the benefits of mandatory uniforms in school. Do they instill specific values in students? Or perhaps they contribute to a better school environment, as referenced in the sample essays above. What do you think? Write about the benefits/advantages of uniforms for an exciting essay.
For help with this topic, read our guide explaining what is persuasive writing ?
If you are interested in learning more, check out our essay writing tips !

Martin is an avid writer specializing in editing and proofreading. He also enjoys literary analysis and writing about food and travel.
View all posts
Do uniforms make schools better?
by: Marian Wilde | Updated: March 1, 2024
Print article

Schools, parents, and students frequently clash over the issue of regulating what students may and may not wear to school. These controversies often pegged to the culture war of the moment touch on everything from gender and sexuality to politics, race, and religion. In 2021, a group of about 50 students in Georgia protested their middle school’s dress code for being discriminatory against BIPOC girls by wearing t-shirts every Friday emblazoned with the words “sexist,” “racist,” and “classist.” In 2022, a fight between students, staff, and police officers broke out at a Pennsylvania high school when hats and hoodies were banned as part of a revision by the school board to the school’s dress code. And in 2023, two Michigan middle schoolers, via their mother, sued their school district after they were banned from wearing “Let’s Go Brandon” sweatshirts.
Are school uniforms the best solution to this contentious debate? If every student is wearing the same outfit, will a host of campus problems be solved? Researchers are divided over how much of an impact — if any — dress policies have on student learning. There are multiple studies with conflicting conclusions, plus books such as 2018’s The Debate About School Uniforms , but the argument wears on, with a list of pros and cons on each side.
Why do some public schools have uniforms?
In the 1980s, public schools were often compared unfavorably to Catholic schools. Noting the perceived benefit that uniforms conferred upon Catholic schools, some public schools decided to adopt a school uniform policy.
President Clinton provided momentum to the school uniform movement when he said in his 1996 State of the Union speech, “If it means teenagers will stop killing each other over designer jackets, then our public schools should be able to require their students to wear school uniforms.”
The pros and cons of school uniforms
According to proponents, school uniforms:.
- Help prevent gangs from forming on campus
- Encourage discipline
- Help students resist peer pressure to buy trendy clothes
- Help identify intruders in the school
- Diminish economic and social barriers between students
- Increase a sense of belonging and school pride
- Improve attendance
Opponents contend that school uniforms:
- Violate a student’s right to freedom of expression
- Are simply a Band-Aid on the issue of school violence
- Make students a target for bullies from other schools
- Are a financial burden for poor families
- Are an unfair additional expense for parents who pay taxes for a free public education
- Are difficult to enforce in public schools
Uniforms vs. dress codes
Schools and districts vary widely in how closely they adhere to the concept of uniformity.
What’s a dress code?
Generally, dress codes are more relaxed than uniform policies. Sometimes, however, dress codes are quite strict with requirements that are potentially viewed as biased based on race or gender. In 2020, two Black male students in Texas, cousins with West Indian heritage, were suspended for wearing dreadlocks in supposed violation of the district’s hair and grooming policy, part of the dress code. The elder one, a senior, was told he couldn’t attend prom or graduation until his dreads were trimmed. In 2022, girls on the track team at an Albany, NY high school were sent home for wearing sports bras at practice.
Uniforms are certainly easier for administrators to enforce than dress codes, largely because the ACLU (American Civil Liberties Union) can be depended upon to protect a student’s “right to express themselves.” The ACLU believes dress codes are often used to, “shame girls, force students to conform to gender stereotypes… punish students who wear political and countercultural messages. Such policies can be used as cover for racial discrimination… Dress codes can also infringe on a student’s religious rights…” To successfully enforce a dress code, insists the ACLU, the school must prove the student’s attire, “is disruptive to school activities.”
The ACLU’s dress code stance is regularly supported by federal courts , like the 2023 lower court ruling in North Carolina that ended a charter school decree that girls couldn’t wear pants to school. ACLU lawyers claimed this violated Title IX because the dress code “discriminated against female students by limiting their ability to fully participate in school activities, such as using the playground.” The U.S. Supreme Court later declined to take up a case challenging the lower court’s ruling.
Check with your school to see what the dress code is, as they can be fairly specific. In Tulsa, Oklahoma, for example, the dress code prohibits :
- Symbols, mottoes, words or acronyms that convey crude, vulgar, profane, violent, death-oriented, gang-related, sexually explicit, or sexually suggestive messages.
- Symbols, mottoes, words or acronyms advertising tobacco, alcohol, or illegal drugs or drug paraphernalia.
- Symbols, mottoes, words or acronyms identifying a student as a member of a secret or overtly antisocial group or gang or that identifies a student as a member of an organization that professes violence or hatred toward one’s fellow man.
- Visible and permanent tattoos/brands incompatible with the standards set forth herein shall be covered to prohibit their display.
- Excessively large or baggy clothes
What’s a uniform?
School uniforms worldwide can widely range from nondescript to bizarre. (Extreme examples from China, Australia, and the UK on this YouTube video ) Most public school outfits in the USA are quite casual, with a “ common type ” for boys often a polo shirt in a solid color, with pants in khaki, black, or navy blue. A girl’s uniform is often a skirt and a white buttoned-up shirt. Dress shoes are frequently required for both genders.
In the United States, low-income families spend an average of $249 on a child’s school uniform annually, far less than the typical Australian student’s $578. But still, the cost is sometimes viewed as unfair because public education is intended to be free, paid by tax dollars, not “a stress for families on lower incomes.” The ACLU believes that public schools should provide free school uniforms , because the expense is unconstitutional, and it increases wealth inequity.
What research says about school uniforms
In 2006, Virginia Draa, professor at Youngstown State University, reviewed the impact of school uniforms at 64 public high schools that had larger percentages of economically disadvantaged and minority students than other urban schools. Her conclusion surprised her: “I really went into this thinking uniforms don’t make a difference, but I came away seeing that they do… I was absolutely floored.” Her analysis determined that the schools with uniforms improved their students attendance, and graduation rates rose an average almost 11 percent.
In 2022, Ohio State University and University of Pennsylvania researchers reached a contrary opinion in their report titled “ School Uniforms and Students Behavior: Is There a Link? ” Their view was that, in general, evidence that school uniforms improve social skills in the students was “inconclusive.” The solitary praise they provided to uniform-wearing was noting there was “some indication that low-income students in schools that required uniforms demonstrated better school attendance than low-income students in schools that did not.”
What to believe? Jury is still out.
What do students think about uniforms?
A student discussion: pros and cons of uniforms
Editor’s note: This video is part of our high school milestones series about communication skills. The students in this video discuss the pros and cons of school uniforms.
A University of Nevada, Reno, survey of 1,848 middle school students, published in 2022, revealed that 90 percent did not like wearing a uniform to school . Only 30 percent believed the uniforms “might reduce discipline issues, a mere 17 percent thought the uniform helped them focus at school, 34 percent believed their school was safer due to the uniforms and 37 percent said, “I worry less about my appearance” due to the uniform requirement.”
An earlier study, also in Nevada, displayed similar unpopularity with newly instituted uniforms among middle school students. However, when the researchers looked into school discipline and local police records and compared them to the prior year’s data, discipline referrals were down 10 percent, there were 63 percent fewer police log reports, and incidences of graffiti, fights, and gang-related activity were all down.
It’s a big issue
A new trend is the mounting pressure to establish dress codes for teachers. Apparently, the same casual mindset toward revealing outfits is cropping up in the ranks of our teachers.
The debate over uniforms in public schools encompasses many larger issues than simply what children should wear to school. It touches on issues of school improvement, freedom of expression, and hot-button culture wars. It’s no wonder the debate rages on.
Homes Nearby
Homes for rent and sale near schools

Why your neighborhood school closes for good – and what to do when it does

5 things for Black families to consider when choosing a school

6 surprising things insiders look for when assessing a high school
Surprising things about high school
Yes! Sign me up for updates relevant to my child's grade.
Please enter a valid email address
Thank you for signing up!
Server Issue: Please try again later. Sorry for the inconvenience
Argumentative Essay Example: Why We Should Wear School Uniforms
It is often said that school uniforms are important, but why are uniforms important? Uniforms are important because of the educational purposes, the major focus on school, requirements of our goals and for equality. In other countries it’s strictly about school uniforms because we have different points of view and because they want to put student’s futures first. The real question is, why is it so important? Why do most countries have the same rules when it comes to student's school uniforms? And what difference does it make? How does it represent our country, school, motto and ourselves? And in today’s society there are a lot of variations of different opinions on whether we should have school uniforms or not and therefore we should allow students to wear school uniforms.
First off, it is worth considering inappropriate clothing. As much as we agree on wearing whatever we want, there is a limit. Personally, I do not think the dress code is enough, people should wear appropriate clothing for school and that is something school uniforms can help with improving. Besides, wearing inappropriately has a bad influence on the students and their outcome of inappropriate dressing. In the opinion of the people it classifies as distracting and disrespectful.
Another point worth noting is that bullying in school is one of the school's biggest rules. Bullying has expanded over the past few years. The leading cause of bullying is especially if you are poor or different, yet we do nothing to prevent it. We talk about in meetings and in class how we should have equality in school and how bullying affects other people. It makes sense that the way we dress has a big impact on whom we are. I encourage students to embrace themselves and not change depending on other people's opinions. The Uniforms in school give some kind of equality which can also be used as a protection for further bullying. According to other countries, it's important to wear school uniforms to represent their school, country and tradition from way back in history, to show themselves as a part of the school and as a sign of equality. The students seem alright with that and have an understanding for themselves, others and the surrounding society.
Although I know this is true that many people claim they want to show themselves and point out their dressing as a part of their personality. Loads of people argue about freedom of speech and express their concern about bullying and that is understandable. However, I don't see it that way. I believe that there is a way to stop the major issue and put it to an end. With the help of school teachers and all the school staff helping students but also parents can make the bullying stop. Some of us are talking about freedom of speech, but there is a difference between what you are wearing and, what you are talking about. Freedom of speech is that you have the right to your opinion and express your opinion, but it’s different from wearing and expressing your personality or style, that is not freedom of speech. I do agree with being able to wear the way you would describe yourself but to a certain extent.
Lastly, the student's focus increases. The students don't have to think about what to wear or stress themselves out. It is an important matter. Student’s creativity is in fact necessary but should be used outside school. According to school laws we can express ourselves and our creativity in other ways such as our personality and the way we talk, the way we present, the things we do or create and the way we show ourselves in school. A lot of students try to hide their insecurities by wearing whatever they want which does not seem professional. I claim that with the help of school uniforms it shows us that the focus leads to better understanding in school and not only on what to wear. In my humble opinion, not focusing on how to dress or what to dress and instead focusing on school will give you better results, which has also been proven. A factor of poor results is caused by stress and pressure.
In conclusion, wearing school uniforms helps the students feel safer, less stressed and less about changing in society because of other opinions. It also minimizes the chances of getting bullied. The goal is to show equality in school and the people around us as one. People have no hope in this and most of them disagree because they fear not being able to express themselves, which is not the case. In school, there are varieties of ways to express and show yourself, to stand out. School is for the student’s education for the future and must not focus on clothing since that does not matter. In school, you can find a good deal of help, future, education, equality and hope of a better future. That is why we should definitely encourage students to wear school uniforms at school.
Related Samples
- The Education System Should Be Changed Argumentative Essay
- The Importance Of Education Essay Sample
- Community Service in High Schools Persuasive Essay Example
- Homeschooling is it really the best option?
- Argumentative Essay on Against School Dress Code
- National Junior Honor Society Essay Example
- Application Essay Example: University of Wisconsin 2022
- Iowa State's College Experience Essay Sample
- China’s New Restrictions on Private Tutoring Essay Example
- Argumentative Essay Example: School Should Give Us Less Homework
Didn't find the perfect sample?

You can order a custom paper by our expert writers
- Trying to Conceive
- Signs & Symptoms
- Pregnancy Tests
- Fertility Testing
- Fertility Treatment
- Weeks & Trimesters
- Staying Healthy
- Preparing for Baby
- Complications & Concerns
- Pregnancy Loss
- Breastfeeding
- School-Aged Kids
- Raising Kids
- Personal Stories
- Everyday Wellness
- Safety & First Aid
- Immunizations
- Food & Nutrition
- Active Play
- Pregnancy Products
- Nursery & Sleep Products
- Nursing & Feeding Products
- Clothing & Accessories
- Toys & Gifts
- Ovulation Calculator
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- How to Talk About Postpartum Depression
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
The Pros and Cons of School Uniforms for Students
SolStock / Getty Images
Student Safety
Focus on education, attendance rates, discipline issues, dress code enforcement, cost for families, impact on self-esteem.
The debate over whether students should wear school uniforms has been going on for more than a decade. Some people argue that uniforms have a positive impact on the school environment by promoting inclusivity, confidence, and a sense of belonging. Others fear that school uniforms prevent kids from expressing themselves through their clothing choices.
The research on school uniforms is often mixed. While some schools have found uniforms to be beneficial, other research has found that they have little effect. Some studies have even reached the conclusion that requiring school uniforms can be harmful for students.
Let's take a closer look at some of the potential benefits, as well as the challenges, of requiring students to wear uniforms.
Some people think that school uniforms can help make schools safer for kids. When Long Beach, CA, required all students in grades K–8 to wear uniforms, reports of assault and battery decreased by 34%.
Additionally, assault with a deadly weapon decreased by 50%, fighting incidents declined 51%, and sex offenses dropped by 74%. Possession of weapons dropped by 52%, possession of drugs went down 69%, and vandalism was lowered by 18%.
The Sparks Middle School in Nevada reported a decrease in gang activity after instituting a uniform policy. They also reported a drop in fights, graffiti, property damage, and battery. Overall, there was a 63% drop in police reports.
Other proponents of school uniforms report that it prevents students from concealing weapons under clothing. And some also believe intruders would be recognized faster, making the students and staff safer in the event someone from the community tries to enter the school.
Not all studies have found that uniforms reduce discipline issues, however. In fact, a peer-reviewed study found that school uniforms increased the average number of assaults by about 14 per year in the most violent schools. The Miami-Dade County Public Schools Office of Education Evaluation and Management found that fights in middle schools nearly doubled within one year of making uniforms mandatory.
For many students, clothing can be a major source of stress. Not having certain brand name clothing or not wearing fashionable items could lead to feelings of insecurity.
Some people feel students are better able to concentrate on school when they all wear the same clothing. Researchers in Australia noted that students who wear uniforms had improved discipline and academic performance.
Not all studies have found that uniforms improve grades, however. In fact, at least one study found that school uniforms had a negative effect on achievement.
Kids may show up to school more often when they’re wearing uniforms. A study by researchers at the University of Houston found that the average attendance rate for girls in middle and high school increased by 0.3 to 0.4 percent after school uniforms became mandatory. A study by Youngstown State University also found that attendance rates increased and suspensions decreased once students began wearing uniforms.
Students may also be more likely to show up to school on time when they have to wear uniforms. If they don’t have to spend time choosing what to wear every morning, students are able to get out the door more quickly. This means fewer late arrivals.
Proponents of uniforms report that it can improve behavior in students. One school that found this to be true is the John Adams Middle School in Albuquerque, NM. When they mandated school uniforms, discipline referrals dropped from 1,565 in the first semester of the previous year to 405.
An Australian study also concluded that students wearing uniforms were more disciplined and they listened significantly better. Classes were also more likely to start on time.
Not all studies have found this, however. Some research has found that disciplinary issues and bullying didn’t decrease after instituting a mandatory uniform policy.
Many school officials spend a lot of time policing dress codes . Enforcing policies can require a lot of resources as teachers may send kids to the office, and administrators have to determine whether clothing is too baggy, inappropriate, or revealing.
Kids who violate dress codes may spend a lot of time in the office awaiting consequences, or they may receive suspensions for repeated violations. School uniforms can keep kids in the classroom more and prevent staff from wasting time trying to enforce policies.
Parents may spend less money on school clothes when kids wear uniforms. There is less pressure to buy expensive name-brand clothing, and school uniforms might be more affordable.
Opponents of school uniforms, however, say that requiring parents to buy specific articles of clothing goes against the idea that students should be given free education. When public schools force parents to buy uniforms, this could be placing a hardship on some families.
Proponents of uniforms report that they have a positive impact on student self-esteem . Wearing the same clothing as everyone else means that students don’t have to worry about whether their clothing choices will be acceptable to their peers.
But opponents argue that uniforms may have a negative impact on some students’ body image. Research conducted at Arizona State University found that students without uniform policies actually reported higher self-perception scores than students with uniform policies.
When all students wear the same clothing, they may be more likely to compare themselves to their peers as clothing fits differently on everyone’s body.
The Problem With Uniform Research
Although there are many studies that examine the potential benefits and drawbacks of uniforms, many of them revealed correlation, rather than causation. Just because grades went up or behavioral problems went down, there’s no way of knowing that the reason for the change was due to uniform policy. There are many other factors that may have influenced these issues.
A Word From Verywell
Before any school adopts a uniform policy, it may be wise to review the literature. While there certainly may be a lot of benefits to making uniforms mandatory, there are also some potential drawbacks and challenges you might face. Parents, teachers, and administrators may want to weigh the pros and cons before instituting any type of clothing policy for students.
Stanley S. School uniforms and safety . Educ Urban Society. 1996;28(4 ): 424-435. doi:10.1177/0013124596028004003
Nevada Today. College of Education researchers conduct study on impacts of school uniforms .
Granberg-Rademacker JS, Bumgarner J, Johnson A. Do school violence policies matter? An empirical analysis of four approaches to reduce school violence . Southwest J Criminal Justice . 2007;4(1):3-29.
Sun Sentinel. 9 more schools to have students wear uniforms .
Baumann C, Krskova H. School discipline, school uniforms and academic performance . Int J Educ Manage . 2016;30(6):1003-1029. doi:10.1108/IJEM-09-2015-0118
McBrayer S. The school uniform movement and what it tells us about American education: A symbolic crusade, by David L. Brunsma . J Catholic Educ . 2007;11(1). doi:10.15365/joce.1101122013
Gentile E, Imberman S. Dressed for success? The effect of school uniforms on student achievement and behavior . 2011. doi:10.3386/w17337
Draa VAB. School uniforms in urban public high schools . Dissertation: Youngstown State University; 2005.
Lumsden L, Gabriel Miller G. Dress codes and uniforms . Research Roundup: National Association of Elementary School Principals . 2002;18(4):1-5.
Wade KK, Stafford ME. Public school uniforms: Effect on perceptions of gang presence, school climate, and student self-perceptions . Educ Urban Society . 2003;35(4):399-420. doi:10.1177/0013124503255002
By Amy Morin, LCSW Amy Morin, LCSW, is the Editor-in-Chief of Verywell Mind. She's also a psychotherapist, an international bestselling author of books on mental strength and host of The Verywell Mind Podcast. She delivered one of the most popular TEDx talks of all time.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Public Health Rev

Reviewing School Uniform through a Public Health Lens: Evidence about the Impacts of School Uniform on Education and Health
This study uses a public health lens to review evidence about the impacts of wearing a school uniform on students’ health and educational outcomes. It also reviews the underlying rationales for school uniform use, exploring historical reasons for uniform use, as well as how questions of equity, human rights, and the status of children as a vulnerable group are played out in debates over school uniforms. The literature identified indicates that uniforms have no direct impact on academic performance, yet directly impact physical and psychological health. Girls, ethnic and religious minorities, gender-diverse students and poorer students suffer harm disproportionately from poorly designed uniform policies and garments that do not suit their physical and socio-cultural needs. Paradoxically, for some students, uniform creates a barrier to education that it was originally instituted to remedy. The article shows that public health offers a new perspective on and contribution to debates and rationales for school uniform use. This review lays out the research landscape on school uniform and highlights areas for further research.
Despite regular judicial, community, and press scrutiny, there is little consensus on the function of school uniforms, or agreement about evidence of their impact on education and health. Breaches of school uniform policy have resulted in court cases (e.g., [ 1 , 2 ]), and courts note that in focusing on the rights and wrongs of a particular uniform policy, the underlying issues driving uniform design and policy are neglected [ 3 ]. Meanwhile, at the beginning of the school year in many English-speaking countries there are numerous press articles about the cost burden to families of providing school uniforms [ 4 – 8 ], whether they are value for money [ 9 – 11 ], and whether garment design is fit for modern life [ 12 – 17 ]. Discussion seems stymied in a superficial argument about whether school uniforms are good or bad. Rarely do discussions point to empirical evidence about school uniform garment design and policy about uniform use. This situation begs questions as to availability of evidence for school uniform use, its effects on educational or health outcomes, and the underlying rationales for school uniform use.
This article applies a public health lens to review evidence about why we have uniforms and what effects they have on educational and health outcomes. A public health perspective was chosen to review evidence because it is explicitly designed to analyze impacts of broad socio-political forces and determinants of health on individual experiences. Further, public health sees education and health as mutually reinforcing and intrinsically linked. The one determines the success of the other. Consequently, much public health policy aims to optimize wider social policy settings to improve health and education [ 18 ], and encourage equitable outcomes especially for the most vulnerable populations [ 19 ]. It is also why the World Health Organization (WHO) promotes health in all government policies to improve overall population health ([ 20 ]). Therefore, attention to students’ physical and psychosocial health and wellbeing is important for enhancing educational outcomes. This includes evidence for the choice of school uniform garments and individual schools’ policy about uniform and how these affect student wellbeing. The evidence considered here suggests that uniform is of public health concern because its use and effects are prevalent, have impact and are amenable to improvement. Uniform use is prevalent and widespread globally. In their study of 39 PISA countries, Baumann and Kriskova [ 21 ] identify five main geographic/sociocultural groupings where uniform wearing is common: an Anglo-Saxon cluster (United Kingdom, NZ, Australia, United States), Asia, East Asia (South Korea, Japan), the Americas (e.g., Mexico), and Europe. These authors also note that uniform prevalence is increasing. Regarding impact, evidence shows uniforms can impact directly and indirectly on the individual and on society in equity, health and educational domains for better and for worse. The reviewed literature suggests that any harms are amenable to intervention via evidence-based action. Meadmore and Symes [ 22 ] argue that uniforms are not as frivolous as they appear and warrant systematic attention. This article applies that systematic attention through a public health lens. It explores three questions: What is the evidence for the impact of school uniform on students’ academic and health outcomes; what social, cultural and political rationales are made for uniform use; and what human rights may be affected by school uniform choice? For conciseness, “school uniform(s) garments” will be referred to as uniform(s). The practice of wearing/using/mandating a school uniform will be referred to as uniform policy.
Databases that include health and education research were searched for peer-reviewed articles in English using the key word “school uniform” in the title keywords or abstract. The date range searched was from 2000 to (present), being October 2020. The results are detailed in Table 1 .
Database searches October 2020.
Oft -cited peer-reviewed sources that did not appear in the literature searches were also included in the literature review ( n = 25), as well as texts that were found in the initial work for this review. Texts were de-duplicated, yielding 197 texts. Records were screened for relevance and excluded 79 for being out of scope because of time constraints (not in English, PhD theses, conference proceedings). This yielded 118 full text articles to be assessed, of which 26 were excluded because they were off-topic for this review (e.g., industry information about supply chains; school uniform as a basis for a thought experiment; fetishism; reports on forensics; technical information about fabric properties). 92 studies were included in this review.
Note this study examines the breadth of evidence for uniform wearing. Study quality was not part of the analysis.
Articles fell into three broad groups: surveys/studies that elicited stakeholder feedback on some aspect of garment design or policy; or experience of uniform wearing; analyses of large datasets or administrative data; and political, philosophical/ethnographic, and legal analyses of rationale and impact of uniform use.
The first group comprised empirical research that examined data on some aspect of garment design or policy or uniform wearing experience. There was a mixture purposive samples and convenience samples. Studies varied in the number of participants, the number of sites from which participants were taken. Studies elicited views from stakeholders: students, parents, teachers, administrators, social workers, school counselor. Views were gathered via survey and/or focus group. Some surveys formed part of a case study. There were also stand-alone case studies and ethnographies, an RCT and an auto-ethnography.
12 studies examined garment properties for Sun protection, safety, design. The mix of stakeholders varied: students only ( n = 15); students and family/parents/caregivers ( n = 8); multiple stakeholders (students, parents, teachers, and administrators, and/or social workers) ( n = 17). There were three randomized control trials. There were a mixture purposive samples and convenience samples. Studies varied in the number of participants, the number of sites from which participants were taken. The second group comprised analyses of large datasets ( n = 5), and one meta analysis on factors affecting educational outcomes. The third group were non-empirical studies. They included: policy summaries; legal analyses; historical commentaries on uniform’s development; socio-political analyses; political think-pieces; and one economic analysis.
Here, evidence has been arranged according to a public health lens of analysis. First, this section examines the proximate educational and health impacts of uniform garments and uniform policy on students to determine whether there are immediate health or education impacts of uniform use or policy. Second, rationales for uniform use are examined, as well as distal factors that influence student experience. This section examines the broader institutional, and socio-cultural contexts which inform uniform use.
Part 1: Literature for Educational and Health Impacts of Uniform
Does uniform influence educational outcomes.
Starting with the evidence for the impact of uniform on educational outcomes (the core in Figure 1 ), there is little convincing evidence that uniform improves academic achievement. Studies from the United States in the early 2000’s [ 23 , 24 ] note a positive correlation between uniform wearing and academic achievement (e.g., Bodine [ 25 ]). Later, in 2012 Gentile and Ibermann found a positive effect on grades and retention [ 26 , 27 ]. Stockton et al. [ 28 ] noted there was a greater perception of increased attendance and achievement after uniform was introduced. However, studies of large datasets and meta-analyses fail to find a link between uniform and academic achievement. Brunsma and Rockquemore’s (2003) response to Bodine’s assessment of their administrative data review in the late 1990’s reiterated that no overwhelming link exists between uniform wearing and academic outcomes (there were methodological disagreements about which data to choose and how they should be analyzed). Later studies by Yeung [ 29 ] and Creasy and Corby [ 30 ] noted multiple factors for academic achievement—but not uniform. In a synthesis of 800 meta-analyses on effects of all hitherto published variables of educational outcomes, Hattie [ 31 ] demonstrated negligible to no association between uniform and academic achievement itself. However, he notes that the ‘heat and impact of the discussion are as if [uniform] were obviously effective’ (p106) [ 32 ]. In a 2017 update to that study uniform was not listed among the 252 effects on educational outcomes [ 33 ].

