- Call: +44(0)20 7226 1877
- Email: [email protected]
- My basket ({{$root.cartInfo.count}})

Creative Report Writing

There isn’t a right way to write a report, but there are lots of things available to help you make it more accessible, more entertaining and more likely that people will read it right to the very end.
Writing Reports Creatively
You want me to be creative? Report writing is hard enough without this extra pressure!
Read our great tips below for good business report writing, and learn more about our writing courses .
Hey! Remember essay writing in school? There were some weirdos who loved writing essays, but for the majority of students, essay writing was a homework nightmare.
For some of you, effective report writing may be a breeze, not daunting at all. But for a lot of people, those same essay-writing feelings come flooding back:
“Oh my god, I’ve been given a report to write. Now what am I going to do?”
Report Writing Nightmare
Homework nightmare all over again.
Something we’ve noticed with people who hate report writing is that they don’t feel that’s what they were hired to do. They were hired for their expertise, their experience, and their professionalism and didn’t quite take in that creative business writing was going to be part of it all.
See, even if it’s just a tiny part of it all, it can feel really, really BIG, and it’s those exaggerated feelings that can throw people off guard. A lot of people think of creative report writing as an onerous task, which is why creativity hardly gets a look in.
You’re Going To Be Judged
People huff and puff, tear their hair out, cry, leave it to the last minute, try to get someone else to do it for them. Suddenly they’re under the cosh, suddenly they’re going to get ‘graded’.
All those feelings of inadequacy come up: What am I supposed to do? I’m going to be judged. My neck is on the line. I hate writing reports. I didn’t know this was going to be such a big part of the job, etc, etc.
You might be right. That might be what’s going to happen: you may very well be judged, your neck might be on the line. But it’s the overwhelming feelings we’re interested in because they tend to create that blank-page horror: what do I do next?
What Personality?
So this is what people tend to do: they constrain themselves, they lose their unique personality, they become dull, they have to give every piece of information they have and cover all the bases, they shut down and fail to bring their information to life.
OK, maybe it isn’t as dire as all that, but we do see that people tend to rely on their facts, figures, and statistics to tell the story instead of them telling the story and using the facts, figures and statistics to embellish it.
Now, of course, there are some organisations that only want facts and figures. They like the denseness; it makes them feel they’re getting what they paid for. But the reality is that in this day and age, creative report writing has to be more.
Things are changing: an information-packed, fact-packed, dull report usually implies a dull person. Not fair, but there it is.
Bring The Information To Life
See, what report writing is all about is that you’ve taken research and information that you’ve gathered, you’ve assessed it, you’ve brought your expertise to, and then you have to present it to someone else so that they have the information that you have and an understanding of it so that they can then use that information.
What happens, however, is that often people feel they need to ‘park’ their personality and become someone else.
Whereas what you need to be doing, is taking all that information and filtering it through who you are and how you naturally express yourself.
Try This For Some Insight
Here’s an experiment to show what we mean. Pick something you know something about: how much your favourite football team spent on new players this year, how much your council spends on policing, what percentage of your salary goes on mortgage payments/rent/groceries.
Now sit down and write an ‘essay’ about it (it doesn’t have to be a long one!). Read it to yourself. Now find a friend and just tell them about the same subject.
We can pretty much guarantee the two versions won’t be the same. Most people will go into writing mode that’s vastly different from their talking mode.
When relating something to another person you will have a whole collection of skills you use unconsciously that reflects your personality, and your individuality. You’ll enliven your verbal report with anecdotes and the feelings you have about those stories.
The difference is that if you were talking about it, telling someone about it, your voice would be conversational, it would have colour and changes in tone, inflexion, and volume. Your voice would do as much (if not a lot more) to convey your message than the actual words you’d be using.
You’d be using your body, arms, and hands, facial expressions to layer more feelings and expressiveness about your chosen subject.
Writing With Colour
Because the written word is open to interpretation (read, misinterpretation) even more than the spoken word, then it is your job to get the colour, tone, and inflection into your report that would otherwise be missing.
This is what we mean when we say people adopt a report-writing voice. They write with overtly professional, filled with jargon, and complicated, lengthy sentences.
They think that because they are committing themselves to paper and won’t necessarily be around to answer questions and explain something in more detail, they have to present differently than if they were giving the same information face to face.
Give Them Less
That’s what we mean when we say people pack far too much in because they think they need to give the reader everything they know.
They don’t! – You don’t!
It’s like putting on new shoes for an interview that you’ve never worn before. If any of you have ever done that, you’ll know it’s a bad move. No matter how great they looked and felt in the shop, walking in them gives you blisters, takes your attention away from everything else (oh my aching feet!), and makes you wish you had your lovely, old, comfortable, familiar shoes on.
Well, report writing is the same thing. Trying to write in ‘reportese’ is uncomfortable, it takes your attention away from your main message and you wish you could just tell people what you have to say rather than having e to write it.
Reportese vs Conversation
Begin to think of report writing as a conversation. It may feel as though you are doing all the talking but let’s see if we can help you create that voice.
You know how when you’re talking to someone or giving a really fantastic presentation, you can see people nodding in agreement or frowning in disagreement? You’ve hit the target when you can see a non-verbal response. You see how people are reacting.
Well, when you write something you can’t see whether people are nodding in agreement or nodding off to sleep.
Keep Them Awake
YOU HAVE TO KEEP THEM AWAKE, the same way you have to keep people awake during a presentation.
You’re conversing with them but you don’t have their input. What you want is for them to have some kind of reaction: they love it, hate it, agree, disagree, feel comforted, feel panicky, get angry or frustrated. Something is better than apathy, disengagement, and indifference.
Boy, do you know how many dull and turgid reports there are out there that create just that: indifference.
See, it’s even easier for people to get bored and lose their way with the written word. They can allow themselves to get distracted because you’re not there to say, ‘Now read this bit – this is the bit that really tells you what’s going on.’
That’s what you have to be able to do with the written word – give people a really clear road map of what you want them to get from your report. You have to make sure they read ‘this bit’.
People love stories, they do. And for the most part, people love telling stories: they love setting the scene, giving things a big build-up, getting to the punch line, and then finishing up with a ‘tie up all the loose ends’ conclusion.
So tell a story when you’re tasked with creative report writing.
Write With Purpose
OK, maybe we’re going to state the obvious here, but unfortunately, in our experience, it needs to be stated.
You need to know why you’re writing the d**n thing in the first place.
See, we told you it was obvious.
You absolutely must have a message you want people to get. It really isn’t OK just to pile fact upon fact and hope it will make sense to the reader. Part of the purpose of stating your purpose is so you can give the reader a roadmap of your intentions.
If you don’t have a purpose, the reader will give you one you may not want.
Next, have a point of view. Again, if you don’t have one, your readers may well project one onto you.
Some Important Questions
So ask yourself a few questions:
- Who is this report for?
- What do I want it to achieve?
- What do I want to ‘leave’ them with?
- What do they definitely need to know?
- How do I feel about all of this?
Once you’ve answered those questions, you can filter your information through your purpose and your point of view, and this is actually quite a good way to make the material come to life and give it some of your personality.
Lies, Damn Lies And Statistics
Ah, we hear you say. But what about all those statistics?
OK, let’s take statistics.
Here’s a little game. Pick any statistic that you know. Doesn’t matter what it is. Write it down as a ‘cold’ fact. Just the actual statistic. Now do a kind of ‘riff’ on it, embellishing it. Tell a story about it, actually give people some relatively useless information about it but that will pique their interest.
Here’s one that’s a classic in business: In most companies, 80% of their business comes from 20% of their client list. This is the 80/20 rule.
Just The Facts
This is how we could write it if we were just giving you the facts:
- 80% of Impact Factory’s business comes from 20% of our client list
- Our regular clients are A, B, C, D, etc.
- They give us X, Y, Z amount of work each quarter.
- We run marketing campaigns for both our existing client base and potential clients in order to develop the business.
We’ve given you accurate information, but there would be nothing behind it. You wouldn’t actually have the full picture.
Or We Could Try This the Creative Report Writing Way
We have a range of long-term clients including Fidelity Investments, Barnet Council, Merrill Lynch, Lewisham Council, Proximity London, all of which shows the depth and breadth of the kind of people who like our work. We like them in return and enjoy developing our relationships with them.
And this is what we do to ensure a continued interest in what we do: we have unusual marketing campaigns, we give stuff away free, we really listen to the clients’ needs and rectify any mistakes we might make as quickly as we are able, we send interesting email newsletters, we take them to lunch, etc.
80% of our business comes from 20% of our client list. Our clients really love us because we rarely break a promise, we exceed expectations, we communicate with them regularly so they feel connected to us, and they know how much we enjoy working with them.
It’s simply more interesting, and if we then added in the actual figures, they would enhance the story, not be the story. Did you need all that extra information? Probably not. But what it did, was paint a picture of Impact Factory that lets you know how we achieve what we achieve.
Anyone can take a statistic and give it a dry reading; writing it creatively takes something extra. You want people to look forward to reading your stuff.
Who Are You Writing For?
Impact Factory stuff is written by real people for real people. We always have a cartoon on the front page of our documents. It’s a signature (long live The New Yorker magazine!). Our stuff is written colloquially and is filled with stories, anecdotes, analogies and examples.
This means that our work is true to us and our style.
You need to be true to your style rather than producing something that anyone could have written.
For Example
Here’s another story from Robin:
“I once was sitting in the reception of a prospective client and picked up a report that was in a stack for people to read. I realised after five minutes that I hadn’t understood a thing I was reading, and I consider myself very competent when it comes to interpreting statistical material.
One of our clients, Hewitt Bacon & Woodrow, on the other hand, has material that’s clear and really easy to read. On the outside, you might think actuarial information, human resources consultancy – going to be pretty dull.
But their material is written for the customer, rather than for the person writing it.”
Accessible Language
For us, that’s the key. Really good creative report writing is written in language that’s accessible to your readers rather than in your language. Technical reports for the layperson are nearly inscrutable.
The language is dense, and packed with jargon, usually with an assumption that you actually know what they’re talking about. People tend to write from their knowledge rather than from the perspective of the person reading it.
Do you know why there are so many books on the market for computer dimwits? Because most manuals are written for the people who created the programmes, not for the people using them!
The same is often true of reports.
Take care of your audience – coddle them, indulge them, look after them.
Let’s Get Practical
People tell us that one of the hardest things about report writing is getting started. Blank-page syndrome.
One of the problems is that a lot of people think they should be able to just sit down and write something from beginning to end, their thoughts all ordered, the facts and figures tripping off their fingers easily. Ha!
Well, some can. Most can’t.
You may have tried some of these methods, but it’s worth having a go at all of them till you find which one/s help you get more creative.
Forget order. Just throw everything that’s related to your report onto a flip chart or a large piece of paper. OK, OK, a small piece of paper will do. Don’t edit, and don’t try to have the stuff make any sense. Random words will do, phrases, even whole sentences.
Let it be chaotic. Step back. Study it for a while. Then with felt tip pens or coloured pens/pencils, start circling related topics or issues. You can have a great time with arrows, squiggly lines.
Draw (oh no, I can’t draw). No one is ever going to see this stuff. So draw. Stick figures, weird-looking charts and graphs, illustrations. It doesn’t matter. The idea is to start freeing up your creativity, so draw.
Then you can put everything related to each issue or topic together on a separate page. And then you can start with the creative report writing.
Mind Mapping
This is a hugely popular way of ordering information and letting your brain run free at the same time. If you haven’t tried it before. It’s really well worth having a go because it can do wonders for your creativity.
Here’s how it works. Write the topic of your report in the middle of a blank page and draw a circle around it. Then draw lots of lines off from the circle and write along the line anything that pops into your head about that topic. Or you can draw a picture.
Then draw lots of little branches off each of those lines and write (or draw) whatever pops into your mind about each of those subtopics. This can go on for a long time, with branches, sub-branches and more sub-branches.
Free Flowing Ideas
Don’t edit or judge what you’re writing/drawing on each line, if at all possible. You may find yourself repeating yourself under different sub-headings. That’s OK. The idea is to let your ideas free-flow.
At some point, you can stand back and see if you can find any pattern at all in the little off-shoots. Look at the repetitions if there are any.
After that, it really doesn’t matter what format you then use: you can sit down and write up each sub-branch into sentences. You can re-order the information. The important thing is that you’ve accessed your mind in a new way.
Let’s ask google for a few examples
Hi google – Find me some examples of mind maps
Classic Outline Format
Yes, we see nothing wrong with this method either. Anything that works, we say. So, in case you didn’t get this at school, the outline method is:
Report Title
A. Introduction
1. The first piece of information 2. The second piece of information 3. The third piece of information and so on.
B. The first issue to be addressed
1. The first piece of information 2. etc
C. The second issue to be addressed
1. The first piece of information
a. Sub piece of information b. Next sub-piece of information
You get the picture!
Some people really like to work in this format. We, personally, think it might be a little stifling and creativity limiting, but we don’t want to stop people from using it if they find it helps them. We tend to think that’s what you could do after you’ve tried one of the other more fluid techniques.
In other words, once you’ve been a bit anarchic, you can take all your information and order it in outline form.
Technical Aids
One way to overcome the blank-page syndrome is not to write at all (at least at first). Use a Dictaphone to just talk. Much like having a conversation with a friend, use the tape recorder to babble. It most certainly doesn’t need to make sense. Once you replay it and type it up you can have a go at making it make sense.
You don’t even need to have blank-page concerns. Indeed, most of this document was ‘written’ on a Dictaphone. This is a way to let the subject stew away in your brain for a while. If you keep your Dictaphone with you at all times, or if you’re not near a computer, you can at least make a record of your thoughts. Without it, the stew might just bubble away.
Keep the recorder next to your bed as you might wake up in the middle of the night with an idea. Great way to get it ‘off your chest’ if you don’t want to turn on a light to write it down. You might sound like a drunken sailor the next day, but the idea will have been saved.
The next important technical aid is a notebook. Yes, the simple notebook, also kept with you at all times, to jot things down, make notes, and keep tabs on those fabulous ideas that pop up.
30 Second Influencer
A few years ago, we created something called the 30-Second Presentation or 30-Second Influencer. We did this to give our participants a simple model they could use to get information ‘over’ to others in a punchy, enlivening style:
Here it is:
- Get people’s attention
- Make it relevant to them
- Give them your central message
- Use an example they can relate to
- Tell them what you think they should do next/ what the next step should be
The idea is that you write about 60-70 words in total, and if you read it out loud it should take just about 30 seconds. It forces you to get really, really clear using the minimal amount of words.
Here’s an example from Jo Ellen:
I happen to be passionate about recycling and I could go on and on boring you with statistics, who’s doing what where, how everyone should make sure they recycle everything they could. If I go on for too long, I lose my audience. If I give too little, you won’t care.
By starting a report on recycling, using the 30-second influencer, I can lead people into my story before they know it.
Here’s how it could work:
Rubbish! Like me, I bet you use tons of it every week. We could all benefit from recycling more of our rubbish. For instance, in Bury St Edmunds where I live, we have one of the best recycling records in England. Next time you unwrap a package, fold up your newspaper, finish a bottle, think before you toss it into landfill and bin it where it will do some good.
Hopefully, I will have got your attention, whether you agree with me or not. By opening a report on recycling with my 30-second presentation, I’ve given you a precis of my entire report in 5 sentences. Then, it would be my job to enliven those 5 sentences even more with the rest of the report. I might even break down the issues in more detail, and start every section with the 30-second influencer.
What its purpose is, is to get you to distil down everything you want to say in a concise, yet vibrant way.
The Red Editing Pencil
Most people write waaay too much, as we mentioned earlier. They feel they have to stuff their reports with every piece of information they have.
You don’t. So you need to get ruthless, heartless, and pragmatic and start slashing your report. It isn’t as hard as it looks and the advice on the next page might help you see what needs to go.
Looking Good
Looks help.
It’s not just about the information, it’s about the way you present that information.
Long paragraphs don’t work. Give the eye a break! Most people, when they look at a page with very little white space, will already assume it’s going to be boring.
Short punchy paragraphs are better than long technical ones.
Lay things out; be careful of ‘orphans’ and ‘widows’, those single words on a line, or a heading that’s on the bottom of a page with the information on the next page.
If appropriate, use pictures, graphs, and charts to illustrate a point, and then talk people through them. This is a great opportunity to use stories because the facts/statistics will be there in graph/chart form. People can ‘see’ what you’re saying, so you can use your text to bring the facts to life.
And Finally
What a relief. You’ve finished.
Wait! Before you press the print or send button, one last thing to do.
Read it out loud. More than once.
Then, if you have the courage, read it to a friend or colleague. It should flow easily; you should be able to spot mistakes the eye couldn’t see, but your ear can hear. We’d be surprised if after reading it out loud you didn’t want to change a few things, even if they’re minor.
Reading it out loud allows you to put some expression into it – if you find that your words aren’t mirroring that expressiveness, get that red pencil out and start editing like mad!
And Finally Finally
The most important thing to remember about creative report writing is that there is information sitting in your brain that you need to present in such a way so that other people want it to sit in theirs.
When someone finishes reading what you have written they need to have the information you want them to have and the understanding for it to make sense; they know what it is that has to happen next;
It doesn’t matter what the report is about, who it’s for, or what it’s going to be used for if you can keep to that one objective – the transfer of useful information from you to others – then your reports should get easier and a whole lot more creative.
Write Like A Presenter
Do you know that piece of advice that people give to presenters? Tell your audience what you’re going to tell them, tell them, and then tell them what you’ve just told them.
Powerful copywriting is like that too.
You set out your stall, putting it in digestible chunks, perhaps using the 30 Second Influencer. The bulk of your report is what you want/need the readers to know, and then you pack up your stall, summarising the key points.
And like any good verbal presentation, make sure your last couple of paragraphs are the ones they’re going to remember.
There isn’t a right way to write a report, but there are lots of things available to help you make it more accessible, more entertaining, and more likely that people will read it right to the very end.
You will also benefit from understanding the barriers to communication that can impact the way you write as much as the way you speak .
Check out the Harvard Business Review report into How Bad Writing is Destroying Your Companies Productivity
Business Writing Training
Impact Factory runs
Open Professional Development Courses
Tailored Writing Skills Training
Five-Day Elite Communicate With Impact Workshops
and personalised
One-to-One Writing Skills Training
for anyone who is interested in
Communication Issues
Related Articles

Email Reflections: 10 Simple Courtesies
- Writing for Business
Here are some very important tips you will want to know — ten ways to be respectful and courteous to your receiver — before you respond to another email.

Effective Report Writing and Creative Business Writing
Imagine being commended for the clarity of your written communications.

Powerful Digital Copywriting
Power Up Your Web Presence With Powerful Digital Copywriting.
Discuss your requirements
If you like what you've seen, please call us on +44 (0)20 7226 1877 or click the button below to contact us via our contact form.
Privacy Overview
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Data Visualization 10 Report Design Ideas & Tips to Engage Readers
10 Report Design Ideas & Tips to Engage Readers
Written by: Midori Nediger Jun 12, 2023

A good report design encompasses a visually appealing and well-structured layout that effectively communicates information. It involves a clear and logical organization with headings and sections, consistent branding elements , readable typography and a visual hierarchy to emphasize key points.
Ultimately, designing a good report goes beyond aesthetics and encompasses strategic elements that facilitate effective information communication. This includes implementing visually appealing and well-structured layouts.
Ideally, your report should be mobile-friendly too. Sounds like a lot, but I’ve got everything covered in this guide so keep reading or get started right away with one of Venngage’s professionally designed report templates .
How to design a report:
- Balance text with visuals to make your information easy to digest.
- Use a single highlight color to draw attention to key information.
- Create a clear text hierarchy to make your report easy to navigate.
- Incorporate your branding for cohesive report design.
- Visualize your data with bar charts, line charts, bubble charts, and pie charts.
- Use a 2-column layout for optimal readability.
- Leave plenty of whitespace in your report design.
- Apply consistent motifs across every page of your report design.
- Use color blocks to group related information.
- Include an appendix with detailed tables and graphs.
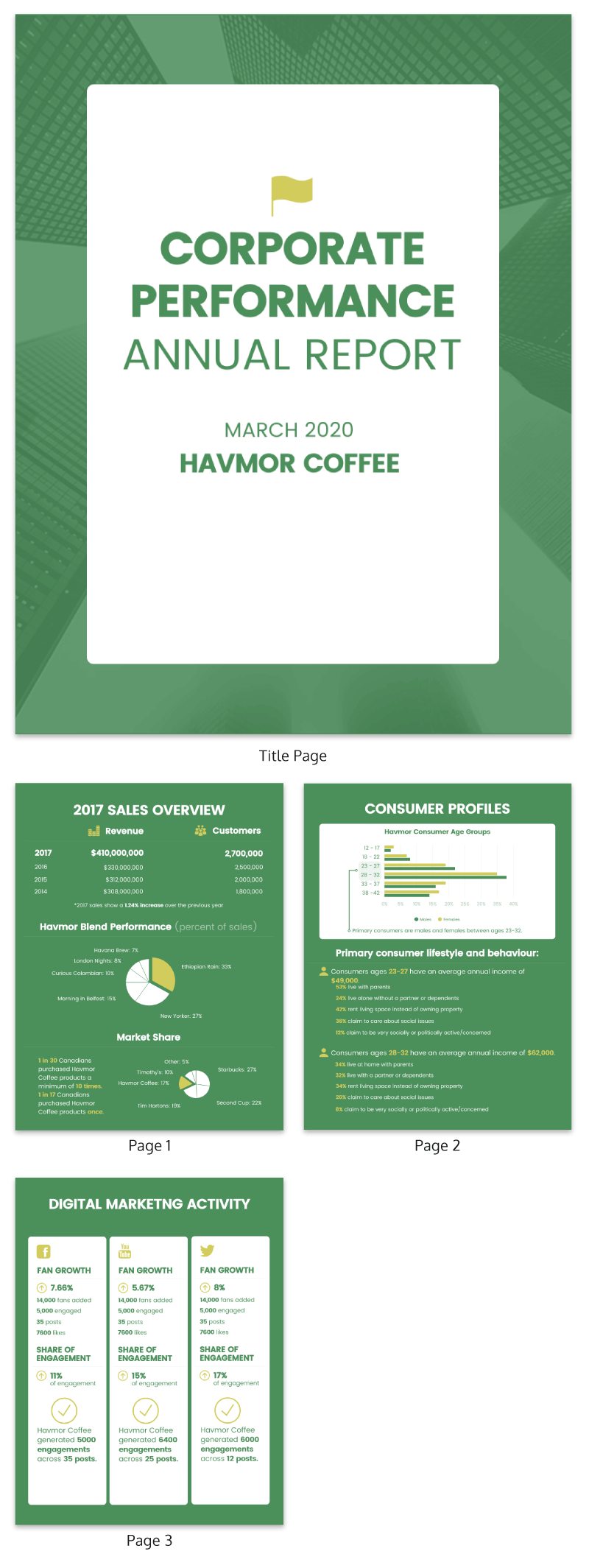
Today I’m going to give you a primer on making reports that are as beautiful as they are functional. We’ll cover the 10 report design best practices you need to know and report design ideas.
When writing a report that uses a lot of data, you should use the IMRaD format . IMRaD is an acronym that stands for Introduction – Method – Results – and – Discussion.
If your report is more text than data-heavy, such as if you were creating an annual report or a nonprofit report about a program of activities, you should broadly follow the IMRaD format too. Although with less emphasis on the ‘method’ section. Instead, focus on showcasing the results of your work.