Organization of evidence about uniform use.
Nonetheless, it appears that uniform may contribute to an environment that fosters academic achievement. Baumann and Kriskova [ 21 ] examined information from the PISA study on student experience of discipline within the classroom environment (listening, noise level, quietening/settling, schoolwork, starting work). This study involved a very large sample of students from across the globe. These researchers found a statistically significant difference related to settling to work between uniform wearing and non-uniform wearing samples. Thus, Baumann and Kriskova [ 21 ] recommend keeping uniforms where already used and introducing them where not used. Similarly, Firmin et al. [ 34 ] found introducing uniform reduced distractions. Writing about the United States, DaCosta’s [ 35 ] study of students noted improved concentration and increased security in the school where uniform was introduced. A South African study reported that uniform helped to maintain classroom discipline [ 36 ].
However, settling to work and classroom discipline are two of many facilitators of learning outcomes [ 21 ], along with class size, funding levels, homework, and, importantly, factors related to the quality of the teacher (qualifications, personality, incentives, mentoring for new teachers). Given that teacher skill and relationship between student and teacher are established as influential factors on learning outcomes [ 33 ], some argue that expecting teachers to enforce school uniform rules detracts from teaching, learning, and good relationships [ 30 , 37 ], notwithstanding the classroom management benefits of uniform-wearing described by Baumann and Kriskova [ 21 ]. Indeed, Da Costa [ 35 ] reports, the introduction of school uniform created opposition and non-compliance, distracting students and teachers from education. There are indications that uniform could create psychological barriers to education for vulnerable students, especially when it is a new phenomenon. Gromova and Hayrutdinova [ 38 ] found that for ethnic-minority newcomers to a school, uniform can simply be another strange element to get used to in a new environment.
One study argues that organisational and classroom management enhanced by uniforms may be achieved at the expense of other educational goals and values. Baumann and Kriskova’s [ 21 ] research ranks Korea and Japan highest in terms of settling to work and removing distractions. Yet Park’s [ 39 ] study found in Korea uniform was linked to stifling creativity, in spite of good academic performance. This is indicative only (a small study from one country), but highlights how much is not known about the impact of uniform on other domains of education.
Another effect of school uniform is that schools socialize students to certain explicit and implicit values and social norms and inculcate social skills that will help them get on in the world. Within that framework, school uniform provides what Vopat [ 40 ] describes as teachable moments (unplanned, yet important learning opportunities) to reflect on norms of society. There is no data that directly addresses non-academic learning outcomes from uniform. However, Vopat’s idea of teachable moments hints at why some administrators prefer a uniform [ 41 , 42 ], and a more formal one at that [ 41 ].
In some contexts, uniform is also instrumental to other goals: school security and students’ physical safety, aids student focus on learning. In South Africa, Wilken and van Aardt [ 36 ] observed that uniforms can make certain students targets of attack outside the school grounds. In South Africa and the United States uniforms are used to easily identify intruders on school premises and to reduce gang violence and theft of designer items outside of school [ 35 , 36 ]. However, in the United States one study found negligible evidence of uniform enhancing security [ 43 ], while another study found introducing uniform created only a lower perception of gang presence [ 44 ].
Overall, it appears that while uniform is a factor that removes distractions from classroom learning, thereby enhancing operational management, it has no direct impact on academic achievement and is not among factors that demonstrably improve educational outcomes. It may enhance school security, and influence schools’ broader educational and socialization goals.
Does Uniform Influence Health Outcomes?
Unlike for educational outcomes, there is a far more direct link between uniform garments and uniform policy and health outcomes. Health impacts can be divided into physical and psycho-social effects, though there is a significant overlap between the two. Physical impacts of school uniform relate to how uniforms facilitate physical activity during the day, whether uniform garments protect the wearer against known environmental hazards, whether the garments promote health and safety, and whether the garments are comfortable to wear. Psycho-social impacts are linked to fitting in (or not) with peers.
One effect uniforms have on physical wellbeing is their limitation or allowance of exercise. Encouraging regular physical activity is part of the WHO’s health promotion concept of health in all policies and settings. Globally, governments are trying increase physical activity among children and young people to reduce child obesity rates [ 45 ]. Additionally, physical activity enhances learning outcomes and improves wellbeing ([ 46 ]), therefore policies that promote planned and incidental physical activity positively influence educational and health outcomes. However, it appears that school uniform design and policy can pose a barrier to incidental exercise, particularly for girls. McCarthy et al. [ 47 ] found primary school girls were more active on sports uniform days and met government recommended daily physical activity levels on those days. Norrish et al.’s [ 48 ] study on the effect of uniform on incidental physical activity among ten-year-olds found that school uniform design could limit physical activity (measured by student self-report and pedometers). Correcting for choice of activity (ballgames, skipping vs imaginary play, verbal games), girls did significantly more activity during breaks on sports uniform days. Likewise, Watson et al. [ 49 ] and Stanley et al. [ 50 ] reported that recommended physical activity for school-aged children was not being met, especially for girls, where restrictive school uniform limited physical activity and created an explicit barrier to lunchtime play. Further, in an age of active transport policy, Hopkins et al. [ 51 ] found that school uniform style and lack of warmth was a barrier to cycling to school for some female secondary students, and Ward et al. [ 52 ] found both garment design and schools’ uniform policy hampered active transport among older teenagers. There are strong indications that uniform garments and policy about which garments can be worn directly impact on students’ physical health outcomes, for female students in particular.
While there is evidence on how uniform facilitates physical activity, there is little evidence on the psychological effects of uniforms on how students feel about doing physical activity in uniform. Unflattering or revealing (sports) uniforms may deter students from participating in sport. Focusing on physical activity, Watson’s et al.’s [ 49 ] study noted the complex social factors that affect physical activity, and how a unisex sport uniform could enhance the feeling of comfort and confidence. For instance, Pausé’s [ 53 ] auto-ethnography highlights the psychological barrier an unflattering sports uniform can pose to fat children’s participation in and enjoyment of physical activity as a good in itself (as opposed to a means to lose weight).
Physical health can be protected against known environmental health hazards by uniform garment design and policy implementation. However, school uniform policy (at national or school level) does not routinely address these hazards. In Australasia, ozone layer degradation results in high UV radiation levels in warmer months. Prolonged UV exposure results in skin damage and over the long term increased rates of moles and skin cancers across the population. Yet Gage et al. [ 54 ] found that uniformed schools had lower total body coverage than non-uniformed schools, albeit with greater neck coverage due to collared uniforms. This is despite evidence that hats with a brim and sun-safe clothing (covered arms and legs) can improve sun protection [ 55 ] while not increasing objective measures of body temperature [ 56 ]. Indeed, modeling from Australia indicates that slightly longer garments significantly alter mole patterns [ 57 ]. Of course the effectiveness of uniform garments (or indeed any garments) for sun protection depends on proper implementation of policy. For instance, in New Zealand Sunsmart is a voluntary school policy to optimize protection of children’s skin from sun damage and sunburn. However, Reeder et al. [ 58 ] found that Sunsmart policies were not consistently implemented, even among Sunsmart-accredited schools.
Uniform has also been used as part of measures to combat disease. In Thailand and other countries with endemic dengue, school uniform design, the use of insecticide-treated clothing [ 59 – 62 ], and how uniform is worn [ 63 ] have been investigated extensively in relation to dengue prevention, especially how to stop insecticide washing out of fabric. However, while the use of insecticide-treated clothing is supported by parents in these countries, willingness to pay for the uniform is linked to parental monthly income. Governmental willingness to subsidize treated uniforms is linked to overall cost, irrespective of effectiveness or potential health gain [ 64 , 65 ]. It appears that good garment design that protects against environmental hazards cannot be separated from good policy implementation and a financial subsidy if garment cost is high.
Interestingly, while environmental hazards and their impact on health were considered, no peer reviewed articles were found related to safe garment design e.g., Inflammable materials, removing strangling risks. The only information found on uniform policy and garment safety did not relate to garments but accessories (not uniform proper). It was from the United Kingdom, where the Health and Safety Executive found that schools had incorrectly applied health and safety legislation to ban certain non-uniform items of jewellery that had no link to causing physical harm [ 66 ].
Is it possible to achieve optimal uniform garment design? Researchers have examined different elements of uniform design, some related to health outcomes. There is a particularly interesting body of research emerging about properties of school uniform garments. Researchers have investigated how to standardize sizing [ 67 ], improve garment quality and durability [ 68 ], optimize materials, enhance style, include high visibility/reflectiveness for road safety, and ensure physical comfort irrespective of outside temperature [ 68 – 71 ]. This demonstrates that it is technically possible to design a uniform that meets cost imperatives, is physically safe, comfortable, and enjoyable to wear. These studies showed garment materials do not necessarily prioritize the wearer’s physical comfort. Functionality (durability, ease of care, ease of drying, stain and wrinkle resistance) is often preferred over comfort or safety (Kadolph, 2001 in 36). For example, polycotton is used instead of cotton because it is colourfast and fast-drying, despite not breathing well in hot weather.
It appears that no consensus exists on best practice for uniform design, who should be involved in design decisions, and considerations in policy development and implementation (e.g., health and educational impacts of garment design and policy, gender neutral options, non-physically restrictive garments). There is no data that discusses this point directly though some studies involve parents and students [ 68 , 71 ], and DaCosta [ 35 ] recommends involving students in co-designing the uniform, to develop a uniform that provides choice and flexibility. Gereluk proposes principles for a non-discriminatory environment [ 72 ], which provides helpful guidance on how to accommodate minority concerns into majority spaces. In doing so, he helpfully lists general elements to consider that can be applied to uniform design and policy. These are: health and safety; whether (any religious/cultural garment) is oppressive to (the wearer) or others; whether it significantly inhibits the educational aims of the school; whether (whatever item is not part of the uniform) is essential to one’s identity.
There is evidence that uniforms can be psychosocially protective of health. Uniforms remove “competitive dressing”—the pressure to wear certain (expensive) brands, colors, or styles [ 36 ]. Uniform removes most socio-economic signs of difference [ 73 ]. Wilken and van Aardt [ 36 ] and Jones (for higher socio economic status students) [ 74 ] report that school uniforms take away stress and family arguments about what to wear on school days. The positive psychological effect of removing competitive dressing probably only holds for students with a certain level of material wealth (see discussion below on equity of access to education and uniform cost). Thus, Catherine and Mulgalavi [ 75 ] found in Pakistan that school uniform had a positive effect on students’ self-esteem, particularly if they had the full and correct uniform. It seems for very poor students, school uniform requirements may simply become something else to worry about, but for others uniform removes a barrier to fitting in.
In addition to the ambivalence of wearers’ feelings, there are mixed data on the impact of uniform on bullying. In a study of one school in the United States, Sanchez et al. [ 76 ] found introduction of a uniform did not significantly change the school’s culture before and after a school uniform was introduced, though some females said males treated them better when they wore a uniform. Jones (United States) reported a reduction in bullying after uniform was introduced [ 74 ].
Indeed, Cunningham and Cunningham [ 77 ] note that while uniforms can reduce bullying, there will always be triggers such as girls choosing to wear trousers not skirts. Importantly, any dress is about more than clothing, indicating social relations, self-presentation, and formation in society, and is a sensitive topic in adolescence [ 78 ]. Indeed, Swain’s ethnography found that students who complied with uniform rules risked being socially excluded [ 79 ].
It appears that uniforms can be both protective and harmful, depending on context, how the student pushes the boundaries of uniform rules to fit in, and whether the student is part of a marginalised/socially disadvantaged group. Whatever the context, females are half of the population, and their physical and psycho-social health seems to be routinely and arbitrarily disadvantaged by uniform design.
Overall, in terms of health and education impacts it seems any psycho-social benefits will only hold if other psycho-social and physical harms to girls, and minorities are addressed. Table 2 summarizes the health and education impacts of uniform. From a health and education perspective, uniform’s biggest advantage is that it removes some distractions; it helps students to settle in the classroom and removes the worst of competitive dressing. If garments and policy are well designed, they encourage physical activity and can protect against environmental hazards. Nonetheless, poorly designed garments and uniform policies especially affect girls and minorities.
Uniform’s positive, neutral, and negative impacts on education and health outcomes.
Part 2: Exploring Social, Cultural and Political Rationales for Uniform Use
Since uniforms do not positively influence academic achievement and can have negative physical and psycho-social health impacts, what drives their use? Further, why are known problems in uniform policy and design not addressed? To answer these questions, it is important to consider the broader context in which uniform is used. The literature that addresses these questions can be divided into three groups. The first group examines the role of uniforms in institutions and the community; the second, the interaction between human rights and uniform; the third (dealt with in part 3 below) the relationship of uniforms to the idea of children as a vulnerable class of people who need special protection. Institutions, human rights laws and societal perceptions of children and childhood constitute important upstream/distal determinants of health and educational outcomes. All the above elements contribute to wider social settings that facilitate or prevent access to what people need to enjoy good health and education. Table 3 summarizes rationales for uniform use.
Implicit and explicit rationales for uniform use.
Uniforms as a Reflection of Schools and Communities
Schools are institutional extensions of overlapping communities: geographic, religious, or ethnic. Community norms reflect institutional and wider societal rules. Uniform signals internal culture to students and provides cues to outsiders about the school’s character.
Within schools, uniforms reinforce institutional culture, signaling school values to students [ 80 ], thereby identifying the wearer with objectives beyond the self. Along with school facilities and symbols [ 21 ], a well-disciplined body of students is associated with a certain type of dress. Additionally, some argue that uniforms contribute to a sense of affiliation in students, belonging [ 81 ], and pride in the school, especially after uniform has been recently introduced [ 82 ]. Affiliation is related to solidarity; yet there seems to be a tipping point when solidarity is undermined if the uniform is too expensive and excludes students [ 83 ]. Howell [ 84 ] argues that among charter school students he studied in the United States, uniform is only one element to increase participation and is far less important than other variables like family dynamics. However, claims about uniform fostering solidarity are not supported by empirical research on student feelings about belonging in the school context. Research into school belonging did not find a significant association between school uniform and a sense of belonging to the school community [ 85 ]. Instead, belonging is fostered by a supportive, respectful atmosphere and a sense of achieving.
It has been argued that uniforms communicate messages to those outside the school community. Stephenson [ 86 ] argues the main role of uniform has changed from primarily addressing poverty or removing differences marking class and gender to primarily signaling education standards, and the school’s place in the education market [ 22 , 36 ], showcasing the institutions’ disciplinary philosophy [ 27 ]. Happell [ 87 ] notes that in the United States uniform visually demarcates students and is associated with private education, improving the wider school environment [ 35 ], or maintaining the impression of strictness and safety [ 22 ]. Shao et al. [ 88 ] note that like corporate uniform, school uniform gives cues to the service environment—a more conservative uniform suggests more conservative values, higher socio-economic status, and by association higher academic achievement. Indeed, Bodine [ 89 ] notes that uniform reinforces and delineates social hierarchies and who belongs. Belonging can be inclusive, encouraging broad participation and access, or exclusive by drawing lines between people and putting up practical barriers to access, delineating who is and is not worthy of privilege [ 90 ].
Within institutions uniform is a management tool [ 21 ]. It has the veneer of solidarity, but there is no empirical evidence linking uniform to feelings of belonging to a school. Uniform also signals tradition, and communicates the place in the education market to outsiders, especially a school’s disciplinary and academic climate. The factors affecting a school’s choice to require a uniform is in turn affected by wider forces of socio-political climate and human rights.

Wider Forces: Socio-Political Climate
As illustrated in Figure 1 , the individual health and educational impacts of uniform are nestled in the broader school culture, which in turn is influenced by the wider socio-political context, influenced by the community’s values. A country’s history, power structures, and socio-economic patterns are thus played out through uniforms. Further, dominant societal values are the lens through which human rights and other implicit and explicit values are projected. Uniform wearing can be intrinsic to a greater good, or instrumental in reaching other goals. With this in mind, what data exist on the socio-political factors that influence uniform garment design and policy?
Uniform design and policy slowly changes alongside social and educational policy developments. Thus, New Zealand, uniform design has changed alongside New Zealand’s education policy and socio-political context [ 81 ]. Similarly, in China uniform has gradually incorporated more modern and Western influences in design over time [ 91 ]. In their discussion on the reasons for uniform, Meadmore and Symes argue that uniform wearing is a form of governmentality–the process of unconscious internalization of external values designed to maintain existing power structures. In this way uniform is a “disciplinary tactic” [ 115 ] embodying respectability, cleanliness, modesty, and inoffensiveness. Conformity means meeting the standards of an institution [ 92 ], explicitly in service of an ideal of equality, and implicitly to maintain the societal power dynamics expressed through institutions. Whether a form of governmentality or not, it is clear that uniform is associated with broader societal values.
In some societies, uniform wearing seems intrinsically linked to a greater societal good. Thus, Baumann and Kriskova [ 21 ] argue that high PISA scores are associated with good classroom discipline, which is intrinsically linked to wider societal values. The authors hypothesize that in South Korea and Japan, Confucian values of self-discipline and conformity to ritual inform practical aspects of daily life. Baumann and Kriskova argue that conforming to social norms is part of being a good Confucian; thus, any penalty for breaching uniform standards (a social norm) is explicitly and intrinsically linked to becoming a better Confucian.
Alternatively, uniform wearing can be instrumental in reaching other ends. Hence, when uniform use became common in the Anglosphere in the 1800’s, there seems to have been a (noble) aim of making schools islands of fairness in an unfair world. Craik [ 93 ] states that in England school uniform aimed to equalize social class, creating social camouflage through functional, reasonably priced clothing. However, this rationale ignores wider societal power structures, and that uniform wearing may be mainly instrumental to another goal. Thus, in some post-colonial contexts uniform was part of a transfer of British values and seen as a way to civilize and promote a certain ideology [ 92 ]. In New Zealand, uniforms were inspired by military dress and were intended to encourage empowerment, belonging, and pride, as well as social camouflage [ 92 ]. In South Africa, school uniforms were imposed on the black population as a means of control [ 36 ]. Australian authors have hypothesized that certain types of school uniform historically represented respectability and happiness and promoted social integration. Wearing a school uniform provided a means for migrant children (and their families) to fit in [ 94 ]. Wearing a school blazer has been described as a cultural symbol of reaching and being included in a social ideal of wealth and educational achievement [ 95 ].
Some socio-political rationales are explicit and are part of clear public policy measures to shape society. For instance, Mujiburrahaman [ 96 ] describes uniform as part of Sharia law implementation in schools in Aceh; Moser notes it is part of fostering citizenship and identity in Indonesia’s schools [ 97 ]; and Draper et al. [ 98 ] describe how uniforms that use a hybrid of traditional and modern clothing styles, materials, and manufacturing techniques are part of a cultural revitalization project in Thailand. In the United States, from the mid-1990’s school uniforms have been explicitly promoted as a means to lower danger and violence in schools and remove classroom distractions [ 99 ]. Indeed, in the United States uniforms are often perceived as more neutral than dress codes because everyone wears the same [ 100 ], as opposed to judgements being made about clothing items against a standard. Overall it appears that uniform use is often driven by goals beyond health or education as values in themselves.
Part 3: Human Rights and Uniform Use
Human rights legislation supporting equity and freedom from religious or gender discrimination and protecting the rights of children has been discussed in conjunction with school uniform. In cases of disagreement about garment design or uniform policy and where institutional policy or social norms do not provide a solution, human rights law has been invoked to help reconcile different rights and values.
Human rights are overarching, universal entitlements that preserve the dignity of humans. Theoretically, human rights are interrelated and indivisible and should not be separated from each other [ 101 ]. Practically, the experience with uniform shows that simultaneously giving effect to different human rights is not straightforward. Social context influences how human rights are interpreted and given legal standing. Looking at the United States, Ahrens [ 102 ] notes that in the 1970’s uniform was of great constitutional concern (impinging of First Amendment right of freedom of expression), whereas nowadays few legal or constitutional problems with uniform are discussed, possibly because the overwhelming concern is student safety; the importance of identifying intruders outweighs concern over freedom of expression [ 103 ].
Equality vs. Equity
The human rights notion that all humans are equal is important to school uniform policy. As noted earlier, the idea that equality of access to education is enhanced by “social camouflage” is a principal historic and current rationale for uniform [ 36 , 89 ]. Proponents of uniform argue it creates equality and emphasize the benefits of homogeneity that outweigh any negative impacts: unity, a sense of belonging (although this point has not been demonstrated empirically), and group identity. In their view, the human right to equal treatment is enhanced by removing outward signs of social differences [ 36 , 89 ]. This may explain why in Malaysia, Woo et al. found that while students thought uniform unattractive, they conceded it reduced outward markers of differing socio-economic status [ 73 ].
However, an equality focus in uniform policy sidesteps the issue of who bears the brunt of equality as “sameness”. Equality focuses on same treatment, while equity focuses on outcomes, sometimes requiring different treatment to achieve similar outcomes [ 104 ]. Data show that uniforms are not intrinsically equitable. The cost of uniforms can affect students’ rights to access education. In addition to inequity of physical activity by gender and barriers for minority groups, the cost of uniform garments themselves is a determinant of access to education, and clearly unequally felt across society. The cost barrier that uniform poses to attending school is widespread, particularly in low and middle-income countries. Using Mongolia as an example, Sabic-el Rayess et al, [ 83 ] note that in countries where the very poor cannot afford uniforms, they do not attend school. Likewise, Simmons-Zuilkowski [ 105 ] found that in South Africa enrollment rates among the very poor are lower because of cost of uniforms. In Kenya, Mutengi [ 106 ] found a statistically significant link between uniform cost and education access, and Green et al. [ 107 ], Sitieni and Pillay [ 108 ] and Cho et al. [ 109 ] describe free uniform as part of support and incentive packages for at-risk children to attend school [ 110 ]. In Ghana, Alagbela [ 111 ] and Akaguri [ 112 ] show that uniform cost creates a barrier to education for the very poor. One contradiction to this trend comes from Hidalgo et al. in one study in Ecuador [ 113 ]. The authors found that providing uniform decreased attendance. However, the authors note that the study was not conducted as anticipated; some families promised uniforms were not supplied with them, and many in the study group had already purchased a uniform (it was therefore a sunk cost), so uniform cost was not a factor that decided school attendance. Cost is also a likely concern among all parents in high-income countries. In the United Kingdom, Davies [ 114 ] examined uniform cost and supply and surveyed parents who were happiest when uniform could be sourced from a mixture of designated shops and high street/generic stores and found that uniforms were cheapest when items could be brought from anywhere. However, as in low income countries, uniform creates an unequal cost burden across the population. In the United States, Da Costa [ 35 ] highlights the economic burden on the poor of buying a school uniform. In South Korea and the United States, poorer parents spend a higher percentage of their income on uniforms [ 36 ]. In New Zealand, a survey of parents [ 115 ] found school uniform cost is a significant burden for poorer families. In Scotland, Naven et al. [ 116 ] reported how uniform cost created such a barrier to education that the state changed its clothing grant policy to help ease the financial burden on families.
Of course cost is not the only equity issue in uniform use, but it is an important one. Davies’ [ 114 ] United Kingdom report on uniform supply and cost found that garment quality was a main influence on purchasing decisions, followed by availability and cost. Surveying parents’ and educators’ attitudes to uniforms, for both groups Davies found uniforms were considered worthwhile because they are a long-term investment: generally long-lasting, infrequently replaced, and cheaper over the student’s career than non-uniform alternatives. However, Davies’ and other data (e.g., Gasson et al., Naven et al., Catherine and Mugalavai, Simmons-Zuilkowski) suggest the large initial upfront cost is a barrier for poorer families. Another reason for concern is that sameness does not result in equity or improve human rights protection. Deane [ 117 ] argues that justifications for uniform based on equity are not well considered because the mere wearing of uniform does not create equity, and does not magic away other differences [ 117 ]. In practical terms, equity through uniforms is inevitably an imperfect idea: even if uniform policy allows students to choose to wear any items from a list so long as items comply with style or color rules, expensive branded items, or other garment choices would inevitably signal differences in economic status, wearer style, and individual preferences. It seems for the very poor/marginalized in any society, uniform can be simply another barrier to education because of the focus on equality, not equity. Ironically, those most in need of education may be denied it via a mechanism that was originally instituted to remove barriers to education.
Uniform and Freedom of Religion
In addition to general rights to equal treatment, specifically protected rights are of concern when considering uniform, particularly freedom of religion and the right to non-discrimination because of gender. Uniform rules and the right to freedom of religion is an example of where courts are asked to reconcile seemingly conflicting rights with each other. For instance, the Convention on the Rights of the Child (Art 14) protects freedom of religion [ 118 ]. Nonetheless, this right is not unfettered and can be limited if others’ rights are impinged, and its application depends on how individual countries legislate to support human rights.
Theoretically, uniforms should not impinge on religious freedom. Practically, the situation is not so clear-cut. Complex questions about how religion is represented and how it is recognized are often played out through uniform [ 119 ], especially in liberal democracies. For some, adhering to a school uniform policy means not observing religious requirements. In Australia, where states are required to have a uniform policy, direct and indirect discrimination on the basis of religion is forbidden. Yet there is no clarity on whether a school can have a policy that is silent on students’ religious beliefs and practices [ 120 , 121 ]. Australian courts have found that exceptions to uniform rules can be made to avoid injury to religious sensibilities, doctrines, beliefs, or principles (e.g., allowing wearing yarmulke or hijab). In England (which has a longstanding uniform tradition), the case of Begum sought to balance religious freedom to wear Sharia-appropriate clothes against the right to education, school uniform policy [ 122 , 123 ], and women’s rights. In Begum the court found that social cohesion, protecting minority rights, and ensuring religious freedom must be balanced [1 , 124 – 126 . In Begum , the judgment shows how tricky it is to reconcile all human rights in themselves, let alone apply them within the context uniform policy requirements.
Whatever the social context, outward signs of faith can challenge both uniform rules and wider societal values such as secularity in public institutions. Gereluk [ 72 ] argues for reasonable accommodation and mechanisms to redress potential unequal treatment of minorities. What constitutes “reasonable accommodation” appears to be context-dependent.
Uniform and Gender
Similarly to promoting equity and freedom of religion, human rights protect non-discrimination by gender. The discussion so far has shown that whatever the rationale, uniform garment design has a greater impact on girls, particularly on their physical health. This differential effect has been addressed by human rights legislation. For instance, The New Zealand Human Rights Commission agreed with a complaint of discrimination on gender grounds by two female-identified students [ 127 ] who argued that the requirement to wear a skirt disadvantaged them because it restricted their movement. Settlement was reached when the school added culottes (shorts that look like skirts) to the school uniform. In this example, human rights legislation allowed schools to have uniform codes for males and females, providing uniforms do not disadvantage one gender or group.
Differential treatment by gender is underpinned by historical and some current thought, though it is rarely discussed in relation to uniform. This is possibly because it is linked to deeply entrenched and normalized gender roles. Political and philosophical research addresses this point. Dussel [ 128 ] argues that school uniforms hamper, restrain, and try to domesticate girls’ bodies. Happel [ 87 ] argues that school uniform is linked to gendered performance, where school uniforms underpin sex and gender roles, because they restrict movement and confirm traditional gender identities. Happel [ 87 ] argues that because skirts allow for exposure of underwear, buttocks, and genitals, girls are taught modesty/immodesty through a garment. Girls are thus objectified because they have to curb their behavior because of another’s gaze. In this review no evidence was found of any of the above restrictions caused by boys’ uniform. Notably, girls’ uniforms tend to be more expensive [ 106 , 114 ], illustrating that even here there is a “pink tax” for female-oriented products that perform the same function as a unisex/male alternative [ 114 , 129 ]. Further, normalized gender roles affect gender-diverse students, already a group at risk of exclusion. For gender diverse students, non-inclusive uniform policies are particularly problematic [ 130 ] and affect them disproportionately [ 17 ]. Non-inclusive uniform policy relies upon the idea that clothing is an essential element of gender identity and that any fluidity or flexibility in dress rules risks undermining individual and collective gender identity. There is no evidence of gender identity being so fragile [ 131 ]. In practical terms, Henebery [ 132 ] argues that even if uniforms have unisex options, they are still split by gender, where skirts are limited to biological girls. Interestingly, Bragg [ 133 ] notes that a school uniform policy that strictly enforces male/female uniforms is in stark contrast with the broader and more fluid social understanding and representations of gender that students are exposed to, especially in Western countries.
It appears that uniforms place a physical restriction and price premium on girls, and policy does not routinely consider gender diverse students. This is driven by socio-cultural norms and negatively impinges on their human rights, despite the overarching right to equal treatment irrespective of gender.
Uniform and Children and Young People’s Freedom of Expression
Freedom of expression is another area of human rights that often clashes with uniform. The right to freedom of expression (Art 13 UNCRC [ 134 ]) can be restricted in respect of the rights and reputations of others, protection of national security, and public order. Article 12 (UNCRC, 1989) details that free expression is given weight in accordance with the age and development of the child. Some hold that school uniforms are inherently restrictive, arguing that school uniform hampers expressive rights and normal identity exploration, constitutes intrusive control of group behavior (e.g., 35), and symbolizes oppression [ 131 ]. Conversely, others argue argues that it is nonsensical to say that uniforms crush self-expression when there are many other creative outlets [ 89 ]. There is no empirical evidence on this point. Vopat takes a different approach and considers children’s moral and psychological development. Looking at expression and developmental stage, Vopat [ 40 ] separates self-expression into two categories: mere expression, and substantive expression. Mere expression is simply about what a person likes/dislikes, whereas substantive expression is an outer manifestation of deeply held values or another specific intention. Vopat [ 40 ] argues that small children lack the cognitive ability for substantive expression because they do not have the psychological capacity for it yet. Nonetheless, Vopat [ 40 ] suggests that uniform may be a learning point for students. Children need thinking time to become their moral selves. School uniforms provide explicit teachable moments, opportunities to think using different moral frameworks to examine the utility of different social attire and freedom of expression in context, and children’s understanding of and critical thinking about social appropriateness of dress [ 135 ], which enhances learning outcomes [ 40 ]. Conversely, and despite these learning opportunities, Deane [ 117 ] argues that uniform’s blindness to or suppression of difference implicitly dampens the ability think about and discuss difference; thought is constrained because uniform creates an implicit understanding that strangers should be the same as oneself, and where there is difference, there is danger. Consequently, uniform suppresses recognition and discussion about differences in ethnicity, religion, or class [ 117 ].
There is no empirical evidence either way that uniform constrains freedom of expression. There are hypotheses that uniform provides a teaching opportunity about appropriate dress, and socializes people to a particular dress standard. Other ideas suggest that uniform allows students to rebel in safe confines [ 81 ].
Children’s Rights and Minors as a Vulnerable Group
The rights of children sit alongside other rights. These rights protect children because the wider socio-political climate identifies children and minors as a vulnerable class of people who need protection.
However, there is no agreement about what rights of children exactly should be protected, and many wider concerns about children are projected onto uniform [ 89 ]. Through an institution limiting clothing choice or requiring certain clothing, Bodine [ 89 ] argues that uniform protects childhood by protecting children from sending messages with their clothing choices that they do not fully understand. However, exactly what is protected is unclear. Vopat [ 40 ] argues protection should be linked to the child’s moral development and ability to reason, balanced against Article 12 of UNCROC, which includes the duty to consider children’s voice in decisions that affect them. Some [ 87 ] argue that uniform should be done away with altogether because of harm to children’s human rights. Irrespective of children’s vulnerability and human rights, Brunsma and Rockquemore [ 136 ] argue that even if uniforms do not harm, and young children cannot yet exercise their rights, there is no justification for imposing uniforms in an educational context, especially if uniforms do not improve educational goals.
Overall, while human rights are universal, the way they are expressed in particular cultural contexts varies, driven by socio-political forces. It appears that the idea that uniform is inherently equitable is flawed. It does not level social class, and is not blind to religion, gender, and socio-economic status. It does not necessarily consider cultural and individual identity or diversity. Data on human rights and uniform show that uniform policies result in unequal impact of garment design and policy on girls and religious minorities. Data on freedom of expression is equivocal. Whatever the case, wider sociocultural issues are clearly played out through uniforms, and it appears that uniforms can become a proxy for other issues, particularly considering the special status of children and young people. Blanket approaches to uniform policy can be repressive of cultural identity/diversity and ignore entrenched power imbalances [ 22 , 131 ]. By scrutinizing the outcomes of uniform policy, it is clear that many uniform policies have neutral/minimal impact for the majority, but the minority must compromise cultural or religious values to comply with uniform rules. Females make up half the population, yet uniform design limits their ability to participate in incidental physical activity, a proven enhancer of health and educational outcomes.
This review demonstrates that far from being a “trivial relic” [ 22 ], school uniform is an important yet neglected public health issue that affects all students who are required to wear it. As a preliminary review, this study maps the conceptual landscape of school uniform garment design and policy in a public health framework, and brings evidence together to show health and education impacts of school uniform use. The review shows that school uniform is important, but not for commonly believed reasons. First, there persists a belief that school uniform in itself enhances academic outcomes. This is unsupported by evidence—there is no direct link between uniform and academic achievement [ 33 ]. However, uniform does contribute to a more settled classroom environment [ 21 ], which facilitates learning. Second, some studies argue uniform can distract from a good rapport between students and teachers, which is linked to improved learning (30,37). Third, despite common belief, uniform has no empirically supported impact on enhancing a feeling of belonging to a school [ 85 ]. Notably, there is a general paucity of evidence for use and a gap between what is believed about uniform and what is supported by empirical evidence. It appears that uniform use and policy is a neglected area of research: given its widespread use there is surprisingly little empirical evidence about its use or effects at all.
Concerningly, psychological and physical health impacts of uniform have been neglected. Positively, uniform removes the psycho-social barrier of competitive dressing. Indeed, well-designed uniform garments that are comfortable to wear, do not restrict physical activity for all students, that protect against environmental hazards, plus a uniform policy that is inclusive of all students (irrespective of gender/gender identity) can enhance student physical and psychological health [ 47 , 48 , 54 ]. Neutrally, uniform can both increase and decrease bullying. Negatively, inflexible uniform policies and garment design disadvantage girls, gender-diverse students, and overweight students because they do not feel confident in participating in physical activity while wearing uniform garments (47–51,53). From a physical health perspective, empirical evidence demonstrates that girls’ physical health is particularly disadvantaged. Girls make up around half the school-aged population, so the demonstrated link between poor uniform design and worse physical and psycho-social health for girls is of concern. Physically restrictive uniforms can hamper girls’ physical and social participation in school, especially physical activity during breaks and on the journey to school. Poorly designed sports uniform may also deter girls’ and overweight children’s participation in timetabled physical education. For all students, there is no evidence of systematic consideration in uniform policy of health and safety and protection from environmental hazards that permits students to wear garments to suit the weather conditions, or that ensures garments are comfortable to wear.
Further, gender-based inequity is inherent in uniform; girls’ uniforms are more expensive and more restrictive. Inequity exists for religious minorities and gender-diverse students who have to dress to fit the uniform policy rather than dress so they feel physically comfortable. Because garment design reflects the norms of the dominant culture, religious and ethnic minorities, and gender-diverse students often have to compromise beliefs and identity to comply with uniform rules.
This review shows that uniform garment design and policy focus on equality (same treatment) at the expense of equity (different treatment to achieve similar outcomes). While uniform removes the psycho-social pressure on individuals and families of competitive dressing and outward signs of socio-economic differences between students, it does not eliminate inequity. Paradoxically, uniforms can worsen inequity. Worldwide, for the very poorest students, the cost of a uniform may be prohibitive, creating a barrier to education before the students even arrive on school grounds [ 83 , 105 – 107 , 109 – 112 , 114 – 116 , 137 ]. For some students the disadvantages will be cumulative. Using the public health lens of analysis highlights this avoidable inequity.
Why do we compel children to wear uniforms and persist with policies that detract from physical and psycho-social health, and that disadvantage poorer students? This review has highlighted that uniform has become a proxy for many issues. Financial and political economies are projected onto uniform policy and garment design. An organisation’s history, institutional stewardship, values, and traditions are often embodied in uniform, which is possibly why certain designs and materials are so enduring. Uniform signals a school’s place in the education market and gives external and internal indications of the school culture (22, 26, 36). Uniform also appears to enhance school operations (21). In classrooms it helps students settle to task and help identify intruders and improve security (36,43), or the perception of security (44).
A public health lens helps to shed light on uniforms, and their impact on health and education. The public health frame of analysis brings together and organizes data from different disciplines to illuminate questions that are important to population health, illustrating proximate factors and distal factors to individual experiences. It has also shown that uniform merits public health interest: if uniform use is prevalent, its use impacts on health and educational outcomes, and, importantly, school uniform garments and policies regulating their use are amenable to improvement, with an eye to improving equity.
This study’s principal limitation is that data is only drawn from English-language research largely focused on the Anglosphere or where articles were available in English, yet much of the world that wears uniform is not Anglophone. Potentially important data may have been missed. Further this study’s primary data are primarily peer-reviewed articles, which ensures rigor, but leaves out a depth of information from other sources. Further, articles of all types (including commentaries) were included because this research focused on evidence about uniform use, rather than the quality of that evidence. For time constraints conference proceedings and PhD theses were excluded. Note that there were variations in the types of studies done. For instance, the physical impacts of uniform use (e.g., on physical activity of wearers, protection against environmental hazards) were measured using quantitative or qualitative/quantitative mixes of design with larger sample sizes. For instance Norrish et al’s [ 48 ] work on physical activity for girls was one of the few that included objective and subjective measures of the phenomena under investigation, with a repeated measures crossover design (same group tested in two different conditions). Finally, as with other areas of inquiry, philosophical pieces or commentaries often argue against the status quo rather than defend it. It is possible that there exist more positive or neutral impacts of uniform on education and health than have been hitherto documented, especially in empirical research.
Limitations notwithstanding, this research will be of interest to those within the public health community, those involved in uniform regulation and design, and those involved in educational management. It will also be of special interest to the general public, who will be better informed about the evidence for what uniform achieves, and what can be done about making it better. Conceptually, issues related to uniform design are of interest to researchers of other populations (e.g., prisoners, military) with diminished capacity or whose choice of clothing is restricted.
This review has important implications for future research. It has highlighted gaps in knowledge about garment design and uniform policy and their impacts.
Regarding garment design, more information is required on different priorities that inform design choices: durability, serviceability, safety of materials, quality, and comfort to the wearer, particularly with an eye to protection against environmental hazards, and how to make garment styles enduring over time as well as inclusive, comfortable, and health-promoting.
Other issues like cost, value for money, environmental sustainability and ethical sourcing of materials may be of interest. Furthermore, different stakeholder (student, parent, teacher, school administrator) perspectives could be measured to further explore what factors influence garment design, how those different factors inform uniform use policy within schools, extending on multi stakeholder studies similar to that done by Wilken and van Aardt [ 42 ] or McCarthy et al [ 41 ]. Regarding uniform use policy, there is little information about how school rules are developed and what principles might look like to ensure uniform use is education and health promoting. Regarding impacts of design and policy, further studies are required with objective and subjective measures of whatever phenomenon related to uniform is being investigated. In particular, more studies are required on the health and psycho-social impacts of uniforms. For instance studies such as Hopkins [ 51 ], Norrish et al. [ 48 ] and Watson et al. [ 49 ] could be replicated in other jurisdictions and cultural settings.
In terms of public policy, there is little peer-reviewed evidence on supply chains, competition law, and profits that drive uniform costs. There is little evidence about how to reduce the cost barrier of uniforms for the poor; how different societal values are incorporated into uniform design (e.g., environmental protection and school/community tradition, or, given the impacts of uniform on health and access to education, whether any form of government regulation of upfront cost, uniform policy or garment design is required (especially for state-funded schools).
An important practical implication is making the evidence about uniform’s education and health impacts available in a form easily accessible to school administrators and governors to inform their uniform garment and policy decisions. After all, educators are experts in education, not garment design or uniform policy development, so it is unsurprizing that, left alone to organize uniform, they may not develop the most health and education-promoting garments or policies.
Uniform use is deceptively simple. It is so commonplace and ordinary, however, the questions it sparks are complex and are related to deeply held views of what is normal, traditional, and socially acceptable. Yet uniform use has real impacts on health and education, for better and for worse. This review shows that uniforms may be the right diagnosis for creating an equitable learning environment, providing cost-effective garments over a student’s learning career, and easing the psychological pressure of competitive dressing. However, this review shows the importance of getting the prescription right. The efficacy and effectiveness of uniforms as a vehicle for equitable access to education and good health depends on the right prescription for uniform policy and garment design that remove potential negative effects of poor garment design and policy.
A public health lens reveals that much school uniform garment design and use policy negatively affects the poor, girls, religious and ethnic minorities, and gender-diverse students. It is a sad irony that these are the very groups who could benefit most from the equitable access to education that uniform is supposed to facilitate. This review also shows how environmental hazards, health and safety concerns, and garment comfort are neglected for all uniform wearers. There is no natural reason why any of this should be so.
Fortunately, any negative educational and health impacts of school uniform garment design and policy are amenable to change. The clarity that this review provides about the evidence for uniform’s impact on health and education may provide a starting point to ensure uniform is as healthy and education-promoting as possible and to build on the advantages uniform offers. By examining evidence of how uniform and uniform policy impacts on students’ health and wellbeing, perhaps it will be easier to establish a common idea about school uniform’s purpose(s), with a view to improving wearer experience. If the educational and health impacts of uniform are clear it could be possible to improve wearer experience to ensure that garments are desirable, equitable, healthy, and safe [ 22 ], and that both policies and garments enable all students to learn and thrive in modern life.
Author Contributions
The author undertook this entire project.
Time spent on this research was funded from my ordinary teaching salary.
Conflict of Interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Find anything you save across the site in your account
The Downsides of School Uniforms
By Mark Oppenheimer