Watch: How to create an annual report
Once you feel confident and inspired, you can jump to our reports templates page to start designing your own custom report! Keep reading for some report design ideas.
1. Balance text with visuals for a digestible report design
As humans, we’re much better at grasping information presented in the form of visuals than written text. So when designing a text-heavy report, look for opportunities to summarize information by transforming text into visuals to make your information more engaging and easier to digest.
Don’t use words if the same information can be presented visually.
Aim for at least a 50/50 balance between text and images. At least half of each page should be dedicated to visuals like charts, diagrams, and helpful images.
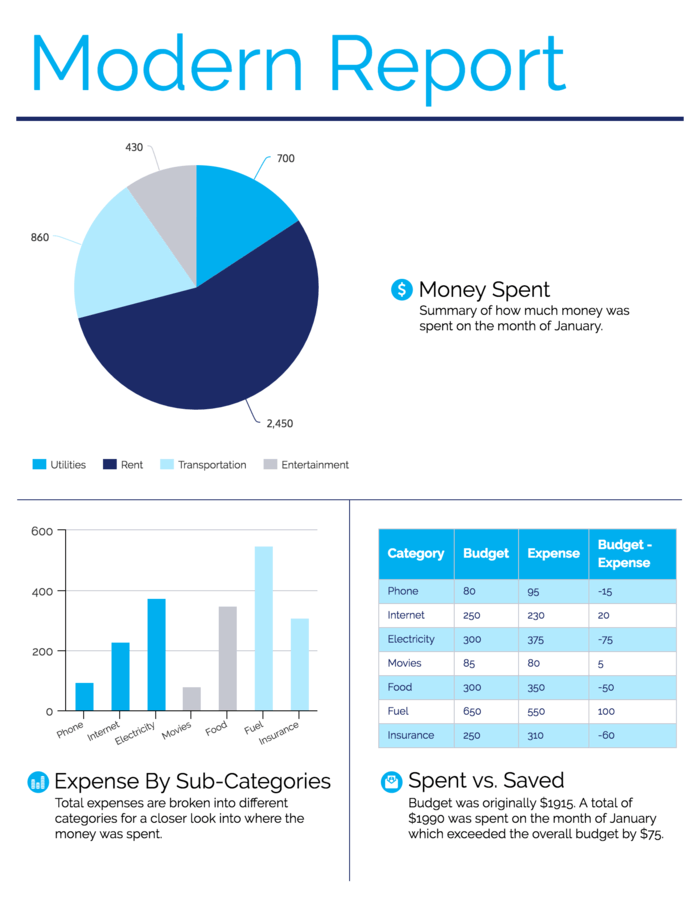
As with the simple report design above, every chunk of text in the report should be accompanied by a representative visual. The visual should communicate the bulk of the information, and the accompanying text should list the major takeaways.
Even if your report requires a more text-heavy approach, try to scatter visuals between the longer paragraphs of text. Alternating text with visuals will help keep your readers engaged from page to page like in this report design idea:

Just remember, functionality should always come first. Visuals should be used to enhance understanding–to categorize, highlight, and emphasize information–not just to break up the text. Choose visuals that make your content easier to understand.
Our progress report templates are ideal for businesses and consultants to showcase the right data and ignore all the minutiae in the process.
Our consulting report templates are another good resource.
2. Use a single highlight color to draw attention to key information
Color is one of the most important elements of any design.
Besides playing a role in the overall look and feel of a design, color can be even be used to control where our readers look. We can use bold color accents to draw our readers’ attention to any key facts and figures that we think are particularly important.
As shown in the modern report design below, color is a powerful tool for highlighting significant data points and drawing attention to report headers.

Just make sure you use highlight colors with restraint. Many bright, contrasting colors will compete with each other and overwhelm the senses, distracting from the message you’re trying to communicate.
Sticking with a single highlight color will enhance your readers’ comprehension, and even help to tie your document together.

3. Create a clear text hierarchy for an easy-to-navigate report design
Similar to the way we can use color to tell our readers what to look at first, we can use text size to tell our readers what to read first.
This is what a typographic hierarchy is all about–sizing and styling text so that readers can easily navigate our reports with just a quick glance.

Every report should have at least three levels of text hierarchy, and this hierarchy should be applied to the entire document.
Your text hierarchy should contain, at the very least:
- Header text
- Subheader text
- Paragraph text
As seen in the report design below, headers should be big and bold enough to grab your reader’s attention, and a bit stylized. Subheaders should be a little smaller, and a little less stylized. Paragraph text should be more minimal in style, and highly readable.

Check out our guide on choosing fonts for more information on creating text hierarchies.
4. Incorporate your branding for a cohesive report design
It’s usually a good idea to take your company’s branding into account when you create your reports.
Using your brand elements will help you stick with a single visual theme from start to finish, which is critical to creating a report design that feels like one cohesive document.
As seen in this example from IPG Media below, consistently applying company brand colors can have a dramatic effect.
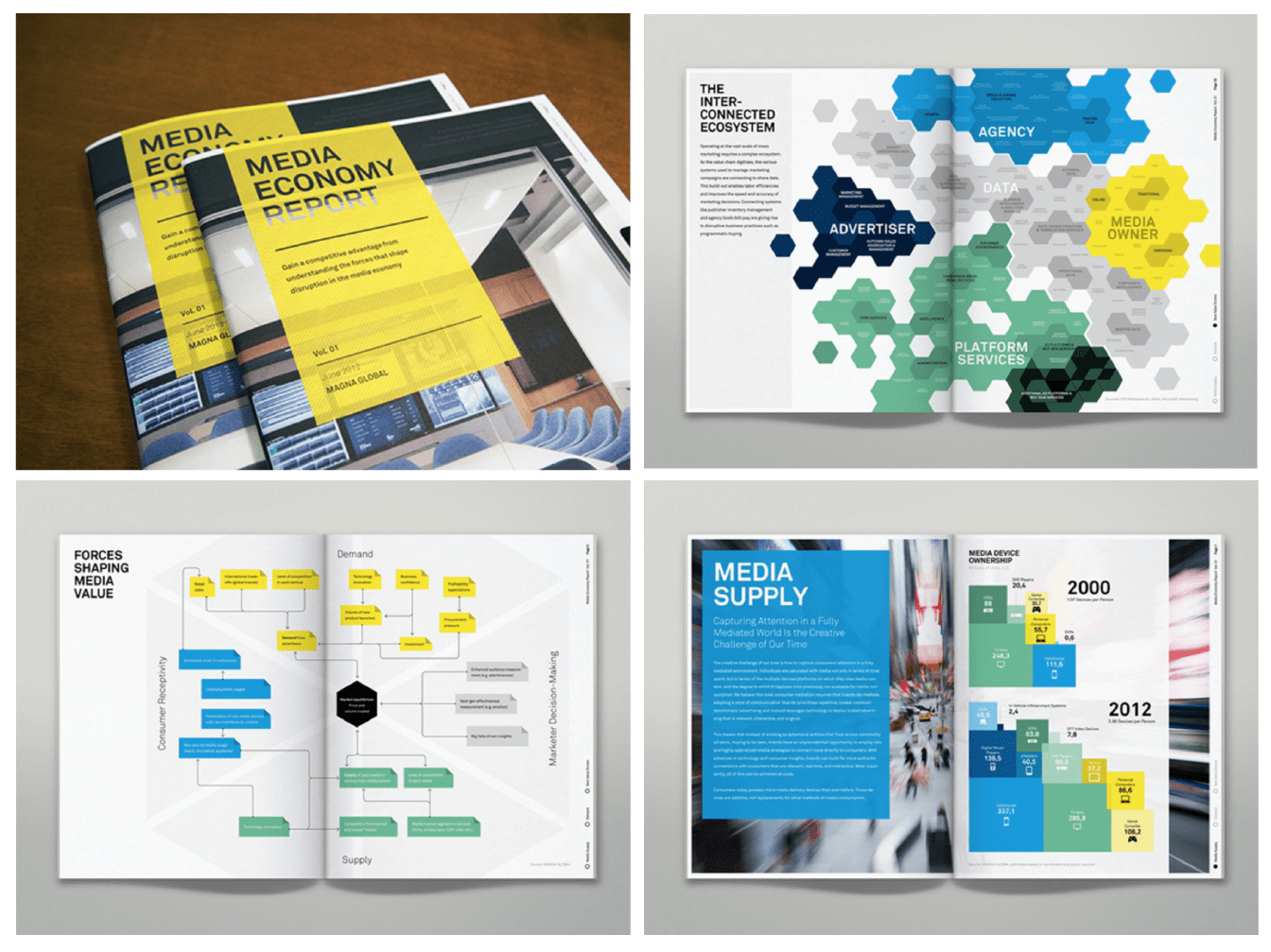
But don’t be afraid to add your own personal touch! Just because your design is consistent with your company’s branding doesn’t mean you have no creative freedom.
You can riff on your company’s core brand elements to create a fun design that still meets the brief. This report design from Maine Tourism mixes some secondary colors with the core brand colors to give the report a unique feel.

If you haven’t already, check out Venngage’s My Brand Kit . We’ve made it even easier to apply your company’s brand colors, fonts, and logos to all of our report templates!
Just upload your company logo, and add your company’s fonts and brand colors, then generate branded report templates with one click!

Once you’re happy with your report design, use the Venngage Business Account to invite your team to comment on your design and get some good feedback. You can even save your annual report as a template to use next year!
5. Visualize your data with bar charts, line charts, bubble charts, and pie charts
Data visualizations in a long report don’t have to be fancy. In fact, simpler is usually better!
And that’s why knowing the basics of chart design can be a game changer for your report design.
Using simpler charts like line charts, bar charts, bubble charts, and big number charts means that you won’t run the risk of confusing your readers, and they won’t have to work to interpret your charts.
These basic charts can even be quite engaging if incorporated cleverly into your overall design. Check out this annual report design from the Hall Family Foundation, which uses very basic data visualization techniques (big number charts and bar charts) to great effect.

Just make sure you’re using charts that are appropriate for the type of data that you have and the message you’re trying to convey.
Here are a few guidelines on how to choose the right type of chart :
- Use line charts to highlight trends over time
- Use bar charts and bubble charts to show difference among categories
- Use big number charts to emphasize key performance indicators
Watch: How to Pick The Right Chart For Your Data
One final tip for visualizing data in reports: include descriptions for all charts or tables to add context for readers. As seen below, each chart should have some accompanying text (a header, at the very least) that provides clarification and explains important trends.

If you’re not sure of the best way to visualize your data, look for inspiration in our statistical infographics . Many of the same visualization techniques used in data-heavy infographics work surprisingly well in report designs, too.
6. Use a 2-column layout for optimal readability
Messy, disorganized reports not only look unprofessional, they can be confusing!
Keep your reports organized by building them on a grid–ideally, a 2-column grid, as seen in this report design from the Global Fund for Children . A grid gives a report some visual structure, prevents visual clutter, and creates a satisfying sense of rhythm in the design.
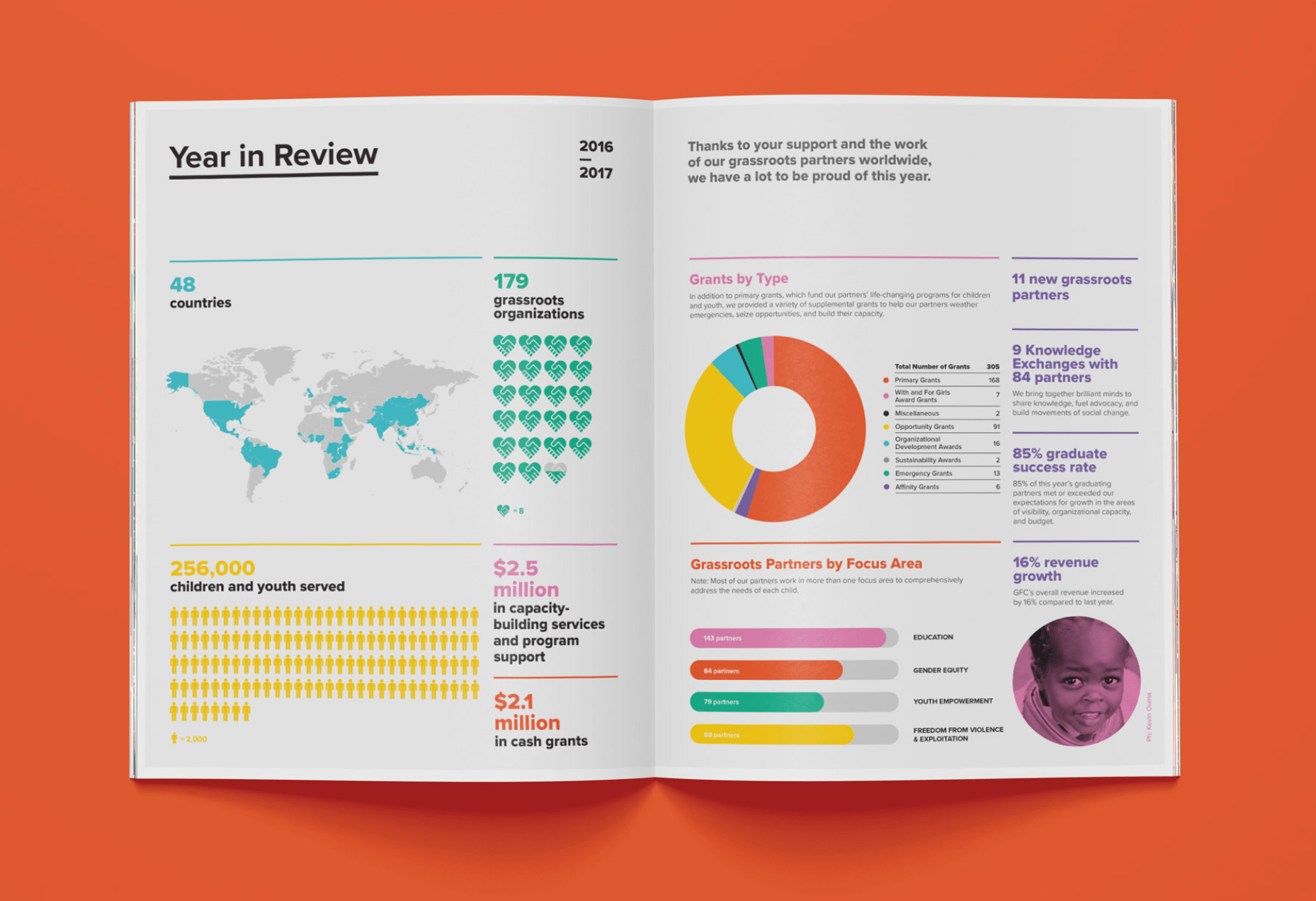
Designing on a 2-column grid will also prevent your paragraphs from getting too wide. The optimal line length of readability is about 60-70 characters per line, which usually works out about right in most 2-column layouts.

7. Leave plenty of whitespace in your report design
Whitespace, the empty space around every piece of content on a page, is an essential element of good design.
The perfect amount of whitespace makes a design feel balanced and pleasing, while a lack of whitespace makes a design feel cramped and unfinished. Just take a look at what a difference a bit of whitespace makes in a simple design:

This report from Samsung Fire & Marine Insurance is a bit of an extreme example of whitespace in practice, but you get the point. The blank space around the text, numbers, and images helps a design feel light, polished and balanced:

When it comes to adding whitespace to your reports, keep in mind that readers might get turned off when faced with large walls of text. Try to summarize your information , break text up into smaller sections and space those sections out to prevent pages from getting too busy.

Whitespace is especially important in information-dense reports, which can easily look heavy and overwhelming in the page. By leaving generous margins around text sections and charts, we can prevent our reports from looking too formidable.
8. Apply the same visual motifs across every page of the report design
Consistency is crucial to a great report design. Since your text and visuals are changing from page to page, for the pages of a report to feel like they belong together, they must have similar design elements that remain consistent from page to page.
These consistent design elements (or motifs) could be images, illustrations, icons , or even just shapes!
Check out the annual report design below. The simple band along the right side of the page creates that essential visual consistency to tie the design together.

To add motifs to your report designs in Venngage, head to our Icon Library in the left panel of the editor. You can browse the library by category:

Or search for specific icons by keyword with our search bar. When using the search, you can even filter your search to find multicolored icons or single color icons (which can be customized to any color)!

9. Use color blocks to group related information
The layout and design of a report should support readers’ understanding of the information within that report.
For example, we can use basic design elements (like blocks of color, lines, and borders) to indicate which information belongs together, making it easier for our readers to quickly interpret that information.

Let’s take a look at how this can help us design data-heavy pages of our reports.
Data-heavy pages can easily get visually overwhelming, with a ton of data points, lines, and bars all competing for our attention. By dividing these pages into defined sections, we can create a dashboard-style report design that’s much easier to take in:

Never underestimate the power of a color block!
10. Include an appendix with detailed tables and graphs
To avoid overwhelming readers with too much information at once, detailed tables and graphs should be left out of the main body of the report and included in an appendix instead.
This gives interested readers the opportunity to explore your content in greater depth while keeping your core report short and sweet.
When creating tables for your appendices, there are a few design tips you should keep in mind:
- Use a bright color to clearly distinguish header rows from body rows.
- Alternate the color of body rows between white and light grey to make the table easy to scan.
- Use brightly-colored boxes to draw attention to important values in the table.
Designing an effective report is all about including the right amount of information. Your goal in the body of the report should be to state any key takeaways and back up those statements with supporting visuals. Any information beyond that should be relegated to an appendix.
Bonus: Add an attractive cover
“Don’t judge a book by its cover” might be good advice in your daily life, but the truth is that people still do it—and you need to take that into account if you want people to walk away with a positive impression of your report.
For printed documents, consider using a report cover page or book cover with an engaging photo, illustration, or other design on it. Make sure it’s an image that expresses the brand voice or subject matter associated with the report. You’ll also want something that matches the report’s overall tone; if it’s optimistic, sobering, or conflicted, choose an image that helps to convey those feelings.
Even if your report cover takes a fairly minimalist approach (with a design comprised of little more than the title of the report), that still adds a great deal more professionalism than there would be with no cover at all.
PS: If you’re an HR professional, you can use our HR report templates to create anything from incident reports to performance reviews.
Related: 20 Professional Report Cover Page Examples & Templates [100% Customizable]
Even if the content of your report is dry, the design of the report doesn’t have to be. With these report design best practices in mind, you can create documents that make the information they contain easy to digest and a pleasure to read.
Get a head start on your next report design ideas with one of our many report templates and our easy-to-use report creator .
More report design guides:
- 90+ Annual Report Design Templates, Inspirational Examples & Design Tips [2024]
- What is a Marketing Plan & How to Create One [with Examples]
- 21 Engaging Performance Review Examples [+ Tips From an HR Manager]
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
👀 Turn any prompt into captivating visuals in seconds with our AI-powered design generator ✨ Try Piktochart AI!
- Piktochart Visual
- Video Editor
- AI Design Generator
- Infographic Maker
- Banner Maker
- Brochure Maker
- Diagram Maker
- Flowchart Maker
- Flyer Maker
- Graph Maker
- Invitation Maker
- Pitch Deck Creator
- Poster Maker
- Presentation Maker
- Report Maker
- Resume Maker
- Social Media Graphic Maker
- Timeline Maker
- Venn Diagram Maker
- Screen Recorder
- Social Media Video Maker
- Video Cropper
- Video to Text Converter
- Video Views Calculator
- AI Brochure Maker
- AI Document Generator
- AI Flyer Generator
- AI Infographic
- AI Instagram Post Generator
- AI Newsletter Generator
- AI Report Generator
- AI Timeline Generator
- For Communications
- For Education
- For eLearning
- For Financial Services
- For Healthcare
- For Human Resources
- For Marketing
- For Nonprofits
- Brochure Templates
- Flyer Templates
- Infographic Templates
- Newsletter Templates
- Presentation Templates
- Resume Templates
- Business Infographics
- Business Proposals
- Education Templates
- Health Posters
- HR Templates
- Sales Presentations
- Community Template
- Explore all free templates on Piktochart
- Course: What is Visual Storytelling?
- The Business Storyteller Podcast
- User Stories
- Video Tutorials
- Need help? Check out our Help Center
- Earn money as a Piktochart Affiliate Partner
- Compare prices and features across Free, Pro, and Enterprise plans.
- For professionals and small teams looking for better brand management.
- For organizations seeking enterprise-grade onboarding, support, and SSO.
- Discounted plan for students, teachers, and education staff.
- Great causes deserve great pricing. Registered nonprofits pay less.
How to Write a Report (2023 Guide & Free Templates)

You have a report due in a few days, but you’re still procrastinating like a pro.
Sounds familiar?
If you’ve been staring at a blank page, wondering how to write a report the best way possible, you’re not alone. For many, writing a report, especially for the first time, can feel like rolling a giant boulder uphill.
The good news is that from a first draft to creating reports that people love to read is a skill you can develop and polish over time.
Whether you’re a student, a professional, or someone who wants to up their report-writing game, keep reading for a 2023 guide and step-by-step instructions on how to write a report. Plus, learn about the basic report format.
You’ll also get access to report templates that you can edit and customize immediately and learn about a tool to make reports online (no need to download software!). You can also jump right into customizing templates by creating a free account .
What is report writing?
Report writing is a way of communicating information, data, insight, or analysis. It’s an essential skill that will come in handy in various settings, from academic research or diving into historical events to business meetings.
But creating a report can be a bit intimidating at first.
In its simplest form, report writing starts with researching and gathering all the information, analyzing your findings, and presenting it in a way that’s easy for your audience to understand.
Sounds easy enough, right?
Well, there’s a bit more to it than that. We’ll guide you through every step of the process to write an entire report from a rough draft and data in the next section.
But first, let’s get to know the different types of reports.
Types of reports
Reports come in all shapes and sizes, and the type of report you write will depend on your specific goals and audience. Each type of report has its unique purpose, format, and style.

The most common types of reports are:
- Academic report – These include school reports, book reports, thesis reports, or analytical reports between two opposing ideas.
- Business report – Business reports range from annual reports to SWOT analyses . The goal of business reports is to communicate ideas, information, or insights in a business setting.
- Research report – Research reports are often more scientific or methodological in nature. They can take the form of case studies or research papers.
Learn more : 20 Types of Reports and When to Use Them (Plus Templates)
How to write a report without feeling overwhelmed
Breaking down the report writing process into three stages can make it much more manageable for you, especially if it’s your first time to create one.
These three stages are:
- Pre-writing stage
- Writing stage
- Post-writing stage
Let’s take a look at the steps for each stage and how to write a good report in 2023 that you can be proud of.
Stage 1: Pre-writing
The pre-writing stage is all about preparation. Take some time to gather your thoughts and organize your main idea. Write a summary first.
Here are important steps to help you deal with the overwhelm of creating an insightful report.
Understand the purpose of your report
Knowing your purpose will help you focus and stay on track throughout the process. Dig into the why of your report through these questions:
- Who is your intended reader? Are you familiar with your audience’s language and how they think?
- What are you trying to achieve with your report? Are you trying to inform, persuade, or recommend a course of action to the reader?
Research your topic
It’s time to gather as much information as you can about your topic. This might involve reading books, articles, and other reports. You might also need to conduct interviews with subject matter experts.
Pro tip on how to write a report : Pick reputable sources like research papers, recently-published books, and case studies by trustworthy authors.
Make a report outline
An outline is a roadmap for your report. It covers your title, introduction, thesis statement, main points, and conclusion. Organizing your thoughts this way will help you keep focus and ensure you cover all the necessary information.
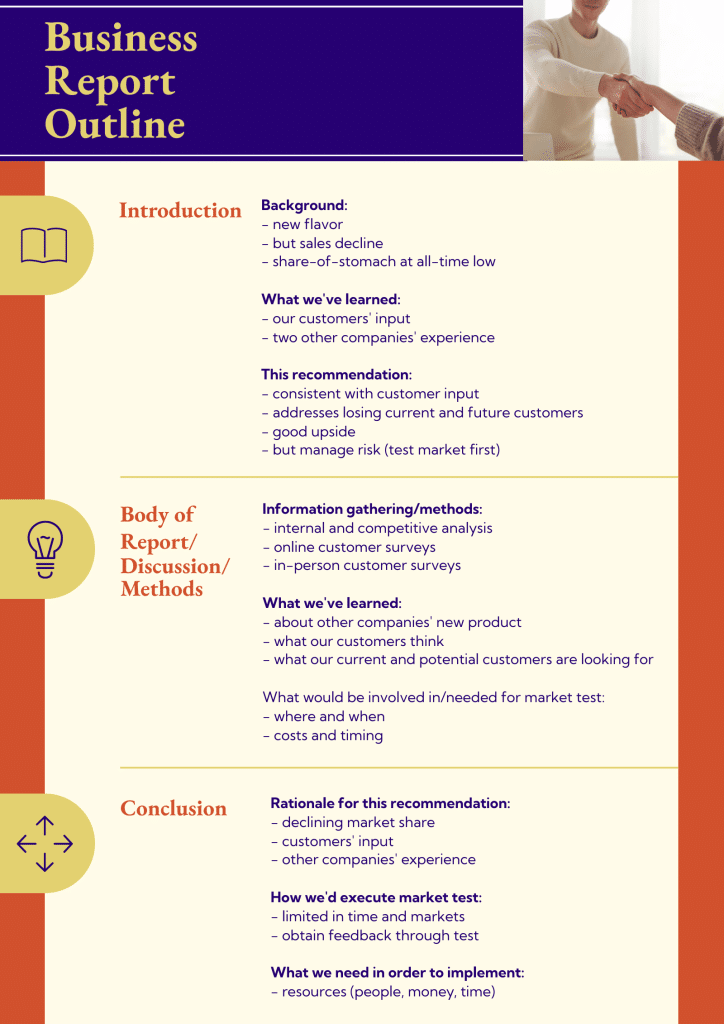
While you can create a report without creating an outline, you could write a better report with an outline. An outline helps you organize your facts and important points on paper.
Stage 2: Writing
Once you have completed the pre-writing stage, it’s time to write your report.
Follow the proper report writing format
You will feel a lot of resistance at this point because this is where most of the tedious work of report writing happens. However, the process can be a breeze if you follow a proper structure and report writing format.
The structure of your report can vary depending on the type of report you’re creating, but the report writing format below can serve as a guide for anyone.
- Title page. This is the first page of your report and should include the report’s title, the author’s name, the date of presentation or submission, and any other relevant information, such as your name or the organization’s name.
- Table of Contents (TOC ). This section contains subsections of your report and their corresponding page numbering. A well-written TOC will help readers navigate your report easily and find the information they need.
- Brief summary . This part provides an overview of the report’s particular purpose, subject, methodology, key findings, and recommendations. This section is often called the executive summary in corporate reports.
- Introduction . The introduction should provide background information about the topic and explain why the report was written. It should also state the aims and objectives of your report and give an overview of the methodology used to gather and analyze the data. Make sure you include a powerful topic sentence.
- Main body. The main body of the report should be divided into subsections, each dealing with a specific aspect of the topic. These sections should be clearly labeled and organized in a logical order. In most reports, this is also the part where you explain and present your findings, analysis, and recommendations.
- Conclusion. Summarize the main points of your report and provide a final summary, thought, or suggestions. Review your thesis statement. The conclusion also includes any limitations of the study and areas for further research or future action.
- References . This section should include a list of all the sources cited in the report, like books, journal articles, websites, and any other sources used to gather information on your subject.
- Appendices . In the appendices section, you should include any additional information relevant to the report but not in the article’s main body. This might consist of raw data, event details, graphs, charts, or tables.
With all these key report elements, your readers can look forward to an informative, well-organized, and easy-to-read report.
Pro tips: Remember to use clear and concise language in your essay. It is also required to follow a specific type of formatting set by your organization or instructor.
Plus, use the active voice when you can because it helps improve clarity. To write a report essay in a passive voice makes it sound less concise.
Reports should usually be written in the third person.
Edit and proofread the article
Once you have completed your first essay draft, take some time to edit and proofread your work. Look for spelling mistakes and grammar errors, as well as any areas where the flow of your article could be improved. Review your topic sentence.
If hiring a professional editor isn’t possible, have a colleague or someone else read your rough draft and provide feedback. You can also use tools like Grammarly and the Hemingway App .
Stage 3: Post-writing
You’re almost there! This stage is about finalizing your report and ensuring it is ready to be shared.
Format your report
Ensure your report is formatted correctly, with clear and easy-to-read fonts, headings, and subheadings.
Incorporate visuals
Adding visuals to your report article is another great way to help your audience understand complex information more easily.
From charts to illustrations, the right visual can help highlight and explain key points, events, trends, and patterns in your data, making it easier for the reader to interpret the information.