My daughter’s school uniform, required by the public magnet middle school where she began sixth grade last week, is perfectly nice. It’s not so much a single uniform as a broad wardrobe of coördinated prep-wear: skirts or pants, paired with piqué polo shirts, all in “goldenrod yellow,” navy, or white, topped off by a fleece zip-up (on which the school crest is optional). For her first day, she chose the navy skirt with the white polo. As she walked to the corner to catch the bus, I was reminded of a time when our schools were orderly, our teachers respected, and our children all above average.
That was an imaginary time, of course, but nostalgia for it has helped to create the modern school-uniform movement, which has won the kind of broad—indeed, nearly uniform—support that exists for no other educational policy, or social policy, that one can think of. Although there isn’t a scholarly consensus that uniforms do anything to improve student achievement or school climate, about one-fifth of all public-school students now wear them. They are one of the few interventions on which charter-school advocates and anti-charter activists agree.
Even the students have gone along, in one of the great surrenderings of liberty in modern history. For, although we think of uniforms as a reclamation of the olden days, they are relatively new in this country. Against British Commonwealth traditions, we were the free and easy New World, the country where children dressed themselves. For the most part, the appearance of students was governed only by the nagging of parents (“Get a haircut!”); informal norms (T-shirts were for athletics, not the school day); and deference to teachers and principals, who had wide discretion to tell a boy that he looked like a hoodlum, or tell a girl that her hemline was inappropriately short.
In the sixties, students fought for more autonomy in dress, to signal allegiance to a particular band or clique or general attitude toward the world. They saw dress as a mode of expression in schoolyard politics, and in world politics: in 1969, in Tinker v. Des Moines, the Supreme Court upheld high-school students’ rights to wear black armbands to protest the Vietnam War. That case was the capstone for an emerging jurisprudence of freedom-in-attire, coming after court decisions in New York and Idaho striking down bans on women wearing pants, and a decision in New Hampshire ending a ban on bluejeans. These cases helped solidify a trend toward more freedom for young people to dress how they wished. And so it was, from the nineteen-seventies into my childhood, in the nineteen-eighties.
Then Bill Clinton happened. In 1996, Clinton, running for reëlection and eager to shore up his conservative credentials, championed mandatory school uniforms “as the kind of small-bore, low-cost, common-sense policy initiative that might appeal to a broad cross-section of voters,” as the legal scholars Deborah M. Ahrens and Andrew M. Siegel write, in their forthcoming paper “Reconsidering the Constitutionality of Student Dress Restrictions.” Clinton plugged uniforms in his State of the Union address that year and had his Department of Education issue a manual for schools that were transitioning to require uniforms. While some schools had experimented with uniforms in the eighties and nineties, it’s clear, Ahrens and Siegel argue, that “the modern enthusiasm for uniforms can be traced pretty directly to the 1996 Clinton administration initiative.”
Expecting some pushback, the Department of Education issued guidelines for making the new uniform policies able to withstand lawsuits. Except the free-expression lawsuits never came. As with other policies favored by conservatives, such as law-and-order policing and mass incarceration, Clinton’s support gave cover to liberals, desperate for any policies that might help the inner cities, to join the act. As one might expect, school uniforms, while growing in popularity everywhere, have really become a feature of poor schools. According to a 2016 study by the National Center for Education Statistics, school uniforms are required at fifty-three percent of schools where three-quarters of students are eligible for free or reduced lunch. But, of schools where fewer than a quarter of students are so eligible, only four per cent require uniforms.
These uniforms have become a rich revenue source for kiddie-clothing companies like French Toast, which has a verbose Web site dedicated to their magical properties. One typical section makes the argument that “school uniforms bring an image of success to students and teachers.” But that depends how one defines success. In Silicon Valley, on Ivy League campuses, and even in a growing number of white-shoe firms, the rule is to dress down. While once upon a time each profession had its uniform—the gray-flannel suit, the white coat—today, the most successful people wear what they want, especially in the more creative industries.
On the Web site for my daughter’s school, the hyperlink “Click here for more information about student uniforms!” redirects to Lands’ End. Once known for its middle-quality oxford button-downs, Lands’ End has become a major player in the school-uniform game, and not by accident. It has aggressively formed partnerships with school systems, often becoming their main uniform purveyor, and it has helped fund some of the questionable research adduced to show that uniforms improve schools. In 2013, Lands’ End helped pay for a survey by the National Association of Elementary School Principals that found that eighty-five per cent of principals “and other school leaders” believed that uniforms improved classroom discipline.
Many school leaders believe that uniforms help, although they can’t seem to agree on why. It’s student achievement, or “school pride,” or a perceived reduction in fighting. When independent researchers have tried to quantify such claims, they have had mixed results. One widely cited study, on schools in Long Beach, California, showed a decrease in school crime after the introduction of uniforms, but the city had taken many other measures to reduce violence at the same time, so it’s hard to tease out how much uniforms mattered. Many studies show no change in school culture, and some even show negative results: in one 2007 study , the introduction of uniforms accompanied an increase in the average number of assaults in one district’s violent schools.
One good friend of mine, a superintendent of a charter-school network, who spoke to me off the record, swears that introducing uniforms where he works changed the culture overnight, increased respect, and improved students’ ability to learn. He may be right. And, if uniforms are viewed positively by students, parents, and administrators alike—as they are—then it can seem precious to object to them. To some extent, enthusiasm about school culture is a good in itself; even if it doesn’t yield higher test scores or graduation rates, perhaps it leads to better teacher retention or recruitment. Maybe the aesthetics of color-coördinated order just make everyone in the building happier. One 2002 study of Texas middle-school students found that those in uniform had a stronger sense of “belonging” in their school community. That’s worth something.
But, so long as the evidence for these claims is thin, I am more concerned about what we know to be true: that uniforms are yet one more way that the surveillance of the un-powerful—the poor, people of color, and that great unheard group of the young—has become increasingly acceptable. “Campuses increasingly subject students to police surveillance techniques, including drug-sniffing dogs, metal detectors, surveillance cameras, random sweeps for contraband including bag searches, and drug tests,” Ahrens and Siegel write. As students become “proper subjects for policing,” they argue, it’s no surprise that we presume to tell them what to wear.
Uniforms can be liberating, in the way that the absence of choice is. My daughter is only a few days into her school year, yet she already says that uniforms simplify her morning. But, as our society reckons once more with the costs and burdens of free expression, we should remember that not so long ago teen-agers fought for their right to black armbands. While in theory the right to such overt political expression—the armband, the political button or patch—would still be upheld by courts, the spirit behind that freedom has disappeared. We’ve stopped thinking of our sons and daughters as citizens whose independence we want to cultivate by, as much as possible, getting out of the way.
By signing up, you agree to our User Agreement and Privacy Policy & Cookie Statement . This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

By Neal Katyal

Home » Tips for Teachers » Why Students Should Not Wear Uniforms: A Thoughtful Exploration with 9 Reasons, Studies and Statistics
Why Students Should Not Wear Uniforms: A Thoughtful Exploration with 9 Reasons, Studies and Statistics
In the ongoing debate about school uniforms, a significant voice often goes unheard – that of the students themselves. The argument against mandatory school uniforms is not just about fashion or personal preferences; it delves deeper into fundamental issues of self-expression, equity, and the very purpose of education. This article, “Why Students Should Not Wear Uniforms,” seeks to uncover the less discussed but crucial aspects of this debate, presenting a comprehensive view that challenges the traditional perspective favoring uniforms.

At the core of the anti-uniform stance is the belief in the importance of individuality and personal growth during the formative years of schooling. Uniforms, often seen as a tool for homogenization, can stifle the self-expression and creativity that are essential in nurturing young minds. By enforcing a standard mode of dress, schools may inadvertently suppress the diversity and individuality that should be celebrated within educational environments. Moreover, the imposition of uniforms can raise significant financial burdens for families, create unnecessary resistance to authority, and overlook important cultural and religious considerations.
I am seething about this poor young girl who has been put in isolation because she’s not wearing a school uniform bought from the right place, school uniforms are far too expensive for a lot of people in this country in the most ridiculous you can get just as good from supermarke — James Whale (@THEJamesWhale) September 17, 2023
This article aims to explore these perspectives, offering insights into why the policy of mandatory school uniforms might be an outdated approach that overlooks the broader objectives of education and personal development. As we delve into this topic, we invite readers to reconsider the conventional wisdom on school uniforms and reflect on the potential benefits of a more flexible and inclusive approach to student attire.
After reading this article you’ll know:
- Educator and Industry Expert Perspectives →
- 9 Reasons Why Students Should Not Wear Uniforms →
- Opposing Perspectives on School Uniforms →
Uniforms in Education: Educator and Industry Expert Perspectives
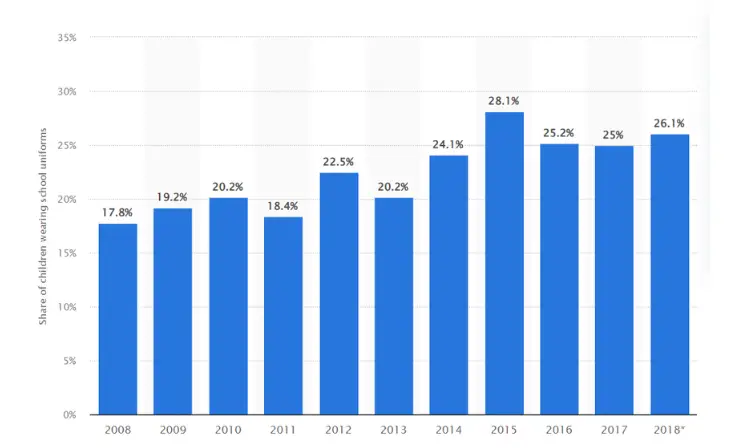
Teachers and educational experts are increasingly questioning the rising trend of school uniforms in U.S. public schools. While the period from 1999-2000 to 2017-18 saw an increase from 12% to 20% in schools adopting uniforms, there’s growing concern about their impact on student individuality and expression. In 2015-2016, uniform policies were enforced in 25% of public primary schools, 20% of middle schools, and 12% of high schools, with a notable prevalence in urban and high-poverty schools . Experts argue that such policies, while aiming for uniformity, might inadvertently suppress student creativity and self-identity, vital for holistic educational development.
Here’s the perspective of educational field experts on the matter:
“I completely disagree with uniforms on every level. Supporters of uniforms say that they reduce bullying with regards to fashion, but there is a great deal of evidence that says it just pushes that bullying underground. Instead of being bullied about something superficial like the shirt you are wearing, bullies just go to the tried and true body image shaming. Glass? Overweight? Acne? Too many freckles? Hair colour? Too tall? Too short? What school administrators see is a surface level reduction in bullying, followed by them patting themselves on the back and ignoring the problem completely.” — Scooter Campbell , assistant language teacher
“While uniforms are supposed to build a sense of community, they may have the opposite effect. Fashion is one way that students express themselves, and that may be an important part of the school experience. When students can’t show their individuality, they may not feel like they belong as much. School uniforms may not be the most effective way to improve student behavior and engagement.” — Arya Ansari, assistant professor of human sciences at The Ohio State University
“I really don’t care whether or not a student’s shirt is tucked in, as long as they are learning. I don’t care whether or not a student has on the right belt, as long as I can’t see their underwear. I don’t care if a boy has earrings, facial hair, or painted nails, as long as he’s not painting them in my class. I don’t care if a girl has bright pink hair, a tank top, and ripped jeans, as long as bosoms and butt cheeks are covered and secure. I don’t like hoodies on heads in my classroom because it makes it too easy to hide Airpods, but I don’t care if the sweatshirt has a hood. As long as it’s not a top hat or sombrero that blocks the view of the students behind them, I don’t care if my students wear hats or beanies in my class.” — New Orleans Mom Guest Author
The video below explores the debate on the impact of school uniforms on academic performance. It delves into whether mandating uniforms in schools truly enhances students’ learning and overall academic success.
Want to know how to be a strict teacher? Read our dedicated article .
9 Reasons Why Students Should Not Wear Uniforms
Let’s explore the reasons against mandating school uniforms for students. Understanding these arguments provides valuable insights into the broader educational and social implications of uniform policies.
1. Expression of Individuality
The concept of “Expression of Individuality” in the context of school uniforms is a vital aspect of student development and autonomy. When schools impose uniforms, they inadvertently restrict a key channel through which students express their individuality and creativity. This freedom of expression is not merely about fashion or aesthetics; it’s a crucial part of a student’s journey towards self-discovery and confidence building.

Key aspects of individuality expression through clothing include:
- Personal Identity Formation: Choosing what to wear allows students to explore and affirm their personal identities and tastes.
- Creativity and Innovation: Fashion is a form of art. Allowing students to select their own clothes fosters creativity and innovation, skills highly valued in many aspects of life and work.
- Cultural Expression and Diversity: Clothing can be a powerful expression of cultural heritage. A diverse dress code celebrates and acknowledges the rich tapestry of cultures in the student body.
Beyond these points, individuality in clothing choices helps prepare students for future environments where they must make decisions about their personal and professional presentation. In many modern workplaces, the ability to express oneself appropriately through attire is valued and can impact career progression and personal branding.
Furthermore, enforcing a uniform policy can subtly imply that conformity is more important than individual thought and expression. This is at odds with the educational goal of fostering independent, critical thinkers who will contribute uniquely to society.
In essence, the freedom to choose one’s attire is not just a matter of personal taste but a crucial element in nurturing confident, creative, and culturally aware individuals. Schools, by embracing this diversity in student clothing, can enhance the educational experience and better prepare students for the varied and diverse world beyond their gates.
2. Financial Burden
The requirement of school uniforms can impose a significant financial burden on families, an aspect that often gets overlooked in the uniform policy debate. In the United States, over half of parents , at 55%, perceive school uniforms to be costly. This financial strain is not just about the initial cost of purchasing uniforms, but also encompasses several hidden expenses that accumulate over time.
Key points illustrating the financial burden of school uniforms include:
- Initial and Replacement Costs: Uniforms, especially those with specific designs or logos, can be expensive to buy. Additionally, as children grow or uniforms wear out, they often need replacing, adding to the financial strain.
- Multiple Sets Requirement: To maintain a clean and presentable appearance throughout the week, families typically need to purchase multiple sets of uniforms, further escalating the cost.
- Special Care and Maintenance: Some uniforms require special laundering or care, which can add to the overall expense, either in terms of higher home utility bills or professional cleaning services.
Moreover, these costs can be particularly burdensome for families with multiple children or those on a limited income. Research from the University of York highlighted that school uniforms present unmanageable costs for low-income families. The study found that purchasing uniforms imposed sudden and significant financial burdens, leading families to make sacrifices on essentials like food and heating, and in some cases, to enter into debt.
In addition to the direct financial impact, there’s also the consideration of opportunity cost. Money spent on uniforms could have been allocated to educational resources, extracurricular activities, or savings for future educational expenses.
In conclusion, the mandatory school uniform policy can lead to significant and often underappreciated financial pressures on families, making it a substantial reason for reconsidering such policies, especially in schools that serve economically diverse or disadvantaged communities.
3. Comfort and Practicality
The issue of comfort and practicality is a significant concern in the debate against mandatory school uniforms. Students spend a substantial part of their day in school, and their attire plays a crucial role in their overall comfort and ability to engage effectively in various school activities.

Key aspects highlighting the importance of comfort and practicality include:
- Physical Comfort: Uniforms, often designed with a one-size-fits-all approach, may not suit every body type, leading to discomfort. Comfortable clothing is essential for students to focus and participate actively in their learning.
- Suitability for Varied Activities: School life involves a range of activities, from sitting in classrooms to physical education and outdoor play. Uniforms might not be practical for all these diverse activities, impacting students’ ability to participate fully.
- Weather Appropriateness: Uniforms may not be designed for all weather conditions, which can affect students’ comfort and health. For example, a uniform might be too warm for summer months or insufficiently protective during colder weather.
Additionally, practicality concerns extend to the maintenance of uniforms. They often require regular washing and ironing, which can be time-consuming for families. Also, the need for specific uniform attire for different school events or days (e.g., physical education uniforms) adds to the complexity and impracticality of the uniform system.
In essence, prioritizing comfort and practicality in student attire is not only a matter of convenience but also impacts their academic engagement and well-being. Allowing students to wear clothing that is comfortable, suited to a variety of activities, and appropriate for the weather can enhance their school experience, making them more receptive to learning and participating in school life.
4. Lack of Preparation for Real World
The argument that school uniforms do not adequately prepare students for the ‘real world’ is increasingly relevant in today’s diverse and flexible professional environment. In many modern workplaces, the ability to choose and present oneself appropriately is a valued skill, reflecting individual judgment and adaptability.
Key points underscoring this lack of preparation include:
- Diversity in Workplace Attire: Modern workplaces often have varied dress codes, ranging from formal to casual. Uniform policies do not expose students to the decision-making process involved in dressing for different occasions and environments.
- Personal Branding: In many careers, personal style is an integral part of professional branding. Uniforms do not allow students to explore and develop their personal style, which can be a disadvantage in professions where self-presentation is key.
- Adaptability and Decision-Making: Choosing appropriate attire for different settings teaches adaptability and decision-making skills. Uniforms eliminate these daily choices, potentially leaving students less prepared to make such judgments post-graduation.
Norman Isaacs, the principal at Millikan Middle School in Sherman Oaks, California, opposes school uniforms . He argues that students should be taught to make decisions and choices rooted in their own values instead of adhering to arbitrary rules. He believes this approach is essential for students to develop independent thinking and self-discipline.
In conclusion, while uniforms might simplify wardrobe decisions during school years, they can inadvertently hinder the development of skills necessary for navigating the varied and often nuanced dress codes encountered in adult life, especially in professional settings. Allowing students the freedom to choose their attire is more aligned with preparing them for the real-world scenarios they will face after graduation.
5. Equality Issues
The topic of equality in relation to school uniforms is multi-faceted and complex. While uniforms are often championed as a tool for promoting equality, they can, in fact, inadvertently highlight and exacerbate existing socioeconomic disparities among students.

Key points illustrating the equality issues associated with school uniforms include:
- Highlighting Economic Disparities: The quality, newness, and upkeep of uniforms can become a marker of economic status. Students from less affluent backgrounds may struggle to keep their uniforms in pristine condition, inadvertently highlighting socio-economic differences.
- Access to Uniforms: The cost of uniforms can be prohibitive for some families, particularly those with multiple school-age children, leading to inequality in access.
- Uniform Assistance Programs: While some schools offer uniform assistance programs, reliance on such programs can inadvertently stigmatize students, creating a sense of otherness rather than unity.
Moreover, the notion that uniforms inherently promote a sense of equality among students is debatable. While uniforms may superficially level the playing field by unifying student attire, true equality and respect among students stem from an inclusive school culture that values diversity, not just from masking individual differences with standard clothing. For example, in schools like Archer , the uniform policy doesn’t restrict branded shoes or accessories, allowing students to display wealth through these items. This often leads to a sense of inequality, as students become aware of and feel pressured by the presence of expensive items, undermining the supposed leveling effect of uniforms.
In summary, while the intention behind school uniforms may be to create a level playing field, they can sometimes have the opposite effect by highlighting economic disparities and creating barriers to access. A more effective approach to promoting equality in schools involves addressing these deeper issues directly, rather than masking them with a uniform policy.
6. Resistance to Authority
The imposition of school uniforms can sometimes foster resistance to authority among students, particularly as they grow older and seek to assert their independence and individuality. This resistance is not just a matter of rebellion; it often stems from deeper feelings of autonomy and self-expression being suppressed.
Key points related to resistance to authority include:
- Asserting Independence : As children mature into teenagers, they naturally seek to express their individuality. Uniforms can be perceived as a restriction on this expression, leading to resistance as a form of asserting independence.
- Questioning Rules and Uniformity: Older students often begin to question the rationale behind various rules, including dress codes. Mandatory uniforms can become a focal point of this questioning, symbolizing a broader struggle against perceived unnecessary authority.
- Impact on Student-Teacher Relationships: Strict uniform policies can create an adversarial dynamic between students and school authorities, impacting the overall school environment and student-teacher relationships.
The resistance to uniforms and, by extension, to school authority, can have wider implications. It can detract from the educational experience, creating an environment of conflict and tension rather than one of learning and growth. Additionally, this resistance can carry over into other aspects of school life, affecting participation in school activities, respect for school rules, and overall school morale.
In essence, while the aim of school uniforms may be to promote discipline and unity, they can sometimes yield the opposite result, particularly among older students. Recognizing and respecting students’ growing need for self-expression and autonomy is crucial in fostering a positive and productive school atmosphere.
7. Cultural and Religious Concerns
Addressing cultural and religious concerns is crucial when considering the impact of mandatory school uniforms. Uniform policies can sometimes conflict with students’ cultural and religious practices, leading to feelings of exclusion and a lack of representation.
Key points highlighting cultural and religious concerns include:
- Respect for Cultural Attire: Many cultures have traditional attire that holds significant meaning. Uniform policies can prevent students from wearing these culturally important garments, leading to a loss of cultural expression.
- Accommodating Religious Dress Requirements: Some religions have specific dress codes, such as headscarves or particular garments. Uniforms that don’t accommodate these requirements can impede religious freedom and expression.
- Impact on Inclusivity and Diversity: A uniform policy that doesn’t consider cultural and religious diversity can create an environment where students feel their identities are not acknowledged or respected.
Furthermore, navigating these cultural and religious nuances requires sensitivity and understanding from educational institutions. When schools fail to accommodate such diversity, it can lead to a sense of alienation among students from different cultural or religious backgrounds. This alienation can affect their sense of belonging and engagement within the school community.
In summary, while school uniforms are often intended to create a cohesive and unified appearance, they can inadvertently undermine the rich cultural and religious diversity within the student body. An inclusive approach that respects and accommodates these differences is essential for fostering an educational environment that values and celebrates diversity.
8. Psychological Impact
The psychological impact of school uniforms on students is an important aspect to consider, particularly as it pertains to their self-image, confidence, and overall mental well-being. Uniforms, by their very nature of imposing a standard appearance, can have various unintended negative psychological effects on students.
Key points regarding the psychological impact include:
- Self-Image and Confidence: Uniforms can affect how students perceive themselves, especially if they feel the uniform is unflattering or doesn’t reflect their identity. This can lead to issues with self-esteem and confidence.
- Conformity vs. Individuality: The emphasis on conformity through uniforms may conflict with a student’s desire for individual expression, leading to internal conflict and stress.
- Stress on Families: The pressure to maintain a set standard of uniform can also place stress on families, particularly if they struggle financially or have time constraints, affecting the student’s home life and mental well-being.
Additionally, unflattering or restrictive uniforms can deter students from participating in sports , creating a psychological barrier. For example, an auto-ethnography highlighted the psychological barrier posed by an unflattering sports uniform to fat children’s participation in and enjoyment of physical activity.
In conclusion, while uniforms are often intended to eliminate distractions and create equality, they can have significant psychological impacts on students. These impacts can range from affecting self-esteem and personal identity to creating stress and anxiety. Considering these factors is crucial in evaluating the overall effectiveness and appropriateness of uniform policies in schools.
9. Not Environmentally Friendly
The environmental impact of school uniforms is an often overlooked yet critical aspect of the debate surrounding their use. The production, maintenance, and disposal of school uniforms carry significant environmental implications, making them a less sustainable option for student attire.

Key points highlighting the environmental concerns include:
- Resource-Intensive Production: The manufacturing of uniforms often involves resource-intensive processes, using materials that are not environmentally friendly and consuming large amounts of water and energy.
- Frequent Replacement and Waste: As children grow, uniforms need frequent replacing, contributing to textile waste. Unlike everyday clothing, which can be handed down or repurposed, specific school uniforms have limited use beyond the school environment.
- Chemical Usage in Maintenance: The maintenance of uniforms, especially those requiring special care, can involve the use of harsh chemicals and detergents, further contributing to environmental harm.
Furthermore, the environmental impact of uniforms extends beyond their production and maintenance. The disposal of outdated or worn-out uniforms poses a challenge, as they are often not made from biodegradable or recyclable materials, adding to landfill waste.
In summary, considering the environmental footprint of school uniforms is essential in the context of growing concerns about sustainability and environmental conservation. Moving towards more eco-friendly clothing options or implementing uniform recycling programs could be steps in mitigating the environmental impact associated with school uniforms.
Addressing Opposing Perspectives on School Uniforms

While the debate around school uniforms has varying opinions, it’s essential to consider the opposing views. Below, we explore common arguments in favor of mandating school uniforms, coupled with counterarguments that provide a different perspective on the issue.
1. Uniforms Save Time
The perceived time-saving aspect of school uniforms is often debated. While it’s argued that uniforms can save time in choosing outfits for school, this benefit is minimal as students still need casual attire for outside school hours.
Furthermore, uniforms can actually add to the workload of teachers . They often spend a significant amount of time enforcing uniform policies and addressing infractions such as improper dress. This enforcement can detract from the primary focus of teaching and reduce the time available for actual lesson delivery.
2. Uniforms Improve Attendance and Discipline
Proponents of school uniforms often claim they instill discipline by requiring students to adhere to dress codes. However, true discipline is more effectively cultivated through internal motivation and understanding the reasons behind rules , rather than mere conformity to a uniform. Encouraging critical thinking and self-discipline is more beneficial for students’ overall development.
This perspective is supported by research using data from the Early Childhood Longitudinal Study , which showed that school uniforms had no effect on students’ behavior across various dimensions, including internalizing and externalizing behavior problems, and social skills. This finding was consistent through kindergarten to the end of fifth grade, even after accounting for a range of factors that could influence behavior.
3. Improving Safety and Security
The argument that uniforms aid in identifying who belongs on campus and enhance security is subject to debate. While it may assist in spotting intruders, a more effective approach to safety involves a robust security system and active community engagement.
Fostering a safe school environment is better achieved through open communication and trust among students, staff, and the community. The effectiveness of uniforms in improving security is not universally acknowledged and is often viewed as a measure to enforce conformity rather than a genuine strategy to enhance safety.
Interested in exploring different teaching methods? Take a look at our comprehensive guide featuring 15 distinct teaching styles.
Useful Resources
- National Center for Education Statistics
- School uniforms: A history of ‘rebellion and conformity’ by BBC
- Educational Statistics by Statista
The case against school uniforms is compelling. Uniforms often fail to achieve their intended goals of promoting equality, saving time, and enhancing safety. Instead, they may inadvertently perpetuate socioeconomic disparities, add burdens to educators and students alike, and provide a false sense of security. Emphasizing personal expression, fostering genuine equality, and focusing on more effective educational strategies would be more beneficial for student development and school environments.
If you want to learn more about dress code for teachers, check out our article “ How to Meet the Teacher Dress Codes in Diverse Learning Environments in 2023″ .
- “Back-to-school: share of children wearing school uniforms in the United States from 2008 to 2018”, Statista
- “School uniforms”, National Center for Educational Statistics
- “Dressed for Success? The Effect of School Uniforms on Student Achievement and Behavior”, National Bureau of Economic Research
- “Do you think students need to wear a school uniform? Why or why not?”, Quora
- Department of Human Sciences, The Ohio State University
- “Dress Code, Stress Mode: A Teacher’s Perspective on the Uniform Debate”, New Orleans Mom
- “School Uniforms Are Expensive Statistics [Fresh Research]”, Gitnux
- “Buying school uniform post-lockdown ‘unmanageable’ for low income families”, phys.org
- “School Uniforms: Do They Reduce Violence–Or Just Make Us Feel Better?”, EdWeek
- “Do uniforms really create socioeconomic equity?: Designer items while in uniform”, The Oracle
- “Reviewing School Uniform through a Public Health Lens: Evidence about the Impacts of School Uniform on Education and Health”, Public Health Reviews
- “School uniforms save time”, Parlia
- “Early Childhood Longitudinal Program (ECLS)”, National Center for Educational Statistics
- “School Uniforms: A Safety and Security Issue”. The Raider Voice
- Recent Posts

Simona Johnes is the visionary being the creation of our project. Johnes spent much of her career in the classroom working with students. And, after many years in the classroom, Johnes became a principal.
- 28 Exciting Yarn Crafts for Preschool Kids: Igniting Creativity and Fine Motor Skills - April 29, 2024
- 16 Engaging and Educational Cause and Effect Activities for Preschoolers to Boost Cognitive Development - April 24, 2024
- 25 Innovative and Engaging Parts of Speech Activities for Middle School: Fun Grammar Games to Enhance Learning - April 14, 2024
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Your Health
- Treatments & Tests
- Health Inc.
- Public Health
Why writing by hand beats typing for thinking and learning
Jonathan Lambert

If you're like many digitally savvy Americans, it has likely been a while since you've spent much time writing by hand.
The laborious process of tracing out our thoughts, letter by letter, on the page is becoming a relic of the past in our screen-dominated world, where text messages and thumb-typed grocery lists have replaced handwritten letters and sticky notes. Electronic keyboards offer obvious efficiency benefits that have undoubtedly boosted our productivity — imagine having to write all your emails longhand.
To keep up, many schools are introducing computers as early as preschool, meaning some kids may learn the basics of typing before writing by hand.
But giving up this slower, more tactile way of expressing ourselves may come at a significant cost, according to a growing body of research that's uncovering the surprising cognitive benefits of taking pen to paper, or even stylus to iPad — for both children and adults.
Is this some kind of joke? A school facing shortages starts teaching standup comedy
In kids, studies show that tracing out ABCs, as opposed to typing them, leads to better and longer-lasting recognition and understanding of letters. Writing by hand also improves memory and recall of words, laying down the foundations of literacy and learning. In adults, taking notes by hand during a lecture, instead of typing, can lead to better conceptual understanding of material.
"There's actually some very important things going on during the embodied experience of writing by hand," says Ramesh Balasubramaniam , a neuroscientist at the University of California, Merced. "It has important cognitive benefits."
While those benefits have long been recognized by some (for instance, many authors, including Jennifer Egan and Neil Gaiman , draft their stories by hand to stoke creativity), scientists have only recently started investigating why writing by hand has these effects.
A slew of recent brain imaging research suggests handwriting's power stems from the relative complexity of the process and how it forces different brain systems to work together to reproduce the shapes of letters in our heads onto the page.
Your brain on handwriting
Both handwriting and typing involve moving our hands and fingers to create words on a page. But handwriting, it turns out, requires a lot more fine-tuned coordination between the motor and visual systems. This seems to more deeply engage the brain in ways that support learning.

Shots - Health News
Feeling artsy here's how making art helps your brain.
"Handwriting is probably among the most complex motor skills that the brain is capable of," says Marieke Longcamp , a cognitive neuroscientist at Aix-Marseille Université.
Gripping a pen nimbly enough to write is a complicated task, as it requires your brain to continuously monitor the pressure that each finger exerts on the pen. Then, your motor system has to delicately modify that pressure to re-create each letter of the words in your head on the page.
"Your fingers have to each do something different to produce a recognizable letter," says Sophia Vinci-Booher , an educational neuroscientist at Vanderbilt University. Adding to the complexity, your visual system must continuously process that letter as it's formed. With each stroke, your brain compares the unfolding script with mental models of the letters and words, making adjustments to fingers in real time to create the letters' shapes, says Vinci-Booher.
That's not true for typing.
To type "tap" your fingers don't have to trace out the form of the letters — they just make three relatively simple and uniform movements. In comparison, it takes a lot more brainpower, as well as cross-talk between brain areas, to write than type.
Recent brain imaging studies bolster this idea. A study published in January found that when students write by hand, brain areas involved in motor and visual information processing " sync up " with areas crucial to memory formation, firing at frequencies associated with learning.
"We don't see that [synchronized activity] in typewriting at all," says Audrey van der Meer , a psychologist and study co-author at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology. She suggests that writing by hand is a neurobiologically richer process and that this richness may confer some cognitive benefits.
Other experts agree. "There seems to be something fundamental about engaging your body to produce these shapes," says Robert Wiley , a cognitive psychologist at the University of North Carolina, Greensboro. "It lets you make associations between your body and what you're seeing and hearing," he says, which might give the mind more footholds for accessing a given concept or idea.
Those extra footholds are especially important for learning in kids, but they may give adults a leg up too. Wiley and others worry that ditching handwriting for typing could have serious consequences for how we all learn and think.
What might be lost as handwriting wanes
The clearest consequence of screens and keyboards replacing pen and paper might be on kids' ability to learn the building blocks of literacy — letters.
"Letter recognition in early childhood is actually one of the best predictors of later reading and math attainment," says Vinci-Booher. Her work suggests the process of learning to write letters by hand is crucial for learning to read them.
"When kids write letters, they're just messy," she says. As kids practice writing "A," each iteration is different, and that variability helps solidify their conceptual understanding of the letter.
Research suggests kids learn to recognize letters better when seeing variable handwritten examples, compared with uniform typed examples.
This helps develop areas of the brain used during reading in older children and adults, Vinci-Booher found.
"This could be one of the ways that early experiences actually translate to long-term life outcomes," she says. "These visually demanding, fine motor actions bake in neural communication patterns that are really important for learning later on."
Ditching handwriting instruction could mean that those skills don't get developed as well, which could impair kids' ability to learn down the road.
"If young children are not receiving any handwriting training, which is very good brain stimulation, then their brains simply won't reach their full potential," says van der Meer. "It's scary to think of the potential consequences."
Many states are trying to avoid these risks by mandating cursive instruction. This year, California started requiring elementary school students to learn cursive , and similar bills are moving through state legislatures in several states, including Indiana, Kentucky, South Carolina and Wisconsin. (So far, evidence suggests that it's the writing by hand that matters, not whether it's print or cursive.)
Slowing down and processing information
For adults, one of the main benefits of writing by hand is that it simply forces us to slow down.
During a meeting or lecture, it's possible to type what you're hearing verbatim. But often, "you're not actually processing that information — you're just typing in the blind," says van der Meer. "If you take notes by hand, you can't write everything down," she says.
The relative slowness of the medium forces you to process the information, writing key words or phrases and using drawing or arrows to work through ideas, she says. "You make the information your own," she says, which helps it stick in the brain.
Such connections and integration are still possible when typing, but they need to be made more intentionally. And sometimes, efficiency wins out. "When you're writing a long essay, it's obviously much more practical to use a keyboard," says van der Meer.
Still, given our long history of using our hands to mark meaning in the world, some scientists worry about the more diffuse consequences of offloading our thinking to computers.
"We're foisting a lot of our knowledge, extending our cognition, to other devices, so it's only natural that we've started using these other agents to do our writing for us," says Balasubramaniam.
It's possible that this might free up our minds to do other kinds of hard thinking, he says. Or we might be sacrificing a fundamental process that's crucial for the kinds of immersive cognitive experiences that enable us to learn and think at our full potential.
Balasubramaniam stresses, however, that we don't have to ditch digital tools to harness the power of handwriting. So far, research suggests that scribbling with a stylus on a screen activates the same brain pathways as etching ink on paper. It's the movement that counts, he says, not its final form.
Jonathan Lambert is a Washington, D.C.-based freelance journalist who covers science, health and policy.
- handwriting
Skip to Content
English alum flunks grades in new book
- Share via Twitter
- Share via Facebook
- Share via LinkedIn
- Share via E-mail
Jesse Stommel compiles two decades of eyebrow-raising in Undoing the Grade: Why We Grade, and How to Stop
It was the summer of 2023, sometime in June or July, and Jesse Stommel (PhD, English ‘10) had big weekend plans.
He said to his husband, “I’m going to write a book this weekend”—a book about grades, in particular, and all the trouble they’ve caused.
It was a tall order for such a short period of time, no doubt, but it wasn’t as though Stommel were starting from scratch. He’d been taking a critical eye to grades for two decades and had published numerous essays on the topic, several of which had been read by tens of thousands of people on his website .

Jesse Stommel (PhD, English ‘10) Undoing the Grade: Why We Grade, and How to Stop partially in response to his realization that grades are performative.
“I was already starting to piece these things out in public and have conversations,” says Stommel, who teaches writing at the University of Denver. “That’s how my writing process always works. All of my books are adapted from previously published stuff. This is because I don't think in a vacuum. I need to think alongside other people.”
All Friday, Saturday and Sunday, Stommel toiled away, editing previously published materials, organizing those materials into chapters, writing three brand-new chapters and then bookending everything with a foreword by Martha Burtis and an afterword by Sean Michael Morris (MA, English ‘05).
“And come Sunday night,” he says, “I had a draft of the book.”
That book, titled Undoing the Grade: Why We Grade, and How to Stop , was published on Aug. 14.
I can give you A’s
Growing up, Stommel loved school. Grades, however—grades he didn’t love.
“I did really well throughout elementary school. I was super engaged,” he says. “Then I hit middle school, where I was being graded in the traditional way for the first time, and I got almost straight D’s and F’s in sixth grade.”
His grades improved the following year, but not by much. Being graded had sapped him of his motivation, he says. “All of a sudden I didn’t want to do any of the work.”
But things changed in eighth grade, thanks to his dad and brother.
“They bet me I couldn’t get straight A’s,” he says. “And so, the first semester of eighth grade, I got straight A’s.”
His teachers couldn’t believe it. They were flummoxed, and perhaps a little suspicious. How could he turn things around so quickly? What on earth was going on?
“They sat me down and asked me what had happened, and I told them about the bet,” says Stommel.
Yet that meeting opened his eyes more than it did his teachers’, he says, because it led him to the realization that grades were performative, character traits of a role he was being asked to play. “If what you want is A’s,” he recalls thinking, “I can give you A’s.”
This discovery, and the good grades that arose therefrom, freed Stommel up, he admits, relieving him of the pressure and judgment that often came with D’s and F’s. But it also made him aware of the stakes involved in the pursuit of high marks, stakes he continues to think about to this day.
“Whenever I see a perfect grade point average, what that represents to me is a willingness to compromise yourself, because that's what we're constantly expected to do in traditional grading systems.”

“Whenever I see a perfect grade point average, what that represents to me is a willingness to compromise yourself, because that's what we're constantly expected to do in traditional grading systems,” says Jesse Stommel.
From grader to ungrading
Stommel began his teaching career as a grader, evaluating the work a professor had assigned to students.
“The experience of doing nothing but grading gave me an interesting perspective on what grading is and how it works,” he says. “It had nothing to do with the relationship between me and students. It was just this abstraction of their work and the quality of their work, as though that can be separated from who they are and who I am.”
Stommel wanted to do something different when he became an instructor of record. But what?
His first source of inspiration was CU Boulder English Professor Marty Bickman , who taught Stommel a total of four times, twice when Stommel was an undergraduate and twice when he was a graduate student.
“I really admired Marty’s approach. He didn’t put grades on individual work. Instead, he had students grading themselves and writing self-reflections.”
Stommel also found inspiration in CU Boulder English Professor R L Widmann , with whom he co-taught courses on Shakespeare. Widmann encouraged Stommel to think of assessment not as a judgment laid down from on high but as a conversation between student and teacher.
“She would develop deep relationships with students and then be able to tell them exactly what they needed to hear at exactly the moment they needed to hear it. And they trusted her.”
Stommel combined Bickman’s and Widmann’s approaches in his own classes, along with what he learned about teaching and learning from books like John Holt’s How Children Fail and Paulo Freire’s Pedagogy of the Oppressed . And thus ungrading, which Stommel defines as “raising an eyebrow at grades as a systemic practice,” was born.
But that’s not to say Stommel believes his ungrading practice is the only viable option. Not even close. In his essay “How to Ungrade,” a revised and expanded version of which appears in Undoing the Grade , he provides a smorgasbord of options for the ungrading-curious, including grading contracts, portfolios, peer assessment and student-made rubrics.
The goal of ungrading, he says, is not to replace one uniform approach to assessment with another. It’s for educators to develop an approach that best fits them and their students.
“The work of teaching, the work of reimagining assessment, is necessarily idiosyncratic.”
Myths and paradoxes
But in a world without grades, wouldn’t academic standards fall? Wouldn’t students lose motivation? Wouldn’t they be rewarded for learning less?
The experience of doing nothing but grading gave me an interesting perspective on what grading is and how it works. It had nothing to do with the relationship between me and students. It was just this abstraction of their work and the quality of their work, as though that can be separated from who they are and who I am.”
Questions like these, Stommel says, reflect the cultural anxiety surrounding grades. And while it’s important to remember that this anxiety is itself real—“It’s based in real feelings that we have as human beings,” says Stommel—it’s equally important to remember that the problems from which it stems may not be.
Take grade inflation, or the awarding of higher grades for the same quality of work over long periods of time, as an example. Like Alfie Kohn , author of Punished by Rewards , Stommel calls grade inflation a myth, but he also believes concern over it points to a real phenomenon: the desire for education to be taken seriously.
“We're seeing all kinds of pushes on the education sector,” he says. “People are saying that education isn't doing what it's supposed to be doing, or it’s actually doing harm.”
That many teachers’ jobs lack stability, especially in higher education, doesn’t help, Stommel adds.
“When you see the utter precarity of educators—where most educators are not making a living wage; where 70% of educators in higher education are adjunct or on one-year contracts, sometimes even on one-semester contracts. When you see all of that happening, there is a desire to have some relief. And I think that’s when we talk about something like grade inflation.”
Nevertheless, Stommel argues, the claim that lower grades means better teaching is a misleading one. High standards and high grades are not mutually exclusive.
Stommel cites a former student to prove it. “Jesse’s class was one of the hardest I’ve taken in my life,” this student wrote of one of Stommel’s classes. “It was an easy ‘A.’”
Did you enjoy this article? Subcribe to our newsletter. Passionate about English? Show your support.
Related Articles

Making movies that people love watching

The Loch Ness monster: myth or reality?

Employer-labor relations in the balance
- Division of Arts and Humanities

The Unpunished: How Extremists Took Over Israel
After 50 years of failure to stop violence and terrorism against Palestinians by Jewish ultranationalists, lawlessness has become the law.
Supported by
- Share full article

By Ronen Bergman and Mark Mazzetti
- May 16, 2024
This story is told in three parts. The first documents the unequal system of justice that grew around Jewish settlements in Gaza and the West Bank. The second shows how extremists targeted not only Palestinians but also Israeli officials trying to make peace. The third explores how this movement gained control of the state itself. Taken together, they tell the story of how a radical ideology moved from the fringes to the heart of Israeli political power.
By the end of October, it was clear that no one was going to help the villagers of Khirbet Zanuta. A tiny Palestinian community, some 150 people perched on a windswept hill in the West Bank near Hebron, it had long faced threats from the Jewish settlers who had steadily encircled it. But occasional harassment and vandalism, in the days after the Oct. 7 Hamas attack, escalated into beatings and murder threats. The villagers made appeal after appeal to the Israeli police and to the ever-present Israeli military, but their calls for protection went largely unheeded, and the attacks continued with no consequences. So one day the villagers packed what they could, loaded their families into trucks and disappeared.
Listen to this article, read by Jonathan Davis
Who bulldozed the village after that is a matter of dispute. The Israeli Army says it was the settlers; a senior Israeli police officer says it was the army. Either way, soon after the villagers left, little remained of Khirbet Zanuta besides the ruins of a clinic and an elementary school. One wall of the clinic, leaning sideways, bore a sign saying that it had been funded by an agency of the European Union providing “humanitarian support for Palestinians at risk of forcible transfer in the West Bank.” Near the school, someone had planted the flag of Israel as another kind of announcement: This is Jewish land now.
Such violence over the decades in places like Khirbet Zanuta is well documented. But protecting the people who carry out that violence is the dark secret of Israeli justice. The long arc of harassment, assault and murder of Palestinians by Jewish settlers is twinned with a shadow history, one of silence, avoidance and abetment by Israeli officials. For many of those officials, it is Palestinian terrorism that most threatens Israel. But in interviews with more than 100 people — current and former officers of the Israeli military, the National Israeli Police and the Shin Bet domestic security service; high-ranking Israeli political officials, including four former prime ministers; Palestinian leaders and activists; Israeli human rights lawyers; American officials charged with supporting the Israeli-Palestinian partnership — we found a different and perhaps even more destabilizing threat. A long history of crime without punishment, many of those officials now say, threatens not only Palestinians living in the occupied territories but also the State of Israel itself.