Want to check out more templates? Get access to the template gallery today .
However, it’s important to use visuals sparingly and ensure they are relevant and effectively support the texts. You will learn more about effectively incorporating visuals into your report as you scroll down below to the next sections.
Share your report
Once your report is complete, share it with your audience. This might involve submitting it to your boss, presenting it to a group, or sharing it online.
A final note for this section: Remember to take your time, stay organized, and most importantly, have fun! Writing a report can be a rewarding experience, especially if you get positive feedback when you present.
How to add visuals to your report
Adding visuals to your report is more than just putting a graph or chart for every piece of information.
There are no hard and fast rules but use the pointers below as guidelines:
- Each visual in your report should have a purpose. Don’t just add a pie chart or bar graph for the sake of adding one. Your visual of choice should offer clarity to readers that’s impossible to achieve with words alone. Piktochart’s report maker lets you search for free stock images and illustrations to add to any page with drag and drop.
- Add captions, legends, or arrows to your visuals when possible. For more technical reports, graphics are either Tables or Figures. Number them in order of appearance (Figure 1, Figure 2, Table 1, etc.) and give each a descriptive title.
- Place the visual close to the relevant text on the page.
- Document the source of the visual, citing it in both the caption and references section if necessary.
- Make the graphic stand out with colors, borders, boxes, spacing, and frames.
Learn more : How to Improve Your Data Visualization Design in 6 Steps
Write reports like a pro with Piktochart’s easy-to-edit report templates
Creating reports from scratch can be time-consuming. The great news is you don’t have to make reports from scratch like how it used to be in the 90s and early 2000s. Organizations of all shapes and sizes now understand that you can also create the perfect report with the help of templates.
For example, Piktochart offers a variety of fully customizable templates, allowing you to easily add your branding, colors, and text within the online editor. You can visualize your thesis statement and first draft in less than an hour. It’s also possible to start writing directly in the tool, adding graphics page by page.
These templates range from reports for school presentations to sales reports. By editing them, you can create professional-looking reports without the hassle of formatting and design.
Here are some examples of Piktochart’s professionally-designed templates. If you can’t pick one that matches your report writing format and needs, create a free Piktochart account to get access to more templates.
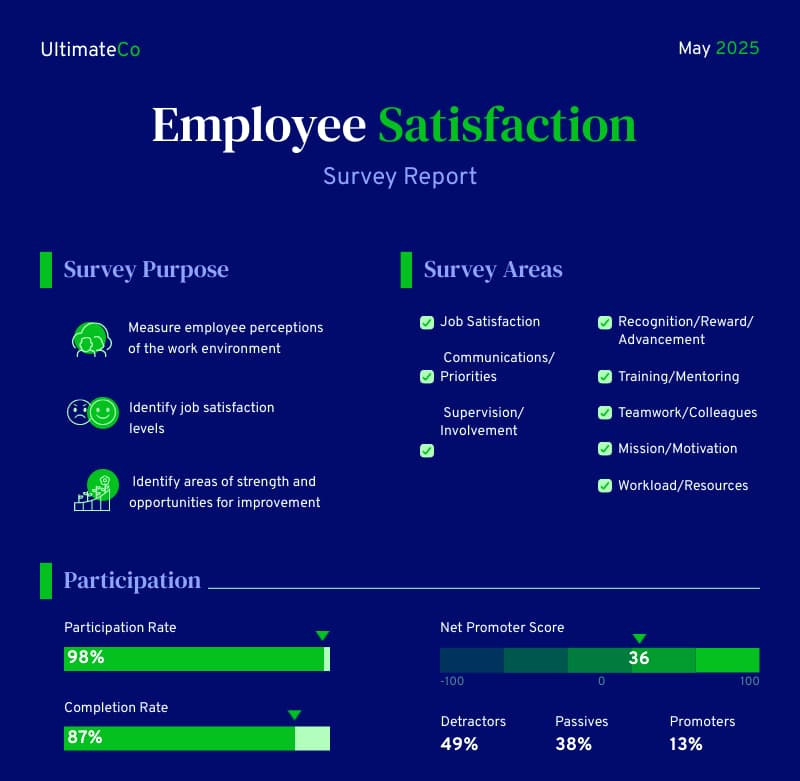
Survey report template
This survey report template includes clear visualizations, making your report findings easier to understand. From customer surveys to employee satisfaction reports, this template is quite versatile.
Research report template
This research report template is perfect for anyone looking to create a thorough and professional research report. The template includes all the necessary sections to help you easily organize your research and present your findings in a concise document.

Corporate report template
Looking for a corporate report template example with an editable table of contents and foreword? This template is the perfect fit!
Whether you’re presenting to investors or sharing information with your team, this corporate report template will help you create a polished and informative executive summary for any corporate organization.

Case study report template
Whether you’re conducting a business case study or an academic case study, this case study report template can help you earn your readers’ trust. This template is specifically designed with fashion as its main theme, but you can edit the photos and details to make it more on-brand with your niche.

Marketing report template
Use this template to create comprehensive marketing reports. The template includes editable sections for social media, data from search engines, email marketing, and paid ads.

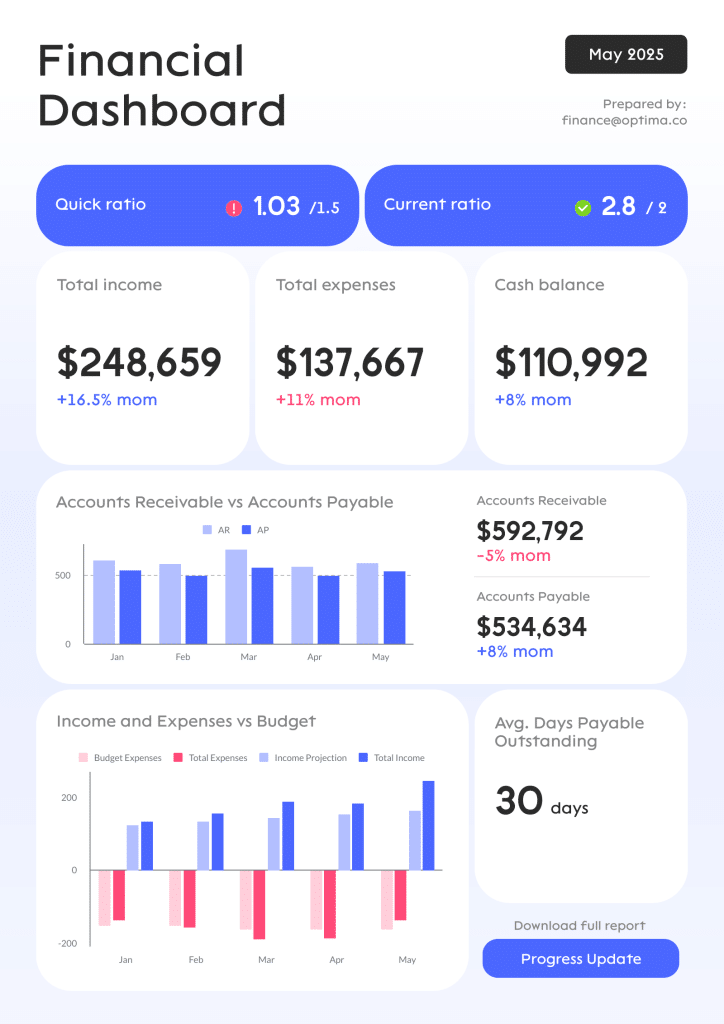
Financial report template
With this customizable finance report template, you don’t need to make a financial report from scratch. Once you’ve written your content, save your report in PDF or PNG formats.
Annual report template
This annual report template is the right template for creating a professional and informative executive summary of your organization’s performance over the past year. This template was designed for HR annual reports, but you can also repurpose it for other types of yearly reports.

See more report templates by creating a free Piktochart account .
Quick checklist for better report writing
Before you submit or present your report, use the quick checklist below to help ensure that your report is well-structured, accurate, clear, and properly cited. Most of all, you must ensure that your report meets your audience’s expectations and has all the information and details they need.
Purpose and audience
- Does the report address its purpose and meet the needs of the intended audience?
Structure and organization
- Is the material appropriately arranged in sections?
- Have irrelevant details been removed?
Accuracy and analysis
- Has all the material been checked for accuracy?
- Are graphs and tables clearly labeled? Check the page numbers too.
- Is the data in graphs or tables analyzed and explained in words?
- Does the discussion or conclusion show how the results relate to the objectives mentioned in the introduction?
- Have the results been compared with existing research from the literature survey?
Writing style and clarity
- Is the report written in a tone that’s indicated in the brand style guide (for corporate reports)? Does it avoid colloquialisms or contractions?
- Does it follow the organization’s specific guidelines for writing style?
- Is it jargon-free and clearly written? Have you translated technical terms into simpler words?
- Use the active voice when you can because it helps improve clarity. A written report in a passive voice may make it sound less concise.
Acknowledgment and citation
- Have all ideas and event data taken from or inspired by someone else’s work been acknowledged with a reference?
- Have all illustrations and figures taken from someone else’s work been cited correctly?
Proofreading
- Has the report been carefully proofread for typos, spelling errors, and grammatical mistakes?
Make engaging and effective reports quickly with Piktochart
Writing a report is a must-have skill for anyone looking to communicate more effectively in their personal and professional lives.
With the steps we’ve provided in this guide, anyone can learn how to write a report that is informative, engaging, and comprehensive.
Plus, the free templates we highlighted are valuable for individuals looking to create reports quickly and efficiently. They can also be used to transform a longer report filled with texts into something more engaging and easy to digest.
Sign up for a free Piktochart account today, and look forward to writing reports with its library of modern, customizable report templates.
Piktochart offers professionally designed templates for all your visual communication needs. It is your one-stop shop for presentations , posters , logos , email signatures , infographics , and more. Customize all templates according to your brand assets in seconds. Get started for free today.

Other Posts
10 Best Sales Report Templates for Tracking Revenue, KPIs & Growth

10 Types of HR Reports (With Templates and Examples)

7 Captivating Report Design Ideas And Tips (With Templates and Examples)
Filter by Keywords
How to Write a Report for Maximum Clarity and Impact
Sudarshan Somanathan
Head of Content
January 26, 2024
If you’re a professional in any industry, you know that sharing ideas and findings through well-crafted reports is a skill that will set you apart from your peers.
But writing a compelling report may seem daunting at first. It requires a well-thought-out approach.
What elements or sources should you incorporate to ensure your report is comprehensive and engaging? And how do you organize each section for maximum impact?
In this guide, we’ll explore the ins and outs of report writing, breaking it down step by step. We’ll also introduce you to some game-changing features in ClickUp, a platform that will make your report-writing journey smoother and more collaborative. Let’s dive in!
Understanding Report Writing
Different types of reports and report writing, key components of report writing, how to write a report, utilizing templates for report writing, wrapping up.
Before we explore the intricacies of how to write a report, let’s establish a solid understanding of what report writing entails. Report writing encompasses the art and science of transforming raw information into a cohesive and structured document.
A well-crafted report is more than a collection of facts; it’s a narrative that provides clarity, insight, and direction. In business, accurate and insightful reports help with informed decision-making.
Adept report writing is a strategic skill that distills complex data into understandable insights. Whether documenting project progress, detailing financial metrics, or analyzing market trends, reports provide a medium.
Reports take various forms in academic and professional settings. In academia and business, research reports provide insights into scientific studies. Policy-makers rely on book reports, and field study reports for ground-level information.
A project report or summary is a comprehensive document that outlines a project’s objectives, progress, challenges, and outcomes. Writing effective project reports demands attention to clear objectives, systematic data collection, and a concise presentation of findings.
Progress, technical, functional, marketing, academic, sales reports, and case studies serve diverse purposes. Each type is purposefully crafted to fulfill specific objectives, catering to the distinct needs within organizations.
Despite their differences in subject, these reports adhere to common attributes, principles, and formats in report writing.
Here, we’ll explore five common types of reports and explain their distinct characteristics. We’ll also show you how to write a report for successful outcomes in your respective fields.
1. Research reports
Research reports meticulously explore a specific topic, utilizing surveys, experiments, or literature reviews. Geared toward contributing to existing knowledge, these reports offer a detailed and authoritative understanding of the subject.
Key features include an extensive literature review, a well-defined methodology, a systematic presentation of findings, and conclusive insights derived from rigorous research.
When writing a research report, start with a clear and focused research question. Conduct thorough literature reviews to identify existing gaps.
Define a precise methodology, outlining your approach step by step. Present your findings in a structured manner, ensuring clarity in your delivery. Employ conclusive insights to draw actionable conclusions.
2. Business reports
Business reports intricately analyze business-related information, which includes financial performance, project updates, and strategic plans.
They inform stakeholders, investors, or internal teams about business operations and performance metrics.
A comprehensive report includes financial statements and concise summaries of ongoing projects. It also provides strategic recommendations tailored to the specific needs and interests of the target audience.
Start with a clear executive summary, move on to financial analysis, offer insights into profitability and performance indicators.
Prioritize clarity and brevity to communicate complex information effectively. Use data visualization tools when necessary to enhance understanding.
3. Technical reports
Technical reports convey complex technical information, procedures, or analyses. Predominantly utilized in science and engineering, these reports aim to communicate intricate technical details.
Specialized language, detailed procedures, and precise data presentation are hallmarks of technical reports, requiring a certain level of expertise for comprehension. These reports often serve as valuable technical references, aiding decision-making, troubleshooting, and further research.
As a professional, ensure your technical reports cater to the specific needs of your audience.
Leverage technical writing software and tools to enhance the precision and effectiveness of your communication. They help maintain a delicate balance between technical depth and clarity for seamless comprehension.
Detail procedures meticulously, leaving no room for ambiguity and aiding professionals in replicating processes or methodologies. Precisely present data, graphs, or tables to reinforce findings.
4. Incident reports
Incident reports involve the meticulous documentation of unexpected events or issues. They’re typically written down, outlining real events, the sequence of events, and the corresponding responses.
These are designed to analyze incidents thoroughly, learn from them, and establish preventive measures for future occurrences.
Detailed descriptions of the incident and its immediate and potential impact form the core of incident reports. Recommendations for improvement ensure a comprehensive understanding and proactive approach.
When drafting incident reports, ensure a detailed chronology of events and responses.

Incident report templates guide professionals in crafting detailed narratives, ensuring comprehensive documentation.
Consider the templates for documentation and to enhance preparedness, minimize risks, and cultivate a safer and more resilient environment in your field.
5. Progress reports
Progress reports track the ongoing development of a project or initiative, documenting achievements, challenges, and future plans.
They’re primarily geared toward providing decision-makers with valuable insights and relevant data, enabling informed decision-making.
These reports include milestone tracking, performance indicators, project reports, and a narrative that details the project’s progress and outlines anticipated future milestones.
To create an effective progress report, focus on quantifiable achievements and challenges. Tailor the report to decision-makers, providing them with a concise and forward-looking overview.
Now, let’s delve deeper into the essential components of a well-structured report.
To write impactful reports, you need to grasp the basics. From the initial impression set by the title page to the nuanced details in appendices and executive briefs, each element plays a vital role in improving the report’s effectiveness and readability.
Here are the key components contributing to a comprehensive report’s structure and depth.
1. Title page
Serves as the face of the report, providing crucial information at a glance. It includes title, author’s name, date, and relevant institutional information.
2. Abstract or executive summary
Summarizes the report’s main points. Offers a quick overview for readers with time constraints, acting as a stand-alone summary highlighting key findings and recommendations.
3. Table of contents
Outlines the structure and organization of the report, aiding readers in navigation. Accuracy in page references is vital, ensuring a reliable roadmap for easy access to specific content areas.
4. Introduction
Acts as the opening chapter, setting the stage for the report. States the report’s purpose and scope, offering a concise yet comprehensive overview of what follows. Guides readers toward a clear understanding of the report’s objectives and what they can expect within its content.
5. Methodology or approach
Details of how the research or analysis was conducted. Essential for transparency, allowing others to replicate the study and verify its validity.
6. Findings or results
Presents the main outcomes or discoveries derived from the research. Backed by data, evidence, or examples, ensuring the credibility and reliability of the presented findings.
7. Discussion or analysis
Interprets the report findings, providing context and deeper understanding. Offers insights and potential implications, elevating the report beyond a mere presentation of facts.
8. Recommendations
Suggest actions based on the report’s findings. Provides decision-makers clear directions on how to respond to the presented information.
9. Conclusion
Summarize the report’s key points. Reinforces the main theme, leaving a lasting impression on the reader.
10. References or bibliography
Cites sources used for reference in the report, ensuring its credibility and allowing for further exploration. Adheres to a standardized citation format for most reports, enhancing the report’s professionalism and academic integrity.
Let’s explore a few additional components that enhance a report’s completeness. Incorporating these into your report ensures it is a valuable and impactful document in your professional endeavors.
- Appendix: Houses supplementary materials such as charts, graphs, or detailed data to enhance comprehensiveness and provide additional information
- Acknowledgments: Conveys gratitude to those who contributed and ensures proper recognition to foster a collaborative and appreciative tone within the report
- Glossary of terminology: Defines technical terms or jargon for better reader comprehension, especially in reports with specialized language
- Visual elements: Incorporates visuals like charts, graphs, or images. Aids in presenting complex data or concepts, enhancing reader engagement and understanding
- Executive brief: Offers a condensed executive summary version, providing a quick snapshot of the report’s key elements for efficient decision-making
- Quality assurance or peer review: Involves a thorough review process to catch errors or inconsistencies, ensuring the information presented is accurate and trustworthy
- Action plan: Propose a step-by-step plan based on recommendations to help execute the next steps effectively, translating recommendations into tangible results
- Monitoring and evaluation: Establish a system for ongoing assessment after the report’s implementation. Ensures continuous improvement, allowing for adjustments based on real-world outcomes
You need the right tools and a systematic approach to write effective reports. Let’s explore the intricacies of report creation.
Here are the practical steps to craft a good report that grabs attention and delivers impact:
1. Define your purpose and audience
Before you start writing a report, clearly define why you’re creating the report and who will be reading it.
Ask yourself: What is the main objective of the report or article? Is it to inform, persuade, or analyze? Understanding your audience is paramount.
Tailor your language, tone, and content to cater to your readers’ specific needs, expectations, and level of expertise.
2. Research thoroughly
Gather all necessary information through extensive research and credible sources, ensuring a well-rounded understanding of your subject matter. To expedite this process, leverage ClickUp AI features . Utilize its advanced capabilities to quickly summarize lengthy documents, extracting key insights efficiently.
Explore a diverse array of over a hundred meticulously crafted and research-backed AI tools, offering tailored solutions for every role and use case.
Incorporating AI streamlines your research and improves the precision of data extraction.
3. Plan your structure
Before you start writing, plan the structure of your report. Develop a comprehensive roadmap outlining each section, ensuring your narrative’s logical flow and coherence.
A well-structured outline acts as a guide, facilitating seamless transitions between ideas and topics. To simplify this task, use ClickUp AI’s intuitive features to create organized outlines.
This optimization refines your report’s structure, enhancing readability, overall quality, and impact.
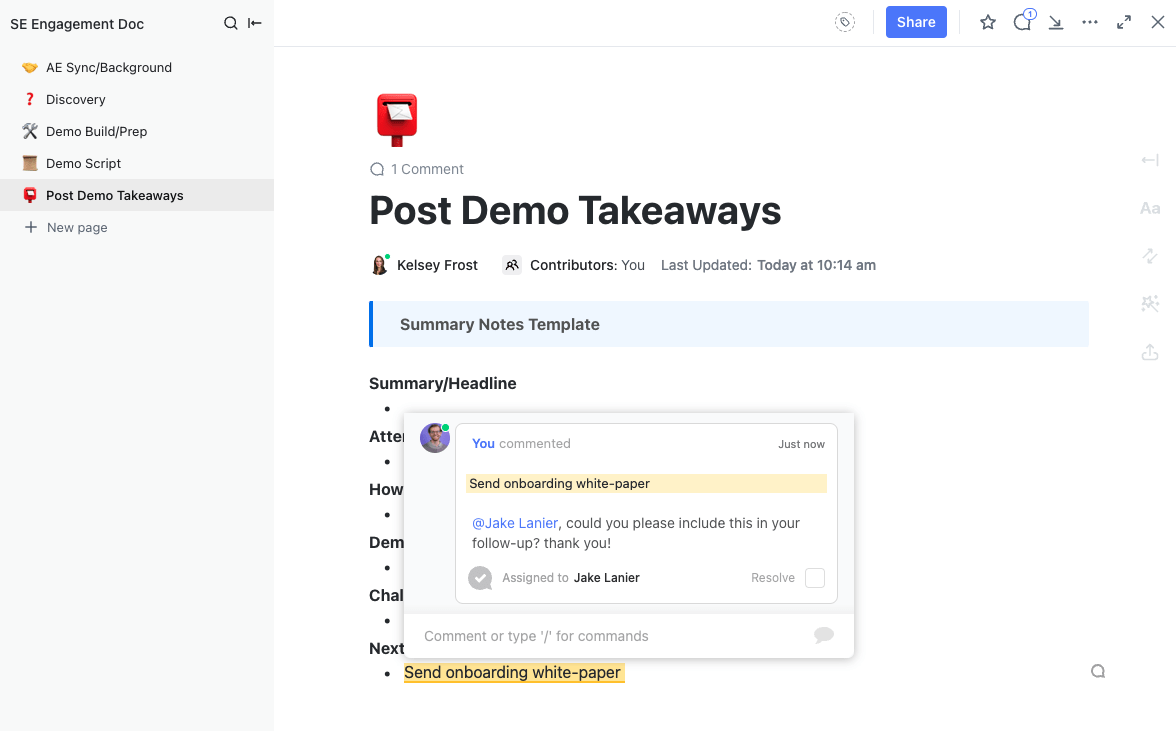
4. Utilize ClickUp’s features for drafting
Leverage ClickUp Docs for a seamless writing experience beyond traditional document creation. Take advantage of the platform’s collaborative features like Assigned Comments for efficient teamwork.
Here’s how to utilize ClickUp Docs to expedite your workflow and enrich your work experience.
- Integration with workflows: Link Docs and tasks together for centralized access. Enhance workflows by adding widgets to update project statuses, assign tasks, and more—all within the document editor
- Tagging and task assignment: Simultaneously edit documents with your team in real time. Tag team members with comments, assign action items, and convert text into trackable tasks for seamless idea management
- Efficient document management: Quickly access document templates for immediate drafting. Save frequently used documents as templates for convenient access in the future
- Advanced document settings: Customize font type, size, height, page width, and more according to your preferences. Keep track of essential metrics, including character count, word count, and reading time for each page in your Doc
- Enhanced document customization: Customize your document’s appearance with an overview and headers. Ensure a structured and visually appealing layout for a more engaging reader experience
5. Leverage AI writing tools and start organizing with checklists
Unleash your creativity and conquer writer’s block with various advanced AI writing tools like ClickUp AI. It provides a dynamic solution for brainstorming, generating content, and breaking creative barriers.
Utilize ClickUp’s Checklists to ensure a systematic approach to your tasks, covering all necessary points seamlessly. Stay on top of your progress and deadlines, enhancing your productivity and reducing the risk of overlooking crucial details.
Keep all your work organized by categorizing Docs within ClickUp, facilitating easy access and searchability. Ensure the security of your Docs with privacy and edit controls, allowing you to manage who can access and edit your documents.
6. Revise and edit
After completing your first draft, reviewing your report for clarity, coherence, and accuracy is crucial. Ensure your ideas flow seamlessly, maintaining a logical structure throughout the document. Utilize writing assistant software for valuable insights into your writing style. Whether refining grammar, improving sentence structure, or fine-tuning vocabulary, the best writing assistant software is a virtual guide. These advanced tools also suggest improvements, enhancing your report’s overall readability.
To enhance your editing process, leverage ClickUp’s advanced commenting features. Solicit feedback from colleagues directly within the document to promote constructive input.
Ensure there are no grammatical mistakes or typos. ClickUp’s collaborative features make it easy for multiple eyes to review.
7. Format professionally
Attention to formatting is pivotal for a polished and professional-looking report. Ensure consistency in font styles, headings, spacing, and alignment throughout the body of the report.
ClickUp’s versatile templates are an excellent starting point, offering pre-designed layouts that can significantly enhance your report’s visual appeal.
From case study templates and daily report templates to annual report templates , ClickUp offers a variety of templates for quick content creation.
Leveraging these templates streamlines the formatting process, providing a structured framework.
8. Finalize and distribute with confidence
Once you’ve confirmed that all the data in your report aligns with your standards, proceed to the finalization step. Double-check all components, including content, formatting, and accuracy.
Confirm that your report aligns with the initial purpose and effectively communicates your findings. Once satisfied, proceed to distribute your report to the intended audience.
Consider the most appropriate channels for dissemination, ensuring accessibility and relevance to the recipients. Whether through email, a shared platform, or a presentation, choose a method that aligns with your audience’s preferences.
Templates are a game-changer when it comes to report writing. They provide a structured starting point, saving you time and ensuring consistency.
With predefined structures, formats, and prompts, content writing templates help streamline your writing workflow. Whether a seasoned writer or tackling a new project, incorporating free content writing templates into your toolkit can significantly boost productivity.
Here are some ClickUp templates to leverage:
1. Report cover template

The Report Cover Template in ClickUp efficiently creates professional and visually appealing covers for various reports. It streamlines the design process and customization options, allowing users to:
- Create modern, stylish covers for reports
- Customize fonts and colors, and include logos or images
- Maintain consistency in branding across marketing reports
Steps to use the Report Cover Template involve setting the tone, selecting suitable designs, adding necessary details, finalizing, and printing. Collaboration, brainstorming, and progress tracking are facilitated within ClickUp’s workspace.
2. Report requirements template

The Report Requirements Template by ClickUp offers an efficient and organized approach to creating comprehensive reports. It streamlines the process by:
- Providing a consistent format for data collection, ensuring accuracy, completeness, and improved efficiency
- Offering structured elements like custom statuses, fields, views, and project management tools
- Guiding users through steps like defining the report’s purpose, establishing timelines, gathering resources, outlining content, and reviewing the final report
This template helps you:
- Clearly define report objectives and structure content
- Assign tasks, set timelines, and monitor progress
- Collect, organize, and analyze data for cohesive reports
- Facilitate collaboration among team members and ensure efficient communication throughout the report creation process
The Report Requirements Template facilitates project requirement documentation for business analysts. Integrating this template into your ClickUp Workspace helps maintain cohesion and clarity within teams, streamlining the process from report conceptualization to delivery.
3. Project reporting template

Project reporting is crucial for a project manager to gauge a project’s health and address critical areas needing attention. The Project Reporting Template comprehensively overviews high-level Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and overall project performance.
It assists in monitoring essential project elements such as tasks, expenses, and pending action items. Click Up’s Project Reporting Template is a centralized tool for project managers, providing insights into the project’s progress and potential bottlenecks.
With a clear snapshot of crucial project metrics, managers make informed decisions and allocate resources effectively to ensure project success. Streamline your project reporting with this template, covering key project elements.
By incorporating these templates into your report-writing process, you save time. You benefit from a proven framework designed to enhance the clarity and organization of your report.
In today’s dynamic professional environment, proficient communication through reports is indispensable. Whether conveying research findings, business updates, or project progress, mastering the art of report writing can elevate your career. ClickUp AI features and Click Up Docs transform the writing process into an efficient, collaborative, and enjoyable journey. So, when you undertake your next report-writing venture, follow the steps, embrace the templates, and let ClickUp be your ally in crafting impactful reports.
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months
How To Write a Report: A Detailed Guide [+AI Method]
![creative writing for report How To Write a Report: A Detailed Guide [+AI Method]](https://assets-global.website-files.com/5f7ece8a7da656e8a25402bc/645b8df737dcc500780779ca_How%20to%20Draft%20a%20Winning%20Report.jpg)
- Table of contents

Catherine Miller
Writers often wonder how to stand out from the crowd when writing a professional report.
Unlike articles or blogs, the informative, formal nature of reports can make them feel stiff and boring. And whether you want a top grade or to make an impact on your audience, another dull report probably won’t help.

In my career I’ve written a range of reports for both internal and external audiences—and regularly read reports from industry leaders, too. Top reports are informative and educational, summarizing key information quickly so it’s easy to digest. But the best examples also use high-quality research and concise but compelling language to bring the subject matter to life.
In this article, I’ll focus on general thematic reports, the kind you may be asked to write at college or work. I’ll give you the lowdown on how to write an effective report that still packs in the facts.
Types of reports
The term “report” comprises a wide genre of documents. If you’re used to other kinds of academic writing, it will help to understand the key qualities that reports share.
What sets reports apart
Reports are similar to other kinds of academic writing in many ways: you’ll still need strong research in the background, clear citations, and a formal language style , for example.
But several details set reports apart from other forms. Reports:
- Stick to the facts rather than veering into personal opinion or argument
- Save interpretation and recommendations for the end of the piece
- Use clear organizational techniques like bullet points, heading and subheadings, and charts or graphics
- Use concise, clear language that can be easily skimmed
Common types of reports
Reports are used in a wide range of contexts, so make sure you’re writing the right kind of report for your purposes. Here’s an overview of some common types.

Pre-writing steps
Before you set pen to paper, it’s important to do your research and plan your report carefully. Giving yourself plenty of time for this stage will make the actual writing quicker and less rambling.
1. Define the audience and purpose of the report
If you haven’t already been given a purpose for the report, be sure to define this before you begin. This can help you decide on the type of research you need to do and check if your report is fulfilling its goals while you draft.
Examples of common report aims:
- To demonstrate your understanding of an academic topic or text
- To improve understanding of the work your department is doing, so other departments in the same organization can build on your success
- To raise awareness of a particular problem that your organization can solve
On top of this, ask yourself who your audience is and what is their level of prior knowledge relative to yours. Within a hierarchy, such as a company or school, the audience may be more senior than you (vertical reporting), or at the same level as you (lateral reporting). This can affect what information is relevant to include.
Additionally, note whether it’s an internal or external publication and what your audience might do with the information they learn from your report.

Read the full article: Use AI to better define your audience
2. establish goals and objectives.
If you are writing your report for school or university, check the assessment guidelines for the report before you begin. You’ll need to include all the required elements.
If you are writing for professional purposes, however, the goals and objectives may be up to you or your department to define. An objective for your report should ideally be SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant and Time-Bound).
For example, a lead-generating report can be used for the aim of securing meetings with interested buyers by highlighting a problem that your company can solve, and the impact of your report can be measured by the number of downloads and subsequent meetings within a certain time period.
An internal report could be used to inform a strategy meeting, and the impact could be measured in how many strategic recommendations are made as a result.
Read the full article: Develop your strategy and goals
3. research and gather information.
A report needs to be based on factual evidence, so the research stage is absolutely key to producing an informative piece. Firstly, you should review the major literature on the topic to make sure you can define and explain key terms and set out any needed context.
For academic reports, your professor or institution may be able to provide a recommended reading list. Use your college library and make sure you find out which academic journals your institution subscribes to. You can often access these online using sites like JSTOR and Google Scholar .
You may also want to include primary sources to add originality to your report and make it more appealing to your audience. These could include:
- Original research such as interviews
- Statistics you’ve compiled
- Details of experiments, tests, or observations you’ve made
It’s really helpful to keep organized notes during your research. Note any key quotations with page numbers, plus publication and author details for each text you reference or read. This will make it much easier to create your citations and bibliography later on.
You could do this on paper or using flexible software like Notion or Evernote or specialist software like Mendeley or Zotero .
Read the full article: 8 Must-Have Tools for Researchers in 2023 (Including AI)
4. outline your report structure.
Creating an outline before you begin writing is key to successfully drafting a report.
Start by noting down a skeleton framework, i.e. the main points you want to cover, which you will then develop as you write. In some cases, if you’re clear on what you might include in your report, this step might come before you start researching; alternatively, your main points might change during your research phase.
Although the exact layout of your report will depend on your objectives, a report should include the following sections:
- Introduction
- Summary of context
- Summary of your main topic or text
- Bibliography
Additional sections that you may want to include, depending on context:
- An abstract — used in academic contexts.
- A summary of your findings — useful if you include your own original research (such as interviews or statistics)
- Recommendations for further action or research
Read the full article: How to Properly Write an Outline Using AI
5. write the draft of your report.
Your first draft is your chance to develop the ideas you noted down during outlining. You might need to continue researching as you go, especially if you find that certain areas need more evidence or explanation.
Write your title and abstract
The title of your report should clearly and concisely state what it is about. Your audience may need to quickly select it from a list of other publications, so make sure to use keywords to make your work easy to identify. Remember that this is also your audience’s first impression of your writing!
You may also need to create an abstract for your work: a short summary of your research and findings, giving a quick statement about the problem and/or potential solution, a concise explanation of what you did to investigate it, and your findings in brief. You will probably want to write your abstract after finishing the rest of the report.
Create a table of contents
The table of contents should direct readers to each section of the report with page numbers. You may want to include hyperlinks to relevant sections if you are presenting your document electronically.
Prepare your sections
Developing each section in full will form the bulk of your drafting work. Make sure each section is adding value to your report.

Balance analysis with facts
Report writing should be factual. There will be times when you need to draw conclusions and make recommendations. However, this analysis should not overwhelm the factual content of your report. Remember, this is not a persuasive opinion piece. Make sure your analysis is grounded in evidence, and keep your recommendations concise.
Use clear language
A report should clearly inform the audience about the topic at hand. Keep your language precise and easy to understand. Keep sentences and paragraphs at a sensible length. If you use technical terms your audience might not know, include definitions. Try to avoid emotive language that can make the report sound like a persuasive essay.
Sometimes it can be difficult to achieve all this while writing the first draft, so feel free to come back to improve on it in later drafts.
Use visuals to keep it interesting
Many reports use visuals like graphs, charts, photographs, or infographics. These can convey information quickly and engage your audience by breaking up the text.
Simple graphs and charts can usually be made in spreadsheet software, but you may want to call on the skills of a graphic designer if your organization has the resources. Make sure to caption and number your graphics.
Cite your sources
Your institution or organization may stipulate a citation model, so double-check what is required before you begin. In general, quotations or anything else taken from another source should be properly cited, including the author’s name, title, and page number, plus other information, depending on format. Citations may be in-text or footnotes.
It’s a good idea to add citations as you write, because going back and putting them in afterwards can be very fiddly and time-consuming.
At the end of your report you will also need to provide a bibliography, which lists the texts you have cited. Citation software like Zotero or a bibliography generator like MyBib can make this easier.
Follow an appropriate format
Make sure to check the style guidelines provided by your academic institution or work organization. These might determine the page formatting you need to use (e.g. page numbering, page size, use of images, etc.). If no such guidelines exist, look at other reports from your field to determine what will be clear and useful for your audience.
Read the full article: Essay writing guide
6. edit, review and revise.
Reviewing and revising your work is one of the most important parts of the writing process, so make sure you give yourself plenty of time for this part and avoid rushing to meet a deadline. Review your content first, checking that each section has enough evidence and development, before moving on to editing for clarity and technical accuracy.
Using a reading and writing assistant like Wordtune can make editing at the phrase, sentence, or word level quicker and easier. Wordtune not only finds spelling, punctuation, and grammar errors, but it can also suggest changes to your vocabulary and sentence structure that make your work clearer and more compelling. You can even specify whether you want a more formal or casual tone — most reports should be formal in nature.
Read the full article: The complete editing guide
Writing a report using an ai prompt (chatgpt + wordtune).
You can use this prompt to generate a useful report:
Please generate a comprehensive report on the topic "[Your Specific Topic Here]". Ensure the report adheres to the following structure and guidelines: Title: Craft a concise and descriptive title that encapsulates the essence of the report. Abstract: Provide a succinct summary (100-150 words) that encapsulates the main objectives, methodology, findings, and significance of the report. Table of Contents: List all the sections and relevant sub-sections of the report for easy navigation. Introduction: Introduce the topic, its background, relevance in today's context, and the primary objectives of this report. Body: Dive deep into the topic. This should include: Background/History: A brief history or background of the topic. Current Scenario: Present relevant data, facts, and figures. Analysis/Discussion: Discuss the implications of the data, any patterns observed, and their significance. Conclusion: Summarize the main findings, discuss their implications, and suggest recommendations or potential future research directions. Additionally, ensure that the content is: - Well-researched and cites reputable sources. - Coherent and logically structured. - Free from jargon, unless necessary, and is accessible to a general audience.
Make sure your next report has an impact
Whether your report is for academic or business purposes, you need to make sure it is well-researched, clearly expressed, and conveys the main points quickly and concisely to your audience. Careful planning and organization can make this process much easier, as well as leaving time to review and revise your work, either manually or with the help of software like Wordtune. Following these tips, your first report is sure to make an impact — and the more you write, the easier it will get.
Share This Article:
.webp)
Eight Steps to Craft an Irresistible LinkedIn Profile
.webp)
7 Common Errors in Writing + How to Fix Them (With Examples)

How To Prepare For Studying Abroad (From Someone Who’s Done It)
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.

What Is Creative Writing? (Ultimate Guide + 20 Examples)
Creative writing begins with a blank page and the courage to fill it with the stories only you can tell.
I face this intimidating blank page daily–and I have for the better part of 20+ years.
In this guide, you’ll learn all the ins and outs of creative writing with tons of examples.
What Is Creative Writing (Long Description)?
Creative Writing is the art of using words to express ideas and emotions in imaginative ways. It encompasses various forms including novels, poetry, and plays, focusing on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes.

Table of Contents
Let’s expand on that definition a bit.
Creative writing is an art form that transcends traditional literature boundaries.
It includes professional, journalistic, academic, and technical writing. This type of writing emphasizes narrative craft, character development, and literary tropes. It also explores poetry and poetics traditions.
In essence, creative writing lets you express ideas and emotions uniquely and imaginatively.
It’s about the freedom to invent worlds, characters, and stories. These creations evoke a spectrum of emotions in readers.
Creative writing covers fiction, poetry, and everything in between.
It allows writers to express inner thoughts and feelings. Often, it reflects human experiences through a fabricated lens.
Types of Creative Writing
There are many types of creative writing that we need to explain.
Some of the most common types:
- Short stories
- Screenplays
- Flash fiction
- Creative Nonfiction
Short Stories (The Brief Escape)
Short stories are like narrative treasures.
They are compact but impactful, telling a full story within a limited word count. These tales often focus on a single character or a crucial moment.
Short stories are known for their brevity.
They deliver emotion and insight in a concise yet powerful package. This format is ideal for exploring diverse genres, themes, and characters. It leaves a lasting impression on readers.
Example: Emma discovers an old photo of her smiling grandmother. It’s a rarity. Through flashbacks, Emma learns about her grandmother’s wartime love story. She comes to understand her grandmother’s resilience and the value of joy.
Novels (The Long Journey)
Novels are extensive explorations of character, plot, and setting.
They span thousands of words, giving writers the space to create entire worlds. Novels can weave complex stories across various themes and timelines.
The length of a novel allows for deep narrative and character development.
Readers get an immersive experience.
Example: Across the Divide tells of two siblings separated in childhood. They grow up in different cultures. Their reunion highlights the strength of family bonds, despite distance and differences.
Poetry (The Soul’s Language)
Poetry expresses ideas and emotions through rhythm, sound, and word beauty.
It distills emotions and thoughts into verses. Poetry often uses metaphors, similes, and figurative language to reach the reader’s heart and mind.
Poetry ranges from structured forms, like sonnets, to free verse.
The latter breaks away from traditional formats for more expressive thought.
Example: Whispers of Dawn is a poem collection capturing morning’s quiet moments. “First Light” personifies dawn as a painter. It brings colors of hope and renewal to the world.
Plays (The Dramatic Dialogue)
Plays are meant for performance. They bring characters and conflicts to life through dialogue and action.
This format uniquely explores human relationships and societal issues.
Playwrights face the challenge of conveying setting, emotion, and plot through dialogue and directions.
Example: Echoes of Tomorrow is set in a dystopian future. Memories can be bought and sold. It follows siblings on a quest to retrieve their stolen memories. They learn the cost of living in a world where the past has a price.
Screenplays (Cinema’s Blueprint)
Screenplays outline narratives for films and TV shows.
They require an understanding of visual storytelling, pacing, and dialogue. Screenplays must fit film production constraints.
Example: The Last Light is a screenplay for a sci-fi film. Humanity’s survivors on a dying Earth seek a new planet. The story focuses on spacecraft Argo’s crew as they face mission challenges and internal dynamics.
Memoirs (The Personal Journey)
Memoirs provide insight into an author’s life, focusing on personal experiences and emotional journeys.
They differ from autobiographies by concentrating on specific themes or events.
Memoirs invite readers into the author’s world.
They share lessons learned and hardships overcome.
Example: Under the Mango Tree is a memoir by Maria Gomez. It shares her childhood memories in rural Colombia. The mango tree in their yard symbolizes home, growth, and nostalgia. Maria reflects on her journey to a new life in America.
Flash Fiction (The Quick Twist)
Flash fiction tells stories in under 1,000 words.
It’s about crafting compelling narratives concisely. Each word in flash fiction must count, often leading to a twist.
This format captures life’s vivid moments, delivering quick, impactful insights.
Example: The Last Message features an astronaut’s final Earth message as her spacecraft drifts away. In 500 words, it explores isolation, hope, and the desire to connect against all odds.
Creative Nonfiction (The Factual Tale)
Creative nonfiction combines factual accuracy with creative storytelling.
This genre covers real events, people, and places with a twist. It uses descriptive language and narrative arcs to make true stories engaging.
Creative nonfiction includes biographies, essays, and travelogues.
Example: Echoes of Everest follows the author’s Mount Everest climb. It mixes factual details with personal reflections and the history of past climbers. The narrative captures the climb’s beauty and challenges, offering an immersive experience.
Fantasy (The World Beyond)
Fantasy transports readers to magical and mythical worlds.
It explores themes like good vs. evil and heroism in unreal settings. Fantasy requires careful world-building to create believable yet fantastic realms.
Example: The Crystal of Azmar tells of a young girl destined to save her world from darkness. She learns she’s the last sorceress in a forgotten lineage. Her journey involves mastering powers, forming alliances, and uncovering ancient kingdom myths.
Science Fiction (The Future Imagined)
Science fiction delves into futuristic and scientific themes.
It questions the impact of advancements on society and individuals.
Science fiction ranges from speculative to hard sci-fi, focusing on plausible futures.
Example: When the Stars Whisper is set in a future where humanity communicates with distant galaxies. It centers on a scientist who finds an alien message. This discovery prompts a deep look at humanity’s universe role and interstellar communication.
Watch this great video that explores the question, “What is creative writing?” and “How to get started?”:
What Are the 5 Cs of Creative Writing?
The 5 Cs of creative writing are fundamental pillars.
They guide writers to produce compelling and impactful work. These principles—Clarity, Coherence, Conciseness, Creativity, and Consistency—help craft stories that engage and entertain.
They also resonate deeply with readers. Let’s explore each of these critical components.
Clarity makes your writing understandable and accessible.
It involves choosing the right words and constructing clear sentences. Your narrative should be easy to follow.
In creative writing, clarity means conveying complex ideas in a digestible and enjoyable way.
Coherence ensures your writing flows logically.
It’s crucial for maintaining the reader’s interest. Characters should develop believably, and plots should progress logically. This makes the narrative feel cohesive.
Conciseness
Conciseness is about expressing ideas succinctly.
It’s being economical with words and avoiding redundancy. This principle helps maintain pace and tension, engaging readers throughout the story.
Creativity is the heart of creative writing.
It allows writers to invent new worlds and create memorable characters. Creativity involves originality and imagination. It’s seeing the world in unique ways and sharing that vision.