Many of the people we interviewed, some speaking anonymously, some speaking publicly for the first time, offered an account not only of Jewish violence against Palestinians dating back decades but also of an Israeli state that has systematically and increasingly ignored that violence. It is an account of a sometimes criminal nationalistic movement that has been allowed to operate with impunity and gradually move from the fringes to the mainstream of Israeli society. It is an account of how voices within the government that objected to the condoning of settler violence were silenced and discredited. And it is a blunt account, told for the first time by Israeli officials themselves, of how the occupation came to threaten the integrity of their country’s democracy.
The interviews, along with classified documents written in recent months, reveal a government at war with itself. One document describes a meeting in March, when Maj. Gen. Yehuda Fox, the head of Israel’s Central Command, responsible for the West Bank, gave a withering account of the efforts by Bezalel Smotrich — an ultraright leader and the official in Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu’s government with oversight over the West Bank — to undermine law enforcement in the occupied territory. Since Smotrich took office, Fox wrote, the effort to clamp down on illegal settlement construction has dwindled “to the point where it has disappeared.” Moreover, Fox said, Smotrich and his allies were thwarting the very measures to enforce the law that the government had promised Israeli courts it would take.
This is a story, pieced together and told in full for the first time, that leads to the heart of Israel. But it begins in the West Bank, in places like Khirbet Zanuta. From within the village’s empty ruins, there is a clear view across the valley to a tiny Jewish outpost called Meitarim Farm. Built in 2021, the farm has become a base of operations for settler attacks led by Yinon Levi, the farm’s owner. Like so many of the Israeli outposts that have been set up throughout the West Bank in recent years, Meitarim Farm is illegal. It is illegal under international law, which most experts say doesn’t recognize Israeli settlements in occupied land. It is illegal under Israeli law, like most settlements built since the 1990s.
Few efforts are made to stop the building of these outposts or the violence emanating from them. Indeed, one of Levi’s day jobs was running an earthworks company, and he has worked with the Israel Defense Forces to bulldoze at least one Palestinian village in the West Bank. As for the victims of that violence, they face a confounding and defeating system when trying to get relief. Villagers seeking help from the police typically have to file a report in person at an Israeli police station, which in the West Bank are almost exclusively located inside the settlements themselves. After getting through security and to the station, they sometimes wait for hours for an Arabic translator, only to be told they don’t have the right paperwork or sufficient evidence to submit a report. As one senior Israeli military official told us, the police “exhaust Palestinians so they won’t file complaints.”
And yet in November, with no protection from the police or the military, the former residents of Khirbet Zanuta and five nearby villages chose to test whether justice was still possible by appealing directly to Israel’s Supreme Court. In a petition, lawyers for the villagers, from Haqel, an Israeli human rights organization, argued that days after the Oct. 7 Hamas attack, a raiding party that included settlers and Israeli soldiers assaulted village residents, threatened murder and destroyed property throughout the village. They stated that the raid was part of “a mass transfer of ancient Palestinian communities,” one in which settlers working hand in hand with soldiers are taking advantage of the current war in Gaza to achieve the longer-standing goal of “cleansing” parts of the West Bank, aided by the “sweeping and unprecedented disregard” of the state and its “de facto consent to the massive acts of deportation.”
The Supreme Court agreed to hear the case, and the relief the villagers are seeking — that the law be enforced — might seem modest. But our reporting reveals the degree to which decades of history are stacked against them: After 50 years of crime without punishment, in many ways the violent settlers and the state have become one.
Separate and Unequal
The devastating Hamas attacks in Israel on Oct. 7, the ongoing crisis of Israeli hostages and the grinding Israeli invasion and bombardment of the Gaza Strip that followed may have refocused the world’s attention on Israel’s ongoing inability to address the question of Palestinian autonomy. But it is in the West Bank where the corrosive long-term effects of the occupation on Israeli law and democracy are most apparent.
A sample of three dozen cases in the months since Oct. 7 shows the startling degree to which the legal system has decayed. In all the cases, involving misdeeds as diverse as stealing livestock and assault and arson, not a single suspect was charged with a crime; in one case, a settler shot a Palestinian in the stomach while an Israel Defense Forces soldier looked on, yet the police questioned the shooter for only 20 minutes, and never as a criminal suspect, according to an internal Israeli military memo. During our review of the cases, we listened to recordings of Israeli human rights activists calling the police to report various crimes against Palestinians. In some of the recordings, the police refused to come to the scene, claiming they didn’t know where the villages were; in one case, they mocked the activists as “anarchists.” A spokesman for the Israeli National Police declined to respond to repeated queries about our findings.
The violence and impunity that these cases demonstrate existed long before Oct. 7. In nearly every month before October, the rate of violent incidents was higher than during the same month in the previous year. And Yesh Din, an Israeli human rights group, looking at more than 1,600 cases of settler violence in the West Bank between 2005 and 2023, found that just 3 percent ended in a conviction. Ami Ayalon, the head of Shin Bet from 1996 to 2000 — speaking out now because of his concern about Israel’s systemic failure to enforce the law — says this singular lack of consequences reflects the indifference of the Israeli leadership going back years. “The cabinet, the prime minister,” he says, “they signal to the Shin Bet that if a Jew is killed, that’s terrible. If an Arab is killed, that’s not good, but it’s not the end of the world.”
Ayalon’s assessment was echoed by many other officials we interviewed. Mark Schwartz, a retired American three-star general, was the top military official working at the United States Embassy in Jerusalem from 2019 to 2021, overseeing international support efforts for the partnership between Israel and the Palestinian Authority. “There’s no accountability,” he says now of the long history of settler crimes and heavy-handed Israeli operations in the West Bank. “These things eat away at trust and ultimately the stability and security of Israel and the Palestinian territories. It’s undeniable.”
How did a young nation turn so quickly on its own democratic ideals, and at what price? Any meaningful answer to these questions has to take into account how a half-century of lawless behavior that went largely unpunished propelled a radical form of ultranationalism to the center of Israeli politics. This is the history that is told here in three parts. In Part I, we describe the origins of a religious movement that established Jewish settlements in the newly won territories of Gaza and the West Bank during the 1970s. In Part II, we recount how the most extreme elements of the settler movement began targeting not only Palestinians but also Israeli leaders who tried to make peace with them. And in Part III, we show how the most established members of Israel’s ultraright, unpunished for their crimes, gained political power in Israel, even as a more radical generation of settlers vowed to eliminate the Israeli state altogether.
Many Israelis who moved to the West Bank did so for reasons other than ideology, and among the settlers, there is a large majority who aren’t involved in violence or other illegal acts against Palestinians. And many within the Israeli government fought to expand the rule of law into the territories, with some success. But they also faced harsh pushback, with sometimes grave personal consequences. Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin’s efforts in the 1990s, on the heels of the First Intifada, to make peace with Yasir Arafat, chairman of the Palestine Liberation Organization, gave rise to a new generation of Jewish terrorists, and they ultimately cost him his life.
The disagreement over how to handle the occupied territories and their residents has bred a complex and sometimes opaque system of law enforcement. At its heart are two separate and unequal systems of justice: one for Jews and another for Palestinians.
The West Bank is under the command of the I.D.F., which means that Palestinians are subject to a military law that gives the I.D.F. and the Shin Bet considerable authority. They can hold suspects for extended periods without trial or access to either a lawyer or the evidence against them. They can wiretap, conduct secret surveillance, hack into databases and gather intelligence on any Arab living in the occupied territory with few restrictions. Palestinians are subject to military — not civilian — courts, which are far more punitive when it comes to accusations of terrorism and less transparent to outside scrutiny. (In a statement, the I.D.F. said, “The use of administrative detention measures is only carried out in situations where the security authorities have reliable and credible information indicating a real danger posed by the detainee to the region’s security, and in the absence of other alternatives to remove the risk.” It declined to respond to multiple specific queries, in some cases saying “the events are too old to address.”)
According to a senior Israeli defense official, since Oct. 7, some 7,000 settler reservists were called back by the I.D.F., put in uniform, armed and ordered to protect the settlements. They were given specific orders: Do not leave the settlements, do not cover your faces, do not initiate unauthorized roadblocks. But in reality many of them have left the settlements in uniform, wearing masks, setting up roadblocks and harassing Palestinians.
All West Bank settlers are in theory subject to the same military law that applies to Palestinian residents. But in practice, they are treated according to the civil law of the State of Israel, which formally applies only to territory within the state’s borders. This means that Shin Bet might probe two similar acts of terrorism in the West Bank — one committed by Jewish settlers and one committed by Palestinians — and use wholly different investigative tools.
In this system, even the question of what behavior is being investigated as an act of terror is different for Jews and Arabs. For a Palestinian, the simple admission of identifying with Hamas counts as an act of terrorism that permits Israeli authorities to use severe interrogation methods and long detention. Moreover, most acts of violence by Arabs against Jews are categorized as a “terror” attack — giving Shin Bet and other services license to use the harshest methods at their disposal.
The job of investigating Jewish terrorism falls to a division of Shin Bet called the Department for Counterintelligence and Prevention of Subversion in the Jewish Sector, known more commonly as the Jewish Department. It is dwarfed both in size and prestige by Shin Bet’s Arab Department, the division charged mostly with combating Palestinian terrorism. And in the event, most incidents of settler violence — torching vehicles, cutting down olive groves — fall under the jurisdiction of the police, who tend to ignore them. When the Jewish Department investigates more serious terrorist threats, it is often stymied from the outset, and even its successes have sometimes been undermined by judges and politicians sympathetic to the settler cause. This system, with its gaps and obstructions, allowed the founders of groups advocating extreme violence during the 1970s and 1980s to act without consequences, and today it has built a protective cocoon around their ideological descendants.
Some of these people now run Israel. In 2022, just 18 months after losing the prime ministership, Benjamin Netanyahu regained power by forming an alliance with ultraright leaders of both the Religious Zionism Party and the Jewish Power party. It was an act of political desperation on Netanyahu’s part, and it ushered into power some truly radical figures, people — like Smotrich and Itamar Ben-Gvir — who had spent decades pledging to wrest the West Bank and Gaza from Arab hands . Just two months earlier, according to news reports at the time, Netanyahu refused to share a stage with Ben-Gvir, who had been convicted multiple times for supporting terrorist organizations and, in front of television cameras in 1995, vaguely threatened the life of Rabin, who was murdered weeks later by an Israeli student named Yigal Amir.
Now Ben-Gvir was Israel’s national security minister and Smotrich was Israel’s finance minister, charged additionally with overseeing much of the Israeli government’s activities in the West Bank. In December 2022, a day before the new government was sworn in, Netanyahu issued a list of goals and priorities for his new cabinet, including a clear statement that the nationalistic ideology of his new allies was now the government’s guiding star. “The Jewish people,” it said, “have an exclusive and inalienable right to all parts of the land of Israel.”
Two months after that, two Israeli settlers were murdered in an attack by Hamas gunmen near Huwara, a village in the West Bank. The widespread calls for revenge, common after Palestinian terror attacks, were now coming from within Netanyahu’s new government. Smotrich declared that “the village of Huwara needs to be wiped out.”
And, he added, “I think the State of Israel needs to do it.”
Birth of a Movement
With its overwhelming victory in the Arab-Israeli War of 1967, Israel more than doubled the amount of land it controlled, seizing new territory in the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, the Sinai Peninsula, the Golan Heights and East Jerusalem. Now it faced a choice: Would the new land become part of Israel or be bargained away as part of a future Palestinian state? To a cadre of young Israelis imbued with messianic zeal, the answer was obvious. The acquisition of the territories animated a religious political movement — Gush Emunim, or “Bloc of the Faithful” — that was determined to settle the newly conquered lands.
Gush Emunim followers believed that the coming of the messiah would be hastened if, rather than studying holy books from morning to night, Jews settled the newly occupied territories. This was the land of “Greater Israel,” they believed, and there was a pioneer spirit among the early settlers. They saw themselves as direct descendants of the earliest Zionists, who built farms and kibbutzim near Palestinian villages during the first part of the 20th century, when the land was under British control. But while the Zionism of the earlier period was largely secular and socialist, the new settlers believed they were advancing God’s agenda.
The legality of that agenda was an open question. The Geneva Conventions, to which Israel was a signatory, forbade occupying powers to deport or transfer “parts of its own civilian population into the territory it occupies.” But the status of the territory was, in the view of many within and outside the Israeli government, more complex. The settlers sought to create what some of them called “facts on the ground.” This put them into conflict with both the Palestinians and, at least putatively, the Israeli authorities responsible for preventing the spread of illegal settlements.
Whether or not the government would prove flexible on these matters became clear in April 1975 at Ein Yabrud, an abandoned Jordanian military base near Ofra, in the West Bank. A group of workers had been making the short commute from Israel most days for months to work on rebuilding the base, and one evening they decided to stay. They were aiming to establish a Jewish foothold in Judea and Samaria, the Israeli designation for the territories that make up the West Bank, and they had found a back door that required only the slightest push. Their leader met that same night with Shimon Peres, then Israel’s defense minister, who told the I.D.F. to stand down. Peres would treat the nascent settlement not as a community but as a “work camp” — and the I.D.F. would do nothing to hinder their work.
Peres’s maneuver was partly a sign of the weakness of Israel’s ruling Labor party, which had dominated Israeli politics since the country’s founding. The residual trauma of the Yom Kippur War in 1973 — when Israel was caught completely by surprise by Egyptian and Syrian forces before eventually beating back the invading armies — had shaken citizens’ belief in their leaders, and movements like Gush Emunim, directly challenging the authority of the Israeli state, had gained momentum amid Labor’s decline. This, in turn, energized Israel’s political right.
By the late 1970s, the settlers, bolstered in part by growing political support, were expanding in number. Carmi Gillon, who joined Shin Bet in 1972 and rose by the mid-1990s to become its director, recalls the evolving internal debates. Whose responsibility was it to deal with settlers? Should Israel’s vaunted domestic security service enforce the law in the face of clearly illegal acts of settlement? “When we realized that Gush Emunim had the backing of so many politicians, we knew we shouldn’t touch them,” he said in his first interview for this article in 2016.
One leader of the ultraright movement would prove hard to ignore, however. Meir Kahane, an ultraright rabbi from Flatbush, Brooklyn, had founded the militant Jewish Defense League in 1968 in New York. He made no secret of his belief that violence was sometimes necessary to fulfill his dream of Greater Israel, and he even spoke of plans to buy .22 caliber rifles for Jews to defend themselves. “Our campaign motto will be, ‘Every Jew a .22,’” he declared. In 1971, he received a suspended sentence on bomb-making charges, and at the age of 39 he moved to Israel to start a new life. From a hotel on Zion Square in Jerusalem, he started a school and a political party, what would become Kach, and drew followers with his fiery rhetoric.
Kahane said he wanted to rewrite the stereotype of Jews as victims, and he argued, in often vivid terms, that Zionism and democracy are in fundamental tension. “Zionism came into being to create a Jewish state,” Kahane said in an interview with The Times in 1985, five years before he was assassinated by a gunman in New York. “Zionism declares that there is going to be a Jewish state with a majority of Jews, come what may. Democracy says, ‘No, if the Arabs are the majority then they have the right to decide their own fate.’ So Zionism and democracy are at odds. I say clearly that I stand with Zionism.”
A Buried Report
In 1977, the Likud party led a coalition that, for the first time in Israeli history, secured a right-wing majority in the country’s Parliament, the Knesset. The party was headed by Menachem Begin, a veteran of the Irgun, a paramilitary organization that carried out attacks against Arabs and British authorities in Mandatory Palestine, the British colonial entity that preceded the creation of Israel. Likud — Hebrew for “the alliance” — was itself an amalgam of several political parties. Kach itself was still on the outside and would always remain so. But its radical ideas and ambitions were moving closer to the mainstream.
Likud’s victory came 10 years after the war that brought Israel vast amounts of new land, but the issue of what to do with the occupied territories had yet to be resolved. As the new prime minister, Begin knew that addressing that question would mean addressing the settlements. Could there be a legal basis for taking the land? Something that would allow the settlements to expand with the full support of the state?
It was Plia Albeck, then a largely unknown bureaucrat in the Israeli Justice Ministry, who found Begin’s answer. Searching through the regulations of the Ottoman Empire, which ruled Palestine in the years preceding the British Mandate, she lit upon the Ottoman Land Code of 1858, a major effort at land reform. Among other provisions, the law enabled the sultan to seize any land that had not been cultivated by its owners for a number of years and that was not “within shouting distance” of the last house in the village. It did little to address the provisions of the Geneva Convention, but it was, for her department, precedent enough. Soon Albeck was riding in an army helicopter, mapping the West Bank and identifying plots of land that might meet the criteria of the Ottoman law. The Israeli state had replaced the sultan, but the effect was the same. Albeck’s creative legal interpretation led to the creation of more than 100 new Jewish settlements, which she referred to as “my children.”
At the same time, Begin was quietly brokering a peace deal with President Anwar Sadat of Egypt in the United States at Camp David. The pact they eventually negotiated gave the Sinai Peninsula back to Egypt and promised greater autonomy to Palestinians in the occupied territories in return for normalized relations with Israel. It would eventually win the two leaders a joint Nobel Peace Prize. But Gush Emunim and other right-wing groups saw the accords as a shocking reversal. From this well of anger sprang a new campaign of intimidation. Rabbi Moshe Levinger, one of the leaders of Gush Emunim and the founder of the settlement in the heart of Hebron, declared the movement’s purposes on Israeli television. The Arabs, he said, “must not be allowed to raise their heads.”
Leading this effort would be a militarized offshoot of Gush Emunim called the Jewish Underground. The first taste of what was to come arrived on June 2, 1980. Car bombs exploded as part of a complex assassination plot against prominent Palestinian political figures in the West Bank. The attack blew the legs off Bassam Shaka, the mayor of Nablus; Karim Khalaf, the mayor of Ramallah, was forced to have his foot amputated. Kahane, who in the days before the attack said at a news conference that the Israeli government should form a “Jewish terrorist group” that would “throw bombs and grenades to kill Arabs,” applauded the attacks, as did Rabbi Haim Druckman, a leader of Gush Emunim then serving in the Knesset, and many others within and outside the movement. Brig. Gen. Binyamin Ben-Eliezer, then the top I.D.F. commander in the West Bank, noting the injuries suffered by the Palestinian mayors under his watch, said simply, “It’s a shame they didn’t hit them a bit higher.” An investigation began, but it would be years before it achieved any results. Ben-Eliezer went on to become a leader of the Labor party and defense minister.
The threat that the unchecked attacks posed to the institutions and guardrails of Jewish democracy wasn’t lost on some members of the Israeli elite. As the violence spread, a group of professors at Tel Aviv University and Hebrew University in Jerusalem sent a letter to Yitzhak Zamir, Israel’s attorney general. They were concerned, they wrote, that illegal “private policing activity” against the Palestinians living in the occupied territories presented a “threat to the rule of law in the country.” The professors saw possible collusion between the settlers and the authorities. “There is a suspicion that similar crimes are not being handled in the same manner and some criminals are receiving preferential treatment over others,” the signatories to the letter said. “This suspicion requires fundamental examination.”
The letter shook Zamir, who knew some of the professors well. He was also well aware that evidence of selective law enforcement — one law for the Palestinians and another for the settlers — would rebut the Israeli government’s claim that the law was enforced equally and could become both a domestic scandal and an international one. Zamir asked Judith Karp, then Israel’s deputy attorney general for special duties, to lead a committee looking into the issue. Karp was responsible for handling the most delicate issues facing the Justice Ministry, but this would require even greater discretion than usual.
As her team investigated, Karp says, “it very quickly became clear to me that what was described in the letter was nothing compared to the actual reality on the ground.” She and her investigative committee found case after case of trespassing, extortion, assault and murder, even as the military authorities and the police did nothing or performed notional investigations that went nowhere. “The police and the I.D.F. in both action and inaction were really cooperating with the settler vandals,” Karp says. “They operated as if they had no interest in investigating when there were complaints, and generally did everything they could to deter the Palestinians from even submitting them.”
In May 1982, Karp and her committee submitted a 33-page report, determining that dozens of offenses were investigated insufficiently. The committee also noted that, in their research, the police had provided them with information that was incomplete, contradictory and in part false. They concluded that nearly half the investigations opened against settlers were closed without the police conducting even a rudimentary investigation. In the few cases in which they did investigate, the committee found “profound flaws.” In some cases, the police witnessed the crimes and did nothing. In others, soldiers were willing to testify against the settlers, but their testimonies and other evidence were buried.
It soon became clear to Karp that the government was going to bury the report. “We were very naïve,” she now recalls. Zamir had been assured, she says, that the cabinet would discuss the grave findings and had in fact demanded total confidentiality. The minister of the interior at the time, Yosef Burg, invited Karp to his home for what she recalls him describing as “a personal conversation.” Burg, a leader of the pro-settler National Religious Party, had by then served as a government minister in one office or another for more than 30 years. Karp assumed he wanted to learn more about her work, which could in theory have important repercussions for the religious right. “But, to my astonishment,” she says, “he simply began to scold me in harsh language about what we were doing. I understood that he wanted us to drop it.”
Karp announced she was quitting the investigative committee. “The situation we discovered was one of complete helplessness,” she says. When the existence of the report (but not its contents) leaked to the public, Burg denied having ever seen such an investigation. When the full contents of the report were finally made public in 1984, a spokesman for the Justice Ministry said only that the committee had been dissolved and that the ministry was no longer monitoring the problem.
A Wave of Violence
On April 11, 1982, a uniformed I.D.F. soldier named Alan Harry Goodman shot his way into the Dome of the Rock mosque in Jerusalem, one of the most sacred sites for Muslims around the world. Carrying an M16 rifle, standard issue in the Israeli Army, he killed two Arabs and wounded many more. When investigators searched Goodman’s apartment, they found fliers for Kach, but a spokesman for the group said that it did not condone the attack. Prime Minister Begin condemned the attack, but he also chastised Islamic leaders calling for a general strike in response, which he saw as an attempt to “exploit the tragedy.”
The next year, masked Jewish Underground terrorists opened fire on students at the Islamic College in Hebron, killing three people and injuring 33 more. Israeli authorities condemned the massacre but were less clear about who would be held to account. Gen. Ori Orr, commander of Israeli forces in the region, said on the radio that all avenues would be pursued. But, he added, “we don’t have any description, and we don’t know who we are looking for.”
The Jewish Department found itself continually behind in its efforts to address the onslaught. In April 1984, it had a major breakthrough: Its agents foiled a Jewish Underground plan to blow up five buses full of Palestinians, and they arrested around two dozen Jewish Underground members who had also played roles in the Islamic College attack and the bombings of the Palestinian mayors in 1980. But only after weeks of interrogating the suspects did Shin Bet learn that the Jewish Underground had been developing a scheme to blow up the Dome of the Rock mosque. The planning involved dozens of intelligence-gathering trips to the Temple Mount and an assessment of the exact amount of explosives that would be needed and where to place them. The goal was nothing less than to drag the entire Middle East into a war, which the Jewish Underground saw as a precondition for the coming of the messiah.
Carmi Gillon, who was head of Shin Bet’s Jewish Department at the time, says the fact that Shin Bet hadn’t learned about a plot involving so many people and such ambitious planning earlier was an “egregious intelligence failure.” And it was not the Shin Bet, he notes, who prevented the plot from coming to fruition. It was the Jewish Underground itself. “Fortunately for all of us, they decided to forgo the plan because they felt the Jewish people were not yet ready.”
“You have to understand why all this is important now,” Ami Ayalon said, leaning in for emphasis. The sun shining into the backyard of the former Shin Bet director was gleaming off his bald scalp, illuminating a face that looked as if it were sculpted by a dull kitchen knife. “We are not discussing Jewish terrorism. We are discussing the failure of Israel.”
Ayalon was protective of his former service, insisting that Shin Bet, despite some failures, usually has the intelligence and resources to deter and prosecute right-wing terrorism in Israel. And, he said, they usually have the will. “The question is why they are not doing anything about it,” he said. “And the answer is very simple. They cannot confront our courts. And the legal community finds it almost impossible to face the political community, which is supported by the street. So everything starts with the street.”
By the early 1980s, the settler movement had begun to gain some traction within the Knesset, but it remained far from the mainstream. When Kahane himself was elected to the Knesset in 1984, the members of the other parties, including Likud, would turn and leave the room when he stood up to deliver speeches. One issue was that the continual expansion of the settlements was becoming an irritant in U.S.-Israel relations. During a 1982 trip by Begin to Washington, the prime minister had a closed-door meeting with the Senate Committee on Foreign Relations to discuss Israel’s invasion of Lebanon that year, an effort to force out the P.L.O. that had been heavy with civilian casualties. According to The Times’s coverage of the session, Senator Joseph R. Biden Jr. of Delaware, then in his second term, had an angry exchange with Begin about the West Bank, telling him that Israel was losing support in this country because of the settlements policy.
But Israeli officials came to understand that the Americans were generally content to vent their anger about the issue without taking more forceful action — like restricting military aid to Israel, which was then, as now, central to the country’s security arrangements. After the Jewish Underground plotters of the bombings targeting the West Bank mayors and other attacks were finally brought to trial in 1984, they were found guilty and given sentences ranging from a few months to life in prison. The plotters showed little remorse, though, and a public campaign swelled to have them pardoned. Foreign Minister Yitzhak Shamir also made the case for pardoning them, saying they were “excellent, good people who have erred in their path and actions.” Clemency, Shamir suggested, would prevent a recurrence of Jewish terrorism.
In the end, President Chaim Herzog, against the recommendations of Shin Bet and the Justice Ministry, signed an extraordinary series of pardons and commutations for the plotters. They were released and greeted as heroes by the settler community, and some rose to prominent positions in government and the Israeli media. One of them, Uzi Sharbav, now a leader in the settlement movement, was a speaker at a recent conference promoting the return of settlers to Gaza.
In fact, nearly all the Jews involved in terror attacks against Arabs over the past decades have received substantial reductions in prison time. Gillon, the head of the Jewish Department when some of these people were arrested, recalls the “profound sense of injustice” that he felt when they were released. But even more important, he says, was “the question of what message the pardons convey to the public and to anyone who ever thinks about carrying out acts of terror against Arabs.”
Operational Failures
In 1987, a series of conflicts in Gaza led to a sustained Palestinian uprising throughout the occupied territories and Israel. The First Intifada, as it became known, was driven by anger over the occupation, which was then entering its third decade. It would simmer for the next six years, as Palestinians attacked Israelis with stones and Molotov cocktails and launched a series of strikes and boycotts. Israel deployed thousands of soldiers to quell the uprising.
In the occupied territories, reprisal attacks between settlers and Palestinians were an increasing problem. The Gush Emunim movement had spread and fractured into different groups, making it difficult for Shin Bet to embed enough informants with the settlers. But the service had one key informant — a man given the code name Shaul. He was a trusted figure among the settlers and rose to become a close assistant to Rabbi Moshe Levinger, the Gush Emunim leader who founded the settlement in Hebron.
Levinger had been questioned many times under suspicion of having a role in multiple violent attacks, but Shaul told Shin Bet operatives that they were seeing only a fraction of the whole picture. He told them about raids past and planned; about the settlers tearing through Arab villages, vandalizing homes, burning dozens of cars. The operatives ordered him to participate in these raids to strengthen his cover. One newspaper photographer in Hebron in 1985 captured Shaul smashing the wall of an Arab marketplace with a sledgehammer. As was standard policy, Shin Bet had ordered him to participate in any activity that didn’t involve harm to human life, but figuring out which of the activities wouldn’t cross that line became increasingly difficult. “The majority of the activists were lunatics, riffraff, and it was very difficult to be sure they wouldn’t hurt people and would harm only property,” Shaul said. (Shaul, whose true identity remains secret, provided these quotes in a 2015 interview with Bergman for the Israeli Hebrew-language paper Yedioth Ahronoth. Some of his account is published here for the first time.)
In September 1988, Rabbi Levinger, Shaul’s patron, was driving through Hebron when, he later said in court, Palestinians began throwing stones at his car and surrounding him. Levinger flashed a pistol and began firing wildly at nearby shops. Investigators said he killed a 42-year-old shopkeeper, Khayed Salah, who had been closing the steel shutter of his shoe store, and injured a second man. Levinger claimed self-defense, but he was hardly remorseful. “I know that I am innocent,” he said at the trial, “and that I didn’t have the honor of killing the Arab.”
Prosecutors cut a deal with Levinger. He was convicted of criminally negligent homicide, sentenced to five months in prison and released after only three.
Shin Bet faced the classic intelligence agency’s dilemma: how and when to let its informants participate in the very violent acts the service was supposed to be stopping. There was some logic in Shin Bet’s approach with Shaul, but it certainly didn’t help deter acts of terror in the West Bank, especially with little police presence in the occupied territories and a powerful interest group ensuring that whoever was charged for the violence was released with a light sentence.
Over his many years as a Shin Bet mole, Shaul said, he saw numerous intelligence and operational failures by the agency. One of the worst, he said, was the December 1993 murder of three Palestinians in an act of vengeance after the murder of a settler leader and his son. Driving home from a day of work in Israel, the three Palestinians, who had no connection to the deaths of the settlers, were pulled from their car and killed near the West Bank town Tarqumiyah.
Shaul recalled how one settler activist proudly told him that he and two friends committed the murders. He contacted his Shin Bet handlers to tell them what he had heard. “And suddenly I saw they were losing interest,” Shaul said. It was only later that he learned why: Two of the shooters were Shin Bet informants. The service didn’t want to blow their cover, or worse, to suffer the scandal that two of its operatives were involved in a murder and a cover-up.
In a statement, Shin Bet said that Shaul’s version of events is “rife with incorrect details” but refused to specify which details were incorrect. Neither the state prosecutor nor the attorney general responded to requests for comment, which included Shaul’s full version of events and additional evidence gathered over the years.
Shaul said he also gave numerous reports to his handlers about the activities of yet another Brooklyn-born follower of Meir Kahane and the Jewish Defense League: Dr. Baruch Goldstein. He earned his medical degree at Albert Einstein College of Medicine in the Bronx and in 1983 immigrated to Israel, where he worked first as a physician in the I.D.F., then as an emergency doctor at Kiryat Arba, a settlement near Hebron.
In the years that passed, he gained the attention of Shin Bet with his eliminationist views, calling Arabs “latter-day Nazis” and making a point to visit the Jewish terrorist Ami Popper in prison, where he was serving a sentence for the 1990 murder of seven Palestinians in the Tel Aviv suburb Rishon LeZion. Shaul said he regarded Goldstein at the time as a “charismatic and highly dangerous figure” and repeatedly urged the Shin Bet to monitor him. “They told me it was none of my business,” he said.
‘Clean Hands’
On Feb. 24, 1994, Goldstein abruptly fired his personal driver. According to Shaul, Goldstein told the driver that he knew he was a Shin Bet informer. Terrified at having been found out, the driver fled the West Bank immediately. Now Goldstein was moving unobserved.
That evening marked the beginning of Purim, the festive commemoration of the victory of the Jews over Haman the Agagite, a court official in the Persian Empire and the nemesis of the Jews in the Old Testament’s Book of Esther. Right-wing Israelis have often drawn parallels between Haman and Arabs — enemies who seek the annihilation of Jews. Goldstein woke early the next day and put on his I.D.F. uniform, and at 5:20 a.m. he entered the Cave of the Patriarchs, an ancient complex in Hebron that serves as a place of worship for both Jews and Muslims. Goldstein carried with him his I.D.F.-issued Galil rifle. It was also the Muslim holy month of Ramadan, and on that morning hundreds of Muslims crowded the hall in prayer. Goldstein faced the worshipers and began shooting , firing 108 rounds before he was dragged down and beaten to death. The massacre killed 29 Muslim worshipers and injured more than 100.
The killings shocked Israel, and the government responded with a crackdown on extremism. Kach and Kahane Chai, the two political organizations most closely affiliated with the Kahanist movement, were outlawed and labeled terrorist groups, as was any other party that called for “the establishment of a theocracy in the biblical Land of Israel and the violent expulsion of Arabs from that land.” Rabin, in an address to the Knesset, spoke directly to the followers of Goldstein and Kahane, who he said were the product of a malicious foreign influence on Israel. “You are not part of the community of Israel,” he said. “You are not partners in the Zionist enterprise. You are a foreign implant. You are an errant weed. Sensible Judaism spits you out. You placed yourself outside the wall of Jewish law.”
Following the massacre, a state commission of inquiry was appointed, headed by Judge Meir Shamgar, the president of the Supreme Court. The commission’s report, made public in June 1994, strongly criticized the security arrangements at the Cave of the Patriarchs and examined law-enforcement practices regarding settlers and the extreme right in general. A secret appendix to the report, containing material deemed too sensitive for public consumption, included a December 1992 letter from the Israeli commissioner of police, essentially admitting that the police could not enforce the law. “The situation in the districts is extremely bleak,” he wrote, using the administrative nomenclature for the occupied territories. “The ability of the police to function is far from the required minimum. This is as a result of the lack of essential resources.”