Consistency
Consistency maintains a uniform tone, style, and voice.
It means being faithful to the world you’ve created. Characters should act true to their development. This builds trust with readers, making your story immersive and believable.
Is Creative Writing Easy?
Creative writing is both rewarding and challenging.
Crafting stories from your imagination involves more than just words on a page. It requires discipline and a deep understanding of language and narrative structure.
Exploring complex characters and themes is also key.
Refining and revising your work is crucial for developing your voice.
The ease of creative writing varies. Some find the freedom of expression liberating.
Others struggle with writer’s block or plot development challenges. However, practice and feedback make creative writing more fulfilling.
What Does a Creative Writer Do?
A creative writer weaves narratives that entertain, enlighten, and inspire.
Writers explore both the world they create and the emotions they wish to evoke. Their tasks are diverse, involving more than just writing.
Creative writers develop ideas, research, and plan their stories.
They create characters and outline plots with attention to detail. Drafting and revising their work is a significant part of their process. They strive for the 5 Cs of compelling writing.
Writers engage with the literary community, seeking feedback and participating in workshops.
They may navigate the publishing world with agents and editors.
Creative writers are storytellers, craftsmen, and artists. They bring narratives to life, enriching our lives and expanding our imaginations.
How to Get Started With Creative Writing?
Embarking on a creative writing journey can feel like standing at the edge of a vast and mysterious forest.
The path is not always clear, but the adventure is calling.
Here’s how to take your first steps into the world of creative writing:
- Find a time of day when your mind is most alert and creative.
- Create a comfortable writing space free from distractions.
- Use prompts to spark your imagination. They can be as simple as a word, a phrase, or an image.
- Try writing for 15-20 minutes on a prompt without editing yourself. Let the ideas flow freely.
- Reading is fuel for your writing. Explore various genres and styles.
- Pay attention to how your favorite authors construct their sentences, develop characters, and build their worlds.
- Don’t pressure yourself to write a novel right away. Begin with short stories or poems.
- Small projects can help you hone your skills and boost your confidence.
- Look for writing groups in your area or online. These communities offer support, feedback, and motivation.
- Participating in workshops or classes can also provide valuable insights into your writing.
- Understand that your first draft is just the beginning. Revising your work is where the real magic happens.
- Be open to feedback and willing to rework your pieces.
- Carry a notebook or digital recorder to jot down ideas, observations, and snippets of conversations.
- These notes can be gold mines for future writing projects.
Final Thoughts: What Is Creative Writing?
Creative writing is an invitation to explore the unknown, to give voice to the silenced, and to celebrate the human spirit in all its forms.
Check out these creative writing tools (that I highly recommend):
Read This Next:
- What Is a Prompt in Writing? (Ultimate Guide + 200 Examples)
- What Is A Personal Account In Writing? (47 Examples)
- How To Write A Fantasy Short Story (Ultimate Guide + Examples)
- How To Write A Fantasy Romance Novel [21 Tips + Examples)
How to Create Professional Reports and Documents in Microsoft Word
This guide examines the elements of a professional report and reviews the structuring, styling, and finalizing of your document in Microsoft Word.
If Microsoft Office had been a country, it would have been the third most populous country in the world. 1.2 billion people using a single suite of apps is mind-boggling. And, they "speak" 107 languages!
But right now, you and I are speaking in English and we are going to talk about the most popular tool in the Microsoft Office arsenal -- Microsoft Word 2016 .
This document editor is used for writing a variety of documents. From a simple application to the necessary resume. From a plain bucket list to an office memo. We think we can work with Word. But it is when we sit down to write a serious professional report, we discover an important fact.
Professional report writing needs a different set of skills.
So, ask yourself this -- can you make the leap from a single document to a lengthy report? Do you know all the Microsoft Word features that will help manage this large scale document project? Can you collaborate on the work with other team members?
You may be a student, a small business owner, or an office worker...you will need to create a report or a professionally formatted document of some kind. This MakeUseOf guide will help you update your techniques and sharpen your design approach.
In this guide:
Writing a Report -- Introduction | The Report Checklist
Useful Microsoft Word Tools -- Paste Special | Researcher | Freeze Parts of Your Document
Work on the Layout & Design -- Intro | Cover Page | Table of Contents | Header and Footer | Page Numbers | Font Styling | Paragraph Styling | Page Breaks | Styles and Themes | Captions | Quick Parts | Page Borders
References and Collaboration -- Index | Bibliographies | Cross-Referencing | Comments
Finalize Your report -- Signatures | Watermarks | Read Only | Print to PDF
The Next Step -- Conclusion
Writing a Report
Report writing involves research and then publishing the outcome of that analysis. In the professional world, the "look" or appearance of what you publish is paramount. The eye-pleasing final result could burnish your reputation and enhance your personal brand.
The steps below will handhold you through the expert features in Microsoft Word 2016. Spend a lot of time on a plan. Start with these guidelines…
Step 1: Decide the Purpose
Before you begin the report, you must first know why you are writing it in the first place. Reports are of many kinds but they are either meant to inform or persuade. It can be meant for describing a technical process, sharing background information, or demonstrate progress on a project.
Ask yourself – What and Why . This will help you distill the purpose to the one main point and stick to it instead of rambling on with unnecessary details.
Step 2: Identify Your Audience
The second important consideration is to evaluate your audience. Will they be able to understand what you are talking about? Are there different levels of readers who will read the report? The reader's knowledge of the subject will greatly influence the information that you need to include.
Decide on the primary audience and then script the report at the adequate technical level. The secondary audience can be supported with supplemental information at the end of the report.
Step 3: Know Your Topic
You must know what you are talking about. So, research the topic, and include all the relevant information to prove your point. Make sure that you come to a conclusion based on facts and not personal opinion. The information must be correct, current, and well-referenced.
Also use a variety of resources such as journals, newspaper articles, books, websites, brochures, raw data, annual reports, and speeches to help support your point. Just don't stick to Wikipedia.
Step 4: Outline the Report
You have done the research. There's a ton of information that is waiting to be typed and printed. But wait! Don't drown before you enter the water. Prepare the final outline of the report which will be the chart of waypoints to help you navigate from start to finish. The outline is the blueprint. It will give you a bird's eye view of the land and also show you where you need to fill in the details.
The structure of an idea report can include the following elements:
- Executive Summary
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- The Body of the Report
- Recommendations
- Bibliography and References
Microsoft Word's Document Outline is a powerful feature that can help you organize a document even before you start filling it with research. Take advantage of brainstorming and mind-mapping templates too.
Step 5: Write, Edit, Proofread, and Finish
Once you have structured your report, it is time to fill out the headers with content. I personally find it best to tackle a little bit of each section, and then bulk it up with information. You can do that if you want, or finish each section as you go down the report structure. Make sure you focus on presenting your ideas and using supportive evidence rather than spelling and grammar first. Outline your argument and write a few sentences that cast your main ideas. If you find something worth quoting, quote it.
Once the majority of your text is written, it is now time to read through it and make sure it flows well. Make sure you guide the reader's understanding with transition words such as "This information shows…", "In other words…", "Similarly…" and do highlight relevant and key points.
Finally, spend time to proofread, check for grammar and spelling , and double-check all relevant information and its logical flow. It is best to leave at least one day to check and proofread your work. Don't try to edit it straight after you think you have finished, as you will tend to miss read what you have written. Get some sleep, and proofread it the next day.
The Report Checklist
Before you go and submit or hand in your report that you have worked so hard on, make sure you have done the following:
- Completed the title page with the Title, Your Name, Date, Who the report is for, and a possible description of what the report is about.
- The contents page has appropriate headings and pages numbers are correct.
- Make sure the introduction covers key points, the scope of the report, and the objective it wants to meet.
- You have added captions above tables and below images/graphs.
- Does the content of the report present the information in a clear way, logical, factual, stay on topic, is to the point?
- Does the conclusion state the results, restate main idea's, and does not include any new information?
- Are the headings and sub headings clearly labeled?
- Are quotes relevant, up-to-date, and correctly referenced?
- Have you used page breaks where appropriate?
Now, let's launch Microsoft Word and take you through the features that will help piece together the draft of your report and present it as a professional document.
Useful Microsoft Word Features for Report Writing
Take these as bite-sized tips and master them one by one.
Microsoft Word is a big howitzer with many nuts and bolts. Let's focus on the key skill sets and the tools you will need to plan, prepare, and present the professional report. The Microsoft Word features we will cover below are also productivity shortcuts that will make your job easier.
Tip: Use Microsoft Word 2016's "Tell Me" assistant to learn more about new features in the Office suite.
Let's start with three preliminary tools...
Use Paste Special
For most of us, when we need to copy text or an image into Word, the CTRL+V shortcut does just fine. But sometimes we might want to paste the copied data into another format, such as Excel data as an image. With the Paste Special command you can discard or specify the format when you paste a picture, presentation data, table, or object from any other program into Word.
You will work a lot with Excel tables and charts in a professional document.
If you just copy what you want and click paste, you will notice that it will insert the data as tables. But, if it is a large area of cells you want to paste, and you do not want to edit it, you may want to paste it as an image, with the extra option to edit it.
In Microsoft Excel: Select and highlight the cells that you want to copy > Press CTRL+C.
In Microsoft Word: Go to Home > Paste > Paste Special . Select Paste Special and from the dialog select Microsoft Office Excel Worksheet Object .
You can resize the data as it was an image, and if you double click, you will be able to edit the values. You can change the table or chart and redesign it. And, if you update the data in the chart or table in Excel, you can automatically refresh the chart in Word.
Try the right-click context menu too. The Paste Special menu pops up:
There are more options to import data from Excel into Word . The Microsoft Office Support page also describes them in detail.
Use the Researcher
Yes, there is Google and Wikipedia. But constantly switching from Word to your browser can hamper your productivity. Office 2016 brings in powerful research integration to this grunt work. The Researcher can not only help you find content from within Microsoft Word but also help you quickly add citations. It uses the Bing Knowledge Graph to find the right content to support your document.
Go to Ribbon > References tab and c Choose Researcher . A pane will open on the right with the search options.
Type a keyword for the topic want to search for and press Enter.
The Results pane shows a list of sources you can use in your document. Choose a topic to explore in detail.
Add the topic to your Microsoft Word document with a click on the plus sign on the top-right. You can also click the plus sign on any result to cite the source in your research document. The cite source helps you support your research with web sources and books.
As we will see later, an annotated bibliography is one of the toughest parts of a document. The Researcher is an intelligent assistant who steps in.
Freeze Part of Your Word Document
Let's take for granted that your professional report will be a long and complex work. You can split the Word window into two panes so that you can view two different parts of a document at the same time. It is a valuable time saver when you want to copy and paste parts from one place to another or refer to one part of the document while working in another.
Go to Ribbon > View tab > Split .
To remove the split, click on Remove Split in the same tab.
The Windows group gives you several options to change the way you work with two or more documents. The features are self-explanatory.
To scroll both documents at the same time, click Synchronous Scrolling in the Window group on the View tab. You can also click on View Side by Side to put two parts of the document next to each other.
Tip: Use Split View to display two different layouts – for instance, Print and Outline. Set the split. Then, click in the pane that you want to change, and then select a different layout on the View tab.
Work on the Layout & Design
The presentation of a report is what gets someone to read a report in the first place, and that is why it is crucial that your report is well presented. If you had the choice of four reports to read, what will you choose?
- A hand written report.
- A document printed in black and white.
- A report printed on normal A4 paper in color.
- A report printed in color, with a catchy title page, neatly bounded, and slick?
You will pick up the fourth report because it will pull you towards it by the visual appearance alone.
The front cover is not the only reason. A well-designed report is easier to read. It is also easier to scan when you don't have time to read. That is why you need to spend some time on your headers and footers, and the different styles and themes. In short – the formatting of every element in the report.
Formatting may seem like a difficult chore, but it is a fun exercise that will exercise all your creative muscles. The key takeaways will be the skills you can apply to anything in Microsoft Office going forward. And the time you will save with all the productivity tips learned here.
Microsoft Word 2016 has a wealthy set of features. These are only some of the ways that your report design can stand out from the rest and be professional. So, let's break down the layout and design skills.
This section will cover these features step-by-step:
- Start with a Cover Page
- Make a Table of Contents
- Create Your Header and Footer
- Add Page Numbers
(Format the Content)
- Pick the Right Fonts
- Style the Paragraphs
- Control Page Breaks
- Use Styles and Themes
- Use Quick Parts
- Decorate with Page Borders
1. Start With a Cover Page
The first page is the first point of contact with your reader. It is also your opportunity to make a favorable impression. Don't let your lack of artistic skills be an excuse because Word takes up the job with its in-built gallery of title pages. All you have to do is marry one to the theme of the report.
Microsoft Word 2016 offers you 16 pre-formatted templates and three more on Office.com.
Go to Insert > Pages Group > Cover Page .
The cover page appears at the beginning of the document by default.
As there are only 16 "official" templates on offer, you may find that all your other peers have the same cover page. So, why not customize it, and make it a bit more unique.
You can design a title page (or cover page) in Microsoft Word that can be an original in the stack. Save it as a template or easily change the design on the fly.
2. Make a Table of Contents
Casual readers scan. Good readers scan first and then dive deep. A table of contents provides the waypoints that help both. When it is a long and complicated document, wouldn't you rather check the lay of the land before you head to the section that interests you?
Consider a Table of Contents (TOC) if your document is more than 10 pages long. You should first make sure you don't need to rearrange any pages in your document before creating the TOC.
In Microsoft Word, you don't have to write the entire TOC by hand. There's a Table of Contents automatic tool under the References tab which takes your outline and designs it for you. Also, you can easily keep it updated when you want to change something.
There are also templates you can download and fit it around the nature of the content. For instance, a TOC for a thesis will look different from that of a company's annual report.
We have a complete tutorial on how to create a table of contents page in Word .
The gist of it is this:
Create the outline and use heading styles to organize the hierarchy. Apply the automatic TOC tool to the heading styles. Word 2016 searches for those headings and then inserts the table of contents into your document. Then you can automatically update your TOC if you make changes in your document.
For more hands-on control, you can also use the Manual Table of Contents style. Word inserts placeholder text and you have to insert and format each content in the list.
3. Create Your Header and Footer
Headers and Footers are important in reports as the main purpose is to provide information about the report on every page. They are the common display areas for page numbers. The header of the document should contain the title of the report, and possibly the name of who created it. The title of the current section is helpful.
The footer, on the other hand, should include the page numbers, date of publication, and other administrative information that is required. Do note that some style guides have special guidelines for headers and footers .
Let's start with the header in your document and give it a unique look.
Select Insert , then select either Header or Footer from the group. The built-in gallery shows you several options you can choose from.
The header and footer space is inserted in your document with placeholder text or table. The Header & Footer Tools opens on the Ribbon for other formatting work like the date, time, or picture.
Enter your text and then select Close Header and Footer .
You can start with a blank header and footer. If you have the design skills, use the Header & Footer Tools to design your own. Master the header and footer space if you want to create custom letterheads for your organization. You can use brand elements like company or organization logos at the top and neatly formatted footnotes at the bottom
Let's try with and modify one of the inbuilt headers. I selected Facet from the gallery.
The final look took two minutes to put together with simple text effects and an icon sourced from the Microsoft Office icon gallery.
The header and footer are in place. But, how do you know where you are in the document? Insert page numbers as the next important signpost.
4. Add Page Numbers
Page numbers look best in the footer (unlike in the header as in the image above). You can add a basic page number from the Insert > Page Number button on the Ribbon. You can also add it from the Design tab that appears when you add the header and the footer.
You have a lot of control over page numbers. Choose from a wide range of number formats and customize them to your needs. In this case, we are adding the number to the footer, but you can put them at the top or even at the margins. In this example, I have placed the page number at the bottom left. But, I would like to change the default look and the format.
For example: Using a "Page X of XXX" makes for a better indicator on a long document.
Select the page number. Go to Insert > Quick Parts . From the drop-down menu, select Field . You can also reach the Field dialog from the Header and Footer Design tab.
Choose NumPages from the long list of field names. From the box on the right, you can pick a specific format. I selected the usual 1, 2, 3. Click OK , and the number of the number of pages will appear. Now all you have to do is add your text such as Page X of XXX, and change the look of the numbers with the usual text formatting tools available from the Home tab.
It now looks like this:
Design the look on any page number in your document and Word updates all the remaining automatically. Page numbers are the most common elements in a footer, but it can also hold any other information like the header. From the options in the Insert group, you can add the date and time, document info, pictures, and more to your header or footer.
Next, we're heading into formatting the content.
The visual draw of your professional report comes together with the "beautification" you apply to the content. Formatting is also an essential step for a document that flows well. So, you must focus a lot of energy on picking the right font, paragraph space, and the colors.
Don't worry. Even, the artistically challenged will find this part easy because Microsoft Word comes packaged with default themes and visual styles. Let's start with the most basic element of a document.
5. Pick and Style the Right Font
Your choice of font in a professional Word report not only determines how the text stands out but also how it is printed. You want both for maximum impact.
You can apply a typeface (i.e. the visual look of the font) to either an entire document or to specific parts of a document. All font choices are available from the Home tab. Go to Home > Font .
The default font in Microsoft Word 2016 is Calibri. Look beyond that as you have lots of others to choose from. If you choose Times New Roman, you may be considered lazy, if you choose Windings, well… I don't think I need to explain that. So make sure you choose a font that is easy to read and suits the report. To play it safe, pick from one of these professional-looking Google fonts ; they're available for free.
Tip: Baskerville and Georgia are good alternatives to the over-used Times New Roman
Try different font pairing for the body text and Headings (and Subheadings). Several websites like FontJoy and TypeWolf will help you experiment with font pairings. You can download and use custom fonts too. But remember the thumb-rule -- never use more than three different typefaces in a document.
For that extra bit of pizazz, try a drop cap to enhance your text .
6. Style the Paragraphs
If you want to have your lines double spaced, or single spaced, you need to change the format of the paragraphs. By changing the spacing, you can make a document easier to read or give the impression that it is longer and that you have put more work into it.
To change the paragraph for the whole document, it is best that you select each block of text; otherwise, if you are using headers in your report, they will change too. Another better option is if you customize the particular style you are using to format the paragraph.
To do this, go to Home > Styles . Right click on the style you want to change and select Modify . Click on Format > Paragraph which is at the bottom of the dialog box. Now, change the spacing, indentation, and alignment for the paragraph. Click OK to close the dialogs.
When you want to change a smaller portion of the document , select what you want to change. Right click on the highlighted text and select Paragraph . The same dialog box as above will appear.
7. Control Page Breaks
A page break -- by its very name -- splits a continuous block of text across two pages. Page breaks are important structural elements for long documents. Word automatically inserts a page break at the end of the page. But in a long document, you can place page breaks where you want them.
To insert a manual page break, click Insert > Page Break. (Keyboard shortcut: CTRL + Enter)
A page break looks like this when you click on the Show/Hide command in the Paragraph group .
But what if you want to keep a bunch of lines together on a page or column and not have them separate because of a page break? The layout is in your control. Click the tiny arrow you see in the bottom right of the Paragraph group.
In the Paragraph box, click Line and Page Breaks. Select from these four pagination options:
- Widow/Orphan control places at least two lines of a paragraph at the top or bottom of a page.
- Keep with next prevents breaks between paragraphs you want to stay together.
- Keep lines together prevents page breaks in the middle of paragraphs.
- Page break before adds a page break before a specific paragraph.
We've also shown how to remove page breaks when necessary.
8. Use Styles and Themes
Styles and themes are perhaps two of the more underused features in Microsoft Word . But I think you should use them at every opportunity to save a lot of time.
But what is the difference between a theme and a style? Microsoft says:
Themes provide a quick way to change the overall color and fonts. If you want to change text formatting quickly, Word Styles are the most effective tools.
So, as themes control the general look with color, effects, and fonts – start with a good theme for your document first. Then , use Styles to dig into the specific portions you want to change the appearance for.
For Themes: Go to the Design tab. Pick a theme from the gallery. You can see previews of what the color combination is like.
For Styles: Select the part of the text you want to change. Go to the Styles group on the Home tab. You can see previews of what they look like. Choose the Style that is suitable for your content. For instance, choose a heading style for the headings in your document. Or, a particular style for any quotes. You can also modify an existing style and create new styles from scratch.
9. Captions
Every picture, chart, or illustration needs a caption to clearly describe it. It is a single line of text, usually located below a graphic. Captions are also an important reference when you need to mention them in another place. Many documents omit this small detail.
It is easy to add a caption. Right-click the illustration you want to add a caption to. Select Add Caption .
In the dialog box, add your caption text and configure the remaining options. Captions can be automatically referenced in Word.
10. Use Quick Parts
Professional documents can get repetitive. This is why you should start using Quick Parts for boilerplate content you reuse all the time. For instance, let's say there is a contract clause you include with every document. Or, some introductory information. Instead of repeated copy-paste, save them as Quick Parts and re-use them again and again.
Quick Parts is also a type of building block . You can see the gallery of all reusable blocks of content in the Building Block Organizer .
Save and reuse your own Quick Parts in two steps:
- Select the phrase, sentence, or other portion of your document that you want to save to the gallery.
- Go to Insert > Text group > Quick Parts > Save Selection to Quick Part Gallery . Change the name and add a description if you like. Click OK .
Just as easily, you can re-use the saved snippet of content.
Place your cursor where you want to insert a selection from the Quick Parts Gallery. Go to Insert > Text group > Quick Parts . Then click the sentence, phrase, or other saved selection you want to reuse.
You will notice three other categories in the Quick Parts menu.
AutoText: Word 2016 has retained the old AutoText feature. It works like Quick Parts for any block of text that you use a great deal. Example: A note you want to use with every document.
Document Property: A set of constant properties that you can include with every document. Example: Company name or author.
Fields: These are predefined elements that update automatically. Example: Date, time, page numbers etc.
Remember, entries for document property can sometimes include information you wouldn't want to share with everyone. So, keep a close eye on these fields and remove the hidden personal data whenever required.
11. Decorate With Page Borders
Page borders look good not only on flyers and invitations. If done right, they can add a touch of class to a document. A variety of line styles and widths and art borders are available from the Design menu on the Ribbon.
Go to Design > Page Borders.
In the Borders and Shading box, use the Page Border tab to design your border.
The settings are self-explanatory. Try Shadow or 3-D with the right colors to add a subtle but elegant border. The Art styles with their clip-art borders might be too garish for professional documents.
Use the four corner buttons in the Preview window to select the sides of the page to draw borders. Click these buttons to remove or add borders, as you wish.
Place the cursor on the first page of a document if you want to put a border around only the first page. You can also put borders around certain pages in a section. Place the cursor in the section — either in the first page of that section or in a subsequent page.
References and Collaboration
A Word report can seem like an unmanageable chore. It's like organizing a million piles of hay into neat little stacks. The idea is to know precisely which stack has the pin you are looking for. These features are meant to make it easier.
1. Create an Index
When writing large documents such as a report that contains a lot of information, a contents page may not be enough. An Index should appear at the end of the document, with page numbers to keywords and information in the report. Create an index to help the reader reference the right information with just the page number.
Make an index if your document has more than 20 pages. Microsoft Word 2016 doesn't let the process overwhelm you. It basically has two parts:
- Select the words or information you want to include in the index.
- Place the index at the right place in your document.
You can scroll through the finished document and mark the words or phrases you want to include in the index or mark them as you go along. Either way, select the text you'd like to use as an index entry or click where you want to insert the entry.
1. Click References > Mark Entry .
2. Edit the text in the Mark Index Entry dialog box. You can also add a sub-entry which further defines the main word you used in the index. You can add multiple levels and each appears indented under the main entry.
3. Under Options , you can also create a cross-reference to another main entry. A reader can use this to refer related information elsewhere in the same document.
4. Use the Page number format to decide on the appearance of the page numbers in the index.
5. Click Mark to mark the index entry. To mark this text everywhere it shows up in the document, click Mark All .
6. Repeat the process for all the words and phrases you want to include in the index.
You have now built your index. Insert it at the right place towards the end of the document.
1. Click on the page where you want to insert the index.
2. Click References > Insert Index .
3. The Index dialog box is displayed. Here you can choose to format the text entries, page numbers, tabs, and leader characters.
4. Choose the appearance from the different formats in the list and check the Preview window on the right. Remember, the Preview window doesn't show you actual index. It is just a "simulation" of how it will look like.
5. Click OK . Your Index is now ready.
Sometimes, you may need to add more entries to the index after you have inserted it on the page. Mark the entry and go to References > Update index to include the new mentions.
Also, add a heading for the index because Word doesn't do it automatically.
2. Creating Bibliographies
Your document is almost done. Now, you need to credit all the other research work and ideas which you have referenced in your document. It's time for a bibliography.
A company report might not need a bibliography but an academic paper isn't finished without one. The bibliography is one of the most painstaking jobs in an academic report. You need to have all your citations in order before you sit down to frame the bibliography. Also, decide on the citation style (typically MLA, APA , or Chicago-style ) as per the guidelines of your subject.
Don't hesitate to take advantage of third-party citation and bibliography generators for constructing this section.
But, Microsoft Word 2016 has a complete toolset to make this process as painless as possible. So, go to the point in the document where you would like to place the bibliography. It's good if you have at least one citation to include, but even if you don't, Word 2016 lets you use a placeholder citation and fill in the sources later.
Click References > Bibliography .
Word offers a few bibliography styles that differ only in their heading names. Choose the appropriate style and then insert citations from the button in the Citations & Bibliography group .
The bibliography tool has a few steps to it. For the sake of brevity, I will direct you to the excellent Microsoft Office help page which is a step-by-step guide.
Some academic papers will ask you to create an annotated bibliography . It is a more fleshed out version of a bibliography with a list of citations to journals, books, articles, and other documents followed by a brief paragraph. The paragraph is a description of the source and how it supports your paper.
3. Cross-Referencing
You can use a cross-reference to help the reader navigate through a long document. At any point in a document, you can tell the reader to refer back to a heading, page number, image, chart, footnote, endnote, and paragraph. A cross-reference link is a neat way to connect related information together. The reader just has to click on the link to go that snippet of information.
Here's how you begin:
1. Select the place for the cross-reference and type the text that tells the reader about it. For instance: "Refer to Chart 3 for future trends."
2. Go to Insert > Cross-reference .
3. In the Reference type box, click the drop-down list to select what you want to link to.
4. The options in the Insert Reference to drop-down will change according to your choice above.
5. In the For Which field, go through the choices and tell Word the exact information to link to.
6. Check the Insert as hyperlink box to create the hyperlink for the referenced information.
7. Click on Insert to include the cross-reference in the document.
Remember, our mention of captions? You can make cross-references to equations, figures, graphs, and tables if you used captions below them.
Word cannot create a cross-reference for something that does not exist. Word will let you know about these errors and also update the cross-references automatically when you change the page number or text of the referenced item.
4. Using Comments
A professional report can be a solitary job or you can take the help of a team to prepare the first draft. The humble Comment is one of the most underused tools of a Word document. It is displayed as a rectangular colored balloon in the margin or in the Reviewing Pane.
You can use comments as small "stickies" or self-notes. Leave little notes to yourself in the margins as you write, edit, and revise your way through a report or a manuscript. Be creative – add extra links to other resources, use them for tips and pointers, link to different parts of a document, or set up a feedback link for your readers. And when you finalize, you can easily remove all comments in Word .
Microsoft Word 2016 is also an enhanced collaborative writing tool. Comments play a huge role in communicating feedback across a team. Here's how the comment system works...
1. Highlight the text you want to add a comment to or click at the end of a text block.
2. Go to Insert > Comment . Type your comment in the box. The comments appear in the markup area on the right. The Print Layout view is usually the best way to see the comments alongside the text.
3. Go to the Review tab and see more options for comments. This tab also shows all the controls for tracking changes and comments in a collaborative document. Use the Markup options to display or hide the comments. For instance: No Markup will hide the comments and the markup area on the right.
Finalize Your Report
Once the bulk of your report is completed and saved, it is time to finalize your report. When I say finalize, I don't mean proofread it. That should be done too. Now, you have to take the security measures to protect the report from unauthorized changes and plagiarism.
These security measures will give an extra level of authenticity to your electronic file before you share it.
This section will cover:
- Insert watermarks
- Make the document 'read only'
- Password protect your document
- Print your document to PDF
1. Signatures
You can add text signature for a personal touch to the report. But a simple text signature does not need any authentication. A digital signature is the better way to protect your document from unauthorized access. A digital signature confirms that the document came from the signer and hasn't been tampered in any way.
Let's create a signature line in Microsoft Word 2016.
In the document, place your cursor where you want to create a signature line.
1. Go to Insert > Text group > Signature Line and click Microsoft Office Signature Line .
2. The Signature Setup dialog box is displayed. Fill the fields as indicated. If you are sending the document to someone else for signing, add instructions for the signer in the field reserved for it ( Instructions to the signer ). The signer can also add give the purpose for the signing if the Allow the signer to add comments in the Sign dialog box is checked.
3. Click on OK and the document will now display a placeholder for the signature.
Enter a signature:
When you need to sign a document with a digital signature, go to the signature line and right-click on it.
You will be prompted to sign with a digital ID. If you don't have one, Microsoft will tell you to get one from a signature service partner.
If you don't have a digital ID, you can just insert a textual representation of a signature line . You can use a written signature or an image that doesn't require authentication.
2. Insert Watermarks
A Microsoft Word watermark is a "fake" but still useful visual indicator for the status of the document. For instance, you can use a watermark that says "Drafts" to differentiate it from the final version of the document. Or, use the watermark to suggest the document is "Copyrighted" or "Confidential".
The "Draft" mark is the most common. But, Microsoft Word gives you several other watermarks to choose from.
1. Go to Design > Page Background and choose Watermark . The Watermark button will be enabled in the Print view only.
2. You can choose a picture or a text watermark from the gallery. Both horizontal and diagonal versions are available. The dialog box gives you all the customization options for the final look of the watermark. Try different fonts, layouts, sizes, and colors.
3. You can type your own text in the Text field to create your custom watermark.
4. Choose OK to apply the watermark to your document. Word automatically applies the watermark to every page except the title page.
3. Make Documents "Read Only"
A professional report by its nature should not need to be edited by its readers. Converting the document to a PDF is one way. But, you can also apply a few more restrictions in Microsoft Word and prevent accidental modification or omission of any kind.
There are three ways to protect a document.
First -- Make your document "read only".
This ensures that your document can only be read or copied. It won't prevent anyone from copying the file and making changes to the copy.
1. Go to the File tab > Info > Protect Document > Mark as Final.
2. When readers open a document, a bar on top will prompt readers to treat this document as read only. But, they can click on "Edit Anyway" to open the document in Edit mode.
Second -- Password Protect Your Document.
Protect your document from unwanted edits with a password barrier.
1. Under Protect Document , choose Encrypt with Password . Type a password and click OK .
2. In the Confirm Password box, type the password again, and then click OK . The document will open with the reader prompted for a password.
Microsoft uses the AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), 128-bit key length, SHA1 (a cryptographic hashing algorithm which generates an almost unique 160-bit key to replace the plaintext), and CBC (cipher block chaining) to give a hacker a well-deserved headache.
Third -- Restrict Editing.
This control feature helps you as the author decide which parts of the document others can edit and which will be locked out. Think of it as the bouncer who lets the VIPs in but otherwise bars the door for the common folk.
1. Go to Review > Restrict Editing .
2. Under Editing restrictions , check Allow only this type of editing in the document , and make sure the list says No changes (Read only) .
No changes (Read only) is the default restriction type. For a different restriction level for the document, click the menu and select from Tracked changes, Comments, or Filling in forms.
3. To free some sections from the editing blockade, select the sections for editing without restrictions. To select more than one area, click CTRL while selecting the area using the mouse.
4. You can check Everyone under Exceptions (optional) in the Restrict Editing panel. Or, click More users … and allow only specific users to modify the sections. The allowable areas will be marked with square brackets.
5. Click Yes, Start Enforcing Protection .
Now, type a unique password in the box that opens. You have to type it again to confirm it.
The password is optional. But it ensures that no one can just click Stop Protection and edit the document. If you are still paranoid, go ahead and encrypt your Microsoft Word document as we did in the second process above.
4. Print Your Report to PDF
The Portable Document Format comes with many advantages. Not least is its cross-platform compatibility across all computers. Your document is ready and now you need to share it or send it across to be printed. Many professional reports -- for instance, a legal document -- need to retain the format as intended.
Save or convert a copy to PDF. Microsoft Word 2016 does not need any third-party add-ins.
Go to File > Export > Create PDF/XPS .
Remember, your Word document may contain sensitive information that you do not want to be included in the PDF. Remove it before you publish to PDF. In the Publish as PDF or XPS window, choose Options . Then select Document and clear Document properties . Set any other options you want and choose OK .
Browse to where you want to save the file and click on Publish .
The Next Step...
You are close to the finishing line. The report is ready to be handed over to your readers. But there's one last job left.
Turn the pages and make sure (again) that your report is reader-friendly. Approach it with the eye of the reader. Have you organized your thoughts and written persuasively? Does the information flow well with the charts and illustrations? Can they skim through and find the information quickly? Is the text readable? Use the readability score to gauge the readability level of your documents as a final step.
You also might have noticed we didn't cover some aspects of Microsoft Word. For instance, Microsoft Word Tables are an important tool for data display. Or, the power of lists in information management.
Microsoft Word is more than a quarter of a century old, and packed with little features. At MakeUseOf, we have covered every nook and cranny of this beast. So, do use our resources to learn more about this software for free. Each new feature of Microsoft Word learned will make your life easier.
Make Your Report Shine
As author Nathaniel Hawthorne said,
Easy reading is damn hard writing
Isn't this true for professional report writing too? After all, if given a choice, no one may want to read it. Writing a business report and using it to communicate are two different things. Microsoft Word is just a tool -- it's your job to engage.
For some alternatives, check out the best online word processors . And for more help with professional writing, take a look at how to apologize in an email and mean it .
What are the best practices for writing professional business reports? Tell us in the comments.