In its conclusions, the commission, tracing the lines of the previous decade’s Karp report, confirmed claims that human rights organizations had made for years but that had been ignored by the Israeli establishment. The commission found that Israeli law enforcement was “ineffective in handling complaints,” that it delayed the filing of indictments and that restraining orders against “chronic” criminals among the “hard core” of the settlers were rarely issued.
The I.D.F. refused to allow Goldstein to be buried in the Jewish cemetery in Hebron. He was buried instead in the Kiryat Arba settlement, in a park named for Meir Kahane, and his gravesite has become an enduring place of pilgrimage for Jews who wanted to celebrate, as his epitaph reads, the “saint” who died for Israel with “clean hands and a pure heart.”
A Curse of Death
One ultranationalist settler who went regularly to Goldstein’s grave was a teenage radical named Itamar Ben-Gvir, who would sometimes gather other followers there on Purim to celebrate the slain killer. Purim revelers often dress in costume, and on one such occasion, caught on video, Ben-Gvir even wore a Goldstein costume, complete with a fake beard and a stethoscope. By then, Ben-Gvir had already come to the attention of the Jewish Department, and investigators interrogated him several times. The military declined to enlist him into the service expected of most Israeli citizens.
After the massacre at the Cave of the Patriarchs, a new generation of Kahanists directed their anger squarely at Rabin for his signing of the Oslo agreement and for depriving them, in their view, of their birthright. “From my standpoint, Goldstein’s action was a wake-up call,” says Hezi Kalo, a longtime senior Shin Bet official who oversaw the division that included the Jewish Department at that time. “I realized that this was going to be a very big story, that the diplomatic moves by the Rabin government would simply not pass by without the shedding of blood.”
The government of Israel was finally paying attention to the threat, and parts of the government acted to deal with it. Shin Bet increased the size of the Jewish Department, and it began to issue a new kind of warning: Jewish terrorists no longer threatened only Arabs. They threatened Jews.
The warnings noted that rabbis in West Bank settlements, along with some politicians on the right, were now openly advocating violence against Israeli public officials, especially Rabin. Extremist rabbis issued rulings of Jewish law against Rabin — imposing a curse of death, a Pulsa Dinura , and providing justification for killing him, a din rodef .
Carmi Gillon by then had moved on from running the Jewish Department and now had the top job at Shin Bet. “Discussing and acknowledging such halakhic laws was tantamount to a license to kill,” he says now, looking back. He was particularly concerned about Benjamin Netanyahu and Ariel Sharon, who were stoking the fury of the right-wing rabbis and settler leaders in their battles with Rabin.
Shin Bet wanted to prosecute rabbis who approved the religiously motivated death sentences against Rabin, but the state attorney’s office refused. “They didn’t give enough importance back then to the link between incitement and legitimacy for terrorism,” says one former prosecutor who worked in the state attorney’s office in the mid-1990s.
Shin Bet issued warning after warning in 1995. “This was no longer a matter of mere incitement, but rather concrete information on the intention to kill top political figures, including Rabin,” Kalo now recalls. In October of that year, Ben-Gvir spoke to Israeli television cameras holding up a Cadillac hood ornament, which he boasted he had broken off the prime minister’s official car during chaotic anti-Oslo demonstrations in front of the Knesset. “We got to his car,” he said, “and we’ll get to him, too.” The following month, Rabin was dead.
Conspiracies
Yigal Amir, the man who shot and killed Rabin in Tel Aviv after a rally in support of the Oslo Accords on Nov. 4, 1995, was not unknown to the Jewish Department. A 25-year-old studying law, computer science and the Torah at Bar-Ilan University near Tel Aviv, he had been radicalized by Rabin’s efforts to make peace with Palestinian leaders and had connections to Avishai Raviv, the leader of Eyal, a new far-right group loosely affiliated with the Kach movement. In fact, Raviv was a Shin Bet informant, code-named Champagne. He had heard Amir talking about the justice of the din rodef judgments, but he did not identify him to his handlers as an immediate danger. “No one took Yigal seriously,” he said later in a court proceeding. “It’s common in our circles to talk about attacking public figures.”
Lior Akerman was the first Shin Bet investigator to interrogate Amir at the detention center where he was being held after the assassination. There was of course no question about his guilt. But there was the broader question of conspiracy. Did Amir have accomplices? Did they have further plans? Akerman now recalls asking Amir how he could reconcile his belief in God with his decision to murder the prime minister of Israel. Amir, he says, told him that rabbis had justified harming the prime minister in order to protect Israel.
Amir was smug, Akerman recalls, and he did not respond directly to the question of accomplices. “‘Listen,” he said, according to Akerman, “I succeeded . I was able to do something that many people wanted but no one dared to do. I fired a gun that many Jews held, but I squeezed the trigger because no one else had the courage to do it.”
The Shin Bet investigators demanded to know the identities of the rabbis. Amir was coy at first, but eventually the interrogators drew enough out of him to identify at least two of them. Kalo, the head of the division that oversaw the Jewish Department, went to the attorney general to argue that the rabbis should be detained immediately and prosecuted for incitement to murder. But the attorney general disagreed, saying the rabbis’ encouragement was protected speech and couldn’t be directly linked to the murder. No rabbis were arrested.
Days later, however, the police brought Raviv — the Shin Bet operative known as Champagne — into custody in a Tel Aviv Magistrate Court, on charges that he had conspired to kill Rabin, but he was released shortly after. Raviv’s role as an informant later came to light, and in 1999, he was arrested for his failure to act on previous knowledge of the assassination. He was acquitted on all charges, but he has since become a fixture of extremist conspiracy theories that pose his failure to ring the alarm as evidence that the murder of the prime minister was due not to the violent rhetoric of the settler right, or the death sentences from the rabbis, or the incitement by the leaders of the opposition, but to the all-too-successful efforts of a Shin Bet agent provocateur. A more complicated and insidious conspiracy theory, but no less false, was that it was Shin Bet itself that assassinated Rabin or allowed the assassination to happen.
Gillon, the head of the service at the time, resigned, and ongoing inquiries, charges and countercharges would continue for years. Until Oct. 7, 2023, the killing of the prime minister was considered the greatest failure in the history of Shin Bet. Kalo tried to sum up what went wrong with Israeli security. “The only answer my friends and I could give for the failure was complacency,” he wrote in his 2021 memoir. “They simply couldn’t believe that such a thing could happen, definitely not at the hands of another Jew.”
The Sasson Report
In 2001, as the Second Intifada unleashed a wave of Palestinian suicide bombings against Israeli civilians, Ariel Sharon took office as prime minister. The struggling peace process had come to a complete halt amid the violence, and Sharon’s rise at first appeared to mark another victory for the settlers. But in 2003, in one of the more surprising reversals in Israeli political history, Sharon announced what he called Israel’s “disengagement” from Gaza, with a plan to remove settlers — forcibly if necessary — over the next two years.
The motivations were complex and the subject of considerable debate. For Sharon, at least, it appeared to be a tactical move. “The significance of the disengagement plan is the freezing of the peace process,” his senior adviser Dov Weisglass told Haaretz at the time. “And when you freeze that process, you prevent the establishment of a Palestinian state.” But Sharon was also facing considerable pressure from President George W. Bush to do something about the ever-expanding illegal settlements in the West Bank, which were a growing impediment to any regional security deals. In July 2004, he asked Talia Sasson, who had recently retired as the head of the special tasks division in the state attorney’s office, to draw up a legal opinion on the subject of “unauthorized outposts” in the West Bank. His instructions were clear: Investigate which Israeli government agencies and authorities were secretly involved in building the outposts. “Sharon never interfered in my work, and neither was he surprised by the conclusions,” Sasson said in an interview two decades later. “After all, he knew better than anyone what the situation was on the ground, and he was expecting only grave conclusions.”
It was a simple enough question: Just how had it happened that hundreds of outposts had been built in the decade since Yitzhak Rabin ordered a halt in most new settlements? But Sasson’s effort to find an answer was met with delays, avoidance and outright lies. Her final report used careful but pointed language: “Not everyone I turned to agreed to talk with me. One claimed he was too busy to meet, while another came to the meeting but refused to meaningfully engage with most of my questions.”
Sasson found that between January 2000 and June 2003, a division of Israel’s Construction and Housing Ministry issued 77 contracts for the establishment of 33 sites in the West Bank, all of which were illegal. In some cases, the ministry even paid for the paving of roads and the construction of buildings at settlements for which the Defense Ministry had issued demolition orders.
Several government ministries concealed the fact that funds were being diverted to the West Bank, reporting them under budgetary clauses such as “miscellaneous general development.” Just as in the case of the Karp Report two decades earlier, Sasson and her Justice Ministry colleagues discovered that the West Bank was being administered under completely separate laws, and those laws, she says, “appeared to me utterly insane.”
Sasson’s report took special note of Avi Maoz, who ran the Construction and Housing Ministry during most of this period. A political activist who early in his career spoke openly of pushing all Arabs out of the West Bank, Maoz helped found a settlement south of Jerusalem during the 1990s and began building a professional alliance with Benjamin Netanyahu, who was then the Israeli ambassador to the United Nations and would soon go on to his first term as prime minister. Years later, Maoz would be instrumental in ensuring Netanyahu’s political survival.
“The picture that emerges in the eye of the beholder is severe,” Sasson wrote in her report. “Instead of the government of Israel deciding on the establishment of settlements in the territories of Judea and Samaria, its place has been taken, from the mid-1990s and onward, by others.” The settlers, she wrote, were “the moving force,” but they could not have succeeded without the assistance of “various ministers of construction and housing in the relevant periods, some of them with a blind eye, and some of them with support and encouragement.”
This clandestine network was operating, Sasson wrote, “with massive funding from the State of Israel, without appropriate public transparency, without obligatory criteria. The erection of the unauthorized outposts is being done with violation of the proper procedures and general administrative rules, and in particular, flagrant and ongoing violation of the law.” These violations, Sasson warned, were coming from the government: “It was state and public agencies that broke the law, the rules, the procedures that the state itself had determined.” It was a conflict, she argued, that effectively neutered Israel’s internal checks and balances and posed a grave threat to the nation’s integrity. “The law-enforcement agencies are unable to act against government departments that are themselves breaking the law.”
But, in an echo of Judith Karp’s secret report decades earlier, the Sasson Report, made publicly available in March 2005, had almost no impact. Because she had a mandate directly from the prime minister, Sasson could have believed that her investigation might lead to the dismantling of the illegal outposts that had metastasized throughout the Palestinian territories. But even Sharon, with his high office, found himself powerless against the machine now in place to protect and expand the settlements in the West Bank — the very machine he had helped to build.
All of this was against the backdrop of the Gaza pullout. Sharon, who began overseeing the removal of settlements from Gaza in August 2005, was the third Israeli prime minister to threaten the settler dream of a Greater Israel, and the effort drew bitter opposition not only from the settlers but also from a growing part of the political establishment. Netanyahu, who had served his first term as prime minister from 1996 to 1999, and who previously voted in favor of a pullout, resigned his position as finance minister in Sharon’s cabinet in protest — and in anticipation of another run for the top job.
The settlers themselves took more active measures. In 2005, the Jewish Department of Shin Bet received intelligence about a plot to slow the Israeli withdrawal from Gaza by using 700 liters of gasoline to blow up vehicles on a major highway. Acting on the tip, officers arrested six men in central Israel. One of them was Bezalel Smotrich, the future minister overseeing civilian affairs in the West Bank.
Smotrich, then 25, was detained and questioned for weeks. Yitzhak Ilan, one of the Shin Bet officers present at the interrogation, says he remained “silent as a fish” throughout — “like an experienced criminal.” He was released without charges, Ilan says, in part because Shin Bet knew putting him on trial might expose the service’s agents inside Jewish extremist groups, and in part because they believed Smotrich was likely to receive little punishment in any case. Shin Bet was very comfortable with the courts when we fought Palestinian terrorism and we got the heavy punishments we wanted, he says. With the Jewish terrorists it was exactly the opposite.
When Netanyahu made his triumphant return as prime minister in 2009, he set out to undermine Talia Sasson’s report, which he and his allies saw as an obstacle to accelerating the settlement campaign. He appointed his own investigative committee, led by Judge Edmond Levy of the Supreme Court, who was known to support the settler cause. But the Levy report, completed in 2012, did not undermine the findings in the Sasson Report — in some ways, it reinforced them. Senior Israeli officials, the committee found, were fully aware of what was happening in the territories, and they were simply denying it for the sake of political expediency. The behavior, they wrote, was not befitting of “a country that has proclaimed the rule of law as a goal.” Netanyahu moved on.
A NEW GENERATION
The ascent of a far-right prime minister did little to prevent the virulent, anti-government strain inside the settler movement from spreading. A new generation of Kahanists was taking an even more radical turn, not only against Israeli politicians who might oppose or insufficiently abet them but against the very notion of a democratic Israeli state. A group calling itself Hilltop Youth advocated for the total destruction of the Zionist state. Meir Ettinger, named for his grandfather Meir Kahane, was one of the Hilltop Youth leaders, and he made his grandfather’s views seem moderate.
Their objective was to tear down Israel’s institutions and to establish “Jewish rule”: anointing a king, building a temple in place of the Jerusalem mosques sacred to Muslims worldwide, imposing a religious regime on all Jews. Ehud Olmert, who served as Israeli prime minister from 2006 to 2009, said in an interview that Hilltop Youth “genuinely, deeply, emotionally believe that this is the right thing to do for Israel. This is a salvation. This is the guarantee for Israel’s future.”
A former member of Hilltop Youth, who has asked to remain anonymous because she fears speaking out could endanger her, recalls how she and her friends used an illegal outpost on a hilltop in the West Bank as a base to lob stones at Palestinian cars. “The Palestinians would call the police, and we would know that we have at least 30 minutes before they arrive, if they arrive. And if they do arrive, they won’t arrest anyone. We did this tens of times.” The West Bank police, she says, couldn’t have been less interested in investigating the violence. “When I was young, I thought that I was outsmarting the police because I was clever. Later, I found out that they are either not trying or very stupid.”
The former Hilltop Youth member says she began pulling away from the group as their tactics became more extreme and once Ettinger began speaking openly about murdering Palestinians. She offered to become a police informant, and during a meeting with police intelligence officers in 2015, she described the group’s plans to commit murder — and to harm any Jews that stood in their way. By her account, she told the police about efforts to scout the homes of Palestinians before settling on a target. The police could have begun an investigation, she says, but they weren’t even curious enough to ask her the names of the people plotting the attack.
In 2013, Ettinger and other members of Hilltop Youth formed a secret cell calling itself the Revolt, designed to instigate an insurrection against a government that “prevents us from building the temple, which blocks our way to true and complete redemption.”
During a search of one of the group’s safe houses, Shin Bet investigators discovered the Revolt’s founding documents. “The State of Israel has no right to exist, and therefore we are not bound by the rules of the game,” one declared. The documents called for an end to the State of Israel and made it clear that in the new state that would rise in its place, there would be absolutely no room for non-Jews and for Arabs in particular: “If those non-Jews don’t leave, it will be permissible to kill them, without distinguishing between women, men and children.”
This wasn’t just idle talk. Ettinger and his comrades organized a plan that included timetables and steps to be taken at each stage. One member even composed a training manual with instructions on how to form terror cells and burn down houses. “In order to prevent the residents from escaping,” the manual advised, “you can leave burning tires in the entrance to the house.”
The Revolt carried out an early attack in February 2014, firebombing an uninhabited home in a small Arab village in the West Bank called Silwad, and followed with more arson attacks, the uprooting of olive groves and the destruction of Palestinian granaries. Members of the group torched mosques, monasteries and churches, including the Church of the Multiplication of the Loaves and Fishes on the banks of the Sea of Galilee. A police officer spotted Ettinger himself attacking a herd of sheep belonging to an Arab shepherd. He stoned a sheep and then slaughtered it in front of the shepherd, the officer later testified. “It was shocking,” he said. “There was a sort of insanity in it.”
Shin Bet defined the Revolt as an organization that aimed “to undermine the stability of the State of Israel through terror and violence, including bodily harm and bloodshed,” according to an internal Shin Bet memo, and sought to place several of its members, including Ettinger, under administrative detention — a measure applied frequently against Arabs.
The state attorney, however, did not approve the request. The U.N. Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) documented 323 incidents of violence by settlers against Palestinians in 2014; Palestinians were injured in 107 of these incidents. By the following year, the Revolt escalated the violence by openly advocating the murder of Arabs.
The Shin Bet and the police identified one of the prominent members of the Revolt, Amiram Ben-Uliel, making him a target of surveillance. But the service failed to prevent the wave of violence that he unleashed. On the night of July 31, 2015, Ben-Uliel set out on a killing spree in a central West Bank village called Duma. Ben-Uliel prepared a bag with two bottles of incendiary liquid, rags, a lighter, a box of matches, gloves and black spray paint. According to the indictment against him, Ben-Uliel sought a home with clear signs of life to ensure that the house he torched was not abandoned. He eventually found the home of Reham and Sa’ad Dawabsheh, a young mother and father. He opened a window and threw a Molotov cocktail into the home. He fled, and in the blaze that followed, the parents suffered injuries that eventually killed them. Their older son, Ahmad, survived the attack, but their 18-month-old toddler, Ali, was burned to death.
It was always clear, says Akerman, the former Shin Bet official, “that those wild groups would move from bullying Arabs to damaging property and trees and eventually would murder people.” He is still furious about how the service has handled Jewish terrorism. “Shin Bet knows how to deal with such groups, using emergency orders, administrative detention and special methods in interrogation until they break,” he says. But although it was perfectly willing to apply those methods to investigating Arab terrorism, the service was more restrained when it came to Jews. “It allowed them to incite, and then they moved on to the next stage and began to torch mosques and churches. Still undeterred, they entered Duma and burned a family.”
Shin Bet at first claimed to have difficulty locating the killers, even though they were all supposed to be under constant surveillance. When Ben-Uliel and other perpetrators were finally arrested, right-wing politicians gave fiery speeches against Shin Bet and met with the families of the perpetrators to show their support. Ben-Uliel was sentenced to life in prison, and Ettinger was finally put in administrative detention, but a fracture was spreading. In December 2015, Hilltop Youth members circulated a video clip showing members of the Revolt ecstatically dancing with rifles and pistols, belting out songs of hatred for Arabs, with one of them stabbing and burning a photograph of the murdered toddler, Ali Dawabsheh. Netanyahu, for his part, denounced the video, which, he said, exposed “the real face of a group that poses danger to Israeli society and security.”
American Friends
The expansion of the settlements had long been an irritant in Israel’s relationship with the United States, with American officials spending years dutifully warning Netanyahu both in public and in private meetings about his support for the enterprise. But the election of Donald Trump in 2016 ended all that. His new administration’s Israel policy was led mostly by his son-in-law, Jared Kushner, who had a long personal relationship with Netanyahu, a friend of his father’s who had stayed at their family home in New Jersey. Trump, in a broader regional agenda that lined up perfectly with Netanyahu’s own plans, also hoped to scuttle the nuclear deal with Iran that Barack Obama had negotiated and broker diplomatic pacts between Israel and Arab nations that left the matter of a Palestinian state unresolved and off the table.
If there were any questions about the new administration’s position on settlements, they were answered once Trump picked his ambassador to Israel. His choice, David Friedman, was a bankruptcy lawyer who for years had helped run an American nonprofit that raised millions of dollars for Beit El, one of the early Gush Emunim settlements in the West Bank and the place where Bezalel Smotrich was raised and educated. The organization, which was also supported by the Trump family, had helped fund schools and other institutions inside Beit El. On the heels of the Trump transition, Friedman referred to Israel’s “alleged occupation” of Palestinian territories and broke with longstanding U.S. policy by saying “the settlements are part of Israel.”
This didn’t make Friedman a particularly friendly recipient of the warnings regularly delivered by Lt. Gen. Mark Schwartz, the three-star general who in 2019 arrived at the embassy in Jerusalem to coordinate security between the Israeli government and the Palestinian Authority. A career Green Beret who had combat deployments in Afghanistan and Iraq and served as deputy commander of the Joint Special Operations Command, the military task force with authority over U.S. counterterrorism special missions units, Schwartz wasn’t short on Middle East experience.
But he was immediately shocked by the landscape of the West Bank: settlers acting with impunity, a police force that was essentially nonexistent outside the settlements and the Israeli Army fanning the tensions with its own operations. Schwartz recalls how angry he was about what he called the army’s “collective punishment” tactics, including the razing of Palestinian homes, which he viewed as gratuitous and counterproductive. “I said, ‘Guys, this isn’t how professional militaries act.’” As Schwartz saw it, the West Bank was in some ways the American South of the 1960s. But at any moment the situation could become even more volatile, resulting in the next intifada.
Schwartz is diplomatic when recalling his interactions with Friedman, his former boss. He was a “good listener,” Schwartz says, but when he raised concerns about the settlements, Friedman would often deflect by noting “the lack of appreciation by the Palestinian people about what the Americans are doing for them.” Schwartz also discussed his concerns about settler violence directly with Shin Bet and I.D.F. officials, he says, but as far as he could tell, Friedman didn’t follow up with the political leadership. “I never got the sense he went to Netanyahu to discuss it.”
Friedman sees things differently. “I think I had a far broader perspective on acts of violence in Judea and Samaria” than Schwartz, he says now. “And it was clear that the violence coming from Palestinians against Israelis overwhelmingly was more prevalent.” He says he “wasn’t concerned about ‘appreciation’ from the Palestinians; I was concerned by their leadership’s embrace of terror and unwillingness to control violence.” He declined to discuss any conversations he had with Israeli officials.
Weeks after Trump lost the 2020 election, Secretary of State Mike Pompeo traveled to Israel for a trip that delivered a number of gifts to Netanyahu and the settler cause. He announced new guidelines requiring that goods imported to the United States from parts of the West Bank be labeled “Made in Israel.” And he flew by helicopter to Psagot, a winery in the West Bank, making him the first American secretary of state to visit a settlement. One of the winery’s large shareholders, the Florida-based Falic family, have donated millions to various projects in the settlements.
During his lunchtime visit, Pompeo paused to write a note in the winery’s guest book. “May I not be the last secretary of state to visit this beautiful land,” he wrote.
A Settler Coalition
Benjamin Netanyahu’s determination to become prime minister for an unprecedented sixth term came with a price: an alliance with a movement that he once shunned, but that had been brought into the political mainstream by Israel’s steady drift to the right. Netanyahu, who is now on trial for bribery and other corruption charges, repeatedly failed in his attempts to form a coalition after most of the parties announced that they were no longer willing to join him. He personally involved himself in negotiations to ally Itamar Ben-Gvir’s Jewish Power party and Bezalel Smotrich’s Religious Zionism Party, making them kingmakers for anyone trying to form a coalition government. In November 2022, the bet paid off: With the now-critical support of the extreme right, Netanyahu returned to office.
The two men ushered into power by this arrangement were some of the most extreme figures ever to hold such high positions in an Israeli cabinet. Shin Bet had monitored Ben-Gvir in the years after Yitzhak Rabin’s murder, and he was arrested on multiple charges including inciting racism and supporting a terrorist organization. He won acquittals or dismissals in some of the cases, but he was also convicted several times and served time in prison. During the Second Intifada, he led protests calling for extreme measures against Arabs and harassed Israeli politicians he believed were insufficiently hawkish.
Then Ben-Gvir made a radical change: He went to law school. He also took a job as an aide to Michael Ben-Ari, a Knesset member from the National Union party, which had picked up many followers of the Kach movement. In 2011, after considerable legal wrangling around his criminal record, he was admitted to the bar. He changed his hairstyle and clothing to appear more mainstream and began working from the inside, once saying he represented the “soldiers and civilians who find themselves in legal entanglements due to the security situation in Israel.” Netanyahu made him minister of national security, with authority over the police.
Smotrich also moved into public life after his 2005 arrest by Shin Bet for plotting road blockages to halt the Israeli withdrawal from Gaza. He made Shin Bet’s Jewish Department a frequent target of criticism, complaining that it was wasting time and money investigating crimes carried out by Jews, when the real terrorists were Palestinians. His ultraright allies sometimes referred to the Jewish Department as Hamakhlaka Hayehudit — the Hebrew phrase for the Gestapo unit that executed Hitler’s Final Solution.
In 2015, while campaigning for a seat in the Knesset, Smotrich said that “every shekel invested in this department is one less shekel invested in real terrorism and saving lives.” Seven years later, Netanyahu made him both minister of finance and a minister in the Ministry of Defense, in charge of overseeing civilian affairs in the West Bank, and he has steadily pushed to seize authority over the territory from the military. As part of the coalition deal with Netanyahu, Smotrich now has the authority to appoint one of the senior administrative figures in the West Bank, who helps oversee the building of roads and the enforcement of construction laws. The 2022 election also brought Avi Maoz to the Knesset — the former housing-ministry official whom Talia Sasson once marked as a hidden hand of Israeli government support for illegal settlements. Since then, Maoz had joined the far-right Noam party, using it as a platform to advance racist and homophobic policies. And he never forgot, or forgave, Sasson. On “International Anti-Corruption Day” in 2022, Maoz took to the lectern of the Knesset and denounced Sasson’s report of nearly two decades earlier, saying it was written “with a hatred of the settlements and a desire to harm them.” This, he said, was “public corruption of the highest order, for which people like Talia Sasson should be prosecuted.”
Days after assuming his own new position, Ben-Gvir ordered the police to remove Palestinian flags from public spaces in Israel, saying they “incite and encourage terrorism.” Smotrich, for his part, ordered drastic cuts in payments to the Palestinian Authority — a move that led the Shin Bet and the I.D.F. intelligence division to raise concerns that the cuts would interfere with the Palestinian Authority’s own efforts to police and prevent Palestinian terrorism.
Weeks after the new cabinet was sworn in, the Judea and Samaria division of the I.D.F. distributed an instructional video to the soldiers of a ground unit about to be deployed in the West Bank. Titled “Operational Challenge: The Farms,” the video depicts settlers as peaceful farmers living pastoral lives, feeding goats and herding sheep and cows, in dangerous circumstances. The illegal outposts multiplying around the West Bank are “small and isolated places of settlement, each with a handful of residents, a few of them — or none at all — bearing arms, the means of defense meager or nonexistent.”
It is the settlers, according to the video, who are under constant threat of attack, whether it be “penetration of the farm by a terrorist, an attack against a shepherd in the pastures, arson” or “destruction of property” — threats from which the soldiers of the I.D.F. must protect them. The commander of each army company guarding each farm must, the video says, “link up with the person in charge of security and to maintain communications”; soldiers and officers are encouraged to cultivate a close and intimate relationship with the settlers. “The informal,” viewers are told, “is much more important than the formal.”
The video addresses many matters of security, but it never addresses the question of law. When we asked the commander of the division that produced the video, Brig. Gen. Avi Bluth, why the I.D.F. was promoting the military support of settlements that are illegal under Israeli law, he directly asserted that the farms were indeed legal and offered to arrange for us to tour some of them. Later, a spokesman for the army apologized for the general’s remarks, acknowledged that the farms were illegal and announced that the I.D.F. would no longer be promoting the video. This May, Bluth was nonetheless subsequently promoted to head Israel’s Central Command, responsible for all Israeli troops in central Israel and the West Bank.
In August, Bluth will replace Maj. Gen. Yehuda Fox, who during his final months in charge of the West Bank has seen a near-total breakdown of law enforcement in his area of command. In late October, Fox wrote a letter to his boss, the chief of Israel’s military staff, saying that the surge of Jewish terrorism carried out in revenge for the Oct. 7 attacks “could set the West Bank on fire.” The I.D.F. is the highest security authority in the West Bank, but the military’s top commander put the blame squarely on the police — who ultimately answer to Ben-Gvir. Fox said he had established a special task force to deal with Jewish terrorism, but investigating and arresting the perpetrators is “entirely in the hands of the Israeli police.”
And, he wrote, they aren’t doing their jobs.
‘Only One Way Forward’
When the day came early this January for the Supreme Court to hear the case brought by the people of Khirbet Zanuta, the displaced villagers arrived an hour late. They had received entry permits from the District Coordination Office to attend the hearing but were delayed by security forces before reaching the checkpoint separating Israel from the West Bank. Their lawyer, Quamar Mishirqi-Assad, noting that their struggle to attend their own hearing spoke to the essence of their petition, insisted that the hearing couldn’t proceed without them. The judges agreed to wait.
The villagers finally were led into the courtroom, and Mishirqi-Assad began presenting the case. The proceedings were in Hebrew, so most of the villagers were unable to follow the arguments that described the daily terrors inflicted by settlers and the glaring absence of any law-enforcement efforts to stop them.
The lawyers representing the military and the police denied the claims of abuse and failure to enforce the law. When a judge asked what operational steps would be in place if villagers wanted to return, one of the lawyers for the state said they could already — there was no order preventing them from doing so.
The next to speak was Col. Roi Zweig-Lavi, the Central Command’s Operations Directorate officer. He said that many of these incidents involved false claims. In fact, he said, some of the villagers had probably destroyed their own homes, because of an “internal issue.” Now they were blaming the settlers to escape the consequences of their own actions.
Colonel Zweig-Lavi’s own views about the settlements, and his role in protecting them, were well known. In a 2022 speech, he told a group of yeshiva students in the West Bank that “the army and the settlements are one and the same.”
In early May, the court ordered the state to explain why the police failed to stop the attacks and declared that the villagers have a right to return to their homes. The court also ordered the state to provide details for how they would ensure the safe return of the villagers. It is now the state’s turn to decide how it will comply. Or if it will comply.
By the time the Supreme Court issued its rulings, the United States had finally taken action to directly pressure the Netanyahu government about the violent settlers. On Feb. 1, the White House issued an executive order imposing sanctions on four settlers for “engaging in terrorist activity,” among other things, in the West Bank. One of the four was Yinon Levi, the owner of Meitarim Farm near Hebron and the man American and Israeli officials believe orchestrated the campaign of violence and intimidation against the villagers of Khirbet Zanuta. The British government issued its own sanctions shortly after, saying in a statement that Israel’s government had created “an environment of near-total impunity for settler extremists in the West Bank.”
The White House’s move against individual settlers, a first by an American administration, was met with a combination of anger and ridicule by ministers in Netanyahu’s government. Smotrich called the Biden administration’s allegations against Levi and others “utterly specious” and said he would work with Israeli banks to resist complying with the sanctions. One message that circulated in an open Hilltop Youth WhatsApp channel said that Levi and his family would not be abandoned. “The people of Israel are mobilizing for them,” it said.
American officials bristle when confronted with the question of whether the government’s actions are just token measures taken by an embattled American president hemorrhaging support at home for his Israel policy. They won’t end the violence, they say, but they are a signal to the Netanyahu government about the position of the United States: that the West Bank could boil over, and it could soon be the latest front of an expanding regional Middle East war since Oct. 7.
But war might just be the goal. Ehud Olmert, the former Israeli prime minister, said he believes that many members of the ultraright in Israel “want war.” They “want intifada,” he says, “because it is the ultimate proof that there is no way of making peace with the Palestinians and there is only one way forward — to destroy them.”
Additional reporting by Natan Odenheimer.
Top photograph: A member of a group known as Hilltop Youth, which seeks to tear down Israel’s institutions and establish ‘‘Jewish rule.’’ Photograph by Peter van Agtmael/Magnum, for The New York Times.
Read by Jonathan Davis
Narration produced by Anna Diamond
Engineered by David Mason
Peter van Agtmael is a Magnum photographer who has been covering Israel and Palestinian territories since 2012. He is a mentor in the Arab Documentary Photography Program.
Ronen Bergman is a staff writer for The New York Times Magazine, based in Tel Aviv. His latest book is “Rise and Kill First: The Secret History of Israel’s Targeted Assassinations,” published by Random House. More about Ronen Bergman
Mark Mazzetti is an investigative reporter based in Washington, D.C., focusing on national security, intelligence, and foreign affairs. He has written a book about the C.I.A. More about Mark Mazzetti
Our Coverage of the Israel-Hamas War
News and Analysis
Israel said that it would send more troops to Rafah, the southernmost city in Gaza and the current focal point in the war between Israel and Hamas. Fighting in the city has closed off a vital border crossing, forced hundreds of thousands to flee and cut off humanitarian aid.
President Biden is pushing for a broad deal that would get Israel to approve a Palestinian nation in return for Saudi recognition of Israel. But officials need to overcome Israeli opposition.
The Arab League called for a United Nations peacekeeping force to be deployed in the Gaza Strip and the Israeli-occupied West Bank until a two-state solution can be negotiated , in a statement that also called for the U.N. Security Council to set a time limit for that process.
FIFA Delays a Vote: Soccer’s global governing body postponed a decision to temporarily suspend Israel over its actions in Gaza, saying it needed to solicit legal advice before taking up a motion submitted by the Palestinian Football Association.
PEN America’s Literary Gala: The free-expression group has been engulfed by debate over its response to the Gaza war that forced the cancellation of its literary awards and annual festival. But its literary gala went on as planned .
Jerusalem Quartet Will Perform: The Concertgebouw in Amsterdam, one of the world’s most prestigious concert halls, said that it would allow the Jerusalem Quartet to perform , two days after it had canceled the ensemble’s concerts amid security concerns.
A Key Weapon: When President Biden threatened to pause some weapons shipments to Israel if it invaded Rafah, the devastating effects of the 2,000-pound Mark 84 bomb were of particular concern to him.
Advertisement