30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Report Writing

- Updated on
- Nov 4, 2023

The term “report” refers to a nonfiction work that presents and/or paraphrases the facts on a specific occasion, subject, or problem. The notion is that a good report will contain all the information that someone who is not familiar with the subject needs to know. Reports make it simple to bring someone up to speed on a subject, but actually writing a report is far from simple. This blog will walk you through the fundamentals of report writing, including the structure and practice themes.
This Blog Includes:
What is a report, reporting formats, newspaper or magazine reports, business reports, technical reports, what is report writing, report writing: things to keep in mind, structure of report writing, magazine vs newspaper report writing format, report writing format for class 10th to 12th, report writing example, report writing for school students: practice questions, report writing slideshare.
- Report Writing in 7 steps
Also Read: Message Writing
A report is a short document written for a particular purpose or audience. It usually sets out and analyses a problem often recommended for future purposes. Requirements for the precise form of the report depend on the department and organization. Technically, a report is defined as “any account, verbal or written, of the matters pertaining to a given topic.” This could be used to describe anything, from a witness’s evidence in court to a student’s book report.
Actually, when people use the word “report,” they usually mean official documents that lay out the details of a subject. These documents are typically written by an authority on the subject or someone who has been tasked with conducting research on it. Although there are other forms of reports, which are discussed in the following section, they primarily fulfil this definition.
What information does reporting contain? All facts are appreciated, but reports, in particular, frequently contain the following kinds of information:
- Information about a circumstance or event
- The aftereffects or ongoing impact of an incident or occurrence
- Analytical or statistical data evaluation
- Interpretations based on the report’s data
- Based on the report’s information, make predictions or suggestions
- Relationships between the information and other reports or events
Although there are some fundamental differences, producing reports and essays share many similarities. Both rely on facts, but essays also include the author’s personal viewpoints and justifications. Reports normally stick to the facts only, however, they could include some of the author’s interpretation in the conclusion.
Reports are also quite well ordered, frequently with tables of contents of headers and subheadings. This makes it simpler for readers to quickly scan reports for the data they need. Essays, on the other hand, should be read from beginning to end rather than being perused for particular information.
Depending on the objective and audience for your report, there are a few distinct types of reports. The most typical report types are listed briefly below:
- Academic report: Examines a student’s knowledge of the subject; examples include book reports, historical event reports, and biographies.
- Identifies data from company reports, such as marketing reports, internal memoranda, SWOT analyses, and feasibility reports, that is useful in corporate planning.
- Shares research findings in the form of case studies and research articles, usually in scientific publications.
Depending on how they are written, reports can be further categorised. A report, for instance, could be professional or casual, brief or lengthy, and internal or external. A lateral report is for persons on the author’s level but in separate departments, whereas a vertical report is for those on the author’s level but with different levels of the hierarchy (i.e., people who work above you and below you).
Report formats can be as varied as writing styles, but in this manual, we’ll concentrate on academic reports, which are often formal and informational.
Also Read: How to Write a Leave Application?
Major Types of Reports
While the most common type of reports corresponds to the ones we read in newspapers and magazines, there are other kinds of reports that are curated for business or research purposes. Here are the major forms of report writing that you must know about:
The main purpose of newspaper or magazine reports is to cover a particular event or happening. They generally elaborate upon the 4Ws and 1H, i.e. What, Where, When, Why, and How. The key elements of newspaper or magazine report writing are as follows:
- Headline (Title)
- Report’s Name, Place, and Date
- Conclusion (Citation of sources)
Here is an example of a news report:
Credit: Pinterest
Business reports aim to analyze a situation or case study by implementing business theories and suggest improvements accordingly. In business report writing, you must adhere to a formal style of writing and these reports are usually lengthier than news reports since they aim to assess a particular issue in detail and provide solutions. The basic structure of business reports includes:
- Table of Contents
- Executive summary
- Findings/Recommendations
The main purpose of the technical report is to provide an empirical explanation of research-based material. Technical report writing is generally carried out by a researcher for scientific journals or product development and presentation, etc. A technical report mainly contains
- Introduction
- Experimental details
- Results and discussions
- Body (elaborating upon the findings)
Must Read: IELTS Writing Tips
A report is a written record of what you’ve seen, heard, done, or looked into. It is a well-organized and methodical presentation of facts and results from an event that has already occurred. Reports are a sort of written assessment that is used to determine what you have learned through your reading, study, or experience, as well as to provide you with hands-on experience with a crucial skill that is often used in the business.
Before writing a report, there are certain things you must know to ensure that you draft a precise and structured report, and these points to remember are listed below:
- Write a concise and clear title of the report.
- Always use the past tense.
- Don’t explain the issue in the first person, i.e. ‘I’ or ‘Me’. Always write in the third person.
- Put the date, name of the place as well as the reporter’s name after the heading.
- Structure the report by dividing it into paragraphs.
- Stick to the facts and keep it descriptive.
Must Read: IELTS Sample Letters
The format of a report is determined by the kind of report it is and the assignment’s requirements. While reports can have their own particular format, the majority use the following general framework:
- Executive summary: A stand-alone section that highlights the findings in your report so that readers will know what to expect, much like an abstract in an academic paper. These are more frequently used for official reports than for academic ones.
- Introduction: Your introduction introduces the main subject you’re going to explore in the report, along with your thesis statement and any previous knowledge that is necessary before you get into your own results.
- Body: Using headings and subheadings, the report’s body discusses all of your significant findings. The majority of the report is made up of the body; in contrast to the introduction and conclusion, which are each only a few paragraphs long, the body can span many pages.
- In the conclusion, you should summarize all the data in your report and offer a clear interpretation or conclusion. Usually, the author inserts their own personal judgments or inferences here.
Report Writing Formats
It is quintessential to follow a proper format in report writing to provide it with a compact structure. Business reports and technical reports don’t have a uniform structure and are generally based on the topic or content they are elaborating on. Let’s have a look at the proper format of report writing generally for news and magazines and the key elements you must add to a news report:
To Read: How to Learn Spoken English?
The report writing structure for students in grades 10 and 12 is as follows.
- Heading : A title that expresses the contents of the report in a descriptive manner.
- Byline : The name of the person who is responsible for drafting the report. It’s usually included in the query. Remember that you are not allowed to include any personal information in your response.
- (introduction) : The ‘5 Ws,’ or WHAT, WHY, WHEN, and WHERE, as well as WHO was invited as the main guest, might be included.
- The account of the event in detail : The order in which events occurred, as well as their descriptions. It is the primary paragraph, and if necessary, it can be divided into two smaller paragraphs.
- Conclusion : This will give a summary of the event’s conclusion. It might include quotes from the Chief Guest’s address or a summary of the event’s outcome.
Credit: sampletemplates.com
Credit: SlideShare
Now that you are familiar with all the formats of report writing, here are some questions that you can practice to understand the structure and style of writing a report.
- You are a student of Delhi Public School Srinagar handling a campus magazine in an editorial role. On the increasing level of global warming, write a report on the event for your school magazine.
- On the Jammu-Srinagar highway, a mishap took place, where a driver lost his control and skidded off into a deep gorge. Write a report on it and include all the necessary details and eyewitness accounts.
- As a reporter for the Delhi Times, you are assigned to report on the influx of migrants coming from other states of the country. Take an official statement to justify your report.
- There is a cultural program in Central Park Rajiv Chowk New Delhi. The home minister of India is supposed to attend the event apart from other delegates. Report the event within the 150-200 word limit.
- Write today’s trend of COVID-19 cases in India. As per the official statement. include all the necessary details and factual information. Mention the state with a higher number of cases so far.
- In Jawaharlal Nehru Stadium in New Delhi, a table tennis tournament was held between Delhi Public School New Delhi and DPS Punjab. Report the event in 250-300 words.
Also Read: Formal Letter Format, Types & Samples
Credits: Slideshare
Report Writ ing in 7 steps
- Choose a topic based on the assignment
- Conduct research
- Write a thesis statement
- Prepare an outline
- Write a rough draft
- Revise and edit your report
- Proofread and check for mistakes
Make sure that every piece of information you have supplied is pertinent. Remember to double-check your grammar, spelling, tenses, and the person you are writing in. A final inspection against any structural criteria is also important. You have appropriately and completely referenced academic work. Check to make sure you haven’t unintentionally, purposefully, or both duplicated something without giving credit.
Related Articles
Any business professional’s toolkit must include business reports. Therefore, how can you create a thorough business report? You must first confirm that you are familiar with the responses to the following three questions.
Every company report starts with an issue that needs to be fixed. This could be something straightforward, like figuring out a better way to organise procuring office supplies, or it could be a more challenging issue, like putting in place a brand-new, multimillion-dollar computer system.
You must therefore compile the data you intend to include in your report. How do you do this? If you’ve never conducted in-depth research before, it can be quite a daunting task, so discovering the most efficient techniques is a real plus.
Hopefully, this blog has helped you with a comprehensive understanding of report writing and its essential components. Aiming to pursue a degree in Writing? Sign up for an e-meeting with our study abroad experts and we will help you in selecting the best course and university as well as sorting the admission process to ensure that you get successfully shortlisted.
Ankita Mishra
A writer with more than 10 years of experience, including 5 years in a newsroom, Ankita takes great pleasure in helping students via study abroad news updates about universities and visa policies. When not busy working you can find her creating memes and discussing social issues with her colleagues.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
26 Best Report Writing Topics For Students
Stumped while brainstorming report writing topics ? We’ve got your back. Take a look at our list of interesting-to-research report topics for students .
Completing a research report for a high school or college English class can be a great way to show off your smarts or interest in a topic, but figuring out where to start can be challenging. Choosing a topic that interests you is an essential part of getting started. The more curious you are about your chosen topic, the more interested you’ll be in the research process.
Choose from our list of sample essay topics below to show off your writing skills — we have options that work for several types of report writing formats. If you’re still stuck picking your next essay topic, check out our round-up of essay topics about education .
1. Technology’s Effect on Society
2. gun control in america, 3. anxiety and social media, 4. present-day slavery, 5. should assisted suicide be legal, 6. the draft’s history in america, 7. no child left behind: did it work, 8. the bp oil spill: 12 years later, 9. parental leave around the world, 10. the insanity plea, 12. trans rights: at what age should a person be legally allowed to transition, 13. should school uniforms be mandatory, 14. compare the uk and us education systems, 15. discuss the pros and cons of violent tv shows for teens, 16. analyze how peer pressure impacts teenagers, 17. does music have healing powers, 18. analyze the causes of wildfires, 19. discuss the impact of global warming on the environment, 20. how does single parenting impact the upbringing of a child, 21. what are the social impacts of the covid-19 pandemic, 22. the effects of urbanization on wildlife, 23. mental health impact of social media on teens, 24. sustainable farming practices and food security, 25. the rise of e-learning, 26. impact of plastic waste on marine life.

Technology makes our lives easier in many ways, but today’s tech-heavy society can also have detrimental effects. Some people find they must always be reachable due to constant access through email and cell phones, while others appreciate instant access to the people closest to them.
In a research report on how technology affects today’s society, you can focus on both sides, touching on how technology makes life easier and affects relationships and work-life balance. Discuss how technology has positively affected medical care and how the overuse of technology has contributed to health issues (including an increasingly sedentary lifestyle). Be sure to back up your points with background information based on research.
Gun control in the United States is a controversial topic. This type of academic report can either be written as a report that presents both sides of a story or as a persuasive report that argues one side. People who are for gun control argue that access to guns increases the risk of violence in the United States. In contrast, people against gun control argue that guns aren’t responsible for deaths and violence.
While presenting this topic in a formal report, discuss the history of gun control in the United States. You may also want to consider comparing gun violence rates in the United States with gun violence in other countries and comparing gun control laws in the U.S. to gun control laws in other countries. Be sure to check your sources carefully when writing about gun control, and choose unbiased sources as often as possible.

It’s tough to avoid social media in today’s day and age. While many people find social media a valuable tool for keeping in touch with family and friends, others find apps like Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok to induce stress. Research shows that using social media can have an addictive effect, as scrolling through a social media app affects the brain’s levels of dopamine, a feel-good chemical.
The high associated with scrolling social media can become addictive. People may find themselves stuck in the downward spiral of scrolling for a dopamine hit, followed by comparing themselves to others, negatively affecting their self-esteem. In a paper on this topic, explore how cutting down on social media can relieve adolescent anxiety and explain how social media can also be used to boost self-esteem positively.
While many think of slavery as a thing of the past, the concept is still sadly alive today. This can be an emotional and tough topic to research and write about. Still, it can educate your readers about the harsh reality of present-day slavery, bringing attention to an issue that often goes ignored.
According to antislavery.org , nearly 50 million people live in modern-day slavery, and approximately 25% of modern-day enslaved people are children. There are many forms of modern-day slavery, including forced marriage, domestic servitude, forced labor, human trafficking, and descent-based slavery (when enslaved children are also forced to work as enslaved people). For your research report on present-day slavery, you may focus on one of these areas or explore the concept of modern-day slavery as a whole.
Many people who have experienced the death of a loved one have struggled to watch them suffer and have wished that there was something they could do to help them end their suffering. In some states in America, assisted suicide has become legal . This means that a person who is terminally ill can work with their medical treatment team to develop a plan to die on their own terms.
Some people are against assisted suicide and believe people should be unable to choose how and when they’ll die. In contrast, others feel that allowing people to choose their time of death following a diagnosis of a terminal illness allows them to pass away with dignity.
This report writing topic for students can work as an informational or persuasive essay. If you have strong feelings on the topic, be sure to present both sides of the argument and your personal opinion on your point of view. You’ll also want to be sure to touch on the history of assisted suicide in the United States and views on assisted suicide around the world, as the practice is common in many areas of the world.
The draft in the United States dictates that any male over the age of 18 can be called to military service in times of war. While some people believe that the draft is outdated and should be left behind , others believe that the draft still has a place in America.
This topic can work either as a research report or a persuasive essay. If you can, talking with a military veteran who began their service due to the draft can help bring realism to your report. You may also want to talk with people who left the country to avoid the draft.
While the draft currently can only bring men to military service, some people believe that women should also be able to be drafted. Discussing this aspect of the history of the draft in the United States can add an exciting aspect to your report.
No Child Left Behind was enacted by President George W. Bush and was in effect from 2002-2015. The law rewarded teachers and schools for having high-performing classrooms and penalized schools that did not perform up to par. While some people felt that the law was the right thing to keep schools accountable for student progress, others felt that it kept disadvantaged students at a disadvantage instead of providing teachers and schools with the support they needed to achieve.
While some schools rose to the challenges of No Child Left Behind, others struggled. In an essay on the topic, you’ll need to form your own opinion on whether NCLB was an effective law for education in the United States. You may want to interview educators and administrators working in schools during the No Child Left Behind era to get firsthand opinions on whether the laws were adequate.
Also known as the Deepwater Horizon oil spill , the BP oil spill occurred on April 20, 2021, and spilled more than 130 million gallons off the Gulf of Mexico near the New Othe Orleans, Louisiana coast. The effects of the BP oil spill are still being felt in the area more than a decade later.
You can go in several different directions while reporting on the effects of the BP oil spill. The animal and plant life in the area is still suffering from the spill’s effects. People in the area are also struggling, especially those who made a living fishing off the coast. Tourism in the area has also been affected, leaving many people in New Orleans struggling to make ends meet.
The length of your research paper will determine how in-depth you can go with the topic. If you’re writing a shorter research paper, it’s wise to choose one of the topics (how the spill has affected the area’s economy, wildlife, tourism, etc.). If you’re writing a longer research paper, split it into subheadings so you can fully delve into each facet of the topic.
Many parents in the United States struggle to make ends meet following the birth of a child due to the short time that companies are required to give parents after they welcome a baby into their home. While the United Nations recommends that mothers have at least four months to recover after giving birth, the United States has no federal requirement for parental leave .
While researching this issue, it’s key to explain the differences between how new parents are treated in the United States compared to other countries and how this treatment affects both the stress levels and job performance of new parents. You’ll want to be sure to look at both sides of the issue, also explaining how the lack of a federally mandated parental leave policy can affect companies.
In the United States, a person can be found not guilty of a crime because of insanity. This means that the person accused of a crime isn’t found innocent—the court has decided that they could not understand the severity of the crime. Some people argue that people should not be able to plead insanity after committing a crime, as the crime occurred whether they understood their actions or not. Others argue that the insanity defense is necessary to protect people who do not understand the consequences of their actions.
When writing a research paper on the insanity defense, it’s key to include examples from real-life legal cases, such as the Steven Steinberg case (1981) . Mr. Steinberg claimed he was sleepwalking and dreaming about a break-in to his home when he stabbed and killed his wife. Steinberg was found not guilty due to temporary insanity, as the jury decided he was not in his right mind when the crime occurred.

Transgender health has received a lot of attention in the news recently, and one of the most commonly debated topics in the transgender health medical community is at what age it makes sense for people who are transgender to begin taking hormones and undergo surgical procedures that allow their body to be in alignment with their gender identification.
According to AP News , “The World Professional Association for Transgender Health said hormones could be started at age 14, two years earlier than the group’s previous advice, and some surgeries are done at age 15 or 17, a year or so earlier than previous guidance.”
Digging into the current research on transgender health and gender dysphoria can help you determine your position on this issue. Be sure that the news sources you use are current, as research in this area constantly evolves. You’ll want to be sure you’re basing your opinion on the most up-to-date information from the medical community.
In most US schools, school uniforms aren’t mandatory; instead, the school enforces a dress code. Dress codes define the clothing the school board finds acceptable for students. The dress code can vary from school to school, but for the most part, it requires students to wear appropriate clothing that is not overly short, formal, or dressy. Some argue that allowing students to choose their clothing for school promotes individuality and confidence.
In other countries in the world, a school uniform is mandatory. The purpose of a school uniform is to eliminate any class issues where some children may be able to afford more fashionable clothes than others. A uniform ensures all students look the same and can be argued to promote a feeling of self-confidence and a sense of belonging amongst the students, removing the pressure on deciding what to wear and meeting peer expectations regarding fashion. Choose a side and argue your case in your report, citing sources and studies.
The education systems in the US and the UK have pros and cons. Some argue that the US approach allows for confidence building through more extracurricular activities, while others argue that the UK prioritizes subjects like Math and English from a younger age.
Study the differences in both education systems and choose which one you think is most beneficial to children. Does one education system set students up for success more than the other? Answer this in your own words to create an engaging argument.
Violent TV shows can have positive and negative impacts on teens worldwide. This report discusses the pros and cons of violent TV shows. Some pros include reinforcing morals and prior beliefs that violence is wrong and has negative consequences. However, some argue that violent TV shows can justify violence in the viewer’s mind.
In your report, analyze both sides of this argument and conclude by discussing your views. Include studies and data to support your arguments, looking at how violence can be perceived.
Peer pressure is one of the biggest challenges that teens face. Peer pressure can be severe, such as peer pressure to drink alcohol underage. However, it can also show up in milder ways, such as pressure to dress a certain way, listen to specific music, or follow the crowd.
In your report, discuss the impact of peer pressure on teenagers’ self-esteem and examine how individuality can be challenging to achieve. Discuss factors contributing to peer pressure, like social media, bullying, etc.
Music is argued to be a healing power for mental health, and physical conditions and can even help plants grow. Study this theory and use research data to determine whether this is true. In your report, describe how music can be healing, but also look at the limitations. To create a compelling report, source real data on how music has been used to heal a health condition and discuss how much it can help.

Wildfires are becoming increasingly common all around the world. In particular, the US sees a high number of wildfires every year. In August 2002, devastating wildfires across California left many people without homes.
This report, discusses the causes and effects of wildfires across the globe. Use this report as an opportunity to bring attention to the noticeable effects of global warming and include ways in which governments can work to reduce wildfires.
Global warming is becoming increasingly common, making it an essential topic for argumentative and analytical reports. In your report, discuss the climate changes and how they have impacted the environment.
For example, examine the glaciers and ice sheets shrinking, wildfires across the globe, and the overall temperature increase in countries worldwide. Use scientific data to back up your report, keeping it factual and informative.
Parenting is a common topic for research reports, examining how upbringing and circumstance can help or hinder a child’s development and well-being. Study the effects of living in a single-parent household versus a joint-parent household on the well-being and success of children. There are many arguments both for and against single parenting.
Some pros include that the child creates an excellent bond with the parent or the absent parent could negatively affect the child, so they shouldn’t be within the household. However, some cons can include the single parent becoming dependent on childcare. Discuss the effects of single parenting and look at both the positive and negative effects.
The Covid-19 pandemic has changed the world; with it, social issues have come into focus. Some of the most impactful social challenges of the pandemic are the increasing rates of anxiety and depression . In your report, research and identify the main social challenges that we have faced since the pandemic and discuss the steps that can be taken to recover. Use this report to discuss your own experiences and the challenges others have faced.
Explanation : Urbanization refers to the growth in population concentration in urban areas and its subsequent effects on the environment, economy, and society. One critical effect is on local wildlife, which can be displaced or endangered due to urban sprawl. Start by researching the local species affected by urban development in your region. They should gather data on species decline, habitat loss, or conservation efforts.
Consider visiting a local wildlife reserve or sanctuary. Interviewing experts or conservationists can provide firsthand insights works too.
The ubiquitous use of social media has led to various mental health concerns among teenagers, including issues related to self-esteem, peer pressure, and isolation. Analyze various scholarly articles and surveys highlighting the psychological effects of prolonged social media use. Contrast this with the potential positive aspects, like connectivity and information dissemination. Survey your school or community to gather primary data on the topic, this can make the report more relevant and localized.
Sustainable farming is a method of farming that incorporates practices that can sustain the farmer, resources, and the community at large. It often interlinks with food security, ensuring everyone can access sufficient, safe, nutritious food. Examine different sustainable farming methods, their benefits, and how they contribute to food security. Highlight challenges and propose potential solutions.
If possible, visit a local farm that employs sustainable practices. Real-world observations can add depth to your report.
E-learning refers to using electronic technologies to access educational content outside of a traditional classroom. With the rise of digital platforms and tools, e-learning has become more prevalent. Assess the advantages of e-learning, such as flexibility and accessibility, against its challenges, like lack of face-to-face interaction and potential distractions. Interview students or educators with firsthand experience with traditional and e-learning settings to provide a balanced view.
Plastic waste often ends up in our oceans, affecting marine life. From microscopic plankton to gigantic whales, marine organisms ingest or get entangled in plastic debris, leading to fatal consequences. Research the plastic journey from land to sea, the species most affected, and the overall ecological repercussions. Investigate potential solutions and conservation efforts.
Incorporate visuals, like photographs or infographics, to show the severity of ocean plastic pollution.
Looking for more advice about report writing topics? Check out our guide on how to write an argumentative essay .

Meet Rachael, the editor at Become a Writer Today. With years of experience in the field, she is passionate about language and dedicated to producing high-quality content that engages and informs readers. When she's not editing or writing, you can find her exploring the great outdoors, finding inspiration for her next project.
View all posts
ON YOUR 1ST ORDER
How To Write A Report Introduction: An Academic Guide
By Laura Brown on 27th July 2023
You are definitely here to learn how to write an introduction to a report. So let’s answer it directly!
Well, an effective introduction of a report should succinctly introduce the topic, state the purpose and scope of the report, and provide a brief overview of the key points to be discussed . A report introduction should capture the reader’s interest and set the tone for the rest of the document.
This could be the summary of what should be included in a report introduction and how you can write it. But this summary is not enough to understand completely how you are going to start your report.
Since you are here, you must have got an academic report to tackle. Well, let’s start by talking about something that’s often overlooked but absolutely crucial – the introduction! Trust us, nailing the introduction can make a world of difference to your entire report.
Your report introduction is like the friendly handshake you offer to your readers. It sets the tone, gives an overview of what’s to come, and entices them to stick around for the good stuff. A well-crafted intro not only impresses your readers but also shows off your writing chops and analytical skills.
So, let’s dive into the world of introductions and make your reports shine right from the very start! Get ready to captivate your audience and make your mark in the educational realm. Let’s go!

1. First, Understand The Purpose Of Your Report
To embark on successful academic writing , it’s crucial to grasp the essence of your report’s purpose. Reports come in various types, including essays, research papers, case studies, and many more! Each type requires a tailored approach to crafting a report introduction that captivates your readers.
Once you have identified the type of report you have got to prepare, the second most important thing is to understand why you have been given this report. What is the purpose, and what could be the possible outcome of completing this report.
2. Analyse The Target Audience
Audience engagement is a critical aspect of your report! Let’s shine a spotlight on your readers, who are the real heroes, and explore the art of tailoring your report introduction to captivate them.
It is really essential to consider the readers’ background and knowledge. Are they seasoned professors, fellow students, or professionals in a specific field? Understanding their perspectives helps you strike the perfect balance of technicality and simplicity in your introduction.
Crafting an introduction that speaks directly to your audience is the key. Inject enthusiasm, sprinkle relatable examples, and address their pain points . Use audience-savvy techniques, ensuring your introduction resonates with readers and leaves them eager to explore your entire report.
So, let’s dive in and charm your audience with an introduction they won’t forget! Let’s get started with how to write a report introduction!
3. Elements of a Strong Introduction
Before we head directly into how to start a report introduction, we need to understand some basic elements of the introduction of a report. A well-crafted introduction not only piques the interest of the readers but also sets the tone for the entire document. To achieve this, it should incorporate the following essential elements:
• Opening Hook or Attention-Grabber
The first few sentences of your introduction should captivate the reader’s attention and compel them to delve further into your report. An opening hook can take various forms, such as a thought-provoking question, a compelling statistic, a vivid anecdote, or a relevant and surprising fact.
• Contextualising the Report’s Topic
Following the attention-grabber, it is essential to provide the necessary context for your report’s topic. This contextualisation allows readers to grasp the background, relevance, and significance of the subject under investigation. Incorporate relevant historical, theoretical, or practical information to situate the report within its broader academic or real-world context.
• Thesis Statement or Main Objective
The thesis statement, often positioned at the end of the opening paragraph of the report introduction, concisely articulates the main objective or central argument of your report. It should be clear, specific, and focused, guiding readers on what they can expect to explore further in the document. A strong thesis statement sets the direction for the entire report, providing a roadmap for readers to navigate the subsequent sections with a clear understanding of the primary purpose.
• Overview of Report Structure and Sections
To facilitate navigation and comprehension, it is crucial to provide readers with an overview of the report’s structure and its key sections. This section-by-section outline acts as a guide, giving readers a glimpse of the organisation and flow of the report.
By skillfully incorporating these elements, your introduction will establish a strong groundwork for your report, fostering engagement and understanding throughout its entirety. Now we can move on with your actual question, how to write an introduction for an academic report! After reading this guide, if you still find anything difficult, you can always contact our report writing service for 24/7 assistance.
4. Crafting the Opening Hook
The art of crafting an engaging opening hook lies in its ability to seize the reader’s attention from the outset. Anecdotes and real-life examples breathe life into the report , making complex topics relatable and captivating for your readers. As you go on to illustrate the practical implications of the subject matter, your readers can immediately connect with the content. It will allow you to foster a sense of curiosity to explore further.
In addition to anecdotes, you should incorporate relevant statistics or data. It infuses credibility and significance into the introduction. Numbers possess a persuasive power, shedding light on the magnitude of an issue and underscoring the urgency of the report’s focus. Thought-provoking questions, on the other hand, spark introspection and stimulate critical thinking. Coupled with compelling quotes, they entice readers to contemplate the broader implications of the subject matter.
An effective opening hook in the report introduction, whether through anecdotes, statistics, or questions, sets the stage for an intellectually stimulating journey through the report’s core ideas. By capturing your reader’s imagination, the introduction paves the way for a rewarding exploration of the report’s findings and insights.
Since, students often search for how to write an introduction for a report example, here is one for you. The opening of the introduction could be like this:
In the age of digital interconnectedness, social media platforms have revolutionised the way we communicate, share information, and interact with others. The allure of virtual networks, however, comes hand in hand with growing concerns about their impact on mental health. As these platforms become an integral part of our daily lives, it is crucial to examine the intricate relationship between social media usage and its potential consequences on individuals’ psychological well-being, a pressing issue that forms the focal point of this academic report.
5. Providing Context for the Report
A well-contextualised introduction is paramount to the comprehension of the matter of the report. You should first delve into the background and history of the topic to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of its evolution over time. This historical perspective lays the groundwork for appreciating the report’s relevance in the present context.
Moreover, describing the current relevance and significance of the topic bridges the gap between theory and practice. It highlights the practical implications and real-world applications, enticing readers to explore further. In addition to how to write a report introduction, it is essential to address the previous research or related studies to showcase the existing body of knowledge and identify gaps that the current report aims to fill.
By combining historical context, present-day relevance, and existing research, the introduction forges a clear pathway for readers to navigate through the report’s findings, enriching their understanding and appreciation of the subject matter.
Let’s have a look at an example from the sample report introduction:
The exponential rise of social media has transformed the dynamics of social interactions, communication, and information dissemination, transcending geographical boundaries. With billions of users actively engaging on platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and TikTok, the implications on mental health have garnered significant attention from researchers, health professionals, and society at large. This report endeavours to delve into the multifaceted impacts of social media on mental health, analysing its effects on emotional well-being, self-esteem, and psychological distress.
6. Formulating a Clear Thesis Statement
As we go on to learn how to write an introduction of a report, we should know about the thesis statement. A strong thesis statement is like the backbone of your whole work. It’s the core purpose and focus of what you are doing. When you define the main objective and scope in your thesis, it gives your readers a sneak peek into what you are trying to achieve.
To make it effective, keep the thesis concise and specific. Avoid any vagueness or ambiguity . This will help sharpen the direction of the report and guide your readers to understand the main argument better.
When your thesis aligns with the objectives of your report, everything flows more smoothly. It acts as a navigational tool, guiding you and your readers through all the details and helping everyone grasp the subject matter better. So, get ready to make your report shine with a killer thesis statement!
Let’s have an example of a thesis statement from the introduction of a report:
This report aims to explore the complexities of the relationship between social media usage and mental health, considering both positive and negative aspects. By synthesising existing research, psychological theories, and empirical evidence, we seek to shed light on the various mechanisms through which social media can influence mental health outcomes. Ultimately, this examination underscores the importance of promoting digital well-being and fostering responsible social media use for individuals of all ages.
7. Outlining the Report Structure
An effectively outlined report structure serves as a roadmap for readers. It gives readers a clear and organised overview of what’s inside. First off, listing the major sections or points give them a quick glimpse of how it’s all laid out.
And here’s the trick: a brief description of each section helps readers know what to expect. That way, they can read with focus and easily find what they need later.
When you highlight the logical progression of the report, it keeps everything flowing smoothly. Each section builds upon the previous ones, creating a cohesive narrative. This way, readers can get a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Putting it all together, a well-structured report becomes a valuable guide for your readers. It leads them through all the details and ensures a rewarding and informed reading experience.
Do’s & Don’ts of How to Make a Report Introduction
Concluding on how to write a good introduction for a report.
A strong introduction forms the backbone of your report, as it plays a pivotal role in engaging readers and guiding their journey through the study’s contents. By recapitulating the significance of a well-crafted introduction, we underscore how it captivates readers from the outset, fostering their interest and curiosity.
The introduction sets the tone for the entire report, shaping readers’ perceptions and expectations. As this guide highlights the key elements for creating an effective introduction and how to start writing a report introduction, we encourage students to apply these principles to their own reports. By doing so, they can elevate the impact of their work, leaving a lasting impression on their readers.
We hope that this guide will help you through the introduction process. You can further go on to read how to write a conclusion for a report , so that you can create an excellent report for you.

Laura Brown, a senior content writer who writes actionable blogs at Crowd Writer.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
What to Know About Creative Writing Degrees
Many creative writing degree recipients pursue careers as authors while others work as copywriters or ghostwriters.
Tips on Creative Writing Degrees

Getty Images
Prospective writing students should think about their goals and figure out if a creative writing degree will help them achieve those goals.
Many people see something magical in a beautiful work of art, and artists of all kinds often take pride in their craftsmanship. Creative writers say they find fulfillment in the writing process.
"I believe that making art is a human need, and so to get to do that is amazing," says Andrea Lawlor, an author who this year received a Whiting Award – a national $50,000 prize that recognizes 10 excellent emerging authors each year – and who is also the Clara Willis Phillips Assistant Professor of English at Mount Holyoke College in Massachusetts.
"We all are seeing more and more of the way that writing can help us understand perspectives we don't share," says Lawlor, whose recent novel "Paul Takes the Form of a Mortal Girl" addresses the issue of gender identity.
"Writing can help us cope with hard situations," Lawlor says. "We can find people who we have something in common with even if there's nobody around us who shares our experience through writing. It's a really powerful tool for connection and social change and understanding."
Creative writing faculty, many of whom are acclaimed published authors, say that people are well-suited toward degrees in creative writing if they are highly verbal and enjoy expressing themselves.
"Creative imaginative types who have stories burning inside them and who gravitate toward stories and language might want to pursue a degree in creative writing," Jessica Bane Robert, who teaches Introduction to Creative Writing at Clark University in Massachusetts, wrote in an email. "Through formal study you will hone your voice, gain confidence, find a support system for what can otherwise be a lonely endeavor."
Read the guide below to gain more insight into what it means to pursue a creative writing education, how writing impacts society and whether it is prudent to invest in a creative writing degree. Learn about the difference between degree-based and non-degree creative writing programs, how to craft a solid application to a top-notch creative writing program and how to figure out which program is the best fit.
Why Creative Writing Matters and Reasons to Study It
Creative writers say a common misconception about their job is that their work is frivolous and impractical, but they emphasize that creative writing is an extremely effective way to convey messages that are hard to share in any other way.
Kelly Caldwell, dean of faculty at Gotham Writers Workshop in New York City, says prospective writing students are often discouraged from taking writing courses because of concerns about whether a writing life is somehow unattainable or "unrealistic."
Although creative writers are sometimes unable to financially support themselves entirely on the basis of their creative projects, Caldwell says, they often juggle that work with other types of jobs and lead successful careers.
She says that many students in her introductory creative writing class were previously forbidden by parents to study creative writing. "You have to give yourself permission for the simple reason that you want to do it," she suggests.
Creative writing faculty acknowledge that a formal academic credential in creative writing is not needed in order to get writing published. However, they suggest, creative writing programs help aspiring authors develop their writing skills and allow space and time to complete long-term writing projects.
Working writers often juggle multiple projects at once and sometimes have more than one gig, which can make it difficult to finish an especially ambitious undertaking such as a novel, a play for the screen or stage, or a well-assembled collection of poems, short stories or essays. Grants and fellowships for authors are often designed to ensure that those authors can afford to concentrate on their writing.
Samuel Ace, a published poet and a visiting lecturer in poetry at Mount Holyoke, says his goal is to show students how to write in an authentic way that conveys real feeling. "It helps students to become more direct, not to bury their thoughts under a cascade of academic language, to be more forthright," he says.
Tips on Choosing Between a Non-Degree or Degree-Based Creative Writing Program
Experts note that someone needs to be ready to get immersed in the writing process and devote significant time to writing projects before pursuing a creative writing degree. Prospective writing students should not sign up for a degree program until they have reached that sense of preparedness, warns Kim Todd, an associate professor at the University of Minnesota College of Liberal Arts and director of its creative writing program.
She says prospective writing students need to think about their personal goals and figure out if a creative writing degree will help them achieve those goals.
Aspiring writers who are not ready to invest in a creative writing degree program may want to sign up for a one-off writing class or begin participating in an informal writing workshop so they can test their level of interest in the field, Todd suggests.
How to Choose and Apply to a Creative Writing Program
In many cases, the most important component of an application to a writing program is the writing portfolio, writing program experts say. Prospective writing students need to think about which pieces of writing they include in their portfolio and need to be especially mindful about which item they put at the beginning of their portfolio. They should have a trusted mentor critique the portfolio before they submit it, experts suggest.
Because creative writing often involves self-expression, it is important for aspiring writing students to find a program where they feel comfortable expressing their true identity.
This is particularly pertinent to aspiring authors who are members of minority groups, including people of color or LGBTQ individuals, says Lawlor, who identifies as queer, transgender and nonbinary.
How to Use a Creative Writing Degree
Creative writing program professors and alumni say creative writing programs cultivate a variety of in-demand skills, including the ability to communicate effectively.
"While yes, many creative writers are idealists and dreamers, these are also typically highly flexible and competent people with a range of personal strengths. And a good creative writing program helps them understand their particular strengths and marketability and translate these for potential employers, alongside the more traditional craft development work," Melissa Ridley Elmes, an assistant professor of English at Lindenwood University in Missouri, wrote in an email.
Elmes – an author who writes poetry, fiction and nonfiction – says creative writing programs force students to develop personal discipline because they have to consistently produce a significant amount of writing. In addition, participating in writing workshops requires writing students "to give and receive constructive feedback," Elmes says.
Cindy Childress, who has a Ph.D. in English from the University of Louisiana—Lafayatte and did a creative writing dissertation where she submitted poetry, says creative writing grads are well-equipped for good-paying positions as advertising and marketing copywriters, speechwriters, grant writers and ghostwriters.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual compensation for writers and authors was $63,200 as of May 2019.
"I think the Internet, and writing communities online and in social media, have been very helpful for debunking the idea that if you publish a New York Times Bestseller you will have 'made it' and can quit your day job and write full time," Elmes explains. "Unless you are independently wealthy, the odds are very much against you in this regard."
Childress emphasizes that creative writing degree recipients have "skills that are absolutely transferable to the real world." For example, the same storytelling techniques that copywriters use to shape public perceptions about a commercial brand are often taught in introductory creative writing courses, she says. The ability to tell a good story does not necessarily come easily to people who haven't been trained on how to do it, she explains.
Childress says she was able to translate her creative writing education into a lucrative career and start her own ghostwriting and book editing company, where she earns a six-figure salary. She says her background in poetry taught her how to be pithy.
"Anything that we want to write nowadays, particularly for social media, is going to have to be immediately understood, so there is a sense of immediacy," she says."The language has to be crisp and direct and exact, and really those are exactly the same kind of ways you would describe a successful poem."
Searching for a grad school? Access our complete rankings of Best Graduate Schools.
10 Ways to Discover College Essay Ideas

Tags: education , graduate schools , colleges , students
You May Also Like
Get accepted to multiple top b-schools.
Anayat Durrani May 16, 2024

Premeds and Emerging Medical Research
Zach Grimmett May 14, 2024

How to Get a Perfect Score on the LSAT
Gabriel Kuris May 13, 2024

Premeds Take 5 Public Health Courses
Rachel Rizal May 7, 2024

Fortune 500 CEOs With a Law Degree
Cole Claybourn May 7, 2024

Why It's Hard to Get Into Med School
A.R. Cabral May 6, 2024

Pros, Cons of Unaccredited Law Schools
Gabriel Kuris May 6, 2024

An MBA and Management Consulting
Sammy Allen May 2, 2024

Med School Access for Minority Students
Cole Claybourn May 2, 2024

Different jobs with med degree
Jarek Rutz April 30, 2024


From 101 Creative Writing Exercises: Report It
by Melissa Donovan | Jul 21, 2020 | Creative Writing Exercises | 2 comments

“Report It” from 101 Creative Writing Exercises.
Today, I’m sharing an excerpt from my book, 101 Creative Writing Exercises (aff link). It’s packed with writing exercises that are designed to help you explore all forms of creative writing: fiction, poetry, and creative nonfiction. The book will inspire you while imparting useful writing techniques that are fun and practical.
This exercise comes from “Chapter 2: It’s Personal.” The writing exercises in this chapter focus on writing of a personal nature: memoir, journal writing, and personal essays.
I chose this exercise because it’s challenging and fun. It asks you to look at your own life from a fresh perspective and make yourself the subject of a news report.
Is your life newsworthy? Have you ever witnessed, committed, or been the victim of a crime? Have you ever participated in a protest or a performance? Have you ever had an odd or unusual (paranormal or supernatural) experience?
Traditional and professional journalism is concise and factual. It adheres to a set of journalistic ethics, focusing on the facts and details of the story and presenting those facts thoroughly and honestly. True journalism is objective. The ethical journalist does not inject his or her feelings or opinions.
But journalists are human. The news media in general is increasingly accused of using a variety of creative tactics to spin the news in favor of their own religious, political, or philosophical beliefs. For example, in a report, a journalist should not badmouth a suspected criminal, but that journalist can include a quote from a witness who has badmouthed the criminal while intentionally not including a positive quote from some other witness.
Journalists can pick and choose quotes, facts, and even which stories to report.
When you think about the fact that journalists and reporters are responsible for feeding us information about what’s going on in the world and then consider that they are mere human beings, flawed, emotional, and opinionated just like the rest of us, you can only begin to imagine and wonder just how spun all the news actually is.
The Exercise
Your challenge is to revisit your past and write a news report about something you experienced firsthand.
The rules are simple: straight journalism. What does that mean? True journalists are not allowed to include personal emotion or opinion in their writing. Be as objective as possible. Don’t take sides!
Write about the event or incident as if you are a journalist looking in on your own story from the outside. Make sure you include a headline that will attract readers’ attention.
Tips: To get a feeling for how journalism is written (its tone and style), visit a reputable news site and read a few articles.
Variations: Instead of reporting on a story, write a paparazzi piece. Were you spotted while out on a hot date? If you’re at a loss for subject matter, get creative and write a fictional news story; make up something or change something from your past or better yet, write a news story from your future (maybe you win the Pulitzer Prize in ten years).
Applications: The most obvious application is that you could, someday, become a journalist. Journalism in general is an objective style of writing (at least, it’s supposed to be), and this is a style that is difficult to achieve. This exercise encourages you to write about something you care about but to refrain from including your feelings or personal views.