COMMENTS
One of the primary benefits of school uniforms is their ability to promote a sense of equality among students. When all students are required to wear the same uniform, there is less opportunity for socioeconomic differences to be displayed through clothing. This can help to reduce the pressure on students to wear expensive or fashionable ...
Yeung, Ryan. Educational Policy, 2009, Vol. 23. doi: 10.1177/0895904808330170. Abstract: "One of the most common proposals put forth for reform of the American system of education is to require school uniforms. Proponents argue that uniforms can make schools safer and also improve school attendance and increase student achievement.
13 Advantages to Wearing School Uniforms. Put these 13 factors together and it's easy to see why school uniforms are important to creating a team of united students and staff. 1. Create cohesion. When students all wear the same clothing every day at school, it levels out the playing field.
School uniforms deter crime and increase student safety. In Long Beach, California, after two years of a district-wide K-8 mandatory uniform policy, reports of assault and battery in the district's schools decreased by 34%, assault with a deadly weapon dropped by 50%, fighting incidents went down by 51%, sex offenses were cut by 74%, robbery ...
The first reason why school uniforms are good is that they help not to judge students by their clothes. This eliminates comparing each other for what they wear based on their family income. As a result, it promotes equality. Moreover, it prevents financial violence and stops gang activity. Second, it is very affordable.
How to write an essay on a school uniform? Answer: Start with an introduction, discuss the debate going on school uniforms by students, write the cons and pros of school uniforms. Explains the advantages and changes that wearing a school uniform can bring in students. End the essay with a conclusion. Question 3. What is good about school ...
Here are some key ideas you can incorporate in the body of your essay: Explain the essence of having school uniforms on students, teachers, and learning institutions. Issues such as security and safety, uniformity, and promoting togetherness or unity as benefits. It is easy to spot a student in uniform.
School Uniform: Correlation Between Wearing Uniforms and Academic Performance. The combination of colors for example, may affect the students' comfort as well as the public view and perception of the institution The issue of cost should also be put in to check. We will write.
Has a 20% discount. Claim My Discount →. 1. I believe students should not have to wear uniforms. by Evan. "When wearing uniforms, it is a struggle to be an individual. Teachers are always saying how important it is to just be ourselves and not worry about what others might think.
According to proponents, school uniforms: Help prevent gangs from forming on campus. Encourage discipline. Help students resist peer pressure to buy trendy clothes. Help identify intruders in the school. Diminish economic and social barriers between students. Increase a sense of belonging and school pride.
A factor of poor results is caused by stress and pressure. In conclusion, wearing school uniforms helps the students feel safer, less stressed and less about changing in society because of other opinions. It also minimizes the chances of getting bullied. The goal is to show equality in school and the people around us as one.
Student Safety. Some people think that school uniforms can help make schools safer for kids. When Long Beach, CA, required all students in grades K-8 to wear uniforms, reports of assault and battery decreased by 34%. Additionally, assault with a deadly weapon decreased by 50%, fighting incidents declined 51%, and sex offenses dropped by 74%.
CON. School uniforms restrict students' freedom of expression. School uniforms promote conformity over individuality. School uniforms do not stop bullying and may increase violent attacks. School uniforms do not improve attendance, academic preparedness, or exam results. The key findings used to tout the benefits of uniforms are questionable.
School Uniform Essay: People have long debated over the fact if school uniform is necessary. Many educational institutions impose the necessity of wearing school uniforms which has its benefits and disadvantages. Since both the advantages and disadvantages are based on solid ground, the debate on the necessity of school uniform is ongoing. We will discuss […]
10.05.2024. Cite this essay. Download. The ongoing debate about using school uniforms for students has been contentious. Those favouring school uniforms cite benefits such as increased community spirit, discipline, and an improved learning environment. However, opponents take issue with the idea that school uniforms may limit individuality and ...
School Uniform Argument Essay: Since the past few years, the discussion over the execution of school uniform arrangements in educational systems has been seen broadly across the schools. The choice of uniforms being carried out in educational systems is based on the state or the individual school's strategy. The school either can make ...
Judging from the advantages and disadvantages of uniforms, it is clear that all students should wear uniforms as they distinguish students from civilians and enhance equality in the school environment. References. Baumann, Chris, and Hana Krskova. "School discipline, school uniforms, and academic performance.".
Discussion seems stymied in a superficial argument about whether school uniforms are good or bad. Rarely do discussions point to empirical evidence about school uniform garment design and policy about uniform use. This situation begs questions as to availability of evidence for school uniform use, its effects on educational or health outcomes ...
One good friend of mine, a superintendent of a charter-school network, who spoke to me off the record, swears that introducing uniforms where he works changed the culture overnight, increased ...
1. Expression of Individuality. The concept of "Expression of Individuality" in the context of school uniforms is a vital aspect of student development and autonomy. When schools impose uniforms, they inadvertently restrict a key channel through which students express their individuality and creativity.
In kids, studies show that tracing out ABCs, as opposed to typing them, leads to better and longer-lasting recognition and understanding of letters. Writing by hand also improves memory and recall ...
In his essay "How to Ungrade," a revised and expanded version of which appears in Undoing the Grade, he provides a smorgasbord of options for the ungrading-curious, including grading contracts, portfolios, peer assessment and student-made rubrics. The goal of ungrading, he says, is not to replace one uniform approach to assessment with another.
Judith Karp led a 1982 internal government investigation that found Israeli authorities unwilling or unable to confront settler crimes. "We were very naïve," she now recalls. Peter van ...