I am totally stunned by this extracts, it is so funny and good at the same time. But it also very challenging as you’ve said, I’ve tried writing as a journalist but it remains elusive! (it bits me…).
Journalism is a tough nut to crack, that’s for sure.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

Subscribe and get The Writer’s Creed graphic e-booklet, plus a weekly digest with the latest articles on writing, as well as special offers and exclusive content.

Recent Posts
- 12 Character Writing Tips for Fiction Writers
- What is Free-Verse Poetry?
- Grammar Rules: Lay or Lie
- Writing While Inspired
- Thoughts on Becoming a Writer
Write on, shine on!
Pin It on Pinterest
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Free end-of-year letter templates to your students 📝!
42 Creative Book Report Ideas for Students
Inspire your students to share their love of books.

Responding to what you read is an important literacy skill. Reading about other people’s experiences and perspectives helps kids learn about the world. And although students don’t need to dive deeply into every single book they read, occasionally digging into characters, settings, and themes can help them learn to look beyond the prose. Here are 42 creative book report ideas designed to make reading more meaningful.
1. Concrete Found Poem

This clever activity is basically a shape poem made up of words, phrases, and whole sentences found in the books students read. The words come together to create an image that represents something from the story.
2. Graphic Novel
Have students rewrite the book they are reading, or a chapter of their book, as a graphic novel. Set parameters for the assignment such as including six scenes from the story, three characters, details about the setting, etc. And, of course, include detailed illustrations to accompany the story.
3. Book Snaps
Book Snaps are a way for students to visually show how they are reacting to, processing, and/or connecting with a text. First, students snap a picture of a page in the book they are reading. Then, they add comments, images, highlights, and more.
4. Diary Entry
Have your students place themselves in the shoes of one of the characters from their book and write a first-person diary entry of a critical moment from the story. Ask them to choose a moment in the story where the character has plenty of interaction and emotion to share in a diary entry.
5. Character To-Do List

This fun activity is an off-the-beaten-path way to dive deep into character analysis. Get inside the head of the main character in a book and write a to-do list that they might write. Use actual information from the text, but also make inferences into what that character may wish to accomplish.
6. Mint Tin Book Report

There are so many super-creative, open-ended projects you can use mint tins for. This teacher blogger describes the process of creating book reports using them. There’s even a free template for cards that fit inside.
7. Fictional Yearbook Entries
Ask your students to create a yearbook based on the characters and setting in the book. What do they look like? Cut out magazine pictures to give a good visual image for their school picture. What kind of superlative might they get? Best looking? Class clown? What clubs would they be in or lead? Did they win any awards? It should be obvious from their small yearbooks whether your students dug deep into the characters in their books. They may also learn that who we are as individuals is reflected in what we choose to do with our lives.
8. Book Report Cake

This project would be perfect for a book tasting in your classroom! Each student presents their book report in the shape of food. See the sandwich and pizza options above and check out this blog for more delicious ideas.
9. Current Events Comparison
Have students locate three to five current events articles a character in their book might be interested in. After they’ve found the articles, have them explain why the character would find them interesting and how they relate to the book. Learning about how current events affect time, place, and people is critical to helping develop opinions about what we read and experience in life.
10. Sandwich Book Report

Yum! You’ll notice a lot of our creative book report ideas revolve around food. In this oldie but goodie, each layer of this book report sandwich covers a different element of the book—characters, setting, conflict, etc. A fun adaptation of this project is the book report cheeseburger.
11. Book Alphabet
Choose 15 to 20 alphabet books to help give your students examples of how they work around themes. Then ask your students to create their own Book Alphabet based on the book they read. What artifacts, vocabulary words, and names reflect the important parts of the book? After they find a word to represent each letter, have them write one sentence that explains where the word fits in.
12. Peekaboo Book Report

Using cardboard lap books (or small science report boards), students include details about their book’s main characters, plot, setting, conflict, resolution, etc. Then they draw a head and arms on card stock and attach them to the board from behind to make it look like the main character is peeking over the report.
13. T-Shirt Book Report

Another fun and creative idea: Create a wearable book report with a plain white tee. Come up with your own using Sharpie pens and acrylic paint. Get step-by-step directions .
14. Book Jacket
Have students create a new book jacket for their story. Include an attractive illustrated cover, a summary, a short biography of the author, and a few reviews from readers.
15. Watercolor Rainbow Book Report
This is great for biography research projects. Students cut out a photocopied image of their subject and glue it in the middle. Then, they draw lines from the image to the edges of the paper, like rays of sunshine, and fill in each section with information about the person. As a book report template, the center image could be a copy of the book cover, and each section expands on key information such as character names, theme(s), conflict, resolution, etc.
16. Act the Part
Have students dress up as their favorite character from the book and present an oral book report. If their favorite character is not the main character, retell the story from their point of view.
17. Pizza Box Book Report

If you’re looking for creative book report ideas that use upcycled materials, try this one using a pizza box. It works well for both nonfiction and fiction book reports. The top lid provides a picture of the book cover. Each wedge of the pizza pie tells part of the story.
18. Bookmark
Have students create a custom illustrated bookmark that includes drawings and words from either their favorite chapter or the entire book.
19. Book Reports in a Bag

Looking for book report ideas that really encourage creative thinking? With book reports in a bag, students read a book and write a summary. Then, they decorate a paper grocery bag with a scene from the book, place five items that represent something from the book inside the bag, and present the bag to the class.
20. Reading Lists for Characters
Ask your students to think about a character in their book. What kinds of books might that character like to read? Take them to the library to choose five books the character might have on their to-be-read list. Have them list the books and explain what each book might mean to the character. Post the to-be-read lists for others to see and choose from—there’s nothing like trying out a book character’s style when developing your own identity.
21. File Folder Book Report

Also called a lap book, this easy-to-make book report hits on all the major elements of a book study and gives students a chance to show what they know in a colorful way.
22. Collage
Create a collage using pictures and words that represent different parts of the book. Use old magazines or print pictures from the Internet.
23. Book Report Triorama

Who doesn’t love a multidimensional book report? This image shows a 3D model, but Elisha Ann provides a lesson to show students how to glue four triangles together to make a 4D model.
24. Timeline
Have students create a timeline of the main events from their book. Be sure to include character names and details for each event. Use 8 x 11 sheets of paper taped together or a long portion of bulletin board paper.
25. Clothes Hanger Book Report Mobile

This creative project doesn’t require a fancy or expensive supply list. Students just need an ordinary clothes hanger, strings, and paper. The body of the hanger is used to identify the book, and the cards on the strings dangling below are filled with key elements of the book, like characters, setting, and a summary.
26. Public Service Announcement
If a student has read a book about a cause that affects people, animals, or the environment, teach them about public service announcements . Once they understand what a PSA is, have them research the issue or cause that stood out in the book. Then give them a template for a storyboard so they can create their own PSA. Some students might want to take it a step further and create a video based on their storyboard. Consider sharing their storyboard or video with an organization that supports the cause or issue.
27. Dodecahedron Book Report

Creative book report ideas think outside the box. In this case, it’s a ball! SO much information can be covered on the 12 panels , and it allows students to take a deep dive in a creative way.
28. Character Cards
Make trading cards (like baseball cards) for a few characters from the book. On the front side, draw the character. On the back side, make a list of their character traits and include a quote or two.
29. Book Report Booklets

This clever book report is made from ordinary paper bags. Stack the paper bags on top of each other, fold them in half, and staple the closed-off ends of the bags together. Students can write, draw, and decorate on the paper bag pages. They can also record information on writing or drawing paper and glue the paper onto the pages. The open ends of the bags can be used as pockets to insert photos, cut-outs, postcards, or other flat items that help them tell their story.
30. Letter to the Author
Write a letter to the author of the book. Tell them three things you really liked about the story. Ask three questions about the plot, characters, or anything else you’re curious about.
31. Book Report Charm Bracelet

What a “charming” way to write a book report! Each illustrated bracelet charm captures a character, an event in the plot, setting, or other detail.
32. Fact Sheet
Have students create a list of 10 facts that they learned from reading the book. Have them write the facts in complete sentences, and be sure that each fact is something that they didn’t know before they read the book.
33. Cereal Box TV Book Report

This book report project is a low-tech version of a television made from a cereal box and two paper towel rolls. Students create the viewing screen cut-out at the top, then insert a scroll of paper with writing and illustrations inside the box. When the cardboard roll is rotated, the story unfolds.
34. Be a Character Therapist
Therapists work to uncover their clients’ fears based on their words and actions. When we read books, we must learn to use a character’s actions and dialogue to infer their fears. Many plots revolve around a character’s fear and the work it takes to overcome that fear. Ask students to identify a character’s fear and find 8 to 10 scenes that prove this fear exists. Then have them write about ways the character overcame the fear (or didn’t) in the story. What might the character have done differently?
35. Mind Maps
Mind maps can be a great way to synthesize what students have learned from reading a book. Plus, there are so many ways to approach them. Begin by writing a central idea in the middle of the page. For example, general information, characters, plot, etc. Then branch out from the center with ideas, thoughts, and connections to material from the book.
36. Foldables

From Rainbows Within Reach , this clever idea would be a great introduction to writing book reports. Adapt the flap categories for students at different levels. Adjust the number of categories (or flaps) per the needs of your students.
37. Board games
This is a great project if you want your students to develop a little more insight into what they’re reading. Have them think about the elements of their favorite board games and how they can be adapted to fit this assignment. For more, here are step-by-step directions .
38. Comic strips
If you’re looking for creative book report ideas for students who like graphic novels, try comic strips. Include an illustrated cover with the title and author. The pages of the book should retell the story using dialogue and descriptions of the setting and characters. Of course, no comic book would be complete without copious illustrations and thought bubbles.
39. Timeline
Create a timeline using a long roll of butcher paper, a poster board, or index cards taped together. For each event on the timeline, write a brief description of what happens. Add pictures, clip art, word art, and symbols to make the timeline more lively and colorful.
40. Cereal Box
Recycle a cereal box and create a book report Wheaties-style. Decorate all sides of the box with information about the book’s characters, setting, plot, summary, etc.
41. Wanted Poster

Make a “wanted” poster for one of the book’s main characters. Indicate whether they are wanted dead or alive. Include a picture of the character and a description of what the character is “wanted” for, three examples of the character showing this trait, and a detailed account of where the character was last seen.
42. Movie Version
If the book your students have read has been made into a movie, have them write a report about how the versions are alike and different. If the book has not been made into a movie, have them write a report telling how they would make it into a movie, using specific details from the book.
What creative book report ideas did we miss? Come share in our We Are Teachers HELPLINE group on Facebook.
Plus, check out the most popular kids’ books in every grade..

You Might Also Like

Expand Your Readers’ Palates With a Book Tasting
A perfect way for kids to nibble on a book. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

- Business in Society
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Entrepreneurship and Innovation
- Finance & Investing
- Global Business
- Press Releases
- School News
- Student News
- Alumni News
- Faculty News
- Pillars: Philanthropy News
- COVID-19 News
‘What’s Next?’ for Anton Dela Cruz: From Creative Writing to Ethical Leadership at UVA Darden
By David Buie-Moltz
As the University of Virginia Darden School of Business prepares to graduate its Class of 2024, Anton Dela Cruz is set to move from a multifaceted career in operations to a strategic role in healthcare consulting. His time at Darden has fueled significant personal growth and a shift toward ethical leadership and community involvement.
Raised in Westchester, New York, Dela Cruz’s academic and professional journey is a testament to his resilience and adaptability. Initially enrolled in an engineering program at Cooper Union, he discovered a stronger pull toward the sciences and nature, leading him to study creative writing at SUNY Purchase. “I realized I was more interested in pure science and studying nature than the design process of engineering,” Dela Cruz explains.
He began an MFA in creative nonfiction at the University of South Carolina, where he shares he was the program’s only person of color and navigated coming out as queer. Although he left the program unfinished, it marked a significant chapter in his development. He then joined The Free Times , an alternative weekly in Columbia, South Carolina, where he managed ad production during a tumultuous change in ownership. “This experience tested our team but also brought us closer together. It made me think deeply about what it means to lead and make ethical business decisions,” he notes.
A turning point in Dela Cruz’s journey was when he listened to a Darden admissions podcast featuring Professor Ed Freeman , the renowned father of stakeholder theory. This encounter solidified Darden as the ideal platform for him to merge his ethical values with his career aspirations.

At Darden, Dela Cruz has excelled academically and as president of Pride at Darden , enhancing visibility and support for the LGBTQ+ community. Supported by the need-based AccessDarden and a merit scholarship, his Darden education has been integral to his professional formation.
His roles, ranging from IT-managed services to consulting in project management and executive coaching, have further shaped his leadership philosophy. “I was supercharged by a good boss and manager who made me feel like I could do the work,” he says.
Looking forward, Dela Cruz is eager to join Guidehouse’s Healthcare Segment. “The decisions made in healthcare consulting have high stakes as they directly impact patient care and access,” he observes, underscoring his commitment to ethical leadership and social impact in a critical sector.
This is part of a four-part series, “What’s Next?” Discover how Darden shapes the future of its graduates and read about other remarkable stories from the Class of 2024, including those about Kate Grusky , Yonah Greenstein and Sharon Okeke .
The University of Virginia Darden School of Business prepares responsible global leaders through unparalleled transformational learning experiences. Darden’s graduate degree programs (MBA, MSBA and Ph.D.) and Executive Education & Lifelong Learning programs offered by the Darden School Foundation set the stage for a lifetime of career advancement and impact. Darden’s top-ranked faculty, renowned for teaching excellence, inspires and shapes modern business leadership worldwide through research, thought leadership and business publishing. Darden has Grounds in Charlottesville, Virginia, and the Washington, D.C., area and a global community that includes 18,000 alumni in 90 countries. Darden was established in 1955 at the University of Virginia, a top public university founded by Thomas Jefferson in 1819 in Charlottesville, Virginia.
Press Contact
Molly Mitchell Associate Director of Content Marketing and Social Media Darden School of Business University of Virginia [email protected]

Stakeholder: How Ed Freeman’s Vision for Responsible Business Moved From Theory to Reality

‘What’s Next?’ for Yonah Greenstein: From the Basketball Court to the Boardroom at UVA Darden

3 UVA Darden Students Receive ‘Best and Brightest’ Honors

‘What’s Next?’ for Kate Grusky: A Journey of Purpose and Philanthropy at UVA Darden

‘What’s Next?’ for Sharon Okeke: A New Chapter in Investment Banking and a Journey of Growth at UVA Darden
- The Darden Report Get the latest news about Darden and its students, faculty and alumni.
- Ideas to Action Get the latest business knowledge—research, analysis and commentary—from Darden's faculty.
- Please type the characters you see in the box below.
- By checking this box, you consent to Darden sending you emails about our news, events and thought leadership. Your email address also helps us keep your content relevant when you visit our website and social media. We think you will find our content valuable, and you can unsubscribe or opt-out at any time.
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
StarTribune
University of minnesota professor wins $150,000 literary prize.
A Minnesota novelist has won one of the world's richest literary prizes.
V.V. Ganeshananthan, an associate professor of English at the University of Minnesota since 2015, won the Carol Shields Prize for Fiction Monday night for her 2023 novel, "Brotherless Night." Star Tribune reviewer May-Lee Chai called the book, in which a young woman's family is ripped apart during the Sri Lankan Civil War, "a propulsive masterpiece."
Ganeshananthan — who first read Shields' work when she was a teenager — said the experience was "surreal." It was made more special by the fact that she and the other four semifinalists had a chance to meet the family and friends of the late Shields (whose novels include "The Stone Diaries") as well as the star-packed prize jury, which included novelists Laila Lailami and Claire Messud .
Ganeshananthan and fellow finalists Eleanor Catton ( "Birnam Wood" ), Claudia Dey ("Daughter"), Kim Coleman Foote ( "Coleman Hill" ) and Janika Oza ("A History of Burning") spent a couple days together in Toronto before the presentation. The two-year-old award is presented to a female or non-binary writer in the U.S. or Canada in memory of Shields, a fierce advocate for women.
"Women and non-binary folks are certainly not winning a proportionate number of prizes," noted Ganeshananthan, who intends her work to be "explicitly feminist" (her first novel was "Love Marriage").
The professor said she didn't expect to win, so hadn't prepared her 2-minute acceptance speech until "someone I was talking to the night before [the award was presented] said, 'You should really write something down,' and I said, 'I think that's a bad idea.'"
Ganeshananthan, 44, dashed something off, then focused on enjoying time with her fellow writers, which may be why she said, "I'm still a little, 'Really?' And I may feel that way for a while."
Adding to the surreal aspect might be the high profile — and the dollar amount — of the prize. Ganeshananthan has just begun to think about the "respect and care and heft" that come with it.
"I've been fortunate to have a secure job, teaching creative writing to amazing students, and to work with brilliant colleagues. Not all writers have that or want that. But that's quite a bit of privilege," said Ganeshananthan.

She said she's considering a couple ideas for "Brotherless Night" follow-ups. While she's working on that, the writer — who also co-hosts Lithub's "Fiction/Non/Fiction" podcast and is on the boards of the American Institute for Sri Lankan Studies and the Minnesota Prison Writing Workshop — will have the summer and beyond to decide what's next.
"What everyone wants is more time to write," she said. "The idea that this could go to partly supporting that is encouraging and a stroke of luck."

Review: 'Brotherless Night,' by V.V. Ganeshananthan
Interim books editor Chris Hewitt previously worked at the Pioneer Press in St. Paul, where he wrote about movies and theater.
- Minnesotans among least likely to climb income ladder in U.S.
- Trump says Minneapolis would have burned down without him, that he won 'out of control' Minnesota
Guthrie reports a record $3.8 million deficit
- Reusse: 378 pitches of agony at Target Field
- The ultimate patio guide: 60 all-star patios in the Twin Cities

Lainey Wilson wins big at the 2024 Academy of Country Music Awards, including the top honor
What to stream this weekend: 'bridgerton,' billie eilish and zayn malik albums, 'american fiction', pen america, facing ongoing criticism over its response to the mideast war, gathers for annual gala.

Music Review: Billie Eilish's 'Hit Me Hard and Soft' is zealous outsider pop in a league of her own

- University of Minnesota professor wins $150,000 literary prize • Books
- 'A Series of Unfortunate Events' writer Lemony Snicket/Daniel Handler pulls back the curtain • Books
- University of Minnesota professor's book investigates shocking medical research abuse • Books
- Stretching from WW II to the present, Claire Messud's new novel is a 'masterpiece' • Books
- Review: 'Brotherless Night,' by V.V. Ganeshananthan • Books
© 2024 StarTribune. All rights reserved.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Really good creative report writing is written in language that's accessible to your readers rather than in your language. Technical reports for the layperson are nearly inscrutable. The language is dense, and packed with jargon, usually with an assumption that you actually know what they're talking about. People tend to write from their ...
EDIT THIS REPORT TEMPLATE Today I'm going to give you a primer on making reports that are as beautiful as they are functional. We'll cover the 10 report design best practices you need to know and report design ideas. When writing a report that uses a lot of data, you should use the IMRaD format. IMRaD is an acronym that stands for ...
Annual report template. This annual report template is the right template for creating a professional and informative executive summary of your organization's performance over the past year. This template was designed for HR annual reports, but you can also repurpose it for other types of yearly reports. Annual Review.
Report writing encompasses the art and science of transforming raw information into a cohesive and structured document. A well-crafted report is more than a collection of facts; it's a narrative that provides clarity, insight, and direction. In business, accurate and insightful reports help with informed decision-making. Adept report writing ...
It's not a detailed visualization of microbes in a lab, but the report writing format is the same. Customize this report template and make it your own! Edit and Download. 10 Analysis Report Examples. ... Orana is a multi-faceted creative. She is a content writer, artist, and designer. She travels the world with her family and is currently in ...
2. Follow the Right Report Writing Format: Adhere to a structured format, including a clear title, table of contents, summary, introduction, body, conclusion, recommendations, and appendices. This ensures clarity and coherence. Follow the format suggestions in this article to start off on the right foot. 3.
4 How to Write a Report Cover Page. Now we're ready to get started on your report cover page! When you're first working on your cover page, it's a good idea to start with a template.. This helps you to spice up your report design and make it more than a black and white word document. It can also help you design your title page in an aesthetically pleasing way so it stands out to your ...
Edit and Download. Create a defined grid of your choice that allows you to arrange different elements of your report in a nice and aesthetic way. Use the same color palette across the report. Make sure all the padding and margins are consistent in all similar elements (text, images, buttons, cards, etc.).
Pre-writing steps. Before you set pen to paper, it's important to do your research and plan your report carefully. Giving yourself plenty of time for this stage will make the actual writing quicker and less rambling. 1. Define the audience and purpose of the report.
5. Read, read, read. It's a lot harder to get the hang of creative writing if you don't have any references from which to draw. Notable writers throughout history have penned excellent examples of well-written creative work that should be required reading for any budding creative writer.
Creative writing is an art form that transcends traditional literature boundaries. It includes professional, journalistic, academic, and technical writing. This type of writing emphasizes narrative craft, character development, and literary tropes. It also explores poetry and poetics traditions.
This document editor is used for writing a variety of documents. From a simple application to the necessary resume. From a plain bucket list to an office memo. We think we can work with Word. But it is when we sit down to write a serious professional report, we discover an important fact. Professional report writing needs a different set of skills.
Report Writing Format for Class 10th to 12th. The report writing structure for students in grades 10 and 12 is as follows. Heading : A title that expresses the contents of the report in a descriptive manner. Byline: The name of the person who is responsible for drafting the report. It's usually included in the query.
Be sure to back up your points with background information based on research. 2. Gun Control in America. Gun control in the United States is a controversial topic. This type of academic report can either be written as a report that presents both sides of a story or as a persuasive report that argues one side.
Design Eye-Catching Reports Online with Canva. Start Designing a Report. Easy to create and customize. Thousands of free templates and layouts. Professionally designed and formatted. Styles for every industry. Wow your workmates and boss with reports that are easy on the eye and crying out to be read.
Well, an effective introduction of a report should succinctly introduce the topic, state the purpose and scope of the report, and provide a brief overview of the key points to be discussed. A report introduction should capture the reader's interest and set the tone for the rest of the document. This could be the summary of what should be ...
Report by Canva Creative Studio. Generic One-Page Impact Report Charity Report in Pastel Purple Royal Purple Minimalist Monotone Style. Report by Canva Creative Studio. 1 of 12. ... Writing a report can be a complex and challenging task. Not only do you need to worry about having enough information, but also presenting it in a structured ...
Mission. The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
Creative writing program professors and alumni say creative writing programs cultivate a variety of in-demand skills, including the ability to communicate effectively. "While yes, many creative ...
It's packed with writing exercises that are designed to help you explore all forms of creative writing: fiction, poetry, and creative nonfiction. The book will inspire you while imparting useful writing techniques that are fun and practical. This exercise comes from "Chapter 2: It's Personal.". The writing exercises in this chapter ...
15. Watercolor Rainbow Book Report. This is great for biography research projects. Students cut out a photocopied image of their subject and glue it in the middle. Then, they draw lines from the image to the edges of the paper, like rays of sunshine, and fill in each section with information about the person.
Regardless of the specific type of report that you're trying to make, one of our compelling report templates is absolutely the best way to get started. Choose the template that meets your needs and customize it in any way that you wish - you truly won't believe how easy it is. You'll also have a full library filled with countless free stock ...
As the University of Virginia Darden School of Business prepares to graduate its Class of 2024, Anton Dela Cruz is set to move from a multifaceted career in operations to a strategic role in healthcare consulting. His time at Darden has fueled significant personal growth and a shift toward ethical leadership and community involvement. Raised in Westchester, New York, Dela Cruz's academic and ...
Minneapolis writer V.V. Ganeshananthan, who teaches creative writing at the University of Minnesota, won the Carol Shields Prize for Fiction for "Brotherless Night," earning $150,000.